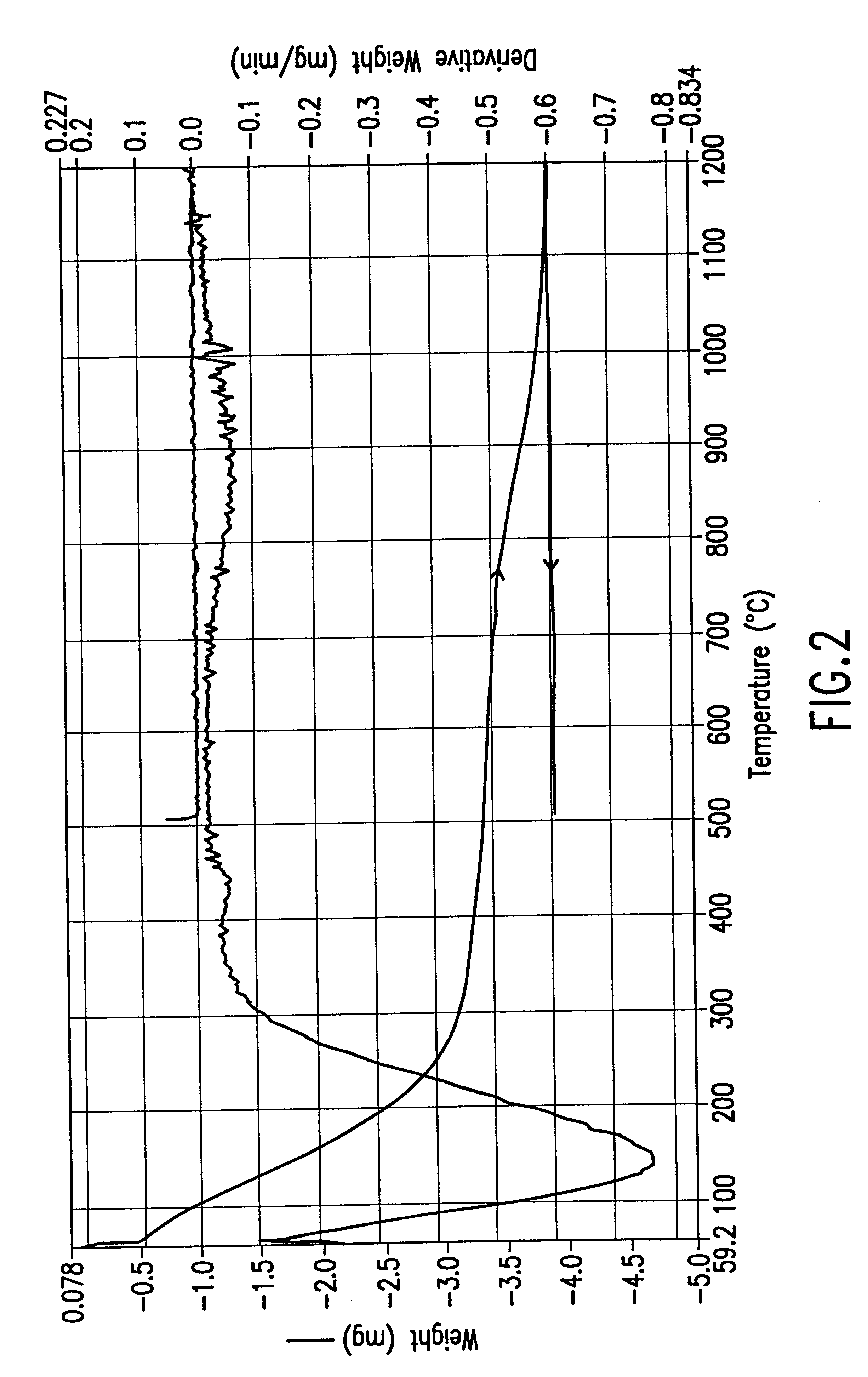
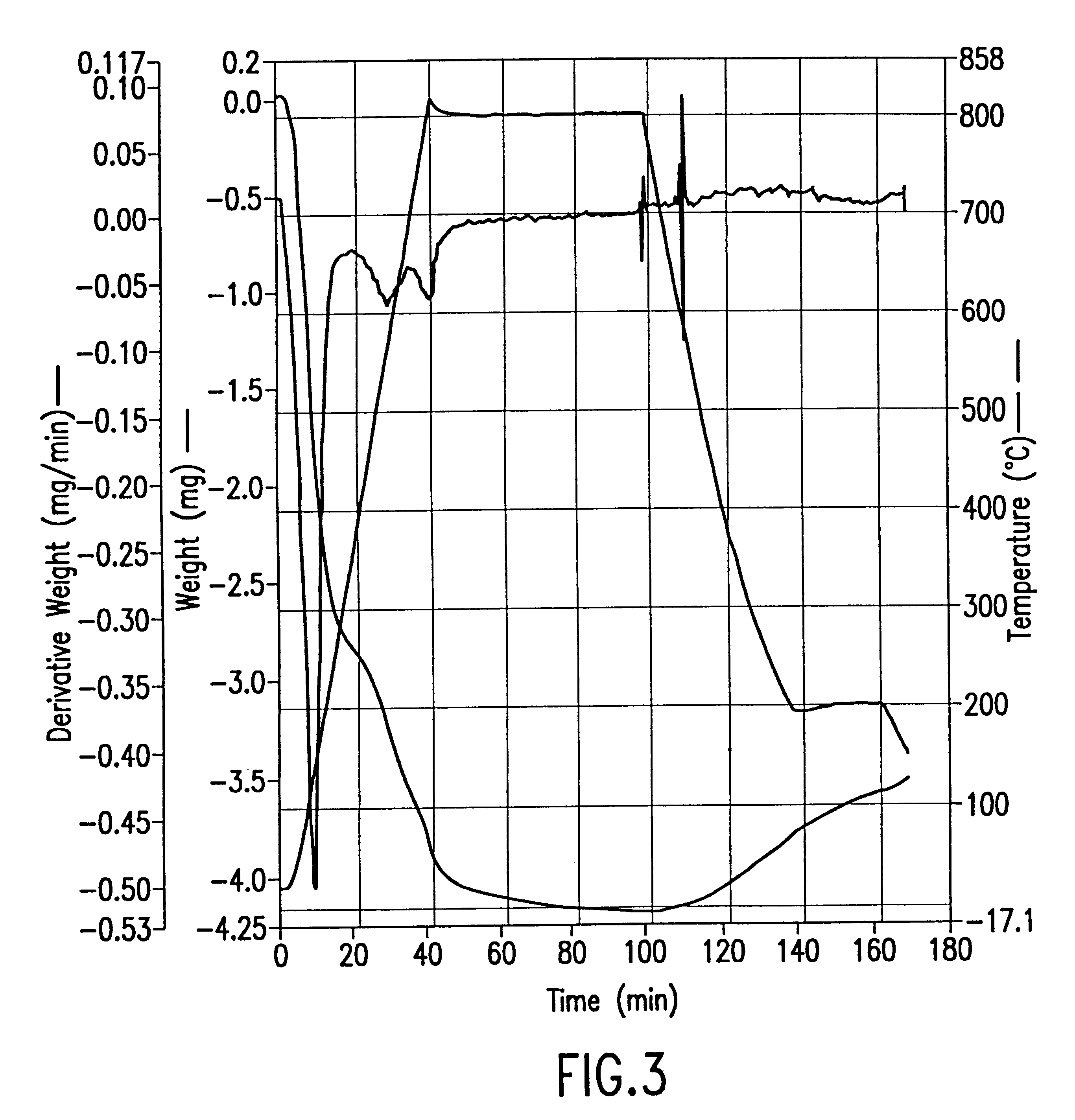
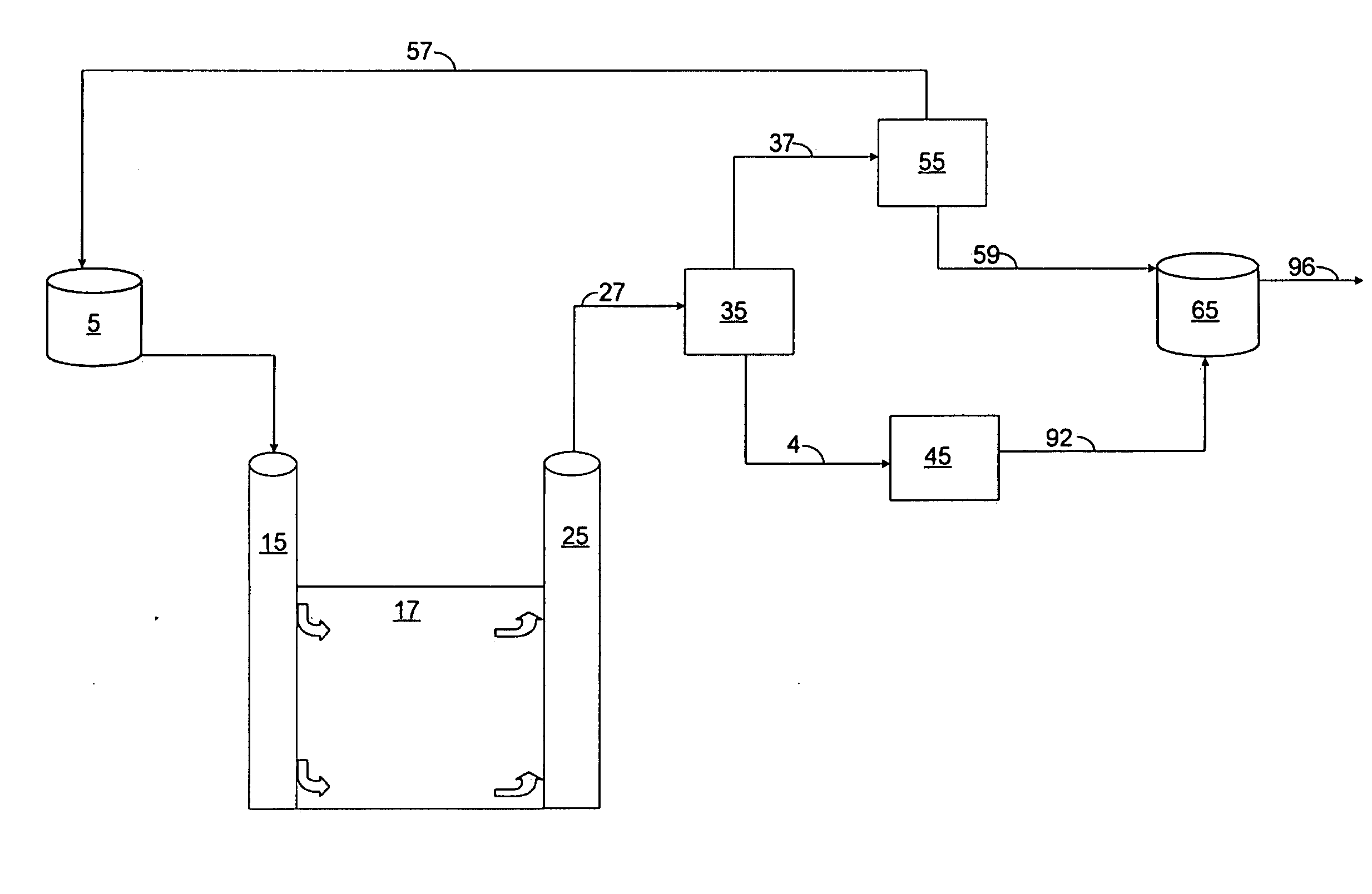
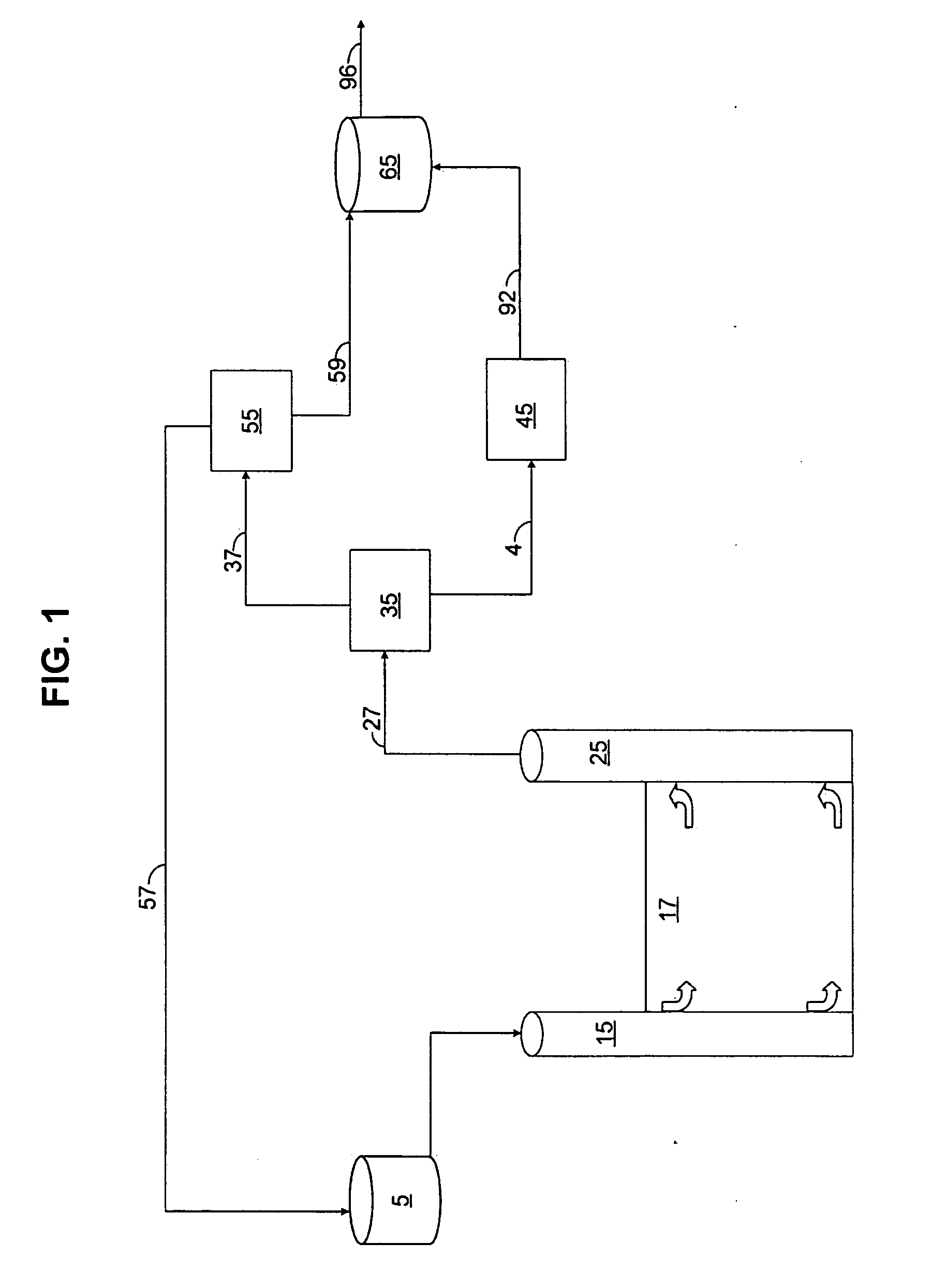
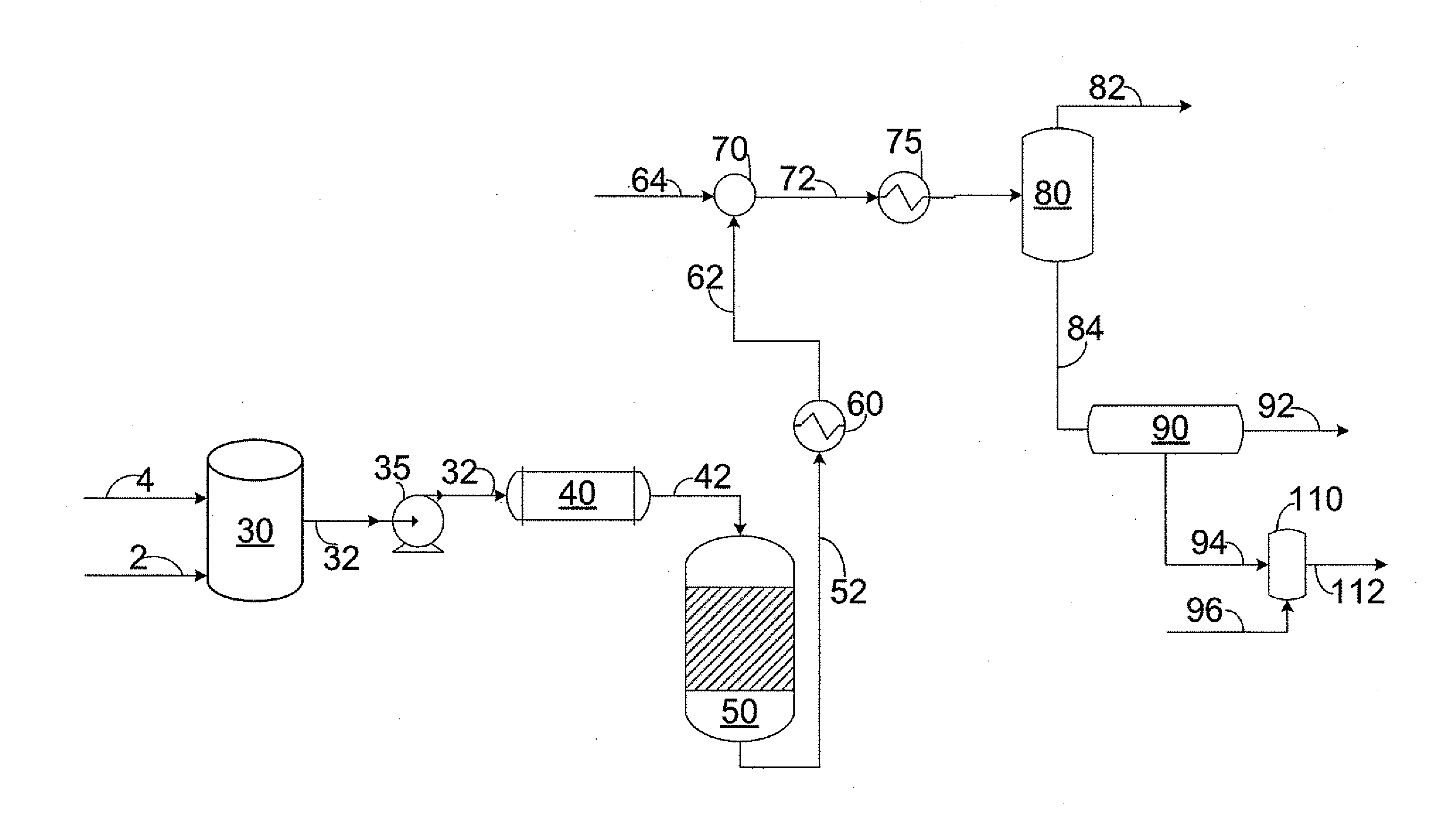
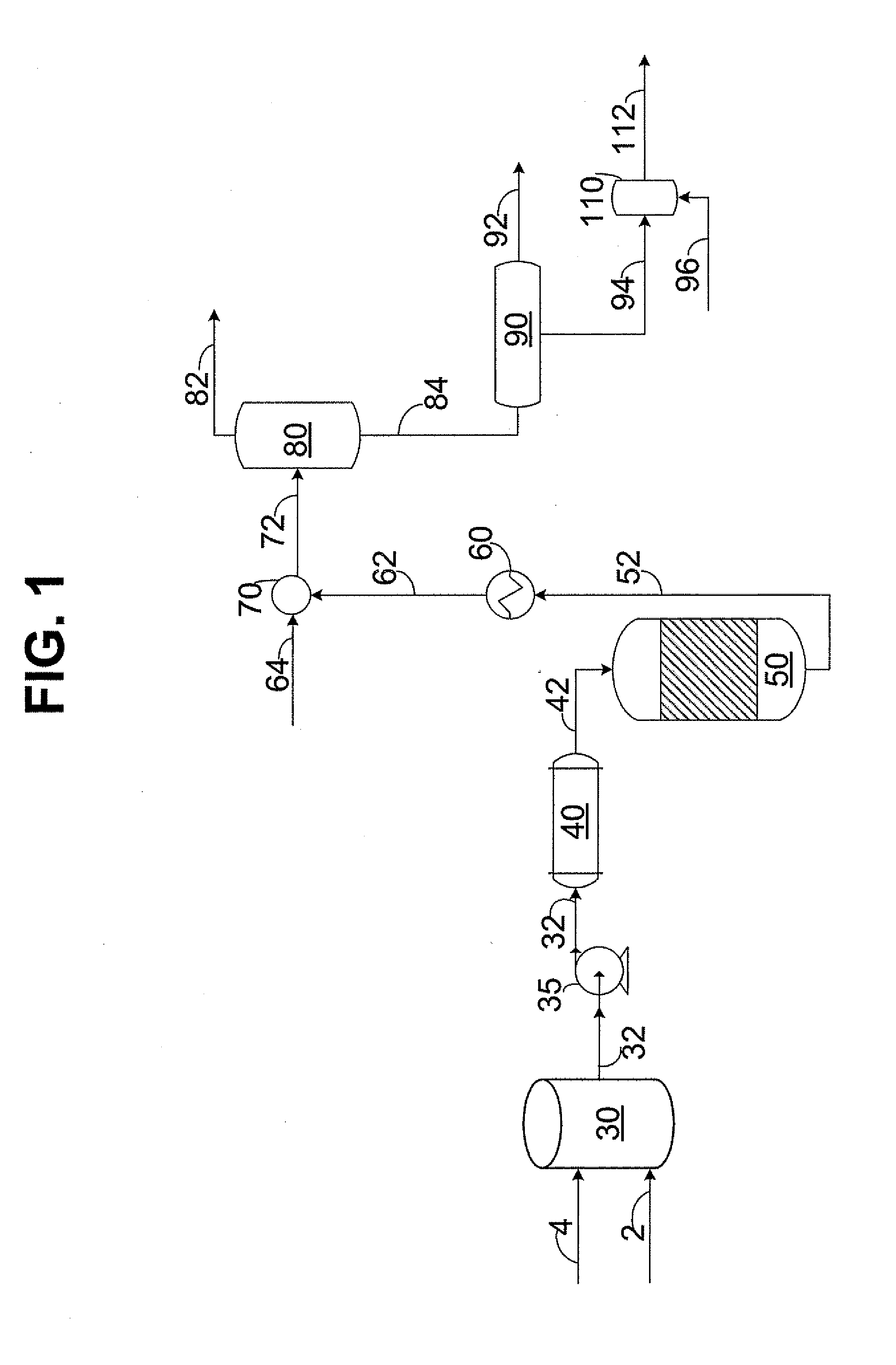
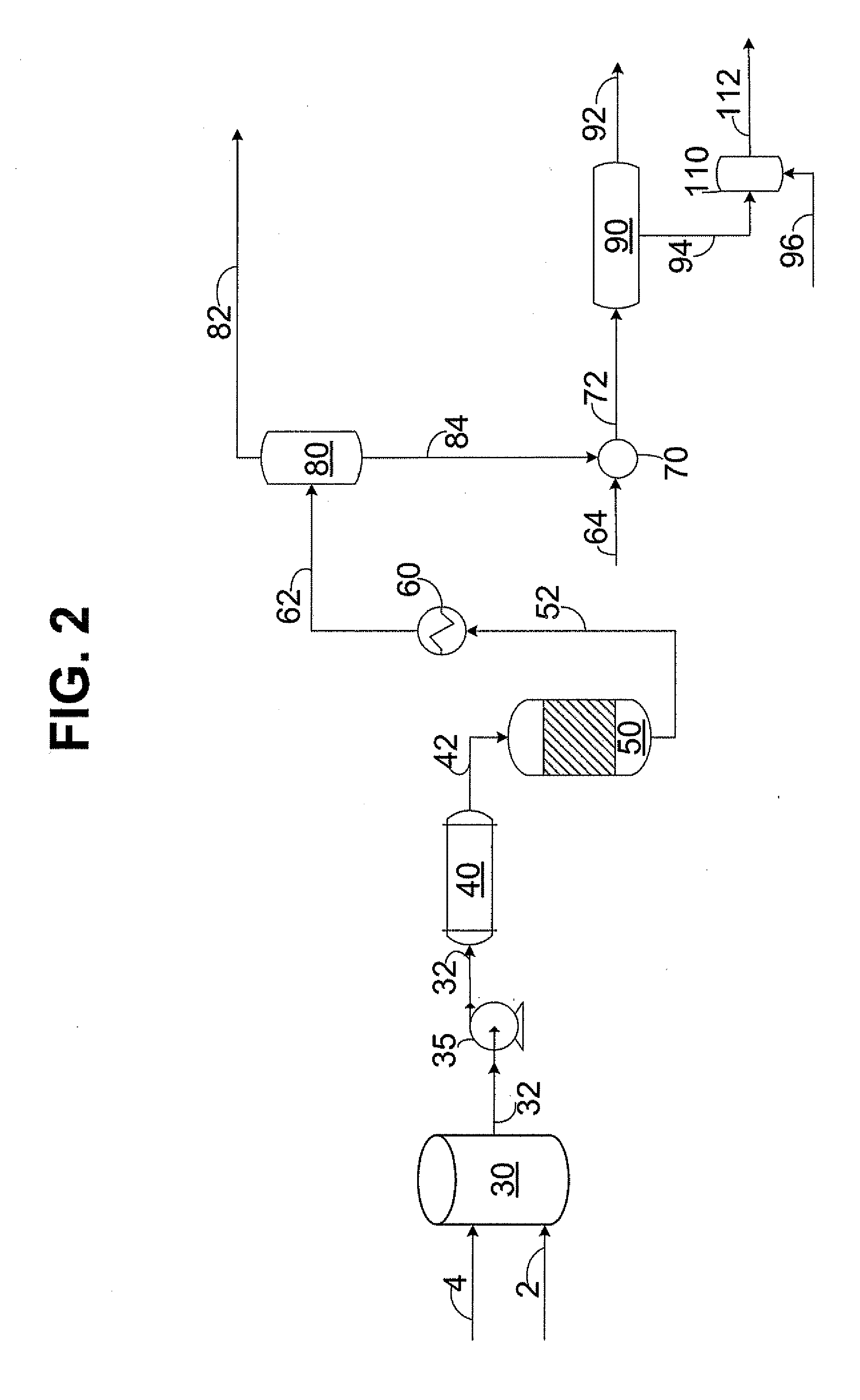
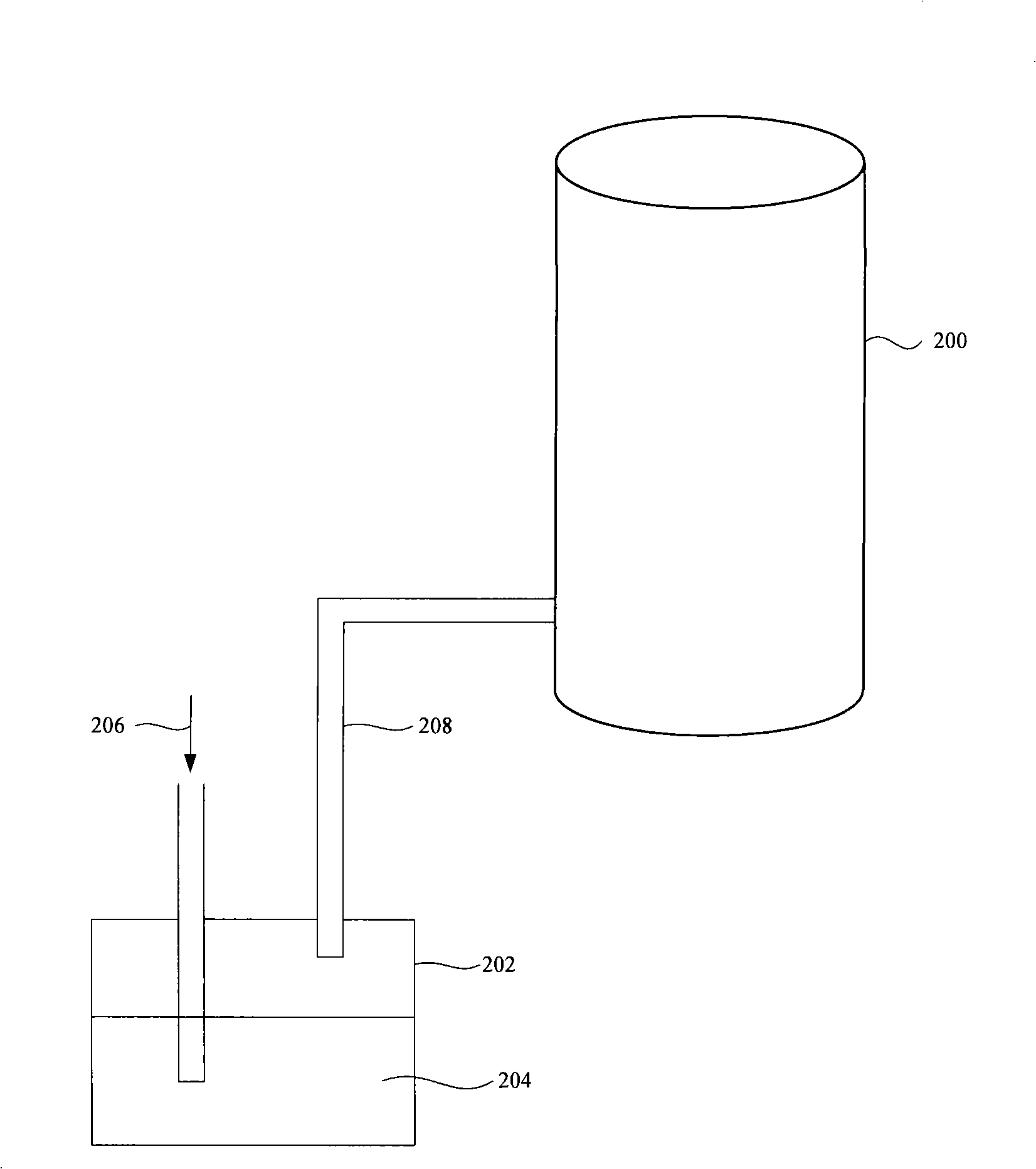
Patents
Literature
527 results about "Metallic impurities" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
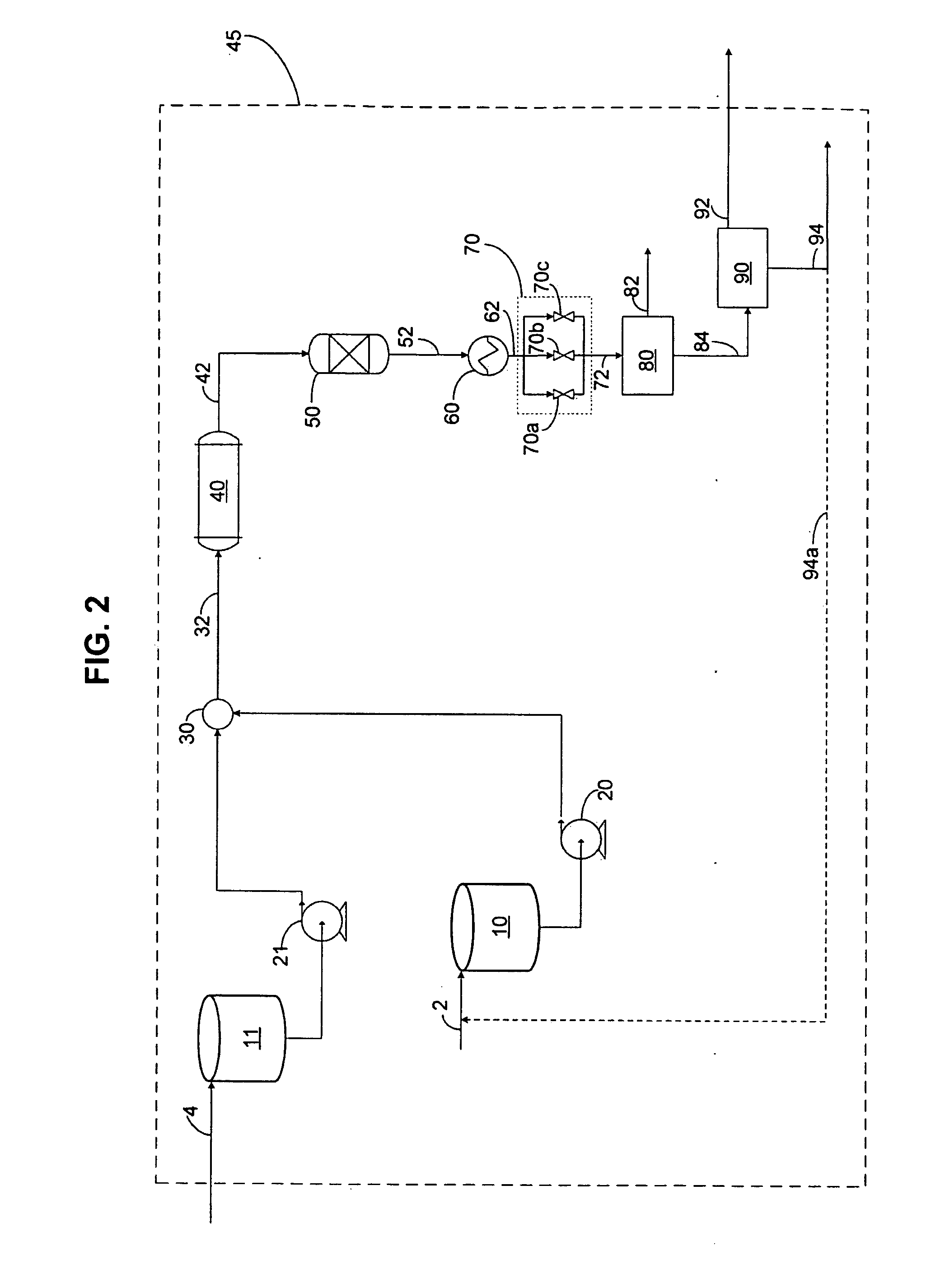
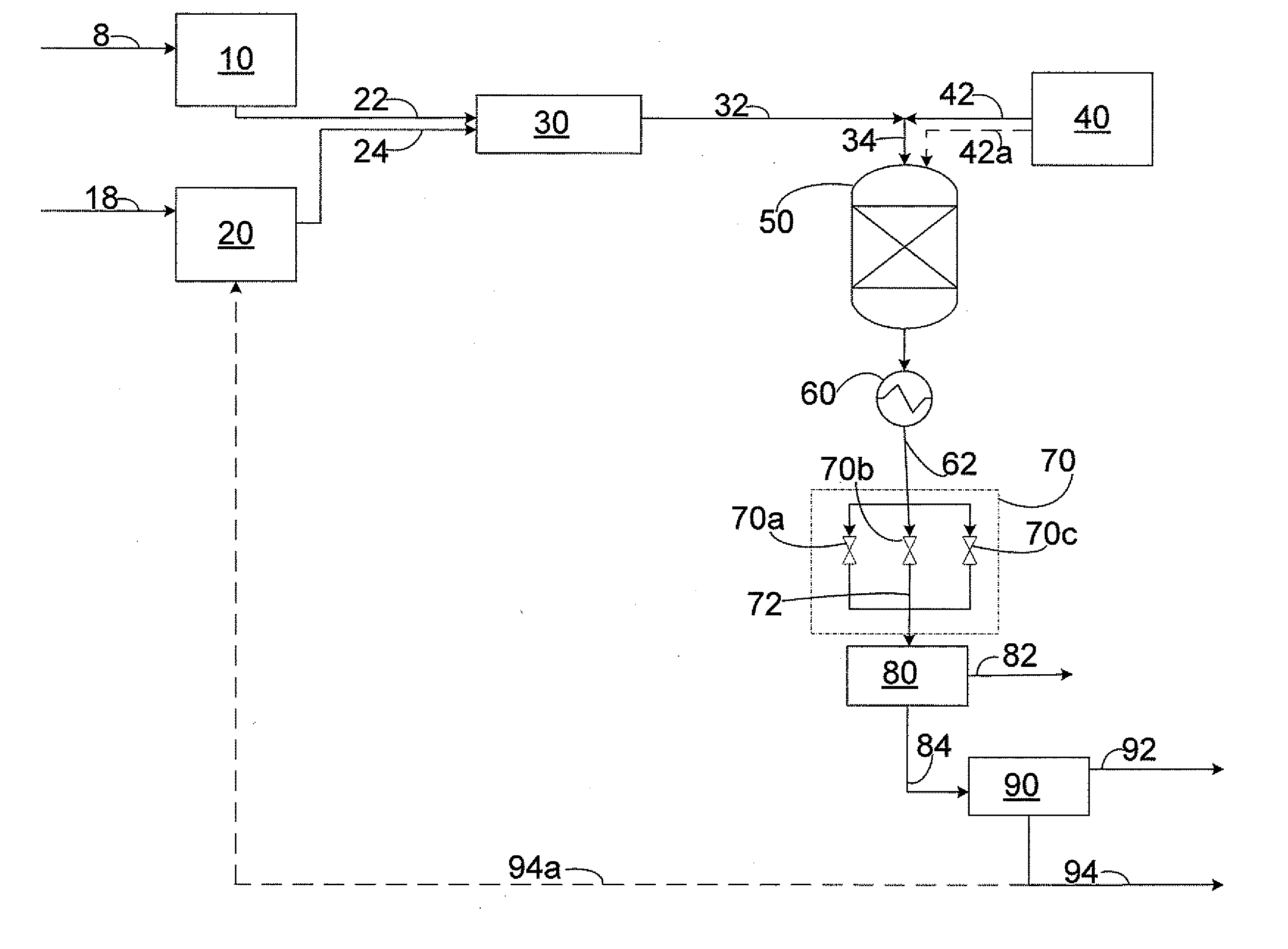
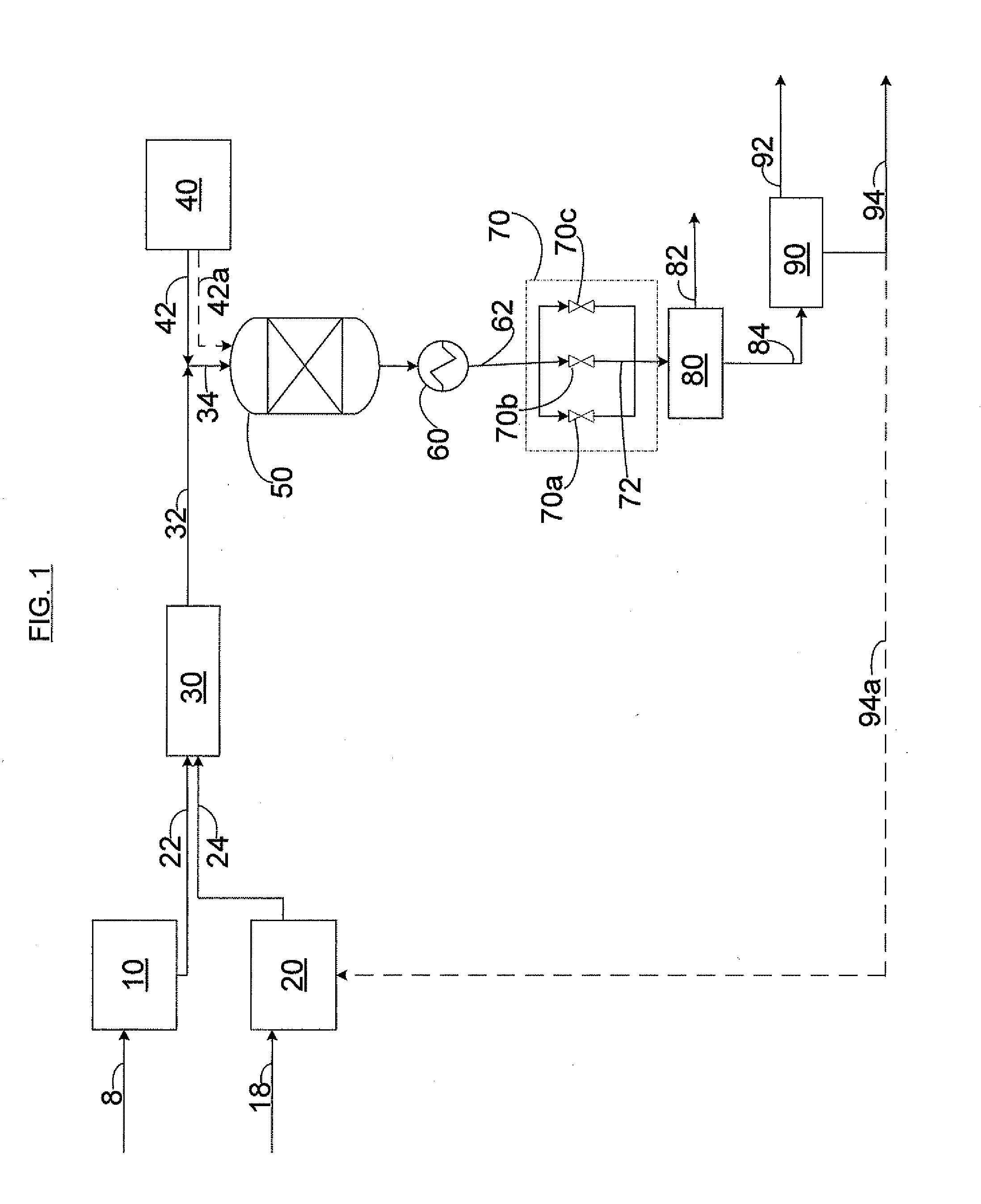
Methods for removal of water from gases using superheated zeolites
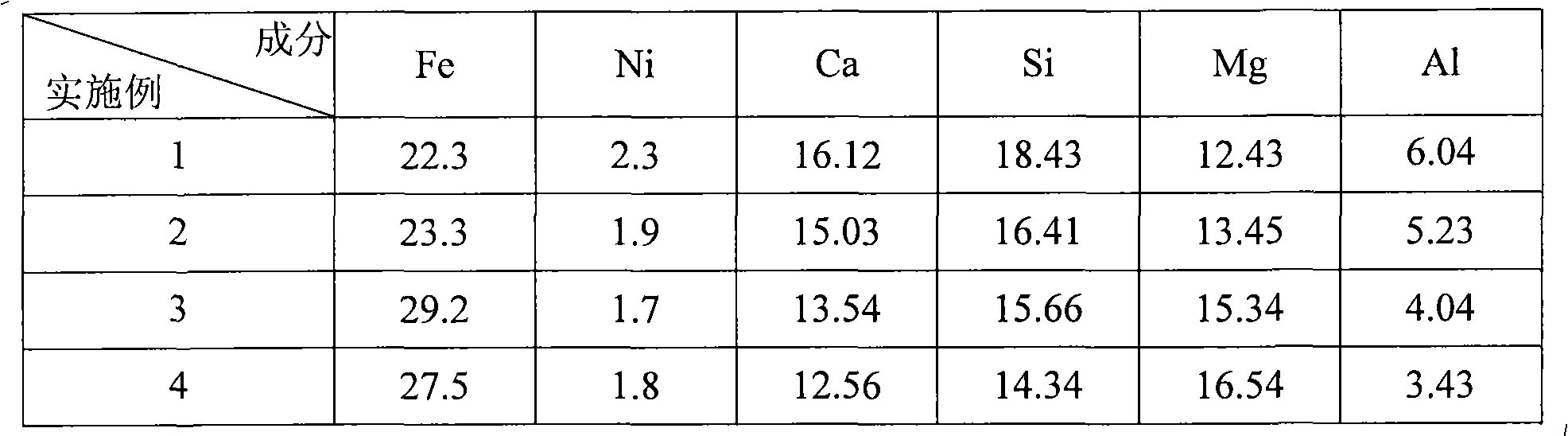
InactiveUS6110258AHigh silica-to-alumina ratioReduce metal contentGas treatmentMolecular sieve catalystsBoiling pointSilicon dioxide
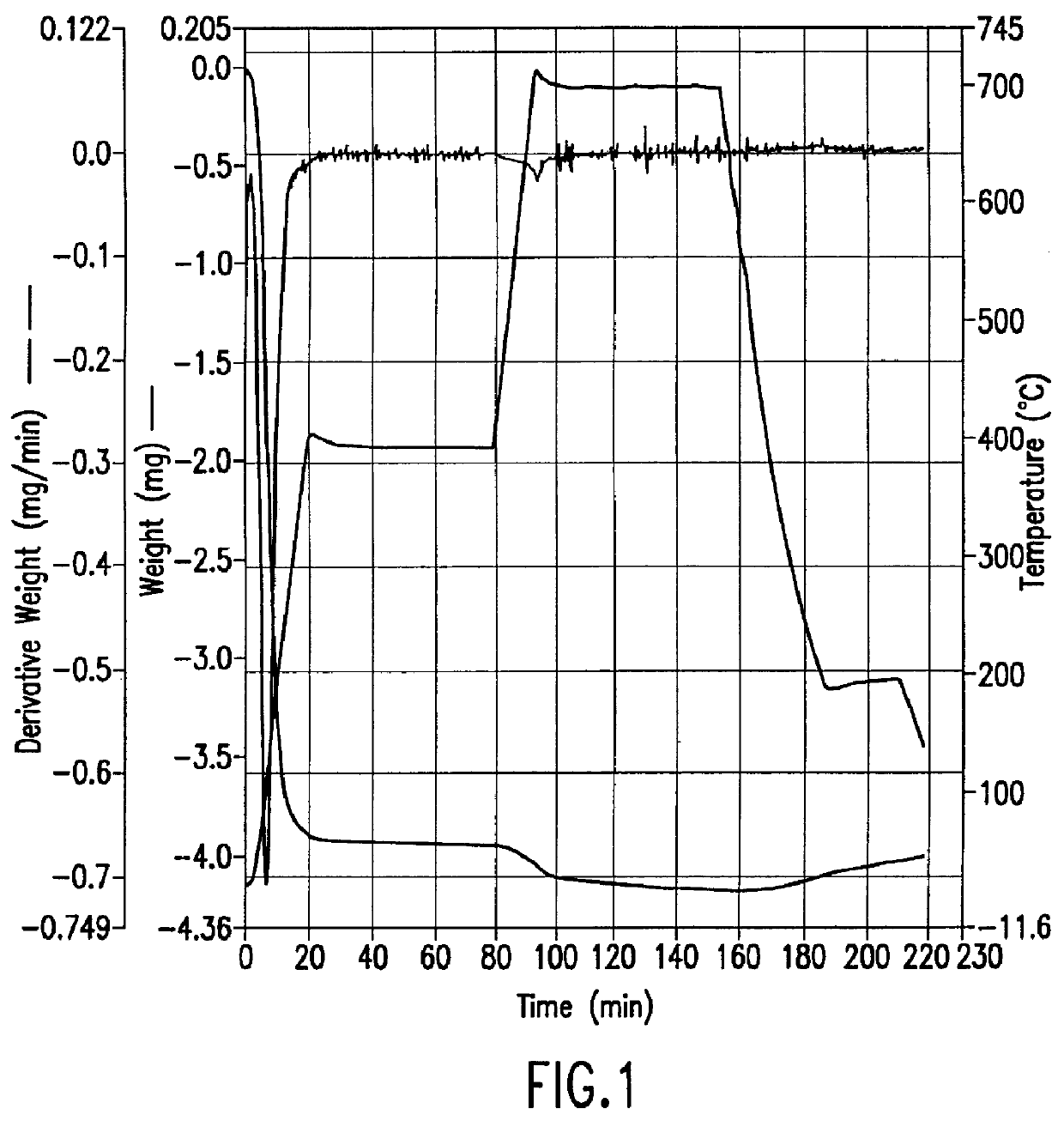
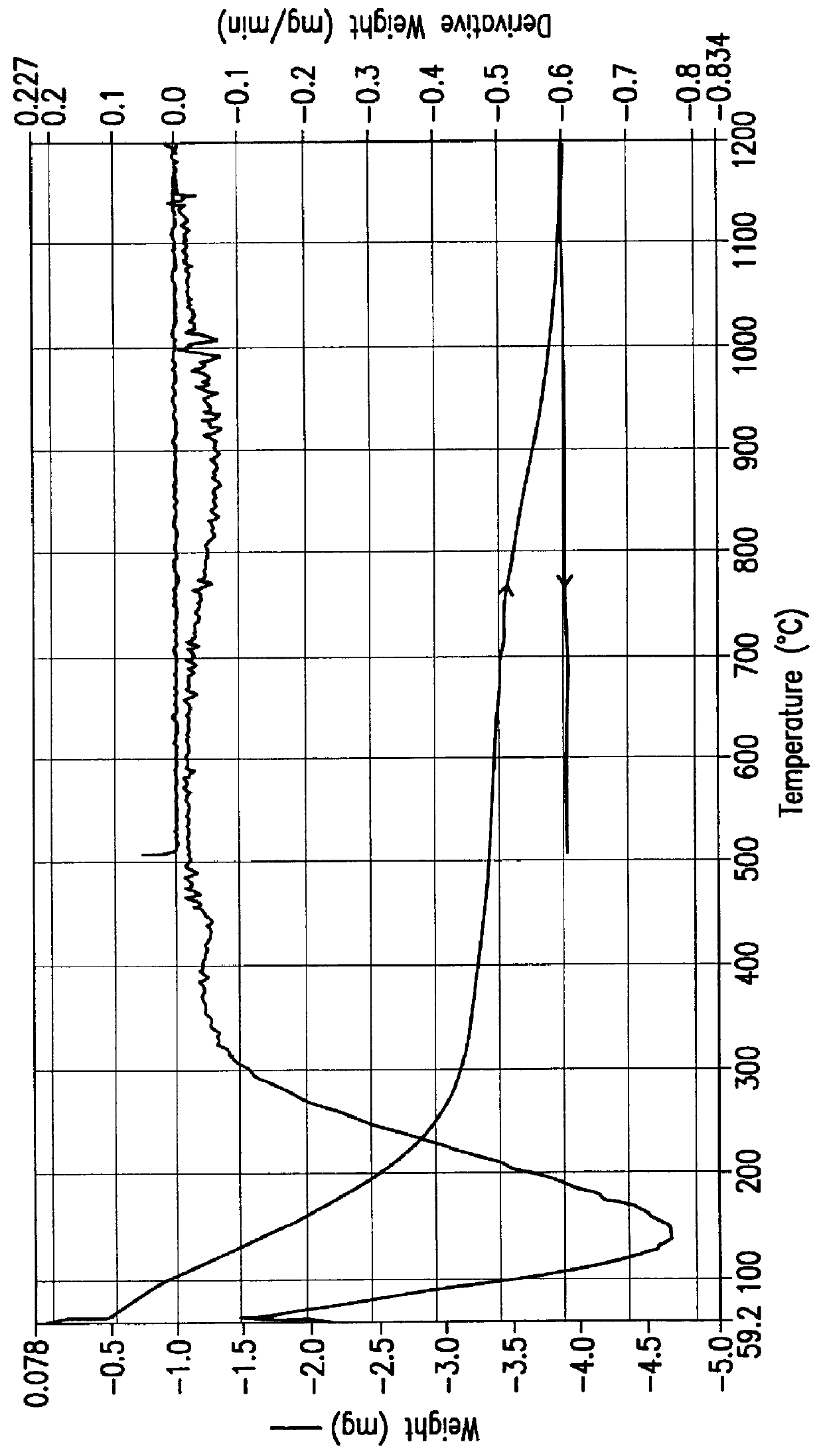
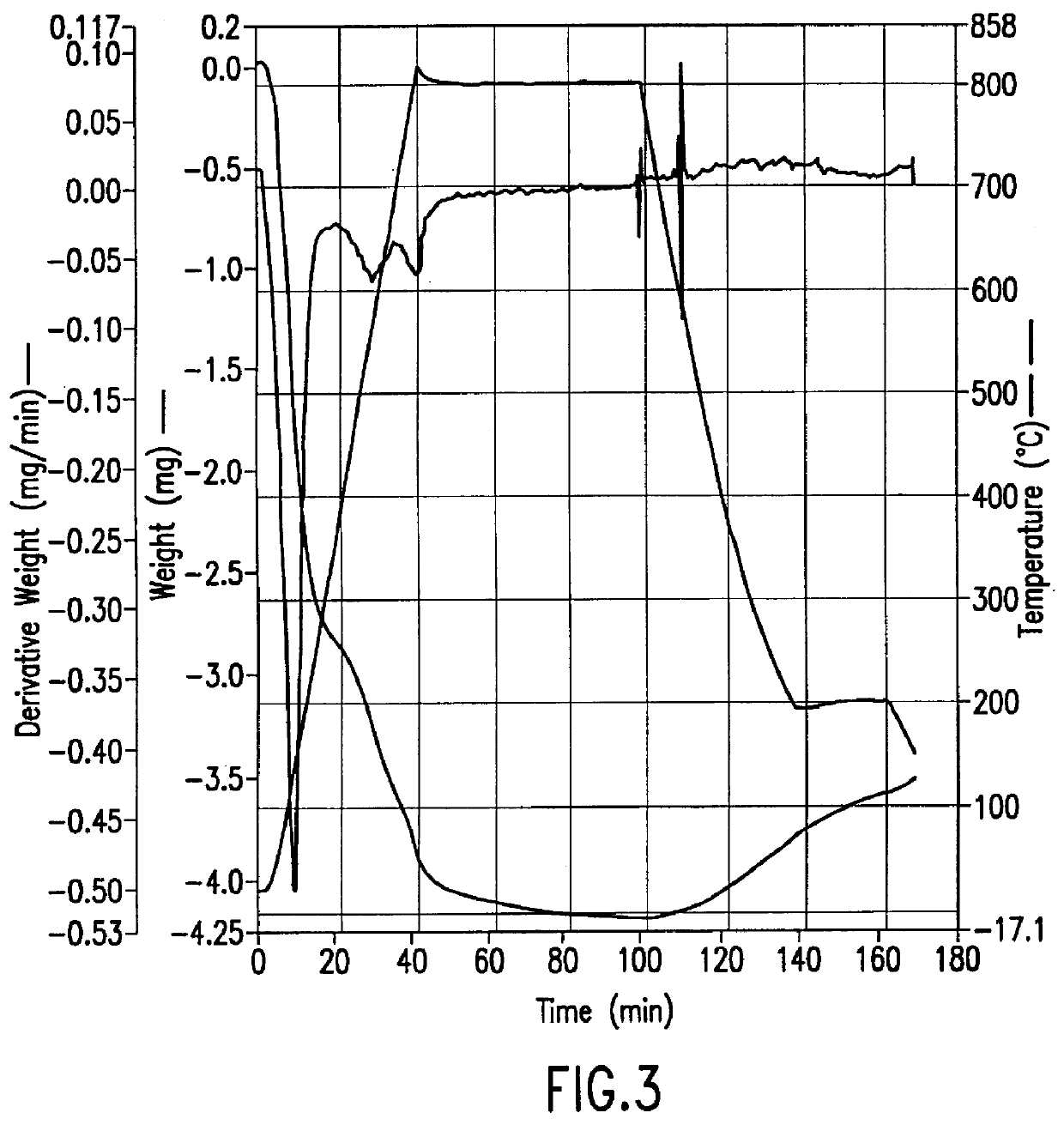
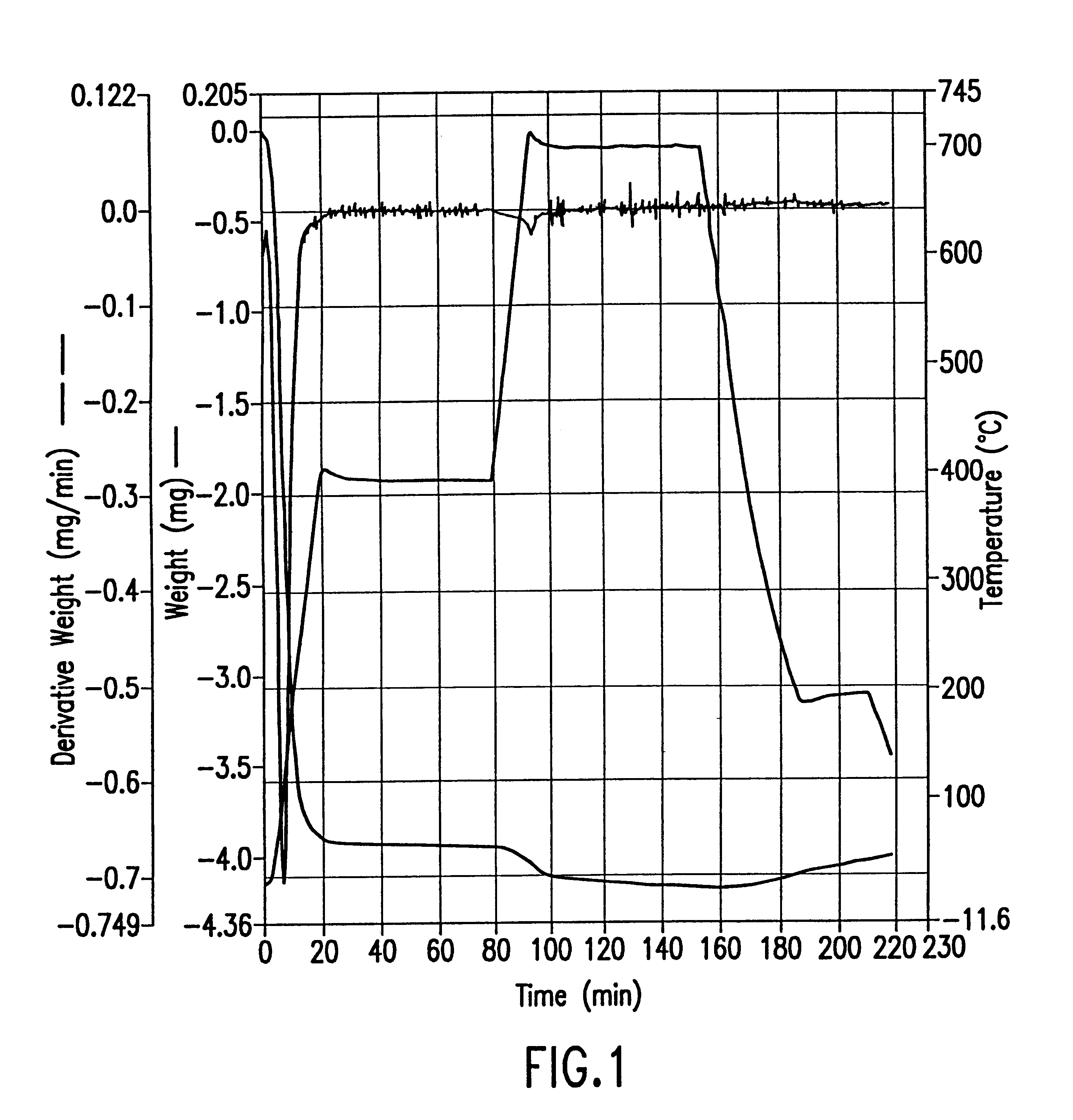
