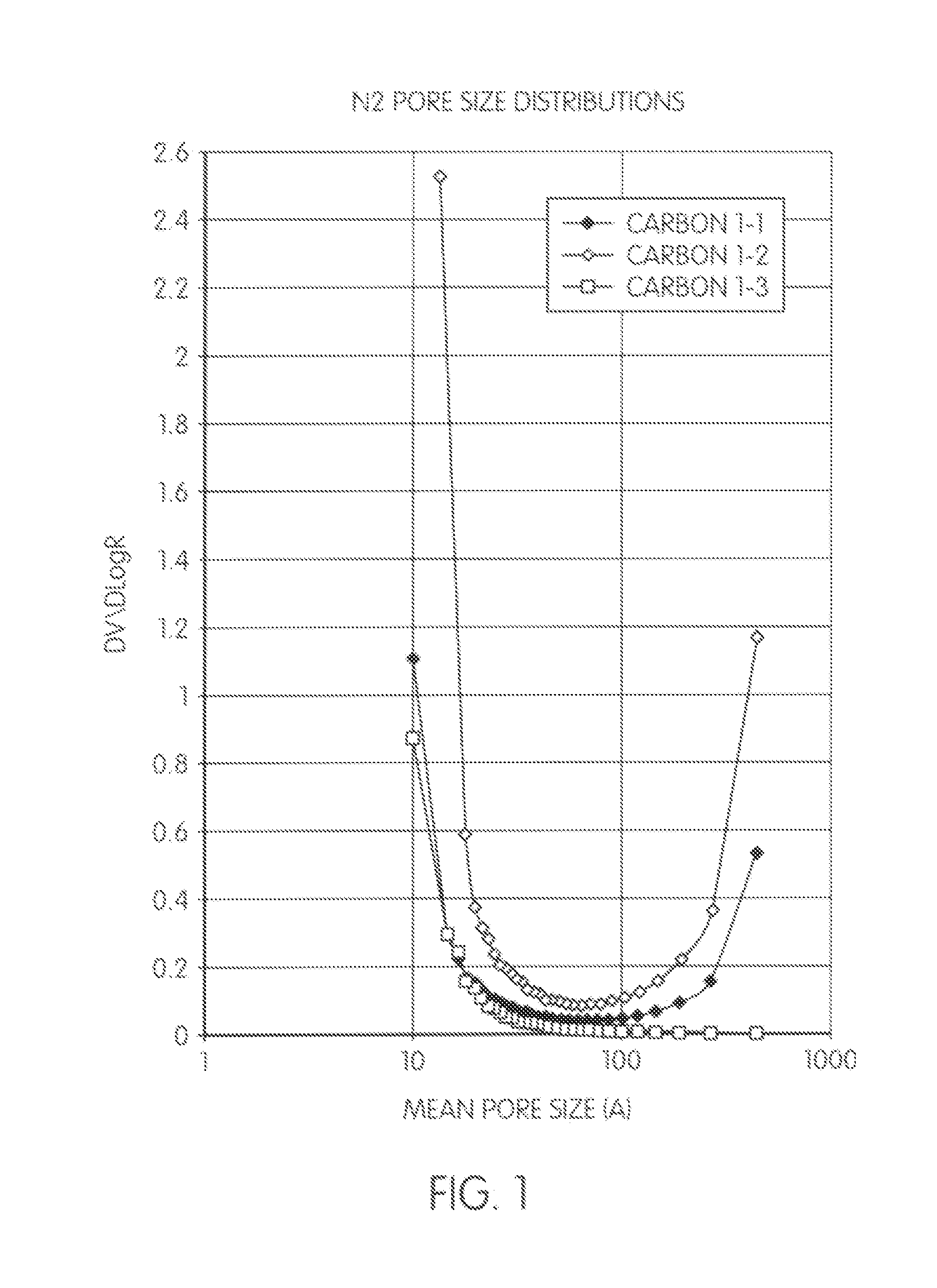Patents
Literature
135 results about "Porosimetry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
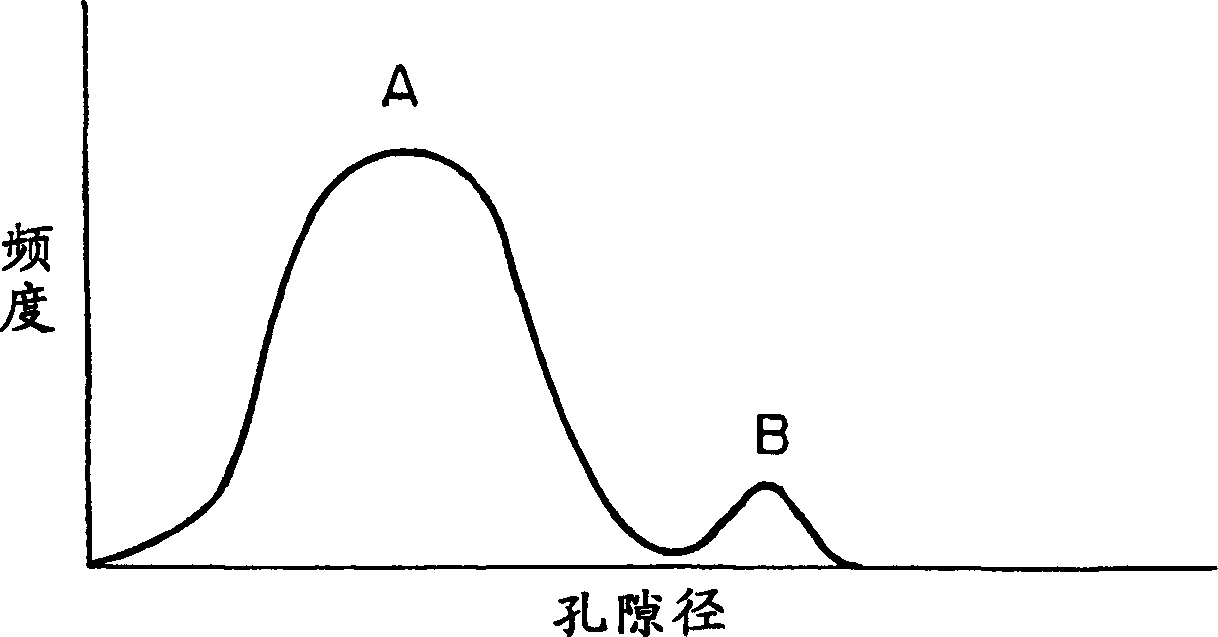
Porosimetry is an analytical technique used to determine various quantifiable aspects of a material's porous nature, such as pore diameter, total pore volume, surface area, and bulk and absolute densities. The technique involves the intrusion of a non-wetting liquid (often mercury) at high pressure into a material through the use of a porosimeter. The pore size can be determined based on the external pressure needed to force the liquid into a pore against the opposing force of the liquid's surface tension.
Nonaqueous electrolyte battery, battery pack and vehicle
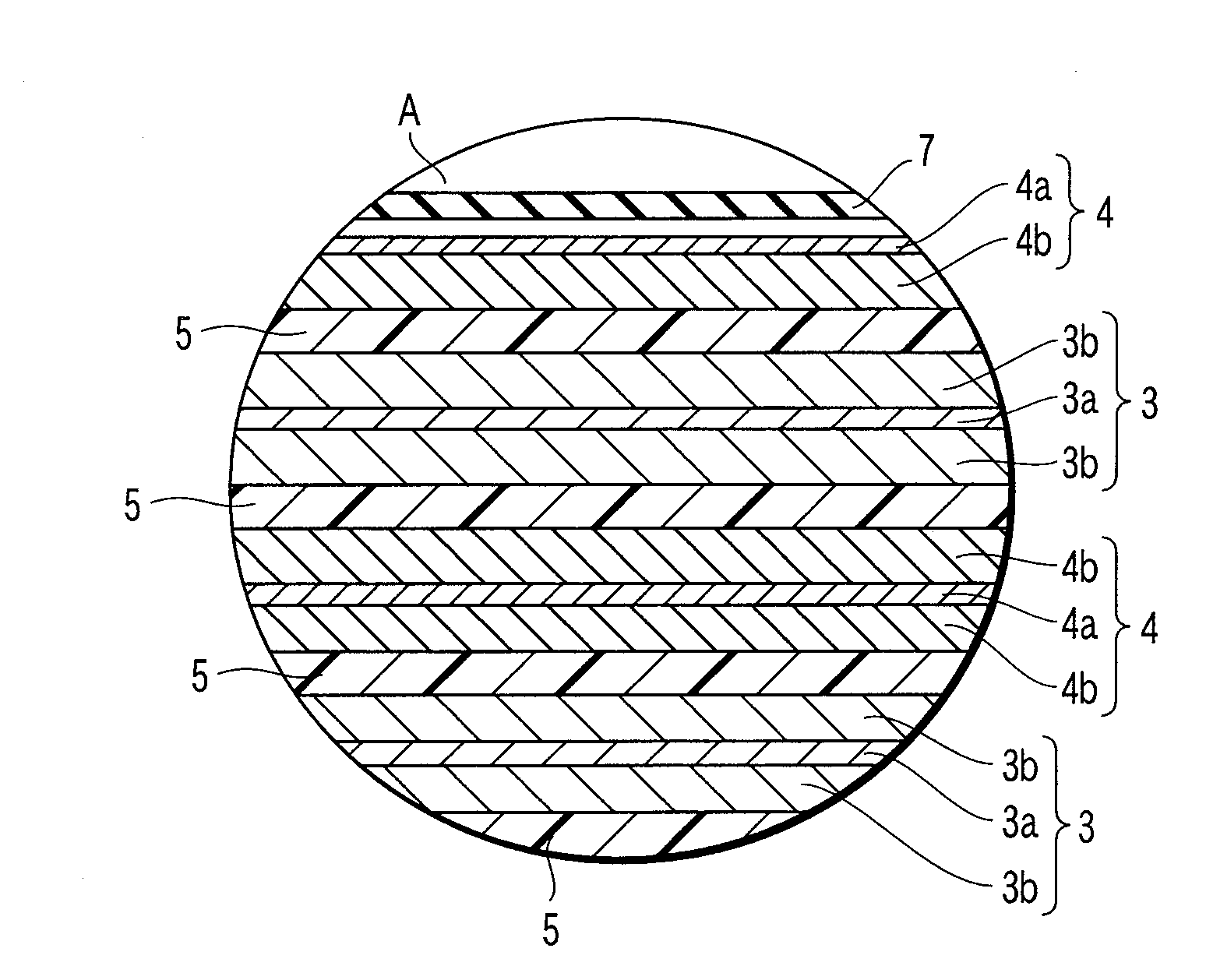
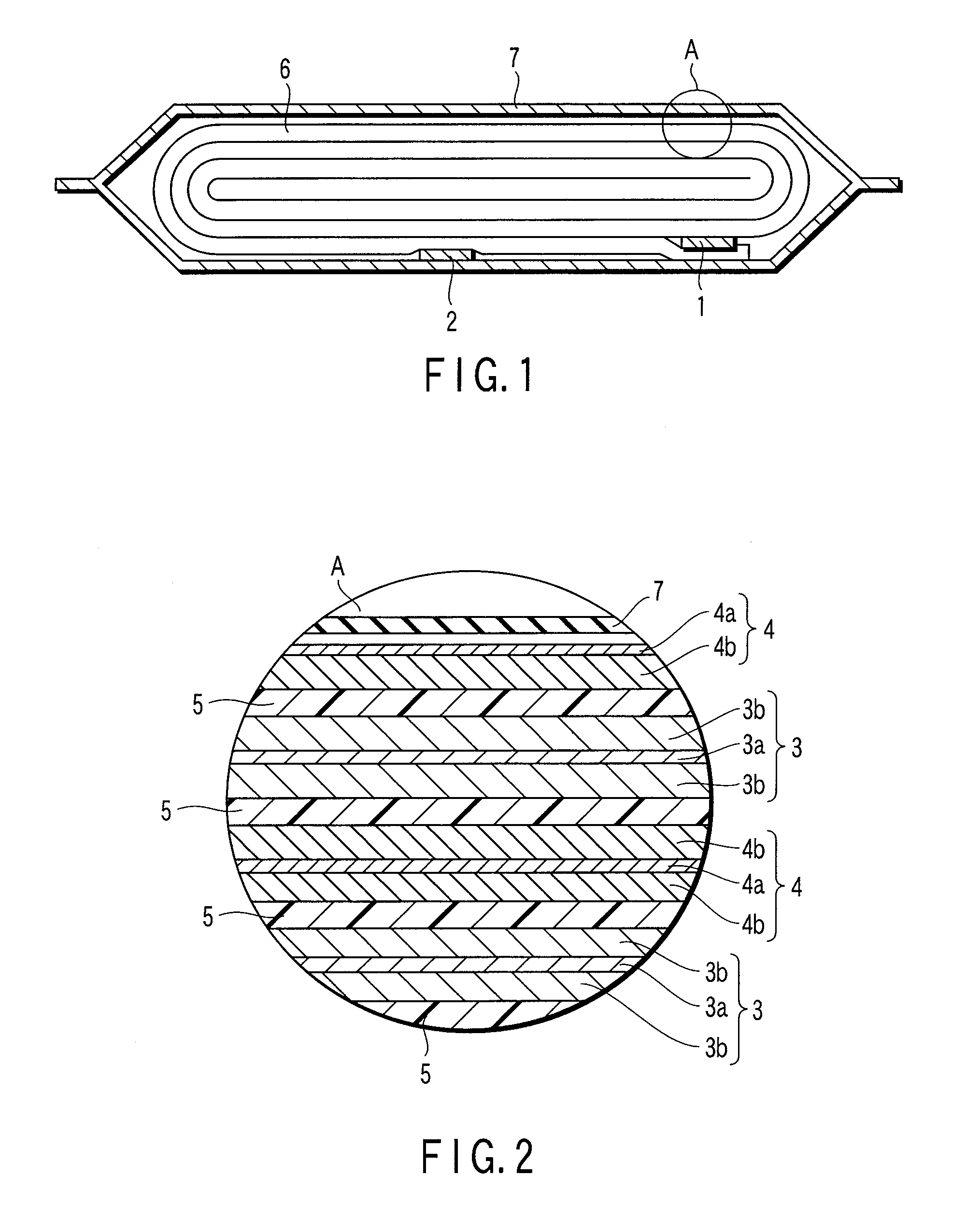
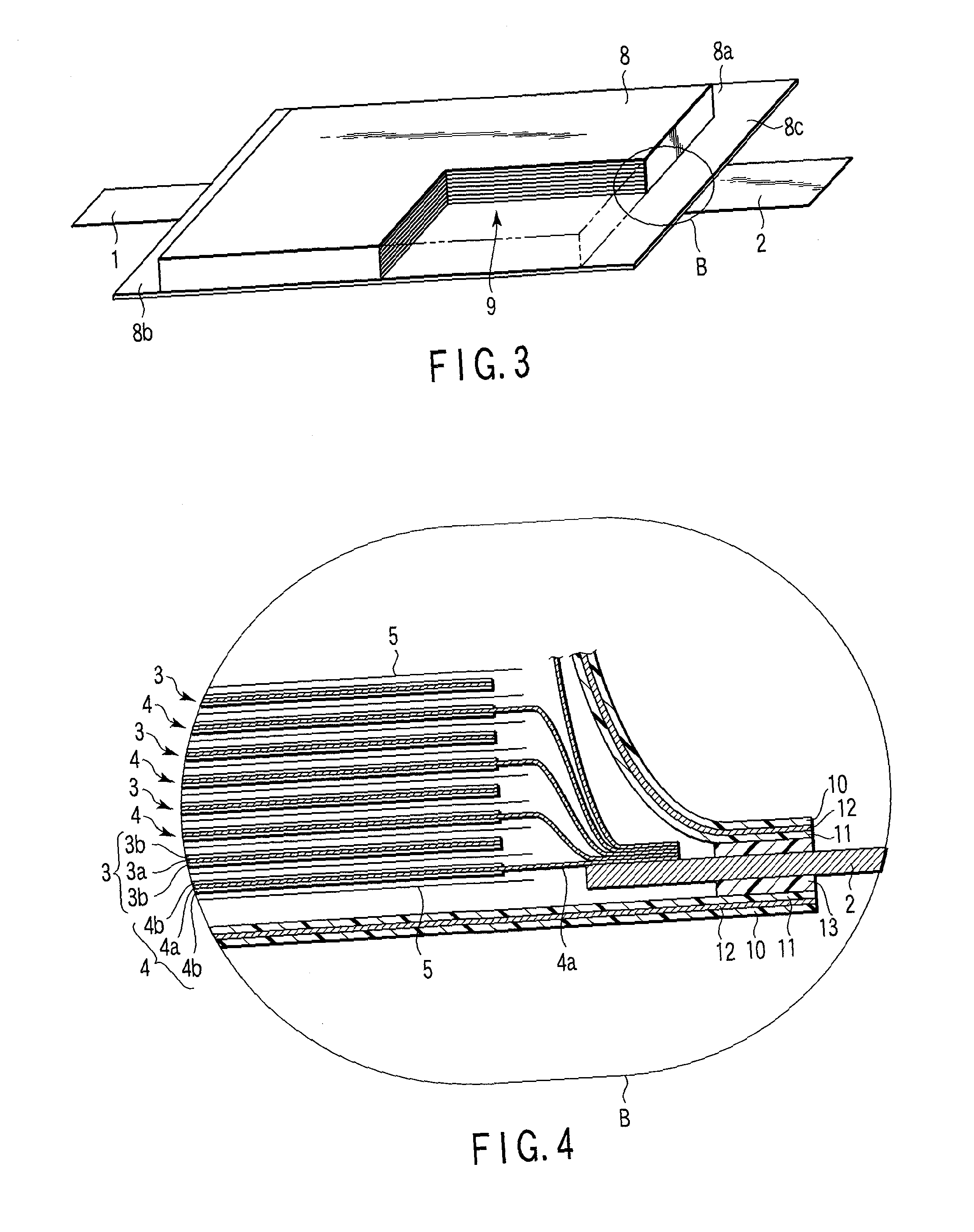
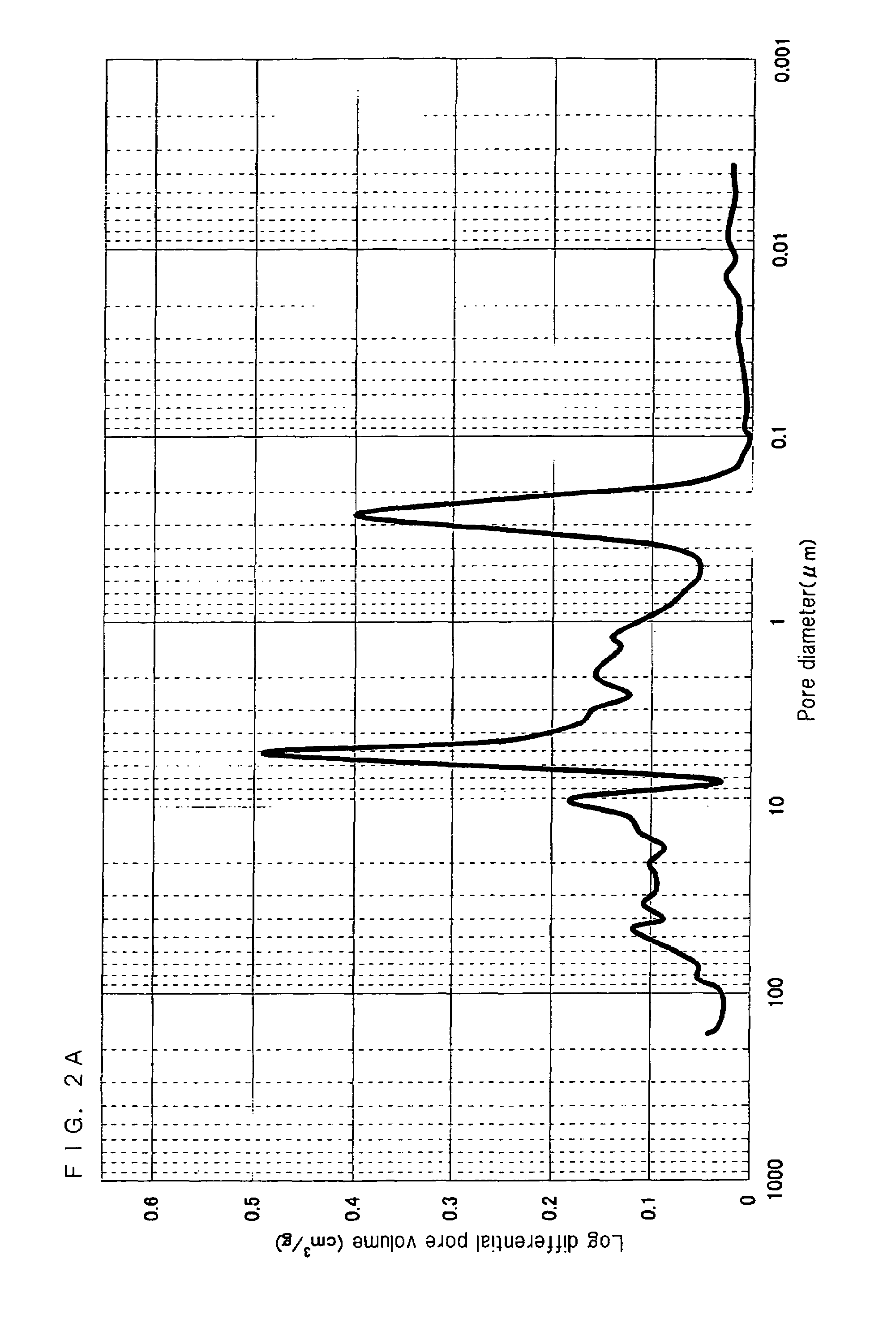
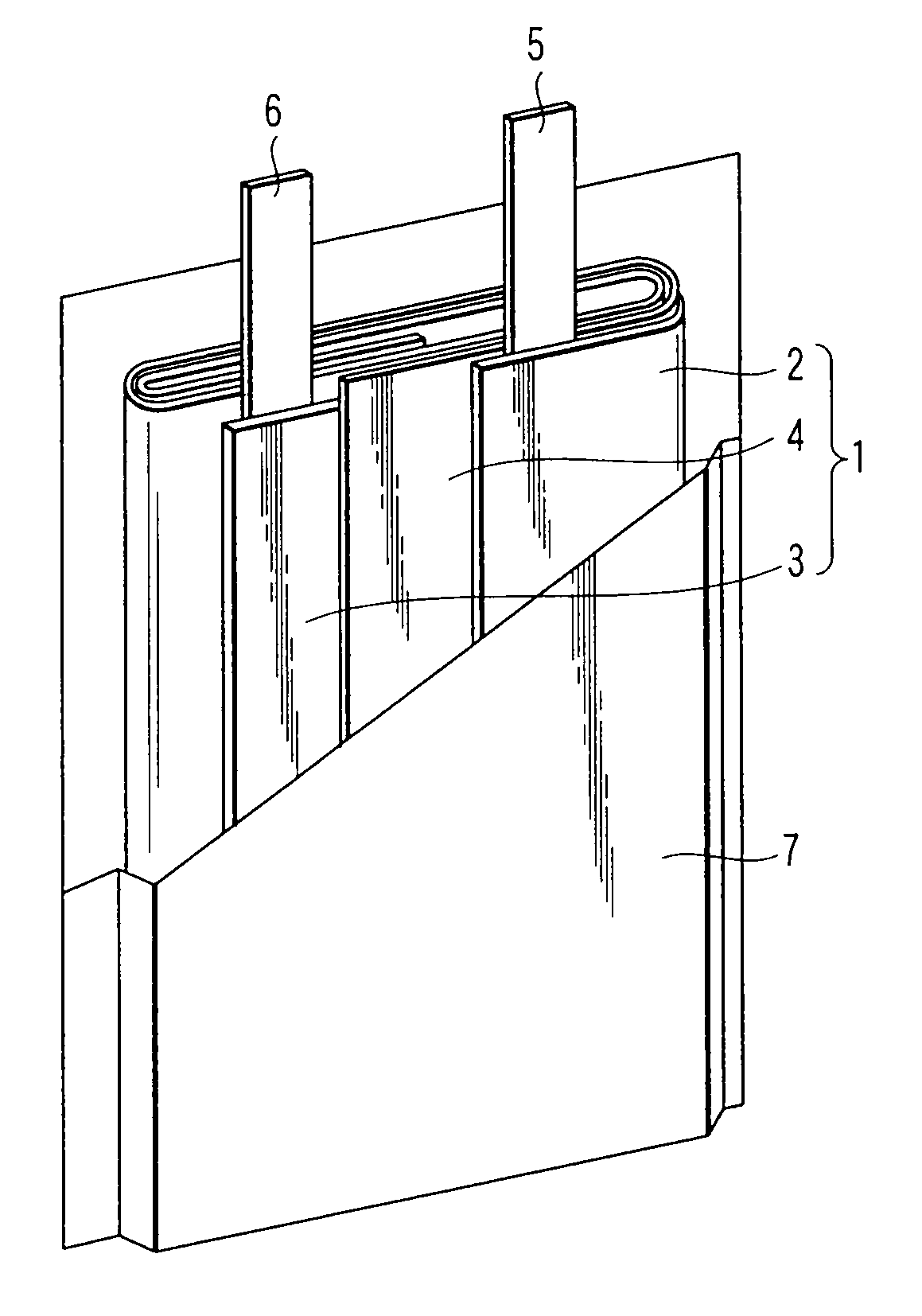
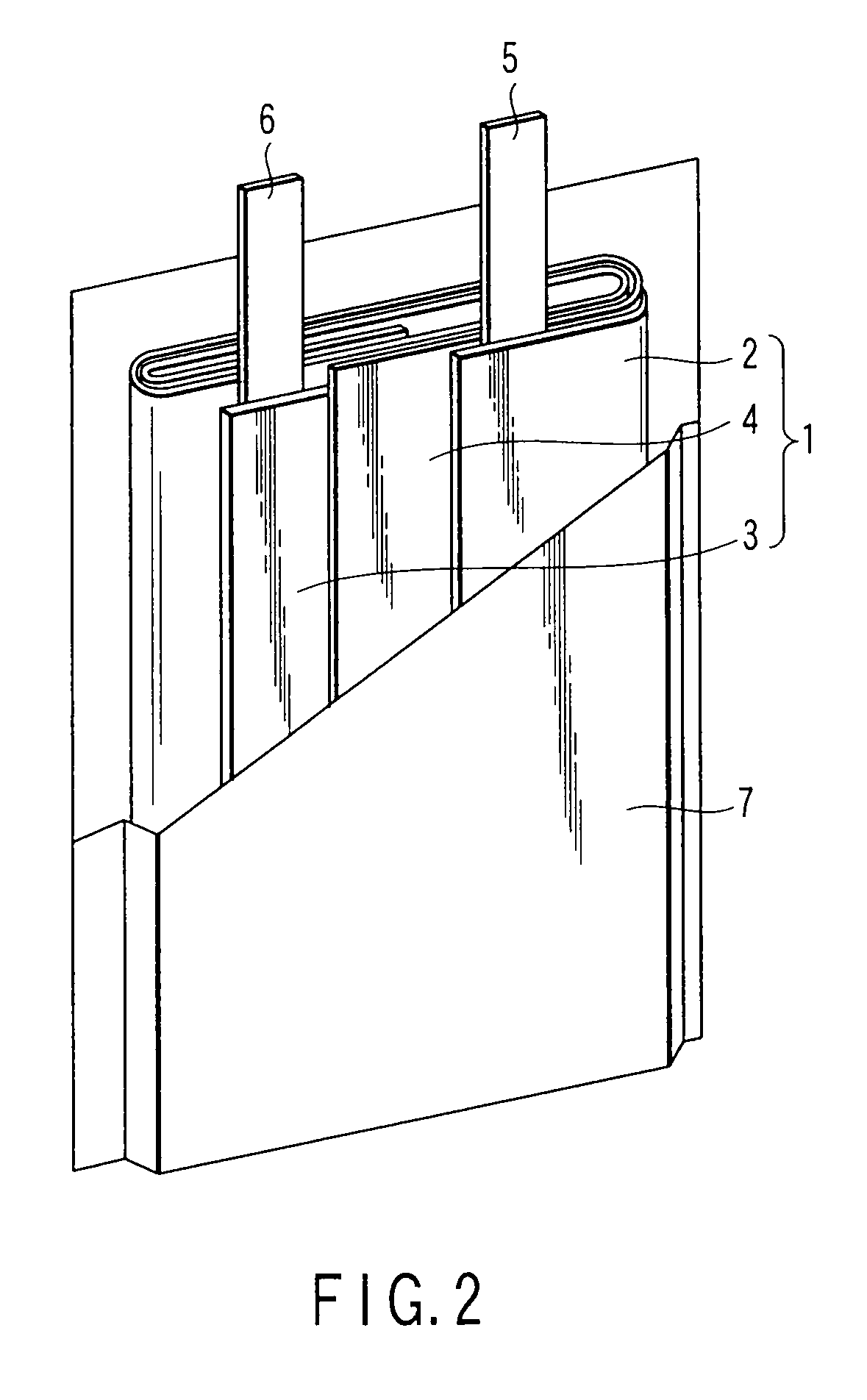
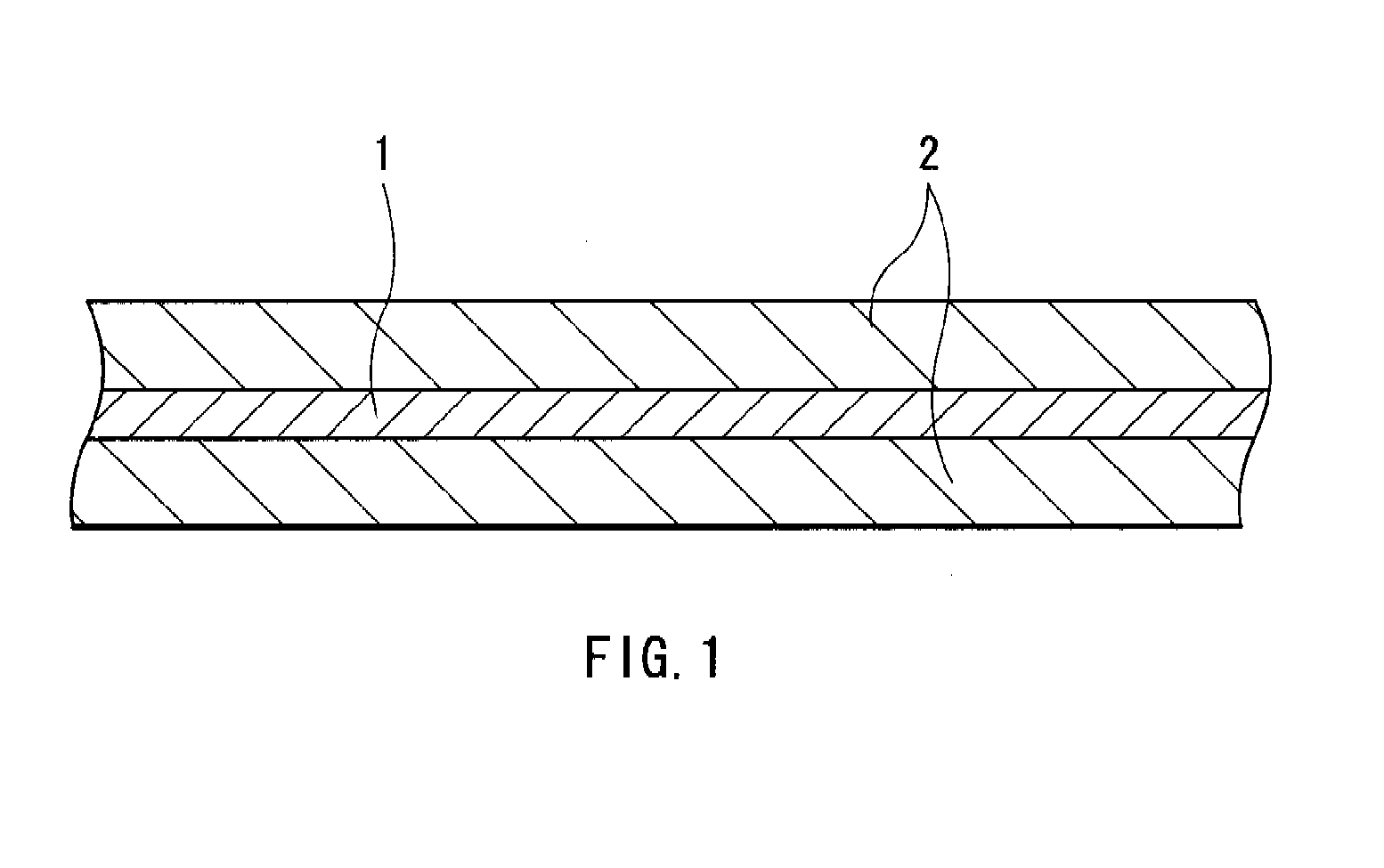
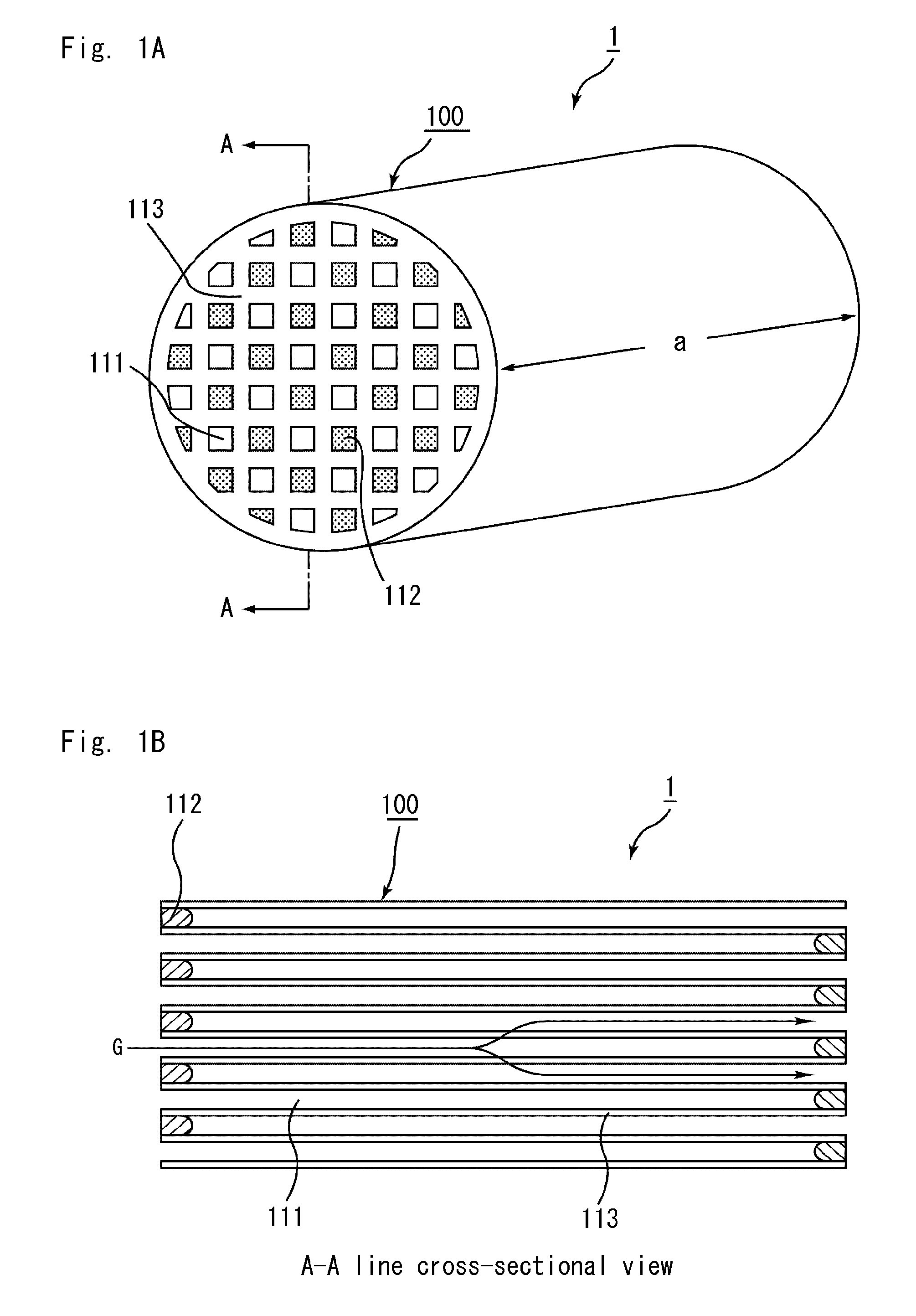
