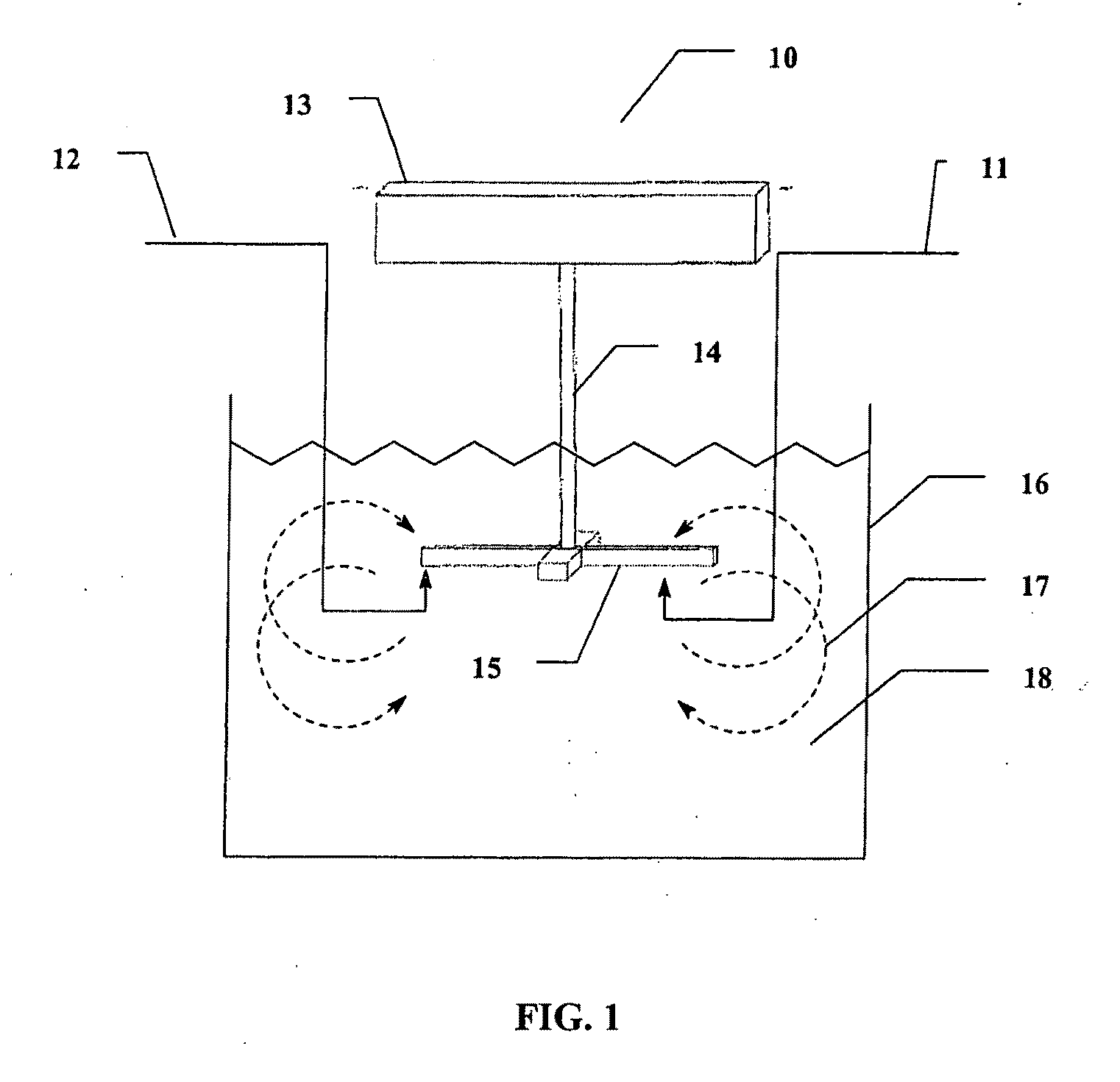
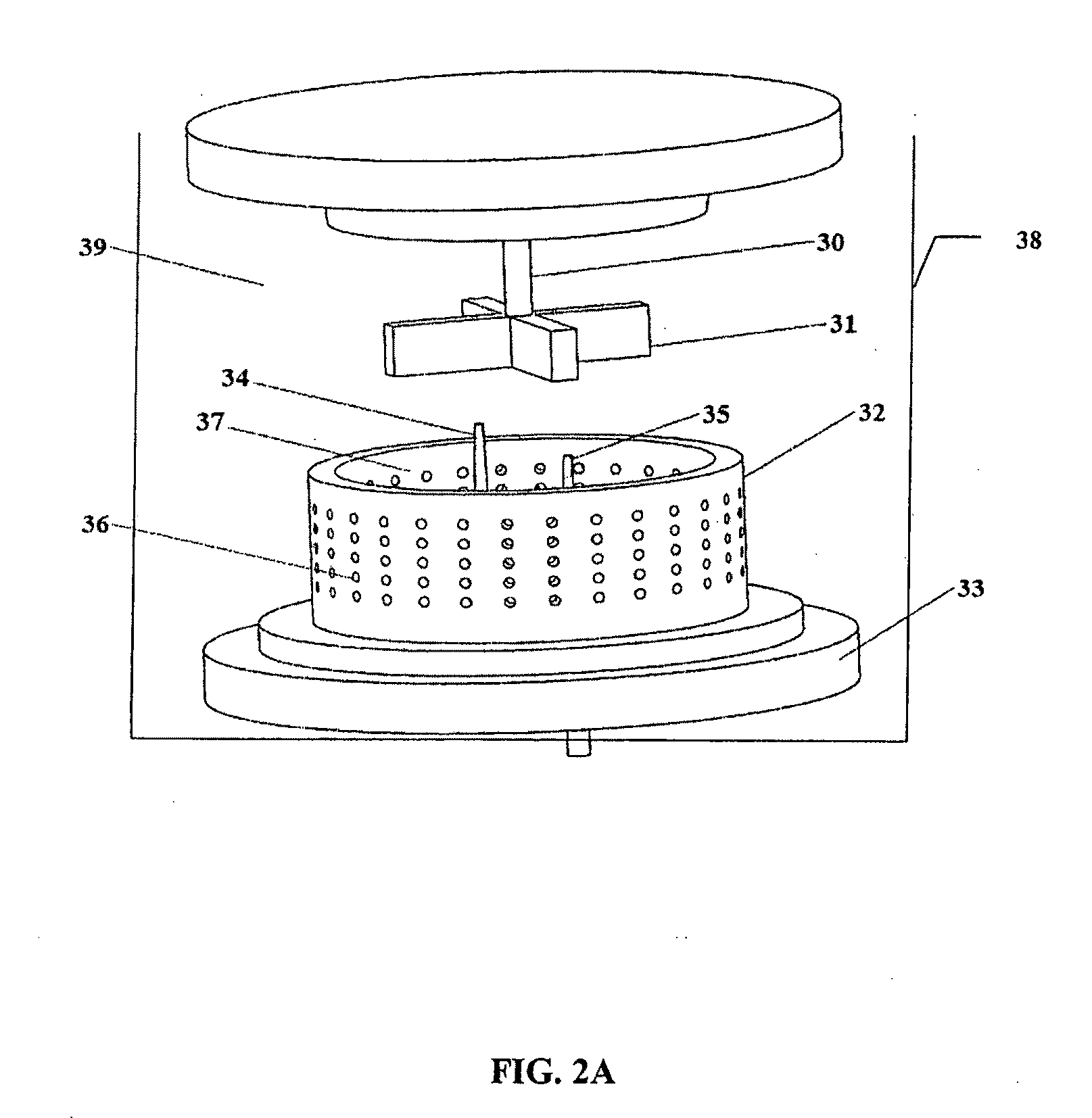
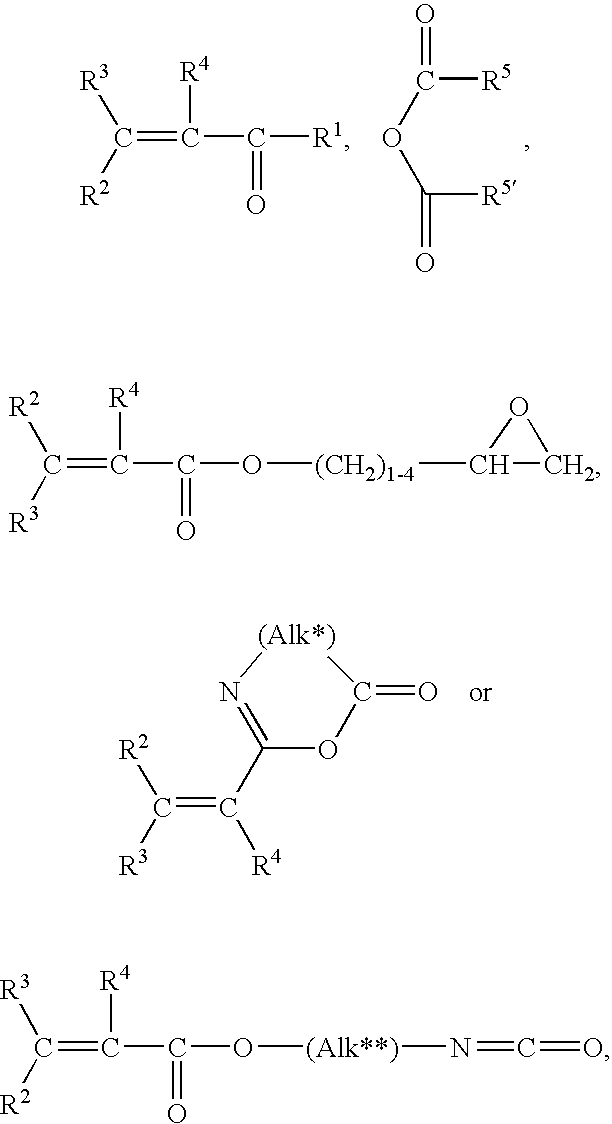
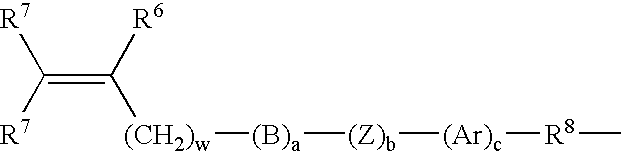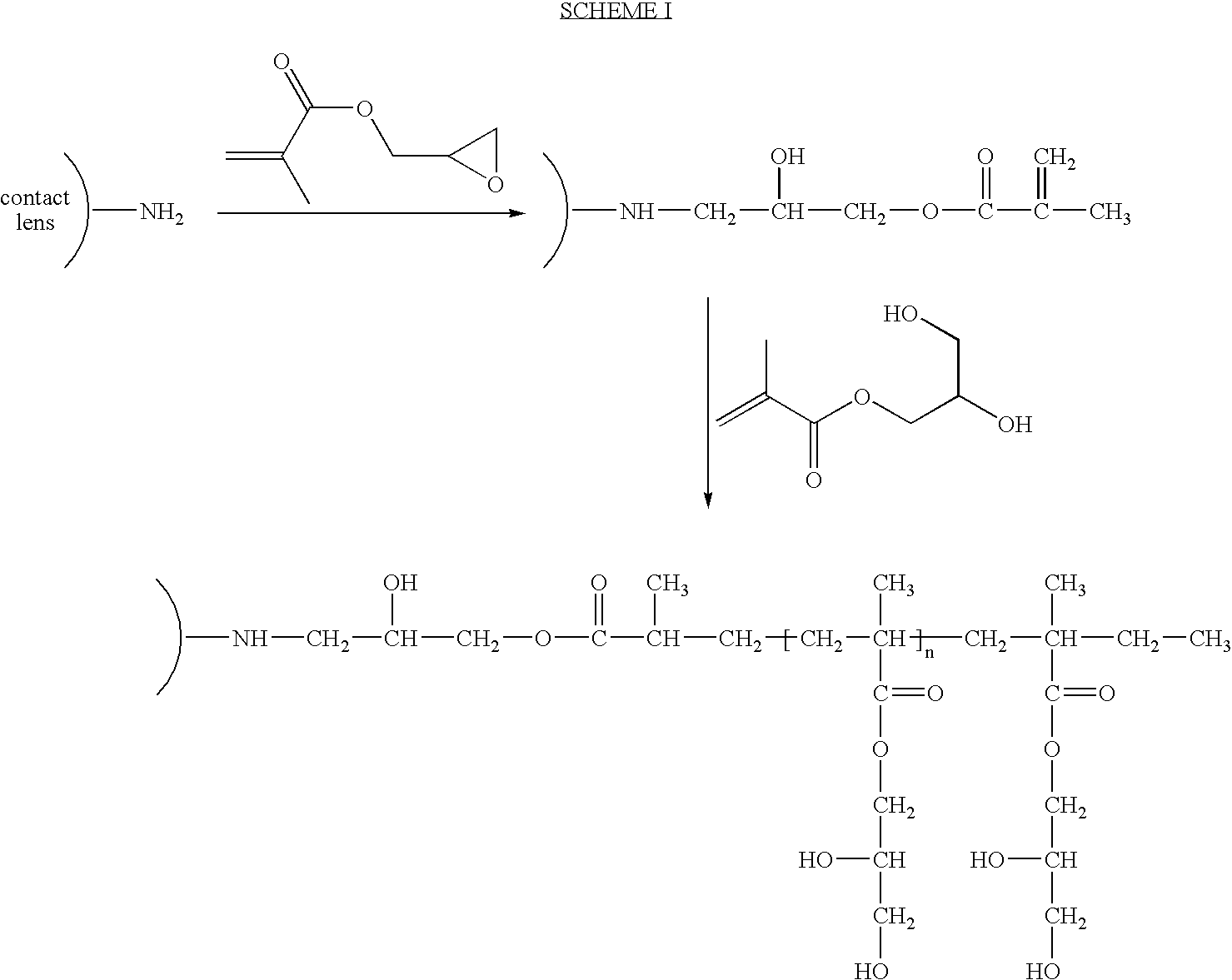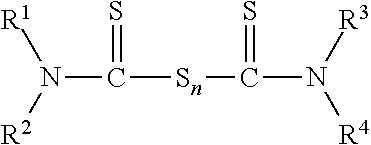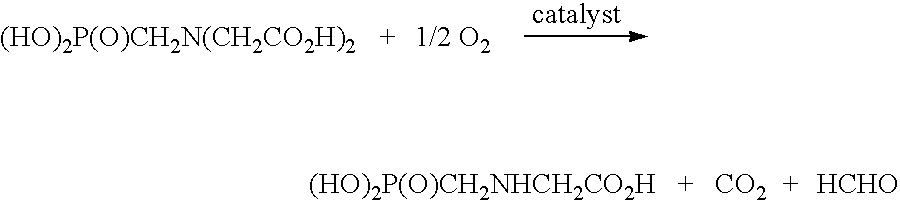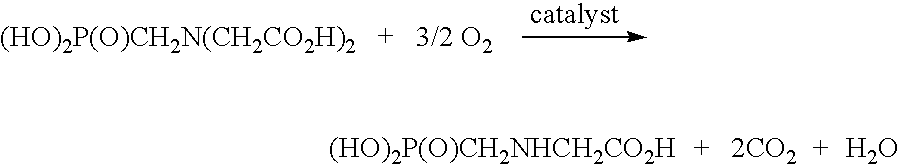Patents
Literature
259 results about "Aqueous reaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
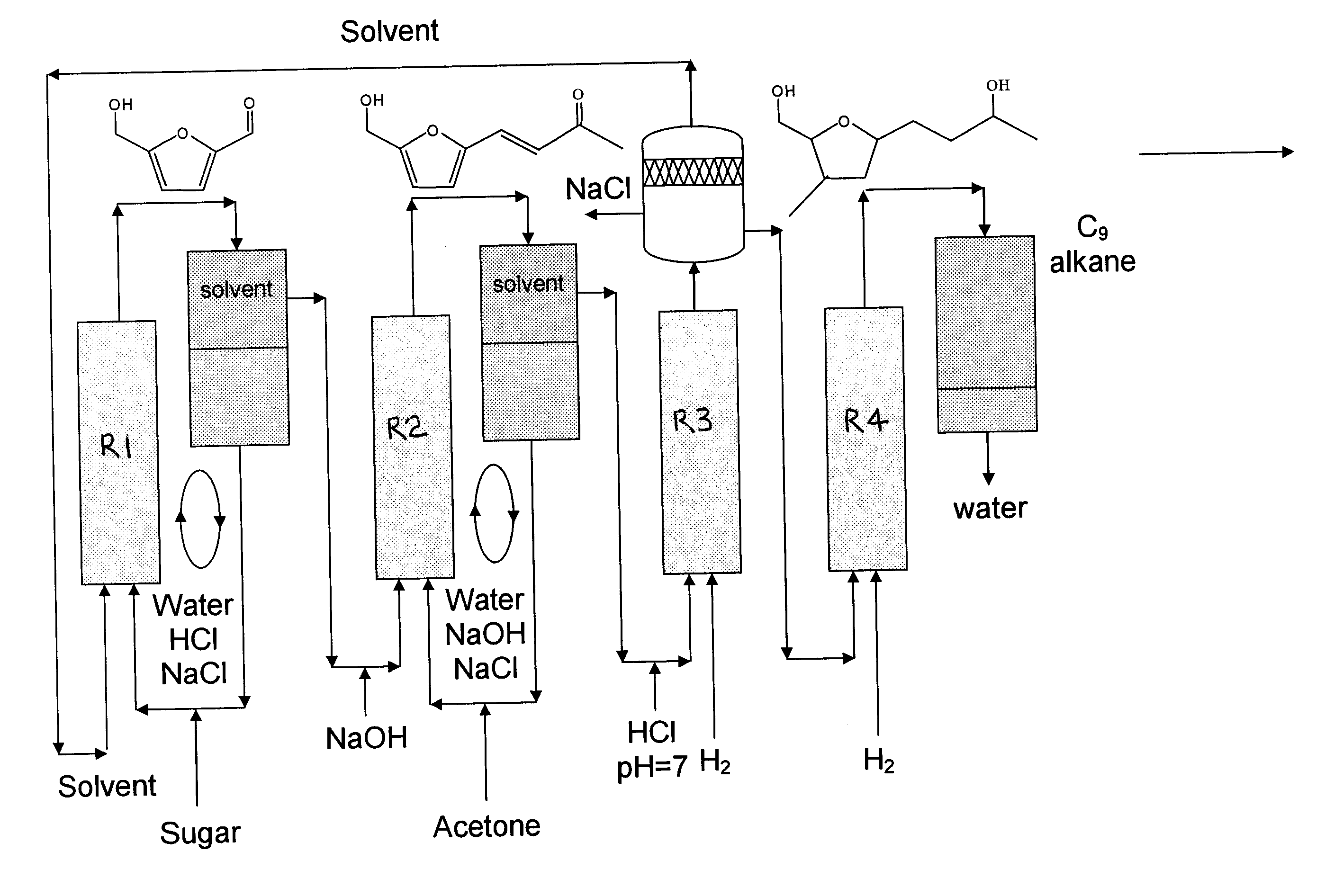
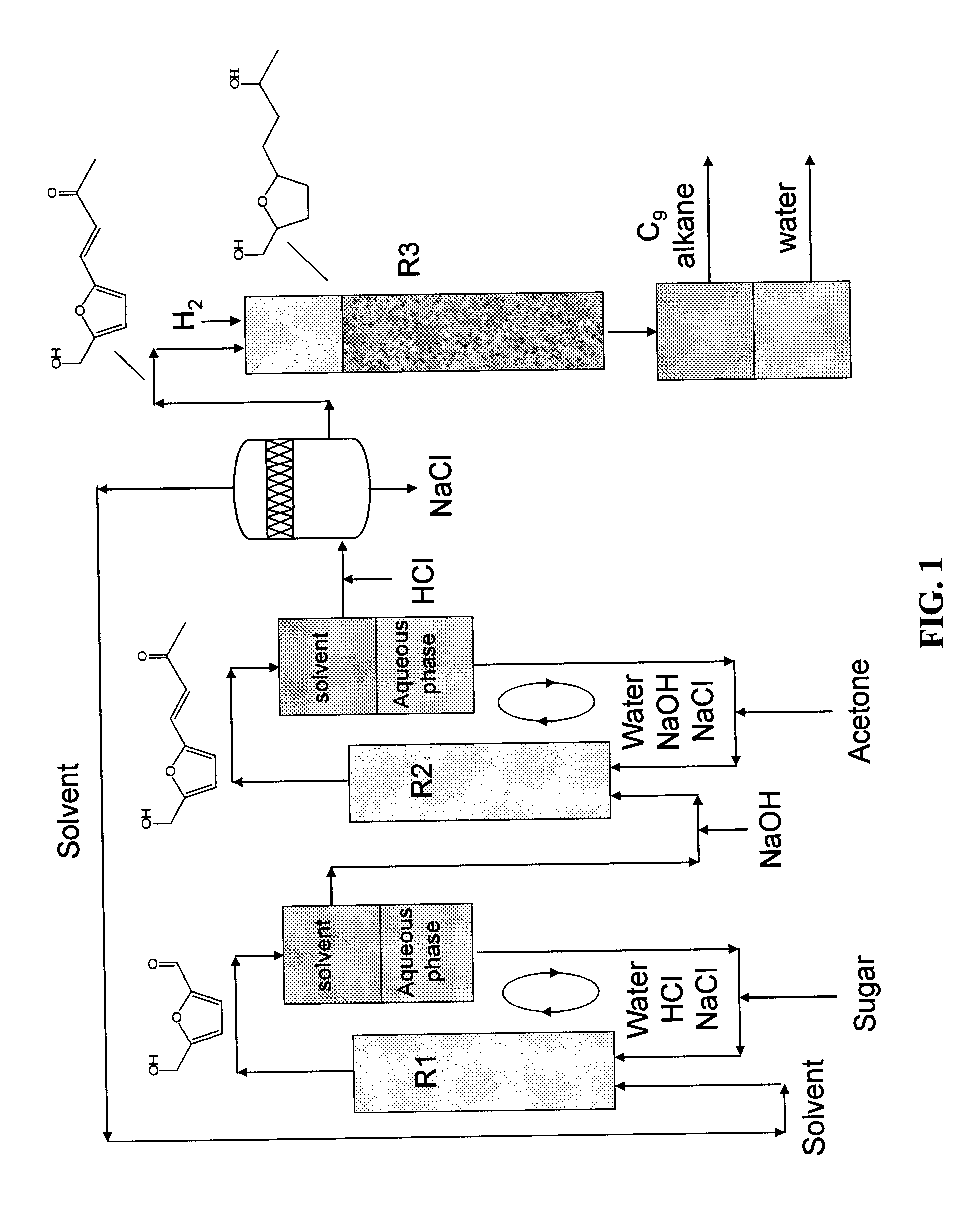
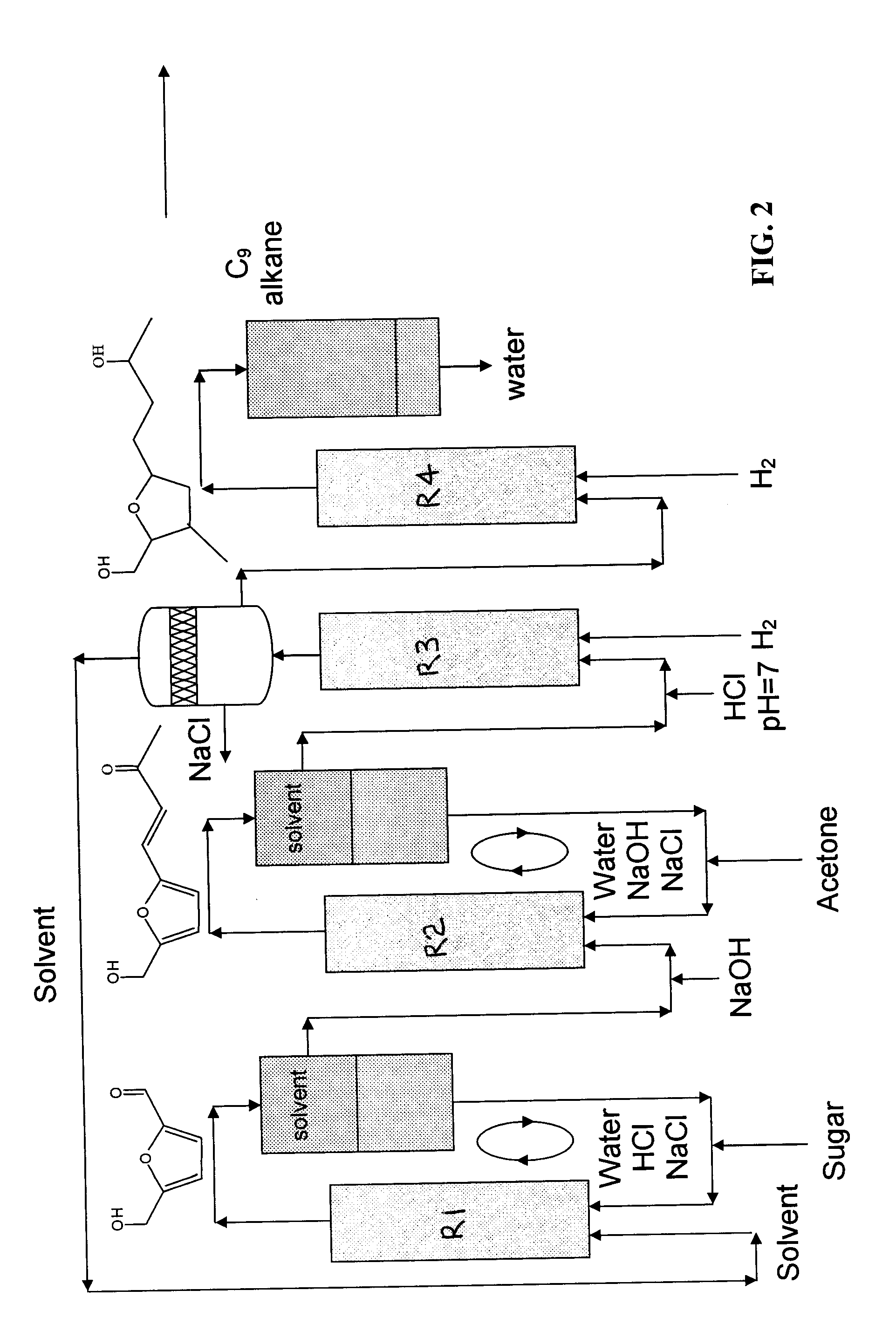
Production of liquid alkanes in the jet fuel range (c8-c15) from biomass-derived carbohydrates
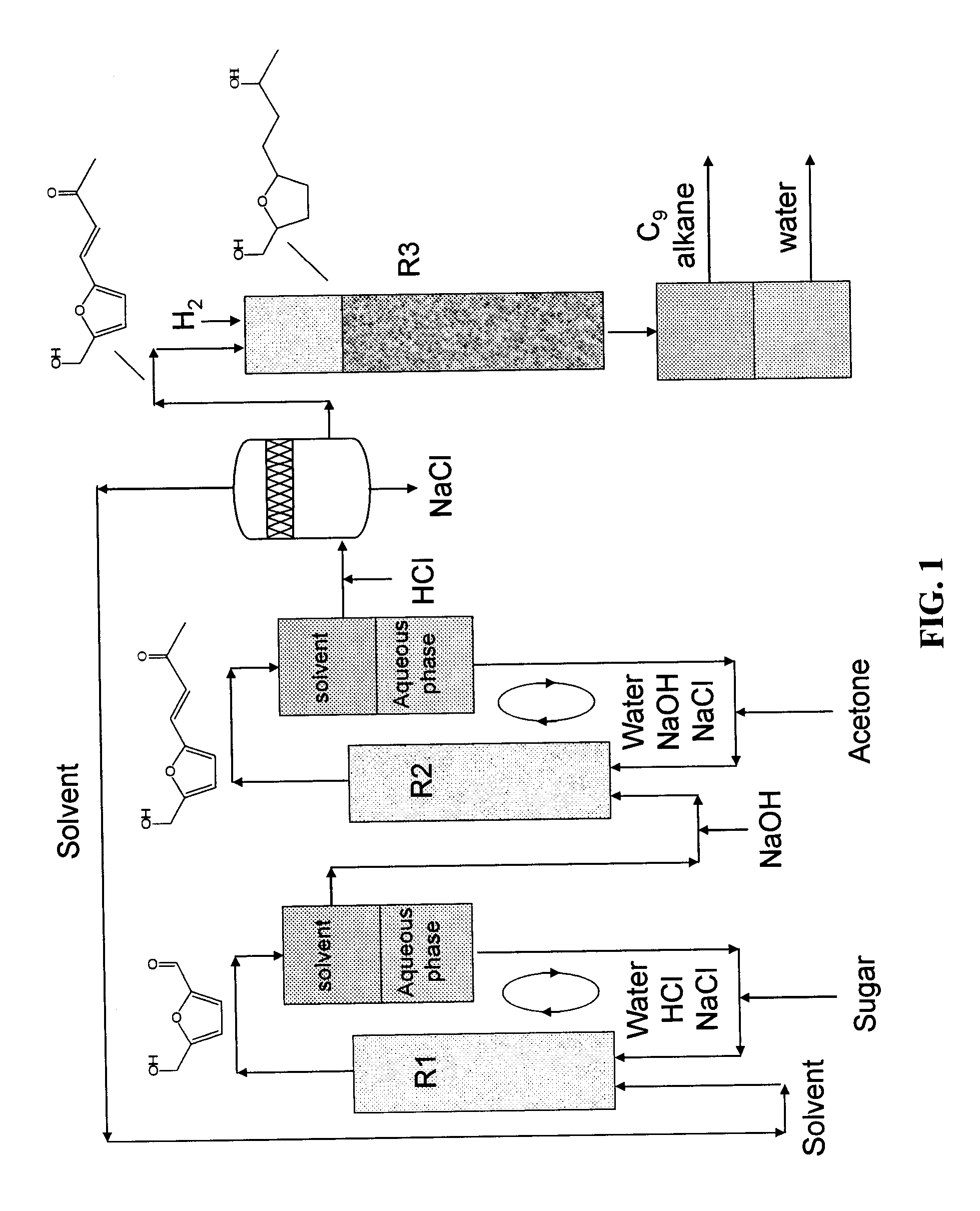
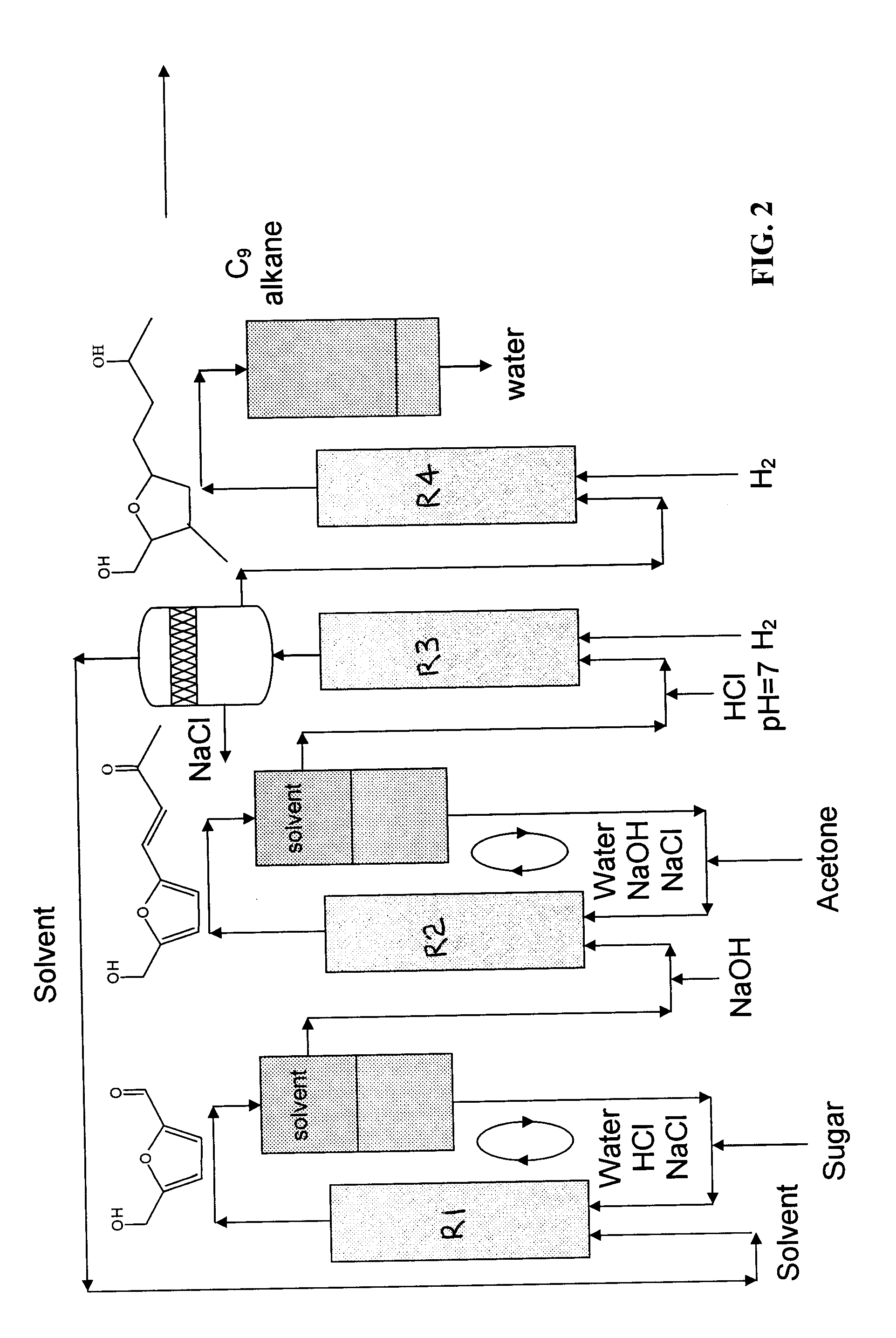
Described is a method for making a composition comprising alkanes. The composition is suitable for use as a liquid transportation fuel in general, and jet fuel in particular. The method includes dehydrating a feedstock solution comprising a carbohydrate, in the presence of an acid catalyst, to yield at least one furan derivative compound, in a reaction vessel containing a biphasic reaction medium: an aqueous reaction solution and a substantially immiscible organic extraction solution. The