Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacterium Q3 and application thereof
A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and degrading bacteria technology, applied in the field of microbial engineering, can solve problems such as difficult to be degraded, complex structure of high-ring polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and increased difficulty of microbial degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
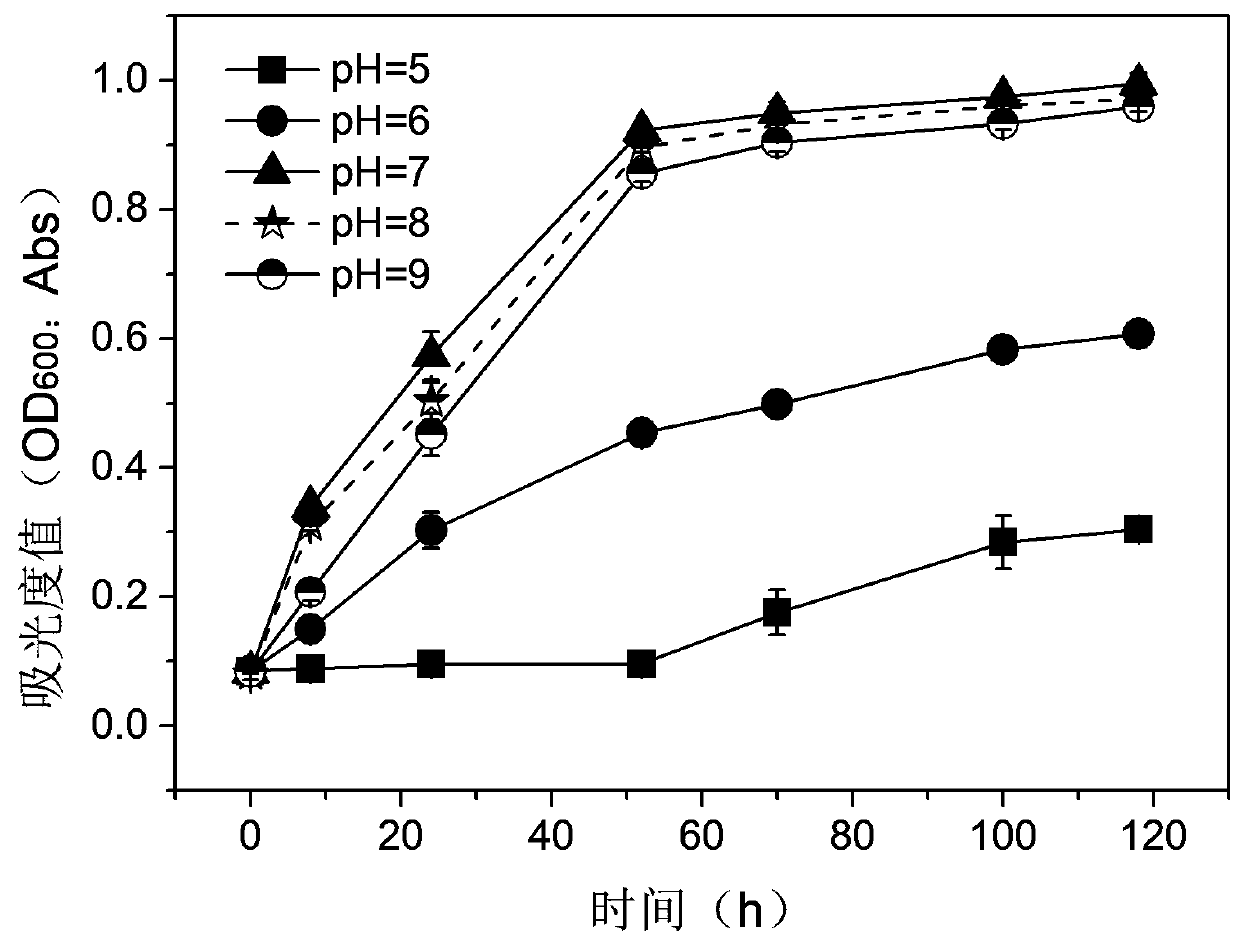
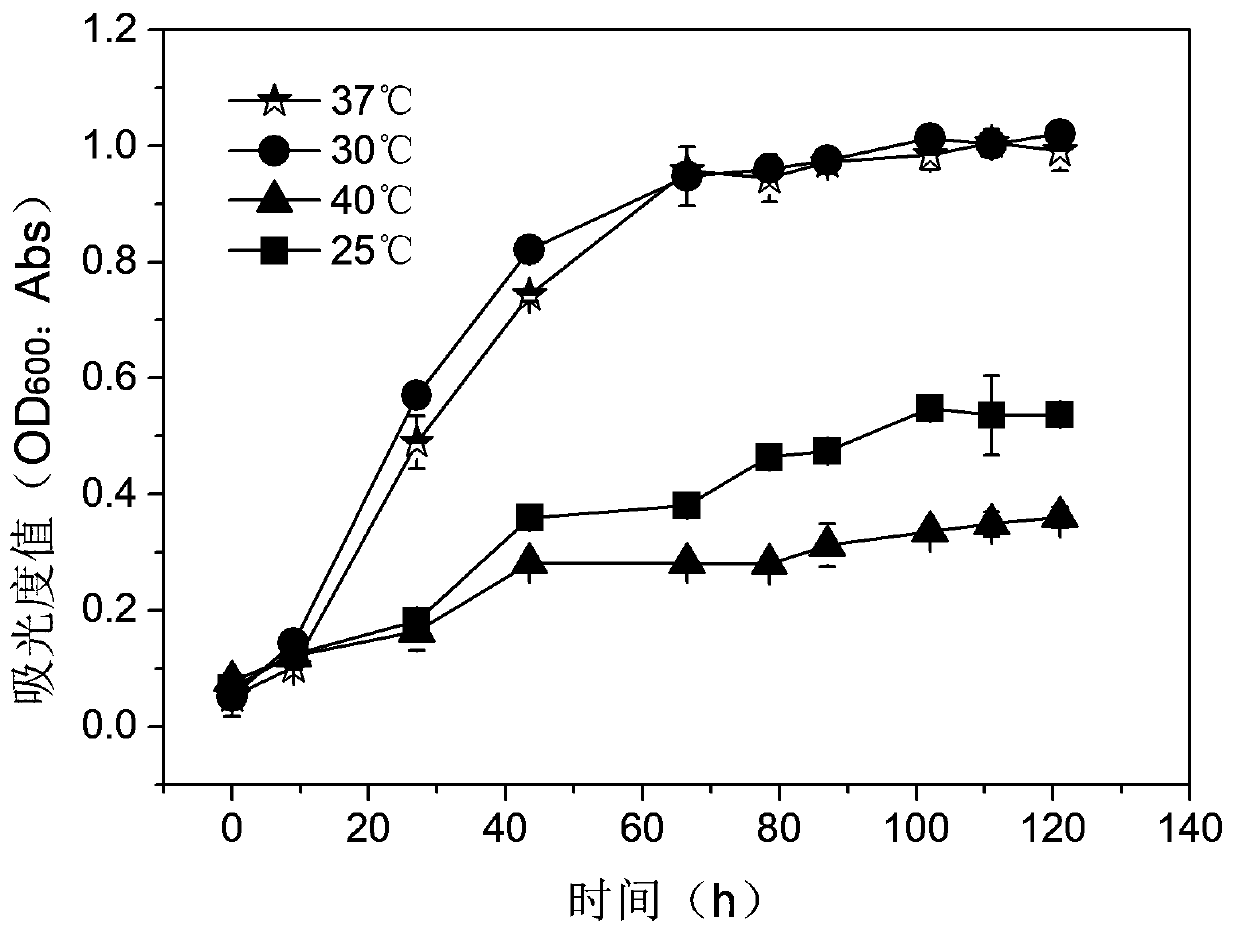
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1: Screening and isolation of bacterial strains
[0034] Taking the PAHs-contaminated soil of Beijing Coking Plant as the bacterial source, 10 g of soil was weighed, and 90 mL of sterile water was added to it at 180 r min -1 , shake in a shaker at 37°C for 3 h, and after standing still for 30 min, take 5 mL of the supernatant and inoculate it into 50 mg L of pyrene -1 In 45 mL of sterilized inorganic salt culture solution, 37°C, 180 rpm -1 Shaker culture. Transfer 5 mL of culture medium every 10 days to 45 mL of pyrene concentration gradient in the form of 100, 200, 300, 500 mg L -1递增 The fresh sterilized inorganic salt culture medium was enriched with PAHs degrading bacteria after 5 transfers. After taking 100 uL of the last enrichment culture solution and coating it on the inorganic salt solid plate, the plate was turned upside down in the beaker containing pyrene, and a layer of pyrene film was spread on the inorganic salt solid plate by sublimation method...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Embodiment 2: bacterial strain is to the degradation of pyrene
