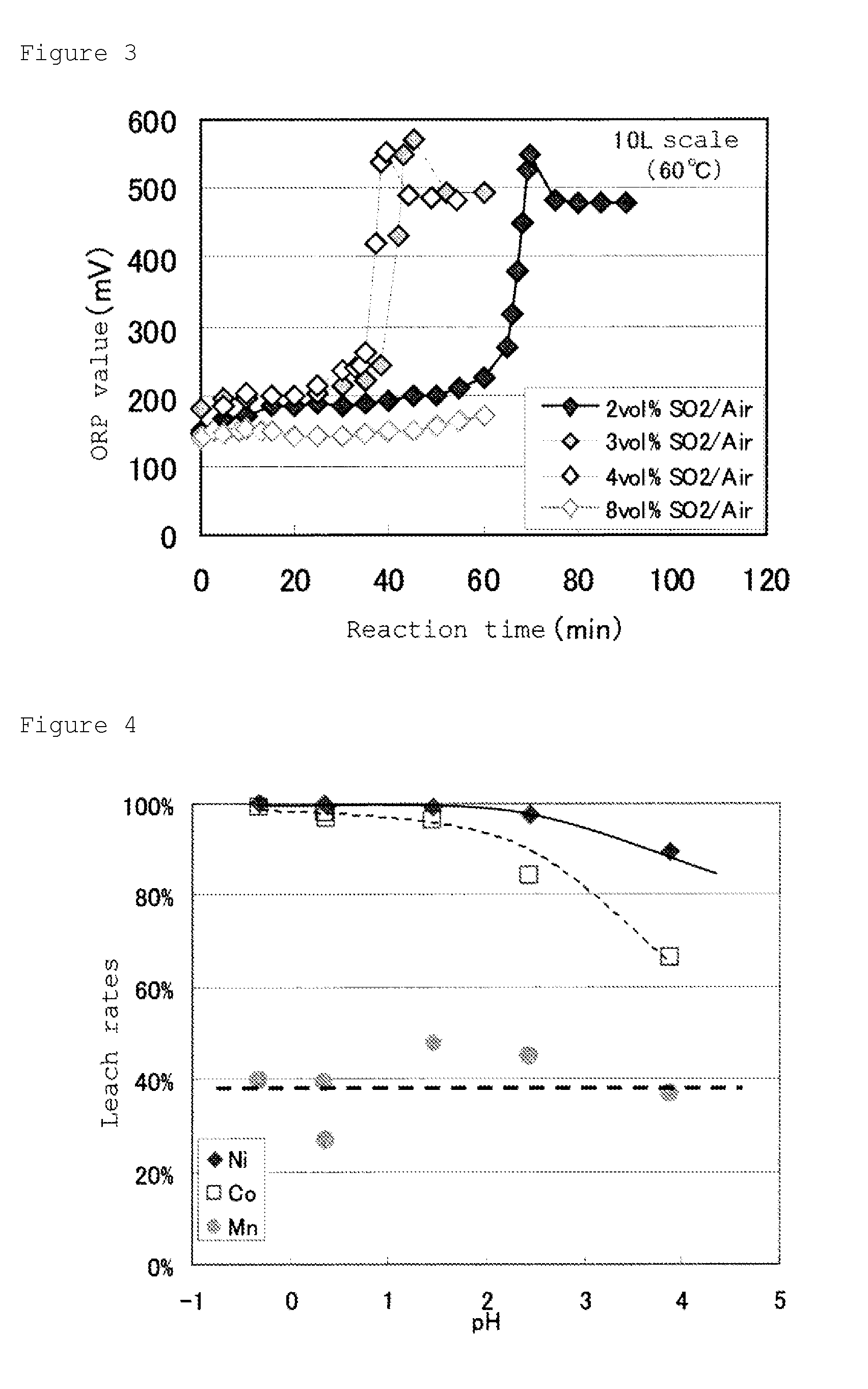
Patents
Literature
52results about "Cobalt compounds preparation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
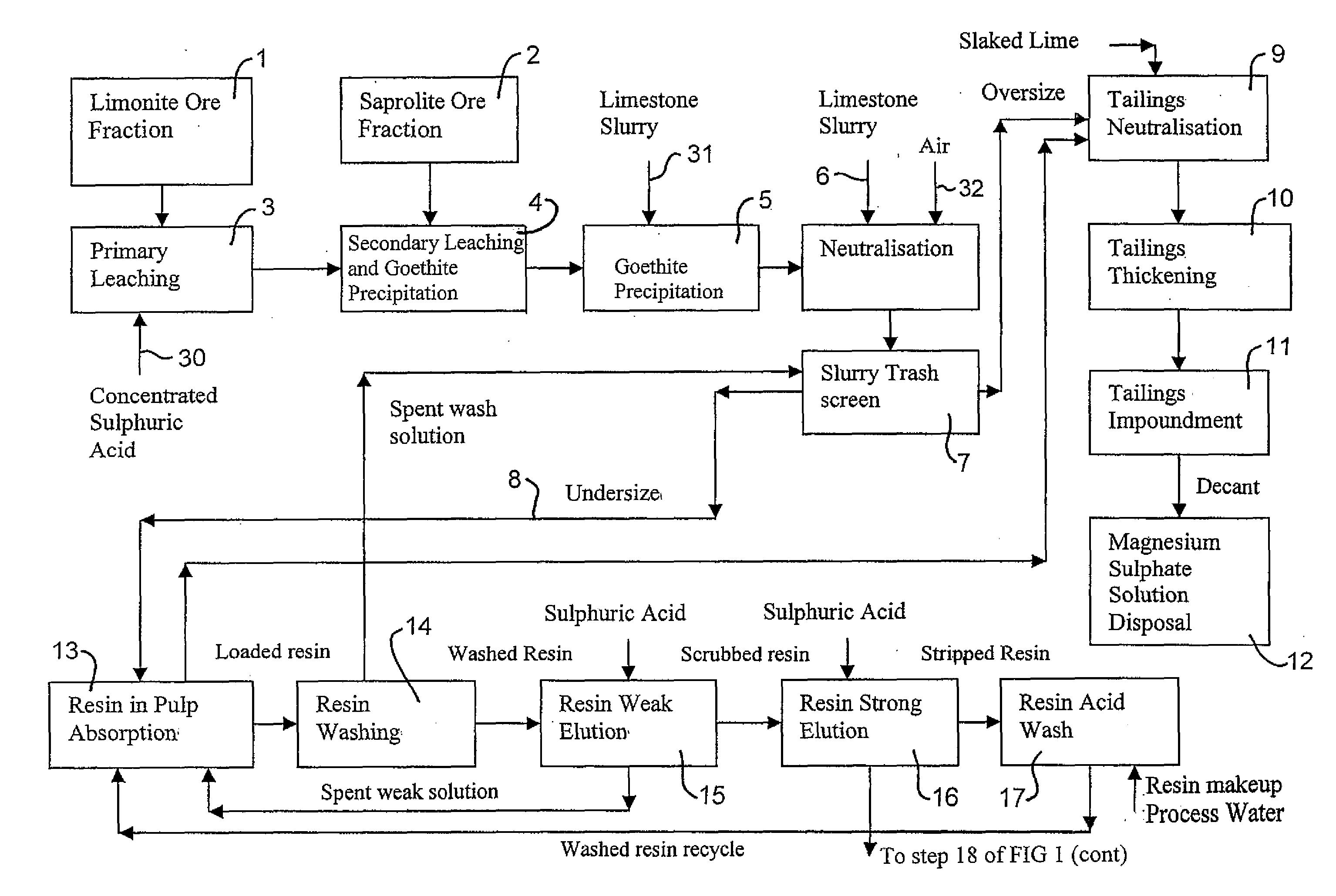
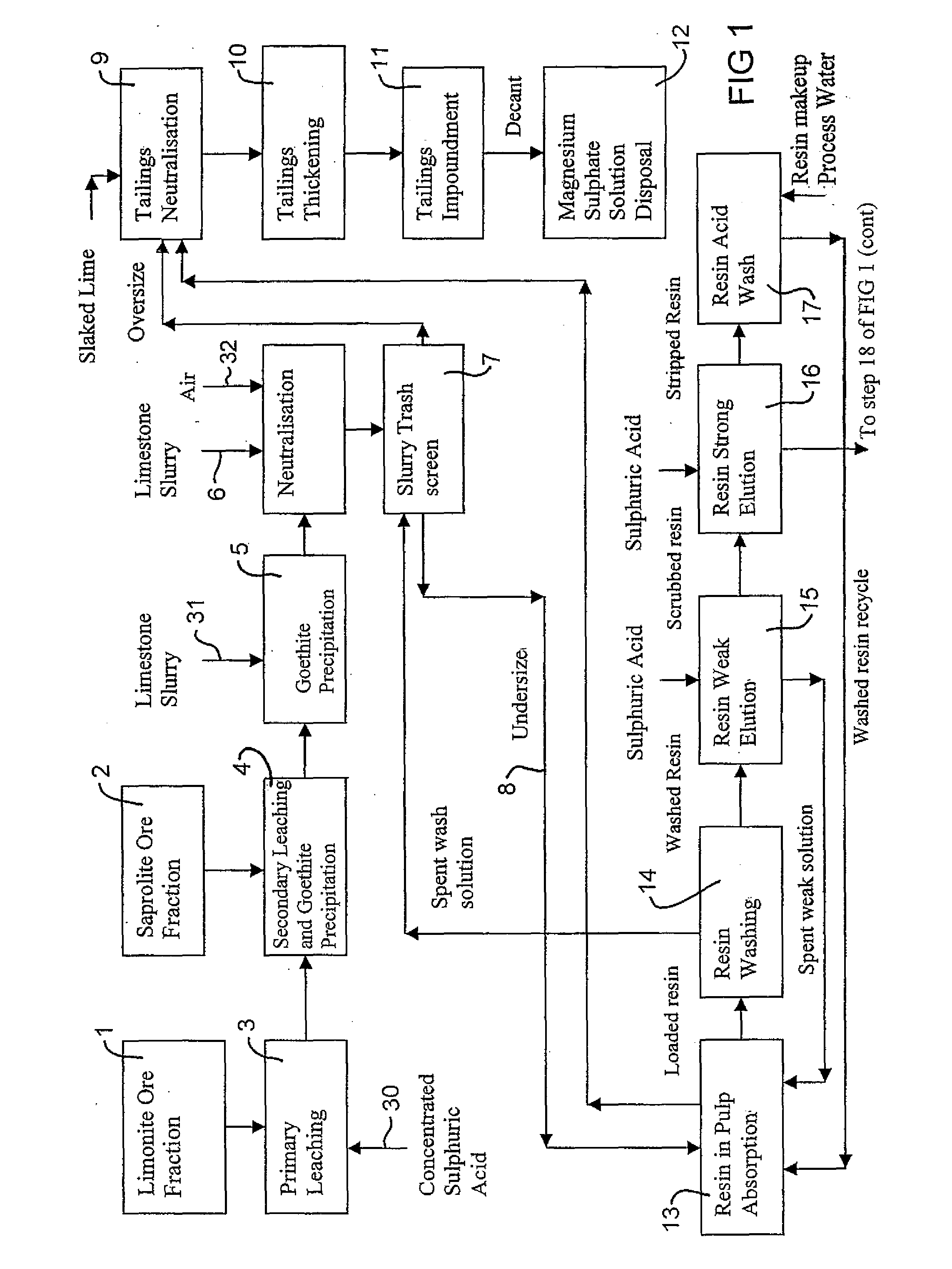
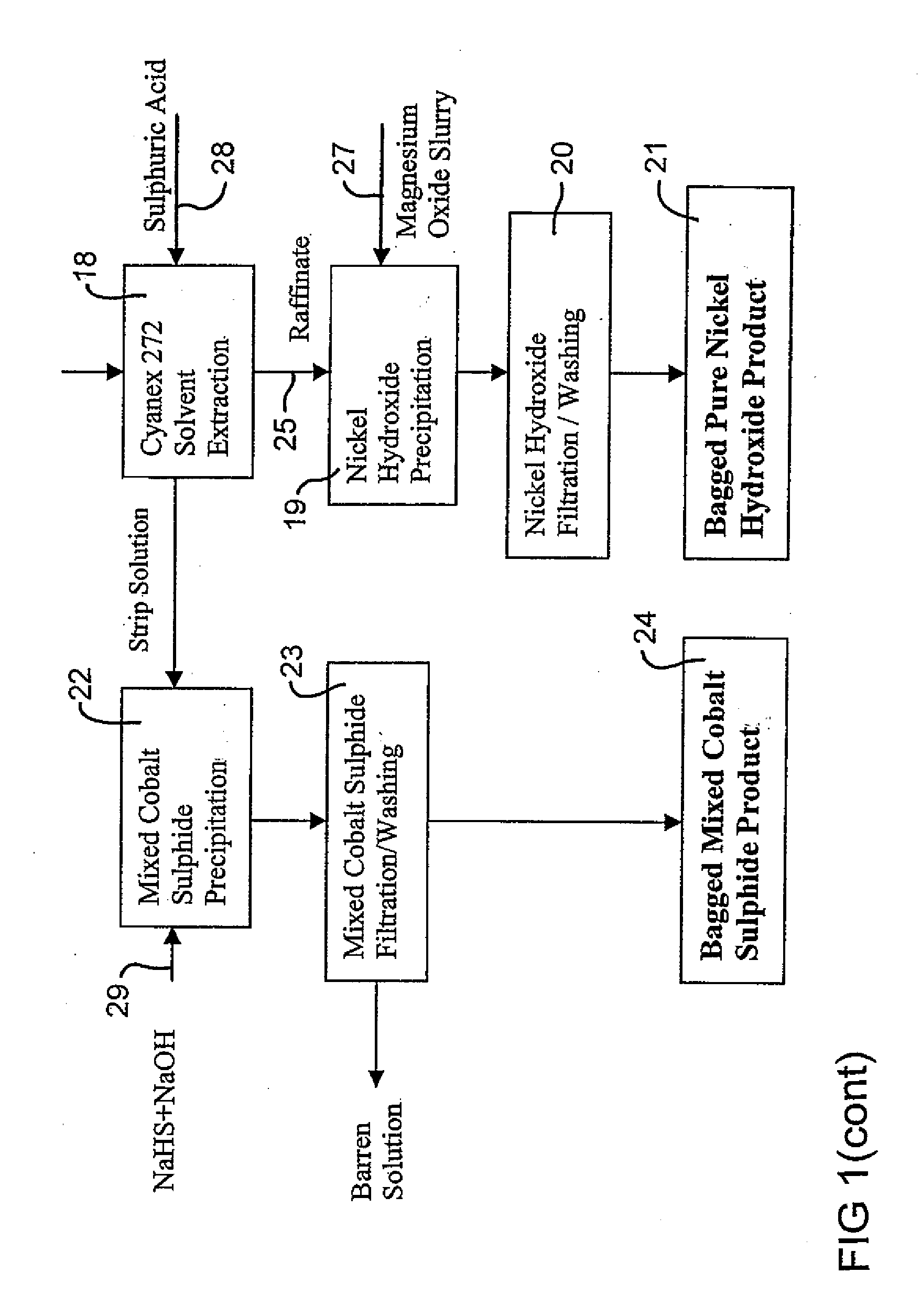
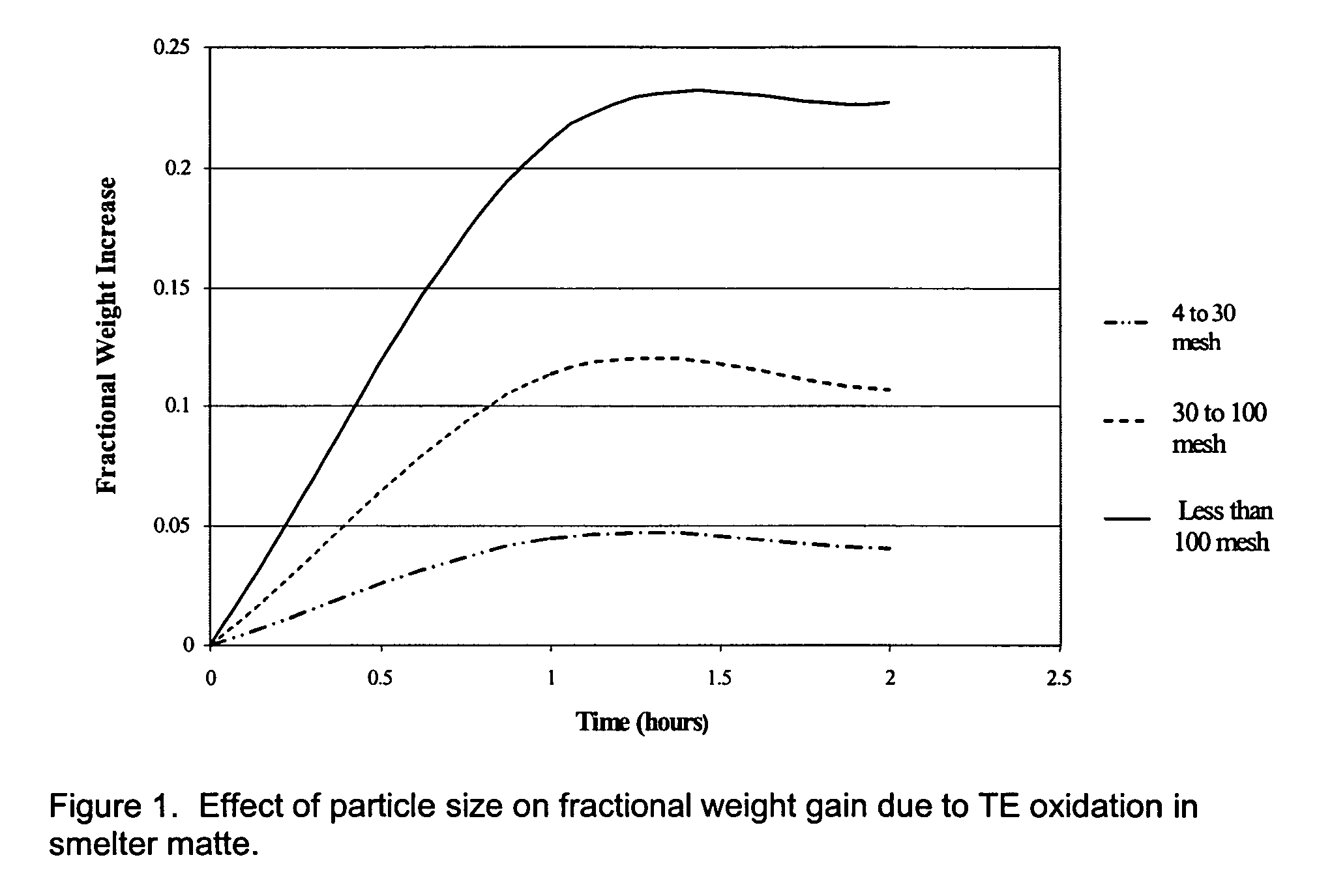
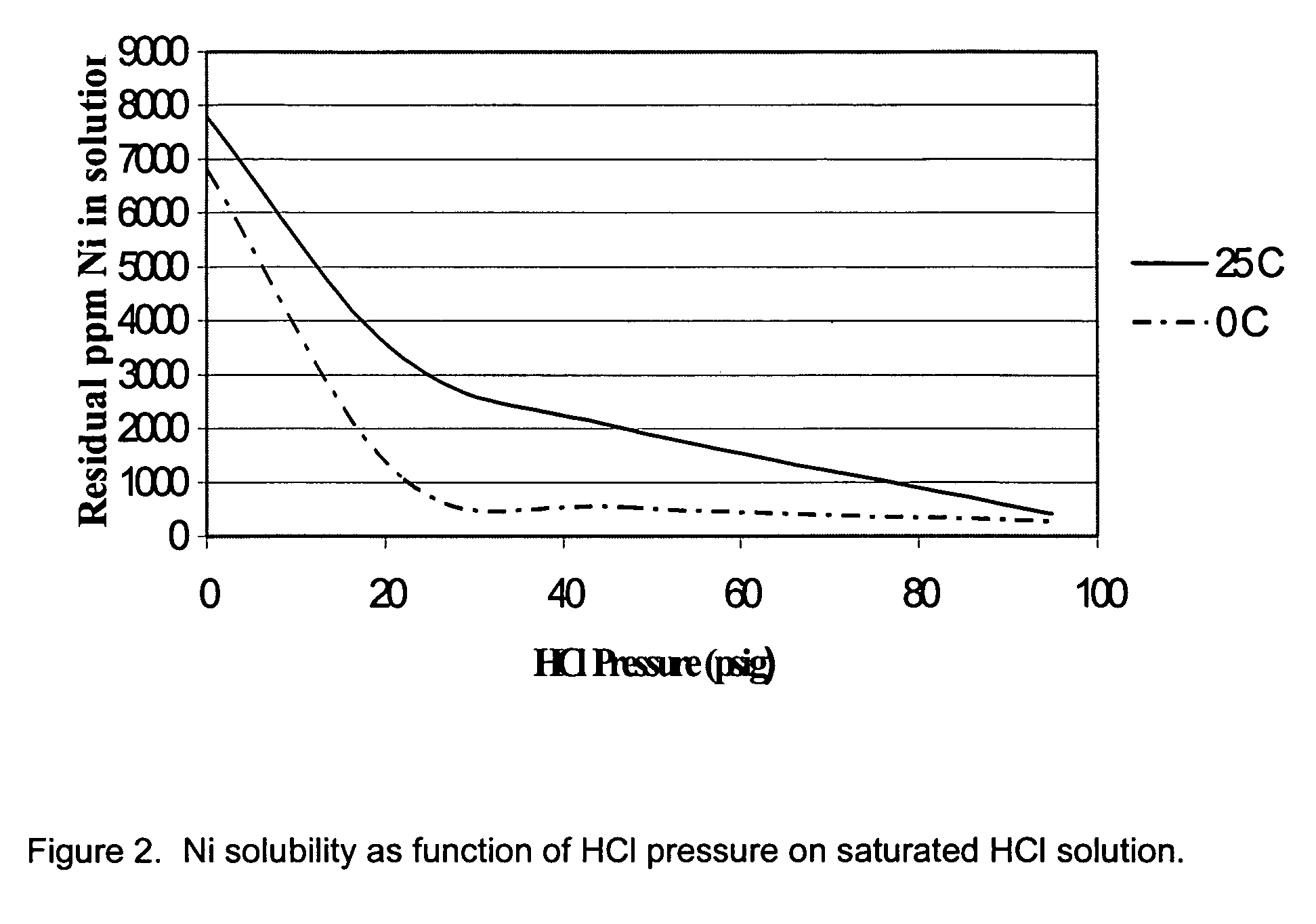
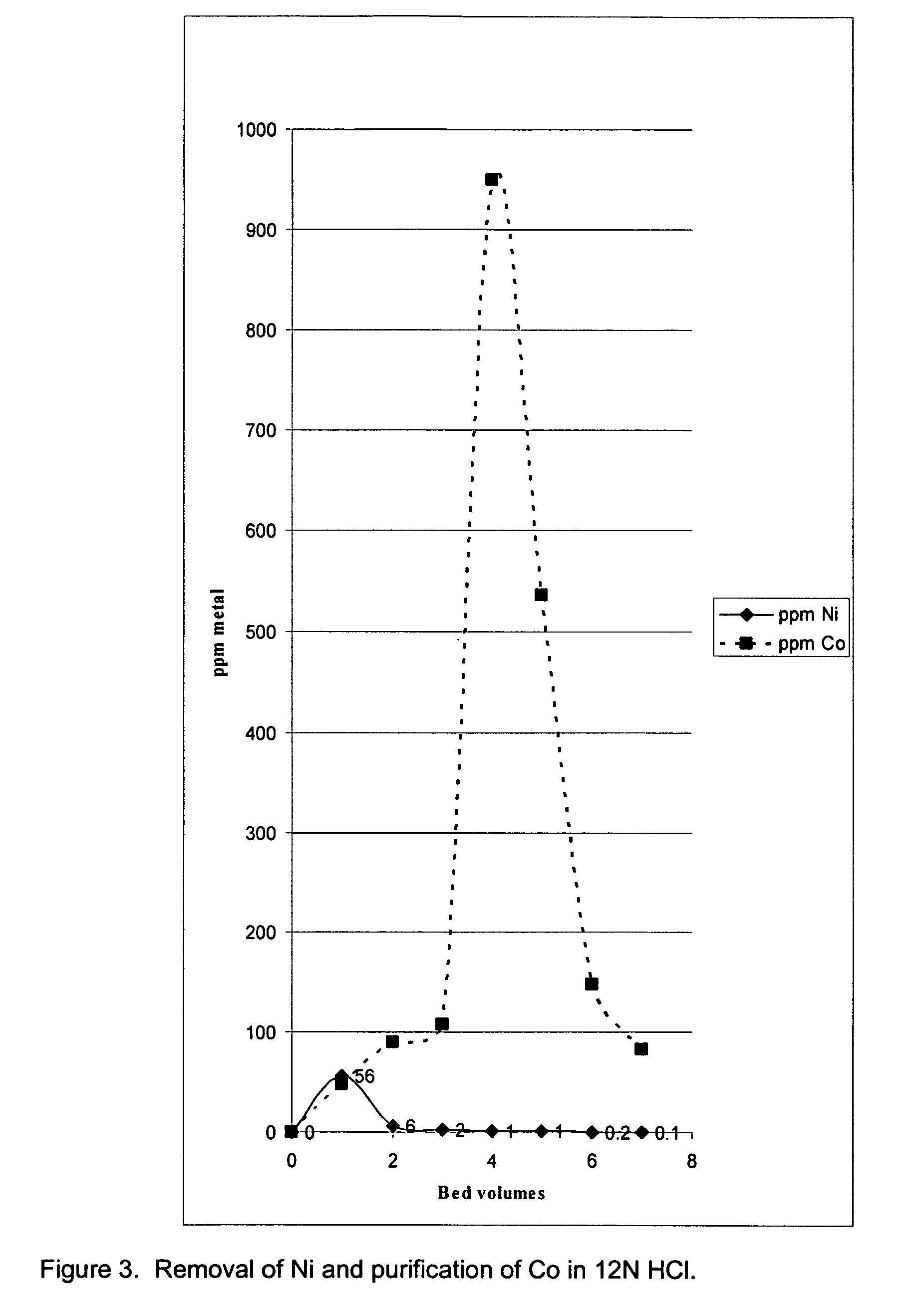
