Patents
Literature
70results about "Zirconium sulfates" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Zirconia porous body and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20060018822A1Dispersed particle separationCatalyst activation/preparationPore distributionEngineering
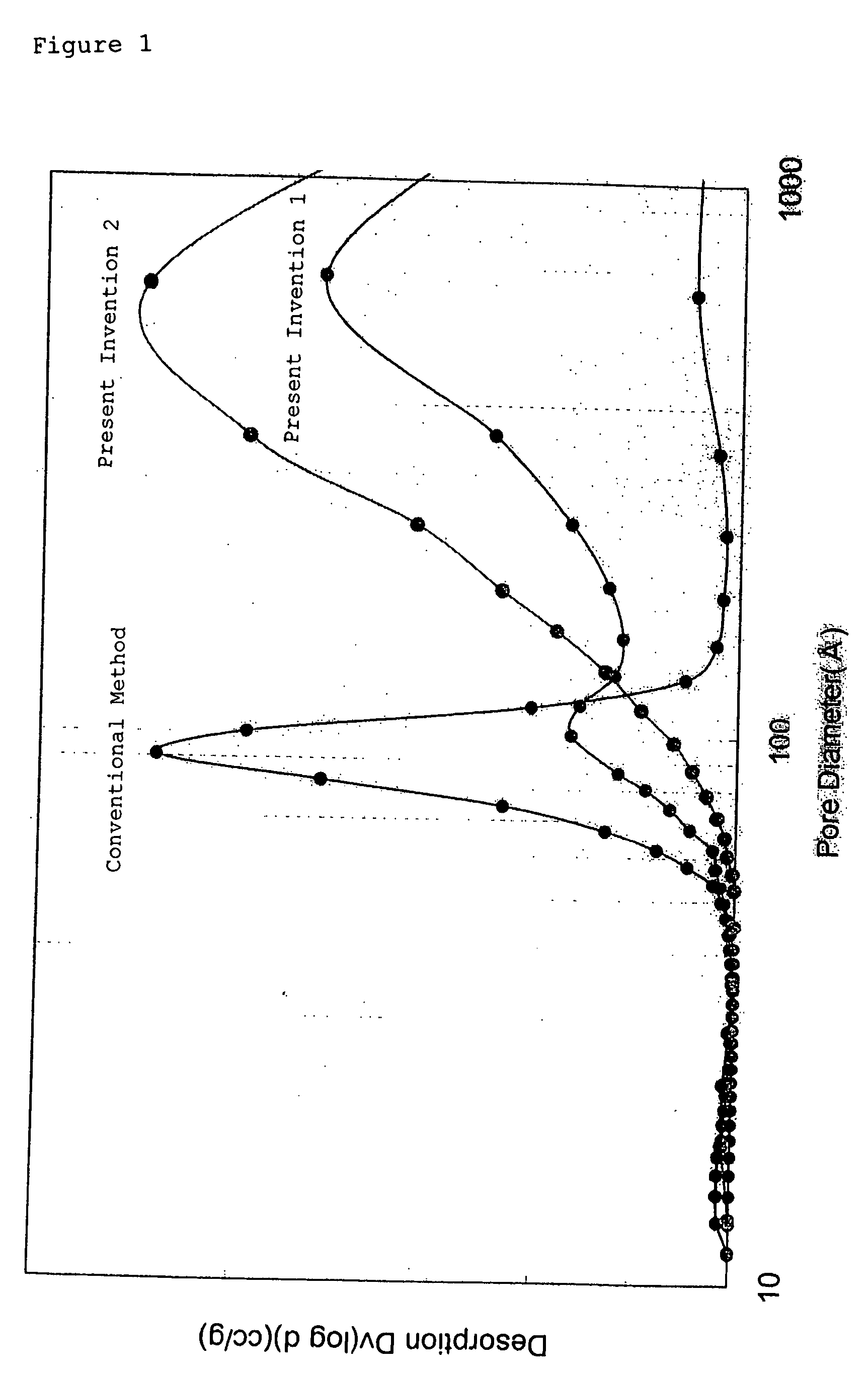
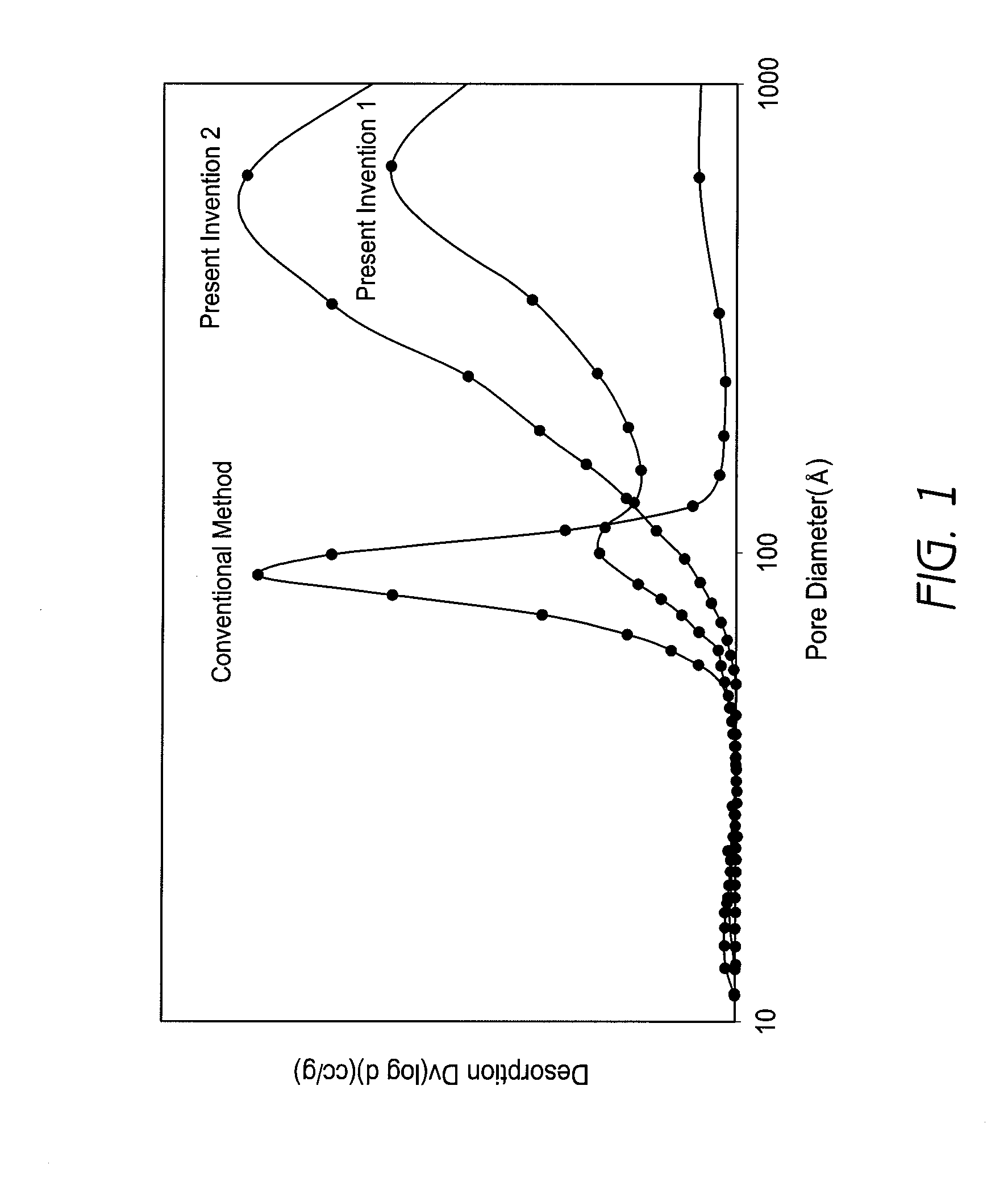
A zirconia porous body with excellent stability of heat resistance is manufactured. This relates to a zirconia porous body having peaks at pore diameters of 8 to 20 nm and 30 to 100 nm in a pore distribution based on the BJH method, with a total pore volume of 0.4 cc / g or more, and to a zirconia porous body having a peak at a pore diameters of 20 to 110 nm in a pore distribution based on the BJH method, with a total pore volume of 0.4 cc / g or more.
Owner:DAIICHI KIGENSO KAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
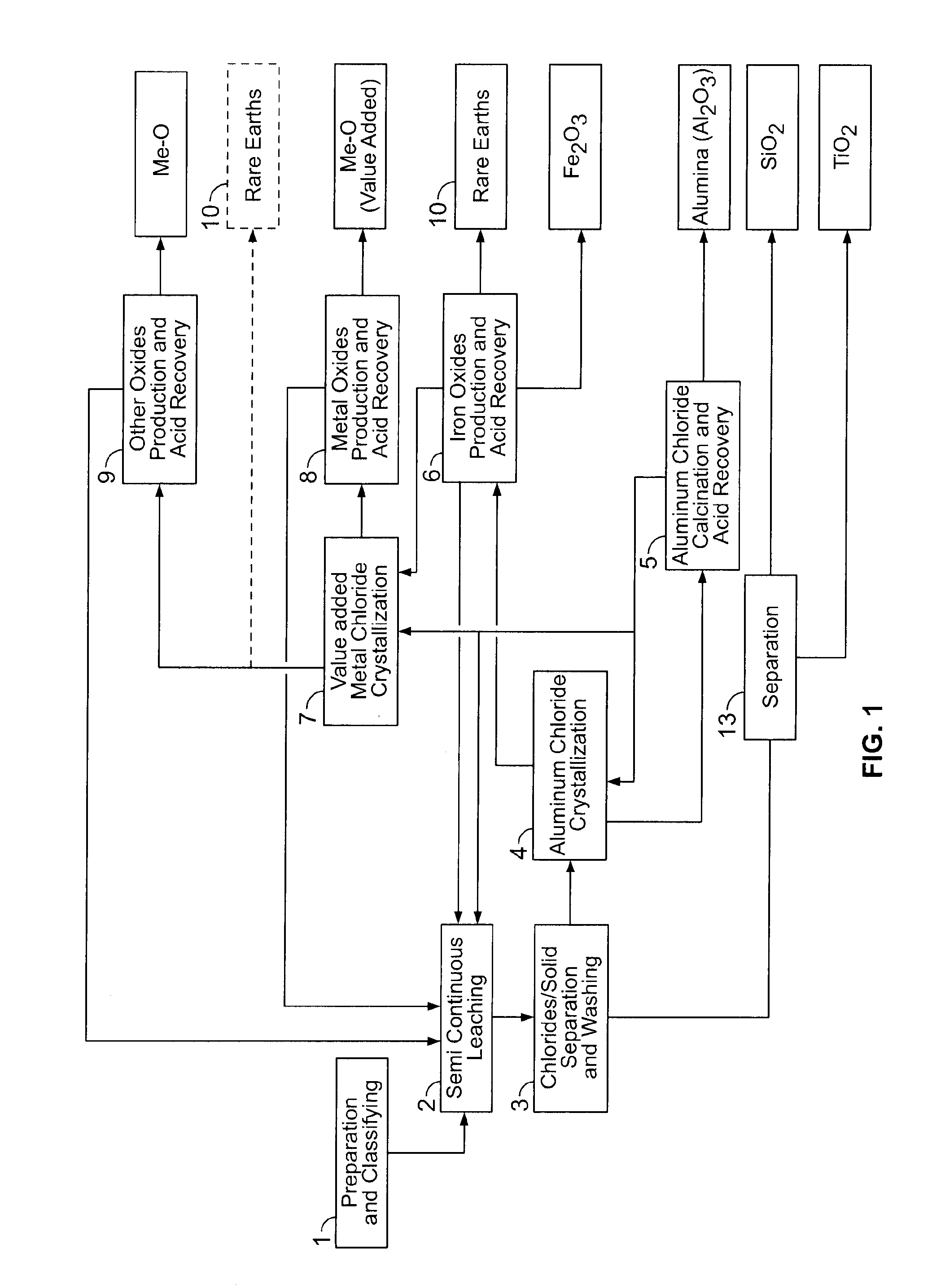
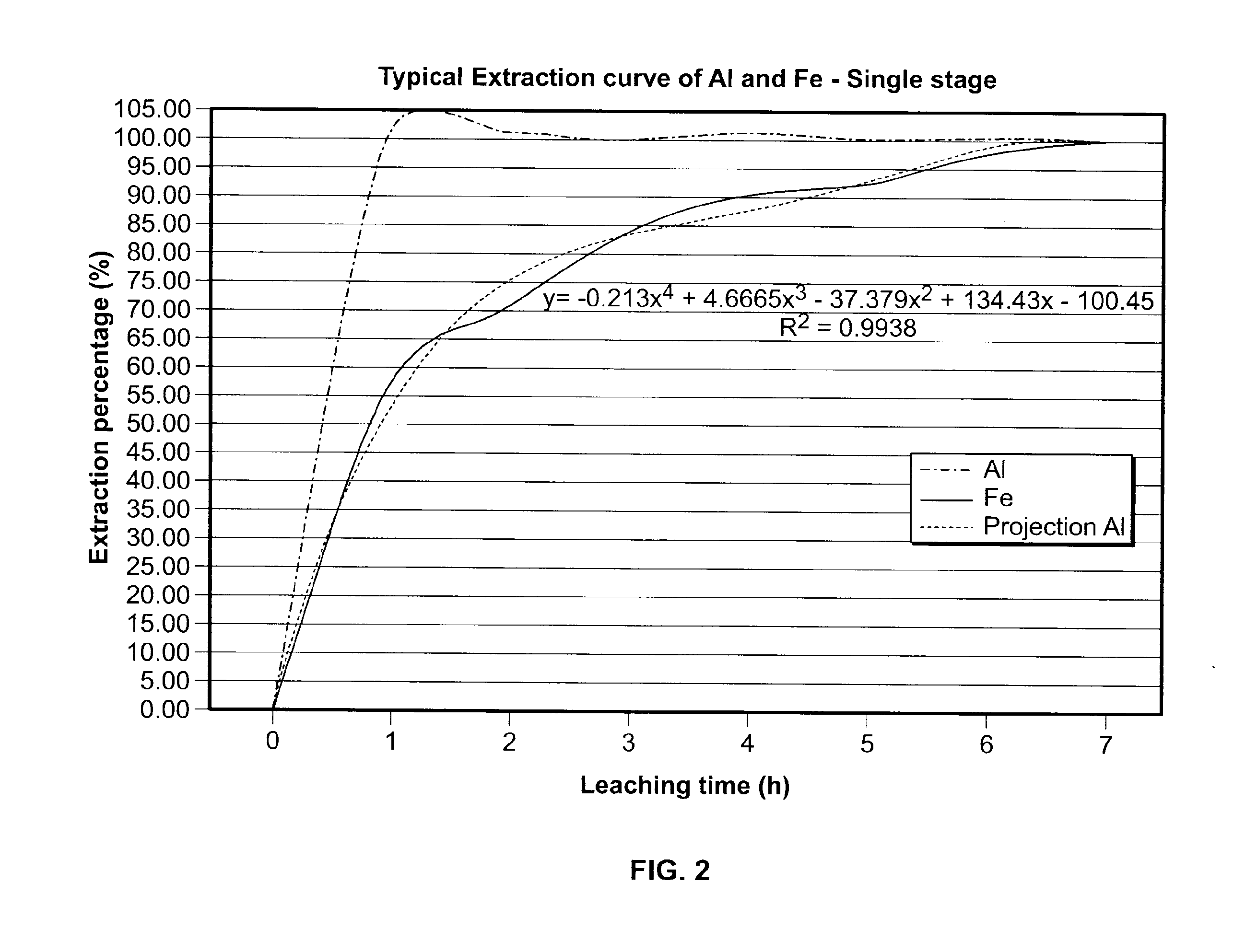
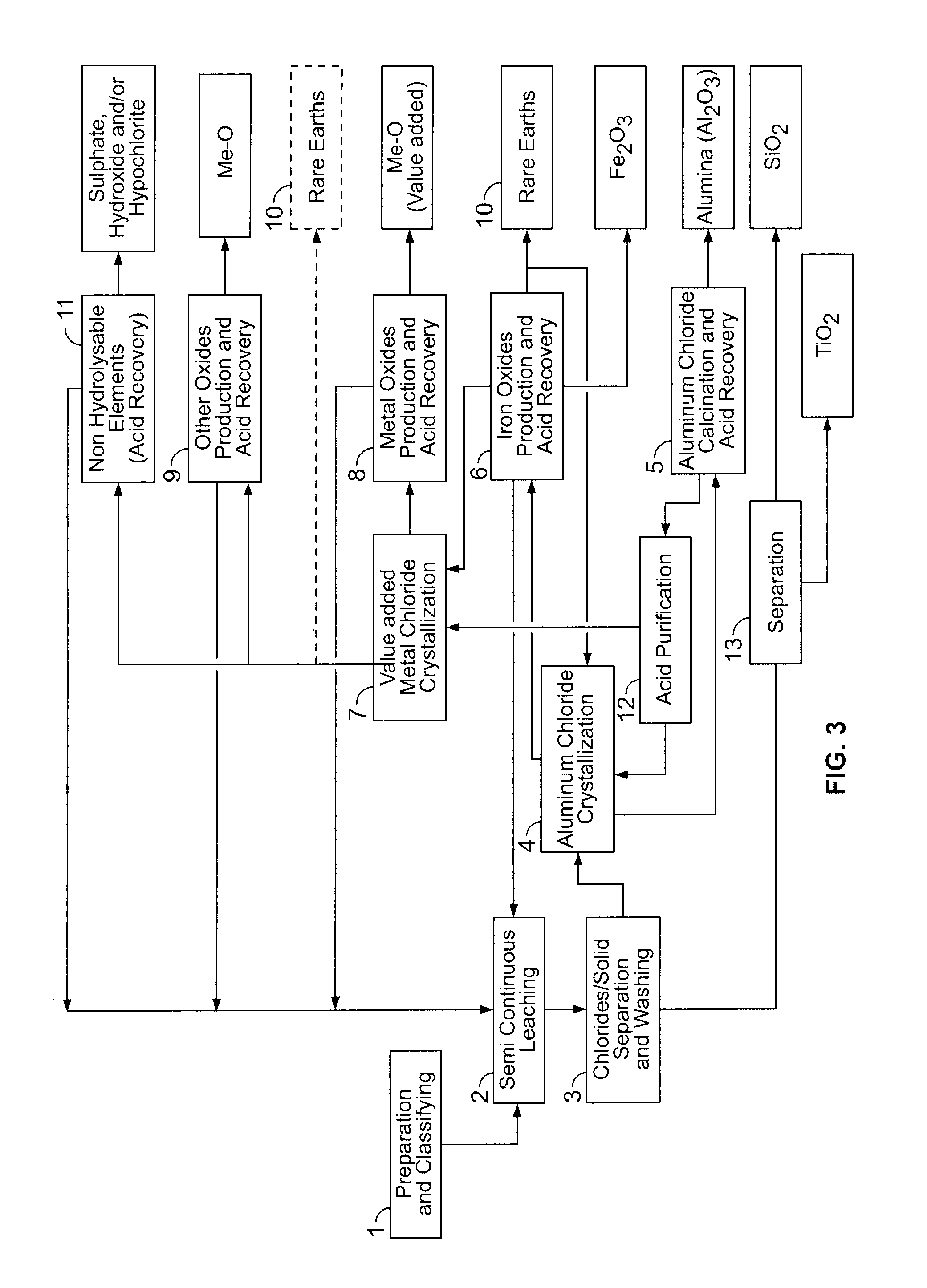
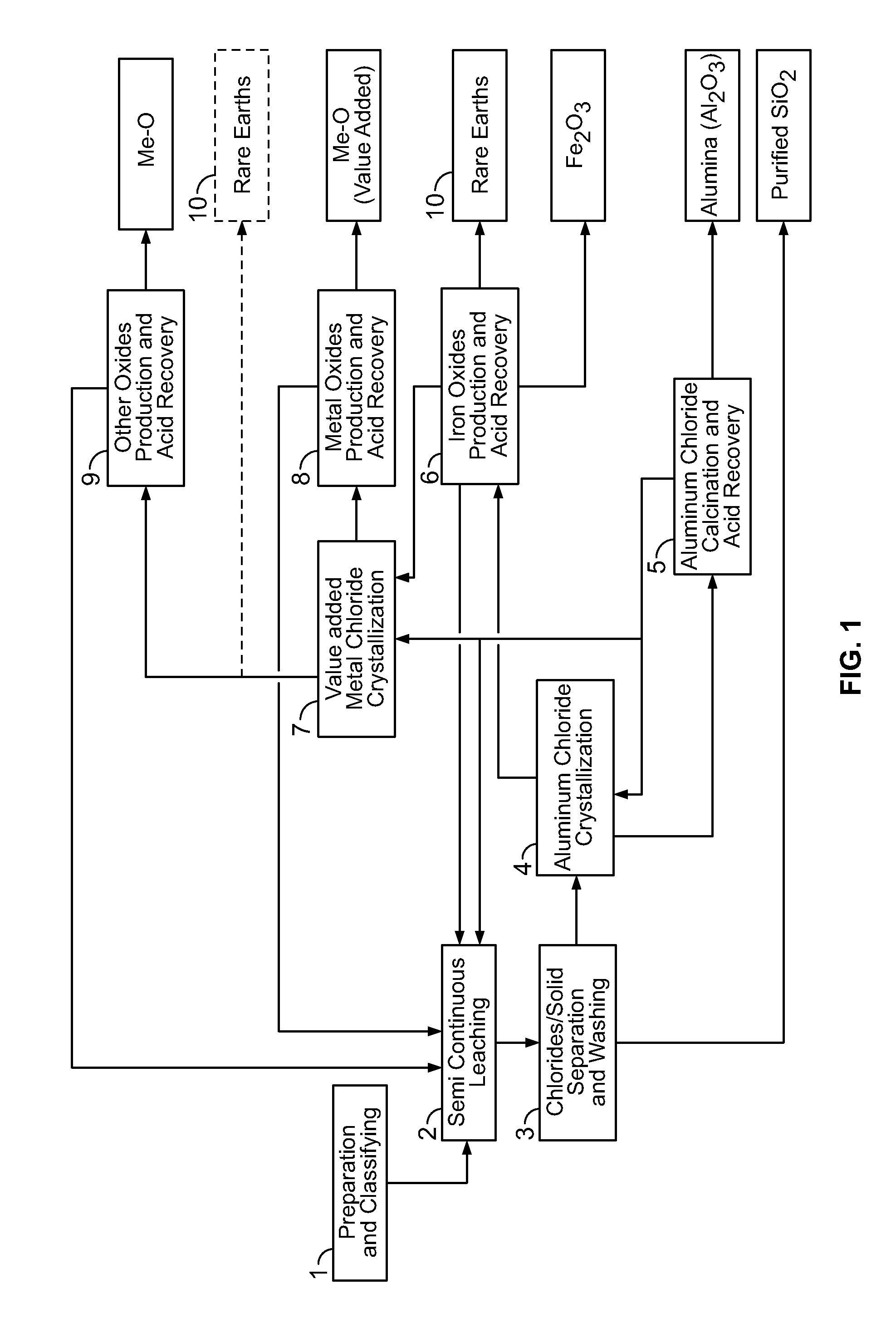
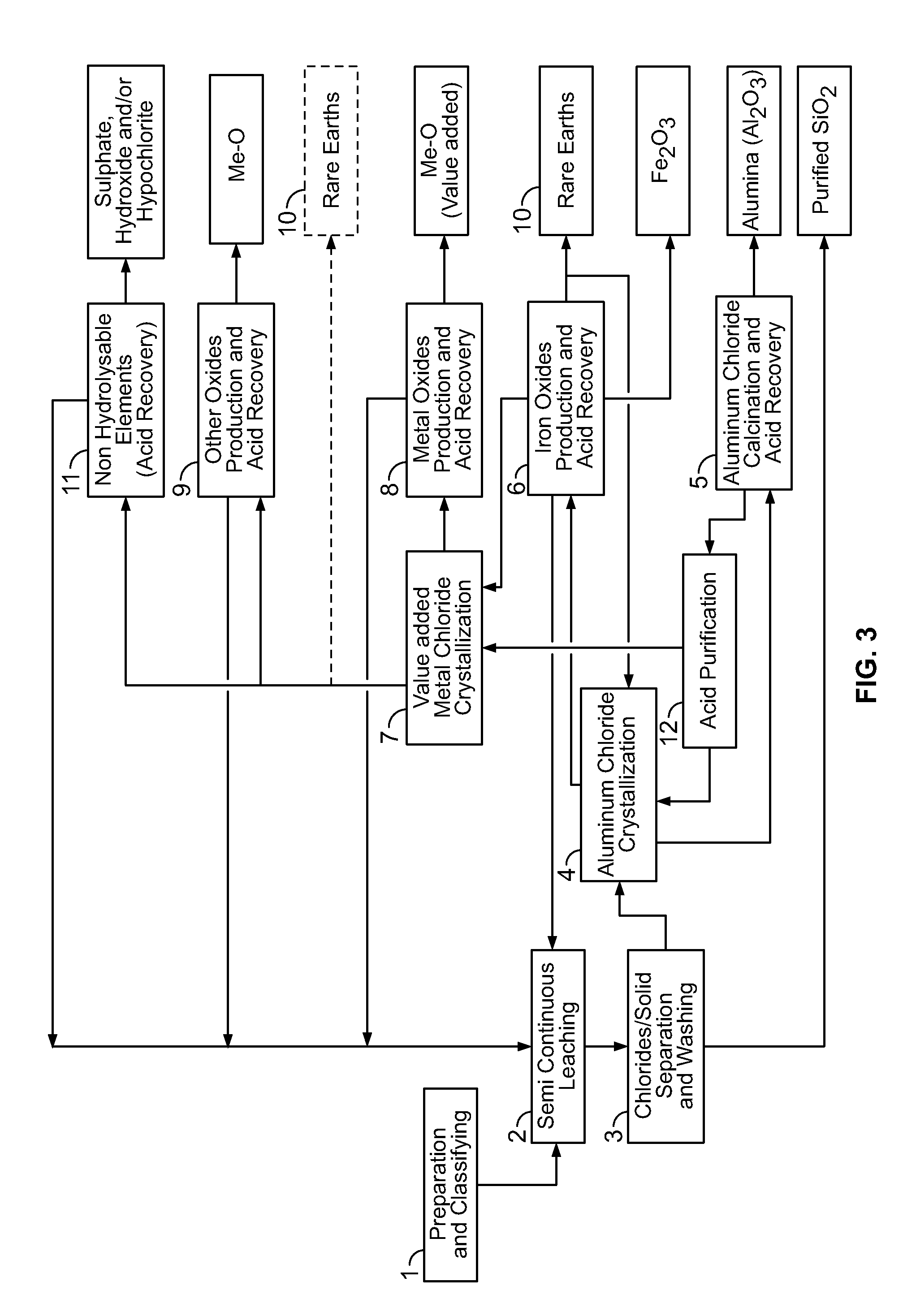
Processes for treating red mud
ActiveUS20140369907A1Simple and efficientLow costAluminium compoundsSolvent extractionPregnant leach solutionRare-earth element
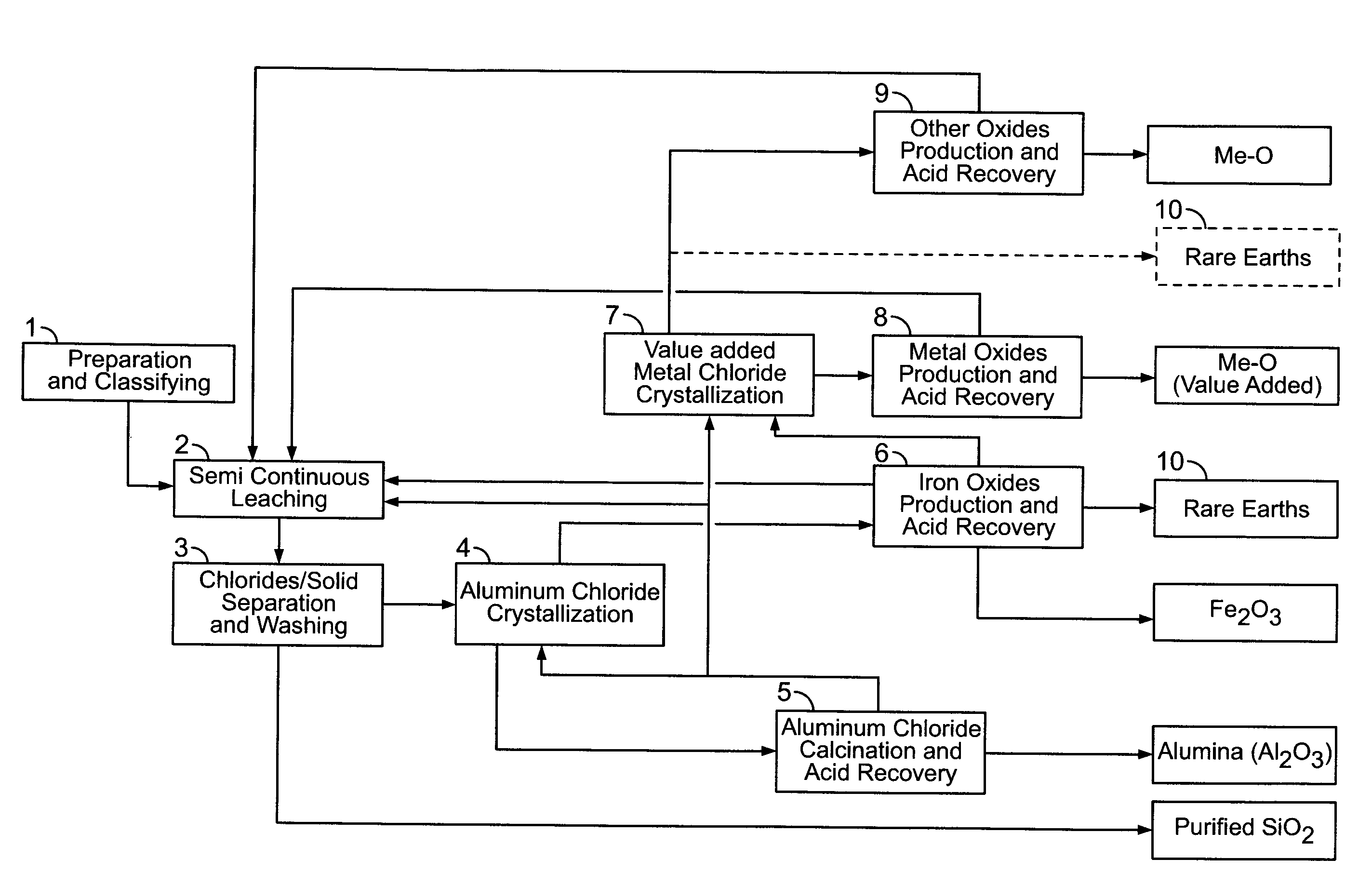
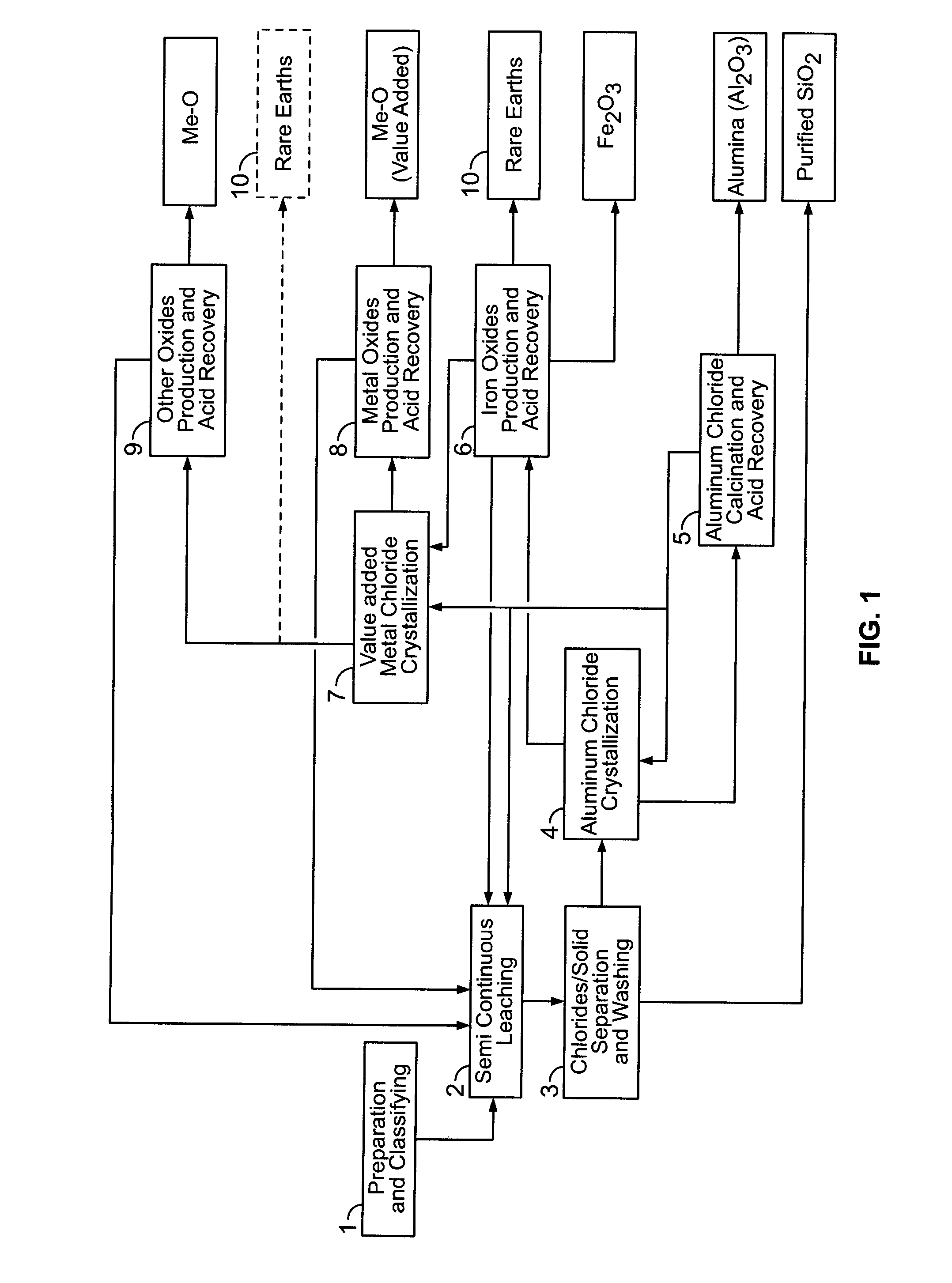
There are provided processes for treating red mud. For example, the processes can comprise leaching red mud with HCl so as to obtain a leachate comprising ions of a first metal (for example aluminum) and a solid, and separating said solid from said leachate. Several other metals can be extracted from the leachate (Fe, Ni, Co, Mg, rare earth elements, rare metals, etc.). Various other components can be extracted from solid such as TiO2, SiO2 etc.
Owner:ORBITE ALUMINAE INC
Cerium oxide-zirconium oxide based composite rare-earth oxide with high specific surface area and high oxygen storage capacity and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103191711ATotal pore volumeFresh specific surface area is highDispersed particle separationCatalyst activation/preparationZirconium hydrideSlurry