furan derivative compound is then subjected to a self-aldol condensation reaction or a crossed-aldol condensation reaction with another carbonyl compound to yield a beta-hydroxy carbonyl compound and / or an alpha-beta unsaturated carbonyl compound. The beta-hydroxy carbonyl and / or alpha-beta unsaturated compounds are then hydrogenated to yield a saturated or partially saturated compound, followed by hydrodeoxygenation (e.g., dehydrating and hydrogenating) of the saturated or partially saturated compound to yield a composition of matter comprising alkanes.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
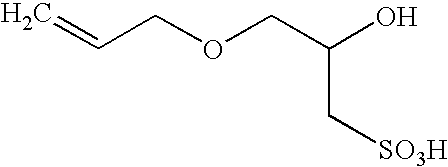
Polymerization of fluoromonomers using a 3-allyloxy-2-hydroxy-1-propanesulfonic acid salt as surfactant
InactiveUS6869997B2Reduce the binding forceOrganic chemistryFibre treatmentFluoropolymerBuffering agent
Fluoropolymers are prepared by a process comprising polymerizing at least one fluoromonomer in an aqueous reaction medium containing monomer, a radical initiator and a 3-allyloxy-2-hydroxy-1-propanesulfonic acid salt as surfactant. The medium may optionally contain one or more of an antifoulant, a buffering agent and a chain-transfer agent.
