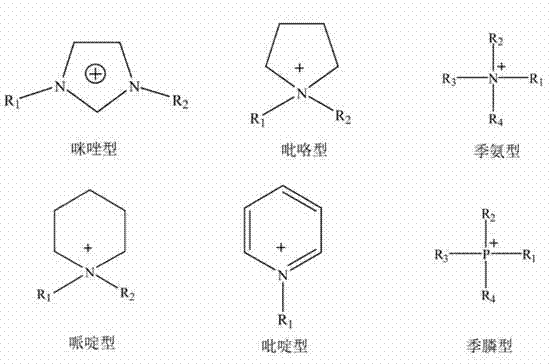
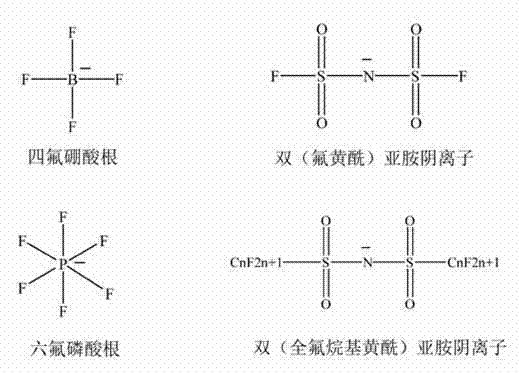
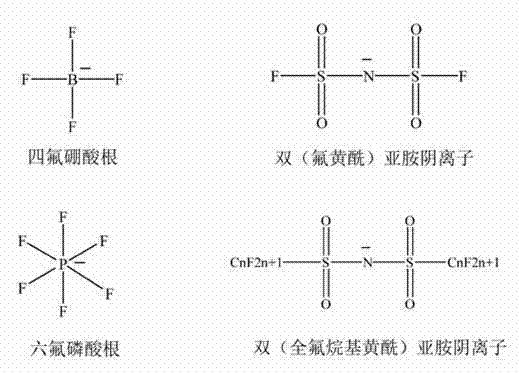
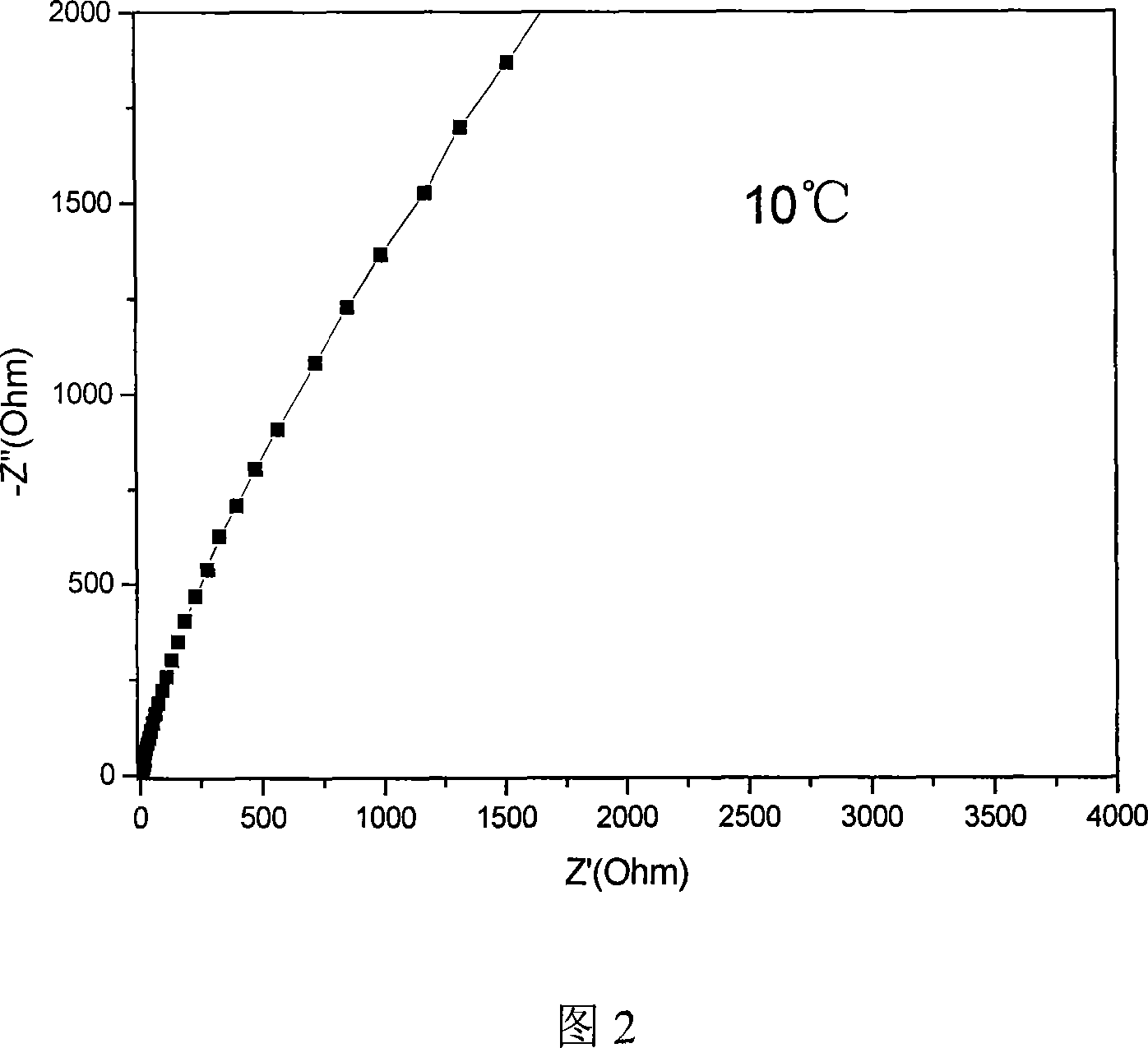
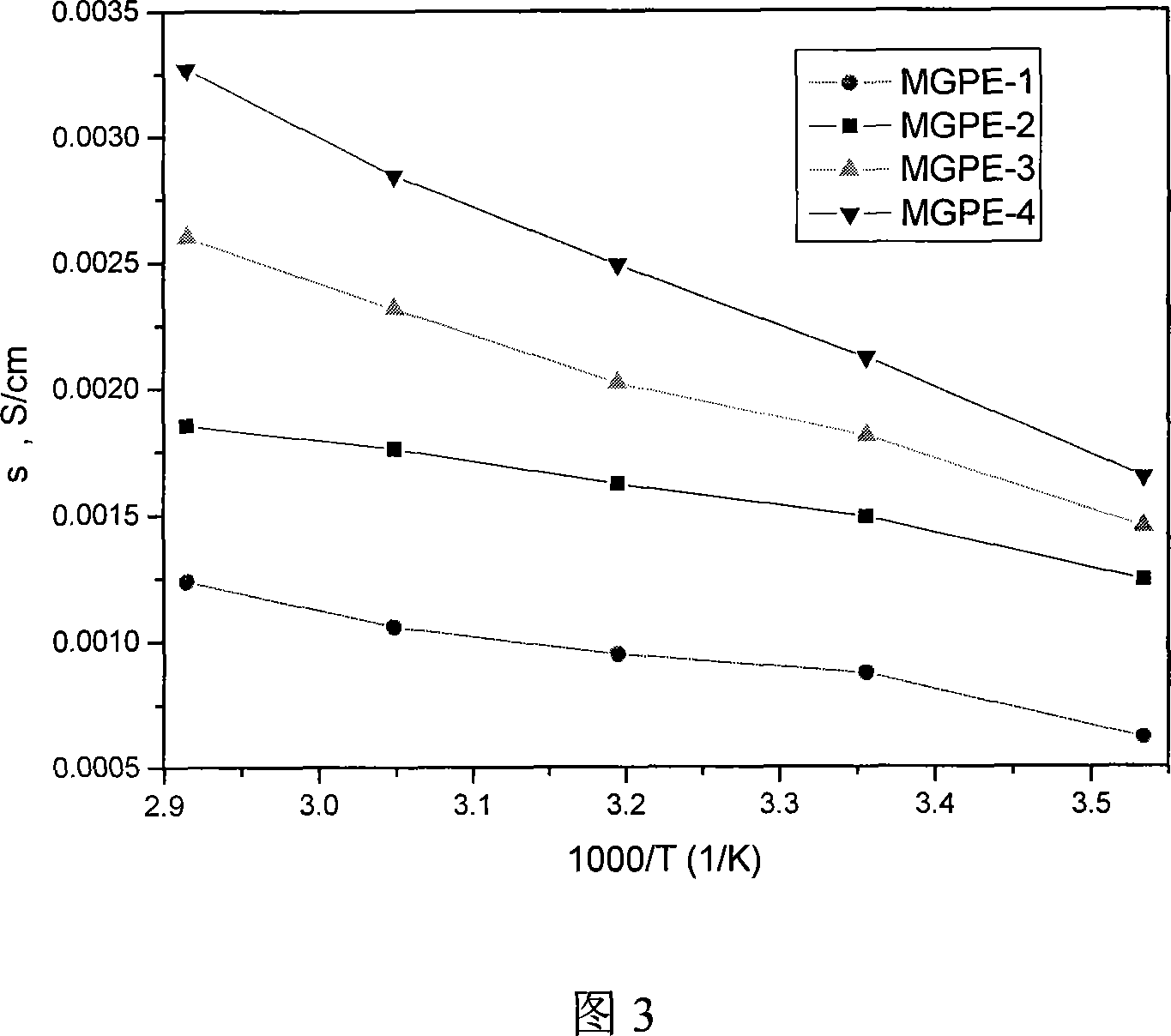
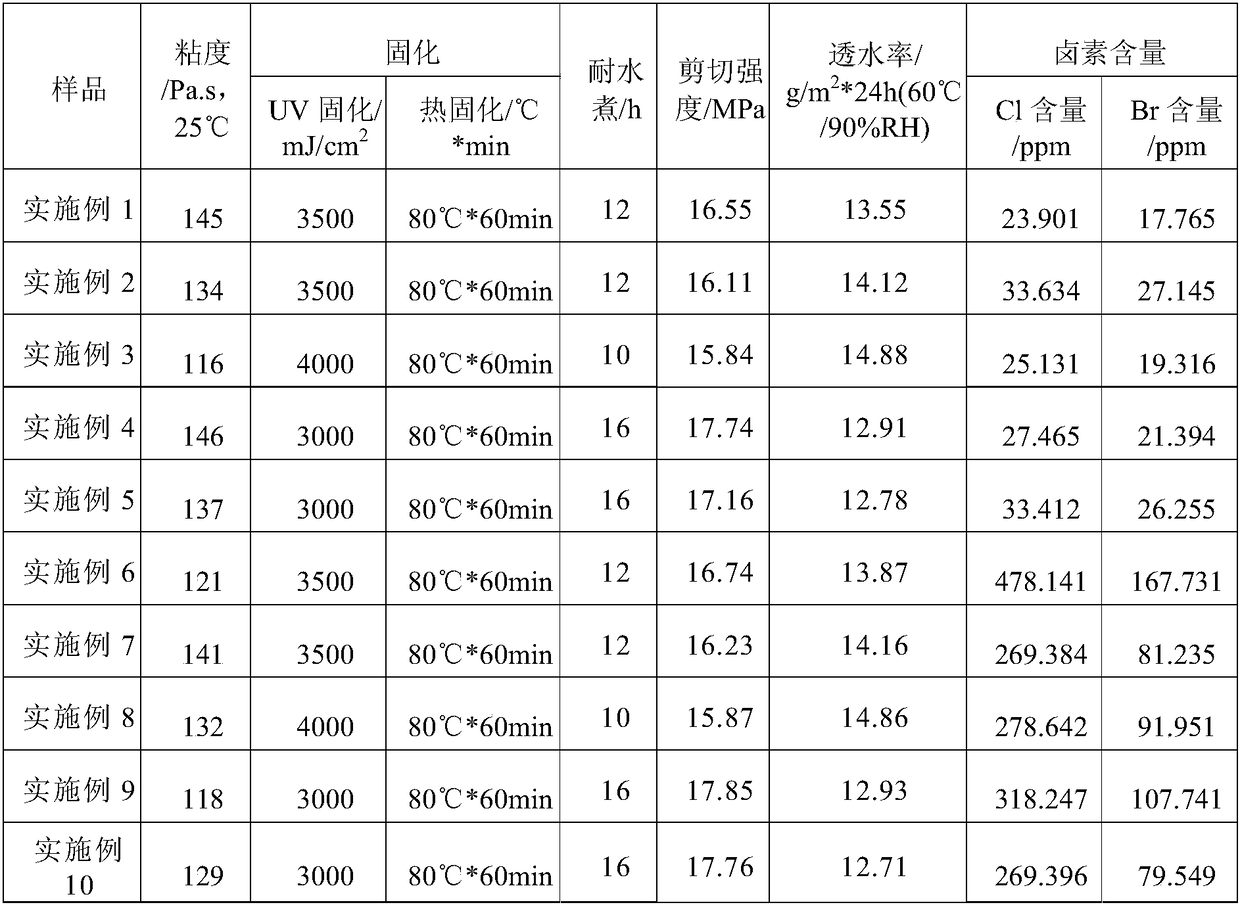
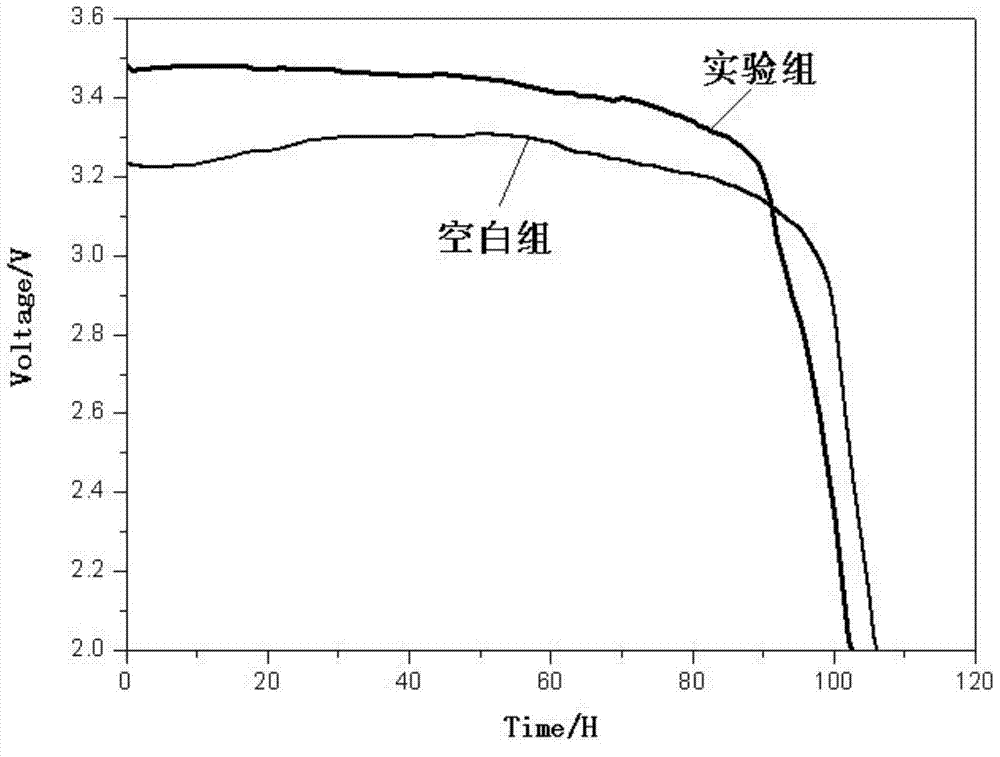
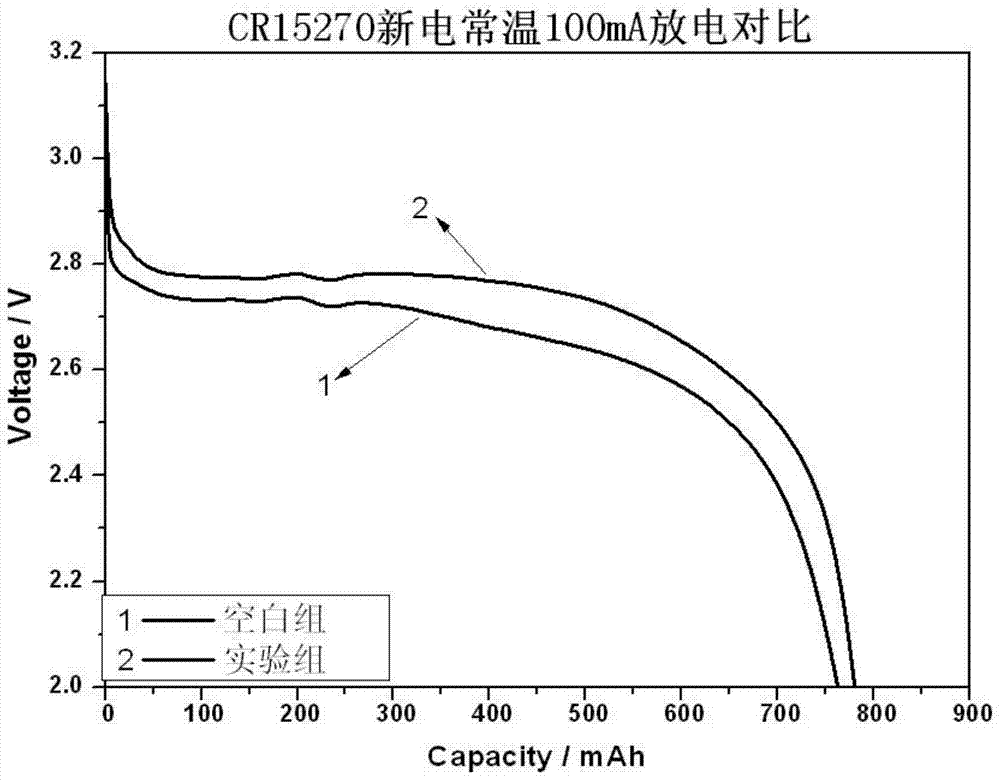
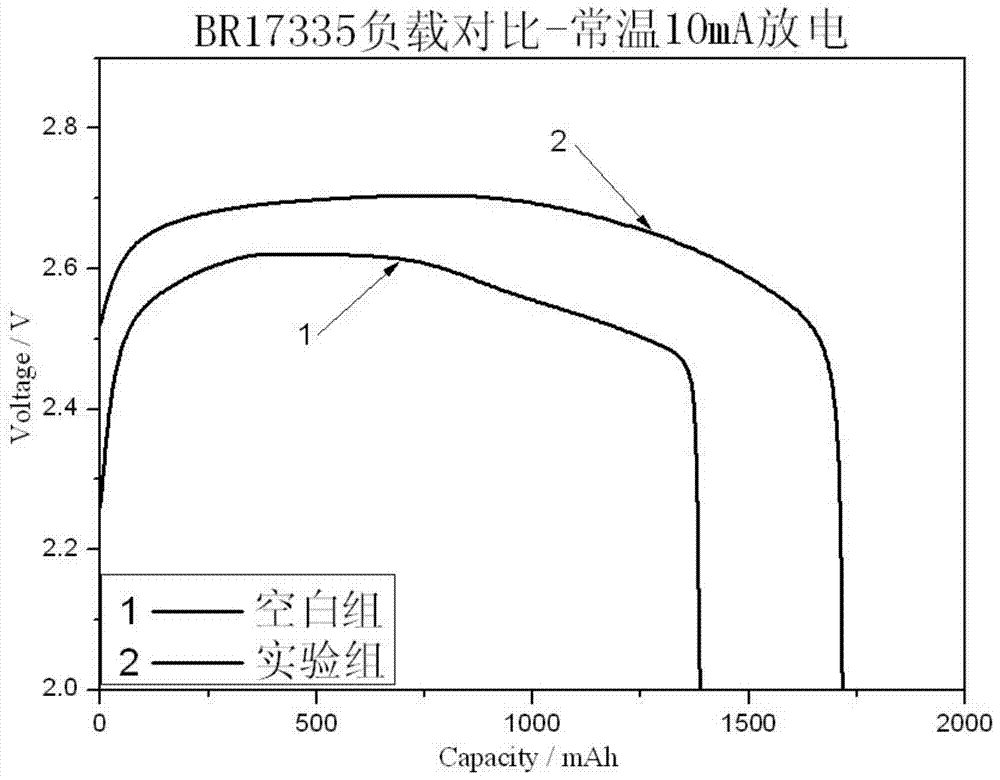