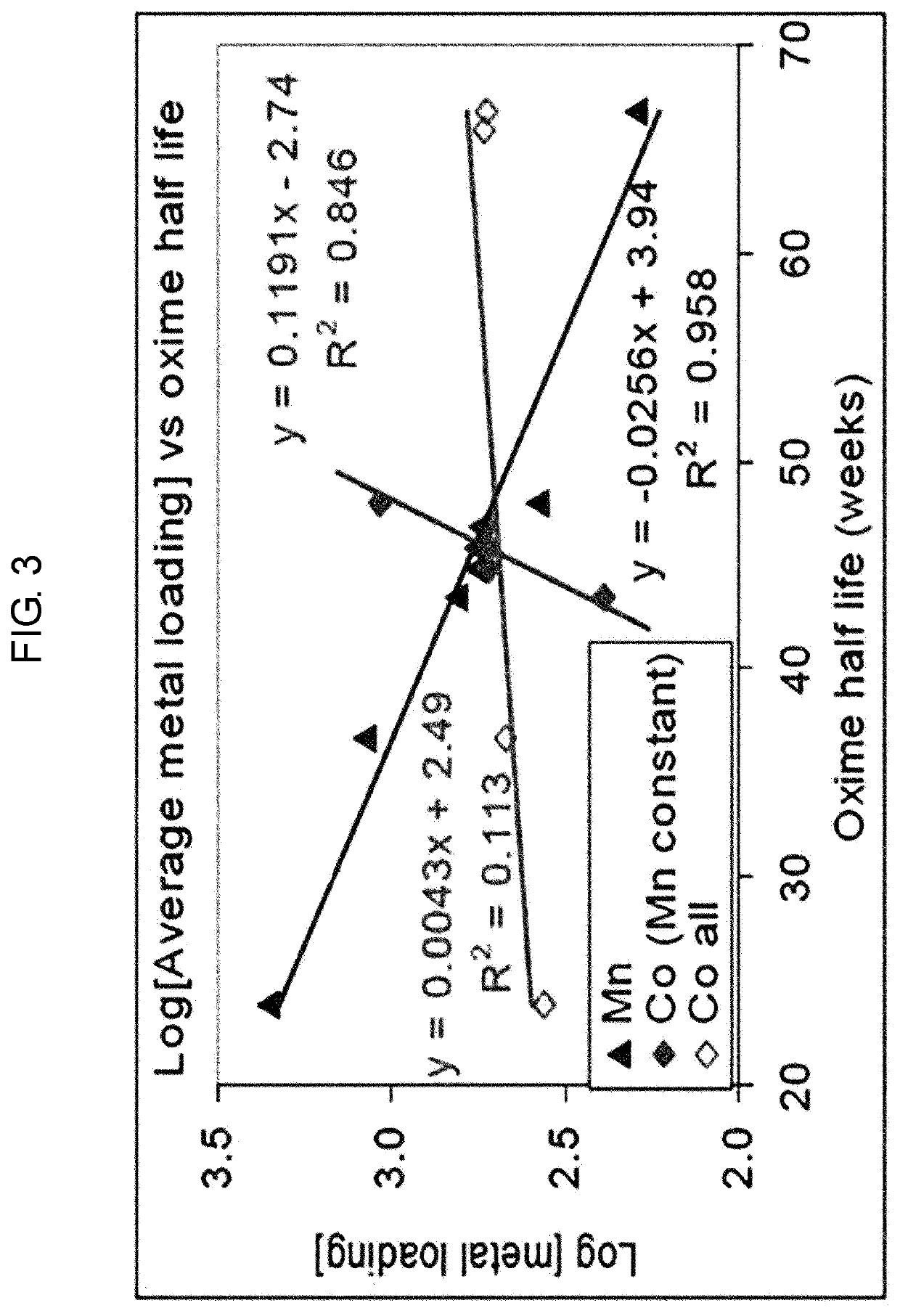
Extraction of Nickel and Cobalt from a Resin Eluate Stream
InactiveUS20070297960A1Easy to transportEasy to disassembleNickel compounds preparationIron compoundsManganeseCopper
A process for the recovery of nickel and cobalt from an acidic resin eluate containing at least nickel and cobalt, said process including the steps of: (a) treating the eluate with an immiscible organic reagent (18) to selectively absorb the majority of the cobalt, and a portion of any copper, zinc and manganese present in the eluate, leaving a raffinate containing the nickel and minor impurities; (b) neutralising the raffinate to precipitate the nickel as nickel hydroxide (19); (c) stripping the cobalt from the organic reagent (22); and (d) recovering the cobalt (23).