Owner:ARKEMA INC
Production of liquid alkanes in the jet fuel range (C8-C15) from biomass-derived carbohydrates
ActiveUS7880049B2High selectivityHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionAlkaneFuran
Described is a method for making a composition comprising alkanes. The composition is suitable for use as a liquid transportation fuel in general, and jet fuel in particular. The method includes dehydrating a feedstock solution comprising a carbohydrate, in the presence of an acid catalyst, to yield at least one furan derivative compound, in a reaction vessel containing a biphasic reaction medium: an aqueous reaction solution and a substantially immiscible organic extraction solution. The furan derivative compound is then subjected to a self-aldol condensation reaction or a crossed-aldol condensation reaction with another carbonyl compound to yield a beta-hydroxy carbonyl compound and / or an alpha-beta unsaturated carbonyl compound. The beta-hydroxy carbonyl and / or alpha-beta unsaturated compounds are then hydrogenated to yield a saturated or partially saturated compound, followed by hydrodeoxygenation (e.g., dehydrating and hydrogenating) of the saturated or partially saturated compound to yield a composition of matter comprising alkanes.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
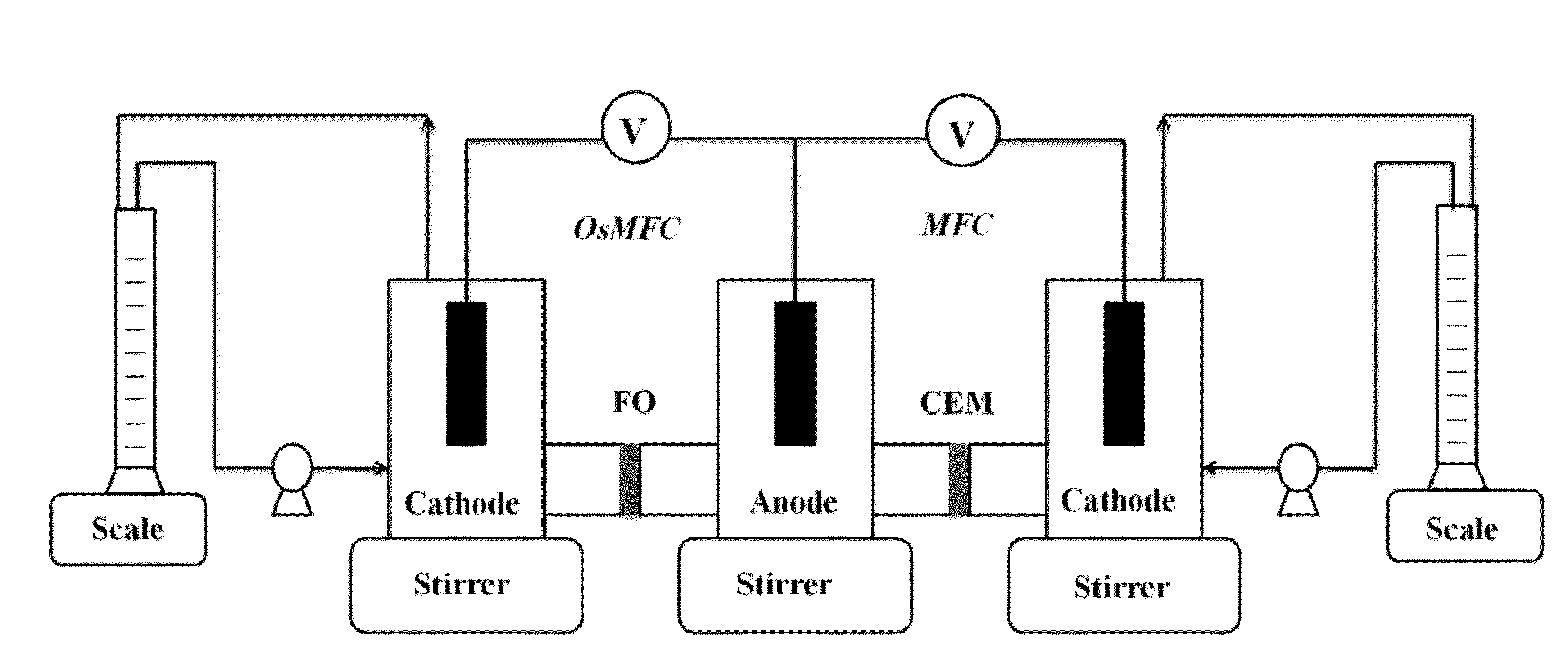
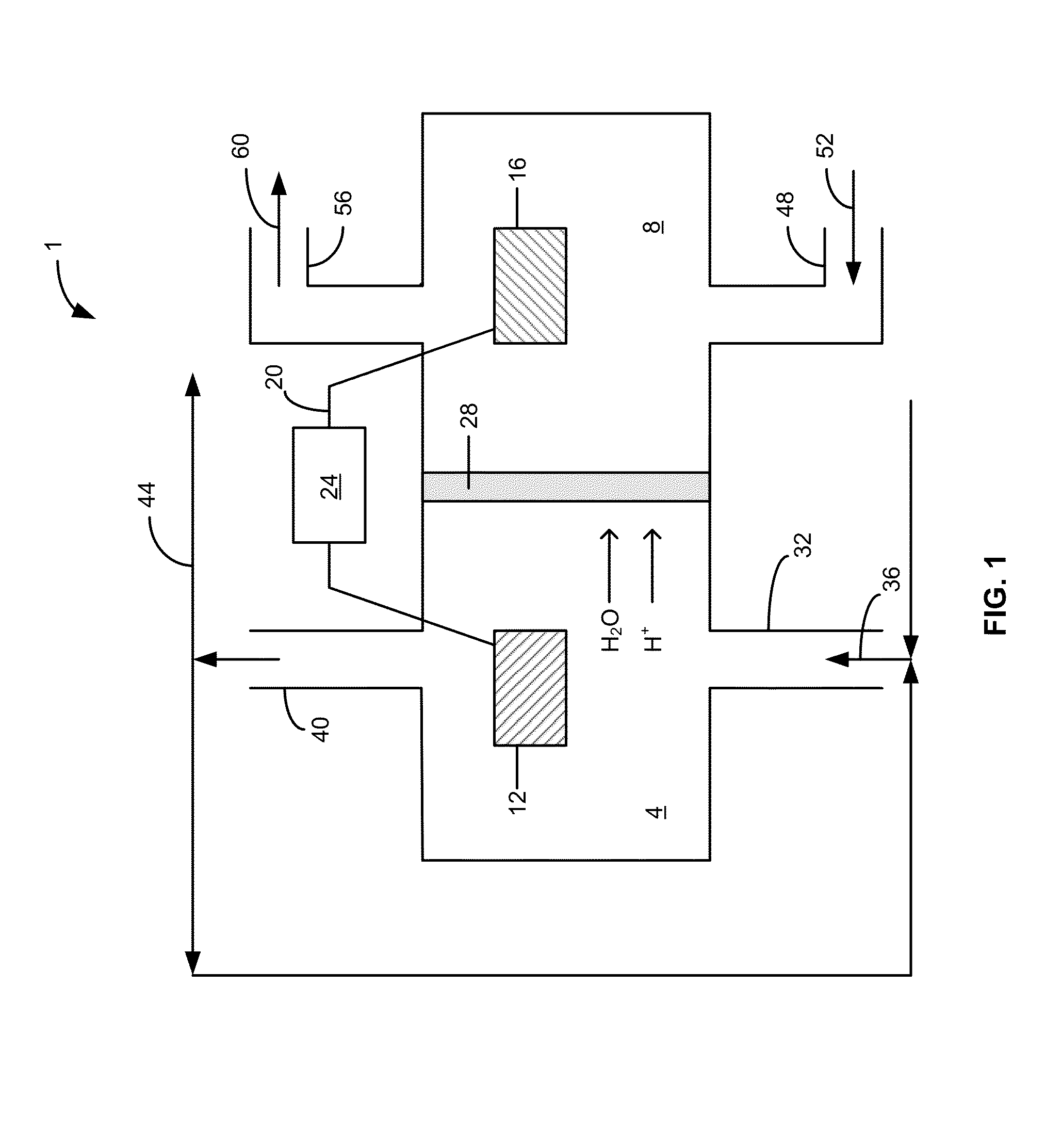
Osmotic bioelectrochemical systems
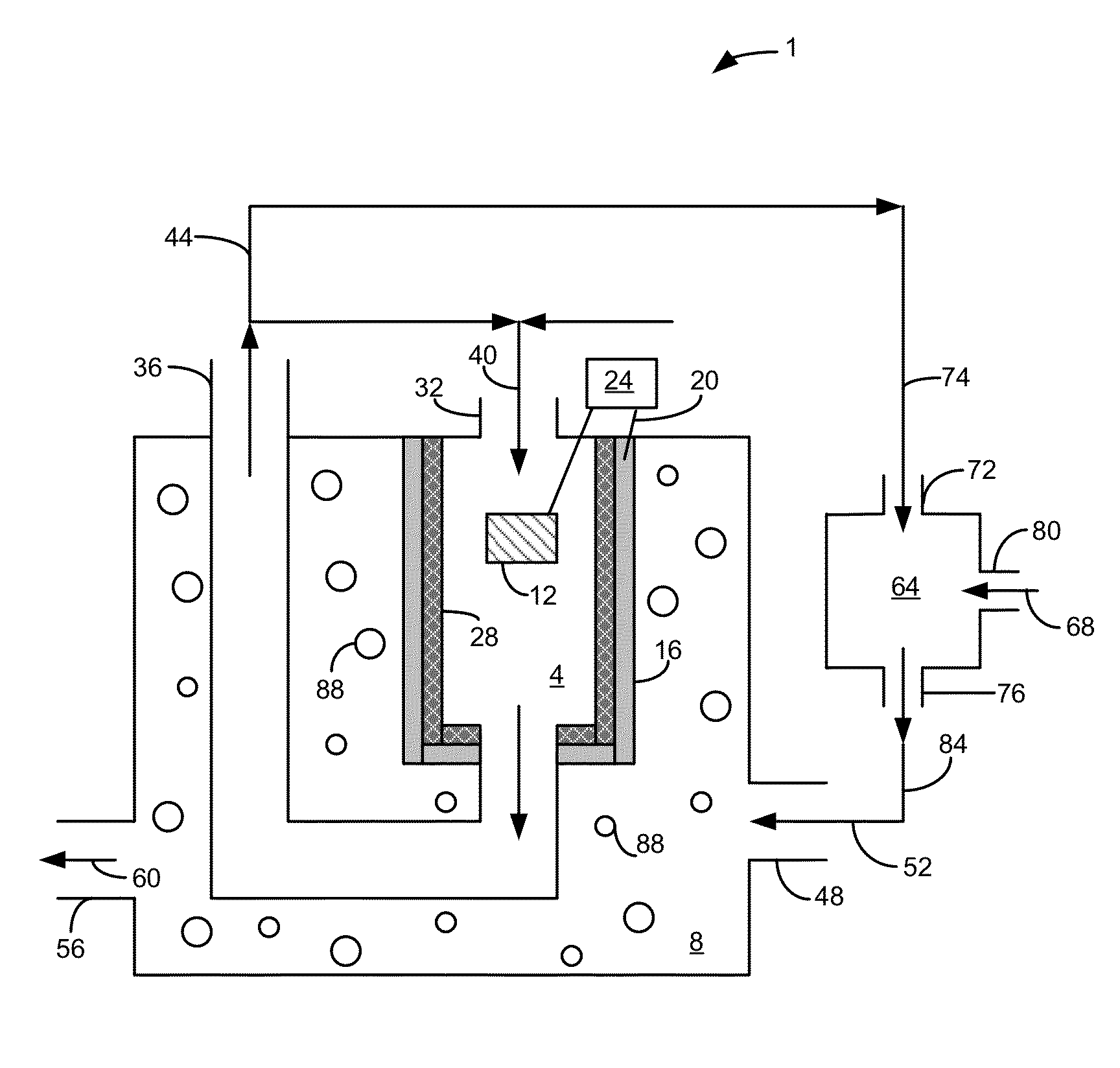
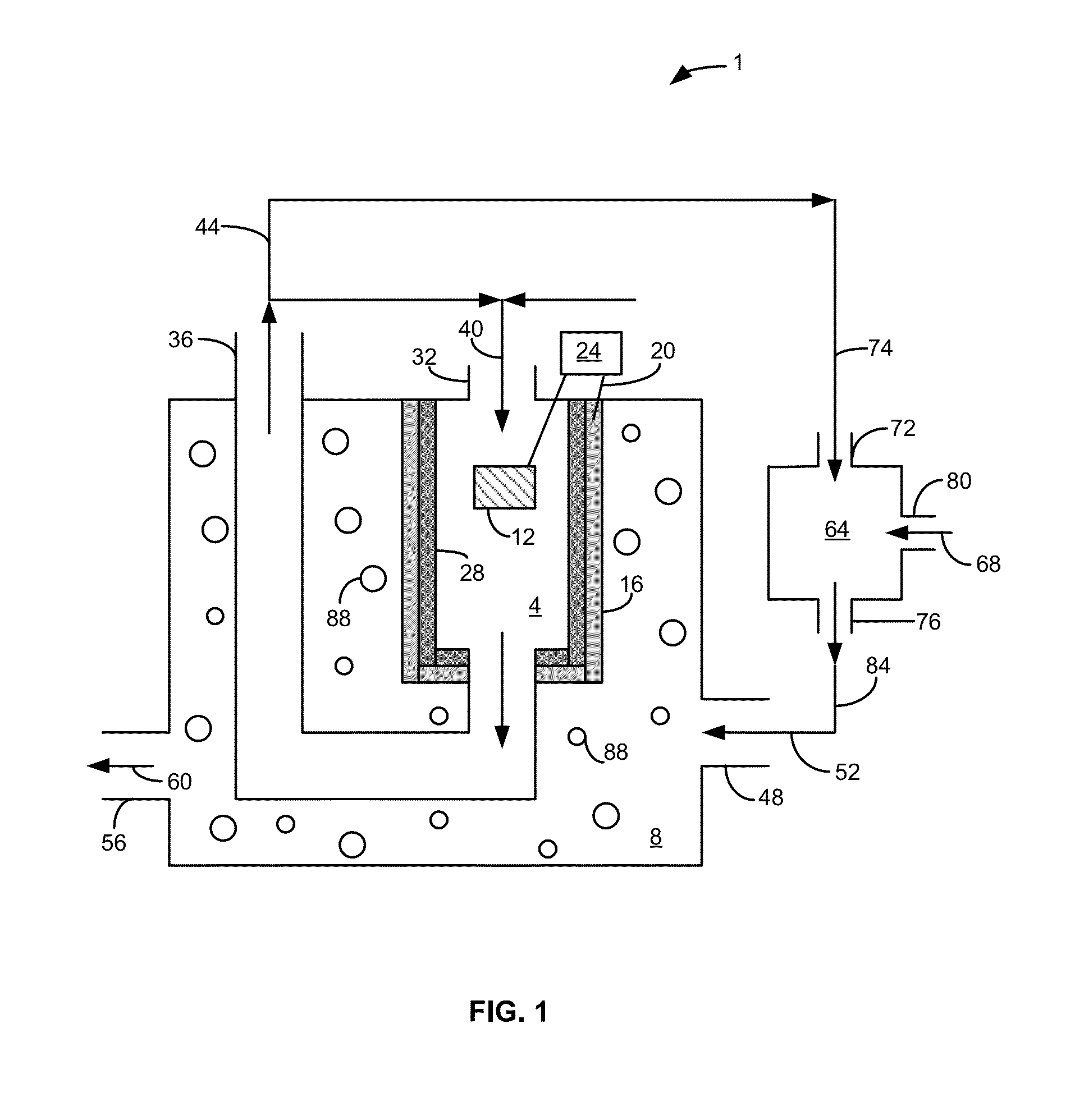
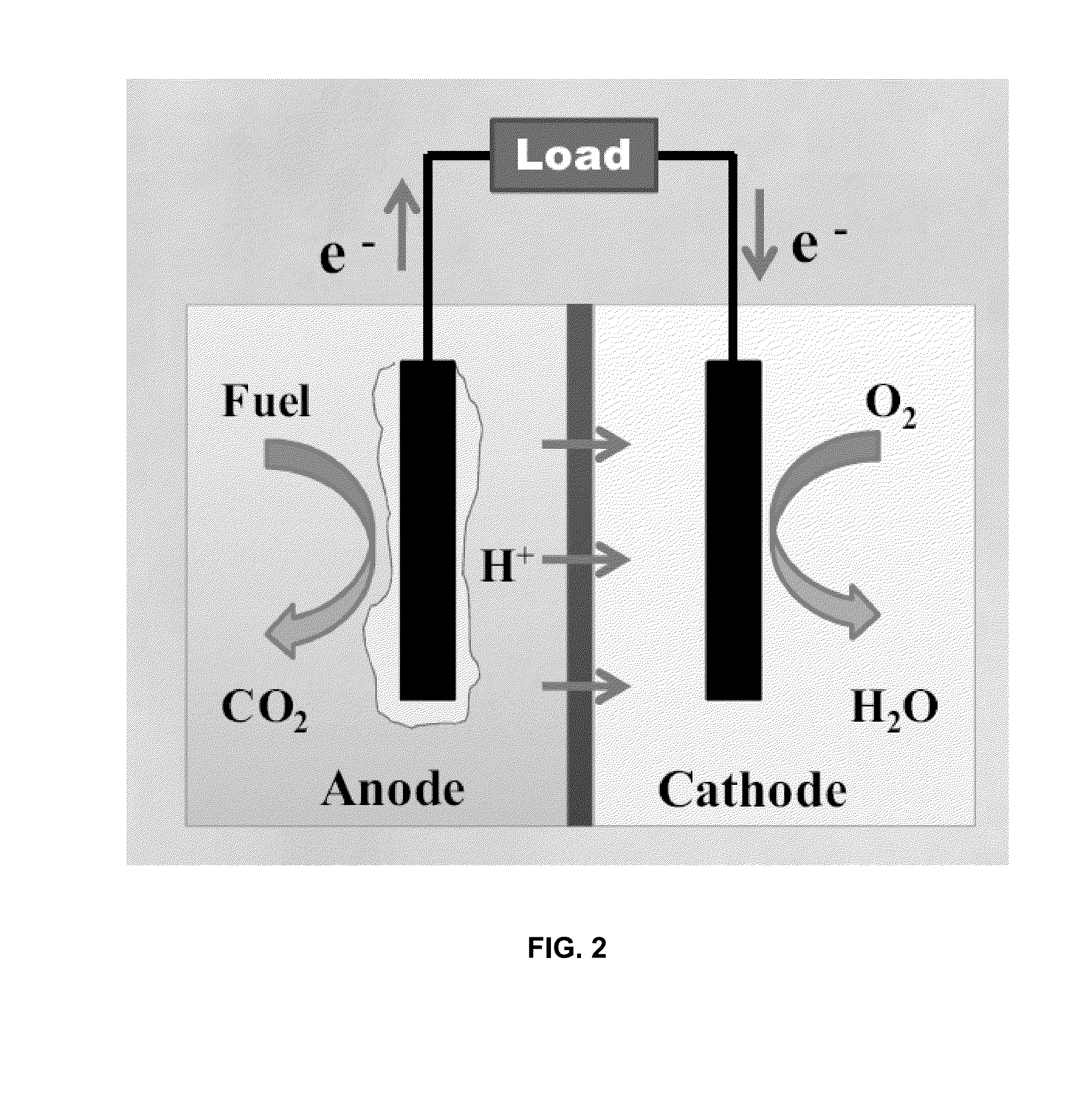
A bioelectrochemical system includes an anode, a saline solution chamber, and a cathode. The anode is at least partially positioned within an anode chamber containing an aqueous reaction mixture including one or more organic compounds and one or more bacteria for oxidizing the organic compounds. The saline solution chamber contains a draw solution and is separated from the anode chamber by a forward osmosis membrane. Water diffuses across the forward osmosis membrane from the aqueous reaction mixture to the draw solution.
