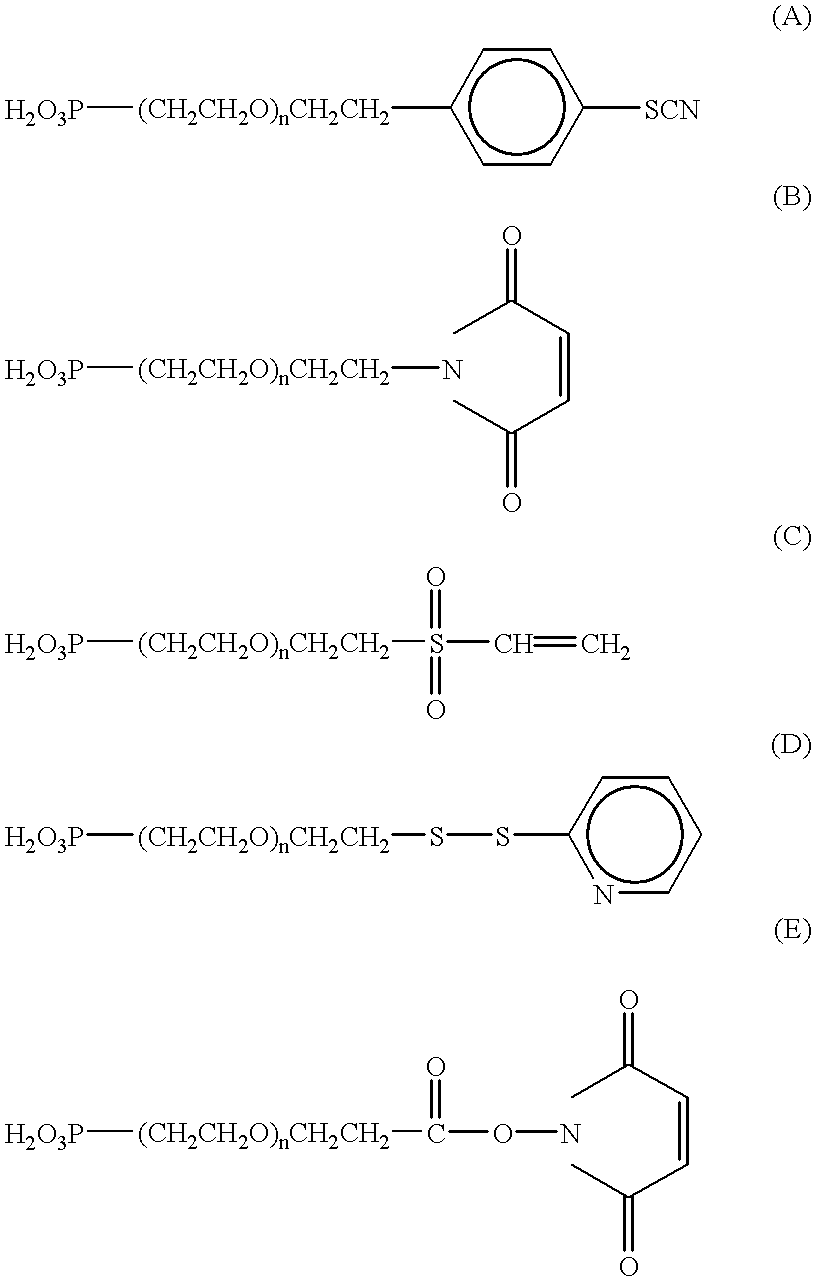
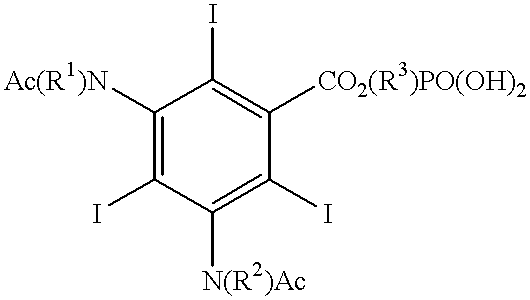
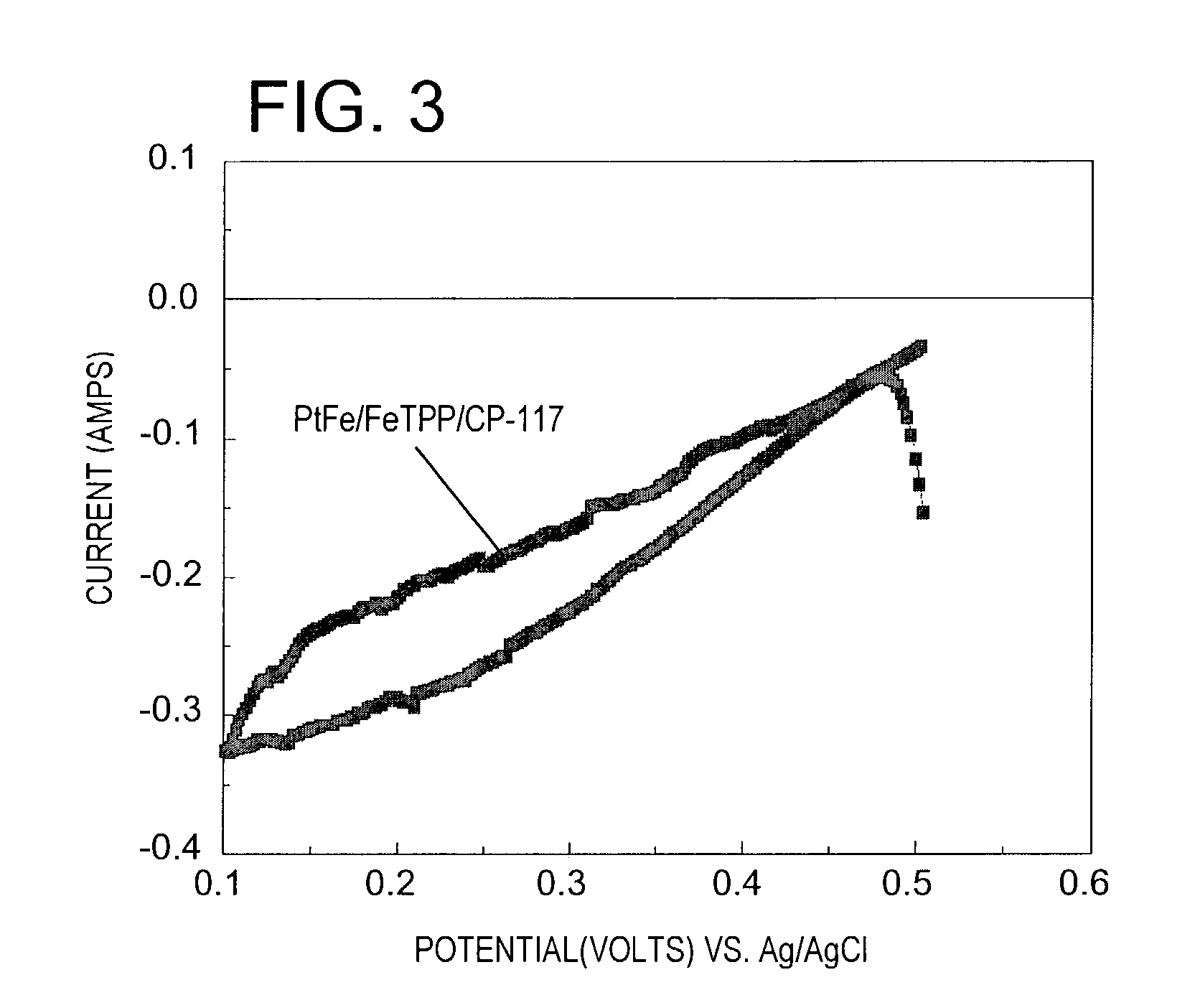
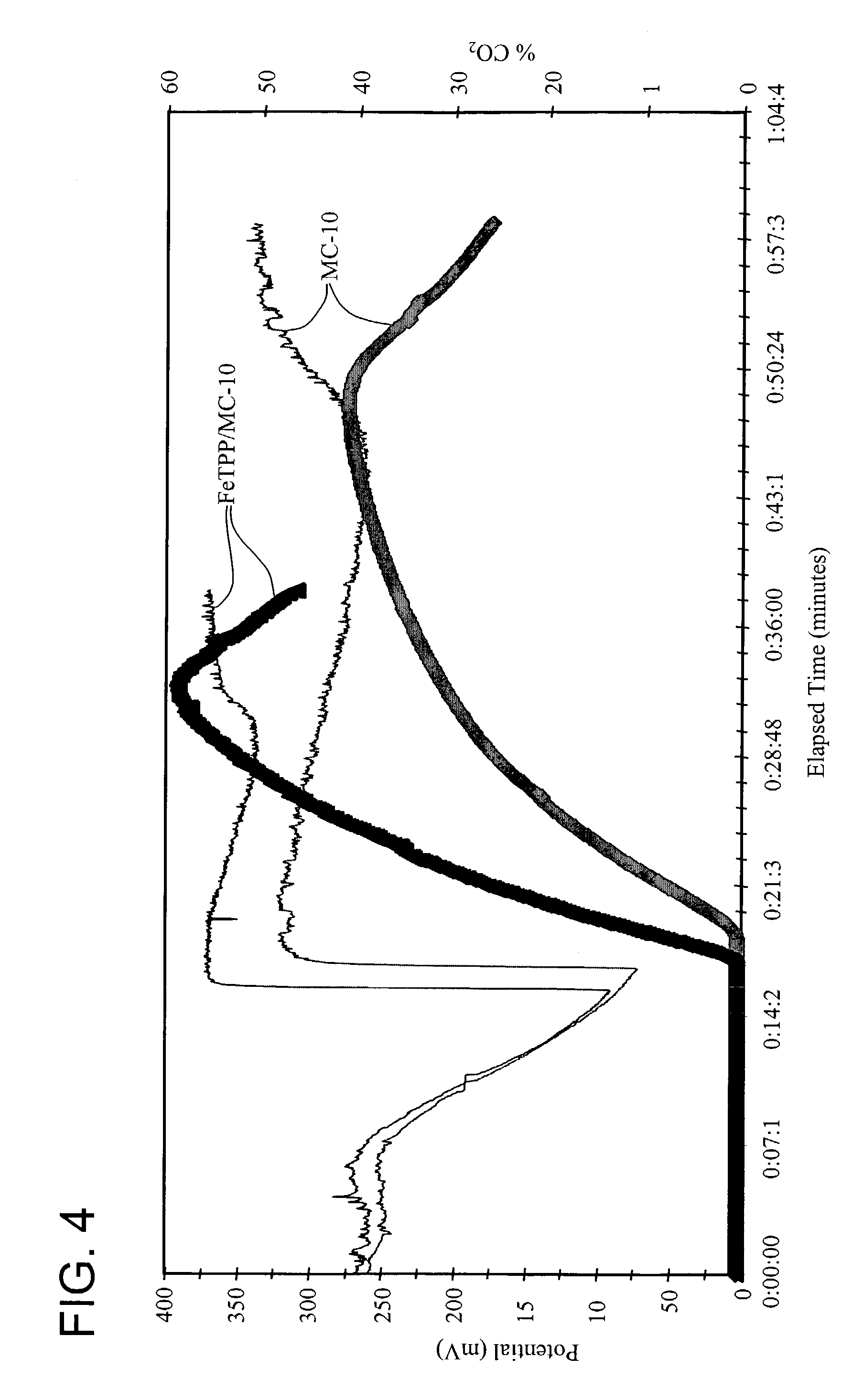
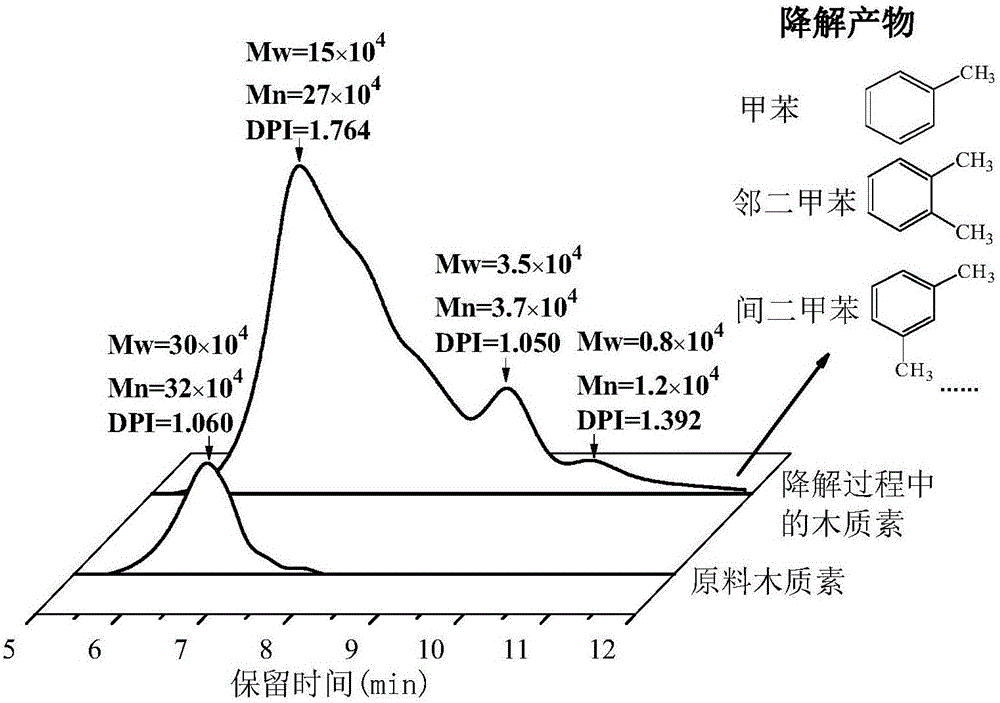
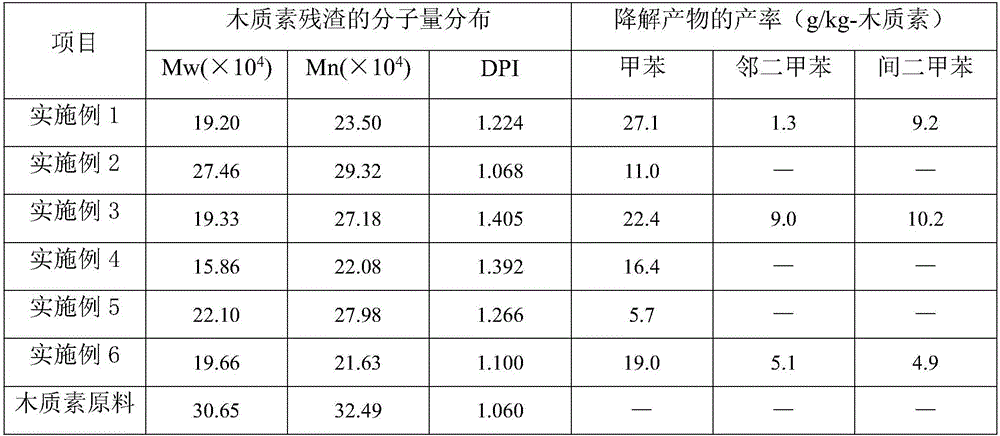
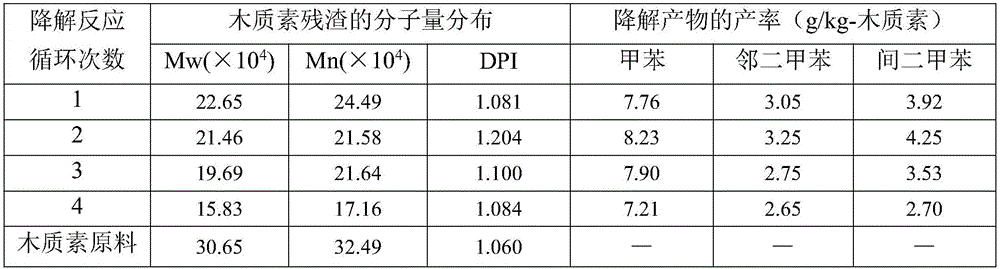
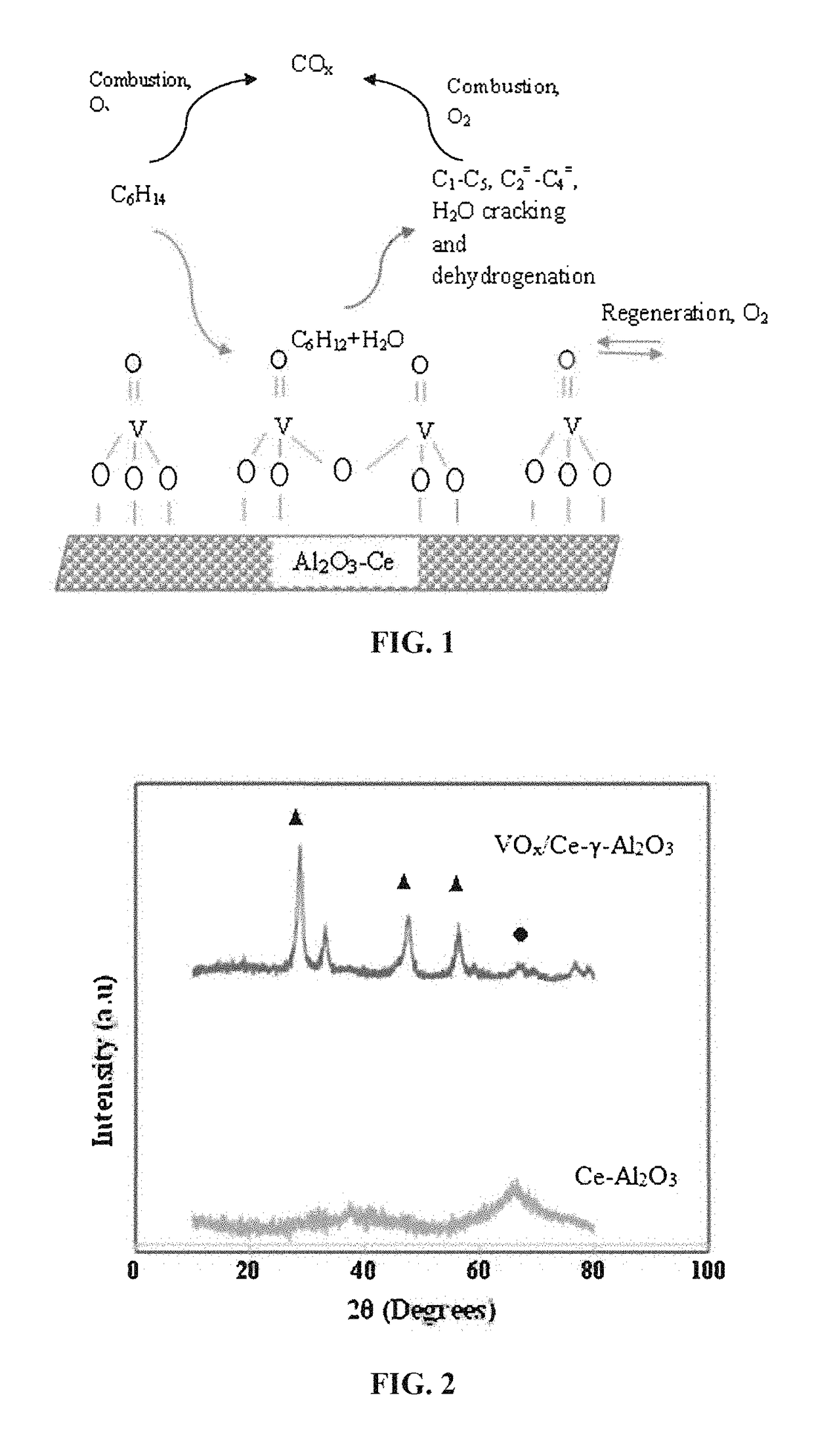
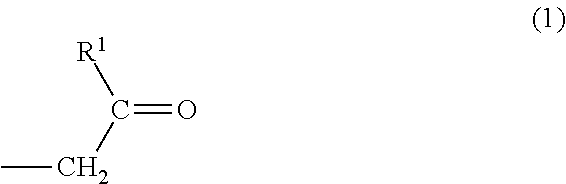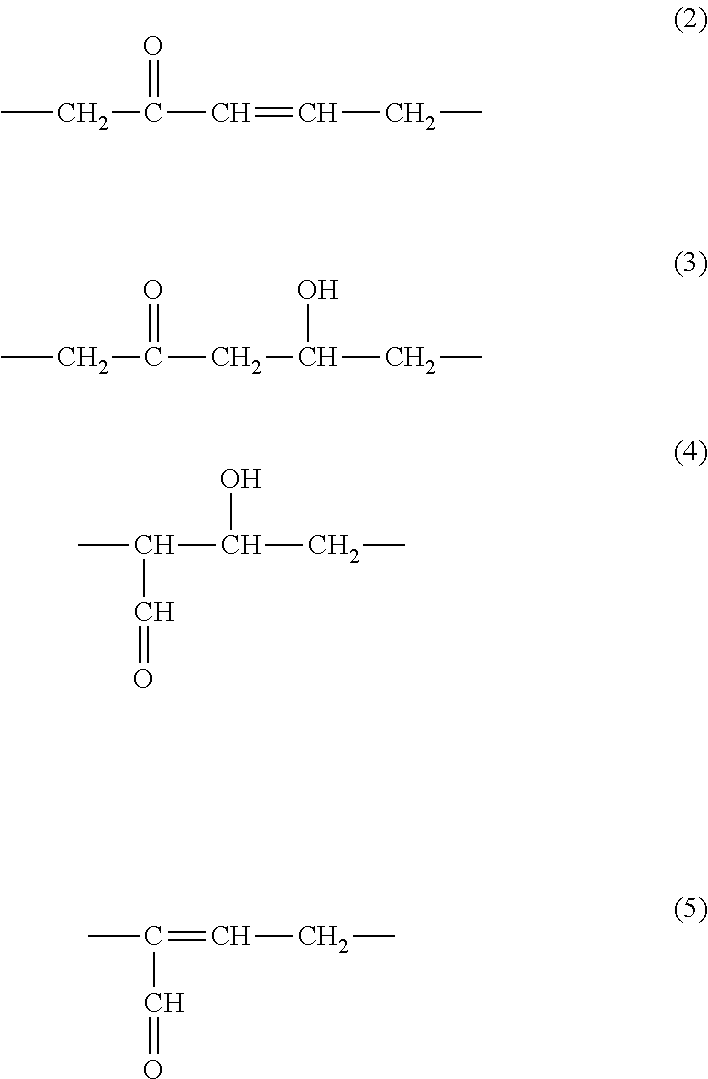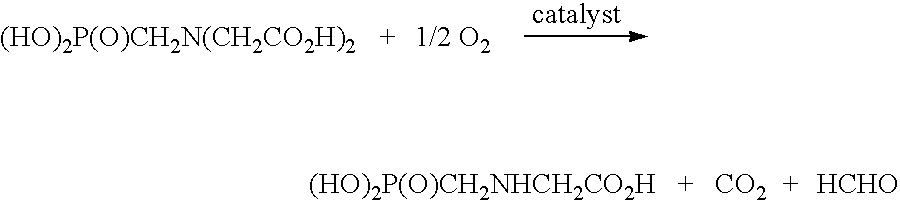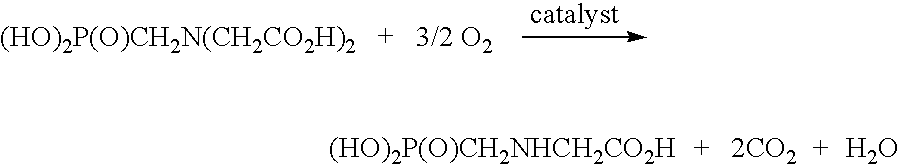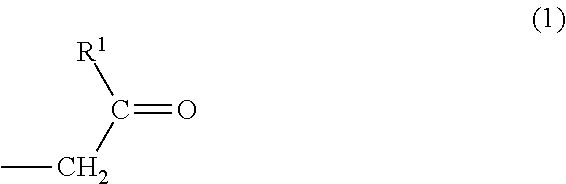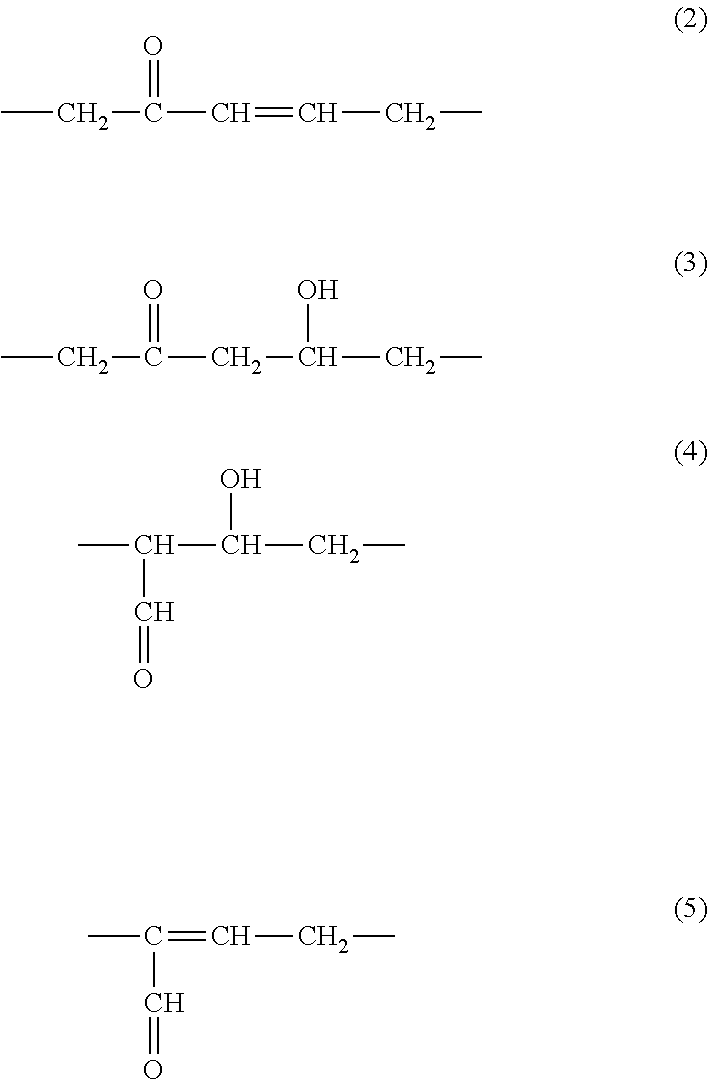Patents
Literature
146 results about "Oxidative cleavage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
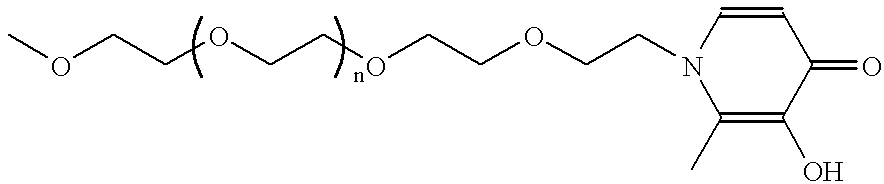
Superparamagnetic contrast media coated with starch and polyalkylene oxides
The invention relates to MR contrast media containing composite nanoparticles, preferably comprising a superparamagnetic iron oxide core provided with a coating comprising an oxidatively cleaved starch coating optionally together with a functionalized polyalkyleneoxide which serves to prolong blood residence.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE AS
Constrast media
InactiveUS6423296B1Increase productionPowder deliveryBiocideOxidative cleavageComposite nanoparticles
The invention relates to MR contrast media containing composite nanoparticles, preferably comprising a superparamagnetic iron oxide core provided with a coating comprising an oxidatively cleaved starch coating optionally together with a functionalized polyalkyleneoxide which serves to prolong blood residence.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE AS
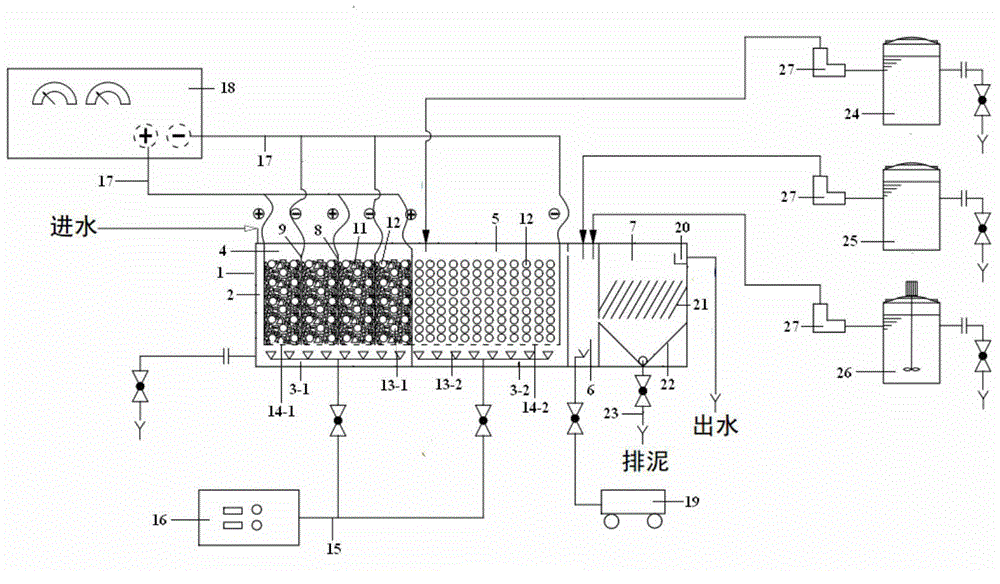
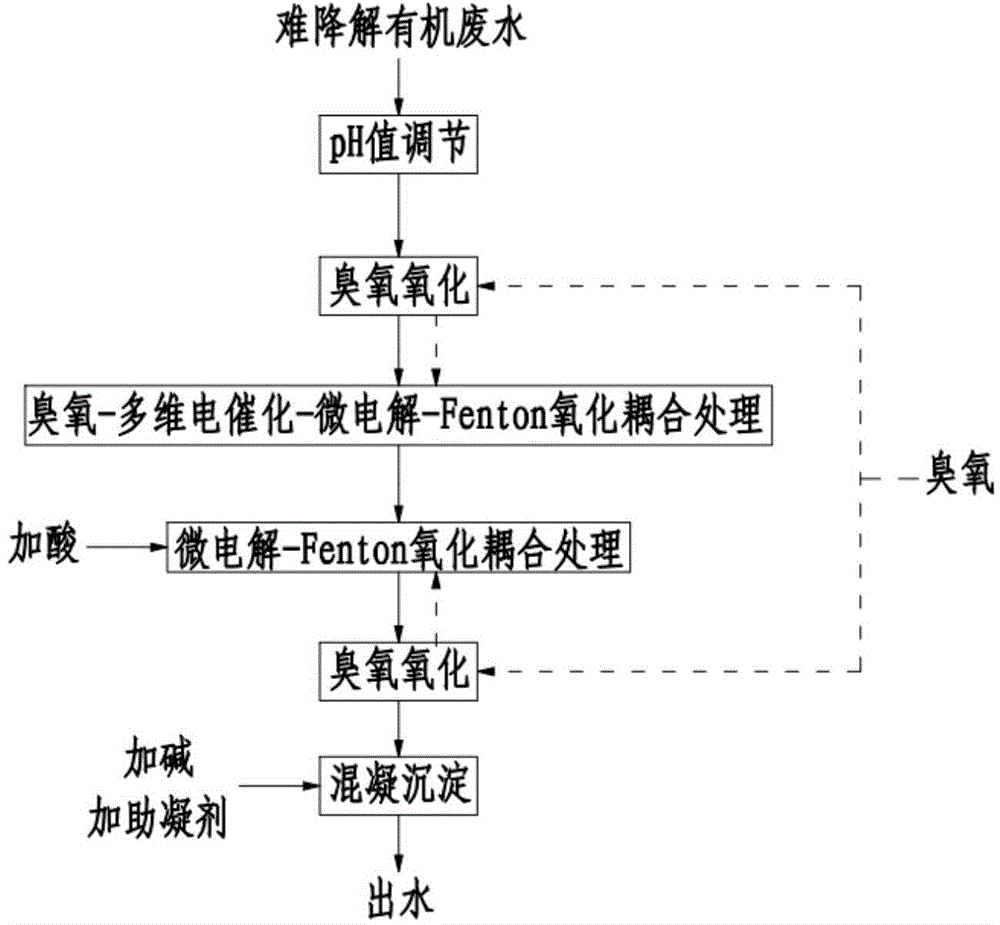