Owner:BHP BILLITON SSM TECH PTY LTD
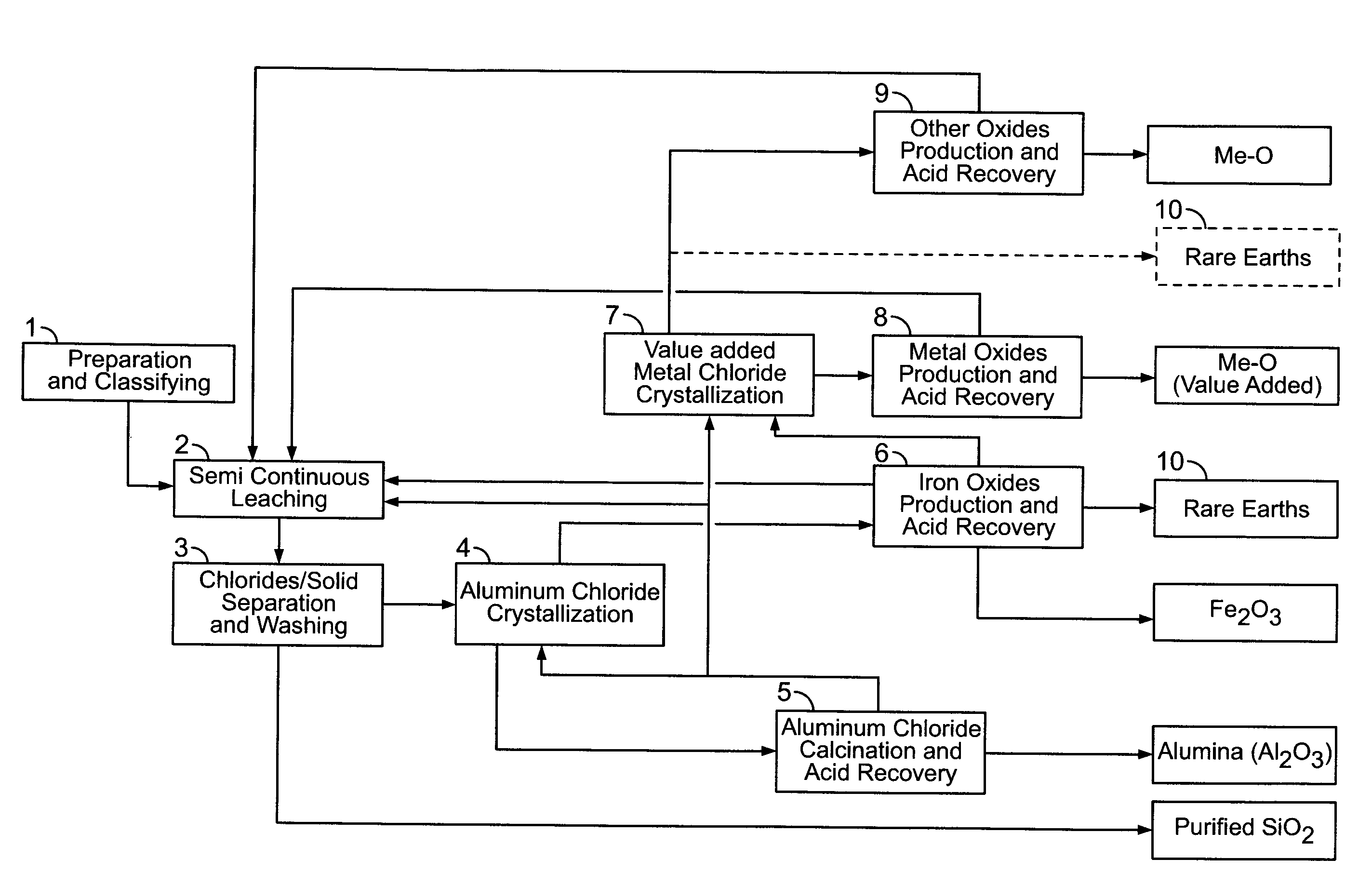
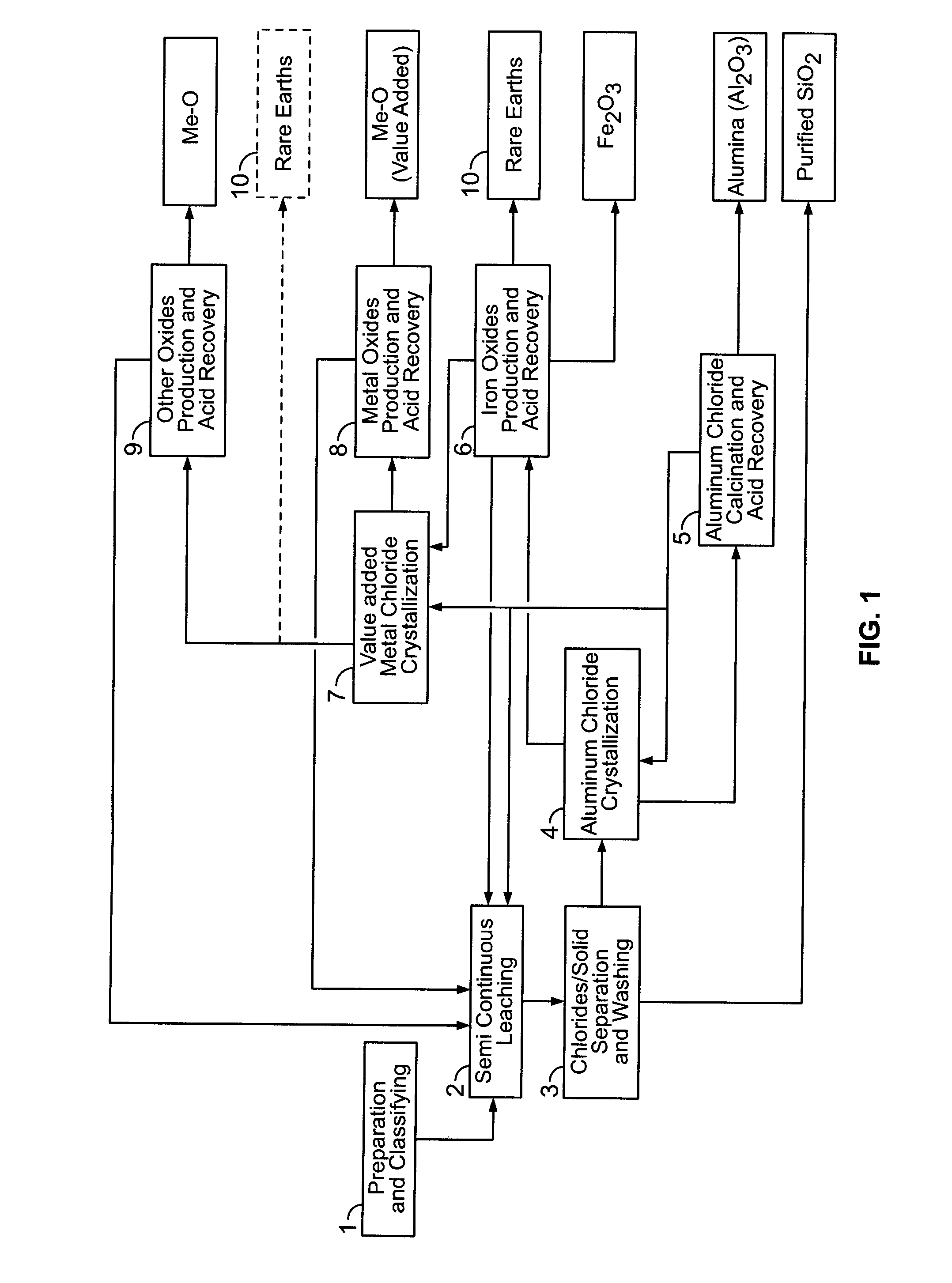
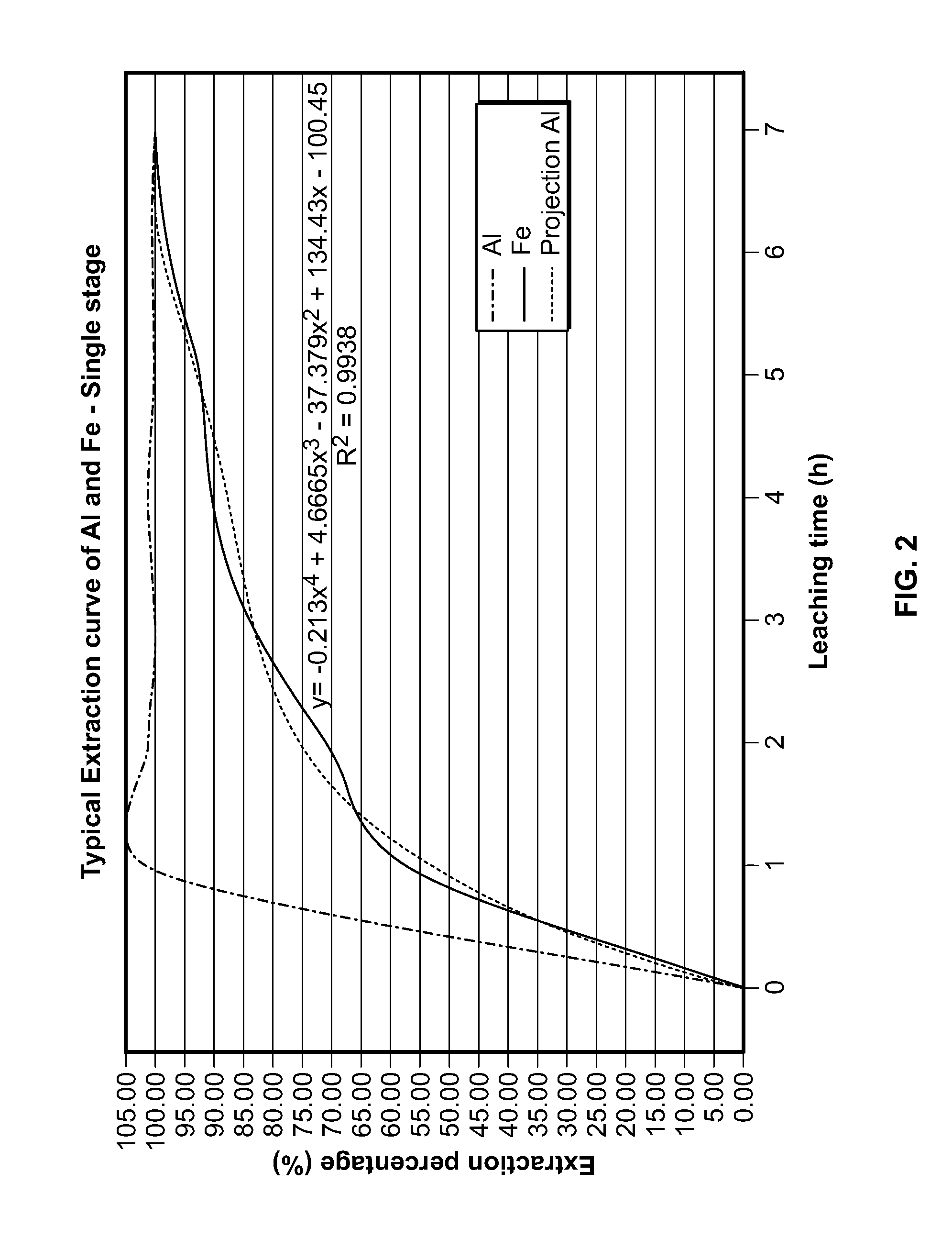
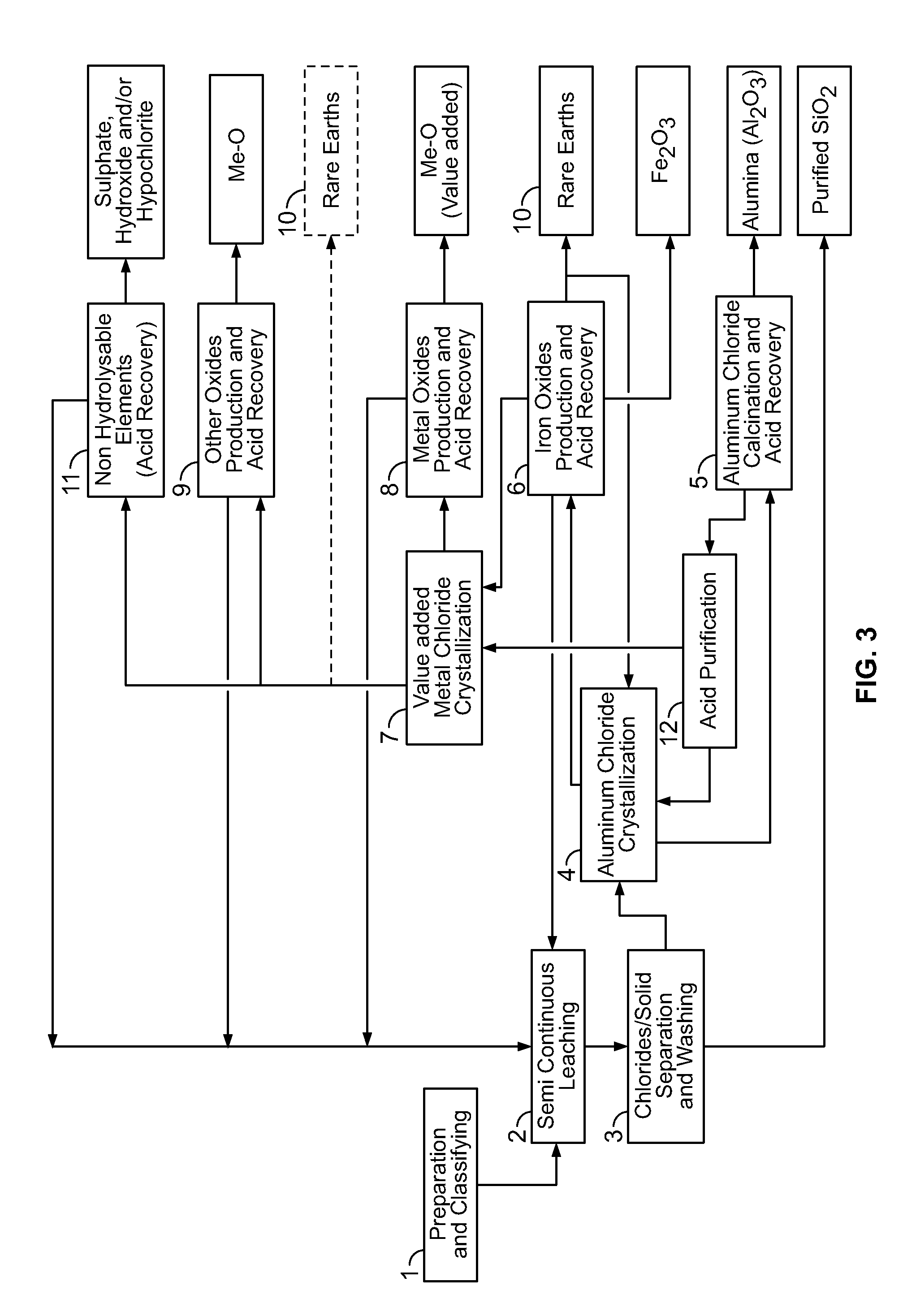
Processes for treating red mud
ActiveUS20140369907A1Simple and efficientLow costAluminium compoundsSolvent