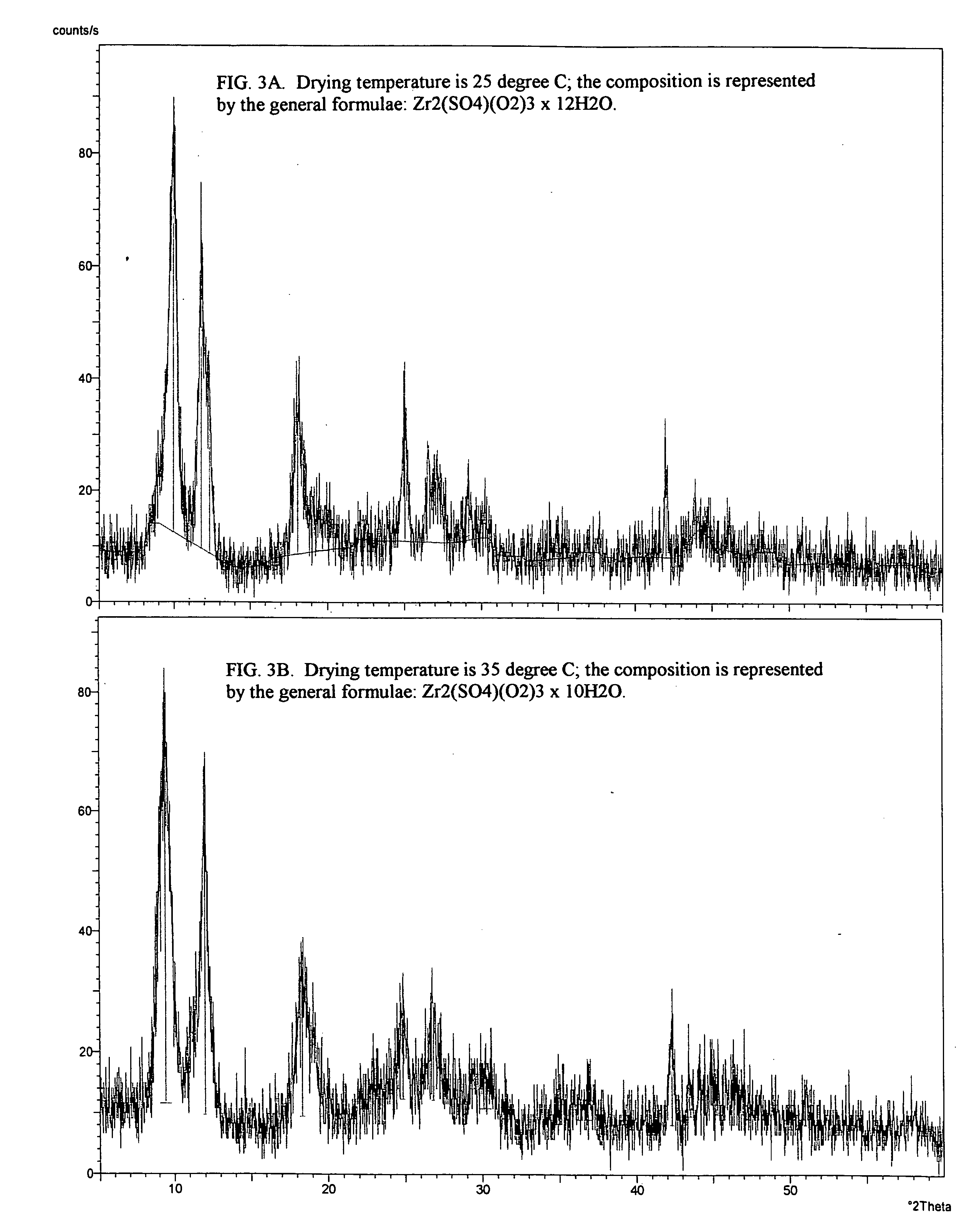
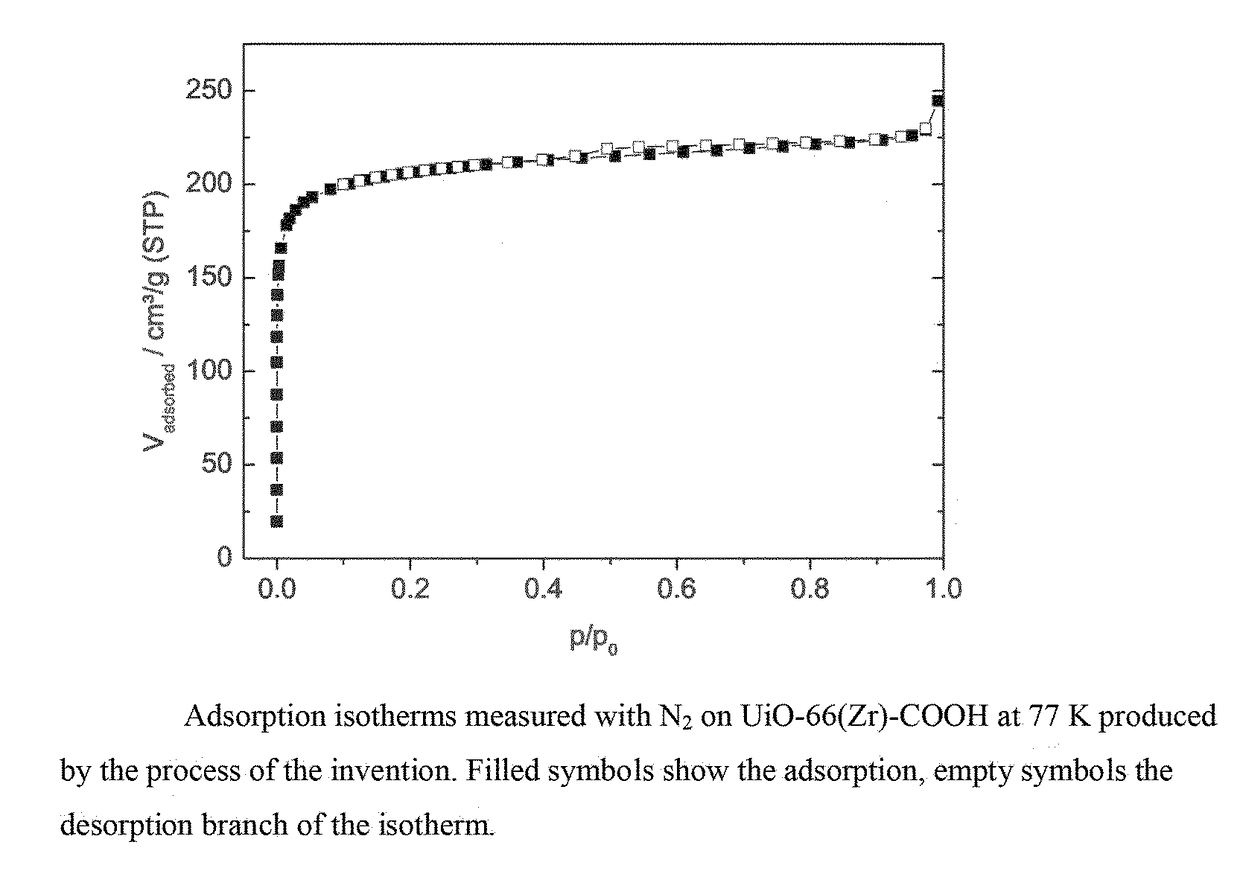
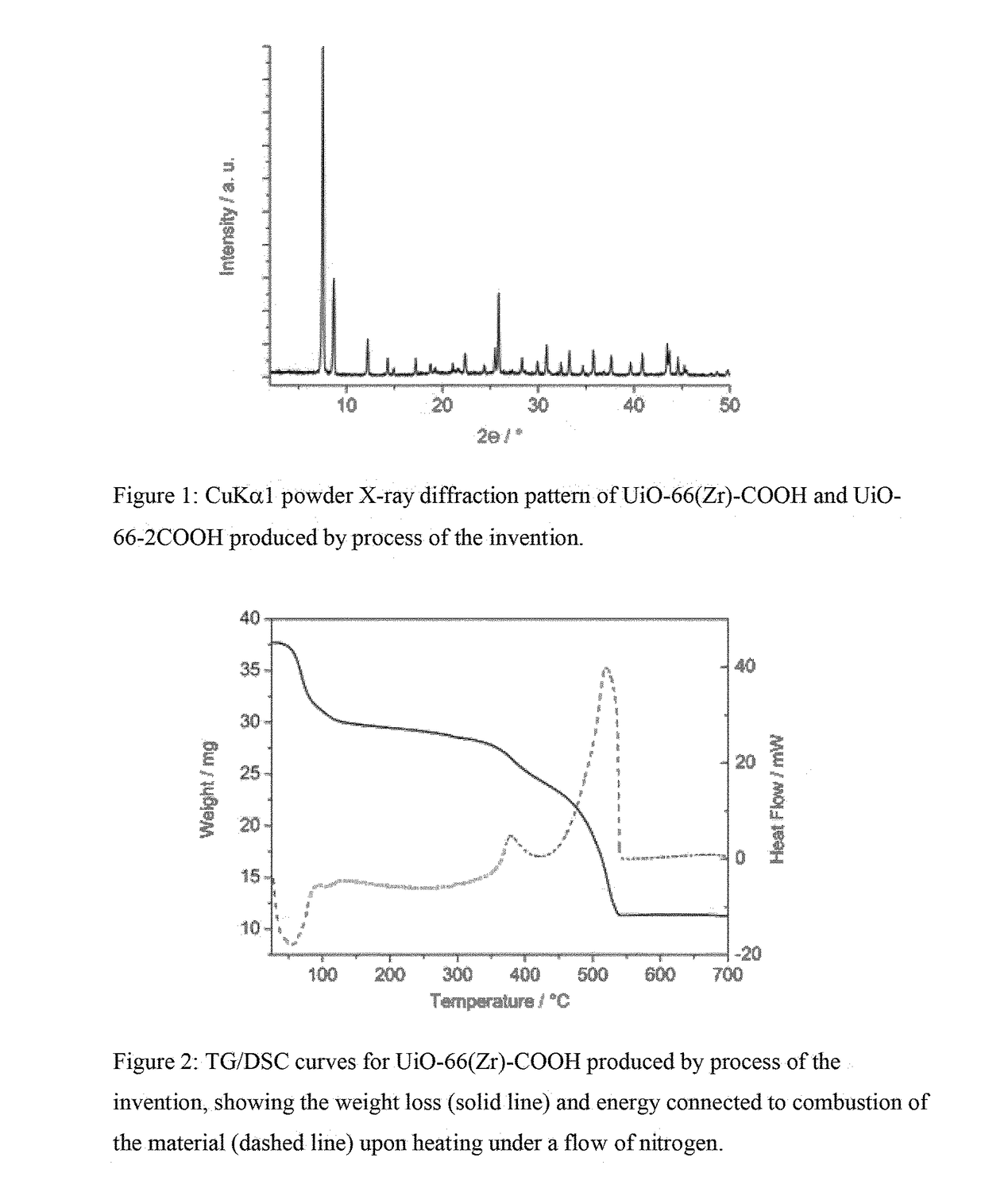
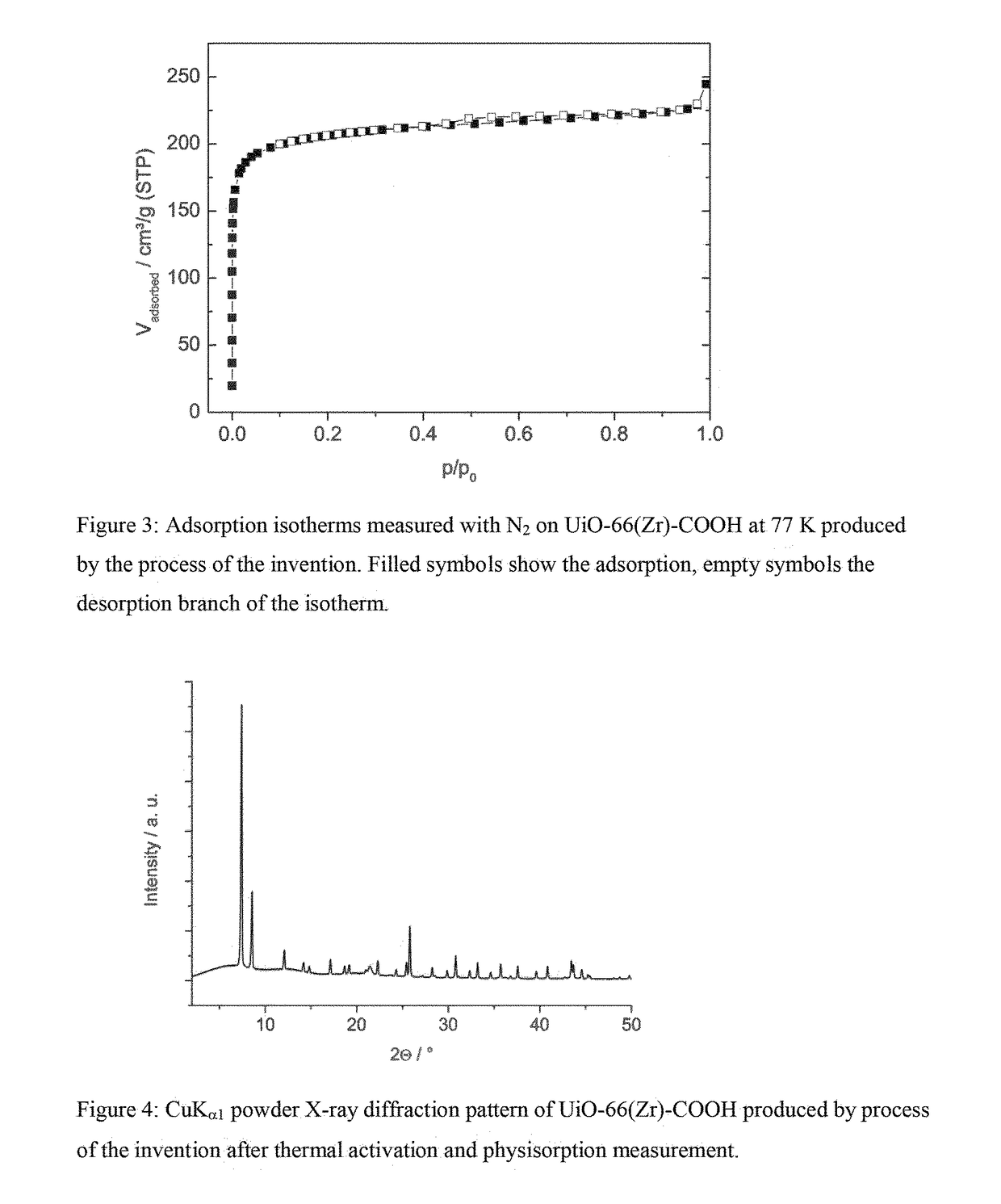
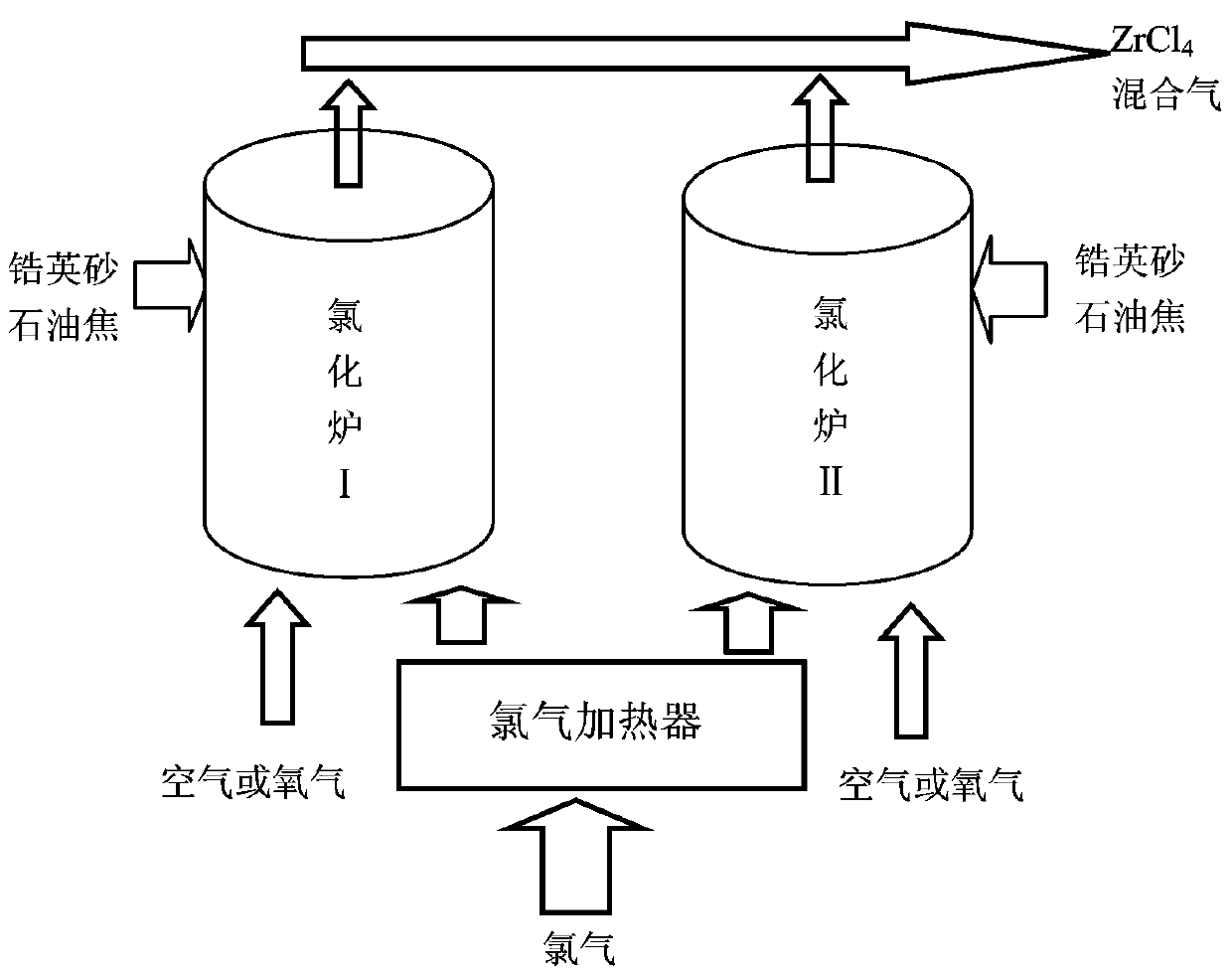
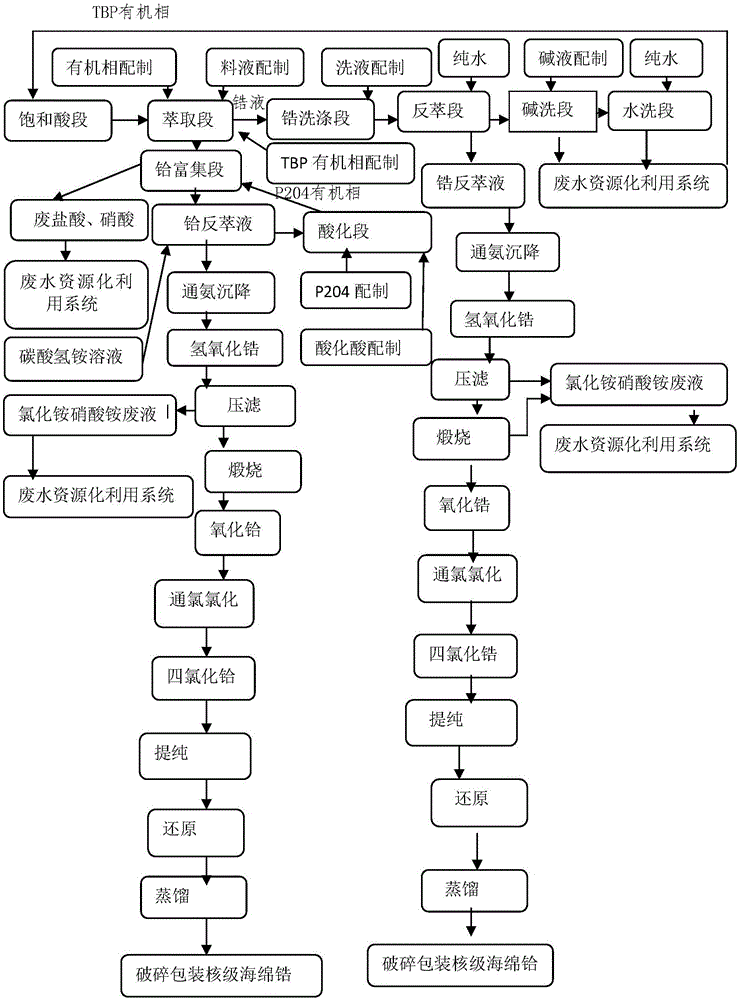
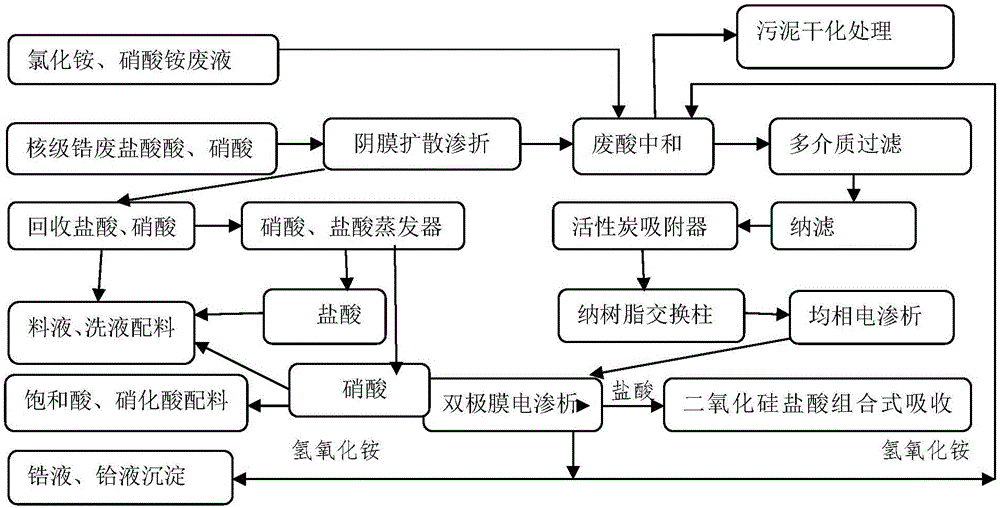
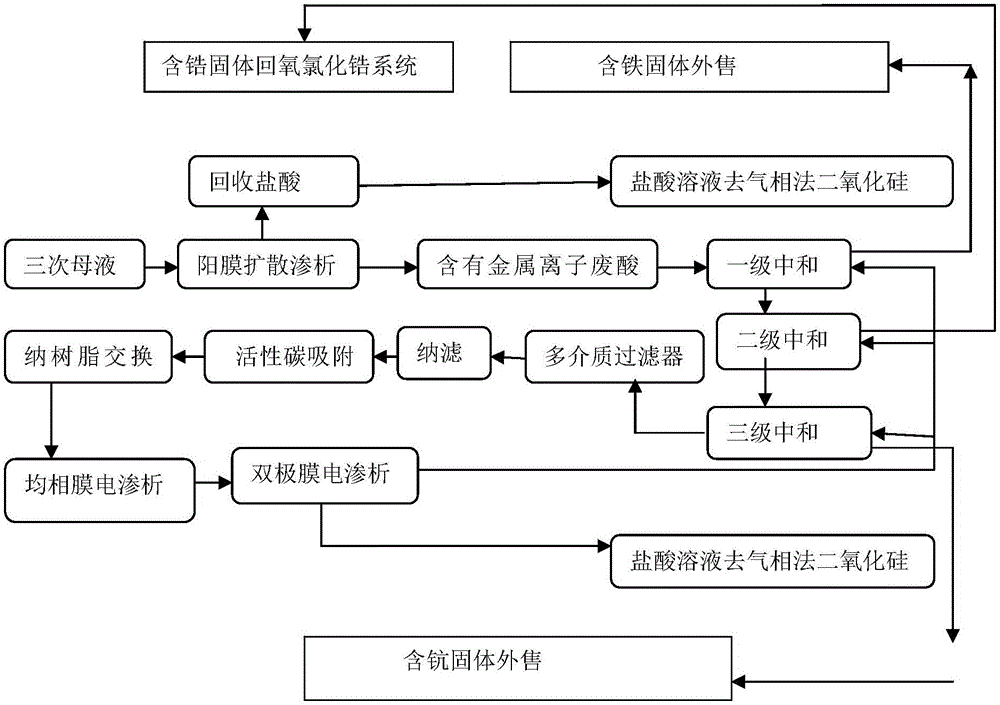
Patents
Literature
163results about "Zirconium halides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
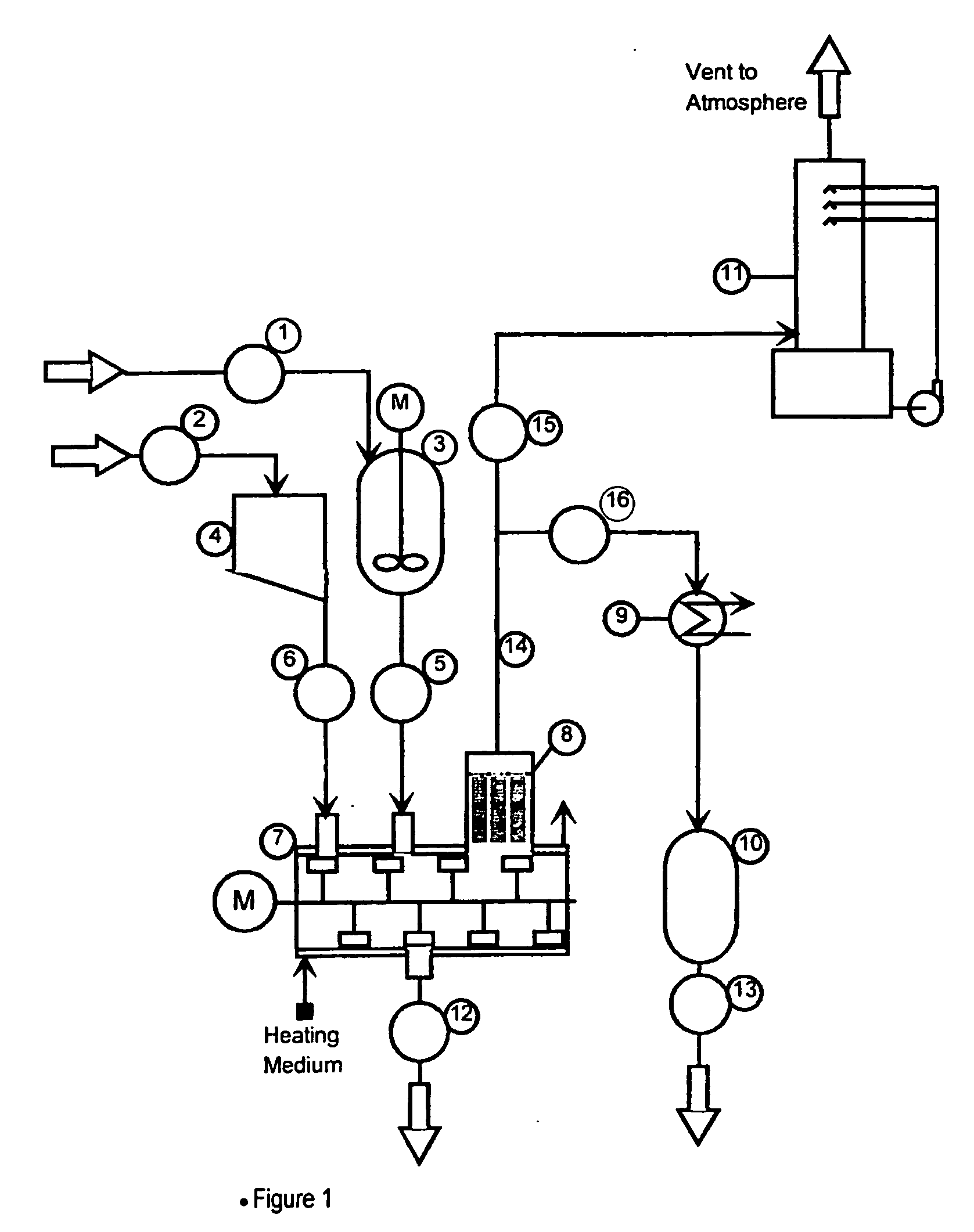
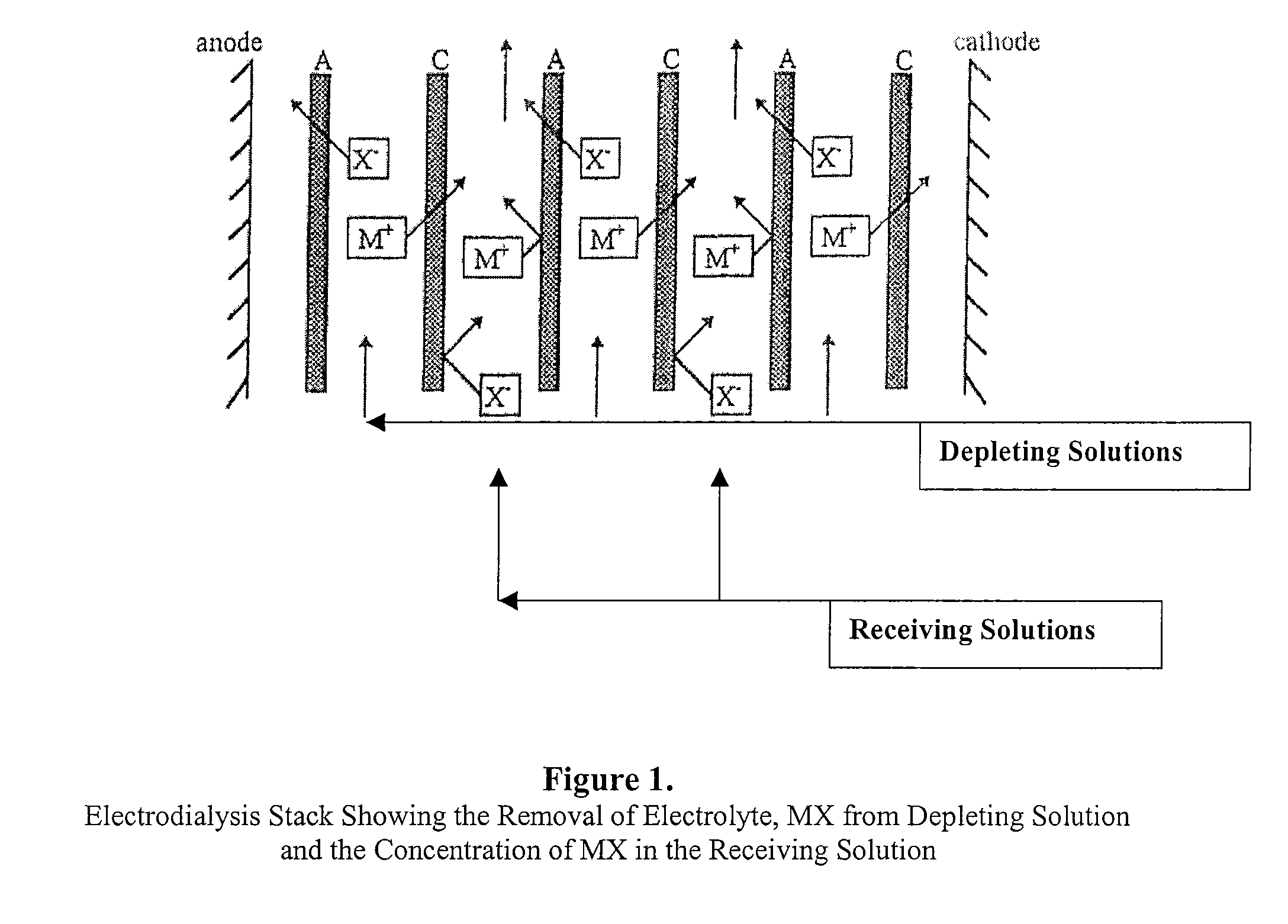
Process for the treatment of waste metal chlorides