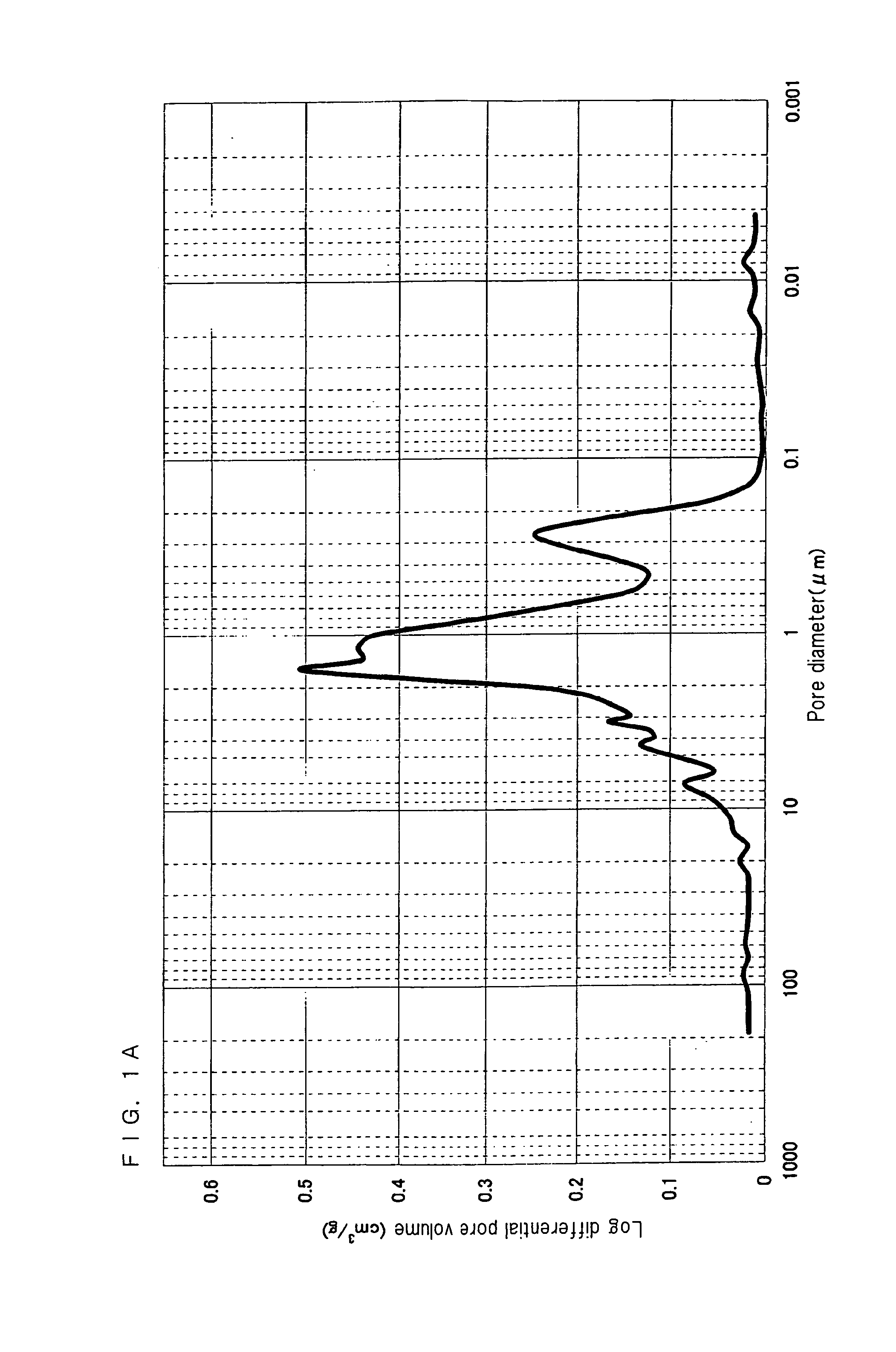
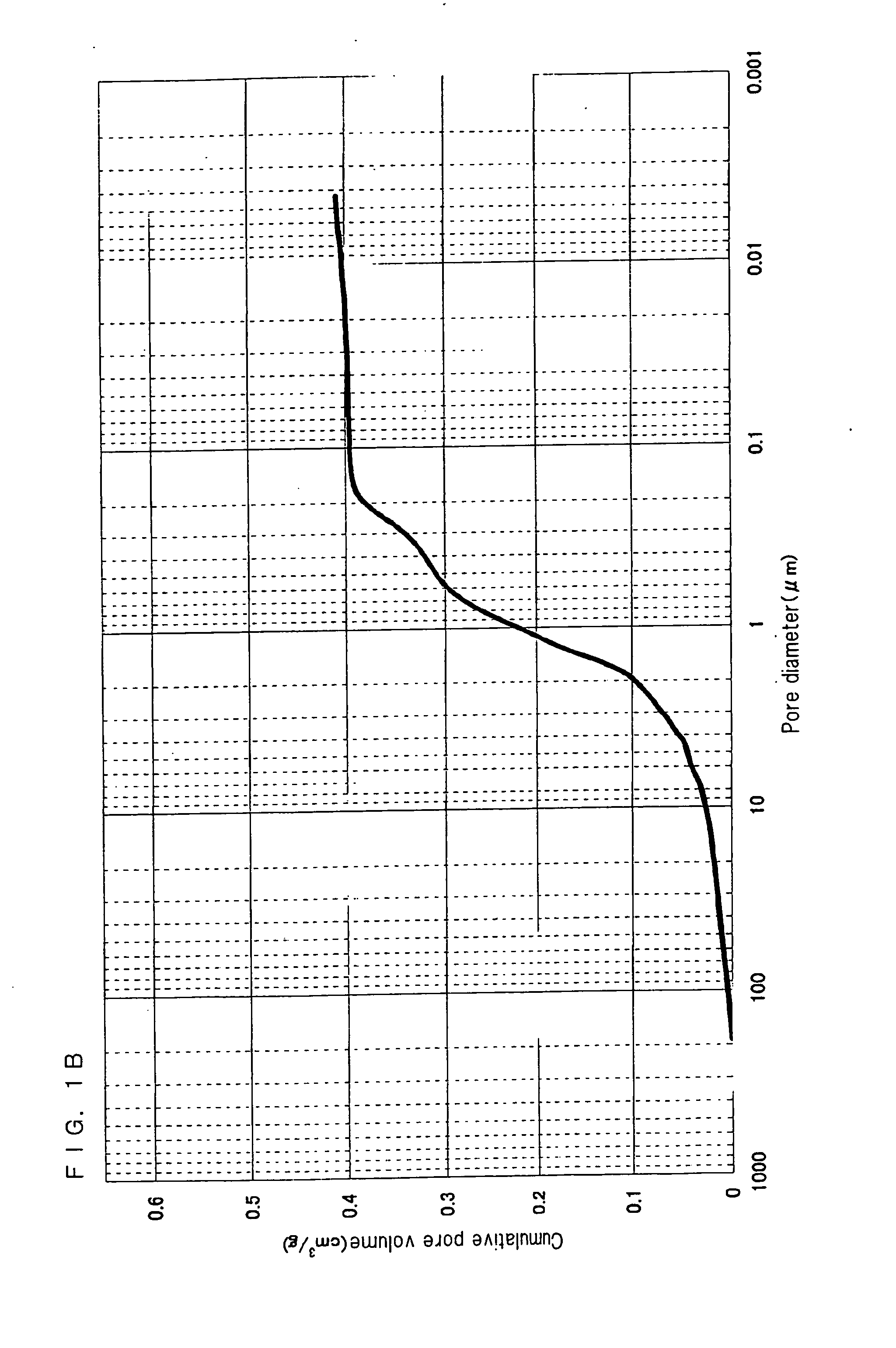
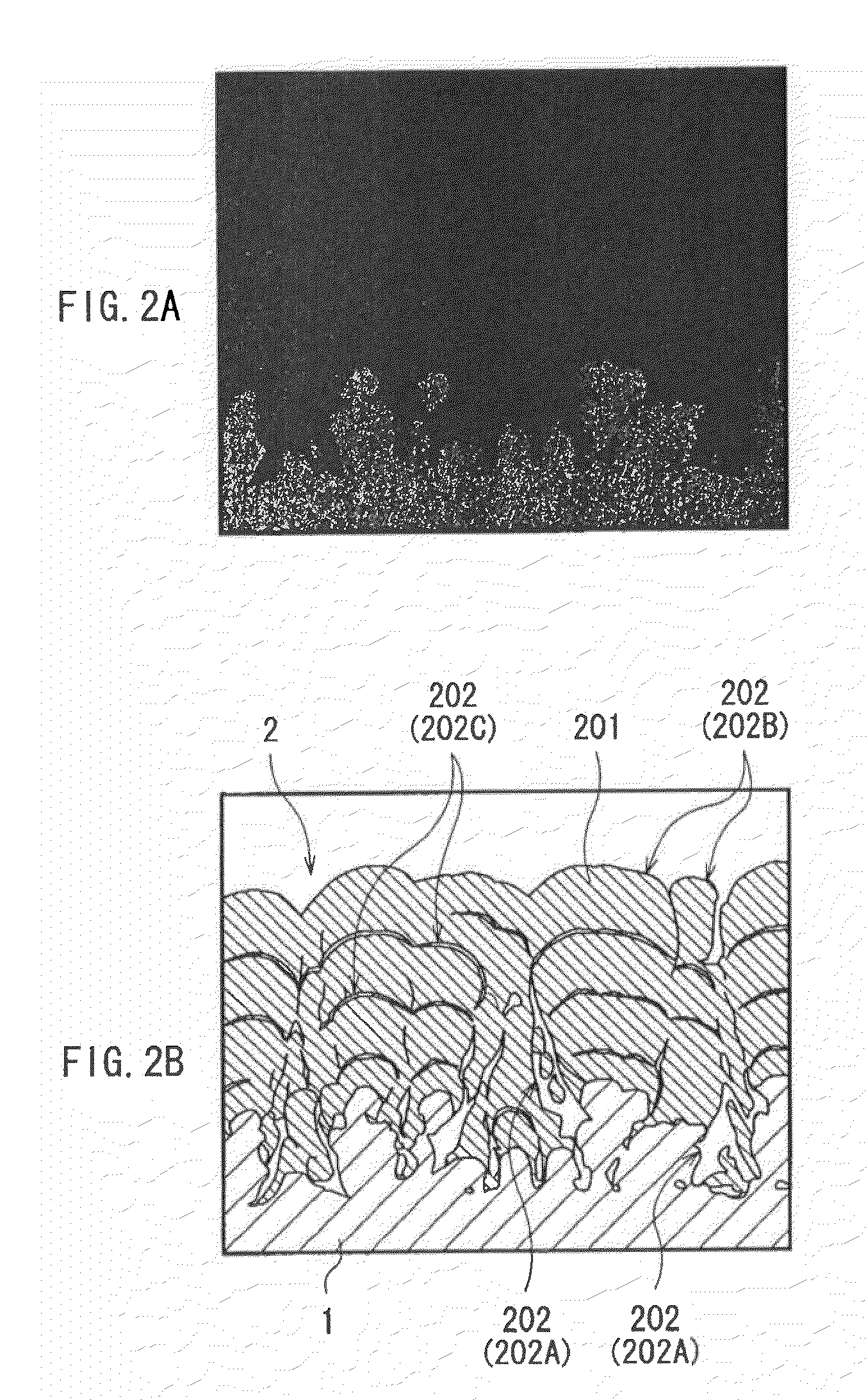
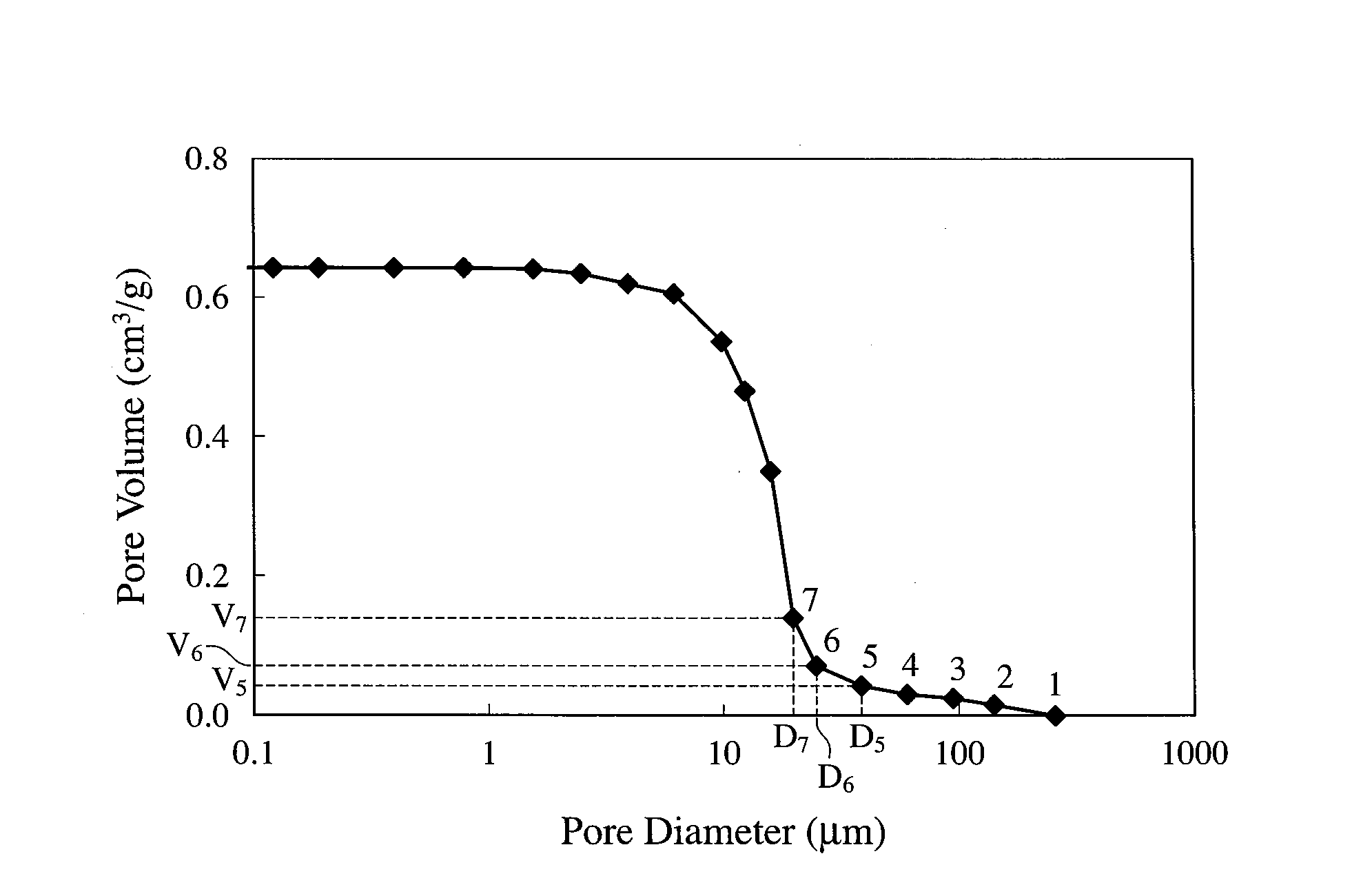
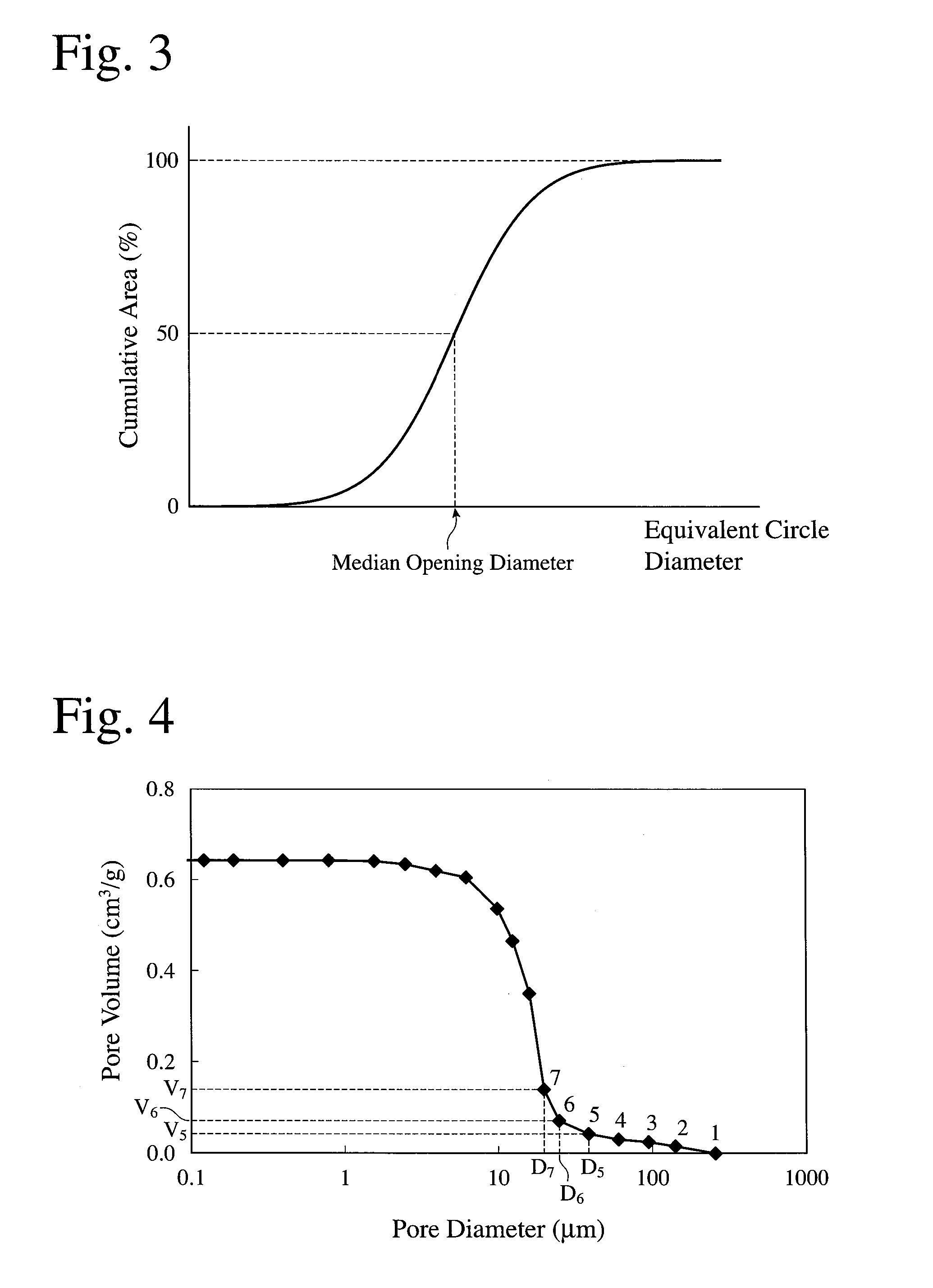
A nonaqueous electrolyte battery includes a negative electrode and a nonaqueous electrolyte. The negative electrode comprises an active material having a lithium ion insertion potential of 0.4V (vs Li / Li+) or more, a conductive agent and a current collector. The nonaqueous electrolyte contains first sultones having an unsaturated hydrocarbon group. A diameter distribution of pores of the negative electrode when measured by mercury porosimetry has a first peak having a mode diameter of 0.01 to 0.2 μm and a second peak having a mode diameter of 0.003 to 0.02 μm. A volume of pores having a diameter of 0.01 to 0.2 μm and a volume of pores having a diameter of 0.003 to 0.02 μm, which are measured by the mercury porosimetery, are 0.05 to 0.5 mL and 0.0001 to 0.02 mL, respectively, per g of the negative electrode excluding the current collector.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
