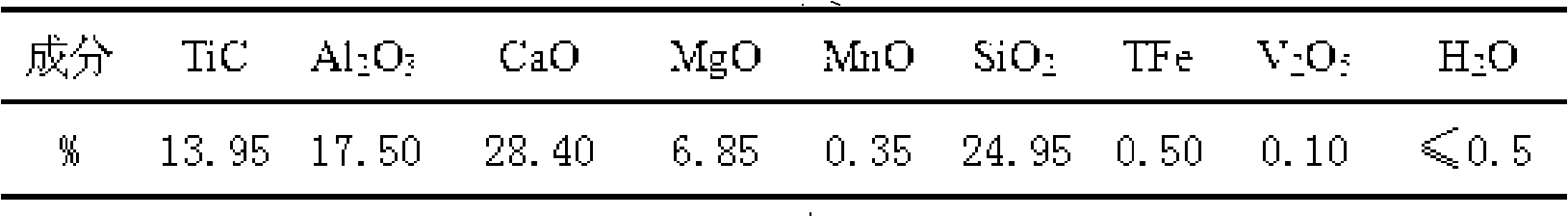Patents
Literature
343results about "Titanium tetrachloride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
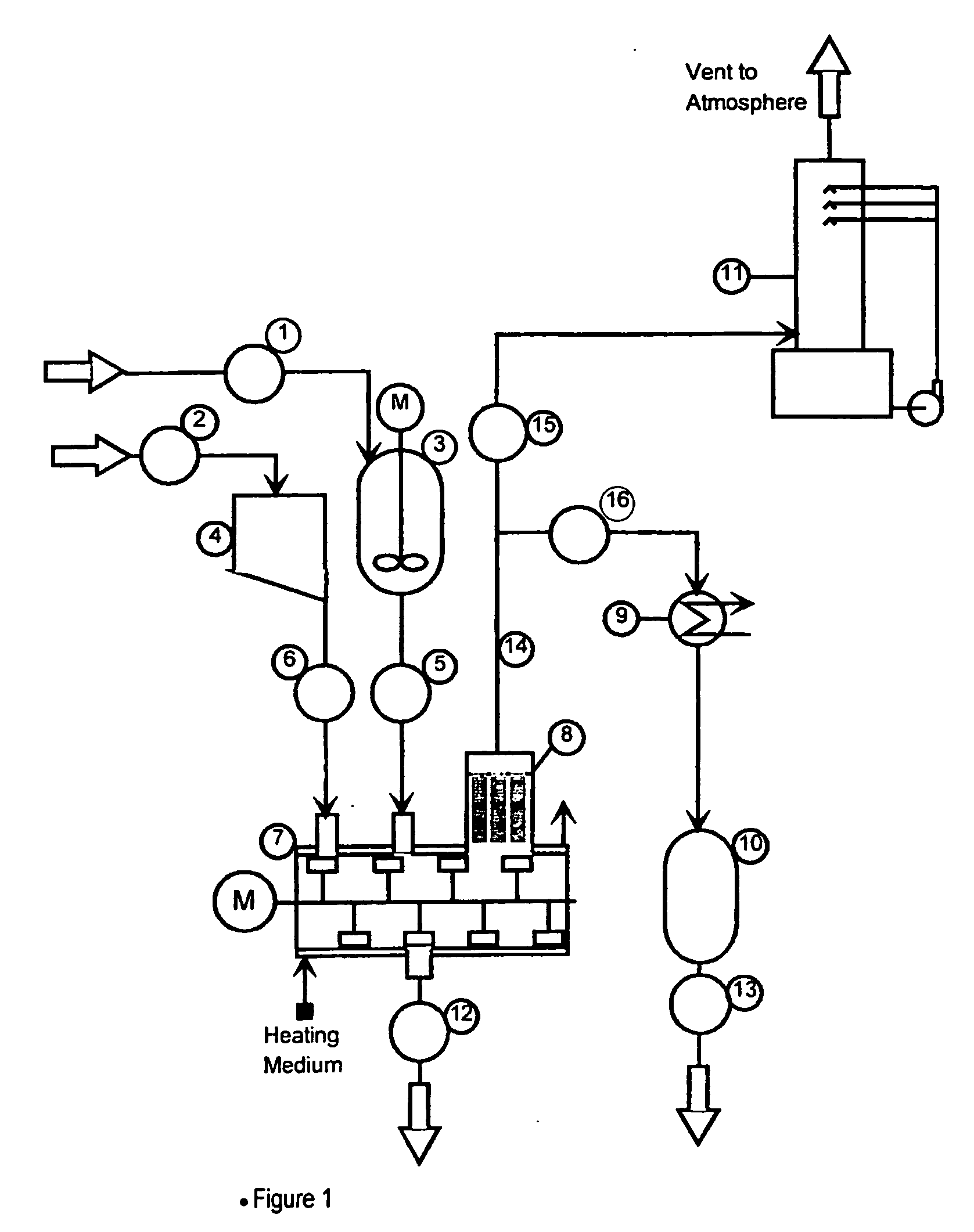
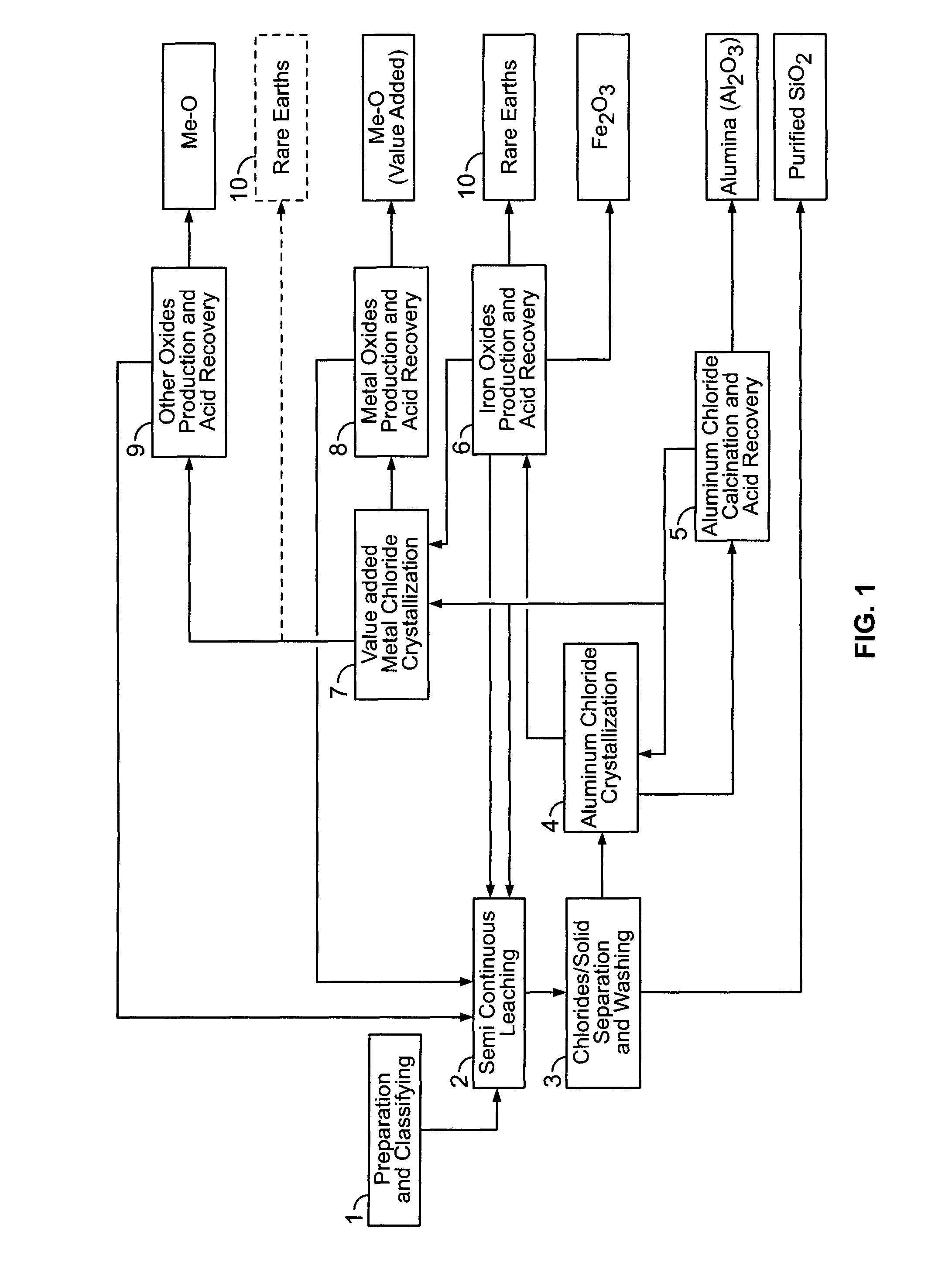
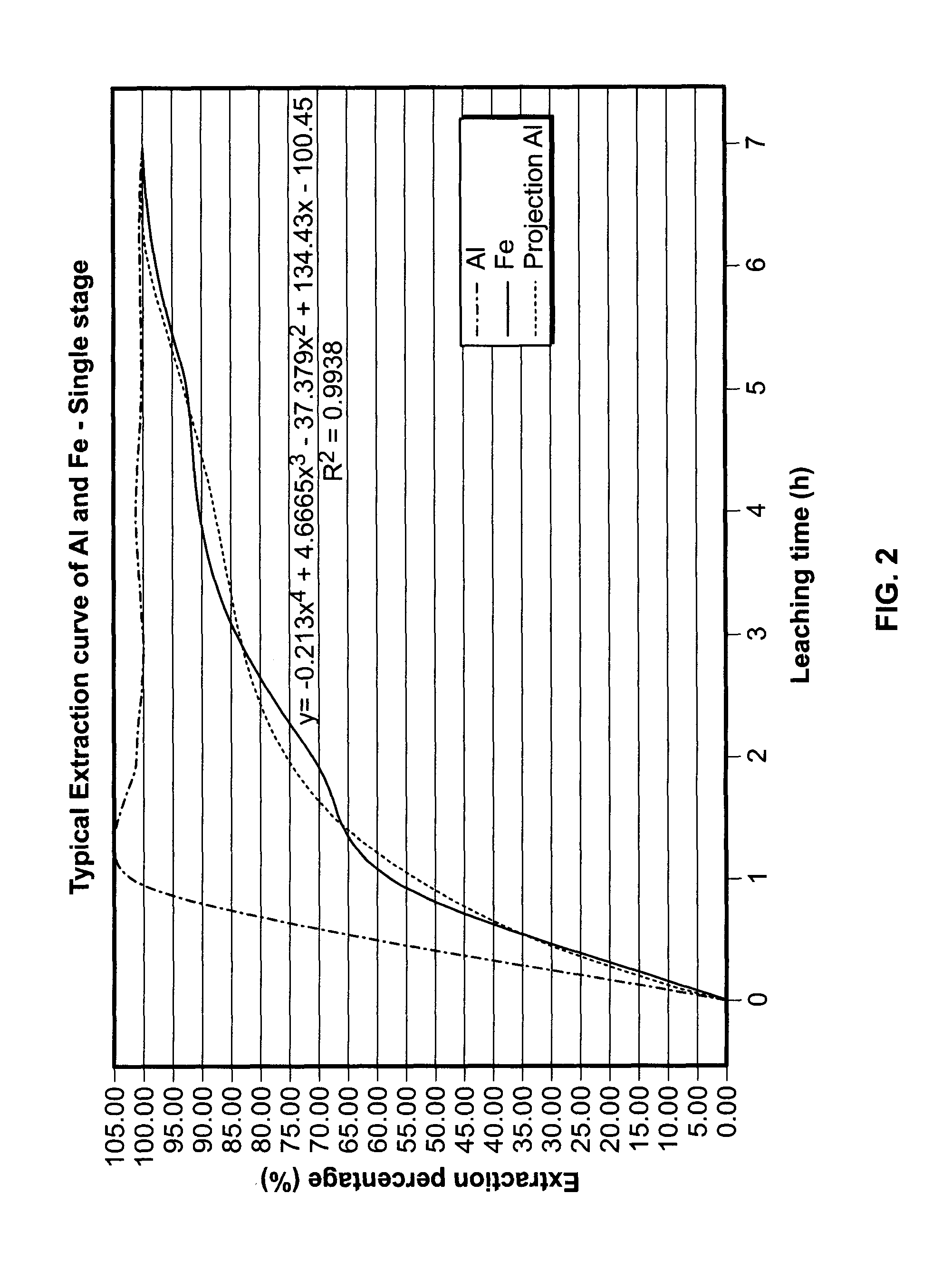
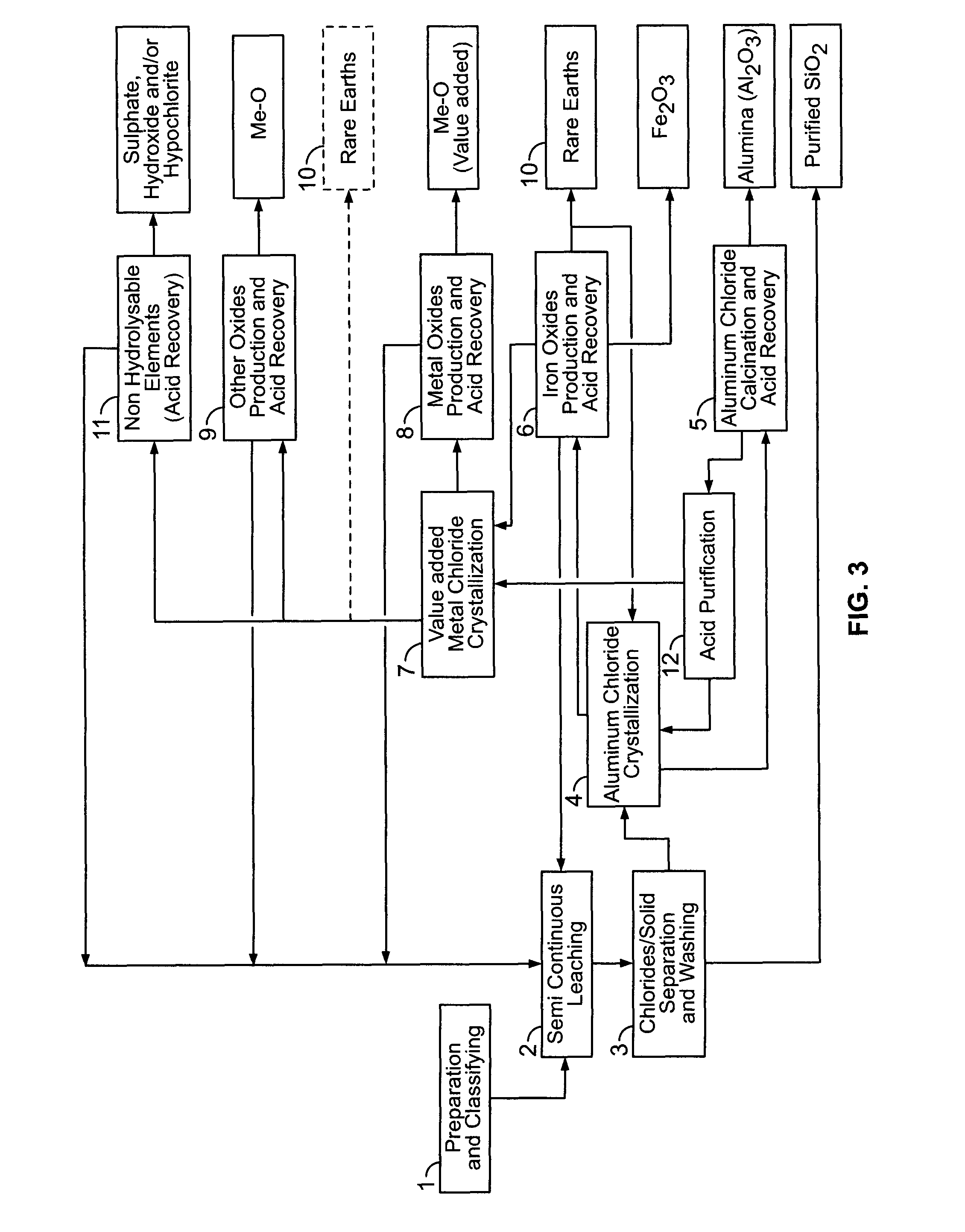
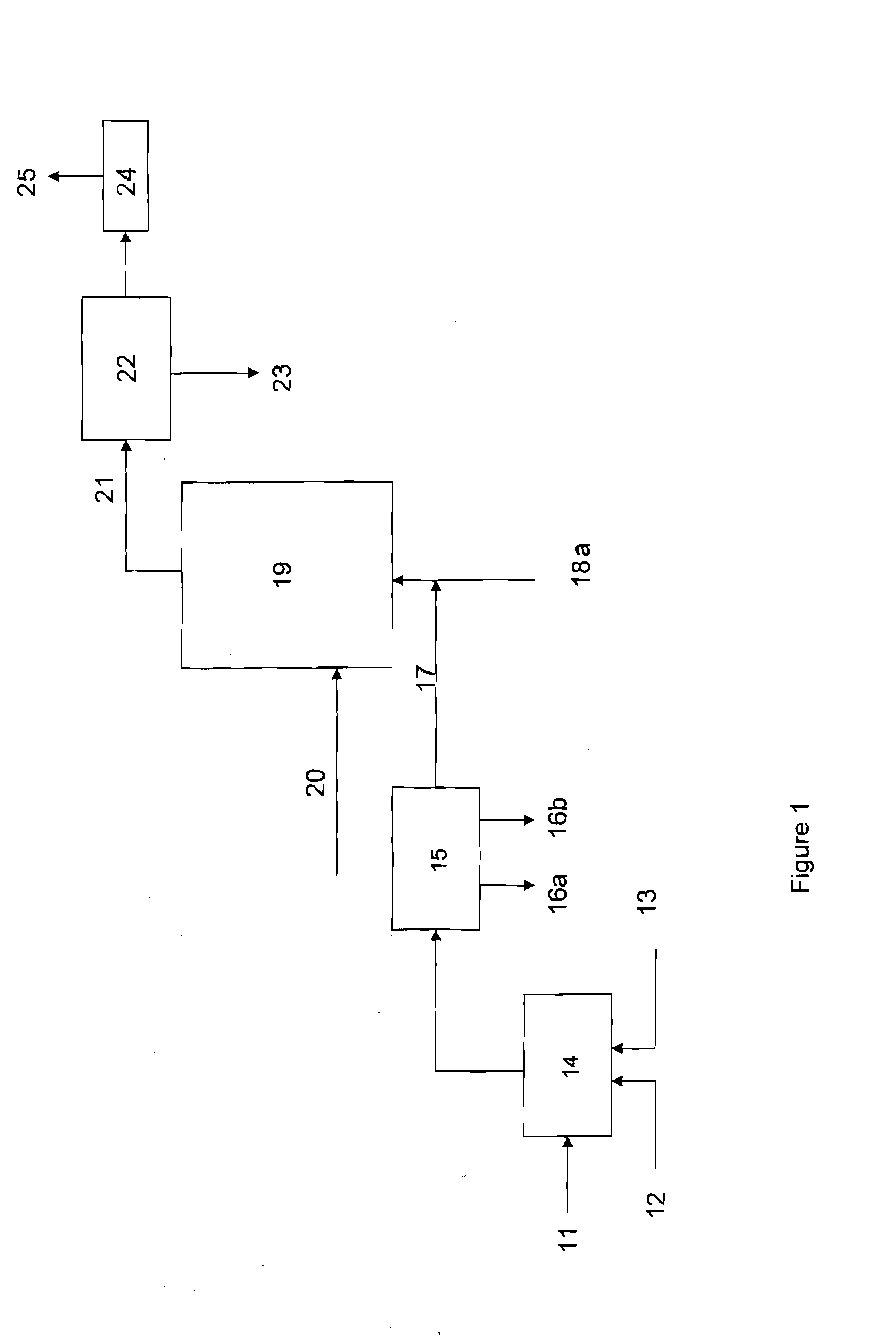
Process for the treatment of waste metal chlorides
InactiveUS20060183958A1Low costMaximize recoveryTitanium tetrachlorideSilicon oxidesMetal chlorideOrganic chloride compound
A process is described for treating the residues from metal chlorination processes wherein valuable volatile metal chlorides or metalorgano chlorides are recovered while low volatility metal chlorides and chloride complexes are reacted with a neutralizing humectant. The resulting neutral, dry solid is suitable for land fill disposal or for recovery of valuable metal constituents by extractive metallurgy techniques.