A method for removing trace moisture from a gas is disclosed. The method involves heating a zeolite having a high silica-to-alumina ratio to about 400 DEG C. to remove physically absorbed water from the zeolite, followed by heating the zeolite to a temperature in excess of 650 DEG C., to form a superheated zeolite. Heating to temperatures of 650 DEG C. or above is believed to cause dehydroxylation of the zeolite. A method for the preparation of a dehydroxylated zeolite is also disclosed. The superheated zeolite is contacted with the gas, thereby adsorbing water from the gas. A dehydroxylated zeolite for removing trace moisture from a gas wherein the zeolite has a high silica-to-alumina ratio and a low level of metallic impurities is also disclosed. The zeolite and methods of the invention are particularly useful for removing trace water from acid gases such as hydrogen chloride and hydrogen bromide.
Owner:MATHESON TRI GAS INC
Methods for removal of impurity metals from gases using low metal zeolites
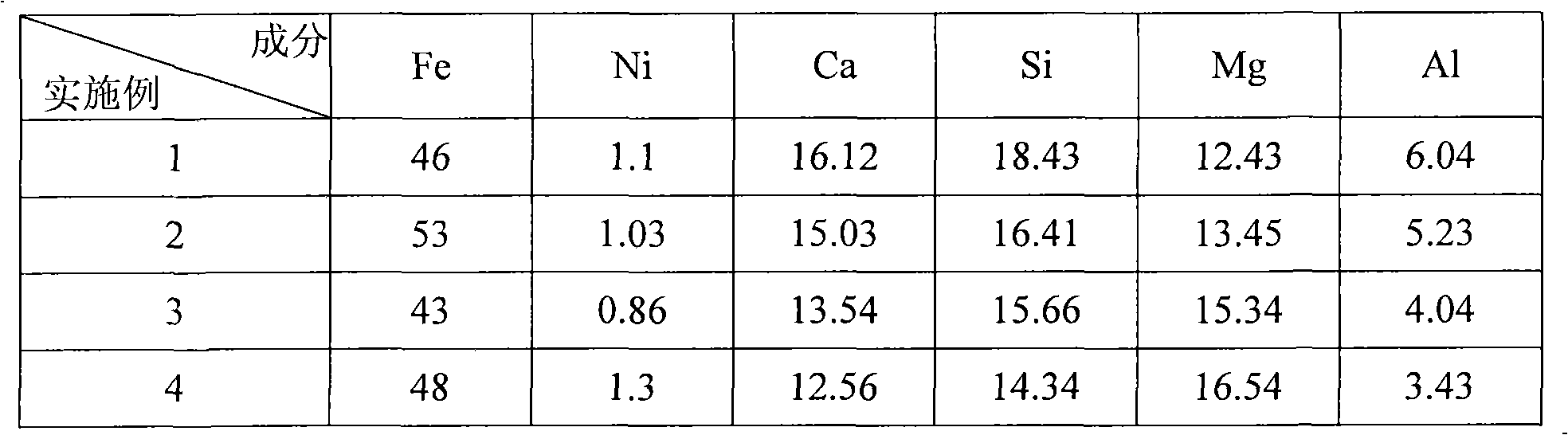
InactiveUS6395070B1High silica-to-alumina ratioReduce metal contentGas treatmentMolecular sieve catalystsBoiling pointTrace metal
A method for removing trace moisture from a gas is disclosed. The method involves heating a zeolite having a high silica-to-alumina ratio to about 400° C. to remove physically adsorbed water from the zeolite, followed by heating the zeolite to a temperature in excess of 650° C., to form a superheated zeolite. The superheated zeolite is contacted with the gas, thereby adsorbing water from the gas. A dehydroxylated zeolite for removing trace moisture from a gas wherein the zeolite has a high silica-to-alumina ratio and a low level of metallic impurities is also disclosed. A method for removing metallic impurities from a gas using the low metals zeolite is also disclosed. The zeolites and methods of the invention are particularly useful for removing trace water and trace metal impurities from acid gases such as hydrogen chloride and hydrogen bromide.
