Method for rapidly locating protein position in guard cell of plant leaf
A technology of guard cells and plant leaves, applied in the field of protein localization in plant cells, can solve the problems of complexity and long cycle, and achieve the effect of simple operation, good repeatability and good labeling effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
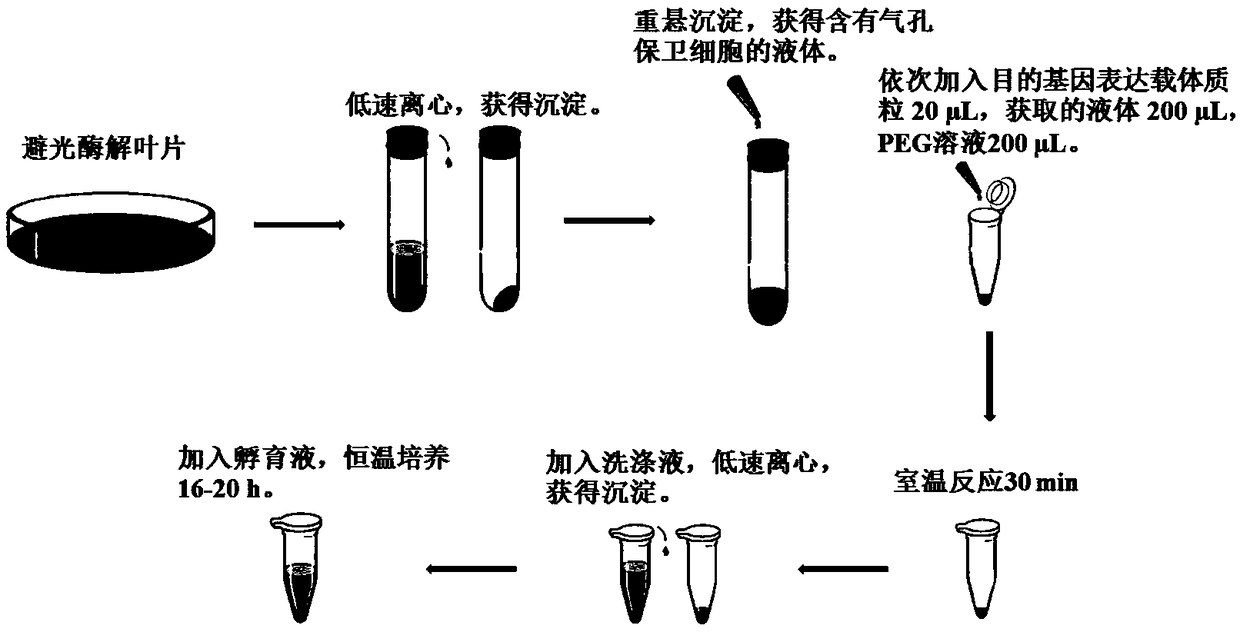
[0032] see figure 1 , the embodiment of the present invention provides a method for rapidly locating the position of a protein in a guard cell of a plant leaf, and the method is carried out according to the following steps:
[0033] 1. Construction of plant expression vector: using high-fidelity enzyme pfu series, design primers for the target gene according to the primer blast in NCBI, and use the cDNA obtained by extracting plant material RNA and inversion as a template, and using PCR technology to clone and sequence the target gene; After the expression vector and the gene fragment are digested and recovered with the same endonuclease, the gene fragment is connected to the expression vector pBI121-EGFP by ligase, and then the target gene expression vector plasmid is prepared; the target gene expression vector plasmid is in pBI121- A vector obtained by excising the GUS gene and replacing it with the EGFP gene on the basis of GUS, using CaMV 35S as the promoter, marking the t...
no. 2 example
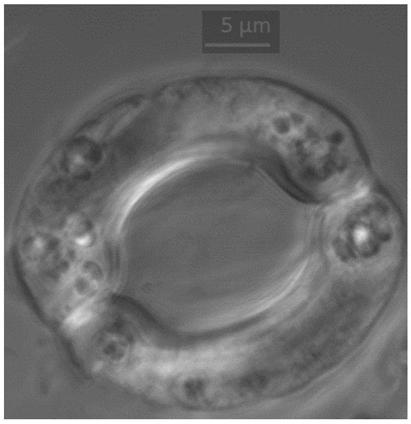
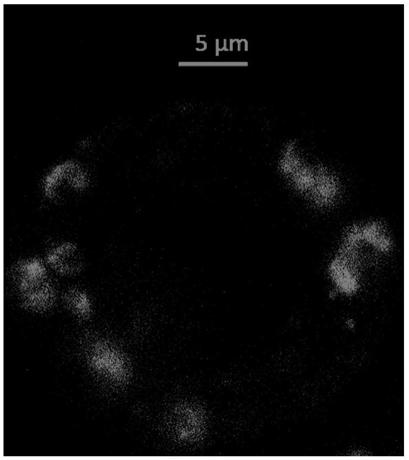
[0040] see image 3 , Figure 4 and Figure 5 , another method for rapidly locating the position of proteins in guard cells of plant leaves provided by the embodiment of the present invention is different from the first embodiment in that the components of the washing solution are 7.2%-7.3% of mannitol and MES (2-morpholinoethanesulfonic acid) 0.04%-0.05%, pH adjusted to 5.7-5.8 with 1M KOH.
no. 3 example
[0042] see image 3 , Figure 4 and Figure 5 , another method for rapidly locating the position of proteins in guard cells of plant leaves provided in the embodiment of the present invention is different from the first and second embodiments in that the composition of the suspension is 0.08% MES by mass fraction -0.1%, Mannitol 7.2%-7.5% and MgCl 2 ·6H 2 O 0.3%-0.4%, adjust pH to 5.7-5.8 with 1 M KOH.
[0043] Wherein, the enzymatic hydrolysis solution is filtered through a 100-120 mesh sieve.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com