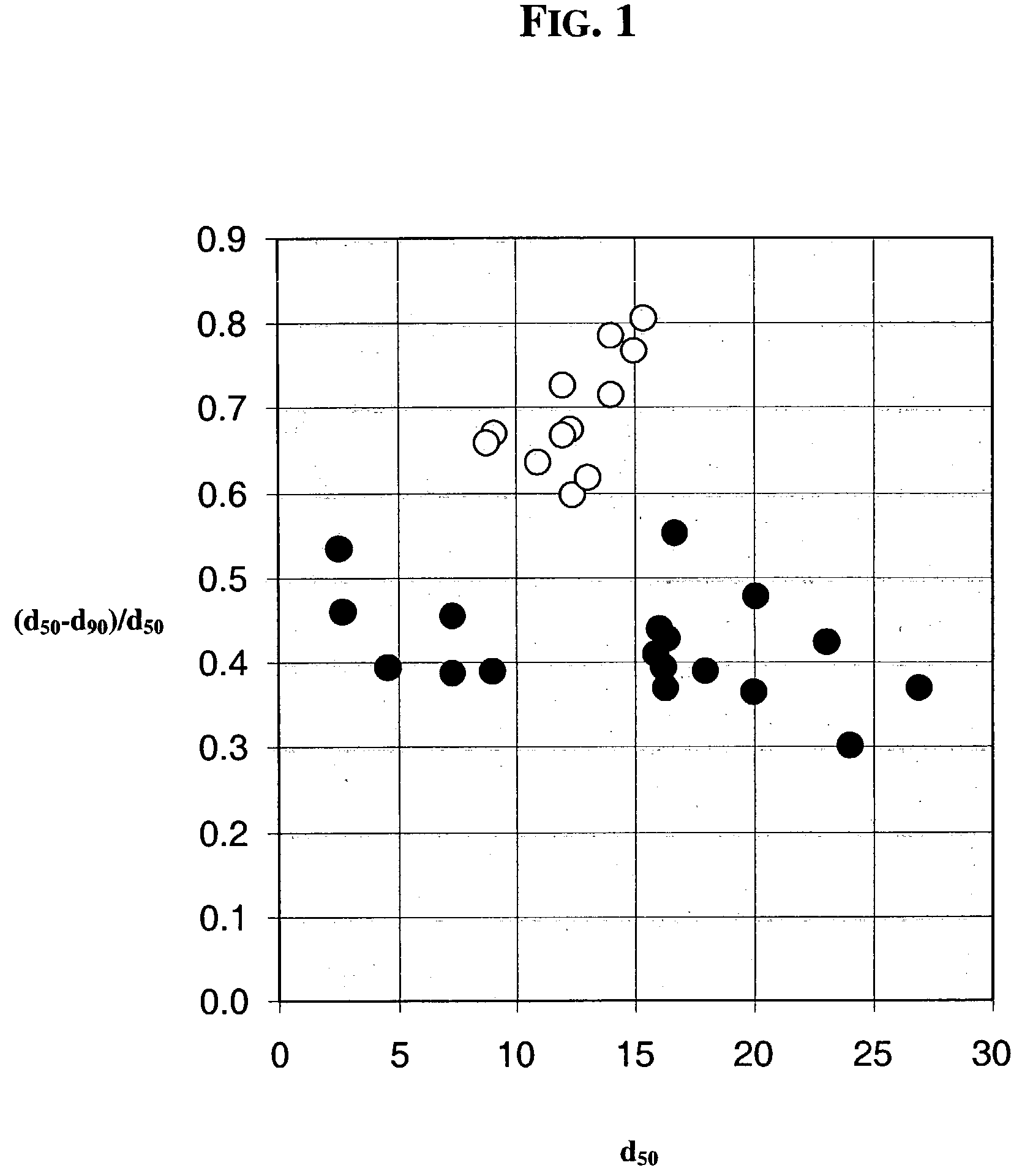
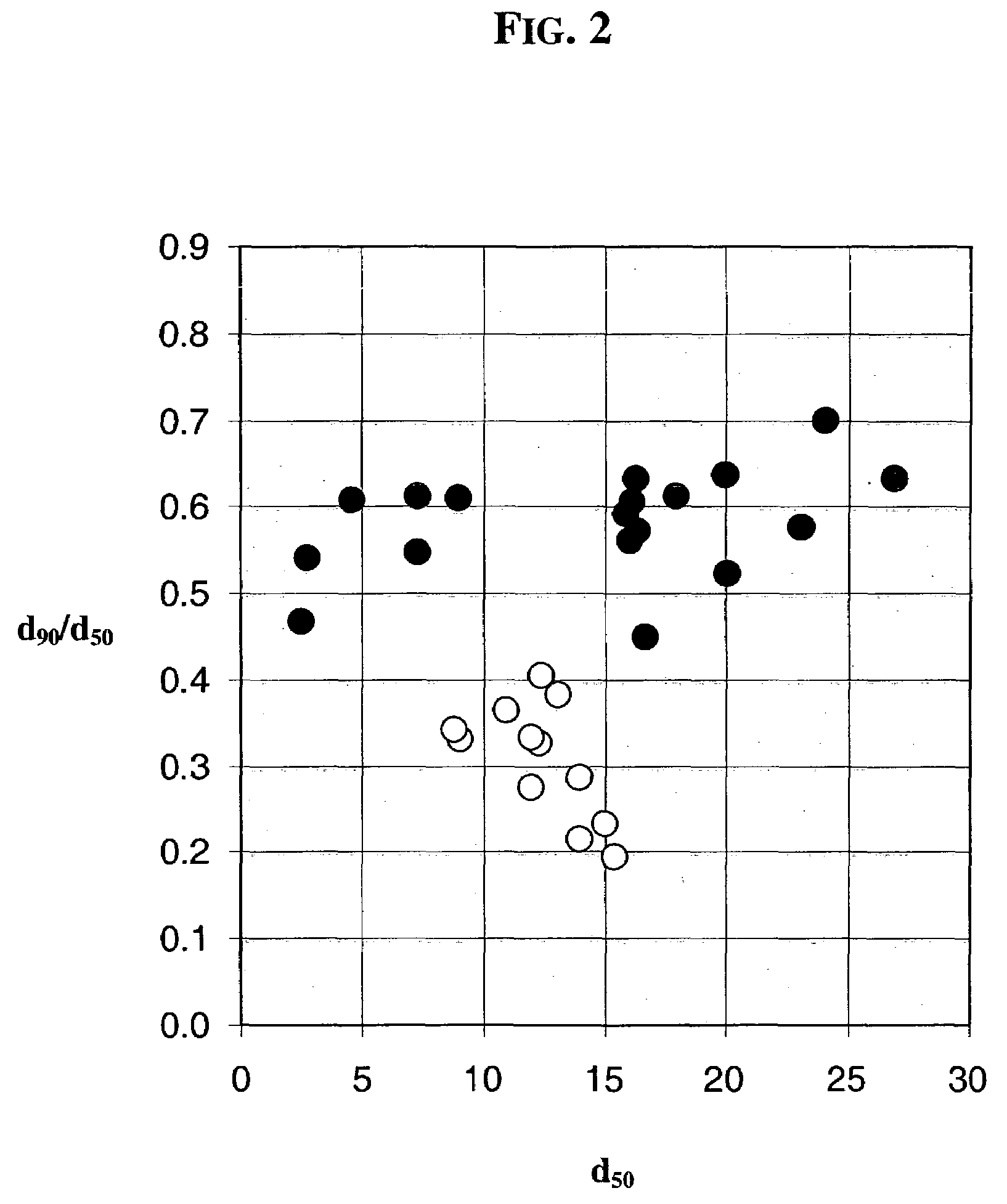
High porosity cordierite composition
ActiveUS20070261378A1Reduce stressImprove filtration efficiencyCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentFiltrationCordierites
Disclosed are ceramic articles, which in one aspect are composed predominately of a cordierite having a composition close to that of Mg2Al4Si5O18. The ceramic articles possess a microstructure characterized by a unique combination of relatively high porosity and relatively narrow pore size distribution, both as measured by mercury porosimetry, that render the ceramic structure useful for ceramic filter applications requiring high thermal durability and high filtration efficiency coupled with low pressure drop along the length of the filter. Such ceramic bodies are particularly well suited for filtration applications, such as diesel exhaust filters or DPFs. Also disclosed are methods for the manufacture of the ceramic articles described herein.