Owner:UMW RES FOUND INC
Synthesis of high activity ZSM-48
ActiveCN101801848AMolecular sieve catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationSilicon dioxideHigh activity
A process for producing ZSM-48 comprises crystallizing an aqueous reaction mixture comprising at least one source of silica, at least one source of alumina, at least one source of hydroxyl ions, at least one source of diquaternary alkylammonium, R2+, ions having the formula: (CH3)3N+(CH2)5N+(CH3)3 and optionally ZSM-48 seed crystals, wherein said reaction mixture has a composition including the following molar ratios: R2+:SiO2 less than 0.1 SiO2:Al2O3 less than 100.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
A continuous process for synthesizing oxamide
ActiveCN102267921ALow costSufficient sourceOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationDehydrogenationNitrogen gas
The invention discloses a continuous process for synthesizing oxamide, which belongs to the fields of catalysis, chemical industry, environmental protection and fertilizer. Coal-based synthesis gas is used to obtain H2≥99.0V% hydrogen and industrial CO through pressure swing adsorption separation technology; N2≥99.0V% nitrogen and industrial O2 are obtained through air through cryogenic separation technology. Use H2≥99.0v% hydrogen and N2≥99.0v% nitrogen to mix according to the ratio of N2:H2=1:3, and send them to the ammonia reaction tower to produce synthetic ammonia; industrial CO gas is sent to react with RONO gas after dehydrogenation, oxygen removal, and water removal The tower catalyzes the synthesis of oxalate, and the NO in the reaction tail gas is reacted with industrial O2 and an alcohol-water solution with an alcohol content of ≥10wt% to generate RONO for recycling; the synthesized oxalate and synthetic ammonia are directly sent to the reactor to synthesize oxamide, a slow-acting nitrogen fertilizer, Substituting urea or ammonium bicarbonate for agricultural and animal husbandry production has good economic and social benefits, and is an important development direction of C1 chemical and nitrogen fertilizer industries.
Owner:陈贻盾
Enzymatic peracid production using a cosolvent
InactiveUS20100087528A1High viscositySubstantial loss of perhydrolytic activityInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic active ingredientsSolubilityBleach
Disclosed herein are two-component enzymatic peracid generation systems and methods of using such systems wherein the first component comprises a formulation of at least one enzyme catalyst having perhydrolysis activity, a carboxylic acid ester substrate, and a cosolvent and wherein the second component comprises a source of peroxygen in water. The two components are combined to produce an aqueous peracid formulation useful as, e.g., a disinfecting or bleaching agent. Specifically, organic cosolvents are used to control the viscosity of a substrate-containing component and to enhance the solubility of the substrate in an aqueous reaction formulation without causing substantial loss of perhydrolytic activity of the enzyme catalyst.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Integrated photo-bioelectrochemical systems
ActiveUS20130017415A1Treatment by combined electrochemical biological processesBiochemical fuel cellsOrganic compoundBioreactor
A bioelectricalchemical system includes an anode, an algal bioreactor, and a cathode. The anode is at least partially positioned within an anode chamber containing a first aqueous reaction mixture including one or more organic compounds and one or more bacteria for oxidizing the organic compounds. The algal bioreactor contains a second aqueous reaction mixture including one or more nutrients and one or more algae for substantially removing the nutrients from the second aqueous reaction mixture. The cathode is at least partially positioned within the algal bioreactor.
Owner:UMW RES FOUND INC
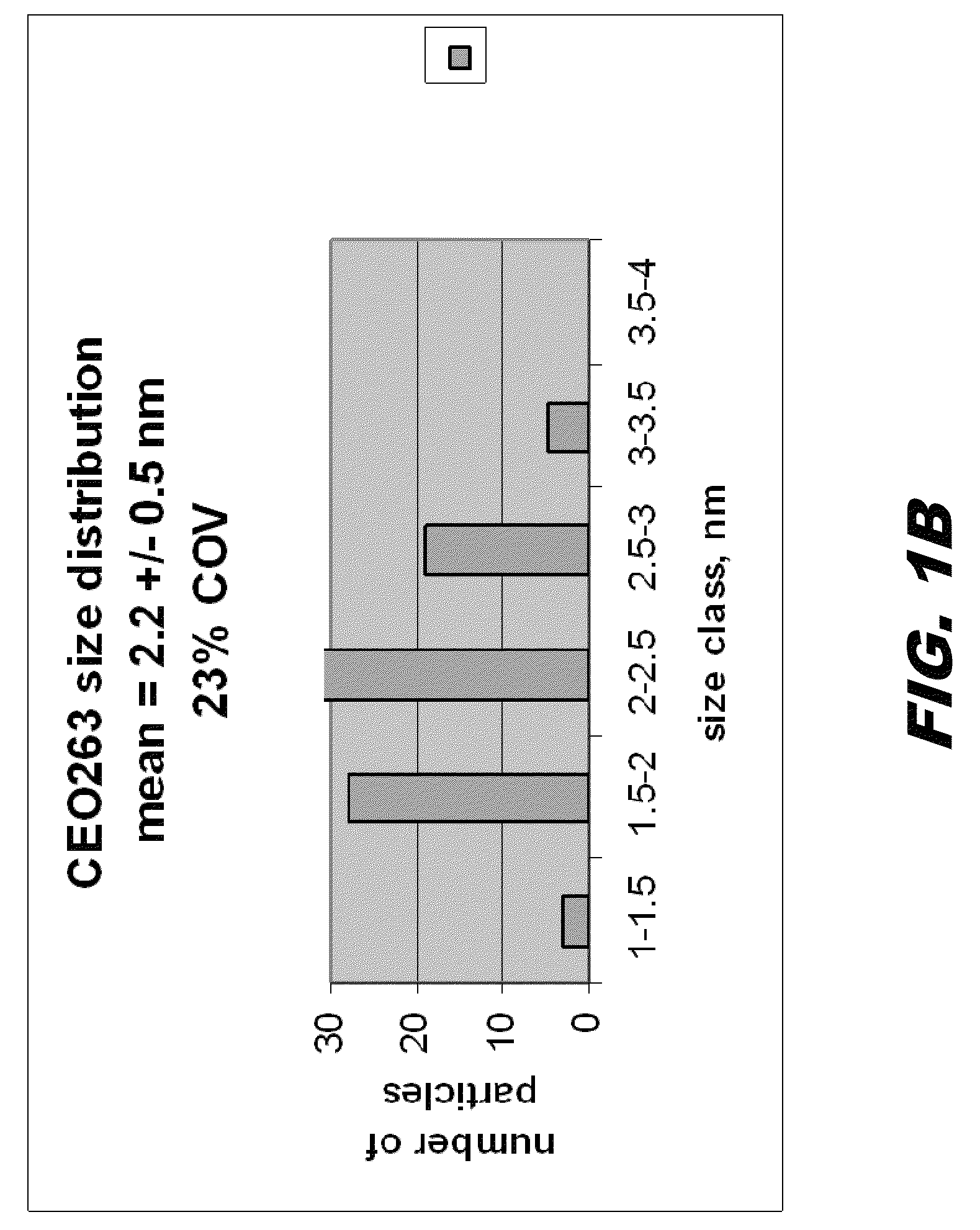
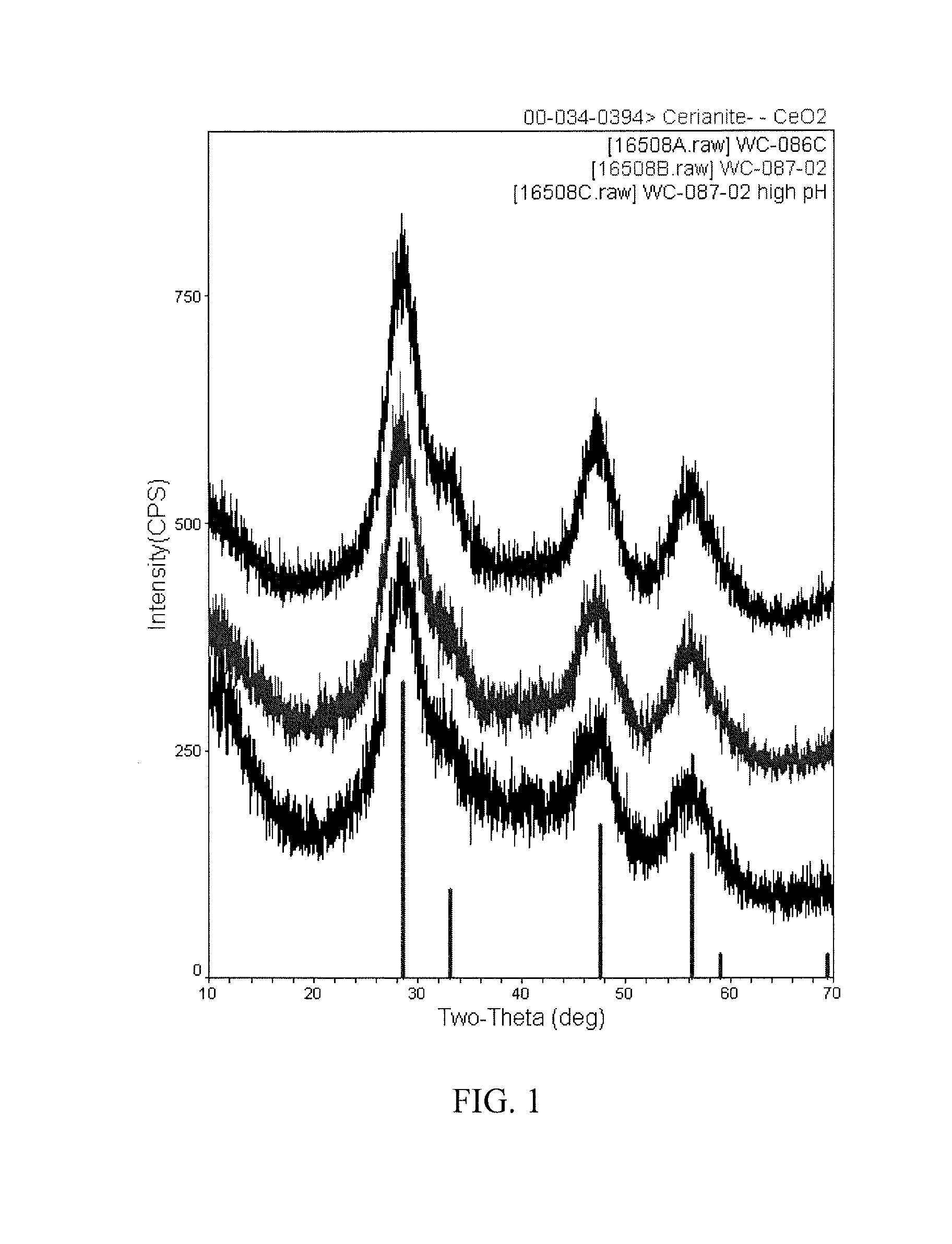
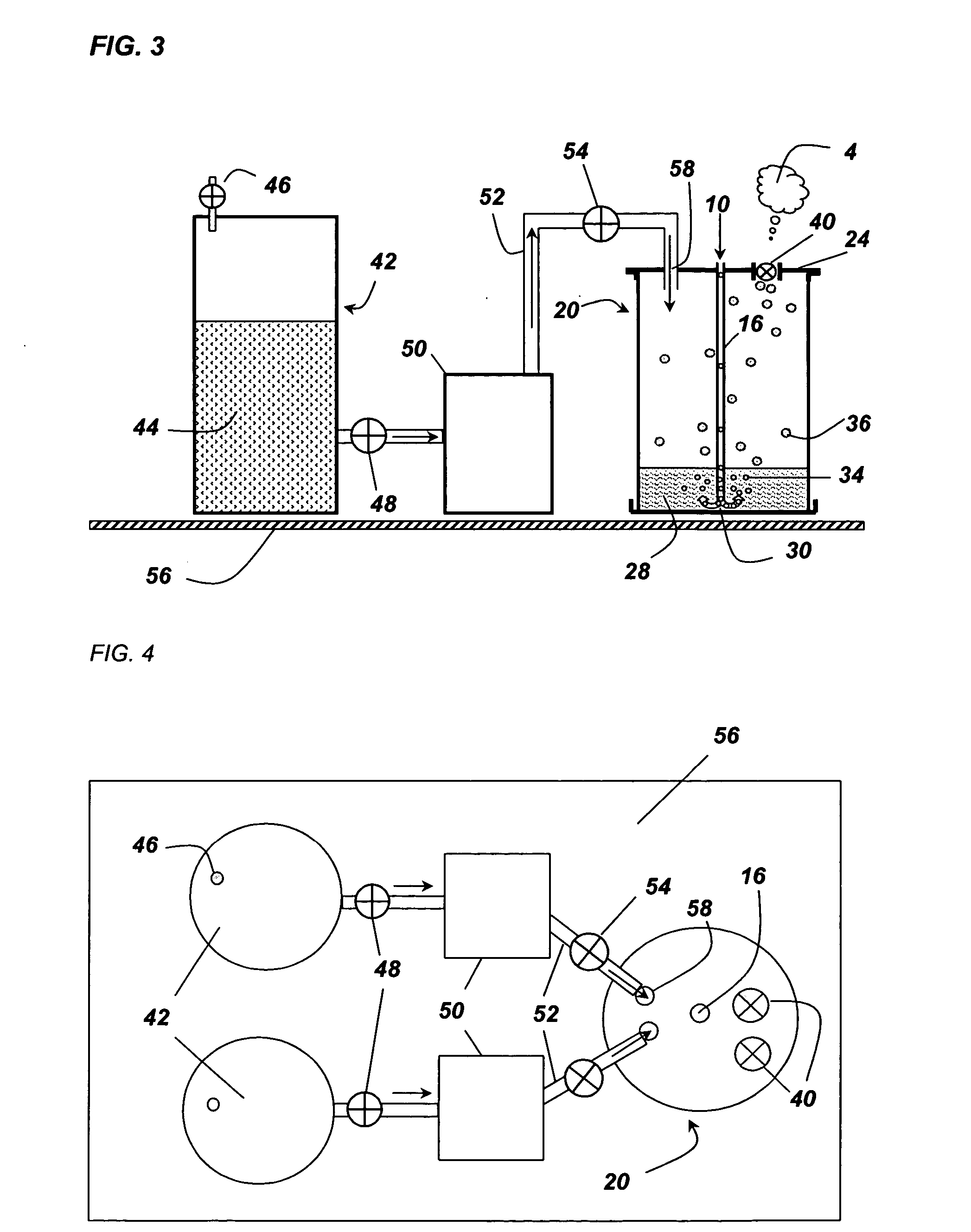
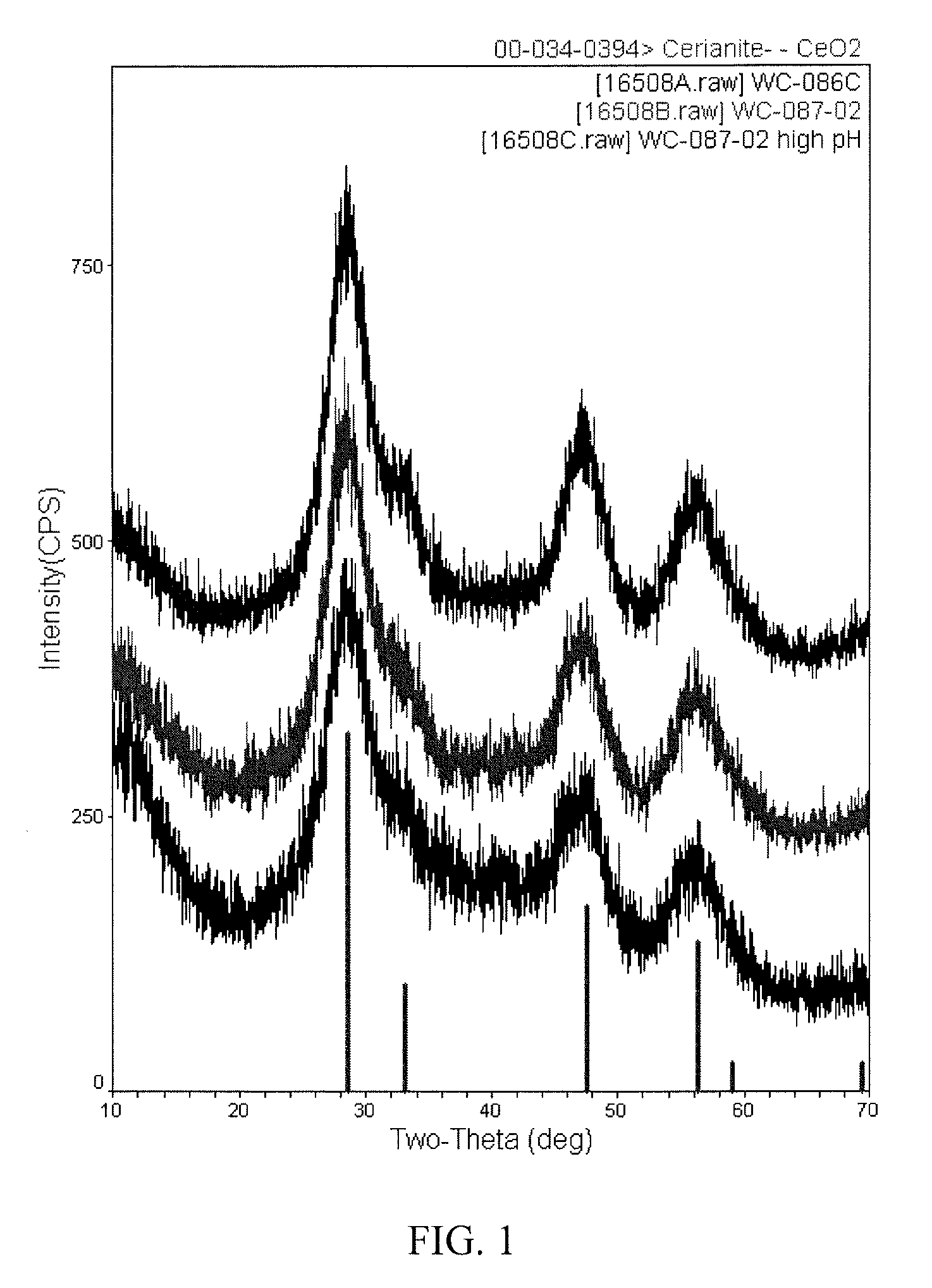
Method of preparing cerium dioxide nanoparticles
A method of making cerium dioxide nanoparticles includes: a) providing an aqueous reaction mixture having a source of cerous ion, a source of hydroxide ion, a nanoparticle stabilizer, and an oxidant at an initial temperature no higher than about 20° C.; b) mechanically shearing the mixture and causing it to pass through a perforated screen, thereby forming a suspension of cerium hydroxide nanoparticles; and c) raising the initial temperature to achieve oxidation of cerous ion to eerie ion and thereby form cerium dioxide nanoparticles having a mean diameter in the range of about 1 nm to about 15 nm. The cerium dioxide nanoparticles may be formed in a continuous process.
