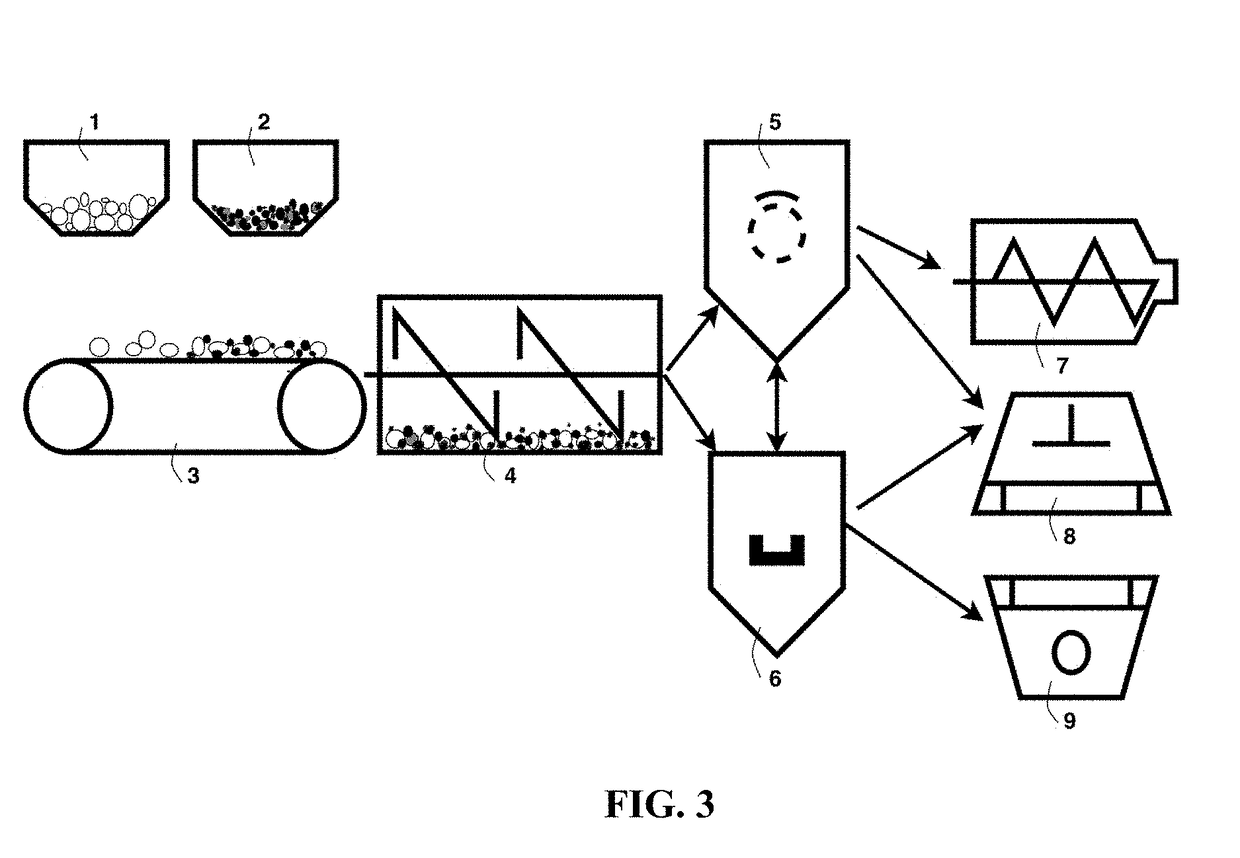
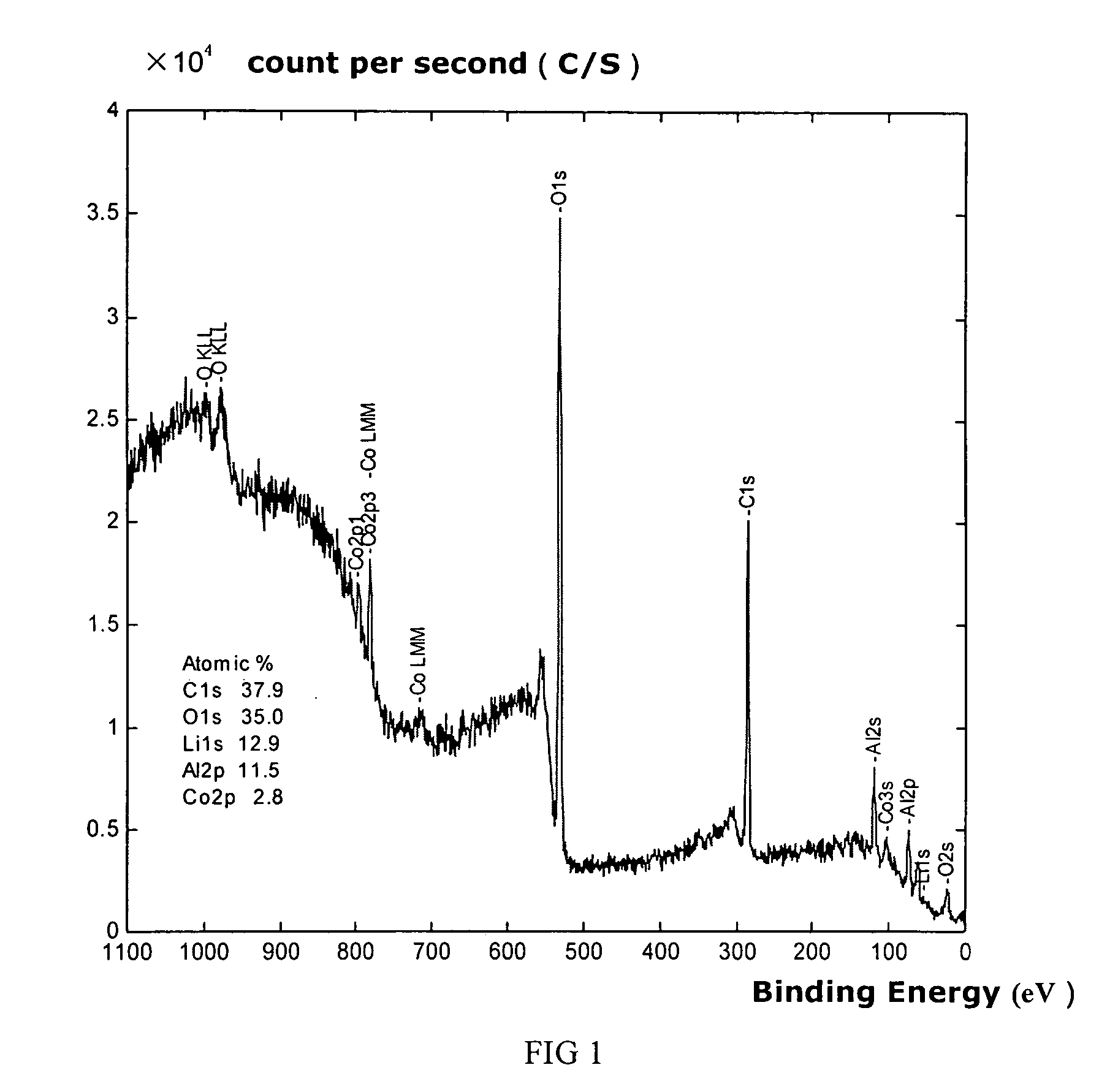
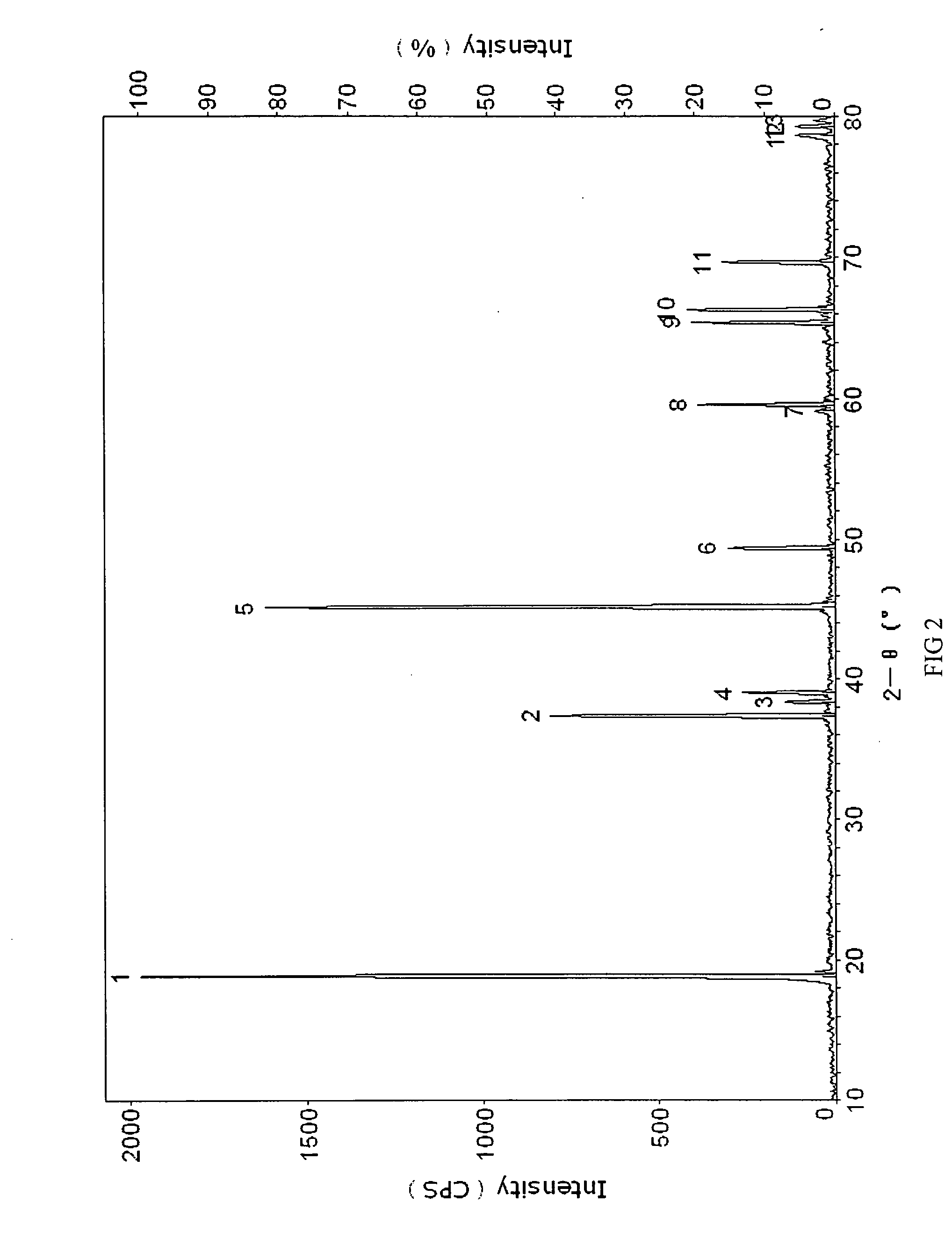
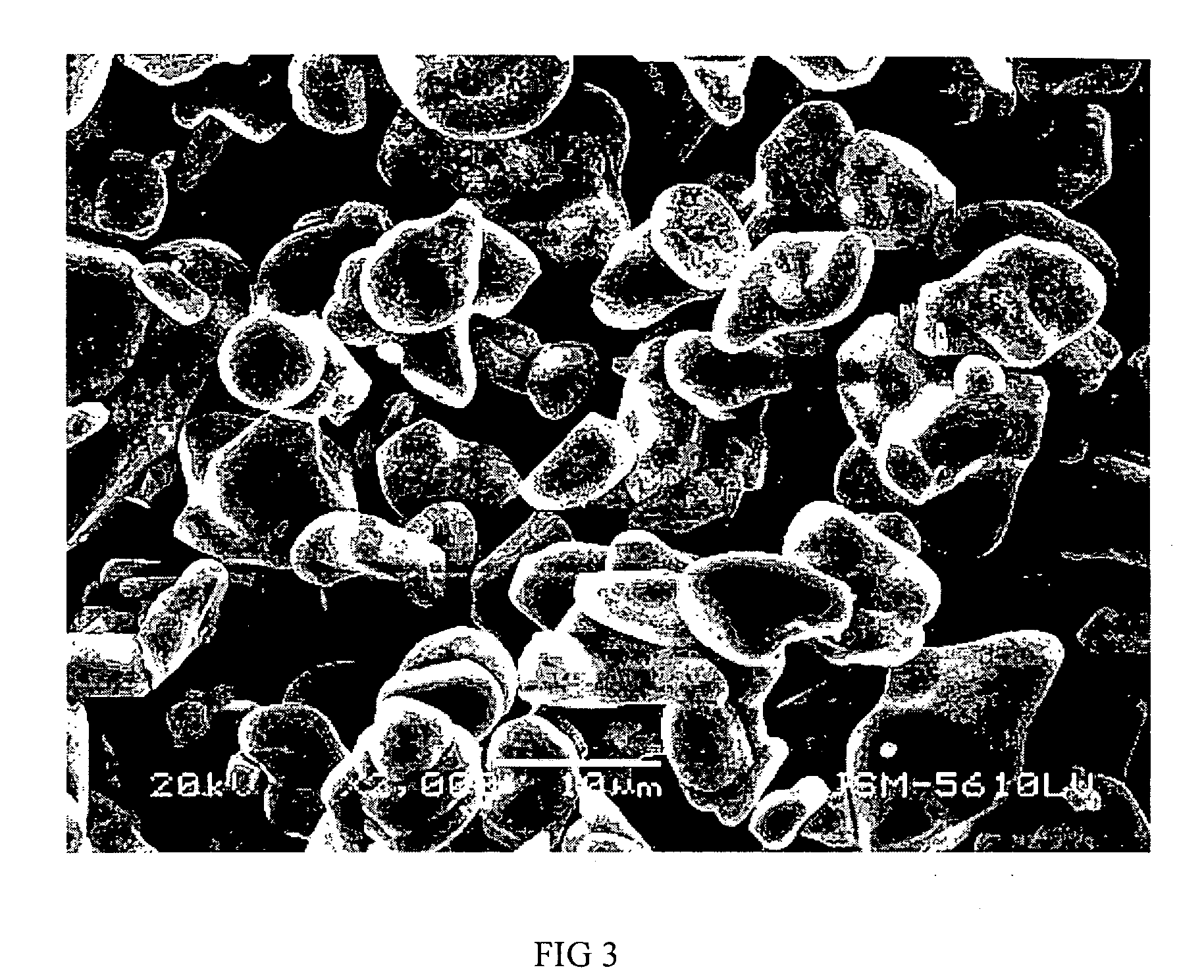
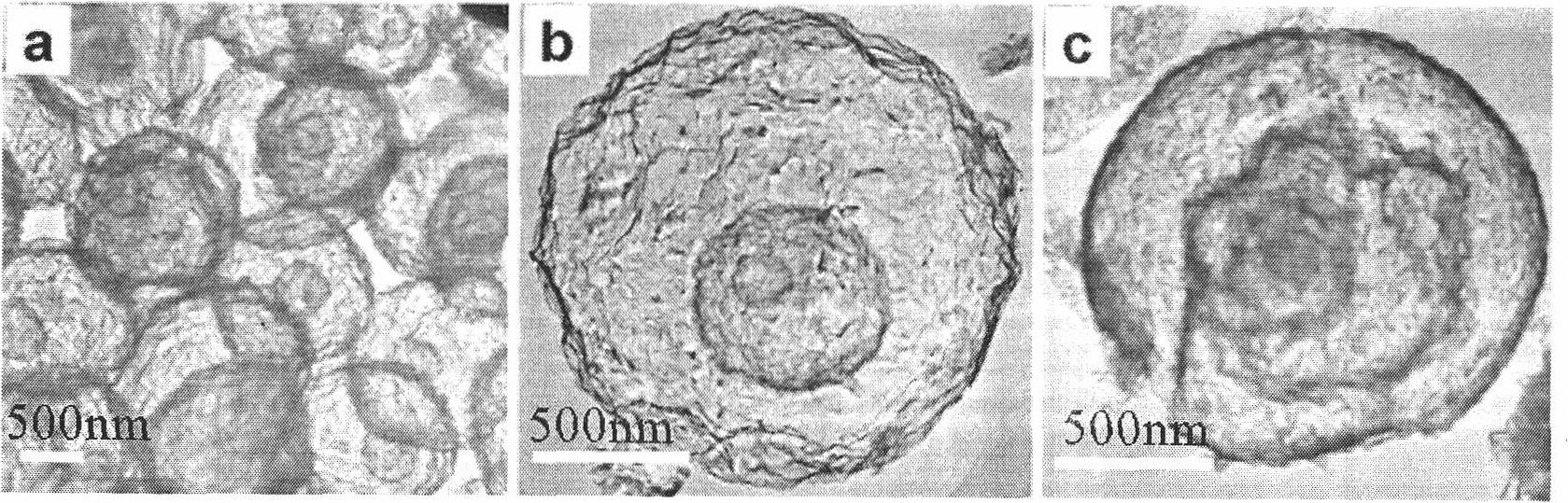
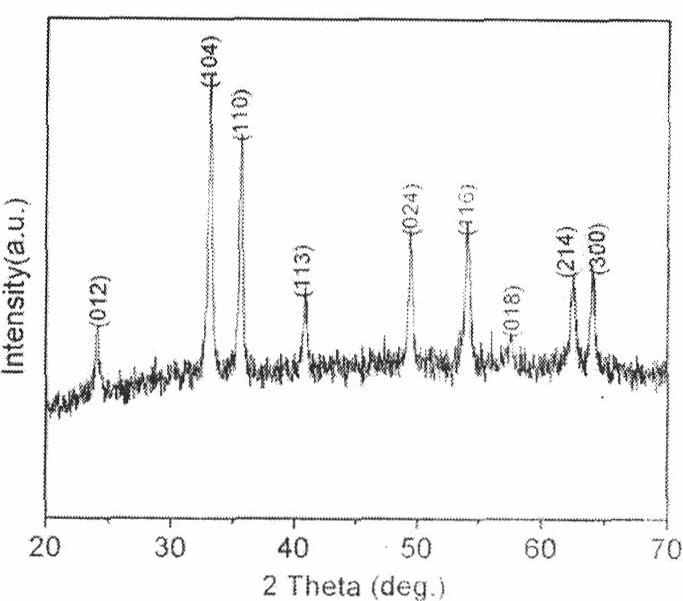
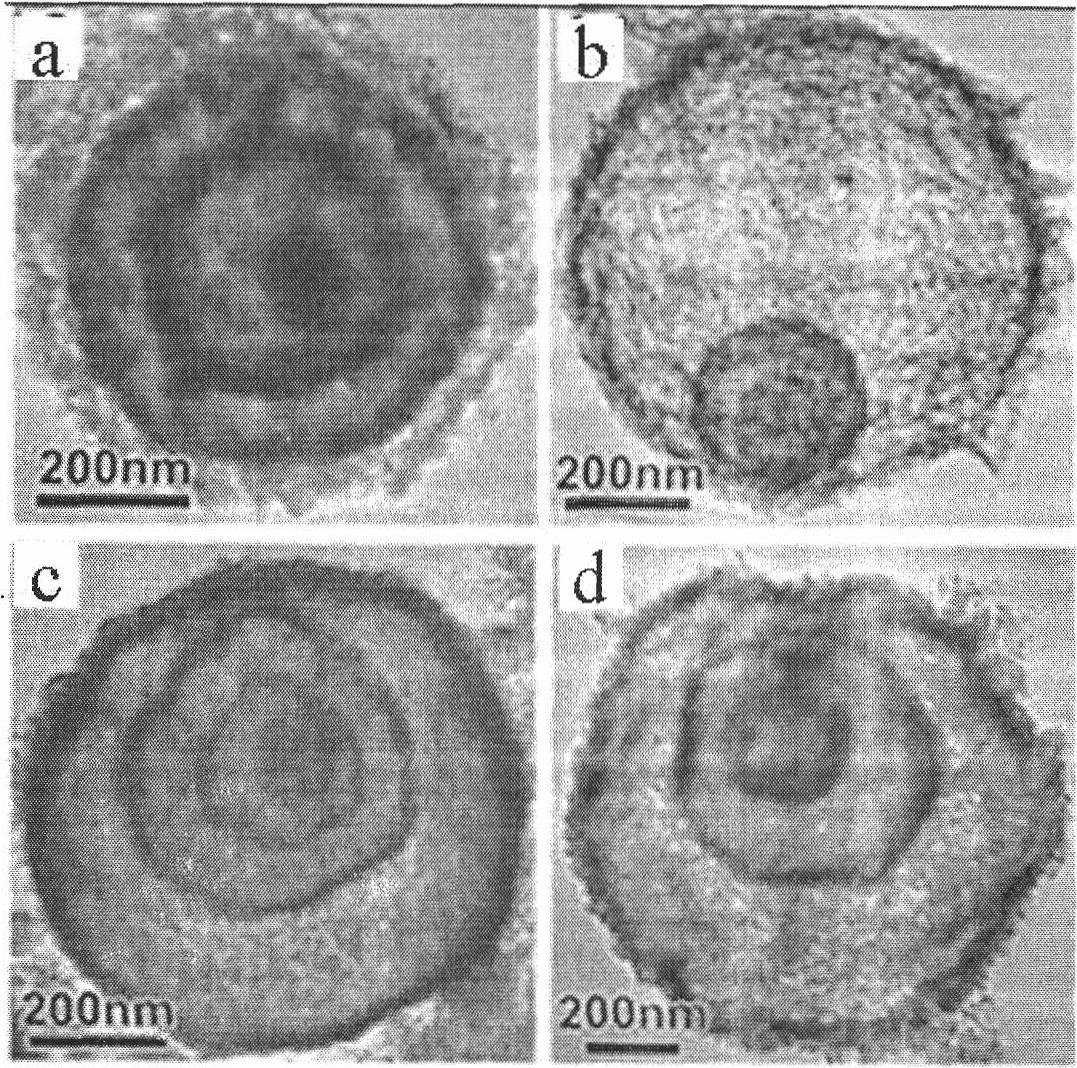
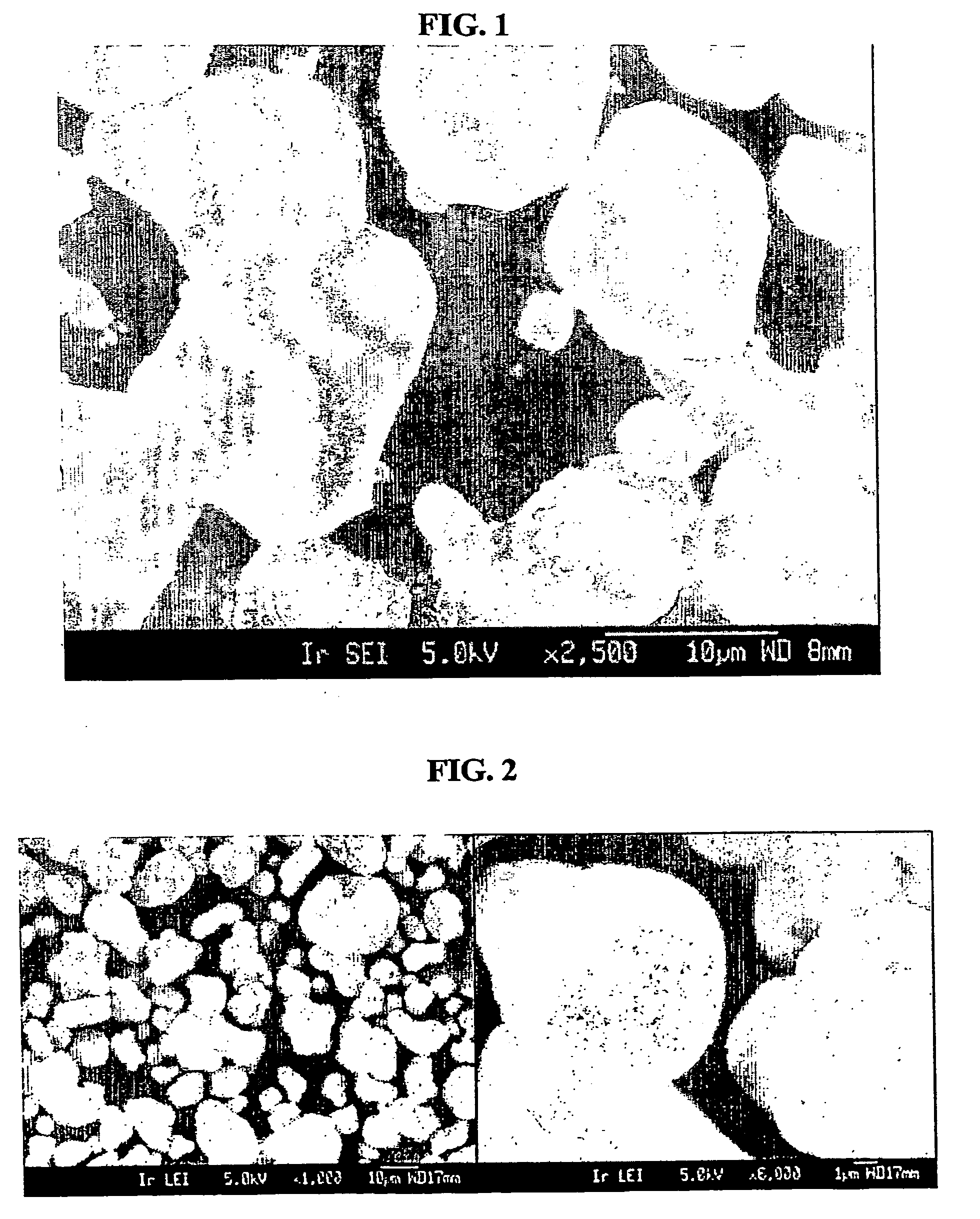
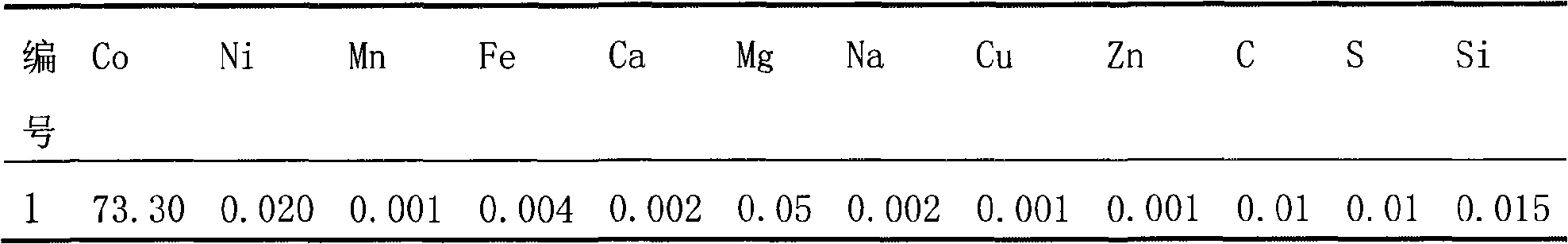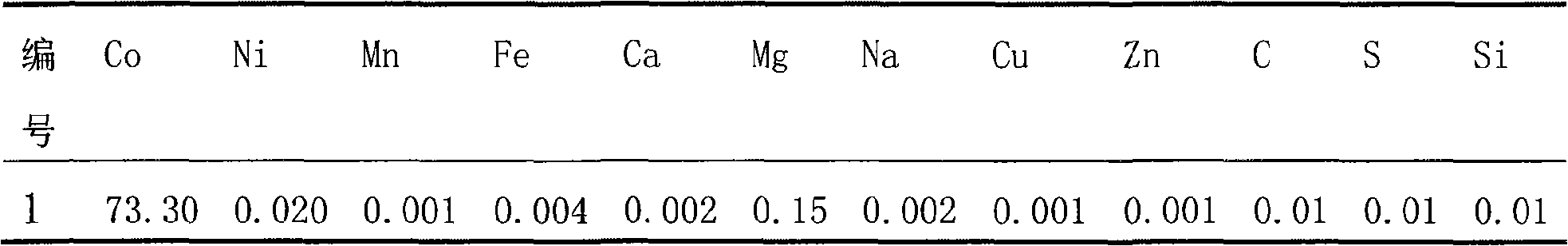Patents
Literature
1764results about "Cobalt oxides/hydroxides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Active material for positive electrode used in lithium secondary battery and method of manufacturing same
InactiveUS6372385B1Easy to implementEvenly dispersedElectrode thermal treatmentActive material electrodesLithium-ion batteryMetal
Disclosed is active material for a positive electrode used in lithium secondary batteries of Formula 1 below and a method manufacturing the same, a surface of the active material being coated with metal oxide. The method includes the steps of producing a crystalline powder or a semi-crystalline powder of Formula 1; coating the crystalline powder or the semi-crystalline powder with metal alkoxide sol; and heat-treating the powder coated with the metal alkoxide sol.where 0<x<=0.3, 0<=y<=0.01, andA is an element selected from the group consisting of Ni, Co and Mn; B is an element selected from the group consisting of Ni, Co, Mn, B, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ti, V, Cr, Fe, Cu and Al; and C is an element selected from the group consisting of Ni, Co, Mn, B, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ti, V, Cr, Fe, Cu and Al.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS DEVICES CO LTD
Positive-electrode active material and nonaqueous-electrolyte secondary battery containing the same
InactiveUS20030170540A1Improve the immunityLarge ion permeabilityIron oxides/hydroxidesElectrode thermal treatmentCrystal structureOxygen
The present invention provides a high-capacity and low-cost non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery, comprising: a negative electrode containing, as a negative electrode active material, a ssubstance capable of absorbing / desorbing lithium ions and / or metal lithium; a separator; a positive electrode; and an electrolyte, wherein the positive electrode active material contained in the positive electrode is composed of crystalline particles of an oxide containing two kinds of transition metal elements, the crystalline particles having a layered crystal structure, and oxygen atoms constituting the oxide forming a cubic closest packing structure.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
Layered Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Composite Oxide Powder For Material Of Positive Electrode Of Lithium Secondary Battery, Process For Producing The Same, Positive Electrode Of Lithium Secondary Battery Therefrom, And Lithium Secondary Battery
ActiveUS20070202405A1Improve securityImprove battery performanceNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsOrganic electrolyte cellsManganeseCobalt