Owner:MATHESON TRI GAS INC
Process to upgrade whole crude oil by hot pressurized water and recovery fluid
ActiveUS20090139715A1Upgraded more easilyLess coke formationThermal non-catalytic crackingRefining by water treatmentSulfurLow nitrogen
A process for upgrading whole crude oil utilizing a recovery fluid, depressurizing an extracted whole crude oil / recovery fluid mixture in a step-wise fashion, and subsequently contacting at least a portion of the whole crude oil with supercritical water fluid to produce high value crude oil having low sulfur, low nitrogen, and low metallic impurities for use as hydrocarbon feedstock.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Petroleum Upgrading Process
ActiveUS20110147266A1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease gravityThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingSulfurLow nitrogen
A process for upgrading a heavy oil stream by completely mixing the heavy oil stream with a water stream prior to the introduction of an oxidant stream. A mixture of the heavy oil stream and the water stream are subjected to operating conditions, in the presence of the oxidant stream, that are at or exceed the supercritical temperature and pressure of water. The resulting product stream is a higher value oil having low sulfur, low nitrogen, and low metallic impurities as compared to the heavy oil stream.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
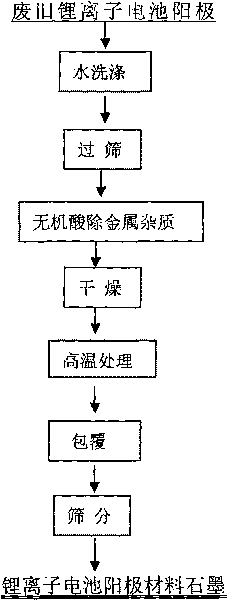
Method for recovering and restoring anode material graphite of waste lithium ion battery
ActiveCN101710632AAchieve recyclingAchieve fixWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingCharge dischargeCopper foil
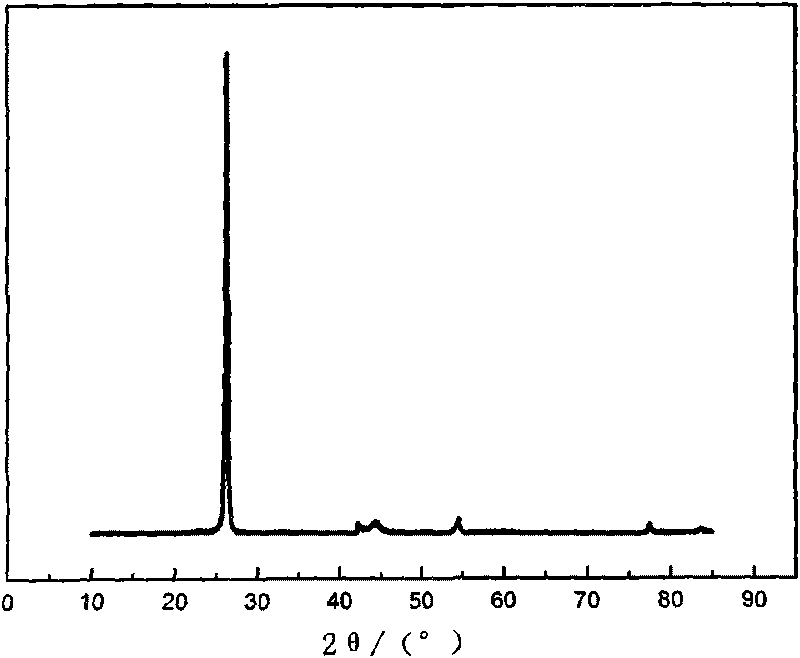
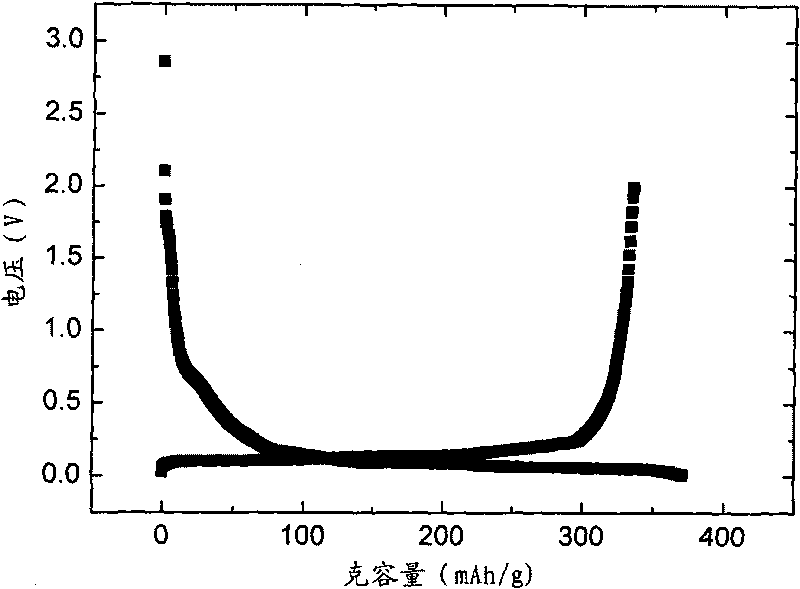
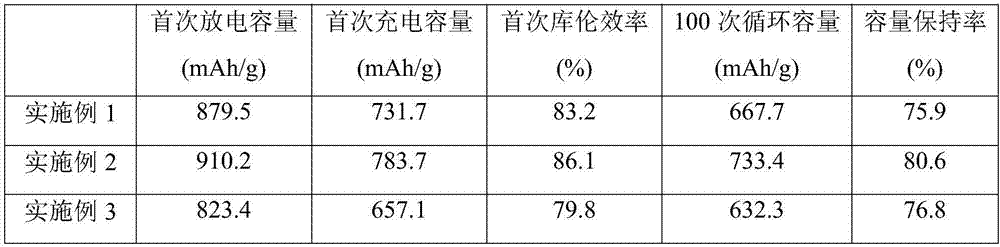
The invention discloses a method for recovering and restoring anode material graphite of a waste lithium ion battery, which belongs to the technical fields of resource cyclic utilization and inorganic material restoration. The method comprises the following steps: (1) separating graphite from copper foil to obtain crude anode material graphite; (2) removing lithium, copper and other metallic impurities in the crude anode material graphite; (3) removing acetylene black and residual organic substances, oxidizing the surface of the graphite; and (4) coating and surface-finishing. The tap density of the graphite obtained in the invention reaches 1.07 g / cm<3>; the first discharge capacity is 335.7 mAb / g; the first charge-discharge efficiency is 90.5%; after circulations for 54 times, the capacity conservation rate is 97.23%; and the properties of the graphite obtained in the invention correspond to the properties of graphite of lithium ion batteries in the market. The invention has the advantages of high graphite recovery rate, high raw material purity, simple technology, low energy consumption and the like, has economic benefit, and also has social benefit of saving finite graphite resources, reducing environmental pollution and the like.
Owner:HUNAN BRUNP RECYCLING TECH
Production process of ultra-high-purity isopropanol
InactiveCN102452897AMild reaction conditionsSimple operation processOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound separation/purificationMolecular sieveDistillation
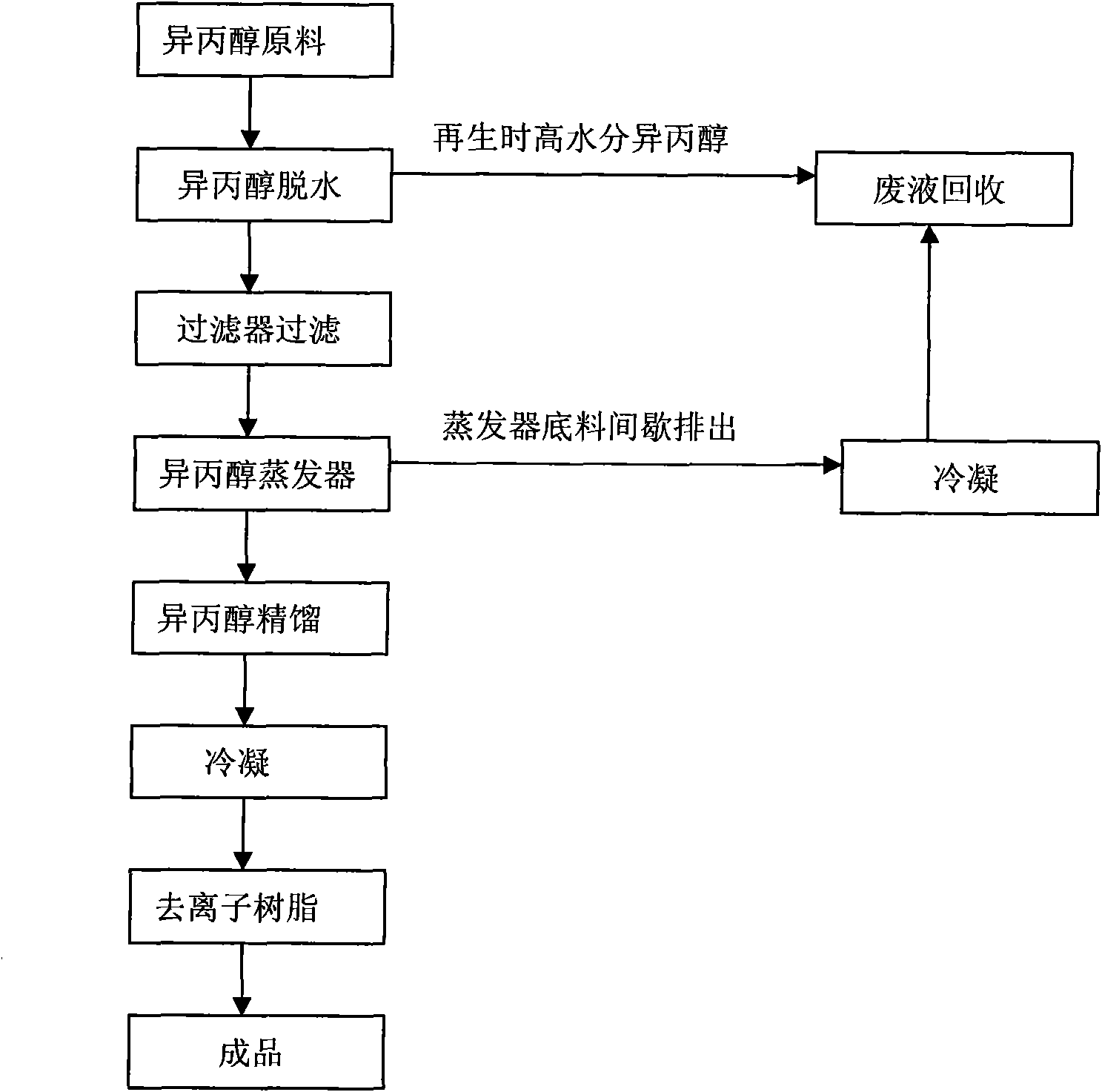
The invention discloses a production process of ultra-high-purity isopropanol, which comprises the following process steps of: (1) delivering a feed stream containing at least 98% of industrial grade isopropanol into a molecular sieve adsorption tower from the bottom of the molecular sieve adsorption tower, dehydrating through a molecular sieve, and then flowing out of the top of the tower to obtain high-purity isopropanol of which the moisture content is less than 100ppm; (2) filtering the high-purity isopropanol taken out of the molecular sieve adsorption tower by using a filter so as to remove particles of which the sizes are more than 1mum; and (3) transferring the high-purity isopropanol which is qualified by filtering into a distillation tower and a rectification column for rectifying, then transferring the rectified high-purity isopropanol into a condenser to be condensed into high-purity liquid isopropanol, enabling the condensed high-purity liquid isopropanol after rectifying to pass through a deionized resin tank, and deionizing through ionic resin so as to obtain ultra-high-purity isopropanol of which the metallic impurity is less than 0.1ppb. The production process disclosed by the invention is carried out under the normal pressure, and has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, simple operation processes and good safety performance.
Owner:JIANGSU DENOIR TECH CO LTD
Seal ring and die corner stress relief pattern design to protect against moisture and metallic impurities
InactiveUS6876062B2Reliable levelingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesStress reliefEngineering
An apparatus and method for protecting die corners in a semiconductor integrated circuit. At least one irregular seal ring having two sides can be configured, wherein the irregular seal ring is located at a corner of a die utilized in fabricating a semiconductor integrated circuit. A dummy configuration for stress relief can then be arranged, wherein the dummy configuration is located at the two sides of the at least one irregular seal ring, thereby protecting the corner of the die against thermal stress and the semiconductor integrated circuit against moisture and metallic impurities. The irregular seal ring can be configured to generally comprise a non-rectangular seal ring. The irregular seal preferably comprises an octangular seal ring.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
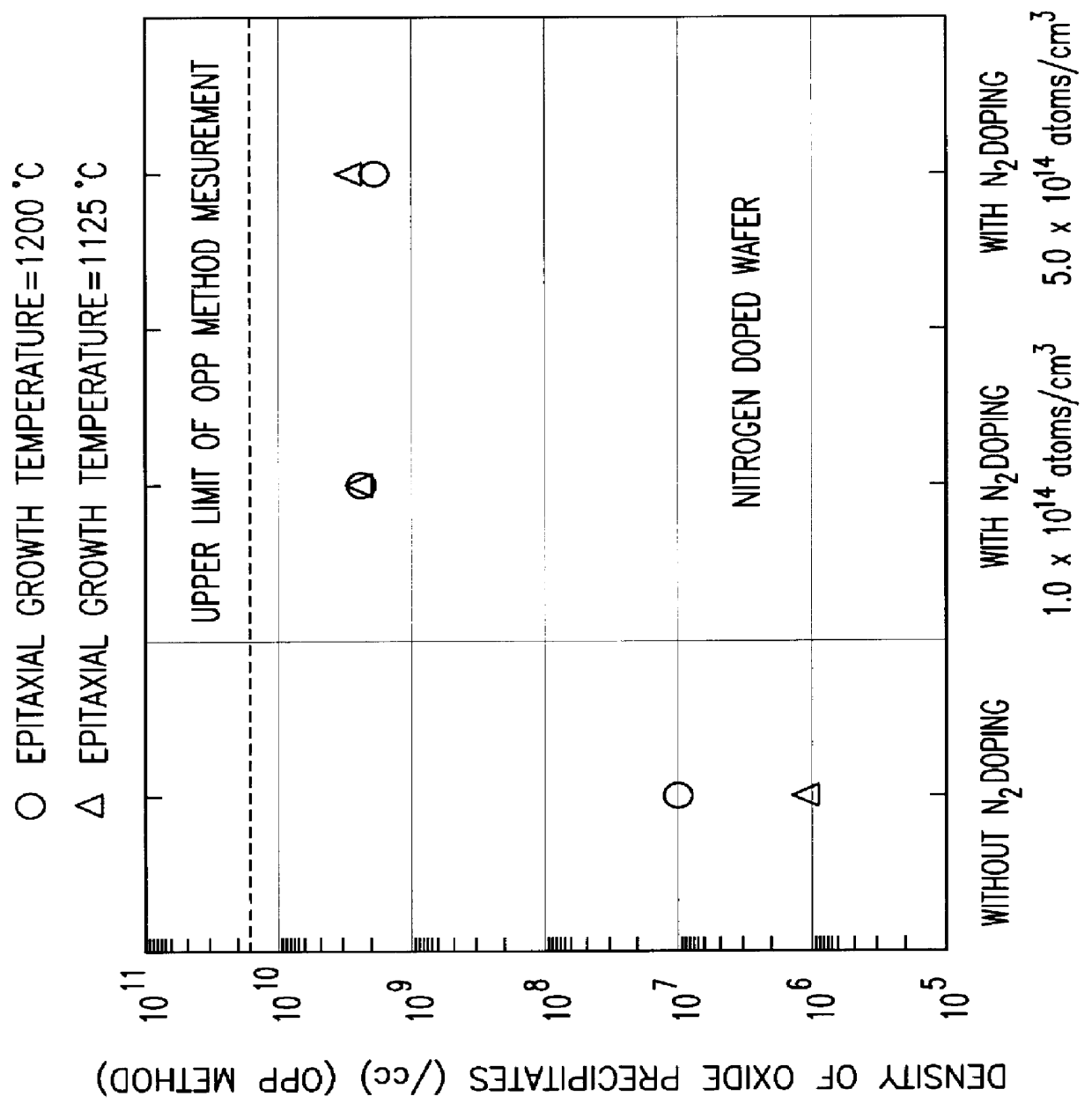
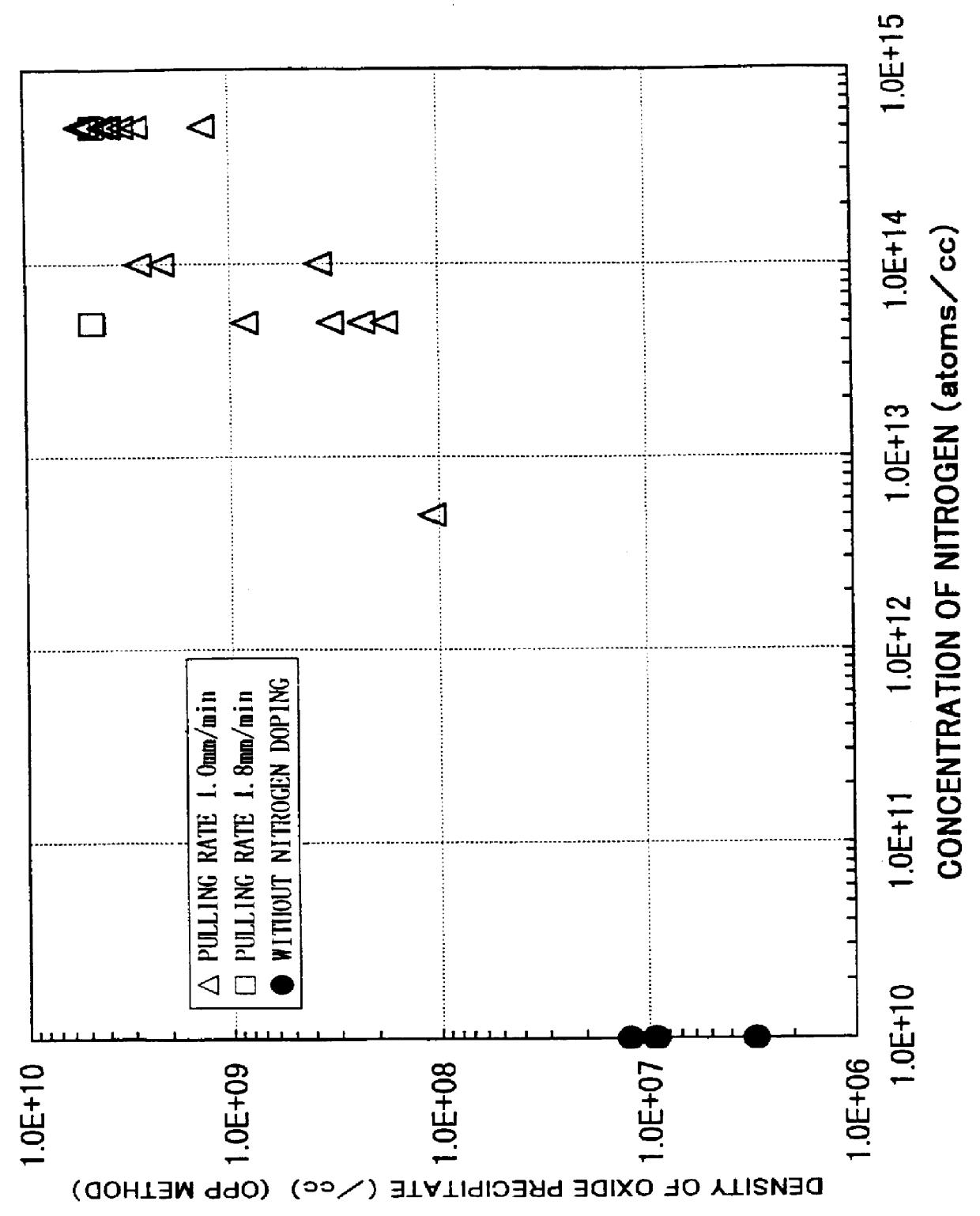
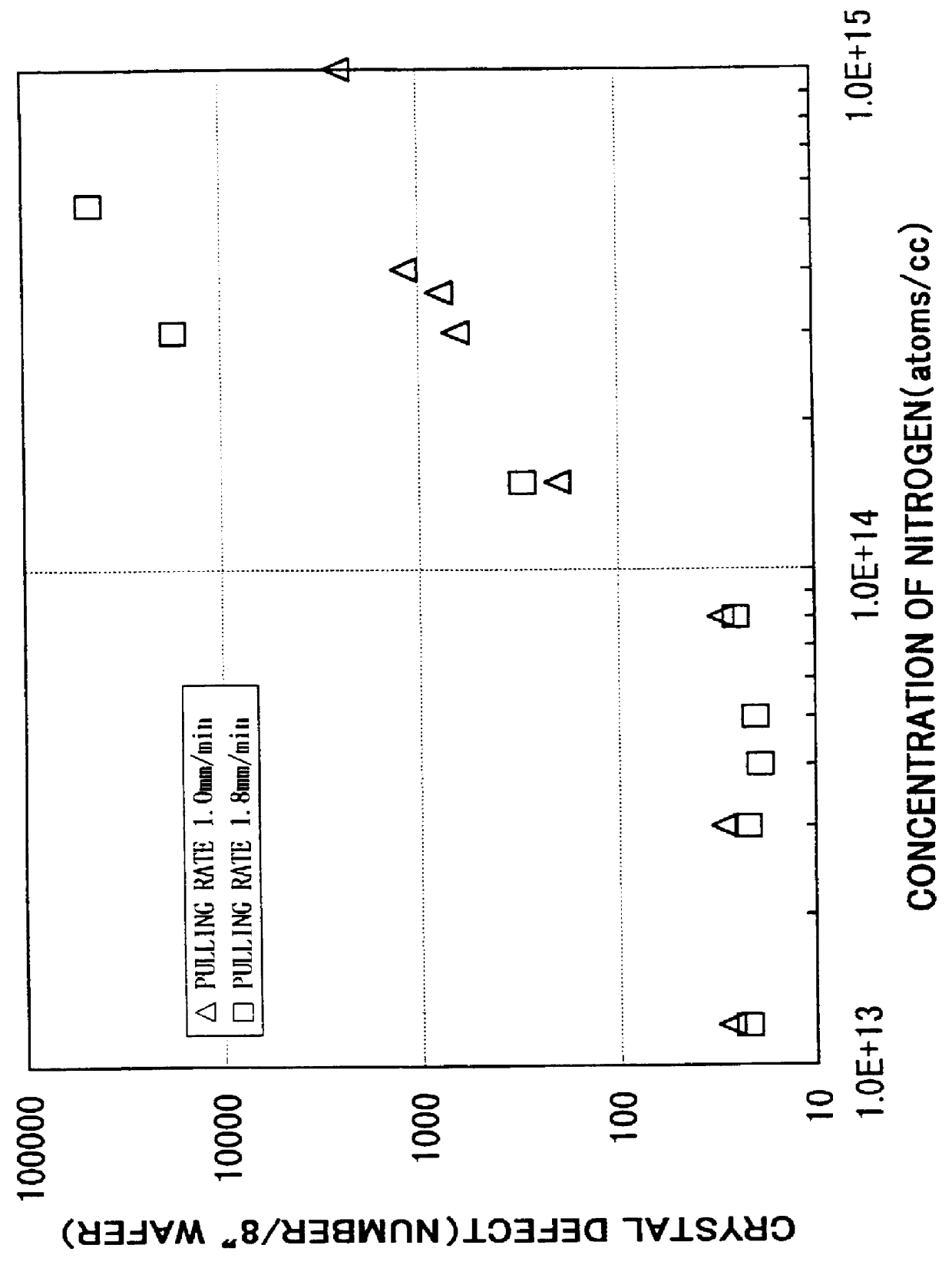
Method for producing an epitaxial silicon single crystal wafer and the epitaxial silicon single crystal wafer
InactiveUS6162708AReduce concentrationEasy to producePolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSingle crystalCrystallinity