Owner:CERION
Method for producing organic acid
InactiveUS20060172401A1Improve filtration efficiencyHigh filtration efficiencyBacteriaOrganic compound preparationOrganic acidOrganic matter
An object to be solved by the present invention is to provide a method for producing organic acid with higher fermentation efficiency. The present invention provides a method for producing organic acid from an organic material by allowing bacterial cell or treated products thereof to act on an aqueous reaction solution containing the above organic material, which is characterized in that after completion of the reaction, the aqueous reaction solution is recovered, cell or treated products thereof are separated from the recovered aqueous reaction solution, and the separated cell or treated products thereof are allowed to act on a fresh aqueous reaction solution, so that the cell or treated products thereof are repeatedly used.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Method for Making Surface Modified Biomedical Devices
InactiveUS20090111942A1Low costFine stepsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationSimple Organic CompoundsPolymer science
Disclosed are methods for making a surface modified biomedical device involving (a) exposing a biomedical device having a plurality of biomedical device surface functional groups to one or more ethylenically unsaturated-containing organic compounds having a reactive group that is co-reactive to the biomedical device surface functional groups of the biomedical device; and (b) graft polymerizing a hydrophilic reactive monomer having a complementary reactive functionality with the ethylenically unsaturated functionalities of the ethylenically unsaturated-containing organic compounds on or near the surface of the biomedical device thus forming a biocompatible surface on the biomedical device. The methods disclosed are two-step methods and do not include any additional surface treatment steps.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Preparation of MFI type crystalline zeolitic aluminosilicate
A process for synthesizing a crystalline aluminosilicate zeolite having an MFI structure comprising crystallizing the zeolite from an alkaline aqueous reaction mixture that comprises SiO2 and Al2O3 or their hydrated derivatives, and an amorphous aluminosilicate nucleating gel with an SiO2 / Al2O3 ratio of from about 10 to less than 20. The reaction mixture does not contain an organic template.
Owner:ALBEMARLE NETHERLANDS BV
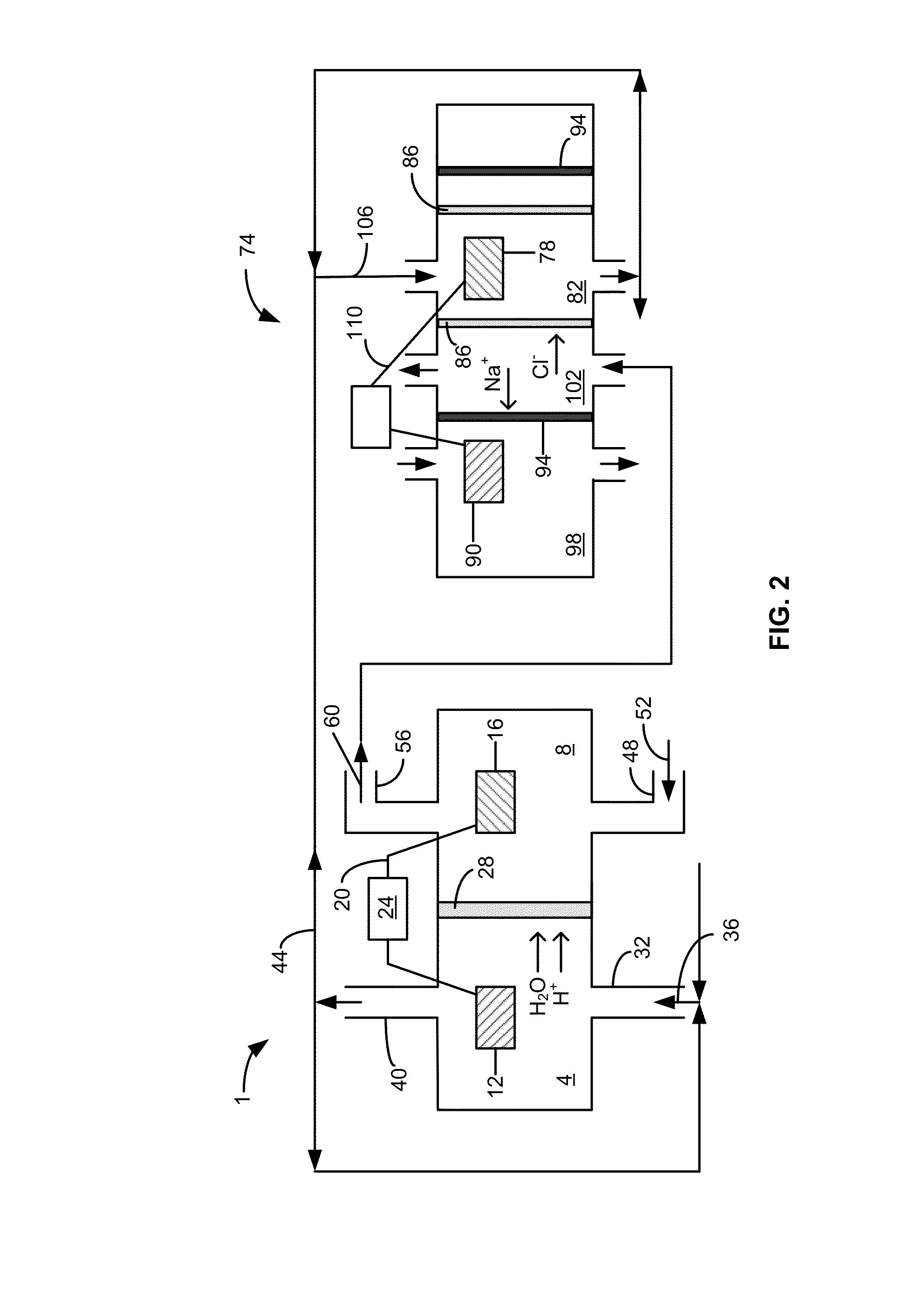
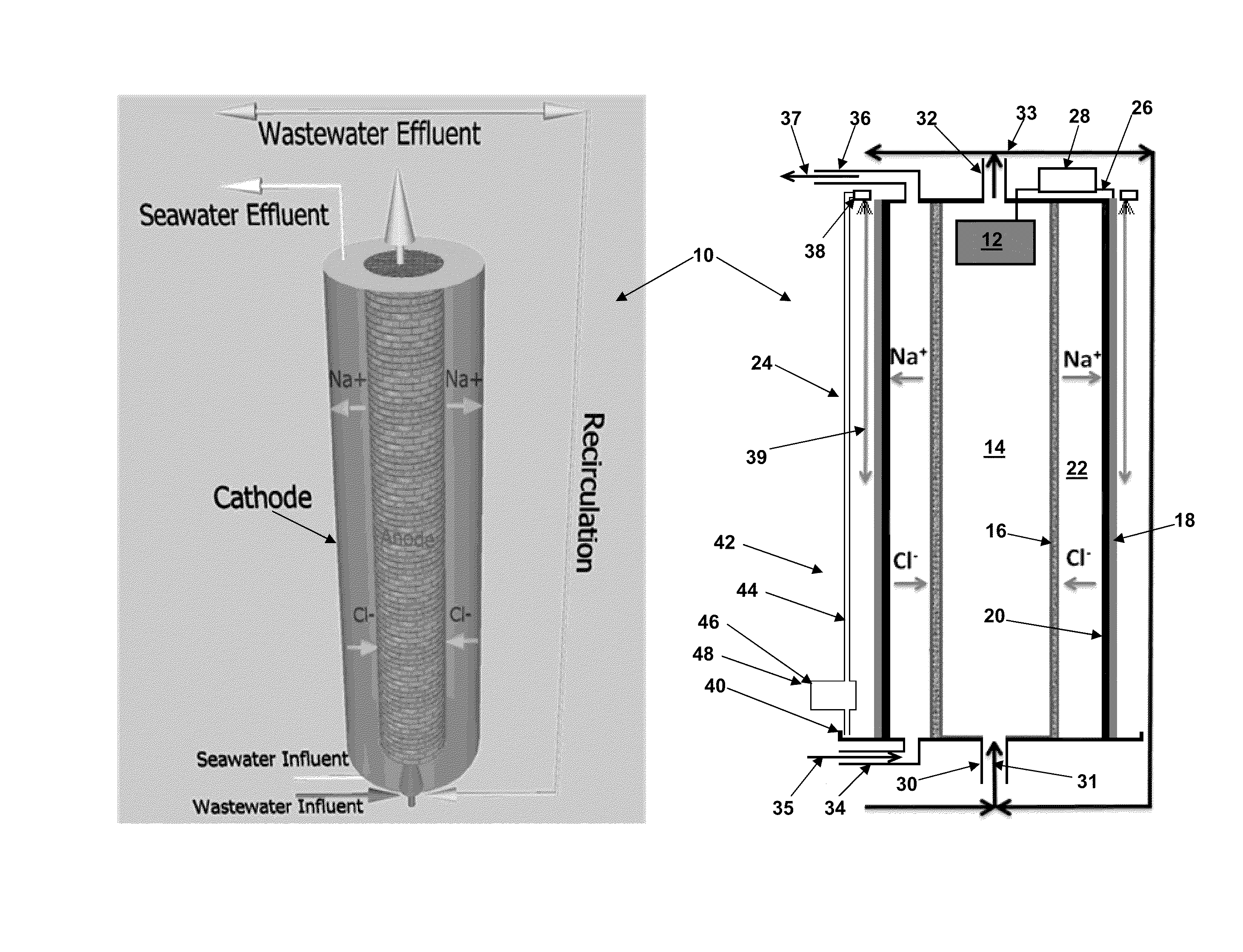
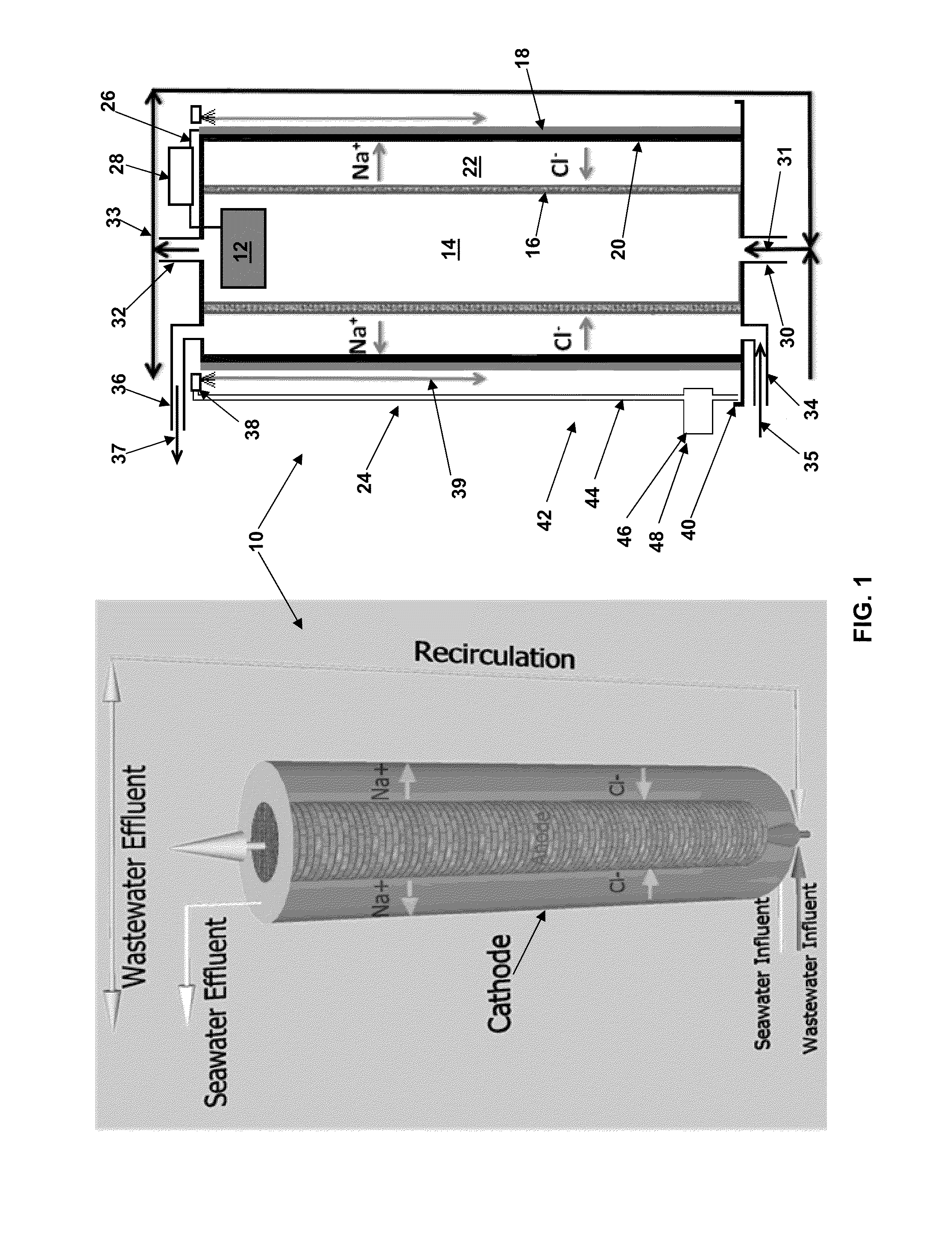
Microbial desalination cells
InactiveUS20110311887A1Other chemical processesTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesSimple Organic CompoundsDesalination
A microbial desalination cell includes an anode, a cathode, a saline solution chamber and a cathode rinsing assembly. The anode is at least partially positioned within an anode chamber for containing an aqueous reaction mixture including one or more organic compounds and one or more bacteria for oxidizing the organic compounds. The cathode is directly exposed to air. The saline solution chamber is positioned between the anode and the cathode, and is separated from the anode by an anion exchange material and from the cathode by a cation exchange material. The cathode rinsing assembly is for rinsing the cathode with a catholyte.