Owner:REC SILICON
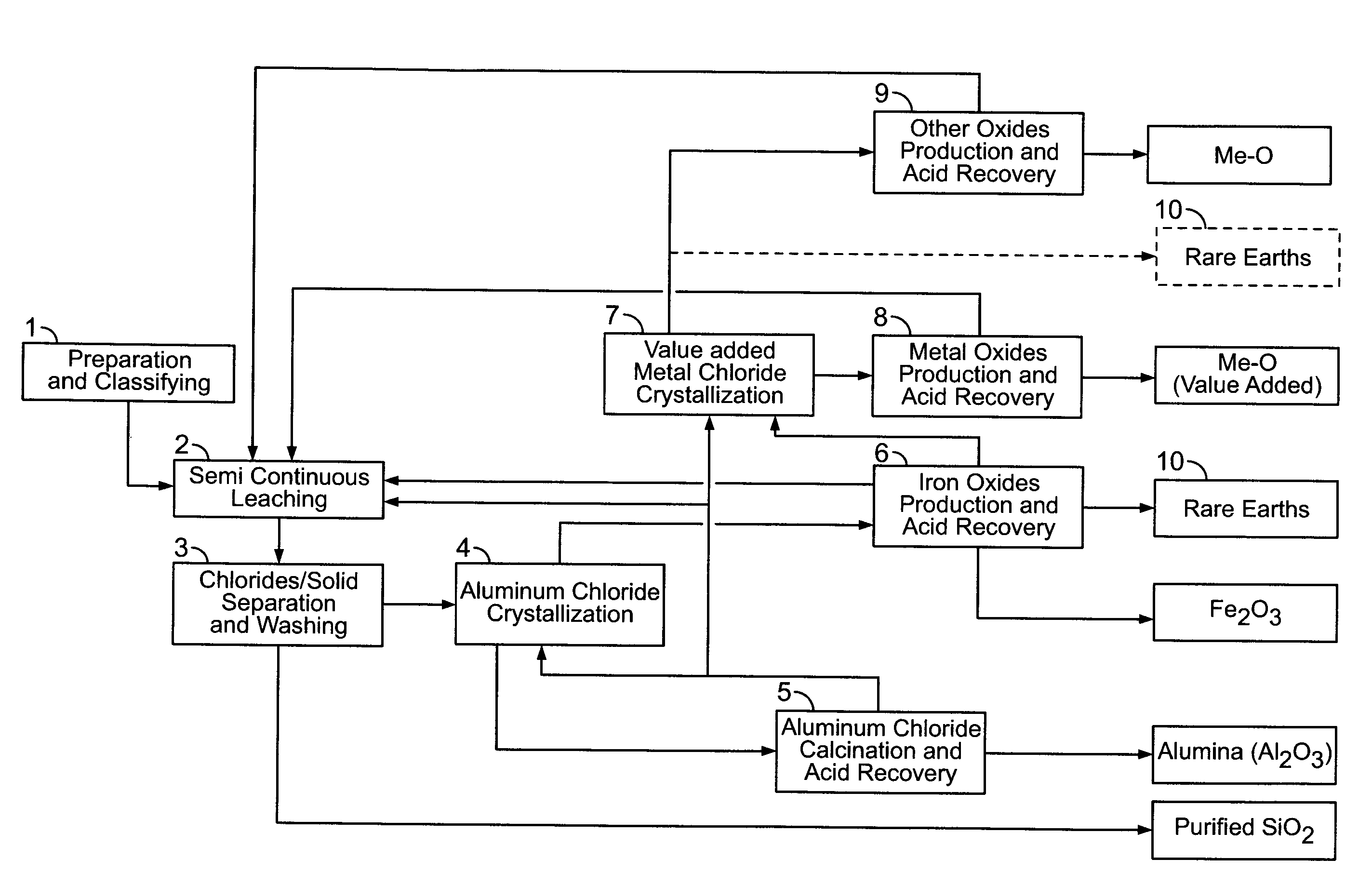
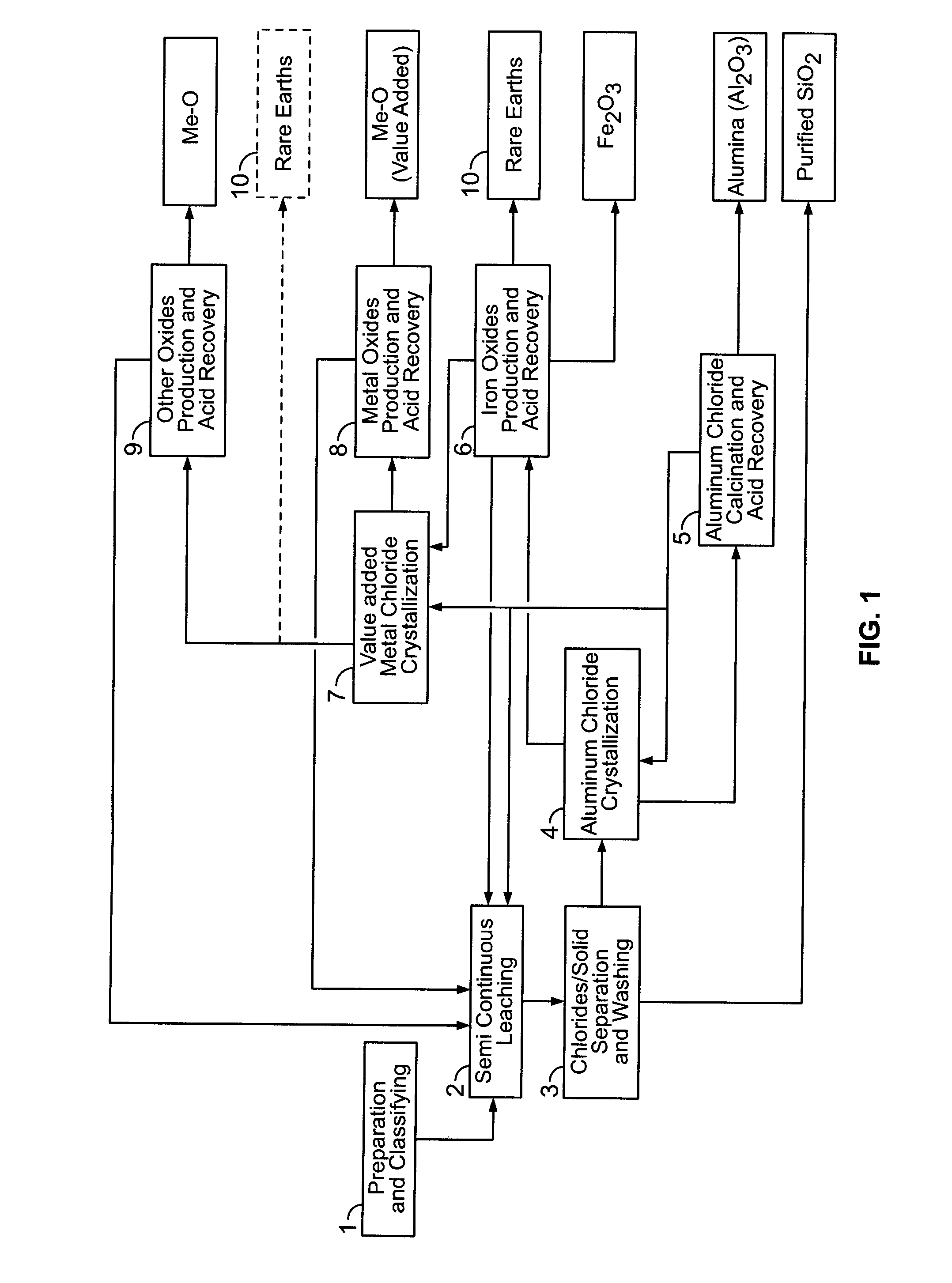
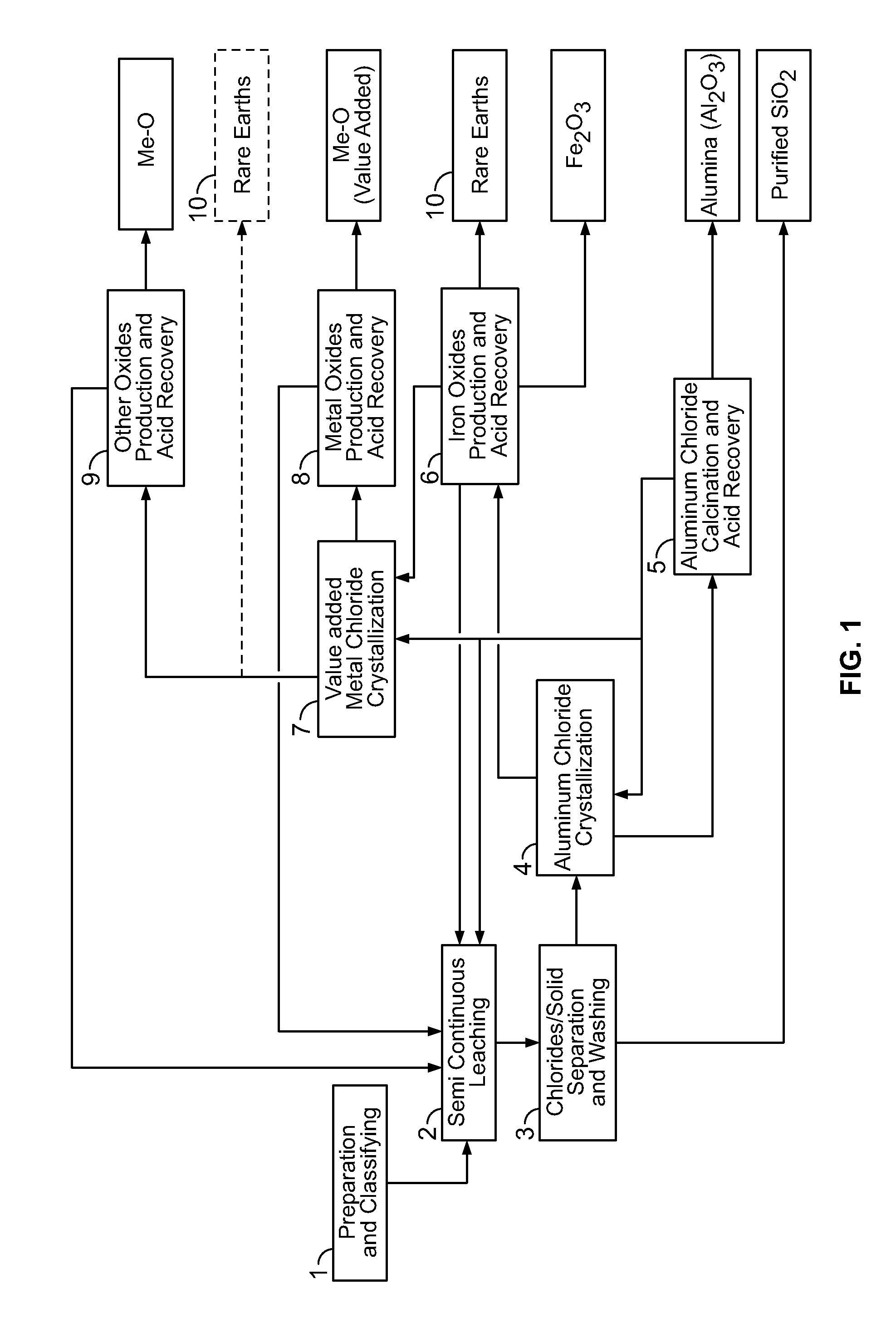
Processes for treating red mud
ActiveUS20140369907A1Simple and efficientLow costAluminium compoundsSolvent extractionPregnant leach solutionRare-earth element
There are provided processes for treating red mud. For example, the processes can comprise leaching red mud with HCl so as to obtain a leachate comprising ions of a first metal (for example aluminum) and a solid, and separating said solid from said leachate. Several other metals can be extracted from the leachate (Fe, Ni, Co, Mg, rare earth elements, rare metals, etc.). Various other components can be extracted from solid such as TiO2, SiO2 etc.
Owner:ORBITE ALUMINAE INC
Metal chlorides and metals obtained from metal oxide containing materials
Method and apparatus for preparing at least one metal chloride from metal oxide containing material comprising calcining the metal oxide containing material under temperature conditions sufficient to obtain a calcined product comprising at least one metal oxide; and selectively chlorinating the calcined product to form at least one metal chloride.
Owner:KEYSTONE METALS RECOVERY
Apparatus for production of metal chloride
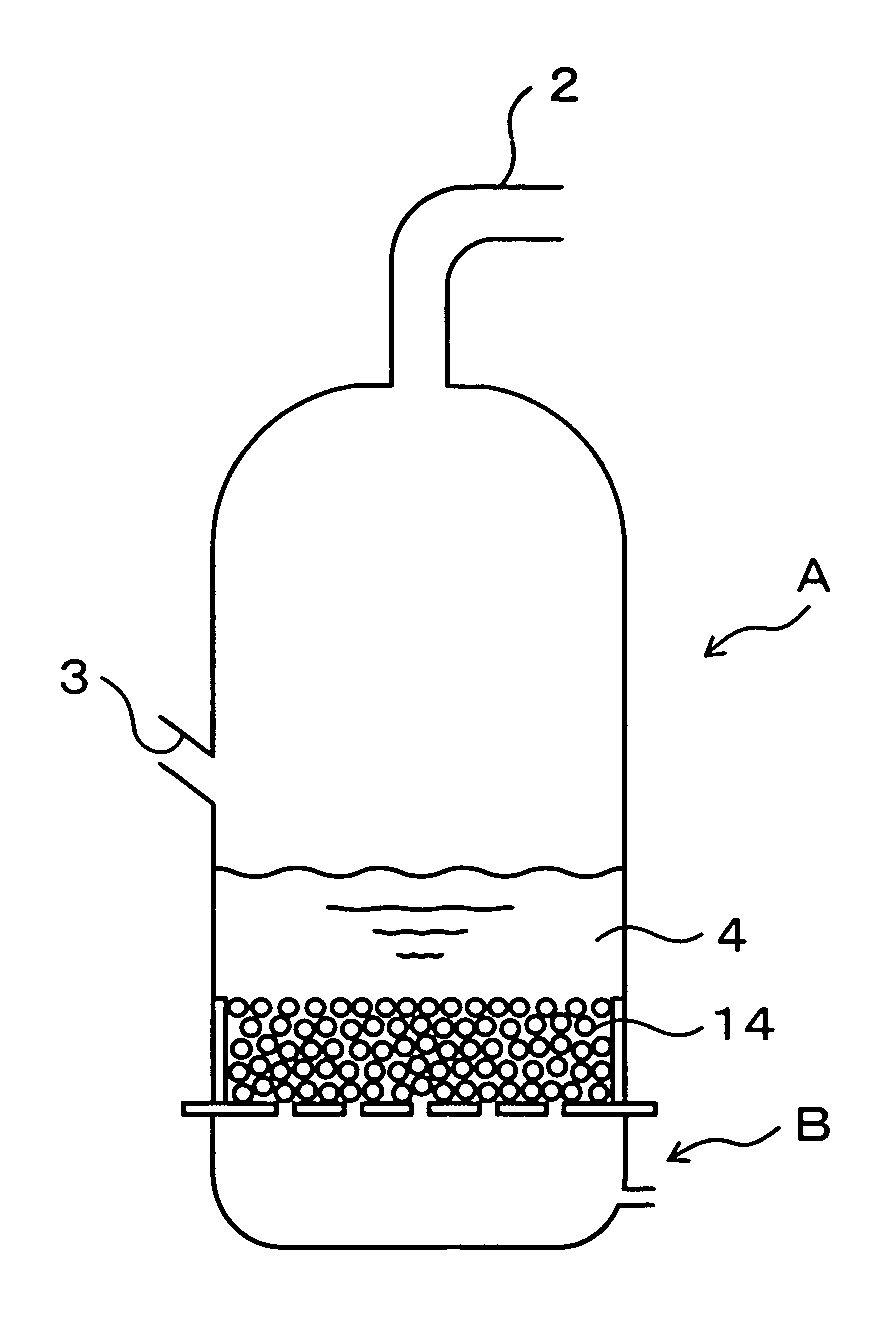
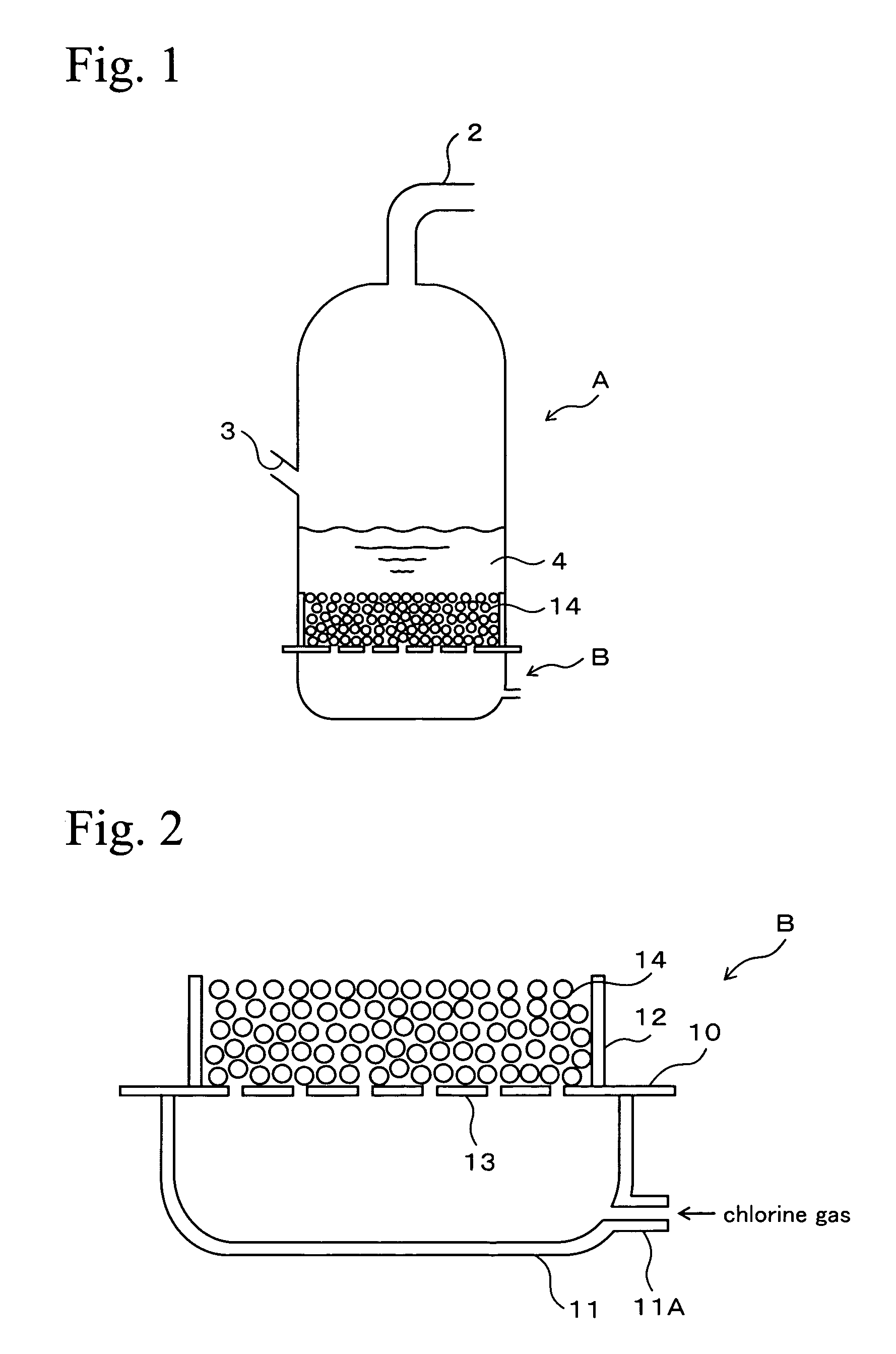
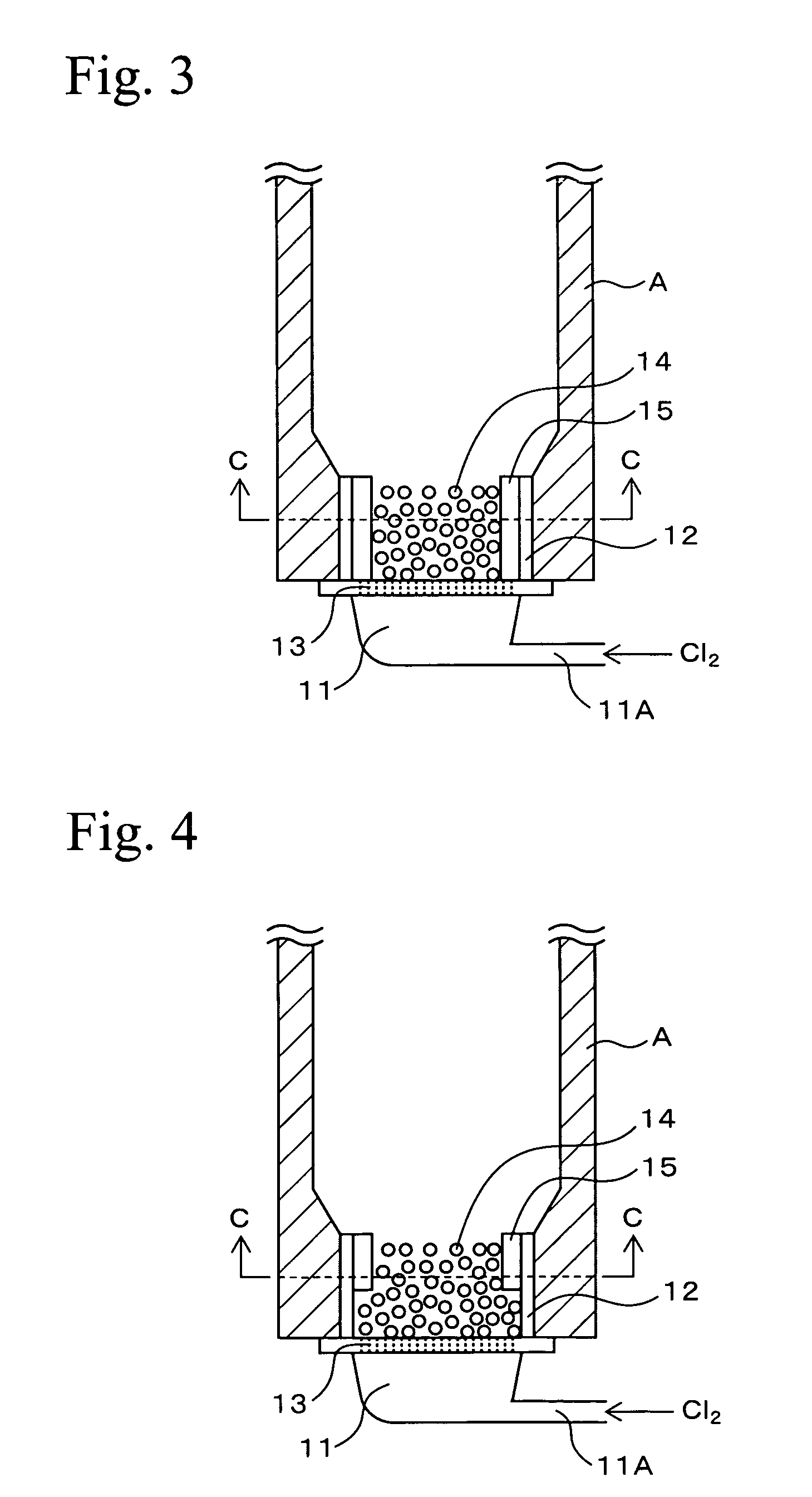
InactiveUS20070178028A1Increased durabilityEfficient productionPhysical/chemical process catalystsChloride preparationMetal chlorideFluidized bed
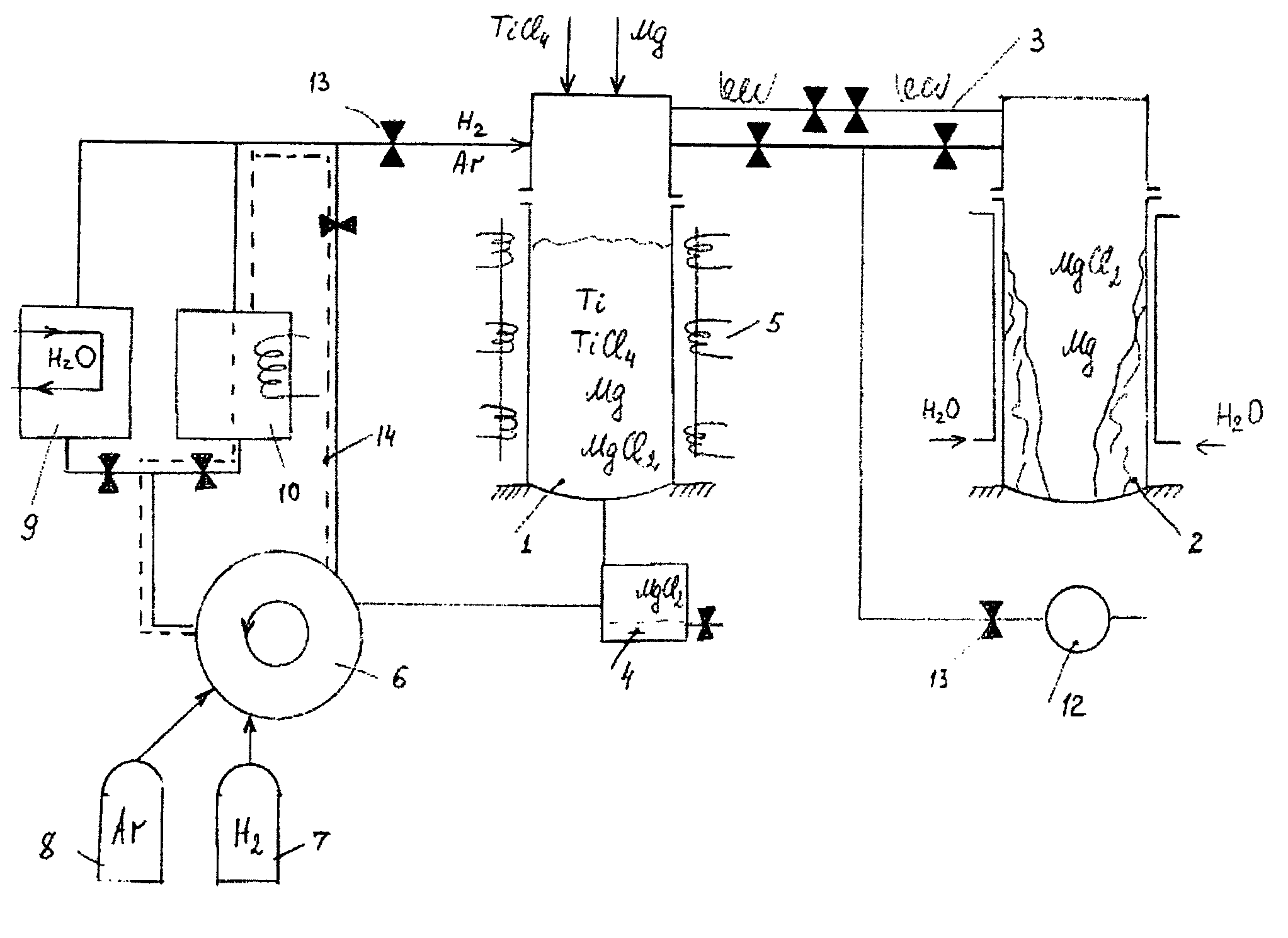
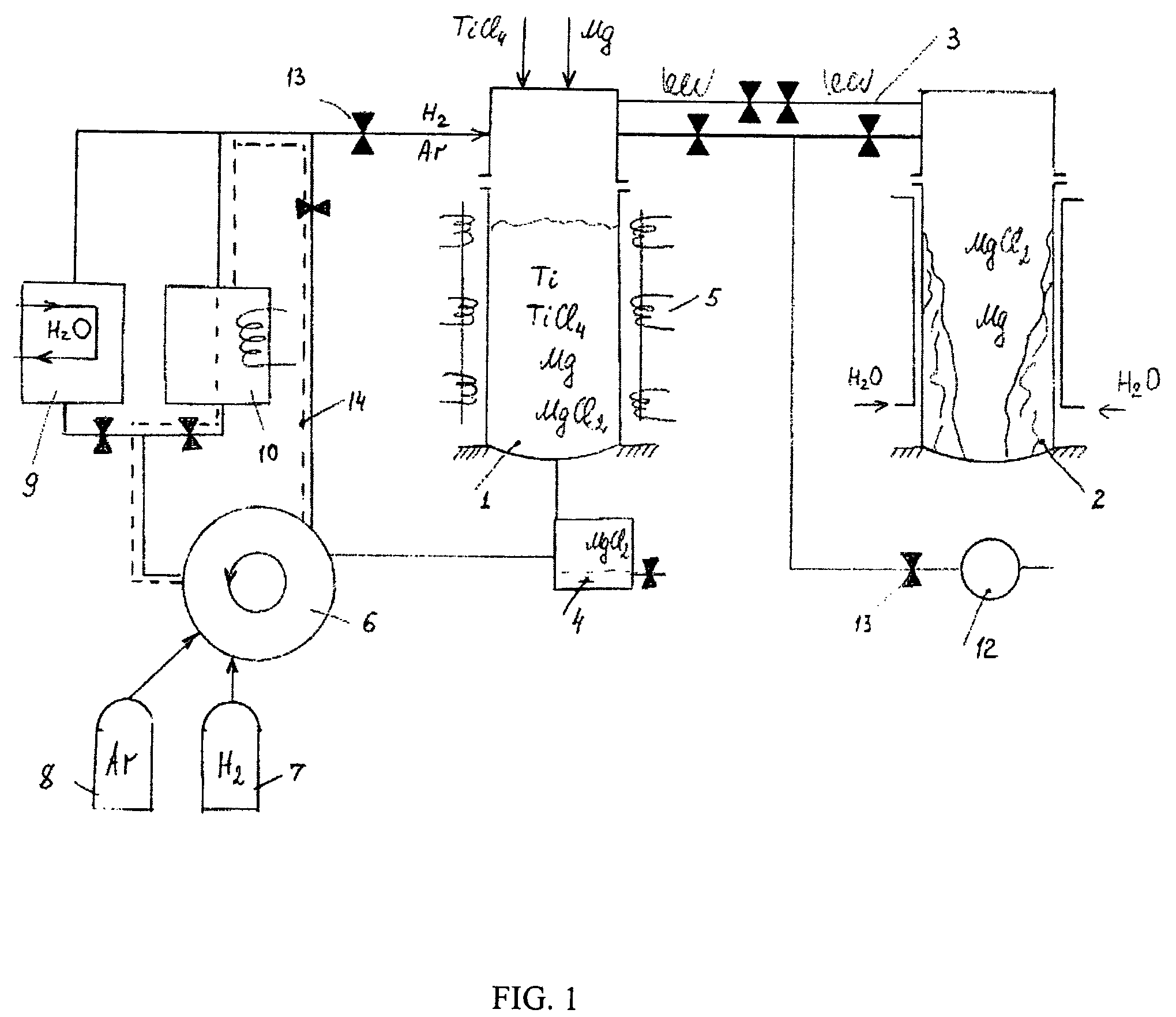
Porous plate 13 is disposed between wind box 11 of dispersion board B and cylindrical vessel wall 12. Filling layer 14 of a structure packed with ceramic particles such as those of fused silica is disposed on the porous plate 13 so as to fill the inside of the cylindrical vessel wall. The filling layer 14 is composed of ceramic particles, so that the corrosion wear by chlorine gas can be inhibited and the durability thereof enhanced. Furthermore, a chlorine resistant member is disposed in a form so as to adhere to the internal surface of the cylindrical vessel wall 12, so that the corrosion wear by chlorine gas of the cylindrical vessel wall 12 can also be effectively inhibited. As a result, damage to the internal wall of the chlorination furnace can be minimized, and the state of allowing chlorine gas to be uniformly dispersed and supplied to fluidized bed 4 containing titanium ore and coke can be maintained for prolonged periods.
Owner:TOHO TITANIUM CO LTD
Resourceful treatment method for fused salt chlorination residues
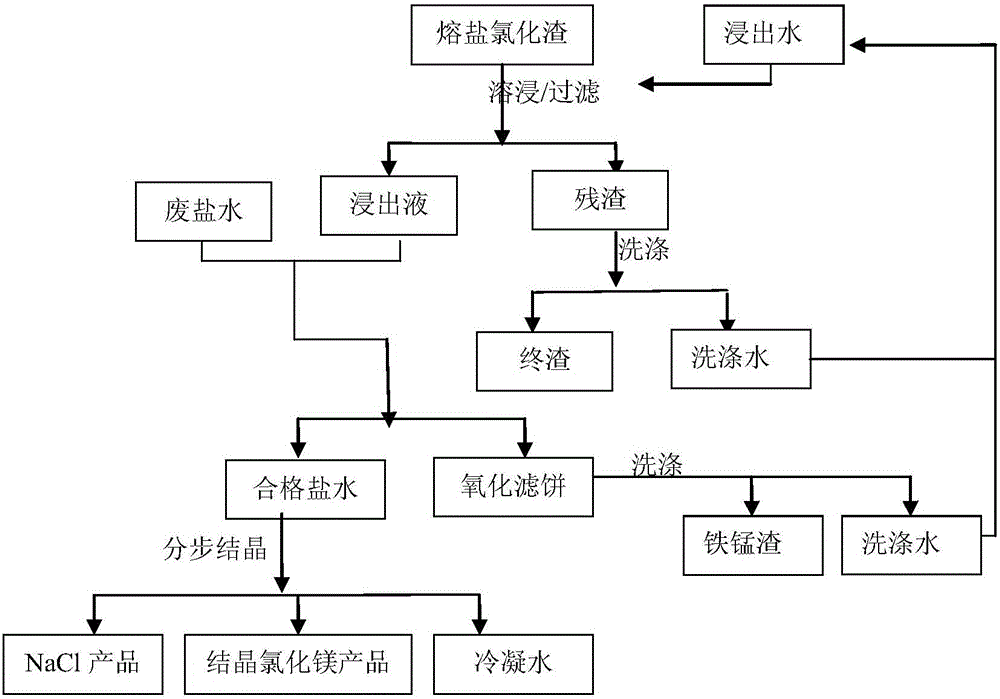
ActiveCN105883911ASimple processReduce processing costsSolid waste disposalTitanium tetrachlorideChemical industryElectrolysis
