Method for identifying haploid regenerated by brassica napus microspores simply, conveniently and quickly
A cabbage rape and microspore technology is applied in the application field of plant cytology to achieve the effects of low cost, easy operation and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
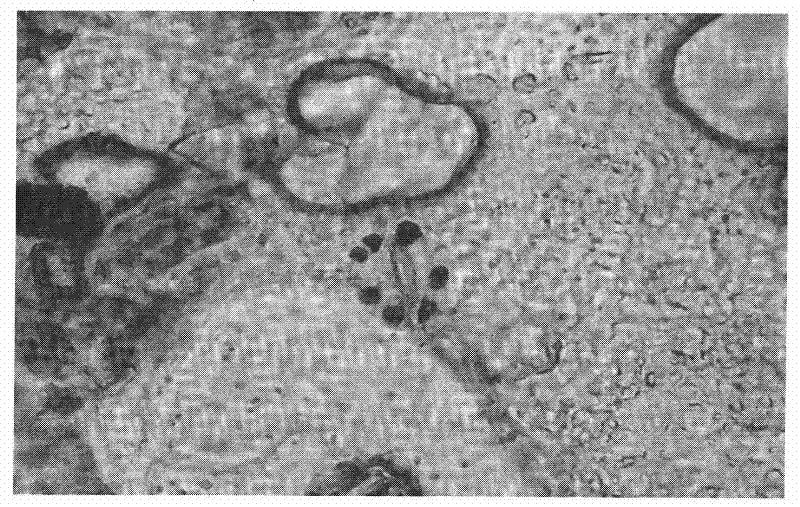
[0025] 1. Cut the leaves of sterile seedlings regenerated from Brassica napus microspores in vitro
[0026] Using the method reported by Shi Shuwen et al. (Shi Shuwen et al., Brassica napus and its interspecific and intergenus hybrid microspore embryoid induction, Huazhong Agricultural University Journal, 1993, 12: 544-550) Brassica napus variety Huashuang 4 , Huashuang No. 2, Huayou No. 8, Huashuang No. 1 and Huahuang No. 1 (the above-mentioned varieties are from the rapeseed laboratory of Huazhong Agricultural University, and have been widely promoted and applied in China). Embryoid bodies, the regenerated embryoid bodies were respectively inoculated on the B5 medium with a pH of 6.0 (B5 medium source: Gamborg et al., Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Experimental Cell Research, 1968, 50 : 151-158) in a 150ml Erlenmeyer flask, cultivated to complete plantlets with roots, stems and leaves (the culture temperature is 24-26°C, the light is 12h ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2 (application embodiment: utilize the method for embodiment 1 to identify and discard the microspore haploid plant that does not set seeds)
[0035] Rapeseed varieties Zhongyou 821 (from the Oil Crops Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, a large-scale promotion variety in China), Huashuang 3 and Huashuang 5 (variety from the rape research laboratory of Huazhong Agricultural University, have been widely promoted and applied in China ) microspores regenerated into embryoid bodies (method reference: Shi Shuwen et al., Induction of microspore embryoid bodies of Brassica napus and its interspecific and intergenus hybrids, Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 1993, 12: 544-550). The obtained embryoid bodies were inoculated into Erlenmeyer flasks containing B5 medium (pH 6.0), and cultivated into plantlets (cultivation temperature was 24-26° C., light was 12 hours per day, and light intensity was 1800 lux). Cut off the 5th lea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com