Owner:UMW RES FOUND INC
Cerium-containing nanoparticles
A process for making cerium-containing oxide nanoparticles includes providing an aqueous reaction mixture containing a source of cerous ion, optionally a source of one or more metal ions (M) other than cerium, a source of hydroxide ion, at least one monoether carboxylic acid nanoparticle stabilizer wherein the molar ratio of said monoether carboxylic acid nanoparticle stabilizers to total metal ions is greater than 0.2, and an oxidant at an initial temperature in the range of about 20° C. to about 95° C. Temperature conditions are provided effective to enable oxidation of cerous ion to ceric ion, thereby forming a product dispersion of cerium-containing oxide nanoparticles, optionally containing one or more metal ions (M), Ce1-xMxO2-δ, wherein “x” has a value from about 0.0 to about 0.95. The nanoparticles may have a mean hydrodynamic diameter from about 1 nm to about 50 nm, and a geometric diameter of less than about 45 nm.
Owner:CERION
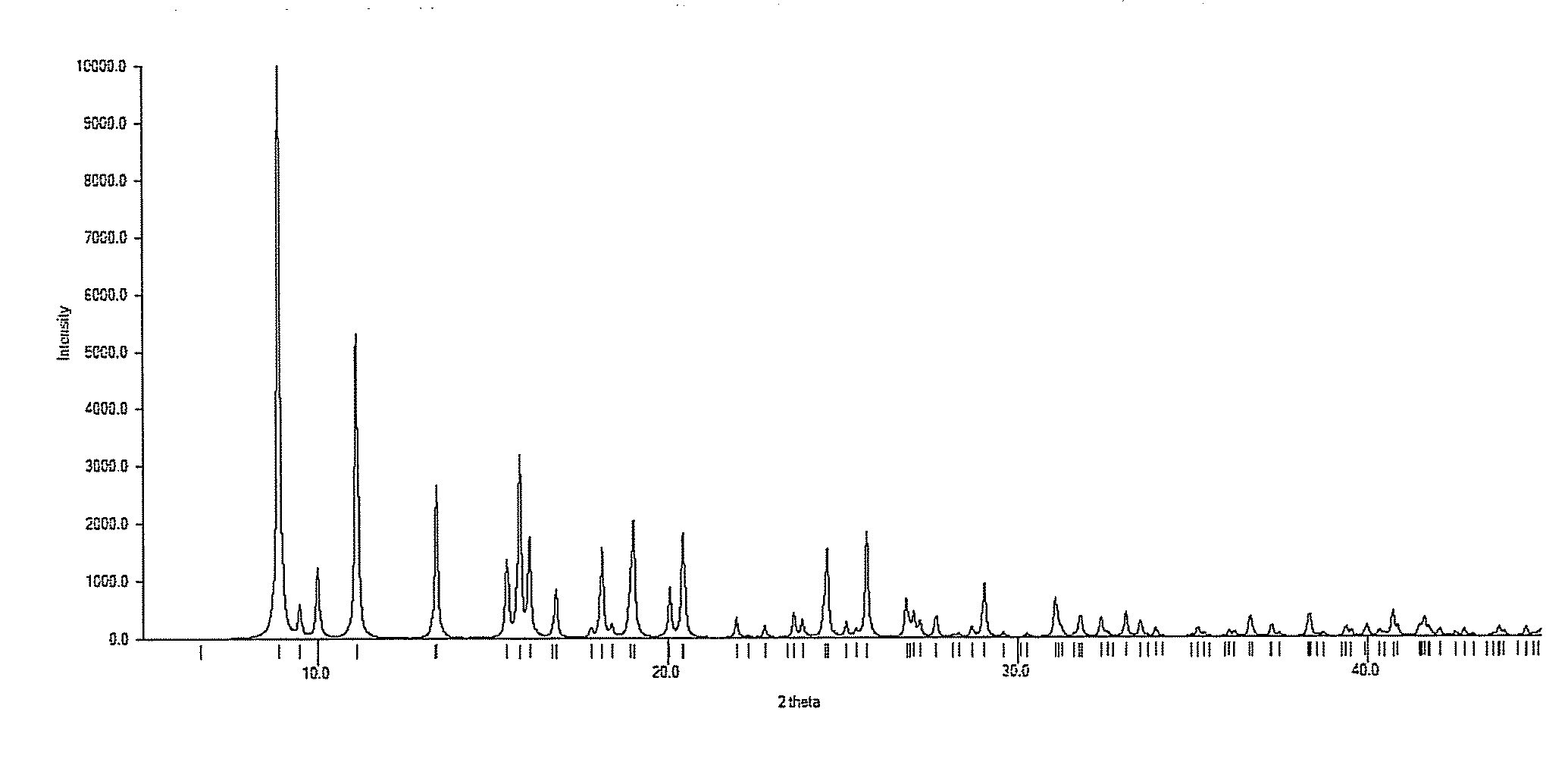
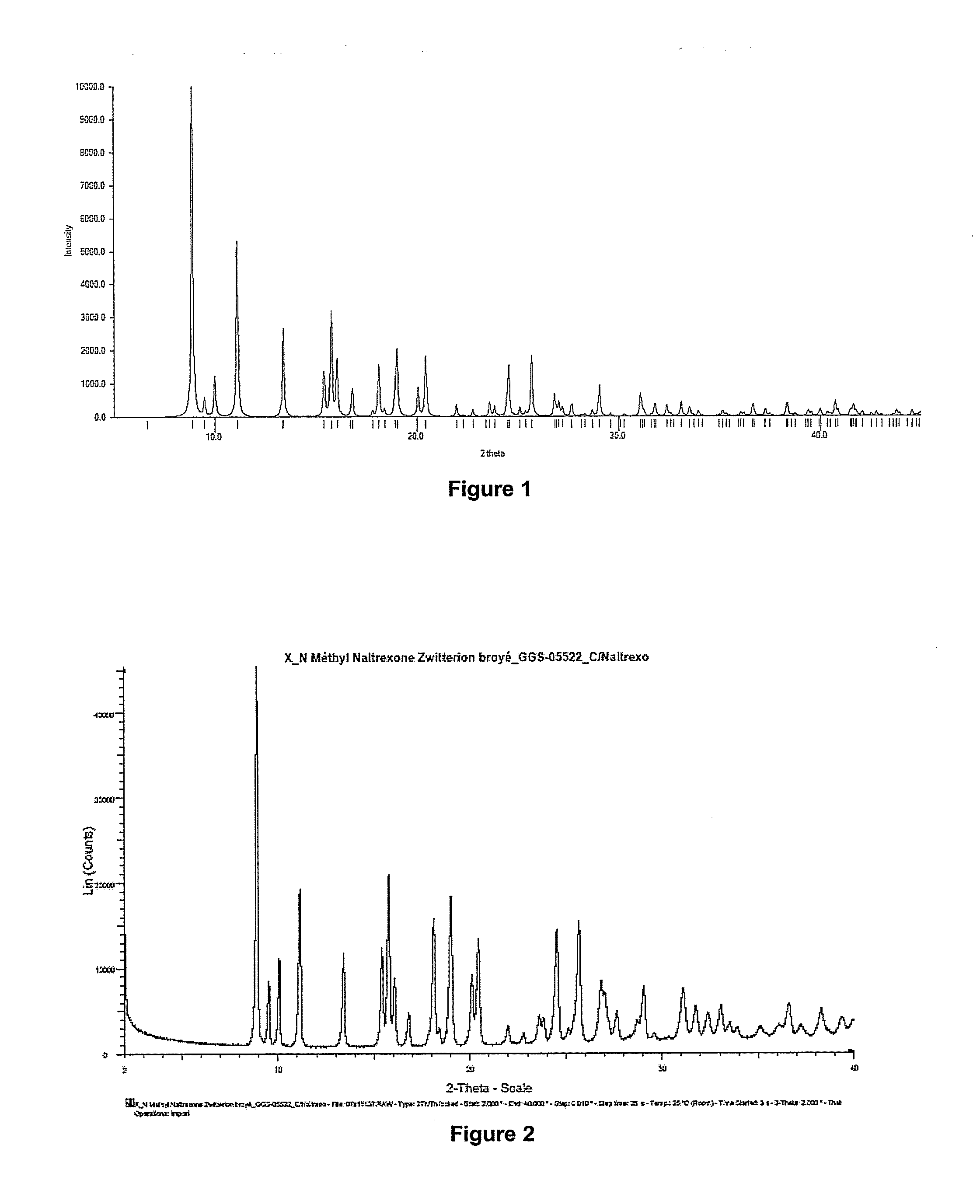
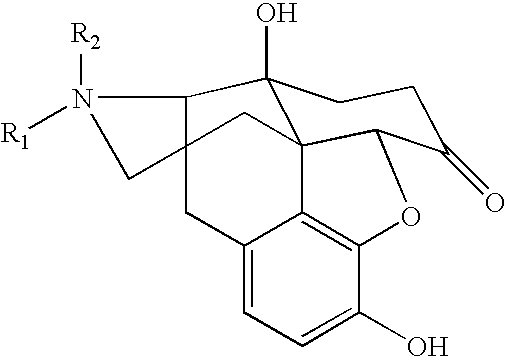
Process for preparing n-alkylnaltrexone halides
The invention relates to a novel process for preparing N-methylnaltrexone bromide, comprising at least the steps consisting in:(i) reacting N-methylnaltrexone methyl sulfate in aqueous solution with an alkaline agent chosen from the group constituted by sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate, cesium carbonate, strontium carbonate and mixtures thereof, for a pH of the aqueous reaction medium of between 7 and 10, and then in(ii) reacting the product thus obtained with hydrobromic acid, which is added for a pH of the aqueous reaction medium of between 0.5 and 5, in order thus to obtain the N-methylnaltrexone bromide.
Owner:SANOFI SA
Method for producing redox-active Ti(IV) coordination compounds
ActiveUS9409842B1Low costMore economical)Organic compound preparationGroup 4/14 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesCompound aMetal
A method for producing an aqueous solution of a redox-active coordination compound of a transition metal which can be used directly as an electrolyte in a flow battery wherein the method comprises reacting a freshly precipitated hydrous transition metal oxide with a chelating agent and a base in an aqueous reaction medium to produce a solution of the corresponding redox-active transition metal coordination compound.
Owner:TRONOX LLC
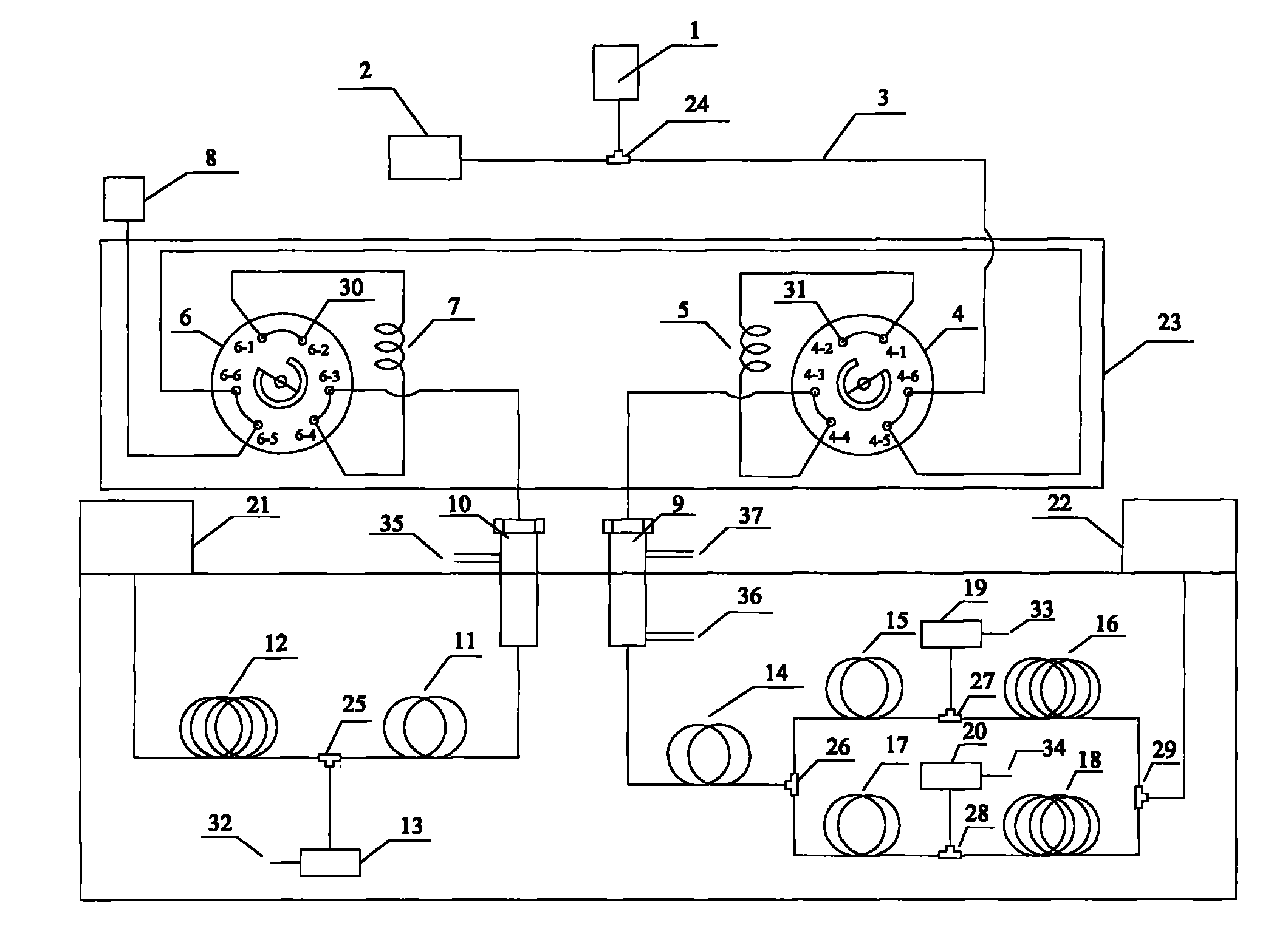
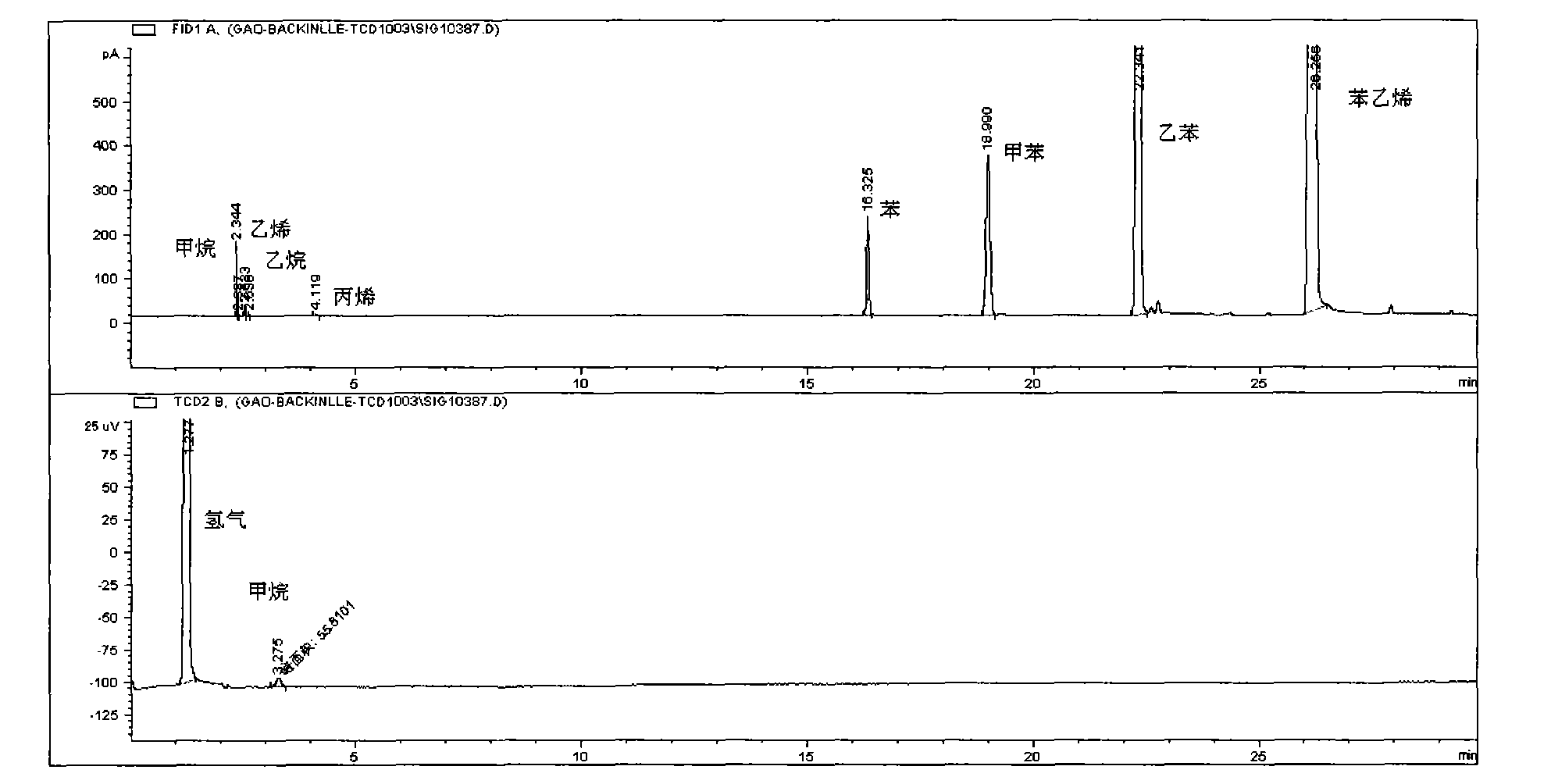
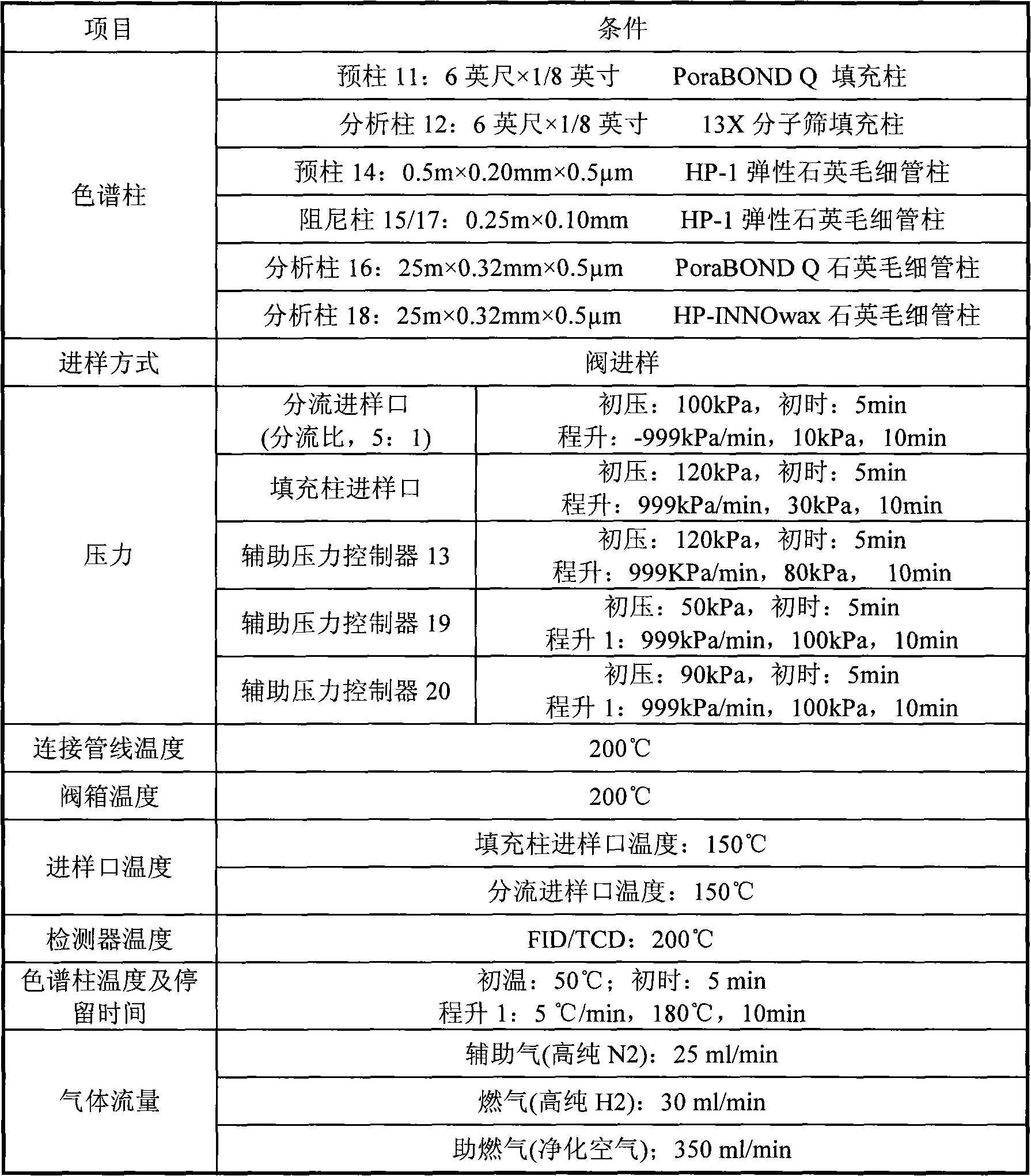
Online chromatographic analysis method
The invention relates to an online chromatographic analysis method, which mainly solves the problem of difficult simultaneous analysis of a mixture of hydrogen / permanent gases, non-aromatic hydrocarbon and aromatic hydrocarbon in the process of analyzing an aqueous reaction system and solves the water interference problem during analysis in the conventional chromatographic analysis technology. A technical scheme of two serially connected analysis systems, namely a hydrogen / permanent gas analysis system and a non-aromatic hydrocarbon and aromatic hydrocarbon analysis system is adopted, so the online chromatographic analysis method well solves the problem of the simultaneous analysis of the mixture of hydrogen / permanent gases, non-aromatic hydrocarbon and aromatic hydrocarbon and the water interference problem during analysis, and can be used for online chromatographic analysis of the aqueous mixture of hydrogen / permanent gases, non-aromatic hydrocarbon and aromatic hydrocarbon.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Apparatus and delivery of medically pure oxygen
Owner:KWIVIK MEDICAL INC
Catalyst To Attain Low Sulfur Gasoline
ActiveUS20090230026A1Catalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsGasoline fuelHydrodesulfurization
This invention relates to a hydrodesulfurization catalyst, a method for preparing the catalyst, and a method for the preparation of low sulfur gasoline fuel with minimal loss of RON. The catalyst particles include a group VIB metal and a support material having relatively high surface area, and optionally includes one or more group VIIIB metal. The method for preparing the catalyst allows for greater loading of the active metal species on the surface of the support material under aqueous reaction conditions.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Nanoceria for the treatment of oxidative stress
