Patents
Literature
221 results about "Gaseous nitrogen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
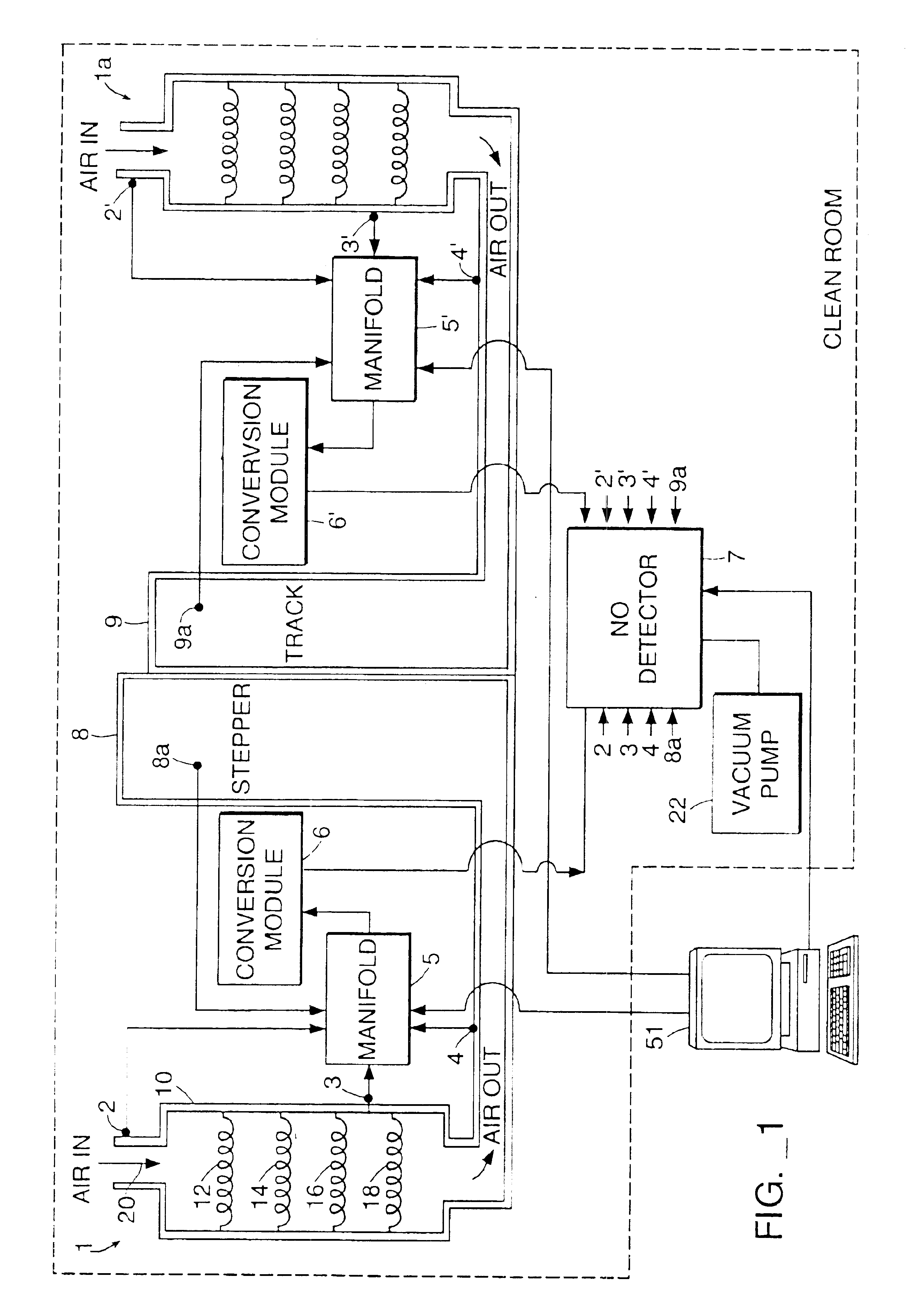
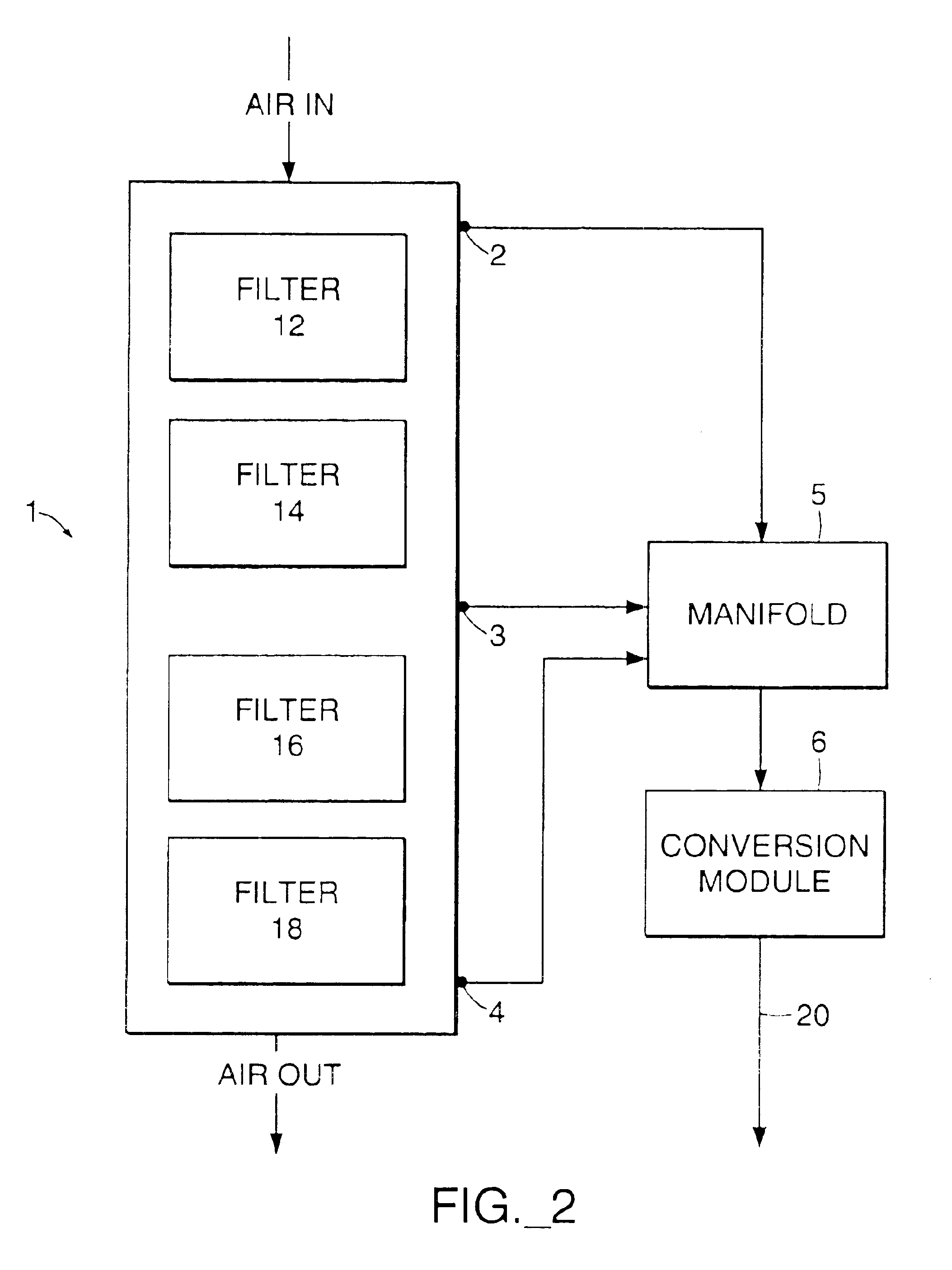
Gaseous Nitrogen. Gaseous Nitrogen is one of the various liquids note 1 added by GregTech 4. It is created by placing a Nitrogen Cell in a Liquid Transposer. It is a form in which Nitrogen can be stored, usually in bulk. It has no use in crafting except to be placed back into an Empty Cell via Liquid Transposer.
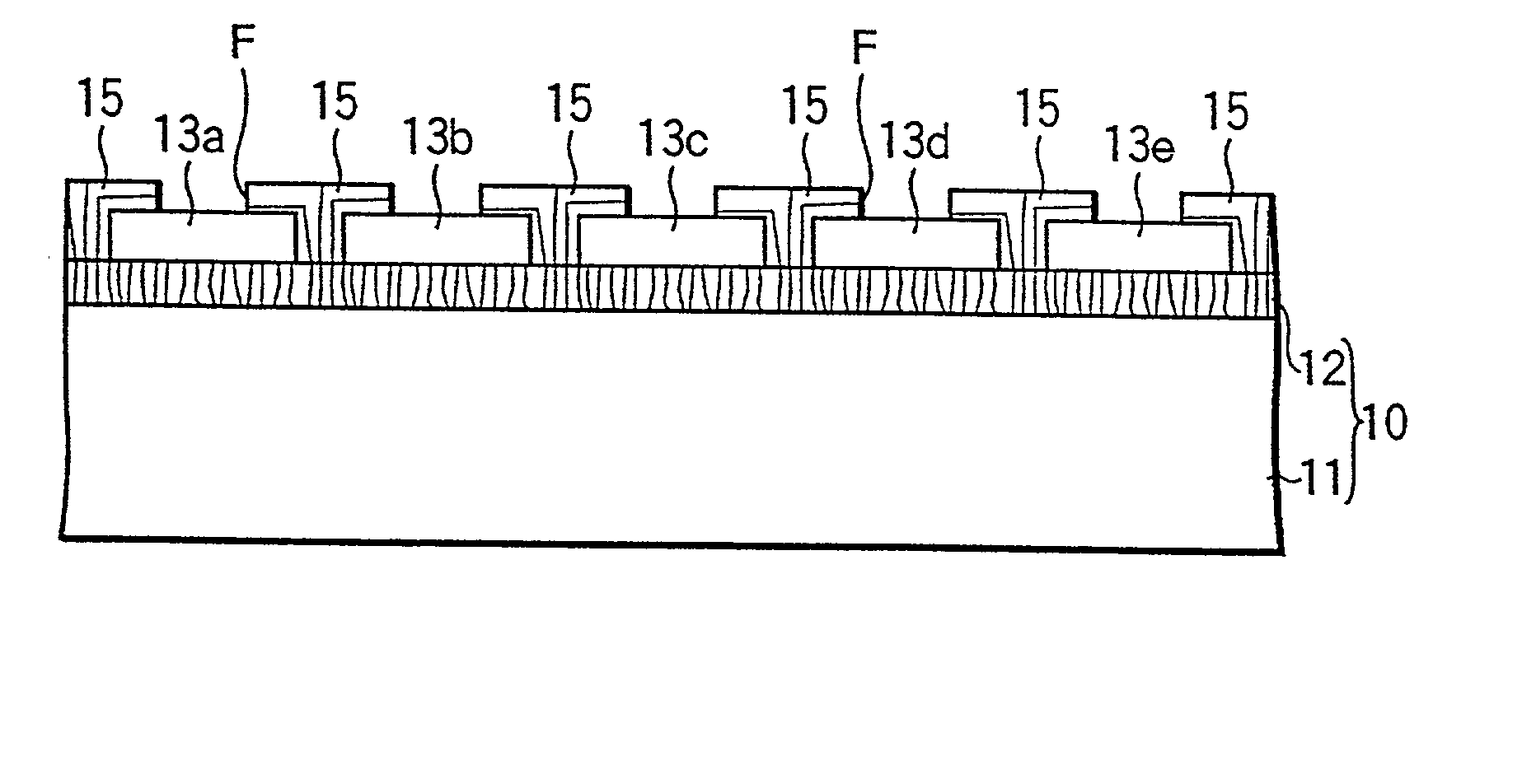
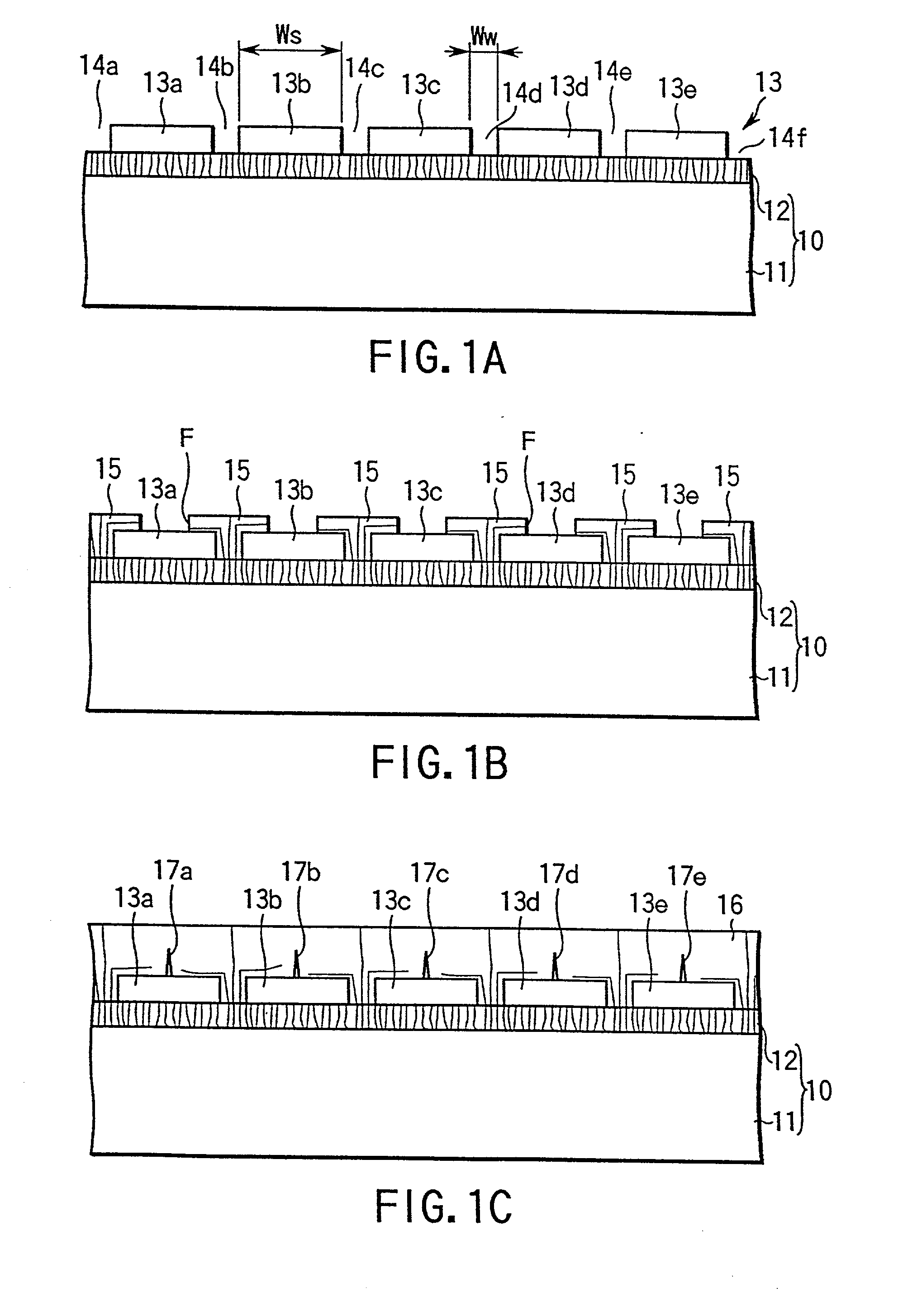
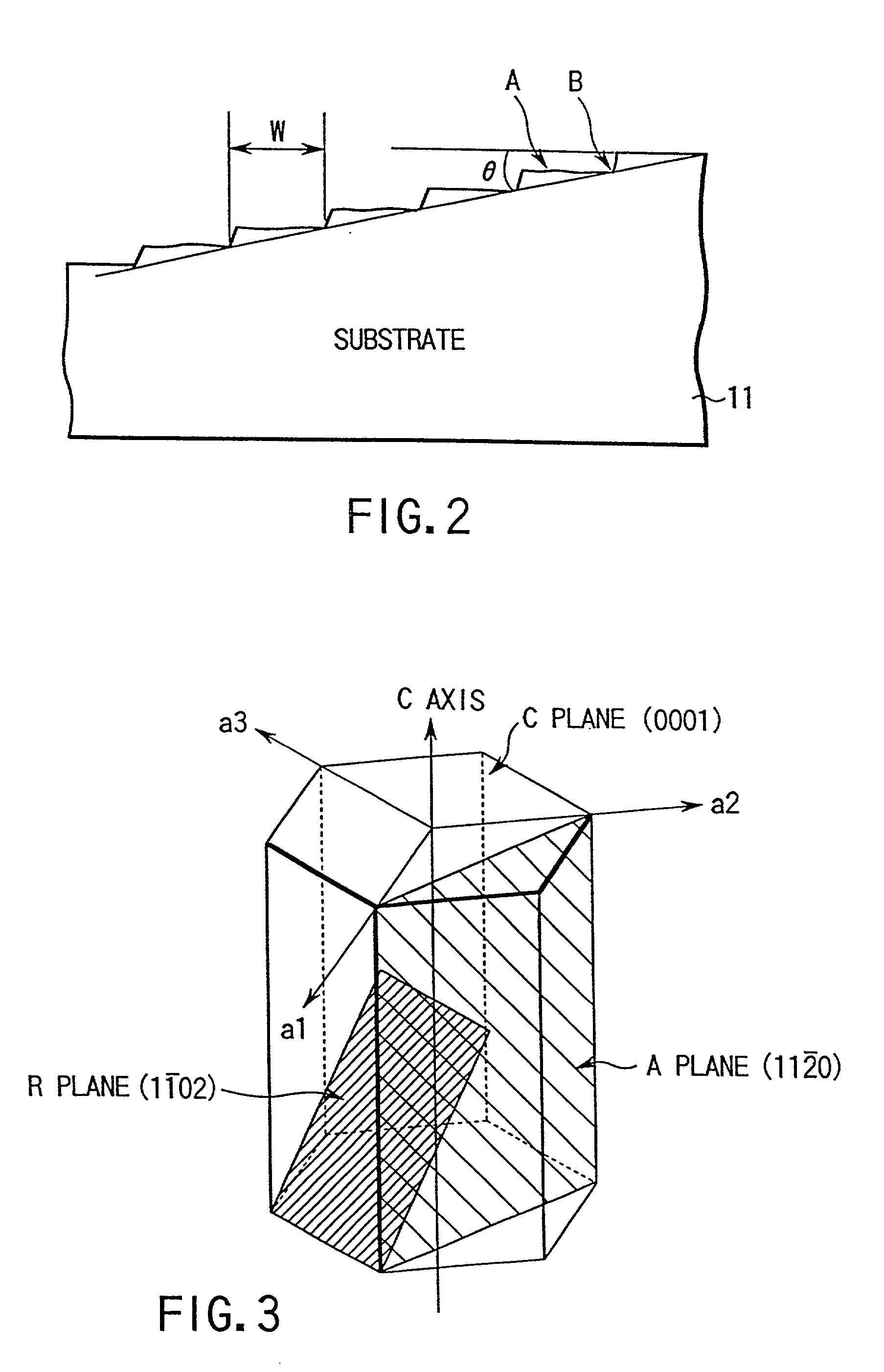
Nitride semiconductor growth method, nitride semiconductor substrate, and nitride semiconductor device
InactiveUS20020046693A1From gel statePolycrystalline material growthCrystallographic defectNitride semiconductors
A method of growing a nitride semiconductor crystal which has very few crystal defects and can be used as a substrate is disclosed. This invention includes the step of forming a first selective growth mask on a support member including a dissimilar substrate having a major surface and made of a material different from a nitride semiconductor, the first selective growth mask having a plurality of first windows for selectively exposing the upper surface of the support member, and the step of growing nitride semiconductor portions from the upper surface, of the support member, which is exposed from the windows, by using a gaseous Group 3 element source and a gaseous nitrogen source, until the nitride semiconductor portions grown in the adjacent windows combine with each other on the upper surface of the selective growth mask.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
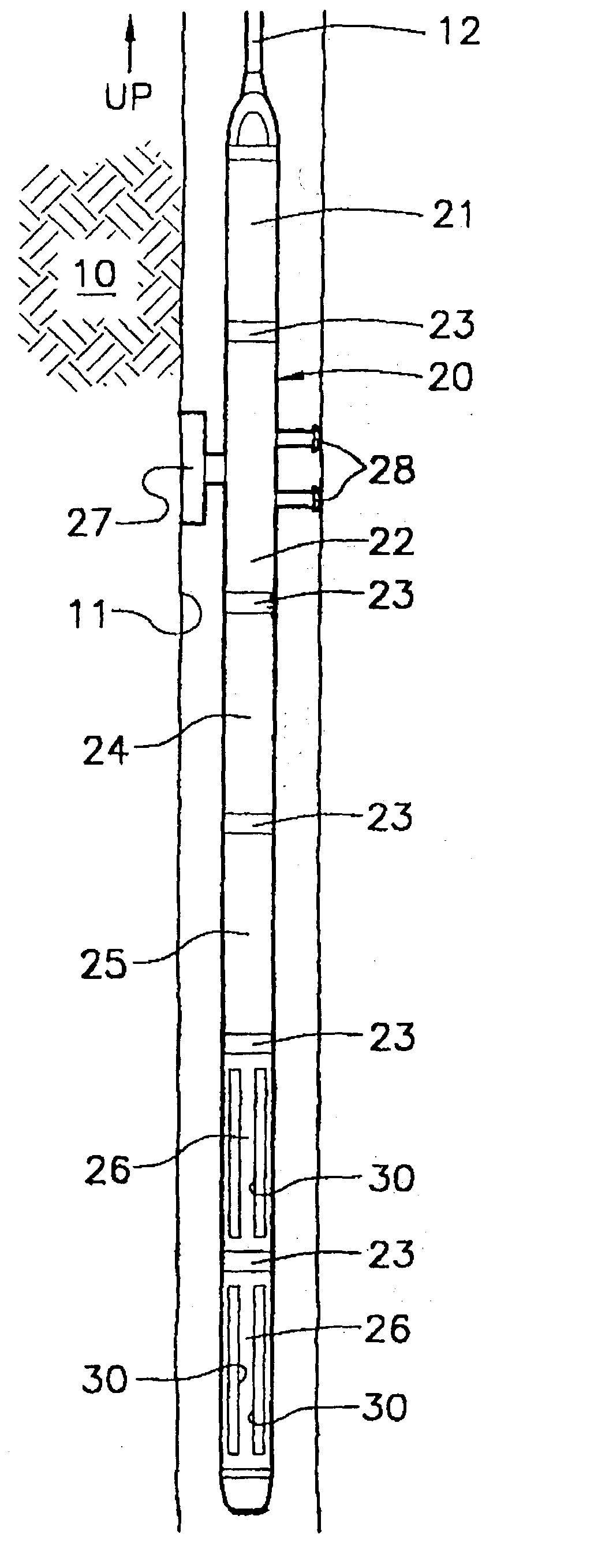
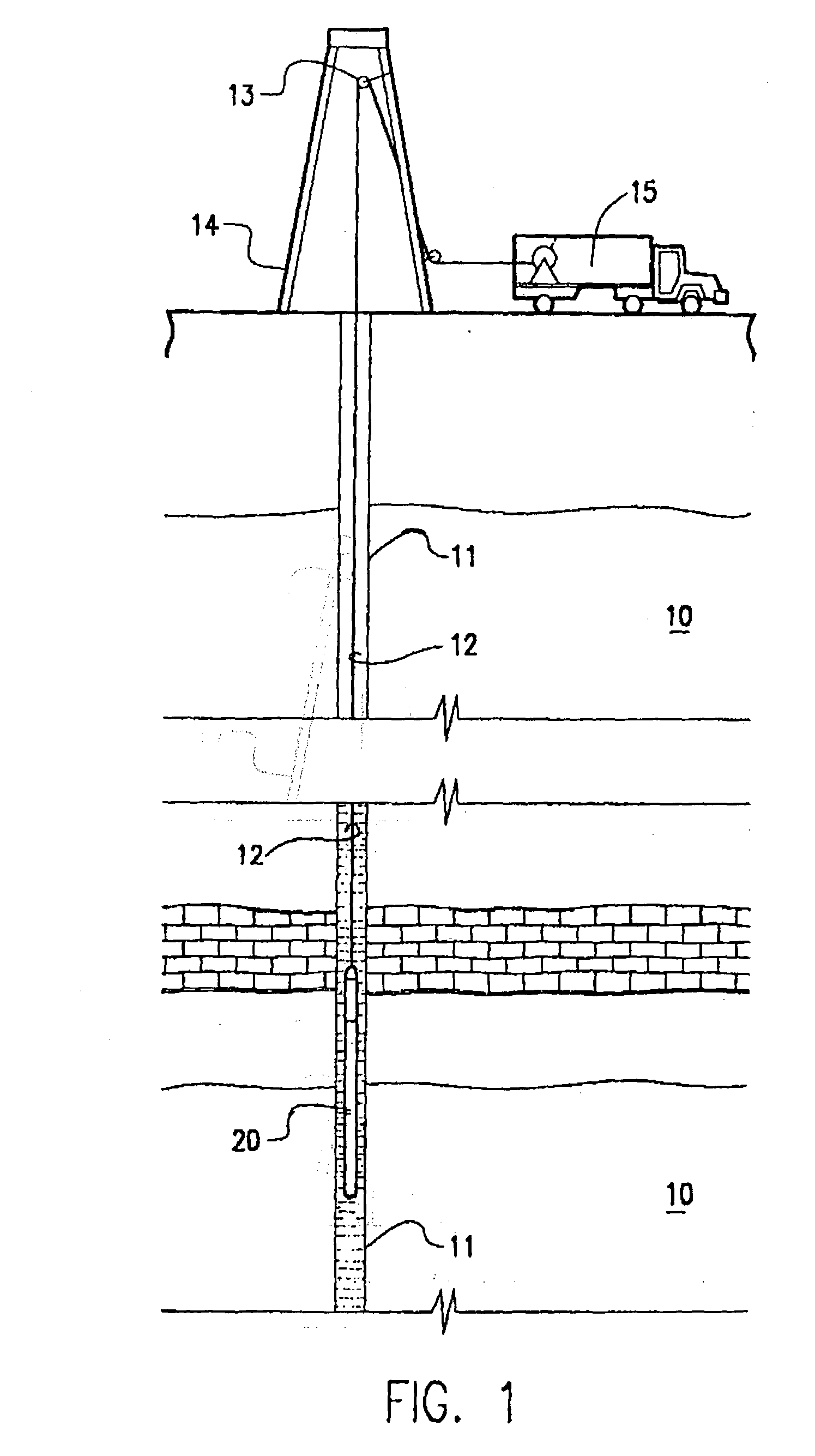
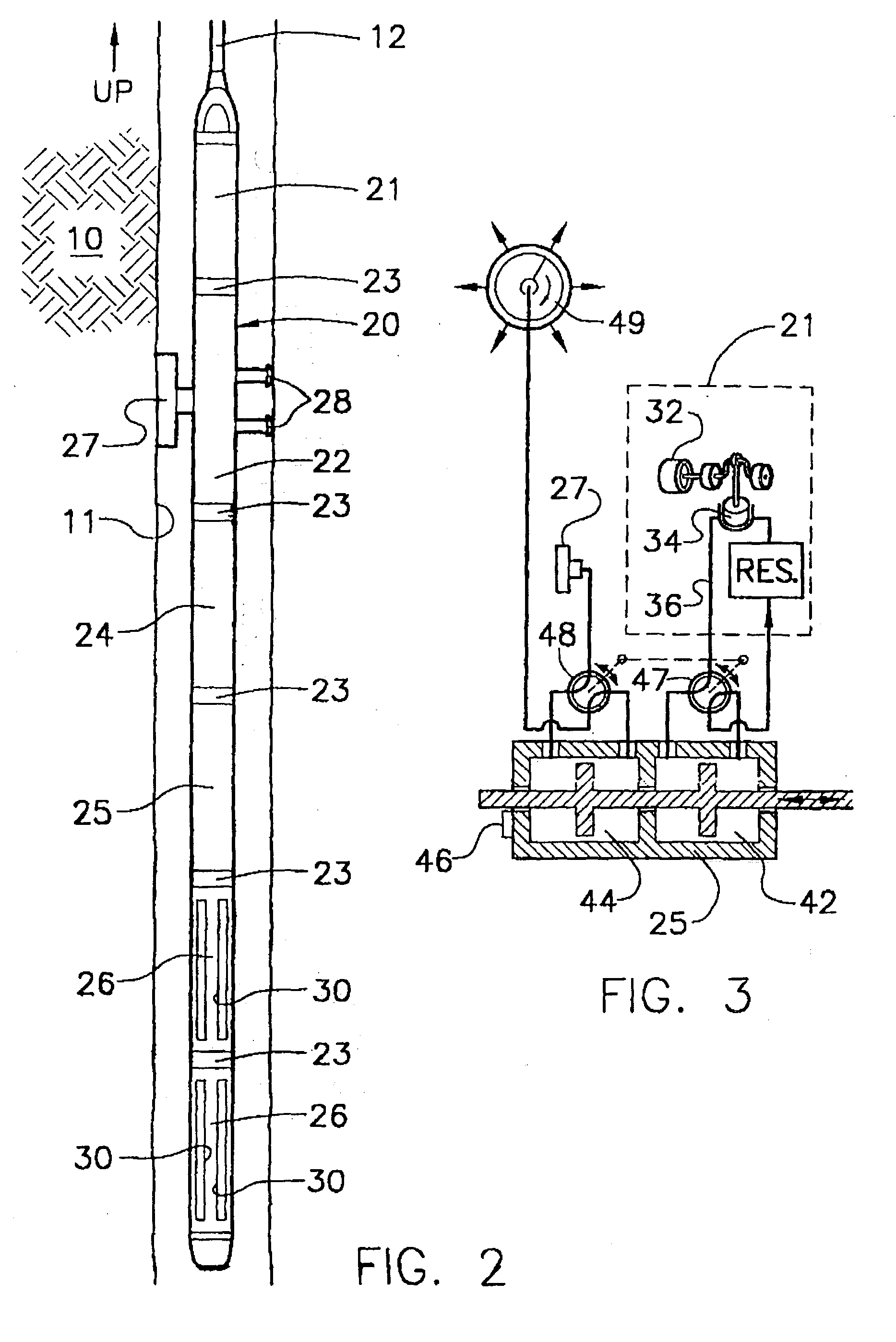
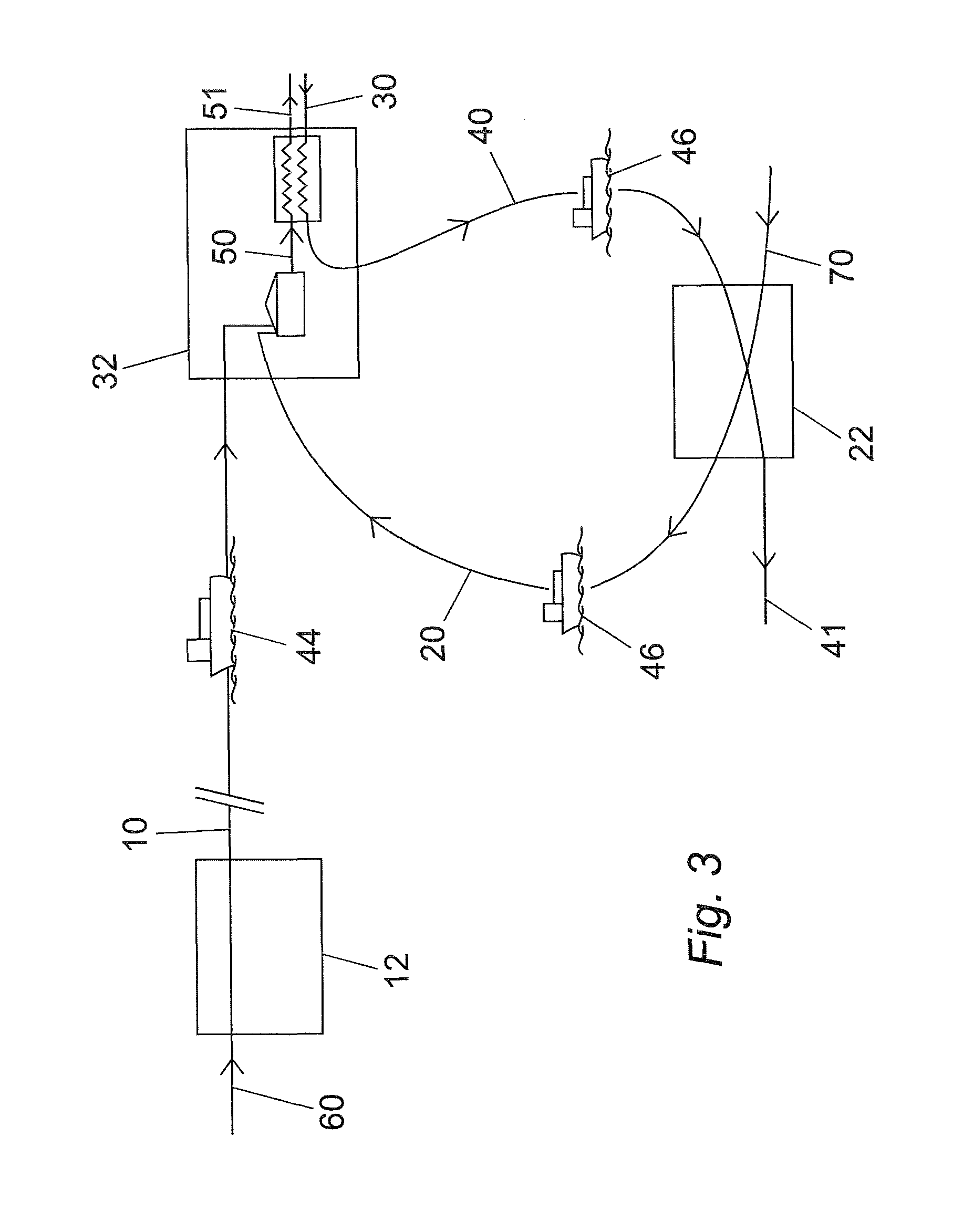
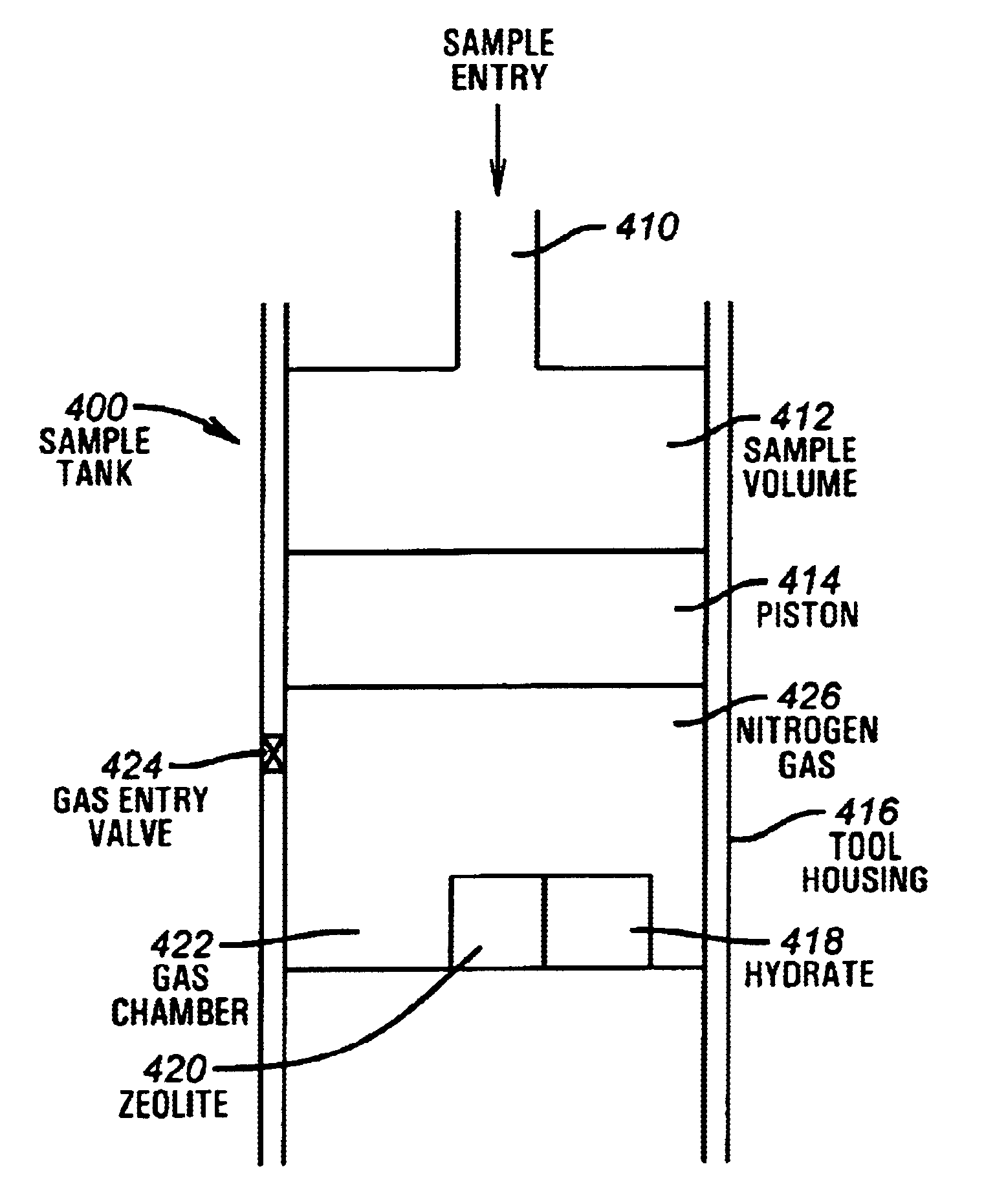
Method and apparatus for supercharging downhole sample tanks
A tank contains both Zeolite and a hydrate in a gas chamber formed beneath a piston in the sample tank. Out of safety considerations, we avoid using source cylinders of nitrogen whose pressures exceed 4000 psi. Thus, the gas chamber of the sample tank is initially pressurized by the source cylinder to no more than 4000 psi of nitrogen at room temperature at the surface. Nitrogen gas is sorbed onto the zeolite at room temperature. As the tank is heated by being lowered downhole, nitrogen desorbs from the zeolite and the gas pressure increases. However, once this tank reaches a temperature high