There is disclosed a method for producing an epitaxial silicon single crystal wafer comprising the steps of growing a silicon single crystal ingot wherein nitrogen is doped by Czochralski method, slicing the silicon single crystal ingot to provide a silicon single crystal wafer, and forming an epitaxial layer in the surface layer portion of the silicon single crystal wafer. There can be manufactured easily and in high productivity an epitaxial silicon monocrystal wafer which has high gettering capability when a substrate having a low boron concentration is used, a low concentration of heavy metal impurity, and an excellent crystallinity.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
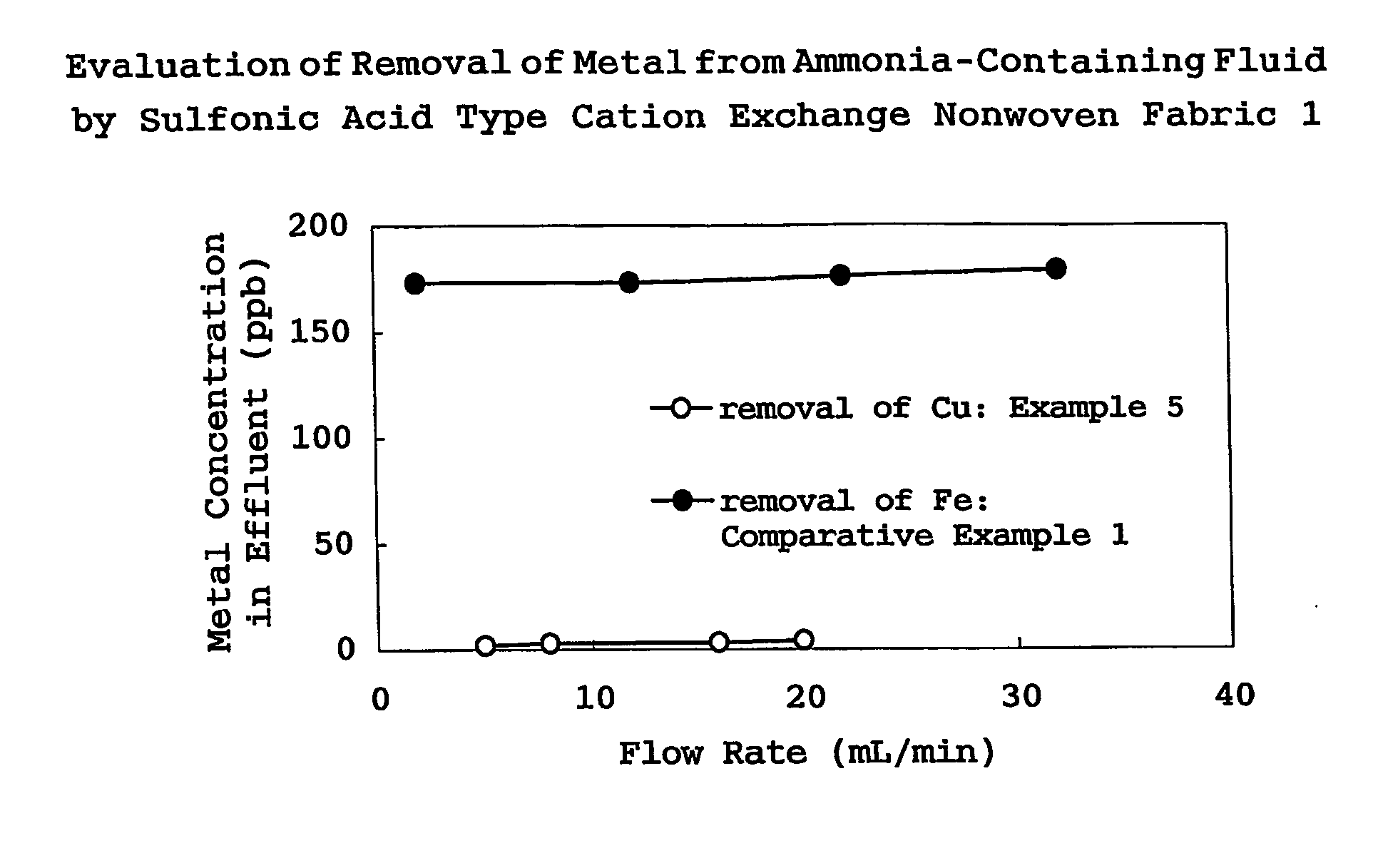
Filter cartridge for fluid for treating surface of electronic device substrate
InactiveUS20070007196A1Suitable for useIon-exchange process apparatusMembranesHydrofluoric acidCompound (substance)
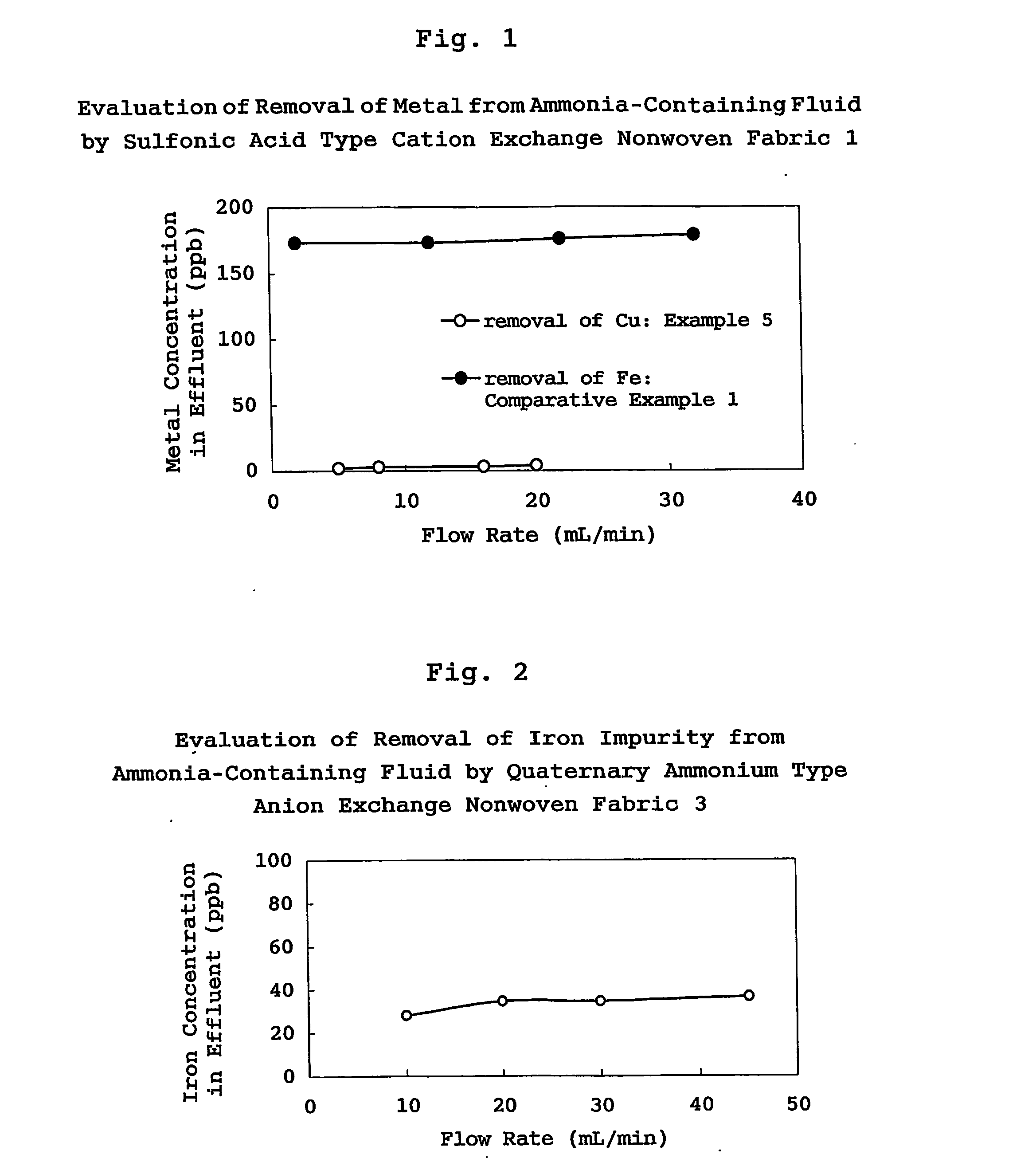
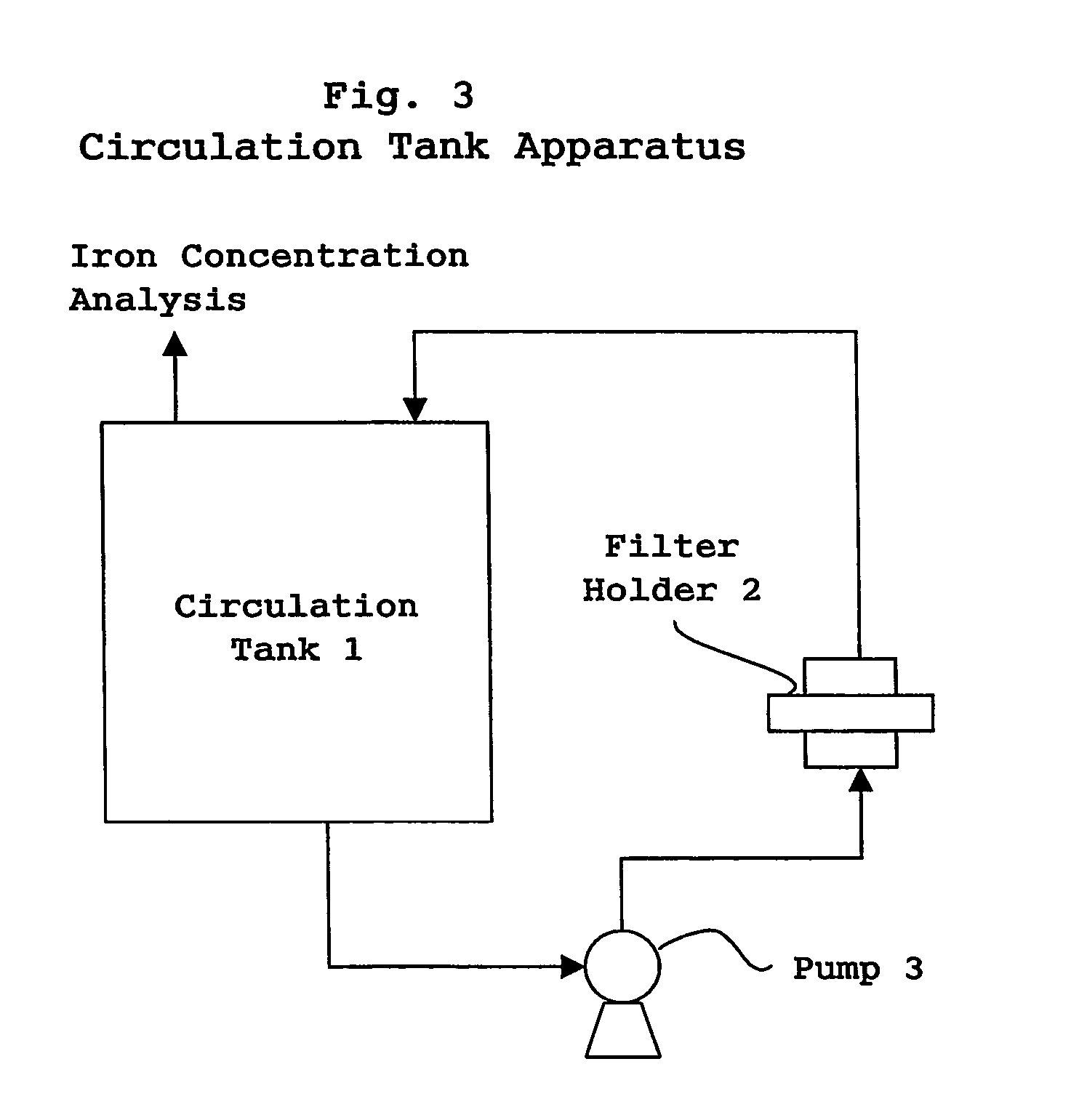
It is the purpose of the present invention to provide filter cartridges which can suitably be utilized in purifying chemical fluids for treating the surface of an electronic device substrate to be used in the semiconductor industry, particularly fluids containing a basic compound such as ammonia and an ammonium salt, or hydrofluoric acid (HF). The filter cartridges relating to the present invention which are used in removing metallic impurities contained in a chemical fluid for treating the surface of an electronic device substrate by treating the chemical fluid, is characterized by having a filter material incorporated therein, into which functional groups compatible with the existing morphology of the metallic impurities to be removed are incorporated in compliance with the constituents of the chemical fluid to be treated and the types of the metallic impurities to be removed.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Method for smelting noble metal
InactiveUS6126720AShorten the timeReduce impurityPhotography auxillary processesSolvent extractionDecompositionMaterials science
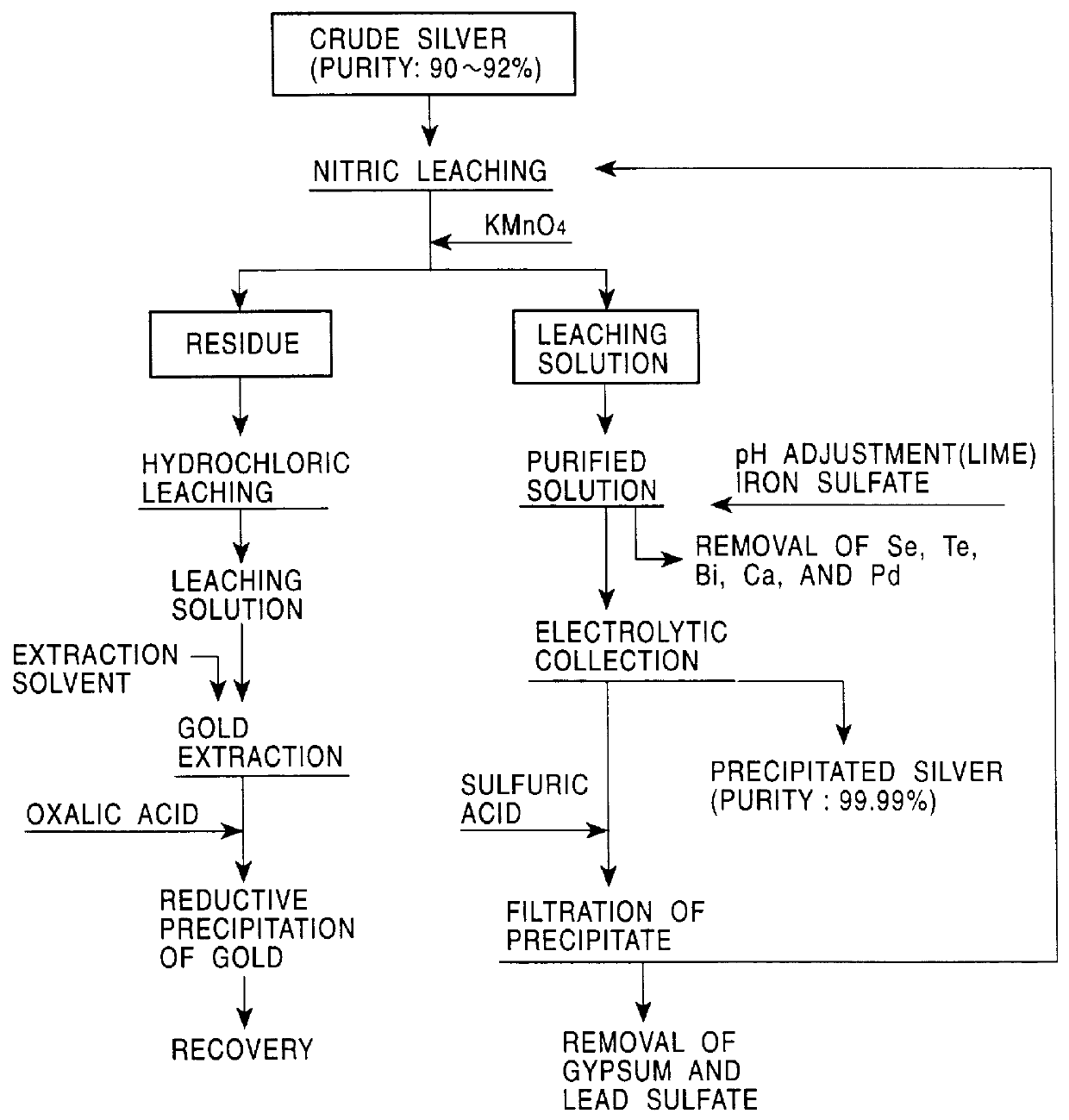
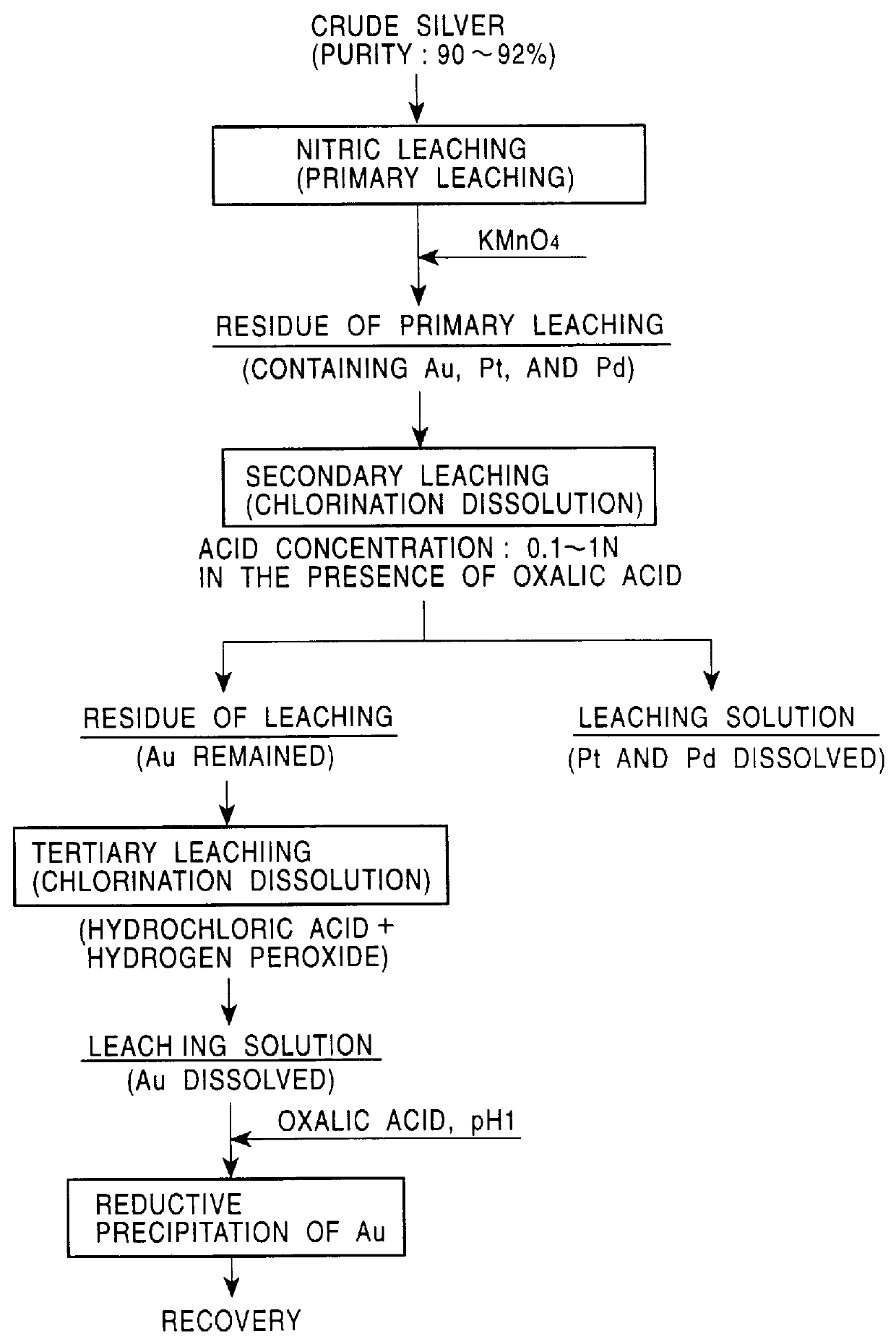
PCT No. PCT / JP98 / 02479 Sec. 371 Date Jan. 15, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Jan. 15, 1999 PCT Filed Jun. 4, 1998 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 58089 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 23, 1998A method for refining noble metals has a silver treating process including a nitric acid leaching step of silver, a purification step of the leaching solution, an electrolytic decomposition step of silver, and a recycling step after the electrolytic decomposition, wherein in the purification step, lime is added in order to precipitate the metallic impurities, such as selenium, tellurium, bismuth, and copper, by neutralization of the leaching solution, and in the recycling step, sulfuric acid is added to the solution after electrolytic decomposition to regenerate nitric acid for recycling use by precipitation of calcium in the solution as gypsum. Preferably, the refining method has a gold recovery process, as well as the silver treating process, wherein the residue of the nitric leaching of the crude silver is dissolved by chlorination and gold is recovered from the leaching solution by solvent extraction or reductive precipitation. High purity gold and silver can be readily obtained, and the refining time for gold is significantly shorter than that in conventional methods.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Removal of sulfur compounds from petroleum stream
ActiveUS20110315600A1Reduce the amount requiredIncreasing API gravityThermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial stages onlyThiolLow nitrogen
A process for upgrading an oil stream by mixing the oil stream with a water stream and subjecting it to conditions that are at or above the supercritical temperature and pressure of water. The process further includes cooling and a subsequent alkaline extraction step. The resulting thiols and hydrogen sulfide gas can be isolated from the product stream, resulting in an upgraded oil stream that is a higher value oil having low sulfur, low nitrogen, and low metallic impurities as compared to the oil stream.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Methods for removing metallic and non-metallic impurities from hydrocarbon oils
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and system for cleaning boiler tube
InactiveCN101327487AEasy to cleanHigh purityHollow article cleaningMaintainance of heating chambersEngineeringCleaning methods
The invention discloses a furnace tube cleaning system and method. Nitrogen gas enters into a cleaning agent tank, wherein, the cleaning agent carried by the nitrogen gas enters into the furnace tube via a pipeline to clean the furnace tube; hydrogen and oxygen are mixed to produce water vapor which enters into the furnace tube to clean the furnace tube. The furnace tube cleaning method of the invention is capable of effectively removing the metallic and non-metallic impurity sediments inside the furnace tubes in the semiconductor calcar pipes.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Methods to purify polymers
InactiveUS6894145B2Efficient removalImprove solubilityDyeing processPolymer dissolutionChemical reaction
The present invention discloses methods to remove impurities in polymeric materials in order to improve the opto-electronic characteristics of devices fabricated from these polymers. The polymers include but not limited to polyarylenes, polyarylenevinylenes, polyaryleneethylnylene, polyfluorenes, polyanilines, polythiophenes, polypyrroles, and any conjugated co-polymers. The methods involve the selection of a scavenger or chelating agent and use it to remove metallic impurities from the polymers. The methods involve dissolving the polymer in a suitable solvent, adding a scavenger, mixing to form a scavenger, containing phase, and finally separating the scavenger containing phase from the polymer phase. According to this invention, it is preferable for the selected scavengers to have functional groups which can chemically react with metallic species and form a coordination compound that is not soluble in a selected solvent. The selected scavenger can be used in a free stand form or carried by either organic or inorganic media.