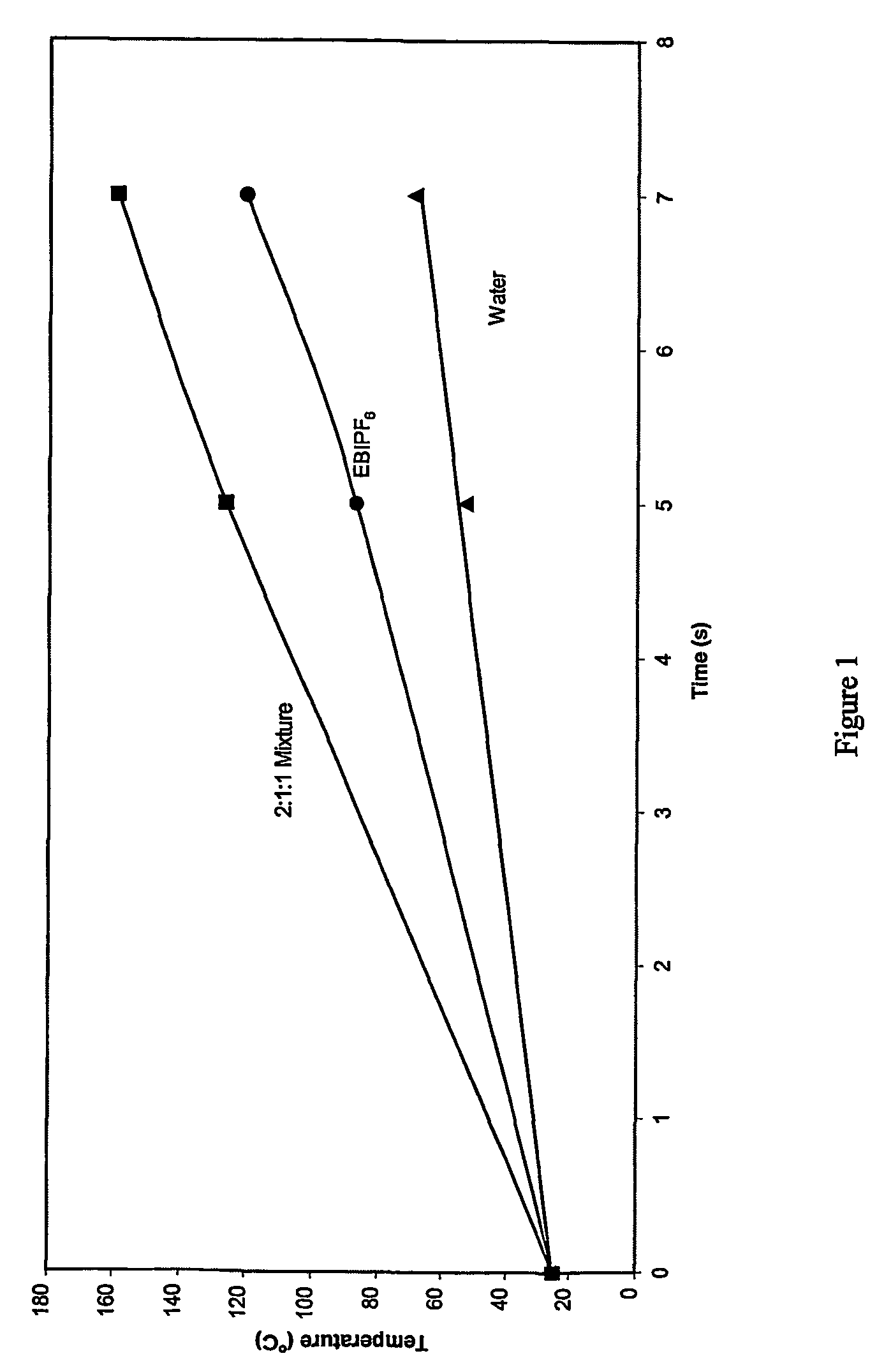
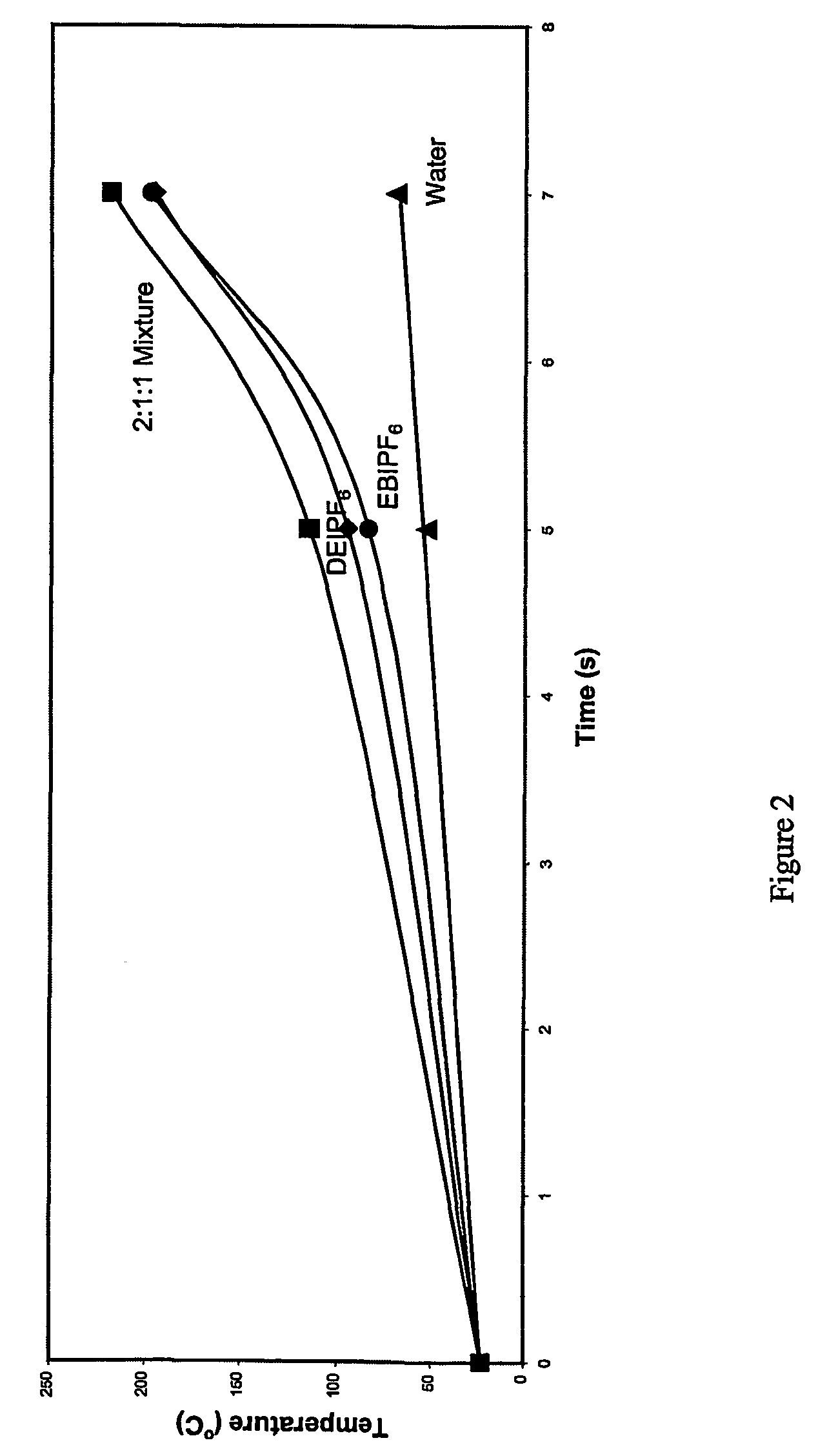
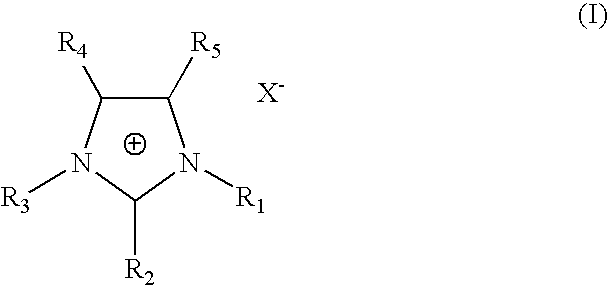
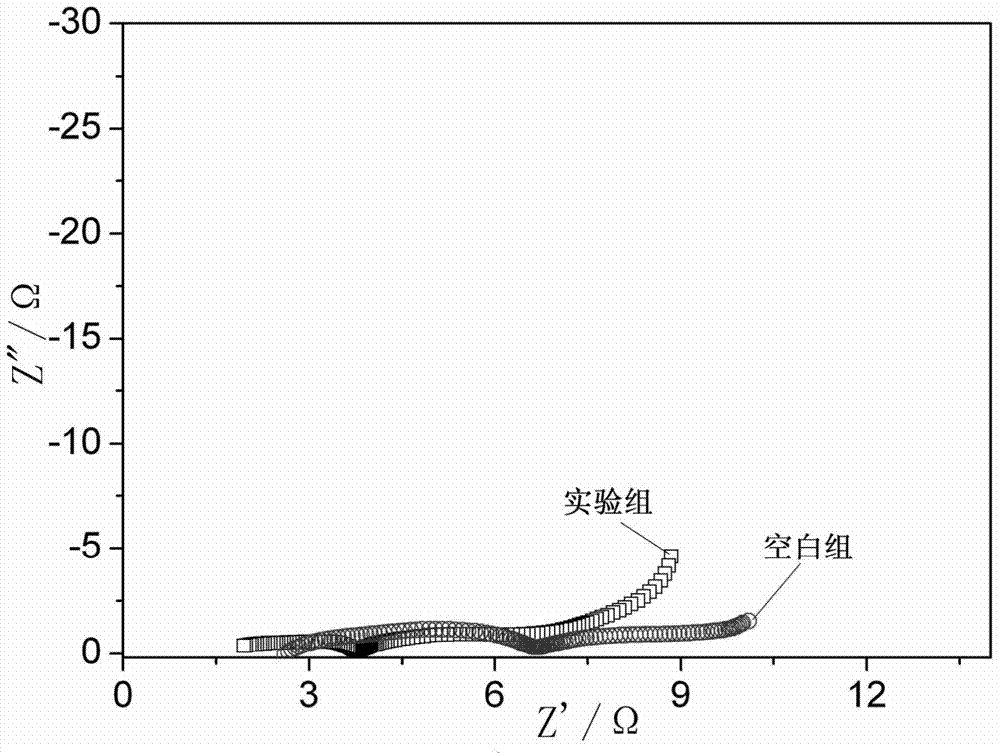
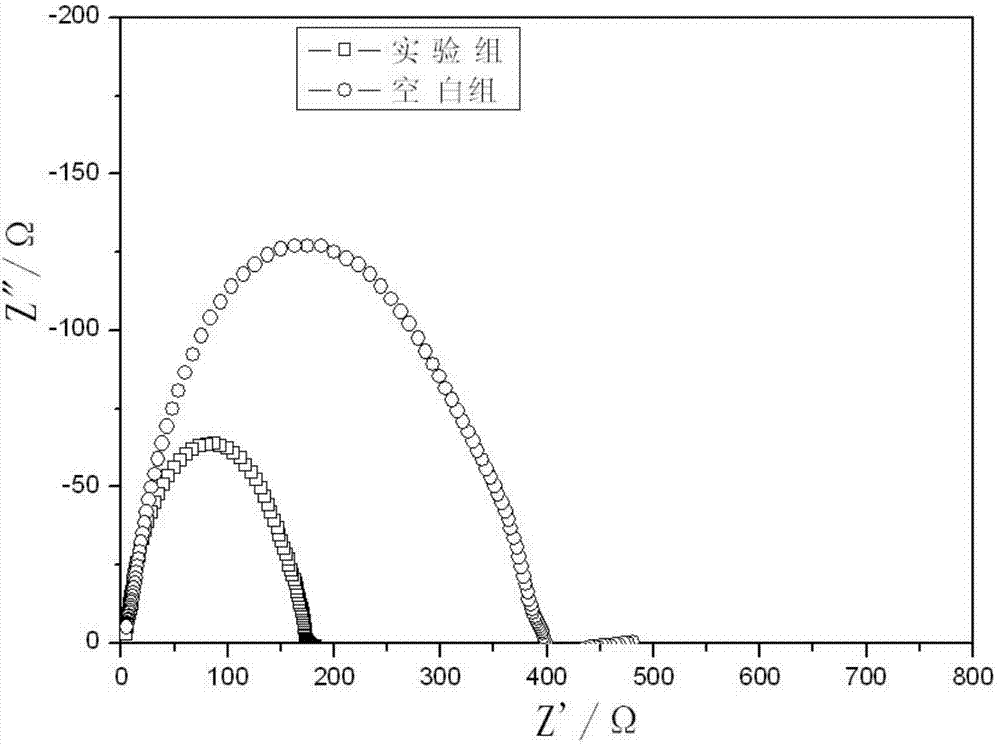
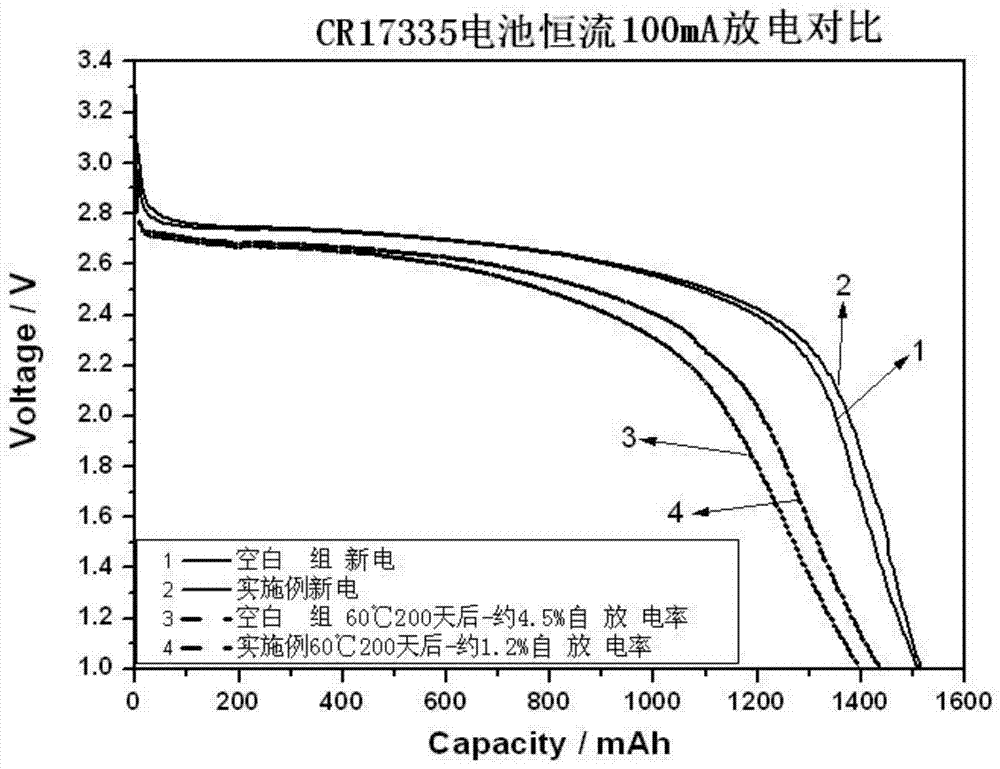
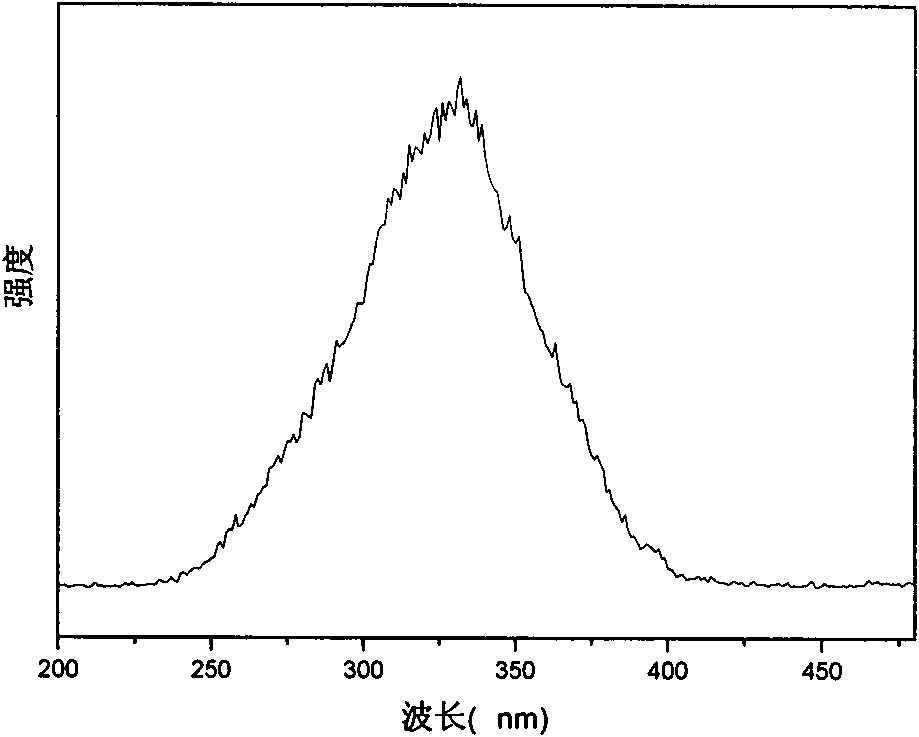
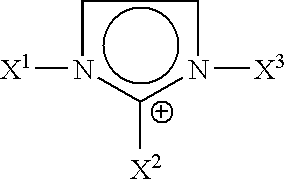Patents
Literature
236 results about "Hexafluorophosphoric acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hexafluorophosphoric acid is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula H₂FPF₆ (also written H₂F[PF₆]). This strong Brønsted acid features a non-coordinating anion, hexafluorophosphate (PF⁻₆). It is formed from the reaction of hydrogen fluoride with phosphorus pentafluoride.
