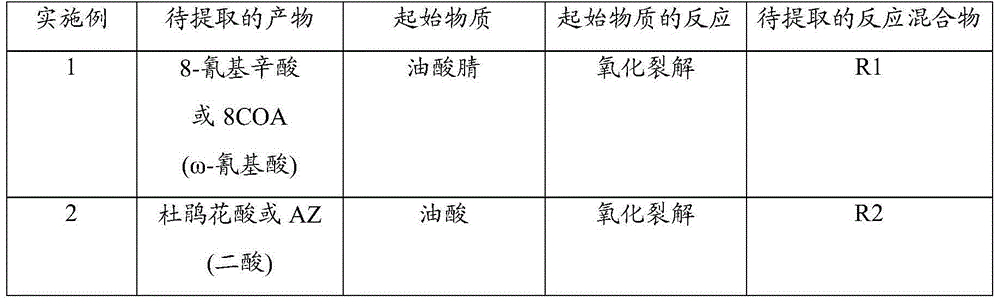
Selective extraction of an omega-functionalised acid after oxidative cleavage of an unsaturated fatty acid and derivatives
An unsaturated fatty acid, selective technology, applied in the field of selective extraction of ω-functionalized acids after oxidative cracking of unsaturated fatty acids and derivatives, can solve difficult and complicated removal problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
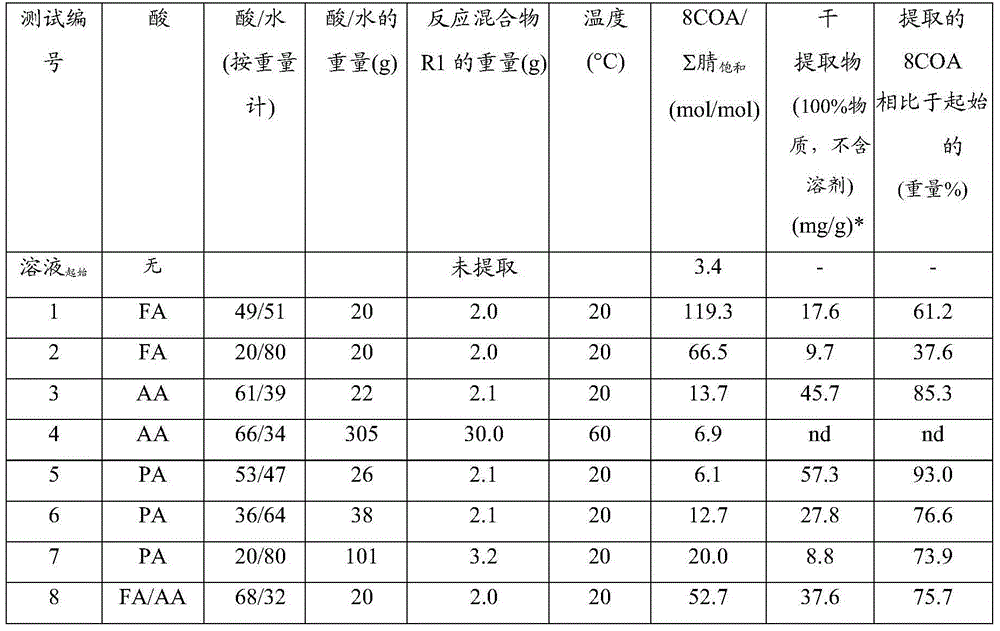
[0064] Example 1 : Extraction of 8-cyanoctanoic acid from reaction mixture R1 derived from oxidative cleavage of oleic acid nitrile
[0065] The reaction mixture R1 used was a solution (according to gas chromatographic analysis) with a composition as presented in Table 2 below.