A powder of a layered lithium-nickel-manganese-cobalt composite oxide for use as a positive-electrode material for lithium secondary battery is provided which, when used as a positive-electrode material for lithium secondary battery, enables a cost reduction and higher safety to be reconciled with improved battery performances. The powder of a layered lithium-nickel-manganese-cobalt composite oxide for use as a positive-electrode material for lithium secondary battery is composed of secondary particles formed by the aggregation of primary particles. It has a composition represented by the following formula (I), has a volume resistivity of 5×105 Ω·cm or lower in the state of being compacted at a pressure of 40 MPa, and has a value of C / S, wherein C is the concentration of carbon contained therein (% by weight) and S is the BET specific surface area thereof (m2 / g), of 0.025 or smaller. The powder has been regulated so as to have a volume resistivity not higher than the specified value and a considerably reduced carbon content while having a composition in a limited range, whereby a cost reduction and higher safety can be reconciled with improved battery performances. Li1+zNixMnyCo1−x−yOδ (I) (0<z≦0.91, 0.1≦x≦0.55, 0.20≦y≦0.90, 0.50≦x+y≦1, 1.9≦δ≦3)
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
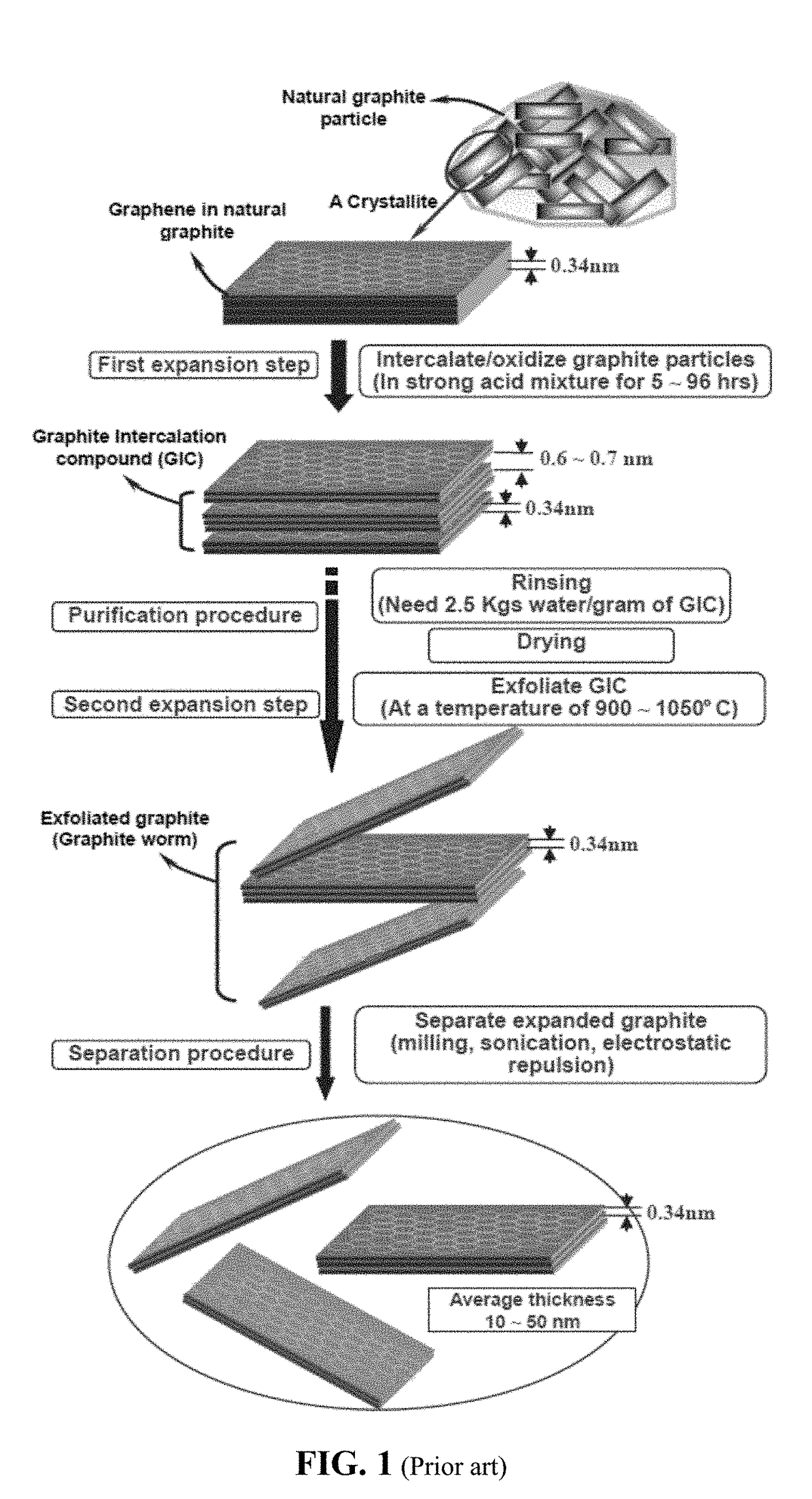
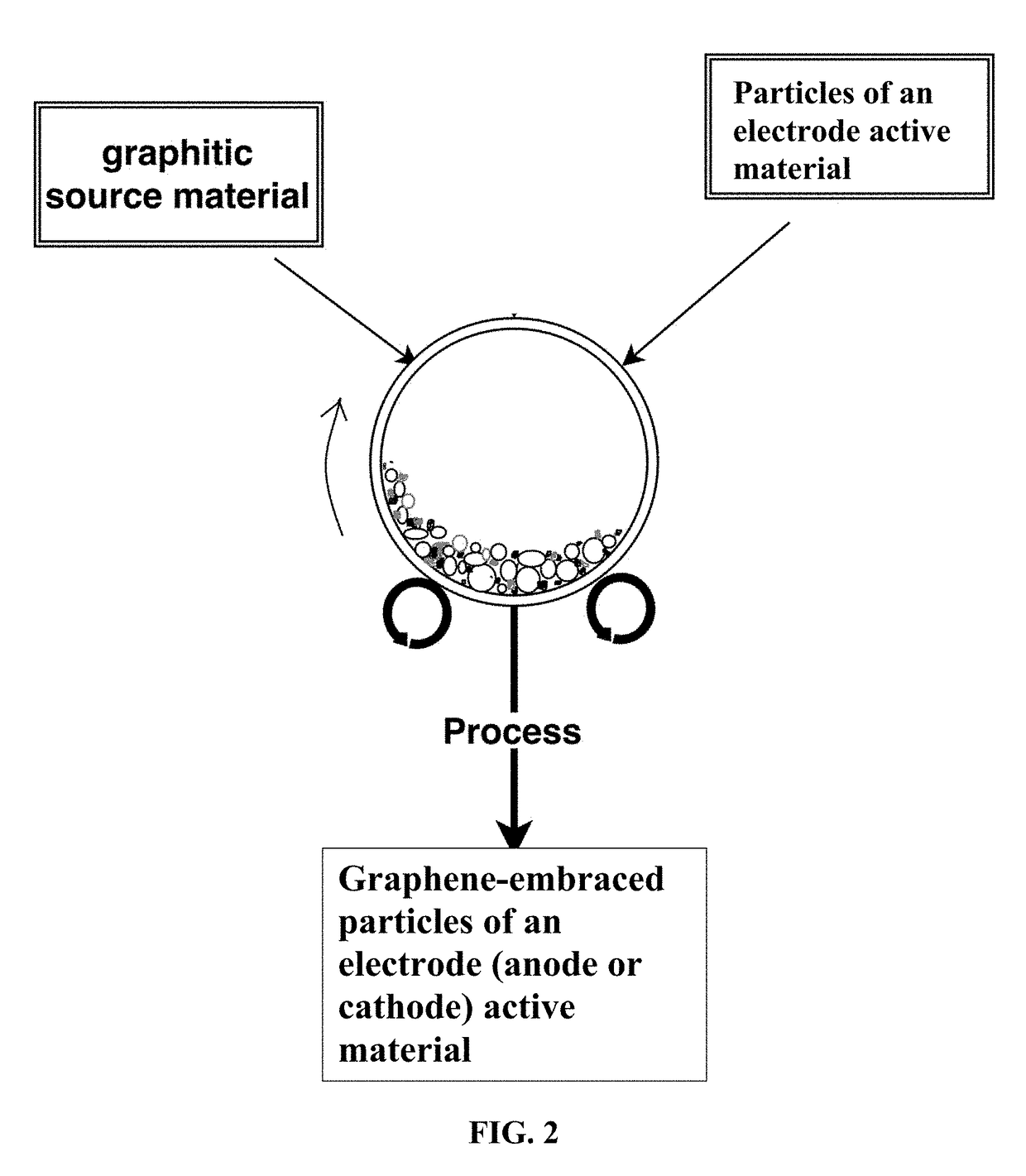
Chemical-Free Production of Graphene-Encapsulated Electrode Active Material Particles for Battery Applications
ActiveUS20170338472A1Improve mechanical propertiesImprove thermal conductivityGrapheneNegative electrodesEnergy impactGraphite
Provided is a simple, fast, scalable, and environmentally benign method of producing graphene-embraced or encapsulated particles of a battery electrode active material directly from a graphitic material, the method comprising: a) mixing graphitic material particles and multiple particles of a solid electrode active material to form a mixture in an impacting chamber of an energy impacting apparatus, wherein the graphitic material has never been intercalated, oxidized, or exfoliated and the chamber contains therein no previously produced graphene sheets and no ball-milling media; b) operating the energy impacting apparatus with a frequency and an intensity for a length of time sufficient for transferring graphene sheets from the graphitic material to surfaces of electrode active material particles to produce graphene-embraced electrode active material particles; and c) recovering the particles from the impacting chamber. Also provided is a mass of the graphene-embraced particles, electrode containing such particles, and battery containing this electrode.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Materials for positive electrodes of lithium ion batteries and their methods of fabrication
InactiveUS20050130042A1Cycle wellEasy dischargeElectrode thermal treatmentSecondary cellsCeriumSolvent
This invention discloses materials for positive electrodes of secondary batteries and their methods of fabrication. Said materials comprise of granules of an active material for positive electrodes coated with an oxide layer. The active material is one or more of the following: oxides of lithium cobalt, oxides of lithium nickel cobalt, oxides of lithium nickel cobalt manganese, oxides of lithium manganese, LiCoO2, LiNi1-xCoxO2, LiNi1 / 3Co1 / 3Mn1 / 3O2, and LiMn2O4. The non-oxygen component in the oxide layer is one or more of the following: aluminum, magnesium, zinc, calcium, barium, strontium, lanthanum, cerium, vanadium, titanium, tin, silicon, boron, Al, Mg, Zn, Ca, Ba, Sr, La, Ce, V, Ti, Sn, Si, and B. Said non-oxygen component of the granules is between 0.01 wt. % to 10 wt. % of said granules of active material. The methods of fabrication for said materials includes the steps of mixing an additive and an active material for positive electrodes uniformly in water or solvent, evaporating said solvent or water, and heat treating the remaining mixture at 300° C. to 900° C. for between 1 hour to 20 hours. The additive is a compound of one or more of the following elements: aluminum, magnesium, zinc, calcium, barium, strontium, lanthanum, cerium, vanadium, titanium, tin, silicon, boron, Al, Mg, Zn, Ca, Ba, Sr, La, Ce, V, Ti, Sn, Si, and B where the element is between 0.01 wt. % to 10 wt. % of said active material. Using the materials of positive electrodes disclosed above or materials for positive electrodes fabricated in the methods disclosed above in batteries produces batteries with excellent cycling and high temperature properties.