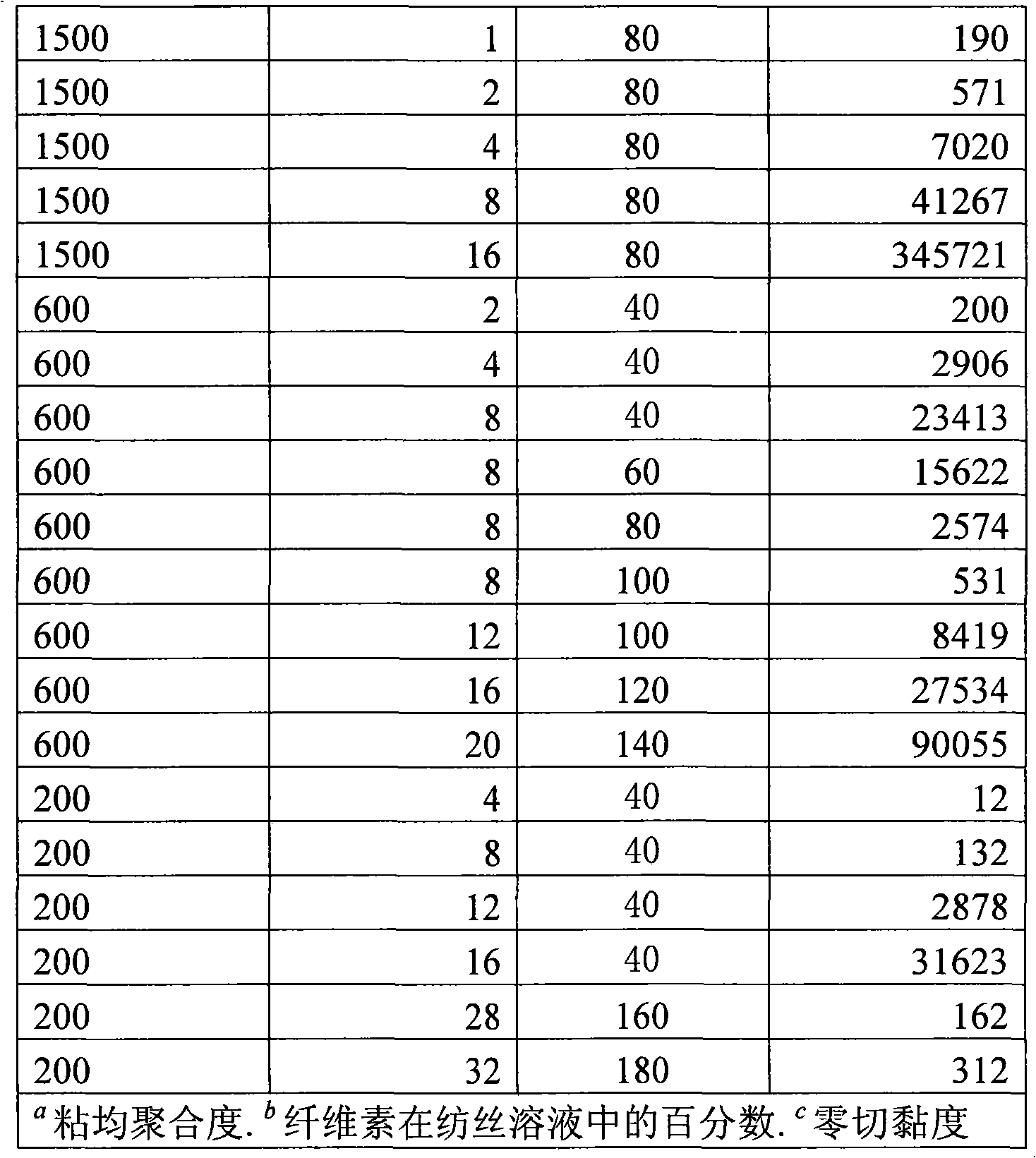
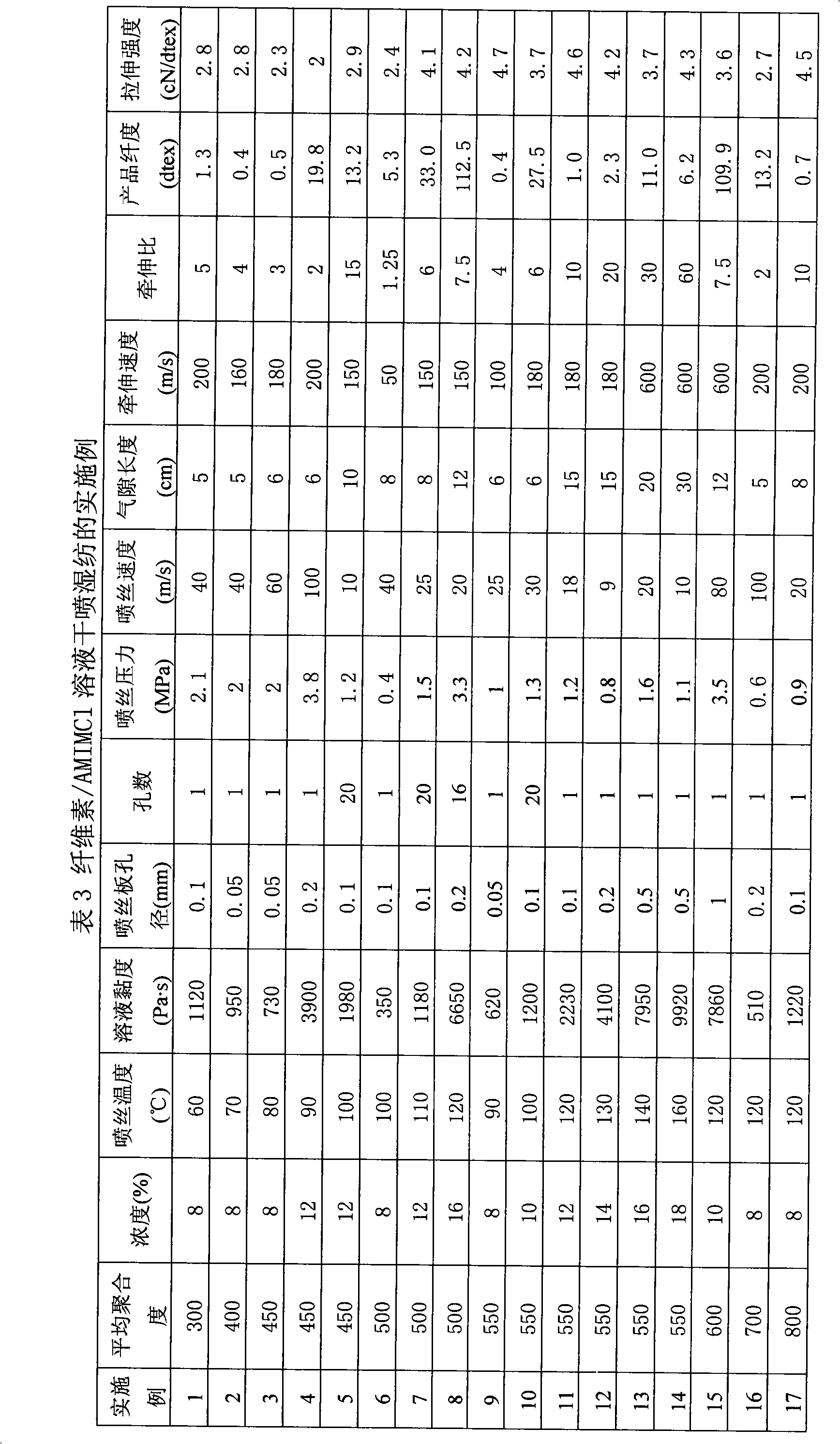
Method for continuously preparing regenerated cellulose fibre
InactiveCN101328626AReduce manufacturing costReduce the temperatureArtificial filament recoveryFibre treatmentPolymer scienceTetrafluoroborate
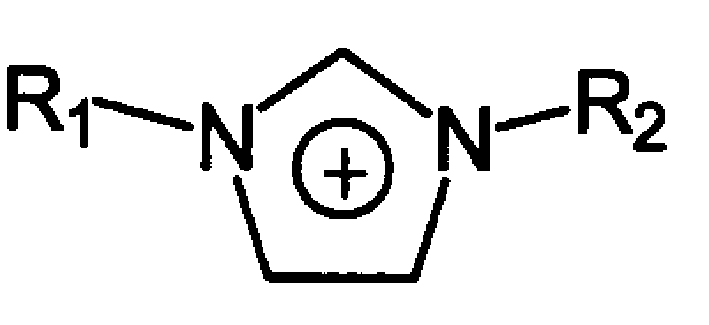
The invention discloses a method for continuously preparing regenerated cellulose fibers through the solvent method, comprising the following steps that: a cellulose raw material is dissolved into an ion liquid to prepare a spinning liquid; gel type regenerated cellulose fibers are obtained through spinning; and the regenerated cellulose fibers are obtained through cleaning, rear draft and drying, wherein, the ion liquid is selected from one or a plurality among the following ion liquids: a). an ion liquid with 1, 3-dialkyl imidazole as a cation and formiate radical, radical vinegar or propionate radical as an anion; and b). an ion liquid with 1-R1-3-R2- dialkyl imidazole as the cation and chlorine, bromine, iodine, formiate radical, radical vinegar, sulfate radical, nitrate radical, tetrafluoroborate radical, thiocyanate radical, hexafluorophosphate radical, p-toluenesulfonate radical or trifluoromethanesulfonic acid radical as the anion. The method has the advantages of wide technological range, mild temperature condition, adequate pressure, quick spinning speed and so on, can prepare the regenerated cellulose fibers with superior performance and complete specifications, and has low production cost, high production efficiency and wide application prospect.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Room temperature ionic liquid containing unsaturated double bond and its prepn and application
InactiveCN1417407AGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPulping with organic solventsSulfate radicalsTriflic acid
The room temperature ionic liquid containing unsaturated double bond has the general expressino of A+B-, where A+ contains R1 being hydroxyl with 1-4 carbon atoms and R2 containing 2-20 carbon atoms and at least one double bond; and B- is one of anions, including chlorate radical, bromate radical, iodate radical, acetate radical, sulfate radical, nitrate radical, tetrafluorobromate radical, etc. Its preparation is to mixture and react olefin halide R1X and N-alkyl imidazole to obtain ionic liquid dialkyl imidazolium halide. The present invention also relates to the application of the ionic liquid in dissolving cellulose and preparing cellulose derivative.
Owner:山东中科恒联生物基材料有限公司
Hydrogenation method for unsaturated block copolymers and hydrogenated unsaturated block copolymers
Use is made, for selectively hydrogenating the olefinic double bonds of block copolymers, at least one block of which comprises olefinic double bonds, using a catalyst based on a metal from Group VIII in a medium comprising an organic solvent for the copolymer and an ionic liquid as solvent for the catalyst, of a water-immiscible ionic liquid, preferably an ionic liquid for which the anion is the hexafluorophosphate anion and the cation is the 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium (bmim+) or 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium (emim+) cation.Applied to poly(styrene)-b-poly(butadiene)-b-poly(methyl methacrylate) block copolymers, the poly(butadiene) block of which predominantly possesses a 1,4-microstructure, this process results in copolymers for which the degree of hydrogenation is at least equal to 50% and which exhibit a melting point of greater than 30 °C.
