Method for recovering titanium (halo) alkoxide from a waste liquid
A technology of alkoxide and alkoxide compound, which is applied in the field of recovering titanium (halogenated) alkoxide from waste liquid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
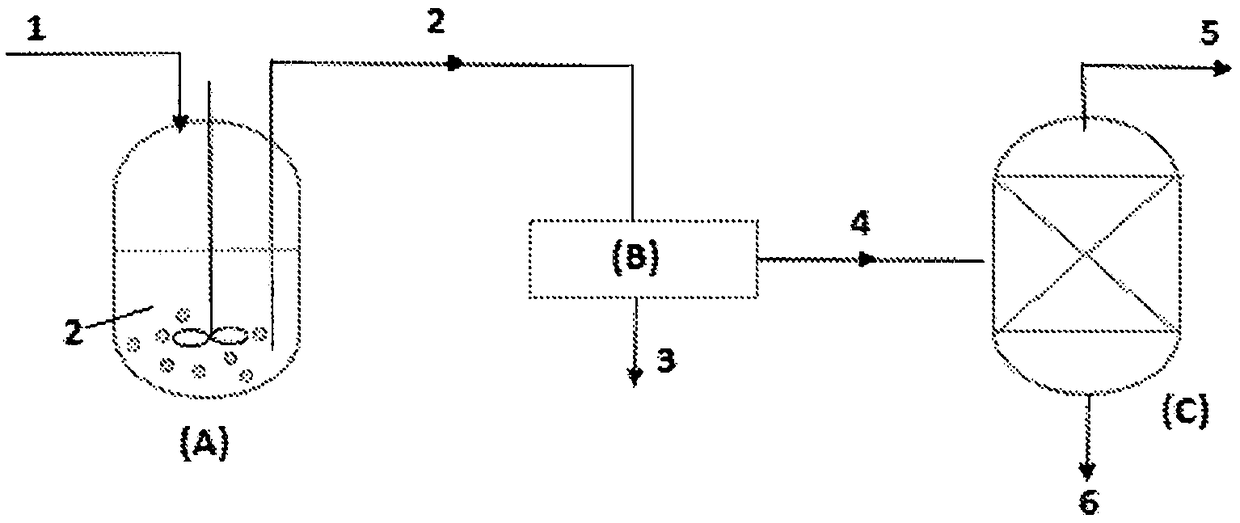
[0027] 900 g of spent liquor 1 from the preparation of Ziegler-Natta catalysts for polypropylene production was subjected to figure 1 The method of the present invention is carried out in the process apparatus illustrated in . The effluent 1 contains about 89% by weight of TiCl 4 , 10% by weight of Ti chloroalkoxide compound and 0.5-1% by weight of diisobutyl phthalate (DiBP) as main components.
[0028] The hot waste liquid 1 leaving the reaction vessel is first cooled with a coolant in the outer cooling jacket of the longitudinally extending crystallizer (A). The temperature inside the crystallizer was maintained at about 10° C. and the spent liquor was continuously stirred at a rate of 400 rpm for 3 hours by a rotor rotating inside the cooling crystallizer. The resulting slurry 2 was then filtered through filter (B), and the isolated crystalline solid 3 was further washed by hexane and dried by gaseous nitrogen to obtain 62 g of white to light yellow crystals containing ...
Embodiment 2
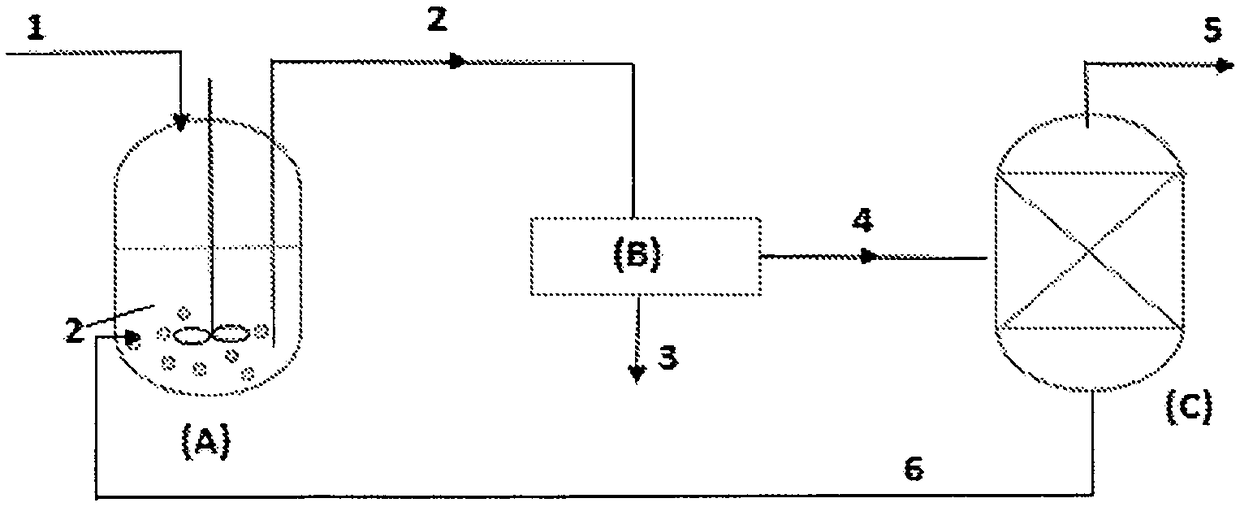
[0031] For another 900 g of effluent from the same Ziegler-Natta catalyst production process, Example 1 was essentially repeated, except that the liquid residue (totalling about 30 g) is delivered back to the crystallizer (A), as figure 2 As shown in , for repeated cooling crystallization treatments under the same operating conditions: the internal temperature was maintained at 10 °C for 3 hours with continuous stirring at a constant rate of 400 rpm. After filtration through filter (B), washing with hexane and subsequent nitrogen drying, 8.2 g of white to pale yellow crystalline solid were obtained, composed of >90% by weight of ethoxylated titanium trichloride (TiCl 3 OC 2 h 5 ) and 4 Composition, as measured by gas chromatography.
Embodiment 3
[0033] 140 kg of spent liquor 1 from the preparation of Ziegler-Natta catalysts for polypropylene production was subjected to figure 1 The method of the present invention is carried out in the process apparatus illustrated in . The effluent 1 contains about 89% by weight of TiCl 4 , 10% by weight of Ti chloroalkoxide compound and 0.5-1% by weight of diisobutyl phthalate (DiBP) as main components.
[0034] The hot waste liquid 1 leaving the reaction vessel is first cooled with a coolant in the outer cooling jacket of the longitudinally extending crystallizer (A). The temperature inside the crystallizer was maintained at about -5°C and the waste liquor was continuously stirred at a rate of 100 rpm for 3 hours by a rotor rotating inside the cooling crystallizer. The resulting slurry 2 was then filtered through filter (B) and the isolated crystalline solid 3 was further washed by hexane and dried by gaseous nitrogen to obtain 4.5 kg of white to light yellow crystals containing ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com