Owner:BYD AMERICA CORP
Lithium metal oxide electrodes for lithium batteries
InactiveUS20060188781A1Increase capacityImprove cycle stabilityActive material electrodesAlkali metal oxidesLithium metalOxidation state
An uncycled preconditioned electrode for a non-aqueous lithium electrochemical cell including a lithium metal oxide having the formula Li(2+2x) / (2+x)M′2x / (2+x)M(2−2x) / (2+x)O2−δ, in which 0≦x<1 and δ is less than 0.2, and in which M is a non-lithium metal ion with an average trivalent oxidation state selected from two or more of the first row transition metals or lighter metal elements in the periodic table, and M′ is one or more ions with an average tetravalent oxidation state selected from the first and second row transition metal elements and Sn, and an uncycled electrode of the formula xLi2M′O3.(1−x)LiMO2, in which 0≦x<1, and in which M is a non-lithium metal ion with an average trivalent oxidation state selected from two or more first-row transition metals or lighter metal elements in the periodic table, and M′ is one or more ions with an average tetravalent oxidation state selected from the first- and second-row transition metal elements and Sn, the electrode being preconditioned in a proton-containing medium with a pH<7.0. Methods of preconditioning the electrodes are disclosed as are electrochemical cells and batteries containing the electrodes.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC +1
Ink-jet printing ink compositions having magnetic properties and specific core/shell binder
InactiveUS6248805B1Improve propertiesImprove magnetic propertiesIron oxides/hydroxidesDuplicating/marking methodsCharge-transfer complexPrinting ink
Specific core-shell binders and magnetic additives for use in ink-jet printing ink compositions are provided. One class of specific core / shell binders has the general formula [AmBnC'p]x, where A and B are hydrophobic components in which A exhibits a glass transition temperature Tg between about -150° and +25° C. and B exhibits a glass transition temperature greater than 25° C., C' is a component that forms hydrophilic or water-soluble component in the polymer chain, and has an ionic or non-ionic structure, m<30 wt %, n>40 wt %, and p<30 wt %, with the total of m+n+p=100 wt %, and x=1 to 100,000. The molecular weight (weight average) of the polymer is between about 1,000 and 2,000,000. The polymers useful in the practice of the invention are prepared by emulsifying the monomers and then conducting a free-radical polymerization in water. The foregoing binder polymer is used in conjunction with magnetic additives comprising either (a) inorganic magnetic compound containing at least one of iron, cobalt, and nickel or (b) organic magnetic complexes containing at least one of iron, cobalt, and nickel or (c) organic charge transfer complexes that exhibit magnetic properties. The ratio of binder (I) to colorant (pigment) is greater that 1 to 10. The concentration of the magnetice additive is within the range of 1 to 30 wt %. The general ink formulation comprises: 5 to 50 wt % water-miscible solvent; 0.5 to 10 wt % colorant; 1 to 30 wt % magnetice additive; and water.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Method of hydrothermal liquid phase sintering of ceramic materials and products derived therefrom