Owner:ATOFINA
Iridium complex phosphor material taking phthalazine derivative as ligand and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102180909AImprove solubilityImprove hole transport abilityGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsLuminescent compositionsQuantum yieldIridium
The invention discloses an iridium complex phosphor material taking a phthalazine derivative as a ligand. The structure of the material is shown as formulas (I) and (II), wherein Ar represents aryl, substituted aryl, heterocycle aryl and substituted heterocycle aryl; R can be one of a halogen atom, alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkoxyl, aryloxy, an alkylthio group, arylthio, aromatic amino, aliphatic amino or a heterocyclic substituent; L^Y can be one of N-COOH, 8-hydroxyquinoline, beta-diketone, N^NH and the like; N^N can be bipyridyl, diquinoline, 1,10-phenanthroline, a derivative of the 1,10-phenanthroline and the like; and Z can be hexafluorophosphate and perchlorate. A dicyclic or ionic iridium complex phosphorescent electroluminescent device taking the phthalazine derivative as the ligand obtained with the preparation method has high internal and external quantum yields, high luminance and high stability. A dicyclic iridium complex is shown as a formula (I), i.e., (C^N)2Ir(L^Y); and an ionic iridium complex is shown as a formula (II), i.e., (C^N)2Ir(N^N)<+>Z<->.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Preparation of phosphorus pentafluoride
A process for the preparation of anhydrous high purity phosphorus pentafluoride in high yield. The process uses an excess of hydrogen fluoride in a reaction with a phosphoric acid to form hexafluorophosphoric acid followed by reaction with a sulfur based acid reactant in a reaction medium containing an excess of hydrogen fluoride.
Owner:LITHDYNE
Ionic liquid mixed electrolyte for lithium ion battery
InactiveCN103094610AImprove solubilityImprove thermal stabilitySecondary cellsTetrafluoroborateQuaternary ammonium cation
The invention discloses an ionic liquid mixed electrolyte for a lithium ion battery. The ionic liquid mixed electrolyte comprises lithium salt, ionic liquid and a non-aqueous organic solvent, wherein the lithium salt is one or mixture of two of lithium bis borate and lithium difluoroborate; cations in the ionic liquid are selected from one of imidazole cations, piperidine cations, pyridine cations, pyrrole cations, quaternary ammonium cations and quaternary phosphine cations; anions in the ionic liquid are selected from one of tetrafluoroborate radicals, hexafluorophate radicals, difluorosulfimide anions and diperfluoroalkylsulfimide anions; and the non-aqueous organic solvent is selected from any one or mixture of several of linear carbonate, cyclic carbonate, linear ether and cyclic ether. The ionic liquid mixed electrolyte is high in thermal stability, wide for an electrochemical stability window, high in conductivity, low in viscosity and good in compatibility with an anode material and a cathode material of the lithium ion battery at the same time.
Owner:JIANGXI YOULI NEW MATERIALS
Porous gel polyelectrolyte thin film and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101062987AEasy to separateIncrease polaritySecondary cellsCoatingsPolyelectrolyteElectrolysis
The invention discloses a multihole gel polymer electrolytic thin film, which comprises the following steps: comprising polyvinylidene fluoride with mass percent at 33-54%, acrylon-methacrylic acid macrogol single dimethyl ether ester copolymer and 43-52% 1M hexafluorophosphoric acid lithium carbonic ester ionogen; synthesizing metyl group acroleic acid carbowax single dimethyl ether ester and acrylic nitrile copolymer; blending and dissolving to N, N-dimethyl acetamine dissolvent with polyvinylidene fluoride; getting multihole thin film through immersed deposition method; absorbing hexafluorophosphoric acid lithium carbonic ester ionogen; getting the product. This invention possesses simple method and high film strength, which possesses good application prospect in polymer lithium ion battery.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Epoxy adhesive for OLED frame encapsulation and preparation method of epoxy adhesive
InactiveCN108546536ACuring shrinkage is smallNot easy to terminateNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesMacromolecular adhesive additivesAntioxidantWater vapor
The invention discloses an epoxy adhesive for OLED frame encapsulation and a preparation method of the epoxy adhesive. The epoxy adhesive is prepared from the following components in parts by weight:50-80 parts of epoxy resin, 5-10 parts of epoxy diluents, 5-10 parts of flexibilizer, 20-40 parts of filler, 1-5 parts of photoinitiator, 0.1-1 part of antioxidant and 0.3-3 parts of additive. The epoxy resin is one or a mixture of more of cycloaliphatic epoxy resin and bisphenol F epoxy resin. The epoxy diluent is one or a mixture of more of oxetane and aliphatic glycidyl ether. The photoinitiator is a cationic photoinitiator which comprises an iron-arene photoinitiator and a hexafluorophosphate photoinitiator. The epoxy adhesive adopts a curing way that ultraviolet exposure and heating are conducted in sequence, has the advantages of less curing agent residue, less volatile component residue, low curing temperature, strong bonding force, boiling resistance, water vapor resistance, oxygenbarrier performance and the like, and reaches the halogen-free standard.
Owner:SHENZHEN FISHER NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for preparing lithium hexafluorophosphate
ActiveCN101570328AImprove product qualityRich sourcesLead-acid accumulatorsPhosphorus compoundsOleumReaction rate
The invention relates to a method for preparing lithium hexafluorophosphate. The method comprises the following steps: (1), enabling anhydrous hydrogen fluoride and phosphorus pentoxide to react underthe protection of inert gas to prepare hexafluorophosphoric acid; (2), adding oleum to the hexafluorophosphoric acid under cooling stirring to prepare phosphorus pentafluoride gas; (3), dissolving high-pure lithium fluoride in an anhydrous hydrogen fluoride solution to form an anhydrous hydrogen fluoride solution containing the lithium fluoride; (4), cooling the phosphorus pentafluoride gas at 40DEG C below zero, guiding the phosphorus pentafluoride gas to the anhydrous hydrogen fluoride solution containing the lithium fluoride, and reacting, crystallizing, separating and drying the phosphorus pentafluoride gas to obtain a pure lithium hexafluorophosphate product; and (5), continuously pumping the unreacted cooled phosphorus pentafluoride gas after a reaction to the other anhydrous hydrogen fluoride solution containing the lithium fluoride and continuously reacting to obtain a lithium hexafluorophosphate finished product. The invention has rich material resources and easily obtainable raw materials, low production cost, high reaction rate, high product quality and thorough reaction and can realize semi-continuous production by the series connection of double kettles.
Owner:DO FLUORIDE CHEM CO LTD
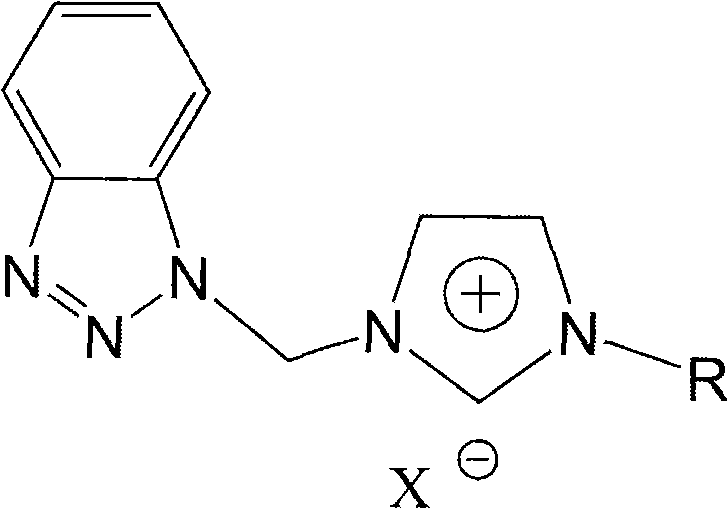
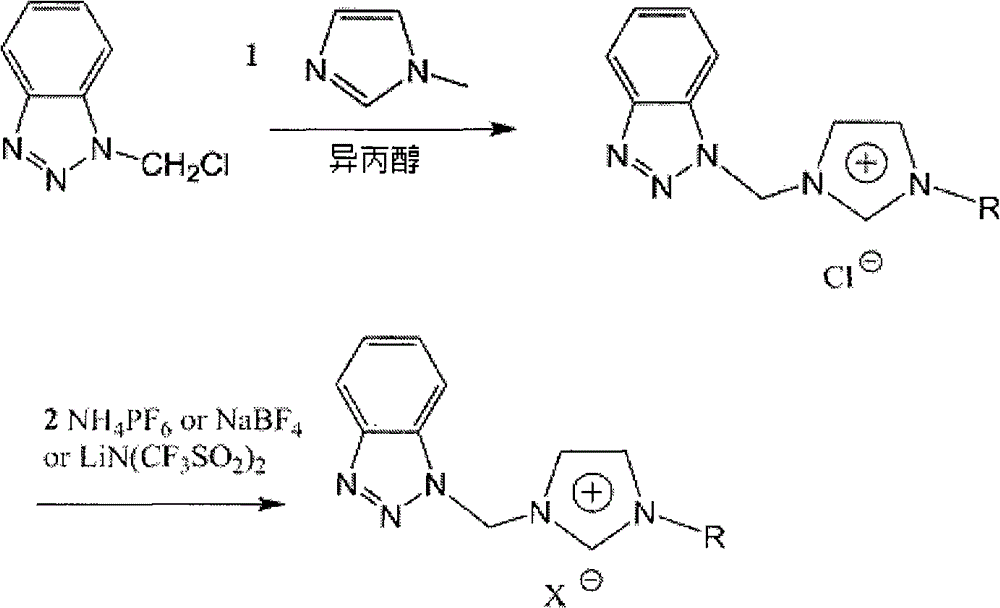
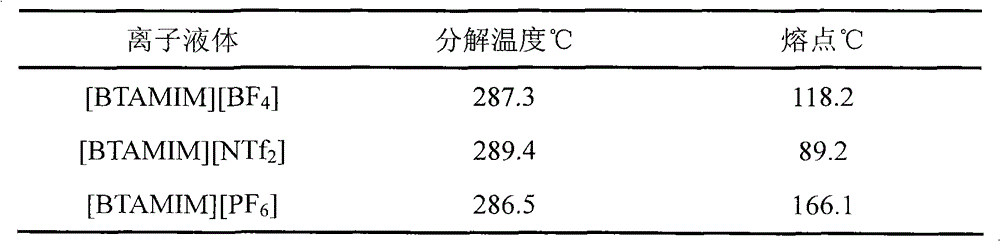
Benzotriazole group-containing ionic liquid and its preparation method and use
InactiveCN102746279AImprove thermal stabilityCorrosion resistanceOrganic chemistryAdditivesImideBenzene
The invention discloses a benzotriazole group-containing ionic liquid and its preparation method and use. The benzotriazole group-containing ionic liquid is characterized in that cations are imidazolium cations; anions are hexafluorophosphate radical, tetrafluoroborate radical or bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide anions; and an imidazole ring-substituted end group contains a benzotriazole group. The benzotriazole group-containing ionic liquid can be used as a lubricant additive or a lubricating grease additive.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of hexafluorophosphoric acid alkali metal salt
InactiveCN106745096AShort staySimple processLithium hexafluorophosphatePhosphorus compoundsChemical synthesisContinuous flow
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical synthesis, in particular to a preparation method of a hexafluorophosphoric acid alkali metal salt. The preparation method comprises the following steps: metering and introducing phosphorus pentafluorine gas and a fluorinated alkali metal salt solution into a microchannel reactor, mixing the phosphorus pentafluorine gas and the fluorinated alkali metal salt solution, carrying out reaction on a mixture, and carrying out crystallization and drying on an obtained reaction solution to obtain the hexafluorophosphoric acid alkali metal salt. According to the preparation method, a continuous flow microchannel reaction technology is adopted to synthesize the high-purity hexafluorophosphoric acid alkali metal salt, so that the reaction time is shortened to dozens of seconds or a few minutes from a few hours, the efficiency is remarkably improved, requirement for additionally configuring a device caused in the conventional intermittent reaction and leakages caused during transferring are prevented, and the safety is improved.