The invention discloses a method for preparing a cerium oxide-zirconium oxide based composite rare-earth oxide. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) heating a zirconium salt solution at room temperature, slowly adding sulfate ions, controlling the temperature rise rate so that the temperature is increased in the range of 90-95 DEG C when the sulfate ions are added completely, and then preserving heat for 20-100 minutes, thereby forming a zirconium basic sulfate composite salt precursor; (2) adding a cerium salt and a rare-earth metal salt to the precursor solution and stirring evenly, thereby obtaining a slurry; (3) settling the slurry by using basic carbonate and / or a basic oxalate solution, thereby obtaining a precipitate; and (4) filtering and washing the precipitate obtained in the step (3), removing purities, and calcining the washed precipitate. The cerium oxide-zirconium oxide based composite rare-earth oxide prepared by the method by controlling raw materials and process conditions has the characteristics of being high in total fine pore volume, high in fresh specific surface area, high in oxygen storage capacity and the like.
Owner:CHAOZHOU THREE CIRCLE GRP
Cerium oxide and zirconium oxide based composite rare earth oxide with favorable ageing resistance and high reduction activity and preparation method of cerium oxide and zirconium oxide based composite rare earth oxide
ActiveCN103191712AHigh reactivityTotal pore volumeCatalyst activation/preparationRare earth metal compoundsReduction ActivityZirconium hydride
The invention discloses a preparation method of a cerium oxide and zirconium oxide based composite rare earth oxide. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) weighting zircon salt with a certain mass and preparing a zircon salt solution; (2) mixing urea and sulfuric acid or sulfate to prepare an activating agent solution; (3) heating the zircon salt solution under the room temperature, meanwhile, slowly and dropwise adding the activating agent solution, controlling the temperature rise speed to ensure that the temperature is raised to 60 DEG C after the addition of the activating agent solution is finished, continuing to raising the temperature to 90-95 DEG C, and keeping the temperature for 20-100min to form a basic zirconium sulfate composite salt precursor solution; (4) preparing soluble cerate and rare earth metal salt, adding the soluble cerate and the rare earth metal salt into the basic zirconium sulfate composite salt precursor solution, and settling by using a soluble hydroxide or an aqueous solution of ammonia; and (5) filtering and cleaning precipitates, and then, calcining the precipitates to obtain the cerium oxide and zirconium oxide based composite rare earth oxide. The cerium oxide and zirconium oxide based composite rare earth oxide prepared by using the method provided by the invention has favorable ageing resistance and high reduction activity.
Owner:CHAOZHOU THREE CIRCLE GRP
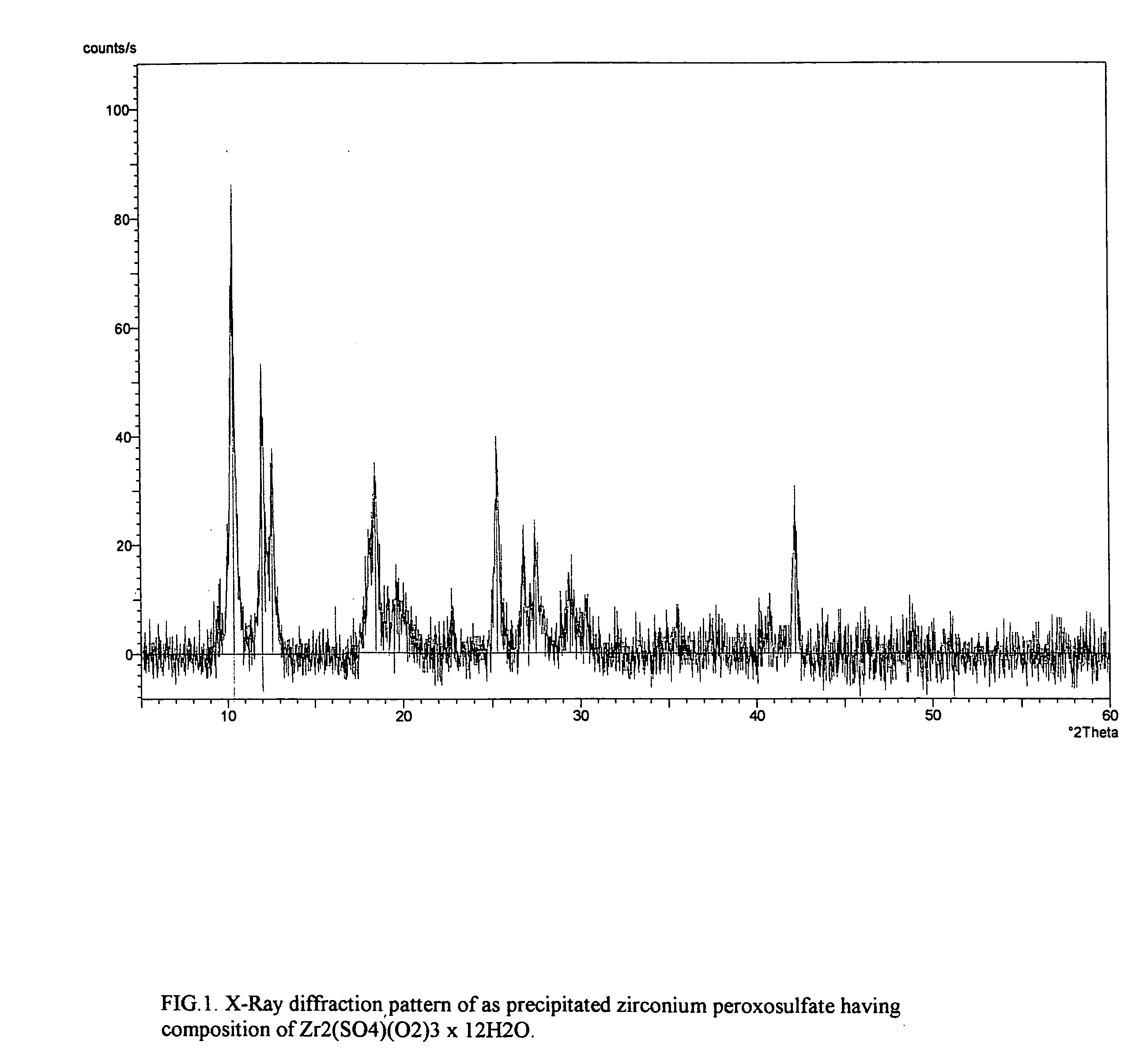
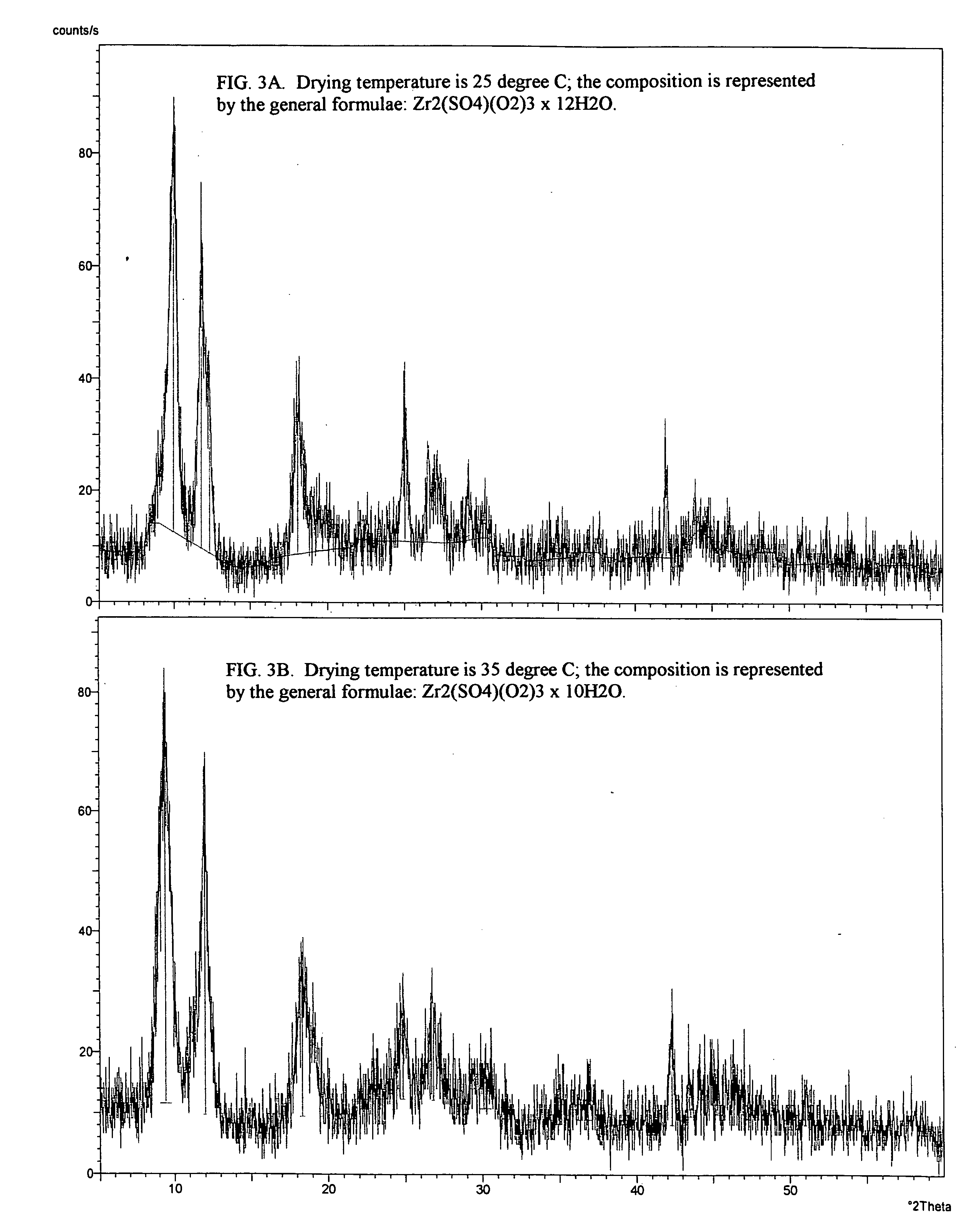
Process for the isolation and purification of zirconium peroxosulfate and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050180911A1High degreeShort processing timePeroxyhydrates/peroxyacidsSulfate preparationPurification methodsZirconium compounds
Provided is a process for isolating zirconium peroxosulfate and its use, either as is or to prepare high purity zirconium compounds including powders of zirconium dioxide and stabilized zirconia. The process is based on precipitating a peroxide compound from an acidic peroxide solution of zirconium and provides a simple, economical method for producing the zirconium peroxosulfate powder and its derivatives with degree of zirconium recovery more than 99%. This process further provides an effective method for the separation and purification of zirconium from a variety of elements and / or naturally occurring ores.