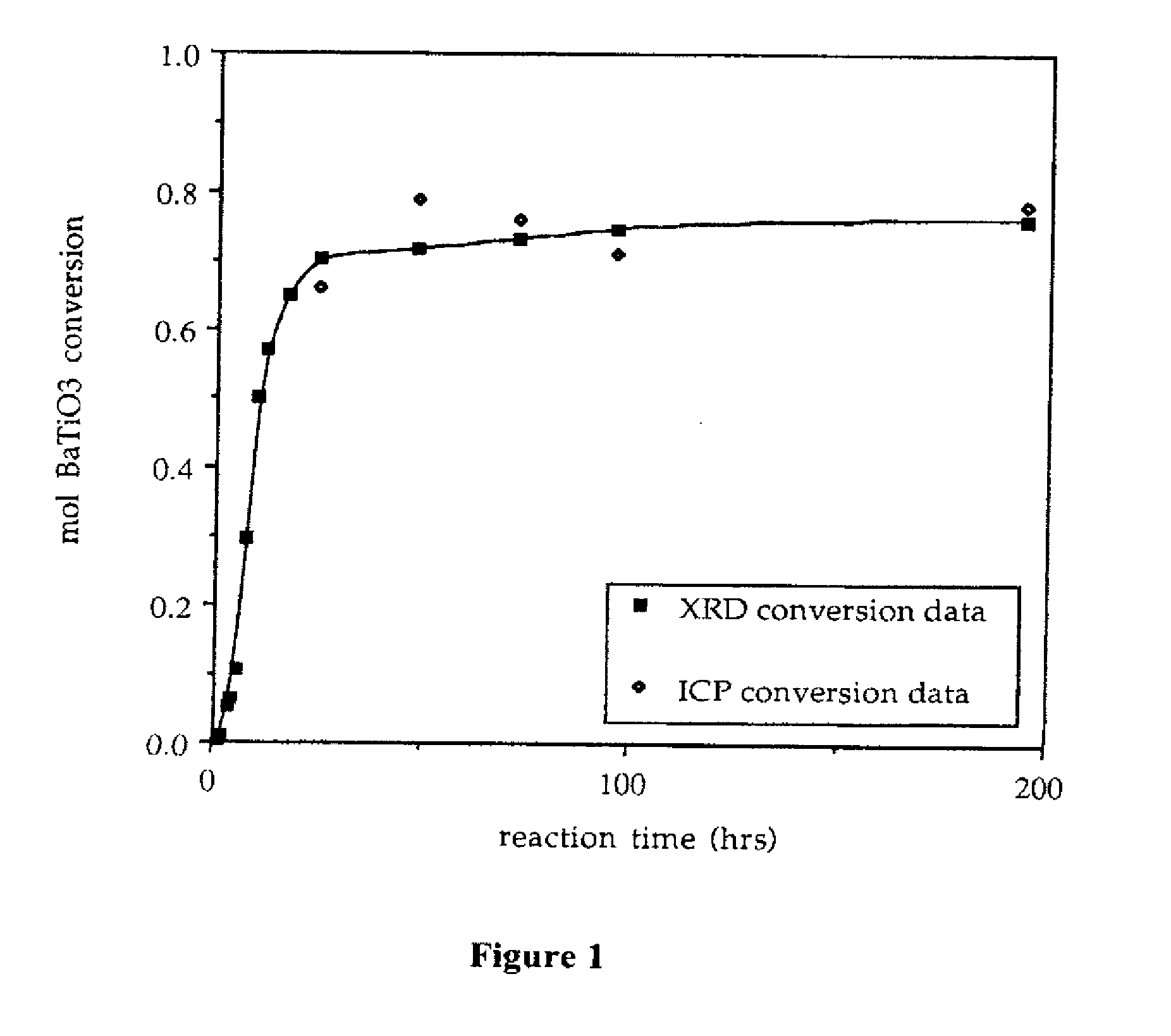
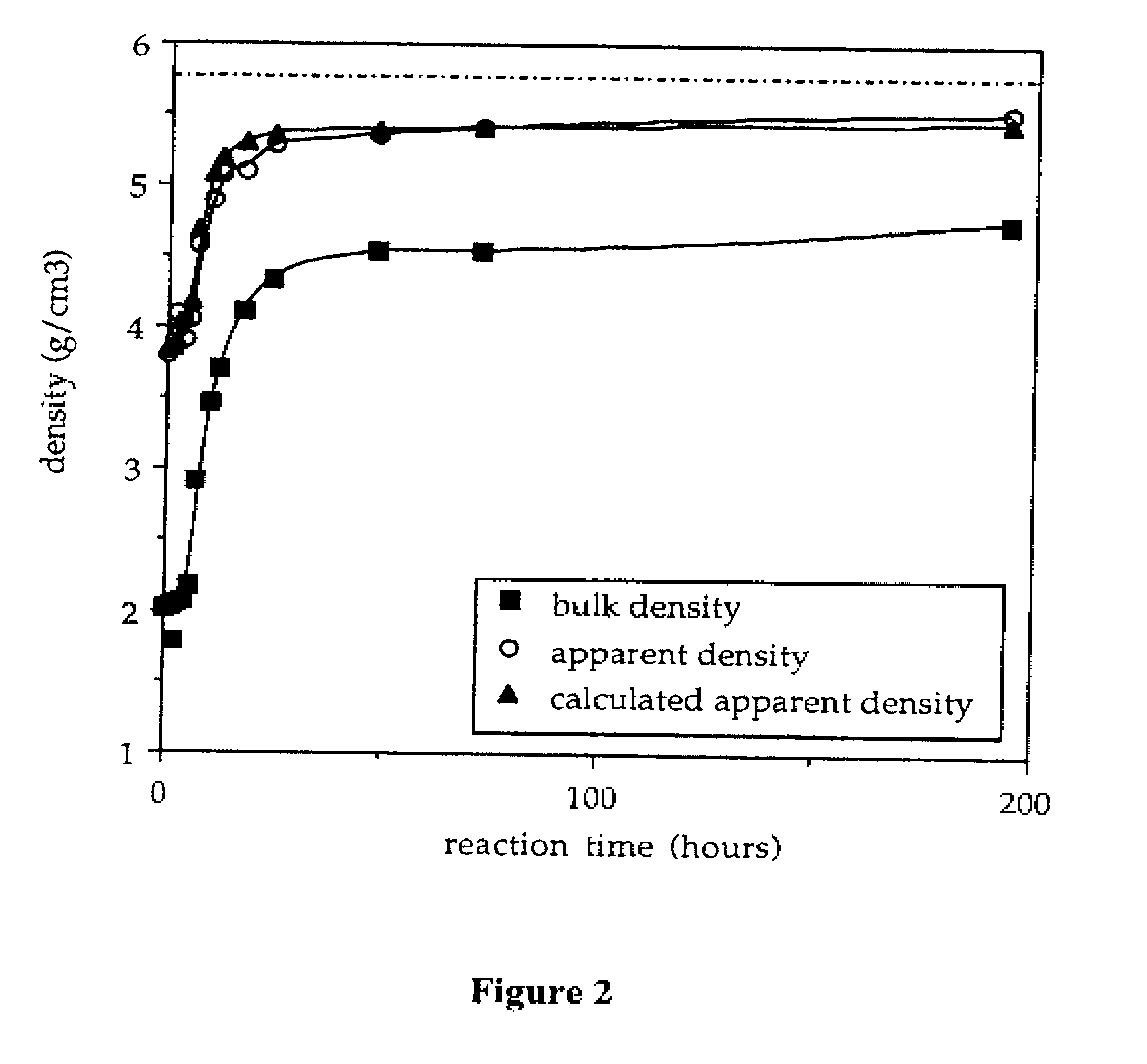
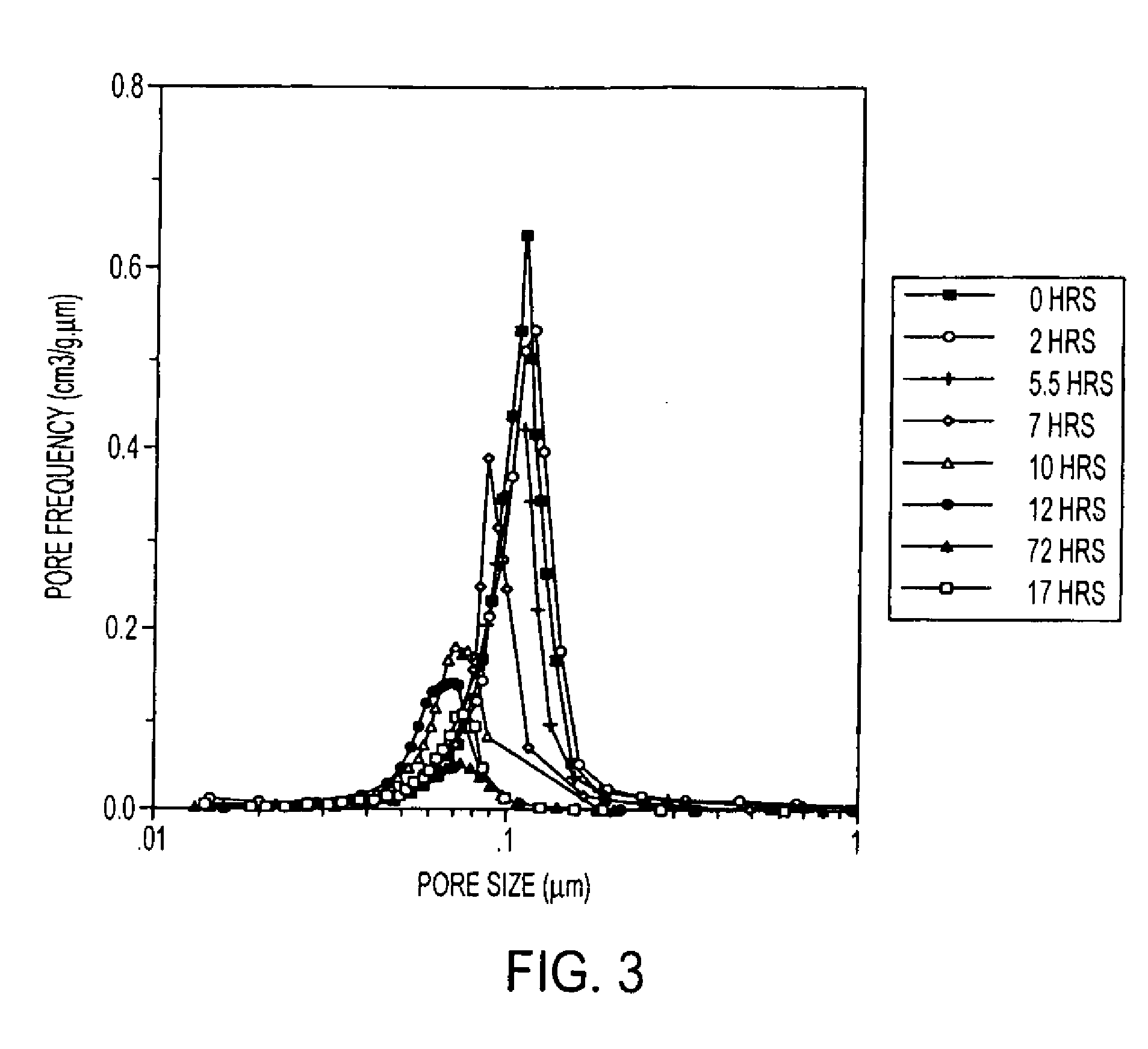
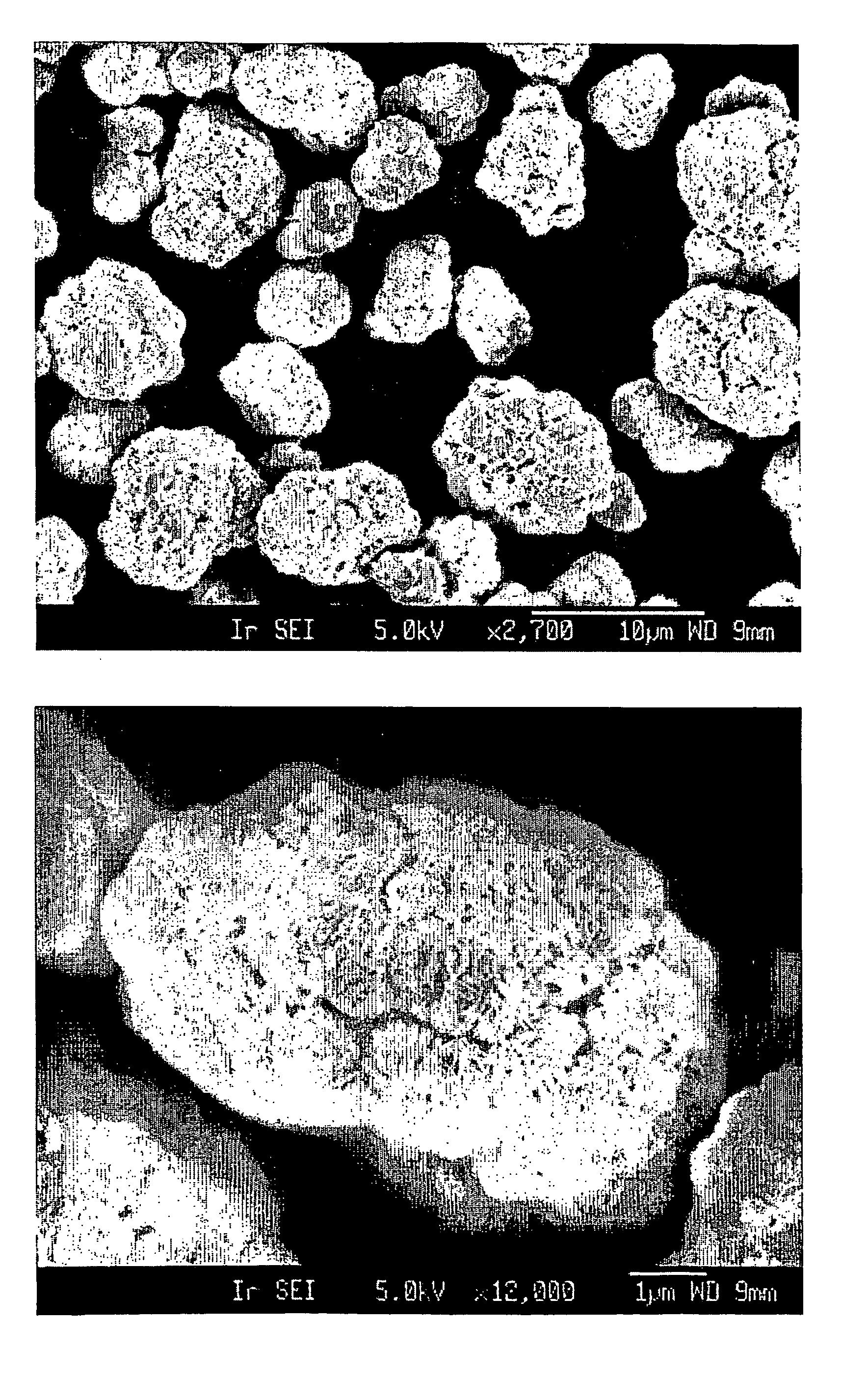
Provided here is a method of producing a monolithic body from a porous matrix, comprising: (i) providing a porous matrix having interstitial spaces and comprising at least a first reactant; (ii) contacting the porous matrix with an infiltrating medium that carries at least a second reactant; (iii) allowing the infiltrating medium to infiltrate at least a portion of the interstitial spaces of the porous matrix under conditions that promote a reaction between the at least first reactant and the at least second reactant to provide at least a first product; and (iv) allowing the at least first product to form and fill at least a portion of the interstitial spaces of the porous matrix, thereby producing a monolithic body, wherein the monolithic body does not comprise barium titanate.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Lithium transition metal oxide with gradient of metal composition
ActiveUS20060105239A1Improve electrochemical performanceIncrease energy densityCell electrodesManganese oxides/hydroxidesManganeseMaterials science
Disclosed are primary materials, precursor materials and final materials as well as methods to prepare these materials. The final materials are mixed lithium transition metal oxides, useful as performance optimized cathode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries. The transition metal is a solid solution mixture of manganese, nickel and cobalt, M=(Mn1-uNiu)1-u-yCoy, with 0.2
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Positive electrode active material and nonaqueous electrolyte secondary cell including the same
InactiveUS20050079416A1Large capacityImprove charge and discharge efficiencyOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideIron oxides/hydroxidesMetallic lithiumManganese
A nonaqueous electrolytic secondary cell produced at low cost and having a large capacity comprises a negative electrode having an active material mainly composed of a material that at least absorbs and releases lithium ions or metallic lithium, a positive electrode, and an electrolyte. The active material of the positive electrode is an oxide containing nickel, manganese, and cobalt, and the contents of the elements are substantial the same.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
Active substance of positive electrode and nonaqueous electrolyte battery containing the same
ActiveUS20050019659A1Increase energy densityImprove high rate discharge performanceSecondary cellsAlkali metal oxidesHigh rateHigh energy
A positive active material is provided which can give a battery having a high energy density and excellent high-rate discharge performance and inhibited from decreasing in battery, performance even in the case of high-temperature charge. Also provided is a non-aqueous electrolyte battery employing the positive active material. The positive active material contains a composite oxide which is constituted of at least lithium (Li), manganese (Mn), nickel (Ni), cobalt (Co), and oxygen (O) and is represented by the following chemical composition formula: LiaMnbNicCodOe (wherein 0<a≦1.3, |b−c|≦0.05, 0.6≦d<1, 1.7≦e≦2.3, and b+c+d=1). The non-aqueous electrolyte battery has a positive electrode containing the positive active material, a negative electrode, and a non-aqueous electrolyte.