Owner:XIAO STEVEN SHUYONG +1
Cleaning solution for substrates of electronic materials
InactiveUS7084097B2Easy to cleanAdsorption of particles can be preventedSurface-active detergent compositionsNon-surface-active detergent compositionsOrganic acidMetallic materials
The present invention relates to a cleaning solution capable of removing efficiently at the same time particles and metallic impurities from a substrate surface without corroding metallic materials.The cleaning solution for cleaning substrates of electronic materials comprises an organic acid compound and at least one selected from the group consisting of dispersants and surfactants.
Owner:KANTO CHEM CO INC
Preparation and application method of graphene-coated porous silicon composite anode material
InactiveCN106920954AThe preparation process is simple and easy to controlLow costCell electrodesSecondary cellsCvd grapheneCarbon source
Preparation and an application method of a graphene-coated porous silicon composite anode material belong to the field of electrode material preparation. According to the preparation, aluminium-silicon, which is used as a raw material, successively undergoes smelting, mechanical milling and chemical etching to prepare porous silicon; and then the porous silicon, graphene oxide and a carbon source undergo ball milling, spray drying and high-temperature pyrolysis to form a graphene-coated porous silicon composite material. Mass percent of silicon in the prepared porous silicon material is 20-80%; mass percent of metal impurities is 20-80%; particle size distribution is 10 nm- 10 microns; pore size distribution is 1-1000 nm; and porosity is 1-90%. According to the obtained graphene-coated porous silicon composite material, particle size is 1-100 microns, the shape is spherical, particle distribution is uniform, and morphology is consistent. When the material is applied to a lithium ion battery anode material, volume expansion of silicon alloying can be effectively prevented, and initial charge-discharge efficiency, theoretical specific capacity, cycle performance and the like are enhanced. The material of the invention is an ideal anode material in the field of lithium ion battery. The preparation has advantages of simple process, low energy consumption, low cost, good reappearance and high yield.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
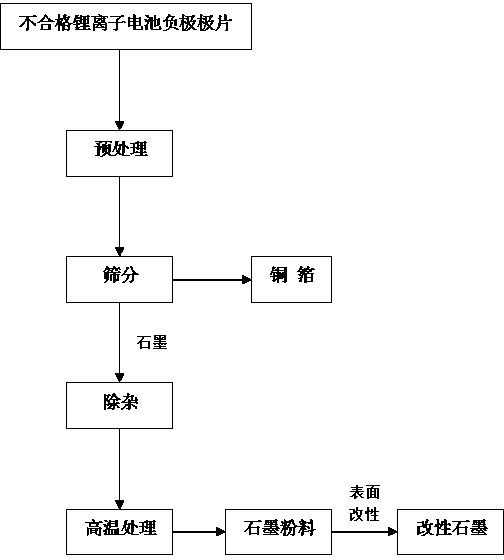
Recycling method for disqualified lithium ion battery negative electrode materials in graphite system
ActiveCN104241723AIncrease contentHigh recovery rateWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingGraphiteMuffle furnace
The invention discloses a recycling method for disqualified lithium ion battery negative electrode materials in a graphite system. The recycling method comprises the following steps that (1) a pole piece of the negative electrode in a disqualified lithium ion battery is put into a separation solvent, a thickening agent between a graphite sheet and a current collector is dissolved, and then the graphite sheet is not firmly attached onto the current collector; (2) graphite and the current collector processed in the step (1) are sieved, and graphite slag is obtained; (3) the graphite slag is subjected to oxidation reaction treatment, metal impurities in the graphite slag are removed, and graphite slurry which is primarily purified is obtained; (4) the graphite slurry is placed in a muffle furnace at 650-700 DEG C and keeps the temperature for 1-2h, impurities in the graphite slurry are removed, and high-purity graphite powder is obtained; and (5) graphite is subjected to surface modification, and graphite powder for electrodes of the battery is obtained. The method can be used for efficiently recycling graphite in negative electrode materials and realizing graphite recovery and cyclic regeneration.
Owner:GUANGDONG BRUNP RECYCLING TECH +1
Method for preparing ternary positive electrode material precursor by virtue of waste batteries
ActiveCN104659438AAchieve recyclingAvoid pollutionReclaiming serviceable partsWaste accumulators reclaimingPhysical chemistryManganese
The invention discloses a method for preparing a ternary positive electrode material precursor by virtue of waste batteries. The method comprises the steps of detaching waste batteries, roasting the detached waste batteries and carrying out sulfuric acid dissolving to obtain a waste battery positive electrode material, then separating and removing metal impurities in the waste battery positive electrode material by virtue of an extraction method to obtain a sulfate solution, supplementing manganese or aluminum to prepare a mixed solution for preparing the ternary positive electrode material precursor, then sequentially adding ammonia water and a sodium hydroxide solution, reacting to generate ternary positive electrode material precursor precipitates, and finally washing and drying to obtain the ternary positive electrode material precursor. According to the method, the cyclic utilization of resources of nickel and cobalt in waste batteries is realized, and the environmental pollution caused by heavy metals is avoided; furthermore, a nickel-cobalt-aluminum precursor and a nickel-cobalt-manganese precursor are produced from the recycled waste batteries, so that the requirements on primary mineral resources are lowered, and the purchase costs of nickel and cobalt are lowered; the method adopts a simple technological process and is applicable to industrial large-scale production.
Owner:广东芳源新材料集团股份有限公司
System for separating and purifying trichlorosilane in production process of polysilicon and operation method thereof
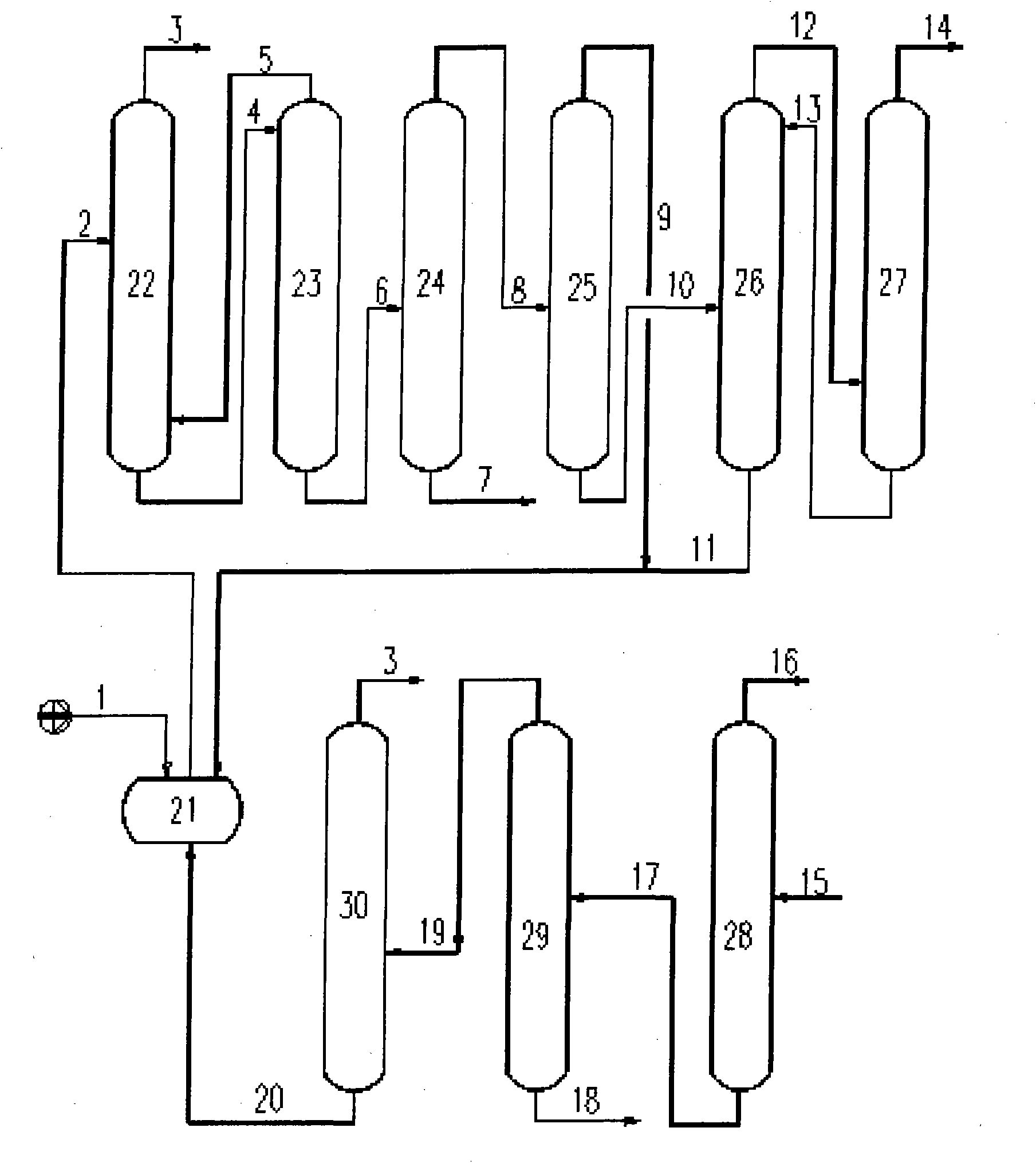
ActiveCN101538044ALow impurity contentMeet production requirementsChemical industryHalogenated silanesProcess engineeringTower
The invention provides a system for separating and purifying trichlorosilane in production process of polysilicon and an operation method thereof. The system consists of a rectification working section and a recovery refining working section; wherein, the rectification working section comprises six towers, and the recovery refining working section includes three towers; the connection mode of the six towers of the rectification working section is that a lightness-removing tower I, a lightness-removing tower II, a weight-removing tower, a secondary lightness-removing tower, a secondary weight-removing tower I and a secondary weight-removing tower II are sequentially connected with each other; the connection mode of the three towers of the recovery refining working section is that a lower-removing tower, a higher-removing tower and a product refining tower are sequentially connected with each other. Chlorsilane rectification technical equipment can be one of main technical bottlenecks limiting the production of the high-quality polysilicon material in China. The invention can achieve the separation requirements and energy-saving aim under the condition that the mass flow rate elastic ratio between feeding of the rectification working section and feeding of the recovery working section is 1:1-1:5. The rectification technique is simplified and optimized, the separation efficiency is improved, the energy consumption of rectification products is reduced, the reliability and stability of system operation can be enhanced, and the content of phosphorus, arsenic, boron and metallic contamination in the rectification products can be lowered.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Recovery method for waste ferric trichloride etching liquid
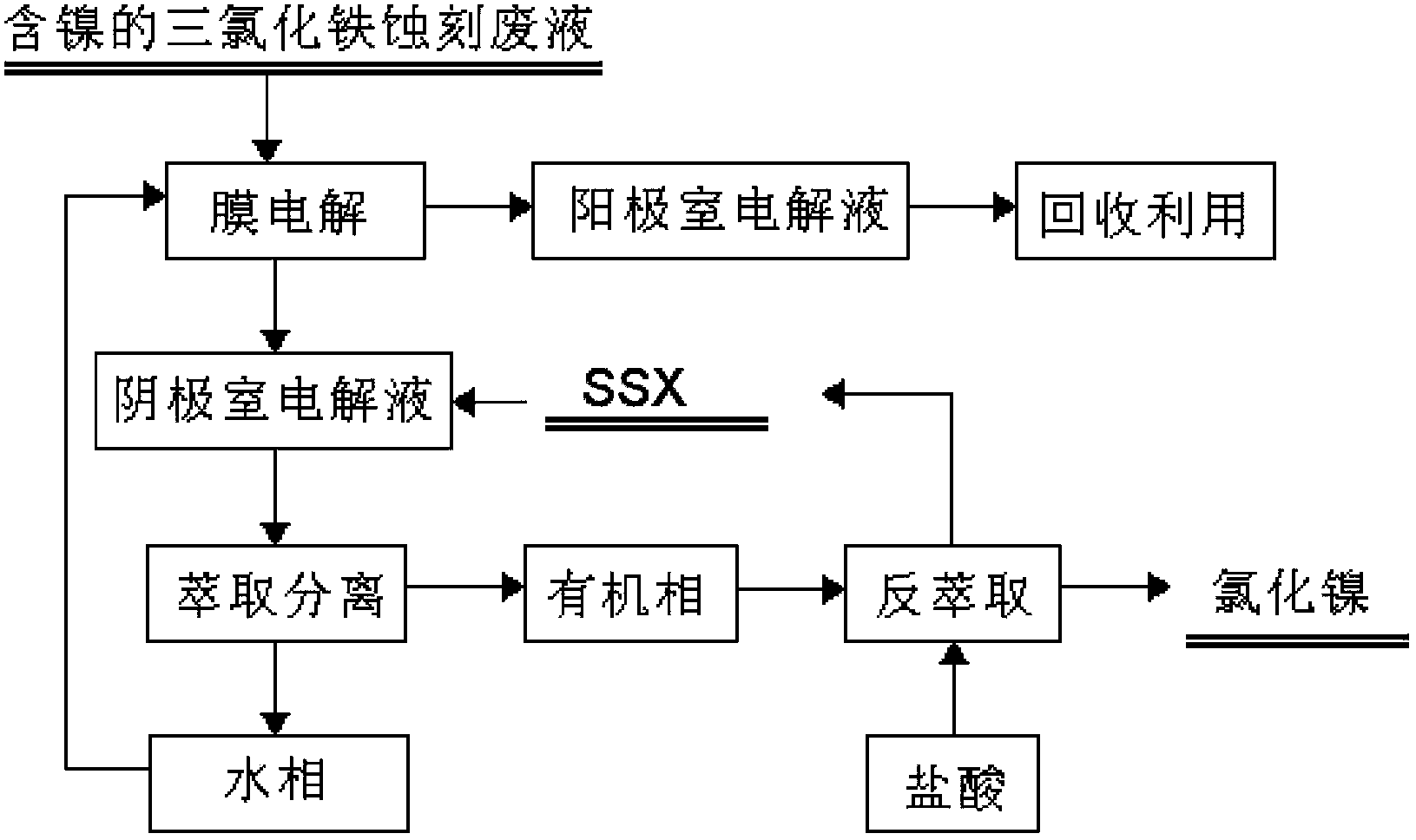
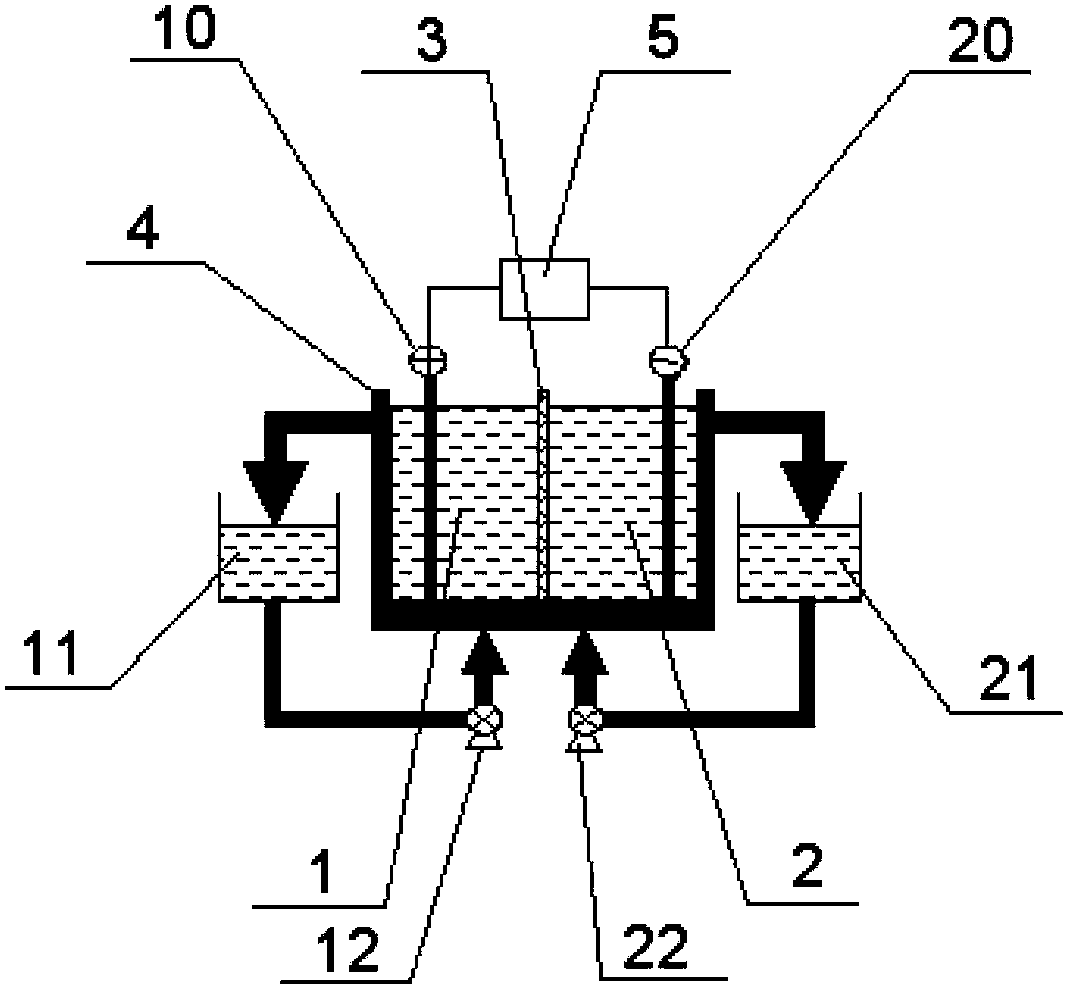
ActiveCN104131285AImprove qualityLow operating costWater contaminantsWaste water treatment from metallurgical processElectrolysisIon-exchange membranes
The invention provides a recovery method for a waste ferric trichloride etching liquid. The method adopts integrated membrane electrolysis and extraction technology and comprises the following steps: providing an electrolytic tank, wherein an ion exchange membrane is arranged in the electrolytic tank to divide the electrolytic tank into an anode chamber and a cathode chamber, and a cathode and an anode are respectively positioned in the cathode chamber and the anode chamber located at two sides of the ion exchange membrane; adding the waste ferric trichloride etching liquid into the cathode chamber and carrying out membrane electrolysis so as to reduce Fe3+ ions into Fe2+ ions; carrying out extraction on a solution obtained after electrolysis in the cathode chamber to remove impurity metals so as to obtain an extract phase solution and a metal impurity-removed phase solution and delivering the metal impurity-removed phase solution to the anode chamber for membrane electrolysis so as to oxidize Fe2+ ions into Fe3+ ions; and recovering a solution obtained after electrolysis in the anode chamber. Compared with conventional processing technology for the waste ferric trichloride etching liquid, the recovery method provided by the invention has the advantages of short and simple process flow, no generation of secondary pollution, no discharge of waste gas, waste water and industrial residue, low production cost, applicability to large-scale treatment, treating capacity of more than ten thousands every year and good environmental and economic benefits.