Owner:BELOV VLADIMIR +1
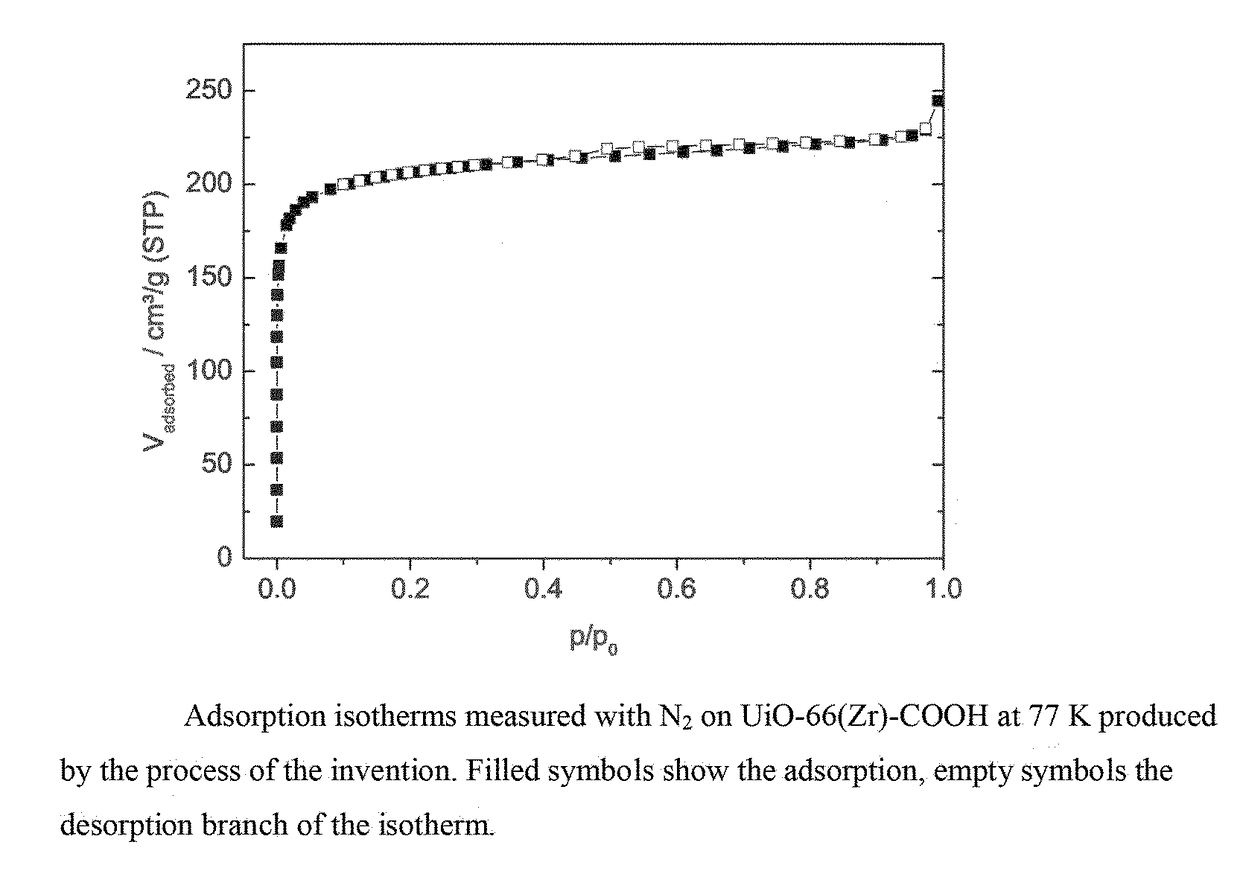
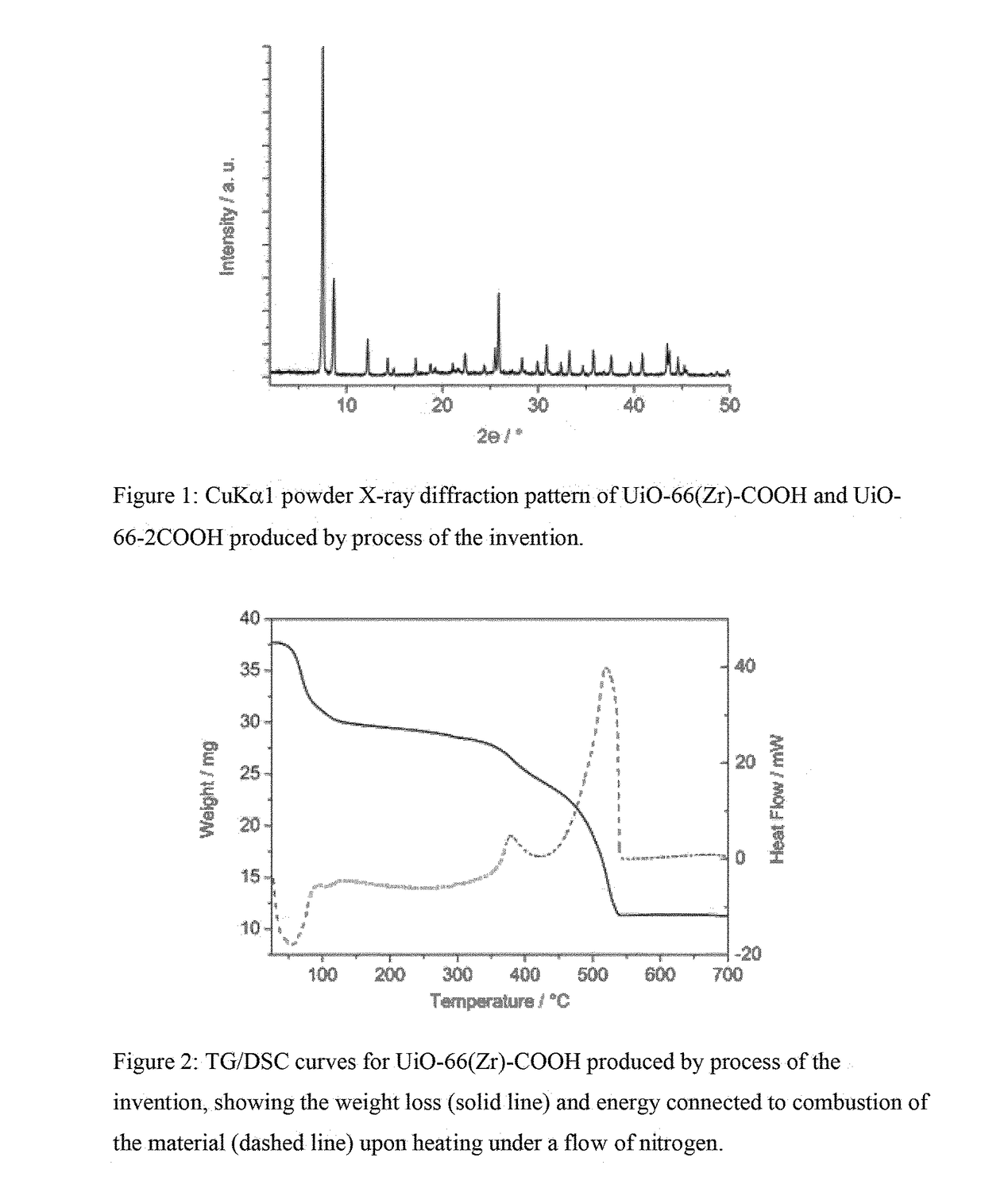
Process for preparing a zirconium-based metal organic framework
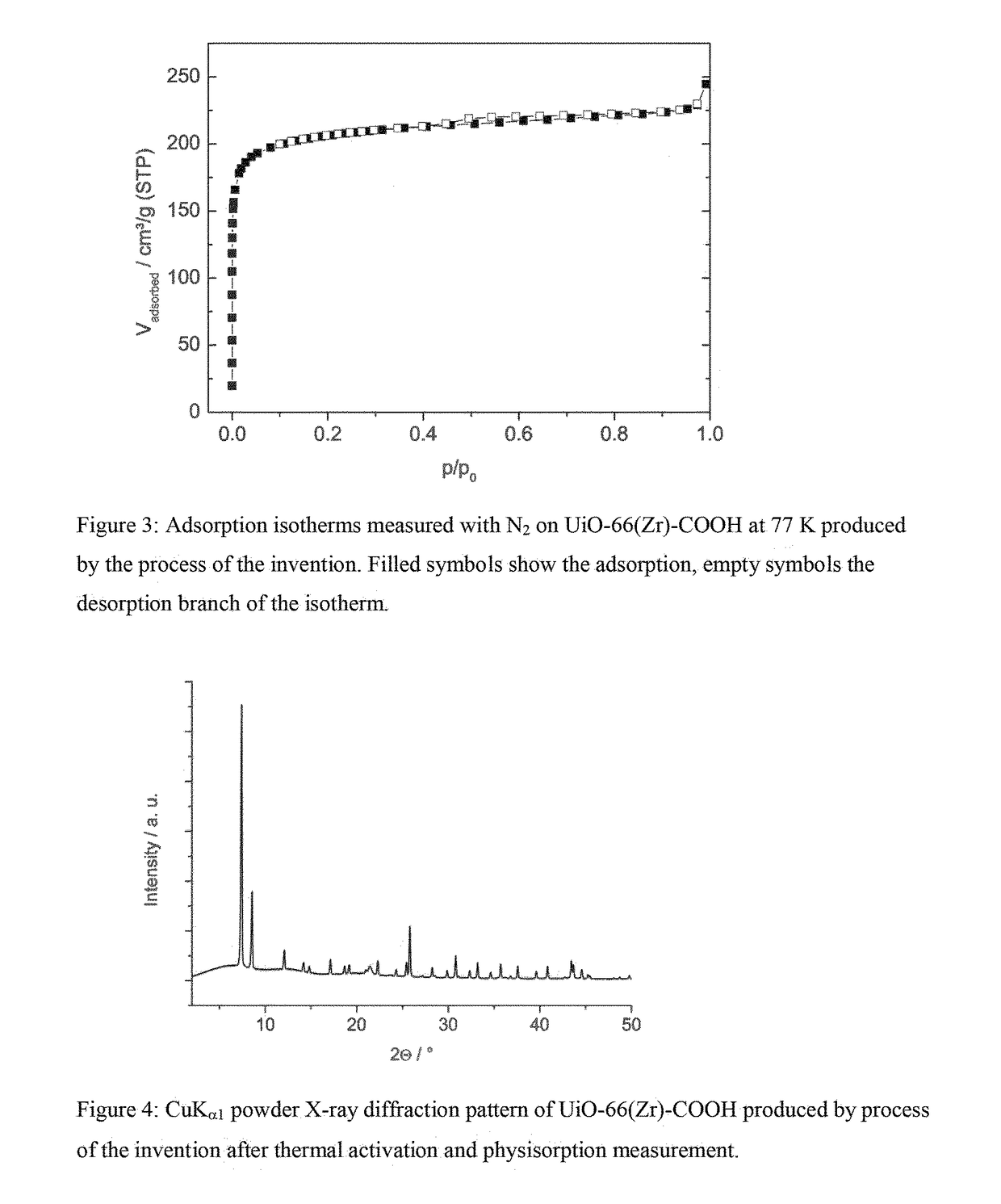
ActiveUS20170291912A1Weakening MOF structureConvenient introductionGroup 4/14 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesZirconium sulfatesChemical compoundMetal-organic framework
There is provided a process for preparing a zirconium-based metal organic framework (Zr-MOF), the process comprising the steps (i) preparing a reaction mixture comprising zirconium ions, sulfate ions and at least one organic linker compound in an aqueous solvent; and (ii) heating the reaction mixture from step (i).
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN +2
Nanostructured titania coated titanium
InactiveUS6835449B2Enhance reliability and lifeConvenient coatingMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentTitaniumNanostructure
A ball valve for use in the pressure acid leaching of nickel ores is disclosed. The valve has a valve body and a ball centrally positioned in the valve body, which has a central passage rotatable in the valve body between open and closed positions. At least one seat is disposed between the ball and the valve body. The ball and seat each comprise a titanium substrate and an ultrafine or nanostructured titania coating. The titania can include from 5 to 45 volume percent of a second phase material that is immiscible with the titania and exhibits corrosion resistance.
Owner:MOGAS IND +1
Preparation method of inorganic fullerene molybdenum disulfide and its application
InactiveCN1752020AImprove anti-wear performanceReduce coefficient of frictionZirconium sulfatesNanoparticlePolyethylene glycol
An inorganic fullerene MoS2 nanoparticle with enclosed nested luminar structure used as the additive of lubricating oil is prepared through proportionally dissolving sodium sulfide and ammonium molybdate in water, reaction while adding the aqueous solution of polyethanediol, dripping hydrochloric acid to obtain MoS3 deposit, centrifugal separation, vacuum drying, hydrodesulfurizing at 500-1000 deg.C in quartz-pipe furnace under protection of Ar gas, and holding the temp for 5-10 hr.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Treatment of a wide range of titanium compounds
InactiveUS20050025687A1Low costEnvironmentally friendlyTitanium halidesProcess efficiency improvementCompound aMicrowave
A process of producing 99% plus titanium dioxide product by using conventional and microwave heating and leaching of the titanium compound feedstock using acid and oxidants. The solid residue from the leaching is used to produce the high quality titanium oxide by froth flotation. Hydrochloric acid can be recovered by multi-stage evaporation. The process can be modified to produce nano-size titanium dioxide product.
