Method for preventing W loss by capturing W catalyst in oxidative cracking reaction
A technology of oxidative cracking and catalyst, which is applied in the direction of metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalyst, physical/chemical process catalyst, chemical instrument and method, etc. It can solve the problems of hydrogen peroxide decomposition and affecting oxidation efficiency, etc., to achieve Effects of avoiding loss, preventing W loss, and improving service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
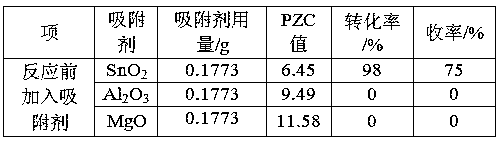
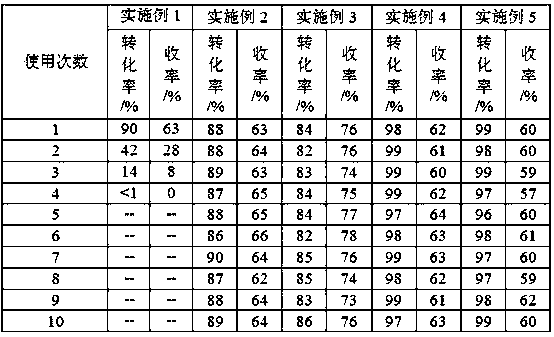
[0020] (Blank experiment) It is used in the reaction of oxidative cracking of epoxy methyl oleate to produce nonanal and nonanalic acid methyl ester without adding solid adsorbent. Weigh 15.6240g epoxy methyl oleate, 0.1160g WO 3 Catalyst and 5.6667g hydrogen peroxide (mass concentration: 30%), mixed evenly, stirred and reacted in a water bath at 80°C for 20 minutes, centrifuged the reaction mixture, and the obtained solid was washed with ethanol and dried, and then reused for the next time For the cracking reaction of epoxy methyl oleate, the recovered solid is recycled as a catalyst to carry out the catalytic reaction. The reaction results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
[0022] It is used in the reaction of oxidative cracking of epoxy methyl oleate to produce nonanal and nonanalic acid methyl ester. Weigh 15.6240g epoxy methyl oleate, 0.4599g SnO 2 , 0.1160g catalyst WO 3 and 5.6667g hydrogen peroxide (mass concentration: 30%), after mixing evenly, stirred and reacted in a water bath at 80°C for 20min, centrifuged the reaction mixture, washed the obtained solid with ethanol, dried it, and continued to reuse it for the next cycle In the cracking reaction of methyl oxyoleate, the recovered solid is recycled as a catalyst to carry out the catalytic reaction, and the reaction results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0024] It is used in the reaction of oxidative cracking of 1,2-cyclopentanediol to produce glutaraldehyde. Weigh 10.0000g 1,2-cyclopentanediol, 3.6034g SnO 2 , 0.4897g Catalyst H 2 WO 4 and 19.9920g of hydrogen peroxide (mass concentration: 50%), mixed evenly, stirred and reacted in a water bath at 90°C for 5 hours, centrifuged the reaction mixture, washed the obtained solid with ethanol, dried, and continued to be used for the next 1 , 2-cyclopentanediol cleavage reaction, so the recovered solid is recycled as a catalyst for catalytic reaction, and the reaction results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com