Method for retarding agricultural non-point source pollution by applying biological carbon and nitrification inhibitor
A technology of agricultural non-point source pollution and nitrification inhibitors, applied in the field of agricultural non-point source pollution research, can solve the problems of restricting the sustainable development of agriculture, excessive nitrogen fertilizer input, degradation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1. Effect of Biochar Application on Nitrous Oxide Emissions and Crop Yield in Rice-wheat Rotation System
[0026] Taking the rice-wheat rotation system in my country as the object, the effect of wheat straw biochar application on N 2 The impact of O emission law; combined with the total output of wheat and rice to evaluate the comprehensive impact on the ecosystem, and provide a scientific basis for the application of biochar to mitigate agricultural non-point source pollution. No nitrogen fertilizer (N0) or 250kg / hm 2 Under the condition of / crop nitrogen fertilizer (N1), field in situ observation wheat season application 0 (B0), 20 (B1), 40t / hm 2 (B2) Biochar to rice-wheat rotation systemN 2 O annual emission and grain yield, set no nitrogen fertilizer, no biochar (N0B0), no nitrogen fertilizer, 20t / hm 2 Biochar (N0B1), nitrogen fertilizer without biochar (N1B0), nitrogen fertilizer and 20t / hm 2 Combined application of biochar (N1B1), nitrogen fertilizer a...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Embodiment two, biochar on soil physical and chemical properties, N 2 Effects on O emissions and vegetable yield
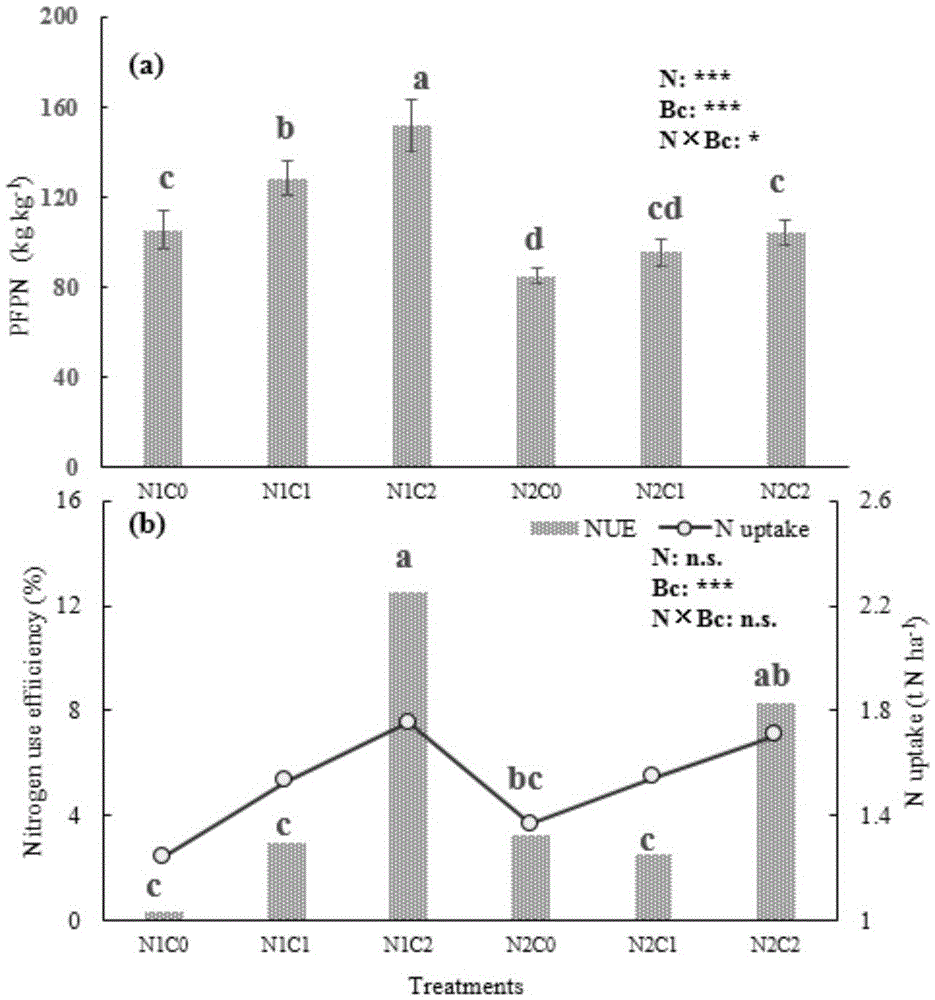
[0031] There are 9 treatments in the field test, the nitrogen fertilizer application level is no nitrogen fertilizer (N0), and the conventional fertilizer application rate is 1200kg / hm for 4 crops per year 2 / yr (N1) and 4 / 3 conventional nitrogen fertilizer application rate (N2), the level of biochar application is no application of biochar (C0), application of 20t / hm 2 Biochar (C1) and application of 40t / hm 2 Biochar (C2). Three replicates were set up for each treatment, and the vegetable planting system, tillage and irrigation level, fertilization method and time were all carried out according to the local management measures. During the test period, nine crops of vegetables were continuously planted, namely amaranth (Amaranthusmangostanus L.), water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica Forssk.), vegetable seedling (Brassica chinensis L.), coriander (Coriandrum s...