[0048] With the Q3 ( Rhodococcus rhodochrous ) were inoculated into LB medium to the logarithmic phase, discarded the supernatant after centrifugation, washed twice by adding 20 mL of sterile water, discarded the supernatant after centrifugation again, harvested the bacteria, and inoculated the bacteria suspension at 600 nm The absorbance value (OD 600 ) were adjusted to 1.0. Inoculate the bacterial suspension of the obtained pure strains (10% inoculum) into the inorganic salt liquid medium containing pyrene, so that the initial content of pyrene is 25, 50, 100, 200 mg L -1 , each sample was repeated 4 times, and a control group was set at the same time. After culturing in a shaker at 37°C and 180 r / min for 8 days, the residual pyrene concentration was measured respectively, and the degradation rate was calculated. The results are shown in Image 6 .
[0049] The results showed that the strain Q3 coul...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Embodiment 3: bacterial strain is to the degradation of PAHs
[0051] As described in Example 2, the Q3 bacterial suspension was prepared, and the resulting bacterial suspension was inoculated (10% inoculum) into inorganic salts containing phenanthrene, pyrene, benzo[b]fluoranthene and benzo[a]pyrene In the liquid medium, the initial concentrations of phenanthrene, pyrene, benzo[b]fluoranthene and benzo[a]pyrene in the medium were 50 mg L -1 , 50 mg L -1 , 10 mg L -1 , 50 mg L -1 , each sample was replicated 4 times, and a control group was set at the same time. After culturing in a shaker at 37°C and 180 r / min for 8 days, the concentrations of residual phenanthrene, pyrene, benzo[b]fluoranthene and benzo[a]pyrene were determined. Calculate the degradation rate. Degradation rate as Figure 7 shown.
[0052] According to the above experimental procedures, the strain Q3 was verified against phenanthrene, pyrene, benzo[a]pyrene, benzo[b]fluoranthene, benzanthracene, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com