Owner:CORNING INC
Honeycomb filter
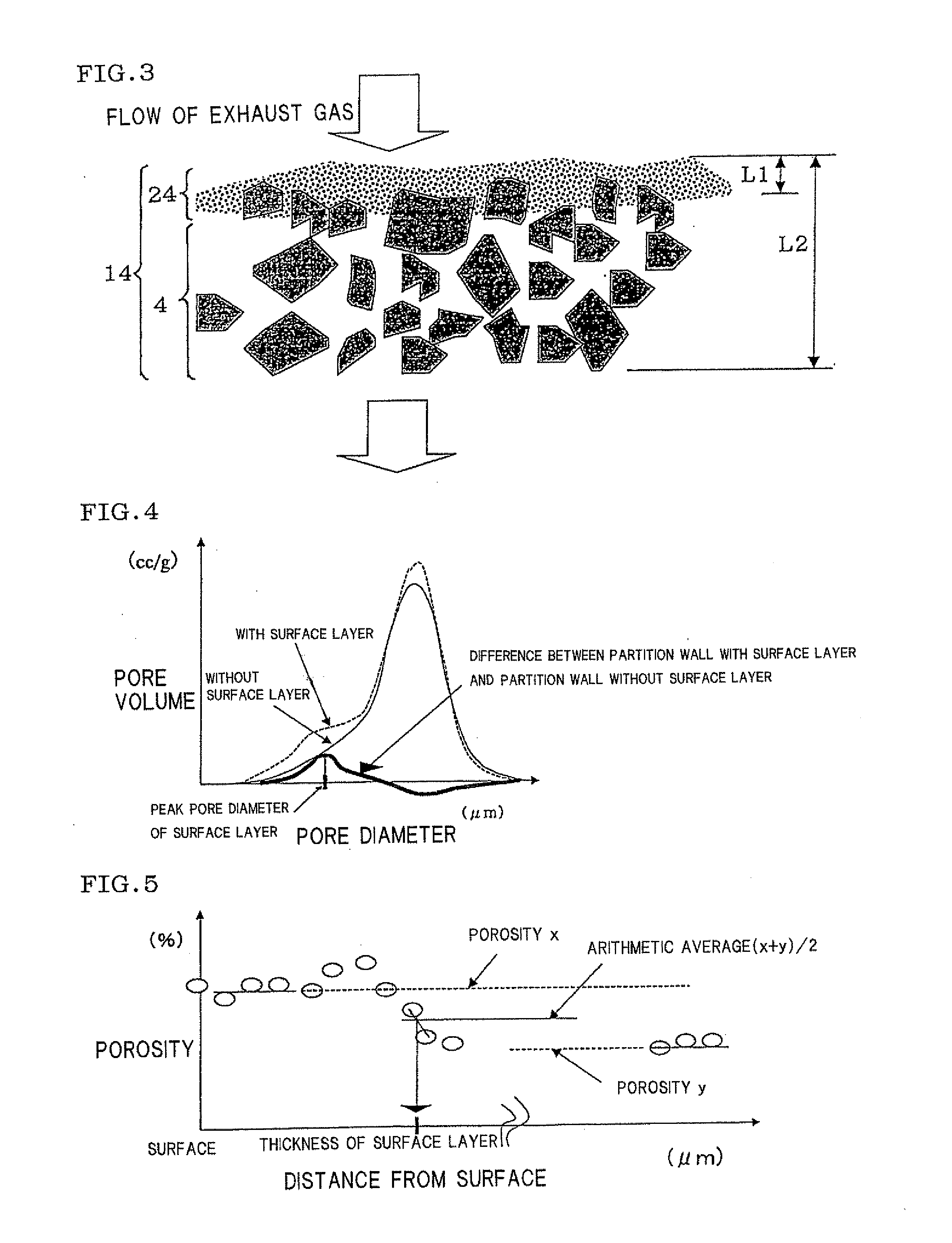
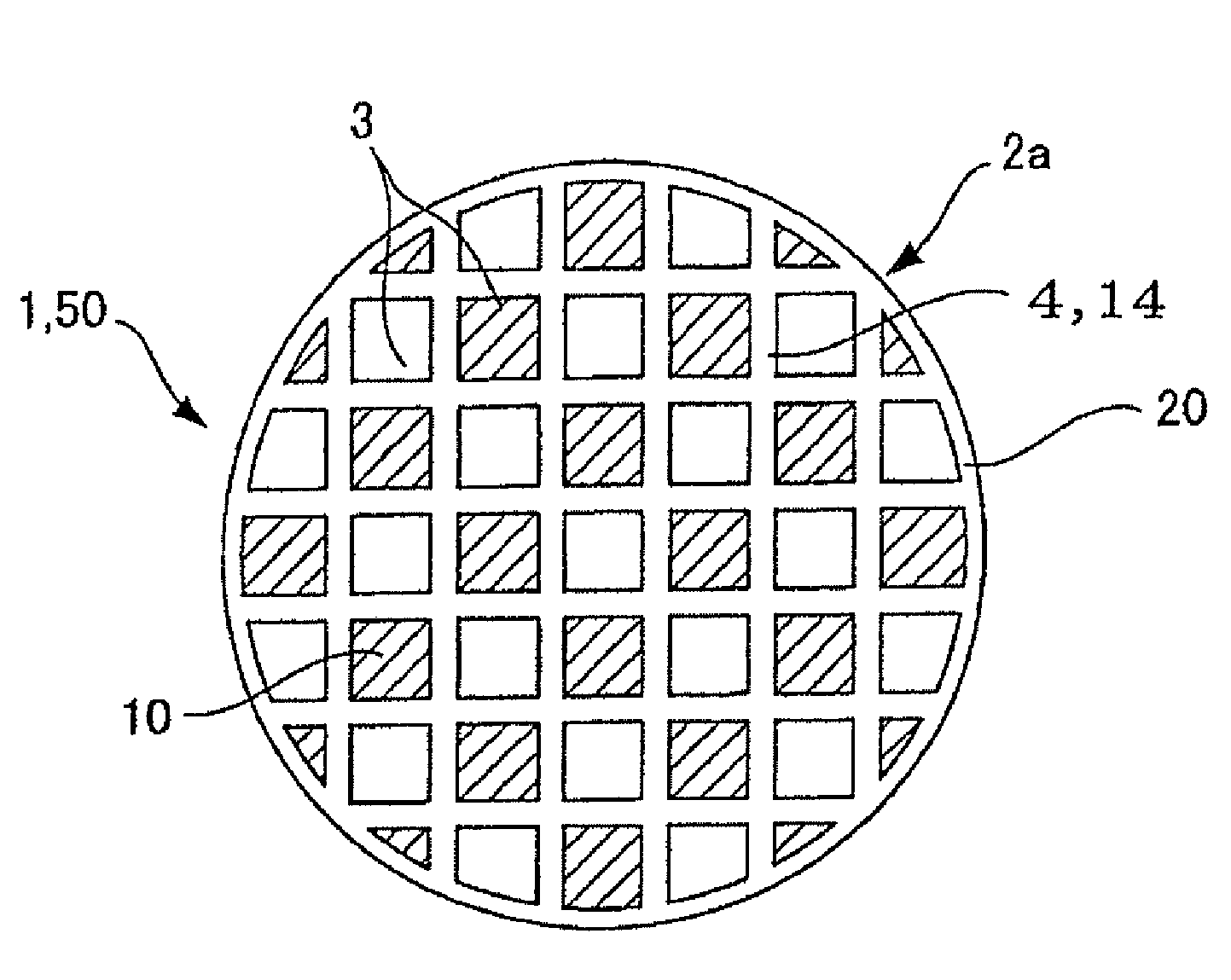
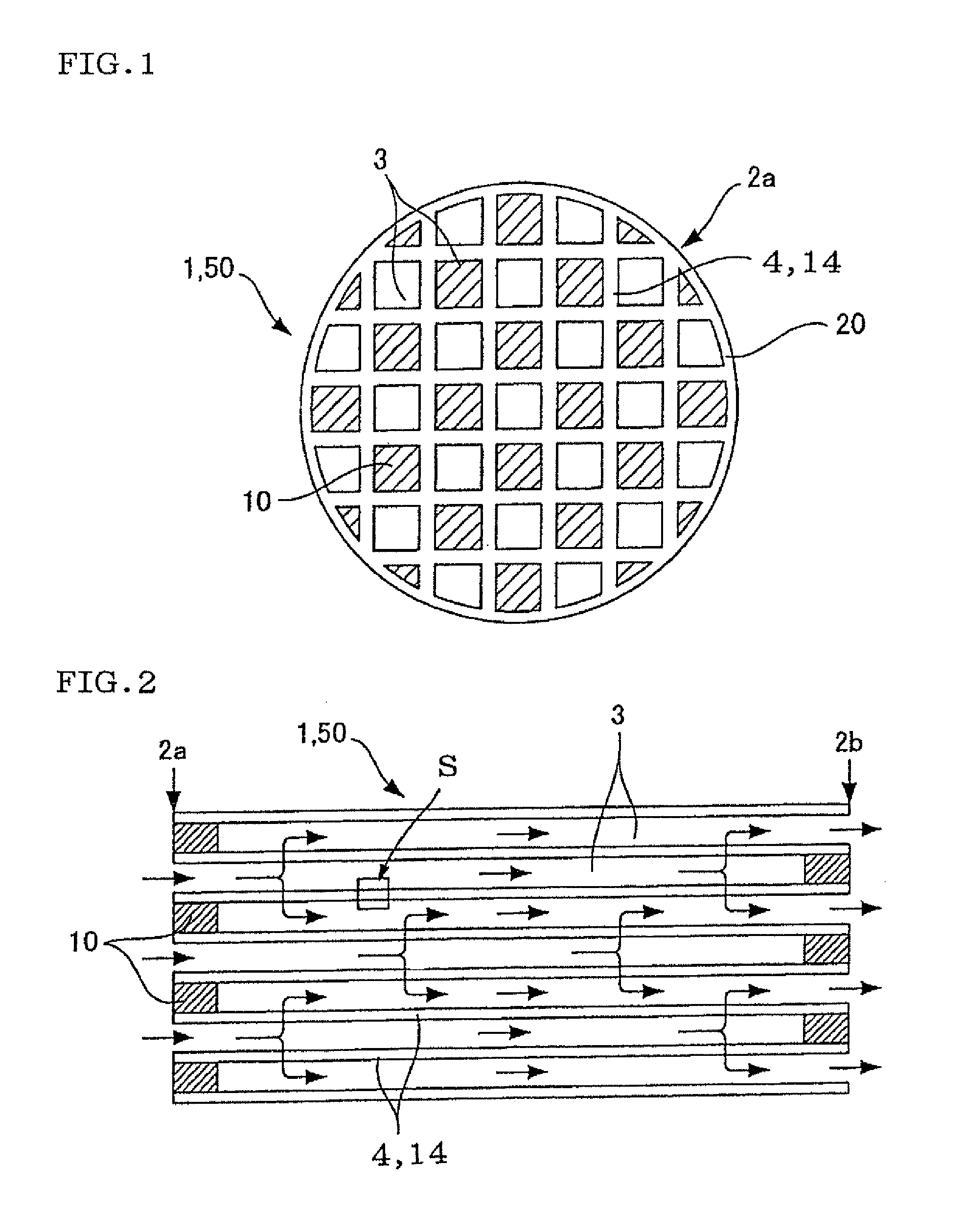
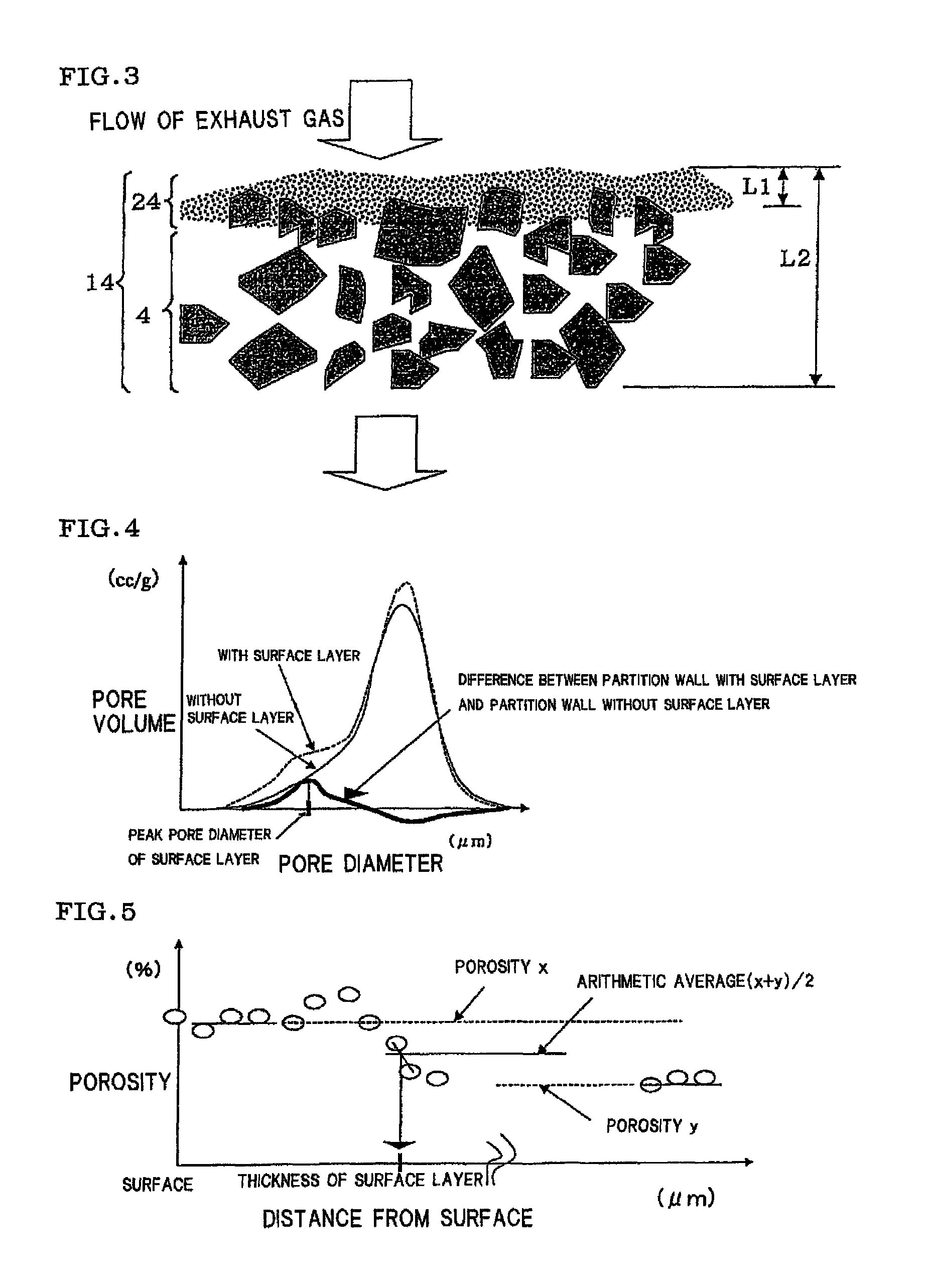
ActiveUS20100135866A1Efficient trappingLower performance requirementsCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationSurface layerFiltration
A honeycomb filter including partition walls having a porous partition wall base material and a surface layer provided on only inflow side or both inflow and outflow sides of the partition wall base material, and satisfying the following conditions capable of using as a DPF. The surface layer has a peak pore diameter of from 0.3 μm to 20 μm (exclusive) being equal to or smaller than the average pore diameter of the base material; the porosity of from 60% to 95% (exclusive) when measured by mercury porosimetry being larger than that of the base material; and the thickness L1 of from 0.5% to 30% (exclusive) of the partition wall thickness L2; and mass per filtration area of from 0.01 mg / cm2 to 6 mg / cm2 (exclusive). The base material has an average pore diameter of from 10 μm to 60 μm (exclusive) and a porosity of from 40% to 65% (exclusive).
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Magnesium aluminum silicate structures for DPF applications
ActiveUS7141089B2Reduce anisotropyGood pore connectivityCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentParticulatesAluminum silicate
A ceramic filter for trapping and combusting diesel exhaust particulates composed of an end-plugged cordierite honeycomb structure exhibiting a pore size distribution as determined by mercury porosimetry in which the quantity d50 / (d50+d90) as related to pore size distribution is less than 0.70, a soot loaded permeability factor Sf, as defined by the equation [d50 / (d50+d90)] / [% porosity / 100], of less than 1.55, and, a coefficient of thermal expansion (25–800° C.) of no greater than 17×10−7 / ° C. The ceramic filter further exhibits a median pore diameter, d50, of at least 4 micrometers and up to 40 micrometers. A method of making the filter is provided.