InactiveUS20060183958A1Low costMaximize recoveryTitanium tetrachlorideSilicon oxidesMetal chlorideOrganic chloride compound
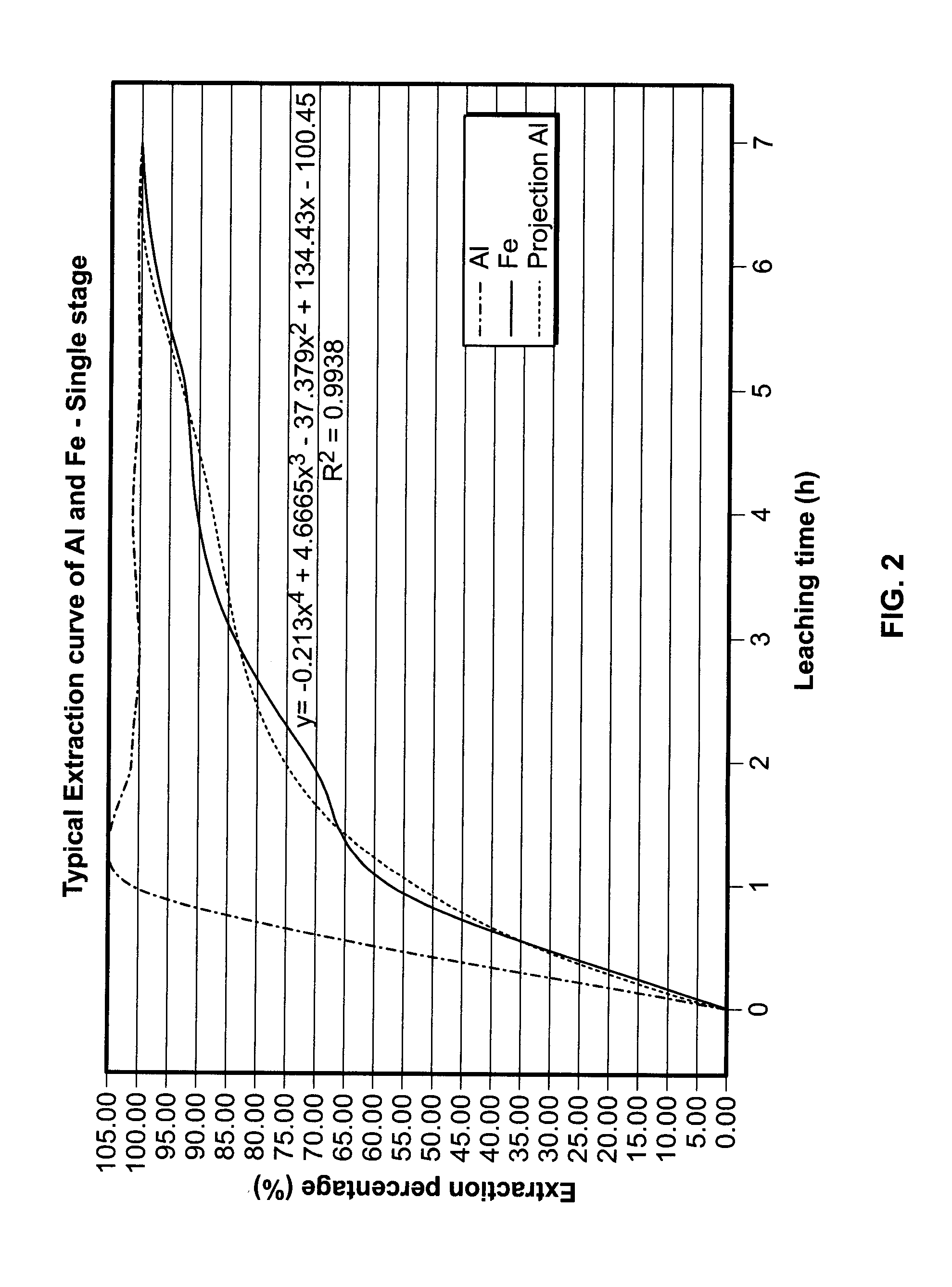
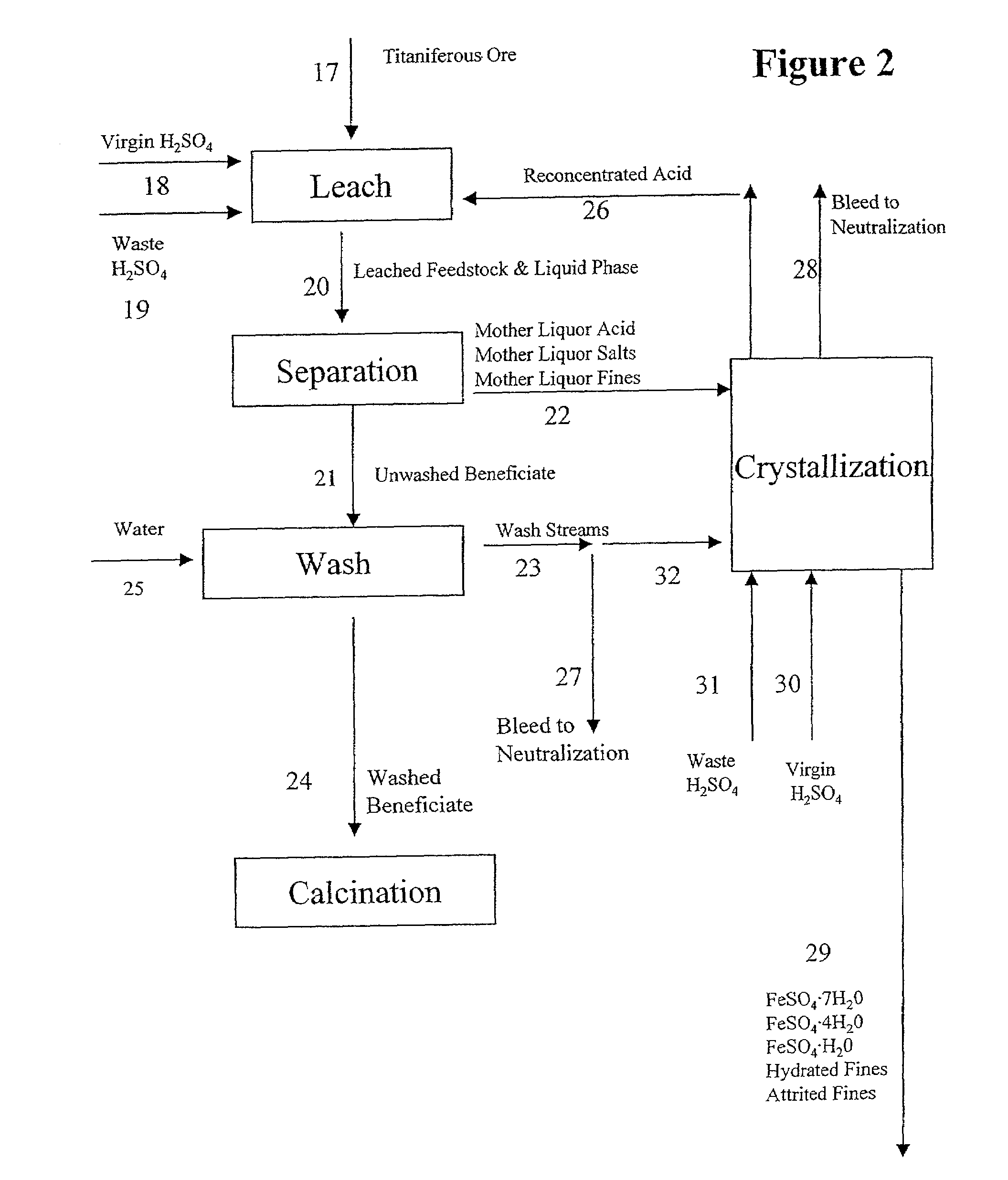
A process is described for treating the residues from metal chlorination processes wherein valuable volatile metal chlorides or metalorgano chlorides are recovered while low volatility metal chlorides and chloride complexes are reacted with a neutralizing humectant. The resulting neutral, dry solid is suitable for land fill disposal or for recovery of valuable metal constituents by extractive metallurgy techniques.