Owner:GS YUASA INT LTD
Cathode active material for lithium secondary battery, process for preparing the same and reactor for use in the same process
ActiveUS20070111098A1Large capacityHigh tap densityElectrode manufacturing processesPhosphatesLithiumHigh rate
The present invention relates to a cathode active material for a lithium secondary battery and a process for preparing the same. In accordance with the present invention, the cathode active material having a high packing density was designed and synthesized and thus provided is a cathode active material for a lithium secondary battery exhibiting structural stability such as improved characteristics for charge / discharge, service life and high-rate and thermal stability, by modifying surface of the electrode active material with amphoteric or basic compounds capable of neutralizing acid produced around the cathode active material.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Lithium-containing composite oxide and nonaqueous secondary cell using the same, and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20030082452A1Stable structureHigh energy density per volumeElectrode thermal treatmentOrganic electrolyte cellsLithiumHigh density
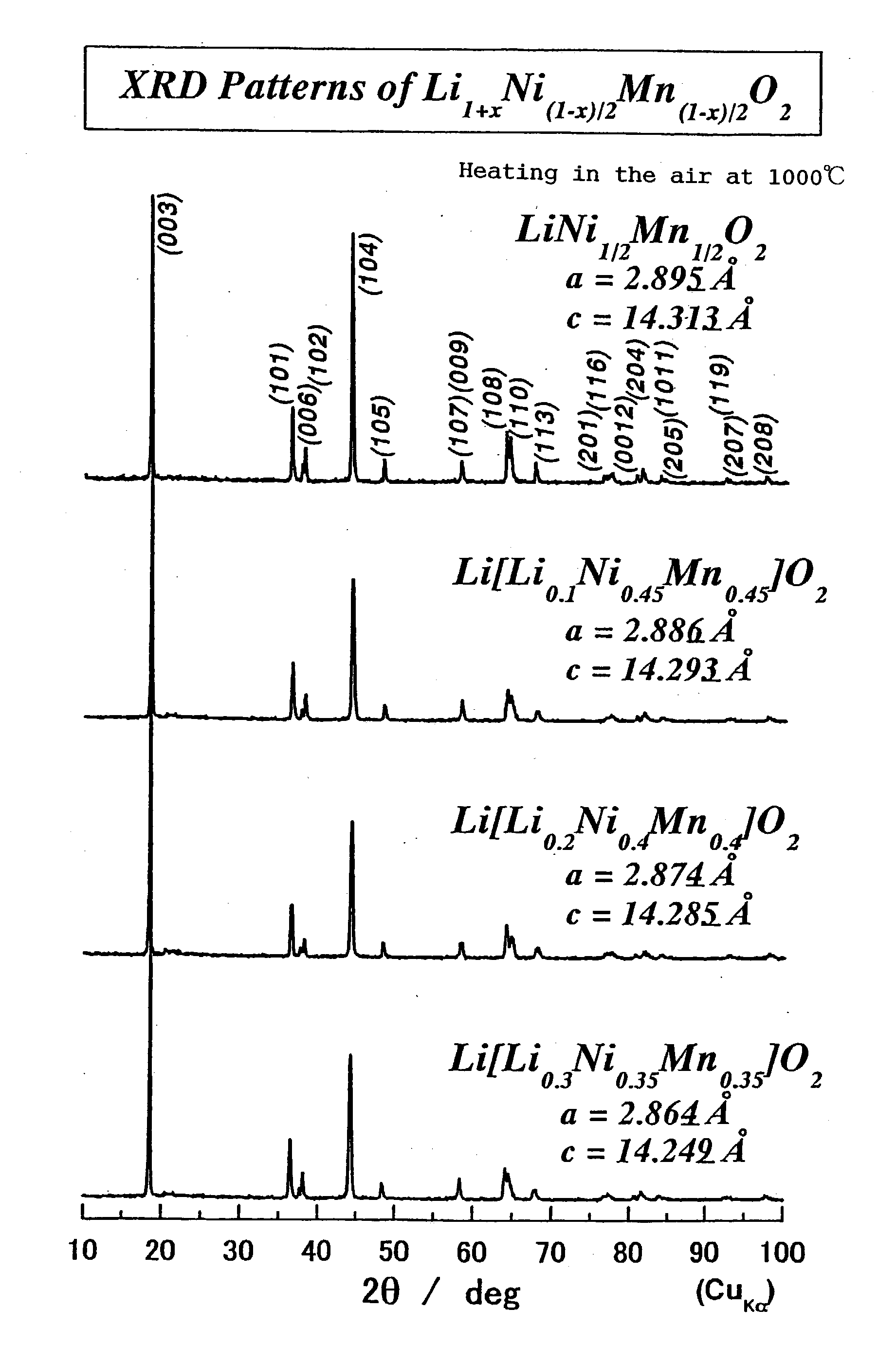
Because of the composition represented by General Formula: Li1+x+alphaNi(1-x-y+delta) / 2Mn(1-x-y-delta) / 2MyO2 (where 0<=x<=0.05, -0.05<=x+alpha<=0.05, 0<=y<=0.4; -0.1<=delta<=0.1 (when 0<=y<=0.2) or -0.24<=delta<=0.24 (when 0.2<=y<=0.4); and M is at least one element selected from the group consisting of Ti, Cr, Fe, Co, Cu, Zn, Al, Ge and Sn), a high-density lithium-containing complex oxide with high stability of a layered crystal structure and excellent reversibility of charging / discharging can be provided, and a high-capacity non-aqueous secondary battery excellent in durability is realized by using such an oxide for a positive electrode.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Lithium composite oxide particle for positive electrode material of lithium secondary battery, and lithium secondary battery positive electrode and lithium secondary battery using the same
InactiveUS20060134521A1Improving low-temperature load characteristicGood paintabilityRuthenium/rhodium/palladium/osmium/iridium/platinum compoundsAlkali metal oxidesElectrical batteryComposite oxide
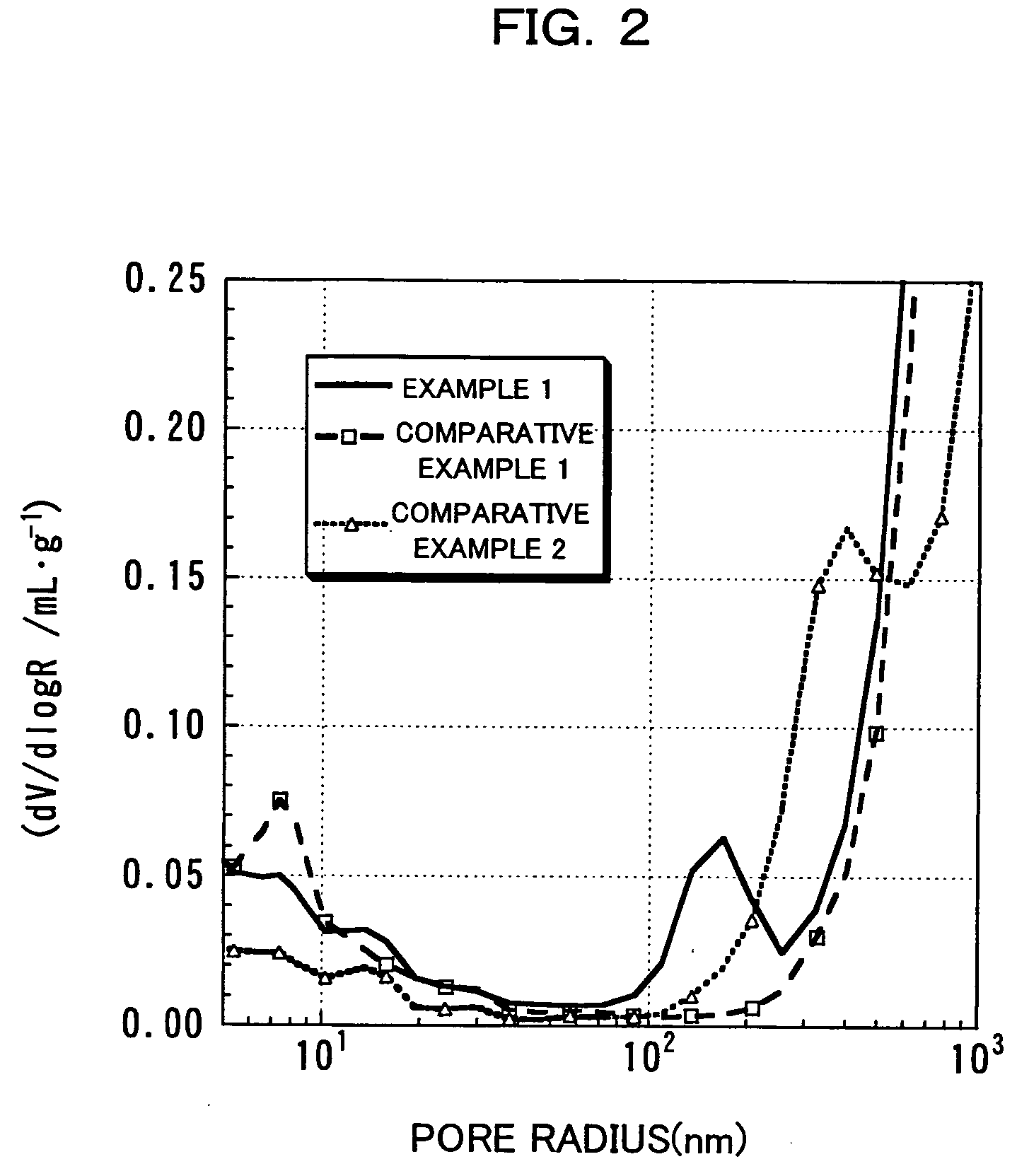
An excellent positive electrode material for a lithium secondary battery is provided that can increase low-temperature load characteristics of the battery as well as improving coatability. When measured by mercury intrusion porosimetry, the material meets Condition (A) and at least either Condition (B) or Condition (C). Condition (A) : on a mercury intrusion curve, the mercury intrusion volume from 50 MPa to 150 MPa is 0.02 cm3 / g or smaller. Condition (B): on the mercury intrusion curve, the mercury intrusion volume from 50 MPa to 150 MPa is 0.01 cm3 / g or larger. Condition (C): the average pore radius is within 10-100 nm, and the pore-size distribution curve has a main peak (with peak top at a pore radius of within 0.5-50 μm) and a sub peak (with peak top at a pore radius of within 80-300 nm).
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
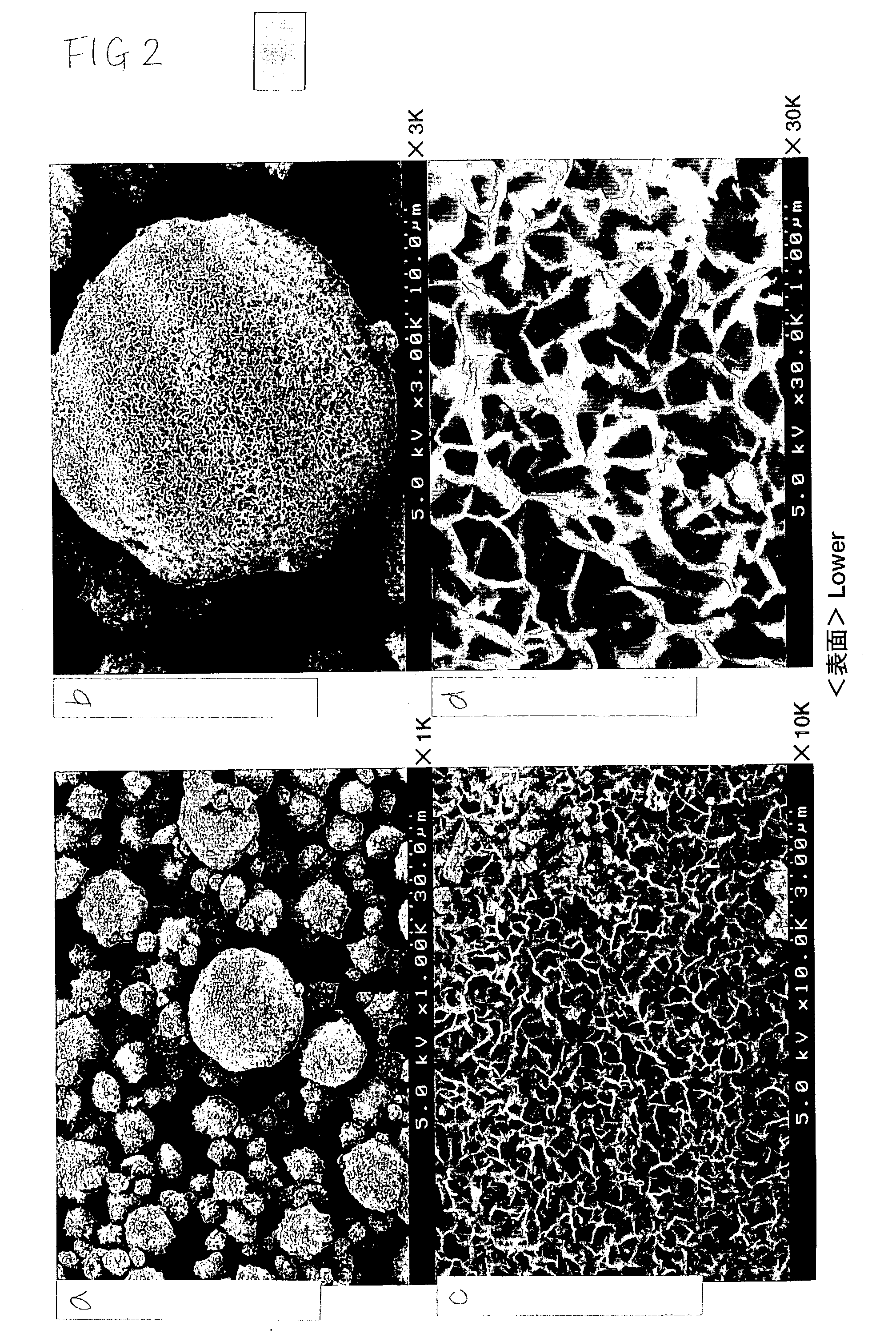
Graphene-supported cobaltosic oxide nano composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101811696ASmall sizeLarge specific surface areaCobalt oxides/hydroxidesCobalt(II,III) oxideCobalt salt
The invention discloses a graphene-supported cobaltosic oxide nano composite material and a preparation method thereof. The graphene-supported cobaltosic oxide nano composite material consists of graphene and cobaltosic oxide, wherein the cobaltosic oxide is loaded on graphene nano sheets; the content of the graphene nano sheets is 2 to 95 weight percent, and the thickness of the graphene nano sheets is 0.3 to 50 nanometers; and the particle size of the cobaltosic oxide is 1 to 200 nanometers and the cobaltosic oxide is ball-shaped or flaky. The preparation method comprises: firstly, mixing solution of graphene oxide, a bivalent cobalt salt and a polymer surfactant; and secondly, mixing the solution obtained by the first step with alkaline solution added with an oxidant, stirring the mixed solution or stirring the mixed solution by ultrasonic waves for 0.2 to 5 hours, transferring the mixed solution to a high-temperature reaction kettle, annealing the reaction product at 100 to 250 DEG C for 3 to 30 hours to obtain a product and washing and drying the product to obtain the graphene-supported cobaltosic oxide nano composite material. The size of the cobaltosic oxide is controllable. The reduction of the graphene oxide and the generation of the cobaltosic oxide are accomplished at the same time.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Multi-shell-layer metal oxide hollow ball and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102464304AHigh specific surface areaSimple processOxide/hydroxide preparationZinc oxides/hydroxidesControllabilityNanoscopic scale
The invention provides a multi-shell-layer metal oxide hollow ball and a preparation method thereof. A hydrothermal method is used for preparing a carbon ball template; metal salts are dissolved in carbon ball suspension liquid, and the gradient distribution, the depth and the number of metal salts entering carbon balls are controlled through regulating adsorption conditions such as metal salt concentration, solution pH value, soaking temperature and time and the like; and the heat treatment is carried out on the carbon balls adsorbing metal ions, and the multi-shell-layer metal oxide hollow ball can be obtained. The shell-layer of the hollow ball prepared by the method is formed by accumulating nanometer crystal particles of metal oxides, the shell layer number can be regulated and changed from two to four, and both the size of the hollow ball and the thickness of the shell layers are controllable. The method provided by the invention is simple and is easy to implement, the controllability is high, the pollution is little, the cost is low, and in addition, the general applicability is realized. The prepared product has a hollow structure and the shell layers with the thickness inthe nanometer level, simultaneously, the internal space can be effectively utilized through the multilayer structure, and the multi-shell-layer metal oxide hollow ball is applied to gas sensitivity and photocatalysis and has the more excellent performance through being compared with the traditional nanometer material and a single-layer hollow ball.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Electrode active material powder with size dependent composition and method to prepare the same
ActiveUS20070122705A1Increased gravimetric energy densityLow costElectrode thermal treatmentActive material electrodesLithiumPhysical chemistry
The present invention relates to a powderous electrode active material of lithium transition metal oxide LiaMbO2, wherein 0.9 < a < 1.1, 0.9 < b < 1.1 and M is dominantly transition metal chosen from Mn, Co and Nickel, having particles with a distribution of sizes, where the composition M varies with the size of the particles, and a preparation method thereof. The present invention also relates to an electrochemical cell, particularly rechargeable lithium battery, using the powderous electrode active material.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Lithium-nickel-cobalt-maganese containing composite oxide, material for positive electrode active material for lithium secondary battery, and methods for producing these
ActiveUS20060083989A1Large capacityExcels in charge-discharge cycle durabilityElectrode rolling/calenderingFluoride preparationManganeseOxygen
Coagulated particles of nickel-cobalt-manganese hydroxide wherein primary particles are coagulated to form secondary particles are synthesized by allowing an aqueous solution of a nickel-cobalt-manganese salt, an aqueous solution of an alkali-metal hydroxide, and an ammonium-ion donor to react under specific conditions; and a lithium-nickel-cobalt-manganese-containing composite oxide represented by a general formula, LipNixMn1-x-yCoyO2-qFq (where 0.98≦p≦1.07, 0.3≦x≦0.5, 0.1≦y≦0.38, and 0≦q≦0.05), which is a positive electrode active material for a lithium secondary cell having a wide usable voltage range, a charge-discharge cycle durability, a high capacity and high safety, is obtained by dry-blending coagulated particles of nickel-cobalt-manganese composite oxyhydroxide formed by making an oxidant to act on the coagulated particles with a lithium salt, and firing the mixture in an oxygen-containing atmosphere.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Electrode material for anode of rechargeable lithium battery, electrode structural body using said electrode material, rechargeable lithium battery using said electrode structural body, process for producing said electrode structural body, and process for producing said rechargeable lithium battery
InactiveUS20050175901A1Prolonged discharging cycle lifeLarge capacityNitrogen compoundsSelenium/tellurium compundsElectrochemical responseParticulates
An electrode material for an anode of a rechargeable lithium battery, containing a particulate comprising an amorphous Sn.A.X alloy with a substantially non-stoichiometric ratio composition. For said formula Sn.A.X, A indicates at least one kind of an element selected from a group consisting of transition metal elements, X indicates at least one kind of an element selected from a group consisting of O, F, N, Mg, Ba, Sr, Ca, La, Ce, Si, Ge, C, P, B, Pb, Bi, Sb, Al, Ga, In, Tl, Zn, Be, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu, As, Se, Te, Li and S, where the element X is not always necessary to be contained. The content of the constituent element Sn of the amorphous Sn.A.X alloy is Sn / (Sn+A+X)=20 to 80 atomic %. An electrode structural body for a rechargeable lithium battery, comprising said electrode material for an anode and a collector comprising a material incapable of being alloyed with lithium in electrochemical reaction, and a rechargeable lithium battery having an anode comprising said electrode structural body.