The invention discloses a resourceful treatment method for fused salt chlorination residues. According to the method, high-oxidizability alkaline waste salt water generated through fused salt chlorination tail gas purification or chloro-alkali chemical industry tail gas absorption waste liquor is used for treating leachate of the fused salt chlorination residues so as to recover NaCl, magnesium chloride hexahydrate and ferro-manganese residues, and low-cost resourceful treatment for the fused salt chlorination residues is achieved. Waste is treated with waste, the pollution problem of the fused salt chlorination residues is solved, NaCl, MgCl2 and ferro-manganese raw materials in the fused salt residues are recovered and used, and the resourceful treatment method has good economic benefits, has great significance in eliminating development bottleneck of technology application of preparing TiCl4 through titanium residue fused salt chlorination, can be widely applied to domestic and overseas fused salt chlorination-magnesium thermal electrolysis titanium sponge and fused salt chlorination titanium sponge enterprises and has wide popularization prospects.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
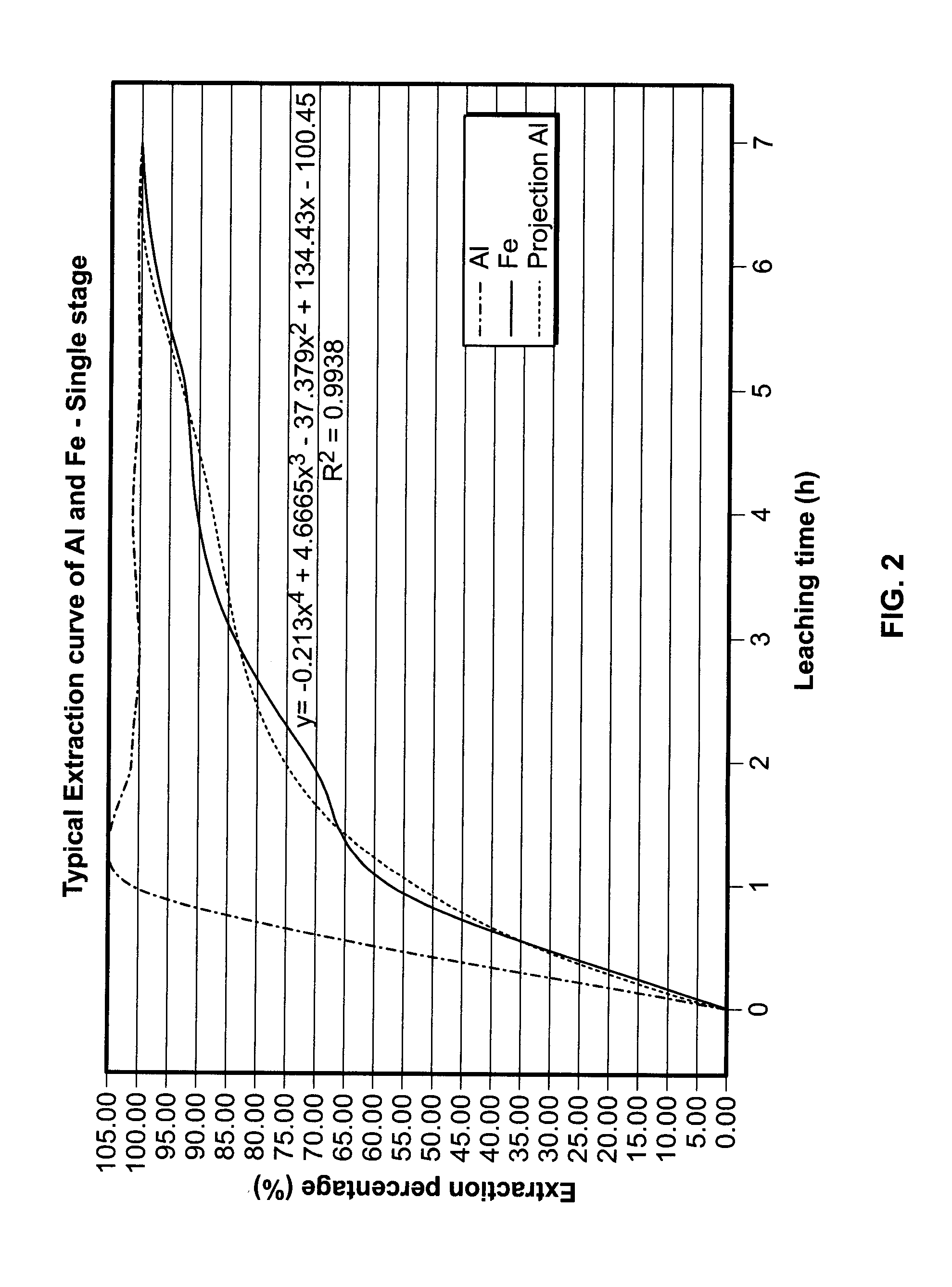
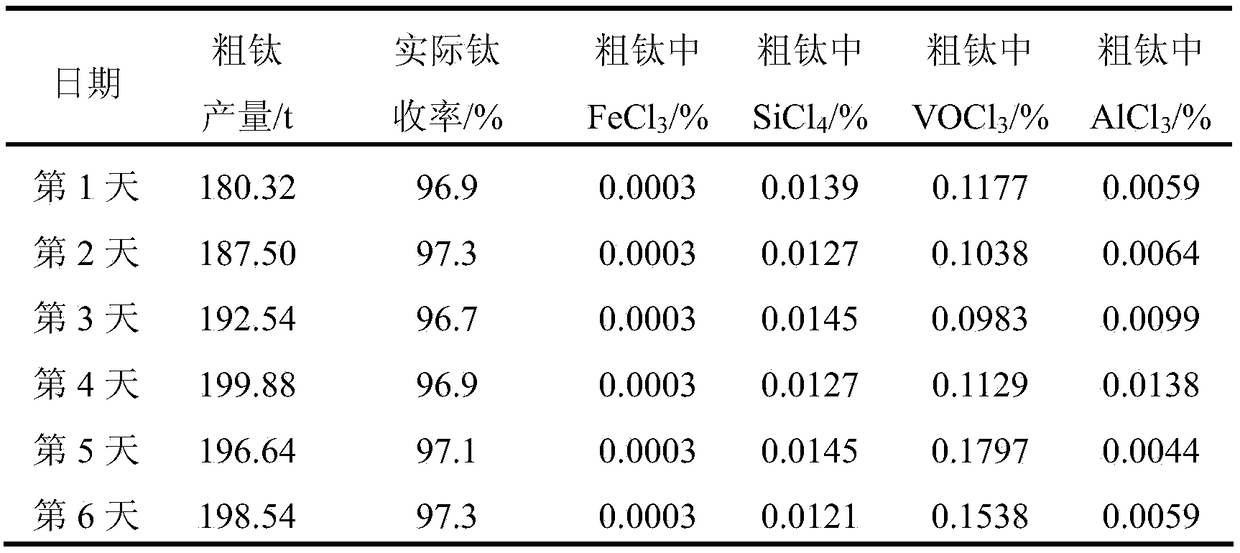
Method for carrying out vanadium removal on coarse titanium tetrachloride
InactiveCN106241860ASlight sticking phenomenonAccelerated settlementTitanium tetrachlorideTitanium tetrachlorideMaterials science
The invention relates to the field of refining of titanium tetrachloride, and discloses a method for carrying out vanadium removal on coarse titanium tetrachloride. The method comprises: (1) carrying out first contact on coarse titanium tetrachloride with vanadium content of 0.3 weight percent or over 0.3 weight percent and an organic vanadium removal reagent, and carrying out solid-liquid separation on a product obtained by the first contact, wherein the first contact enables vanadium content in a liquid phase obtained by the solid-liquid separation to be reduced to 0.2 weight percent or below 0.2 weight percent; (2) carrying out aluminium powder vanadium removal on the liquid phase obtained by the solid-liquid separation. When the method disclosed by the invention is adopted to process the coarse titanium tetrachloride with high vanadium content, the existing aluminium powder vanadium removal integral device is sufficiently utilized, a small quantity of residues is generated, a vanadium removal effect is good, and generated solid has good settleability.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
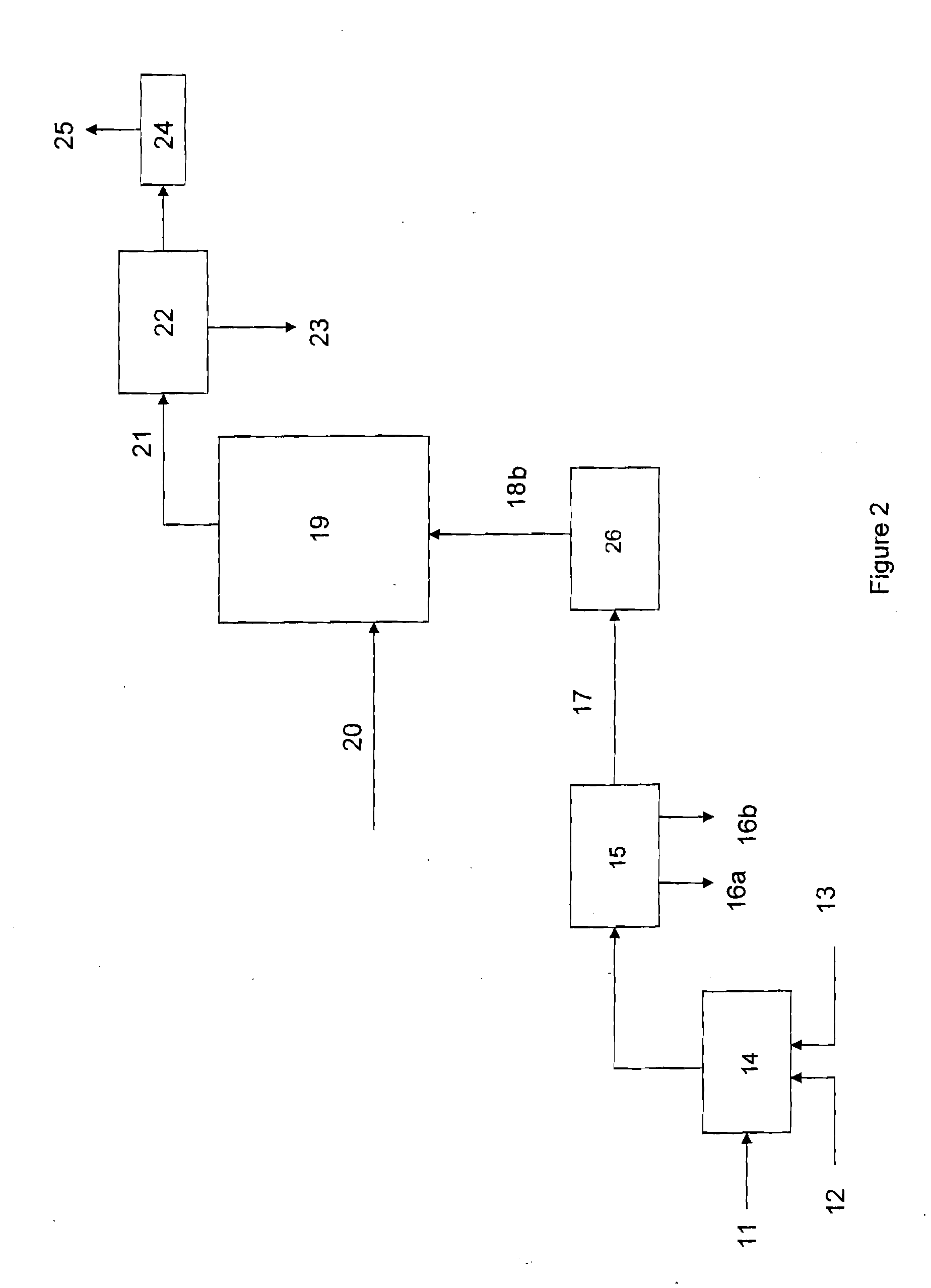
Method and apparatus for the production of metal compounds
ActiveUS20060191372A1Improve responseTitanium trichlorideTitanium tetrachlorideAluminium chlorideReaction zone
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for the production of titanium alloys and titanium-aluminium inter-metallic compounds and alloys. Starting from a precursor material including titanium subchloride (titanium trichloride or titanium dichloride), the precursor material is reduced by aluminium to produce titanium-aluminium intermetallic complexes or alloys and aluminium chloride which is driven away from the reaction zone so as to favour the forward reaction and the production of the titanium-aluminium compounds. Starting from a precursor material of titanium subchloride avoids the problems associated with starting from titanium metal (which is expensive to produce) or titanium tetrachloride (a reaction very difficult to control), and results in the production of powdered forms of titanium-aluminium compounds with controllable composition.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