Owner:REC SILICON
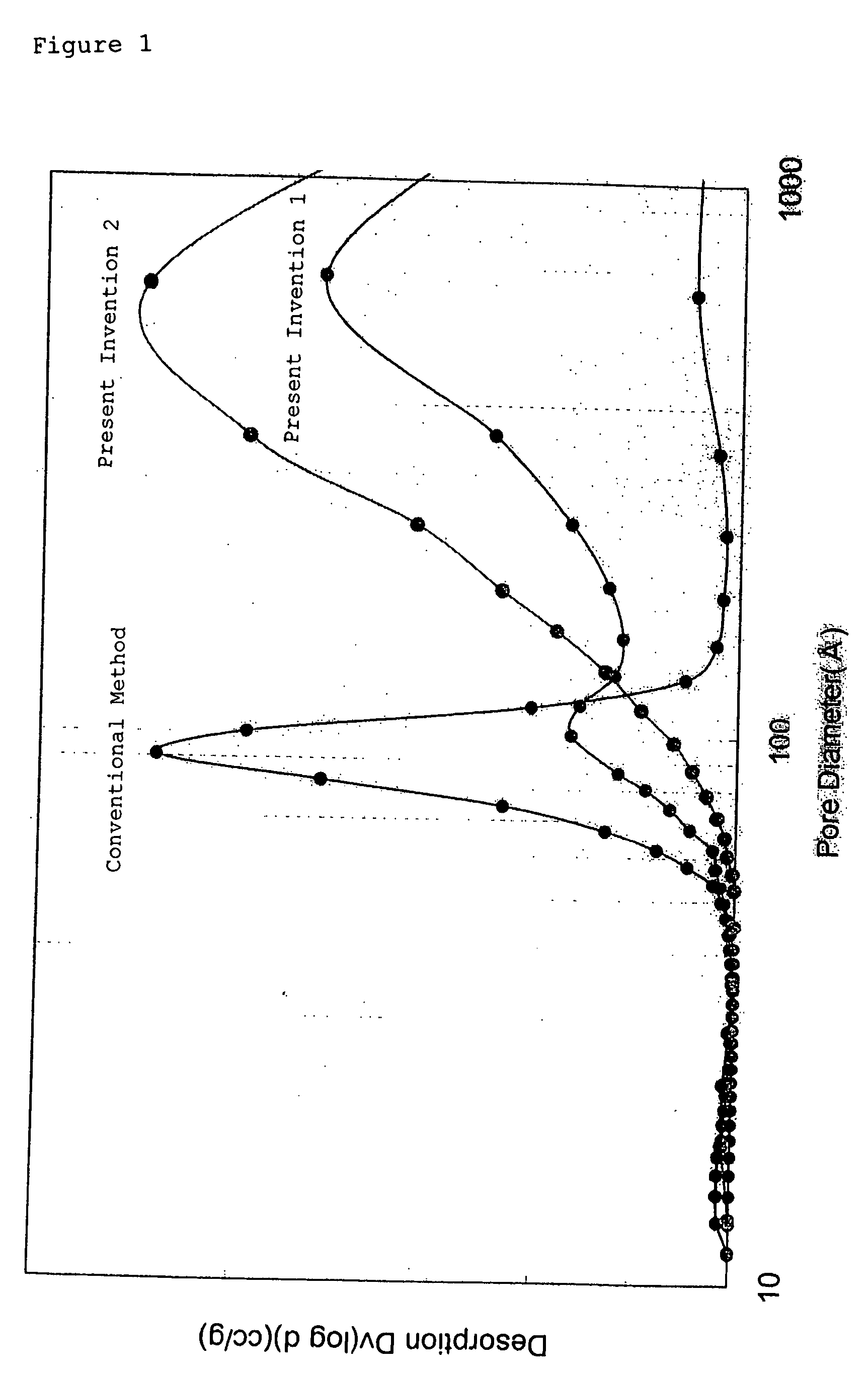
Zirconia porous body and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20060018822A1Dispersed particle separationCatalyst activation/preparationPore distributionEngineering
A zirconia porous body with excellent stability of heat resistance is manufactured. This relates to a zirconia porous body having peaks at pore diameters of 8 to 20 nm and 30 to 100 nm in a pore distribution based on the BJH method, with a total pore volume of 0.4 cc / g or more, and to a zirconia porous body having a peak at a pore diameters of 20 to 110 nm in a pore distribution based on the BJH method, with a total pore volume of 0.4 cc / g or more.
Owner:DAIICHI KIGENSO KAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
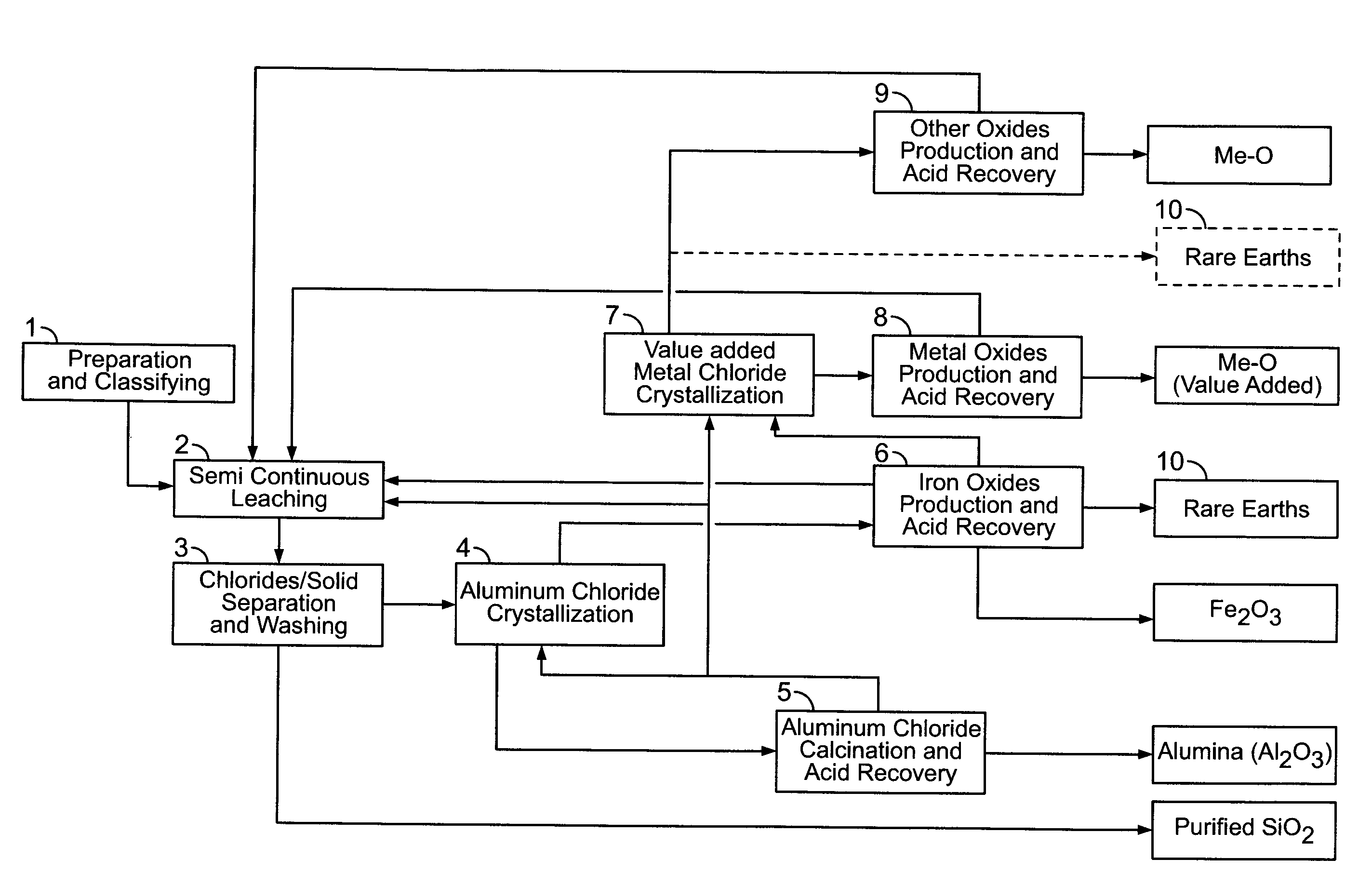
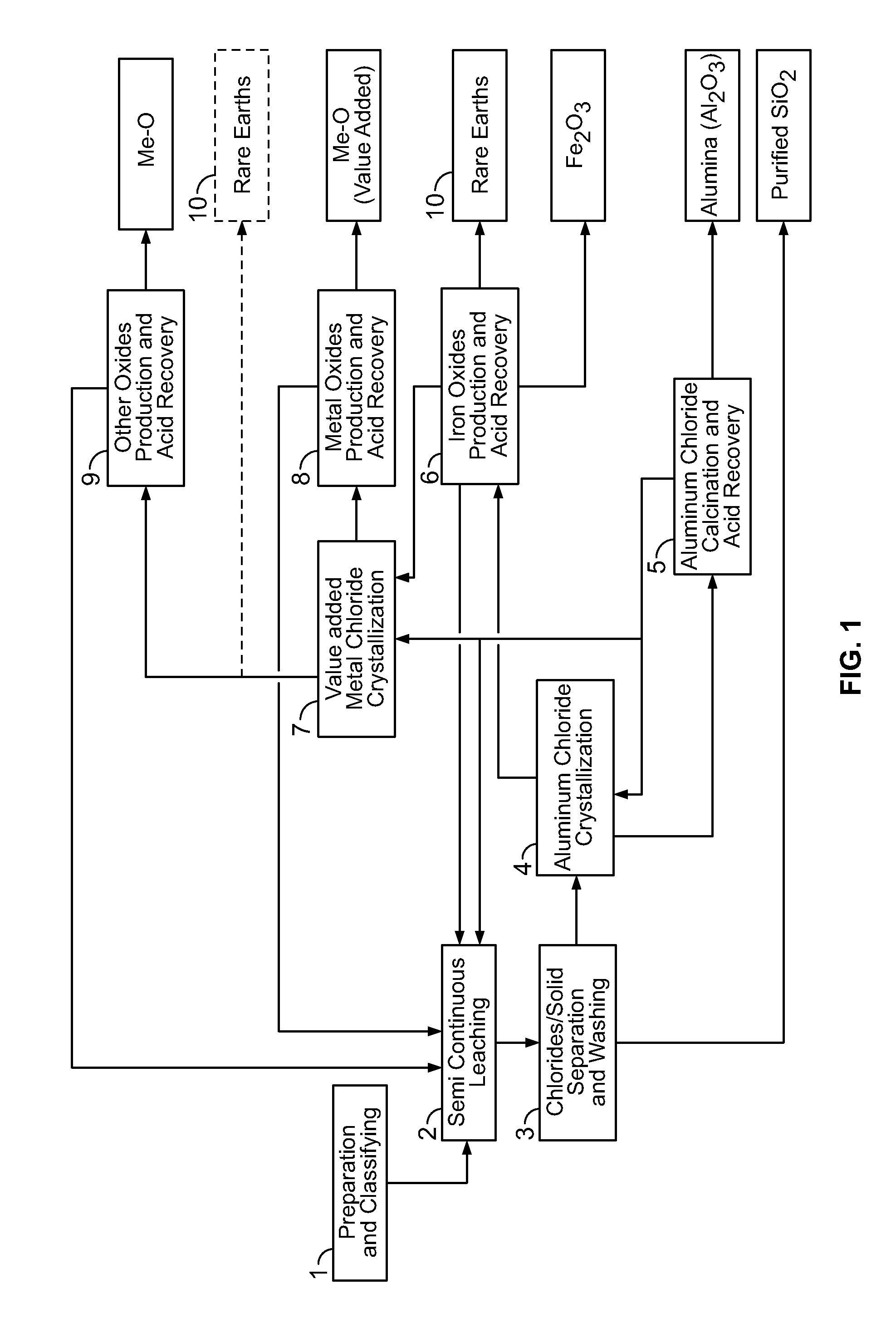
Processes for treating red mud
ActiveUS20140369907A1Simple and efficientLow costAluminium compoundsSolvent extractionPregnant leach solutionRare-earth element
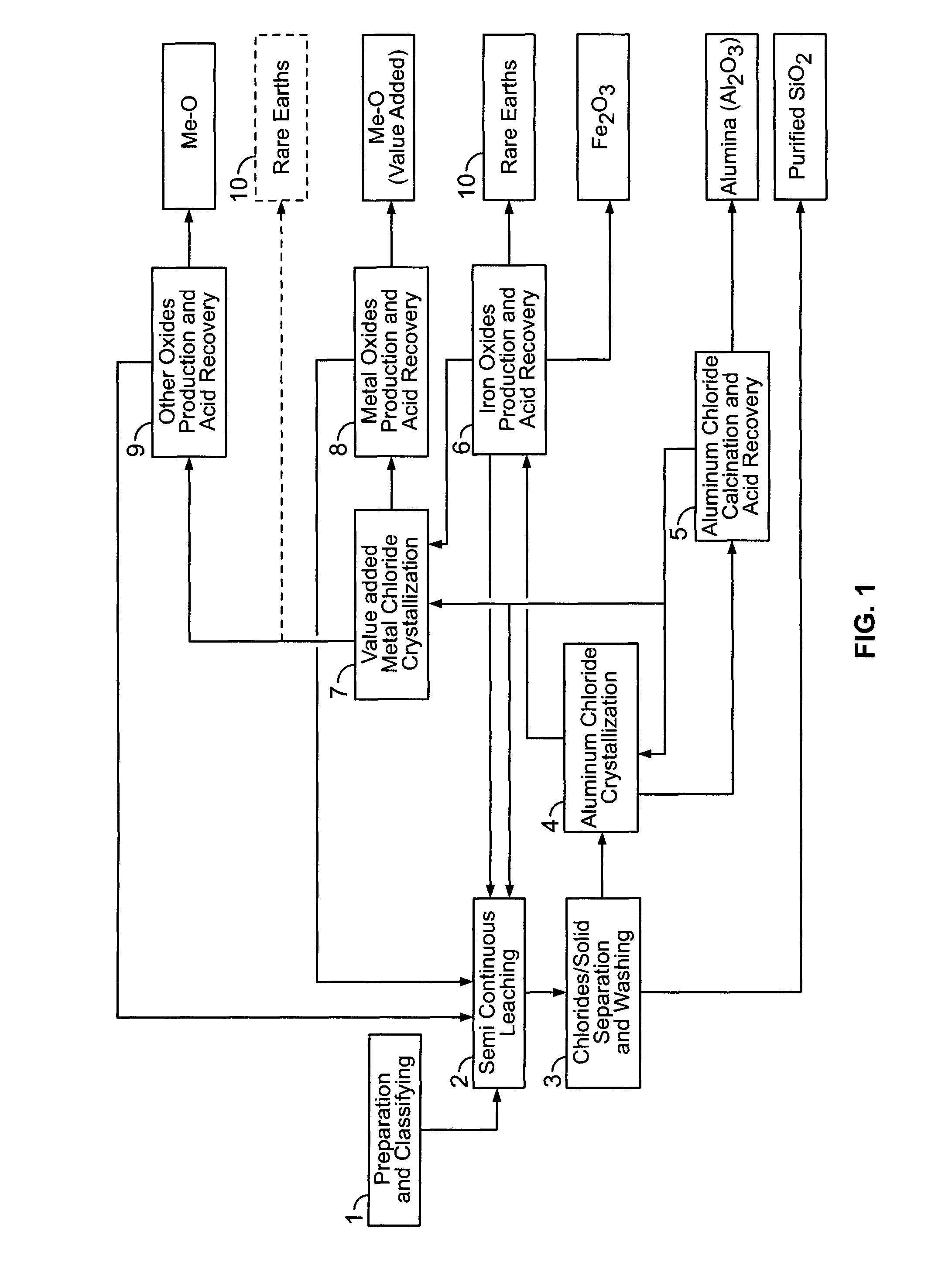
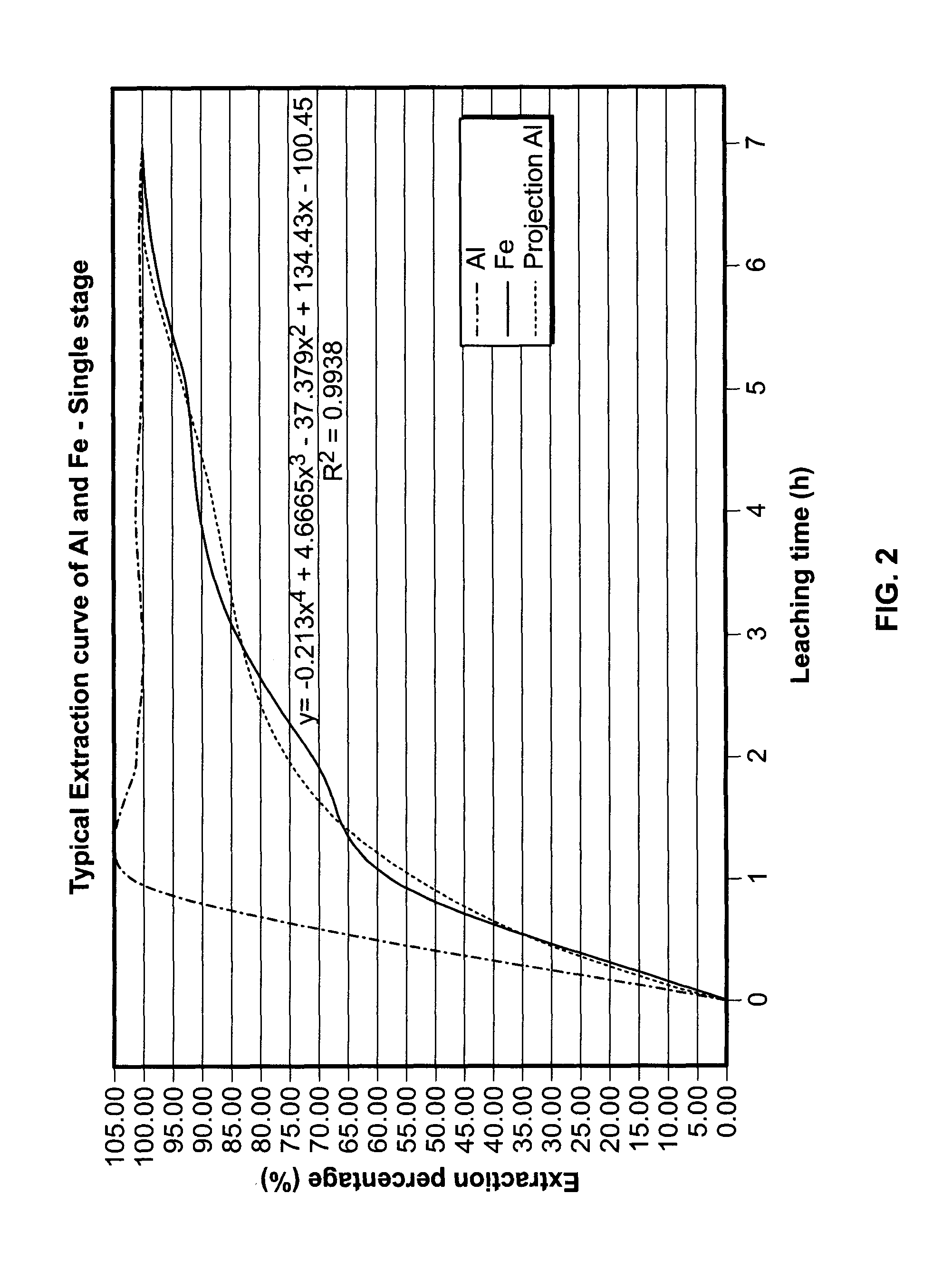
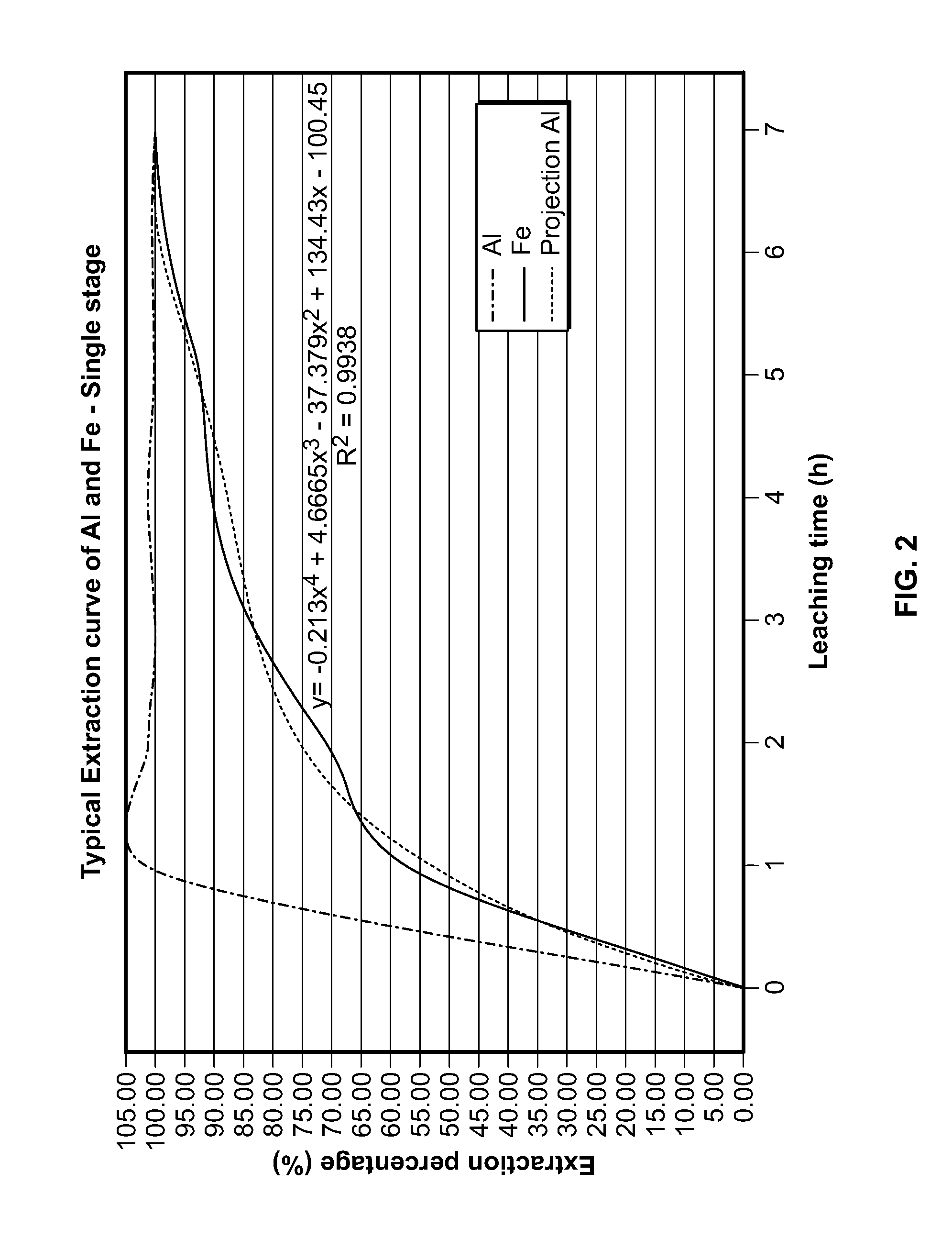
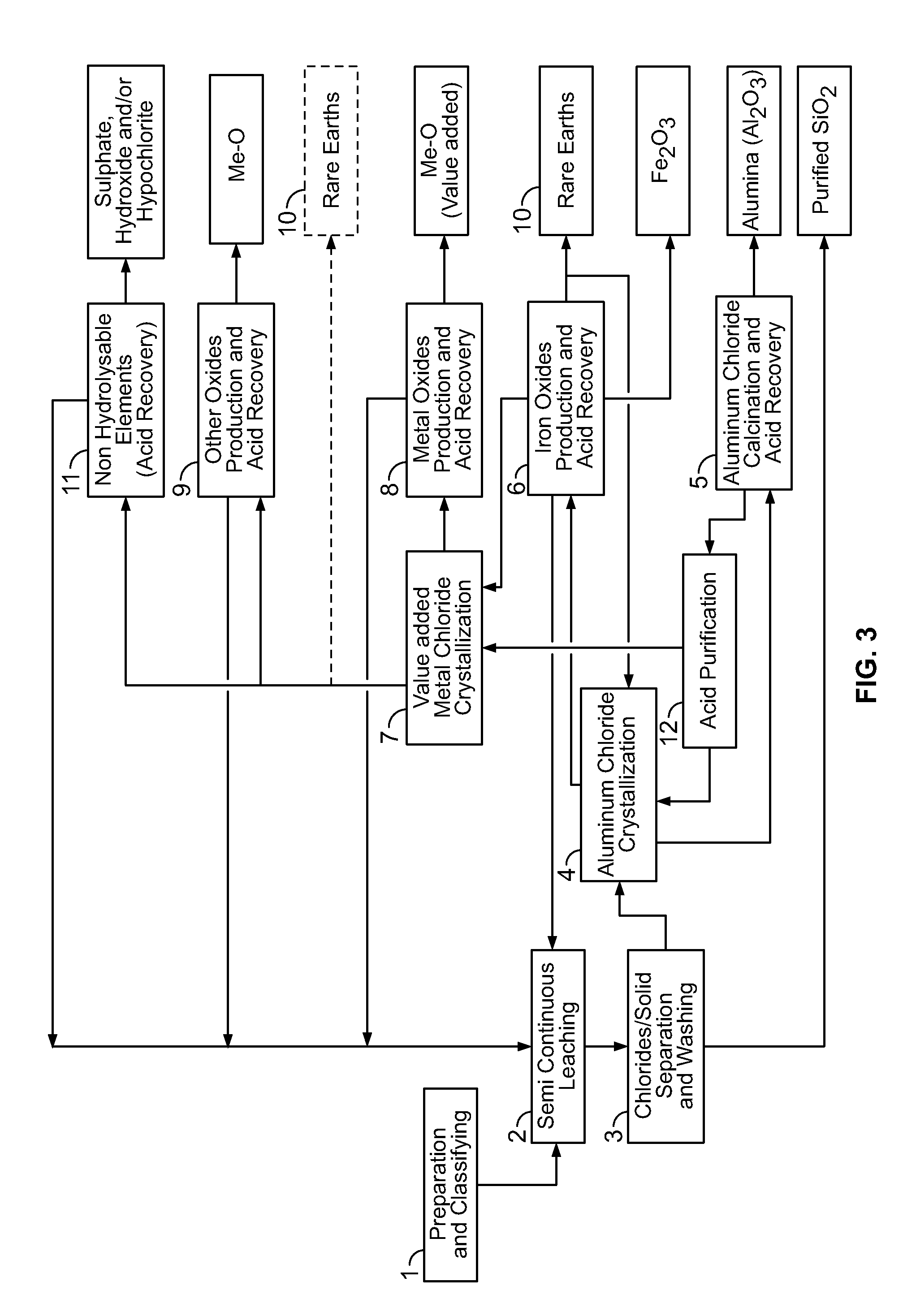
There are provided processes for treating red mud. For example, the processes can comprise leaching red mud with HCl so as to obtain a leachate comprising ions of a first metal (for example aluminum) and a solid, and separating said solid from said leachate. Several other metals can be extracted from the leachate (Fe, Ni, Co, Mg, rare earth elements, rare metals, etc.). Various other components can be extracted from solid such as TiO2, SiO2 etc.
Owner:ORBITE ALUMINAE INC
Method for cooling zirconium tetrachloride produced through fluidizing chlorination method
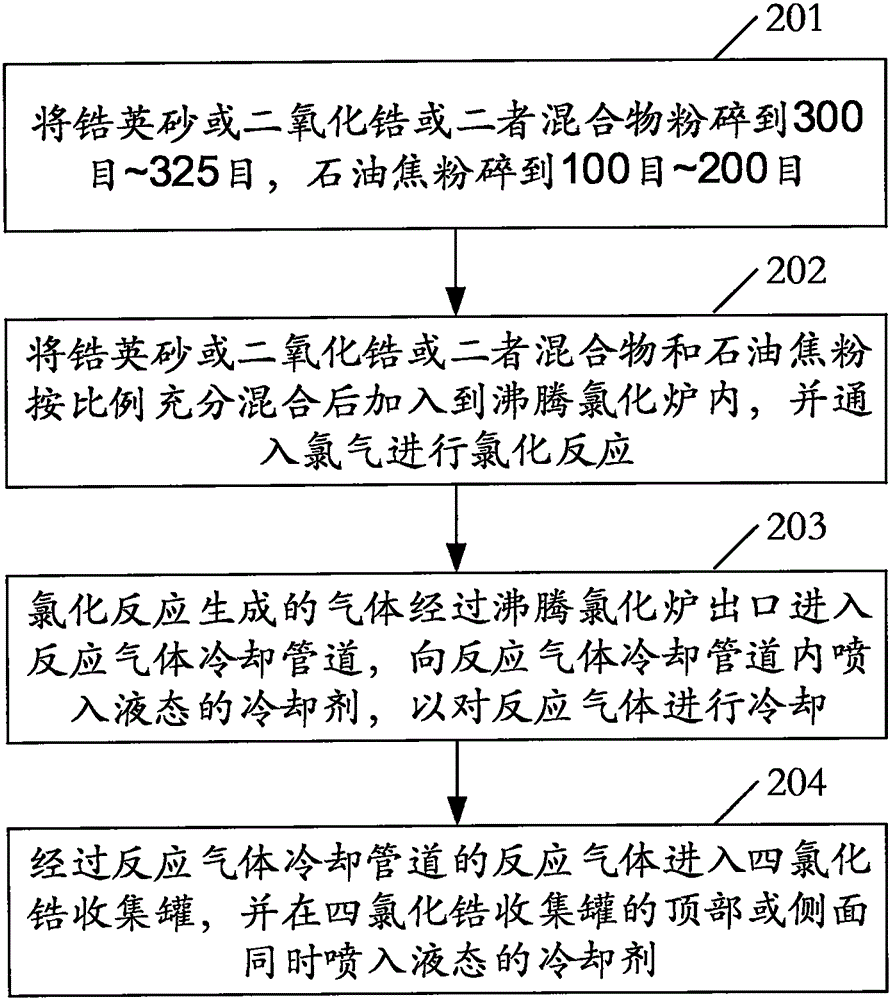