Owner:CANON KK
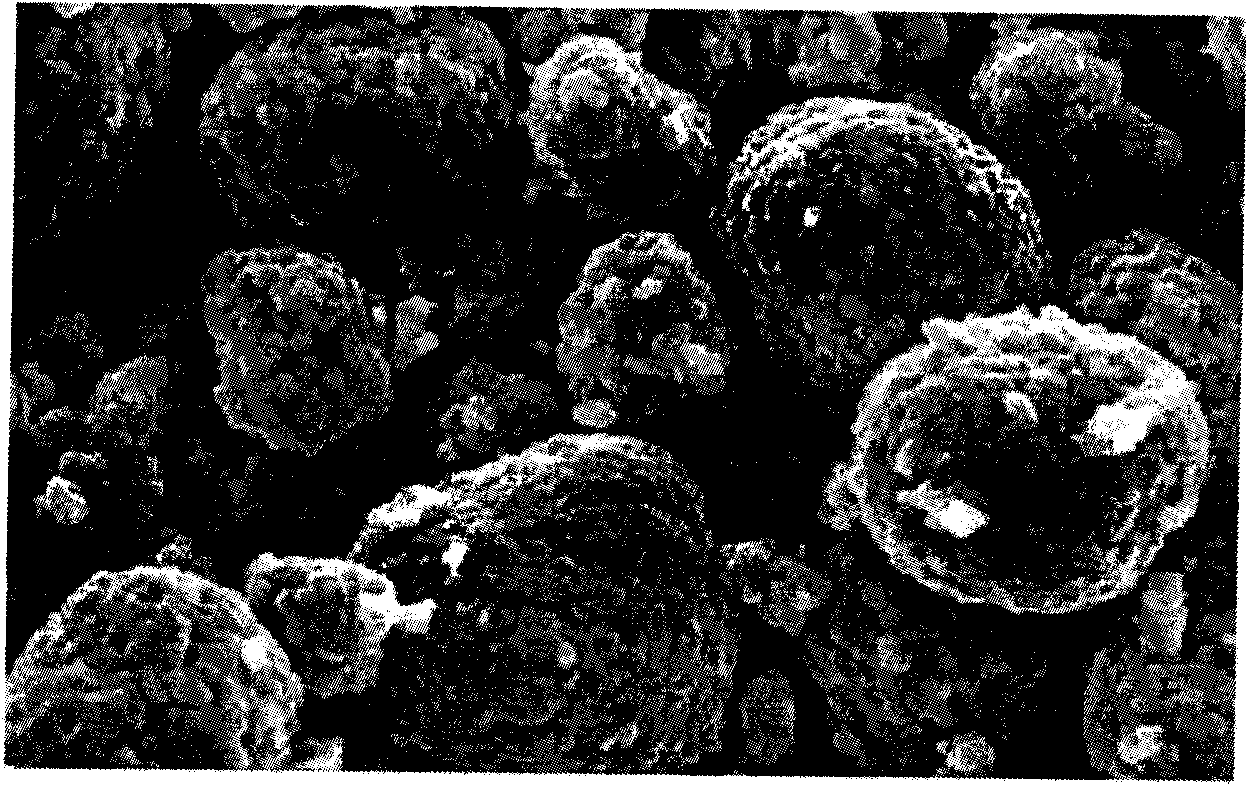
Method for continuously synthesizing precursor of lithium ion battery positive material
InactiveCN102092798AInhibition formationSolve the problem of easy oxidationCell electrodesManganese oxides/hydroxidesSynthesis methodsManganese
The invention provides a method for continuously synthesizing a precursor of a lithium ion battery positive material, relating to an improvement of a synthesis method of a nickle cobalt manganese termary positive material nickle cobalt lithium manganate of the lithium ion battery positive material. The method is characterized in that the synthesis process is as follows: merging a complexing agent ammonia, an aqueous solution of metal nickle cobalt manganese ions and a precipitator sodium hydroxide solution and then continuously adding the substances into a reaction kettle for a synthesis reaction under the strong stirring condition in the presence of protective gas; and aging, filtering and washing the effluent from the reaction kettle, and then drying to obtain the lithium ion battery positive material precursor spherical nickle cobalt manganese termary hydroxide. The method has the advantages that the preparation process is continuous, the particle size of the prepared nickle cobalt manganese compound hydroxide powder is controlled in a range of 5-20 microns, and the prepared nickle cobalt manganese compound hydroxide powder is even in distribution and excellent in electrochemistry property. The method has the advantages of high production efficiency, low production cost and significant economic and social benefits, and the energy is saved.
Owner:LANZHOU JINCHUAN NEW MATERIAL SCI & TECH +1
Graphene nanometer sheet-cobaltous oxide composite negative electrode material of lithium ion battery and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101800302AImprove conductivityIncrease profitNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesCobalt oxides/hydroxidesOxide compositeLithium-ion battery
The invention relates to a graphene nanometer sheet-cobaltous oxide composite negative electrode material of a lithium ion battery and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of batteries. The negative electrode material consists of graphene nanometer sheets and cobaltous oxide, wherein the graphene nanometer sheets are distributed on cobaltous oxide particles in a staggering way; the mass fraction of the graphene nanometer sheets is 5 to 90 percent; the thickness of the graphene nanometer sheets is 1 to 50 nanometers; and the particle size of the cobaltous oxide is 10 to 500 nanometers. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dispersing graphite oxide in alcohol-water solution or aqueous solution with ultrasound or stirring; adding cobalt salt, alkali and a reducing agent into the mixture and pouring the mixture into a hydrothermal kettle after stirring; performing further sealing and synchronous hydrothermal reaction, washing, filtering and drying to obtain a graphene nanometer sheet-cobaltous oxide composite; and processing the graphene nanometer sheet-cobaltous oxide composite in the protective atmosphere to obtain the graphene nanometer sheet-cobaltous oxide composite negative electrode material. In the invention, when the material is charged or discharged by a current of 200mA / g, the reversible specific capacity of the material can be stabilized in a range of over 900mAh / g.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Complex lithium metal oxides with enhanced cycle life and safety and a process for preparation thereof