extractionPregnant leach solutionRare-earth element
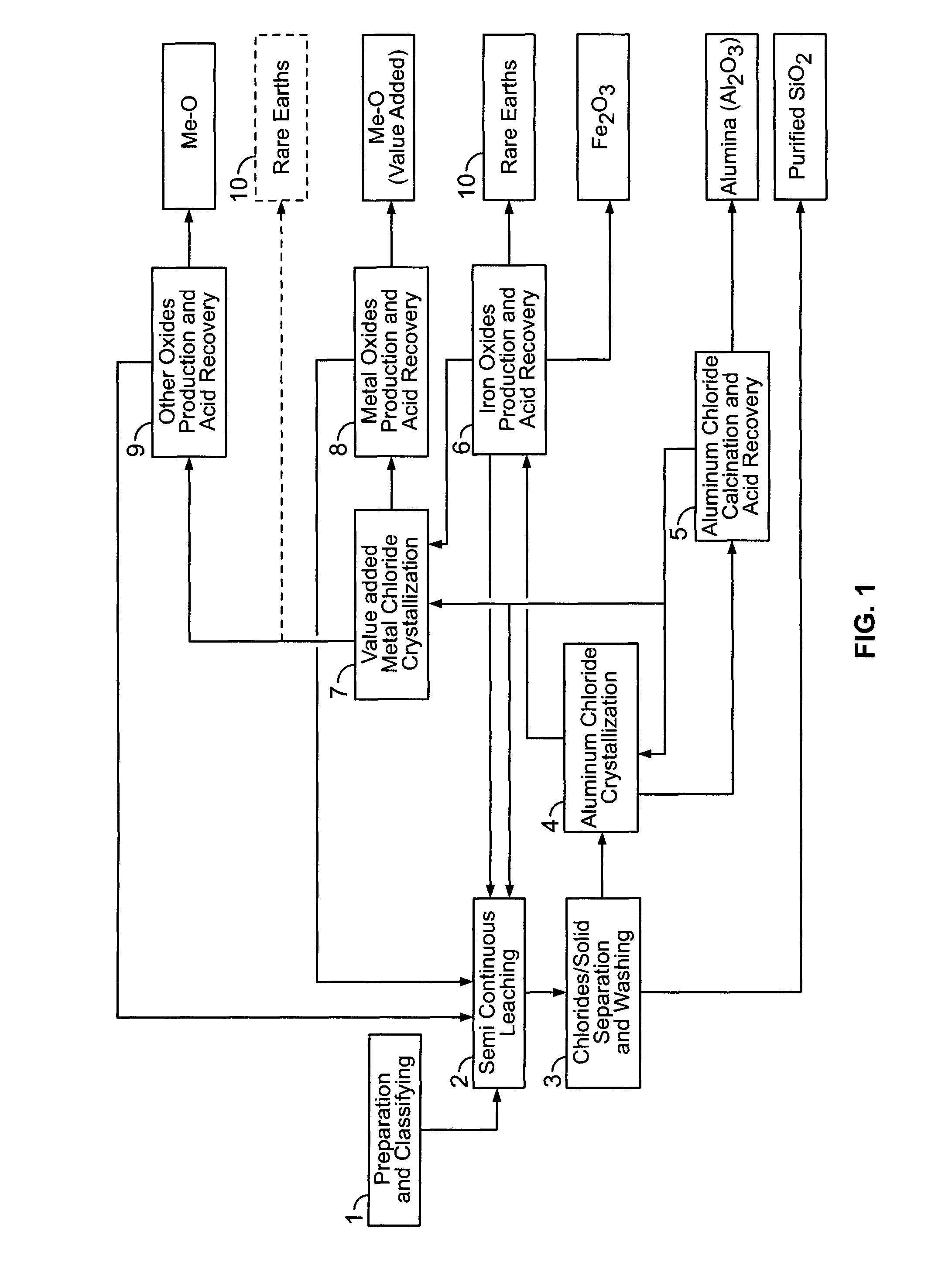
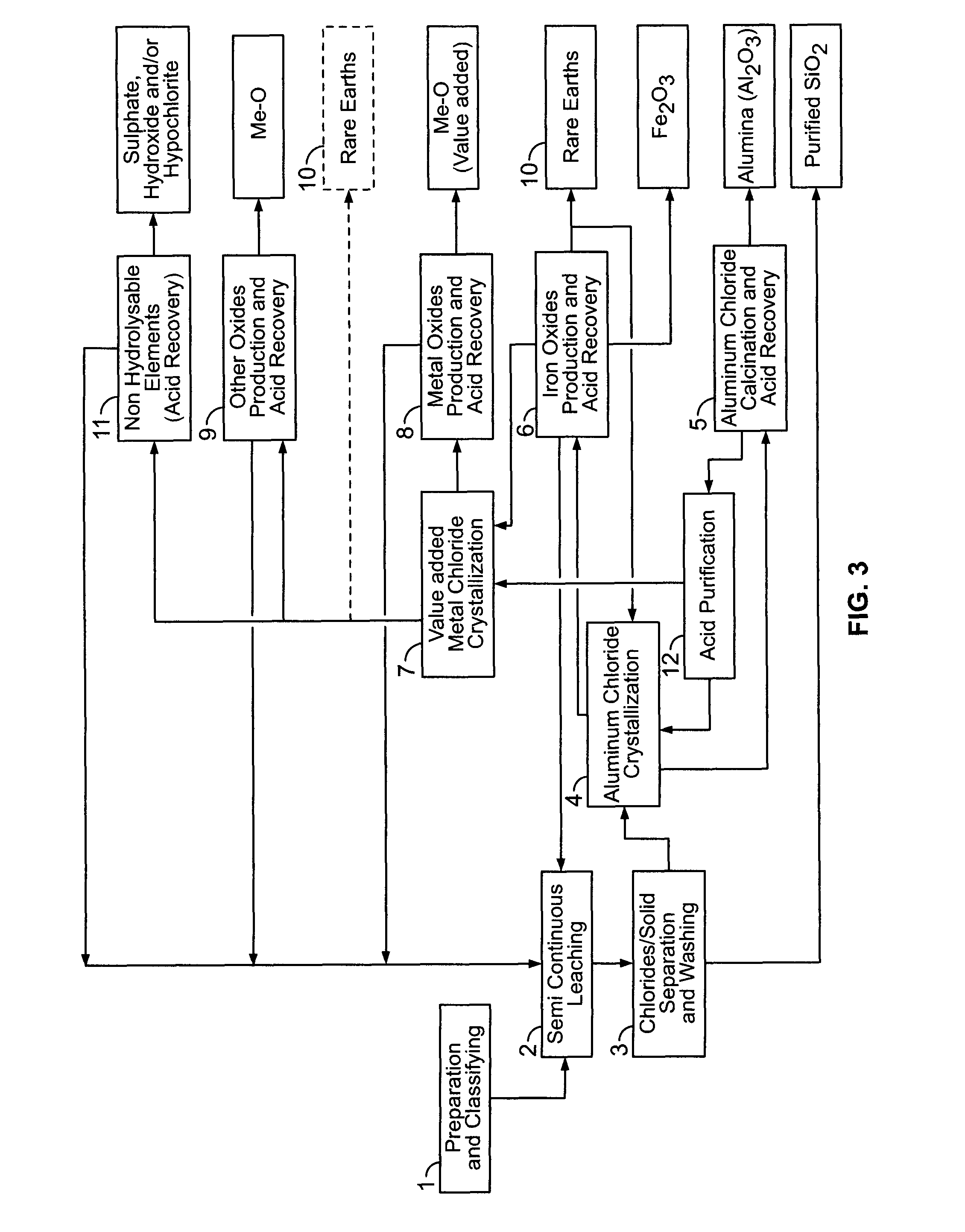
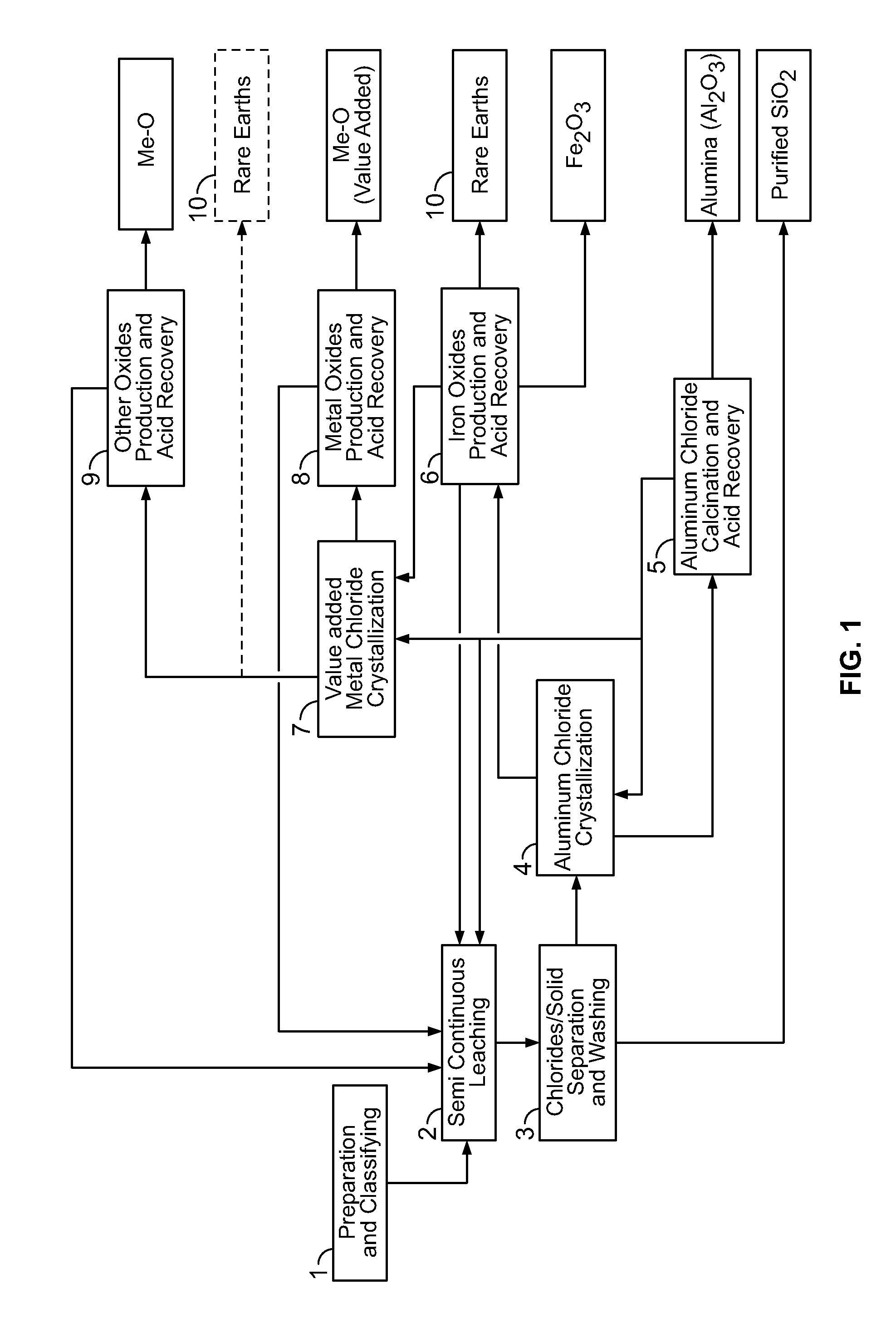
There are provided processes for treating red mud. For example, the processes can comprise leaching red mud with HCl so as to obtain a leachate comprising ions of a first metal (for example aluminum) and a solid, and separating said solid from said leachate. Several other metals can be extracted from the leachate (Fe, Ni, Co, Mg, rare earth elements, rare metals, etc.). Various other components can be extracted from solid such as TiO2, SiO2 etc.
