Plant CO2 sensors, nucleic acids encoding them, and methods for making and using them
A plant organ, plant technology, applied in the field of drought-resistant plants, to achieve the effect of enhanced carbon and water utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 6
[0435]
[0436] a Arabidopsis genome project locus number
[0437] bAccording to Fabre N. et al., (2007) Plant, Cell Environment 30:617-629; or from the Arabidopsis information resource website (Carnegie Institution for Science, Department of Plant Biology, Stanford, CA, National Science Foundation grant) .
[0438] Thus, in alternative aspects, any carbonic anhydrase (carbonic dehydratase) may be used in the practice of the present invention.
[0439] Generating and Manipulating Nucleic Acids
[0440] In alternative aspects, the invention provides, for example isolated, synthetic and / or recombinant encoding novel CO of the invention 2 Nucleic acid and coding sequences of sensor genes that inhibit CO 2 Nucleic acids for sensor gene or messenger expression (eg siRNA, microRNA, antisense nucleic acids), and guard cell specific transcriptional regulatory elements such as promoters. Nucleic acids of the invention can be produced, isolated and / or manipulated by, for exampl...
Embodiment 1
[0496] Embodiment 1: By controlling the CO of the present invention 2 Sensor genetic manipulation of water and carbon dioxide (CO2) through plant stomata 2 )exchange
[0497] The present invention provides for controlling the CO of the present invention 2 Genetic manipulation of sensors via plant stomatal water and carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) method of exchange.
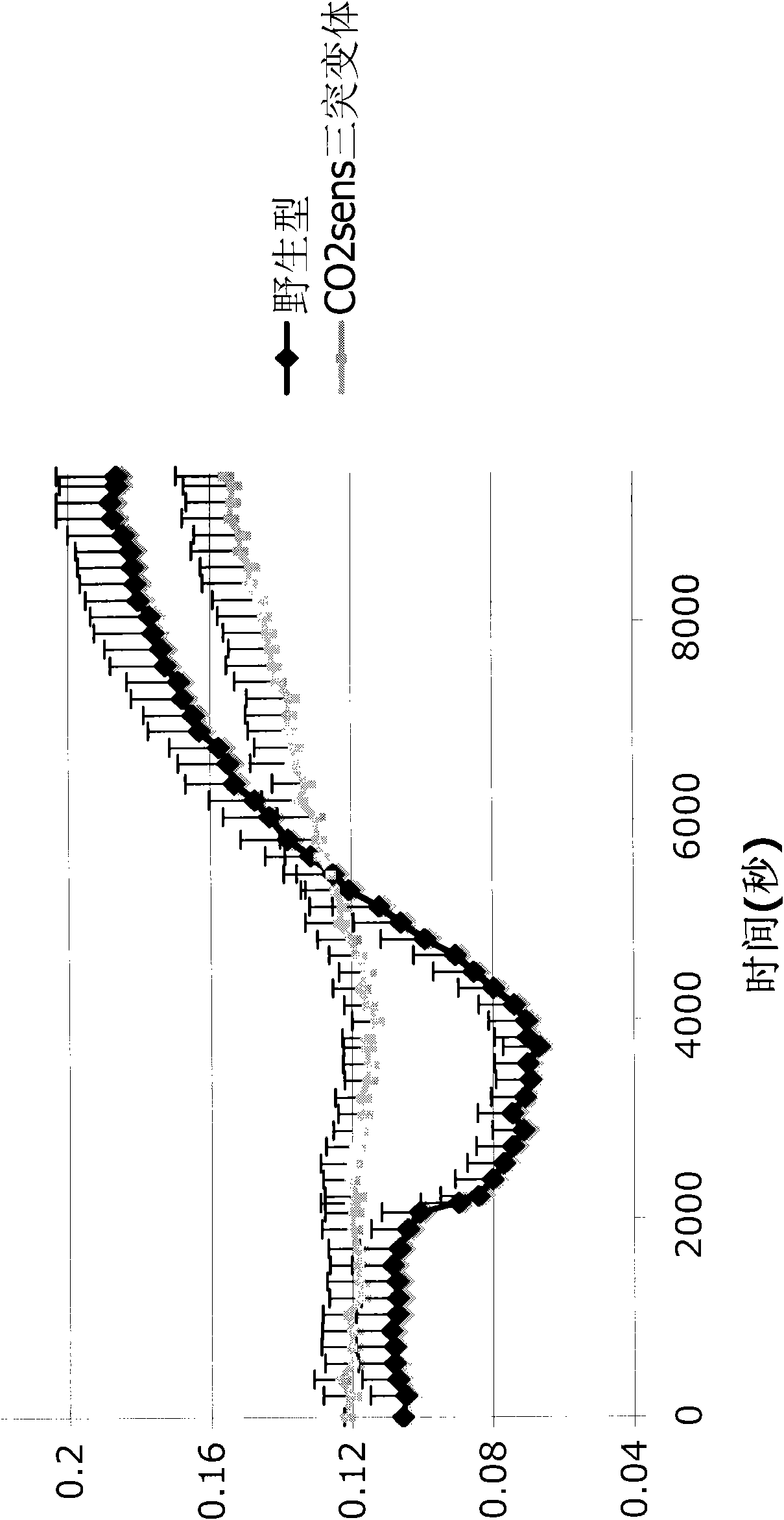
[0498] Construction of an Arabidopsis double mutant: According to cell-specific microarray analysis, this double mutant lacks the full-length expression of two homologous genes, which are highly expressed in wild-type guard cells.
[0499] Arabidopsis double mutants lack full-length expression of homologous genes that are highly expressed in wild-type guard cells, according to cell-specific microarray analysis. CO2Sen double mutants display impaired pair [CO 2 ] altered stomatal response, as determined by real-time gas exchange analysis; [CO 2 ] Change involves 365ppm CO from ambient 2 to an increased 800...
Embodiment 2
[0508] Example 2: Controlling plant CO 2 CO uptake and water use efficiency 2 Receptor Characterization
[0509]The present invention provides compositions and methods for the controlled opening and / or closing of plant stomata. Stomata are formed by pairs of guard cells in the leaf epidermis and are able to control plant water loss and carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) influx into plants. The present invention provides for the control of CO for photosynthetic carbon fixation 2 Compositions and methods for the amount of uptake and control of the amount of water lost through transpiration through these "controllable" stomata. The present invention provides a mechanism for providing guard cell signal transduction to sense CO 2 level, water status, light and other environmental stimuli to adjust stomatal aperture to optimize CO under different conditions 2 Compositions and methods for inflow, water loss and plant growth.
[0510] The present invention provides methods for ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com