enough to release the hydrate's water of hydration, the released water is preferentially sorbed by zeolite, displacing sorbed nitrogen, and causing the pressure in the gas volume to increase even further. Because well temperatures are not high enough to desorb water from zeolite, any water sorbed onto a Zeolite sorption site will permanently block released nitrogen from resorbing at that site. The process of lowering the tank downhole provides the necessary heating to make the entire process occur. Thus, if returned to the surface at room temperature with the original gas-chamber volume, the tank's pressure would not fall back to the original pressure (e.g., 4000 psi) but would be at a substantially higher pressure (e.g., 6000 psi or more depending on the amount of Zeolite used and gaseous nitrogen gas released).
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
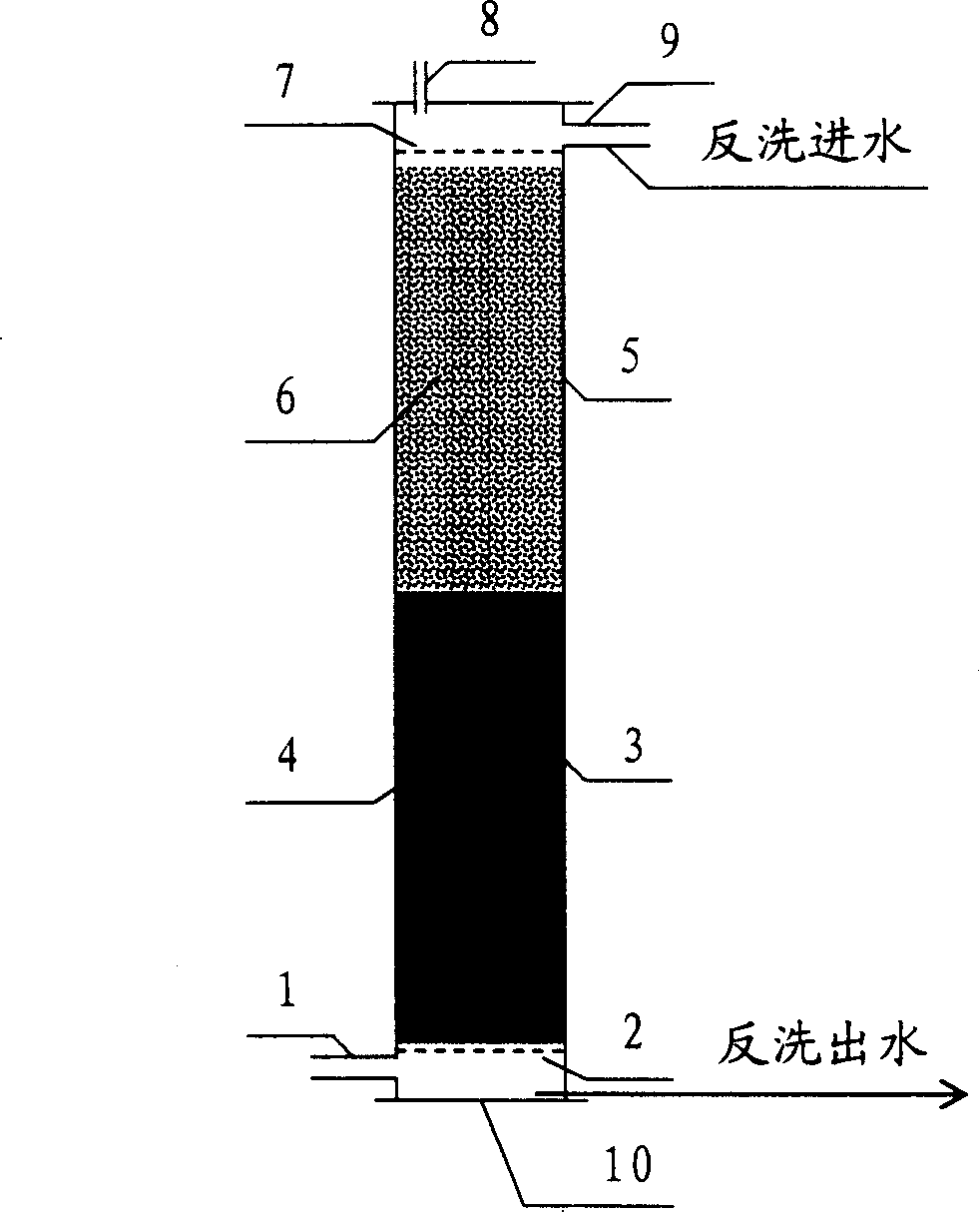
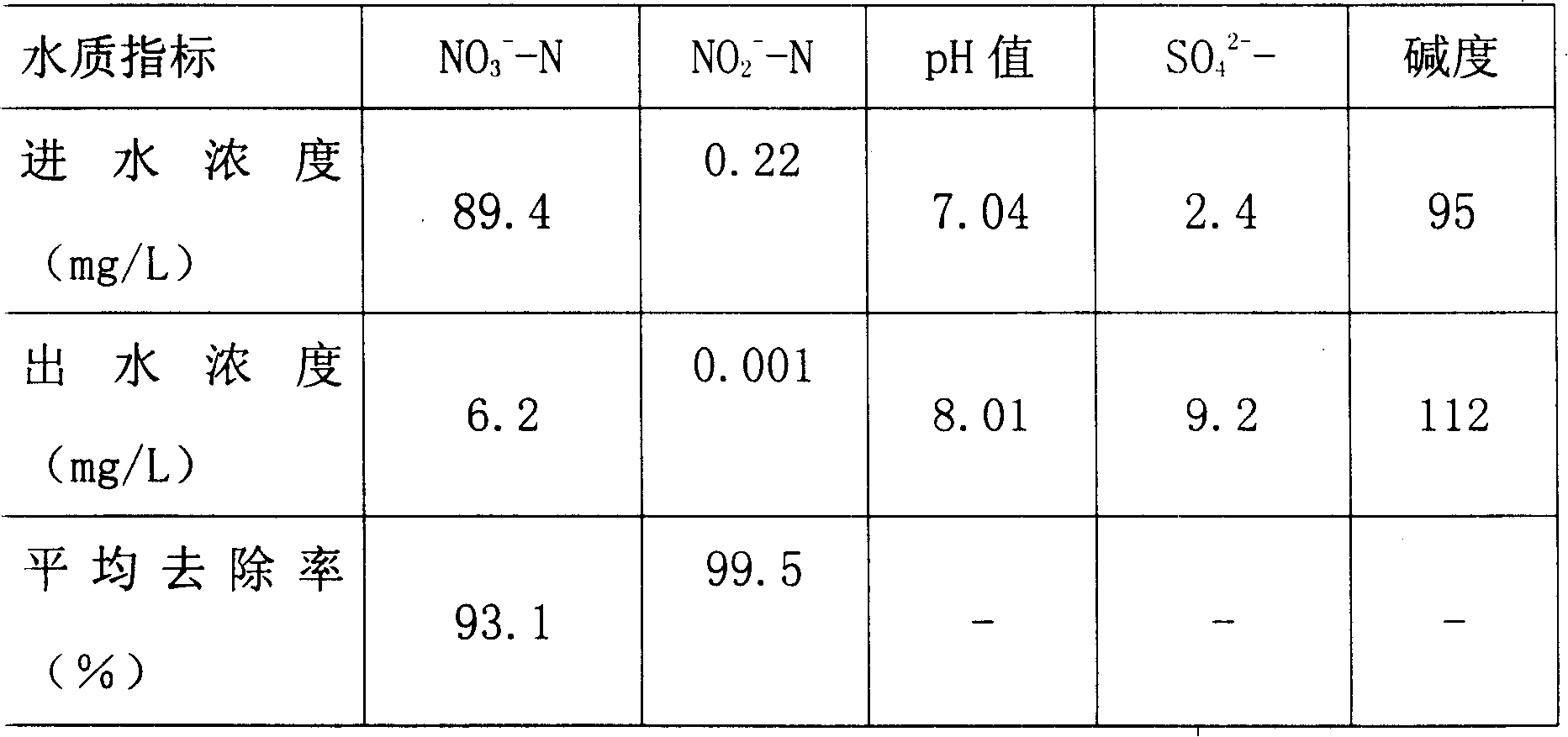
Method for removing nitrate nitrogen from aquaculture water
InactiveCN101200332AImprove effluent qualityEasy working condition controlTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesDevice formBiodegradable polymer
The invention relates to a method of removing nitrate in aquaculture water, relating to treat aquaculture water. The invention comprises a sulfur autotrophic denitrification and biodegradation polymer carbon source heterotrophic denitrification device, the invention is characterized in that: the sulfur autotrophic denitrification section and the biodegradation polymer carbon source heterotrophic section are series-connected from up to down according to the proportion of 1:1 to form a denitrifying device; after the integrated denitrifying device forms film, the aquaculture water enters from the water inlet of the lower part of the integrated denitrifying device, and flows through the filling layer of the sulfur autotrophic denitrification section from up to down to remove partial nitrate, the remained nitrate in the aquaculture water and the sulfate anion generated in the process of the sulfur autotrophic denitrification section enter the filling layer of the biodegradation polymer carbon source heterotrophic section, so as to remove the remained nitrate in the aquaculture water and also generate gaseous nitrogen, the reducing bacteria of the sulfate reduces the sulfate anion to hydrogen sulfur; the treated aquaculture water flows out from the water outlet of the lower part of the integrated denitrifying device; the gaseous nitrogen and hydrogen sulfur are exhausted from exhaust opening.