The invention relates to the field of chemical production, and discloses a method for cooling zirconium tetrachloride produced through a fluidizing chlorination method. The cooling method comprises the following steps: fully mixing zircon sand / zirconium dioxide / a mixture of zircon sand and zirconium dioxide with petroleum coke powder according to a certain ratio, adding the mixture into a fluidizing chlorination furnace, introducing chlorine gas into the furnace to carry out chlorination reactions; introducing the gas generated in the chlorination reactions into a reaction gas cooling channel from the outlet of the fluidizing chlorination furnace, spraying liquid coolant into the reaction gas cooling channel to cool the reaction gas; then introducing the cooled reaction gas into a zirconium tetrachloride collecting tank, at the same time, and spraying liquid coolant into the zirconium tetrachloride collecting tank from top part or lateral side of the zirconium tetrachloride collecting tank so as to cool the reaction gas, wherein zirconium tetrachloride in a gas state is cooled and converted into zirconium tetrachloride powder, and the powder falls on the bottom of the zirconium tetrachloride collecting tank. According to the cooling method, liquid coolant is sprayed to the reaction gas so as to cool the reaction gas, the cooling effect is improved, the yield of zirconium tetrachloride is increased, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:王卓
Process for the isolation and purification of zirconium peroxosulfate and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050180911A1High degreeShort processing timePeroxyhydrates/peroxyacidsSulfate preparationPurification methodsZirconium compounds
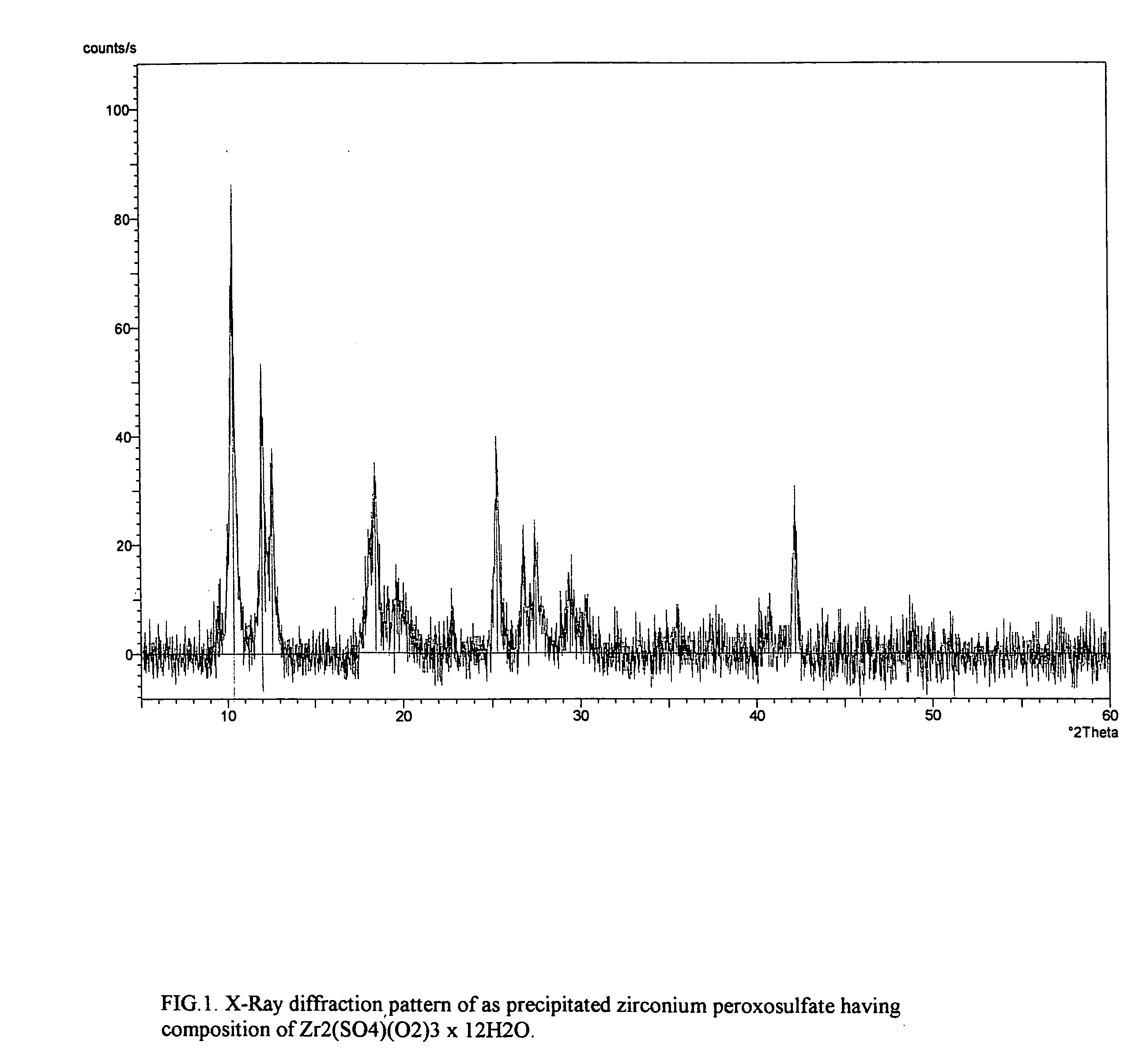
Provided is a process for isolating zirconium peroxosulfate and its use, either as is or to prepare high purity zirconium compounds including powders of zirconium dioxide and stabilized zirconia. The process is based on precipitating a peroxide compound from an acidic peroxide solution of zirconium and provides a simple, economical method for producing the zirconium peroxosulfate powder and its derivatives with degree of zirconium recovery more than 99%. This process further provides an effective method for the separation and purification of zirconium from a variety of elements and / or naturally occurring ores.