Advanced oxidative coupling device and process for treating organic wastewater difficult to degrade
ActiveCN104787941AImprove removal efficiencyLow running costWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsElectrolysisMulti dimensional
The invention discloses an advanced oxidative coupling device and process for treating organic wastewater difficult to degrade. A main device body comprises an ozone oxidation-multi-dimensional electro-catalysis / microelectrolysis area, an ozone oxidation-microelectrolysis / Fenton area, a coagulation area and an inclined plate sedimentation area, wherein the ozone oxidation-multi-dimensional electro-catalysis / microelectrolysis area comprises a multi-dimensional electrolysis / microelectrolysis area at the upper part and an ozone oxidation area at the lower part; the ozone oxidation-microelectrolysis / Fenton area comprises a microelectrolysis / Fenton area at the upper part and an ozone oxidation area at the lower part. The device combines four levels of advanced oxidation systems, and electrocatalytic oxidation, ozone oxidation, Fenton oxidation and a microelectrolysis reaction are mutually coupled in function, so that an organic matter difficult to degrade is subjected to multi-level oxidation to realize complete oxidative cracking; when the device is used for treating the organic wastewater difficult to degrade, the yield and the production rate of *OH are increased, the liquid phase transfer process is accelerated, the overall current efficiency of the device is increased, operation expenses are saved, flexible regulation and control of a process unit are realized, and the device can be used for treating various kinds of organic wastewater difficult to degrade.