Owner:CORNING INC
Agglomerated zeolite adsorbents and process for producing the same
ActiveUS20110105301A1Large hole volumeImprove mass transfer effectMolecular sieve catalystsOther chemical processesSorbentIon exchange
An agglomerated zeolite adsorbent which comprises 95-99.5 mass % of X zeolite and 0.5-5.0 mass % of binder, wherein the exchangeable cationic sites of said X zeolite are occupied by Group IIA metal and / or K, the total pore volume of said adsorbent is no less than 0.26 mL / g as measured by mercury porosimetry, the volume of pores with pore diameters from 100 to 500 nm is at least 60% based on the total pore volume. During shaping, a pore-forming agent is added to this adsorbent, and then the adsorbent is alkali treated for in-situ crystallization, followed by ion exchange. Said adsorbent has high adsorption capacity, fast mass transfer rate and good mechanical strength. Said adsorbent is suitable for liquid phase adsorptive separation of para-xylene from C8 aromatic hydrocarbons and is also suitable for adsorptive separation of other alkyl aromatic hydrocarbons isomers.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Hydrocracking catalyst having a unique silica-alumina substrate
A hydrocarbon conversion catalyst contains at least one silica-alumina having the following characteristics: A content by weight of silica SiO2 of between 10 and 60% by weight; an Na content less than 300 ppm by weight; a total pore volume of between 0.5 and 1.2 m / g measured by mercury porosimetry; a porosity of said silica-alumina wherein: the volume of mesopores whose diameter is between 40 Å and 150 Å, and whose mean diameter varies between 80 and 120 Å represents between 30 and 80% of the total pore volume, and (ii) the volume of macropores, whose diameter is greater than 500 Å and preferably between 1000 Å and 10,000 Å represents between 20 and 80% of the total pore volume; a specific surface area greater than 200 m<2> / g, and at least one hydro-dehydrogenating element selected metals of group VIB and group VIII, and optionally phosphorus, boron, silicon, or elements of group VIIA, VIIB or VB.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Catalyst that comprises a silica-alumina and its use in hydrocracking of hydrocarbon feedstocks
The invention relates to a catalyst that contains at least one silica-alumina, whereby said silica-alumina has the following characteristics: A content by weight of silica SiO2 of between 10 and 60% by weight, an Na content that is less than 300 ppm by weight, a total pore volume of between 0.5 and 1.2 ml / g that is measured by mercury porosimetry, the porosity of said silica-alumina is as follows: i / . The volume of these mesopores whose diameter is between 40 Å and 150 Å, and whose mean diameter varies between 80 and 120 Å represents between 30 and 80% of the total pore volume, ii / . The volume of the macropores, whose diameter is greater than 500 Å and preferably between 1000 Å and 10,000 Å represents between 20 and 80% of the total pore volume, a specific surface area of greater than 200 m2 / g, and at least one hydro-dehydrogenating element that is selected from the group that is formed by the metals of group VIB and group VIII, optionally an element that is selected from the group that is formed by phosphorus, boron and silicon, of group VIIA, the elements of groups VIIB and VB. The invention also relates to the use of this catalyst for the transformation of hydrocarbon fractions, in particular hydrorefining and hydrocracking.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Anode and battery
ActiveUS20080305391A1Small sizeImprove performanceElectrode carriers/collectorsActive material electrodesPeak valueOptoelectronics
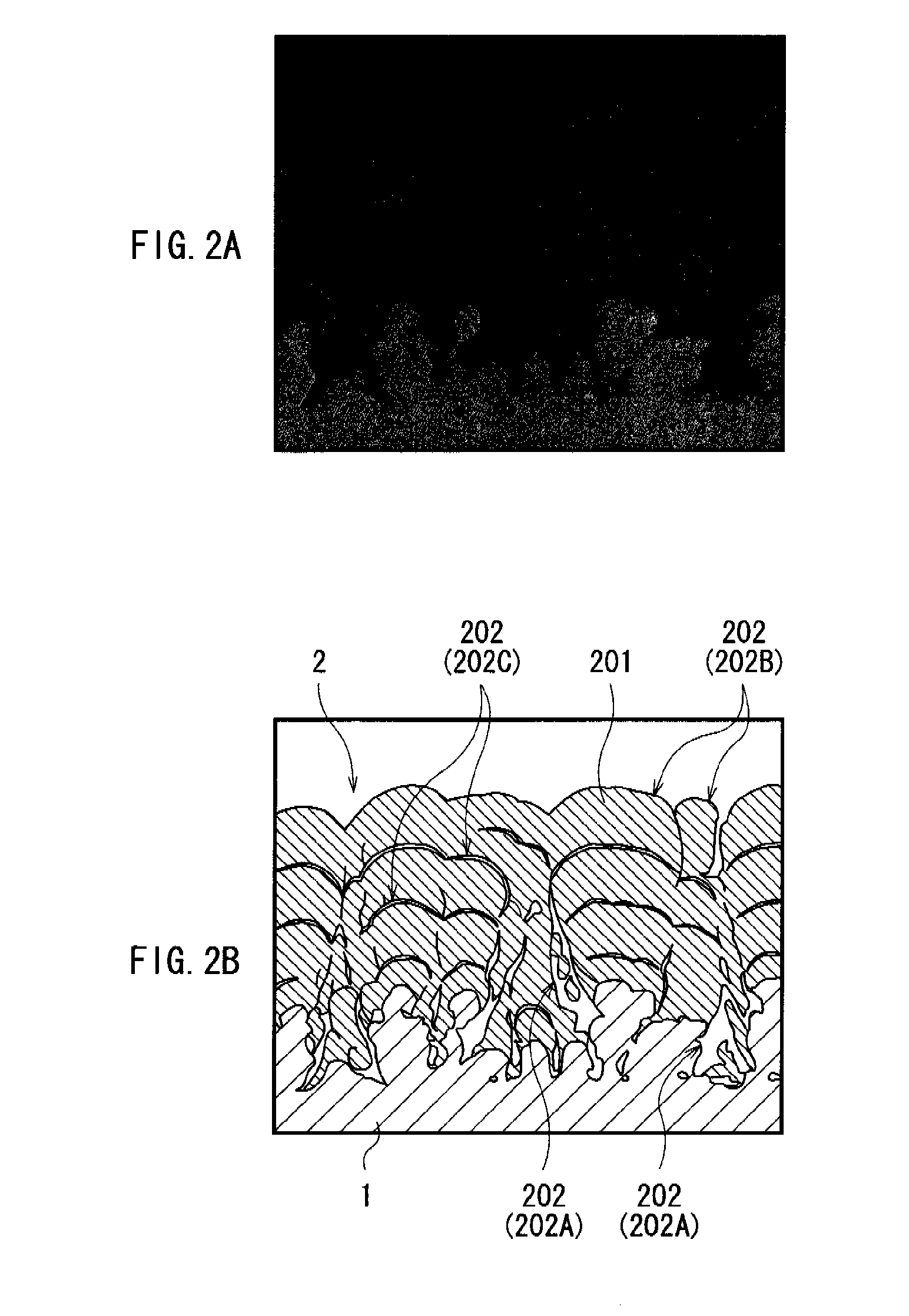
A battery capable of improving cycle characteristics and a manufacturing yield is provided. An anode includes: an anode current collector; and an anode active material layer arranged on the anode current collector, in which the anode active material layer includes an anode active material including a plurality of pores, and the rate of change in the amount of mercury intruded into the plurality of pores is distributed so as to have a peak in a diameter range from 80 nm to 1200 nm both inclusive, the amount of mercury intruded being measured by mercury porosimetry.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Catalyst and process for hydrocracking hydrocarbon-containing feedstocks
ActiveUS20040138059A1Improve spatial resolutionCatalyst carriersOther chemical processesNitrogenPore diameter
This invention relates to silico-aluminum substrates, catalysts, and the hydrocracking and hydrotreatment processes that use them. The catalyst comprises at least one hydro-dehydrogenating element that is selected from the group that is formed by elements of group VIB and group VIII of the periodic table and a non-zeolitic silica-alumina-based substrate that contains an amount of more than 5% by weight and less than or equal to 95% by weight of silica (SiO2) and has the following characteristics: A mean pore diameter, measured by mercury porosimetry, encompassed between 20 and 140 Å, a total pore volume, measured by mercury porosimetry, encompassed between 0.1 ml / g and 0.6 ml / g, a total pore volume, measured by nitrogen porosimetry, encompassed between 0.1 ml / g and 0.6 ml / g, a BET specific surface area encompassed between 100 and 550 m<2> / g, a pore volume, measured by mercury porosimetry, encompassed in the pores with diameters of more than 140 Å, of less than 0.1 ml / g, a pore volume, measured by mercury porosimetry, encompassed in the pores with diameters of more than 160 Å, of less than 0.1 ml / g, a pore volume, measured by mercury porosimetry, encompassed in the pores with diameters of more than 200 Å, of less than 0.1 ml / g, a pore volume, measured by mercury porosimetry, encompassed in the pores with diameters of more than 500 Å, of less than 0.01 ml / g, an X diffraction diagram contains at least the main lines that are characteristic of at least one of the transition aluminas contained in the group that consists of the alpha, rho, chi, eta, gamma, kappa, theta and delta aluminas.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Catalyst for production of ethylene oxide and method for production of ethylene oxide
InactiveUS7560577B2High selectivityOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPore distributionEthylene oxide
A catalyst that enables to produce ethylene oxide in a high selectivity and a method for the production of ethylene oxide using the catalyst are provided. In the catalyst for the production of ethylene oxide, wherein the catalyst component is supported by a carrier, a carrier containing α-alumina as the main component which has at least two peaks in the range of pore diameter of 0.01-100 μm and at least one peak of the above peaks is present in the range of pore diameter of 0.01-1.0 μm in the pore distribution measured by mercury porosimetry is adopted as said carrier.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Active phase bimodal commixed catalyst, process for its preparation and use in hydrotreating residue
InactiveUS20170120229A1Reduce manufacturing costCatalyst activation/preparationAluminium hydroxide preparationHydrogenOxide matrix
A hydroconversion catalyst with a bimodal pore structure:an oxide matrix predominantly of calcined aluminium;a hydro-dehydrogenative active phase of at least one group VIII metal being at least partly commixed within the said oxide matrix mainly made up of calcined aluminium, an SBET specific surface greater than 100 m2 / g, a mesoporous median diameter in volume between 12 and 25 nm inclusive, a macroporous median diameter in volume between 250 and 1500 nm inclusive, a mesoporous volume as measured by mercury intrusion porosimeter greater than or equal to 0.55 ml / g and a total measured pore volume by mercury porosimetry greater than or equal to 0.70 ml / g;a method for preparing a residue catalyst for hydroconversion / hydroprocessing by commixing the active phase with a particular alumina,the use of the catalyst in hydroproces sing, including hydroproces sing heavy feeds.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Nonaqueous electrolyte battery, battery pack and vehicle
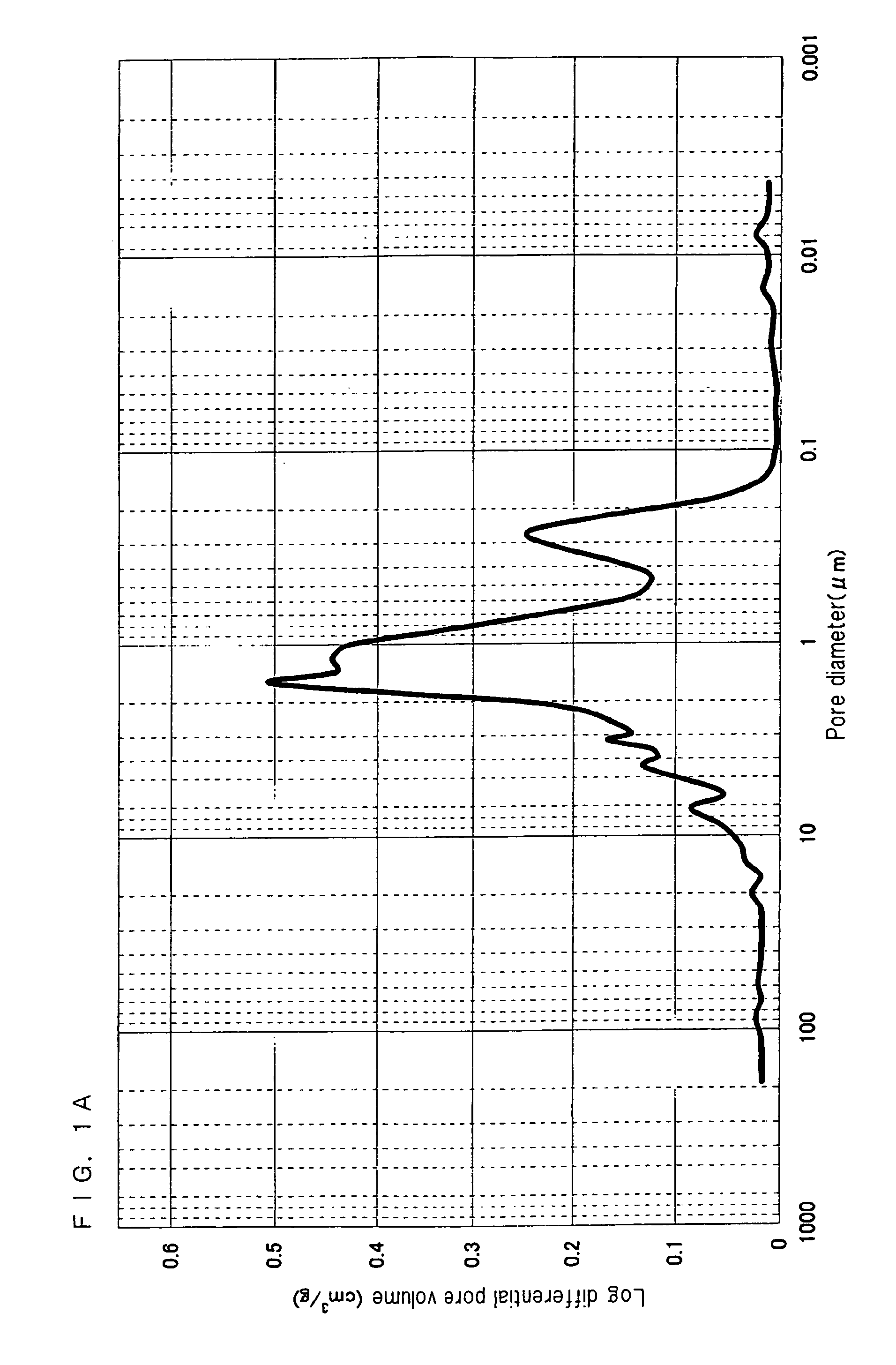
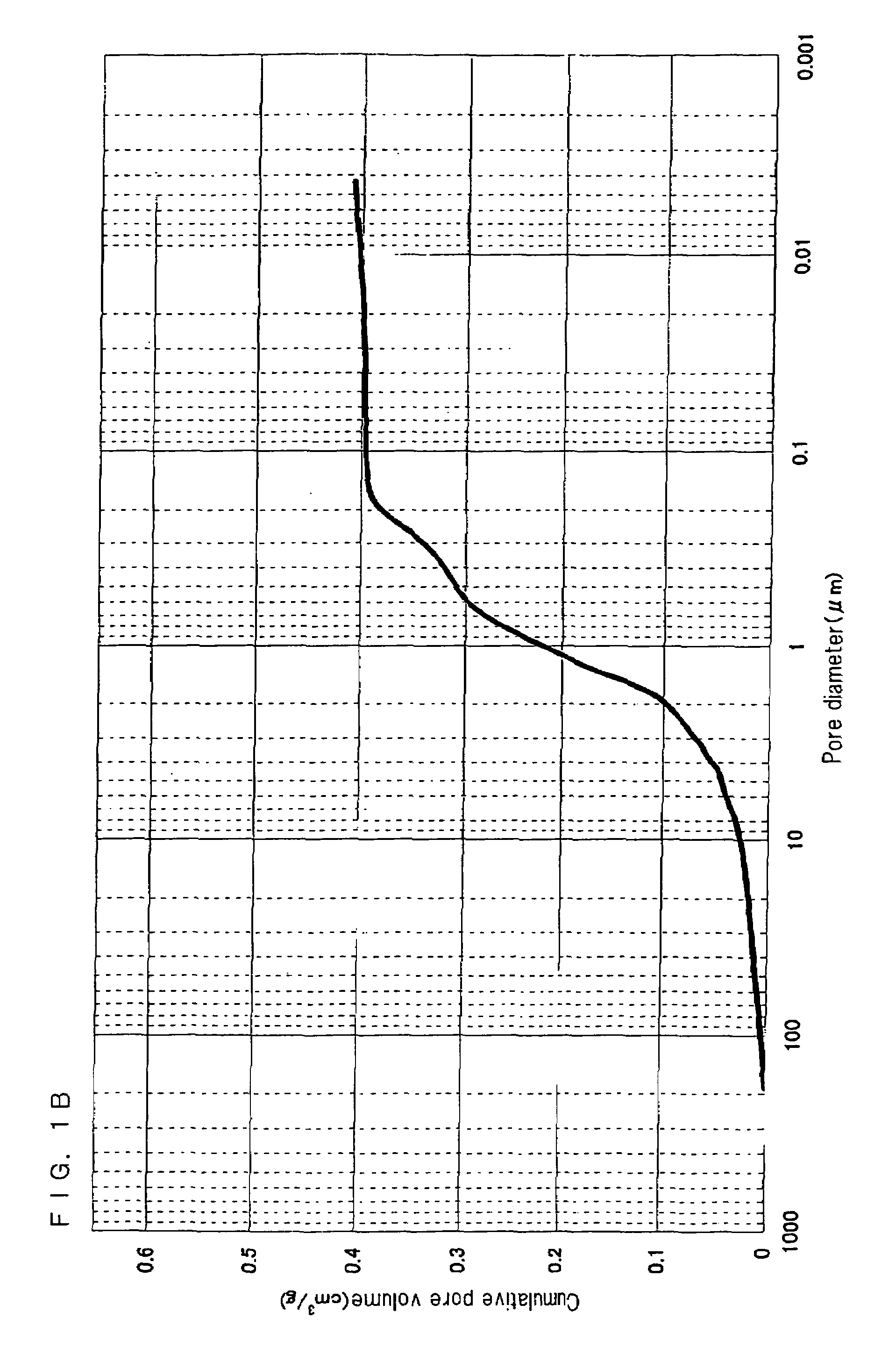
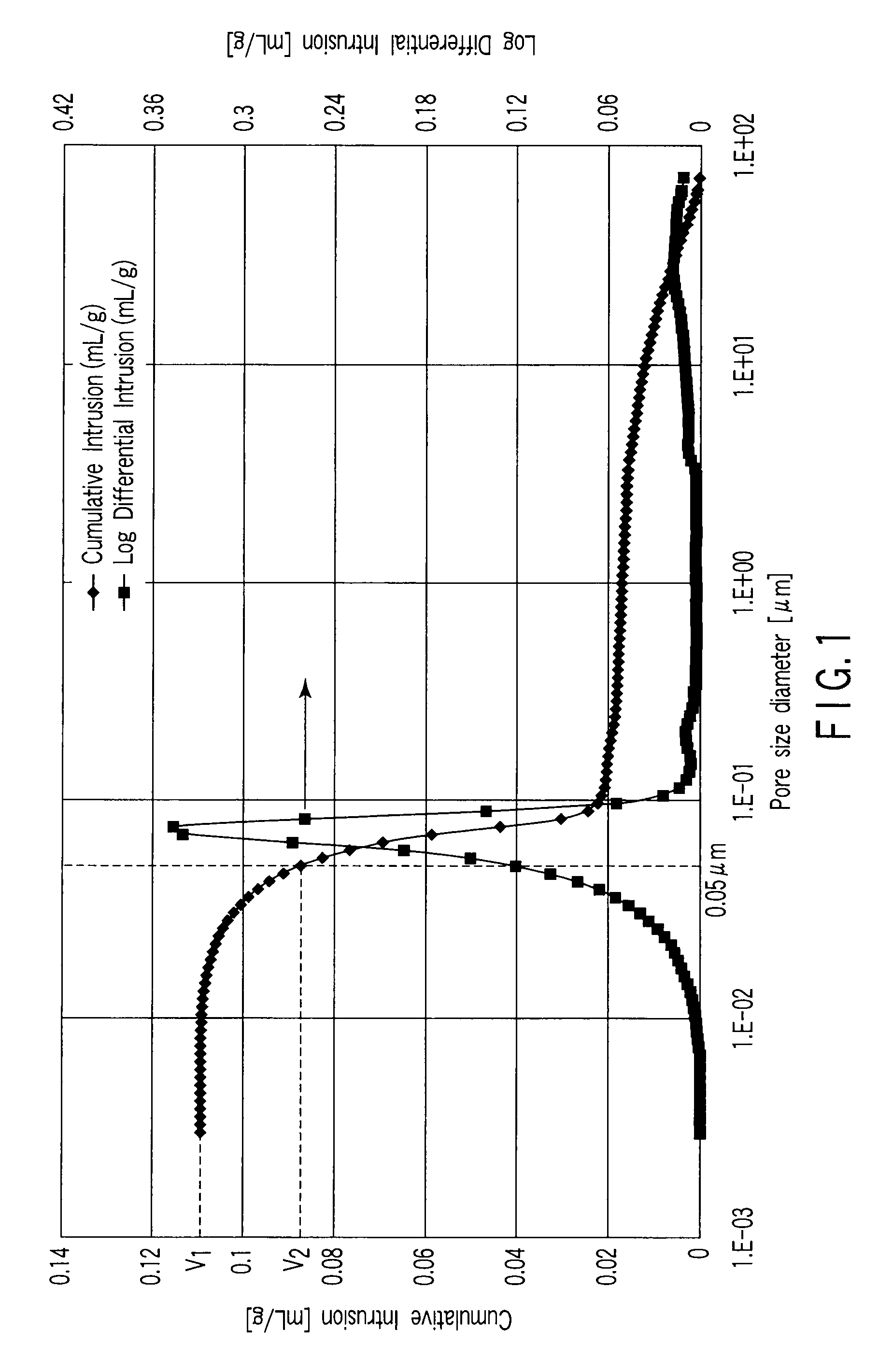
A nonaqueous electrolyte battery includes a positive electrode, a negative electrode and a nonaqueous electrolyte. The negative electrode contains a lithium compound and a negative electrode current collector supporting the lithium compound. A log differential intrusion curve obtained when a pore size diameter of the negative electrode is measured by mercury porosimetry has a peak in a pore size diameter range of 0.03 to 0.2 μm and attenuates with a decrease in pore size diameter from an apex of the peak. A specific surface area (excluding a weight of the negative electrode current collector) of pores of the negative electrode found by mercury porosimetry is 6 to 100 m2 / g. A ratio of a volume of pores having a pore size diameter of 0.05 μm or less to a total pore volume is 20% or more.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Anode and secondary battery
InactiveUS20080305395A1Small sizeImprove performanceElectrochemical processing of electrodesSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsSiliconPorosimetry
A battery capable of improving cycle characteristics is provided. An anode includes: an anode current collector, and an anode active material layer arranged on the anode current collector, in which the anode active material layer includes an anode active material including silicon (Si), and including a pore group with a diameter ranging from 3 nm to 50 nm both inclusive, and the volumetric capacity per unit weight of silicon of the pore group with a diameter ranging from 3 nm to 50 nm both inclusive is 0.2 cm3 / g or less, the volumetric capacity being measured by mercury porosimetry using a mercury porosimeter.