Owner:ORBITE ALUMINAE INC
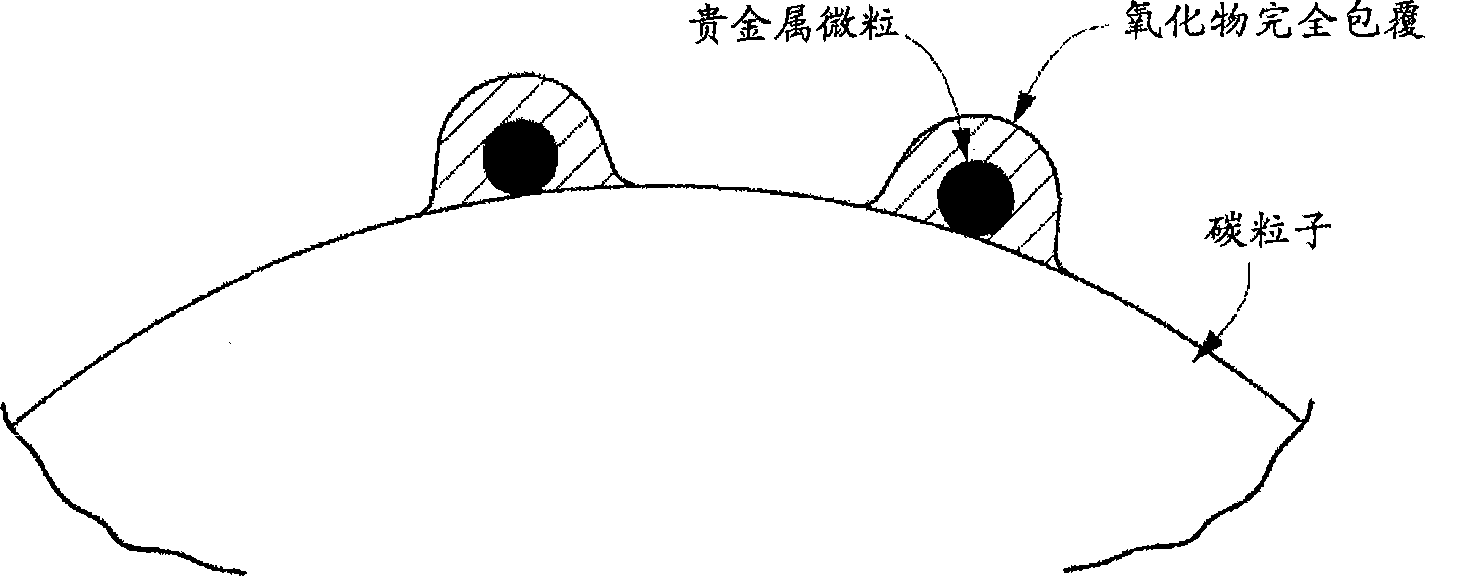
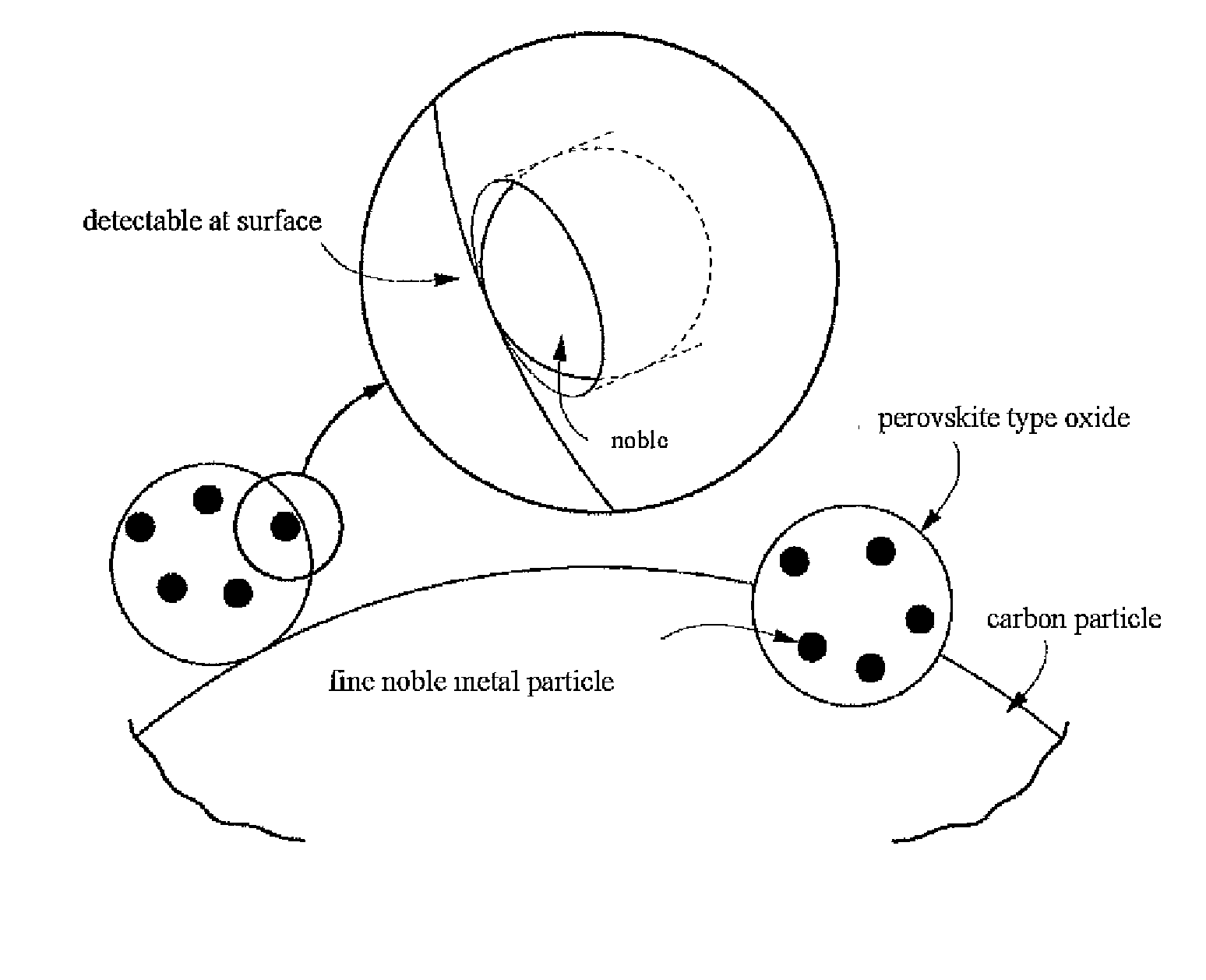