Owner:AEROSPACE KAITIAN ENVIRONMENTAL TECH CO LTD +1
Amplified signal in binding assays
ActiveUS7635571B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalytePhotosensitizer
Methods are disclosed for determining minute quantities of an analyte in a medium suspected of containing the analyte. One method comprises treating a medium suspected of containing an analyte under conditions such that the analyte, if present, causes a substrate having an oxidant cleavable linker and a photosensitizer to come into close proximity. The photosensitizer generates singlet oxygen which oxidatively cleaves the linker to form a product which can be detected in a sandwich detection assay such as LOCI. The amount of product detected is related to the amount of analyte in the medium. Compositions, kits, and compounds are also disclosed.
Owner:DADE BEHRING MARBURG GMBH
Yellowing resistant the polyurethane foam and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a yellowing resistant the polyurethane foam. The polyurethane foam contains composite polyols, and further comprises, with the weight of the polyols as benchmark, 20-80% of aliphatic isocyanate, 1%-6% of a crosslinking agent, 0.5-2.5% of a catalyst, 0.4-8% of a foaming agent, 0.6-2.4% of a foam stabilizer, and 0.8-5% of essential oil; the composite polyols comprises polyether glycol and vegetable oil polyols accounting for 5-30% of the polyether glycol. The polyurethane foam uses aliphatic isocyanate as an isocyanate monomer, avoids oxidized cracking of aromatic isocyanate and improves the yellowing resistance of the foam; the compound polyether glycol and vegetable oil polyols are used as polyols monomers, the vegetable oil polyols can effectively improve the hydrolysis resistance and thermal stability of the foam; and the essential oil can endow the foam with sterilization and ability to purify air. A preparation method adopts a buffer solution containing acid for impregnation, so that the yellowing resistance of the treated foam is further enhanced.
Owner:昆山力普电子橡胶有限公司
Oxidation catalyst and process
InactiveUS7129373B2Promote lowerImprove productivityAmino preparation from aminesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsIminodiacetic acidOxidative cleavage
An oxidation catalyst is prepared by pyrolyzing a source of iron and a source of nitrogen on a carbon support. Preferably, a noble metal is deposited over the modified support which comprises iron and nitrogen bound to the carbon support. The catalyst is effective for oxidation reactions such as the oxidative cleavage of tertiary amines to produce secondary amines, especially the oxidation of N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid to N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Process for producing modified polymer, diene polymer, rubber composition and pneumatic tire
ActiveUS20140364536A1Reduce molecular weightEasily incorporated in main chain structureSpecial tyresPolymer scienceOxidative cleavage
A polymer having a carbon-carbon double bond in a main chain is decomposed by subjecting the carbon-carbon double bond to oxidative cleavage using an oxidizing agent such as periodic acid to decrease the molecular weight, polymer chains of the decomposed polymer are combined by changing acido-basic properties such that a system containing the decomposed polymer becomes basic when acidic and becomes acidic when basic, and a modified polymer in which the structure has been changed is obtained. By this, a functional group can be incorporated in the main chain structure of a polymer. A rubber composition comprising a rubber component containing the modified polymer, and a filler compounded therewith, and a pneumatic tire comprising the rubber composition are provided.
Owner:TOYO TIRE & RUBBER CO LTD
Method for preparing nonane diacid by ozone-hydrogen peroxide mixed oxidant catalysizing
InactiveCN1927806ANo emissionsMild reaction conditionsCarboxylic preparation by ozone oxidationReaction temperatureOrganic compound
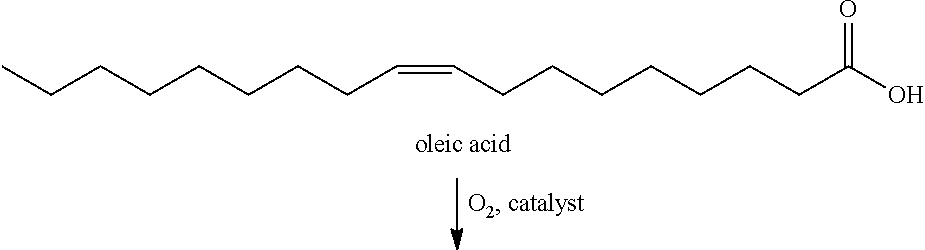
The present invention relates to process of catalytically oxidizing oleic acid or mixed fatty acid obtained through hydrolyzing animal and vegetable grease with mixed oxidant of ozone and hydrogen peroxide to prepare azelaic acid, and belongs to the field of organic compound preparing technology. By using ozone and hydrogen peroxide as mixed oxidant, phosphotungstic acid as catalyst and quaternary ammonium salt as phase transfer reagent, and through the reaction at 60-70 deg.c and normal pressure and the further reaction at 95-105 deg.c for 8-12 hr, the material oleic acid or mixed fatty acid is oxidized and cracked to prepare azelaic acid.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for preparing low carbon olefin by gas-phase oxidation cracking of hydrocarbon with carbon monoxide as a byproduct
InactiveCN1504442AHigh yieldEfficient use ofCarbon monoxideHydrocarbon by hydrocarbon crackingAlkaneCarbon number