Owner:宁波东顺电子科技有限公司
Method and system for refining crude brine
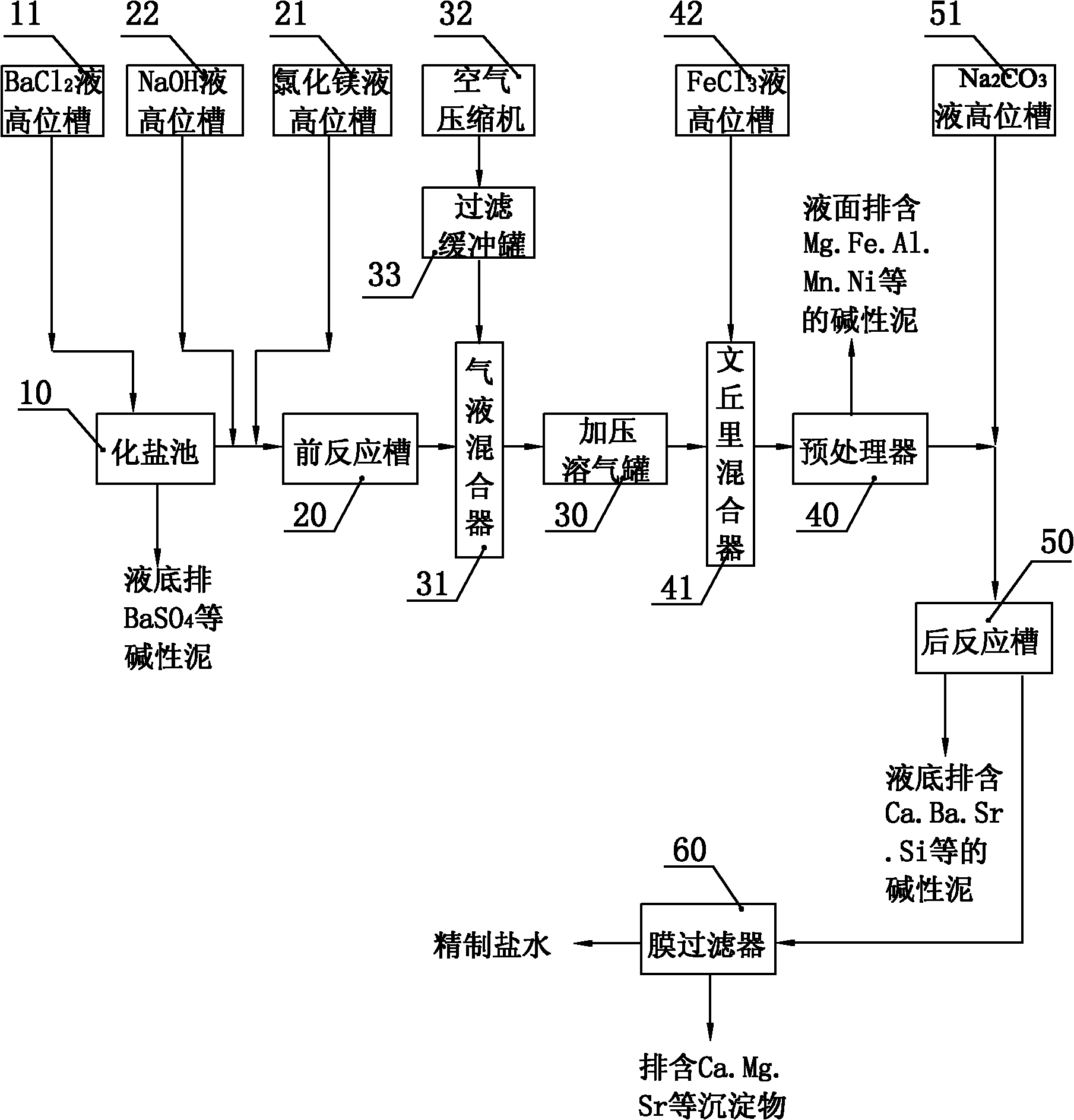
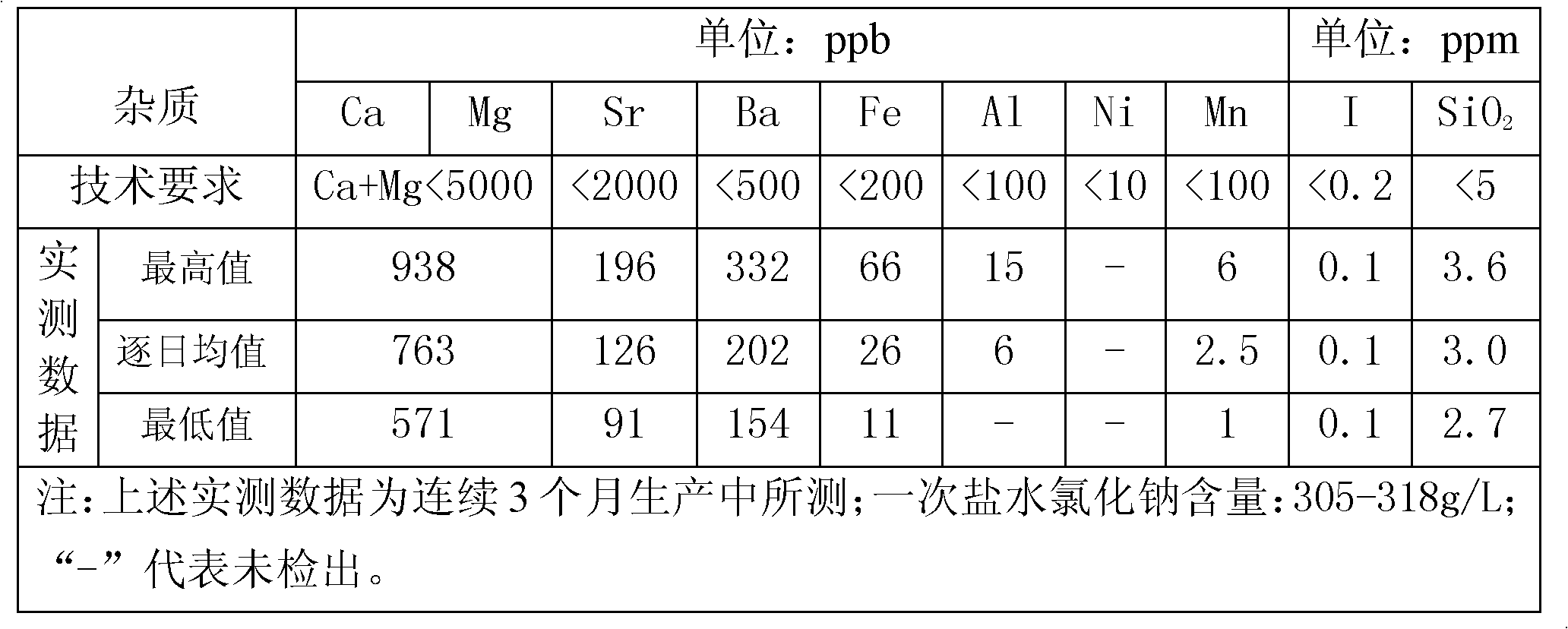
InactiveCN102120590AGood technical effectExcellent and unique refining effectAlkali metal halide purificationIon-exchange membranesSea salt
The invention relates to a method and a system for refining crude brine. The method comprises the following steps of: performing pre-reaction; pressurizing and dissolving gas; pretreating; performing post reaction; filtering by using a membrane; and filtering off residual slag particles by using a membrane filter to obtain the refined brine. By the method and the system for refining crude brine, under the condition of not introducing new impurities, various metal impurity ions are efficiently flocculated and precipitated, so that problems of great mineral salt impurity fluctuation and overproof Fe and Al ions are solved, the high quality of the finished brine product and the high-efficiency and normal operation of subsequent ion-exchange membrane electrolysis can be ensured, and the aim that mineral salt replaces sea salt to serve as chlor-alkali electrolysis raw salt is fulfilled; moreover, brine sludge emission and treatment cost can be obviously reduced, and the method and the system have good emission reduction effect and good environment-friendly property.
Owner:RUYUAN DONGYANGGUANG ELECTROCHEM FACTORY
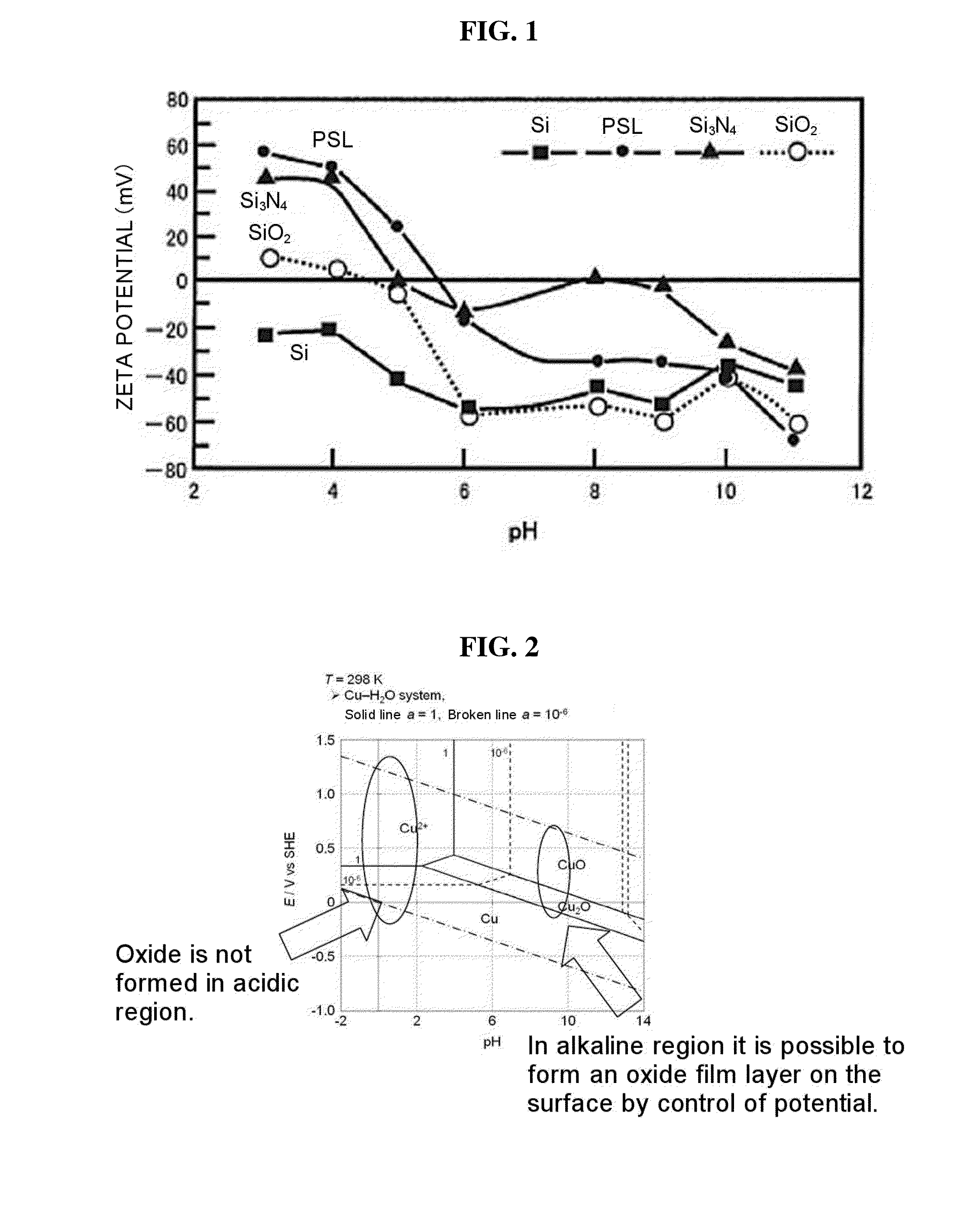
Method of removing impurities from metallurgical grade silicon to produce solar grade silicon
Metallurgical grade silicon is purified by removing metallic impurities and non-metallic impurities. The object is to produce a silicon species that is suitable for use as solar grade silicon. The process involves grinding metallurgical grade silicon containing metallic and non-metallic impurities to a silicon powder consisting of particles of silicon having a diameter of less than about 5 millimeter. While maintaining the ground silicon powder in the solid state, the ground silicon powder is heated to a temperature less than the melting point of silicon (1410 DEG C) under reduced pressure. The heated ground silicon powder is maintained at that temperature for a period of time sufficient to enable at least one metallic or non-metallic impurity to be removed from the metallurgical grade silicon.
Owner:DOW CORNING CORP
Nickel iron smelting process with nickel oxide ore and stainless steel production wastes as raw materials
InactiveCN101353708AAvoid introducingAvoid problems such as burn-throughBlast furnace detailsProcess efficiency improvementMineral SourcesSludge
The invention relates to a ferronickel smelting technology which takes the production waste of nickel oxide ore and stainless steel as raw material. The ferronickel smelting technology comprises the following steps: the nickel oxide ore and the stainless steel with the grain diameter of below 15mm are smelted to remove dust and stainless steel acid cleaning sludge to obtain mixed ore by mixing; the mixed ore and coke powder and industrial honey are mixed to make lump ore; the lump ore is calcined to obtain calcined ore; the calcined ore and coke are sent into an ore heating furnace to obtain the ferronickel by smelting. The technology is a novel ore heating furnace ferronickel-smelting technology, and realizes the recycling and reuse of the production waste of the stainless steel, thus solving the pollution problem of the waste to the environment; simultaneously, elements such as the ferronickel, etc. in the production waste of the stainless steel can be effectively recycled, thus avoiding the waste of mineral resources; traditional solvents such as fluorite and dolomite, etc. are not needed to be used, thus reducing the discharging pollution of fluoride and the possibility of introducing other metallic impurities into the ferronickel; by adopting the technology of the invention, power consumption can be reduced by 300 degrees for producing one ton of the ferronickel.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG POHANG STAINLESS STEEL
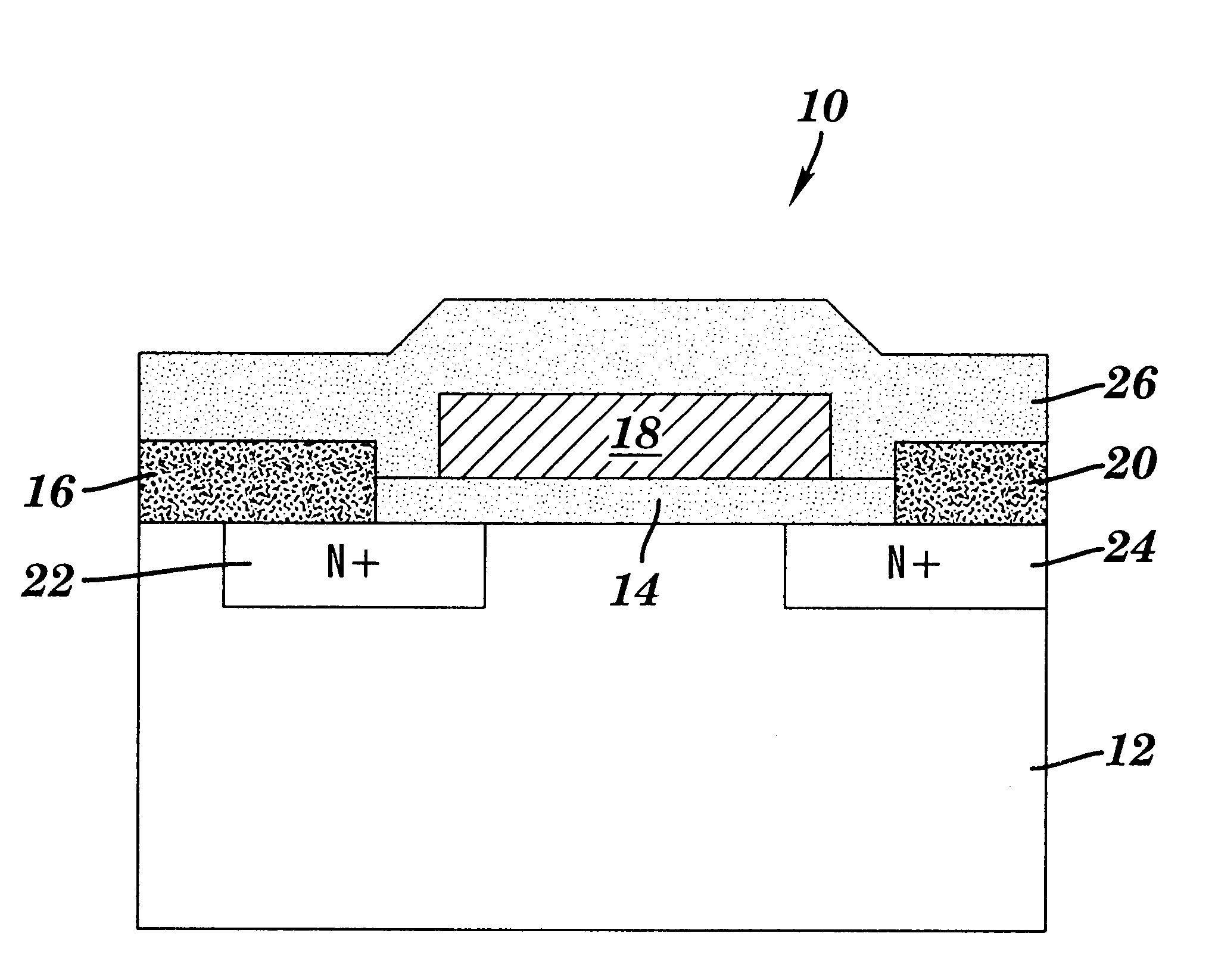
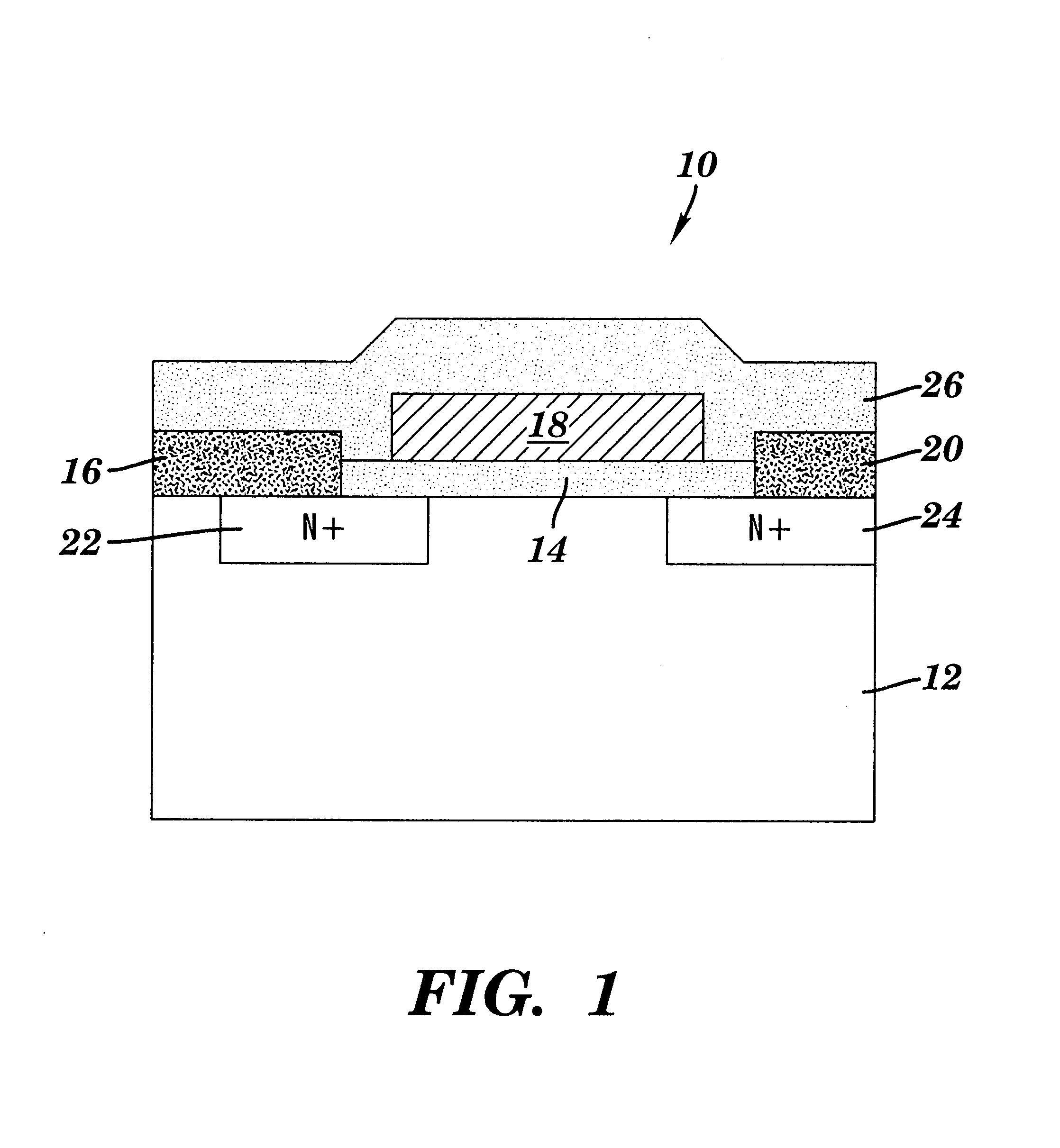
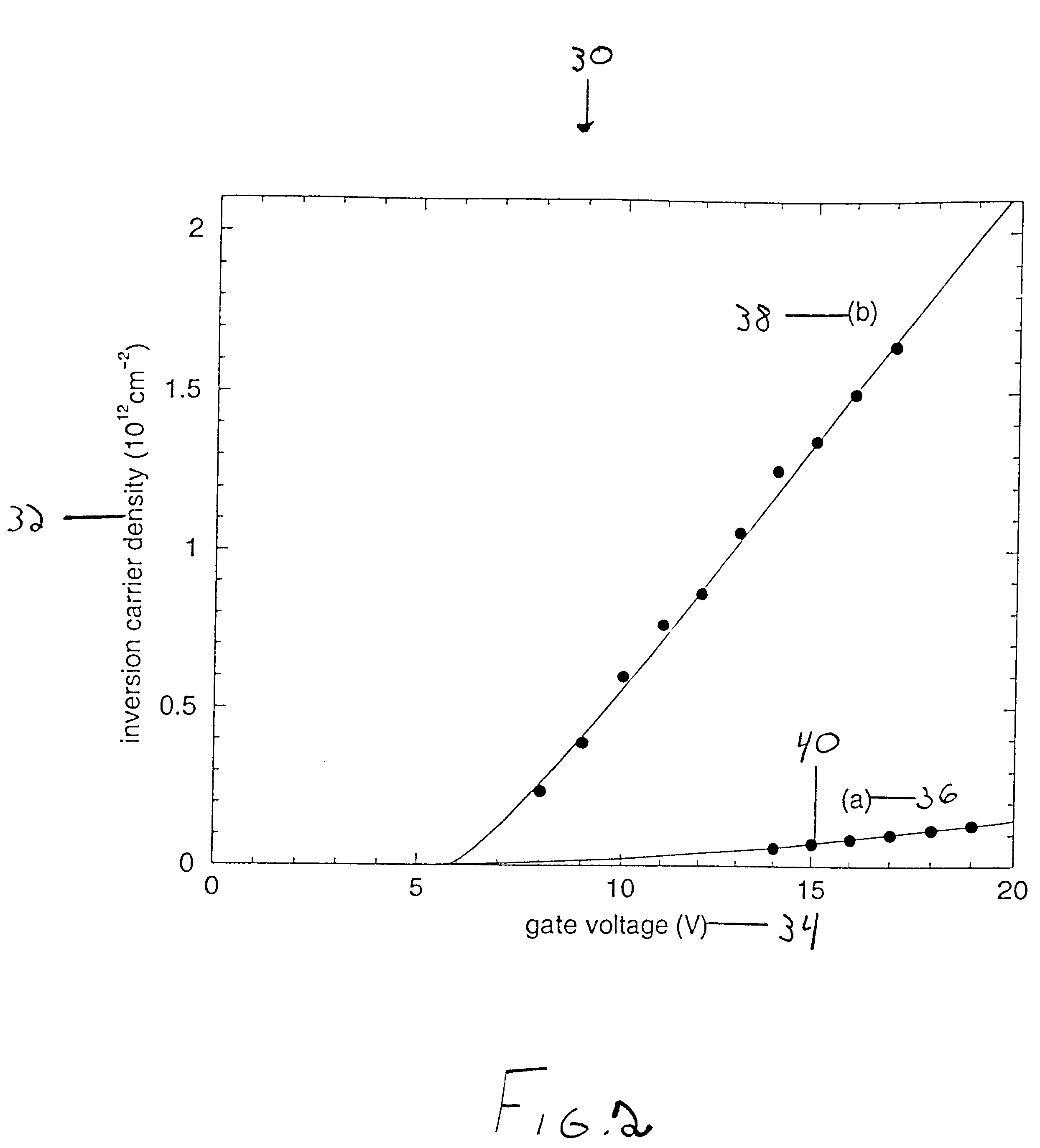
Method for improving inversion layer mobility in a silicon carbide metal-oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor
InactiveUS6559068B2Improve mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETOptoelectronics
A method for improving inversion layer mobility in a silicon carbide metal-oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) is provided. Specifically, the present invention provides a method for applying an oxide layer to a silicon carbide substrate so that the oxide-substrate interface of the resulting SiC MOSFET is improved. The method includes forming the oxide layer in the presence of metallic impurities.