Embodiment 3
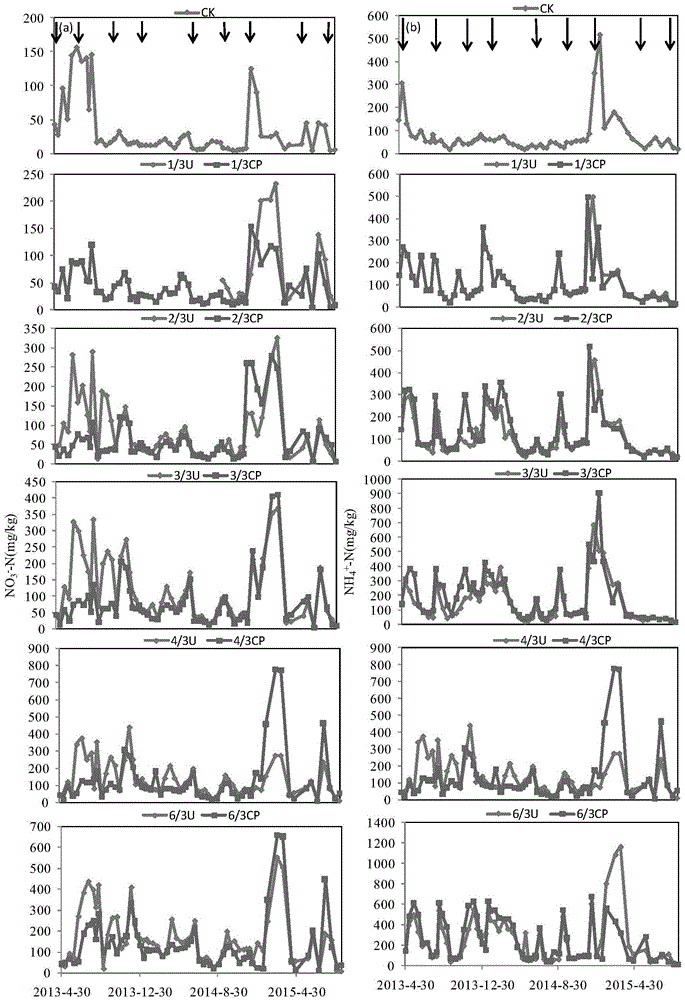
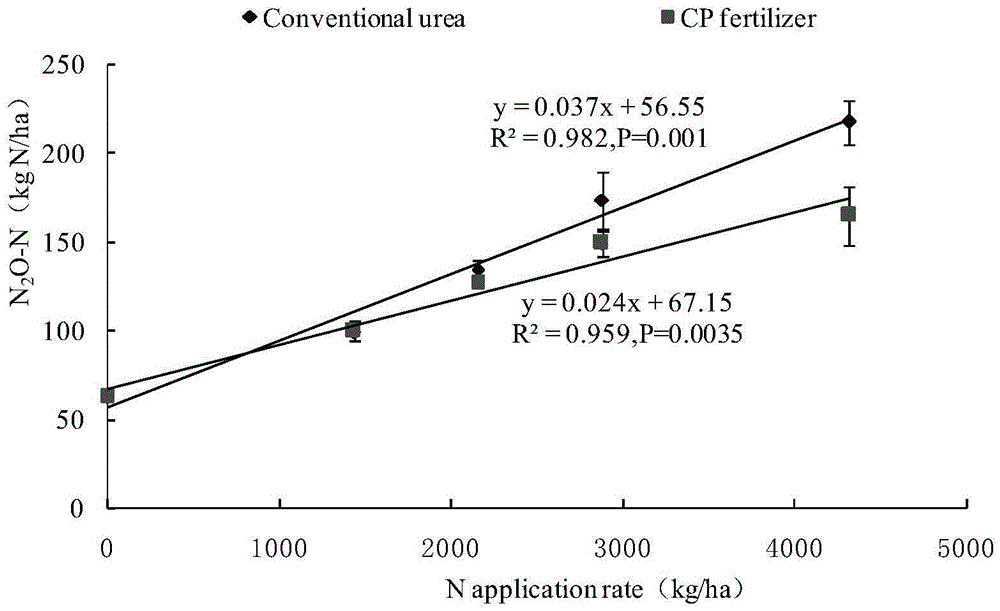
[0044] Embodiment 3, new-type nitrification inhibitors lower vegetable field N in different nitrogen application rates 2 Study on the Influence of O and NO Emissions
[0045] In the field experiment of continuously planting nine-season vegetables in the vegetable field ecosystem in my country, the effect of the new nitrification inhibitor CP nitrogen fertilizer on N 2 The impact of O and NO emissions. The results showed that at nitrogen fertilization levels of 0–480 kgNha -1 crop -1 Lower (0, 80, 160, 240, 320, 480kgNha -1 crop -1 ), the CP nitrogen fertilizer treatment effectively inhibited soil nitrification; compared with conventional urea, the CP nitrogen fertilizer treatment reduced the soil nitrate nitrogen concentration by 18.2%, and the ammonium nitrogen concentration increased by 14.1% ( figure 2 ). Regardless of whether nitrification inhibitors are added to nitrogen fertilizers, N 2 The total amount of O emissions and the amount of nitrogen fertilizer both sh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com