Owner:SHANGHAI FISHERIES UNIV
Apparatus for and method of processing substrate
InactiveUS20120073599A1Avoid damageLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCleaning using liquidsLiquid carbonAtmospheric pressure
A rinsing liquid adheres to a substrate subjected to a cleaning process. The rinsing liquid on the substrate is first replaced with IPA liquid. While the substrate covered with the IPA liquid is held in a dryer chamber, liquid carbon dioxide is supplied to the surface of the substrate. Liquid nitrogen is supplied to cool down the interior of the dryer chamber. This solidifies the liquid carbon dioxide on the substrate into solid carbon dioxide. Thereafter, the pressure in the dryer chamber is returned to atmospheric pressure, and gaseous nitrogen is supplied into the dryer chamber. Thus, the temperature in the dryer chamber increases. The solid carbon dioxide on the surface of the substrate is sublimated, and is hence removed from the substrate. All of the steps are performed while carbon dioxide is not in a supercritical state but in a non-supercritical state.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
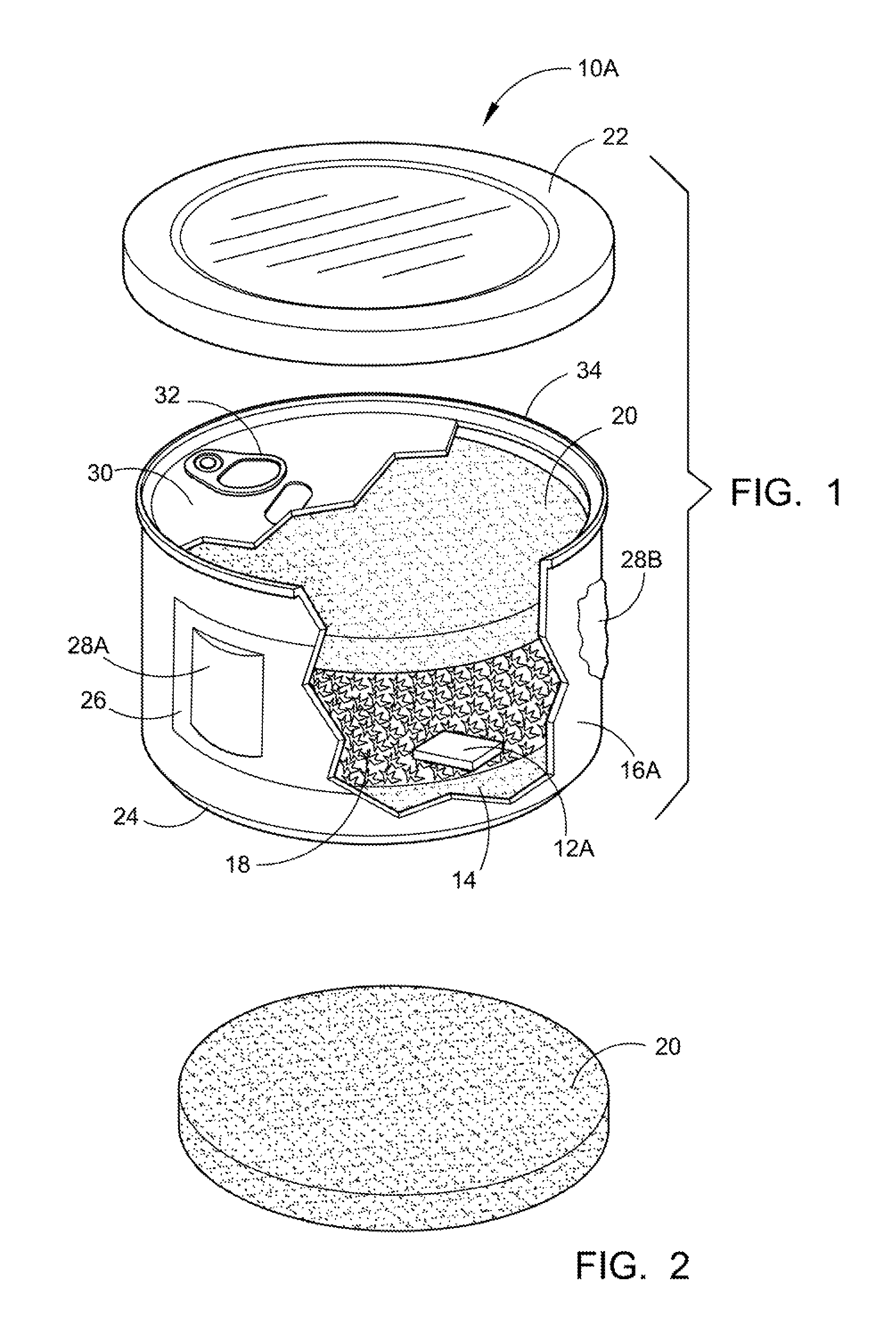
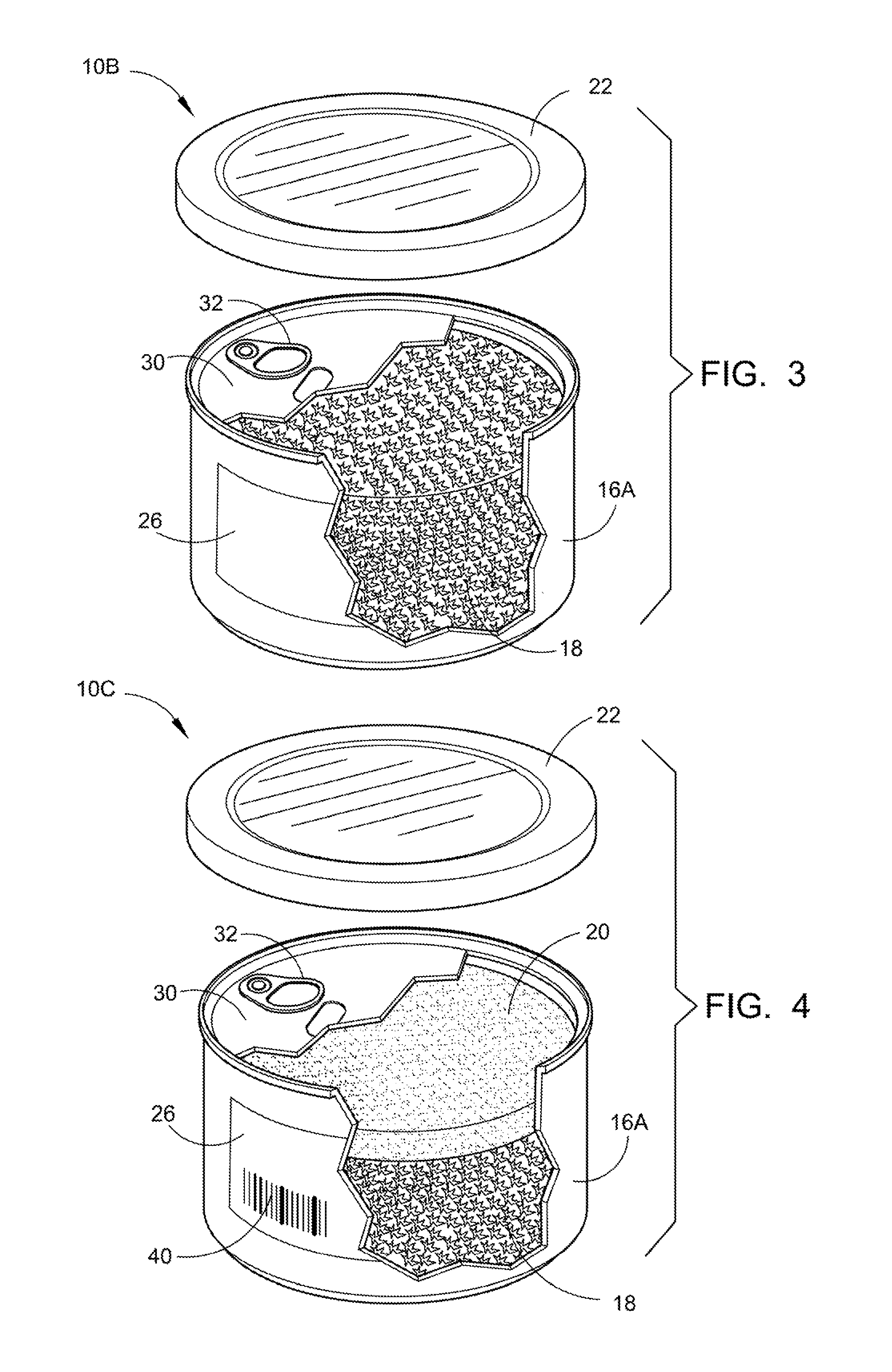
Storage preservation and transport for a controlled substance
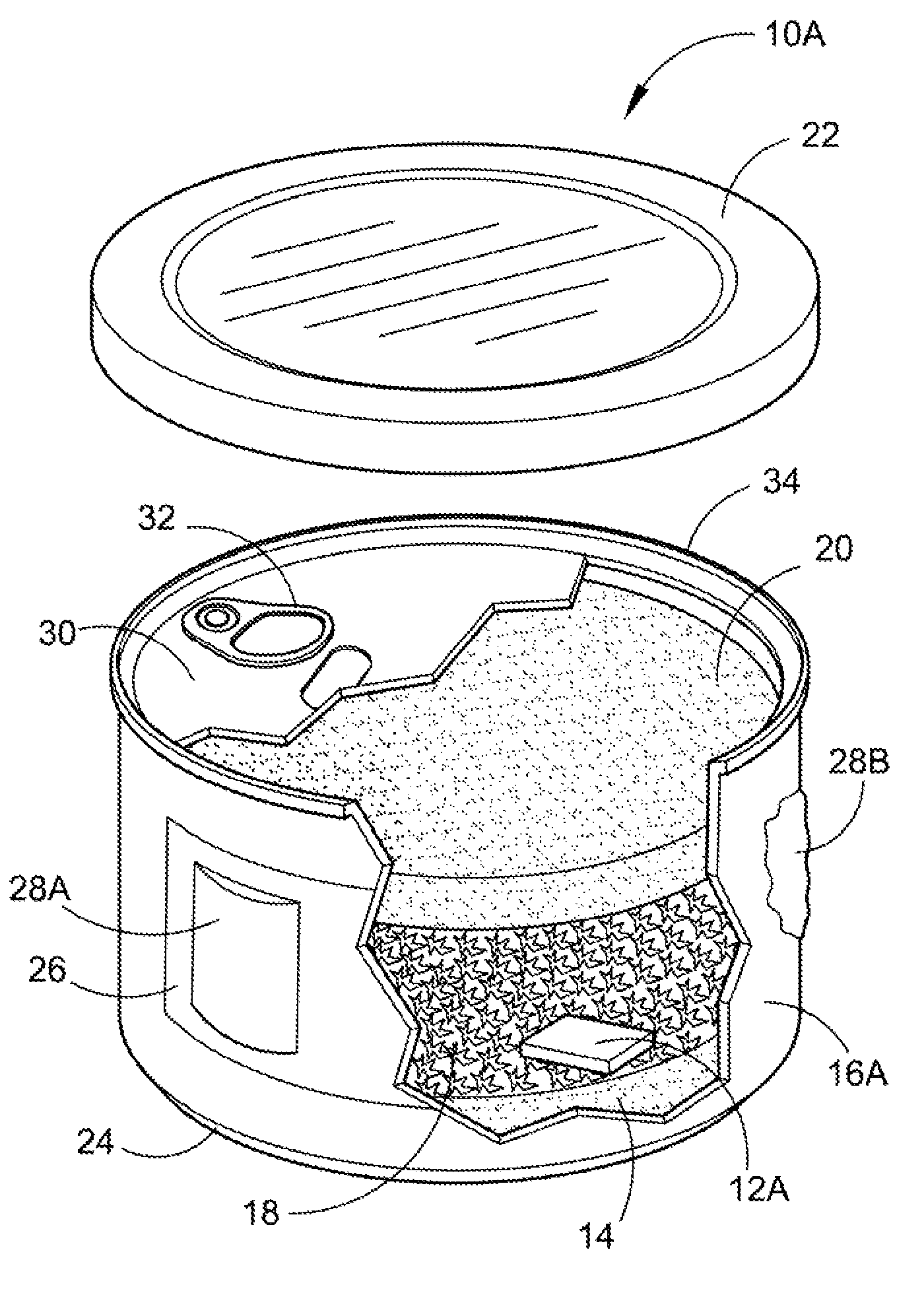
The present application provides a unique process of canning a controlled substance where the cans are hermetically sealed and clearly identified in a number of different ways. The process will begin by inserting a packing and dehumidifying agent, preferably a formed rice cake. The controlled substance is then inserted. In some cases the rice cakes will be eliminated or just a single rice cake will be used on the top or the bottom. If the process of storing the controlled substance in an inert atmosphere is desired, the oxygen in the container is replaced with gaseous nitrogen. After the container has been sealed in the conventional pop-top canning procedure; an identifying scent substance is permanently adhered to the can or label. An internal or external microchip could be used to detect, track and trace the container filled with a controlled substance.
Owner:N2 PACKAGING SYST LLC
Method for precision cleaning and drying flat objects
ActiveUS20090032062A1Improve accuracyKeep clean and drySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFlexible article cleaningLow speedPulp and paper industry
Cleaning and drying of semiconductor wafers is carried out in a single-chamber type cleaning / drying apparatus for flat objects such as semiconductor wafer, where cleaning is carried out by impinging both sides of the wafer which rotates at a relatively low speed with jets of a washing liquid and where subsequent drying is carried out in the same chamber by increasing the rotation speed of the wafer and supplying an isopropyl-alcohol (IPA) mist onto the wafer from the top of the chamber. After the IPA forms a solution with the residue of water on the wafer, the drying process is accelerated by supplying gaseous nitrogen through nozzles arranged on both side of the coaxial with the wafer center. As a result, the IPA-water solution quickly evaporates without leaving traces of water drops on the dried surface.
Owner:PLANAR SEMICON CORP PTE LTD
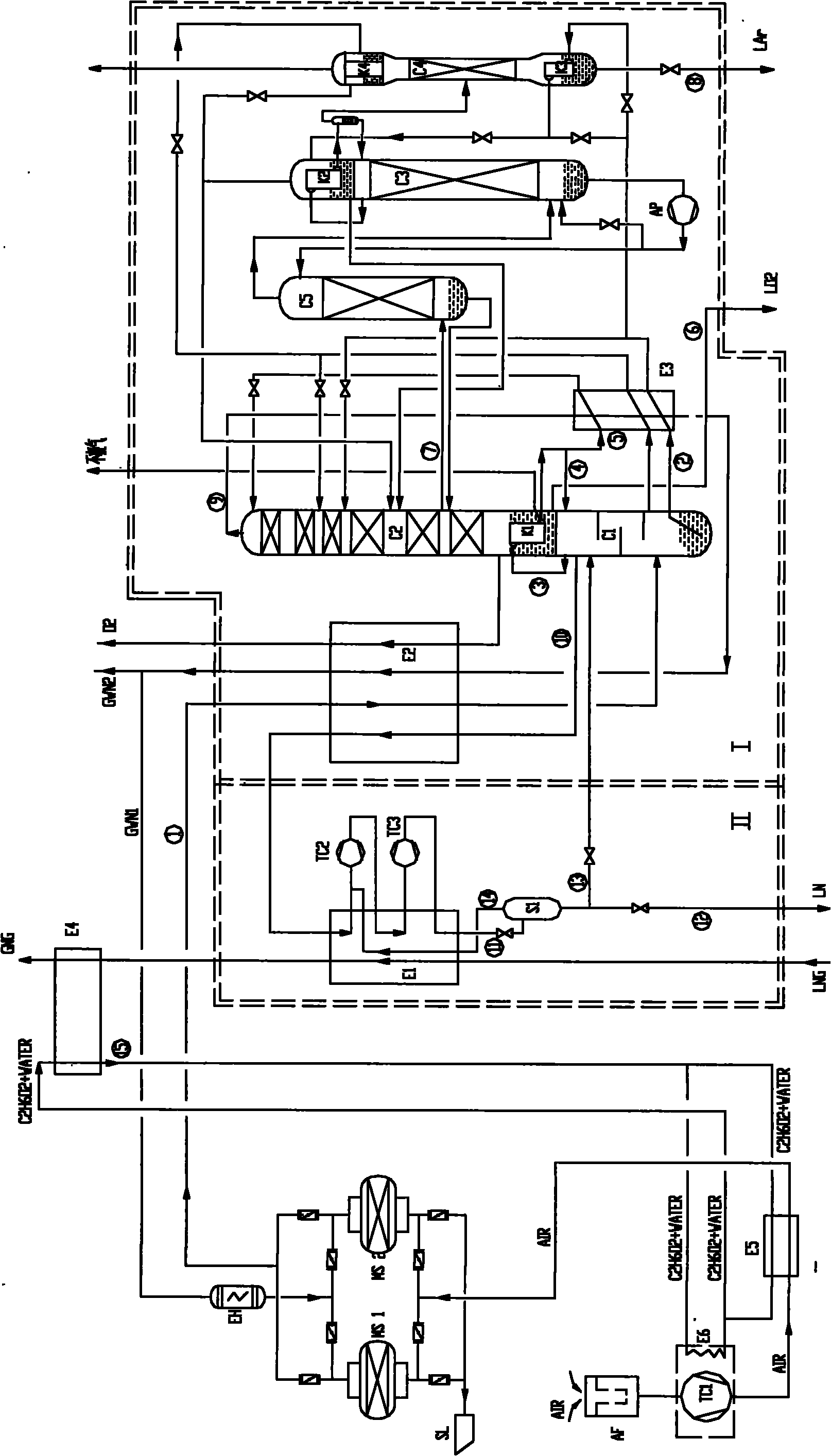
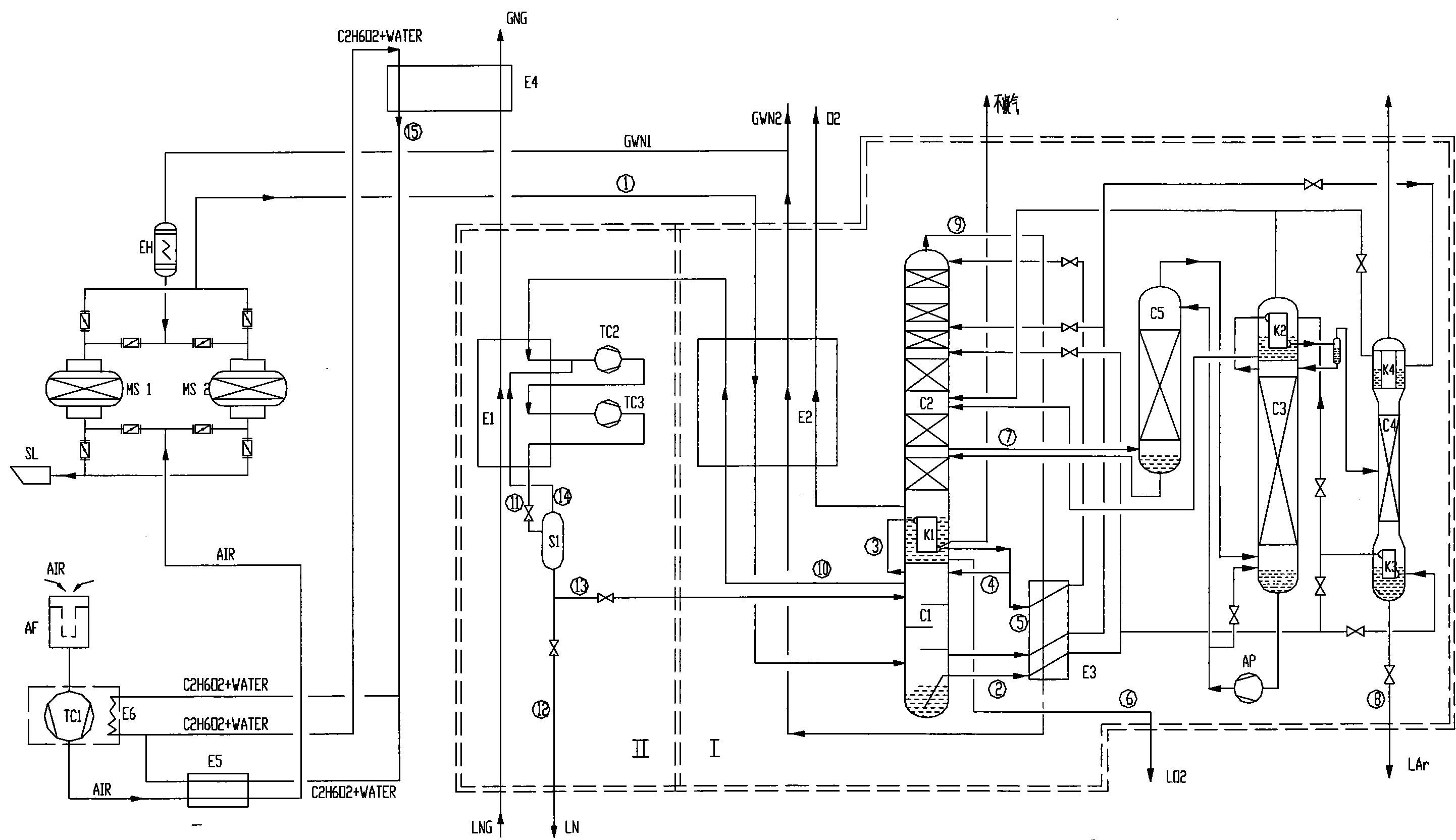
Full-liquid air separation device using cold energy of liquefied natural gas (LNG)
InactiveCN101846436ACompact structureImprove heat transfer efficiencySolidificationLiquefactionComing outAir cleaning
The invention disclose a full-liquid air separation device using the cold energy of the liquefied natural gas (LNG), comprising an air compressing and pre-cooling system, an air purifying system, an air separating system and a nitrogen circulating system capable of recycling the cold energy of the LNG which has the pressure of 8.0MPa or higher. The nitrogen circulating system capable of recycling the cold energy of the LNG comprises a nitrogen compressor, a wound tube heat exchanger and a gas-liquid separator; the gaseous nitrogen coming out of the gas separating system is made to enter the wound tube heat exchanger to exchange heat with the LNG and then is compressed by the nitrogen compressor to have higher pressure; the liquid nitrogen coming out of the wound tube heat exchanger is separated into gaseous nitrogen and liquid hydrogen; the liquid nitrogen coming out of the gas-liquid separator is separated into two branches, wherein one branch of the liquid nitrogen is fed in the air separating system to be used as the return liquid of a lower tower to involve in the rectification of the lower tower and to be made to carry the cold energy in the air separating system, and the other branch of the liquid nitrogen is discharged as the liquid nitrogen product; the gaseous nitrogen coming out of the gas-liquid separator is made to enter the wound tube heat exchanger and reheated to the temperature of the inlet of the nitrogen compressor and then made to enter the nitrogen compressor to circulate. Compared with the prior air separation device of the same scale, the full-liquid air separation device can save the electric energy of more than 50 percent and the consumed water of more than 90 percent.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
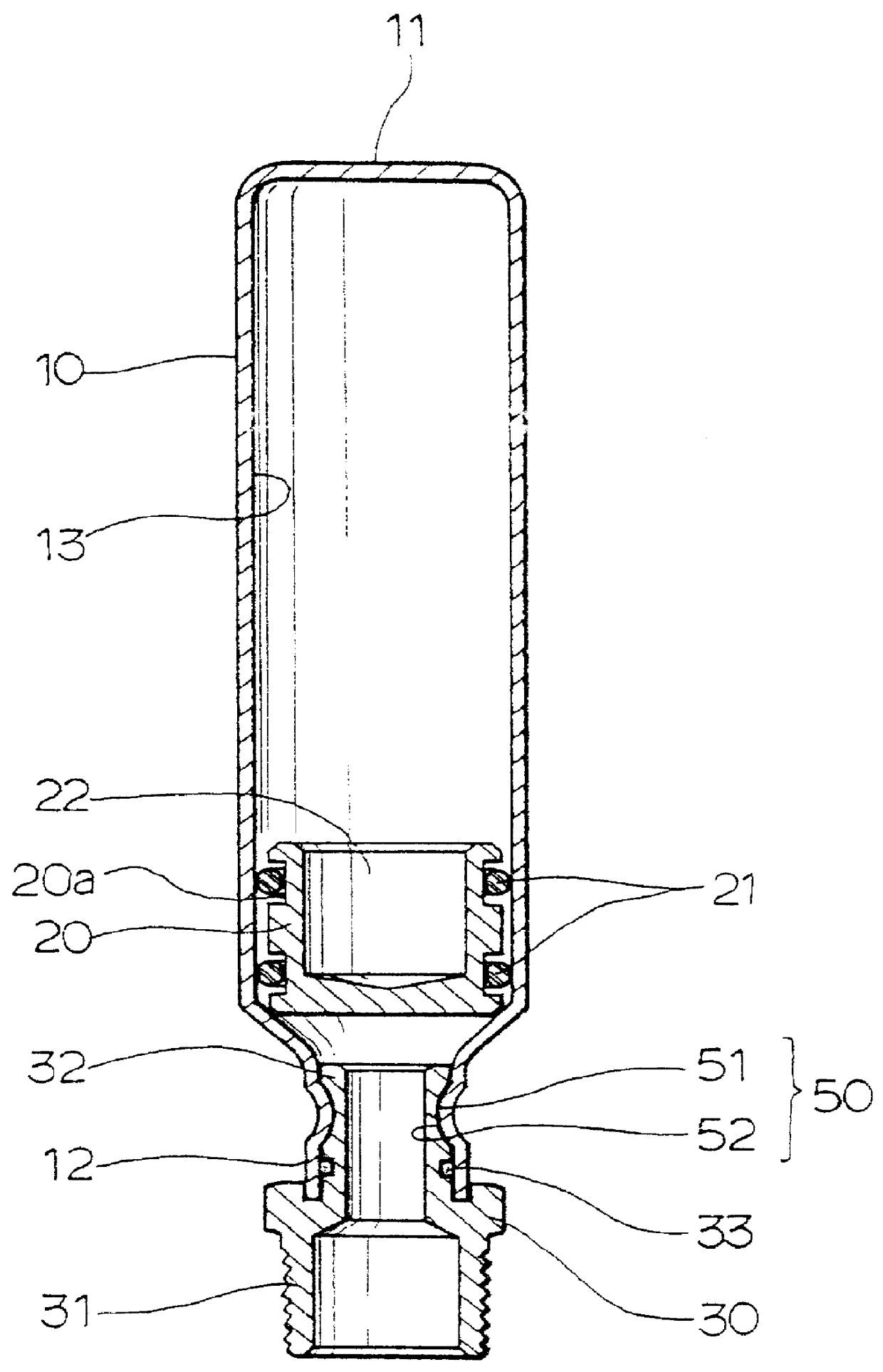
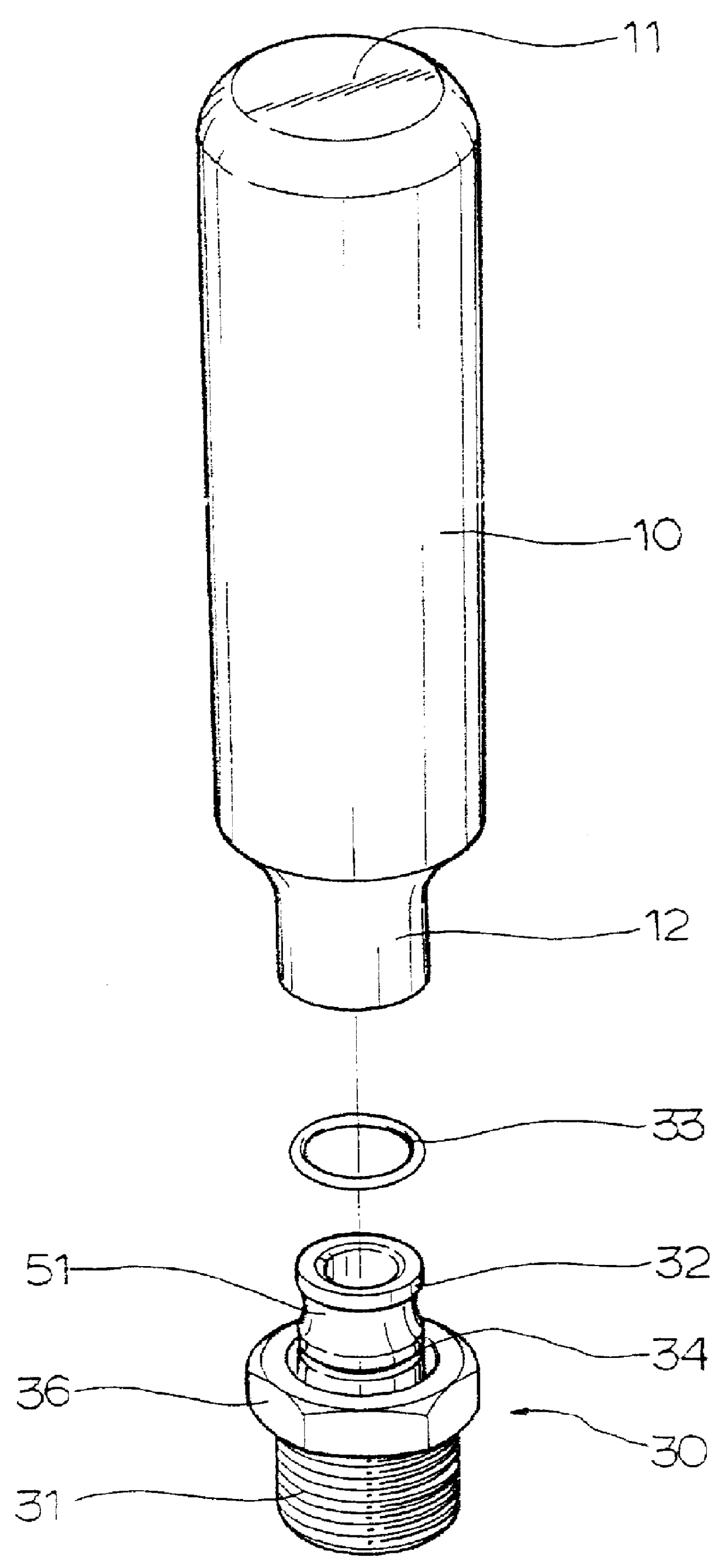
Water hammer arrester
A water hammer arrester constructed with a cylindrical housing having a closed upper end and an internal pressure chamber. A piston slidably installed within the housing to receive a reaction force medium such as gaseous nitrogen, provides a space that communicates with an integral pressure chamber within the closed upper end of the housing. A threaded connector bearing a nipple circumscribed with a plurality of circumferential grooves is crimped into the neck of the lower end of the housing.