Owner:SONY CORP
Examination of porosity by NMR and intrusion porosimetry
ActiveUS20140002081A1Analysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceElectric/magnetic detectionElectromagnetic radiationSpherical equivalent
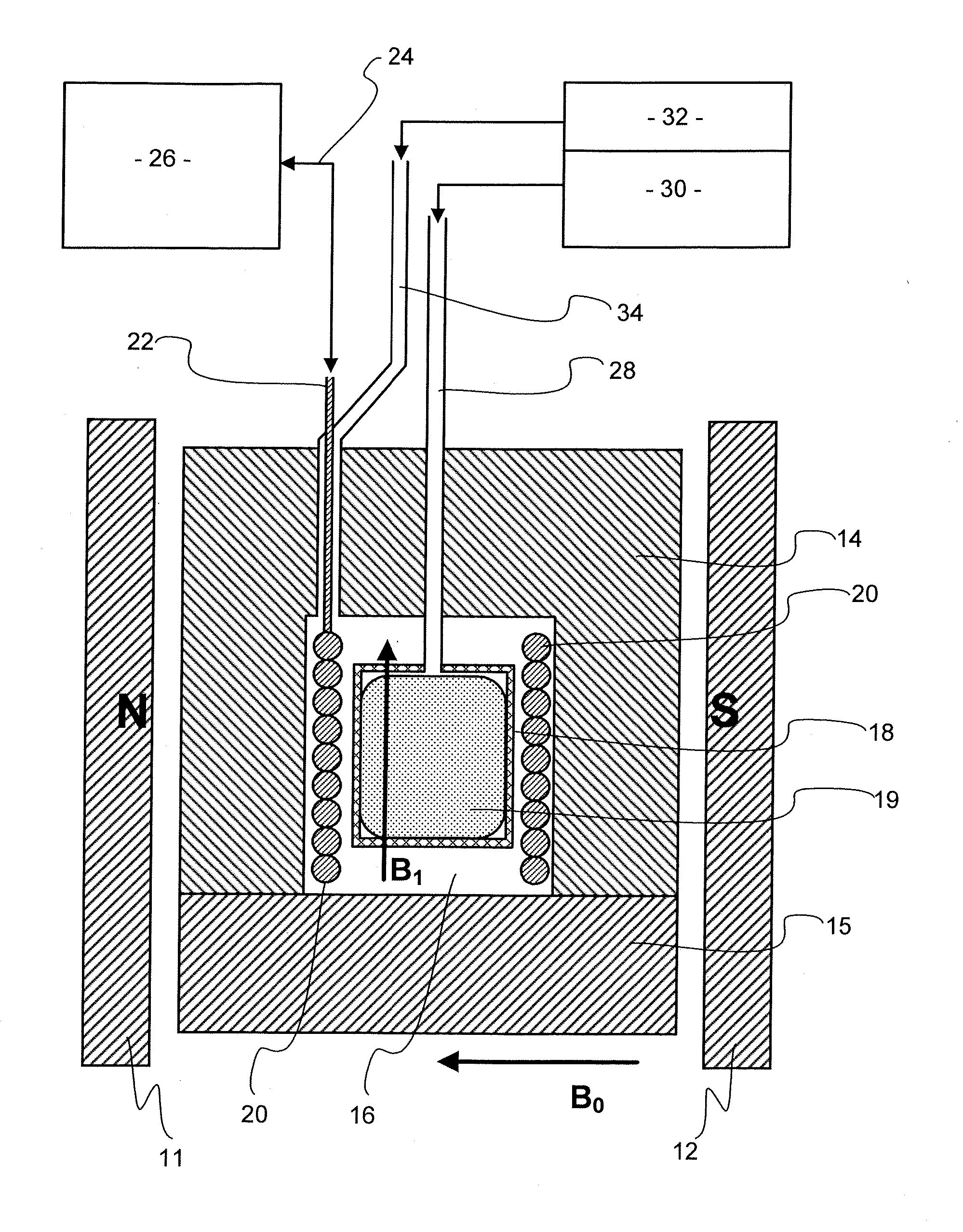
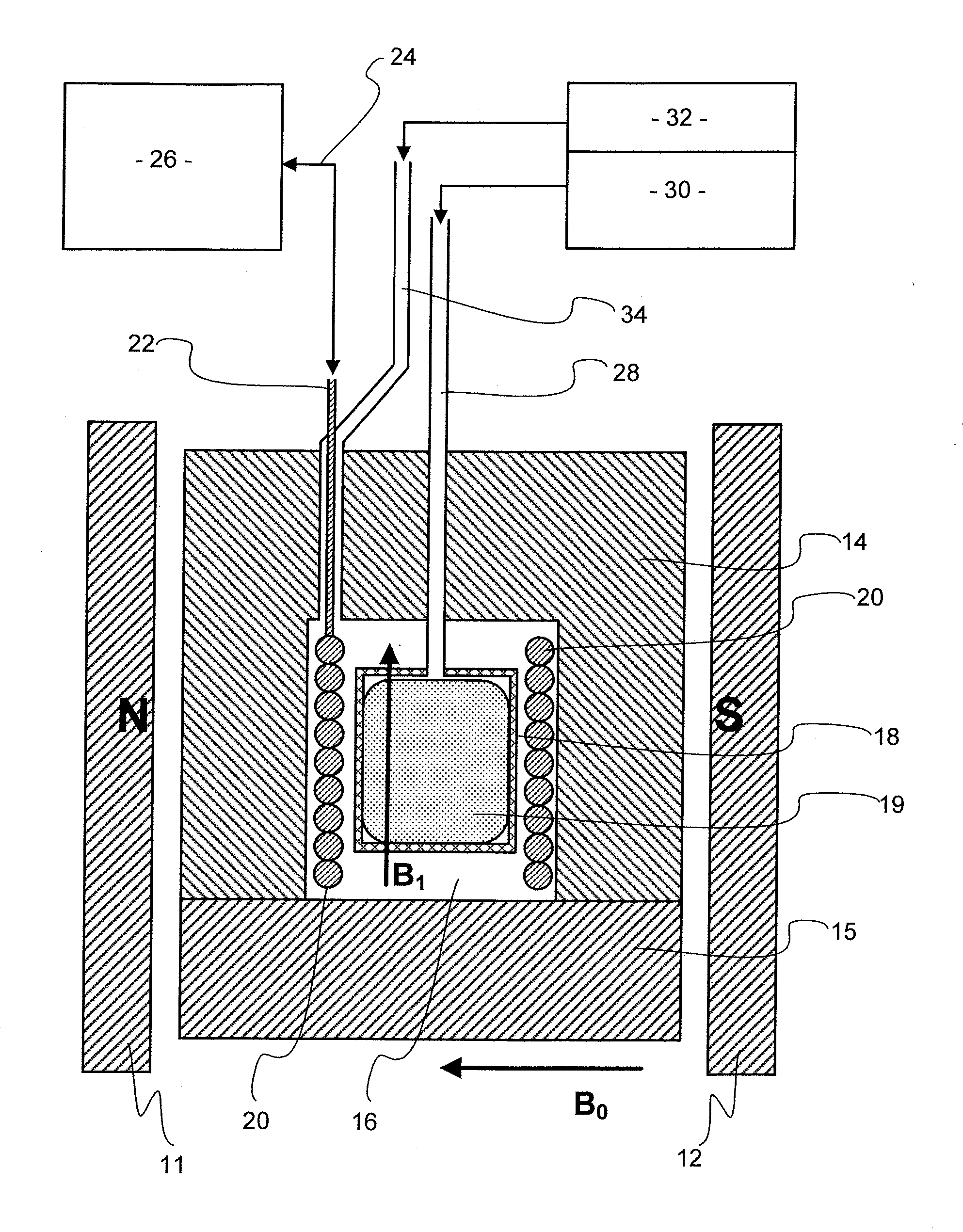
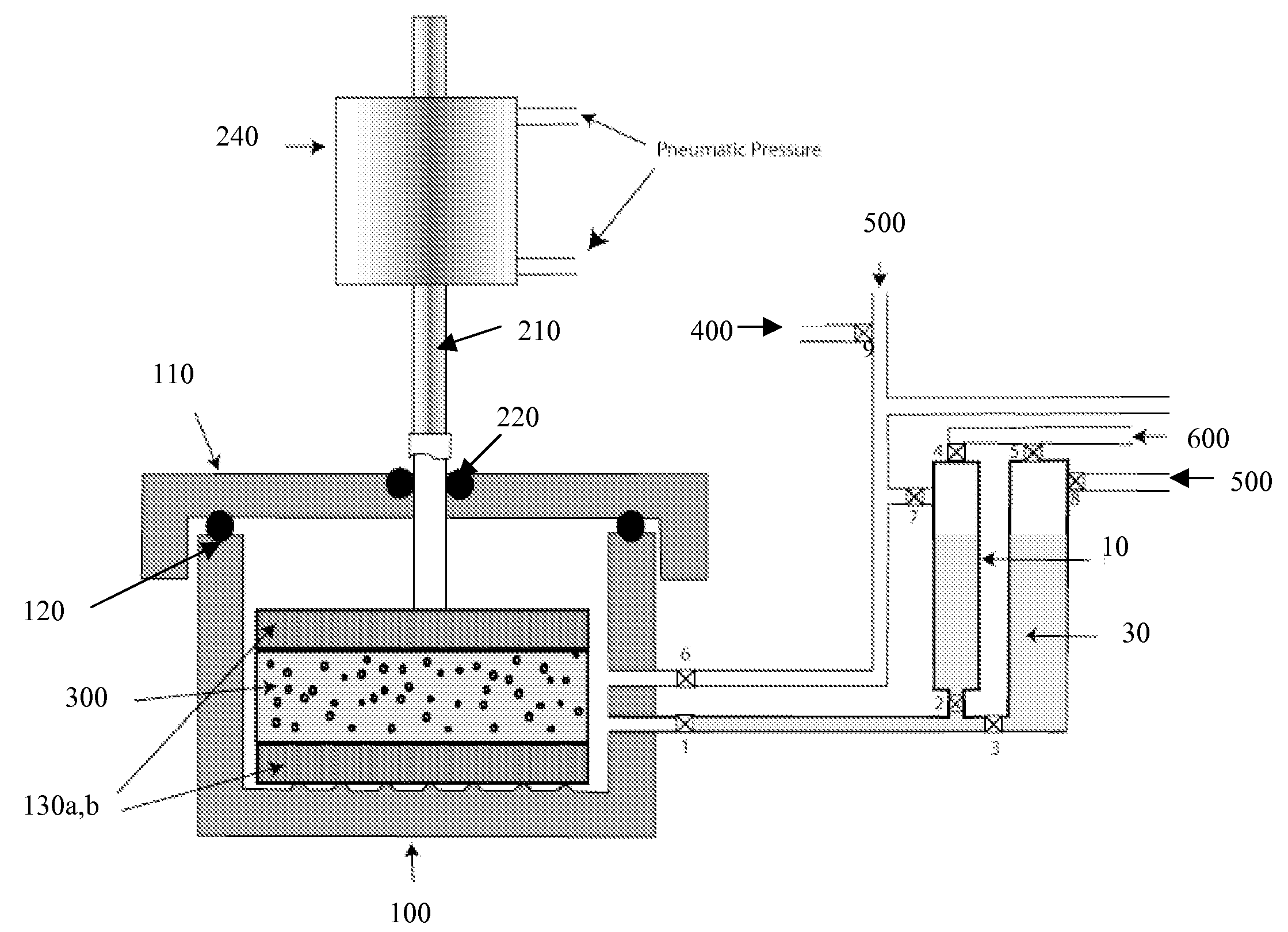
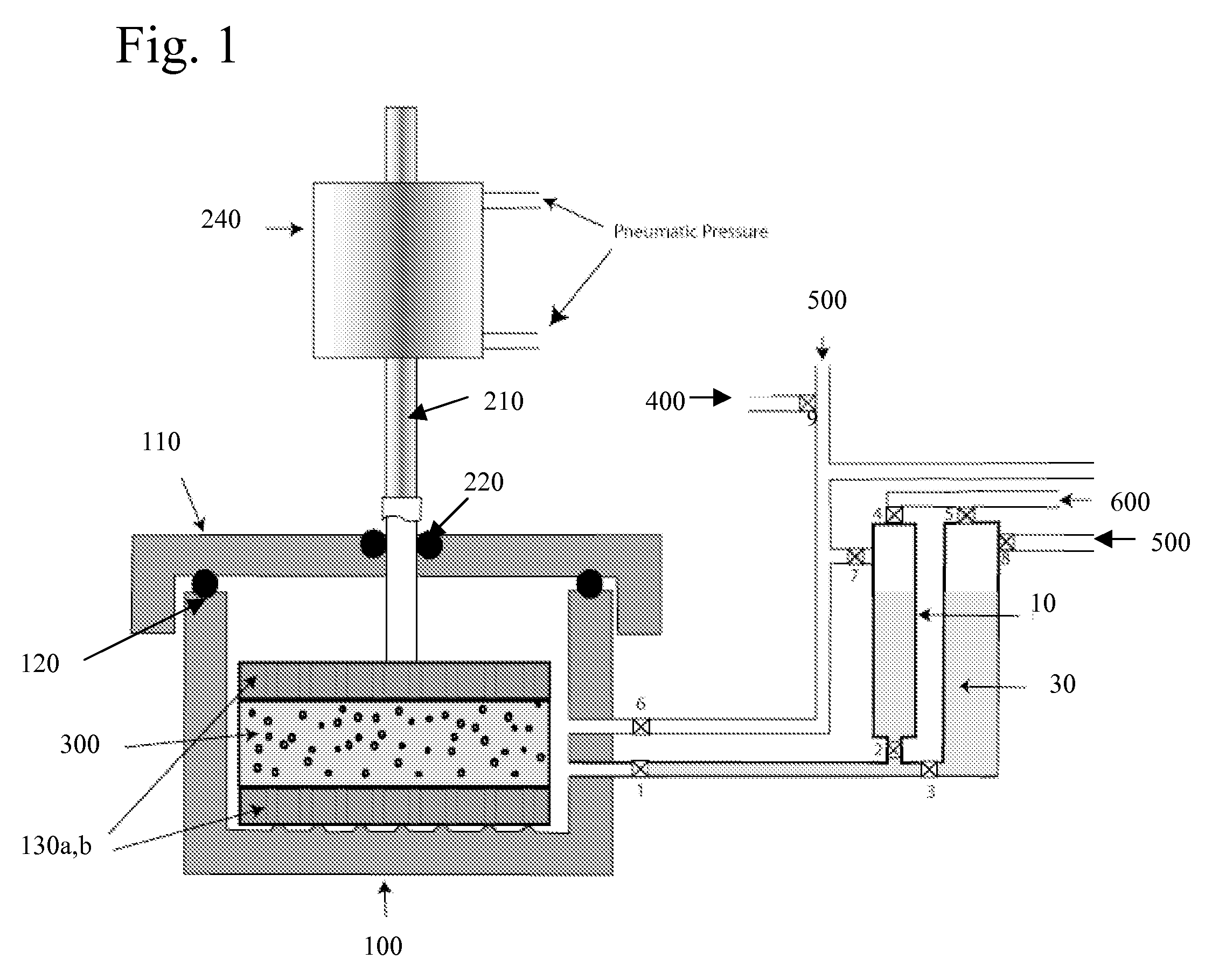
Properties of a porous solid sample 19, which may be a core of rock taken from below ground are carried out using apparatus which performs both nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and porosimetry measurements. The apparatus has a magnet 11,12 providing a magnetic field and a radio frequency coil 20 for transmitting and / or receiving electromagnetic radiation so as to bring about NMR in the magnetic field, a pressure vessel 14, 15 to hold a sample 19 within the magnetic field, a supply of a non-wetting liquid connected to the vessel, means to apply pressure to the non-wetting liquid to force liquid into pores of the sample 19 means to measure applied pressure of the non-wetting liquid and means to measure volume thereof taken up by the sample. The pressure of non-wetting liquid may be increased in steps, using intruded liquid volume at each step to give a measurement of pore throat size using NMR at each step to give a measure of pore size such as diameter of equivalent sphere. The non-wetting liquid may be mercury and NMR may observe the Knight shift of 99 Hg.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Honeycomb filter
ActiveUS8444739B2Efficient trappingLower performance requirementsCombination devicesGas treatmentSurface layerFiltration
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Honeycomb structure, exhaust gas purifying apparatus, and method for producing honeycomb structure
ActiveUS20090238733A1Improve performanceLow pressure lossCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationFiberPore distribution
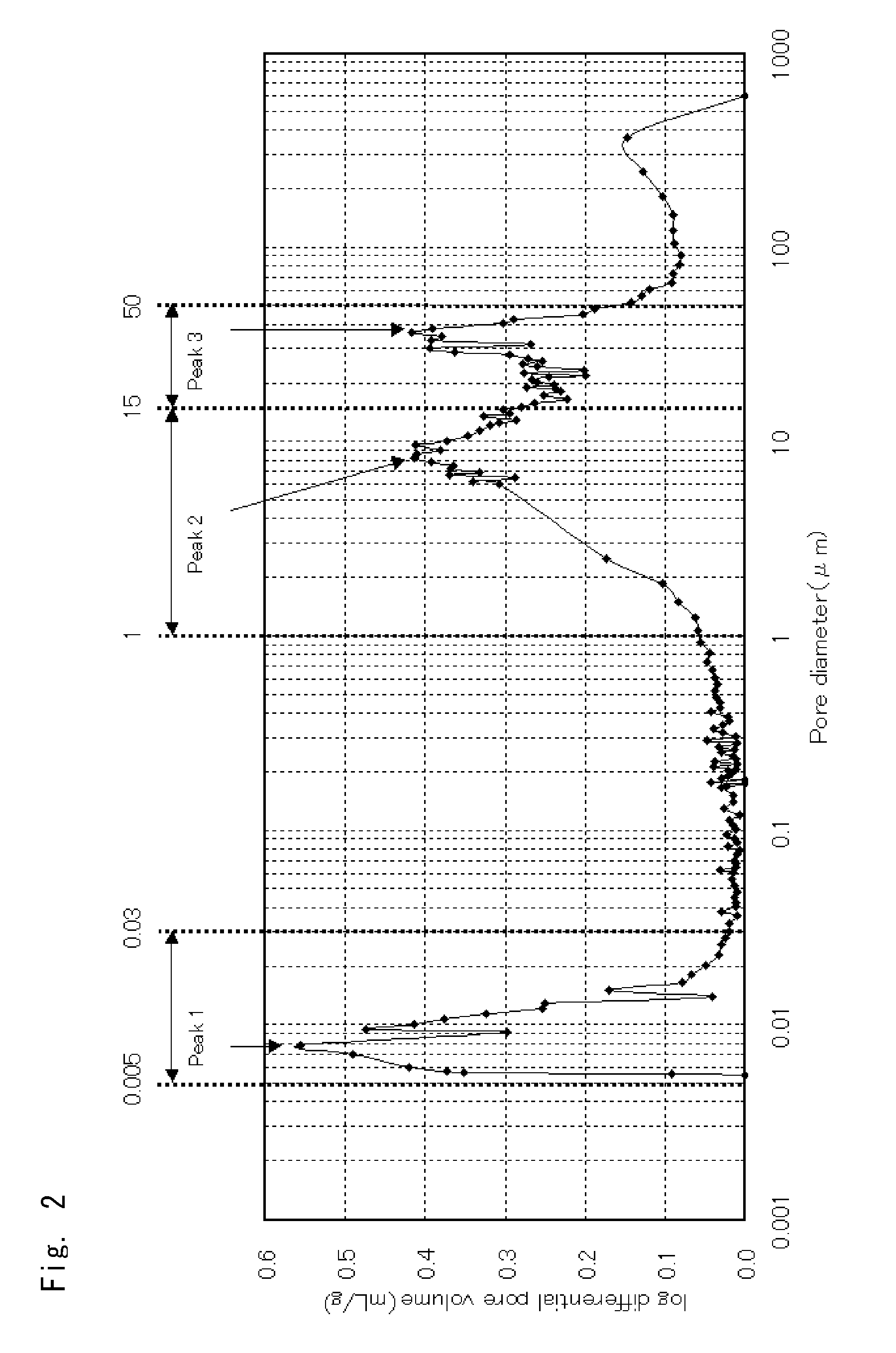
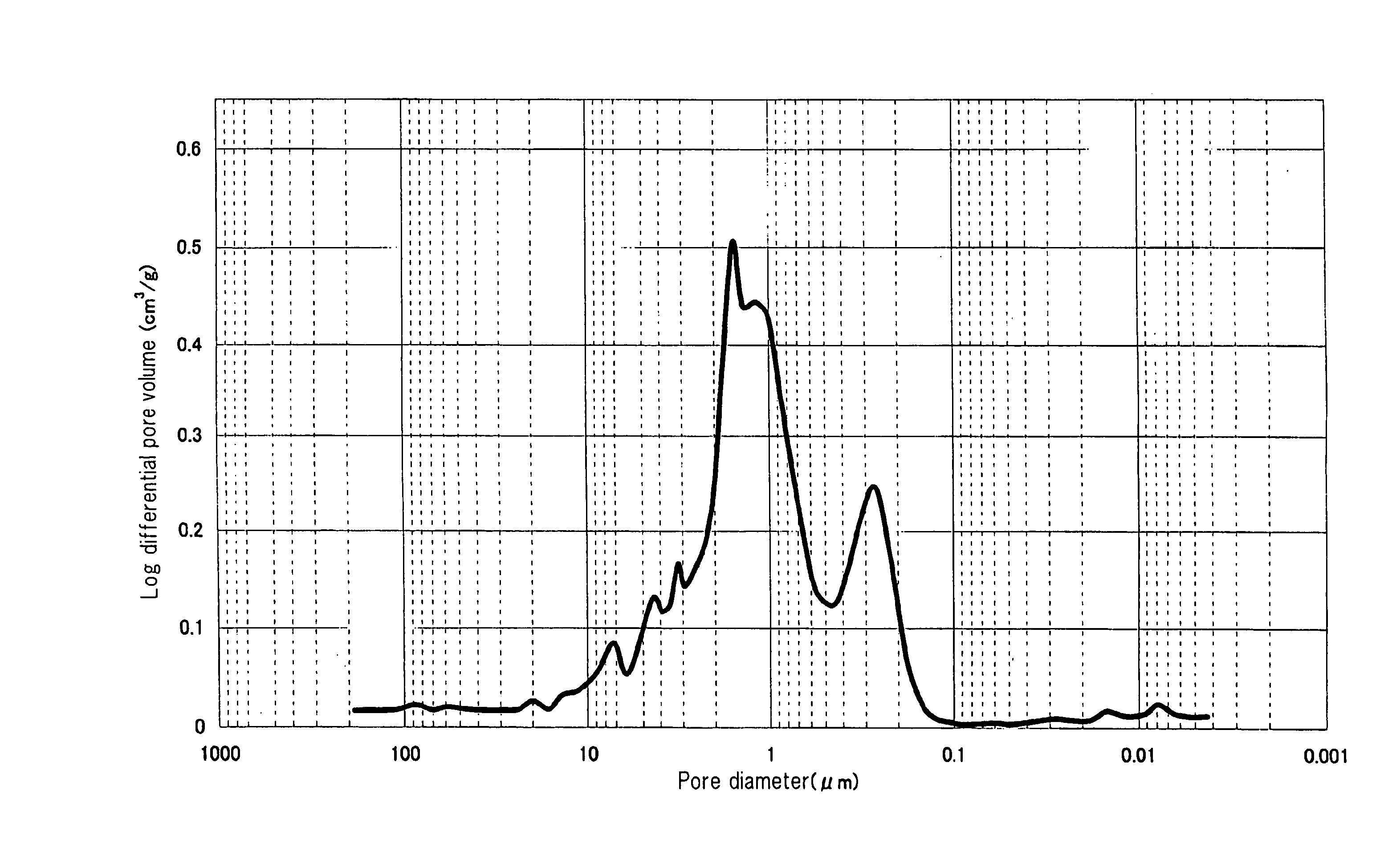
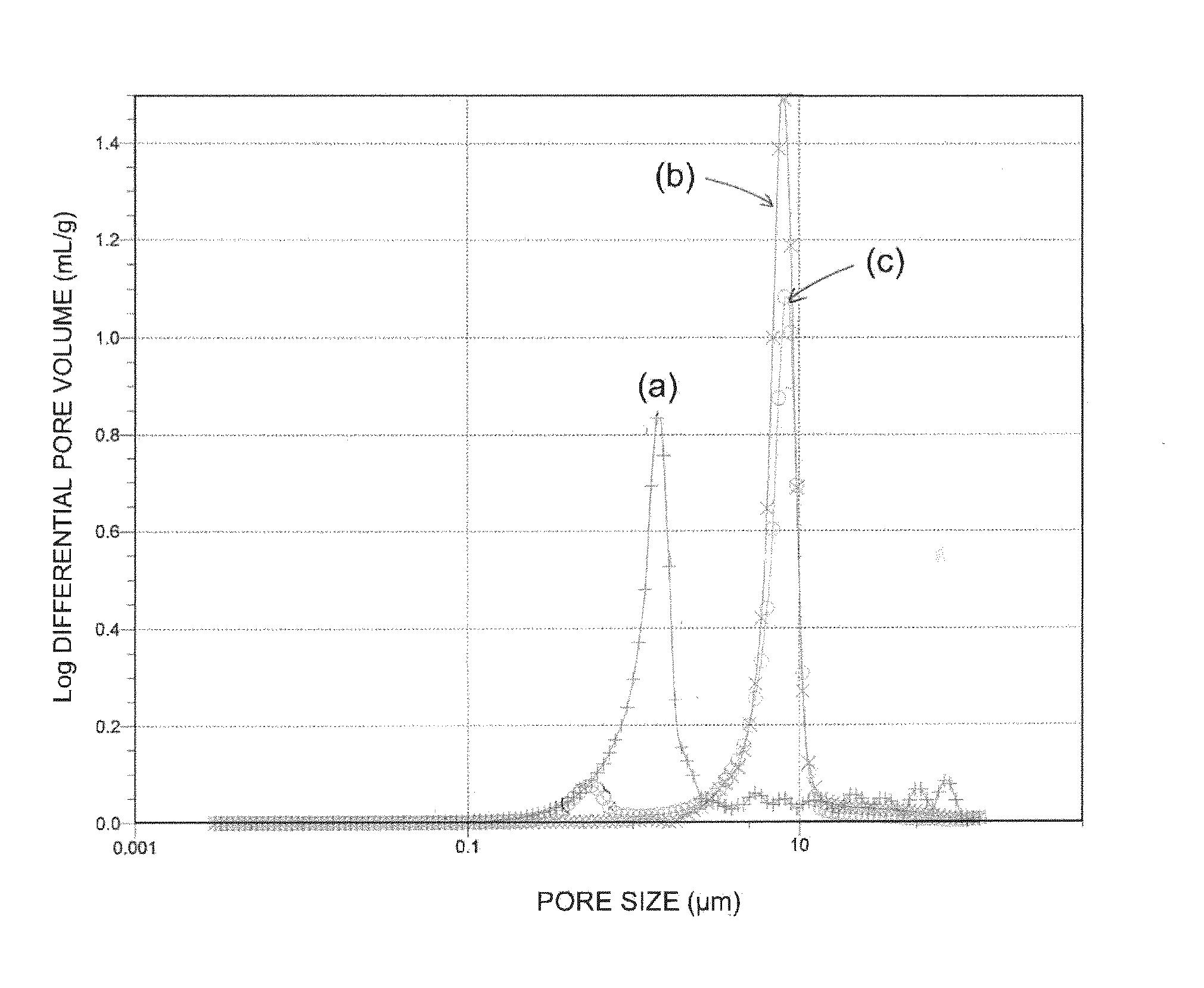
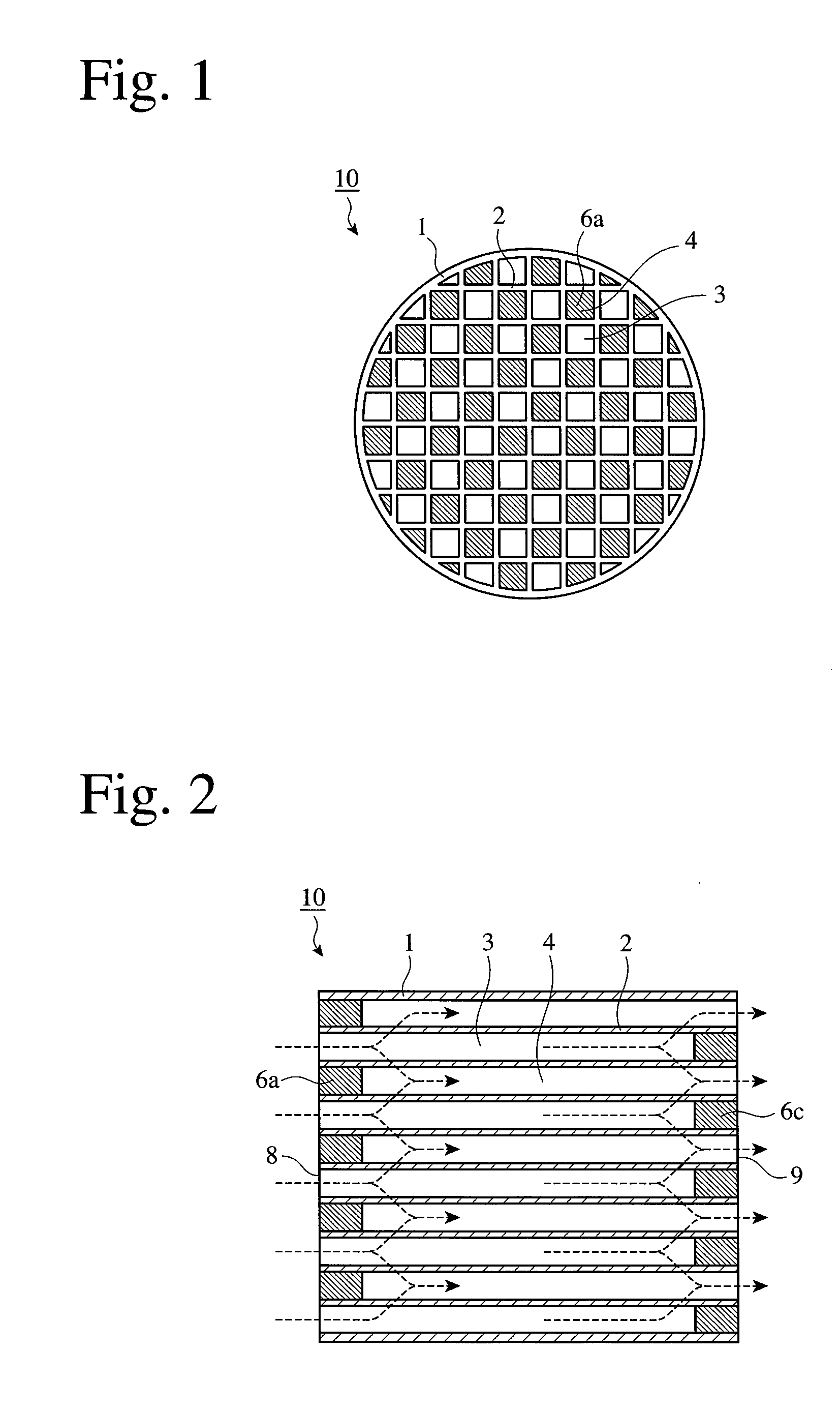
A honeycomb structure includes at least one honeycomb member including inorganic fibers and having walls extending along a longitudinal direction to define cells. A catalyst is provided on the wall in an amount of at least about 100 g and at most about 400 g per liter of volume of the honeycomb structure. The honeycomb member has a pore distribution measured using mercury porosimetry in which a pore distribution curve has a first peak in a range from about 0.005 μm to about 0.03 μm of a pore diameter, a second peak in a range from about 1 μm to about 15 μm of the pore diameter, and a third peak in a range from about 15 μm to about 50 μm of the pore diameter, where the curve is drawn by plotting the pore diameter (μm) on an X-axis and a log differential pore volume (mL / g) on a Y-axis.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Honeycomb filter
ActiveUS20120244042A1Improve performanceEfficient removalCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationPore distributionHoneycomb