A process for preparing lower carbon number hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide through hydrocarbons gas-phase oxidation decomposition, wherein the raw material hydrocarbons are vaporized and mixed with oxygen or air under the temperature of 600-900 deg. C for hydrocarbons oxidation decomposition reaction, the mol ratio of C / O in raw material gas is 1.5-6.0. The invention can substantially lower the activation energy for the process of alkyl group free radical forming through hydrocarbon dehydrogenation, compared with the conventional hydrocarbons thermo-cracking process, the present invention realizes low energy consumption, less discharge, high production capability, low manufacturing cost and reduced investment.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
De-oxygenation treatment for noble metal on carbon catalysts used in liquid phase oxidation reactions
InactiveUS6927304B2Extended service lifeIncrease resistanceGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsLiquid mediumOxidative cleavage
A treatment for de-oxygenating a noble metal on carbon catalyst used in liquid phase oxidation reactions which includes exposing the catalyst to a non-oxidizing environment. The de-oxygenation treatment improves catalyst performance and is particularly suited for noble metal on carbon catalysts used to catalyze the oxidative cleavage of a carboxymethyl substituent from an N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid substrate in an aqueous reaction mixture using an oxygen-containing gas to produce an N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine product. In one embodiment, the catalyst is exposed to a non-oxidizing environment by introducing a non-oxidizing gas and / or reducing gas into a slurry comprising the catalyst in contact with a liquid medium.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Method for preparing aromatic compounds by conducting hydrogenation and depolymerization on spruce lignin through electro-catalysis technology
InactiveCN106676574AIncreased ratio of carbon to hydrogenAvoid complex process conditionsElectrolysis componentsElectrolytic organic productionDepolymerizationElectrolysis
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Fluidizable vanadium catalyst for oxidative cracking of hydrocarbons to olefins in a gas phase oxygen free environment
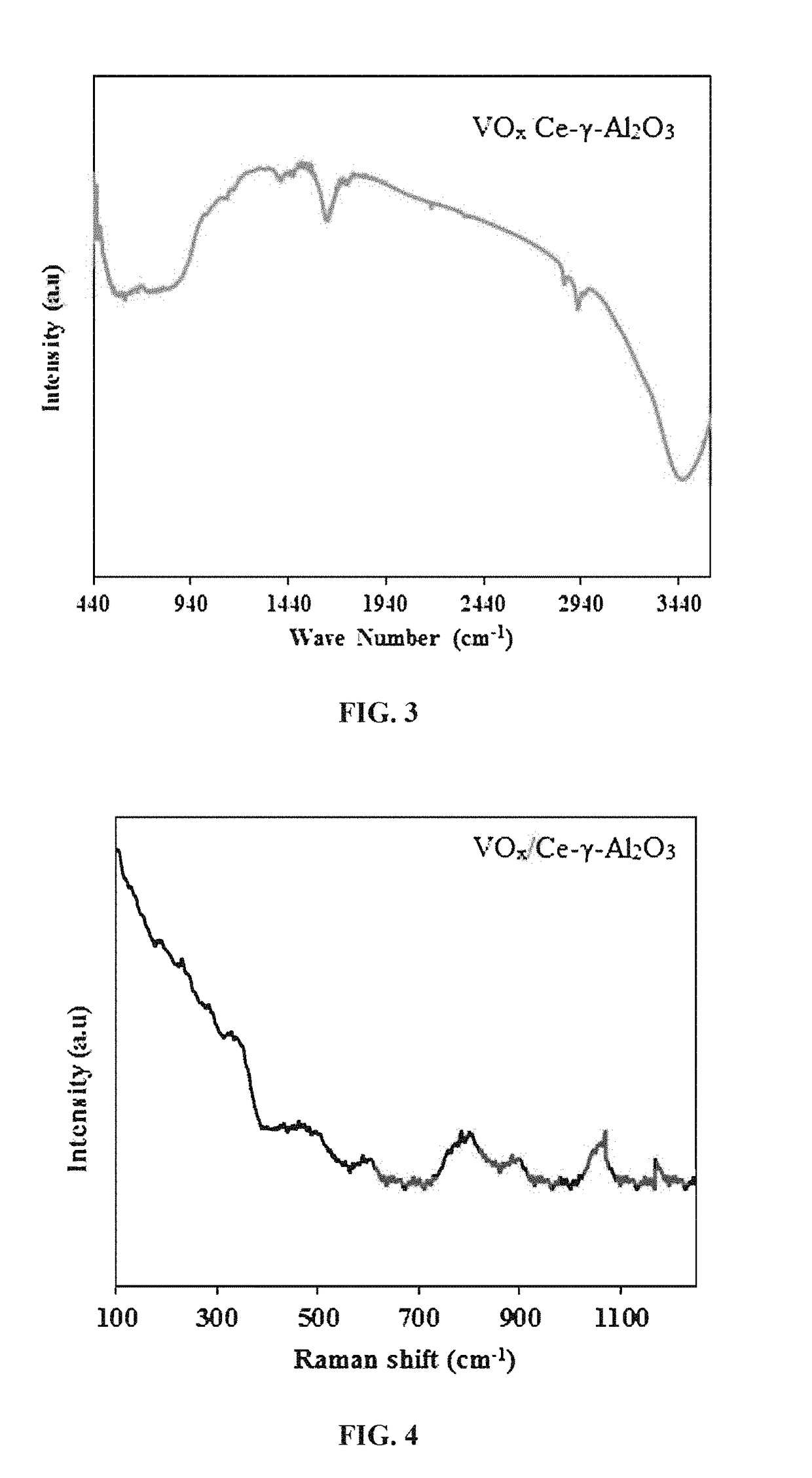
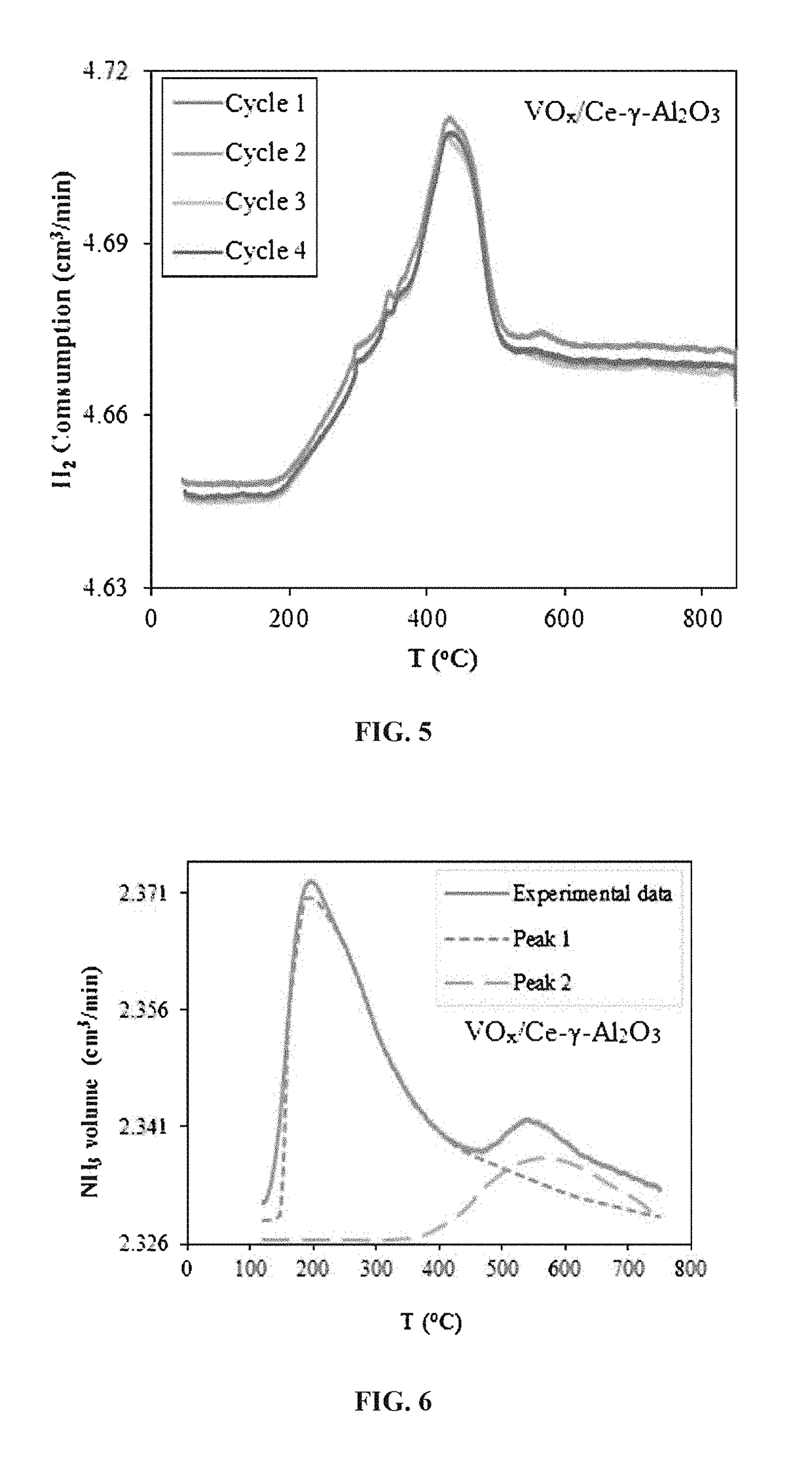
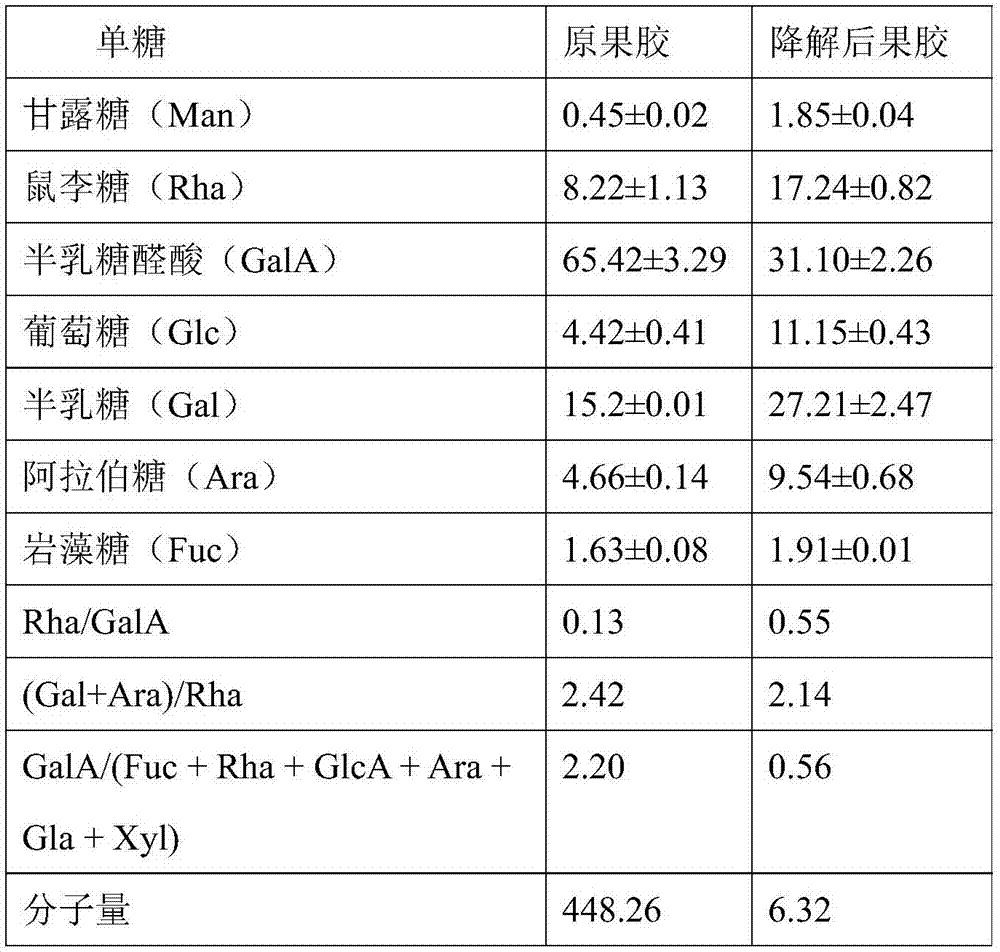
Fluidizable catalysts for the gas phase oxygen-free oxidative cracking of alkanes, such as hexane, to one or more olefins, such as ethylene, propylene, and / or butylene. The catalysts comprise 1-15% by weight per total catalyst weight of one or more vanadium oxides (VOx), such as V2O5. The catalysts are disposed on an alumina support that is modified with cerium to influence catalyst acidity and characteristics of lattice oxygen at the catalyst surface. Various methods of preparing and characterizing the catalyst as well as methods for the gas phase oxygen free oxidative cracking of alkanes, such as hexane, to one or more olefins, such as ethylene, propylene, and / or butylene with improved alkane conversion and olefins product selectivity are also disclosed.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Preparation method of ultralow-molecular-weight pectin rich in RG-I
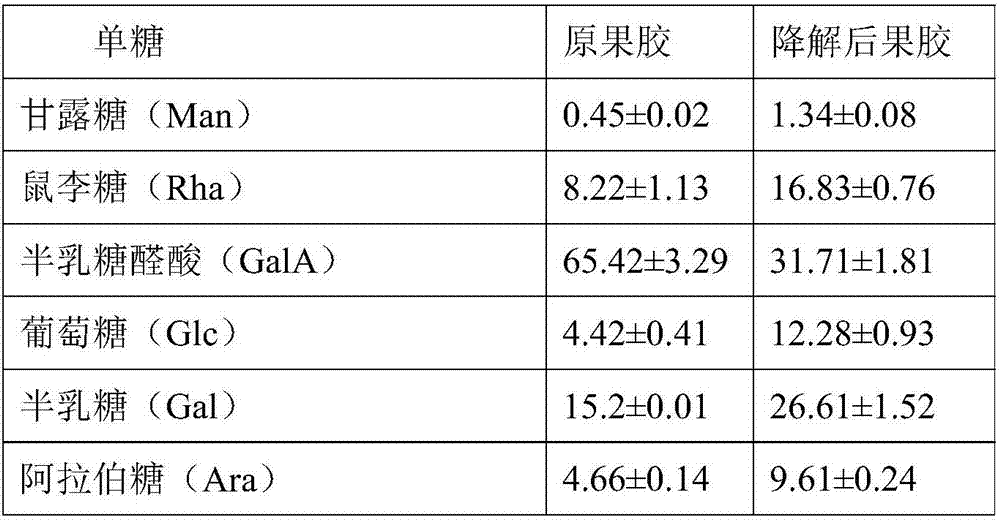
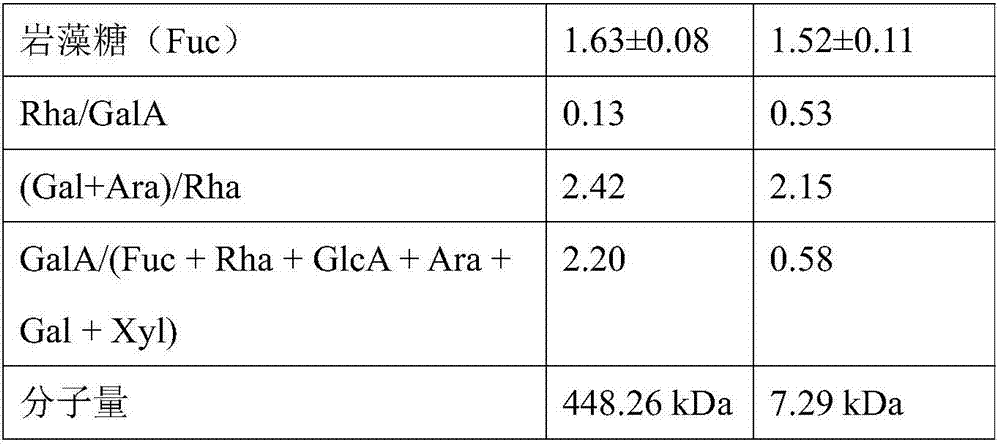
The invention discloses a preparation method of an ultralow-molecular-weight pectin rich in RG-I. The preparation method comprises the steps that Fe<3+> generated in a reaction system is reduced into Fe<2+> through ultrasonic oxidation reaction, re-reaction between the Fe<2+> and hydrogen peroxide is strengthened to produce hydroxyl free radicals, oxidative cleavage of pectin carbohydrate chain is caused, and galacturonic acid in special attack pectin forms the low-molecular-weight pectin rich in RG-I structural domain. The weight-average molecular weight of the pectin is 5-10 kDa, esterification degree is reduced, the product is the ultralow-molecular-weight pectin rich in RG-I, the antioxidant activity is remarkably higher than that of original pectin, and the comprehensive utilization rate is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
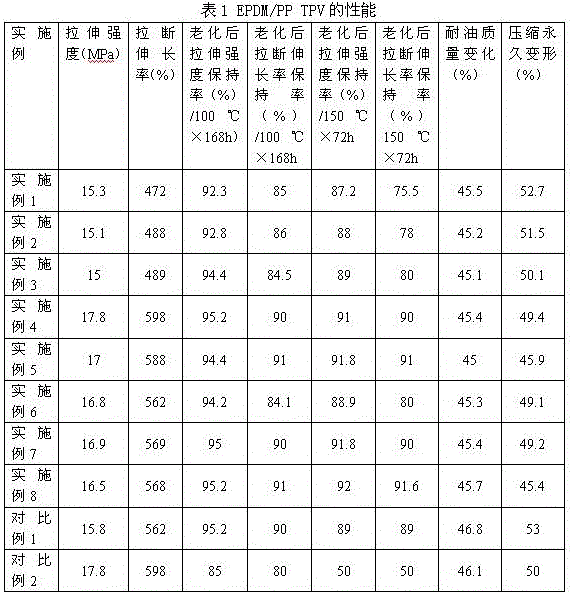
Heat-resistant thermoplastic elastomer and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a heat-resistant thermoplastic elastomer and a preparation method thereof. According to the preparation method, by virtue of a theory that an antioxidant has relatively more lively hydrogen atoms molecules of EPDM and PP, the hydrogen atoms of the antioxidant can easily react with peroxy radicals generated by a blend molecular chain under heat and oxygen in a thermo-oxidative aging process of an EPDM / PP blend, the chain reaction of free radicals is inhibited, and the cleavage and the oxidative cleavage of the molecular chain are prevented, so that the heat resistance of EPDM / PP TPV is improved, and the aging resistance of EPDM / PP TPV is improved. Calcium sulfate whiskers modified by virtue of a silane coupling agent KH-550 form a 'hard core-soft shell' coating structure with EPDM in the blending process of EPDM / PP, and the disperse state of calcium sulfate has a certain blocking effect to gas during thermo-oxidative aging and impedes the conduction of gas and heat, so that the heat resistance stability of EPDM / PP TPV is improved, and the heat aging resistance of EPDM / PP TPV is meliorated.