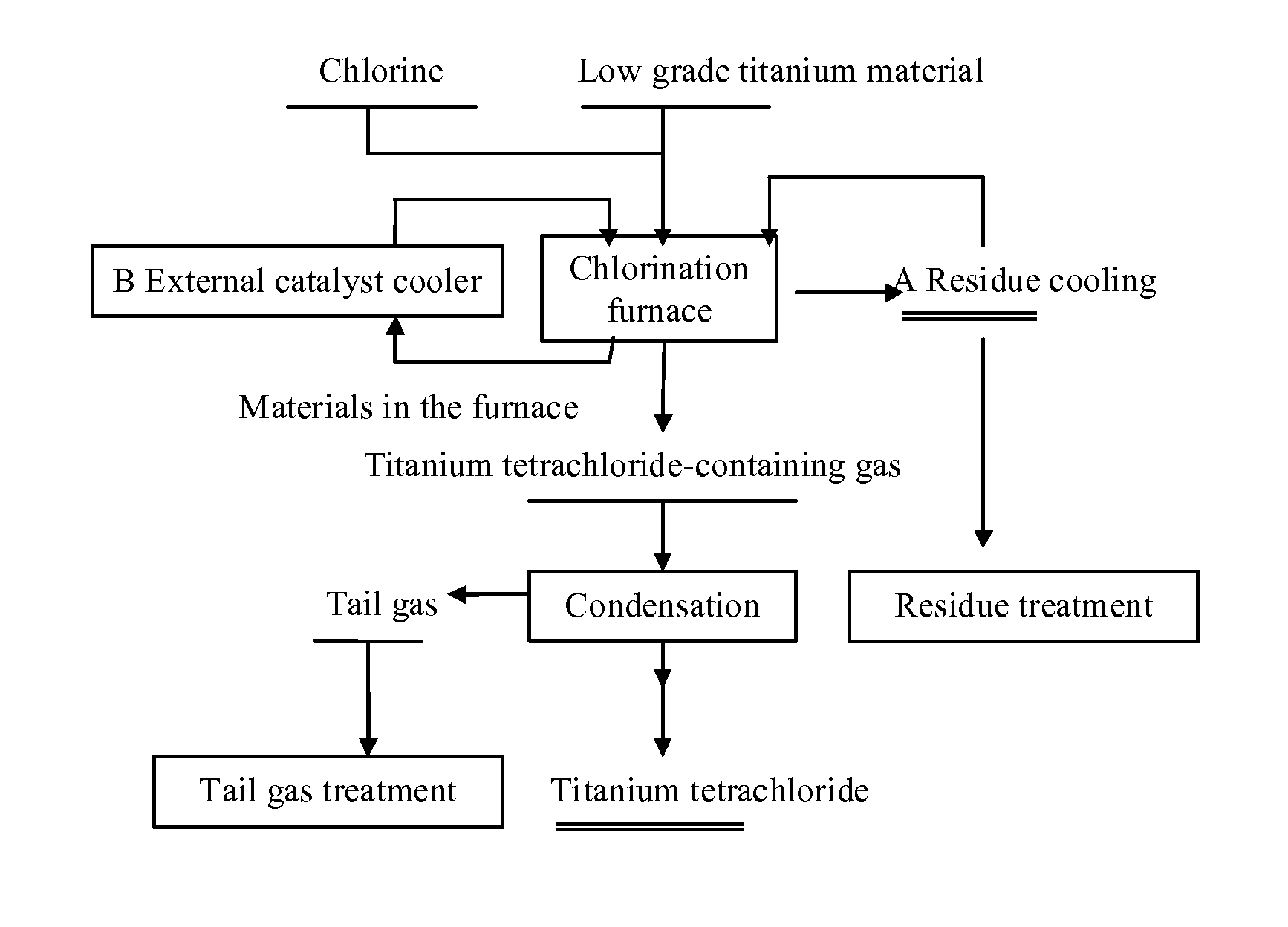
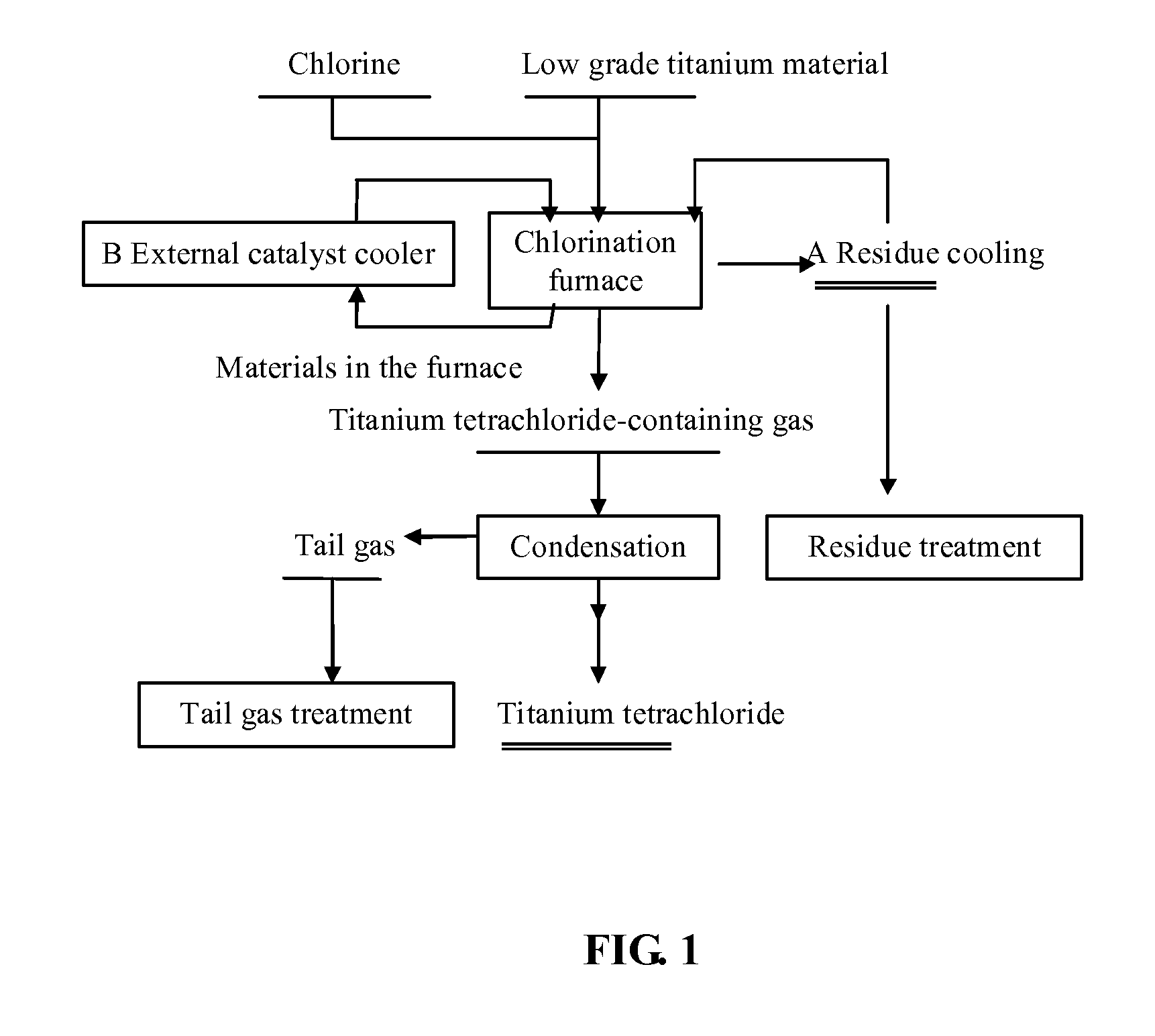
Method for producing titanium tetrachloride using low grade titan raw material
ActiveCN101337689AGuarantee continuous and stable operationRealize industrializationTitanium tetrachlorideLower gradeLow graded
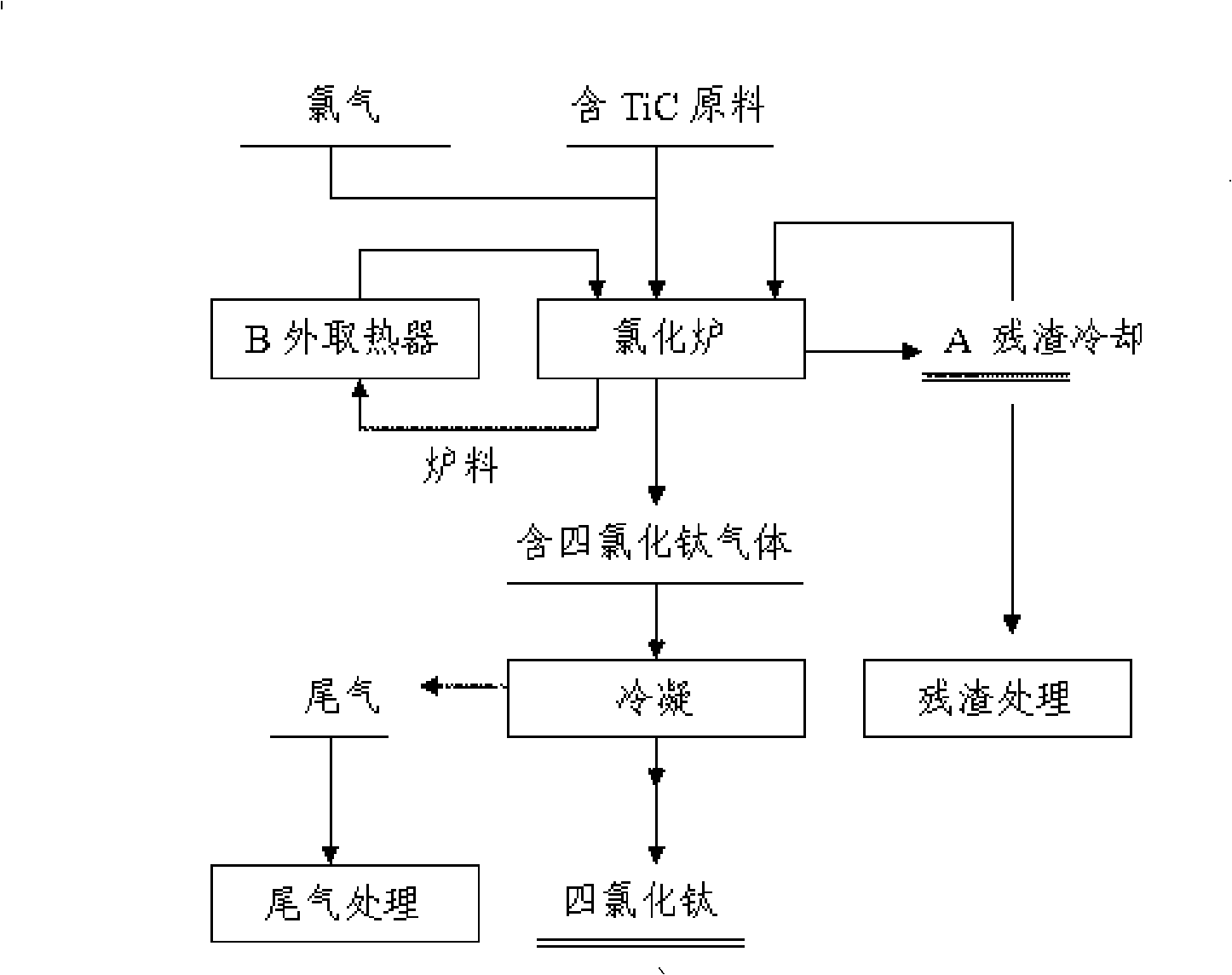
The invention discloses a method for producing titanium tetrachloride by using a low grade titanium material, and belongs to the chemical technical field. The technical problem to be solved is to provide a method for producing titanium tetrachloride by using the low grade titanium material in continuous industrialized production. The method is characterized in that the low grade titanium material containing a certain proportion of titanium carbide is adopted to directly react with chlorine at the temperature of 600 DEG C to 700 DEG C to produce titanium tetrachloride. Long period continuous stable operation can be kept by using the technological parameters of the invention, and chlorination rate of titanium carbide in titanium material reaches above 90 percent, so that the titanium can be better used for producing titanium tetrachloride.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON AND STEEL +2
Method for producing TiCl4 by using low-TiO2-grade titanium slag
InactiveCN104591270AReduce manufacturing costImprove the level of comprehensive utilizationTitanium tetrachlorideBoiling pointMolten salt
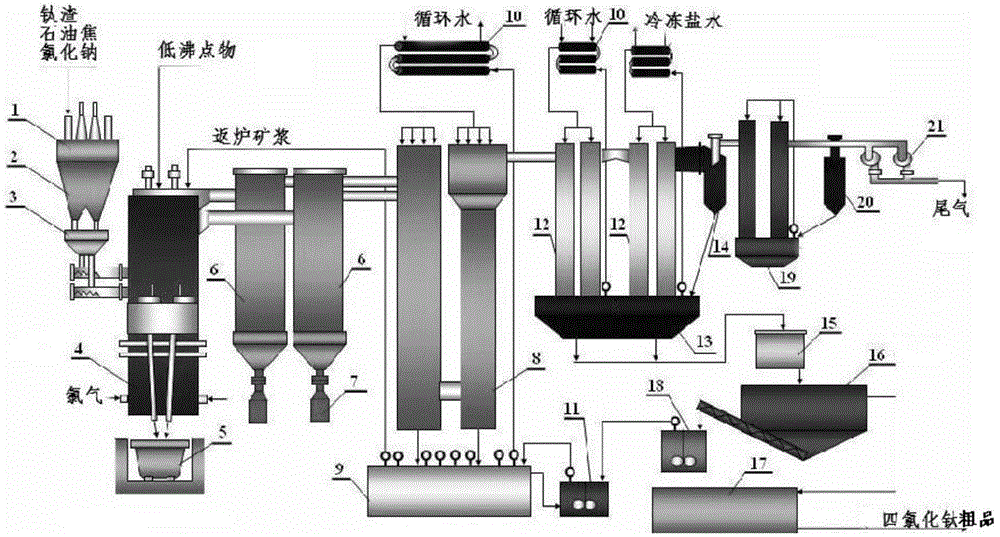
The invention belongs to the field of chemical production, and particularly relates to a method for producing TiCl4 by using low-TiO2-grade titanium slag, solving the technical problems long production of time and high cost. The method for producing TiCl4 by using low-TiO2-grade titanium slag provided by the invention in order to solve the technical problems comprises the following steps: a. adding titanium slag, petroleum coke and sodium chloride to a molten salt chlorinating furnace to react with chlorine at a temperature of 700 to 750 DEG C; and b. conveying a gaseous mixture obtained by reaction from the chlorinating furnace to a dust collection and condensation equipment system, and condensing gaseous TiCl4 into a crude product after removing high-boiling-point impurities. By using the method provided by the invention reduction of the production cost of the TiCl4 crude product is facilitated, the comprehensive utilization level of titanium resources in Panzhihua is improved, and a new development direction for the development of titanium industry of Panzhihua is brought.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP TITANIUM INDAL
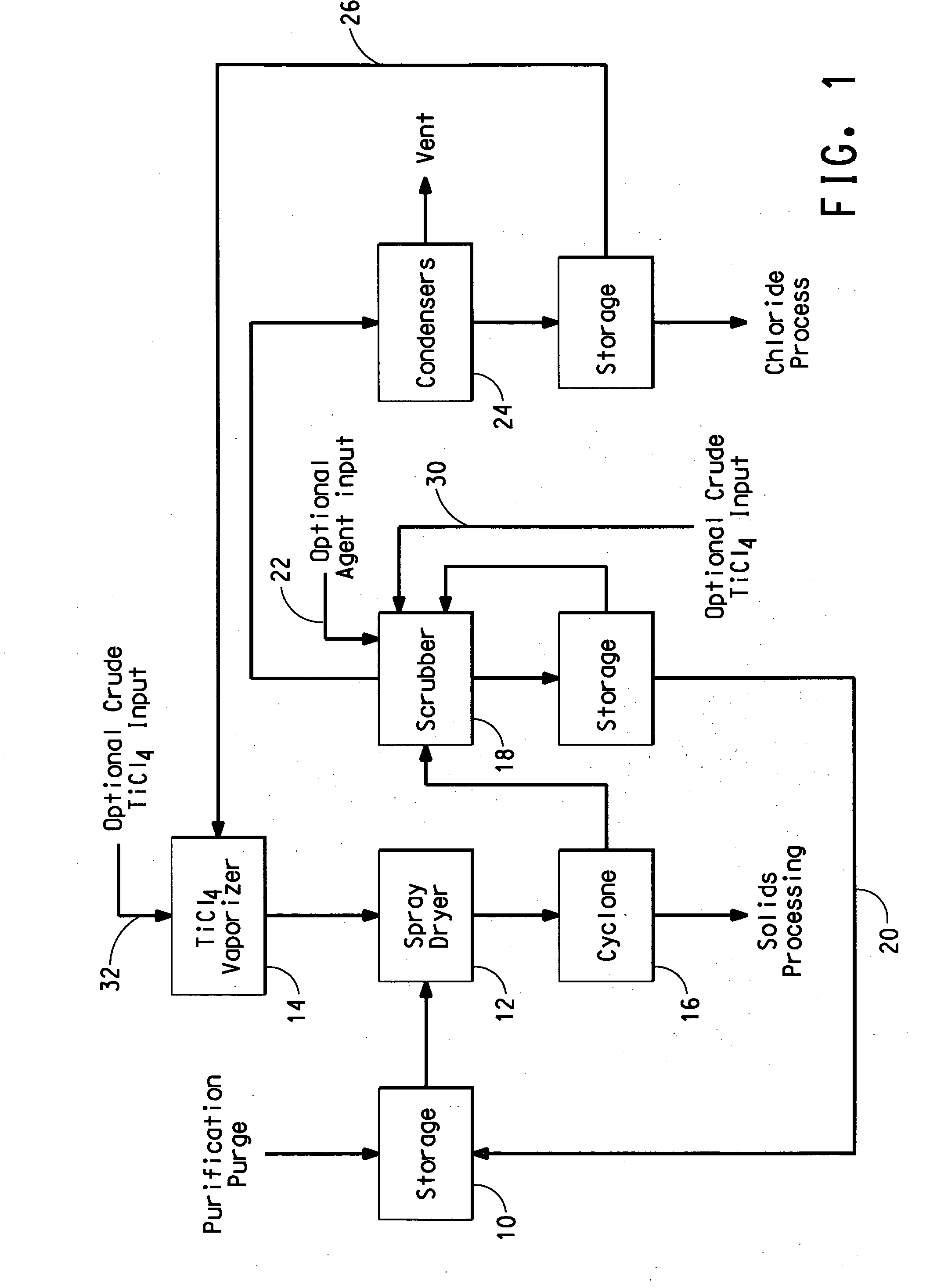
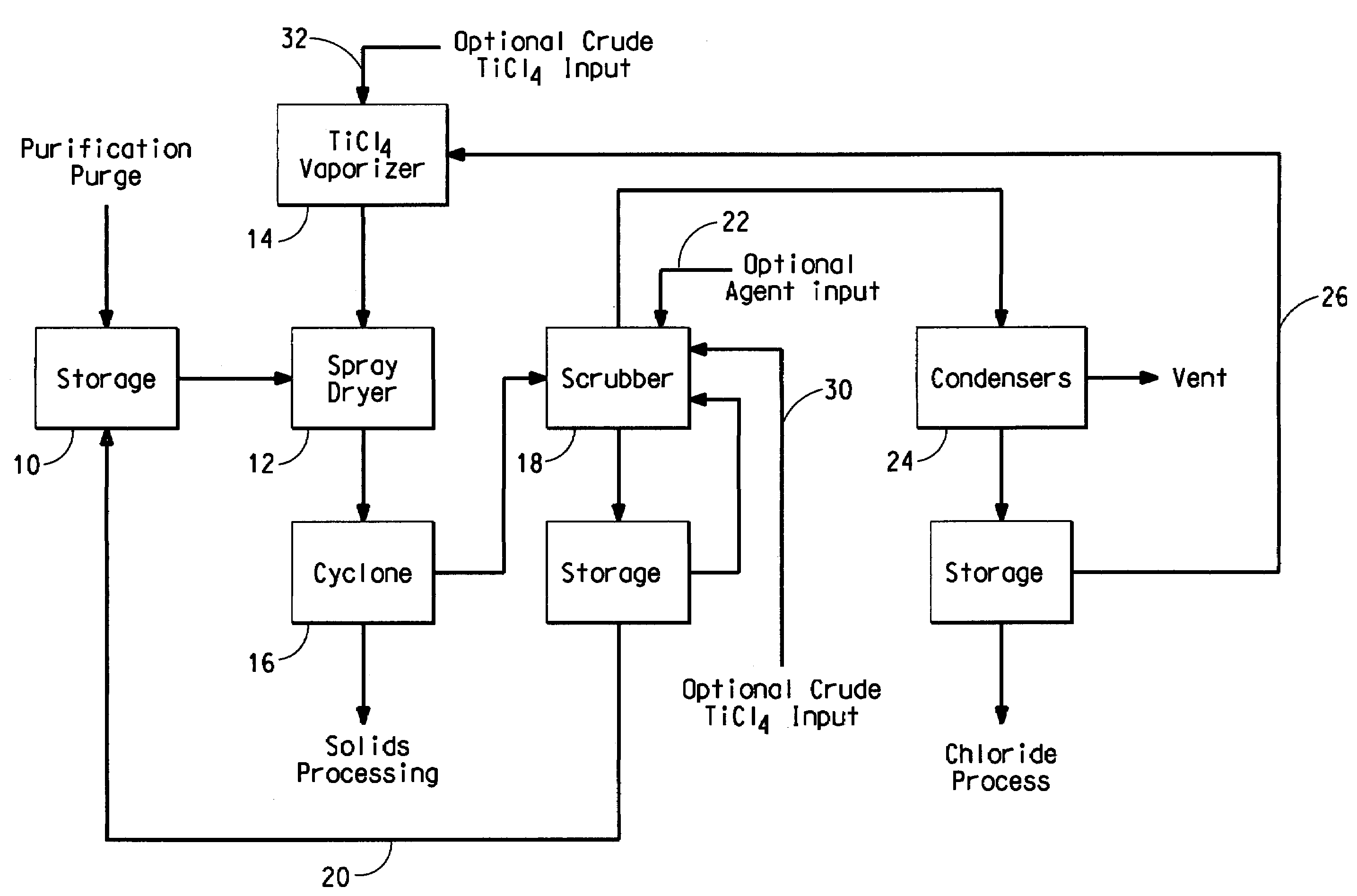