Owner:VLSI TECH LLC
Cleaning liquid composition for electronic device
ActiveUS20130143785A1Improve removabilityPrevent further oxidationCationic surface-active compoundsOrganic detergent compounding agentsParticulatesHydrogen-Ion Concentrations
[Purpose] To provide a cleaning liquid composition that has excellent removability for metallic impurities and particulates, does not cause corrosion of Cu, and can clean a semiconductor substrate having copper wiring in a production process for an electronic device such as a semiconductor device.[Solution means] A cleaning liquid composition for cleaning a semiconductor substrate having copper wiring, the cleaning liquid composition containing one or more types of basic compound containing no metal, and one or more types of phosphonic acid-based chelating agent, and having a hydrogen ion concentration (pH) of 8 to 10.
Owner:KANTO CHEM CO INC
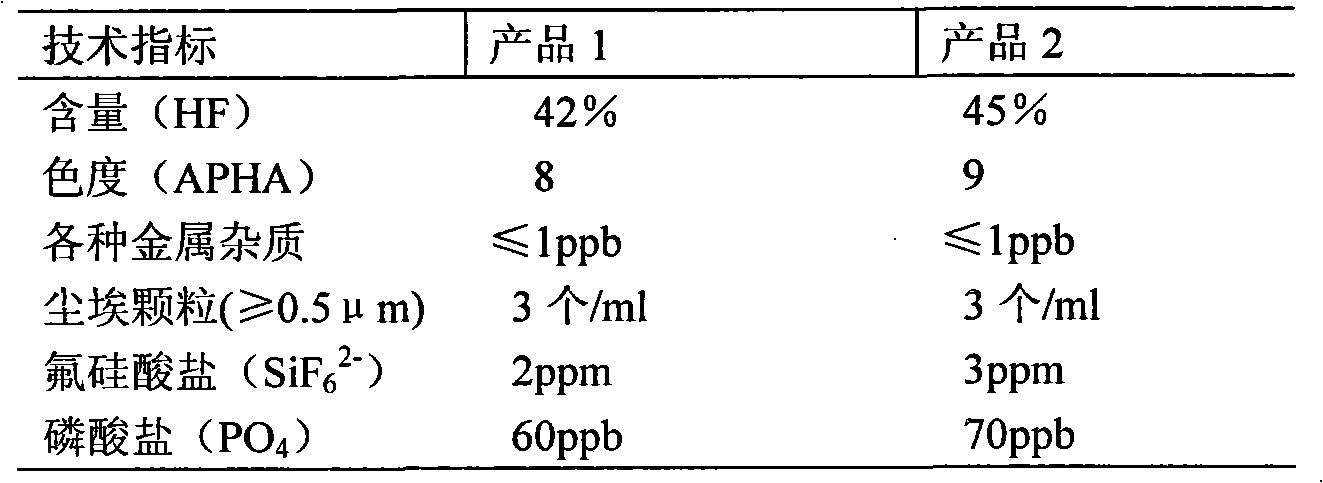
Electron-grade high purity hydrofluoric acid preparation method
The invention discloses an electron-grade high purity hydrofluoric acid preparation method, comprising the following steps: (1) preprocessing liquid anhydrous hydrogen chloride; (2) rectifying liquid anhydrous hydrogen chloride; (3) preparing a hydrofluoric acid semifinished product; (4) preprocessing the hydrofluoric acid semifinished product; (5) removing metal ions in the hydrofluoric acid semifinished product; and (6) obtaining electron-grade high purity hydrofluoric acid. The production technology of the invention avoids the onerous processes of absorbing hydrofluoric acid with anhydrous hydrogen fluoride and re-rectification and directly uses anhydrous hydrogen fluoride liquid for rectification purification; the production technology can effectively remove inorganic impurities such as arsenic trifluoride, SO2, SO3, H2SiF6 and the like, deeply remove various metallic impurities and solid particles, and purify the industrial hydrofluoric acid to refine the ultraclean high purity hydrofluoric acid agent which reaches the quality of ultraclean electron-grade hydrofluoric acid and meets the SIME-C8 standard, thus being applicable to the production of super precision integrated circuit.
Owner:广东光华化学厂有限公司 +1
Preparation of potassium platinochloride
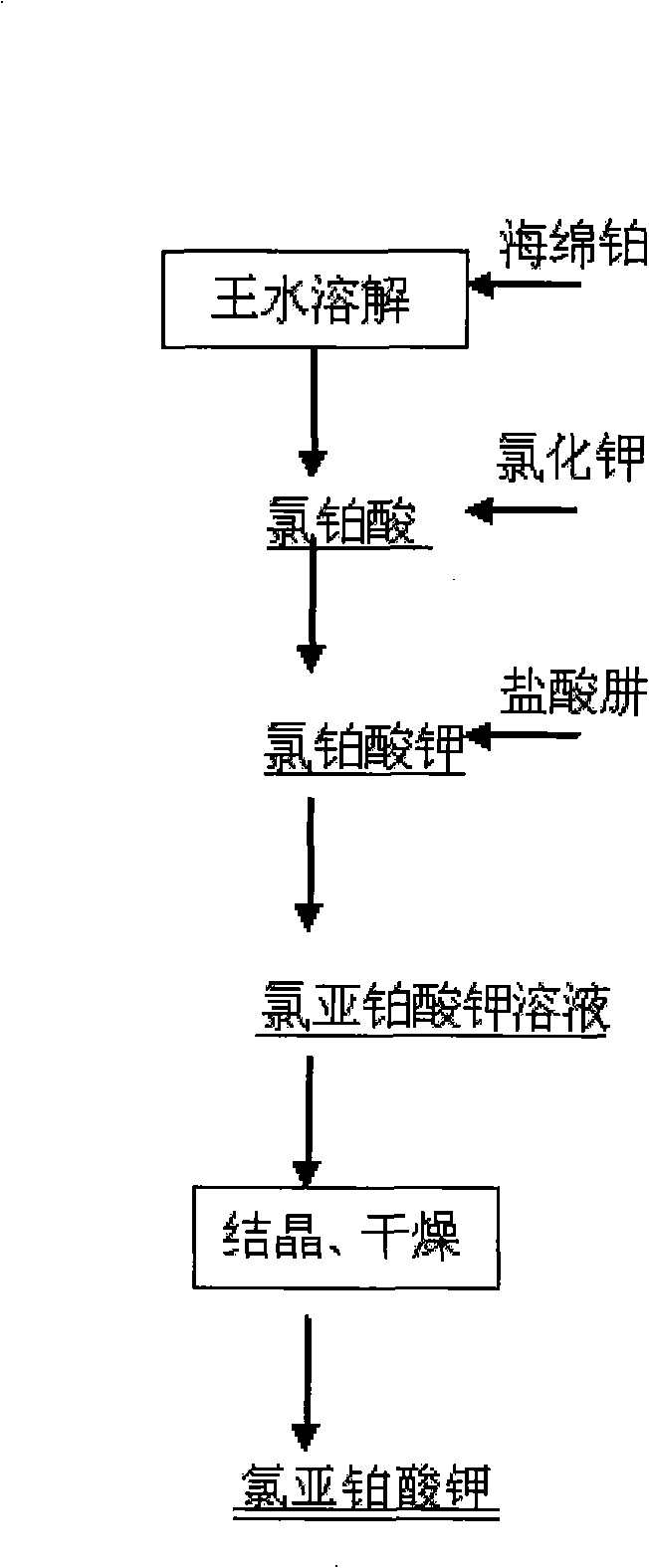
ActiveCN101279772AShort preparation processReduce manufacturing costRuthenium/rhodium/palladium/osmium/iridium/platinum compoundsSodium/potassium compoundsPotassium tetrachloroplatinatePotassium
Disclosed is a method for the production of a potassium platinochloride, which relates to a process for preparing a pharmaceutical intermediate potassium platinochloride. The method of preparation is characterized in that the preparation process adopts a spongy platinum as a material to prepare a chloroplatinic acid solution which is reacted with a potassium chloride solution to prepare the potassium chloroplatinite, then a hydrazine hydrochloride is adopted as a reducing agent to reduce the potassium chloroplatinite for preparing the pharmaceutical intermediate potassium platinochloride. The product adopting the method of the invention has a platinum content of 46.9+-0.2 percent and a potassium content of 19.0+-0.2 percent through a total elemental analysis. The total content of metallic impurity is no more than 0.08 percent.
Owner:兰州金川科技园有限公司
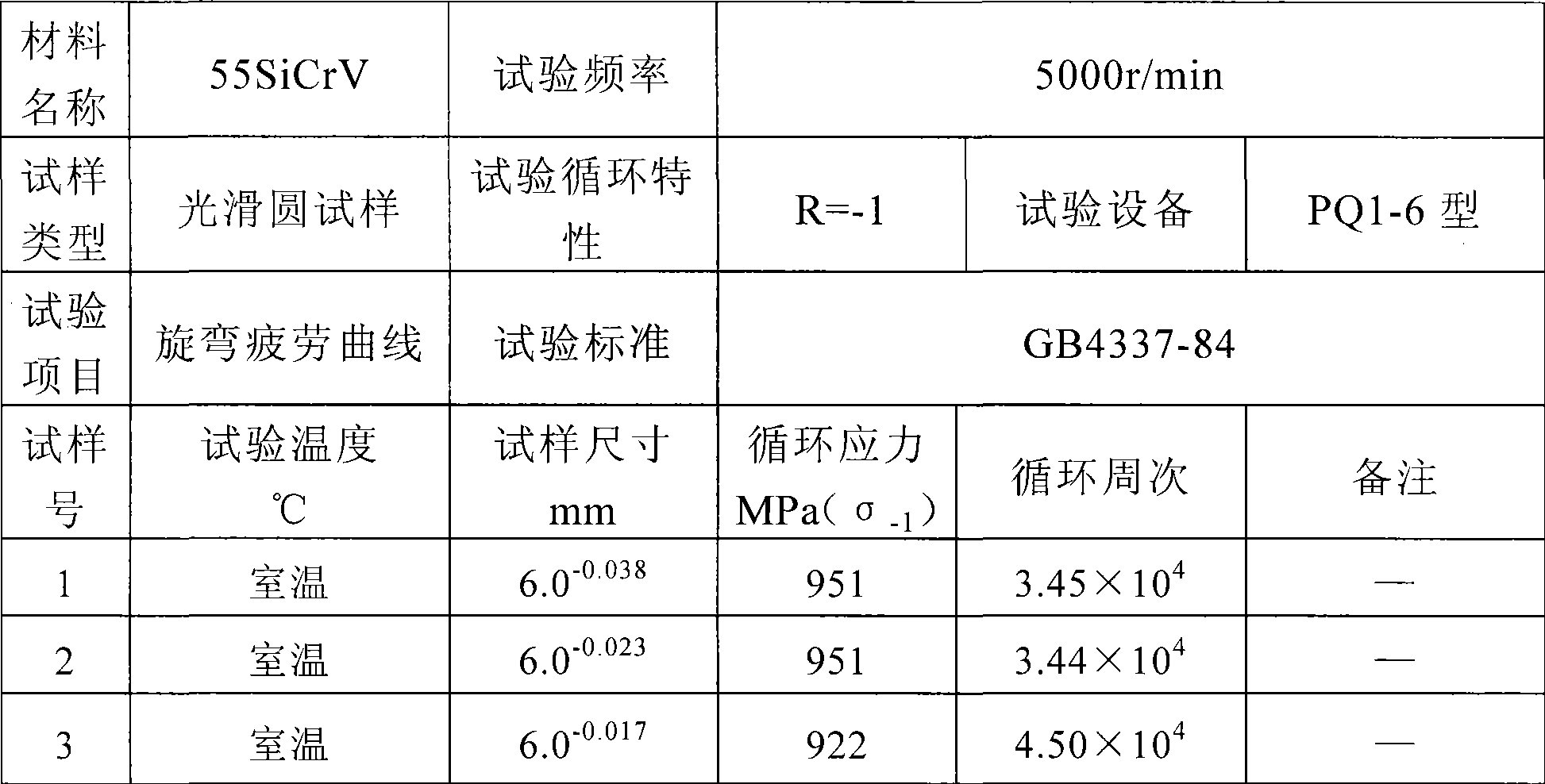
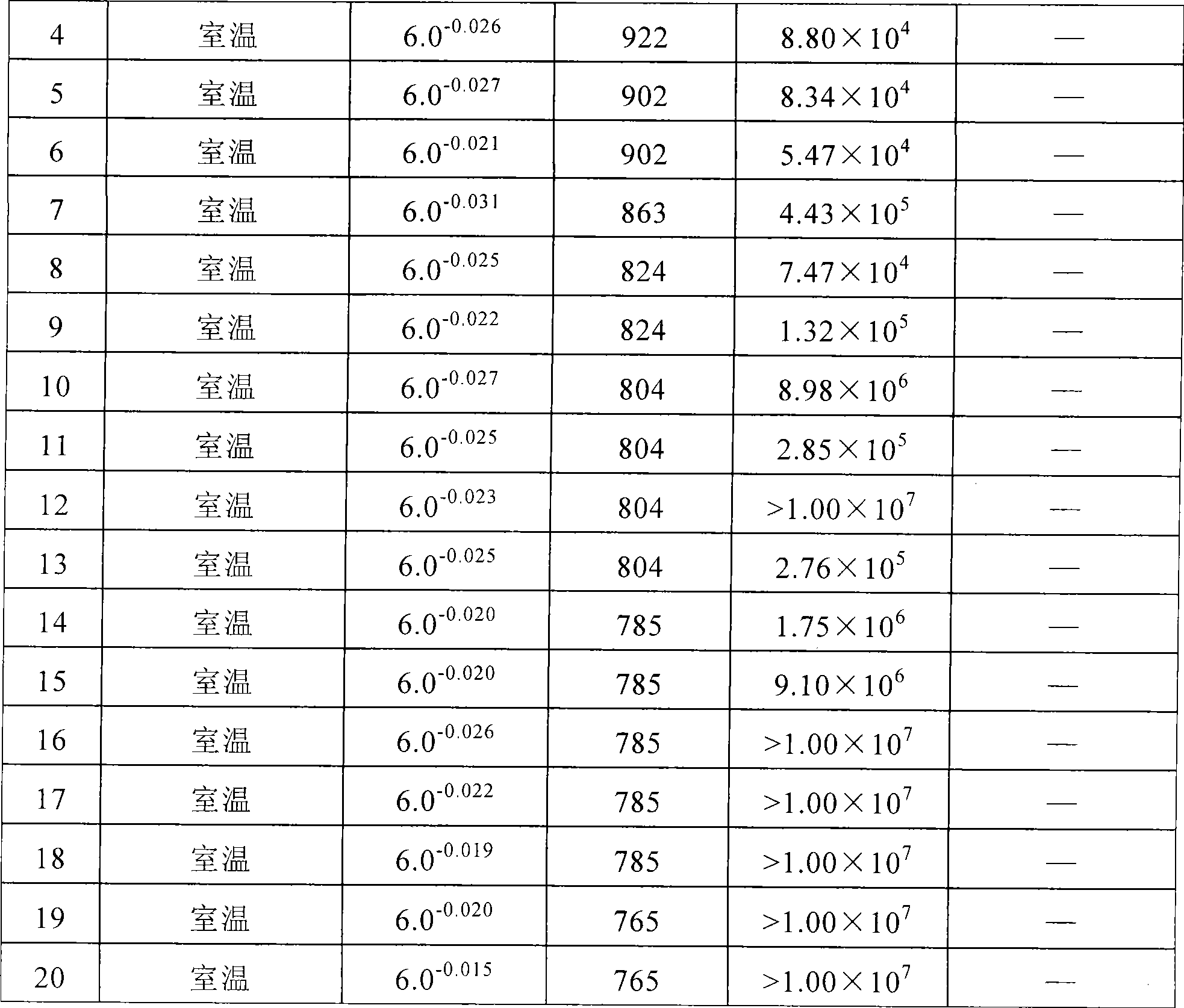
Method for controlling non-metallic impurities in structural alloy steel
ActiveCN101519710AAvoid it happening againFully float to removeProcess efficiency improvementFatigue loadingNon-metallic inclusions
A method for controlling non-metallic impurities in structural alloy steel includes the following steps of: step one: pre-smelting molten steel: (1) batching; (2) slagging in advance in the melting stage; (3) tapping, tapping conditions: (P) is less than or equal to 0.005 percent; (S) is less than or equal to 0.005 percent; and tapping temperature is 1640 DEG C to 1660 DEG C; step two: external refining: at the time of one third of the tapping of a primary smelting furnace, fluxing medium is added into ladles; the heating station of an external refining furnace adopts Si-Fe powder and SiC powder to conduct diffusive deoxidation; oxygen is determined before the ladles enter vacuum degassing, and deoxidizing agent is added; step three: vacuum refining: the vacuum process is kept for longer than or equal to 20min under less than or equal to 66.7Pa; the post-vacuum soft argon blowing time is longer than or equal to 15min; the soft argon blowing intensity is less than or equal to 0.10Mpa; and the post-vacuum crane ladle temperature is 1530 DEG C to 1540 DEG C; and step four: continuous casting. The method improves the purity of steel by improving the composition and size of the non-metallic impurities in steel so as to further meet the requirement on pure steel under high dynamic stress and high cycle fatigue loading.
Owner:宝武特种冶金有限公司
Method for producing high-purity metal chromium by using carbon reduction method
InactiveCN102965526AHigh speedIncrease productivityProcess efficiency improvementImpurityMaterials science
The invention relates to a method for producing high-purity metal chromium by using a carbon reduction method. The method comprises the following steps of: uniformly mixing chromic oxide powder and carbon black powder, adding deionized water or alcohol to form a wet mixed material, carrying out press forming, and drying, thereby obtaining a mixed material block; putting the mixed material block in a vacuum furnace, and enabling chromic oxide to be reduced by carbon black under high-temperature vacuum conditions, thereby obtaining crude chromium; introducing gaseous carbon monoxide, and carrying out heat preservation for 3-8 hours at the temperature of 1,300-1,500 DEG C; introducing gaseous carbon dioxide, and carrying out heat preservation for 3-8 hours at the temperature of 800-1,000 DEG C; and cooling down, and discharging, thereby obtaining a high-purity metal chromium block. According to the method, a gas-solid reduction manner is adopted to remove residual raw materials and non-metallic impurities, so that the production cost is reduced, and the reduction time is shortened; and the produced high-purity metal chromium has the purity of 99.96-99.98%, the oxygen content less than 0.03%, the sulfur content less than 0.01% and the carbon content less than 0.01%, thereby meeting the standards of the high-purity metal chromium.
Owner:JINZHOU NEWROUTE HYPERPURE MATERIAL CO LTD
Cleaning sheet and method for cleaning substrate processing apparatus
InactiveCN1717285ANo pollution in the processReduce pollutionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDetergent materialsEngineeringCleaning methods
A cleaning member which does not contaminate a substrate processing apparatus with an ionic impurity when conveyed into the apparatus for removing foreign materials within the apparatus is disclosed. A cleaning member which does not contaminate a substrate processing apparatus with a metallic impurity when conveyed into the apparatus for removing foreign materials within the apparatus is also disclosed. Specifically, a cleaning sheet characterized in that a cleaning layer wherein pure water extraction amounts (extracted for one hour while boiling at 120 1 / 2 C) of F<->, Cl<->, Br<->, NO2<->, NO3<->, PO4<3->, SO4<2->, Na<+>, NH4<+>, and K<+> are respectively 20 ppm or less is provided on one surface of a supporting body and an adhesive layer is provided on the other surface is disclosed. A cleaning sheet characterized in that a cleaning layer wherein respective contents of Na, K, Mg, Al, Ca, Ti, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn and compounds thereof are 5 ppm (mug / g) or less when calculated in terms of respective metal elements is provided on one surface of a supporting body and an adhesive layer is provided on the other surface is also disclosed.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com