Owner:GUIZHOU MATERIAL IND TECH INSTITUE
Method for preparing mogrol and 11-O-mogrol by combining enzyme hydrolysis and oxidative cracking
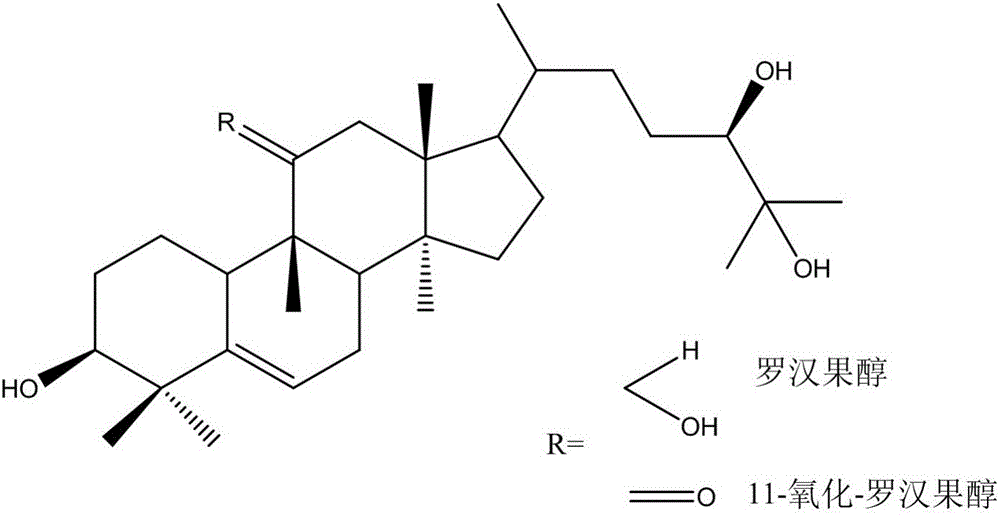
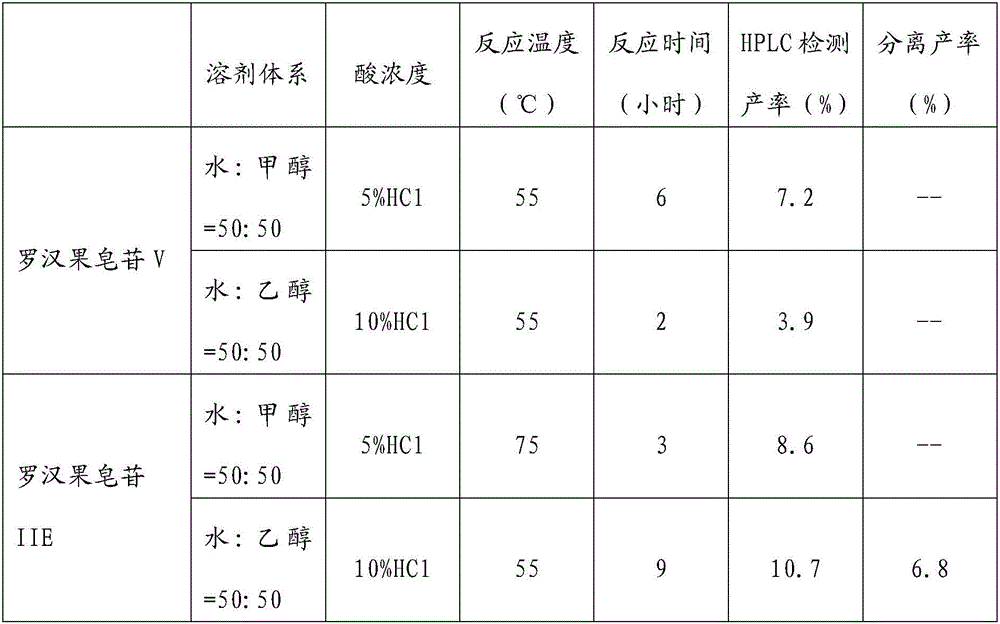
The invention discloses a method for preparing mogrol and 11-O-mogrol by combining enzyme hydrolysis and oxidative cracking, belonging to the technical field of prodrugs or health care products. The method comprises the following steps: 1, carrying out enzyme hydrolysis on mogroside V; 2, carrying out smith degradation: (1) carrying out oxidative cracking on sodium periodate; (2) reducing sodium borohydride; (3) carrying out hydrolysis. The method combines the enzyme hydrolysis and the oxidative cracking for use, firstly removes part of sugar residues of the mogroside V by utilizing the enzyme hydrolysis so as to reduce the complexity of a sugar chain, and then uses the oxidative cracking method to finally obtain the two momordica grosvenori sapogenins i.e., the mogrol and the 11-O-mogrol. The method is suitable for preparing a great deal of samples, is high in yield, and can be used for obtaining the two sapogenins i.e., the mogrol and the 11-O-mogrol at the same time.
Owner:GUANGXI INST OF BOTANY THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
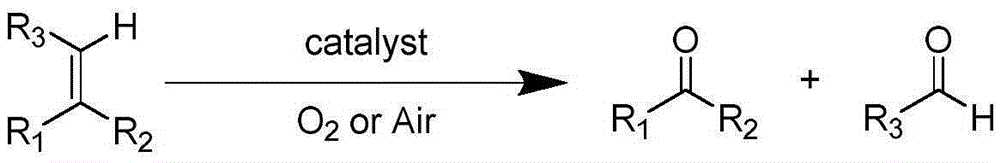
Method for preparing aldehyde ketone by catalyzing carbon-carbon double-bond oxidative cleavage
ActiveCN106831284AOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl group formation/introductionIron saltsOxidative cleavage
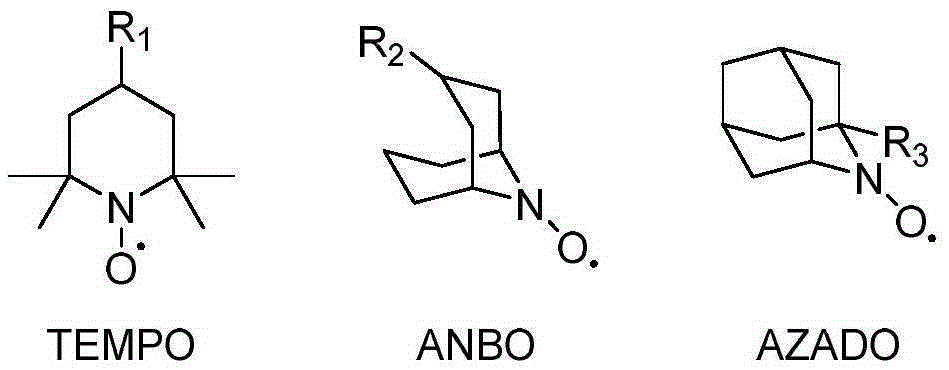
The invention relates to a method for preparing aldehyde ketone by catalyzing carbon-carbon double-bond oxidative cleavage and belongs to the technical field of chemistry and chemical engineering. Particularly, reaction is conducted at a temperature of 30 to 120 DEG C for 1 to 48 hours by taking nitroxide free radical and iron salt as catalysts and air or oxygen as an oxygen source, so that carbon-carbon double bonds (as shown in the description) can be oxidized and broken into corresponding aldehyde or ketone. The system provided by the invention has various advantages of high catalytic activity, high selectivity, mild condition and the like.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for increasing production of propylene and ethylene
InactiveCN102285856AIncrease productionBulk chemical productionHydrocarbon by hydrocarbon crackingAlkaneOxidative cleavage
The invention relates to a method for increasing the output of propylene and ethylene in a steam cracking process. The steam cracking process consists of a cracking furnace and a separation system. On this basis, a catalytic cracking system that uses the C4 fraction produced in the oil refining process as a raw material is added. Through this catalytic cracking system, the mixture of C4 olefins and alkanes is partially converted into propylene-rich And the cracked gas of ethylene, and the separation and purification of the target product is mainly completed by the separation system in the steam cracking process. The feature of the present invention is to fully tap the potential of the separation (recovery) system in steam cracking, only increase the catalytic cracking system composed of catalytic cracking reactor, oxidation cracking reactor and simple separation equipment, and increase low-carbon components such as propylene and ethylene. The output of olefins is conducive to the improvement of the economic benefits of enterprises.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
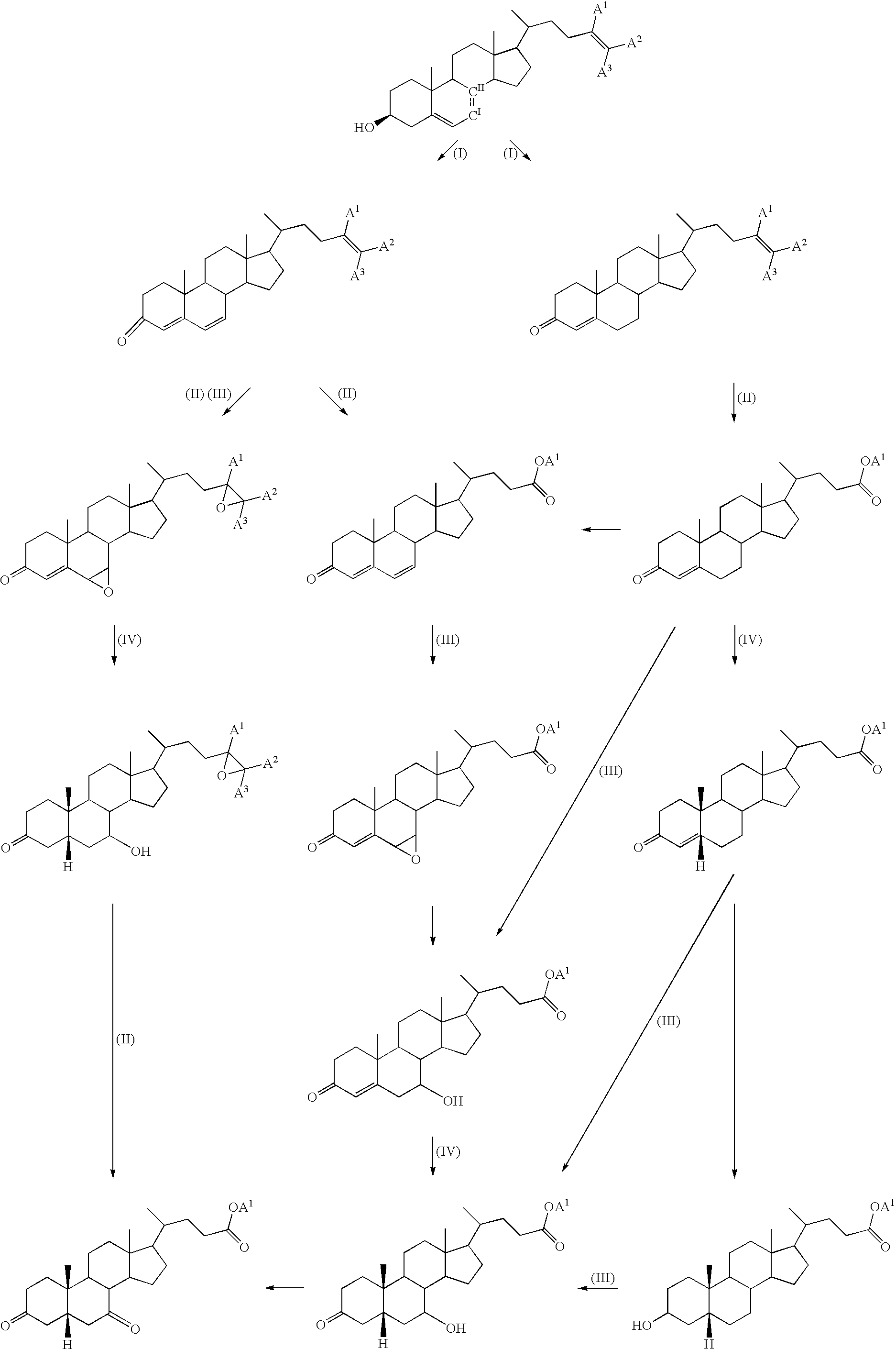
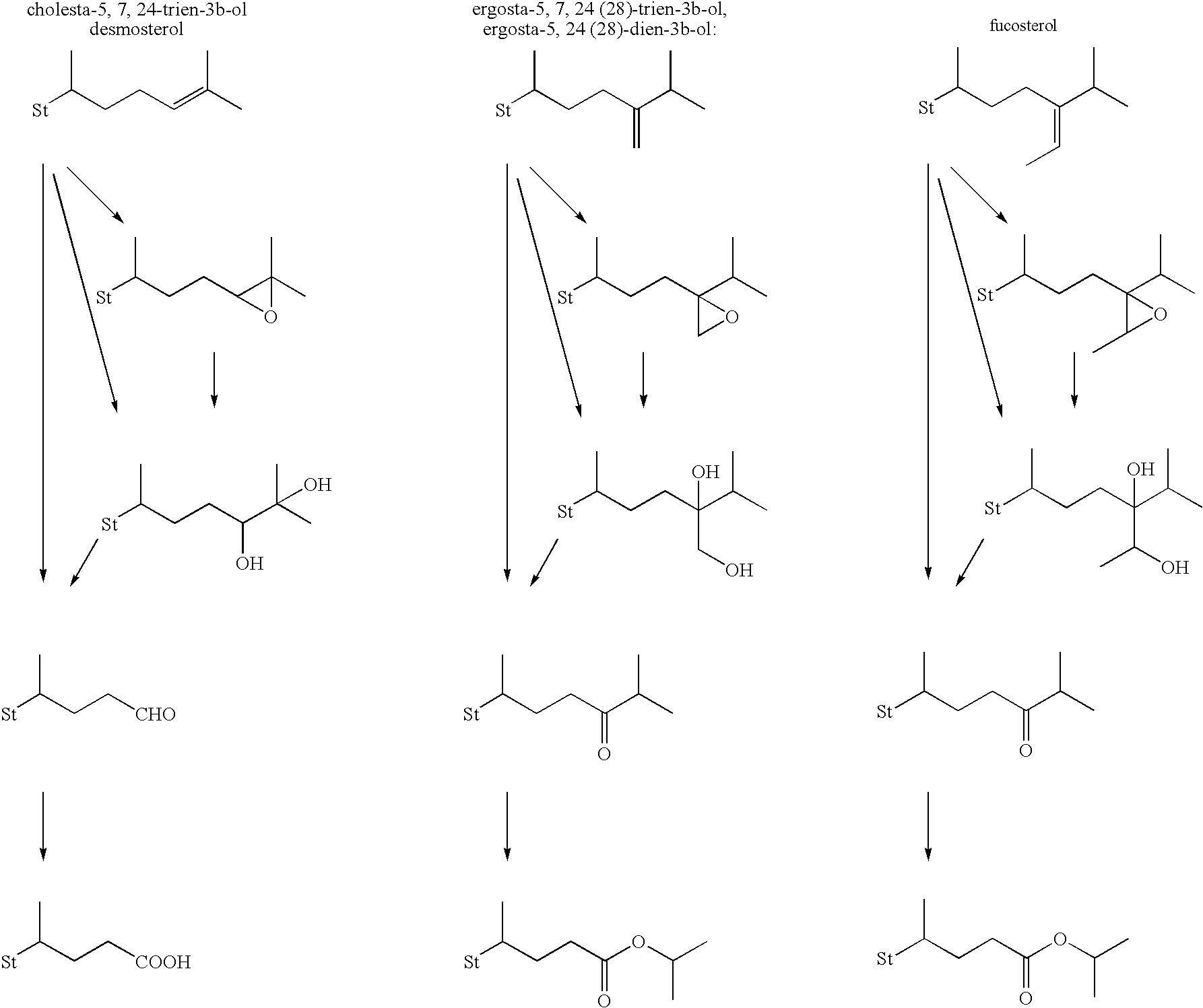
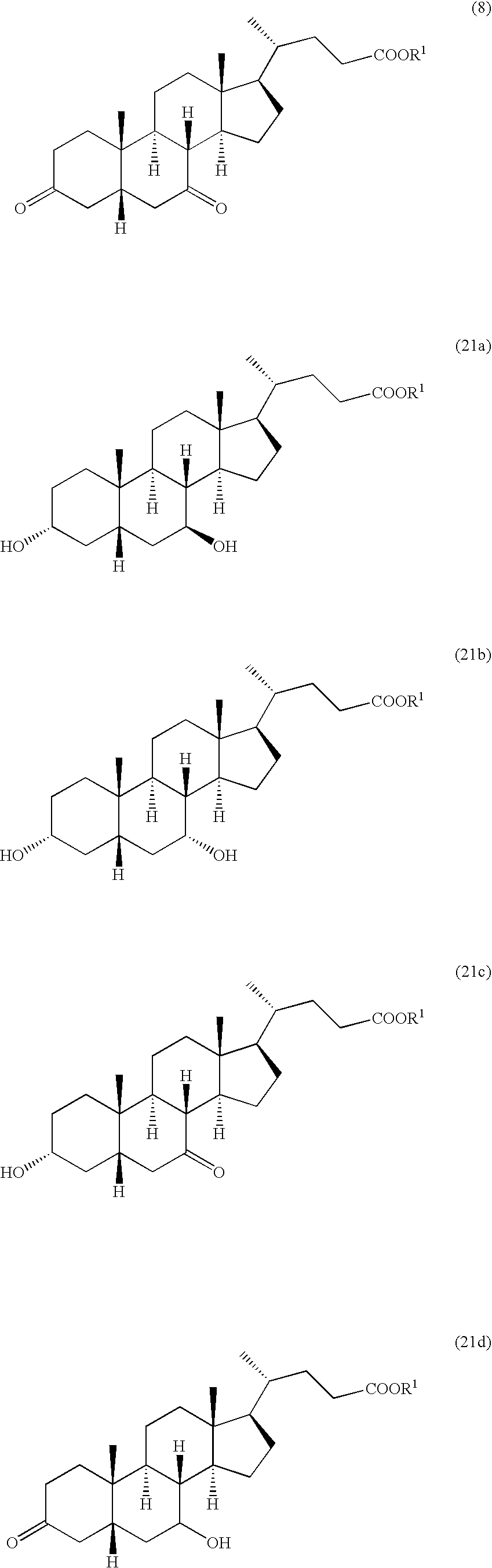
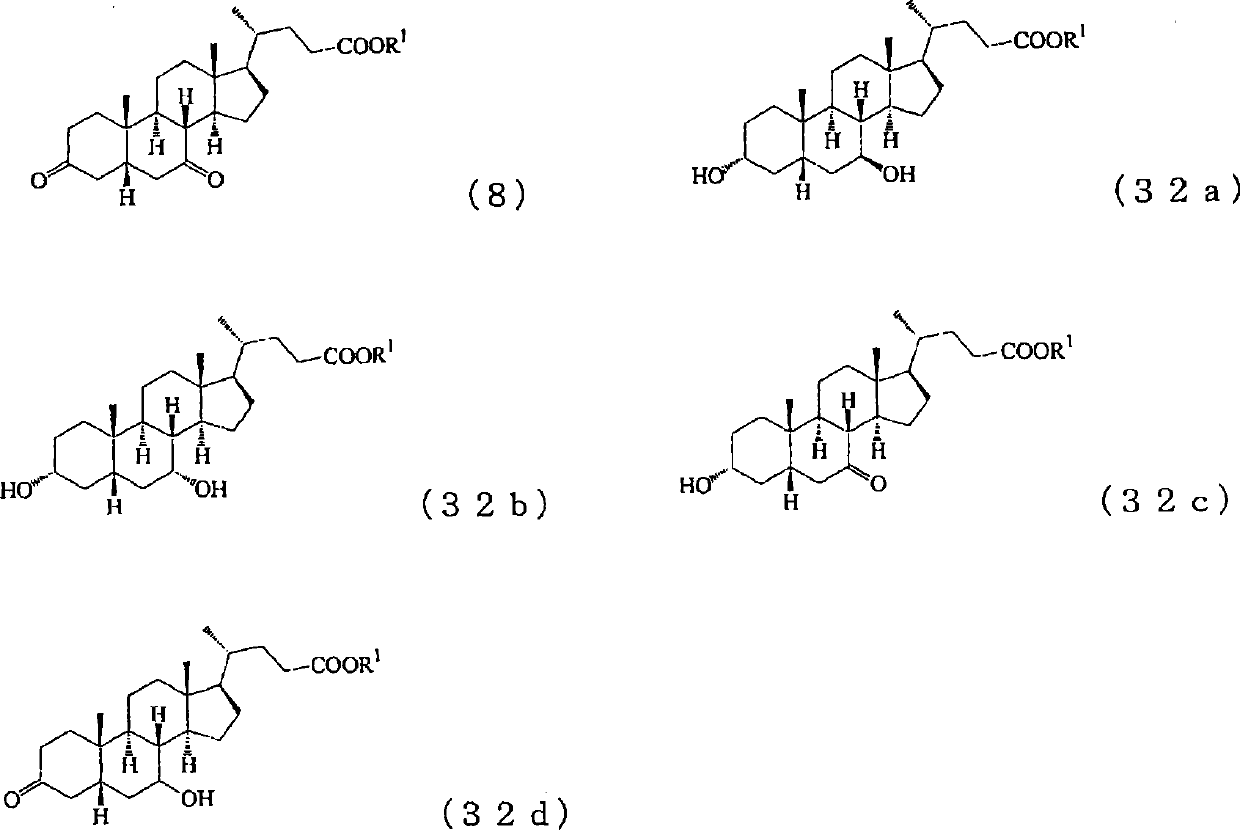
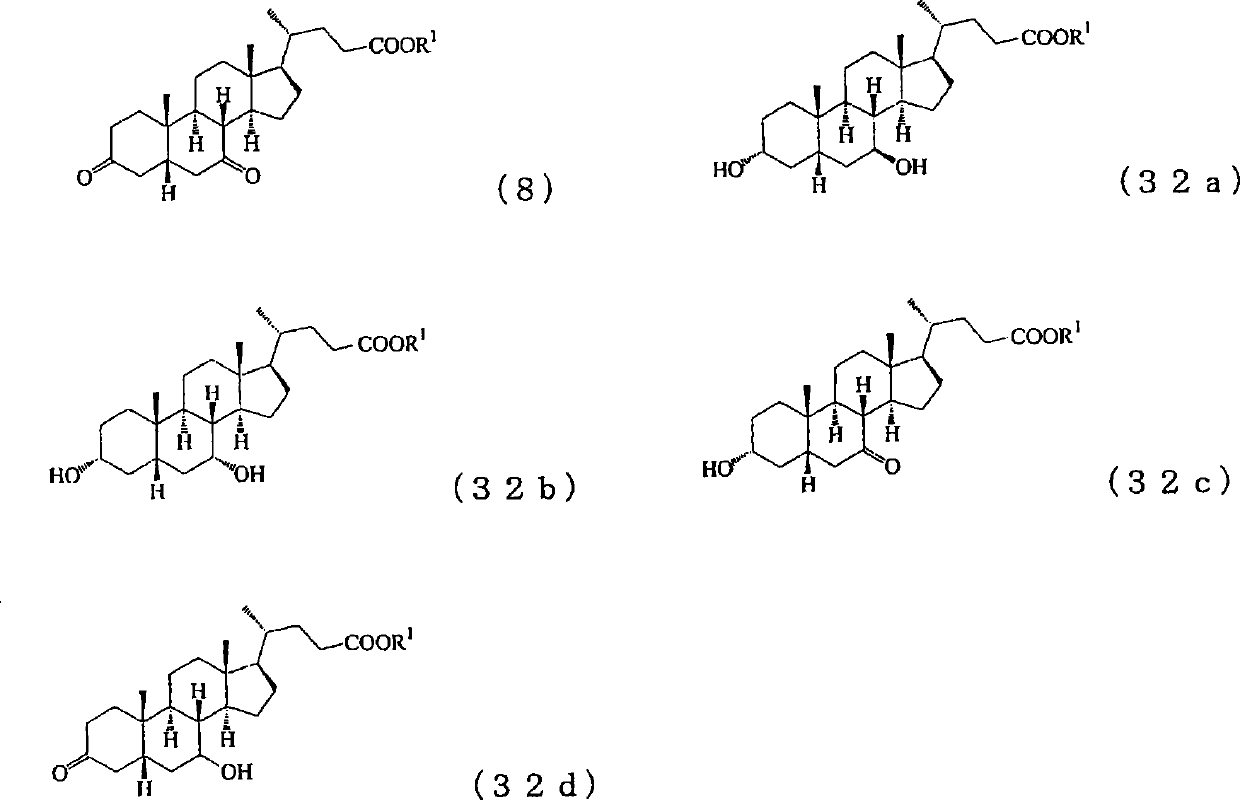
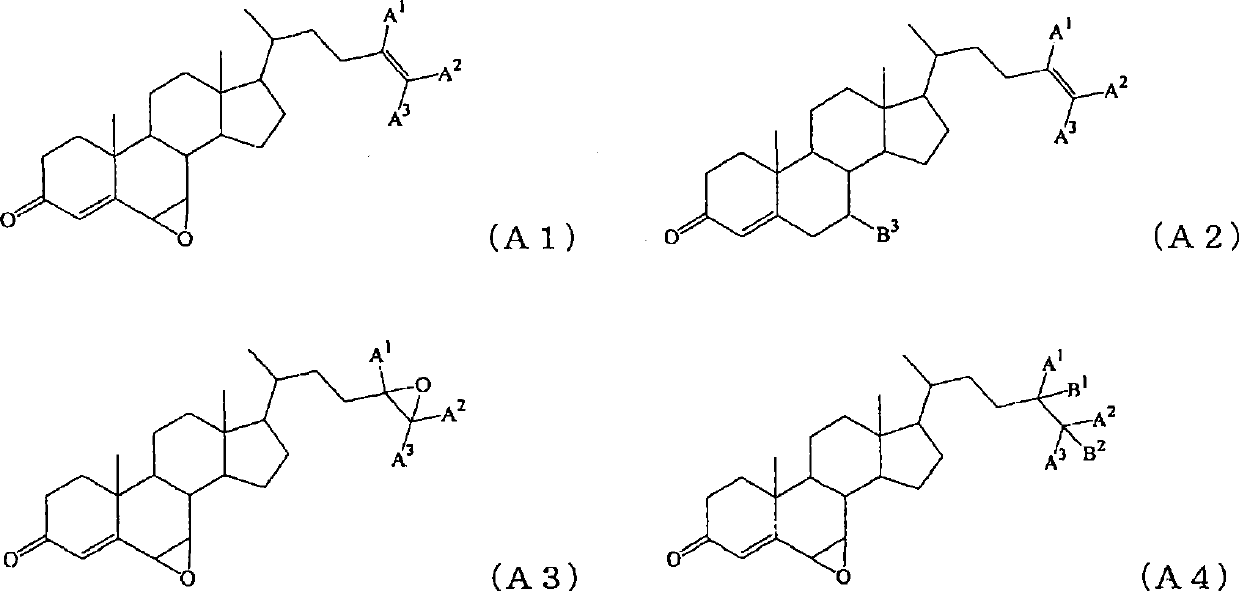
Production method of steroid compound
An object of the present invention is to provide a novel method for producing a steroid compound. The present invention provides a method for producing 3,7-dioxo-5β-cholanic acid or ester derivatives thereof, which uses, as raw materials, sterols having double bonds at positions 5 and 24, such as cholesta-5,7,24-trien-3β-ol, ergosta-5,7,24(28)-trien-3β-ol, desmosterol, fucosterol, or ergosta-5,24(28)-dien-3β-ol, and which comprises the following 4 steps: (I) a step of performing oxidation of a hydroxyl group at position 3 and isomerization of a double bond at position 5 to position 4; (II) a step of converting position 24 to a carboxyl group or an ester derivative thereof by the oxidative cleavage of a side chain; (III) a step of introducing an oxygen functional group into position 7; and (IV) a step of constructing a 5β-configuration by reduction of a double bond at position 4.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