Owner:BELOV VLADIMIR +1
Process for preparing a zirconium-based metal organic framework
ActiveUS20170291912A1Weakening MOF structureConvenient introductionGroup 4/14 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesZirconium sulfatesChemical compoundMetal-organic framework
There is provided a process for preparing a zirconium-based metal organic framework (Zr-MOF), the process comprising the steps (i) preparing a reaction mixture comprising zirconium ions, sulfate ions and at least one organic linker compound in an aqueous solvent; and (ii) heating the reaction mixture from step (i).
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN +2
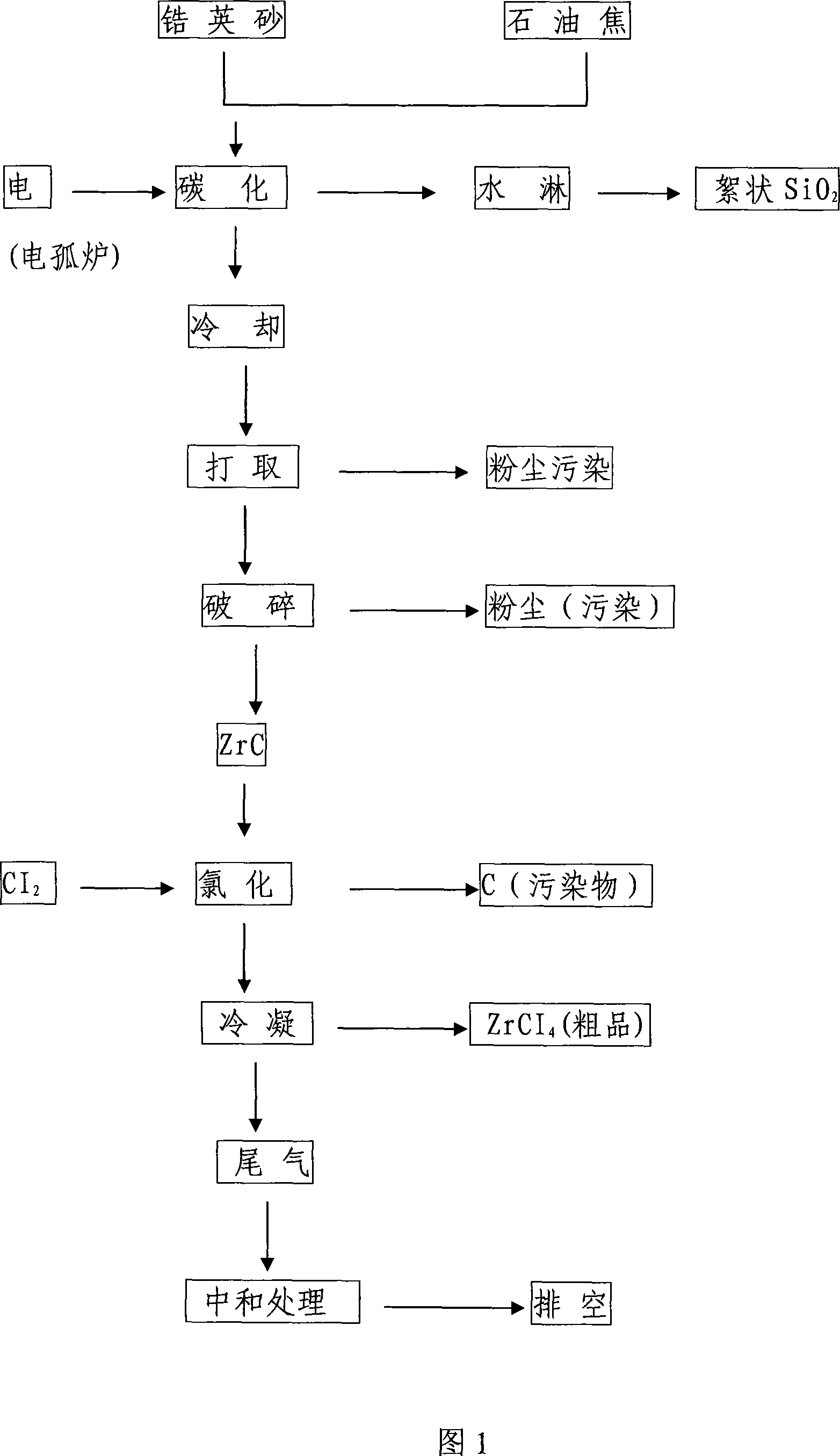
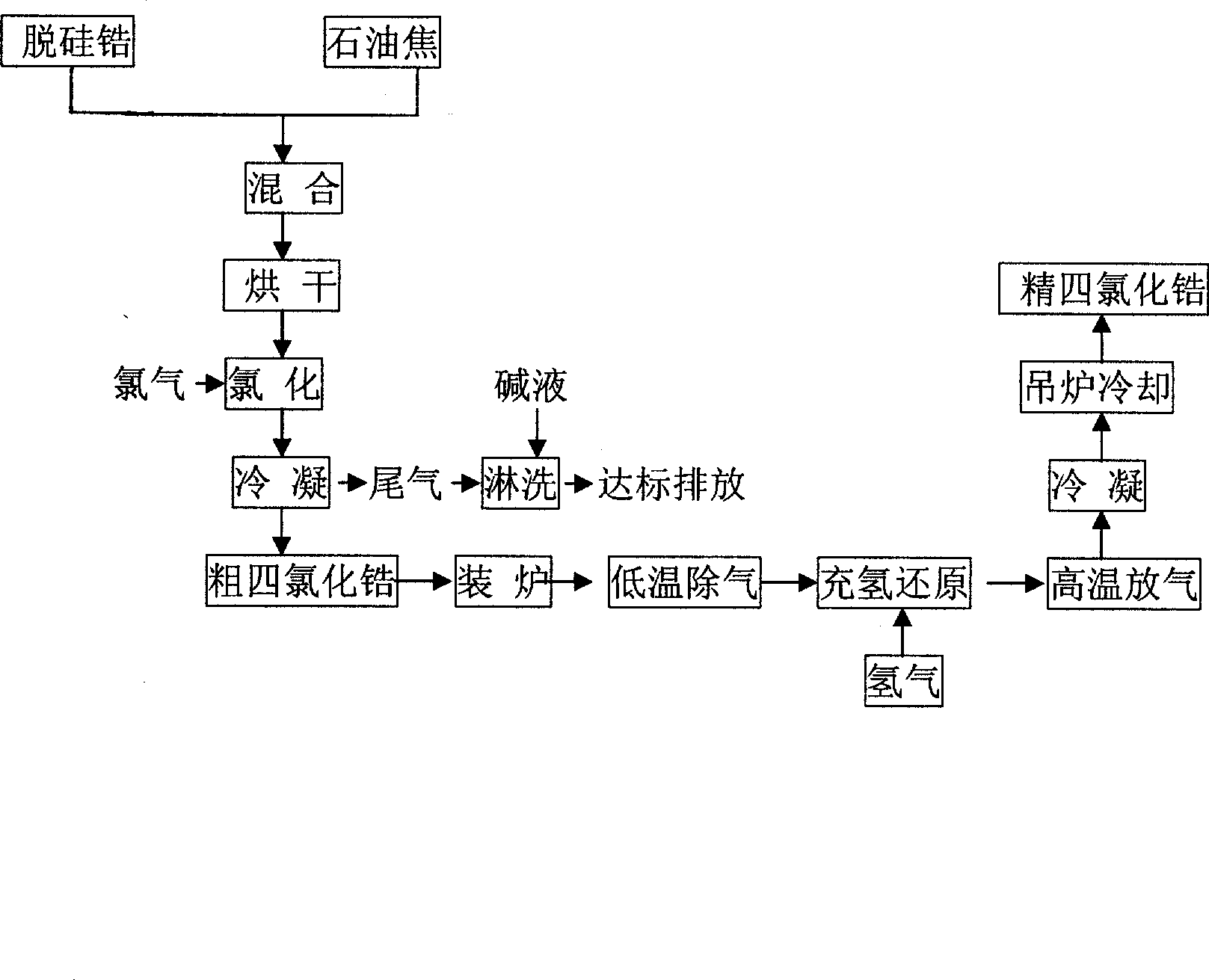
Preparation method of zirconium tetrachloride
InactiveCN101045557AShort processShort production processZirconium halidesTetrachlorideSilicon tetrachloride
A process for preparing ZrCl4 includes such steps as proportionally mixing fine desiliconized zirconium oxide powder with petroleum coke powder, dewatering, loading the mixture into boiling furnace at 900 + / - 5 deg.C while filling chlorine gas, chlorinating reaction at 900-1100 + / - 5 deg.C for 20-21 hr, cooling to 200 + / - 10 deg.C for 8-10 hr, and cooling to 20 + / - 5 deg.C for 3-5 hr.
Owner:CHAOYANG BAISHENG TITANIUM IND CO LTD
Process method for producing zirconium tetrachloride through fluidizing chlorination method
ActiveCN104058454AReduce manufacturing costDo not change frequentlyChemical industryZirconium halidesTetrachlorideSilicon tetrachloride
The invention relates to a process method for producing zirconium tetrachloride through a fluidizing chlorination method. The process method comprises the following steps: smashing zircon sand to 300-325 meshes, smashing petroleum coke to 100-200 meshes, smashing chemical heat supplementing agent to 200-400 meshes, firstly fully mixing the zircon sand and the petroleum coke powder, simultaneously adding the mixture and the heat supplementing agent into a fluidizing chlorination furnace, introducing chlorine to carry out chlorination reaction and keeping the temperature of the fluidizing chlorination furnace at 1100 DEG C, wherein the chemical heat supplementing agent is silica powder or silicon carbide or a mixture of the silica powder and the silicon carbide; the reaction formula of the chemical heat supplementing agent is SiC+2Cl2=SiCl4+C or Si+2Cl2=SiCl4; the main reaction formula of producing the zirconium tetrachloride through zircon sand chlorination is ZrSiO4+4C+4Cl2=ZrCl4+SiCl4+4CO. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the heating problem of a zircon sand fluidizing chlorination furnace can be solved, the production cost of the zirconium tetrachloride is reduced and a byproduct: an important chemical raw material silicon tetrachloride can be produced, so that the process method has the advantages of increasing the working efficiency, saving the energy and reducing the production cost.
Owner:内蒙古自治区浩森新材料开发有限公司
Nanostructured titania coated titanium
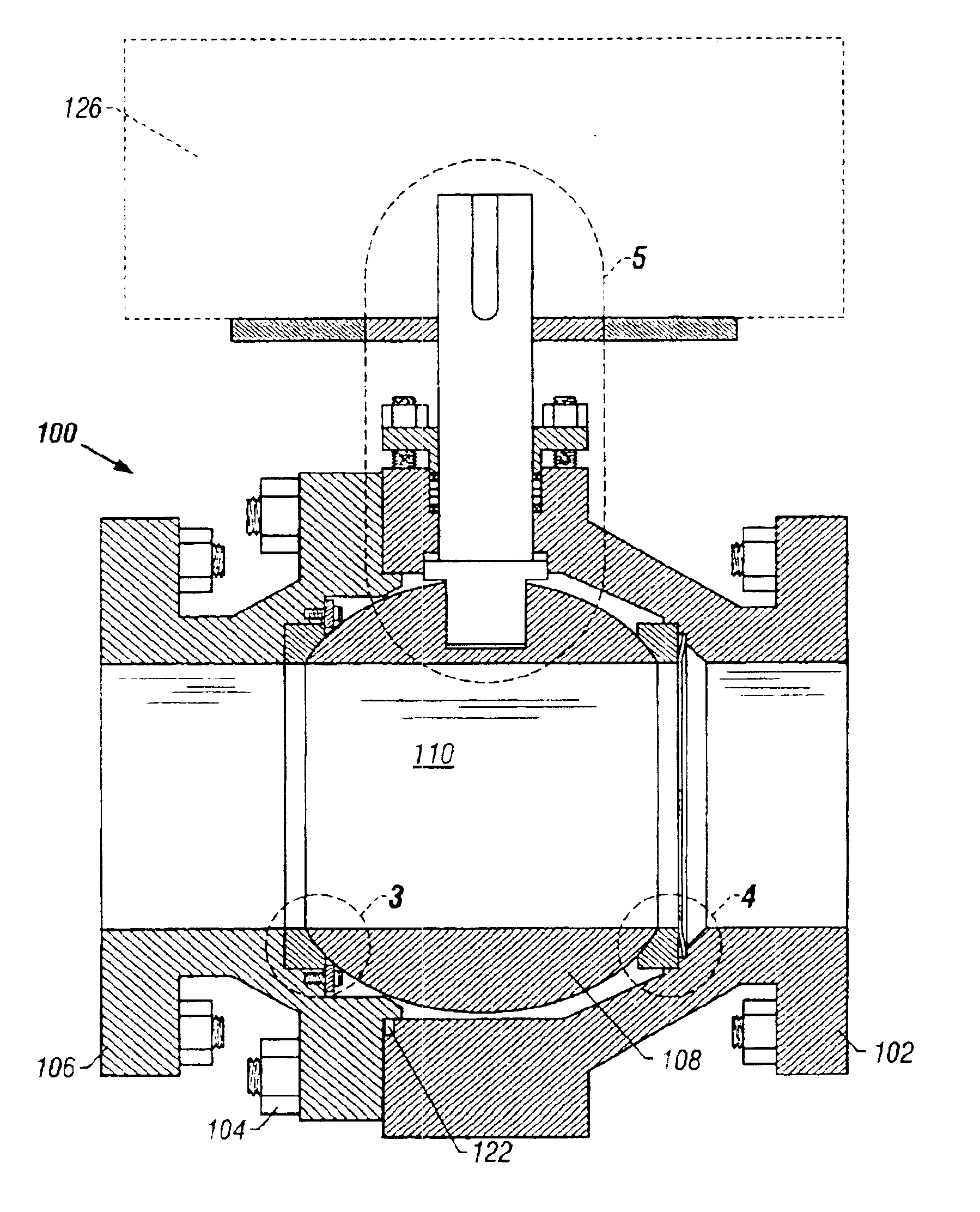
InactiveUS6835449B2Enhance reliability and lifeConvenient coatingMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentTitaniumNanostructure
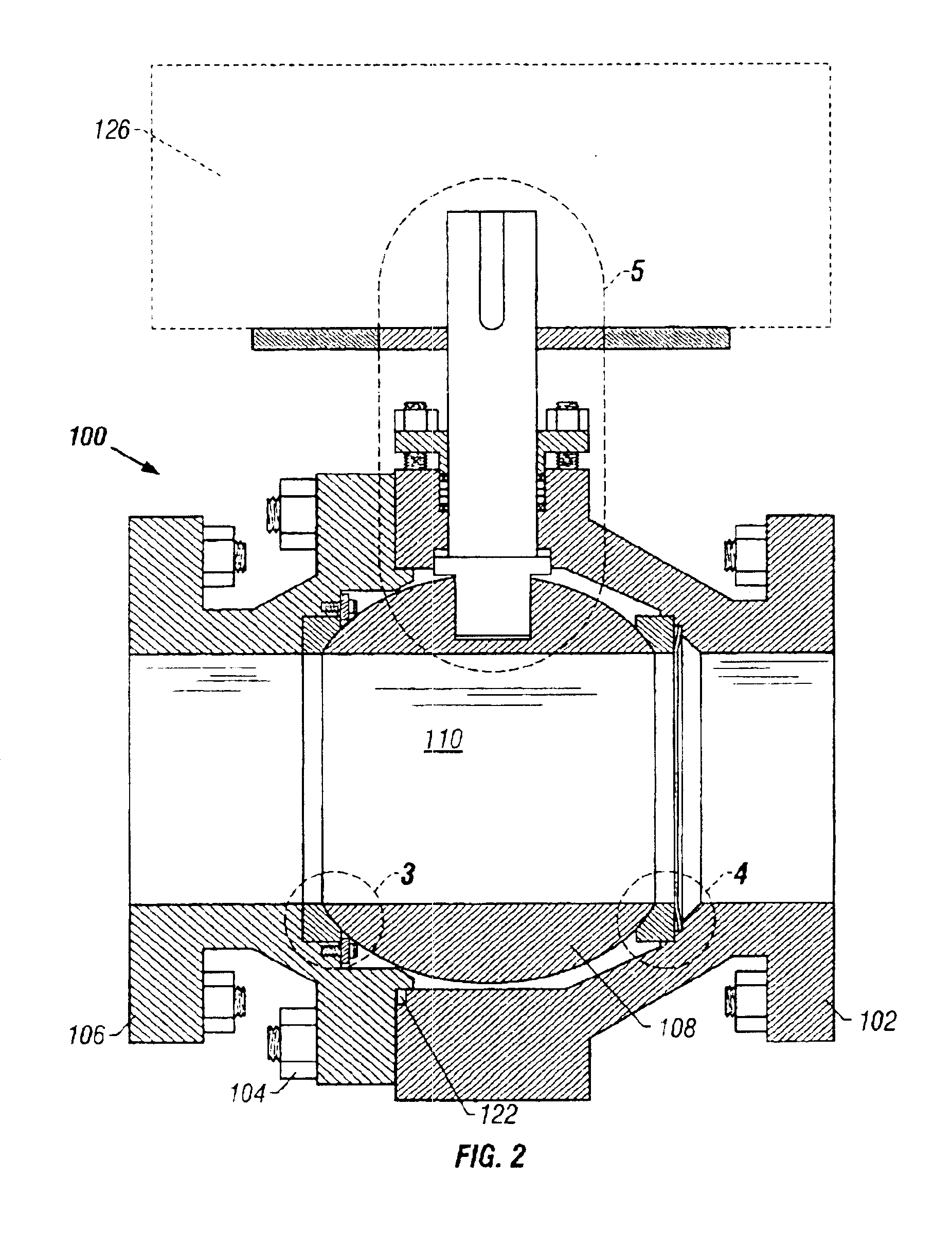
A ball valve for use in the pressure acid leaching of nickel ores is disclosed. The valve has a valve body and a ball centrally positioned in the valve body, which has a central passage rotatable in the valve body between open and closed positions. At least one seat is disposed between the ball and the valve body. The ball and seat each comprise a titanium substrate and an ultrafine or nanostructured titania coating. The titania can include from 5 to 45 volume percent of a second phase material that is immiscible with the titania and exhibits corrosion resistance.