Process for separating solids from a purification purge stream
The disclosure is directed to a process for isolating solids from a purification purge stream comprising an impurity present as a solid, wherein the purification purge stream is substantially free of chlorides other than titanium tetrachloride and vanadium chloride, the process comprising the steps of: (a) atomizing the purification purge stream comprising titanium tetrachloride as a liquid and an impurity present as a solid; (b) drying solids in the atomized purification purge stream by contacting the atomized stream with a titanium tetrachloride vapor stream such that the combined streams reach a temperature of at least about 140° C. to vaporize the liquid titanium tetrachloride, wherein the titanium tetrachloride vapor is substantially free of chlorides other than those of titanium and vanadium, and substantially free of non-condensable gases comprising CO, CO2, N2, or mixtures thereof; and (c) separating the impurity present as a solid from the vaporized titanium tetrachloride. The separated vanadium solids may be further processed to recover valuable by products.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO TT LLC
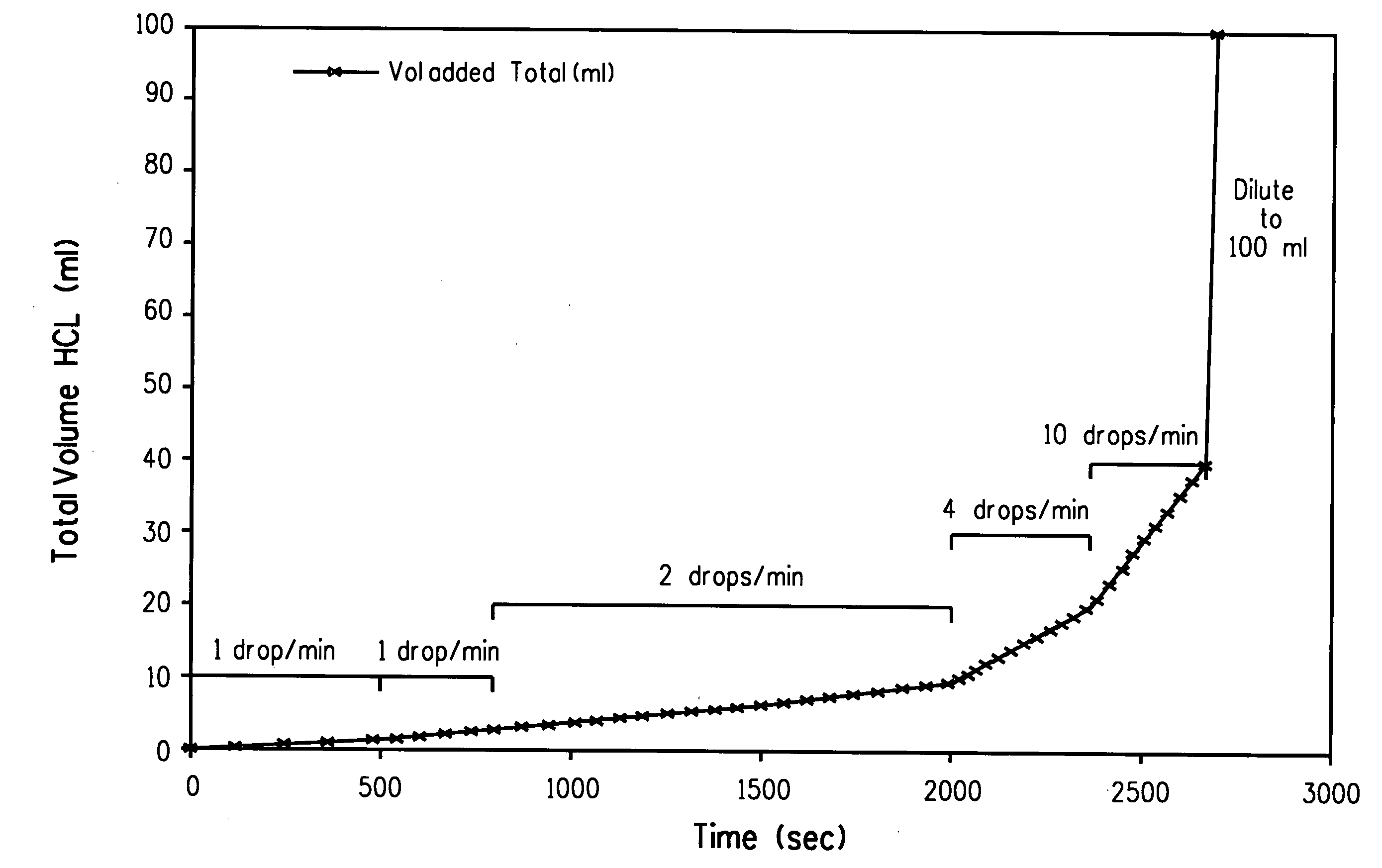
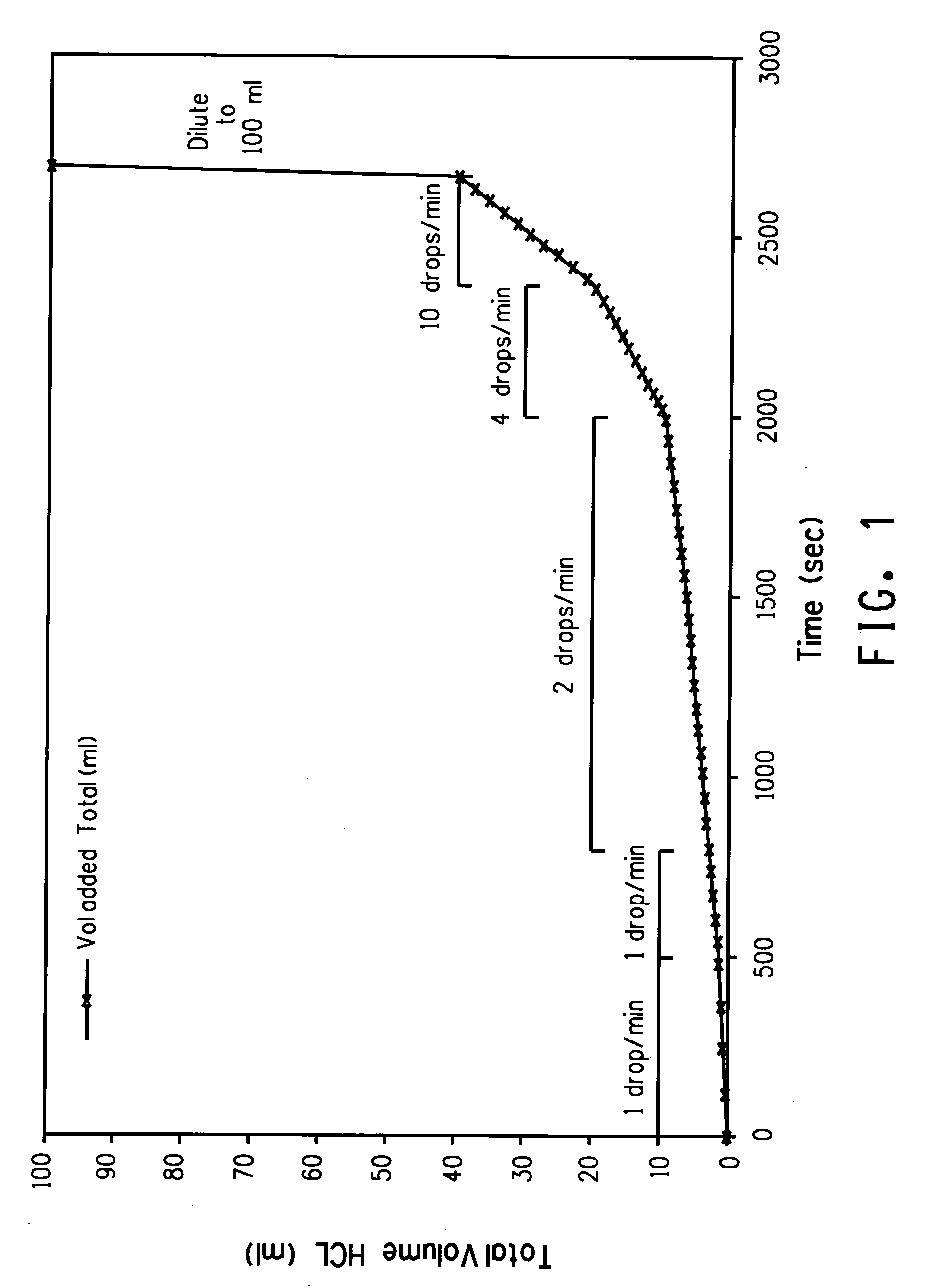
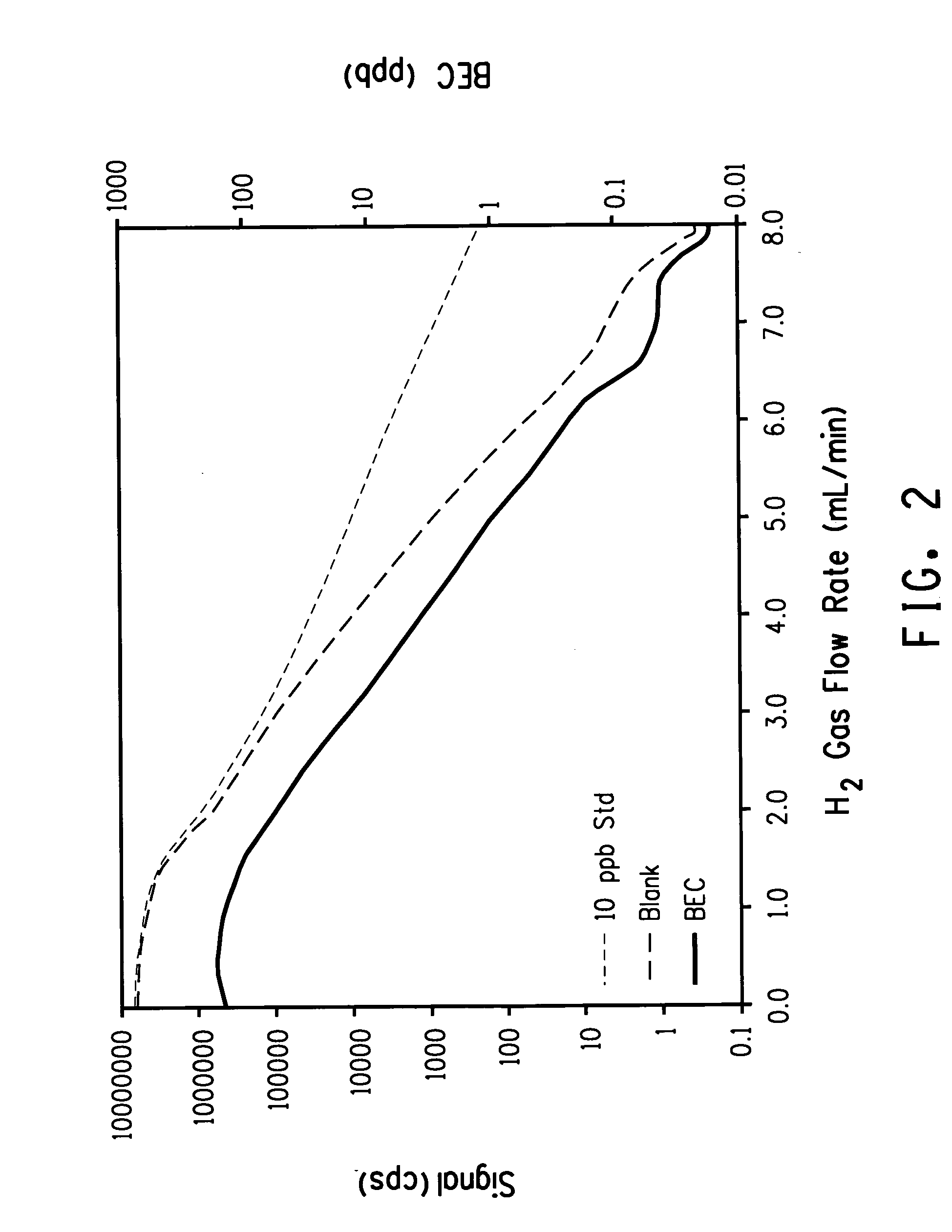
Method for quantification of analytes in a titanium, tin or silcon tetrachloride sample
InactiveUS20070292991A1High degreeImprove throughputSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTitanium tetrachlorideSpectroscopyInductively coupled plasma
This disclosure relates to a method for detecting at least one analyte in a tetrachloride sample comprising titanium, tin or silicon tetrachloride; comprising,(a) adding a mixture of water and acid, typically hydrochloric acid, to the sample under conditions effective for forming an aqueous solution of the sample;(b) introducing the aqueous solution of the sample into an inductively coupled mass spectrometer having a cell selected from the group of a reactive cell and a collision cell or both and producing an analyte ion comprising an interfering species;(c) contacting the analyte ion with a gas to produce a product which is substantially free from the interfering species; and(d) detecting and measuring at least one signal from the analyte in the solution. This disclosure further relates to a method for making an aqueous titanium, tin or silicon tetrachloride sample suitable for analysis in using inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Processes for treating red mud
ActiveUS9023301B2Simple and efficientLow costAluminium compoundsNickel compounds preparationRare-earth elementRed mud
There are provided processes for treating red mud. For example, the processes can comprise leaching red mud with HCl so as to obtain a leachate comprising ions of a first metal (for example aluminum) and a solid, and separating said solid from said leachate. Several other metals can be extracted from the leachate (Fe, Ni, Co, Mg, rare earth elements, rare metals, etc.). Various other components can be extracted from solid such as TiO2, SiO2 etc.