Owner:AH U
Nitride semiconductor growth method, nitride semiconductor substrate, and nitride semiconductor device
InactiveUS20030037722A1Polycrystalline material growthLaser detailsCrystallographic defectNitride semiconductors
A method of growing a nitride semiconductor crystal which has very few crystal defects and can be used as a substrate is disclosed. This invention includes the step of forming a first selective growth mask on a support member including a dissimilar substrate having a major surface and made of a material different from a nitride semiconductor, the first selective growth mask having a plurality of first windows for selectively exposing the upper surface of the support member, and the step of growing nitride semiconductor portions from the upper surface, of the support member, which is exposed from the windows, by using a gaseous Group 3 element source and a gaseous nitrogen source, until the nitride semiconductor portions grown in the adjacent windows combine with each other on the upper surface of the selective growth mask.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
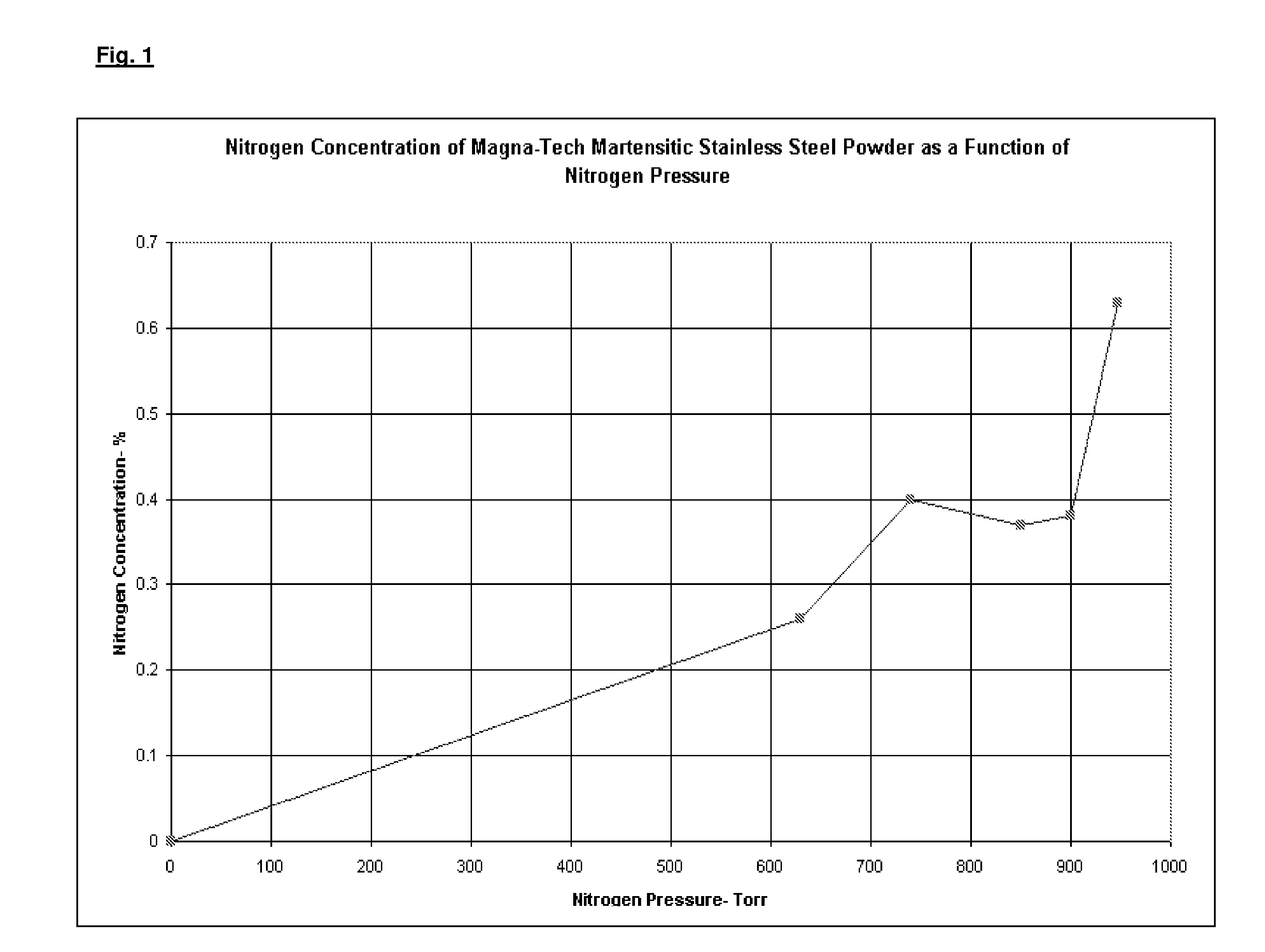
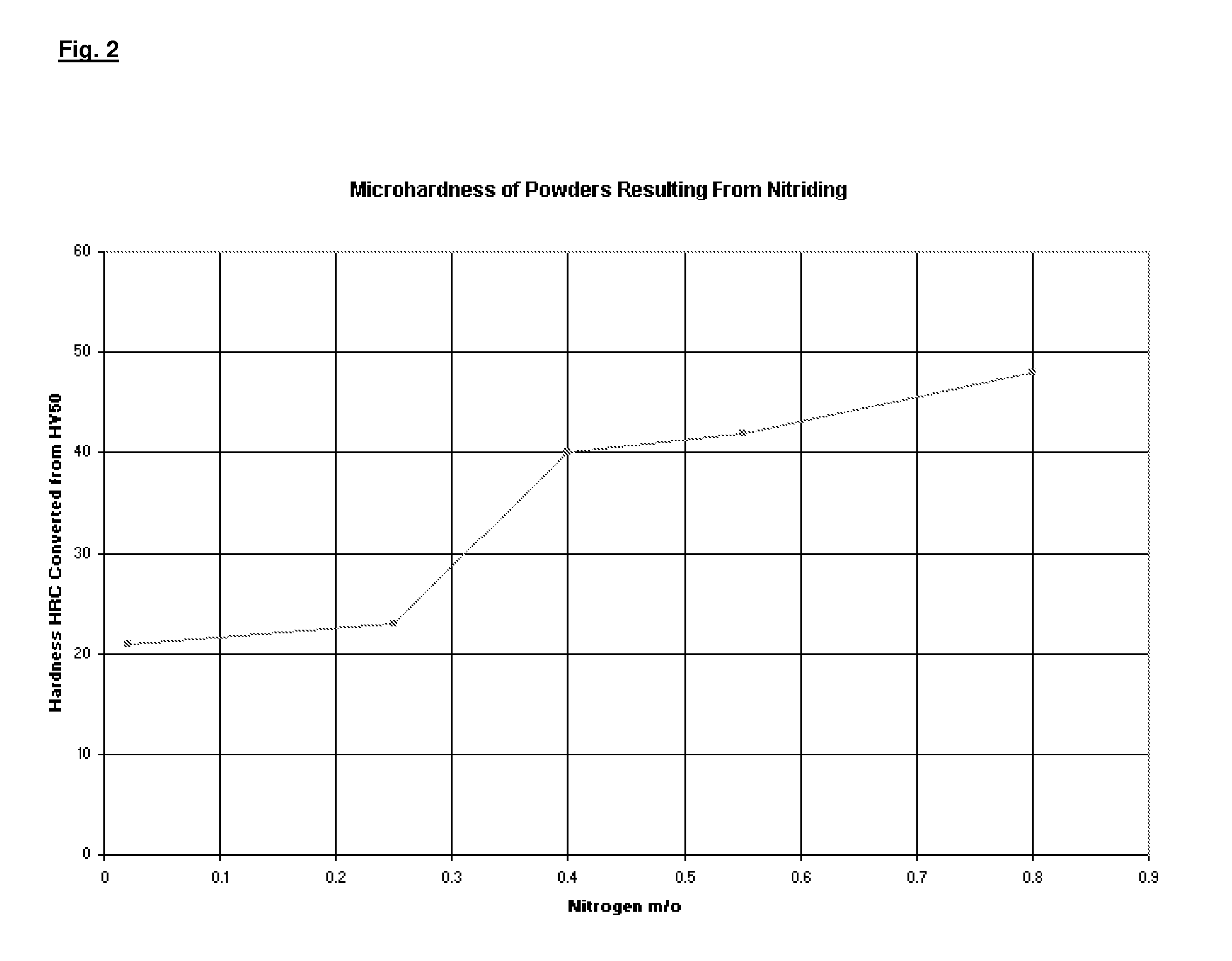
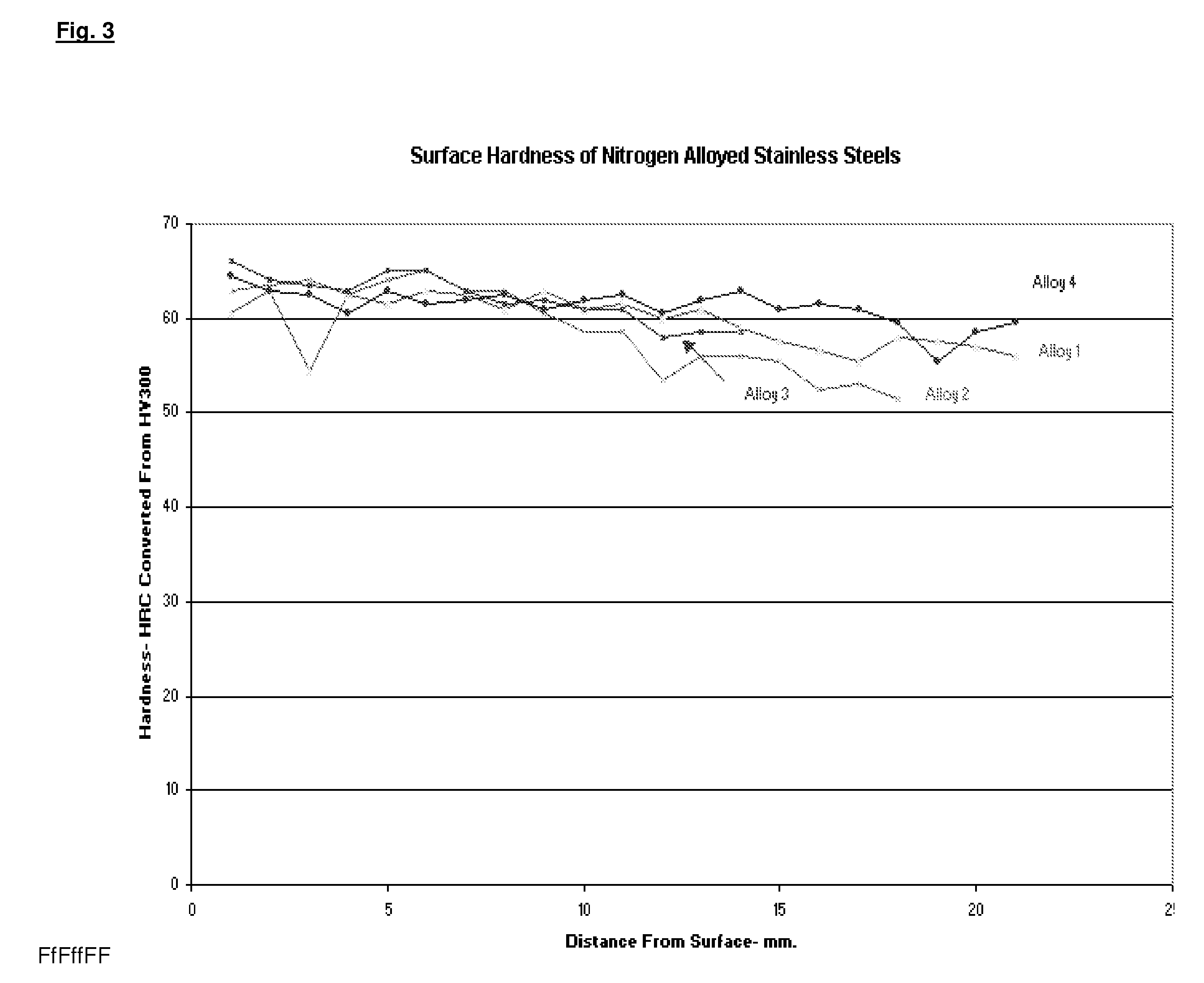
Nitrogen alloyed stainless steel and process
InactiveUS20120082586A1Improved kineticsIncrease resistanceSolid state diffusion coatingMetal layered productsMartensitic stainless steelSS - Stainless steel
The present invention comprises the nitridization of stainless steel with a gaseous nitrogen compound such as nitrogen gas (N2), or ammonia (NH3) at high temperature wherein the reaction pressure is lowered. A base powder with properties similar to those of a martensitic stainless steel is prepared from a molten metal with the subsequent incorporation of selective additives such as cobalt, chromium, boron, copper, vanadium, niobium and mixtures thereof to improve high temperature resistance to scuffing and adhesive wear. The molten mixture is then atomized by water- or air-atomization to yield a base powder which is mixed with nitrogen or ammonia gas at various pressures in a static or fluidized bed to provide a nitrogen alloyed particulate, i.e., a nitrided particulate alloy. The powder is heated in a hot isostatic press under vacuum with argon gas at reduced pressure and later cooled to ambient (room) temperature. A second embodiment of the invention also comprises the use of a wrought iron-based stainless steel or casting as the starting material to be nitrided.
Owner:MAGNA TECH PM LABS
Preparation method of nitrogen-doped graphene
ActiveCN102887498ASimple production processReduce manufacturing costGrapheneDoped grapheneNitrogen doped graphene
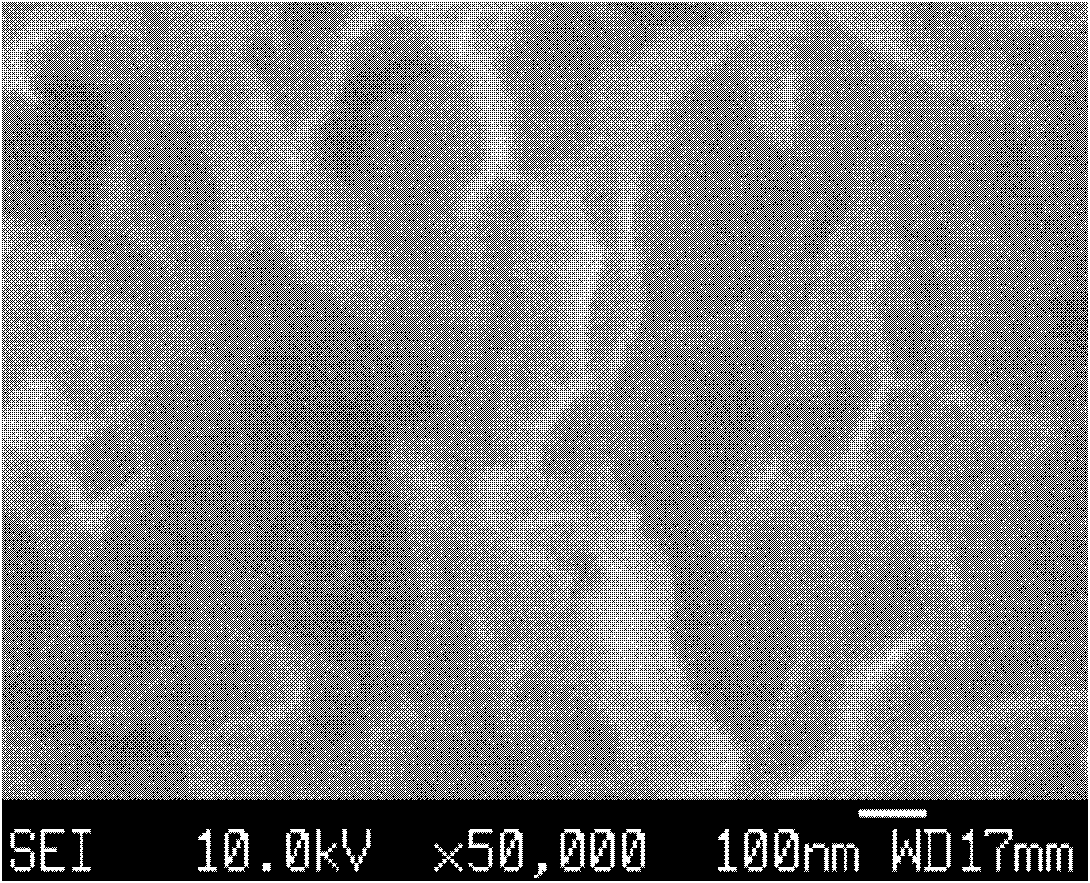
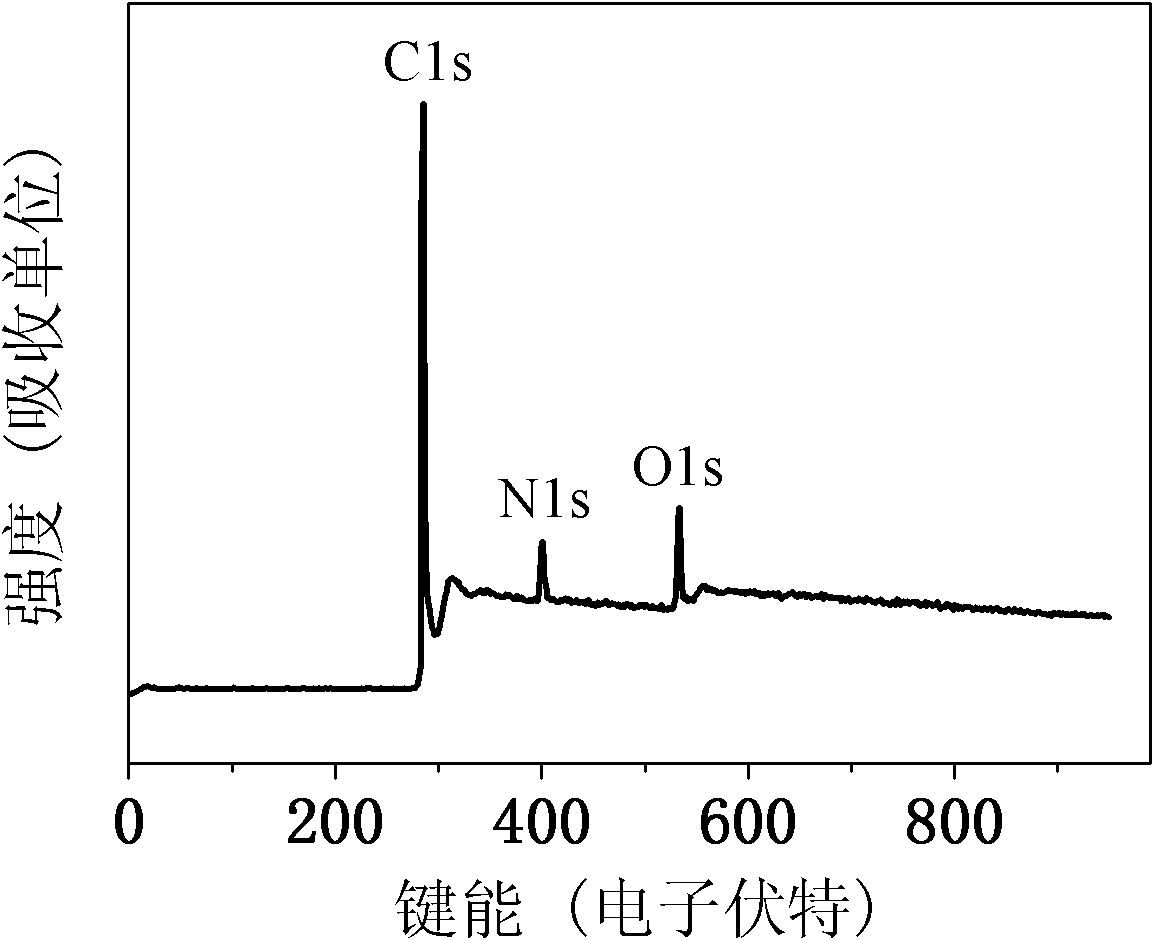
The invention provides a preparation method of nitrogen-doped graphene by a chemical vapor deposition method, which comprises the following steps of: providing a substrate with high temperature resistance, and a solid and / or liquid organic carbon source compound; preparing the organic carbon source compound into solution or suspension; coating the solution or suspension of the organic carbon source compound on the surface of the substrate; heating the substrate coated by solution or suspension containing the organic carbon source compound to 500-1300 DEG C under an oxygen-free and vacuum environment, then leading into gaseous nitrogen compound to react to obtain nitrogen-doped graphene. The preparation method of nitrogen-doped graphene provided by the invention prepares the solid and / or liquid organic carbon source compound into solution or suspension and coats directly on the surface of the substrate to make the organic carbon source compound react with the introduced nitrogen compound. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of having no need of adding a catalyst, simplifying the production process of nitrogen-doped graphene effectively and reducing the production cost. At the same time, the nitrogen-doped graphene prepared by the chemical vapor deposition method enables the doped graphene to be controlled easily in the amount, to be doped uniformly and to be high in electrochemical stability.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
Integration of a liquefied natural gas liquefier with the production of liquefied natural gas
InactiveUS20130205828A1Improve efficiencyLowering net power consumptionSolidificationLiquefactionFractionating columnNitrogen gas
A method for integrating a liquefied natural gas liquefier system with production of liquefied natural gas from a methane-containing gas stream. The liquefied natural gas is produced by feeding a methane-containing gas stream through a heat exchanger to a distillation column and liquefying the natural gas while capturing the gaseous nitrogen. The liquefied natural gas is captured and the nitrogen gas is recovered, fed through the heat exchanger to recover cold and purified.
Owner:LINDE AG
Method for producing silicon nitride films
ActiveUS8357430B2Improve film propertiesIncrease resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenGas phase
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
Nozzle cleaning device and substrate treating device
ActiveCN1669680AEasy dischargeEfficient dischargeLiquid surface applicatorsSpraying apparatusSuction forceEngineering
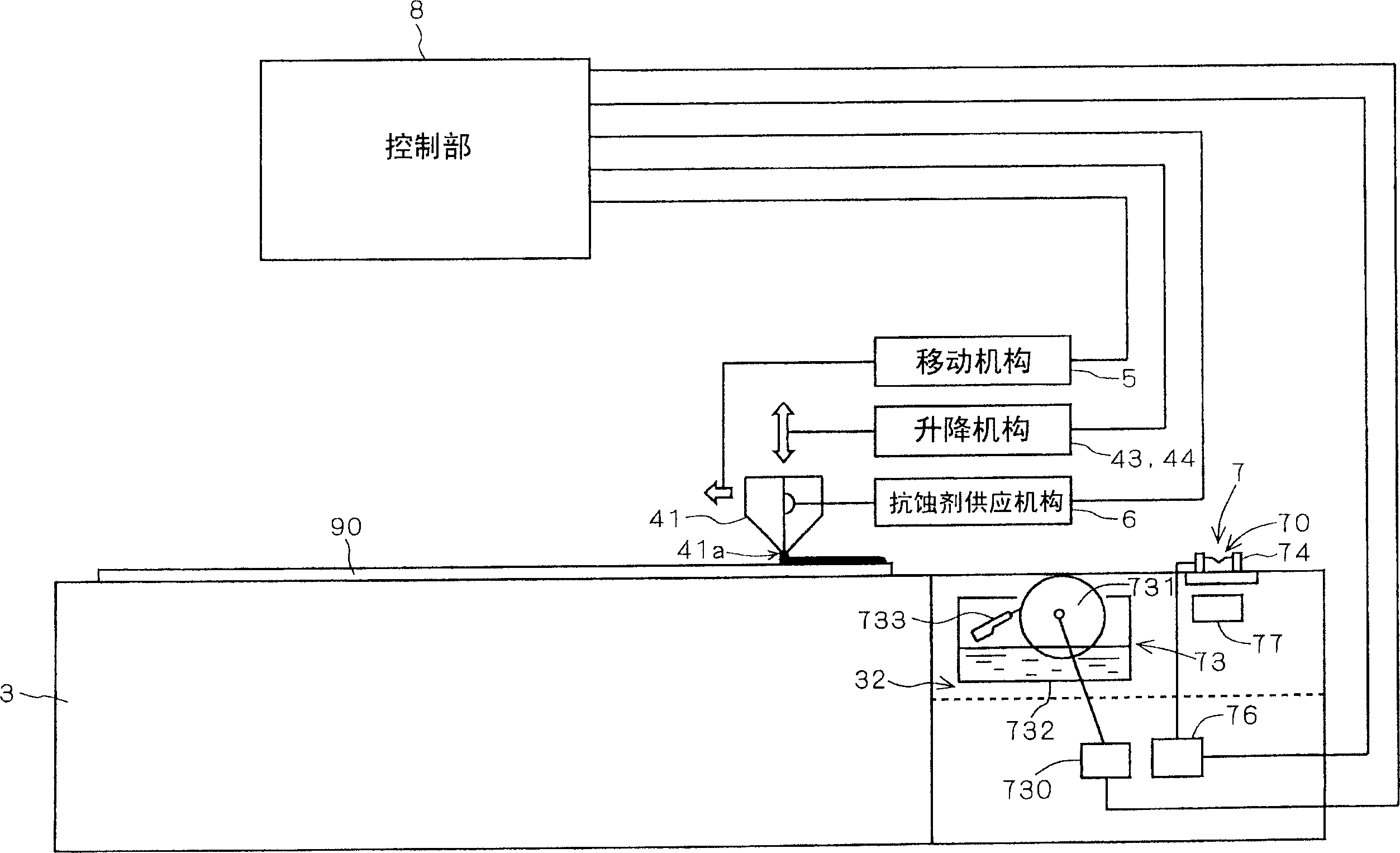
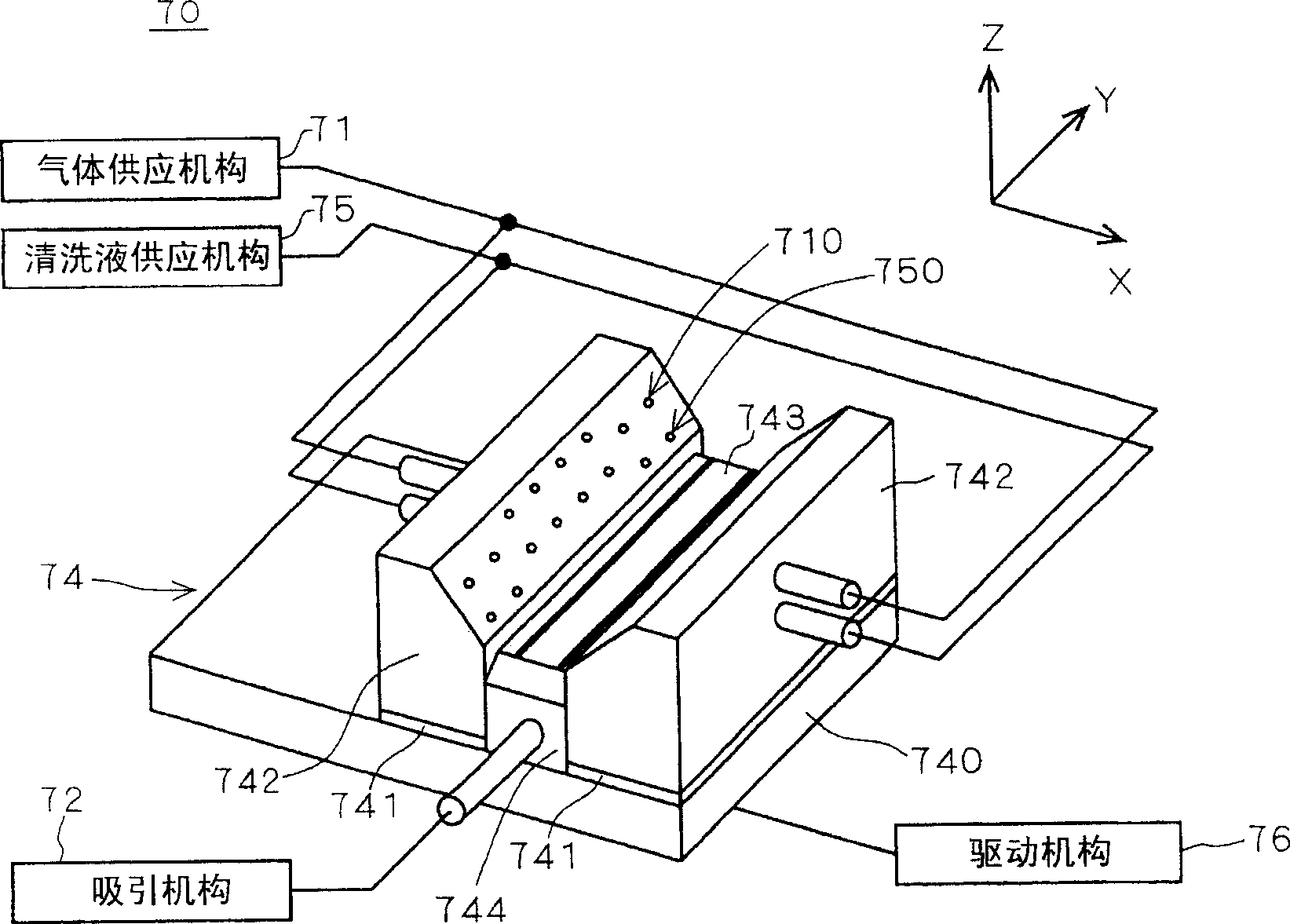
To improve washing effect in washing treatment of a discharge nozzle. A guide block 743 for approaching below a discharge port 41a of a slit nozzle 41 is provided at a washing section 74 for washing a slit nozzle 41. Gas nozzles 710 for blowing gaseous nitrogen and washing nozzles 750 for ejecting rinse liquid LQ are provided and further a suction mechanism sucks the lower part of the discharge port 41a of the slit nozzle 41. Thickness of the guide block 743 in a X-axis direction is made to be larger than the width of the discharge port 41a in the X-axis direction, and thereby adjustment is performed so that suction force by the suction mechanism may not directly act on the discharge port 41a. Thereby suction force of the suction mechanism can be raised and washing effect is improved.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
Storage preservation and transport for a controlled substance
ActiveUS20120061263A1Limit saleContainer decorationsLevel indicationsHermetic sealControl substances
The present application provides a unique process of canning a controlled substance where the cans are hermetically sealed and clearly identified in a number of different ways. The process will begin by inserting a packing and dehumidifying agent, preferably a formed rice cake. The controlled substance is then inserted. In some cases the rice cakes will be eliminated or just a single rice cake will be used on the top or the bottom. If the process of storing the controlled substance in an inert atmosphere is desired, the oxygen in the container is replaced with gaseous nitrogen. After the container has been sealed in the conventional pop-top canning procedure; an identifying scent substance is permanently adhered to the can or label. An internal or external microchip could be used to detect, track and trace the container filled with a controlled substance.