ActiveUS20040200998A1Improve cycle lifeImprove securityElectrode manufacturing processesConductive materialHigh temperature storageLithium metal
This invention relates to complex lithium metal oxides, which are cathode active materials of a lithium or lithium ion secondary battery with enhanced cycle life and safety, and a process for preparation thereof. The core particles are complex lithium metal oxides capable of absorbing, storing and emitting lithium ions, and a coating layer comprised of amorphous complex lithium cobalt oxides that are formed on the surface of the core particle, which is structurally stable and inactive with electrolytes. Because the amorphous complex lithium cobalt oxides are inactive with electrolytes, the oxides stabilize the surface structure of the complex lithium metal oxide and improve on high temperature storage properties, as well as safety and cycle life.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
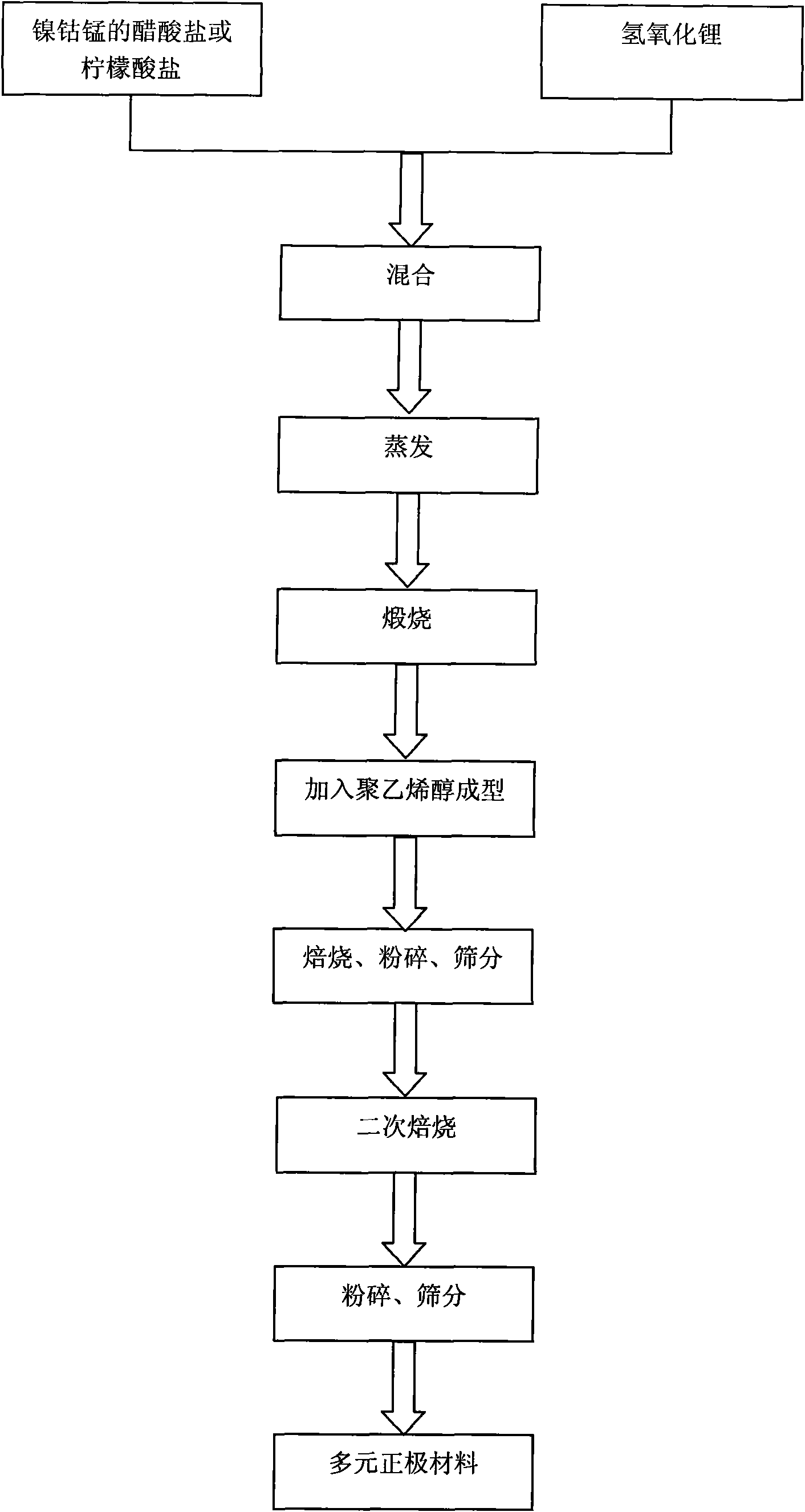
Nickel-cobalt-manganese multi-doped lithium ion battery cathode material and preparation method thereof
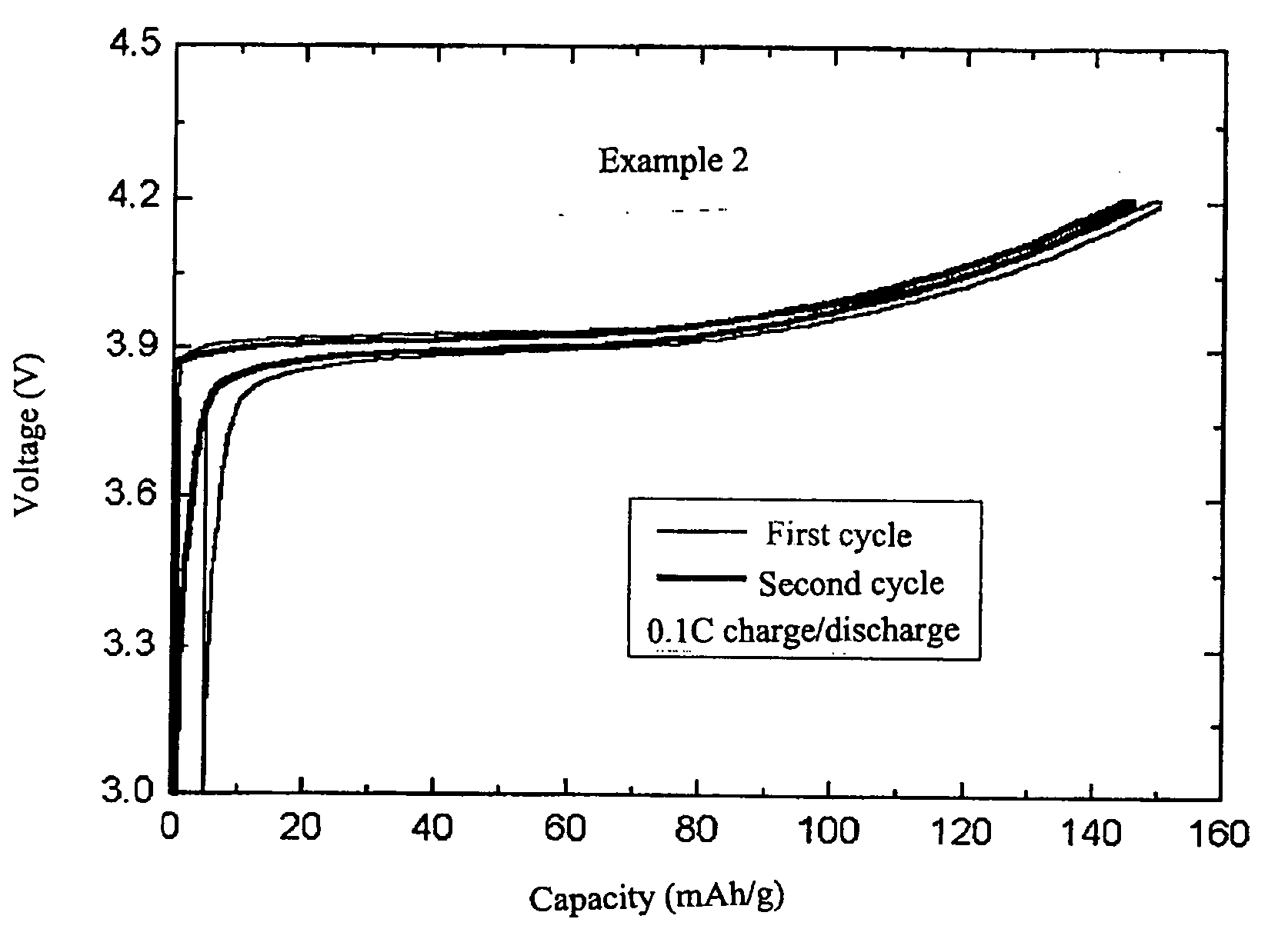
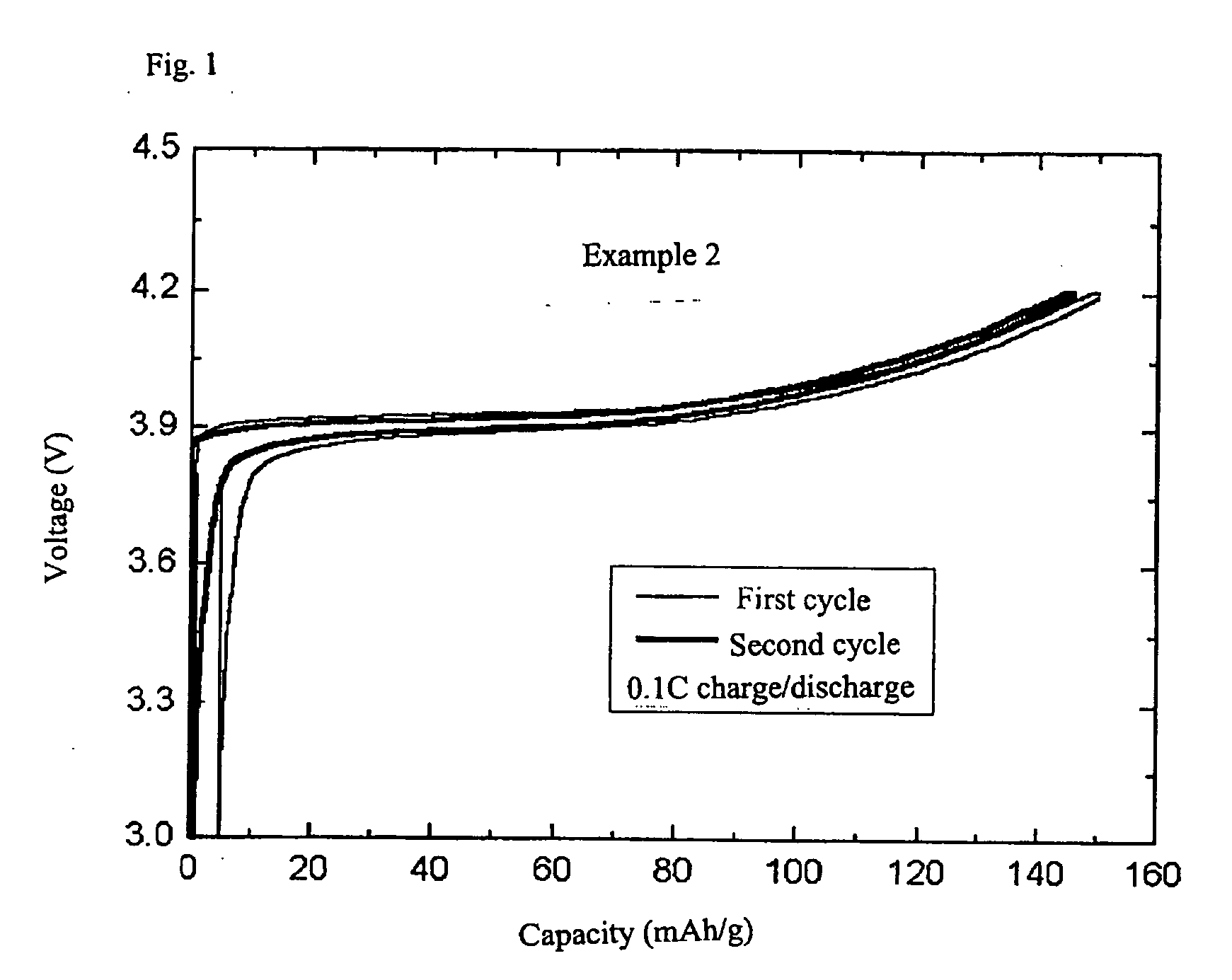
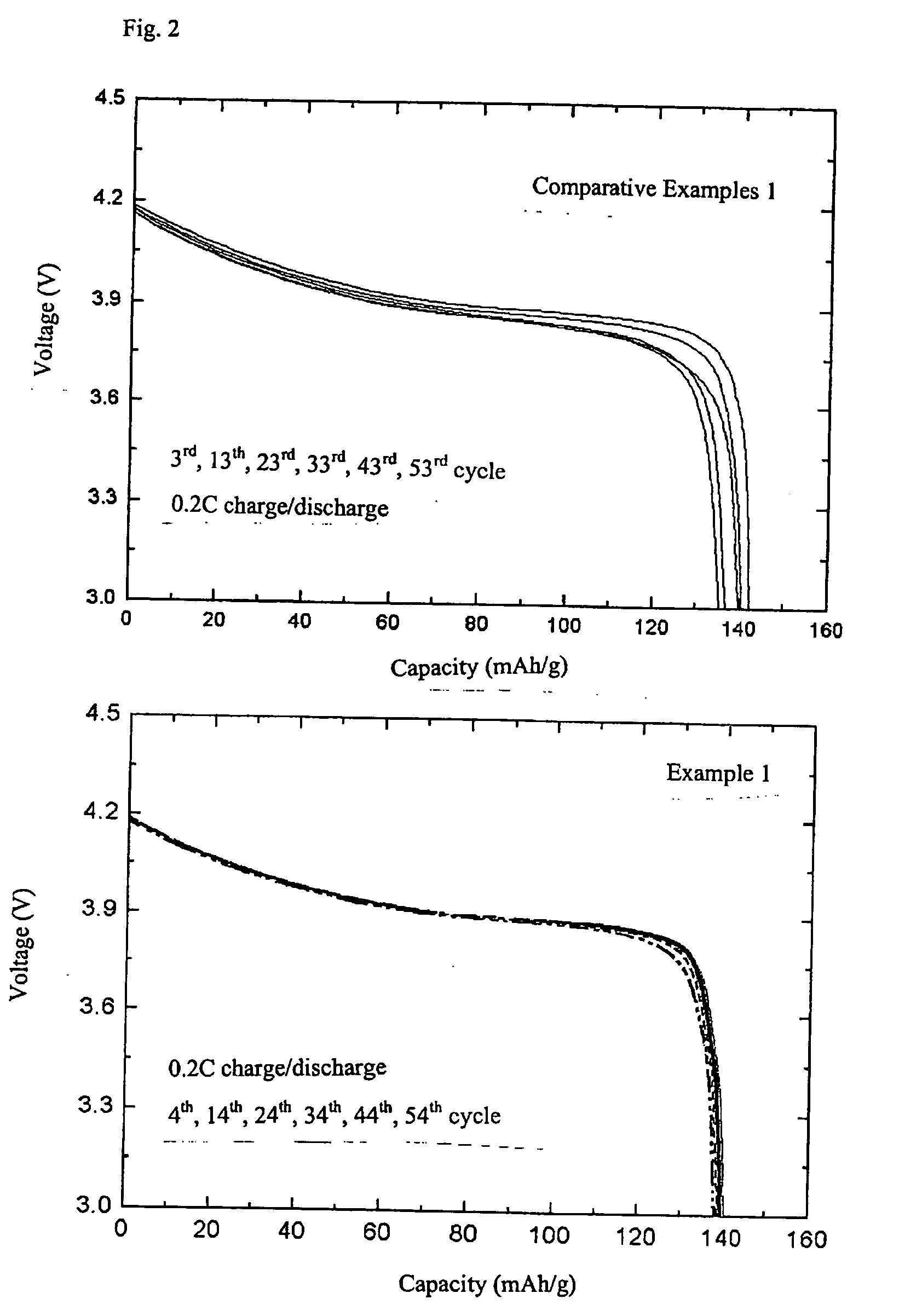
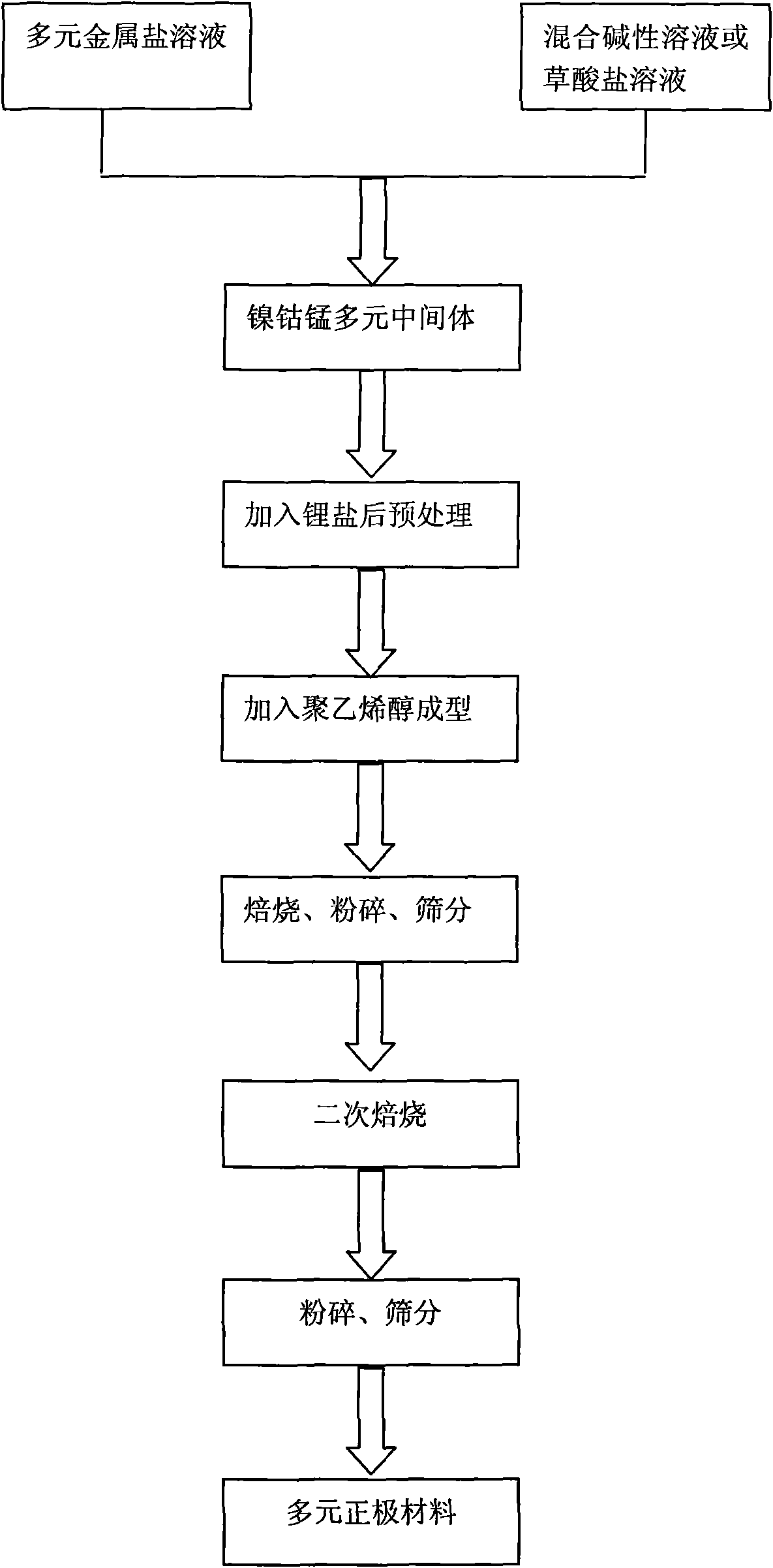
InactiveCN101621125AIncrease compaction densityLow hygroscopicityElectrode manufacturing processesSecondary cellsChemical synthesisPolyvinyl alcohol
The invention discloses a nickel-cobalt-manganese multi-doped lithium ion battery cathode material with high compacted density and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of energy materials. The preparation method of the battery cathode material comprises the following steps: preparing a nickel-cobalt-manganese multi-doped intermediate by a coprecipitation method or a chemical synthesis method; mixing the multi-doped intermediate with lithium salts; after pretreatment, adding polyvinyl alcohol to the obtained mixture; uniformly mixing the polyvinyl alcohol and the mixture and then pressing the mixture into a cake; roasting the cake at 800-950 DEG C; taking the roasted cake out and carrying out cooling, pulverization and 400 meshes of sieving on the cake; then roasting obtained powder at 700-800 DEG C, taking the powder out and carrying out cooling, pulverization and sieving on the powder to obtain the battery cathode material. Granules of the battery cathode material are non-agglomerated single-crystal grains with a grain diameter of 0.6-30 microns, a chemical formula of LiNixCoyMnzM[(1-x-y-z)]O2, a degree of compaction of 3.5-3.7g / cm<3> and a primary discharge capacity of 150-165mAh / g, thus the battery cathode material has good cycle performance and higher safety performance.