Owner:RODOLFO ANTONIO M GOMEZ
Processes for treating red mud
ActiveUS9023301B2Simple and efficientLow costAluminium compoundsNickel compounds preparationRare-earth elementRed mud
There are provided processes for treating red mud. For example, the processes can comprise leaching red mud with HCl so as to obtain a leachate comprising ions of a first metal (for example aluminum) and a solid, and separating said solid from said leachate. Several other metals can be extracted from the leachate (Fe, Ni, Co, Mg, rare earth elements, rare metals, etc.). Various other components can be extracted from solid such as TiO2, SiO2 etc.
Owner:ORBITE ALUMINAE INC
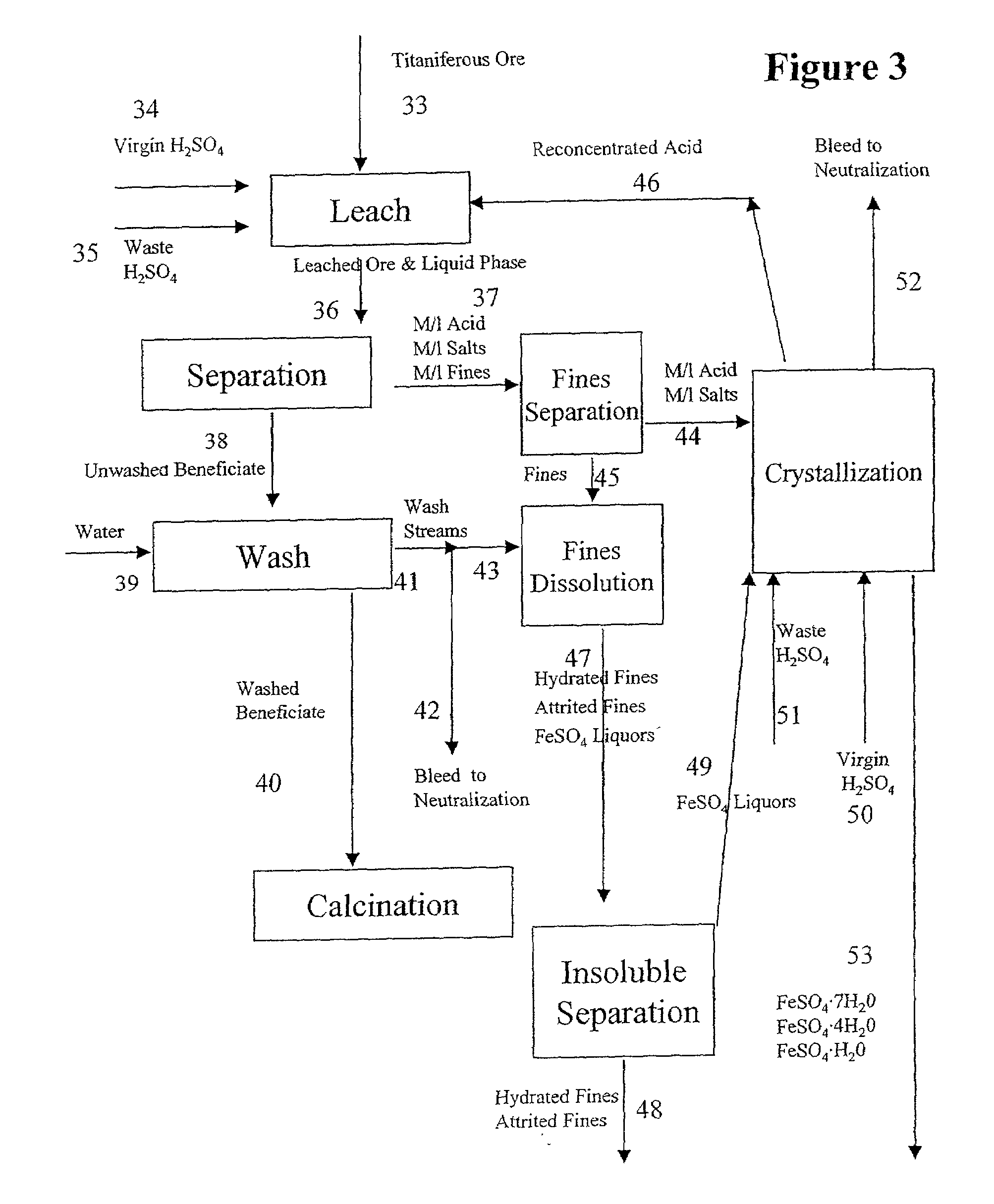
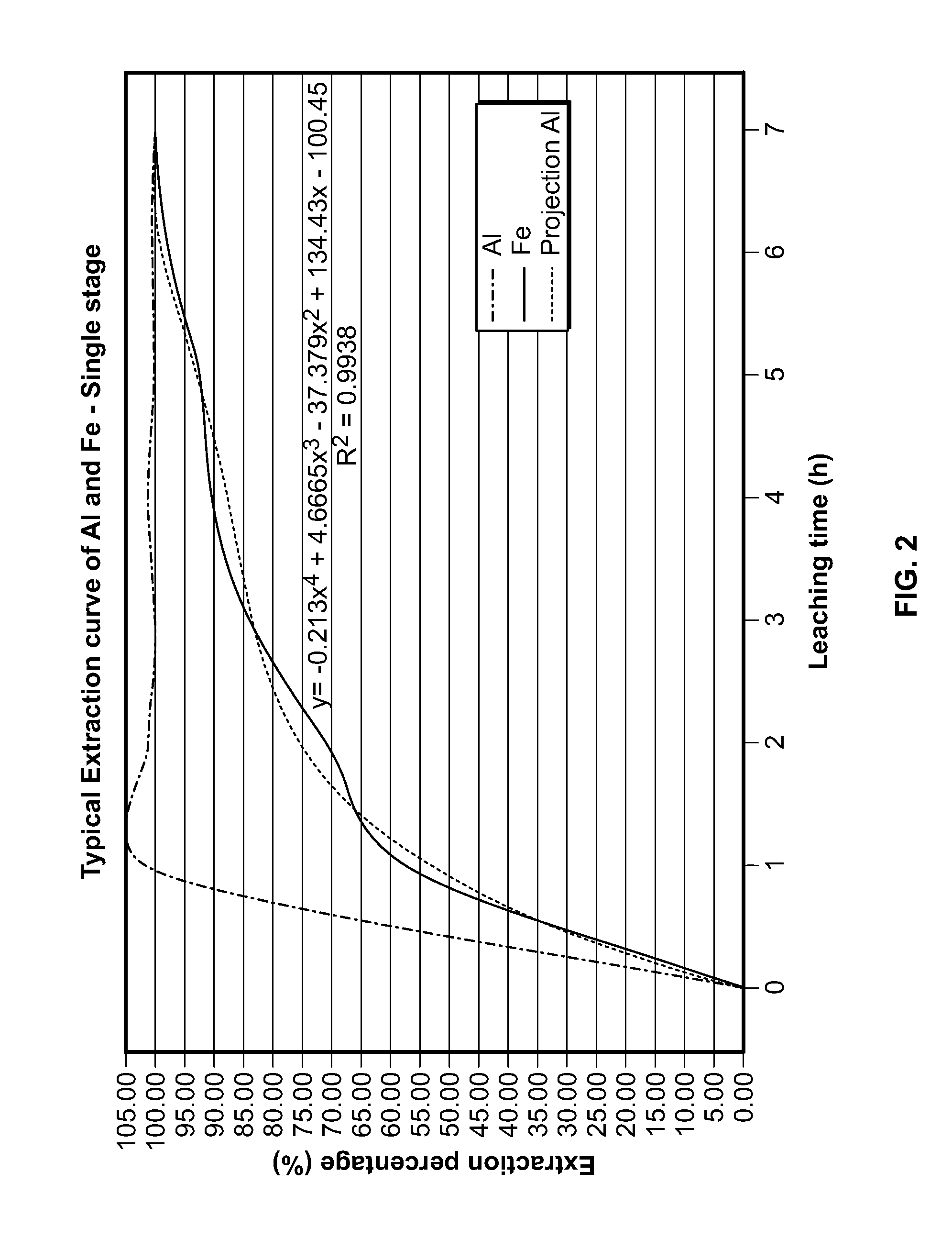
Beneficiation of titaniferous ore with sulfuric acid
InactiveUS7008602B2Low costImprove product qualityTitanium dioxideTitanium halidesTitaniumMaterials science
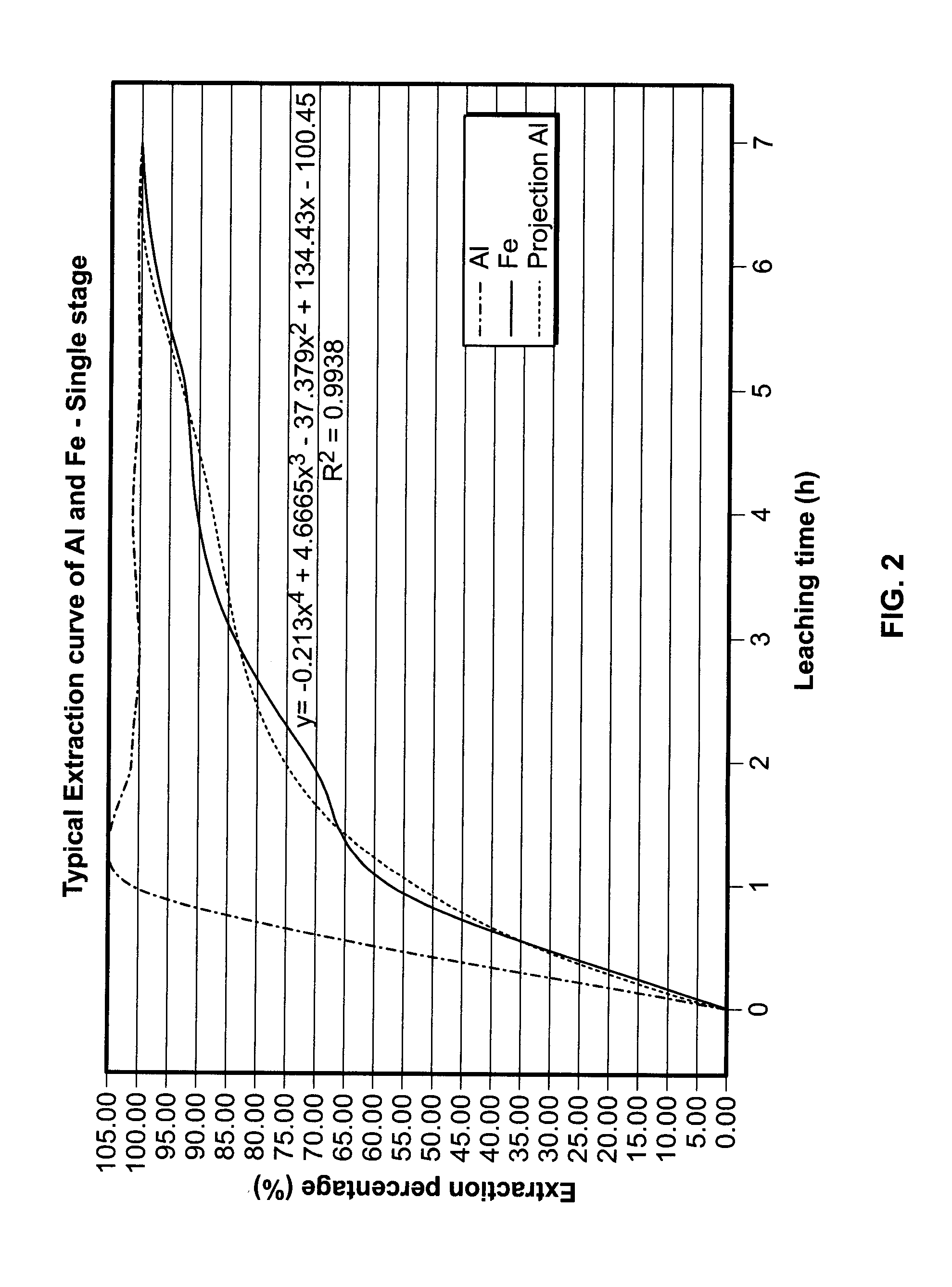
Processes for the efficient and economical beneficiation of titaniferous ore are provided. A unique process for beneficiating ore comprising pretreatment of the ore by oxidation and reduction, followed by acid leaching with sulfuric acid has been developed. The acid used in this process may be recycled, which will thereby increase the efficiency of the process. Preferably the ore treated according to the present invention is ilmenite ore.
Owner:TRONOX LLC
Benefication of titania slag by oxidation and reduction treatment
InactiveUS6803024B1Improve leaching effectTitanium dioxideTitanium halidesReduction treatmentGranularity
This invention relates to a method of treating titania slag to increase the leachability of impurities from the slag consisting of the steps of sizing the titania slag to a particle size from 75 to 850 mum; oxidizing the sized slag particles at a temperature from about 700° C. to below about 900° C. causing the iron present in the slag to concentrate at the exposed surfaces of the slag particles and / or causing an anatase phase to stabilize in the slag, causing a major portion of the iron in the Fe(II) state to convert to the Fe(III) state, and causing the titanium in the Ti(III) state to be converted to the Ti(IV) state; and reducing the oxidized slag in a reducing atmosphere from about 700° C. to about 950° C. to convert a major portion of the iron in the Fe(III) state to the Fe(II) state. The invention also relates to a method of beneficiating titania slag to increase the TiO2 content thereof wherein the above treated slag is leached with acid.