Owner:N2 PACKAGING SYST LLC
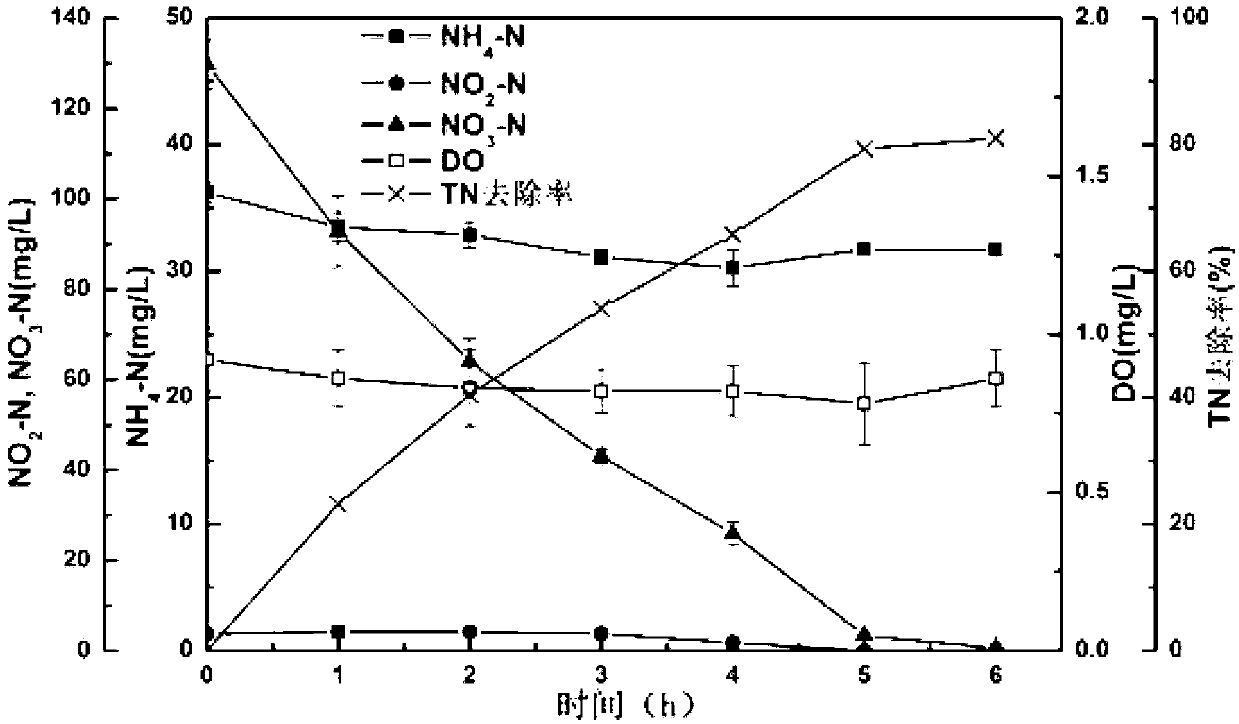
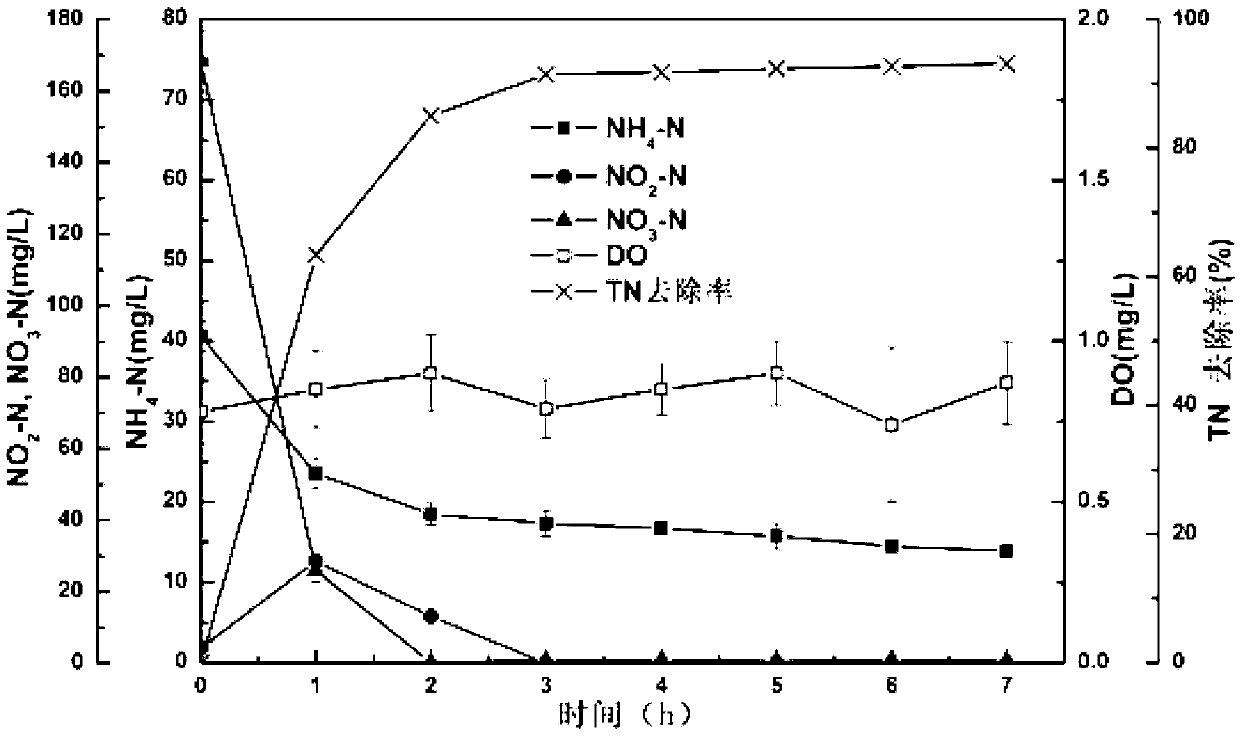
Enrichment of low temperature-resistant heterotrophic simultaneous nitrification-denitrification microbial agent and application thereof in anoxic denitrification of sewage
ActiveCN103342417ABeyond the denitrification effectGood denitrification effectTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesSodium acetateMicrobial agent
The invention relates to enrichment of a low temperature-resistant heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic / anoxic denitrification microbial agent and application thereof in wastewater treatment under an anoxic condition. The microbial agent is capable of realizing simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in an aerobic or anoxic environment, in the presence of both ammonia nitrogen and nitrate, with sodium acetate as a unique organic carbon source under a 10 DEG C low-temperature condition; therefore, inorganic nitrogen in wastewater is transformed into gaseous nitrogen and removal of total nitrogen is realized. The low temperature-resistant microbial agent thoroughly realizes maintenance and stabilization of activity of aerobic nitrification and heterotrophic denitrification bacteria under the low-temperature condition, and also has a very high total nitrogen removal rate under an anoxic condition. Besides, the heterotrophic microbial agent grows quickly and lays a good foundation for quick amplification and actual application. When applied to practical town sewage treatment, the microbial agent is capable of efficiently removing total nitrogen in the low-temperature environment under the single anoxic condition; and therefore, the problem that a traditional treating plant hardly reaches the national class A emission standard of total nitrogen in winter is solved and the utilization potentiality of the microbial agent is huge.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
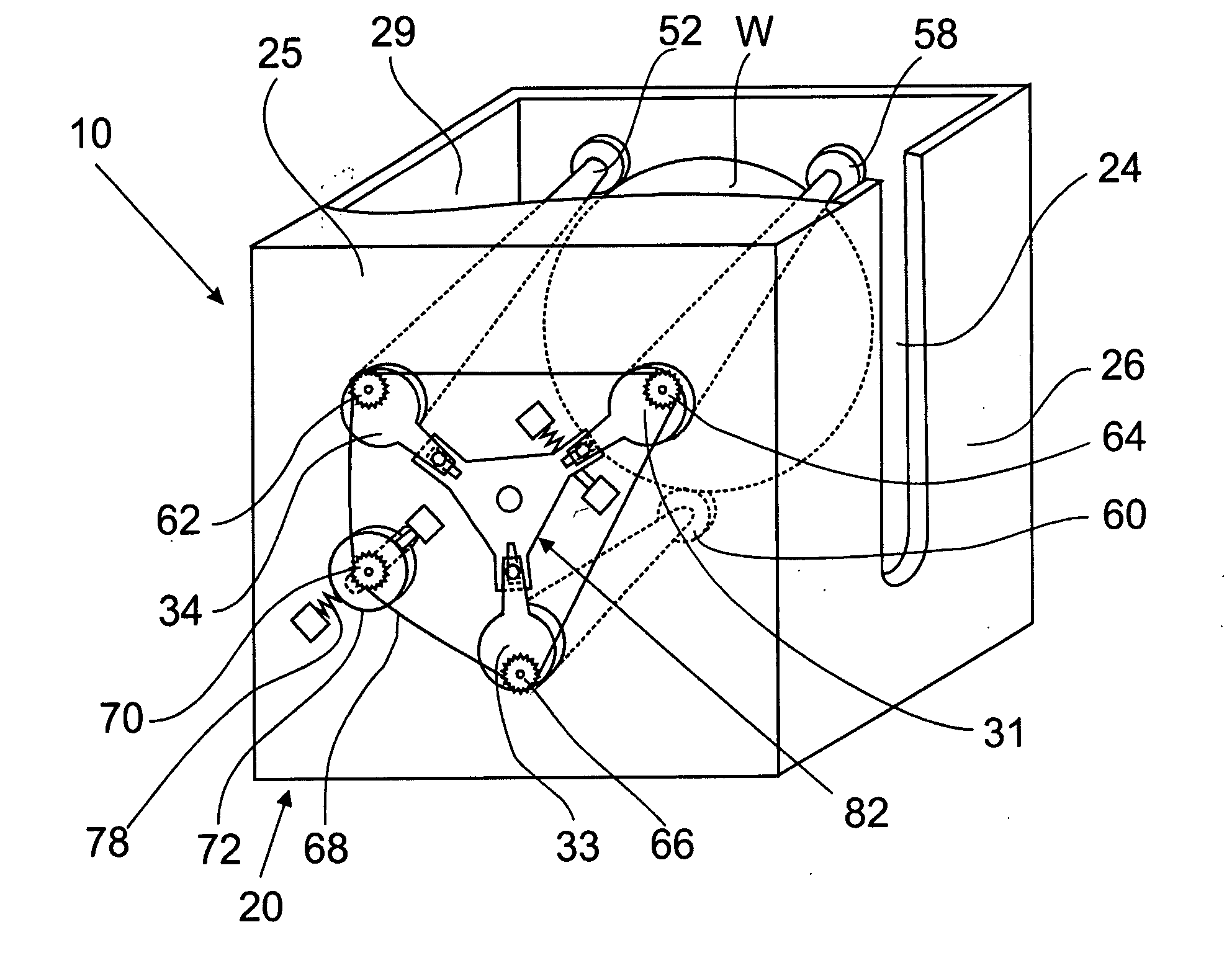
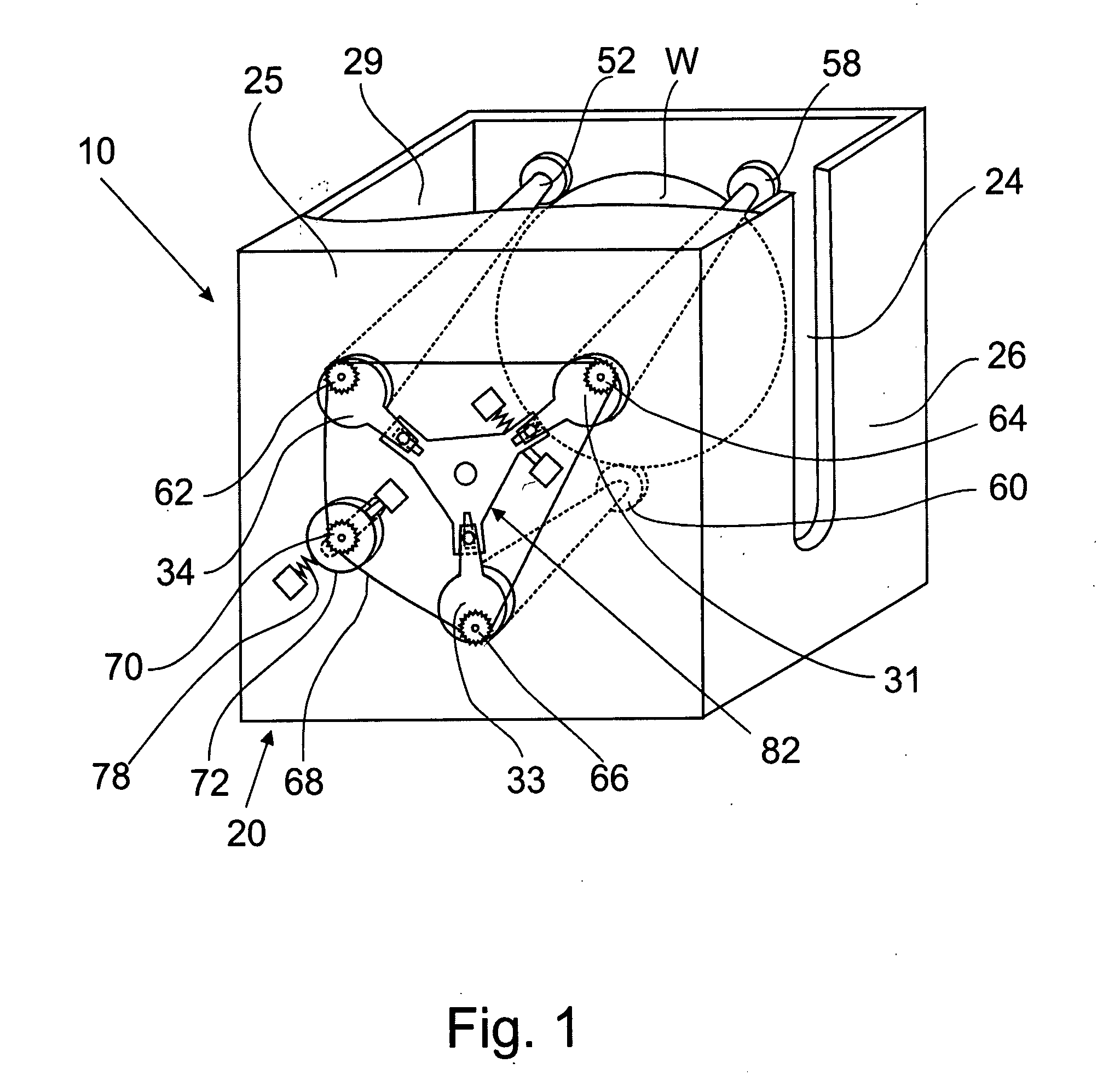
Seal device for tubular member
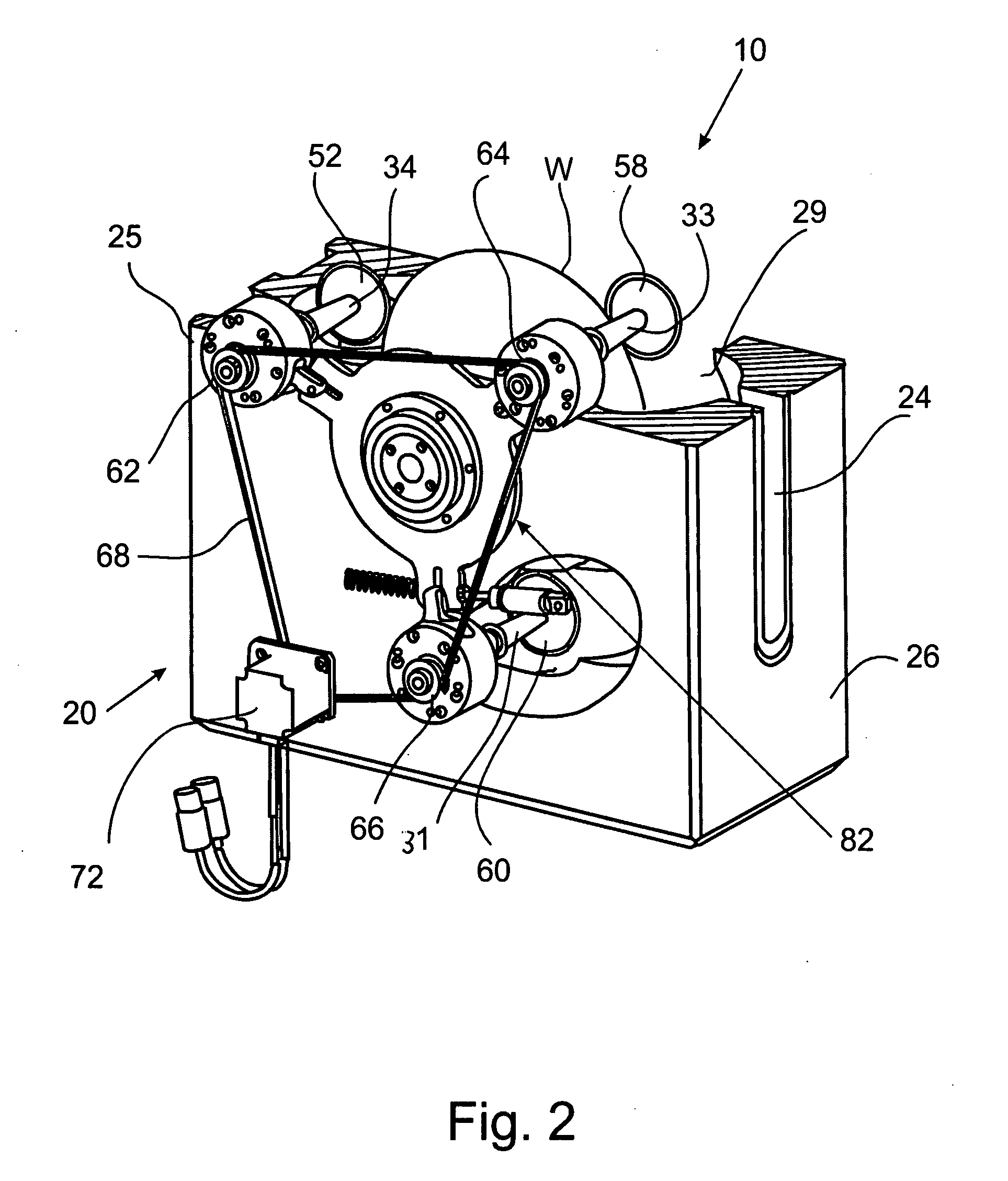
InactiveUS6901966B2Light weightEasy to handleSleeve/socket jointsEngine sealsFront and back endsGaseous nitrogen
A seal device is constituted of a plurality of seal tubes. After a connected-tube body having base members disposed at a fore end and a rear end is inserted into a fluid passage such as a tubular member, the seal tubes are expanded by injecting gaseous nitrogen into each of the seal tubes. The intermediate portions of the seal tubes along a longitudinal direction are press-fitted to the inner surface of the fluid passage over the entire circumference thereof, whereby the fluid passage is sealed. Since the connected-tube body is easily bent in the vicinity of a connecting base member between the tubes, the connected-tube body can be easily curved along the fluid passage, thus facilitating an operation for inserting the connected-tube body into the fluid passage and also enhancing a sealing property with respect to the fluid passage.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
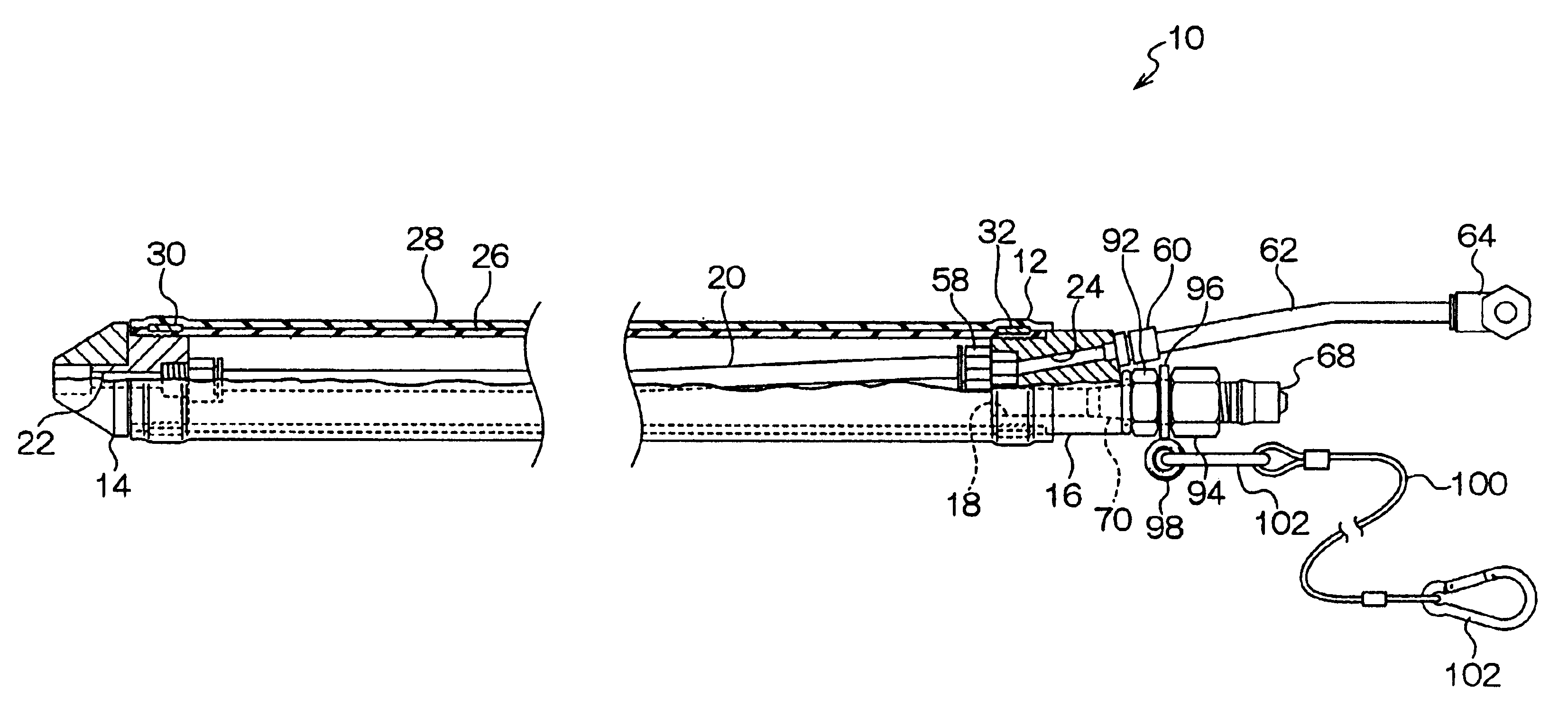
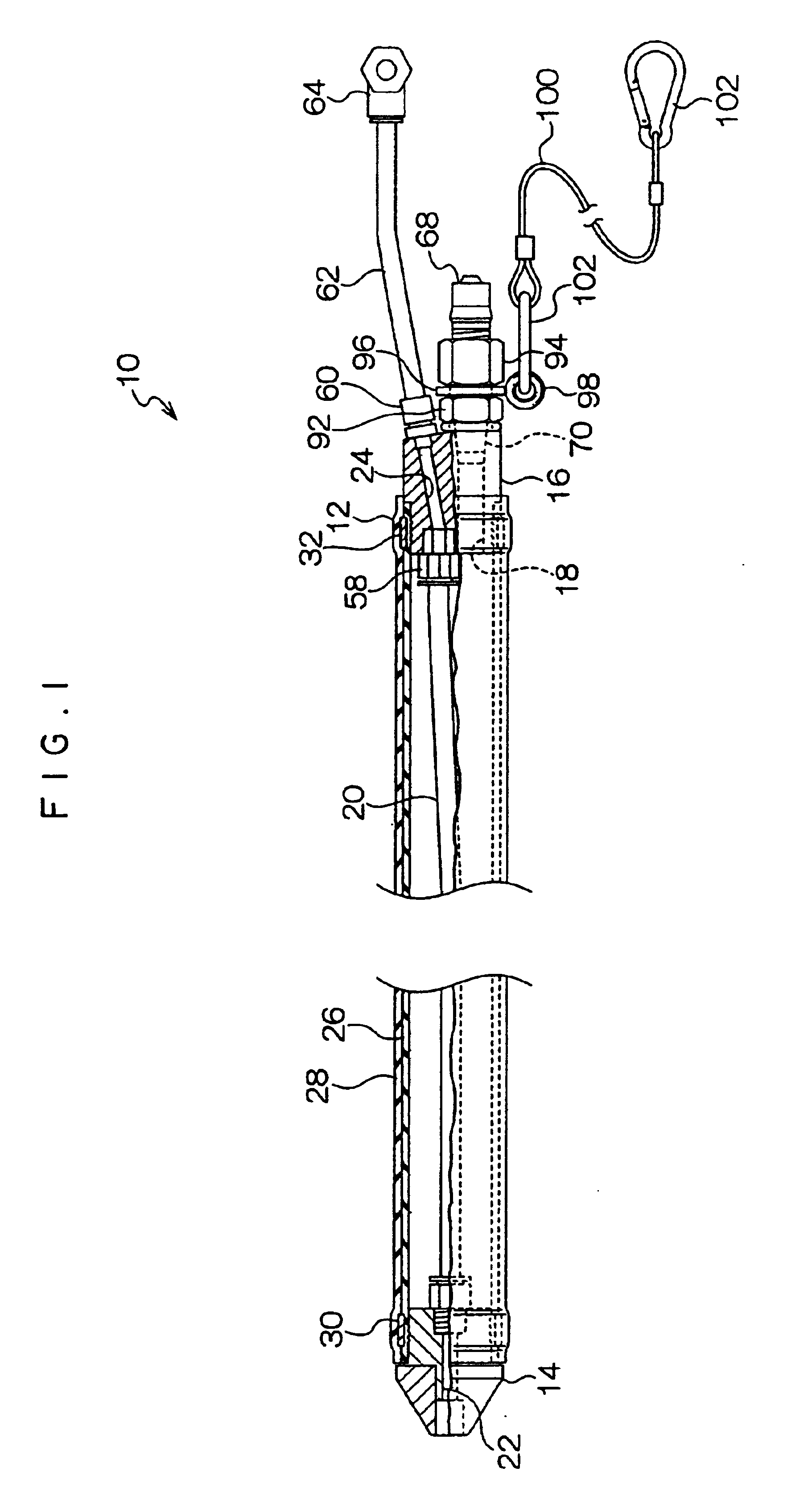
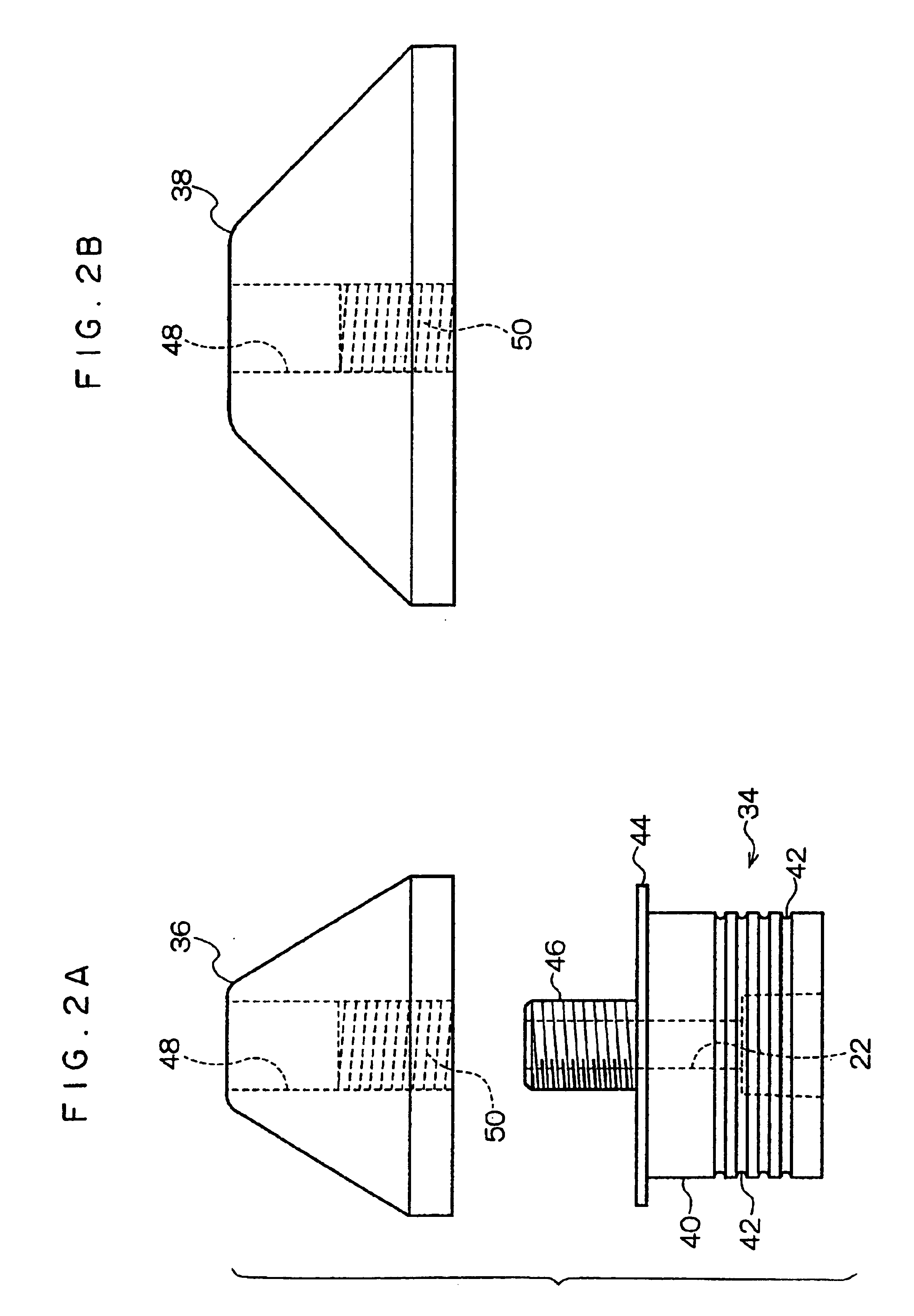
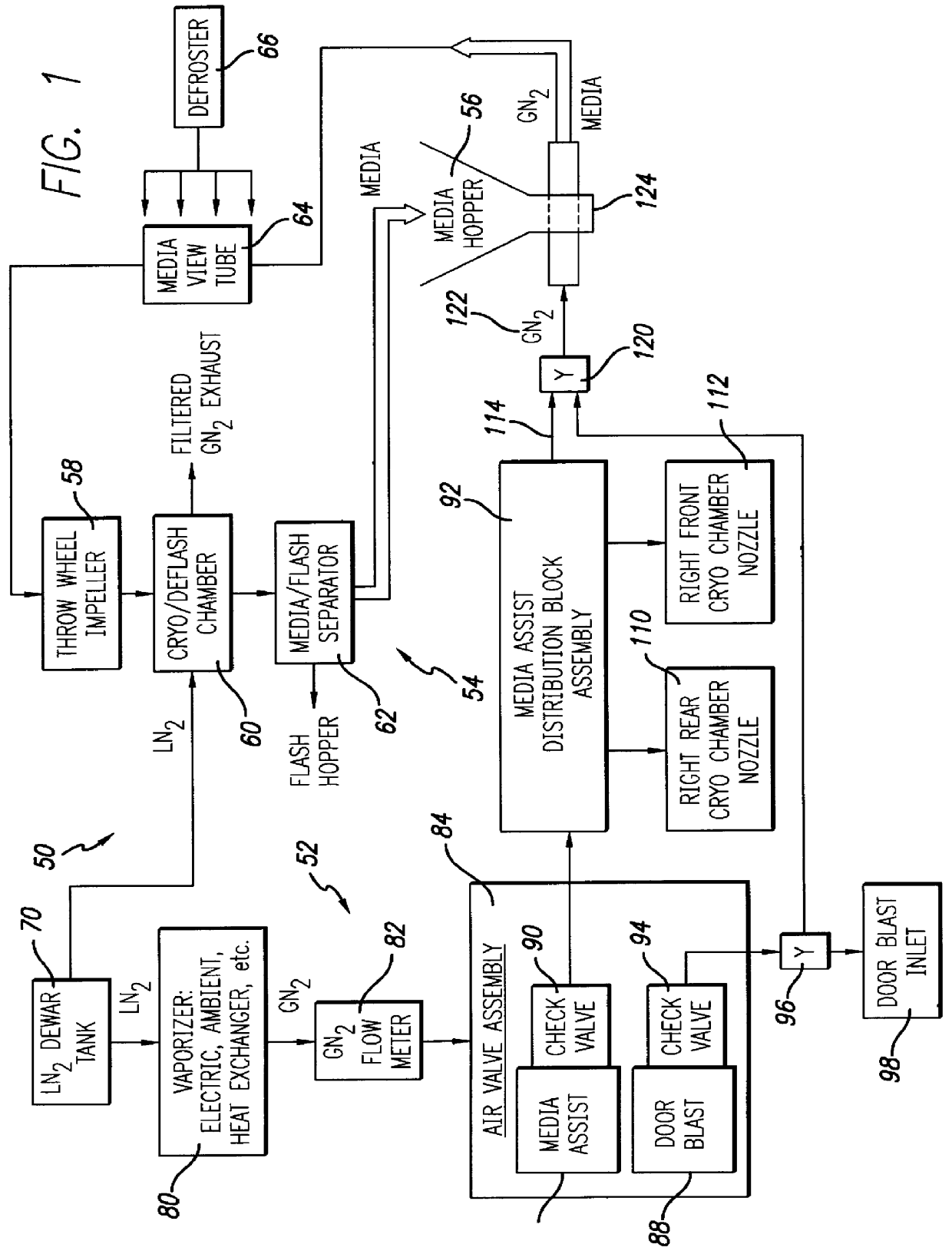
Media assist gaseous nitrogen distribution system for deflashing machine
InactiveUS6099398AAllocation is accurateAbrasive feedersAbrasive machine appurtenancesImpellerDistribution system
A media assist and gaseous fluid flow distribution system for a cryogenic deflashing machine. Dry-nitrogen or other dry gas is supplied to the media assist distribution system of the present invention in order to supply a cryogenic deflashing machine with gas fluid flow. The gaseous nitrogen is distributed into the interior of the cryogenic deflashing chamber as well as serving to propel deflashing media shot into a throw wheel impeller. The throw wheel impeller then propels the media into the cryogenic deflashing chamber to deflash plastic, metal, or other appropriate work pieces. The gas distribution portion of the present invention also supplies a blast of dry nitrogen against the door to ensure that debris collecting nearby is directed towards the drain of the cryogenic deflashing chamber and the media / flash separator. Via the gaseous distribution system of the present invention, the amount of media required for impact deflashing is greatly reduced.
Owner:JACOBSON VENTURES +1