Owner:ORBITE ALUMINAE INC
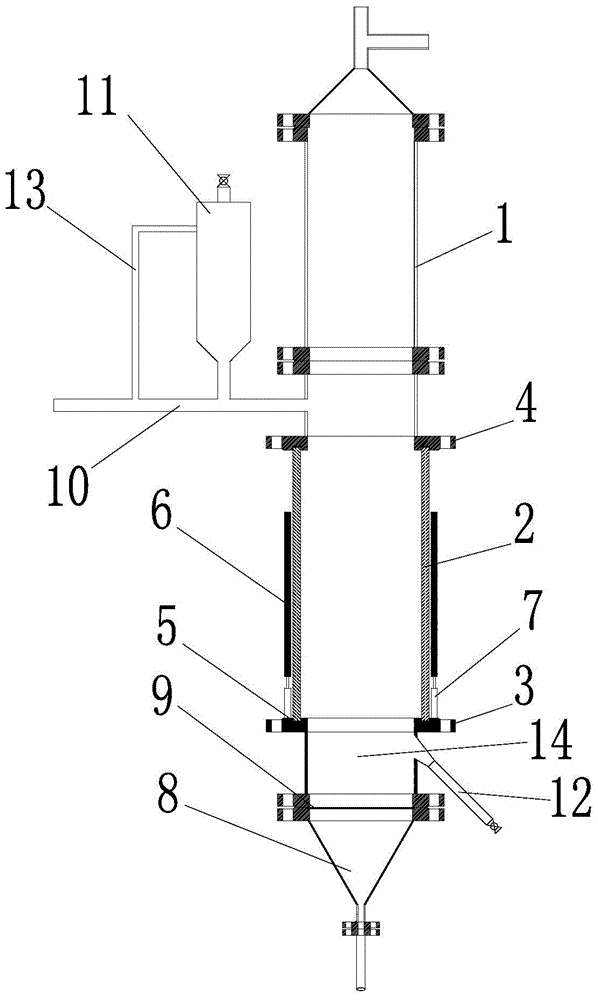
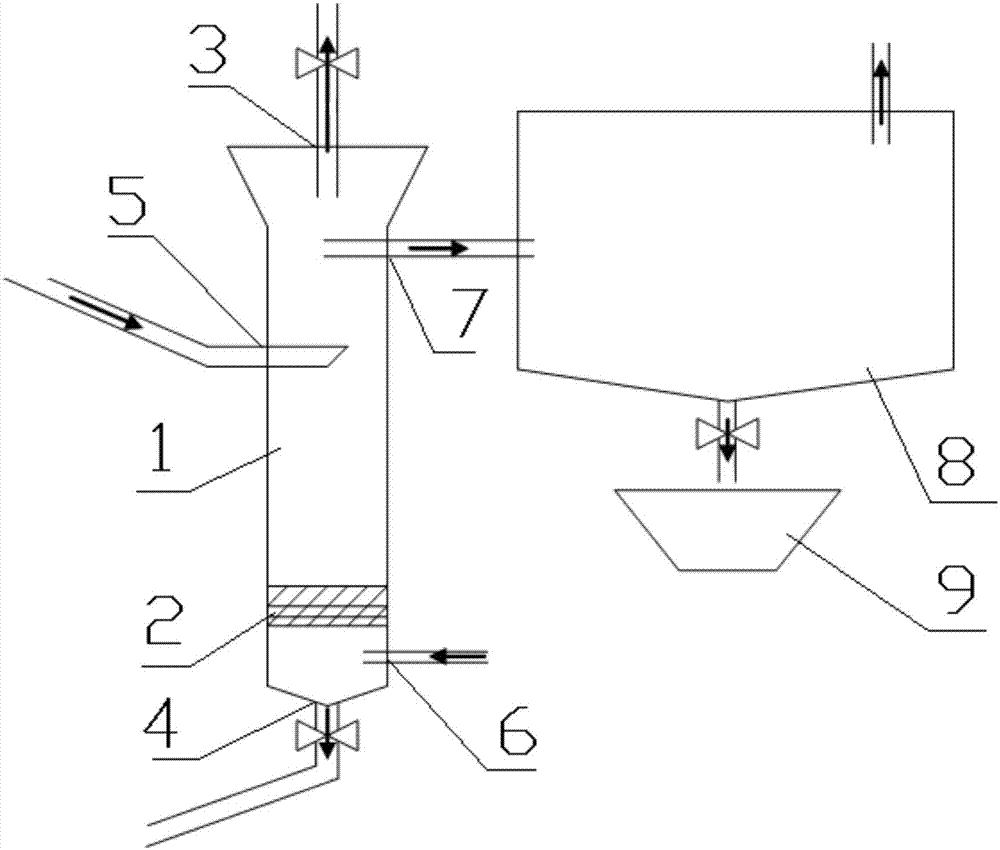
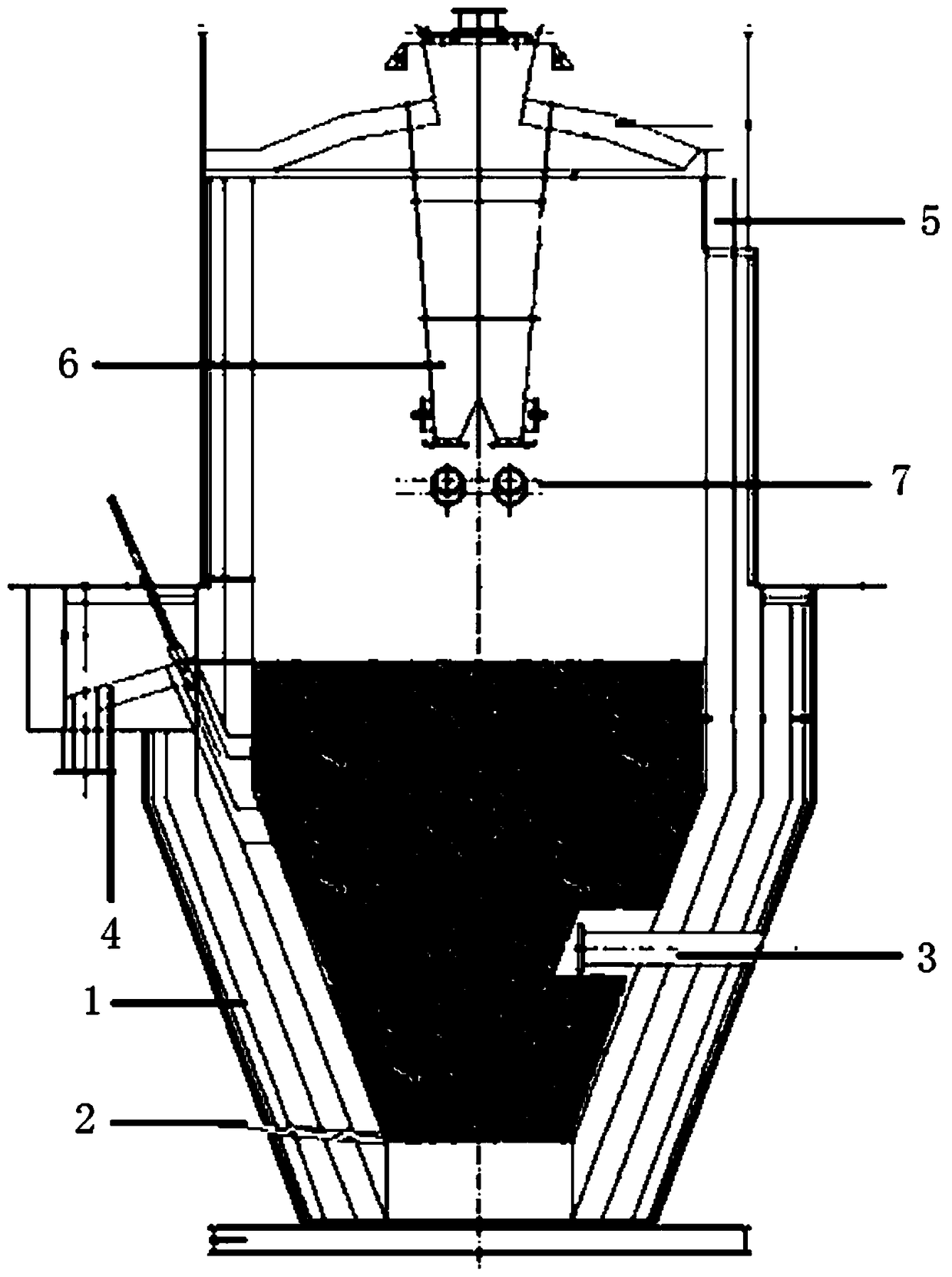
Fluidized chlorination furnace
ActiveCN105236475AResearch FeaturesStudy the state of fluidizationTitanium tetrachlorideSlagFluidization
The invention relates to the field of fluidized chlorination furnaces and discloses a fluidized chlorination furnace. The fluidized chlorination furnace includes a furnace body (1) having an inner chamber, a material feeding inlet, an air inlet, an air outlet and a slag discharge outlet. The inner chamber is respectively connected to the material feeding inlet, the air inlet, the air outlet and the slag discharge outlet. The furnace body (1) includes a reaction part furnace body (2), of which at least one part of the furnace wall is transparent. When a thermal-state test is carried out by the fluidized chlorination furnace, researches can observe reaction situation inside the fluidized chlorination furnace through the transparent part of the furnace wall during the thermal-state test, thereby researching chlorination characters and fluidization state of materials in the fluidized chlorination furnace.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
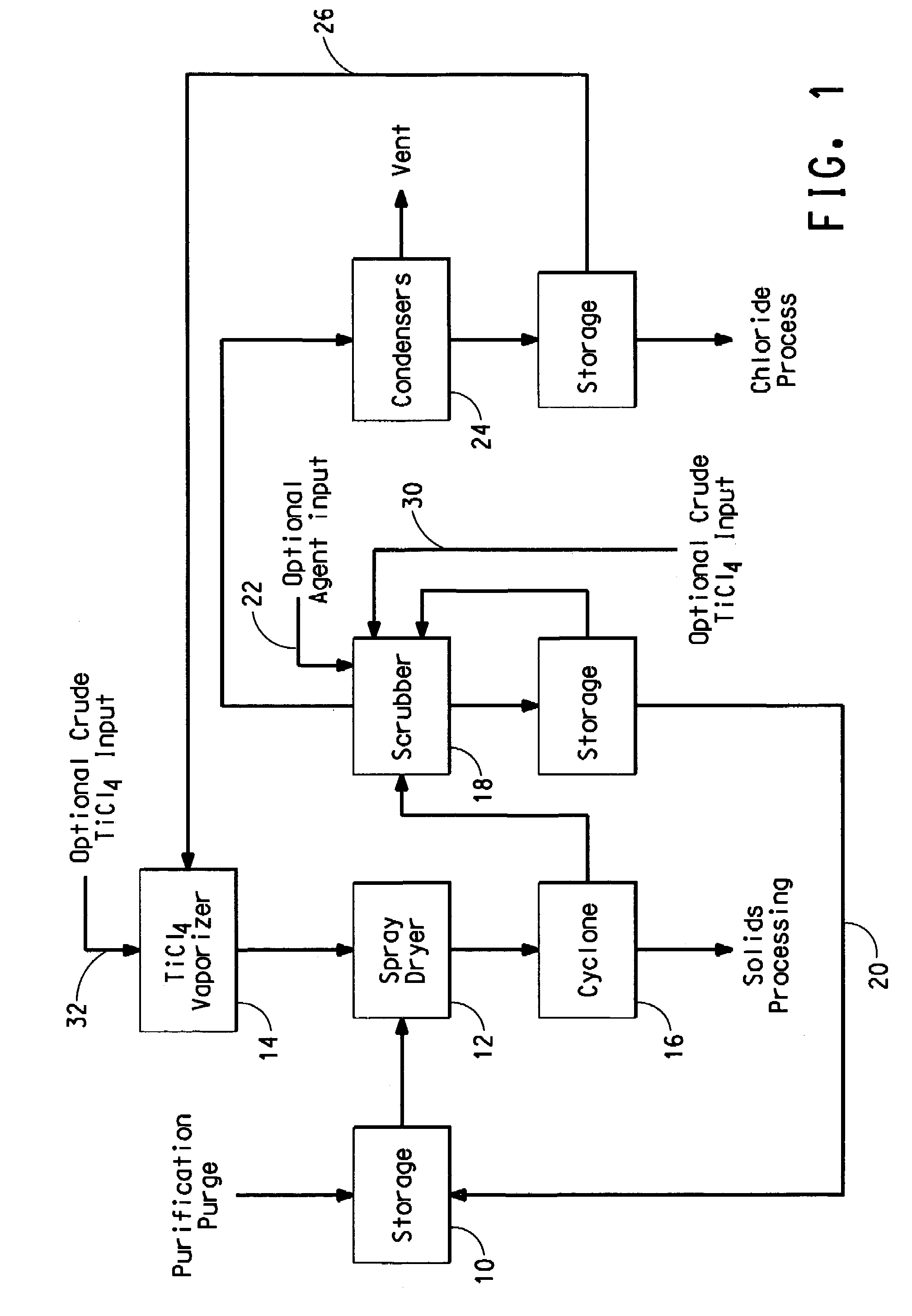
Process for separating solids from a purification purge stream
The disclosure is directed to a process for isolating solids from a purification purge stream comprising an impurity present as a solid, wherein the purification purge stream is substantially free of chlorides other than titanium tetrachloride and vanadium chloride, the process comprising the steps of: (a) atomizing the purification purge stream comprising titanium tetrachloride as a liquid and an impurity present as a solid; (b) drying solids in the atomized purification purge stream by contacting the atomized stream with a titanium tetrachloride vapor stream such that the combined streams reach a temperature of at least about 140° C. to vaporize the liquid titanium tetrachloride, wherein the titanium tetrachloride vapor is substantially free of chlorides other than those of titanium and vanadium, and substantially free of non-condensable gases comprising CO, CO2, N2, or mixtures thereof; and (c) separating the impurity present as a solid from the vaporized titanium tetrachloride. The separated vanadium solids may be further processed to recover valuable by products.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO TT LLC
Method for recovering titanium (halo) alkoxide from a waste liquid
A method for separating one or more titanium (halo) alkoxides from a liquid mixture comprising titanium tetrachloride TiCl4 and at least one titanium (halo) alkoxide, said method comprising: agitatingand cooling the liquid mixture until crystallization of at least one titanium (halo) alkoxide occurs in the liquid mixture; separating the crystallized titanium (halo) alkoxide from the mixture; andoptionally, washing the separated, crystallized titanium (halo) alkoxide with a solvent.