Owner:EXXARO TSA SANDS
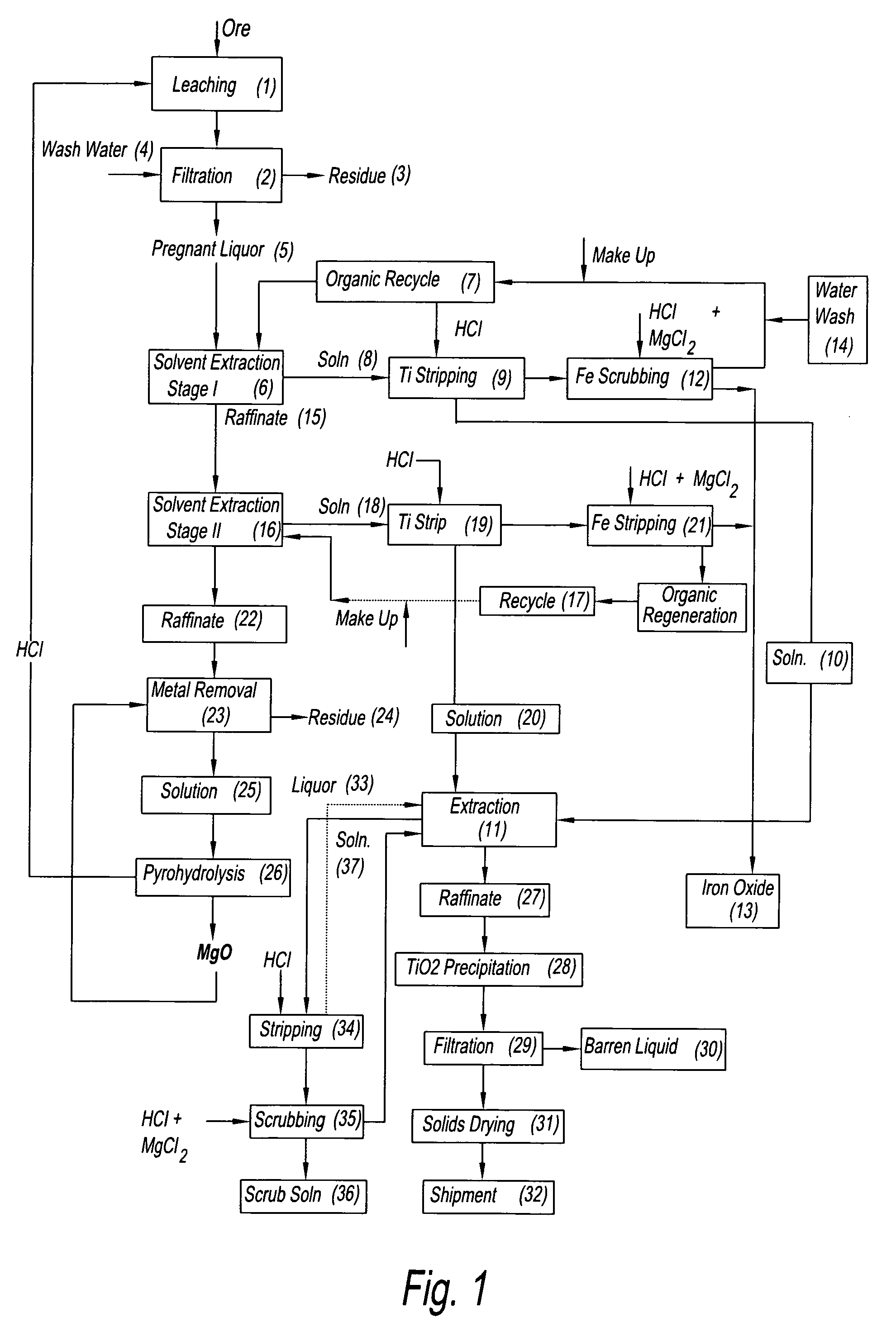
Processes for preparing titanium oxide and various other products
There are provided processes for preparing various products from various materials. For example, such processes are effective for extracting titanium and various other metals from various materials, thereby allowing for preparing products such as titanium chloride and titanium oxide. These processes can comprise leaching the starting material with HCl so as to obtain a leachate and a solid. The solid can be treated so as to substantially selectively extract titanium therefrom while the leachate can be treated so as to substantially selectively recover a first metal chloride therefrom.
Owner:ORBITE ALUMINAE INC
Process for the recovery of titanium in mixed chloride media
Owner:CANADIAN TITANIUM
Agglomeration of titania
InactiveUS7931886B2Conducive to agglomerationImprove bindingPigmenting treatmentIron oxides/hydroxidesChloride process
According to the present invention there is provided a process for the agglomeration of titania slag particles comprising providing titania slag at a d50 particle size of below 106 μm; mixing the slag particles with an organic binder; and agglomerating the mixture of the slag particles and organic binder into agglomerated particles with a d50 particle size in the range from 106 μm to 1000 μm. The agglomerated particles have a (TiO2 and FeO) / C mass ratio of more than 3.4. The invention also relates to such agglomated slag particles and a chloride process for the production of TiO2 wherein such agglomerated titania slag particles are used.
Owner:EXXARO TSA SANDS
Processes for treating red mud
ActiveUS20150275330A1Simple and efficientLow costAluminium compoundsNickel compounds preparationPregnant leach solutionRare-earth element
Owner:AEM TECH INC
Production process of basic zirconium sulphate
The invention provides a direct production process of basic zirconium sulphate from the strong acid salt of zirconium, sulphates, alkali of base or alkaline-earth metal (including ammonium), which comprises, mixing zirconium strong acid salt solid material or sulphate, alkali of base or alkaline-earth metal (including ammonium) by a finite proportion directly, stirring, grinding to result in complete reaction, washing and dewatering to produce the alkali zirconium sulfate.
Owner:柳云珍
Method of separating and purifying zircon fron basic rock
InactiveCN1752019AImprove sorting efficiencyReduce sorting costsZirconium sulfatesDiiodomethaneMagnetic stirrer
A process for separating zircon from basic rock and purifying it includes such steps as crushing and pulverizing basic rock, magnetic stirring while removing strong magnetic substance by U-shaped magnet, using three magnetic rods to respectively remove weak magnetic, strong electromagnetic and weak electromagnetic minerals, using miniature shaker to remove the most of light mineral, electromagnetically fine separation by multi-purpose magnetic analyzer, using heavy diiodomethane solution for separation in separating funnel to remove light minerals and examine by binocular microscope. Its advantages are high purity (more than 99%) and short period.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF GEOCHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
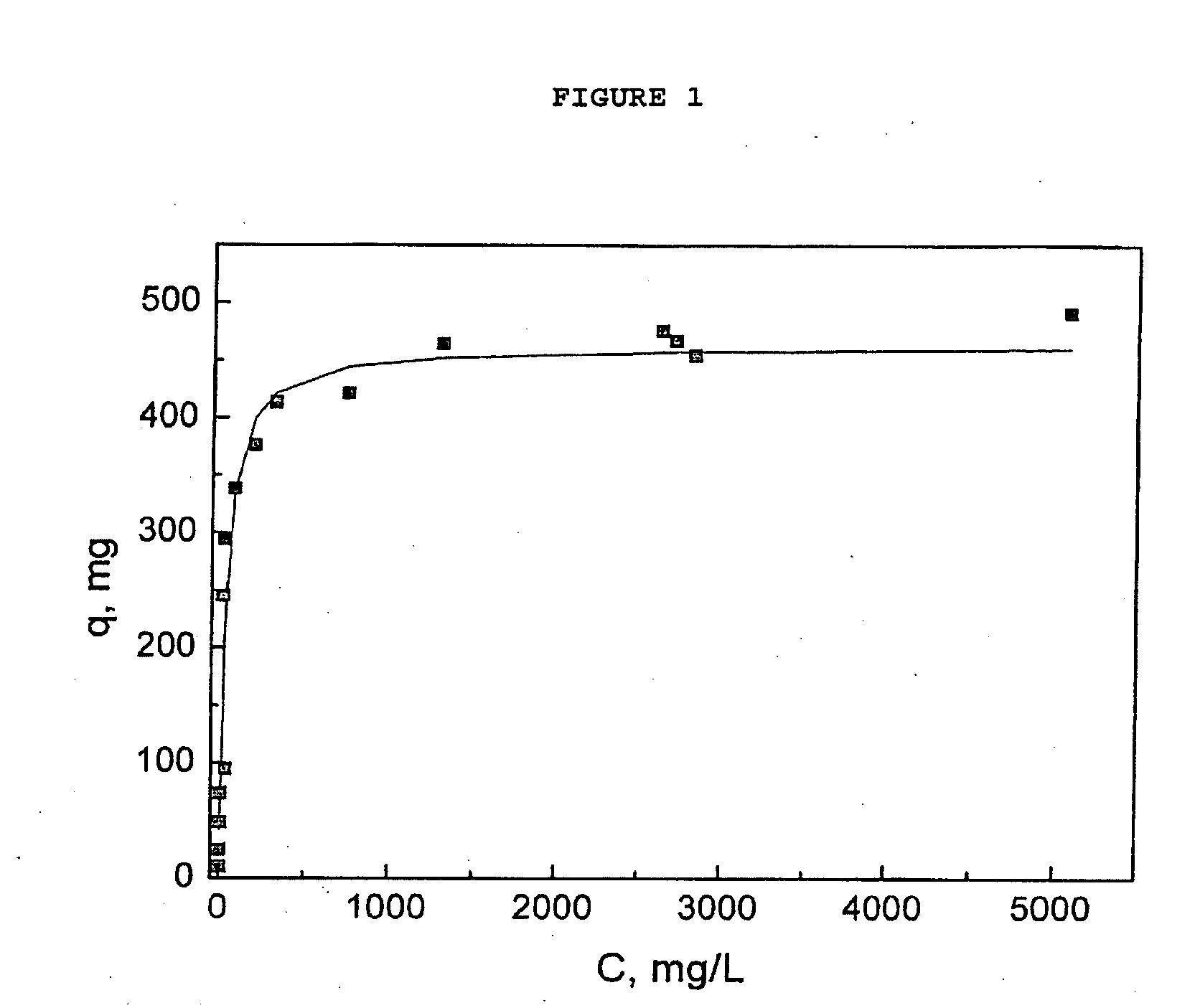
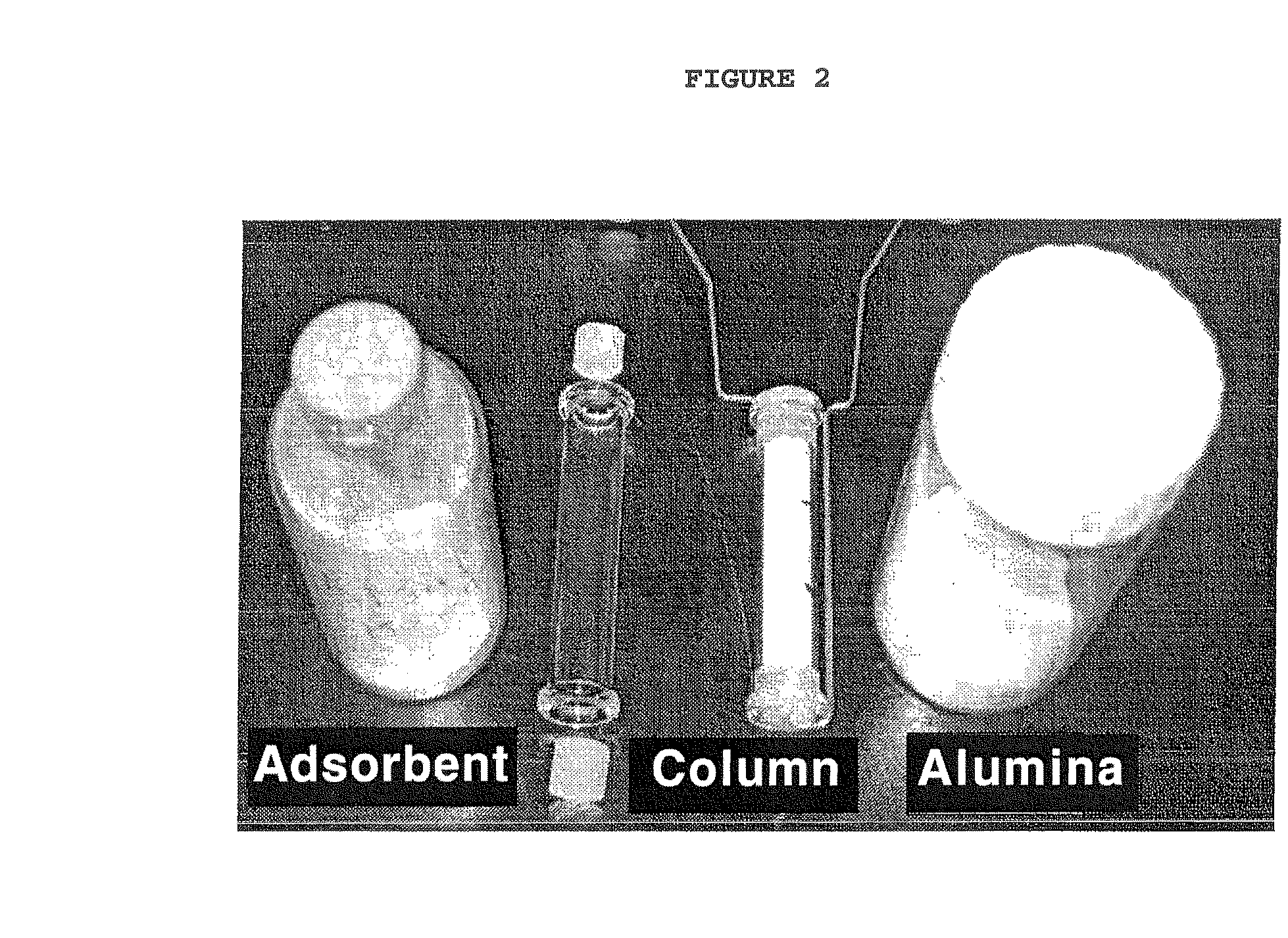
Adsorbents for Radioisotopes, Preparation Method Thereof, and Radioisotope Generators Using the Same
InactiveUS20090277828A1Improve physical stabilityImprove adsorption capacitySpecific isotope recoverySulfate/bisulfate preparationSorbentIsotope
Disclosed is a novel adsorbent for use in a 99Mo / 99mTc generator, which is a medical diagnostic radioisotope generator, and in a 188W / 188Re generator, which is a therapeutic radioisotope generator. The adsorbent composed of sulfated alumina or alumina-sulfated zirconia exhibits adsorption capacity superior to that of conventional adsorbents, and is stable and is thus loaded in a dry state in an adsorption column so that the radioisotope 99Mo or 188W can be adsorbed. Thus, it is possible to miniaturize the column, and such a miniaturized column is small, convenient to use, and highly efficient, and extracts a radioisotope satisfying the requirements for pharmaceuticals, and thus can be useful for radioisotope generators extracting 99mTc or 188Re.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Titaniferous ore beneficiation
ActiveUS20080241026A1Reduced impurity levelsIncrease contentTitanium dioxideTitanium halidesAlkaline earth metalChloride
This invention relates to a process for beneficiating a titaniferous ore. The process comprises calcining the titaniferous ore, at least one alkali or alkaline earth metal salt, and at least one alumina-containing material in the presence of oxygen to form a calcined ore mixture, then leaching the calcined ore mixture with a solution comprising ammonium, sodium or magnesium chloride in the presence of oxygen to form a leached ore mixture, and contacting the leached ore with an acid to form a beneficiated ore.
Owner:UNIV OF LEEDS
Titaniferous ore beneficiation
InactiveUS20070092416A1Reduced impurity levelsTitanium halidesProcess efficiency improvementTitaniumCalcination
This invention relates to a process for beneficiating a titaniferous ore. The process comprises leaching the titaniferous ore with sulfuric acid to form a leached ore, calcining the leached ore in the presence of oxygen to form a calcined ore, and leaching the calcined ore with sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, and / or nitric acid to form a beneficiated ore. The leached ore is not reduced prior to or following calcination.
Owner:TRONOX LLC
Sulfate process
A sulfate process for producing titania from a titaniferous material (as herein defined) including a step of leaching said titaniferous material with a leachant to form a process solution that includes an acidic solution of titanyl sulfate and iron sulfate, wherein said sulfate process further includes a filtration step comprising filtering said leachant to at least substantially remove titanyl sulfate particles from said leachant prior to supplying said leachant to said leach step.