Method of producing a gasified hydrocarbon stream; method of liquefying a gaseous hydrocarbon stream; and a cyclic process
ActiveUS9459042B2Improve cooling effectReduce compressionSolidificationLiquefactionThermodynamicsPetroleum engineering
A first liquefied hydrocarbon stream is provided from a first source and a second liquefied hydrocarbon stream is provided from a second source. The second liquefied hydrocarbon stream has been liquefied by cooling solely against a first cooled nitrogen-based stream. The first and second liquefied hydrocarbon streams are gasified to produce a gasified hydrocarbon stream, thereby cooling a gaseous nitrogen-based stream against the gasifying first and second liquefied hydrocarbon streams to provide a second cooled nitrogen-based stream.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Method and apparatus for supercharging downhole sample tanks
A tank contains both Zeolite and a hydrate in a gas chamber formed beneath a piston in the sample tank. Out of safety considerations, we avoid using source cylinders of nitrogen whose pressures exceed 4000 psi. Thus, the gas chamber of the sample tank is initially pressurized by the source cylinder to no more than 4000 psi of nitrogen at room temperature at the surface. Nitrogen gas is sorbed onto the zeolite at room temperature. As the tank is heated by being lowered downhole, nitrogen desorbs from the zeolite and the gas pressure increases. However, once this tank reaches a temperature high enough to release the hydrate's water of hydration, the released water is preferentially sorbed by zeolite, displacing sorbed nitrogen, and causing the pressure in the gas volume to increase even further. Because well temperatures are not high enough to desorb water from zeolite, any water sorbed onto a Zeolite sorption site will permanently block released nitrogen from resorbing at that site. The process of lowering the tank downhole provides the necessary heating to make the entire process occur. Thus, if returned to the surface at room temperature with the original gas-chamber volume, the tank's pressure would not fall back to the original pressure (e.g., 4000 psi) but would be at a substantially higher pressure (e.g., 6000 psi or more depending on the amount of Zeolite used and gaseous nitrogen gas released).
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
Method of forming gate dielectric layer
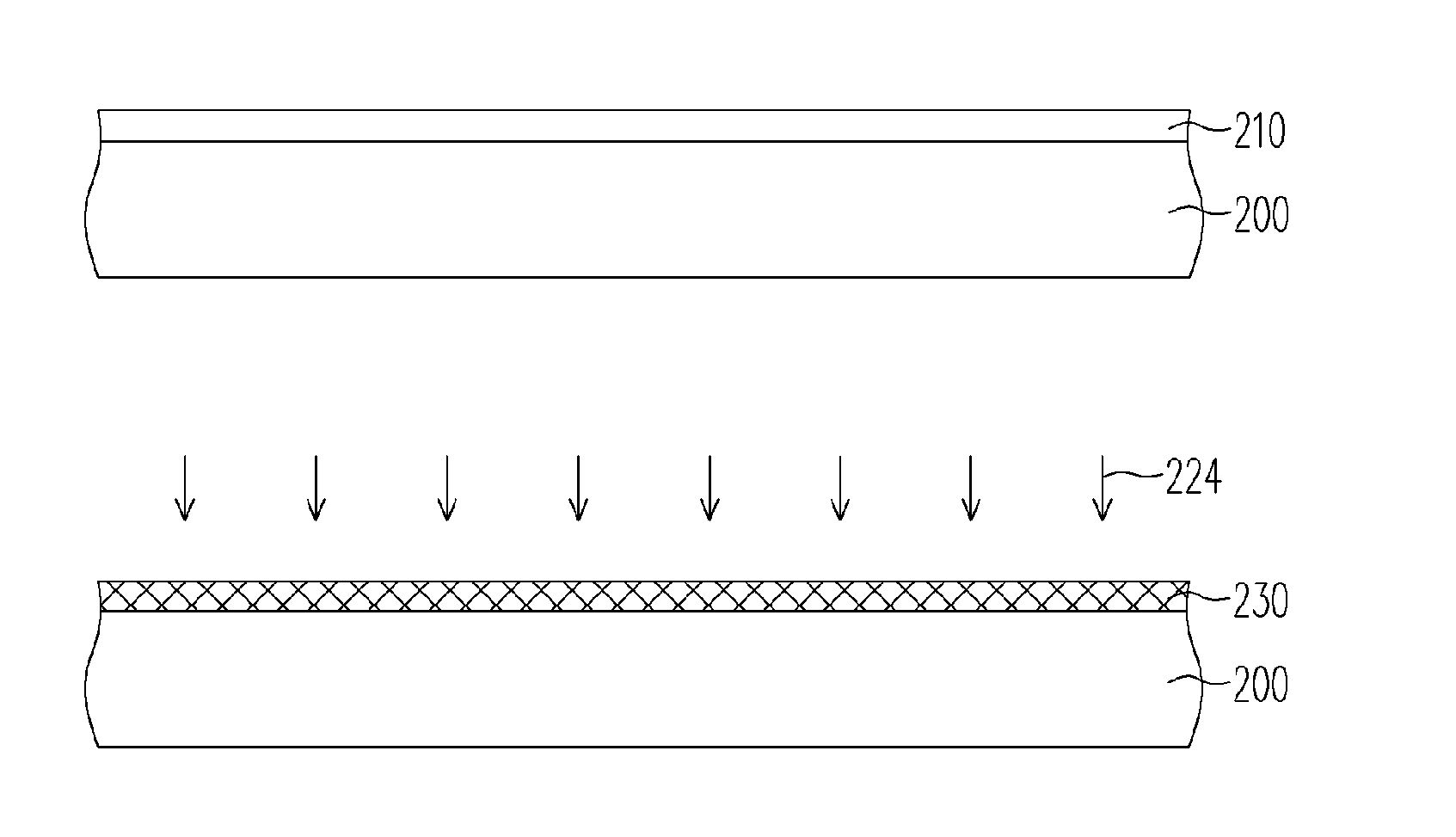
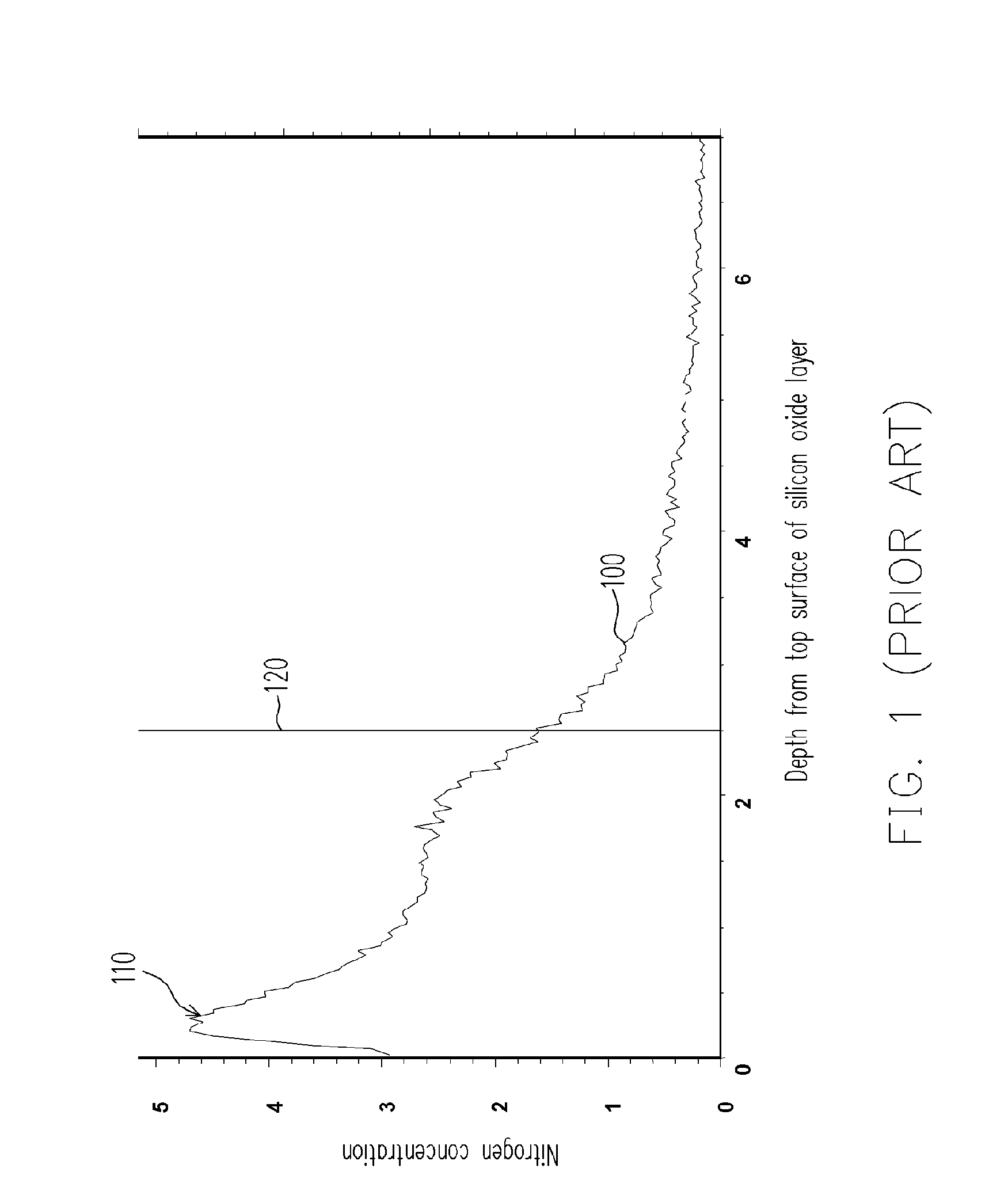
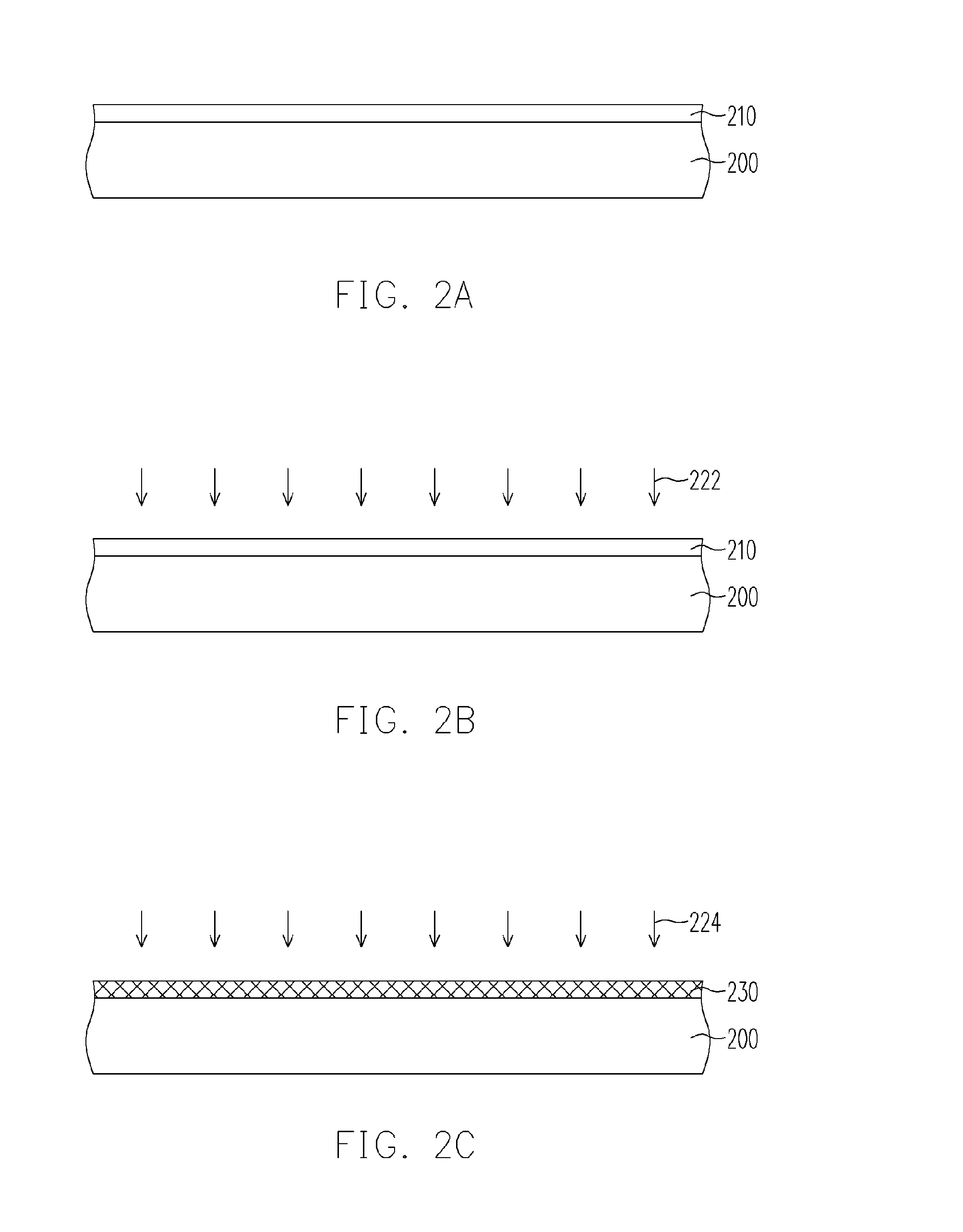
ActiveUS20060172554A1Reduced tunneling currentSolve the real problemSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricSilicon oxide
A method for forming a gate dielectric layer is described. A silicon oxide layer is formed on a semiconductor substrate. Then, a first and a second nitrogen doping processes are performed in sequence to the silicon oxide layer using plasma comprising inert gas and gaseous nitrogen to form a gate dielectric layer. The first nitrogen doping process is performed at a lower power, a lower pressure and a higher inert gas to nitrogen gas ratio than those at the second nitrogen doping process. The combination of the deeper nitrogen distribution of the first nitrogen doping process and the shallower nitrogen distribution of the second nitrogen doping process produces a flatter total nitrogen distribution profile so that leakage current from electron tunneling through the gate dielectric layer can be reduced.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Friction Reduction and Suspension in High TDS Brines
InactiveUS20190112521A1Low viscosityGood suspensionFluid removalDrilling compositionThermodynamicsNitrogen gas
A friction-reducing additive composition that contains a polymeric mixture containing (a) a first polymeric friction reducer that comprises an anionic friction reducer having a molecular weight above 15 million and (b) a second polymeric friction reducer that is either a nonionic or an amphoteric friction reducer. This combination of friction reducers exhibits superior suspensive characteristics for hydrophobically coated proppants in high TDS brines, such as those that reuse fracturing fluids or backwaters. Optionally, gaseous nitrogen can be generated downhole or in the treated field by introducing a two-part system of reactants that chemically interact so as to produce gaseous nitrogen bubbles that help to suspend hydrophobically coated proppants and provide an additional method to control proppant placement within a treated subterranean field.