Owner:CHENGDU JINGYUAN NEW MATERIALS TECH
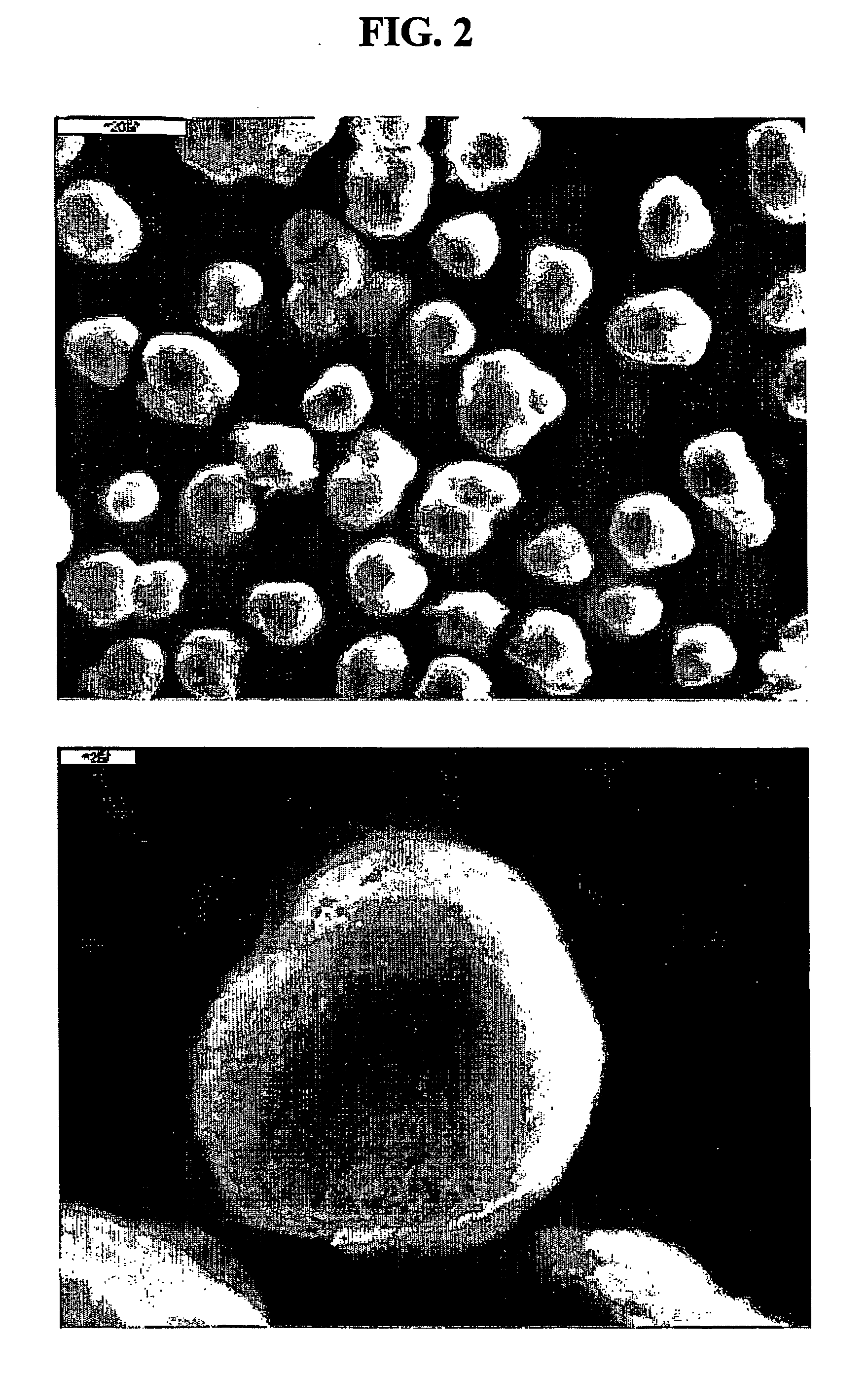
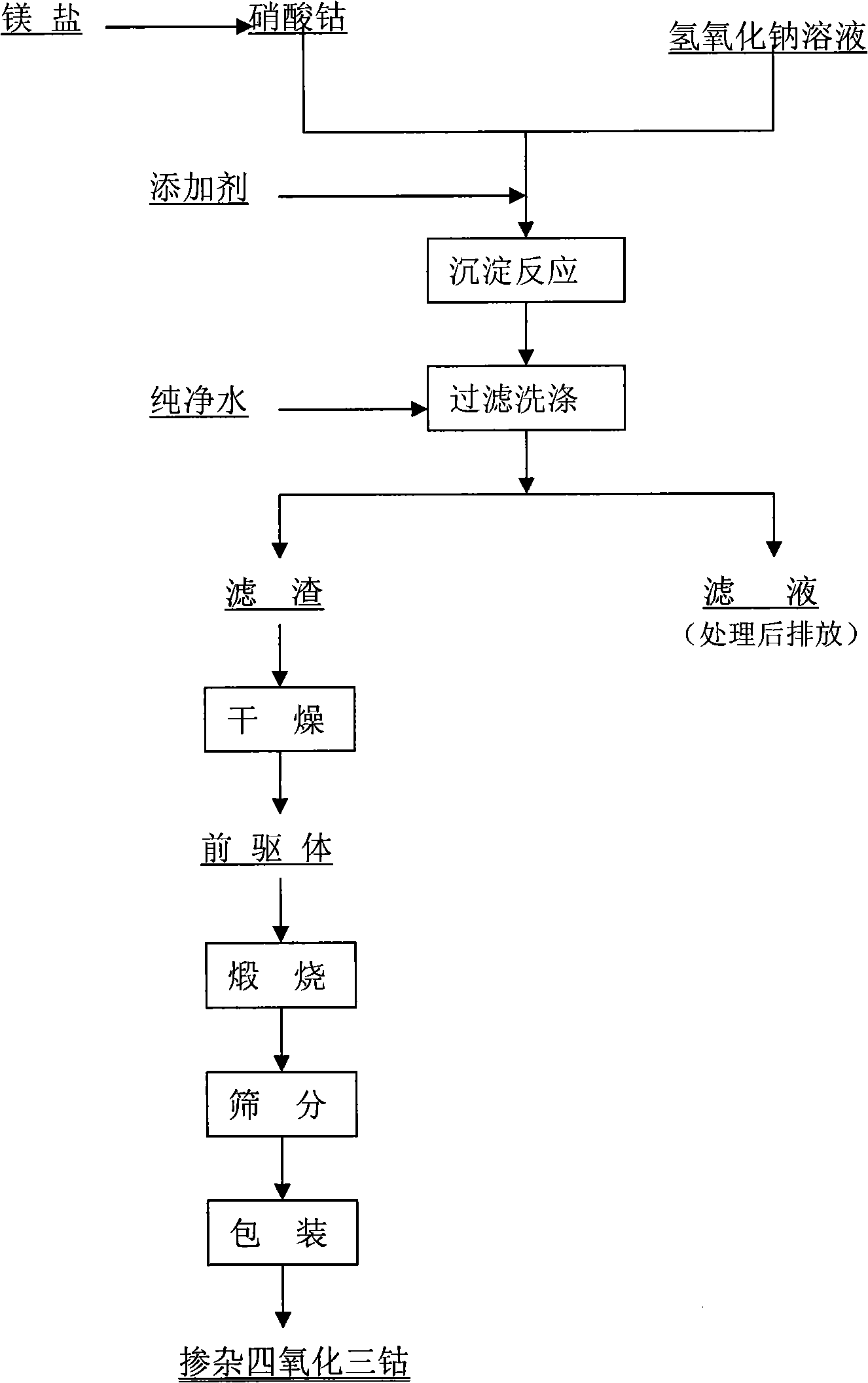
Preparation of doped cobaltic-cobaltous oxide
InactiveCN101279771AImprove stabilityImprove electrochemical performanceCobalt oxides/hydroxidesSal ammoniacNitrate
Disclosed is a process for preparing a doping cobaltosic oxide, which relates to a method for the production of a modified cobaltosic oxide used for a Lithium-ion battery anode material. The method is characterized in that the preparation process comprises: 1) mixing a cobalt nitrate solution containing doped chemical ions with a mixed precipitator solution containing ammonia and sodium hydroxide and making the mixture react for eight to twenty hours at a pH value of between 8.4 to 10 and a temperature of between 40 and 80 DEG C so as to prepare a cobalt hydroxide precipitation containing doped chemical; and 2) washing and drying the cobalt hydroxide precipitation containing the doped chemical and then burning the precipitation for two to six hours at a temperature of between 500 and 800 DEG C so as to obtain the doping cobaltosic oxide. The method of the invention can get even particles with regular shapes after the reaction, the particle sizes of the doping cobalt hydroxide are controllable in a certain range, and the doping cobaltosic oxide can be obtained by calcinations. The method of preparation is characterized in that a magnesium source, an aluminum source, a titanium source, etc. are induced to the cobalt nitrate solution directly, and the process and operation are simple and easy.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
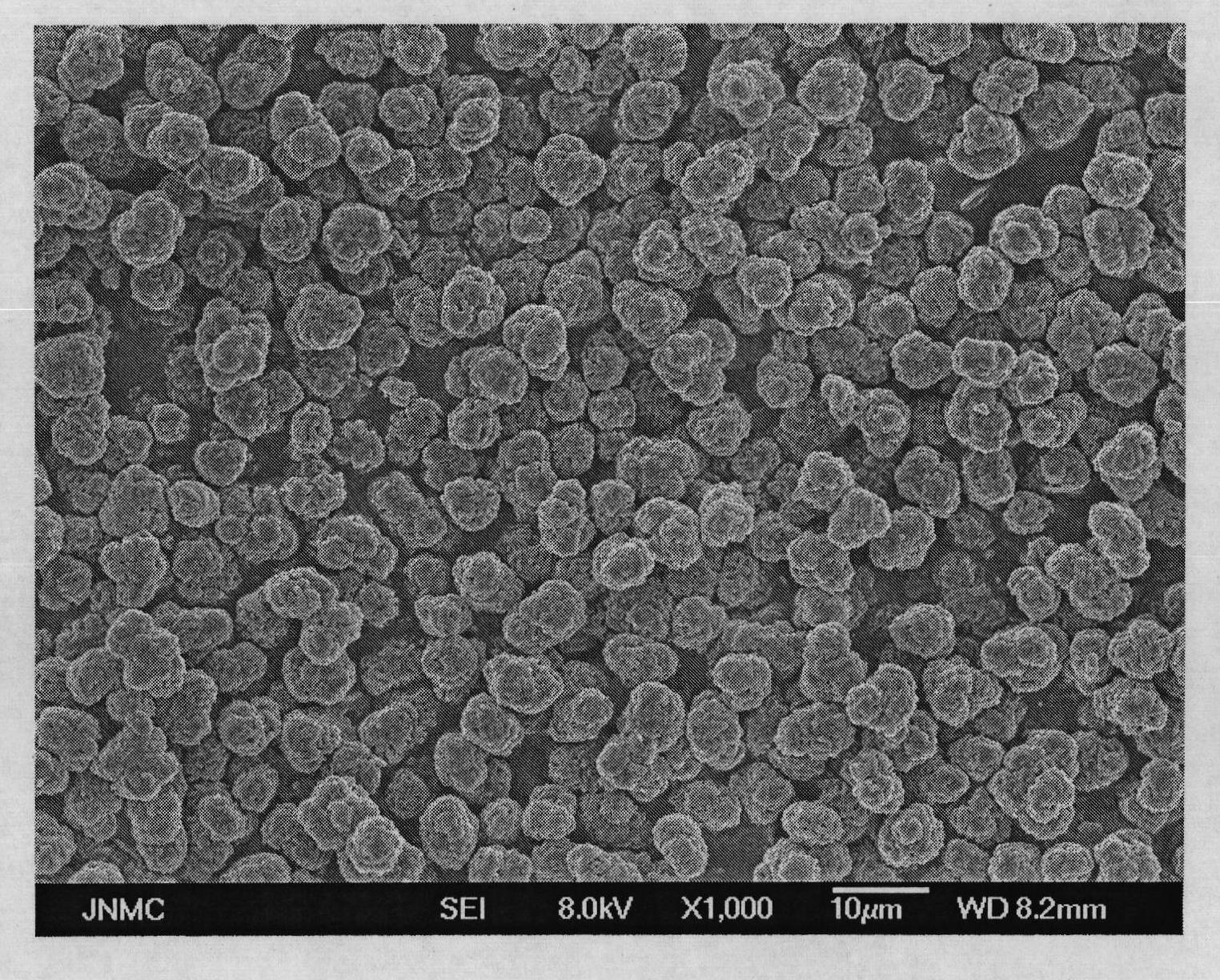
Preparation method of Co3O4 with large grain size and uniformly doped with aluminum
ActiveCN108011101AEvenly distributedUniform particle size distributionCell electrodesCobalt oxides/hydroxidesCobalt(II,III) oxideMicrometer
The invention relates to a preparation method of Co3O4 with large grain size and uniformly doped with aluminum. The invention provides the preparation method of the Co3O4 which is uniformly doped withaluminum and is large in grain size and uniform in particle distribution, and the obtained Co3O4 with the large grain size and uniformly doped with aluminum can completely conform to the requirementof preparation of 4.45V high-voltage lithium cobalt oxide. According to the method, the large-grain size and aluminum-doped cobalt carbonate is synthesized by a wet method, and the problems of difficulty in enlargement of cobalt hydroxide (or hydroxyl cobalt) system grain size and non-uniform particle distribution are solved; with the regard to the problem of uniform aluminum doping of a cobalt carbonate system, a parameter is set from principle, an aluminum compound is prevented from being independently separated out and gathered, the doped Al element can be uniformly distributed in the Co3O4, the grain size reaches 15 micrometers or above, and the particle distribution is uniform; and the lithium cobalt oxide prepared from the aluminum-doped Co3O4 has high specific capacity and excellentcycle property under 4.45V.
Owner:취저우화여우코발트뉴머터리얼컴퍼니리미티드
Microparticles and methods for their production
InactiveUS20050106098A1Improve image qualityThe process is simple and convenientPowder deliveryMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid mediumSource material
Microparticles having a metal-containing core encapsulated in a graphitic shell containing hetero atoms are made by forming, in a liquid medium, colloidal particles containing a metal-oxo species of Fe, Co, Ni and Pd, colloidally stabilized by a surfactant and containing source material of carbon and the hetero atoms. These particles are pyrolyzed in inert gas to yield the microparticles. In an alternative method, silica gel coated particles are formed by colloidally stabilizing particles containing metal species and forming silica at the boundary of the stabilized particle.
Owner:THE UNIV OF READING
Powdered lithium transition metal oxide having doped interface layer and outer layer and method for preparation of the same
ActiveUS7364793B2Use of materialSimple processLiquid surface applicatorsElectrode thermal treatmentInterface layerMechanical stability
The present invention provides a powdered lithium transition metal oxide useful as a major component for cathode active material of rechargeable lithium batteries, comprising a lithium transition metal oxide particle, a doped interface layer formed near the surface of the particle, and a thermodynamically and mechanically stable outer layer, and a method of preparing the same.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Lithium secondary battery with high power
ActiveUS20050271943A1Improves high-temperature cycle characteristicReduce concentrationAlkali metal oxidesIron compoundsElectrical batteryManganese
The present invention provides a non-aqueous electrolyte-based high power lithium secondary battery having a long-term service life and superior safety at both room temperature and high temperature, even after repeated high-current charging and discharging, wherein the battery comprises a mixture of a particular lithium manganese-metal composite oxide (A) having a spinel structure and a particular lithium nickel-manganese-cobalt composite oxide (B) having a layered structure, as a cathode active material.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Titanium comprising nanoparticles and related nanotechnology
ActiveUS7232556B2Increase volumeLow cost productionNitrogen compoundsGermanium dioxideNanoparticleTitanium metal
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Positive electrode active materials for secondary batteries and methods of preparing same
InactiveUS6878490B2Deliver in short periodRetake in short periodAluminium compoundsAlkali titanatesPower capabilityLithium metal
The present invention is a positive electrode active material that can be used in secondary lithium and lithium-ion batteries to provide the power capability, i.e., the ability to deliver or retake energy in short periods of time, desired for large power applications such as power tools, electric bikes and hybrid electric vehicles. The positive electrode active material of the invention includes at least one electron conducting compound of the formula LiM1x−y{A}yOz and at least one electron insulating and lithium ion conducting lithium metal oxide, wherein M1 is a transition metal, {A} is represented by the formula ΣwiBi wherein Bi is an element other than M1 used to replace the transition metal M1 and wi is the fractional amount of element Bi in the total dopant combination such that Σwi=1; Bi is a cation in LiM1x−y{A}yOz; 0.95≦x≦2.10; 0≦y≦x / 2; and 1.90≦z≦4.20. Preferably, the lithium metal oxide is LiAlO2 or Li2M2O3 wherein M2 is at least one tetravalent metal selected from the group consisting of Ti, Zr, Sn, Mn, Mo, Si, Ge, Hf, Ru and Te. The present invention also includes methods of making this positive electrode active material.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com