Owner:JIUJIANG TINCI ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
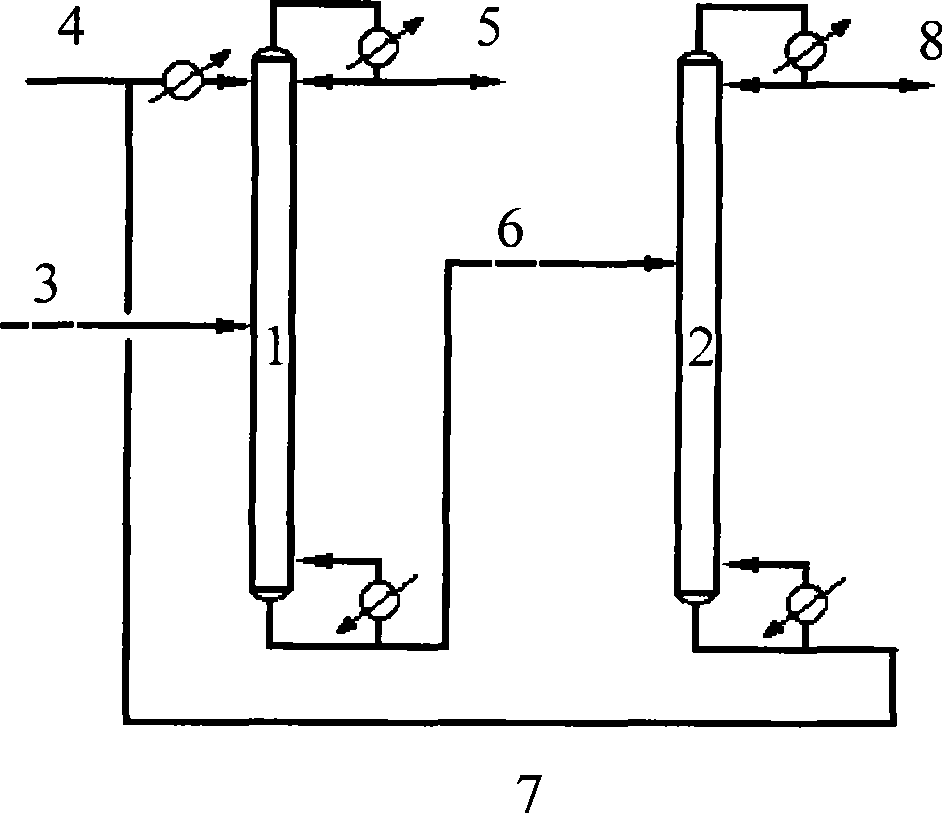
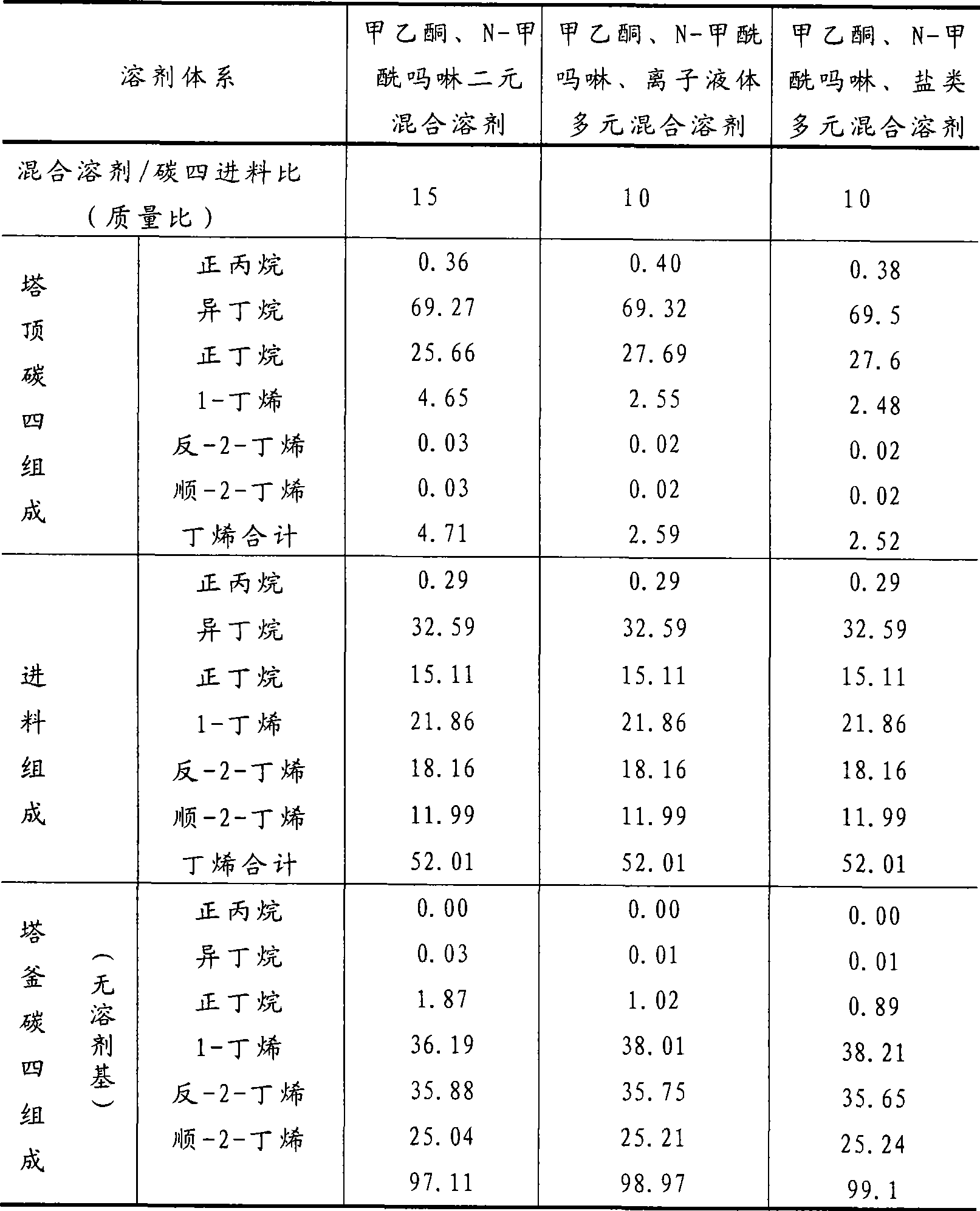
Method for separating butane and butene by using multiple mixed solvent
InactiveCN101417913ARetain solubilityImprove solubilityDistillation purification/separationBulk chemical productionSodium sulfocyanateTetrafluoroborate
The invention relates to a method for spearing butane from butylene with the multicomponent compound of ionic liquid, saline, ethyl methyl ketone and N-formylmorpholine. The content of ionic liquid in the multicomponent compound is 1.0 to 95 percent; the content of the saline in the multicomponent compound is 0.5 to 20 percent; the electropositive ion of the ionic liquid is iminazole electropositive ion, alkyl imidazole electropositive ion or alkyl quaternary ammonium ion, or the compound thereof; the electronegative ion is tetrafluoroborate electronegative ion, hexafluorophosphoric acid electronegative ion, nitrate ion, tetrachloro aluminic acid iron, heptachlor bi aluminic acid iron, chloride ion, bromine electronegative ion or the mixture; and the ionic liquid can be dimethylformamide potassium thiocyanate compound salt, dimethylformamide sodium sulfocyanate compound salt, or the compound; the saline is potassium thiocyanate, sodium sulfocyanate, ammonium thiocyanate, sodium nitrate, potassium nitrate, sodium iodide, potassium iodide, zinc chloride, copper chloride, zinc chloride, potassium bromide, or the compound thereof.
Owner:YANTAI UNIV
Preparation method of lithium hexafluorophosphate
ActiveCN101723346AHigh yieldImprove securityFinal product manufactureElectrolyte accumulators manufactureHydrogen fluoridePhysical chemistry
The invention provides a preparation method of a lithium hexafluorophosphate, which comprises the following steps: firstly, reacting a phosphorus pentachloride with an anhydrous hydrogen fluoride to form mixed liquid of the phosphorus pentachloride and the anhydrous hydrogen fluoride; secondly, preparing anhydrous hydrogen fluoride solution of lithium fluoride; and finally, adding the anhydrous hydrogen fluoride solution of the lithium fluoride into the mixed liquid of the phosphorus pentachloride and the anhydrous hydrogen fluoride, and sequentially performing reaction, crystallization, separation and drying to obtain a pure lithium hexafluorophosphate product. The preparation method of the invention has the advantages of mild reaction, high safety and purity of the lithium hexafluorophosphate product of over 99.9 percent; and the mother liquor can be reclaimed and reused so that the cost is reduced.
Owner:DO FLUORIDE CHEM CO LTD
Phosphorescence iridium complex, preparation method and organic electroluminescent device
InactiveCN102503986AImprove solubilityImprove hole transport abilityGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesIridiumPhenanthroline
The invention discloses a phosphorescence iridium complex by taking a quinazoline derivative as a ligand and an organic electroluminescent device thereof. The structure of the phosphorescence iridium complex disclosed by the invention is represented by the formula (I) or the formula (II) described in the specification, wherein Ar represents aryl, substituted aryl, heterocyclic aryl and substituted heterocyclic aryl; R can be one of a halogen atom, alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkoxy, aryloxy, alkyl sulphanyl, aryl sulphanyl, aromatic amino, fatty amino and heterocyclic substituent; L^Y can be one of N^COOH, N^OH, beta-diketone, N^NH and the like; N^N can be bipyridyl, biquinolyl, phenanthroline and derivatives thereof and the like; and Z can be a hexafluorophosphoric acid radical, a perchloric acid radical and the like. A light-emitting layer of the electroluminescent device disclosed by the invention is prepared by adopting a spin coating and film-preparing method under a specified condition, has the advantages of being low in cost, simple for operation and steady in chemical property, and is beneficial to preparing large-screen electroluminescent devices.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Ionic liquid polymer electrolyte and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104466240AEasy to prepareImprove conductivityElectrolyte accumulators manufactureChemical LinkagePolyethylene oxide
The invention discloses an ionic liquid polymer electrolyte and a preparation method thereof. An ionic liquid polymer is synthesized through using a polymer chemical functionalization process, and the structure of the ionic liquid polymer is represented by formula (1) shown in the specification. The ionic liquid polymer is formed through connecting N-methylimidazole with a polymer by chemical bonds, wherein the polymer can be a linear polymer and a hyperbranched polymer, the linear polymer is polyethylene oxide and polyepoxy chloropropane preferably, and the hyperbranched polymer is hyperbranched polyether preferably; and anion a can be halogen, tetrafluoroborate, hexafluorophosphate and ditrifluoromethyl sulfimide, and N-methylimidazole in the formula (1) can be substituted by a pyridine ring, tributyl amine and a pyrrole ring. The ionic liquid polymer electrolyte is composed of the ionic liquid polymer and a lithium salt, and contains no volatile solvents, and the conductivity at room temperature of the ionic liquid polymer electrolyte can reach 3.5*10<-4>Scm<-1>. The polymer electrolyte can be used in lithium ion secondary batteries, electrochromic devices, supercapacitors and other electrochemical devices.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Preparation method of high purity phosphorus pentafluoride
ActiveCN104261369ALow costNo occupational health hazardPhosphorus halides/oxyhalidesPhosphoric acidSulfur trioxide
The invention provides a preparation method of high purity phosphorus pentafluoride. The preparation method comprises the following steps: step one, taking polyphosphoric acid and waterless hydrogen fluoride as the primary raw materials to prepare a hexafluorophosphoric acid water solution; step two, reacting the hexafluorophosphoric acid water solution obtained in the step one with sulfur trioxide so as to obtain a mixture of hexafluorophosphoric acid and sulfuric acid; step three, directly heating the mixture of the hexafluorophosphoric acid and sulfuric acid obtained in the step two without separation, condensing the generated phosphorus pentafluoride steam so as to obtain a coarse product of phosphorus pentafluoride; step four, refining the obtained coarse product so as to obtain high purity phosphorus pentafluoride with a purity more than 99.5%. The product prepared by the provided preparation method has a high purity and low purity content, wherein the phosphorus pentafluoride content is not less than 99.95%, the waterless hydrogen fluoride content is not more than 50 ppm, the water content is not more than 10 ppm, the metal ion content is not more than 1 ppm, and the content of other purities is not more than 5 ppm.