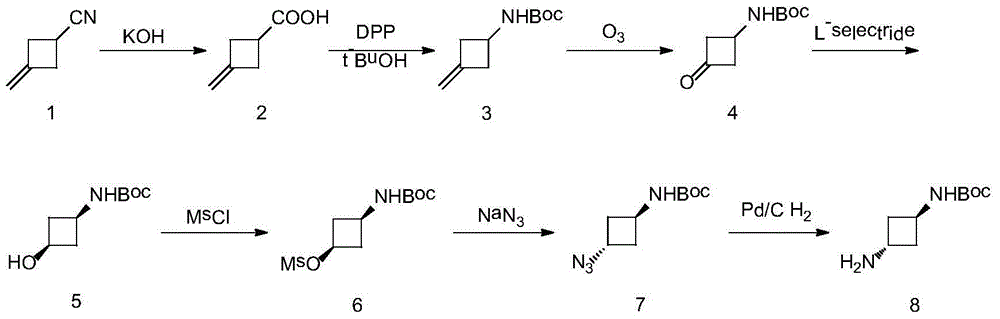
Preparation method of trans-N-Boc-1,3-cyclobutanediamine
InactiveCN104829492ASimple purification methodShort stepsCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationPurification methodsOxidative cleavage
The present invention is a preparation method of trans-N-Boc-1,3-cyclobutanediamine. The method uses easily available 3-methylene-cyclobutyl carbonitrile as a starting material, and conducts 7 steps of reaction including hydrolysis, Curtius rearrangement, oxicracking, reduction, methanesulfonyl chloride protection, substitution and hydrogenation. The invention has the technical characteristics of short reaction step, total yield of up to 49.8% and high purity of the final product (>99%) (the prior art comprises at least 8 steps, and the highest total yield is up to 19%); and N-Boc-1,3-cyclobutanediamine with transconfiguration is selectively synthesized. From the perspective of chemistry, the invention has the characteristics of few steps, simple reaction, high yield, feasible purification method of intermediate and simple operation, and has wide prospect in business application.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Process for production of steroids
InactiveCN101374854ASteroidsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsIsomerizationCarboxyl radical
The invention provides a novel process for the production of steroids, namely, a process for the production of 5ss-3,7 -dioxocholanoic acid or ester derivatives thereof which comprises using as the raw material a sterol having double bonds at the 5- and 24-positions selected from among cholesta -5,7,24-trien-3ss-ol, ergosta-5,7,24(28)-trien-3ss-ol, desmo- sterol, fucosterol, and ergosta-5,24(28)-dien-3ss-ol and conducting the following four steps: (I) the step of conducting the oxidation of 3-position hydroxyl and the isomerization of double bond from the 5-position to the 4-position (II) the step of converting the group at the 24-position into carboxyl or a carboxylic ester group by oxidative cleavage of the side chain, (III) the step of introducing an oxygen-containing functional group to the 7-position, and (IV) the step of constructing 5ss-configuration by reductive saturation of the 4-position double bond.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Method for producing cyclic diketone compound
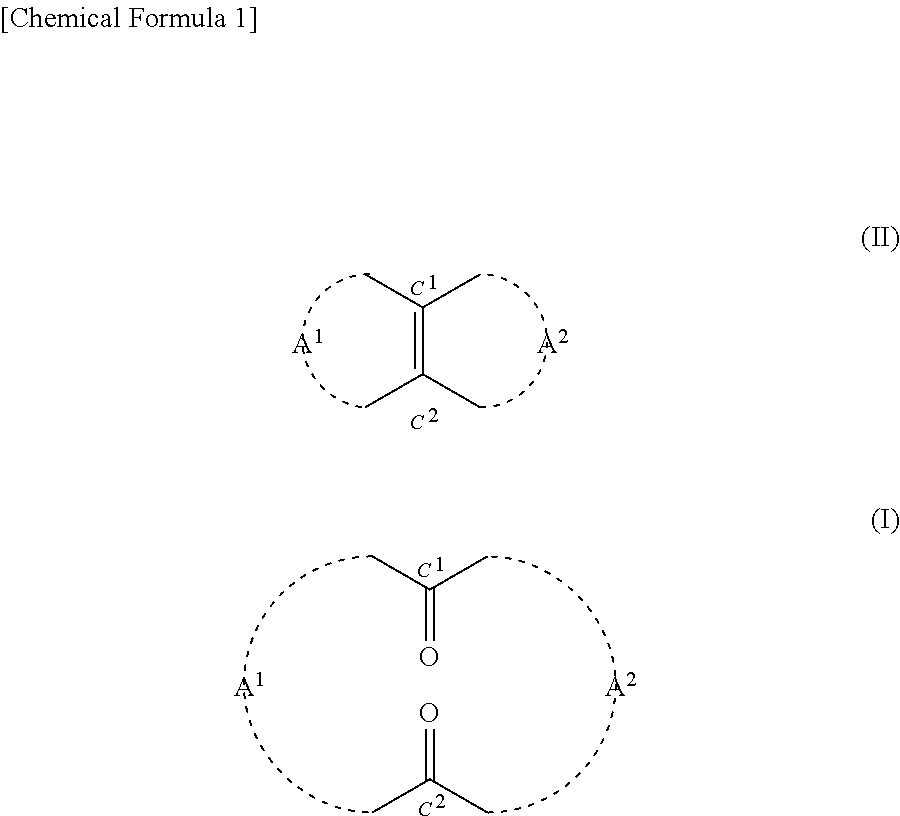
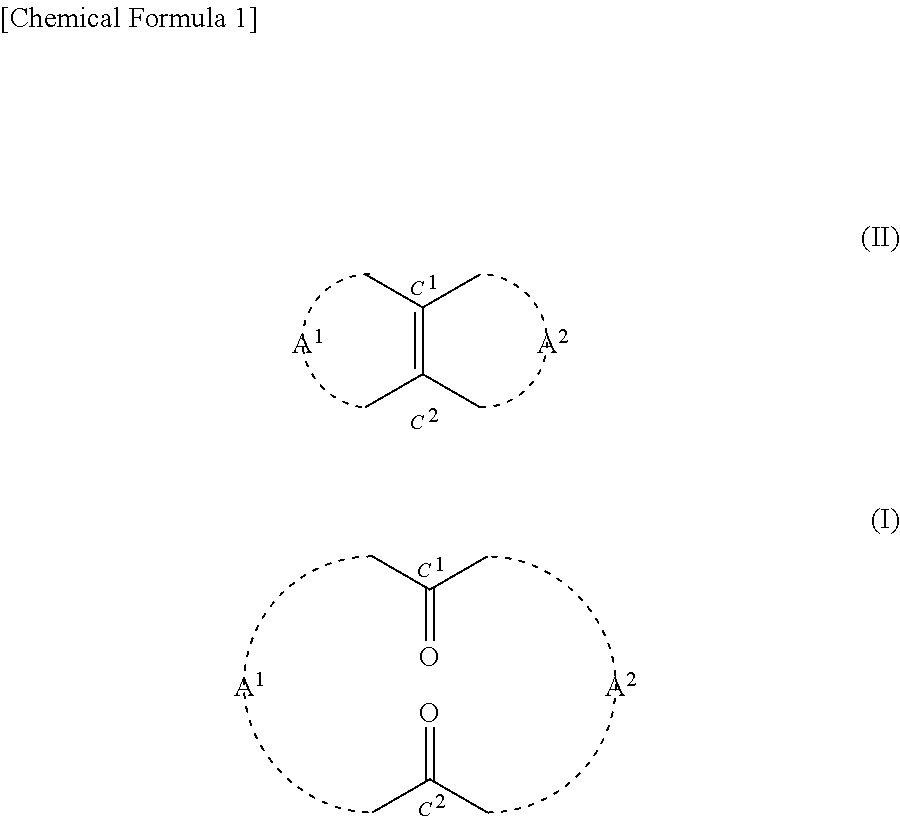
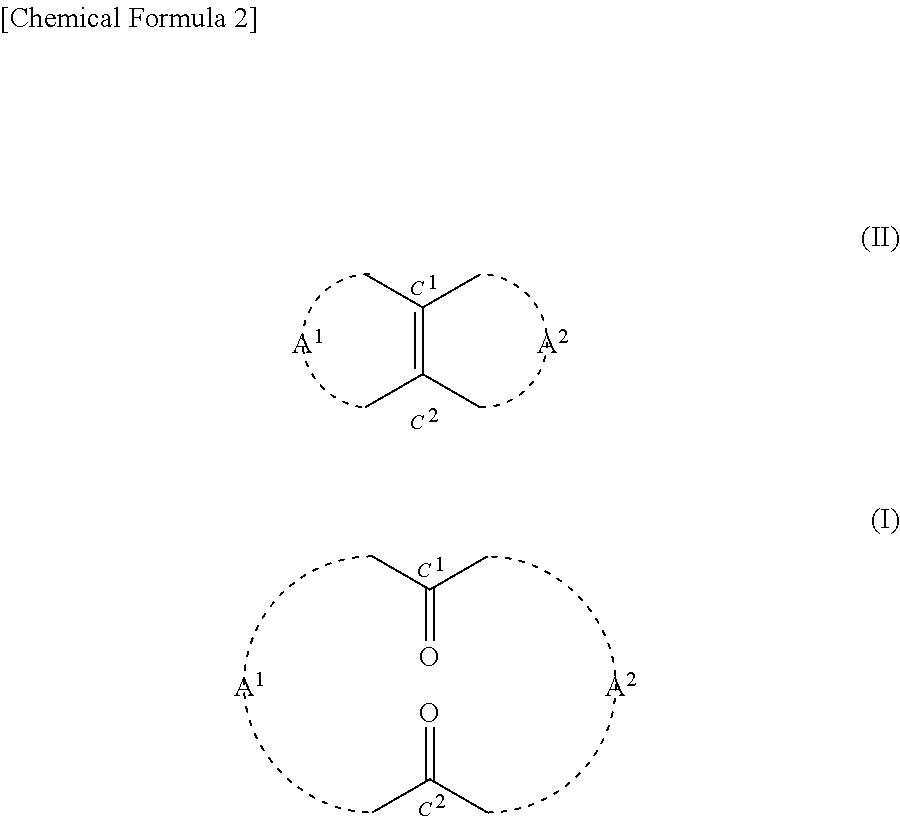
ActiveUS20170362153A1Reduced flexibilityHigh reaction yieldHydrogen peroxideOrganic compound preparationDiketoneOxidative cleavage
Provided is a method for producing a compound represented by general formula (I) by oxidative cleavage of a compound of formula (II), which is a bicyclic tetrasubstituted olefin compound, using hydrogen peroxide. The method for producing a compound represented by general formula (I) includes a step of subjecting a compound represented by general formula (II) to oxidative cleavage using hydrogen peroxide in the presence of an acid catalyst or in the presence of a tungstic acid compound to obtain the compound represented by general formula (I):[In the formulae, formula -A1- (where the front bond denotes a bond that bonds with a carbon atom C1 while the back bond denotes a bond that bonds with a carbon atom C2) is an alkylene group having 2 to 6 carbon atoms that may have been substituted and that may further include an ether bond, an ester bond, a secondary amino group, a thioether group, or these, and formula -A2- (where the front bond denotes a bond that bonds with a carbon atom C1 while the back bond denotes a bond that bonds with a carbon atom C2) is an alkylene group having 4 to 10 carbon atoms that may have been substituted and that may further include an ether bond, an ester bond, a secondary amino group, a thioether group, or these.]
Owner:KAO CORP
Method for catalyzing oxicracking of aryl ethers of lignin model
ActiveCN108947776AReduce dosageMild reaction conditionsOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationArylNitrate
The invention relates to a method for catalyzing oxicracking of aryl ethers of a lignin model. The method is characterized by comprising the step of catalyzing the oxicracking of the aryl ethers of the lignin model by taking two components, i.e., a simple inorganic oxovanadium compound and nitrate as a composite catalyst system and taking molecular oxygen as an oxygen supply. According to the method, the catalyst is simple, cheap and readily available, the reaction conditions are mild, the efficiency of oxicracking is high, and the aryl ethers in lignin can be efficiently cracked by a catalyzed oxidation method.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing butanedioic acid through catalytic oxidation cracking of acetylpropionic acid