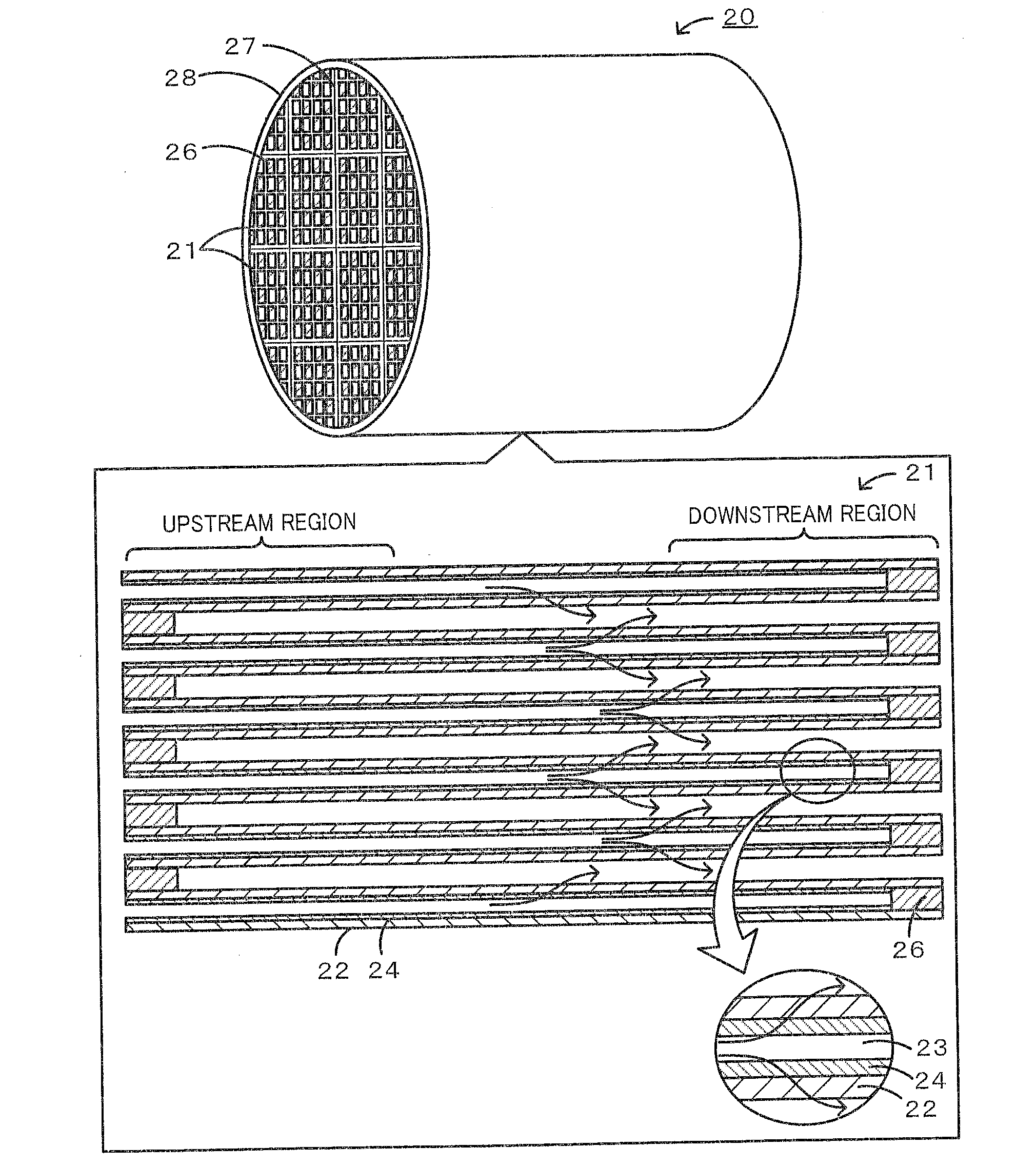
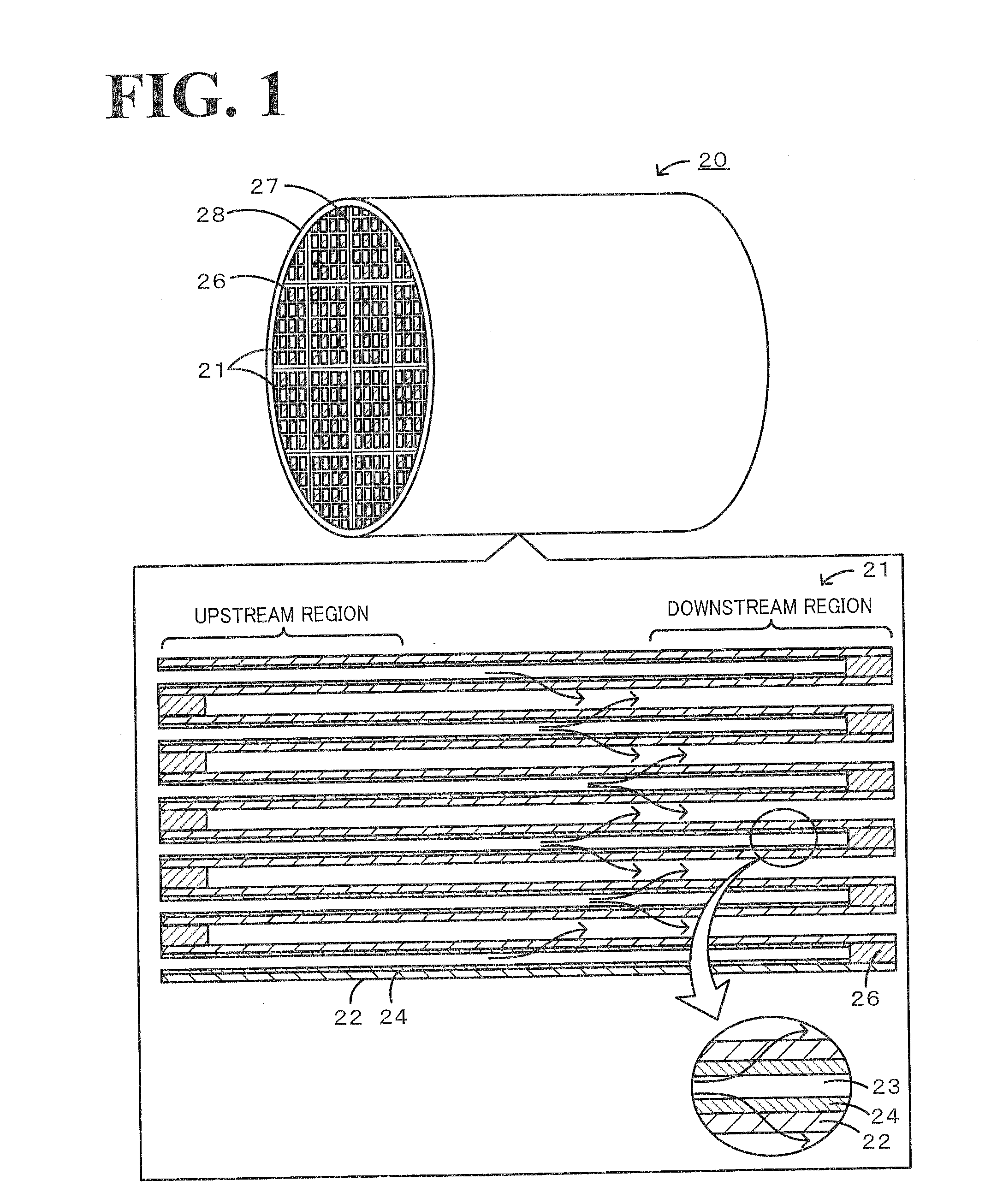
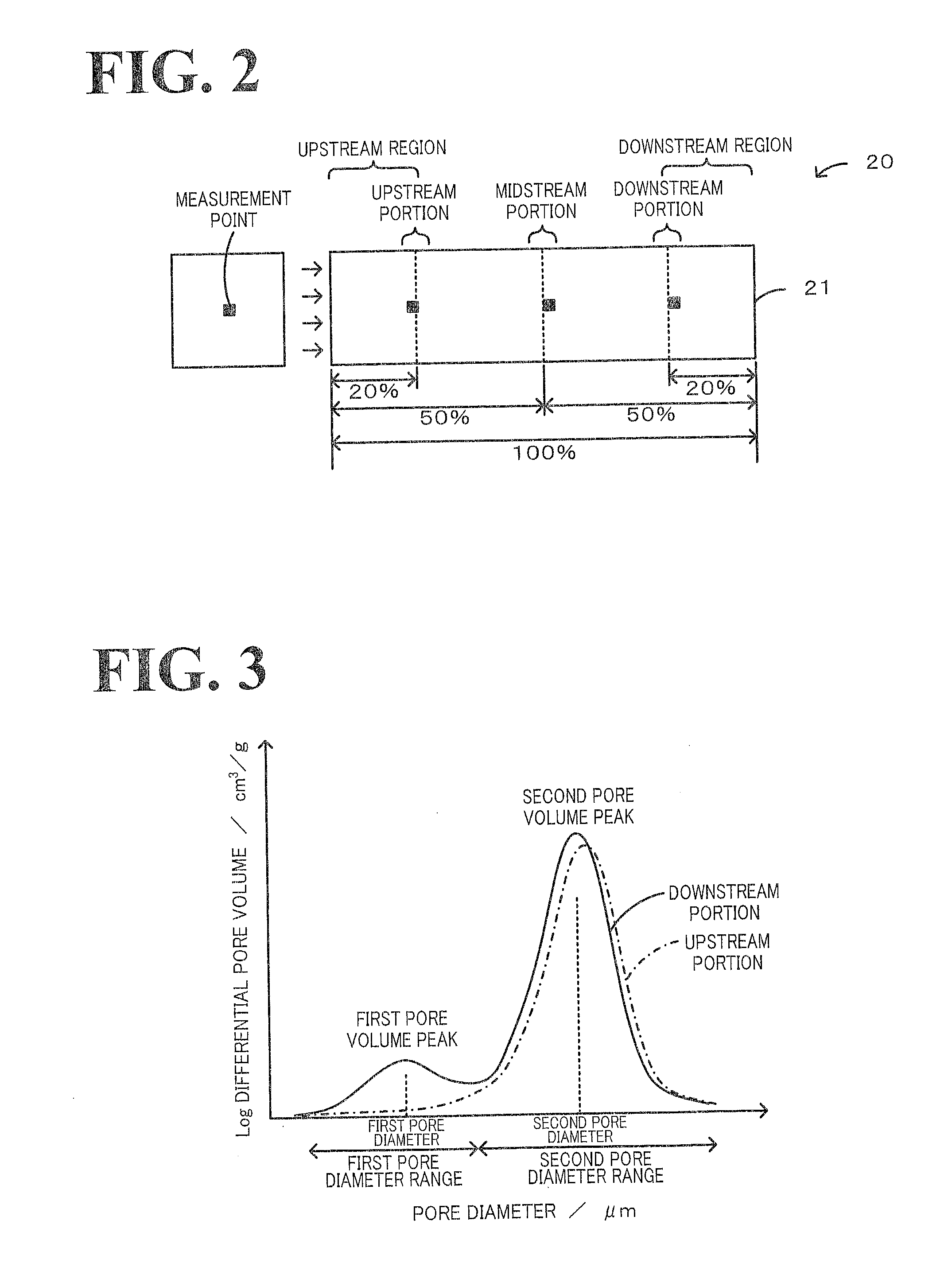
In a honeycomb filter 20, partition portions and trapping layers are formed such that a pore volume difference that is obtained from pore distributions measured by mercury porosimetry and is a difference in volume of pores having a diameter of 10 μm or less between the downstream portion and the upstream portion of the honeycomb filter, is in the range of 0.01 cm3 / g or more and 0.08 cm3 / g or less. In the honeycomb filter, in the downstream portion, a first pore volume peak is present in a first pore diameter range of 2 μm or more and 9 μm or less and a second pore volume peak that is higher than the first pore volume peak is present in a second pore diameter range of 10 μm or more and 25 μm or less.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Catalyst for production of ethylene oxide and method for production of ethylene oxide
InactiveUS20080091038A1High selectivityOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPore distributionEthylene oxide
A catalyst that enables to produce ethylene oxide in a high selectivity and a method for the production of ethylene oxide using the catalyst are provided. In the catalyst for the production of ethylene oxide, wherein the catalyst component is supported by a carrier, a carrier containing α-alumina as the main component which has at least two peaks in the range of pore diameter of 0.01-100 μm and at least one peak of the above peaks is present in the range of pore diameter of 0.01-1.0 μm in the pore distribution measured by mercury porosimetry is adopted as said carrier.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Surface-treated calcium carbonate, method for production thereof and resin composition comprising said calcium carbonate
InactiveCN1692076AImprove adhesionHigh impact strengthCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesOther chemical processesCalcium hydroxideSlurry
A surface-treated calcium carbonate, characterized in that it comprises calcium carbonate surface-treated with an organic agent for surface treatment, and has respective specific ranges of values for a BET specific surface area (Sw), a weight reduction by heat per unit specific surface area (As), an average pore diameter (Dxp) at which an increase in mercury penetration takes a maximum value in a specific range of pore diameter distribution by the mercury porosimetry, and an amount of the average pore diameter [a maximum value of the increase in mercury penetration (Dyp) / an average pore diameter (Dxp)] and a method for producing the calcium carbonate which comprises adding a complex-forming material to a calcium hydroxide slurry, followed by blowing a carbon dioxide gas, to synthesize calcium carbonate, adjusting a calcium carbonate concentration, followed by aging, and treating the surface of the product with an organic agent for surface treatment. The surface-treated calcium carbonate is useful especially for a resin and can be used for producing a resin composition having improved adhesion to an article to be attached and forming a tough coating film.