Owner:JIUJIANG TINCI ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for catalyzing alcohol acid esterification using ion liquid
InactiveCN1880295AReduce dosageHigh catalytic efficiencyOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSulfate radicalsTriflic acid
This invention discloses a method for catalyzing alcohol acid esterification by using an ionic liquid. The ionic liquid A+B- is used as catalyst and solvent, wherein: A+ has the following structural formula, and R could be an alkyl group or alkene group with more than one carbons; B- is selected from the following negative ions: chlorin, bromine, iodine, acetate, sulfate radical, hydrogensulfate radical, phosphate radical, hydrogen phosphate radical, nitrate radical, tetrafluoroboric radical, hexafluorophosphoric radical, p-toluenesulfonic radical, and trifluoromethanesulfonic radical; the catalyst amount added is 0.01%-50% of the total mole of the alcohol and acid added, reaction temperature 20-140Deg C, normal pressure reaction time 0.5-12h.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
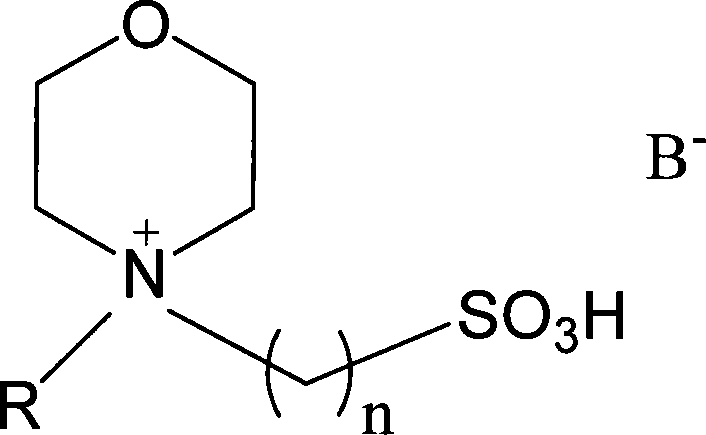
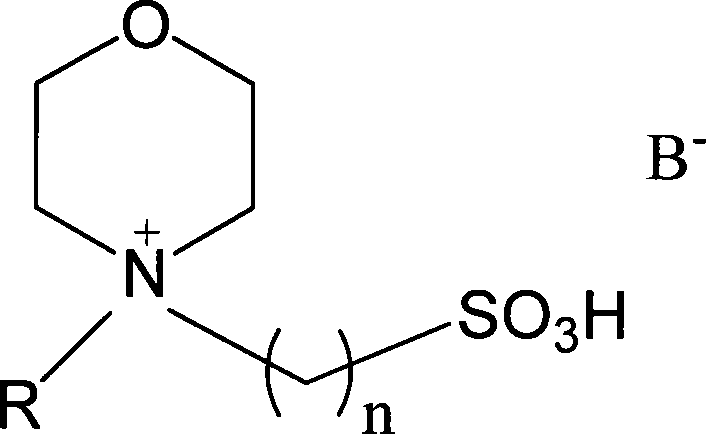
Morpholine quaternary ammonium salt ion liquid and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101157667AImprove thermal stabilityEasy to manufactureOrganic chemistryTetrafluoroborateNitrate
The invention relates to a morpholine quaternary ammonium salt ionic liquid and a preparation method. The ionic liquid has the following structural general formula: A +B-, wherein, the A+ has the structural general formula as the right, in the general formula: R1 is the saturated or unsaturated alkyl containing 1 to 4 carbon atoms, and the R2 is in line with the following rules: a) at least 2 carbon atoms are contained; b) not more than 20 carbon atoms are contained; the B- is selected from one the following anions: chlorine, bromine, iodine, acetate, sulfate, nitrate, tetrafluoroborate, thiocyanate, hexafluorophosphate, p-toluenesulfonic and trifluoromethanesulfonic.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Diacetone acrylic amide type ionic liquid and preparation thereof
InactiveCN1385243AEasy to getLow priceOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsAcetic acidTrifluoroacetic acid
The present invention relates to a new type diacetone acryloamide type ionic liquid and its preparation method. It is made up by using diacetone acryloamide and respectively making it and sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, acetic acid, trifluoroacetic acid, tetrafluoroboric acid or phosphofluoric acid undergo the processes of acid and alkali neutralization and separation. Said invention is low in cost, simple in preparation, has no secondary pollution and is suitable for industrial production and application.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Electrolyte for lithium battery and lithium battery using the electrolyte
InactiveCN103814473AIncrease discharge voltageImprove conductivityFinal product manufacturePrimary cellsEster sulfonateSuccinic acid
The invention discloses an electrolyte for a lithium battery. The electrolyte contains a pyridine ionic liquid, and the pyridine ionic liquid contains cations and anions; the cations are N-alkylpyridine; and the anions are one kind of the anions of a group consisting of halite ions, tetrafluoroboric acid anions, hexafluorophosphoric acid anions, bis(trifluoromethanesulphonyl)imine anions, lactic acid anions, p-methyl benzene sulfonate acid radical anions, acetyl sulfonyl imide anions, saccharin anions, amino acids anions, sulfuric acid ester anions, succinic acid diisooctyl ester sulfonate radical anions, 4,5-dimetridazloe anions, and 5-nitrotetrazolato anions. The electrolyte can change the reaction mechanism of the battery, improve the reduction rate of a cathode active material and the mass transfer rate of the electrolyte, and increase the electrical conductivity of the electrolyte, so the discharge voltage of the lithium battery is improved. Furthermore, the invention further discloses a preparation method for the electrolyte and the lithium battery containing the electrolyte.
Owner:EVE ENERGY CO LTD
Preparation method of lithium hexafluorophosphate
The invention relates to a preparation method of lithium hexafluorophosphate. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: (1) enabling hexafluorophosphate MPF6 to react with a raw material, namely, halogenated lithium salt LiF to obtain fluoride MF and lithium hexafluorophosphate LiPF6, wherein M is Li, Na, K, NH4 and Ag; (2) performing a reaction under a closed condition and in a dry inert gas atmosphere of which the water content is smaller than 10ppm, and stirring for 2-24 hours to generate a lithium hexafluorophosphate solution, wherein the water content of a solvent is smaller than 10ppm, and the reaction temperature is between 0 DEG C and 15 DEG C; and (3) dissolving the MF in the solvent by using the solubility of the MF in the solvent, precisely filtering, removing undissolved substances including the fluoride MF and the like in a filtering manner, condensing and crystallizing to obtain a lithium hexafluorophosphate solid, and drying the lithium hexafluorophosphate solid to obtain a lithium hexafluorophosphate product.
Owner:CNOOC TIANJIN CHEM RES & DESIGN INST +1
One-step process for the preparation of halide-free hydrophobic salts
InactiveUS7253289B2Conveniently separatedImprove ionic conductivityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPropylamineSolvent
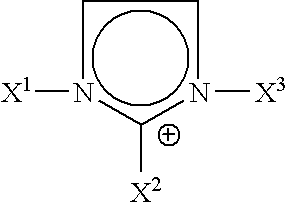
This invention describes a one pot, single-step process for the preparation of halide-free hydrophobic salts comprising polyalkylated imidazolium cations and various anions in accordance with the following structure, where R1 and R3 represent the either the same or different alkyl groups, and R2, R4, and R5 represent either hydrogen atoms, or the same or different alkyl group substituents; X represents a polyatomic anion that is the conjugate base of an acid. By simply mixing aqueous formaldehyde with an alkyl amine such as methylanune, ethylamine, n-propyl oriso-propylamine, or n-butyl-, iso-butyl, or t-butylamine, or by mixing aqueous formaldehyde with two alkyl amines (preferably one being methylamine, ethylamine, n-propyl- or iso-propylamine, or n-butyl-, isobutyl, or t-butylamine) and another being n-propyl- or isopropylaine, or n-butyl-, isbutyl, or t-butylamine), an acid (such as hexafluorophosphoric acid, trifluoroacetic acid, pentafluoropropionic, heptafluorobutyric acid, or the free acid of a bis(perfluoroalkylsulfonyprnide or tris(perfluoroalkylsulfonyl)methide as the source of the anion) and aqueous glyoxal solution, the hydrophobic ionic salts or mixtures thereof thus formed may be conveniently separated directly from the aqueous byproduct layer. Like the single cation hydrophobic salts, these mixed hydrophobic ionic liquids are non-flammable and manifest no detectable vapor pressure up to their decomposition temperature of greater than 300° C. We have also discovered that, surprisingly, ternary mixtures of dialkylated ionic liquids manifest higher ionic conductivities than a single ionic liquid of the mixture alone. This property benefits electrochemical power source applications such as batteries and capacitors. Furthermore, we have discovered that ternary mixtures of dialkylated ionic liquids absorb microwave radiation more efficiently than a single ionic liquid of the mixture alone. This property benefits microwave-induced synthetic reactions. Such physical and chemical properties make it possible to employ inexpensive mixtures of polyalkylated imidazolium cations in an advantageous manner as thermal transfer fluids, high temperature lubricants, and plasticizers, and as solvents in the areas of electrochemistry, synthetic chemistry, catalysis, and separations chemistry.
Owner:COVALENT ASSOCS
Preparation of cobalt adsorbent
InactiveCN105859938AImprove adsorption capacityNot easy to loseOther chemical processesWater contaminantsHexafluorophosphoric acidTrifluoromethyl
The invention relates to preparation of a cobalt adsorbent. The cobalt adsorbent is prepared by introducing bis(pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)cobalticinium hexafluorophosphate, (S,S)-(+)-N,N'-bis(3,5-di-tert-butylsalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediaminocobalt and 1-vinyl-3-buthylimidazolium bis[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]imide in polymerization to be polymerized.
Owner:王金明
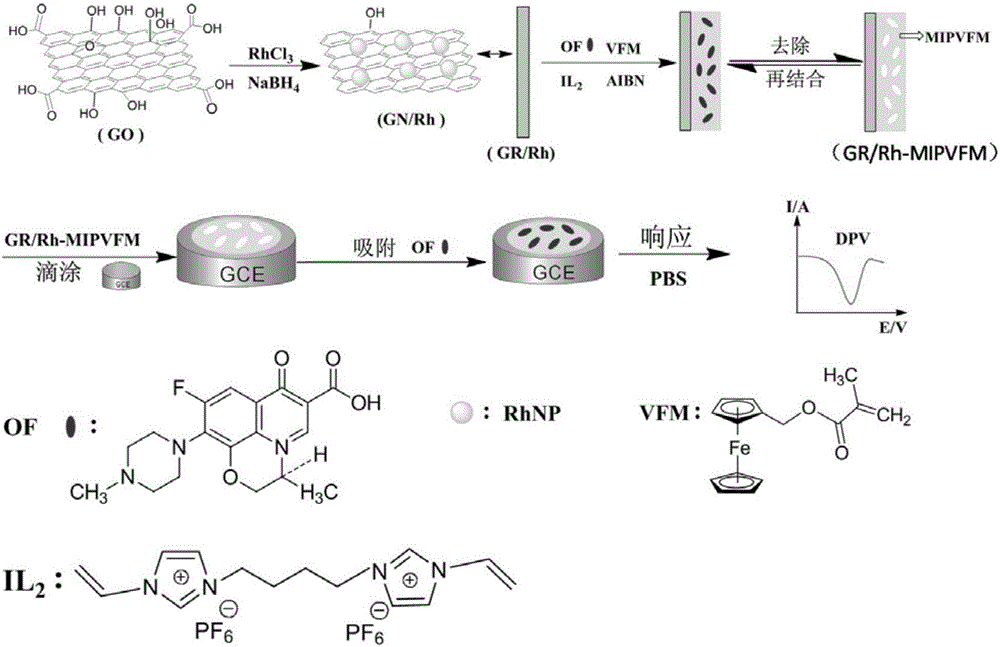
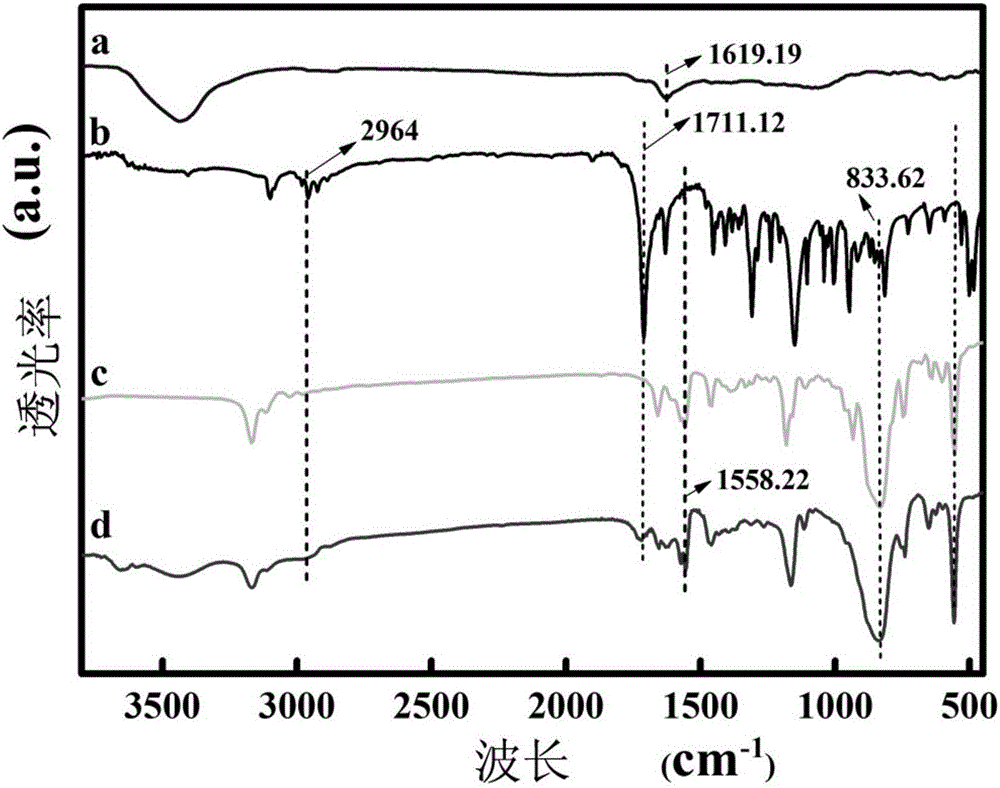
Molecularly imprinted polymer for detecting ofloxacin and preparing method and application thereof
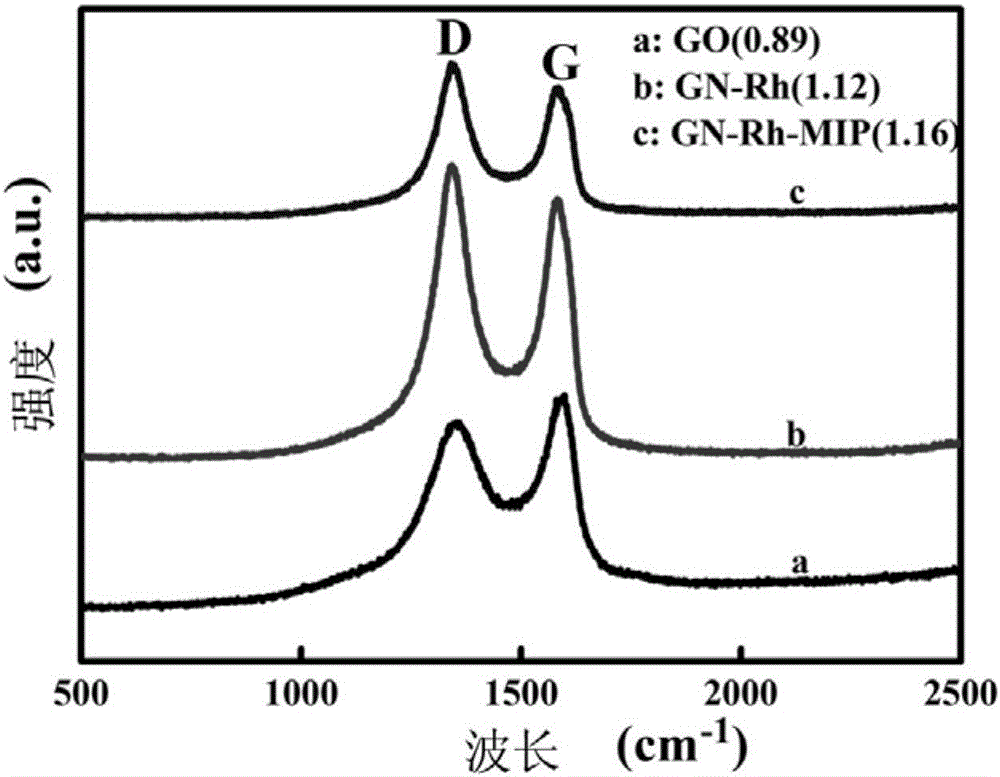
ActiveCN105859988AImprove adsorption capacityGood choiceOther chemical processesMaterial electrochemical variablesFunctional monomerHexafluorophosphoric acid