Owner:PFP TECH
Device and method for testing reverse osmosis membranes
InactiveUS20120234083A1Quick and efficientMembranesSurface/boundary effectReverse osmosisNitrogen gas
The device for testing reverse osmosis membranes provides for the quick and efficient testing of the transport properties of reverse osmosis membranes at a fixed pressure over a fixed period of time. The device includes a first chamber adapted for receiving a volume of de-ionized water and a second chamber adapted for receiving a volume of brine. In use, a reverse osmosis membrane to be tested is clamped between the first and second chambers and a pressurized inert gas, such as gaseous nitrogen, is injected into the second chamber at known pressure to initiate reverse osmosis transport. The transport is carried out at the known pressure for a fixed period of time, after which the concentration of brine volume of water in the first chamber is measured.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Method for retarding agricultural non-point source pollution by applying biological carbon and nitrification inhibitor
InactiveCN105612846AReduce pollutionEasy to operateOther chemical processesOrganic fertilisersAgricultural ecosystemsNitrification inhibitors
The invention relates to a method for retarding agricultural non-point source pollution by comprehensively applying biological carbon and a nitrification inhibitor, belongs to the field of agricultural non-point source pollution research, and is dedicated to retarding non-point source pollution caused by nitrogen gas losses and subsequent atmospheric deposition in a paddy field and vegetable field ecosystem. According to the method, the biological carbon and the nitrification inhibitor are applied in fields of a rice-wheat crop rotation rice field and intensive vegetable cultivation ecosystem, therefore emission of gaseous nitrogen, such as N2O and NOx, is effectively reduced, and the atmospheric deposition is reduced to retard the non-point source pollution; the utilization rate and the yield of crops are increased, and nitrate nitrogen content of soil and migration of nitrate nitrogen to a water body are reduced to retard the non-point source pollution. The method is a brand-new, rapid, simple and efficient non-point source pollution retarding method, can be used for a wide variety of agricultural ecosystems, is convenient to operate and easily available in material, can be widely applied to prevention and control research on the agricultural non-point source pollution to paddy fields and vegetable fields, and provides an effective means for deeply researching the agricultural non-point source pollution.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method and arrangement for processing nitrogen-concentrated effluents in a sequential fractionated cycle biological reactor
ActiveUS7645385B2Easy to adjustControlling the riskBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNitrogen gasChemistry
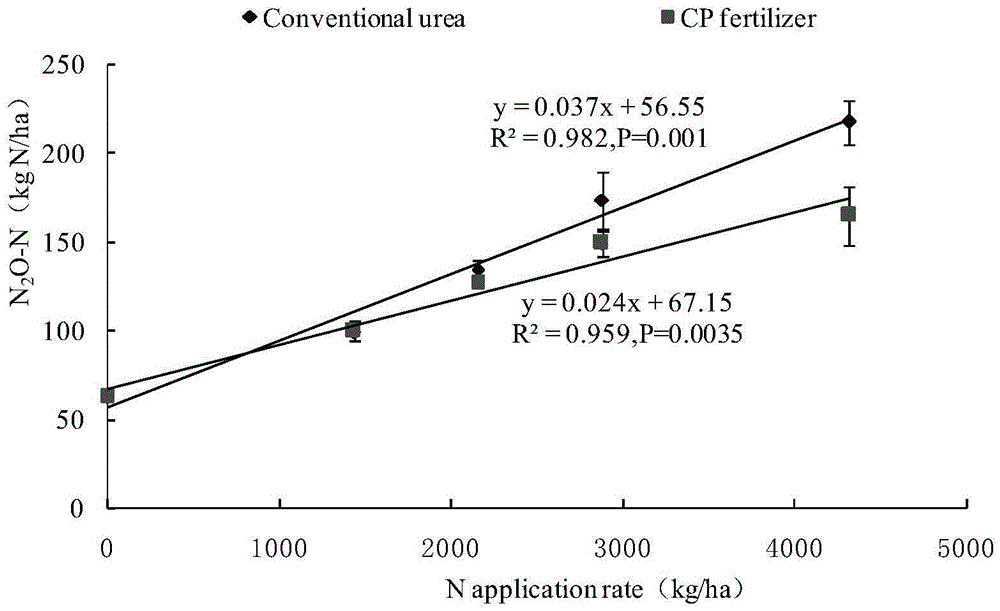
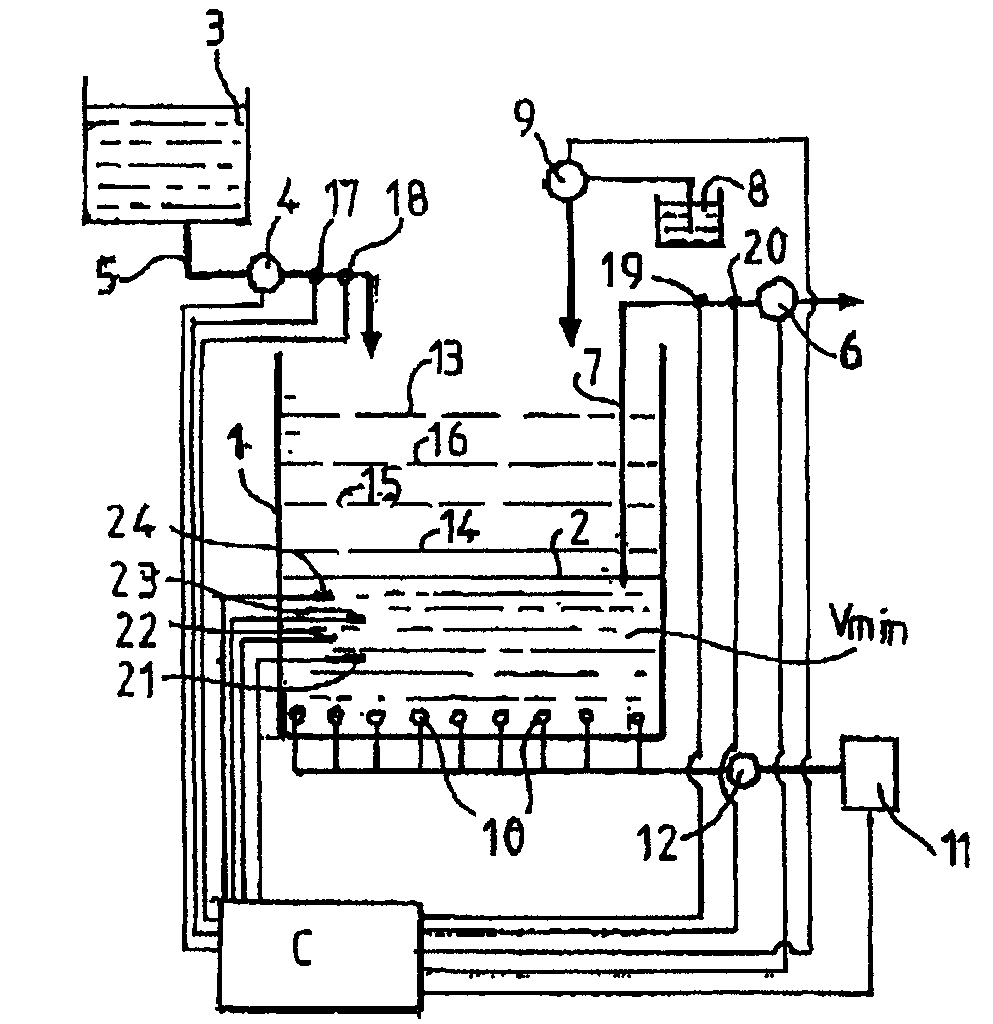
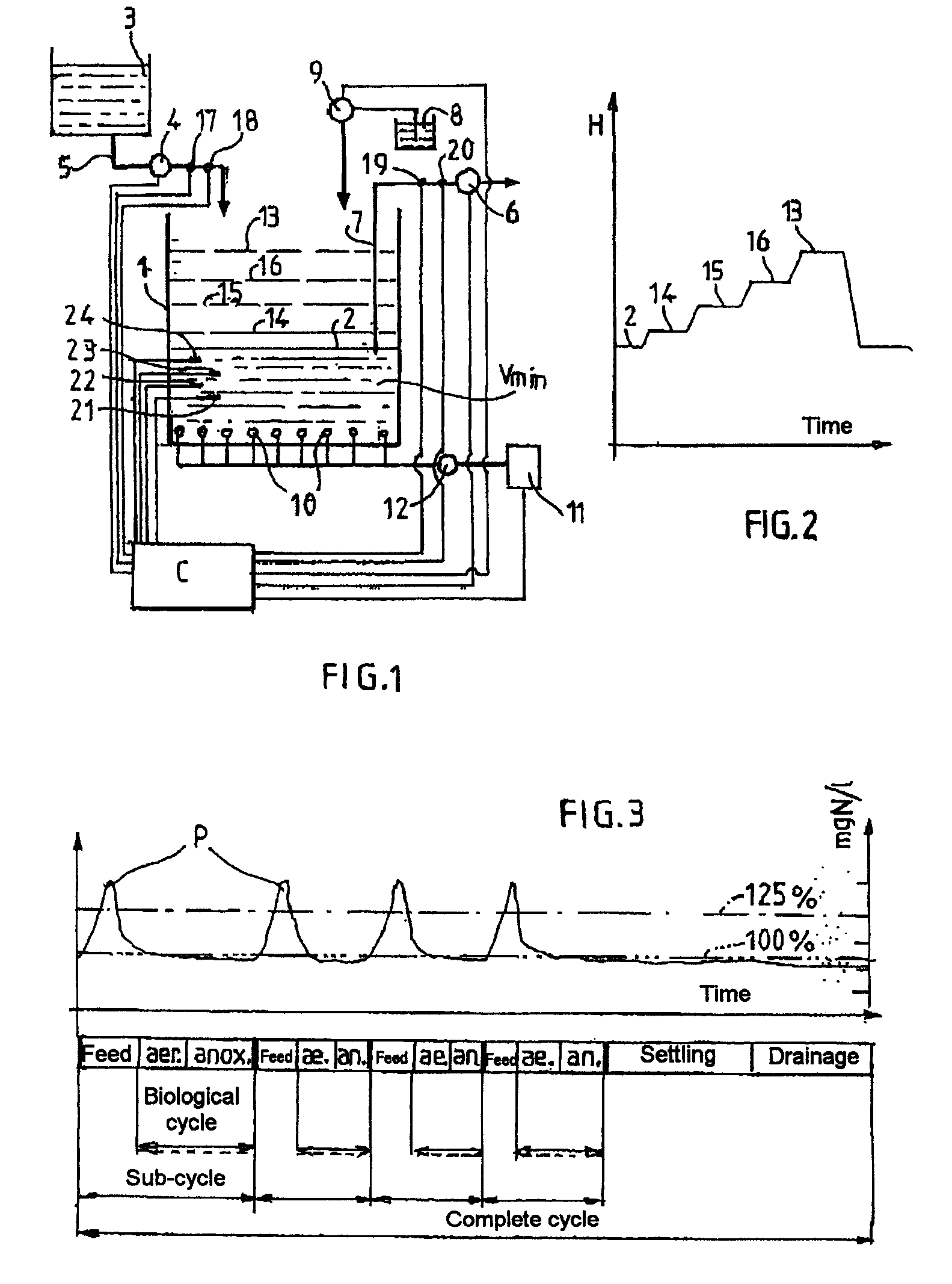
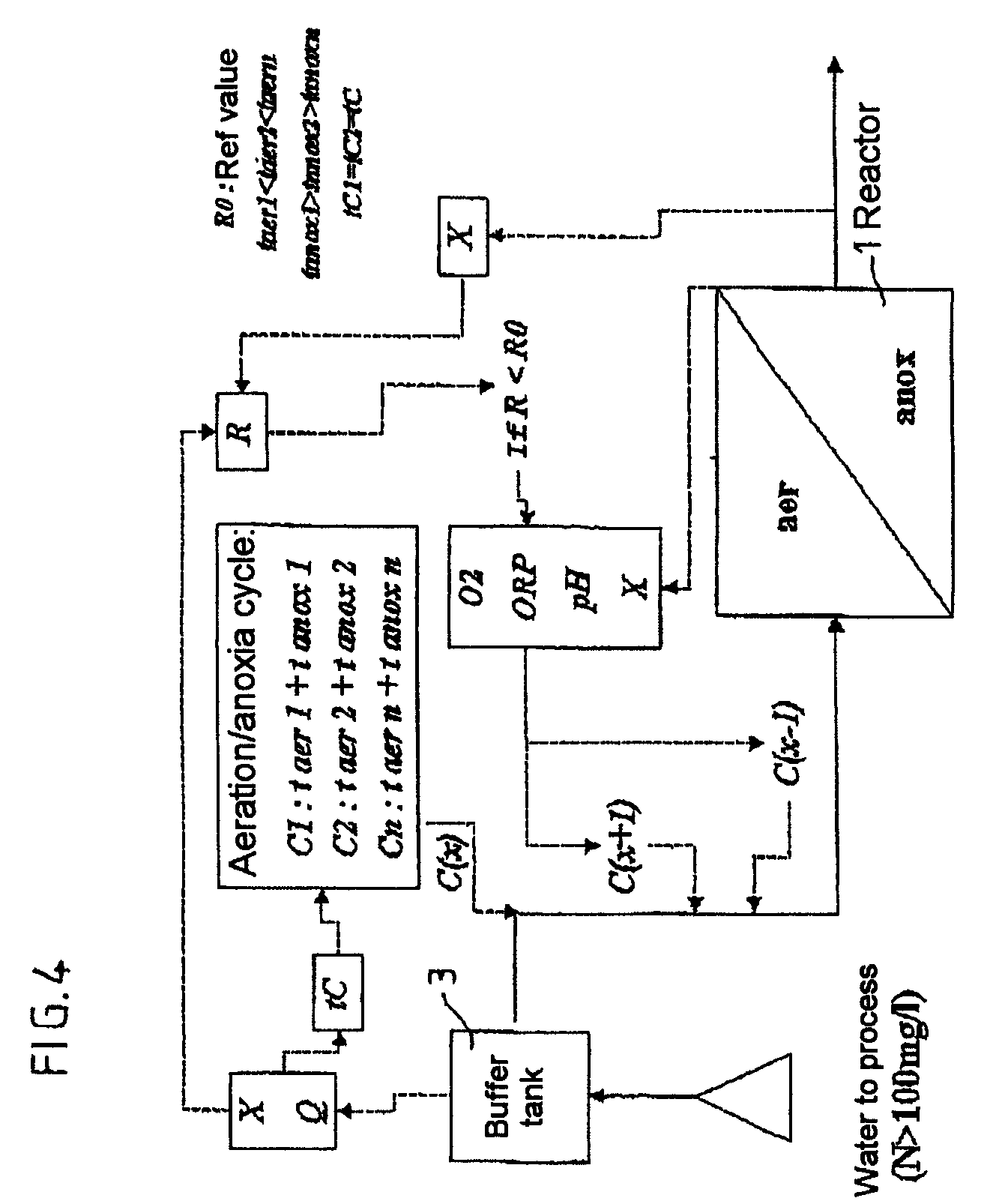
The invention relates to a method for processing nitrogen-concentrated effluents by ammonia oxidation into nitrites followed by nitrite denitritation in a gaseous nitrogen in a sequential biological reactor (1) consisting in pouring a processable effluent volume in to the reactor by successive volume fractions, in dividing the entire processing cycle into successive sub cycles, wherein each sub-cycle comprises a feeding phase, an aeration phase for nitrification and an anoxia phase along which a carbon-containing source is introduced into the reactor for converting nitrites into nitrogen. The inventive method also consists in evaluating a nitrogenous volume charge in the effluent to be processed, mainly by measuring the effluent conductivity (X) and the flow rate (Q) and in determining the number of feeding phases of the entire cycle according to nitrogenous charge and to a minimum volume of liquid in the reactor in such a way that an injected nitrogen concentration is diluted in the liquid volume, wherein the volume phase nitrogenous charge is however sufficient for producing a single shot or peak of the ammonia charge favourable for a nitrating biomass formation in the reactor.
Owner:ONDEO DEGREMONT INC +1
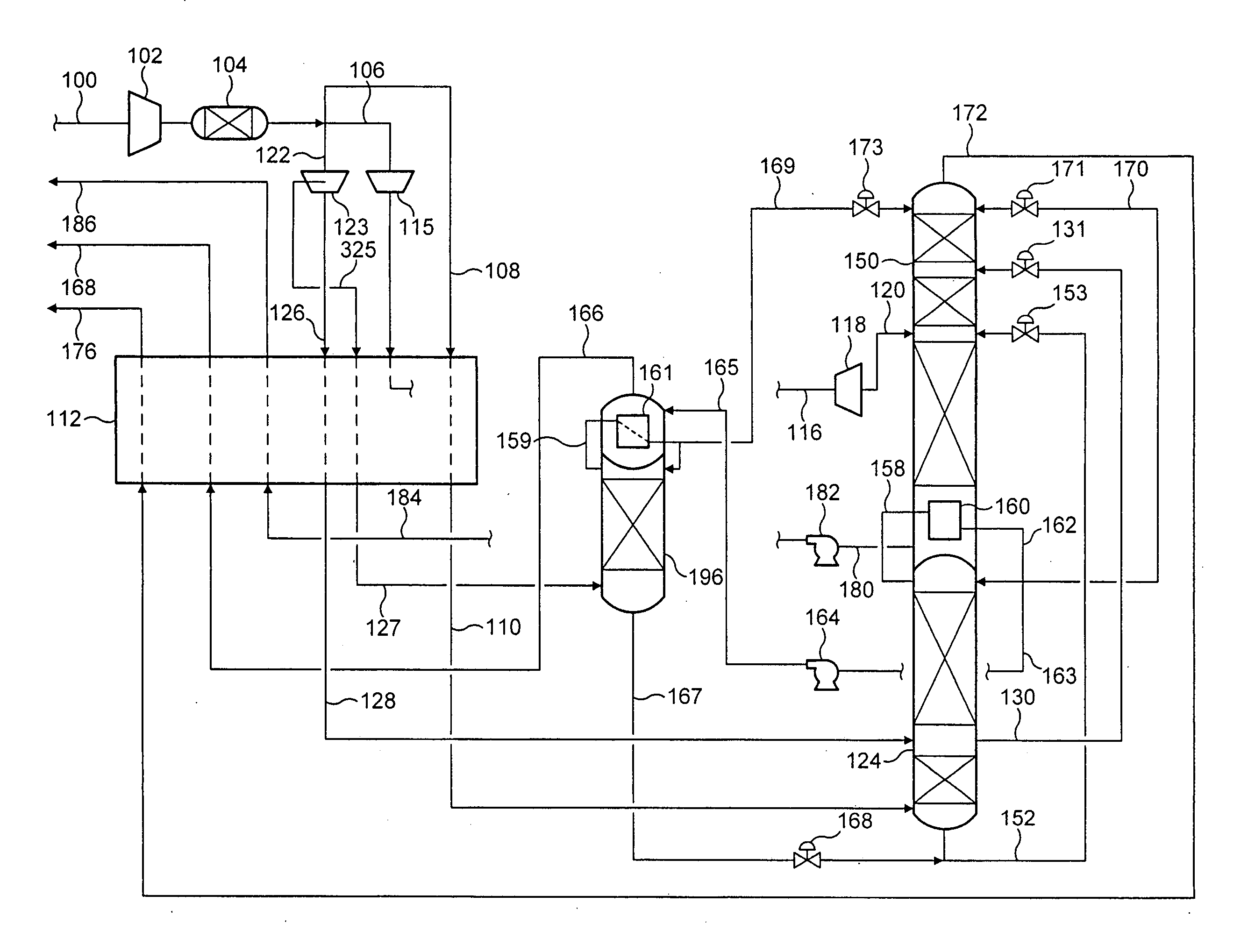
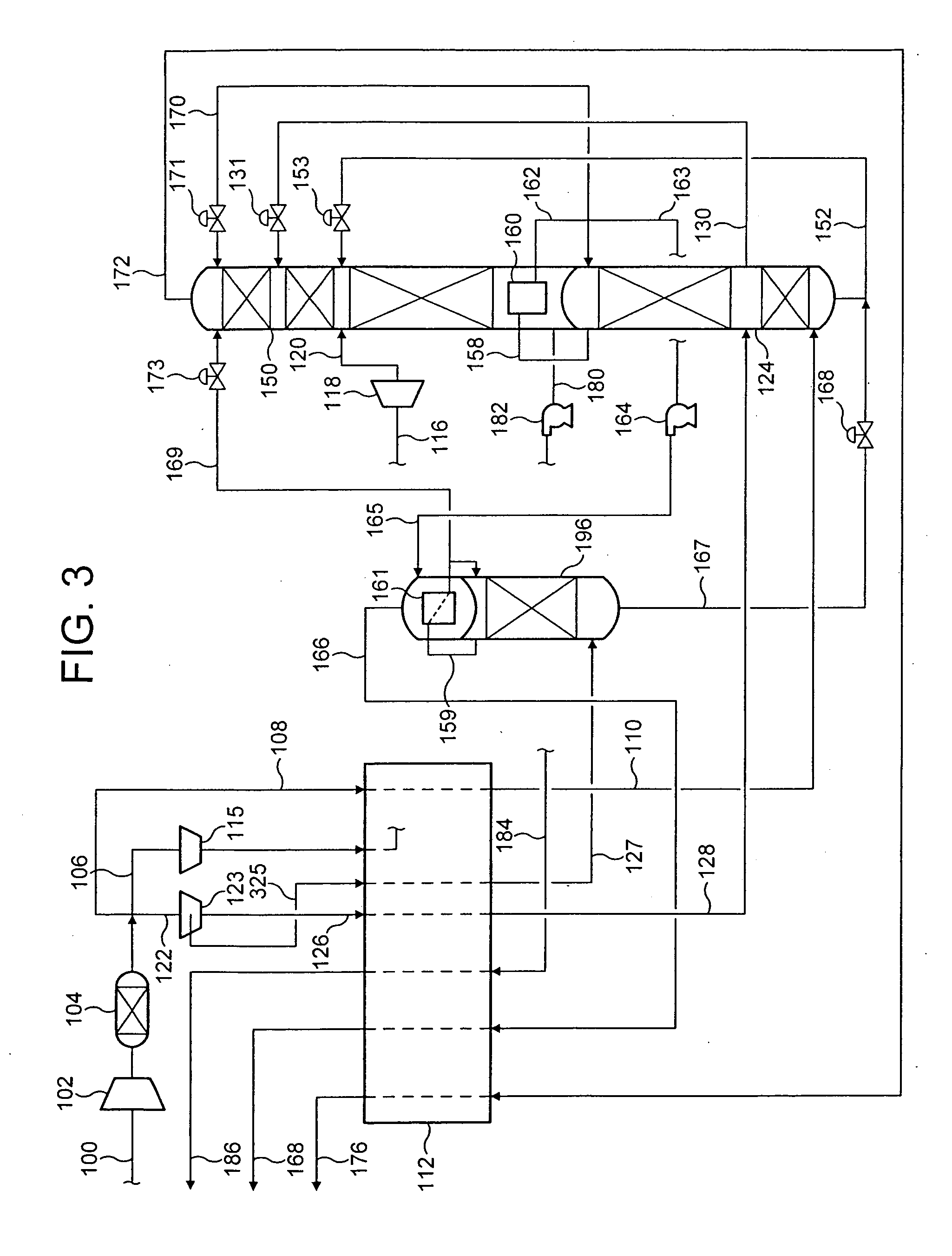
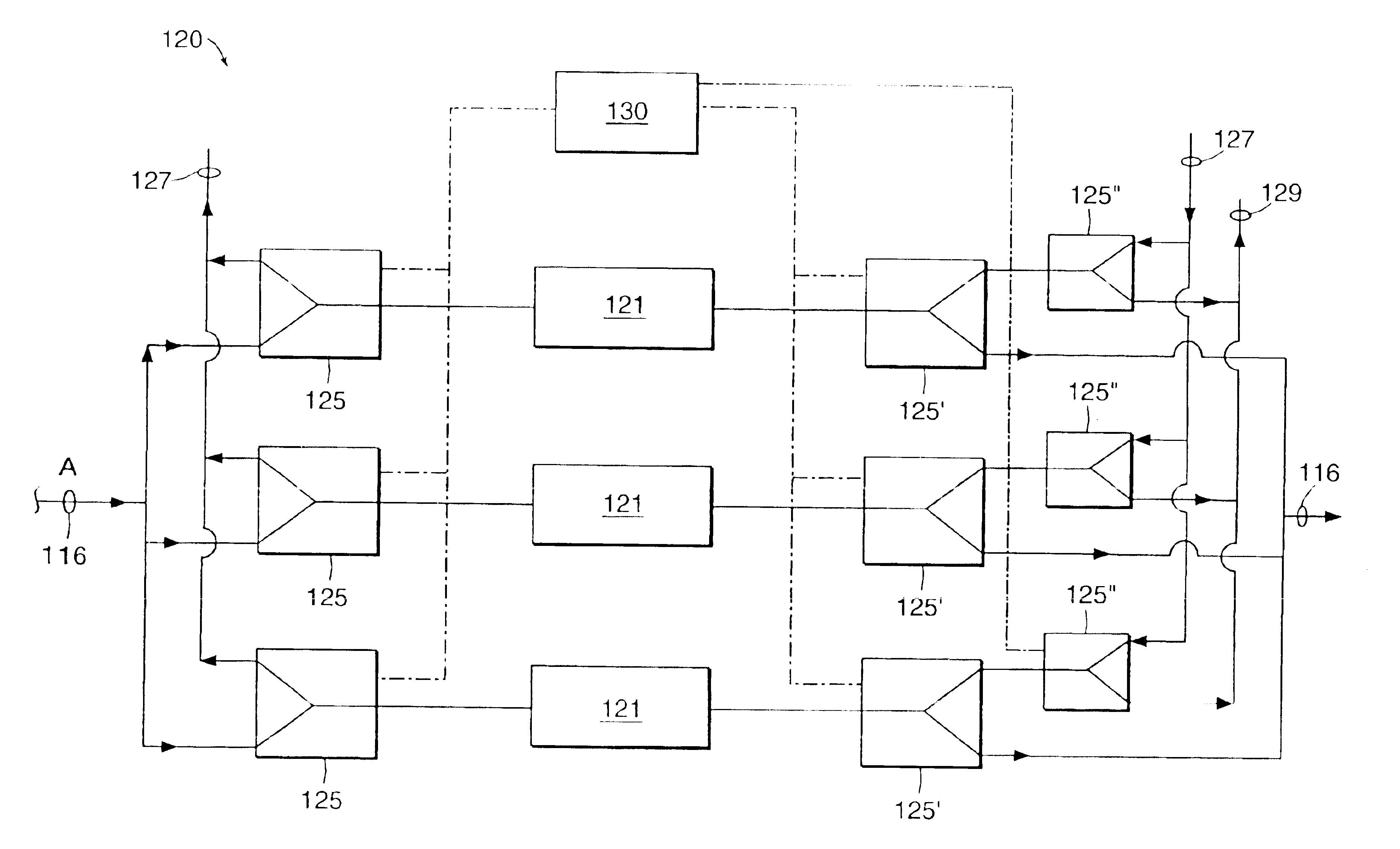
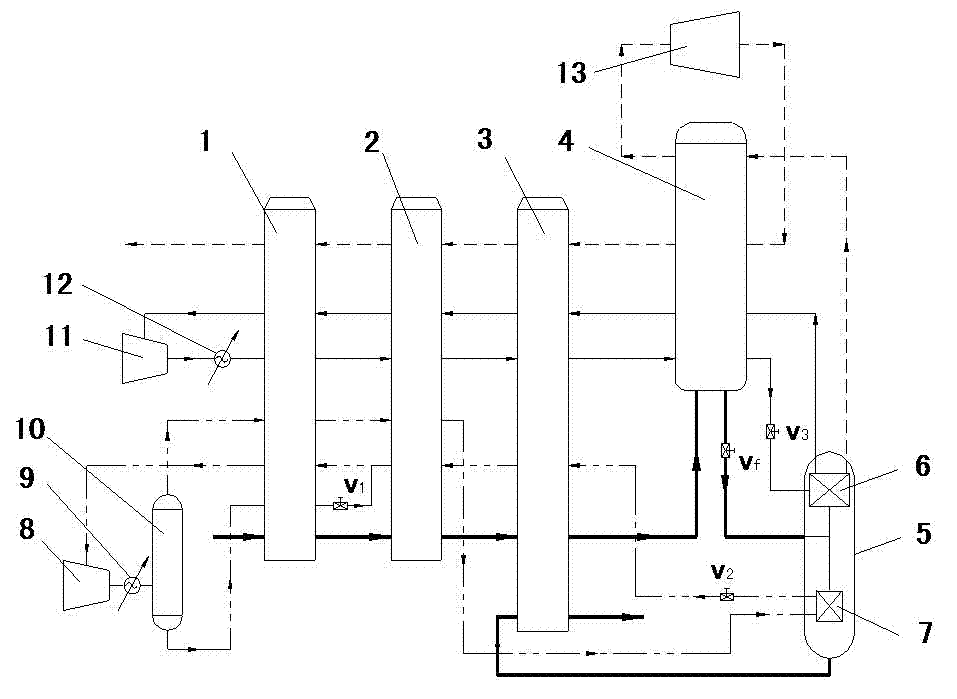
Process for the cryogenic distillation of air
Pressurized gaseous nitrogen (“GAN”) is produced in a process in which liquid nitrogen (“LIN”) is produced in a cryogenic air separation unit (“ASU”). The pressure of at least a portion of the LIN is increased to produce pressurized LIN. A fluid having an oxygen concentration at least equal to that of air is separated in an auxiliary cryogenic distillation column to produce nitrogen-rich overhead vapor and oxygen-enriched bottoms liquid. Heat and optionally mass is transferred between at least a portion of the nitrogen-rich overhead vapor and at least a portion of the pressurized LIN to produce nitrogen-rich liquid and pressurized GAN. At least a portion of said nitrogen-rich liquid is used as reflux to the ASU after suitable pressure adjustment. Such a process allows the production of high purity GAN without the loss of oxygen recovery typically observed in conventional pumped LIN cycles.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Detection of base contaminants in gas samples
InactiveUS6855557B2Measure be usually unsatisfactoryAnalysis using chemical indicatorsChemical analysis using combustionReference sampleControl system
A detection system for detecting contaminant gases includes a converter, a detector, a primary channel for delivering a target gas sample through the converter to the detector, and at least two scrubbing channels for delivering a reference gas sample through the converter to the detector. Each of the scrubbing channels includes a scrubber for removing basic nitrogen compounds from the reference gas sample, while the primary channel preferably transmits the target gas sample without scrubbing. The converter converts gaseous nitrogen compounds in the target gas sample to an indicator gas, such as nitric oxide (NO), and a control system directs the flow of a gas sample among the primary channel and the scrubbing channels. In accordance with one aspect of the invention, the basic-nitrogen-compound concentration can be measured by comparing the concentration of the indicator gas detected in the reference sample with the detected indicator-gas concentration in the target sample. The use of multiple scrubbing channels enables the detection to operate continuously since each scrubber can be alternately purged while another is scrubbing.