Owner:BHP BILLITON INNOVATION PTY LTD
Cerium oxide and zirconium oxide based composite rare earth oxide with favorable ageing resistance and high reduction activity and preparation method of cerium oxide and zirconium oxide based composite rare earth oxide
ActiveCN103191712BHigh reactivityTotal pore volumeDispersed particle separationCatalyst activation/preparationReduction ActivityZirconium hydride
Owner:CHAOZHOU THREE CIRCLE GRP
Production of high-grade synthetic rutile from low-grade titanium-bearing ores
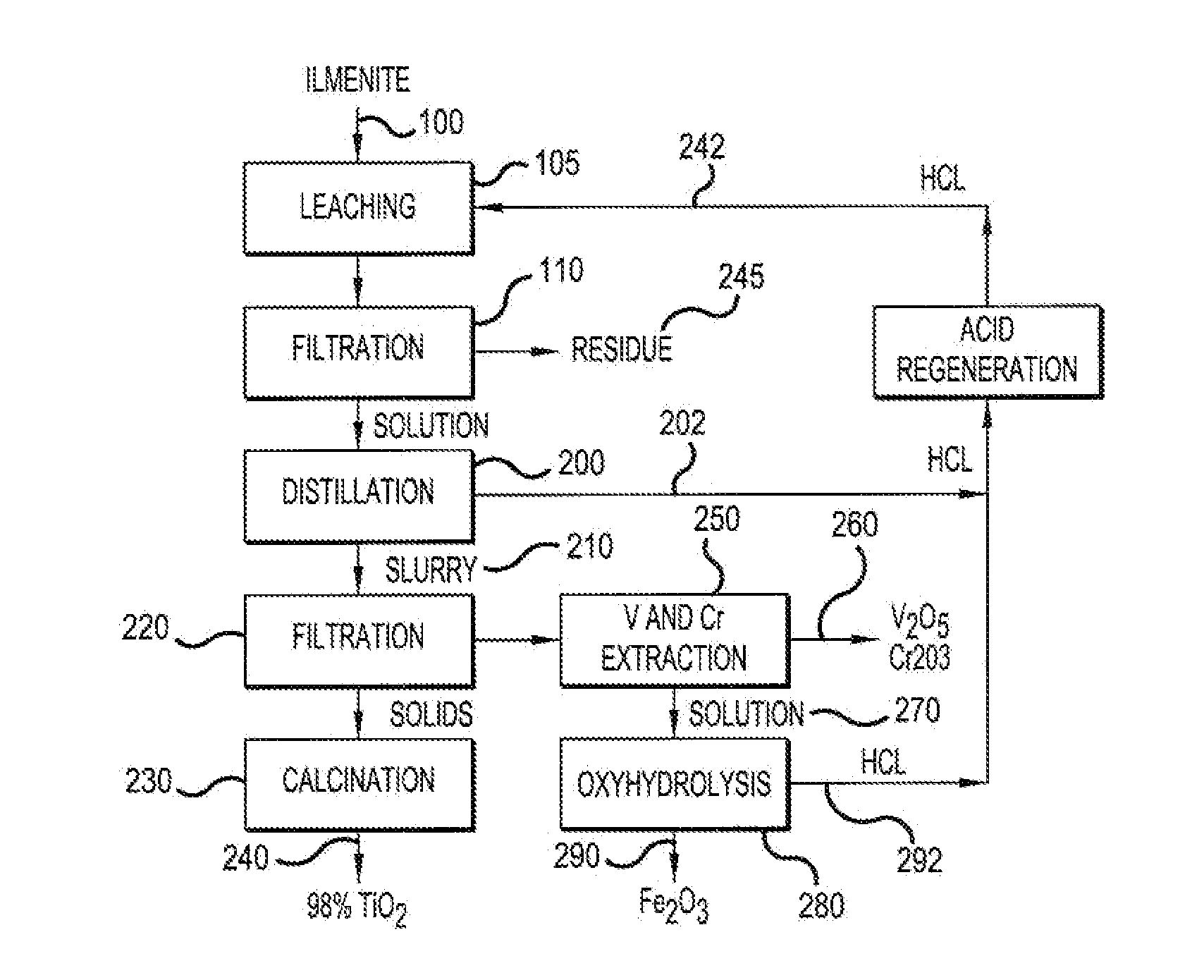
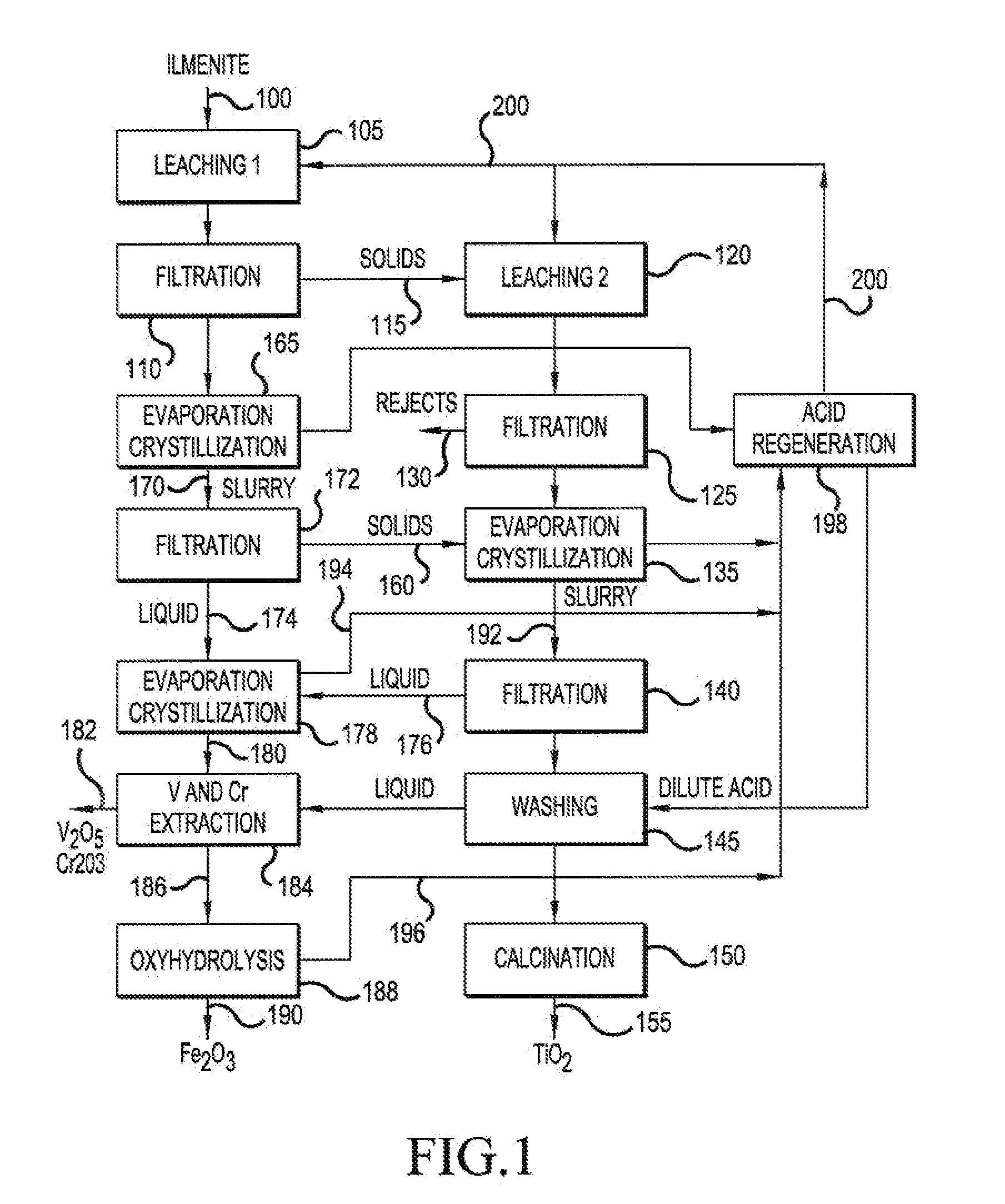
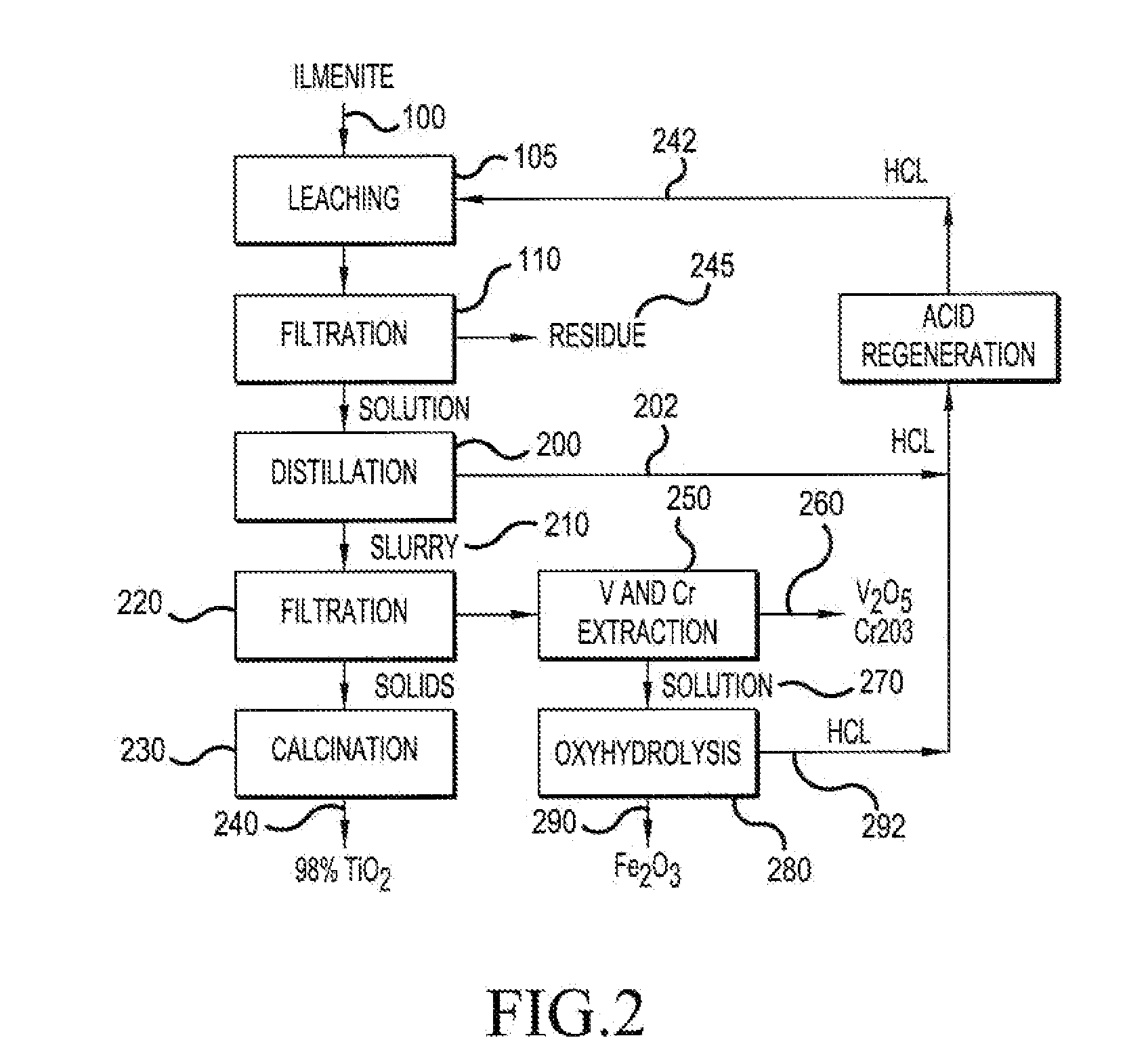
The present invention relates to a two-stage leaching process using concentrated hydrochloric acid that upgrades a variety of inferior quality titanium-iron ores into premium titanium concentrate and iron oxide products. The ground ore is leached with two separate quantities of hydrochloric acid after which the dissolved titanium is precipitated from the filtered liquor by hydrolysis. The still soluble iron chlorides are then optionally subjected to oxyhydrolysis to recover iron oxide and HCl. The process was developed for low-grade ores (under 12% TiO2), and can be naturally applied advantageously to higher grade titanium-bearing ores.
Owner:FFK TECH INC
Removal of contaminants from by-product acids
InactiveUS7704470B2Effective treatmentProvide usageChlorine/hydrogen-chloride purificationSilicaPhosphate ionTitanium
Owner:HAYDOCK CONSULTING SERVICES LC
Process for recovering titanium dioxide
An improved process for recovering a titanium dioxide product from a titanium oxide-containing roasted mass of the type derived from roasting an ilmenite, anatase or perovskite ore by exploiting an organic acid, such as mixture of oxalic acid and ascorbic acid.
Owner:UNIV OF LEEDS
Method for preparing zirconium sulfate tetrahydrate with zirconium carbonate production wastewater
The invention discloses a method for preparing zirconium sulfate tetrahydrate with zirconium carbonate production wastewater. The method comprises the technical steps of: (1) adjusting a pH (Potential of Hydrogen) value of the zirconium carbonate production wastewater with dilute alkali, performing sedimentation, (2) pumping the wastewater into a plate-and-frame filter press for press filtration, purging with compressed air after the press filtration, removing a plate, obtaining zirconium hydroxide, (3) dissolving zirconium hydroxide in sulfuric acid or zirconium sulfate tetrahydrate mother liquor at a mass-volume ratio of 1:(1-3), heating to 50-60 DEG C to completely dissolve zirconium acyl hydroxide, filtering off mechanical impurities, and (4) adding concentrated sulfuric acid into filtrate to adjust a system sulfuric acid concentration to 50-70%, naturally cooling to 40 DEG C for crystallization, centrifuging, and obtaining zirconium sulfate tetrahydrate. The method is simple in technology, prepares zirconium sulfate tetrahydrate with the zirconium carbonate production wastewater, and prevents the zirconium carbonate production wastewater from influencing an environment; obtained zirconium sulfate tetrahydrate is high in purity and is up to a national first grade standard; since the zirconium sulfate tetrahydrate mother liquor is recycled, the production cost is lowered effectively; and environmental resources are saved.