The invention discloses a molecularly imprinted polymer for detecting ofloxacin and a preparing method and application thereof. A carrier, a template molecule, a functional monomer and a crosslinking agent are polymerized under the action of an initiating agent to form a composite material, and the template molecule is removed from the composite material to obtain the molecularly imprinted polymer; graphene / rhodium nano particles serve as the carrier, the template molecule is ofloxacin, the functional monomer is methyl ferrocenyl methacrylate, and the crosslinking agent is 3,3'-(1',4'-butane)-bi-1-vinyl imidazole hexafluorophosphoric acid. The invention further discloses application of an electrochemical transducer made of the molecularly imprinted polymer to ofloxacin detection. The electrochemical transducer made of the molecularly imprinted polymer has good adsorptive property to ofloxacin and is high in selectivity, not prone to interference and wide in detection linear range, and the lower detection limit can reach 0.06 micrometer.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
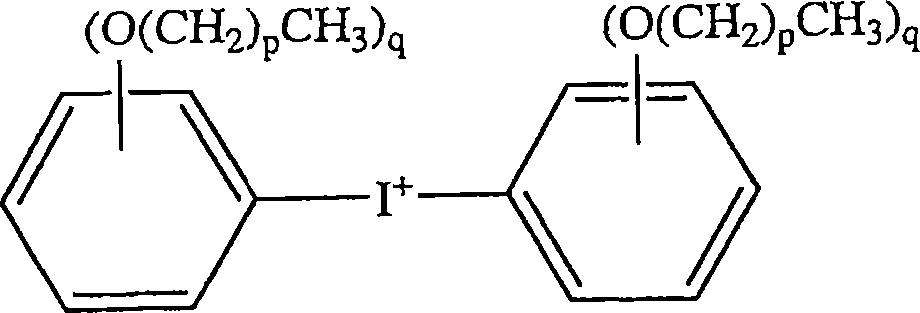
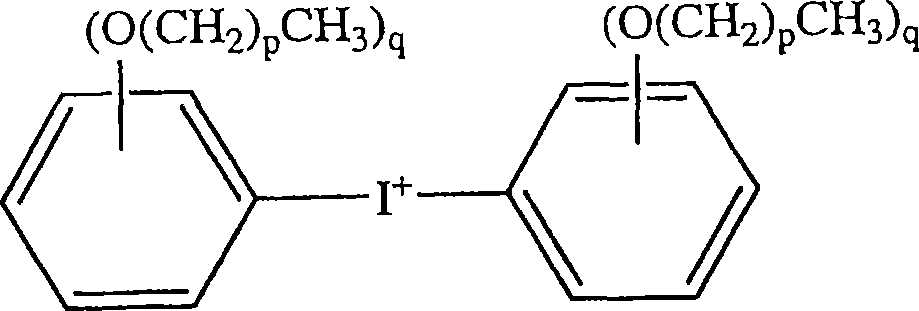
Molding composition and method, and molded article
A curable method useful for encapsulating solid state devices includes (A) an epoxy resin; (B) an effective amount of a cure catalyst comprising (Bl) a first latent cationic cure catalyst comprising a diaryl iodonium hexafluoroantimonate salt; (B2) a second latent cationic cure catalyst comprising (B 2a) a diaryl iodonium cation, and (B 2b) an anion selected from perchlorate, imidodisulfurylfluoride anion, unsubstituted and substituted (C1-C12)-hydrocarbylsulfonates, (C2-C12)-perfluoroalkanoates, tetrafluoroborate, unsubstituted and substituted tetra-(C1-C12)-hydrocarbylborates, hexafluorophosphate, hexafluoroarsenate, tris(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)metliyl anion, bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)methyl anion, bis(trifluoromethylsulfuryl)imide anion, and combinations thereof; and (B3) a cure co-catalyst selected from free-radical generating aromatic compounds, peroxy compounds, copper (II) salts of aliphatic carboxylic acids, copper (II) salts of aromatic carboxylic acids, copper (II) acetylacetonate, and combinations thereof; and (C) about 70 to about 95 weight percent of an inorganic filler, based on the total weight of the curable composition. The composition's cure catalyst allows the use of increased filler loadings, which in turn reduces moisture absorption and thermal expansion of the cured composition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Electrolyte for lithium battery and lithium battery using the electrolyte
ActiveCN103814468AReduce passivationIncrease storage capacityOrganic electrolyte cellsLi-accumulatorsGalliumEster sulfonate
The invention discloses an electrolyte for a lithium battery. The electrolyte contains a pyridine ionic liquid, and the pyridine ionic liquid contains cations and anions; the cations are N-alkylpyridine; the anions are one kind of the anions of a group consisting of aluminum tetrachloride acid radical ions, gallium tetrachloride acid radical ions, tetrafluoroboric acid anions, hexafluorophosphoric acid anions, bis(trifluoromethanesulphonyl)imine anions, lactic acid anions, p-methyl benzene sulfonate acid radical anions, acetyl sulfonyl imide anions, saccharin anions, amino acids anions, sulfuric acid ester anions, succinic acid diisooctyl ester sulfonate radical anions, 4,5-dimetridazloe anions, and 5-nitrotetrazolato anions. The electrolyte can inhabit increasement of a metal lithium surface passivatin layer (an SEI film) in the lithium battery, and can significantly improve storage performance of the battery. Furthermore, the invention further discloses a preparation method for the electrolyte and the lithium battery containing the electrolyte.
Owner:EVE ENERGY CO LTD
Functional ionic liquid and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102180873ALuminous in rich colorsHigh color puritySulfonic acid amide preparationLuminescent compositionsTetrafluoroborateFluorescence
The invention relates to a functional ionic liquid and a preparation method thereof. The structural formula of the ionic liquid is disclosed in the specification, wherein X<-> is Cl<-> (chloride ion), [BF4]<-> (tetrafluoroborate ion), [PF6]<-> (hexafluorophosphate ion) or [Tf2N]<-> (bistrifluoromethanesulfonimide ion), and n=0-15. After being introduced to the cation alkyl side chain of the ionicliquid, a phenanthroline group can coordinate with some metallic ions to form metallic coordination compounds, and can absorb energy and transfer the absorbed energy to the metallic ions so as to coordinate with rare earth ions, thereby being used for preparing a rare earth compound / ionic liquid material. The prepared material has the advantages of colorful emitted light, high color purity, long fluorescence lifetime and high quantum efficiency, and is applicable to the fields of display, new light sources, X-ray intensifying screens and the like.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Catalytic esterification method for sulfonic group functionalization morpholine hyamine ion liquid
InactiveCN101172949AStrong acidThe synthesis process is simpleOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrogen SulfateSulfate radicals
The invention discloses a method for catalyzing and esterifying sulfoacid basal functional ion liquid in the formula (1), wherein, n equals to 2, 3 and 4; R is H or C1 to C4 saturated or unsaturated alkyl of straight chain or branched chain; negative ion B- is chlorine, bromine, iodine, sulfate radical, hydrogen sulfate radical, nitric acid radical, dihydrogen phosphate radical, tetrafluoride boric acid radical, hexaflurate phosphoric acid radical, acetic acid radical, methyl sulfoacid radical, paratoluenesulfonic acid radical, fluoroform sulfoacid radical and trifluoroacetic acid radical. The adding dosage of the ion liquid is 0.5 to 100 percent of the total mol of the alcohol and acid, reacting for 0.5 to 12 hours under the normal pressure and the temperature of 20 to 140 DEG C, the esterifying reaction is catalyzed to produce the ester. Compared with the traditional acidic catalyst, the ion liquid simplifies the separation of the product of the esterifying reaction and provides higher selectivity. The invention is distinctly characterized in that the phase separation between the produced ester and the catalyst is automatically finished, and the ion liquid is reusable after simple or non treatment.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Lithium ion battery flame-retardant electrolyte
ActiveCN106025344AGuaranteed cycle performanceImprove conductivitySecondary cellsTetrafluoroborateTriflic acid
The invention discloses lithium ion battery flame-retardant electrolyte which comprises raw materials of an electrolyte lithium salt, an organic solvent and a flame-retardant additive, wherein the organic solvent is prepared from the following components in parts by volume: 15-40 parts of an organic basic solvent with a high dielectric constant, 5-45 parts of a low-vapor pressure solvent, 10-55 parts of a low-viscosity solvent and 2-35 parts of an indoor temperature ionic liquid; the anion of the indoor temperature ionic liquid is prepared from at least one ion of tetrafluoroborate, hexafluoroborate, trifluoromethanesulfonate, bi-trifluoro sulfonamide and trifluoroacetic acid; the cation of the indoor temperature ionic liquid is ammonium cation; the flame-retardant additive is at least one of fluoroproplylene carbonate, di-fluoroproplylene carbonate, trifluoroproplylene carbonate, fluorobenzene ether, fluoro ether and propyl-2,2,2-trifluoro-ethyl carbonate; the mass of the flame-retardant accounts for 1-20% of the total mass of the electrolyte. By adopting the lithium ion battery flame-retardant electrolyte, not only is the flame-retardant property of the electrolyte remarkably improved, but also the charge and discharge property of a battery is slightly affected.
Owner:DONGFENG COMML VEHICLE CO LTD
Preparation method of difluorophosphoric acid alkali metal salt
ActiveCN105236368AEnsure safetyImprove securityPhosphorus halides/oxyhalidesElectrolytic agentPhosphate
The invention discloses a preparation method of difluorophosphoric acid alkali metal salt. In the method, the difluorophosphoric acid alkali metal salt is produced through a reaction of hexafluorophosphates of alkali metals and corresponding phosphates of the alkali metals in a solid phase or in a non-aqueous solvent, wherein the reaction equation is MPF6+M3PO4=2MPO2F2+2MF (M=Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs), the molar ratio of MPF6 to M3PO4 is 0.8-1.5:1, preferably 1.1-1.2:1, namely, the hexafluorophosphates of alkali metals is excessive properly to ensure reaction of the phosphates to be carried completely. The method can be used for preparing the difluorophosphoric acid alkali metal salt under safe situations, thereby improving safety of the preparation process and ensuring safety of preparation operators. The difluorophosphoric acid alkali metal salt is produced through a reaction of the hexafluorophosphates and the phosphates of the alkali metals, and the target product can be produced whether the reaction is carried out in solid phases or liquid phases under mild conditions without dangerous gas raw materials and generation of acidic gas or water which may damage performances of an electrolyte.
Owner:TIANJIN JINNIU POWER SOURCES MATERIAL +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com