Owner:MYKROLIS CORP
Process for preparing liquefied natural gas (LNG) by low concentration coal bed methane oxygen bearing copious cooling liquefaction
ActiveCN103175381ASolve the blockageAchieve the goal of energy saving and emission reductionSolidificationLiquefaction2-methylbutaneEvaporation
The invention discloses a process for preparing liquefied natural gas (LNG) by low concentration coal bed methane oxygen bearing copious cooling liquefaction. The process for preparing LNG by low concentration coal bed methane oxygen bearing copious cooling liquefaction comprises the following steps: (1), compression and purification process; (2), liquefaction and separation process which comprises a, main procedure process; b, refrigeratory process, wherein the refrigeratory process comprises b1, mixing cryogen process; and b2, nitrogen cryogen process. Nitrogen cryogen sequentially passes through a first level heat exchanger, a second level heat exchanger, a third level heat exchanger and a subcooler for cooling after being compressed and cooled, the nitrogen cryogen after throttling enters an overhead condenser to output cold quantity, and then the gaseous nitrogen cryogen sequentially passes through the subcooler, the third level heat exchanger, the second level heat exchanger, and the first level heat exchanger, the gaseous nitrogen cryogen is warmed gradually to normal temperature, and then flows back to a nitrogen compressor for being circularly used. The mixing cryogen process is used for controlling evaporation capacity at the bottom of a tower, the nitrogen cryogen process is used for controlling condensation capacity at the top of the tower, and independently adjusting purity coefficient and yield coefficient of natural gas products is achieved. The cryogen in a low temperature region only possesses a nitrogen component, and heavy components of isobutane, isopentane and the like do not exist in the low temperature region, and therefore the problems of being free of refrigeration in the process of throttling, or congestion of a cryogen channel are solved.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
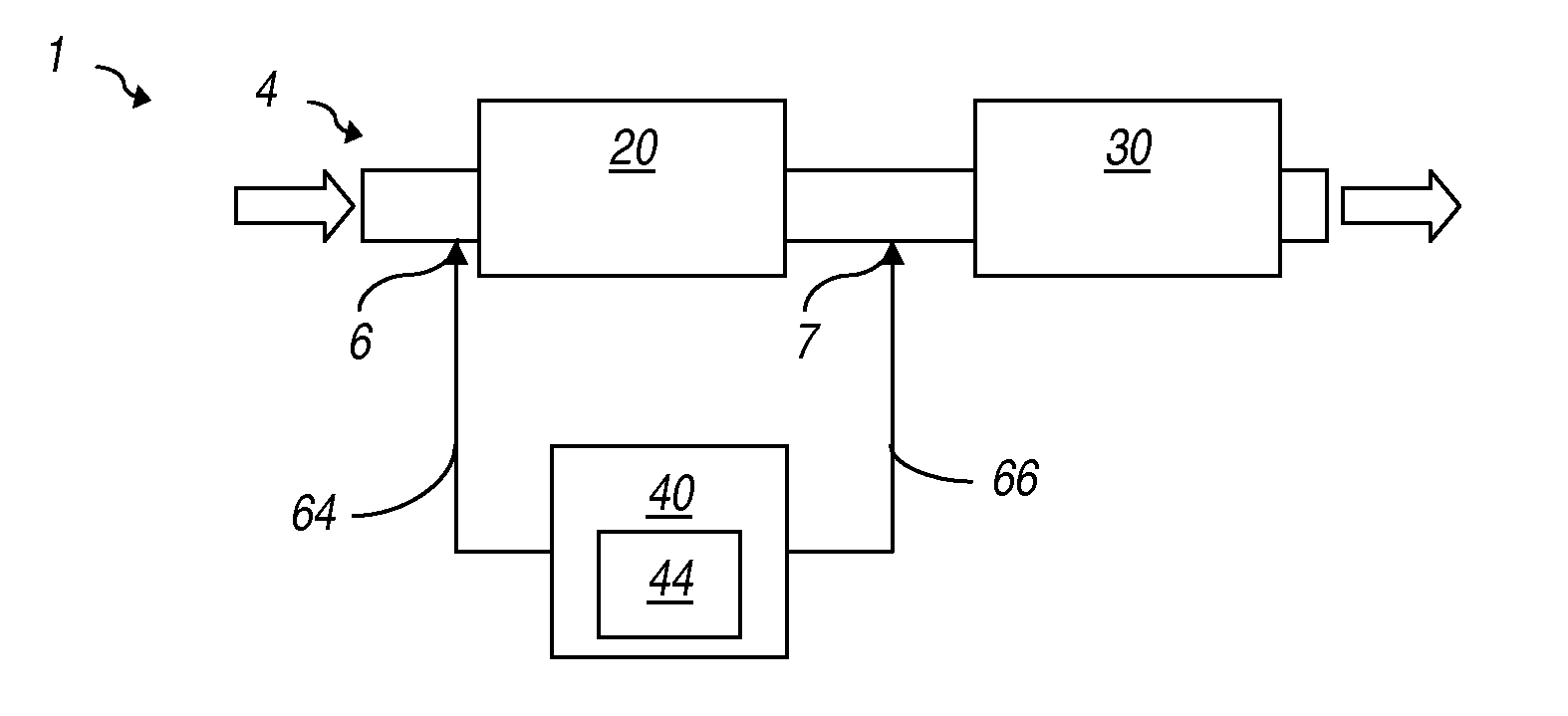
System and method for treating exhaust gases
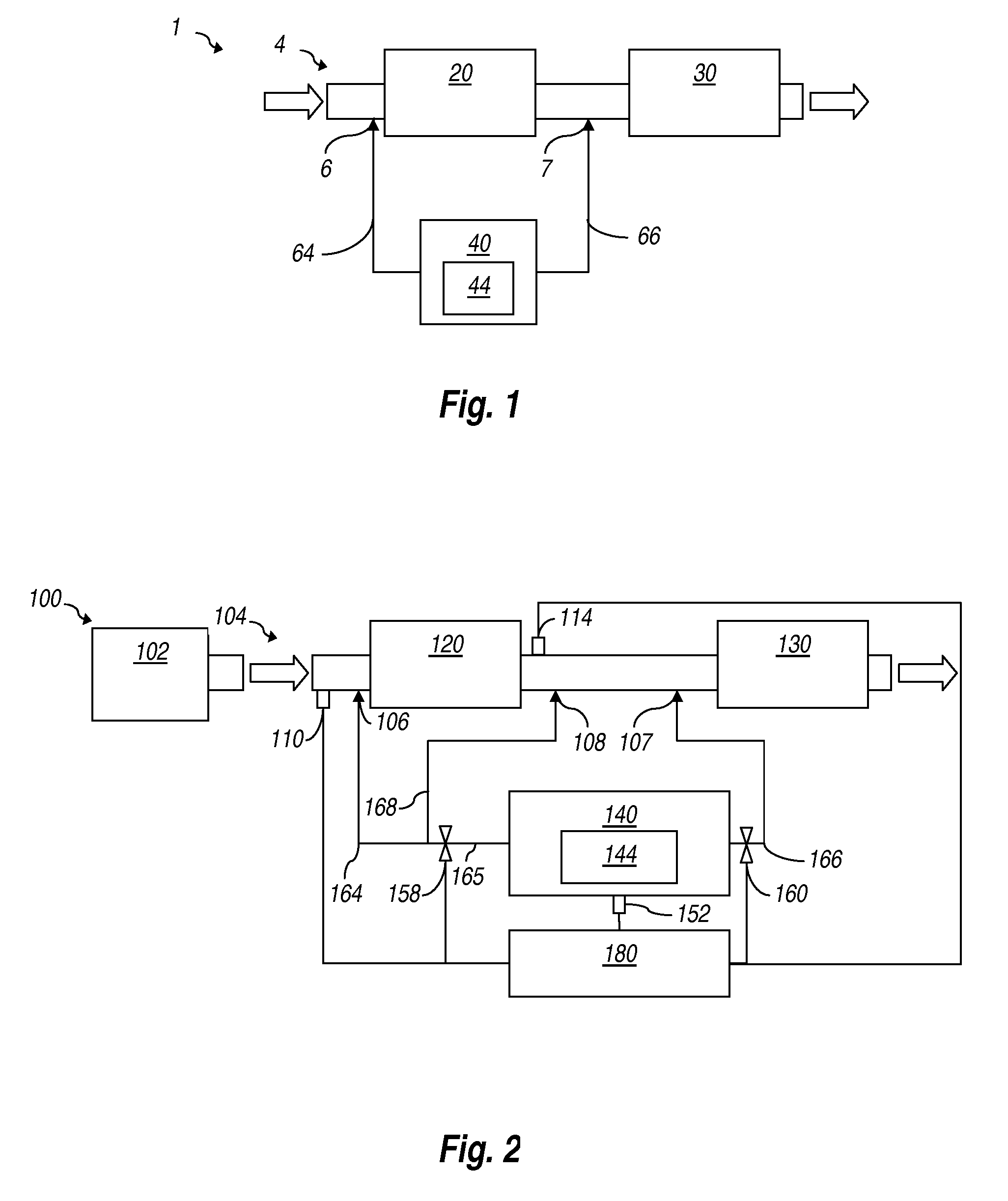
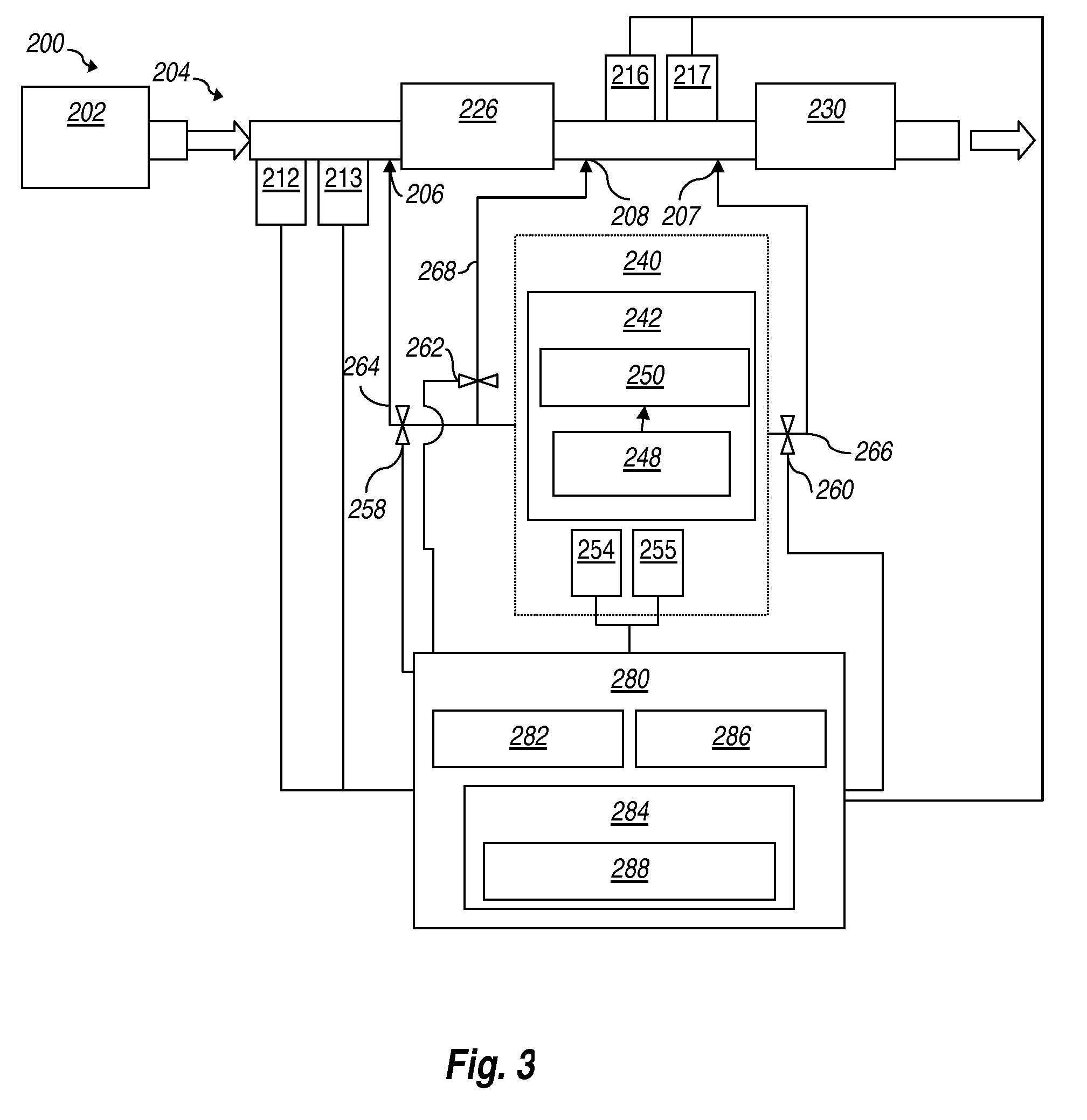
Systems and methods for treating exhaust gases are described. The disclosed systems and / or methods for treating exhaust gases could be used with any power plant, engine, hydrocarbon burning system, other NOx producing system, or combinations thereof. A method (400) for treating exhaust gases is provided. The method (400) may include converting (402) a first quantity of ammonia (44) using an ammonia-SCR catalyst (30) to produce gaseous nitrogen and water and converting (404) a second quantity of ammonia using an ammonia-to-NOx catalyst (20) located upstream of at least a portion of the ammonia-SCR catalyst (30) to produce NOx.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
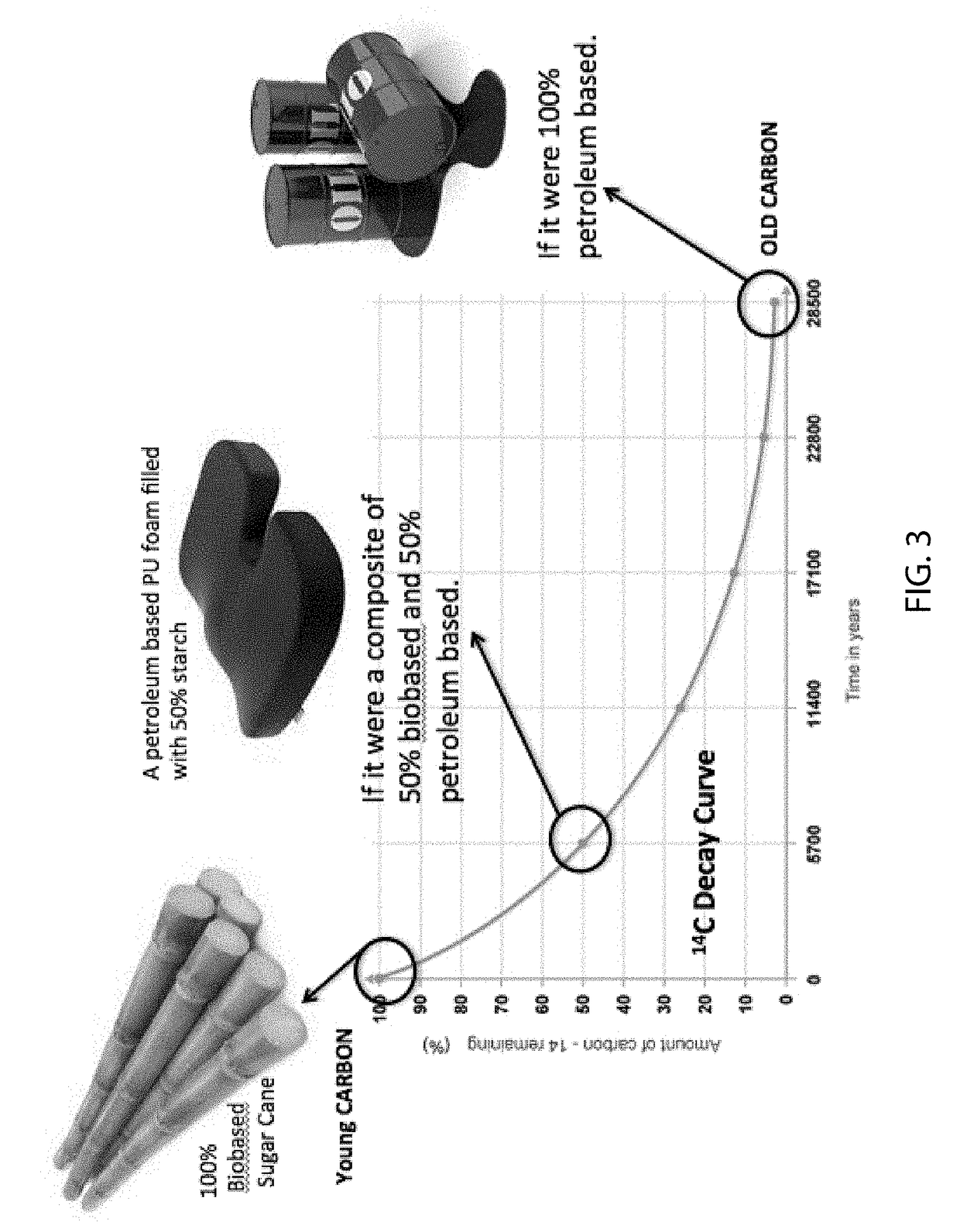
Bio-based and hydrophilic polyurethane prepolymer and foam made therefrom
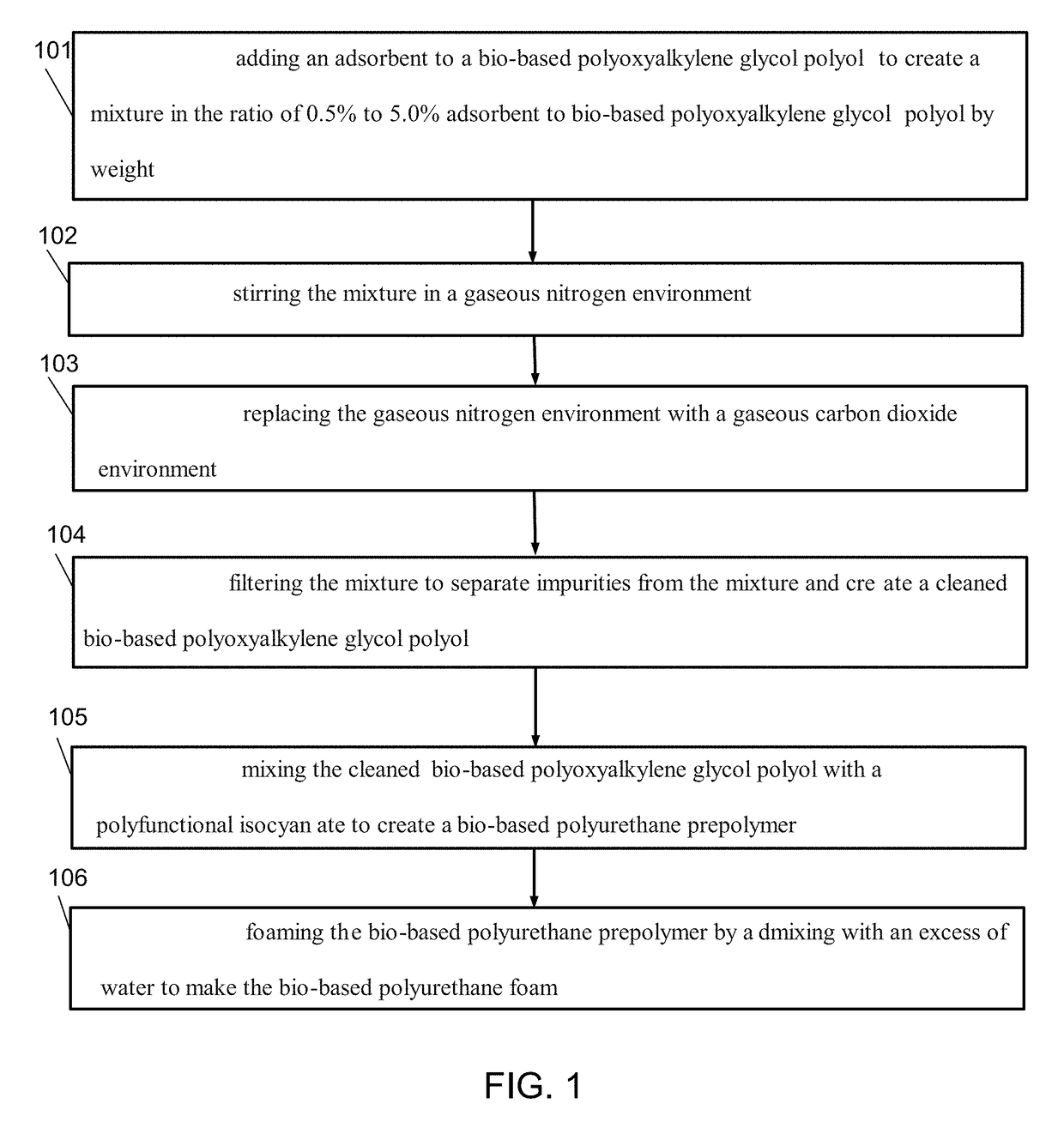
A bio-based polyurethane foam manufactured by a process that involves cleaning a bio-based polyoxyalkylene glycol polyol by a method comprising the steps of adding an adsorbent to the bio-based polyoxyalkylene glycol polyol to create a mixture in the ratio of 0.5% to 5.0% adsorbent to bio-based polyoxyalkylene glycol polyol by weight, stirring the mixture in a gaseous nitrogen environment, replacing the gaseous nitrogen environment with a gaseous carbon dioxide environment, and filtering the mixture to separate impurities from the mixture and create a cleaned bio-based polyoxyalkylene glycol polyol; then mixing the cleaned bio-based polyoxyalkylene glycol polyol with a polyfunctional isocyanate to create a bio-based polyurethane prepolymer; and then foaming the bio-based polyurethane prepolymer by admixing with an excess of water to make the bio-based polyurethane foam.
Owner:BIONANOFOAM LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com