Owner:MOGAS IND +1
Treatment of a wide range of titanium compounds
InactiveUS20050025687A1Low costEnvironmentally friendlyTitanium halidesProcess efficiency improvementCompound aMicrowave
A process of producing 99% plus titanium dioxide product by using conventional and microwave heating and leaching of the titanium compound feedstock using acid and oxidants. The solid residue from the leaching is used to produce the high quality titanium oxide by froth flotation. Hydrochloric acid can be recovered by multi-stage evaporation. The process can be modified to produce nano-size titanium dioxide product.
Owner:RODOLFO ANTONIO M GOMEZ
Method for preparing zirconium tetrachloride through fluidizing chlorination of zircon sand with silicon tetrachloride as byproduct
ActiveCN105565377AEmission reductionReduce manufacturing costCarbon monoxideHalogenated silanesTetrachlorideCollection system
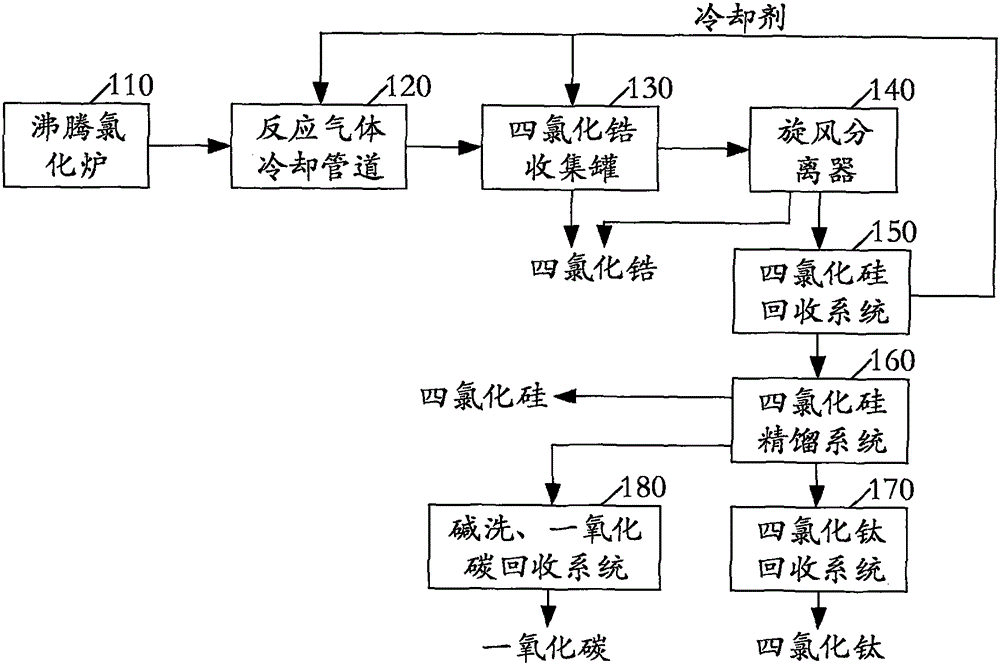
The invention relates to a method for preparing zirconium tetrachloride through fluidizing chlorination of zircon sand with silicon tetrachloride as a byproduct. The method is a preparation method of zirconium halide. A system for realizing the method comprises a zircon sand fluidizing chlorination system, a zirconium tetrachloride condensation and collection system and a silicon tetrachloride rectification system, and also comprises a tail gas recycling system; the tail gas recycling system comprises a tail gas storage device, a chlorine separation and recovery device and a CO recovery and storage device; chlorine in separated and collected tail gas is used as a raw material of a zircon sand fluidizing chlorination reaction, and can be recycled; and the chlorine separated tail gas is used as a raw material of an industrial production apparatus for carrying out a CO participated synthesis reaction. The method for preparing zirconium tetrachloride through fluidizing chlorination of zircon sand with silicon tetrachloride as a byproduct, provided by the invention, has the advantages of effective utilization of Cl2 and CO resources, reduction of discharge of the greenhouse gas CO2, reduction of the product production cost of a zircon sand fluidizing chlorination apparatus, and improvement of the productivity of the apparatus.
Owner:山东广通新材料有限公司
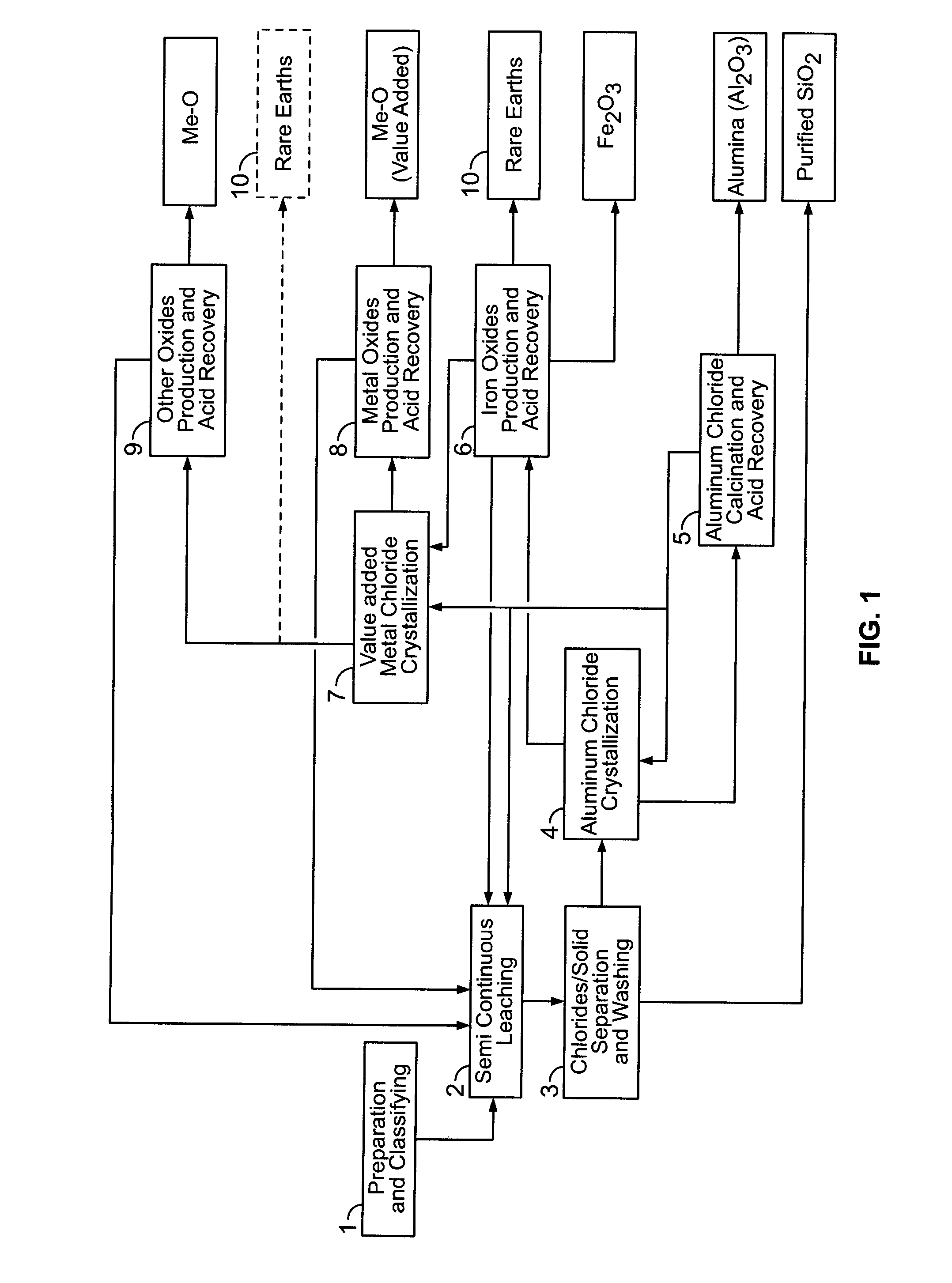
Processes for treating red mud
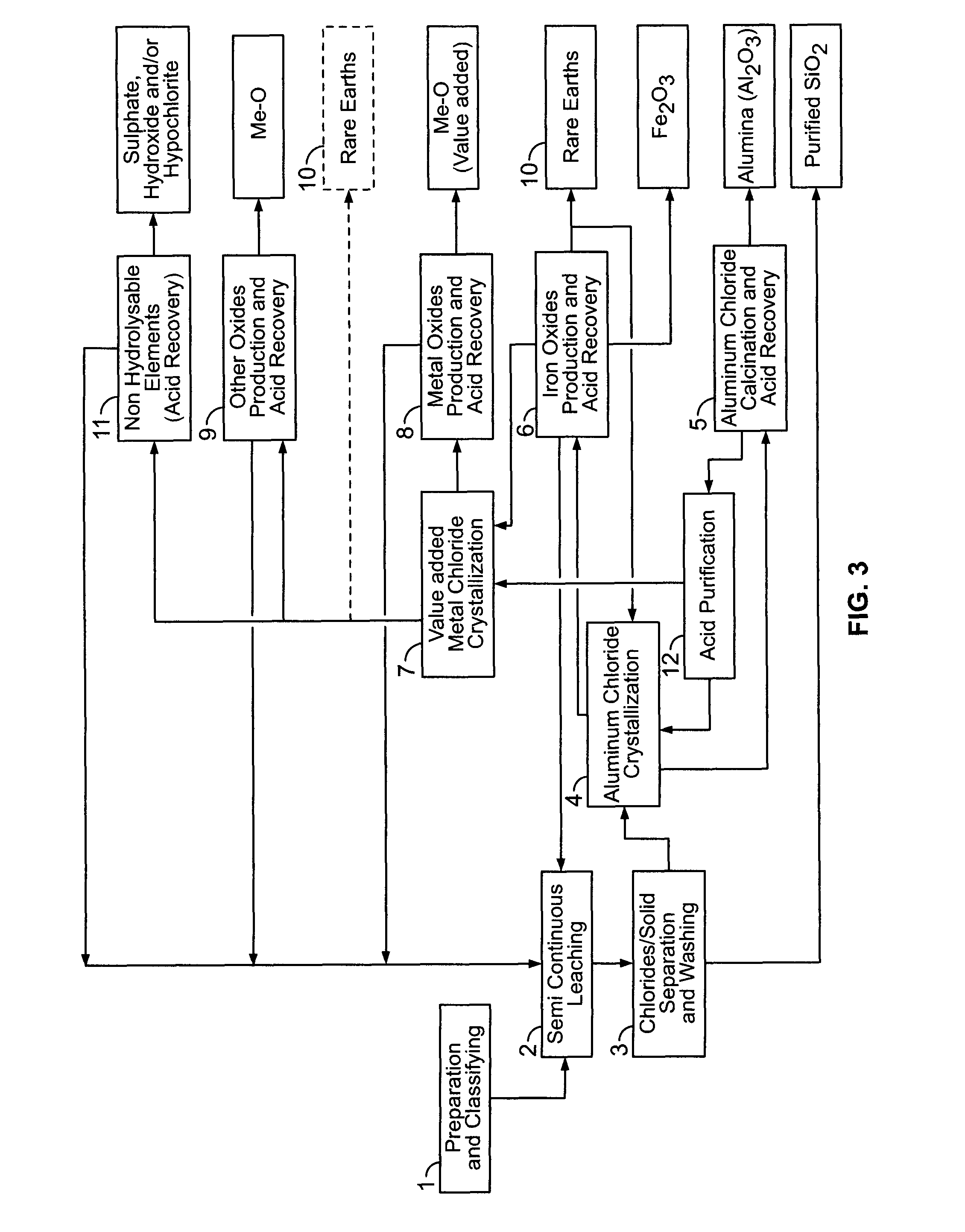
ActiveUS9023301B2Simple and efficientLow costAluminium compoundsNickel compounds preparationRare-earth elementRed mud
There are provided processes for treating red mud. For example, the processes can comprise leaching red mud with HCl so as to obtain a leachate comprising ions of a first metal (for example aluminum) and a solid, and separating said solid from said leachate. Several other metals can be extracted from the leachate (Fe, Ni, Co, Mg, rare earth elements, rare metals, etc.). Various other components can be extracted from solid such as TiO2, SiO2 etc.
Owner:ORBITE ALUMINAE INC
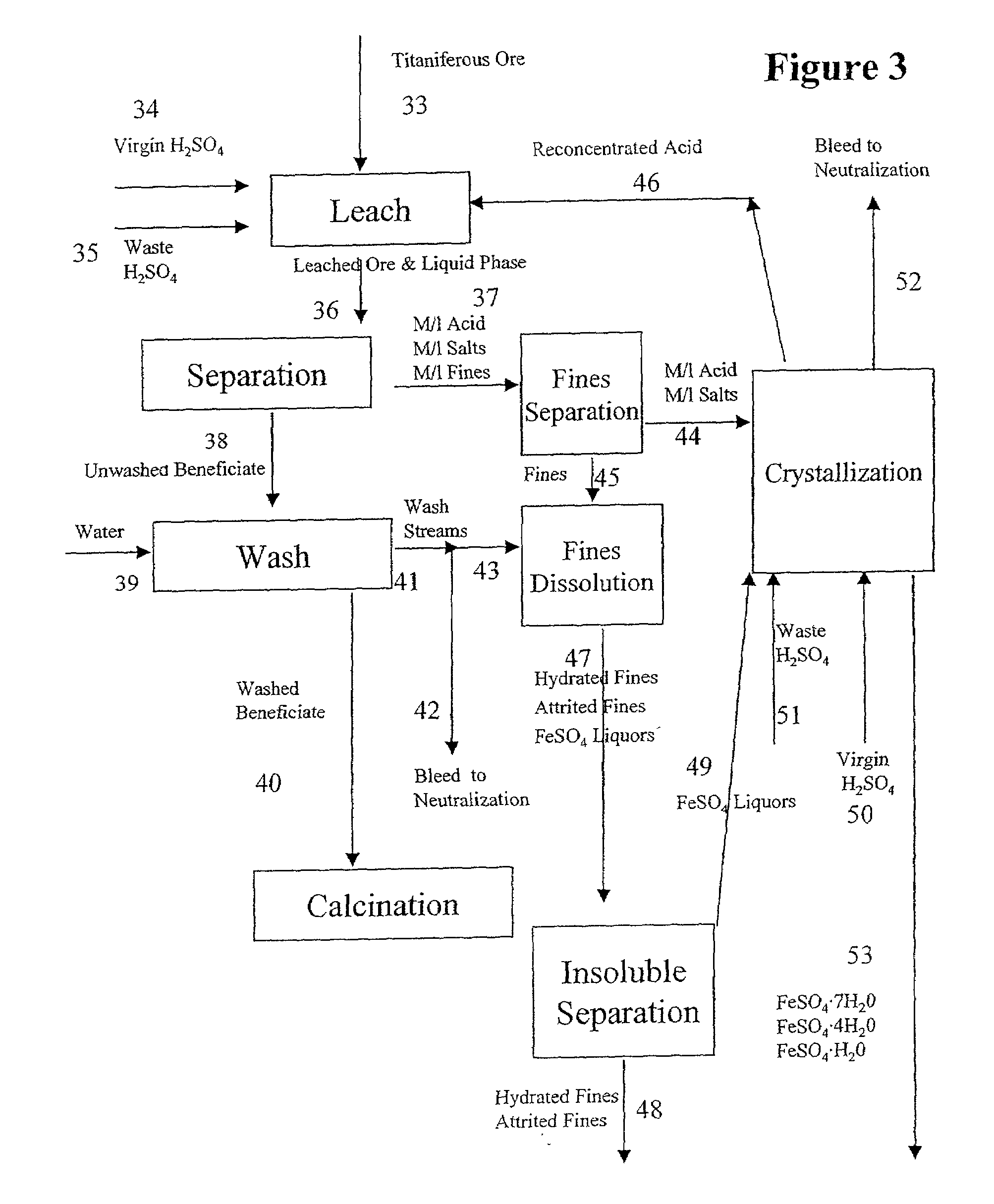
Beneficiation of titaniferous ore with sulfuric acid
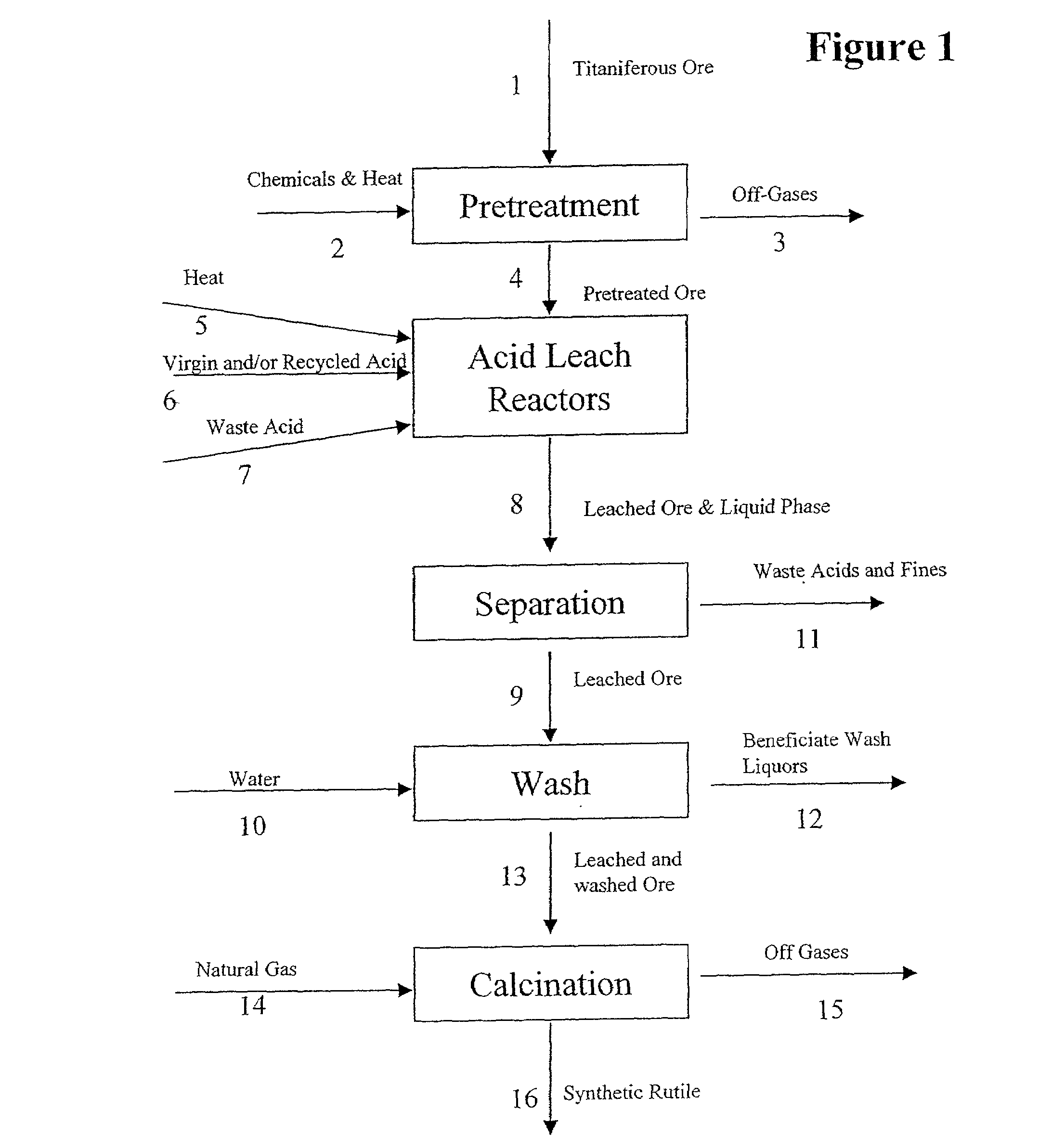
InactiveUS7008602B2Low costImprove product qualityTitanium dioxideTitanium halidesTitaniumMaterials science
Processes for the efficient and economical beneficiation of titaniferous ore are provided. A unique process for beneficiating ore comprising pretreatment of the ore by oxidation and reduction, followed by acid leaching with sulfuric acid has been developed. The acid used in this process may be recycled, which will thereby increase the efficiency of the process. Preferably the ore treated according to the present invention is ilmenite ore.