Owner:CLARIANT INT LTD
Semi-continuous magnesium-hydrogen reduction process for manufacturing of hydrogenated, purified titanium powder
InactiveUS8007562B2Cost-effective and highly-productive manufactureZirconium compoundsTitanium tetrachlorideTitanium chlorideHydrogen atmosphere
The cost-effective hydrogenated, purified titanium powder is manufactured by the semi-continuous process including: (a) magnesium-thermic reduction of titanium chlorides at 830-880° C. in the hydrogen atmosphere characterized by the formation of a hollow porous block of the reaction mass having an open cavity in the center of the block, (b) full thermal-vacuum separation of the hollow block from excessive Mg and MgCl2 at 850-980° C. and residual pressure of 26-266 Pa using a multi-step cycle including: (i) purging hydrogen at 800-950° C. into the reactor at the pressure 10 kPa to 24.5 kPa, (ii) directive squeezing-out of a separated liquid phase containing magnesium and magnesium chloride into an additional vessel, and (iii) application of alternate pressure to small portions of the liquid phase in porous titanium compound from different sides which provides removal of the liquid from small pores of the titanium compound and fast evaporation of said liquid, (c) simultaneous hydrogenation and cooling of the titanium sponge down to 600° C. by purging cold hydrogen using multiple recirculation of hydrogen, (d) holding the hydrogenated porous titanium compound in the hydrogen atmosphere at 450-600° C. for 20-70 minutes, (e) removing the hydrogenated porous titanium compound from the reactor, and (f) crushing and grinding the crushed hydrogenated porous titanium pieces into the powder having a predetermined particle size.
Owner:ADMA PRODS
Method of refining titanium tetrachloride to remove vanadium by employing drainage oil
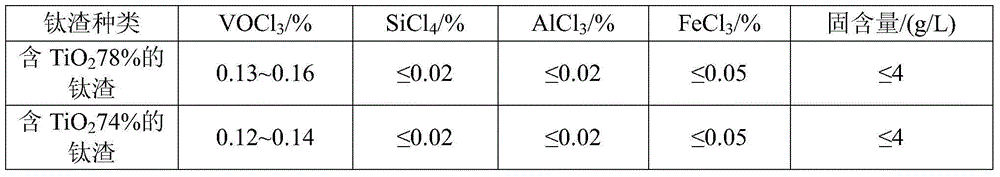
The invention belongs to the field of titanium tetrachloride refining and in particular relates to a method of refining titanium tetrachloride to remove vanadium by employing drainage oil. In order to solve the problems that an existing remove-removal reagent for titanium tetrachloride is high in cost and the like as the drainage oil is great in output and low in cost and is not efficiently utilized, the invention provides the method of refining titanium tetrachloride to remove vanadium by employing drainage oil. The method comprises the following steps of: stirring and mixing the drainage oil and oleic acid in a pre-heating kettle; preheating the mixture to 136-140 DEG C; adding the preheated mixture into a remove-removal rectifying tower; introducing coarse titanium tetrachloride gas; and collecting the refined titanium tetrachloride without vanadium in a remove-removal rectifying tower condenser. By reasonably matching the drainage oil and the oleic acid, the method of refining titanium tetrachloride to remove vanadium not only provides a novel utilization path for cheap drainage oil, but also saves the cost of refining titanium tetrachloride to remove vanadium. The method provided by the invention is simple to operate and low in cost and has an important economical benefit.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP RESEARCH INSTITUTE CO LTD
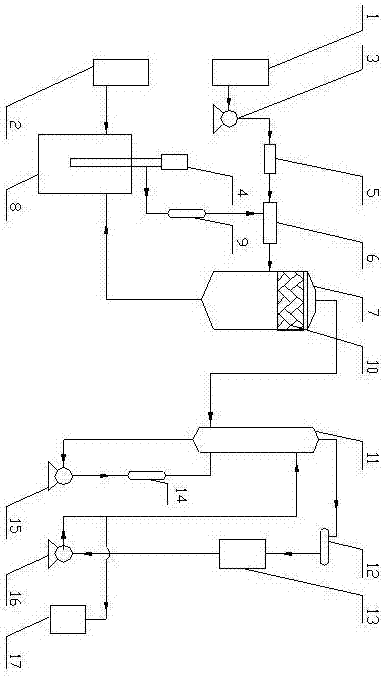
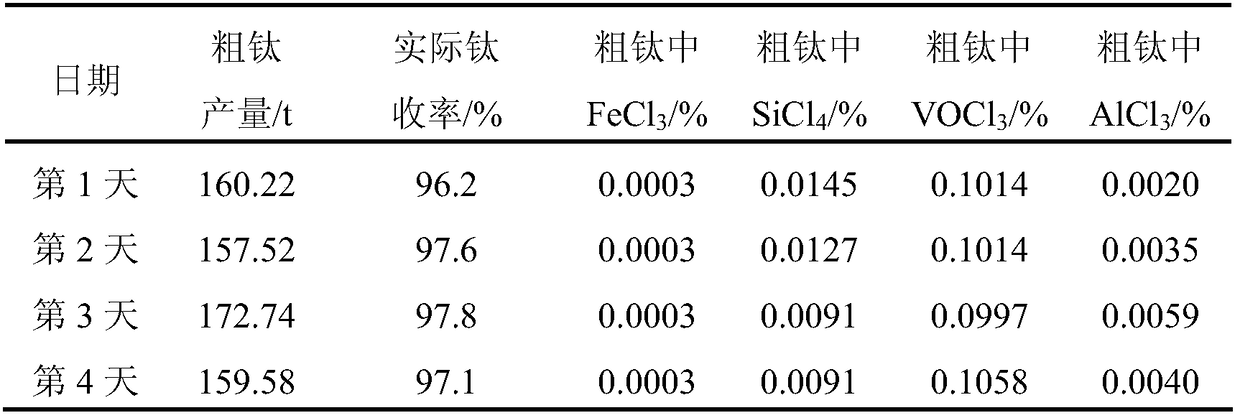
Chemical reaction apparatus and chemical reaction method for removing vanadium from crude TiCl4
InactiveCN106946286AHigh vanadium removal efficiencyProcess control stabilityTitanium tetrachlorideChemical reactionDouble tube
The invention discloses a chemical reaction apparatus for removing vanadium from crude TiCl4. The chemical reaction apparatus comprises, in a successively connected manner, a mixing reactor (6), a flash tank (7), a float valve column (11), a cooler (12), and a reflux tank (13), and also includes a crude TiCl4 storage tank (2), a secondary reactor (8), a double tube-sheet heat exchanger (9), a white oil storage tank (1), a metering pump (3), a flow meter (5), and a vanadium-removed TiCl4 storage tank (17). The invention is direct at a conventional technology of using mineral oil to remove the vanadium from crude TiCl4, wherein the crude TiCl4 heated by the double tube-sheet heat exchanger and precisely metered white oil are uniformly mixed according to ratio in the mixer, so that the two components are rapidly reacted in the mixer to remove the vanadium; the mixture then is fed into the flash tank to perform flash; and the TiCl4, with a VOCl3 impurity being removed, is fed into the high-boiling-point impurity removing float valve column in the form of vapor to further remove high-boiling-point impurities in the TiCl4; and the TiCl4 is cooled to produce a TiCl4 inter-product. The method solves the problems of poor quality stability and high energy consumption in a conventional TiCl4 vanadium removal process, has simple device arrangement and stable process control, and is high in vanadium removal efficiency.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Method for producing titanium tetrachloride by using low-grade titanium material
InactiveUS20110182787A1Long-time continuous and stable operationLong-time continuous and stable and industrializationZirconium compoundsTitanium tetrachlorideLower gradeLow graded
The invention provides a method for producing titanium tetrachloride by using a low grade titanium material, and belongs to the chemical field. The technical problem to be solved is to provide a method for producing titanium tetrachloride by using a low grade titanium material capable of continuous industrialized production. The method is characterized in that the low grade titanium material containing a certain proportion of titanium carbide is caused to directly react with chlorine at 600-700° to produce the titanium tetrachloride. Long-time continuous and stable operation can be realized by using the process parameters of the method, and chlorination rate of the titanium carbide in the titanium material reaches above 90%, so that the titanium material can be better used for producing the titanium tetrachloride.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP VANADIUM TITANIUM & RESOURCES +3
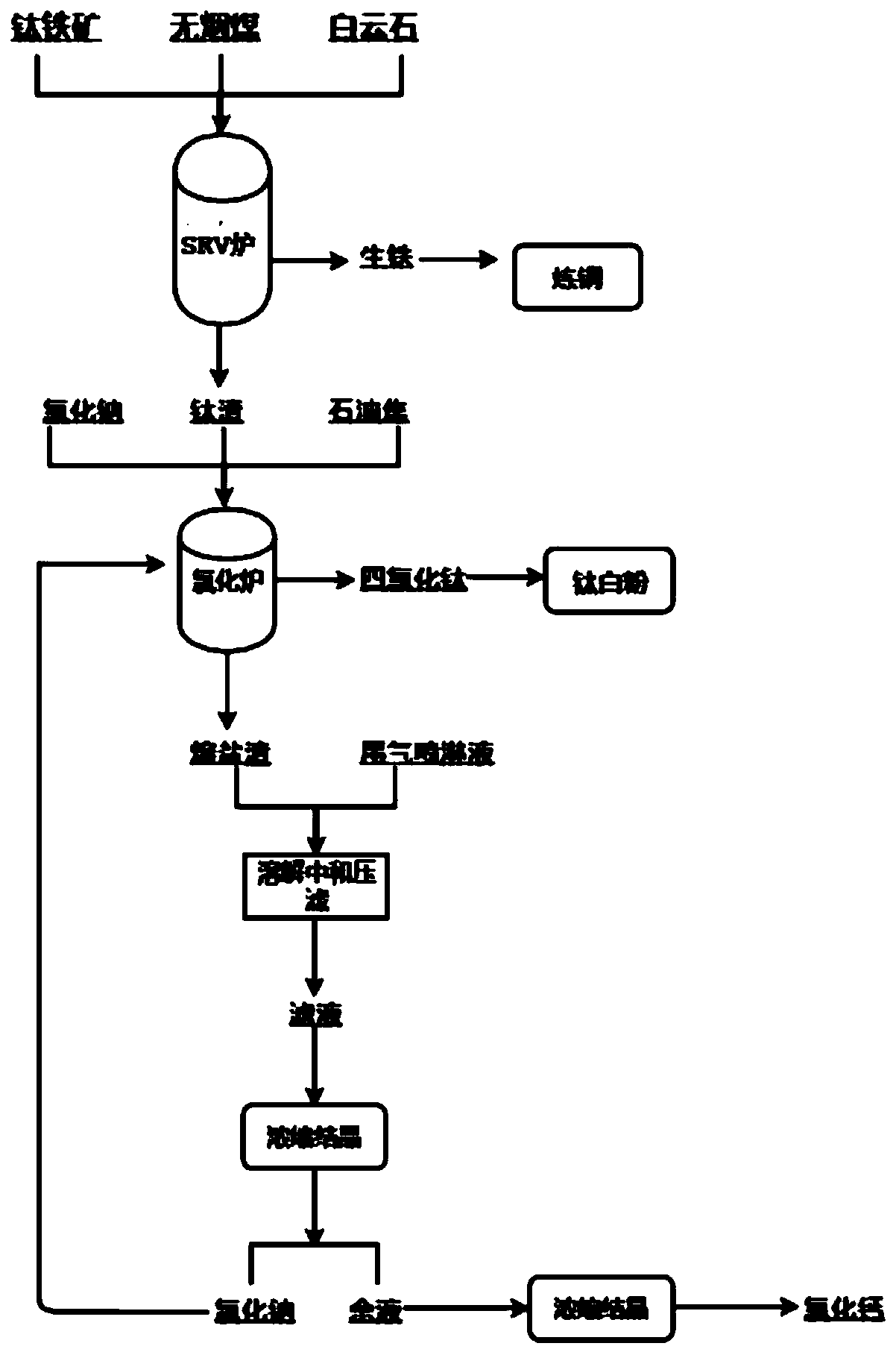
Method for producing titanium slag and titanium white chloride by using Panzhihua ilmenite
InactiveCN110606506AWide applicabilityReduce accumulationCalcium/strontium/barium chloridesTitanium tetrachlorideTitanium tetrachlorideImpurity
The invention discloses a method for producing titanium slag and chlorinated titanium dioxide by using Panzhihua ilmenite, and relates to the field of metallurgy and chemical engineering. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out reduction smelting on ilmenite by utilizing an HIsmelt smelting reduction technology to obtain titanium slag and pig iron; then feeding the titaniumslag as a raw material into a chlorination furnace, producing titanium dioxide by adopting a molten salt chlorination method; recycling and separating molten salt slag obtained in the production process, and returning the separated sodium chloride into the chlorination furnace. In the titanium slag smelting process, ilmenite powder can be directly utilized, wherein a reducing agent can be commonanthracite with low requirements or contains part of bituminous coal; meanwhile, smelting can be conducted at a low temperature, energy consumption is greatly reduced, and the additional value of by-product pig iron is high; in titanium dioxide chloride production by using the titanium slag, the cyclone dust removal device has a good dust collection effect on flue gas, reduces the impurity contentin crude titanium tetrachloride, effectively utilizes the molten salt slag, reduces the accumulation amount of the molten salt slag, and has good green and environment-friendly significance.
Owner:HENAN BILLIONS NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Organic matter vanadium removal mud solid-liquid separation device and separation method
ActiveCN106925009ASimple processReduce energy consumptionTitanium tetrachlorideStationary filtering element filtersOrganic matterTitanium tetrachloride
The invention relates to an organic matter vanadium removal mud solid-liquid separation device and a method for carrying out organic matter vanadium removal mud solid-liquid separation by adopting the device and belong to the field of mixed metallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: inputting organic matter vanadium removal mud into a drying oven through a mud inlet, enabling the organic matter vanadium removal mud to flow through a filtering element in a filter unit, and realizing separation of organic matter vanadium removal residue and titanium tetrachloride in the mud; after filtration, introducing heated inert gas, so that titanium tetrachloride in a filter cake on the filter unit is evaporated, the evaporated titanium tetrachloride gas is recycled by a condenser connected with a condenser connector, so that titanium tetrachloride is obtained; and finally blowing out the dried organic matter vanadium removal residue from a hot gas outlet by virtue of atmospheric flow, and collecting. The device and method which are provided by the invention have the advantages that solid-liquid separation efficiency is more than 99%, and recovery ratio of TiCl4 in the mud is more than 98%; and no chlorinated tailing is doped, so that the separated organic matter vanadium removal residue also can be used for vanadium extraction production, and recycling is realized.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP RESEARCH INSTITUTE CO LTD
Processes for treating red mud
ActiveUS20150275330A1Simple and efficientLow costAluminium compoundsNickel compounds preparationPregnant leach solutionRare-earth element
Owner:AEM TECH INC
Method for discoloring in process of refining coarse titanium tetrachloride from organic substances
InactiveCN104445384ASimple production processAdd lessTitanium tetrachlorideTetrachlorideBoiling point
The invention discloses a method for discoloring in a process of refining coarse titanium tetrachloride from organic substances. The method comprises the following steps: sufficiently mixing the organic substances which account for 0.12%-0.35% of the weight of coarse titanium tetrachloride with coarse titanium tetrachloride to obtain a mixture; adding the mixture into a primary packing tower to remove vanadium, enabling vanadium-removed qualified titanium tetrachloride to pass through a float valve tower to remove low-boiling-point substances, enabling titanium tetrachloride with qualified low-boiling-point substances to pass through a secondary packing tower to remove high-boiling-point substances, and discoloring. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: completely collecting and storing unqualified vanadium-removed tetrachloride in the primary packing tower, not returning unqualified vanadium-removed tetrachloride to the primary packing tower for being subjected to secondary vanadium removal, and adding the collected and stored unqualified vanadium material which accounts for 10-25% of the weight of the qualified vanadium material as well as the qualified vanadium material into the float valve tower and a secondary packing tower, thereby obtaining a qualified fine titanium tetrachloride product. The method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of simple process, less equipment addition and modification, less investment, good effects of discoloring and removing organic substances in titanium tetrachloride, high production efficiency, energy conservation, consumption reduction and the like.
Owner:ZUNYI TITANIUM
TiCl4 preparation process and system
PendingCN108046315AImprove utilizationHigh recovery rateTitanium tetrachlorideMolten stateMolten salt
The invention discloses a TiCl4 preparation process. The process comprises the following steps: mixing vanadic titanomagnetite, a binder and water according to a mass ratio of 100:(1-2.5):(6-9) to obtain raw balls, and carrying out drying, preheating and roasting on the raw balls to obtain oxidized pellets; sending the oxidized pellets into gas-based reduction equipment for direct reduction to prepare vanadium-titanium metallized pellets; sending the vanadium-titanium metallized pellets into a melting furnace for melting, and carrying out slag-iron separation to obtain titanium-containing slag; crushing the titanium-containing slag, carrying out grinding to obtain the titanium slag, adding the titanium slag and a carbon raw material into a chlorination reaction furnace containing a moltensalt with a semi-molten state according to the mass ratio of 100:(11-15), introducing chlorine gas into the chlorination reaction furnace after the molten salt is completely melted, and carrying out chlorination reaction to obtain gaseous TiCl4; condensing the gaseous TiCl4 by a condensing device to obtain crude TiCl4; and carrying out refining process on the crude TiCl4 to obtain refined TiCl4. The method can be used to effectively recover titanium resources, improve the recovery rate of the titanium resources, reduce energy consumption and reduce environmental pollution.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE METALLURGICAL DESIGN INST
Process for preparing titanium tetrachloride using off gases from a silica and zircon carbo-chlorination process
InactiveUS20140154167A1Inhibit wearTitanium tetrachlorideTitanium dioxideEthyl ChlorideSilicon dioxide
This disclosure relates to an improved process for preparing titanium tetrachloride comprising a first carbo-chlorination reaction comprising reacting ores comprising silica and / or zirconium with chlorine and a carbon compound at a temperature of about 900° C. to about 1300° C. to form an unscrubbed off gas comprising carbon monoxide, and using the unscrubbed off gas in a second carbo-chlorination reaction comprising titanium to form titanium tetrachloride.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Production method of titanium carbide slag for preparing titanium tetrachloride
InactiveCN107904408ARealize resource utilizationEfficient use ofTitanium tetrachlorideProcess efficiency improvementMolten stateSlag
The invention discloses a production method of titanium carbide slag for preparing titanium tetrachloride, and belongs to the field of metallurgy. The technical problem to be solved by the invention is to provide the production method of the titanium carbide slag for preparing the titanium tetrachloride by using a low-temperature chlorination process. The production method of the titanium carbideslag for preparing the titanium tetrachloride comprises the following steps: titanium-contained furnace slag is hot filled in an electric furnace in a molten state for heating to 1200-1500 DEG C; a carbon reducing agent is added for continuous heating to a temperature of not lower than 1500 DEG C; when the titanium dioxide conversion rate is not lower than 85%, and the content of titanium carbidein the furnace slag is 9-19%, a slag outlet of the electric furnace is opened; high-pressure water currents are used for water quenching of liquid-state slag in the slag outlet to obtain granular slag; and the granular slag is dehydrated, dried and crushed to obtain the titanium carbide slag. The titanium-contained furnace slag with high calcium and magnesium contents is used as raw materials forpreparing the titanium carbide slag; and titanium resources and calcium resources in the furnace slag are effectively used for realizing the resourceful utilization of the whole titanium-contained furnace slag.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Large-capacity molten salt chlorinating device for treating high-calcium magnesium titanium slag and production method
InactiveCN109052461ALarge diameterImprove distribution uniformityTitanium tetrachlorideGraphite electrodeMolten salt
The invention discloses a large-capacity molten salt chlorinating device for treating high-calcium magnesium titanium slag and a production method in the technical field of metal smelting. The large-capacity molten salt chlorinating device comprises a furnace body, a gas spraying pipe arranged at the bottom of the furnace body, a graphite electrode and a waste salt discharging chute which are arranged on the side surface of the furnace body, and a smoke gas outlet formed in the top of the furnace body, wherein a furnace top bin stretching into the furnace body is arranged on the top of the furnace body; screw feeders are arranged at outlets in the bottom of the furnace top bin; and the screw feeders are rotatably connected with the furnace top bin. Through reasonable design of the furnacebody, the diameter of the furnace body is increased; and through arrangement of the furnace top bin and the screw feeders on the top of the furnace, the distribution uniformity of a gas material and asolid material in the furnace is improved, the chlorination reaction efficiency of the high-calcium magnesium titanium slag is improved, and thus the single furnace capacity is improved.