Owner:MARUO CALCIUM COMPANY
Thermal spray powder
ActiveUS20160244868A1Less poreImprove corrosion resistanceMolten spray coatingElectric discharge tubesThermal sprayingMetallurgy
Provided is a compact thermal spray powder suitable for forming a ceramic thermal spray coating which is compact and excels in durability. The thermal spray powder disclosed herein includes ceramic particles formed of a ceramic material with a melting point equal to or lower than 2000° C. The thermal spray powder is configured such that the peak top of a main peak is in a range of 10 μm or less in a log differential pore volume distribution obtained by a mercury porosimetry, and when the peak top of a second peak is at a fine pore size less than that of the peak top of the main peak, the ratio (H2 / H1) of the height H2 of the second peak to the height H1 of the main peak is 0.05 or less.
Owner:FUJIMI INCORPORATED
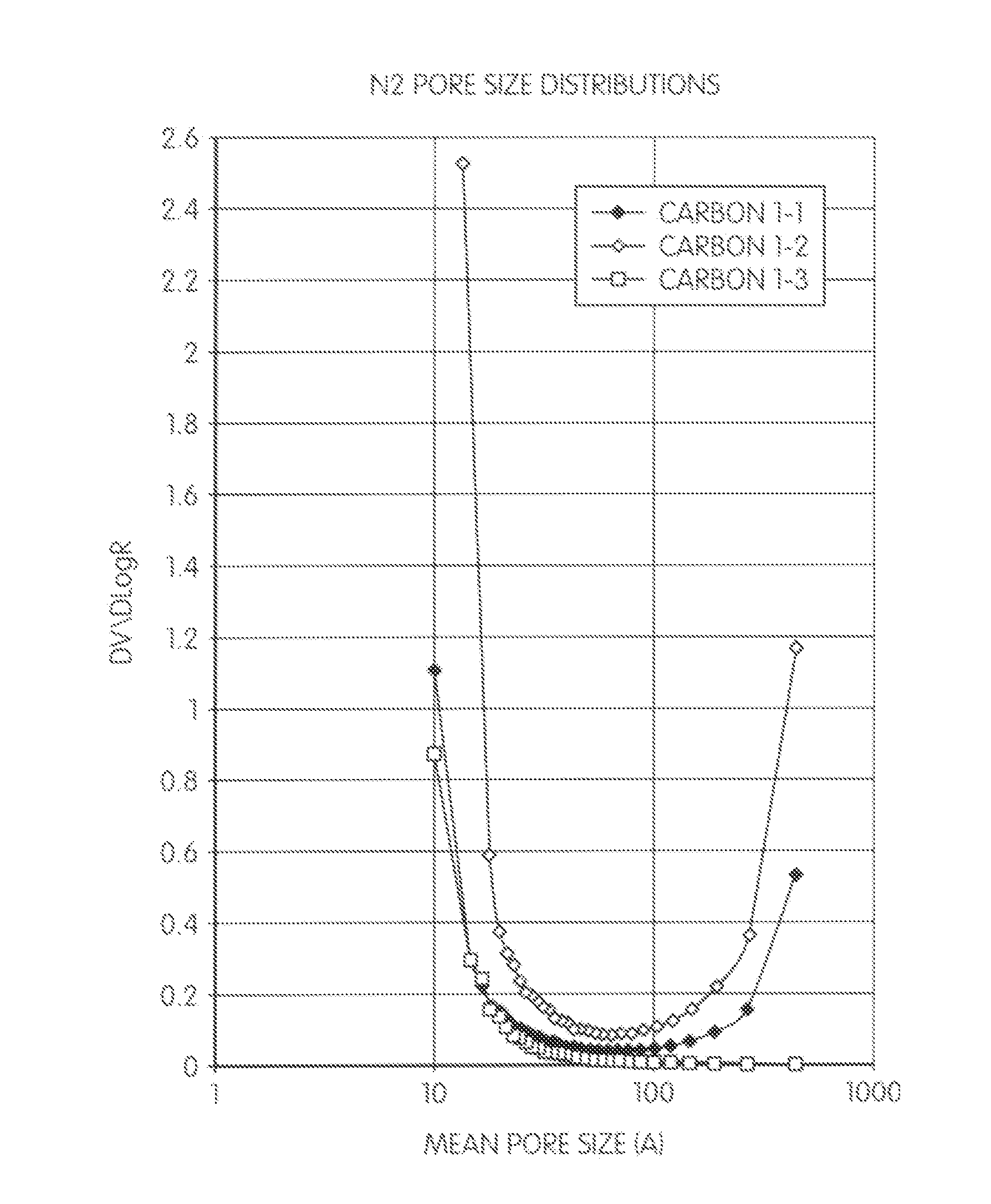
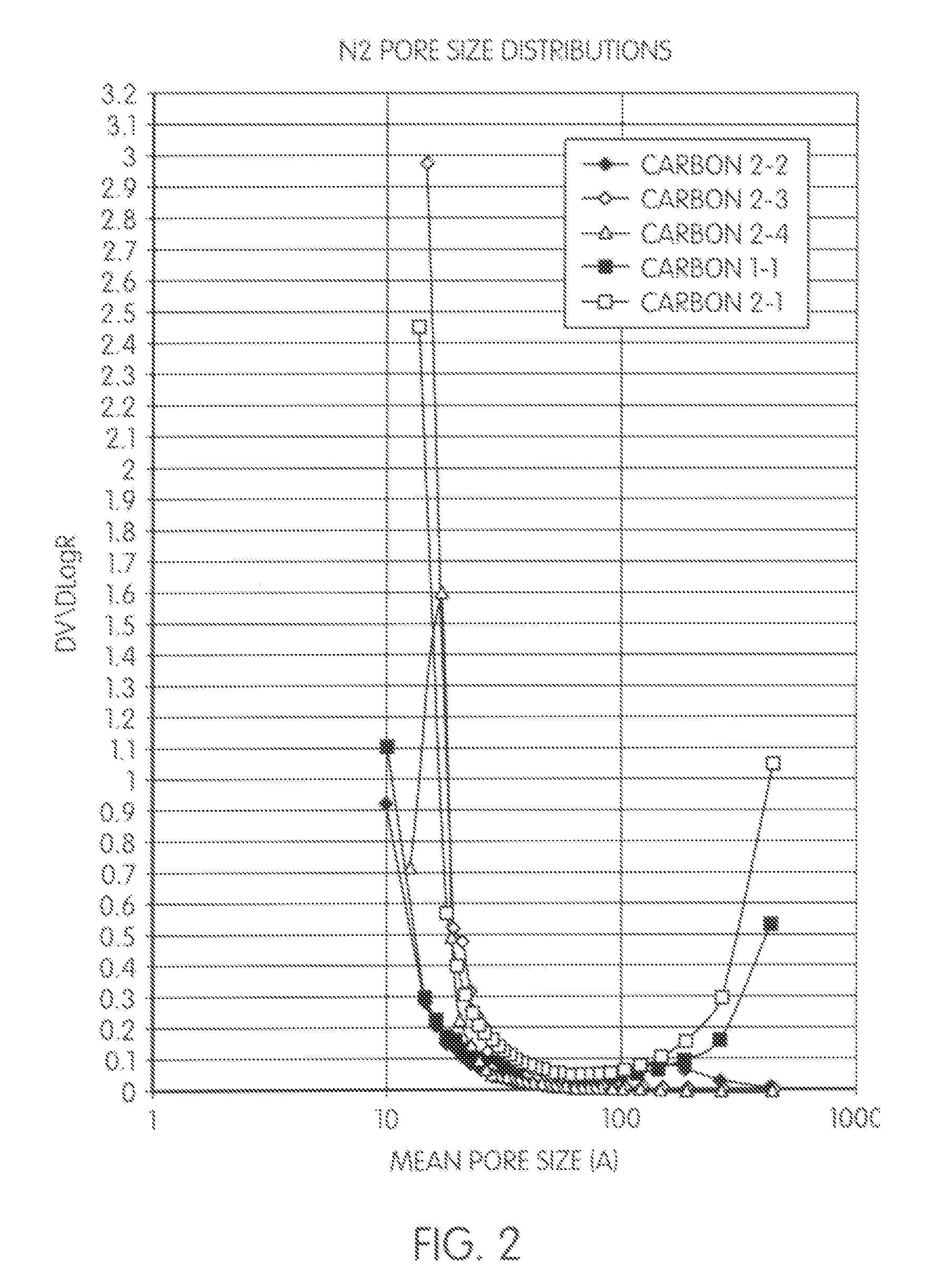
Porous carbons
InactiveUS20110097583A1Improve solubilityGood compatibilitySynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsCross-linkPorous carbon
Porous carbon is provided which is a carbonization and optionally an activation product of a precursor resin, which has a pore structure that, as estimated by nitrogen adsorption porosimetry, comprises micropores and mesopores / macropores, said micropores and mesopores / macropores being in a bimodal distribution with few pores of size 2-10 nm, and the mesopores / macropores providing escape routes for volatile products during carbonisation of the precursor resin.The porous carbon can be made by a method which comprises (a) forming a precursor resin by reacting a nucleophilic component which comprises a phenolic compound or a phenol condensation prepolymer optionally with one or more modifying reagents with an electrophilic cross-linking agent selected from formaldehyde, paraformaldehyde, furfural and hexamethylene tetramine in solution in a pore former e.g. ethylene glycol so that a phase separation occurs between high molecular weight domains and voids of lower molecular weight material and the pore former increases the material in the voids and gives rise to the mesopores in the precursor resin; (b) removing the pore former from the precursor resin; and (c) carbonizing the precursor resin in an inert atmosphere at a temperature from 600° C. upwards, micropores developing during said carbonization so that the carbonized material comprises (a) micropores of diameter of up to 2 nm and (b) mesopores of diameter of 2-50 nm and optionally macropores of diameter >50 nm.
Owner:BRITISH AMERICAN TOBACCO (INVESTMENTS) LTD
Catalyst and process for hydrocracking hydrocarbon-containing feedstocks
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Process for oligomerizing olefins using a silica-alumina based catalyst
An olefin oligomerization process employs a particular silica-alumina catalyst which comprises a non zeolitic support based on silica-alumina containing a quantity of more than 5% by weight and 95% by weight or less of silica (SiO2) and has the following characteristics: a mean pore diameter, measured by mercury porosimetry, in the range 20 to 140 Å; a total pore volume, measured by mercury porosimetry, in the range 0.1 ml / g to 0.6 ml / g; a total pore volume, measured by nitrogen porosimetry, in the range 0.1 ml / g to 0.6 ml / g; a BET specific surface area in the range 100 to 550 m2 / g; a pore volume, measured by mercury porosimetry, included in pores with a diameter of more than 140 Å, of less than 0.1 ml / g; a pore volume, measured by mercury porosimetry, included in pores with a diameter of more than 160 Å, of less than 0.1 ml / g; a pore volume, measured by mercury porosimetry, included in pores with a diameter of more than 200 Å, of less than 0.1 ml / g; a pore volume, measured by mercury porosimetry, included in pores with a diameter of more than 500 Å, of less than 0.1 ml / g; and an X ray diffraction diagram containing at least the principal characteristic peaks of at least one of the transition aluminas included in the group composed of alpha, rho, khi, eta, gamma, kappa, theta and delta aluminas.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Anode and battery
ActiveUS20090035651A1Small sizeImprove performanceFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsSiliconPorosimetry
A battery capable of improving cycle characteristics is provided. An anode includes: an anode active material layer including an anode active material on an anode current collector, the anode active material including silicon (Si) and having a plurality of pores, in which after electrode reaction, the volumetric capacity of a pore group with a diameter ranging from 3 nm to 200 nm both inclusive per unit weight of silicon is 0.3 cm3 / g or less, and the rate of change in the amount of mercury intruded into the plurality of pores is distributed so as to have a peak in a diameter range from 200 nm to 15000 nm both inclusive, the rate of change in the amount of mercury intruded being measured by mercury porosimetry.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Ceramic honeycomb structure and its production method
ActiveUS8636821B2Reduce deteriorationRaise the ratioCombination devicesGas treatmentPore distributionMetallurgy
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Crystallized material with hierarchical porosity containing silicon
InactiveUS20110033375A1Facilitated DiffusionAluminium compoundsMolecular sieve catalystsMaximum diameterNitrogen
Hierarchical porosity material consisting of at least two elementary spherical particles having a maximum diameter of 200 microns, at least one of said spherical particles comprises at least one matrix based on silicon oxide and exhibiting crystallized walls, said material having a macropore volume measured by mercury porosimetry ranging between 0.05 and 1 ml / g, a mesopore volume measured by nitrogen volumetric analysis ranging between 0.01 and 1 ml / g and a micropore volume measured by nitrogen volumetric analysis ranging between 0.03 and 0.4 ml / g. The preparation of said material and use of same as adsorbent or as acidic solid is also described.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
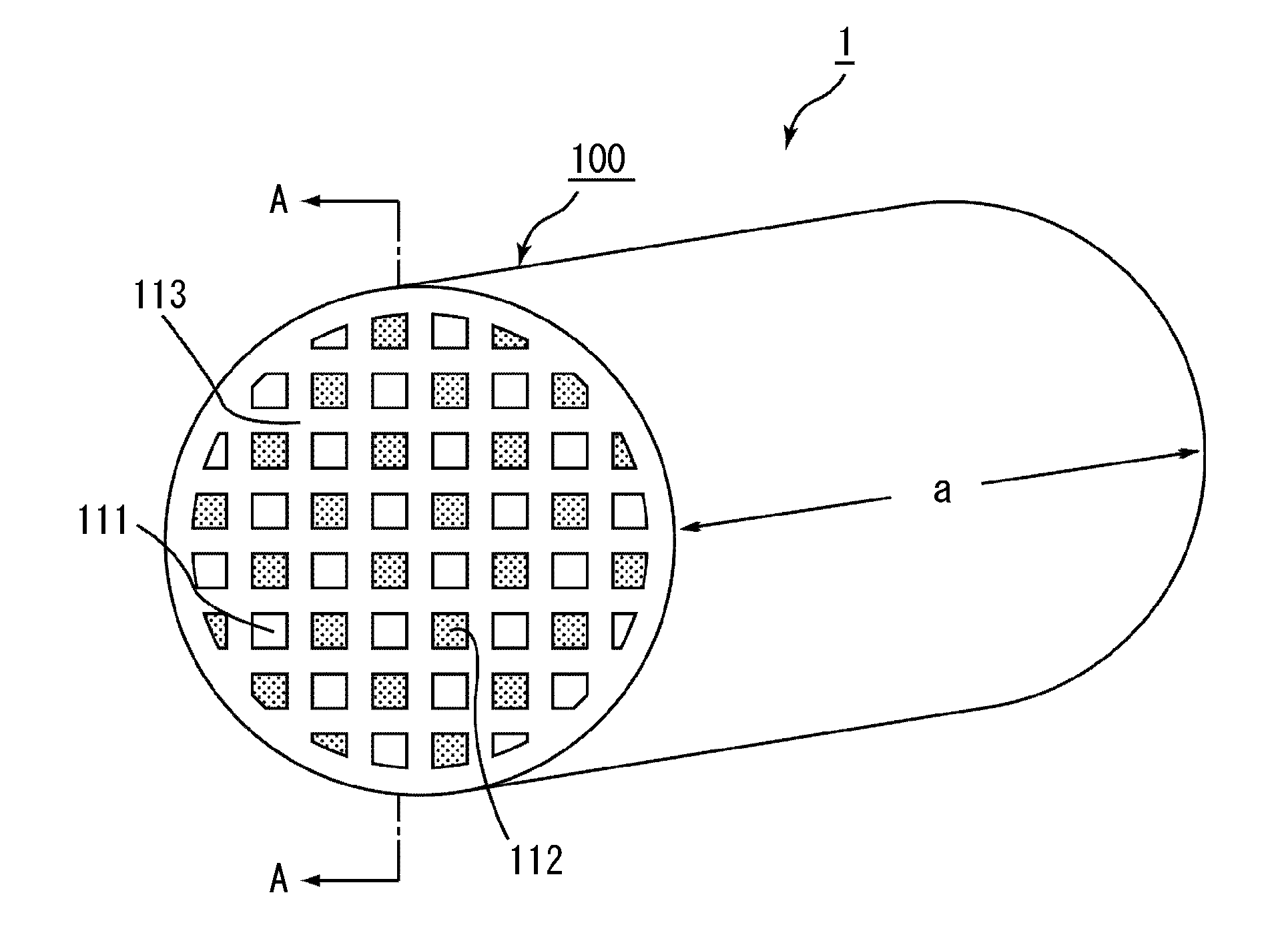
Honeycomb filter and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20060107641A1Increased pressure lossAccurate detectionCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentHoneycombPore diameter
A honeycomb filter includes partition walls forming a plurality of cells extending in one direction, and plugging sections alternately plugging the cells at the ends of the honeycomb filter, the partition walls being formed of a porous base material having a porosity of 45 to 70%. When the average pore size of the base material measured by mercury porosimetry is (A) μm and the average pore size of the base material measured by a bubble point method is (B) μm, the average pore size differential rate expressed by “{(A−B) / B}*100” is 35% or less, and the maximum pore size of the base material measured by the bubble point method is 150 μm or less.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Niobium or tantalum powder and method for production thereof, and solid electrolytic capacitor
InactiveCN1437517AIncrease capacityLower ESRElectrolytic capacitorsTransportation and packagingElectrolysisPore distribution
A niobium or tantalum powder characterized in that it comprises aggregates of primary particles of niobium or tantalum and has a pore distribution having a peak in the range of 1 to 20 mu m as measured by the mercury porosimetry. The niobium or tantalum powder comprises aggregates having large pores, which communicate with voids being present between primary particles and facilitate the permeation of an electrolyte over the whole of the inside of each aggregate. Accordingly, a solid electrolytic capacitor having an anode electrode prepared by using the niobium or tantalum powder has a high capacity and also a low ESR.
Owner:CABOT SUPERMETALS
Hydrocracking process using a zeolite modified by basic treatment
ActiveUS20110108459A1Good choiceHigh degreeAluminium compoundsMolecular sieve catalystsActive phaseChemistry
The present invention describes a hydrocracking and / or hydrotreatment process using a catalyst comprising an active phase containing at least one hydrogenating / dehydrogenating component selected from the group VIB elements and the non-precious elements of group VIII of the periodic table, used alone or in a mixture, and a support comprising at least one dealuminated zeolite Y having an overall initial atomic ratio of silicon to aluminium between 2.5 and 20, an initial weight fraction of extra-lattice aluminium atoms greater than 10%, relative to the total weight of aluminium present in the zeolite, an initial mesopore volume measured by nitrogen porosimetry greater than 0.07 ml·g−1 and an initial crystal lattice parameter a0 between 24.38 Å and 24.30 Å, said zeolite being modified by a) a stage of basic treatment comprising mixing said dealuminated zeolite Y with a basic aqueous solution, and at least one stage c) of thermal treatment.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Compression vacuapore for determination of pore structure characteristics of hydrophobic materials under compressive stress
InactiveUS20080276690A1Accurate pore structure characterizationAccurately applying controlled compressive stressPermeability/surface area analysisTest sampleControl manner
A method for determining pore structure characteristics of hydrophobic porous materials includes placing a test sample of material in the sample chamber of a porosimetry apparatus, creating a partial vacuum and evacuating the sample chamber to remove air, creating a partial vacuum and evacuating the penetrometer and storage vessel above the water level, releasing the vacuum in a controlled manner, so pressure is applied and water in the penetrometer enters the sample chamber and intrudes into pores of the sample, applying a measured amount of intrusion pressure and measuring the change in volume of water in the penetrometer, and determining pore structure characteristics of the sample based on the change in volume of water in the penetrometer. The method further includes an optional step of applying a desired amount of compressive stress on the sample prior to testing. Nonporous plates optionally are used to measure x-y plane pore structure.
Owner:POROUS MATERIALS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com