ActiveCN105712870AReduce adverse effectsHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationChemical recyclingButanedioic acidLevulinic acid
A method for preparing butanedioic acid through catalytic oxidation cracking of acetylpropionic acid is provided; according to the method, a manganese-containing composite oxide material modified by a hydrophobic group is used as a catalyst, molecular oxygen is used as an oxygen source, and acetylpropionic acid is oxidized into butanedioic acid under a solvent-free condition. The hydrophobic properties of the catalyst can inhibit adsorption of oxidation by-product water on the catalyst surface, and the catalyst stability is improved; at the same time, through control of adsorption of raw materials and products on the catalyst surface, the selectivity of the target product butanedioic acid is improved.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of cracking carbon nanotube strengthened copper-based composite material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a cracking carbon nanotube strengthened copper-based composite material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dispersing carbon nanotubes into concentrated sulfuric acid, then adding concentrated phosphoric acid and potassium permanganate for magnetic stirring, cooling to room temperature after heating for heat preservation, then adding deionized water containing hydrogen peroxide in an ice-bath condition, obtaining a cracking carbon nanotube after cleaning, preparing the obtained cracking carbon nanotube and copper acetate intoa precursor in a solution, dropwise adding glucose and hydrazine hydrate under magnetic stirring, carrying out suction filtration, drying and annealing treatment to obtain composite powder, preparingthe composite powder into a block material through SPS sintering, and then obtaining the cracking carbon nanotube strengthened copper-based composite material through heat extrusion and annealing treatment. According to the preparation method, oxidative cracking treatment is carried out on the carbon nanotubes, the length-width ratio controllable cracking carbon nanotube is obtained, and the plasticity of the material can be considered while the strength of the composite material is improved, so that the composite material has good comprehensive mechanical property.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
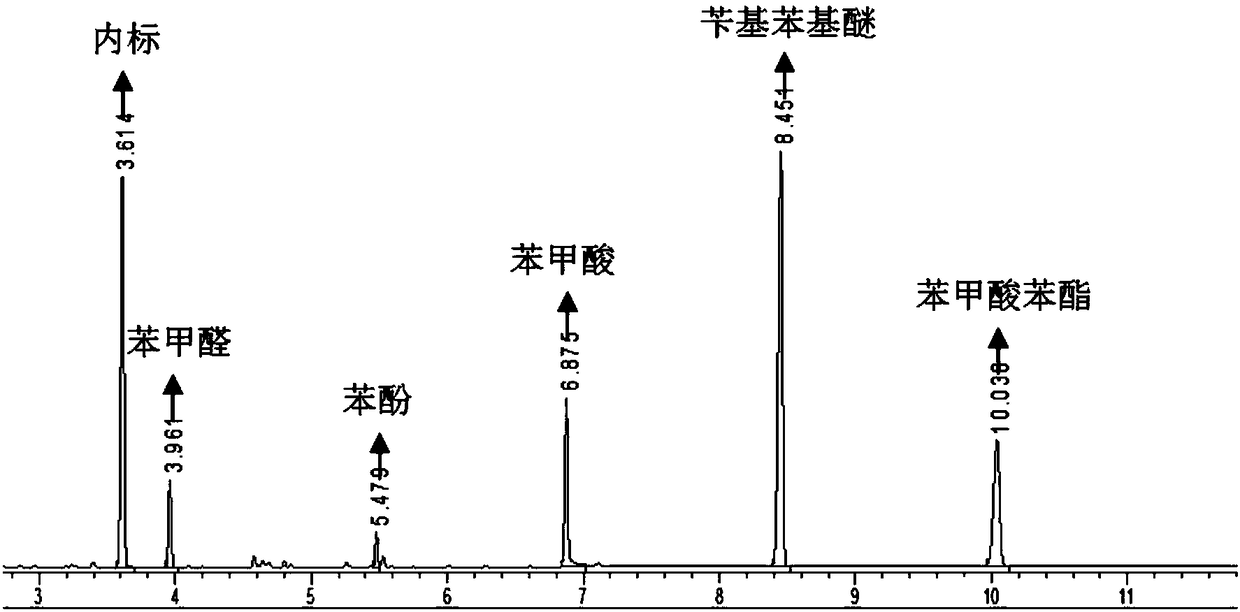
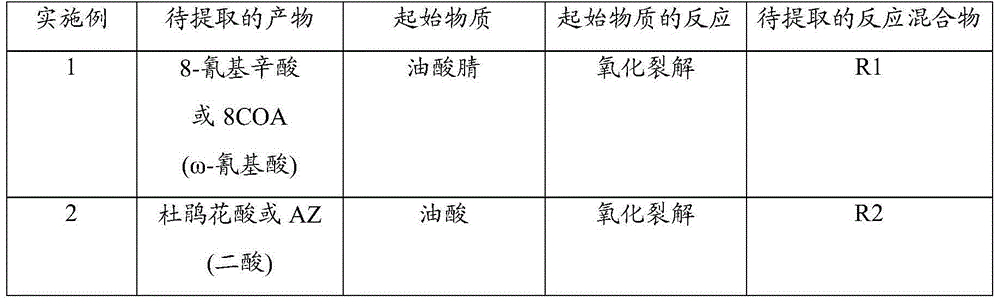
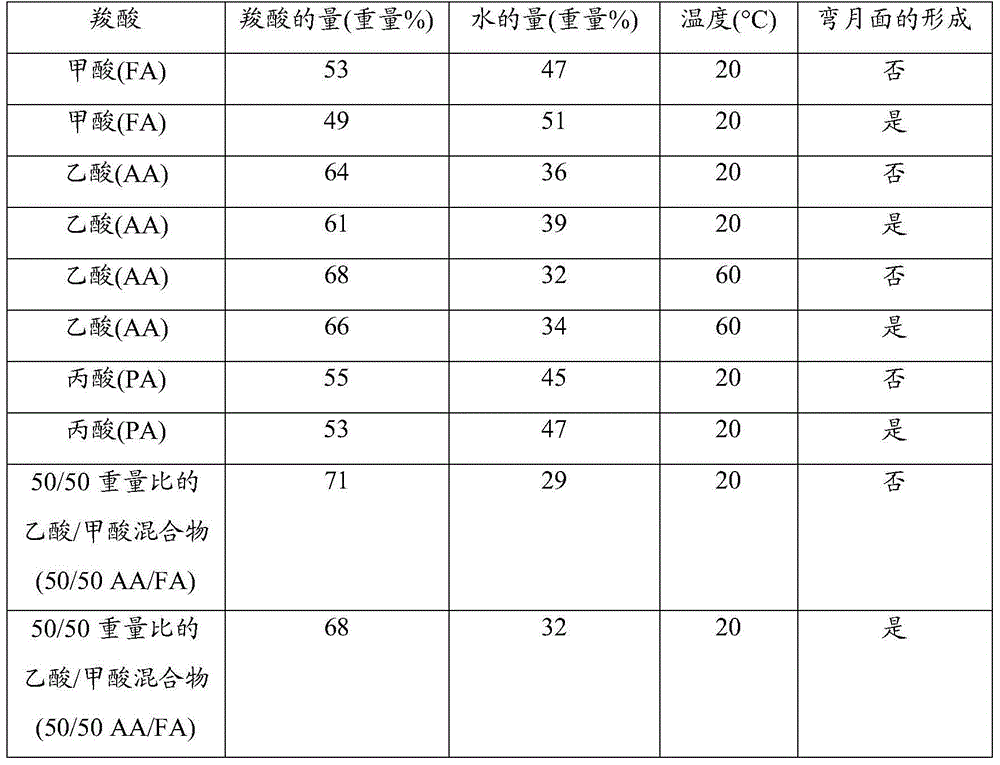
Selective extraction of an omega-functionalised acid after oxidative cleavage of an unsaturated fatty acid and derivatives
InactiveCN104797552ACarboxylic preparation by ozone oxidationCarboxylic acid nitrile purification/separationOxidative cleavagePolyamide
The invention concerns a method for the selective extraction of a reaction product, originating from an oxidative cleavage of an unsaturated fatty acid or of an ester derivative or of an unsaturated nitrile derivative, said reaction product being a co-functionalised acid chosen from the C6 to C15 diacids, ester-acids and nitrile-acids, using, as the selective extraction solvent, a composition comprising a mixture of water and C1-C4 carboxylic acid. The invention also concerns the use of said method and the extraction solvent composition for the preparation of C6 to C15 amino acid, diacid or ester-acid monomers for the production of polycondensation polymers, in particular polyamides.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
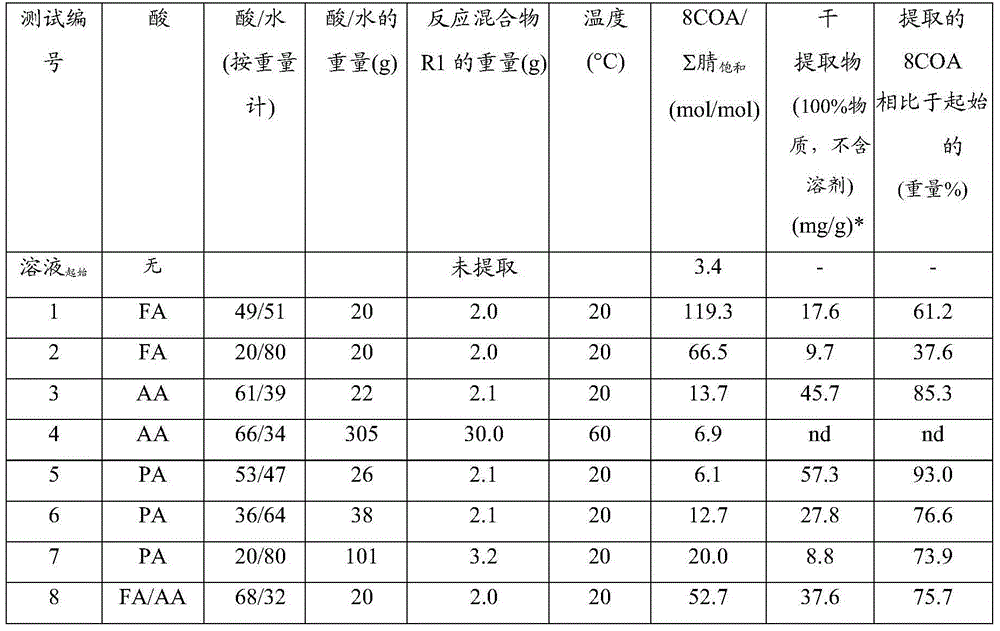
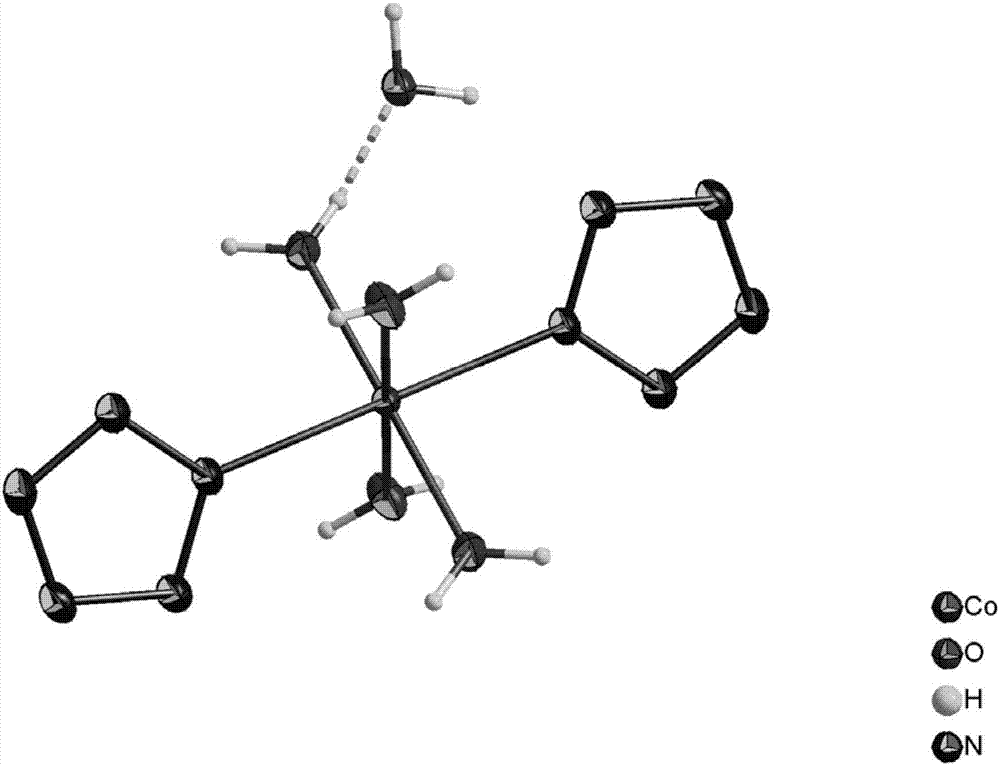
Aqueous metal ion pentazole salts and preparation method thereof
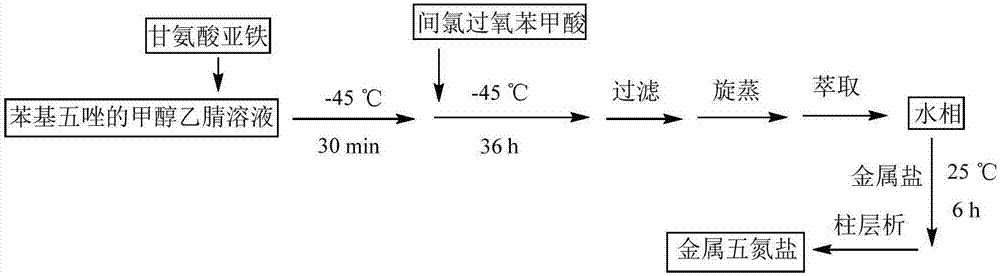
The invention discloses aqueous metal ion pentazole salts and a preparation method thereof. The metal salts have a chemical structural formula of M(N5)x(H2O)y. When M represents a monovalent metal Li, Na, K or Ag, x is 1 and y is 4. When M represents a divalent metal Fe, Co, Ni, Mg, Ca, Ba, Cu, Zn or Pb, x is 2 and y is 8 or 10. The preparation method utilizes metachloroperbenzoic acid and ferrous glycinate as a cleavage reagent and an aid acting with aryl pentazole. Through an oxidative cleavage method, the C-N bond of the aryl pentazol molecule is selectively cut and a metal ion-containing salt is used as a capture reagent in preparation of the aqueous metal ion pentazole salts. The preparation method successfully prepares the metal pentazole salts. The metal pentazole salts can be widely used in the field of energetic materials.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preventing W loss by capturing W catalyst in oxidative cracking reaction