Owner:TRONOX LLC
Production method of nanoscale high-purity zirconium dioxide composite powder
InactiveCN106866142AImprove particle size uniformityEfficient removalMaterial nanotechnologyZirconium halidesDistillationIon exchange
The invention relates to a production method of nanoscale high-purity zirconium dioxide composite powder. The method comprises the following steps: taking zirconium tetrachloride as the raw material, drying the raw material, then removing impurity with boiling point being lower than that of zirconium tetrachloride and impurity with boiling point being higher than that of zirconium tetrachloride through a two-step distillation crystallization method, dissolving zirconium tetrachloride by using a mixed solution of deionized water and alcohol, carrying out separation of zirconium and hafnium in the solution through an MIBK extraction-elution resin filled extraction chromatographic column, then further purifying zirconium tetrachloride through an ion exchange mode, adding chloride into a high-purity zirconium tetrachloride solution to form a zirconium tetrachloride compound solution, then obtaining zirconium hydroxide gel through an ammonia water spraying co-precipitation manner, carrying out hydrothermal reaction of the zirconium hydroxide gel in a high-pressure reactor, and finally filtering, washing and drying to obtain the nanoscale high-purity zirconium dioxide composite powder. The nanoscale high-purity zirconium dioxide composite powder prepared by the method has the advantages of high purity, uniform particle size, high dispersibility and the like and is applicable to industrial production.
Owner:南京金鲤新材料有限公司
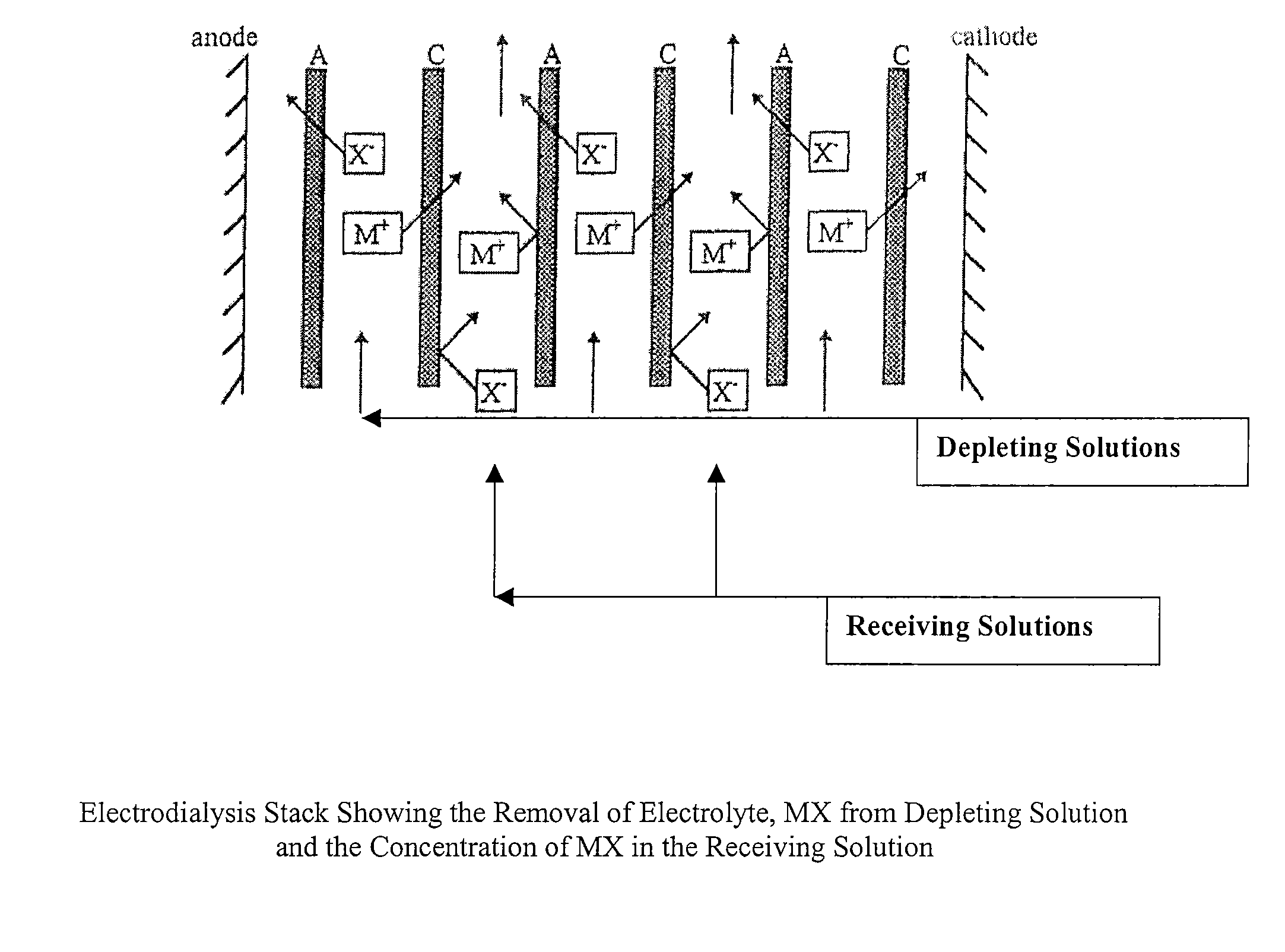
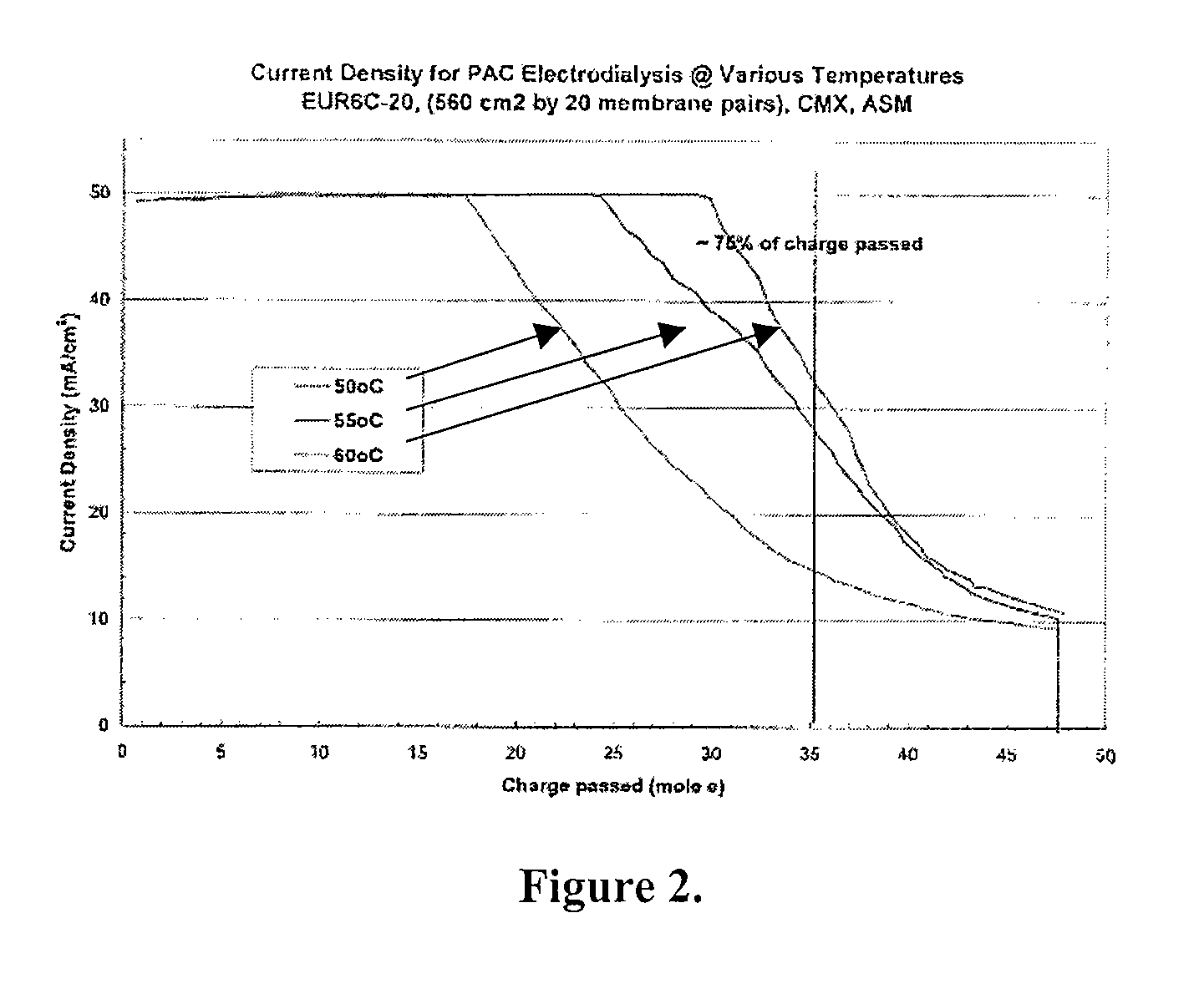
Polyaluminum Chloride and Aluminum Chlorohydrate, Processes and Compositions: High-Basicity and Ultra High-Basicity Products
ActiveUS20070187256A1Increase concentrationIncrease hydroxide contentCosmetic preparationsElectrolysis componentsAntiperspirantsAlkalinity
The invention relates generally to processes for the production of high-basicity and ultr-high basicity polyaluminum chlorides including aluminum chlorohydrate. The processes can produce products of a wide range of basicities and are particularly useful in producing high basicity products. The process can produce a wide range of solution concentrations and are particularly useful in producing high solution concentrations. The processes described generate high purity products, which are free of by-product salt(s). The processes described herein can also be utilized to produce enhanced efficacy polyaluminum chlorides including aluminum chlorohydrate. When compared to conventional processes for manufacturing these compounds the processes disclosed herein are unique in so far as the disclosed processes do not require aluminum metal as a starting material. The products of the processes are suitable in applications including water purification, catalysts, and antiperspirants. In addition, the invention is directed to the products prepared by the processes described herein.
Owner:NEXT CHEM LLC
Benefication of titania slag by oxidation and reduction treatment
InactiveUS6803024B1Improve leaching effectTitanium dioxideTitanium halidesReduction treatmentGranularity
This invention relates to a method of treating titania slag to increase the leachability of impurities from the slag consisting of the steps of sizing the titania slag to a particle size from 75 to 850 mum; oxidizing the sized slag particles at a temperature from about 700° C. to below about 900° C. causing the iron present in the slag to concentrate at the exposed surfaces of the slag particles and / or causing an anatase phase to stabilize in the slag, causing a major portion of the iron in the Fe(II) state to convert to the Fe(III) state, and causing the titanium in the Ti(III) state to be converted to the Ti(IV) state; and reducing the oxidized slag in a reducing atmosphere from about 700° C. to about 950° C. to convert a major portion of the iron in the Fe(III) state to the Fe(II) state. The invention also relates to a method of beneficiating titania slag to increase the TiO2 content thereof wherein the above treated slag is leached with acid.
Owner:EXXARO TSA SANDS
Processes for preparing titanium oxide and various other products
There are provided processes for preparing various products from various materials. For example, such processes are effective for extracting titanium and various other metals from various materials, thereby allowing for preparing products such as titanium chloride and titanium oxide. These processes can comprise leaching the starting material with HCl so as to obtain a leachate and a solid. The solid can be treated so as to substantially selectively extract titanium therefrom while the leachate can be treated so as to substantially selectively recover a first metal chloride therefrom.
Owner:ORBITE ALUMINAE INC
Production device for preparing ultra-pure zirconium oxychloride byproduct silicon tetrachloride by fluidizing chlorination of zircon sand
ActiveCN105540660AEmission reductionReduce manufacturing costChlorine/hydrogen-chlorideCarbon monoxideCollection systemZirconium oxychloride
The invention relates to a production device for preparing ultra-pure zirconium oxychloride byproduct silicon tetrachloride by fluidizing chlorination of zircon sand, belonging to a preparation method of zirconium halogenide. The production device comprises a zircon sand fluidizing chlorination system, a silicon tetrachloride condensation collection system, a silicon tetrachloride rectifying system and a silicon tetrachloride hydrolyzed ultra-pure zirconium oxychloride preparation system. The production device is characterized by also comprising a tail gas recycling system; the tail gas recycling system comprises a tail gas storage device, a chlorine gas separation recycling device and a CO recycling storage device; firstly, the chlorine gas in the tail gas is separated and collected to be used as a raw material for fluidizing chlorination of the zircon sand and to be recycled; and the tail gas after the chlorine gas is separated is used as a raw material of an industrial production device involved in the synthesis reaction participated by CO. By adopting the production device, the Cl2 and CO resources can be efficiently utilized, and the emission of the greenhouse gas CO2 is reduced; and the production cost of products of the zircon sand fluidizing chlorination device can be reduced, and the production capacity of the device can be improved.
Owner:山东广通新材料有限公司
Polyaluminum chloride and aluminum chlorohydrate, processes and compositions: high-basicity and ultra high-basicity products
ActiveUS7846318B2Increase hydroxide contentCosmetic preparationsChloride preparationAntiperspirantsAlkalinity
The invention relates generally to processes for the production of high-basicity and ultra-high basicity polyaluminum chlorides including aluminum chlorohydrate. The processes can produce products of a wide range of basicities and are particularly useful in producing high basicity products. The process can produce a wide range of solution concentrations and are particularly useful in producing high solution concentrations. The processes described generate high purity products, which are free of by-product salt(s). The processes described herein can also be utilized to produce enhanced efficacy polyaluminum chlorides including aluminum chlorohydrate. When compared to conventional processes for manufacturing these compounds the processes disclosed herein are unique in so far as the disclosed processes do not require aluminum metal as a starting material. The products of the processes are suitable in applications including water purification, catalysts, and antiperspirants. In addition, the invention is directed to the products prepared by the processes described herein.
Owner:NEXT CHEM LLC
Process for the recovery of titanium in mixed chloride media
Owner:CANADIAN TITANIUM
Method for producing zirconium tetrachloride by carbochlorination and method for producing zirconium sponge
ActiveCN103466699AShort processReduce power consumptionZirconium halidesTetrachlorideReduction treatment
The invention provides a method for producing zirconium tetrachloride by carbochlorination and a method for producing zirconium sponge. The method for producing zirconium tetrachloride comprises the following steps: mixing 100 parts by weight of zircon sand with 26-45 parts by weight of carbonaceous reducing agent, and adding into a chlorination furnace; preheating a mixture to 1200-1500 DEG C; introducing chlorine at the temperature of 500-1100 DEG C, performing carbon-adding boiling chlorination reaction with the mixture, heating, and controlling the chlorination reaction temperature at 1050-1200 DEG C to obtain a reaction product. The method for producing zirconium sponge comprises the following steps: preparing the reaction product taking zirconium tetrachloride as a main component by using the method for producing zirconium tetrachloride; performing reduction treatment on the reaction product to obtain zirconium sponge. The methods provided by the invention have the beneficial effects of short process flow, low power consumption, low cost and continuous and stable reaction.