A process for making nanoparticles of biocompatible materials is described, wherein an aqueous reaction mixture comprising cerous ion, citric acid and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid in a predetermined ratio, an oxidant, and water is provided along with temperature conditions to directly form, without isolation, a stable dispersion of cerium oxide nanoparticles. These biocompatible cerium oxide nanoparticles may be used to prevent and / or treat oxidative stress related diseases, such as stroke, relapse / remitting multiple sclerosis, chronic-progressive multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and ischemic reperfusion injury.
Owner:CERION
Curable Polymer Latex Compositions for the Manufacture of Rubber Articles
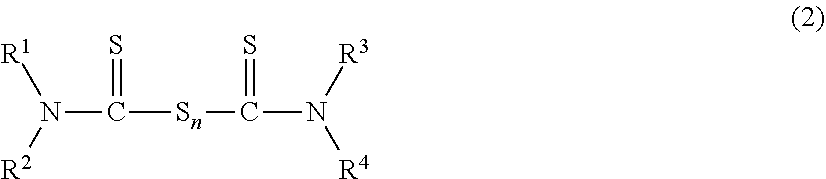
A curable polymer latex composition obtainable by:(a) subjecting a monomer mixture comprisingi. at least one conjugated diene;ii. at least one ethylenically unsaturated nitrile;iii. optionally at least one ethylenically unsaturated acid;iv. optionally at least one further ethylenically unsaturated compound different from any of the compounds (i)-(iii);to free-radical emulsion polymerization in an aqueous reaction medium to form a raw polymer latex; and(b) allowing the obtained raw latex to mature in the presence of at least one thiocarbonyl-functional compound, wherein the at least one thiocarbonyl-functional compound is present in an amount of at least 0.05 wt.-%, based on the total amount of monomers subjected to free-radical emulsion polymerization in step (a), and(c) optionally compounding the matured polymer latex with one or more cross-linking agent. Methods for making such curable polymer latex composition or rubber articles made therefrom, respectively.
Owner:SYNTHOMER SDN BHD
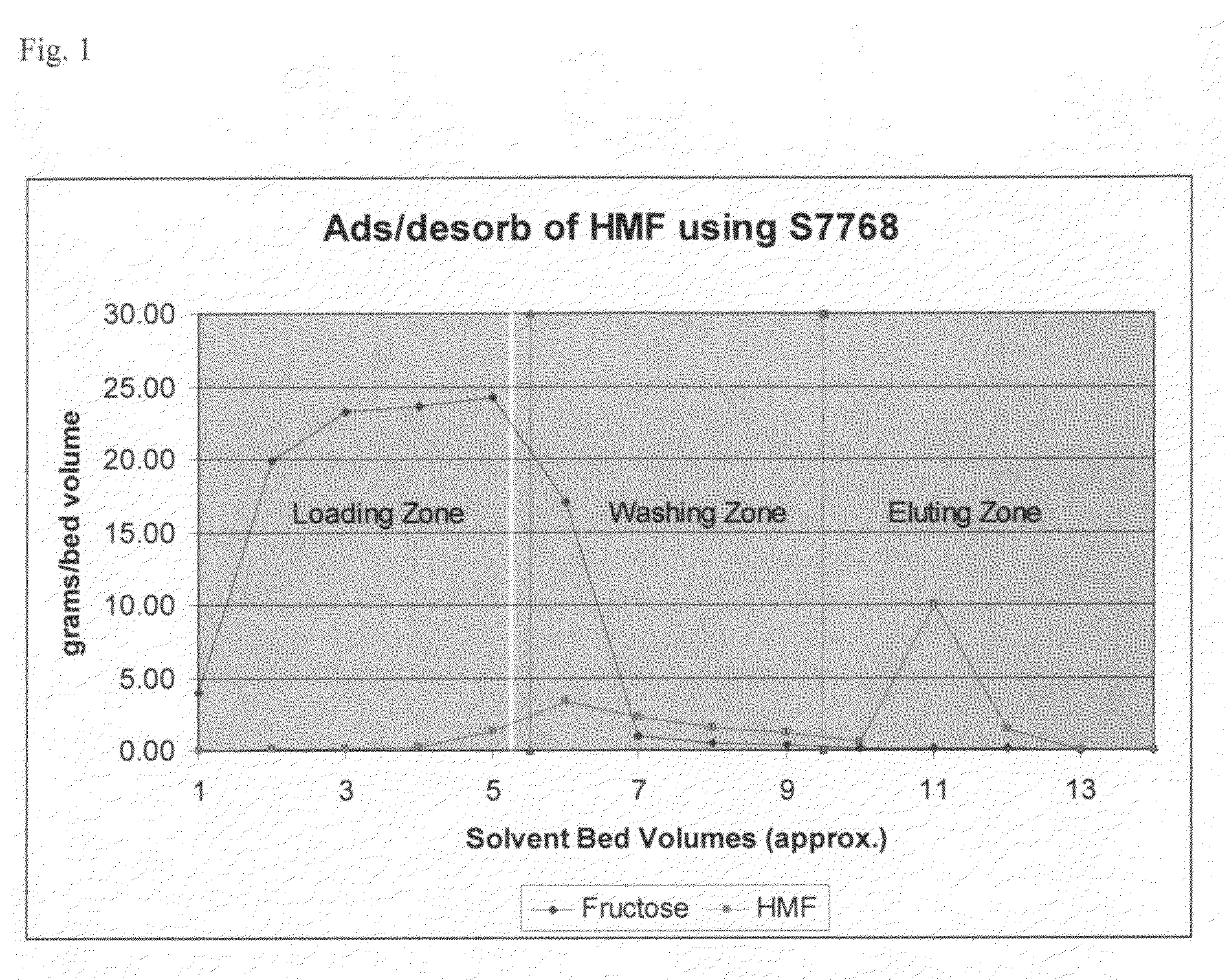
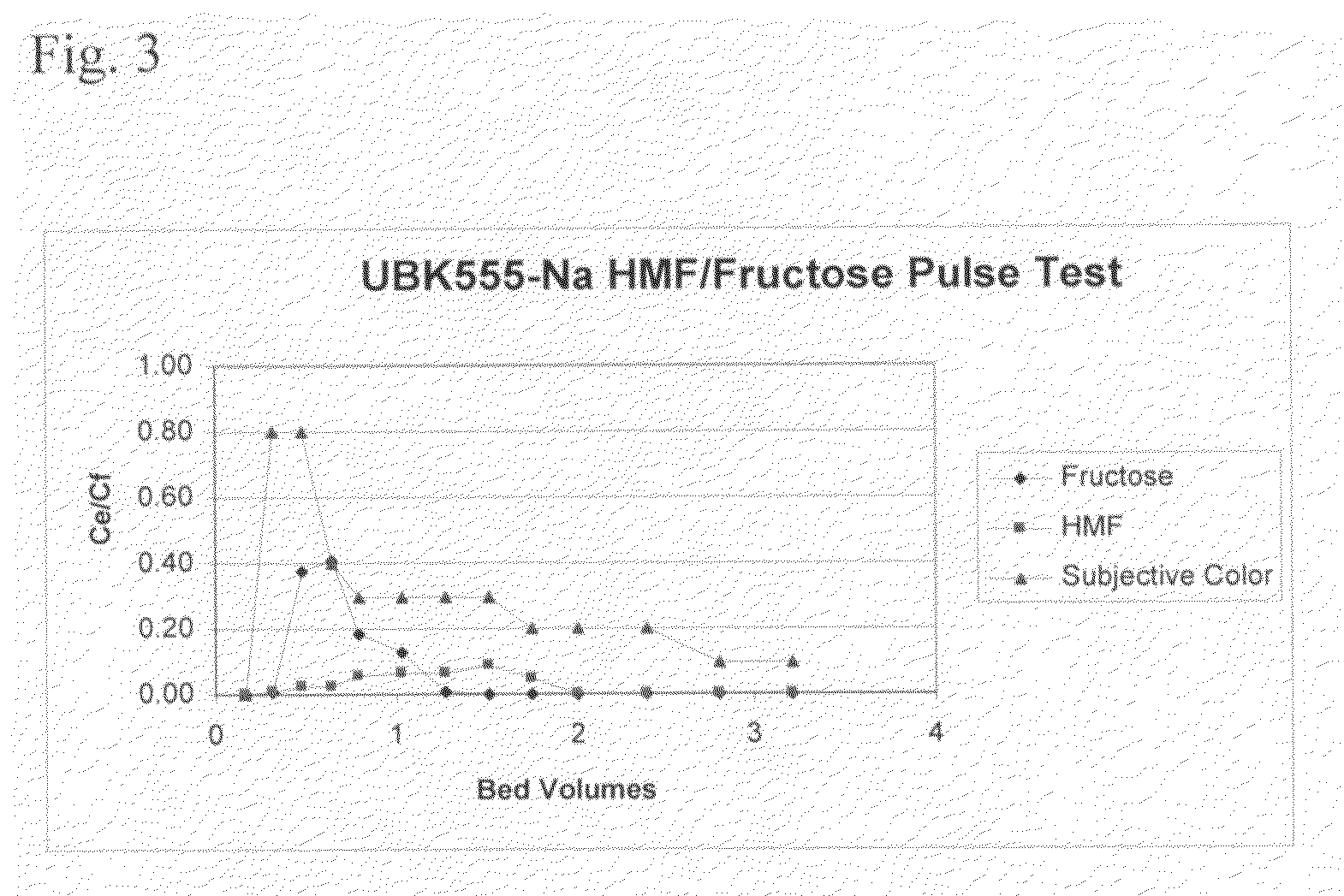
Method for purifying hydroxymethylfurfural using non-functional polymeric resins
ActiveUS7897794B2High puritySubstantial reduction in furfuralOrganic chemistryFructoseOrganic solvent
Disclosed are methods of at least partially purifying HMF from an aqueous mixture containing reactants and products of HMF synthesis from fructose that relies on use of non-functional polymeric resins. A first type of non-functional polymeric resin preferentially adsorbs HMF relative to fructose and is used to remove a majority of fructose from the reaction mixture. HMF is desorbed from the first non-functional polymeric resin with an organic solvent such as acetone. A second type of non-functional polymeric resin preferential adsorbs furfural from an aqueous reaction mixture allowing HMF to pass through. In one embodiment, these non-functional polymeric resins may be used alone in combination with each other to obtain HMF of high purity. In other embodiments, one or more of the foregoing non-functional polymeric resin resins is used in combination with cation exchange chromatography to still further purify the HMF.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
Process for the epoxidation of olefins
The present invention refers to a continuos process for the epoxidation of olefins with hydrogen peroxide in presence of a heterogeneous catalyst promoting the epoxidation reaction, whereby the aqueous reaction mixture comprises: i) an olefin; ii) hydrogen peroxide; iii) less than 100 wppm of alkali metals, earth alkali metals, both irrespective whether in ionic, complex or covalently bonded form, bases or cations of bases having a pkB of less than 4.5, or combinations thereof; and iv) at least 100 wppm of bases or cations of bases having a pkB of at least 4.5 or combinations thereof, whereby the wppm are based on the total weight of hydrogen peroxide in the reaction mixture.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH +1
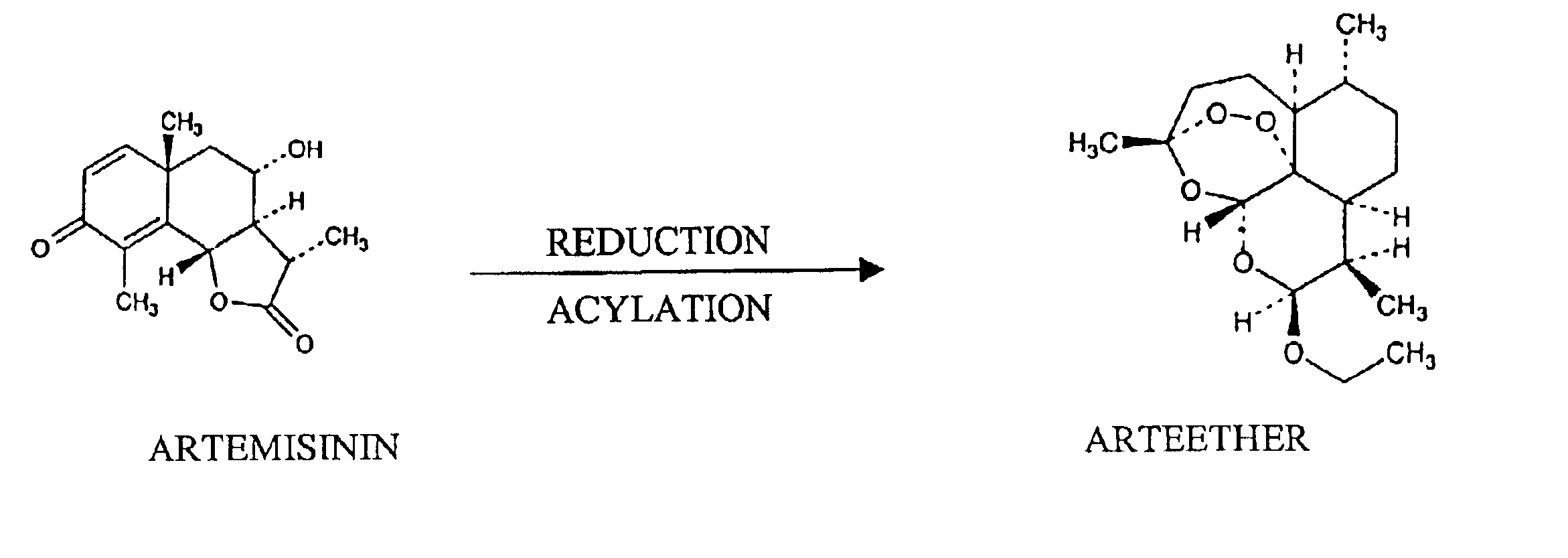
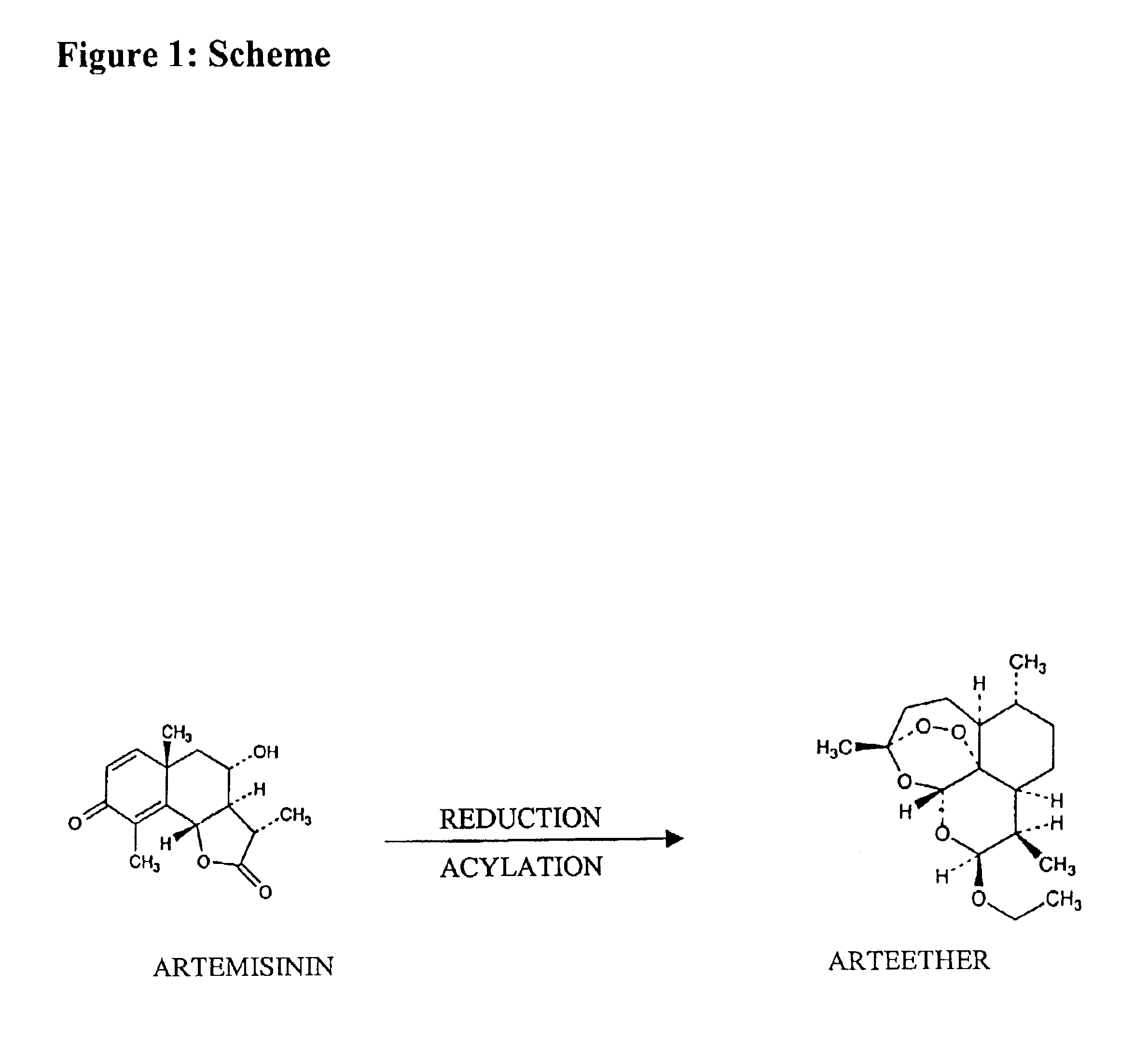
Single pot conversion of artemisinin into arteether
The present invention provides a method for the preparation of arteether from artemisinin in one pot in just about 4 hours comprising reduction of artemisinin into dihydroartemisinin by less quantity of sodium borohydride in ethanol at room temperature in the presence of a novel polyhydroxy catalyst, acylation of dihydroartemisinin in the presence of an acid catalyst, extraction of arteether from an aqueous reaction mixture using 1% ethyl acetate in n-hexane followed by workup and purification of the impure arteether to yield 80-86% (w / w) pure alpha, beta arteether.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Arsenic analysis
InactiveUS6696300B1Increase ratingsSimple methodWithdrawing sample devicesTesting waterArsineImproved method
An improved method for the analysis of arsenic in an aqueous sample, is disclosed. In accordance with the inventive method, arsenic is reduced to arsine gas in an acidic aqueous reaction environment and in the presence of an effective amount of an agent for increasing the rate of arsine gas production. Beneficially, metal cations are used as rate-increasing agents.
Owner:IND TEST SYST
Aqueous polymer dispersion
InactiveUS20070179240A1High viscosityImprove the level ofCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsWater insolublePolymer chemistry