[0066] Table 2 : combination of reaction mixture R1
[0067] Components of reaction mixture R1
weight%
mmol / g
0.7
0.049
Heptanoic acid (A7)
1.9
0.146
Caprylic acid (A8)
1.2
0.080
Nonanoic Acid (A9)
12.4
0.785
Capric acid (A10)
0.5
0.028
7-cyanoheptanoic acid (7CHA)
1.6
0.105
8-cyanoctanoic acid (8COA)
19.8
1.169
9-Cyanononanoic Acid (9CNA)
1.0
0.053
Myristonitrile (14:0)
1.7
0.080
10-cyanodecanoic acid (10CDA)
1.2
0.062
Palmitic acid nitrile (16:0)
4.3
0.182
Stearic acid nitrile (18:0)
1.8
0.068 ...
Embodiment 2
[0085] Example 2 : Extraction of diacid (Azelaic acid: AZ) from reaction mixture R2 obtained by oxidative cleavage of oleic acid
[0086] The reaction for the oxidative cleavage of oleic acid proceeds in a similar manner to the oxidative cleavage of oleic acid nitrile (with oleic acid nitrile being replaced by oleic acid). The oleic acid used was Oleon with a purity of 75%. The reaction takes place at 70 °C with no gas flow and using pure H with 144% relative to pure oleic acid 2 o 2 .
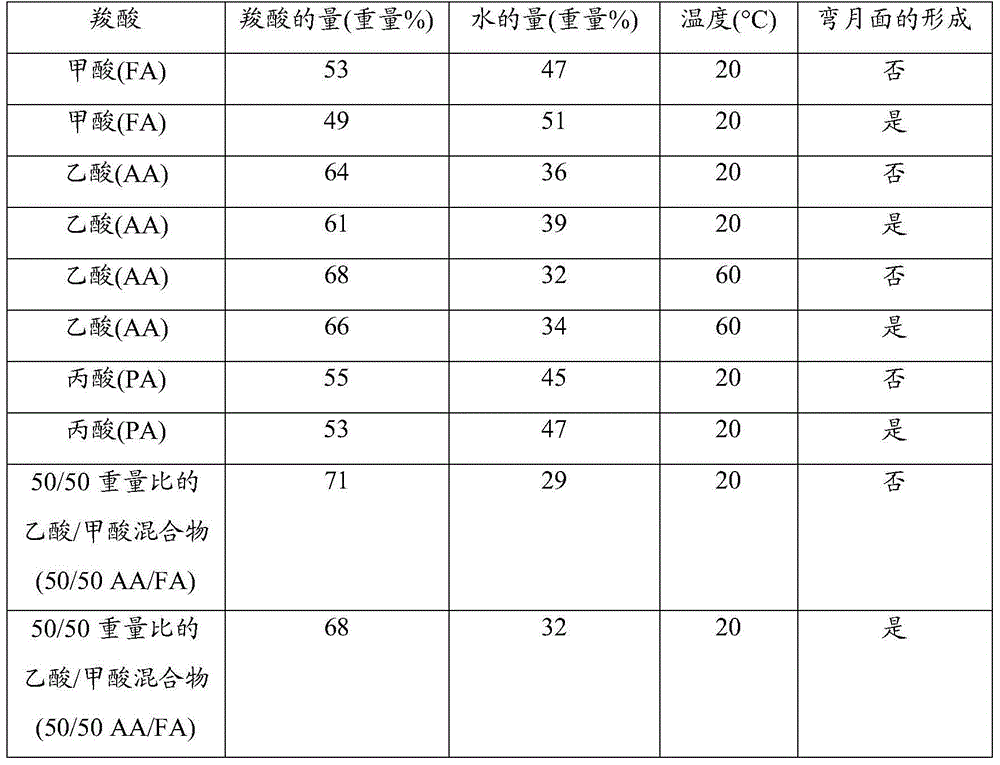
[0087] A sample of the reaction mixture R2 derived from the oxidative cleavage of oleic acid was extracted with the following solvent mixture: acetic acid (AA) / water, corresponding to AA / water = 58 / 42 by weight.
[0088] A weight of 2.1 g of the solution (R2) derived from the oxidative cleavage was brought into contact with a weight of 24.9 g of the AA / water solvent mixture. Thus, azelaic acid, which was initially present at 36.9%, was extracted by this solvent mixture. The composition ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com