Owner:XINJIANG JINGSHUO NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for producing zirconium tetrachloride
InactiveCN104556226AControl reaction temperatureAvoid the tediousness of frequent parking and replacementHalogenated silanesZirconium halidesAutomatic controlReaction temperature
The invention relates to the technical field of chemical processes and in particular discloses a method for producing zirconium tetrachloride. The method comprises the following steps: respectively crushing zircon sand, petroleum coke powder and a chemical auxiliary agent; fully mixing the zircon sand and petroleum coke powder according to a ratio, adding the mixture into a boiling chloridizing furnace, and introducing chlorine for carrying out a chlorination reaction; regulating the amount of the added chemical auxiliary agent by virtue of an automatic control system, so that the temperature of the boiling chloridizing furnace is always preserved to 1100 DEG C. The chemical auxiliary agent accounts for 15-30 percent of the total weight of the zircon sand and petroleum coke powder; the weight ratio of the zircon sand to petroleum coke powder is 10:(1-2.5); and the chemical auxiliary agent refers to metal silicon, silicon carbide or a mixture of metal silicon and silicon carbide. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the reaction temperature can be constantly controlled, the complicated operation of frequently stopping and replacing is avoided, the production efficiency is improved, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:赤峰盛森硅业科技发展有限公司
Method for preparing nuclear-grade sponge zirconium and nuclear-grade sponge hafnium
InactiveCN106435221AAchieve recyclingSolve difficult environmental problemsSilicaProcess efficiency improvementNuclear gradeElectrolysis
The invention relates to nuclear-grade sponge zirconium, in particular to a method for preparing nuclear-grade sponge zirconium and nuclear-grade sponge hafnium. Chlorine generated by hydrochloric acid electrolysis is used for producing zirconium tetrachloride and zirconium oxychloride by a zircon sand boiling chlorination method; zirconium and hafnium are seperated to obtain zirconium oxide and hafnium oxide through a TBP-Hcl-HNO3 extraction method; and then, the chlorination and the purification are performed to obtain the nuclear-grade sponge zirconium and the nuclear-grade sponge hafnium. The method radically solves the environmental protecting environment difficultly treated in the zirconium oxychloride industry and the nuclear-grade sponge zirconium industry, and realizes complete industry chain circulation for combined production of the zirconium oxychloride industry, the gas-phase method silicon dioxide industry, the nuclear-grade sponge zirconium industry and the hydrochloric acid electrolysis industry.
Owner:郭爽
Agglomeration of titania
InactiveUS7931886B2Conducive to agglomerationImprove bindingPigmenting treatmentIron oxides/hydroxidesChloride process
According to the present invention there is provided a process for the agglomeration of titania slag particles comprising providing titania slag at a d50 particle size of below 106 μm; mixing the slag particles with an organic binder; and agglomerating the mixture of the slag particles and organic binder into agglomerated particles with a d50 particle size in the range from 106 μm to 1000 μm. The agglomerated particles have a (TiO2 and FeO) / C mass ratio of more than 3.4. The invention also relates to such agglomated slag particles and a chloride process for the production of TiO2 wherein such agglomerated titania slag particles are used.
Owner:EXXARO TSA SANDS
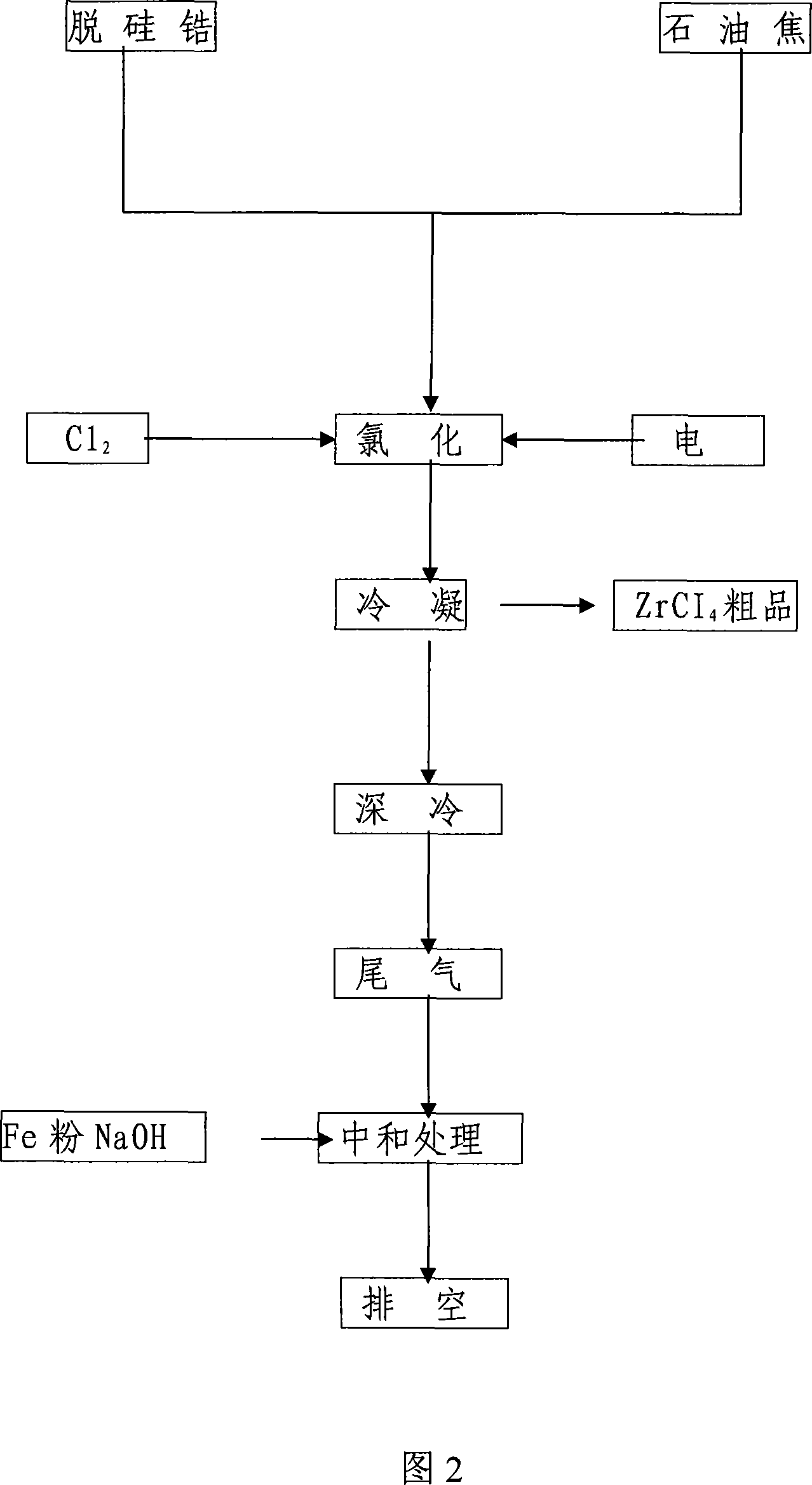
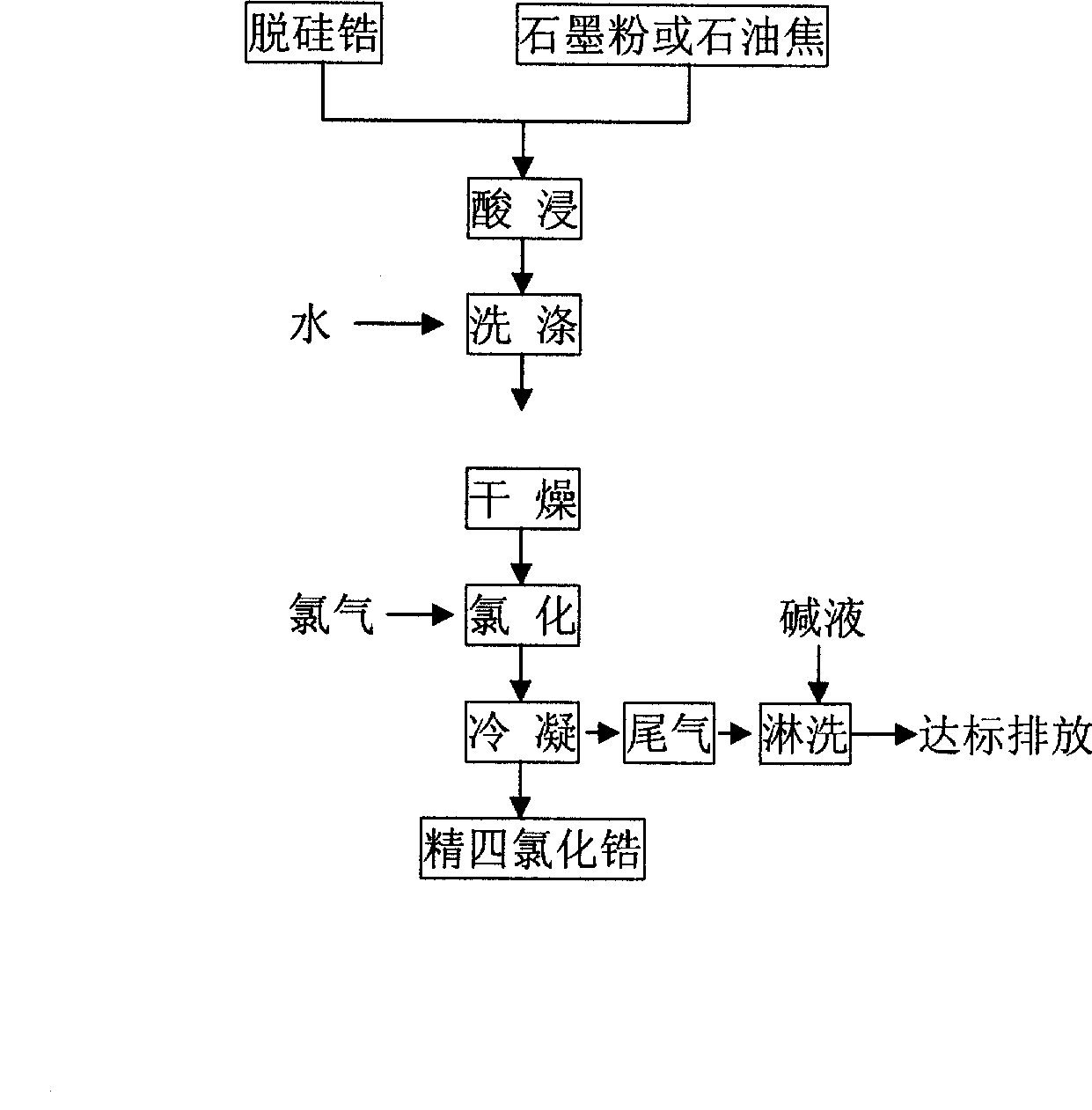
Preparation of refined zirconium tetrachloride
ActiveCN101486490ASave high power consumptionEliminate the purification processZirconium halidesHigh energyPetroleum
The invention adopts a chemical method to remove impurities in raw materials, and a boiling chlorination method to prepare refined zirconium tetrachloride. The preparation method comprises the steps that: desilicated zirconium is ground into fine powder of 300 meshes to 500 meshes and then mixed with petrol coke or graphite of 50 meshes to 200 meshes according to the weight ratio of 100:16-20; then the mixture is added into a container which holds mineral acid with the use concentration of 3 mol / L to 7 mol / L, and reaction is carried out for 0.5 hour to 5 hours at the temperature ranging from 10 DEG C to 60 DEG C so as to remove the impurities; then, the reaction products are washed with water to be neutral, dried at the temperature of 70 DEG C to 120 DEG C and added into a boiling chlorination furnace which is provided with a filter; when the temperature inside the boiling chlorination furnace reaches 800 DEG C to 900 DEG C, chlorine with the flowing rate of 0.6 M / hour to 1.0 M / hour is led into the boiling chlorination furnace to react for 20 hours to 24 hours; and finally, refined zirconium tetrachloride with the content over 98 percent is obtained. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method has the advantages of eliminating the crude zirconium-tetrachloride purifying process with high energy consumption and low yield, shortening process flows, being beneficial to environmental protection and significantly reducing the production cost.
Owner:朝阳东锆新材料有限公司
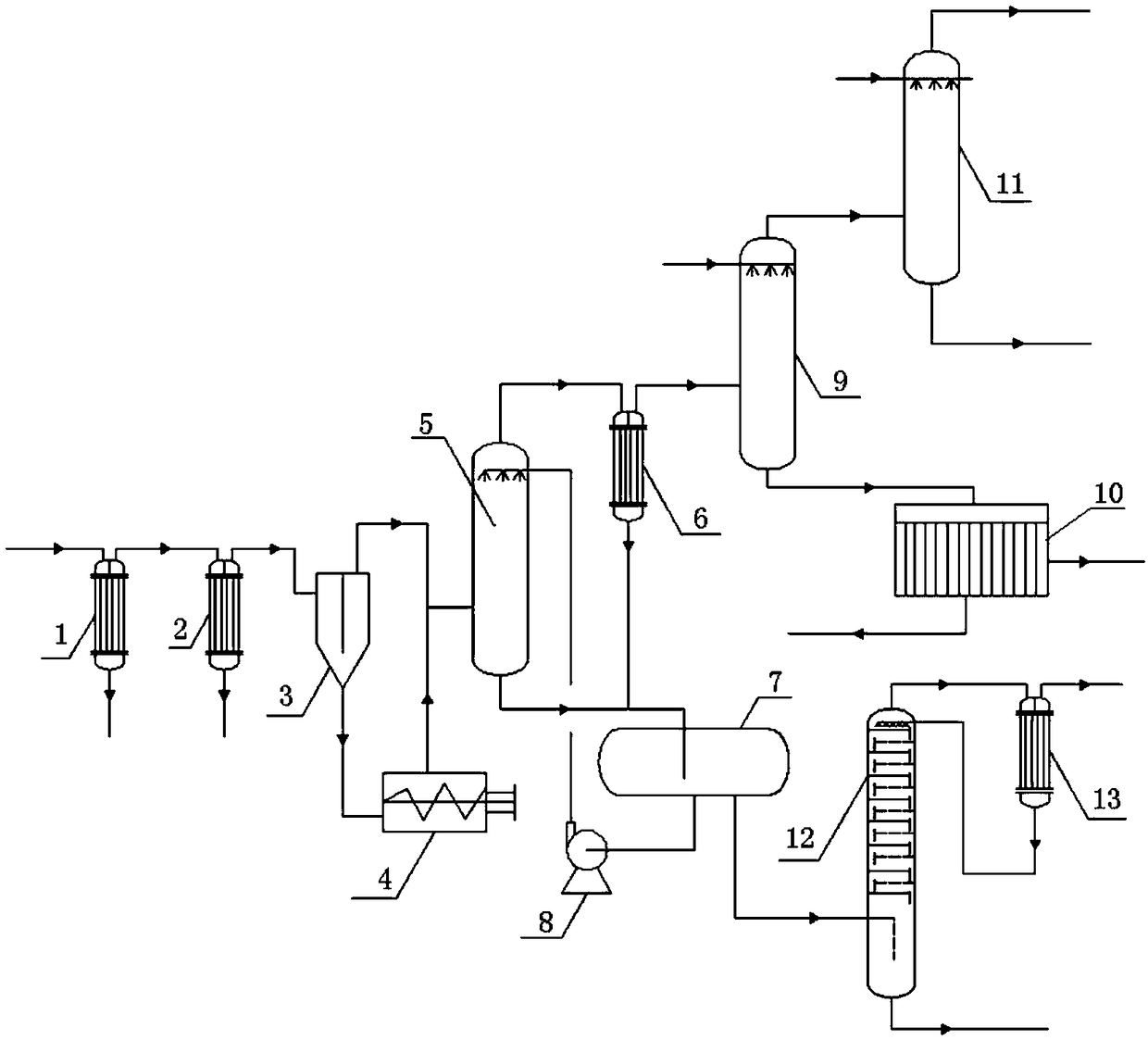
Separation method and device of zirconium tetrachloride synthesis gas
ActiveCN109019684AReduce separation costsReduce the temperatureSilicaCarbon monoxideTetrachloridePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a separation method of zirconium tetrachloride synthesis gas. The zirconium tetrachloride synthesis gas is prepared from zirconium tetrachloride by a chlorination method. The method comprises the following steps of (1) lowering the temperature of the zirconium tetrachloride synthesis gas to 150 to 180 DEG C; separating out first coarse zirconium tetrachloride to obtain first synthesis gas; (2) lowering the temperature of the first synthesis gas to 80 to 120 DEG C; separating out second coarse zirconium tetrachloride to obtain second synthesis gas. The separation methodand device of zirconium tetrachloride synthesis gas provided by the method have the advantages that according to the method, the first coarse zirconium tetrachloride and the second coarse zirconium tetrachloride are respectively cooled and separated through stepped temperature reduction; the first coarse zirconium tetrachloride and the second coarse zirconium tetrachloride can be respectively usedas a coarse product to be used; the temperature used for separating out the first coarse zirconium tetrachloride through temperature reduction is lower; most zirconium tetrachloride in the zirconiumtetrachloride synthesis gasis separated out; the cold quantity is greatly saved; the separation cost of the zirconium tetrachloride synthesis gas is reduced.
Owner:XINTE ENERGY +1
Processes for treating red mud
ActiveUS20150275330A1Simple and efficientLow costAluminium compoundsNickel compounds preparationPregnant leach solutionRare-earth element
Owner:AEM TECH INC
Process for preparing titanium tetrachloride using off gases from a silica and zircon carbo-chlorination process
InactiveUS20140154167A1Inhibit wearTitanium tetrachlorideTitanium dioxideEthyl ChlorideSilicon dioxide
This disclosure relates to an improved process for preparing titanium tetrachloride comprising a first carbo-chlorination reaction comprising reacting ores comprising silica and / or zirconium with chlorine and a carbon compound at a temperature of about 900° C. to about 1300° C. to form an unscrubbed off gas comprising carbon monoxide, and using the unscrubbed off gas in a second carbo-chlorination reaction comprising titanium to form titanium tetrachloride.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Titaniferous ore beneficiation
ActiveUS20080241026A1Reduced impurity levelsIncrease contentTitanium dioxideTitanium halidesAlkaline earth metalChloride
This invention relates to a process for beneficiating a titaniferous ore. The process comprises calcining the titaniferous ore, at least one alkali or alkaline earth metal salt, and at least one alumina-containing material in the presence of oxygen to form a calcined ore mixture, then leaching the calcined ore mixture with a solution comprising ammonium, sodium or magnesium chloride in the presence of oxygen to form a leached ore mixture, and contacting the leached ore with an acid to form a beneficiated ore.
Owner:UNIV OF LEEDS
Titaniferous ore beneficiation
InactiveUS20070092416A1Reduced impurity levelsTitanium halidesProcess efficiency improvementTitaniumCalcination
This invention relates to a process for beneficiating a titaniferous ore. The process comprises leaching the titaniferous ore with sulfuric acid to form a leached ore, calcining the leached ore in the presence of oxygen to form a calcined ore, and leaching the calcined ore with sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, and / or nitric acid to form a beneficiated ore. The leached ore is not reduced prior to or following calcination.
Owner:TRONOX LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com