The invention provides a process for preparing an aqueous dispersion of water insoluble heteropolymeric particles comprising polymerising in an aqueous reaction medium ethylenically unsaturated monomers, said ethylenically unsaturated monomers comprising ionisable ethylenically unsaturated monomers and non-ionisable hydrophilic ethylenically unsaturated monomers, to form said heteropolymeric particles dispersed in said aqueous reaction medium, wherein the monomers in said reaction medium at any point in time comprise less than 5 weight % of ionisable ethylenically unsaturated monomer, wherein for at least a part of the polymerisation the monomers in said reaction medium have a composition which is maintained with an ionisable ethylenically unsaturated monomer content of from 0.5 to less than 5 weight % throughout polymerisation of at least 30 weight % of the total amount of monomers polymerised to form the heteropolymeric particles, and wherein the total amount of non-ionisable hydrophilic ethylenically unsaturated monomers and ionisable ethylenically unsaturated monomers polymerised constitutes at least 75 weight % of the total amount of monomers polymerised to form the heteropolymeric particles, a method of preparing a paint comprising conventional paint additives and the aqueous dispersion of water insoluble heteropolymeric particles of the invention, and a novel aqueous dispersion of water insoluble heteropolymeric particles.
Owner:DULUXGROUP AUSTRALIA
Method and apparatus for microbial decontamination
InactiveUS20050079123A1Simplified generationBiocideLiquid-gas reaction as foam/aerosol/bubblesChlorine dioxideGas release
A process and apparatus is provided for generating chlorine dioxide gas for the fumigation of enclosed spaces that includes adding reactants for generation of chlorine dioxide by dropwise addition to an aqueous reaction medium in a sealed reaction chamber while bubbling a motive gas through the aqueous reaction medium, whereby the motive gas releases the generated chlorine dioxide gas from the aqueous reaction medium and drives the release of chlorine dioxide gas from reaction chamber.
Owner:SHULER ROBERT K
Nanoceria for the treatment of oxidative stress
A process for making nanoparticles of biocompatible materials is described, wherein an aqueous reaction mixture comprising cerous ion, citric acid and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid in a predetermined ratio, an oxidant, and water is provided along with temperature conditions to directly form, without isolation, a stable dispersion of cerium oxide nanoparticles. These biocompatible cerium oxide nanoparticles may be used to prevent and / or treat oxidative stress related diseases, such as stroke, relapse / remitting multiple sclerosis, chronic-progressive multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and ischemic reperfusion injury.
Owner:CERION
Lewis and bronsted-lowry acid-catalyzed production of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) from glucose
Described is a process to make hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) from glucose. The process includes the steps of reacting a feedstock solution comprising glucose, in the presence of a homogeneous Brønsted acid catalyst and a homogeneous Lewis acid catalyst, in a reaction vessel containing a biphasic reaction medium. The reaction medium includes an aqueous reaction solution and a substantially immiscible organic extraction solution. HMF is produced in the aqueous reaction solution and extracted into the organic extraction solution.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +1
De-oxygenation treatment for noble metal on carbon catalysts used in liquid phase oxidation reactions
InactiveUS6927304B2Extended service lifeIncrease resistanceGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsLiquid mediumOxidative cleavage
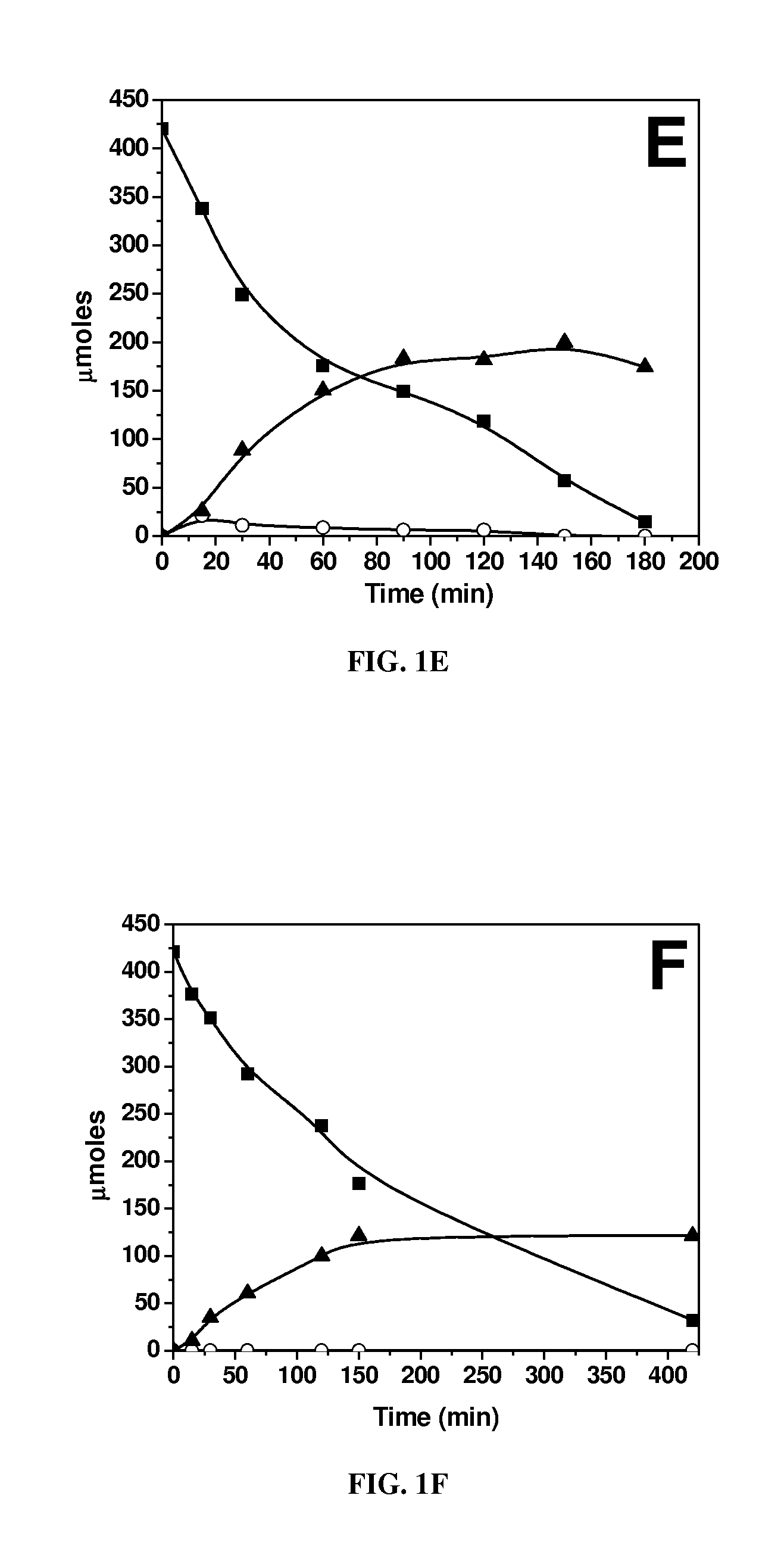
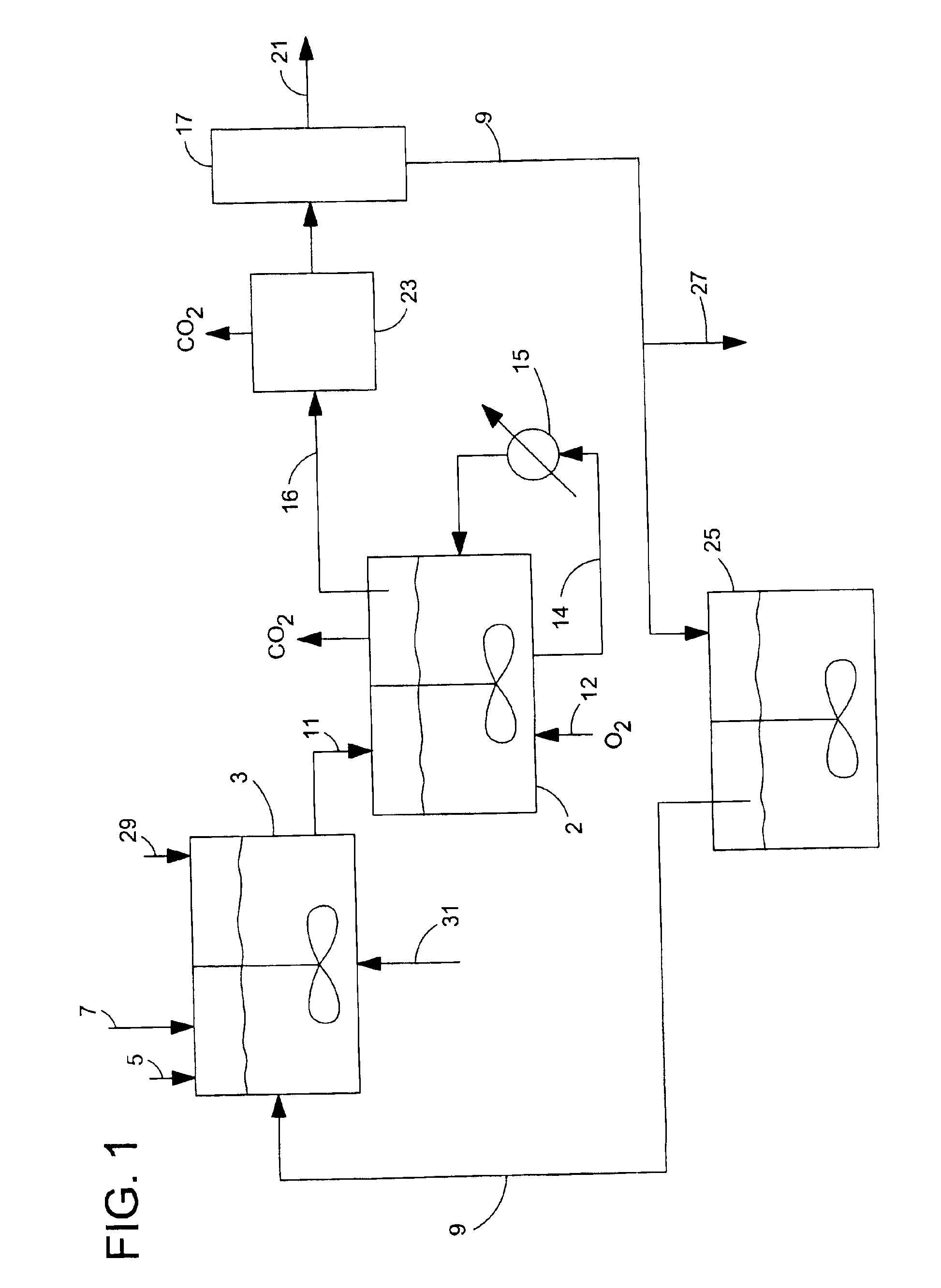
A treatment for de-oxygenating a noble metal on carbon catalyst used in liquid phase oxidation reactions which includes exposing the catalyst to a non-oxidizing environment. The de-oxygenation treatment improves catalyst performance and is particularly suited for noble metal on carbon catalysts used to catalyze the oxidative cleavage of a carboxymethyl substituent from an N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid substrate in an aqueous reaction mixture using an oxygen-containing gas to produce an N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine product. In one embodiment, the catalyst is exposed to a non-oxidizing environment by introducing a non-oxidizing gas and / or reducing gas into a slurry comprising the catalyst in contact with a liquid medium.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com