InactiveCN109126766AActivity does not affectAvoid churnOrganic compound preparationHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsOxidative cleavageSorbent
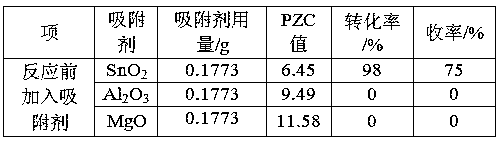
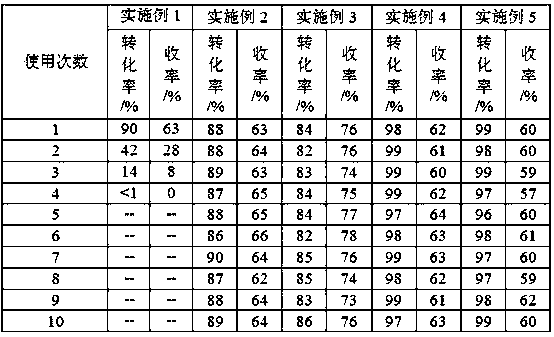
The invention discloses a method for preventing W loss by capturing a W catalyst in oxidative cracking reaction. The method particularly includes the steps: uniformly mixing a solid adsorbent, the W catalyst, hydrogen peroxide and reaction substrates; performing stirring reaction on mixture; centrifugally separating solid after reaction is completed; recycling the solid by a post-processing step;mixing the solid, the hydrogen peroxide and the reaction substrates; repeating catalytic reaction. W dissolved in reaction solution is adsorbed by a SnO2 solid adsorbing agent, a carrier of the W is formed, activity of catalytic reaction cannot be reduced, the W is recycled and then can be repeatedly used for the catalytic reaction, the activity of catalytic reaction cannot be affected by the solid adsorbing agent, the solid adsorbing agent can be repeatedly used, SnO2 cannot decompose the hydrogen peroxide when the SnO2 has a high PZC value, the SnO2 added into WO3 / H2O2 and H2WO4 / H2O2 systems, tungsten-containing negative ions can be effectively dissolved, a new catalyst is combined, the W loss is prevented, and the service life of the catalyst is prolonged.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing adiponitrile by catalytic ammonia oxidation cracking of cyclohexanol
ActiveCN109956888AEasy to separatePreparation by hydrocarbon ammoxidationOxidative cleavageCyclohexanol
The invention relates to a method for preparing adiponitrile by the catalytic ammonia oxidation cracking of cyclohexanol. In the method, ammonia gas is used as the nitrogen source, air and / or oxygen is used as the oxygen source, and cyclohexanol is subjected to the ammonia oxidation cracking to prepare adiponitrile under the catalytic action. According to the method, the ammonia oxidation efficiency is high, and the product yield is high; the air is used as the oxygen source, so that the method is economic and environment-friendly; and the product and the catalyst are easy to separate, and thepost-treatment is simple, so that the method has good application prospect.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for producing modified polymer, diene polymer, rubber composition and pneumatic tire
ActiveUS9365656B2Easily incorporated in main chain structureReduce molecular weightSpecial tyresPolymer scienceOxidative cleavage
A polymer having a carbon-carbon double bond in a main chain is decomposed by subjecting the carbon-carbon double bond to oxidative cleavage using an oxidizing agent such as periodic acid to decrease the molecular weight, polymer chains of the decomposed polymer are combined by changing acido-basic properties such that a system containing the decomposed polymer becomes basic when acidic and becomes acidic when basic, and a modified polymer in which the structure has been changed is obtained. By this, a functional group can be incorporated in the main chain structure of a polymer. A rubber composition comprising a rubber component containing the modified polymer, and a filler compounded therewith, and a pneumatic tire comprising the rubber composition are provided.
Owner:TOYO TIRE & RUBBER CO LTD
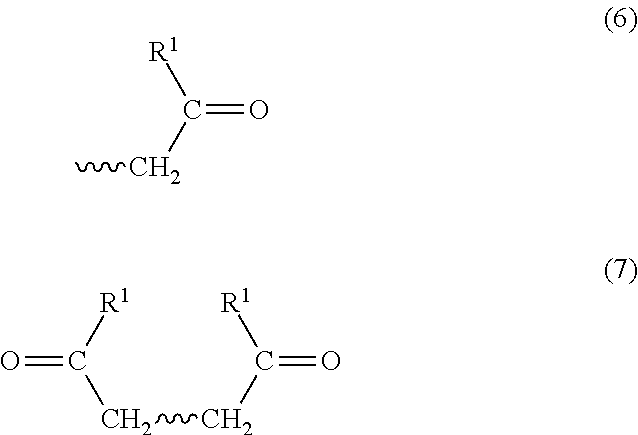
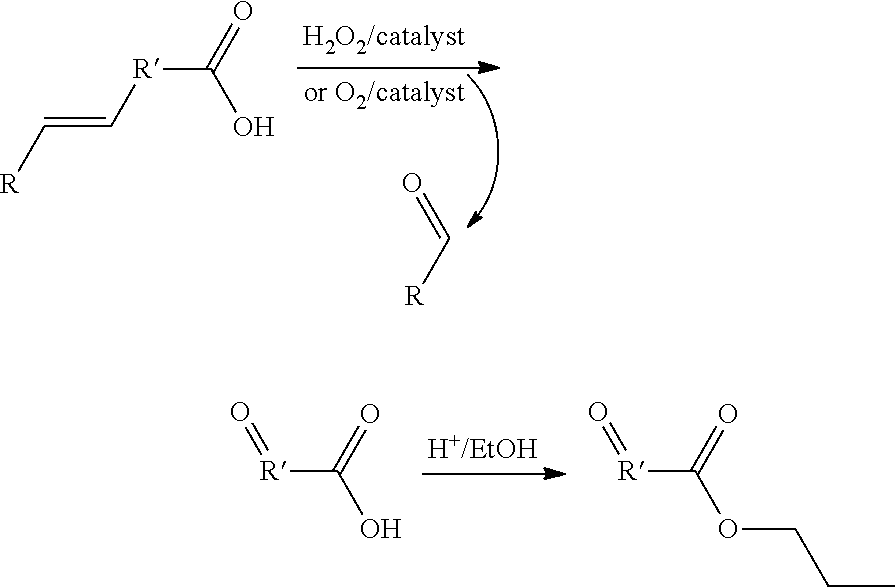
Oxidative cleavage of unsaturated carboxylic acids
InactiveUS20120264956A1Saving expenseSave materialOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationOxidative cleavageDouble bond
Provided are processes for the oxidative cleavage of a double bond in an unsaturated carboxylic acid. The process includes contacting the unsaturated carboxylic acid with a mild oxidizing agent and agitating the unsaturated carboxylic acid and the mild oxidizing agent for a time sufficient to cleave a double bond of the unsaturated carboxylic acid and produce a product comprising an aldehyde. The process is typically carried out in a mill, such as a ball, hammer, attrition, or jet mill.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com