Owner:JIANGXI KINGAN HI TECH
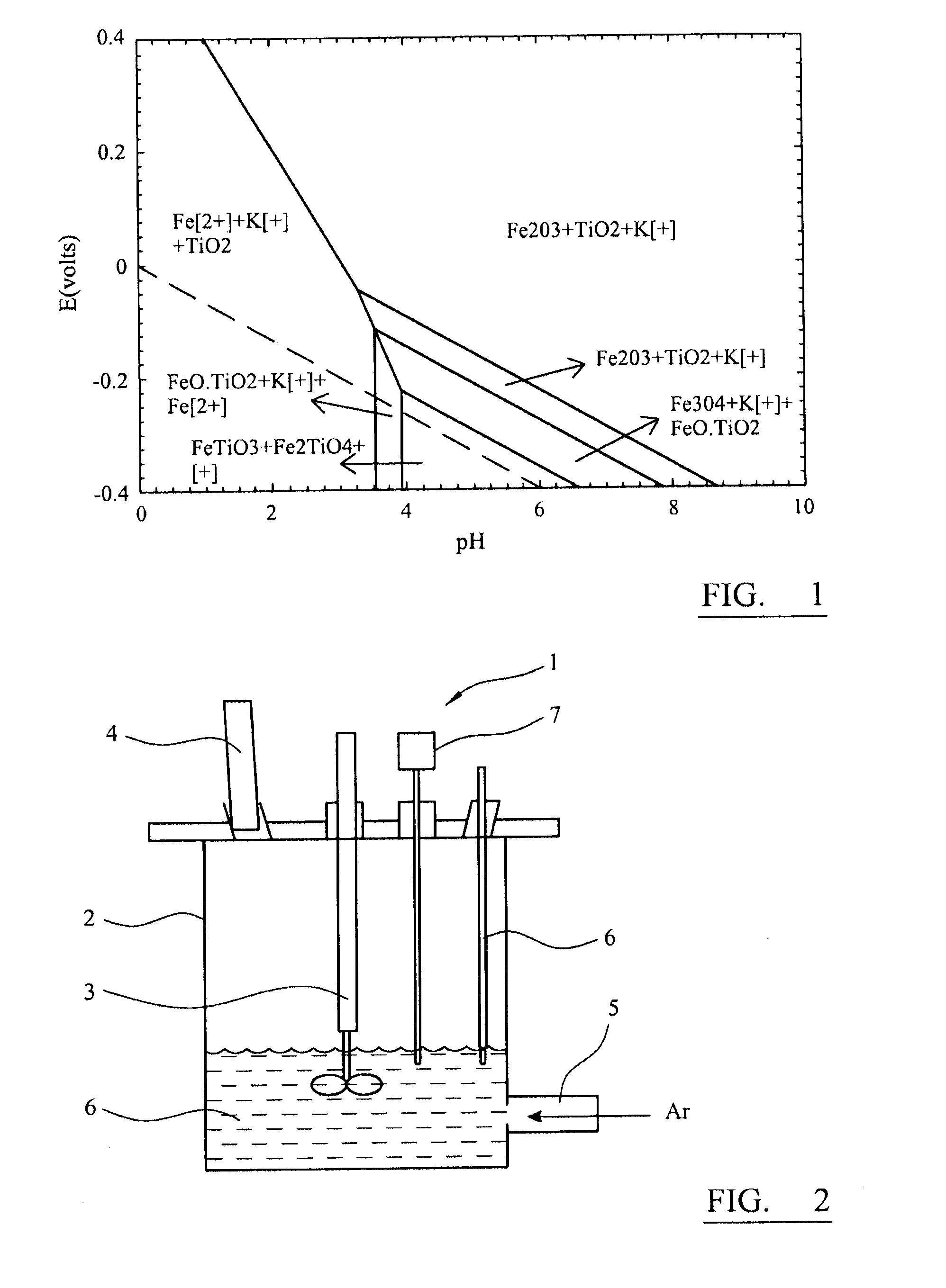
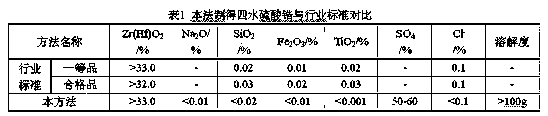
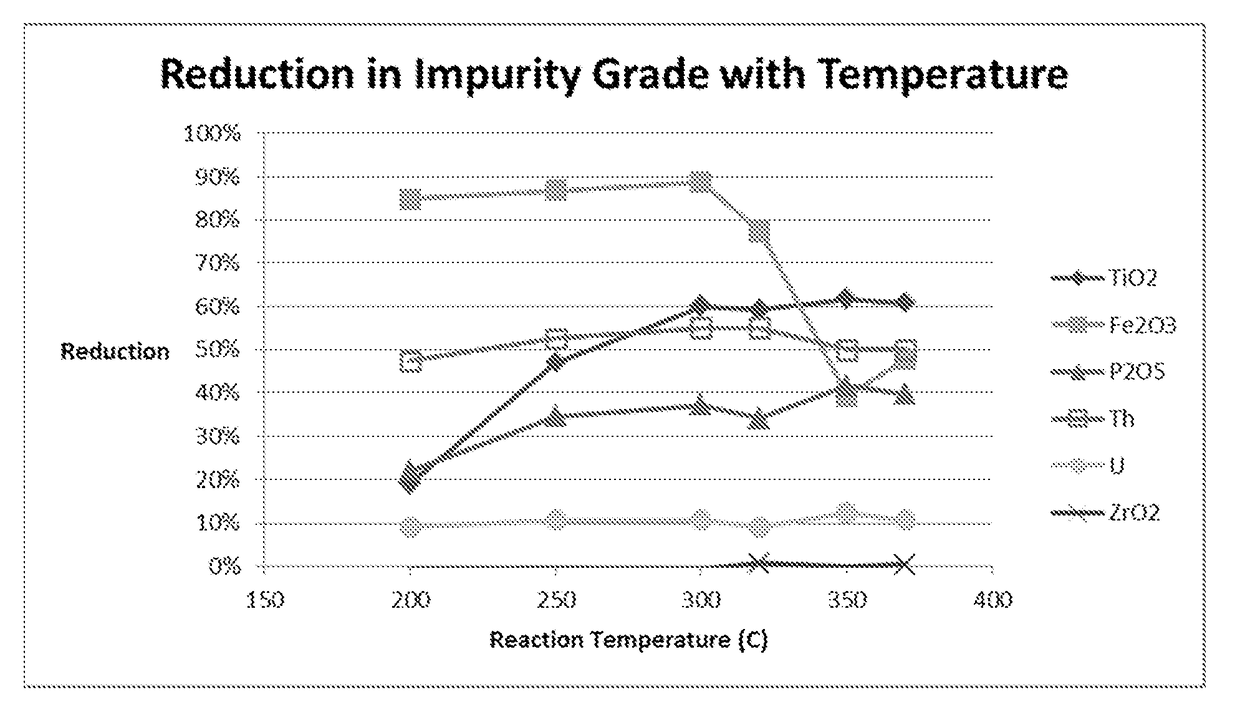
Process for Improving the Grade and Optical Quality of Zircons
ActiveUS20180023170A1Improve Grading QualityImprove optical qualityTitanium and titanyl sulfatesIron sulfatesPregnant leach solutionSulfate
A process for improving the grade and optical quality of zircon, comprising: baking a mixture of a zircon feed and concentrated sulphuric acid at a baking temperature in the range of from 200 up to 400° C., and for a time to form water leachable sulphates with impurities therein including at least iron and titanium; leaching the baked mixture to dissolve the leachable sulphates; and separating the zircon from the leachate containing the leached sulphates, which separated zircon is thereby of improved grade and optical quality.
Owner:ILUKA RESOURCES
Zirconia porous body and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20080312075A1Dispersed particle separationCatalyst activation/preparationPore distributionHeat resistance
A zirconia porous body with excellent stability of heat resistance is manufactured. This relates to a zirconia porous body having peaks at pore diameters of 8 to 20 nm and 30 to 100 nm in a pore distribution based on the BJH method, with a total pore volume of 0.4 cc / g or more, and to a zirconia porous body having a peak at a pore diameters of 20 to 110 nm in a pore distribution based on the BJH method, with a total pore volume of 0.4 cc / g or more.
Owner:DAIICHI KIGENSO KAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
Compositions comprising zirconium hydroxide and graphite oxide and methods for use
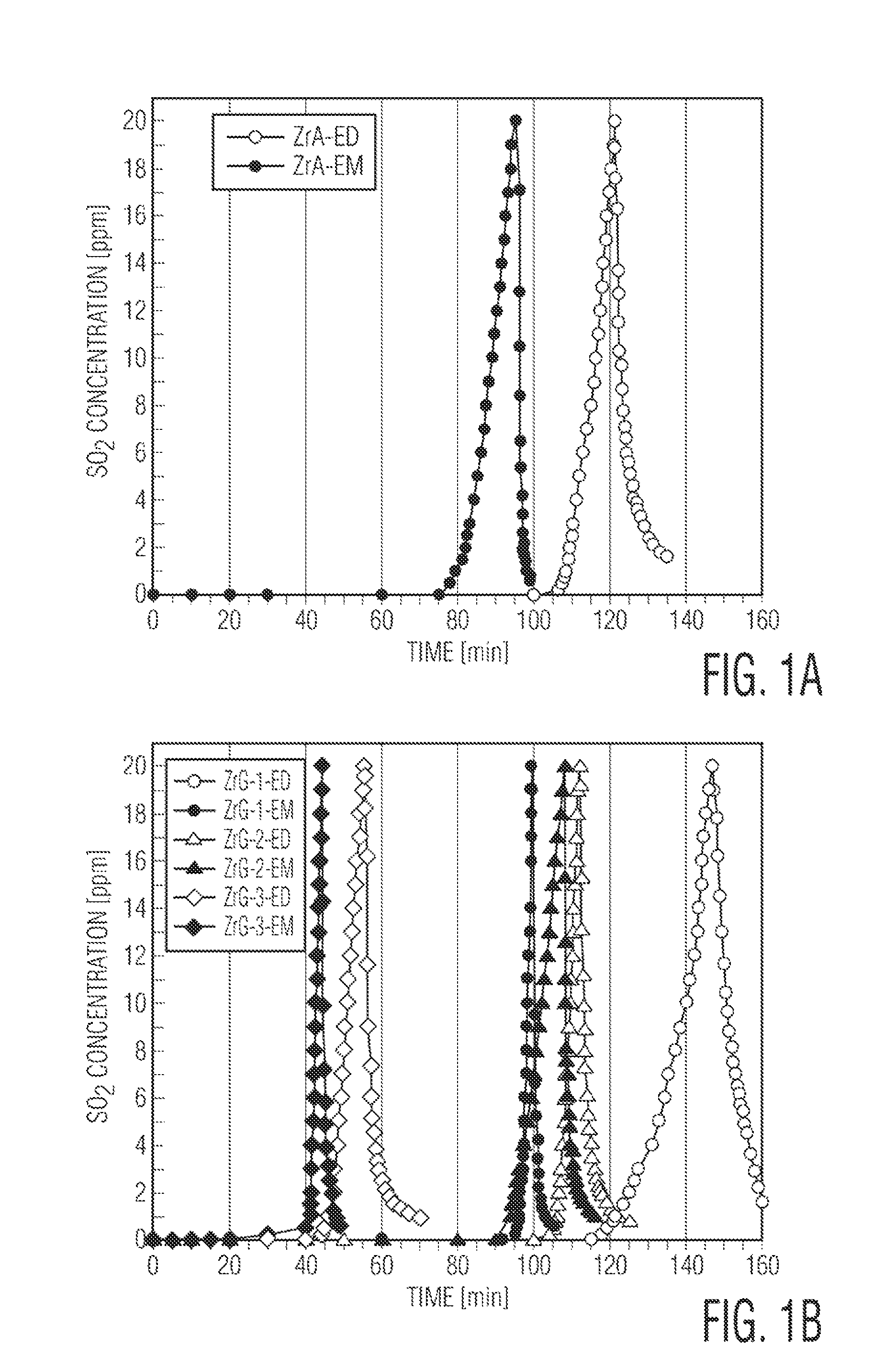
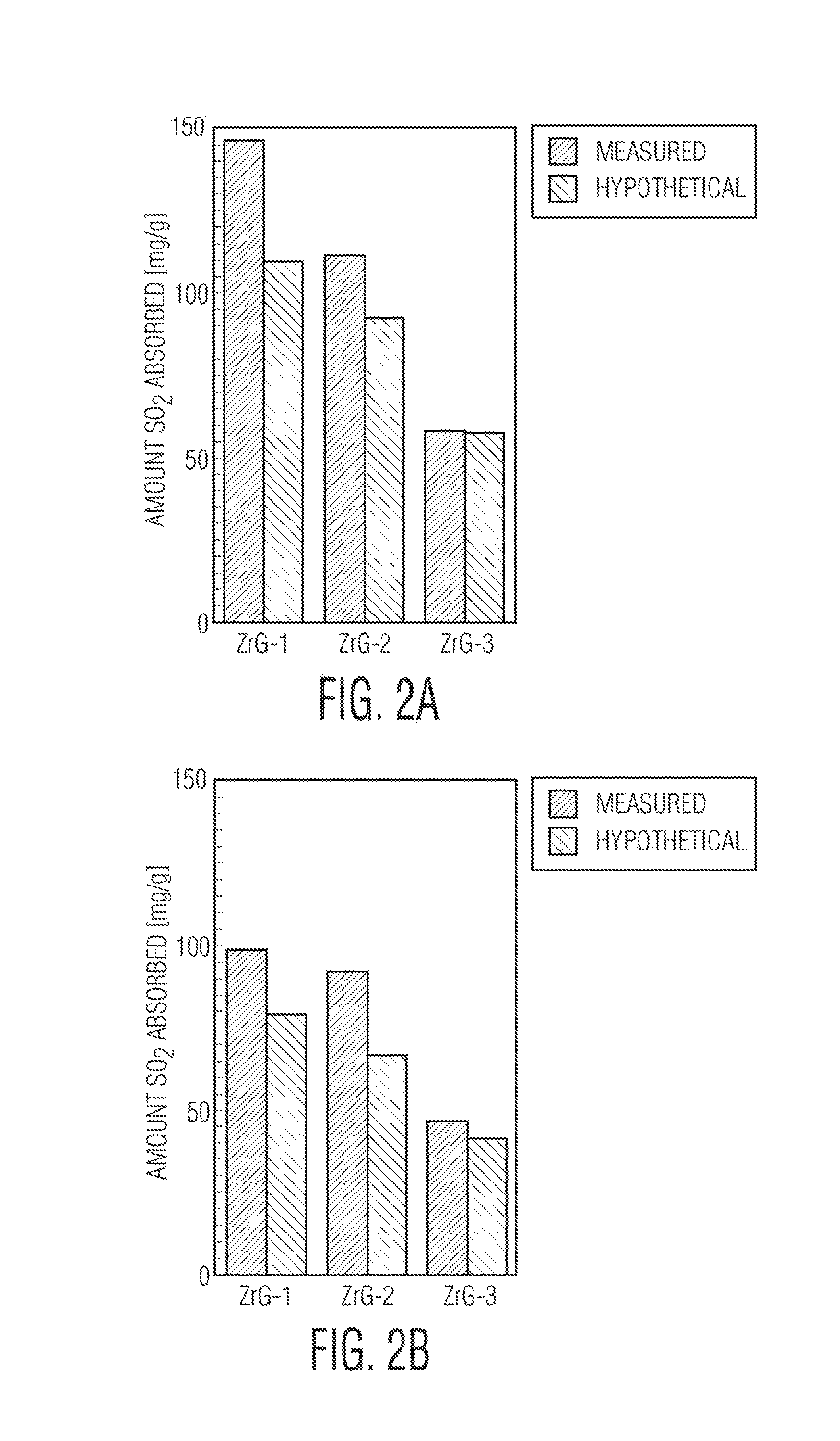
InactiveUS8658555B1Unique propertyImprove adsorption capacityGas treatmentDispersed particle separationCompound (substance)Metal
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com