Owner:CHENGDU ADVANCED METAL MATERIALS IND TECH RES INST CO LTD
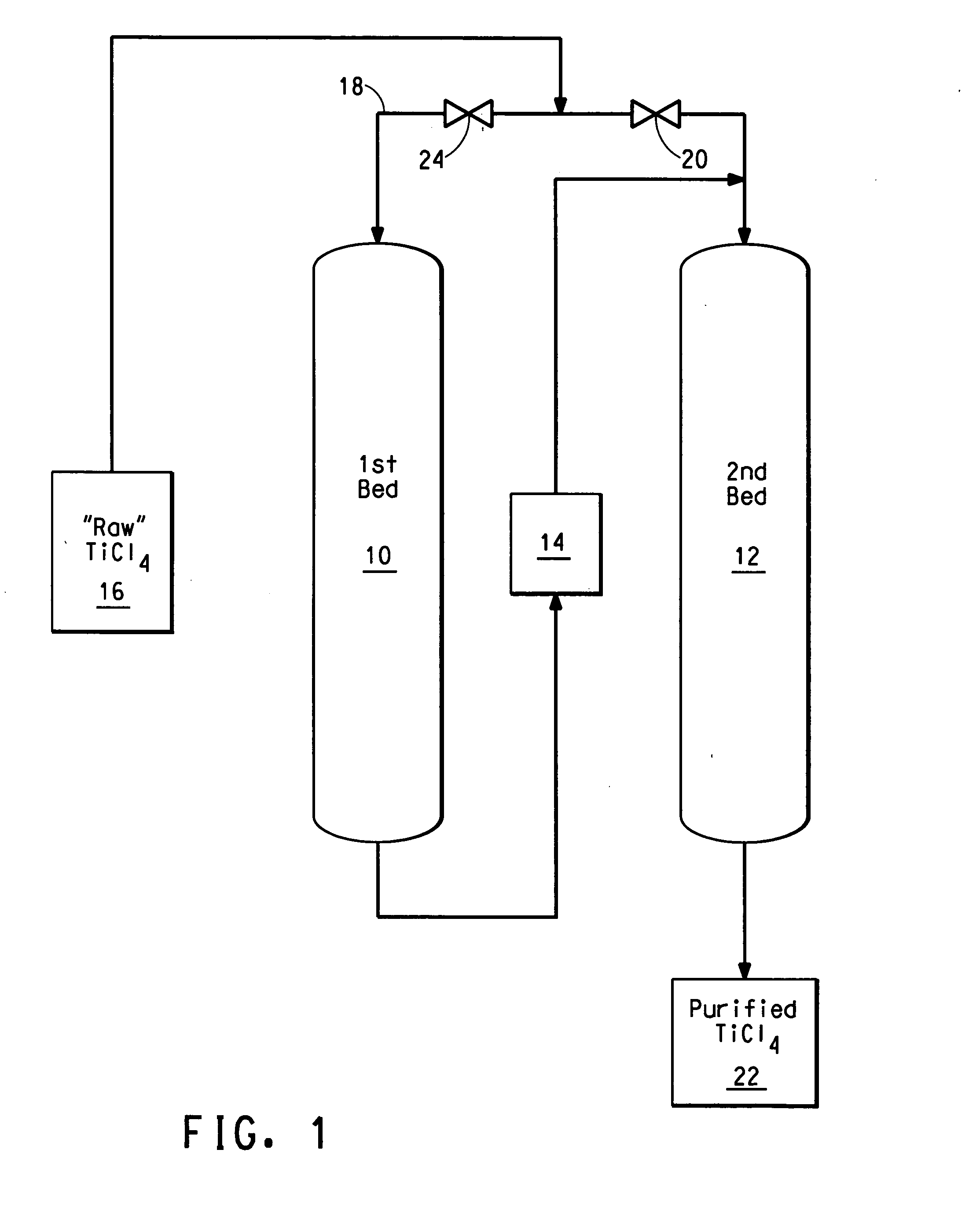
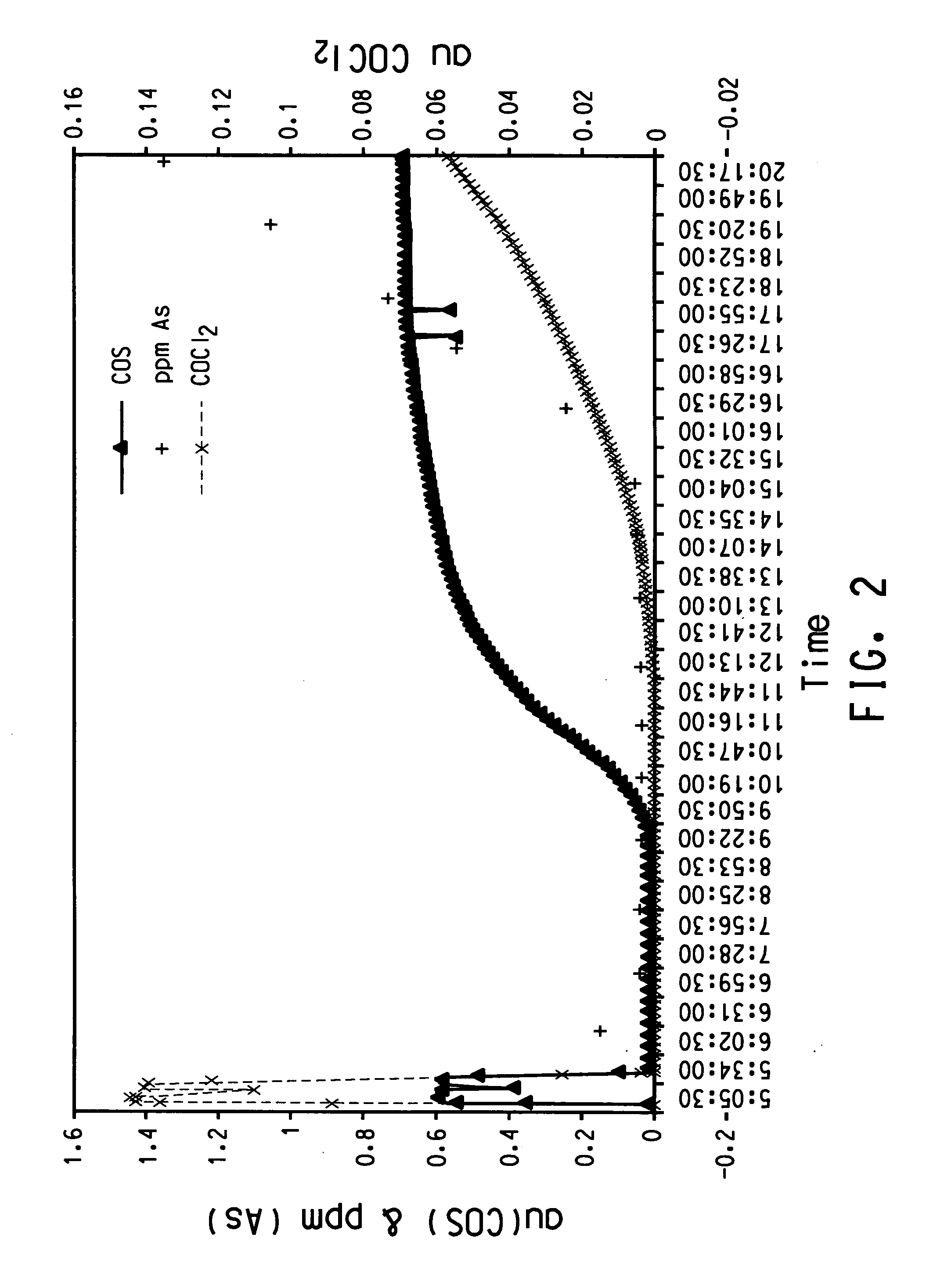
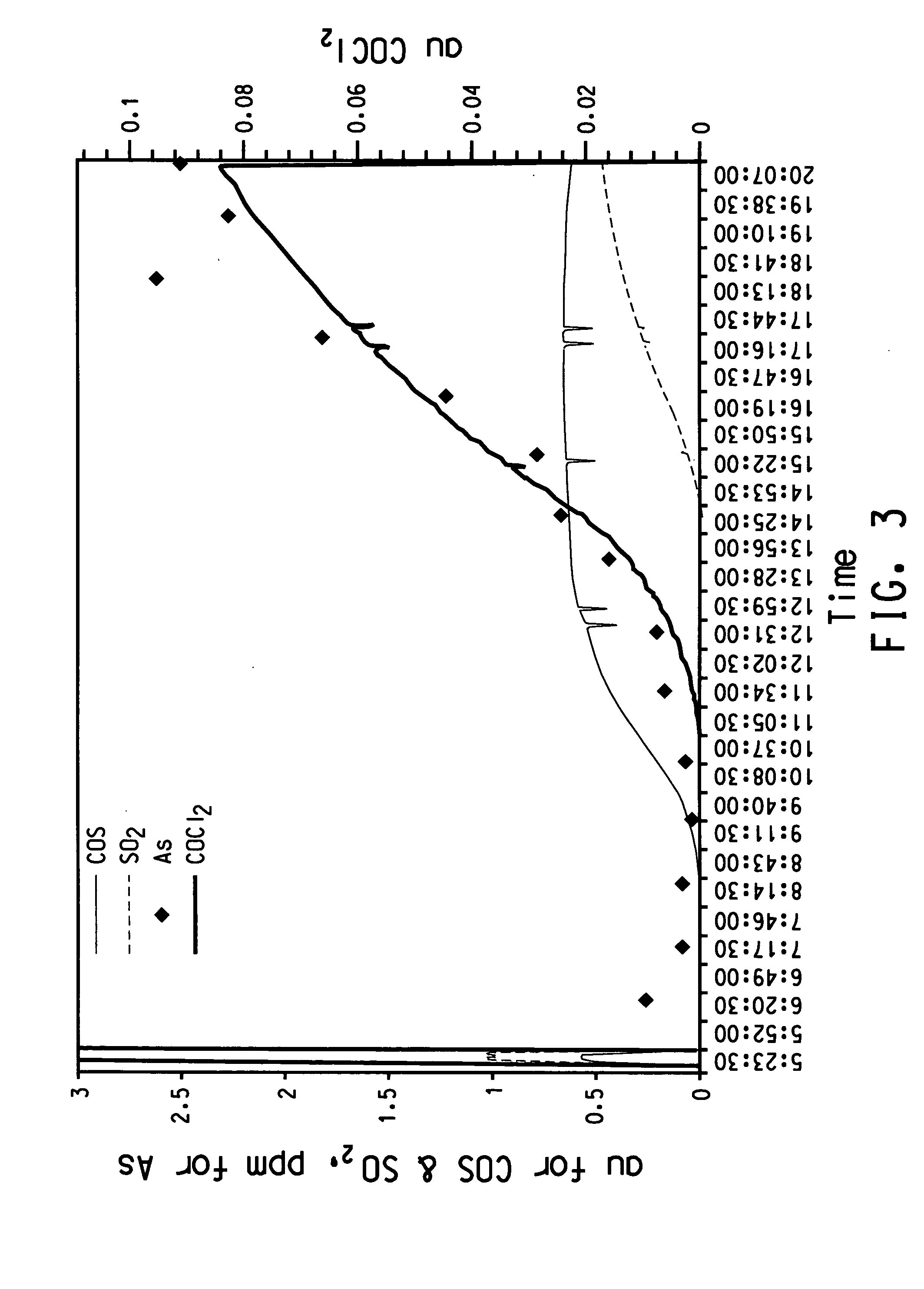
Process for purifying titanium chloride-containing feedstock
InactiveUS20060228292A1Easy to handleClose monitoringSolid sorbent liquid separationTitanium tetrachlorideTitanium chlorideCarbonyl sulfide
The disclosure is directed to a process for purifying a titanium chloride-containing feedstock using an activated carbon bed, comprising: (a) providing the titanium chloride-containing feedstock comprising an impurity, such as arsenic, and at least one tracker species selected from the group consisting of phosgene, carbonyl sulfide, sulfur dioxide, carbon disulfide, thionyl chloride, sulfur chloride, SO2Cl2, carbon dioxide, and hydrochloric acid and combinations thereof; (b) feeding the titanium chloride-containing feedstock to the activated carbon bed; (c) contacting the titanium chloride-containing feedstock with the activated carbon by flowing the feedstock through the activated carbon bed to remove at least a portion of both the tracker species and the impurity from the feedstock to form a treated product; (d) continuing the flow of the titanium chloride-containing feedstock at least until the tracker species is detected in the treated product; and (e) regenerating the activated carbon bed.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for preparing titanium dioxide by using high-titanium-type blast furnace slag
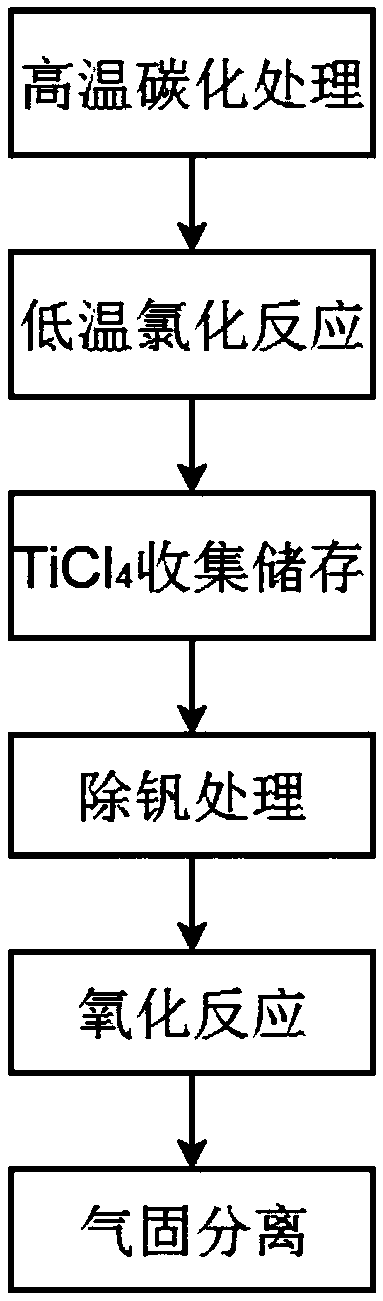
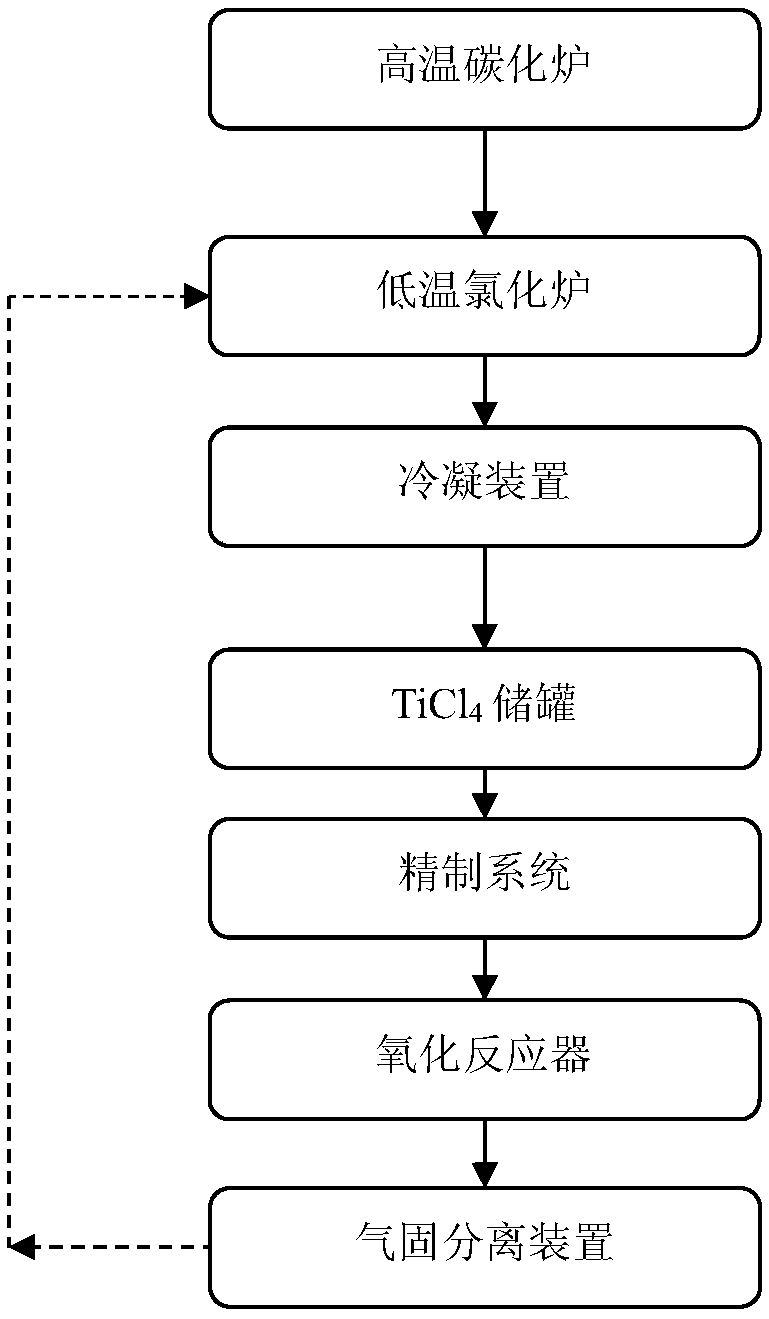
InactiveCN108975393AFully recycleLess chlorine impurity contentTitanium tetrachlorideTitanium dioxideSlagCarbonization
The invention discloses a method for preparing titanium dioxide by using high-titanium-type blast furnace slag, and belongs to the technical field of the steel smelting. In order to adequately recycletitanium on the high-titanium-type blast furnace slag, and avoid resource waste, the provided method for preparing the titanium dioxide by using the high-titanium-type blast furnace slag comprises the following steps: performing high-temperature carbonization treatment on the high-titanium-type blast furnace slag, crushing, to obtain carbonized slag; performing a low-temperature chlorination reaction on the carbonized slag and a chlorine gas, to obtain a chlorination reaction mixture containing a TiCl4 gas, after condensing, to obtain crude TiCl4; performing vanadium removing treatment on thecrude TiCl4 by using fatty acid, rectifying, to obtain fine TiCl4; and performing an oxidization reaction on the fine TiCl4 and O2, to obtain an oxidization reaction mixing product containing TiO2 and Cl2, cooling, filtering, to obtain TiO2 and the chlorine gas. The method is capable of adequately recycling the titanium in the high-titanium-type blast furnace slag, and avoiding the resource waste, low in process cost, and good in product quality.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Purification of titanium tetrachloride
InactiveUS20060051267A1Reduce lossesZirconium compoundsTitanium tetrachlorideAluminium chlorideTitanium tetrachloride
The present invention is a process for reducing raw material yield losses resulting from the passivation aluminum chloride and vanadium chlorides in the chlorinator discharge in a carbochlorination process for making titanium tetrachloride.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com