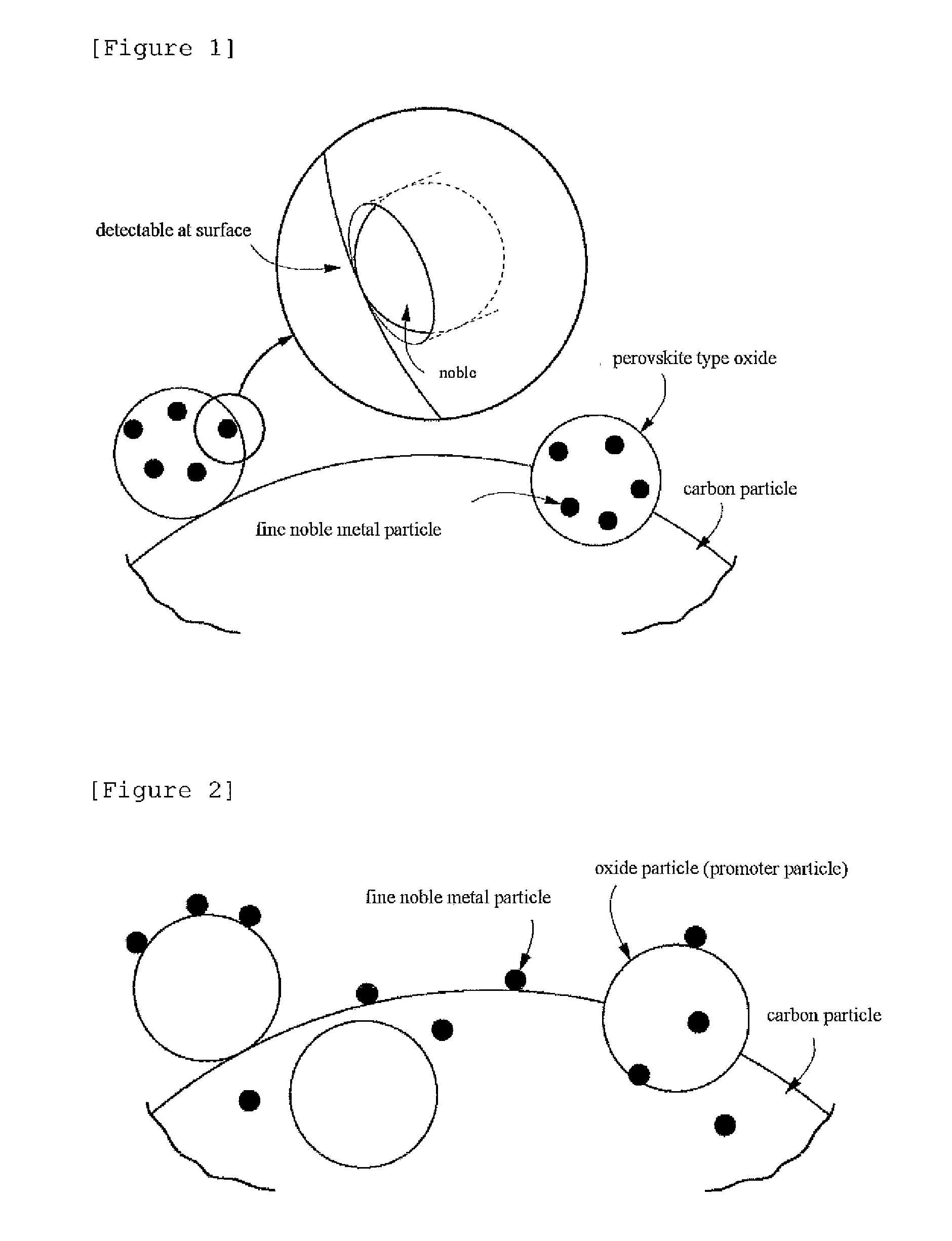
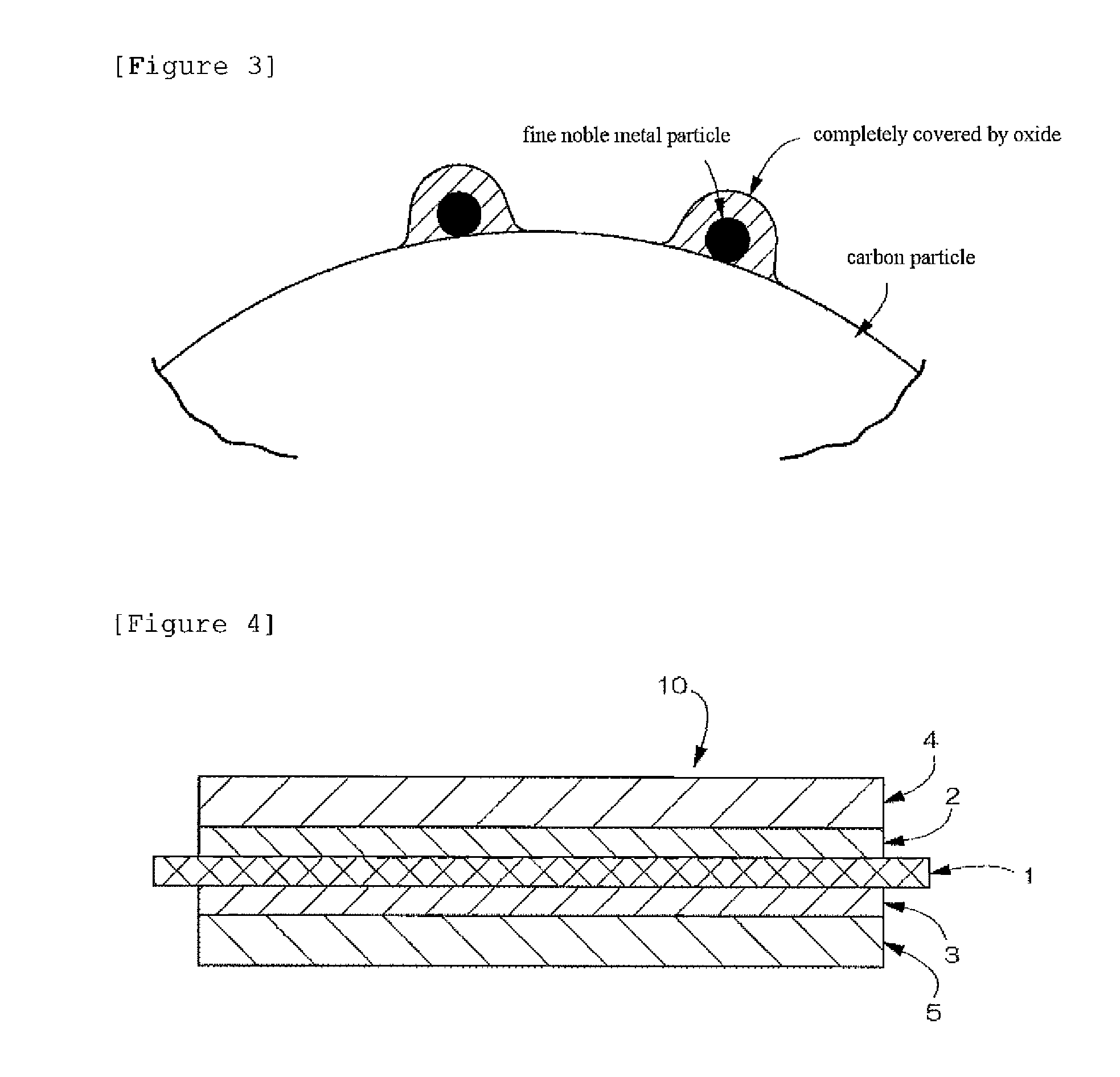
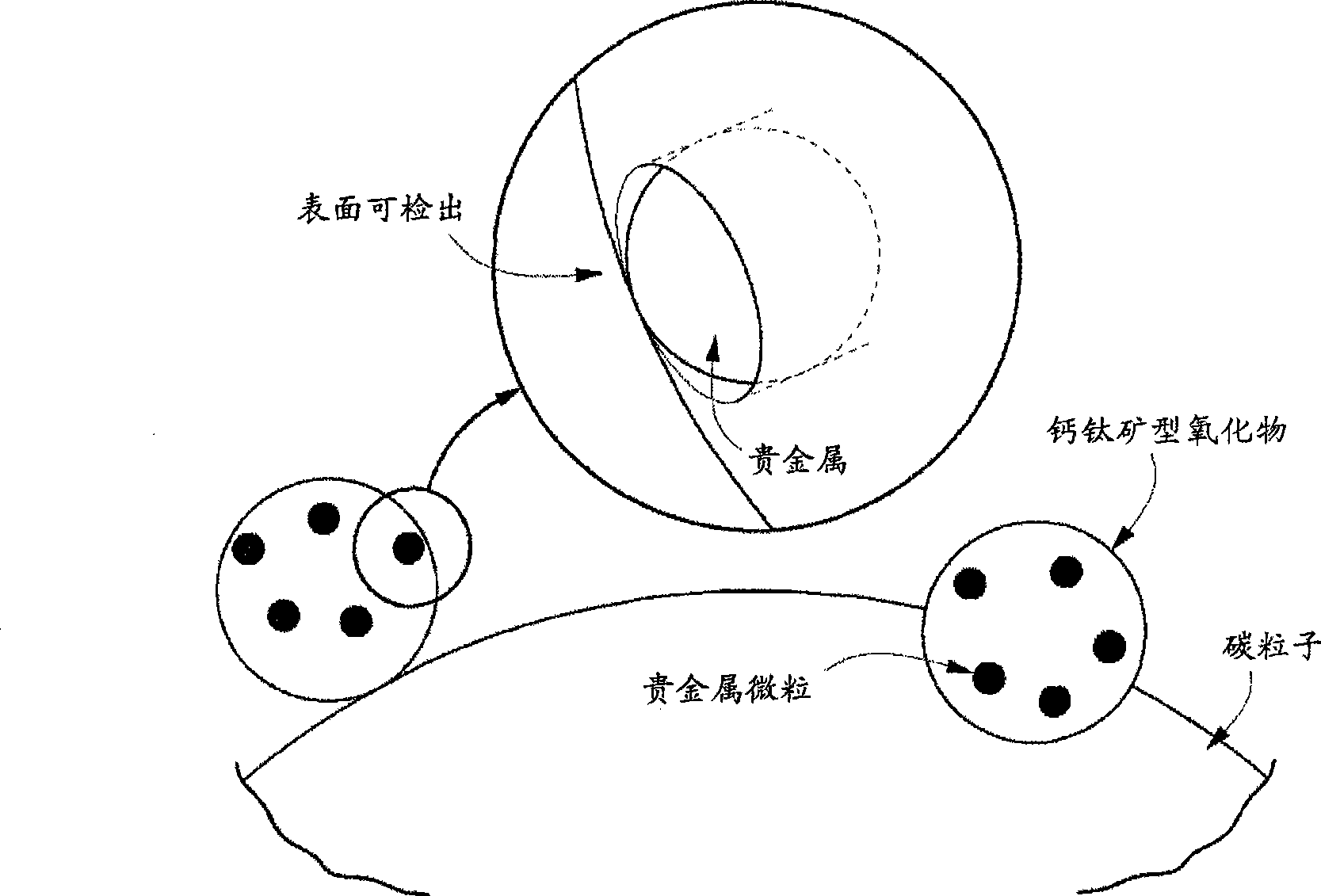
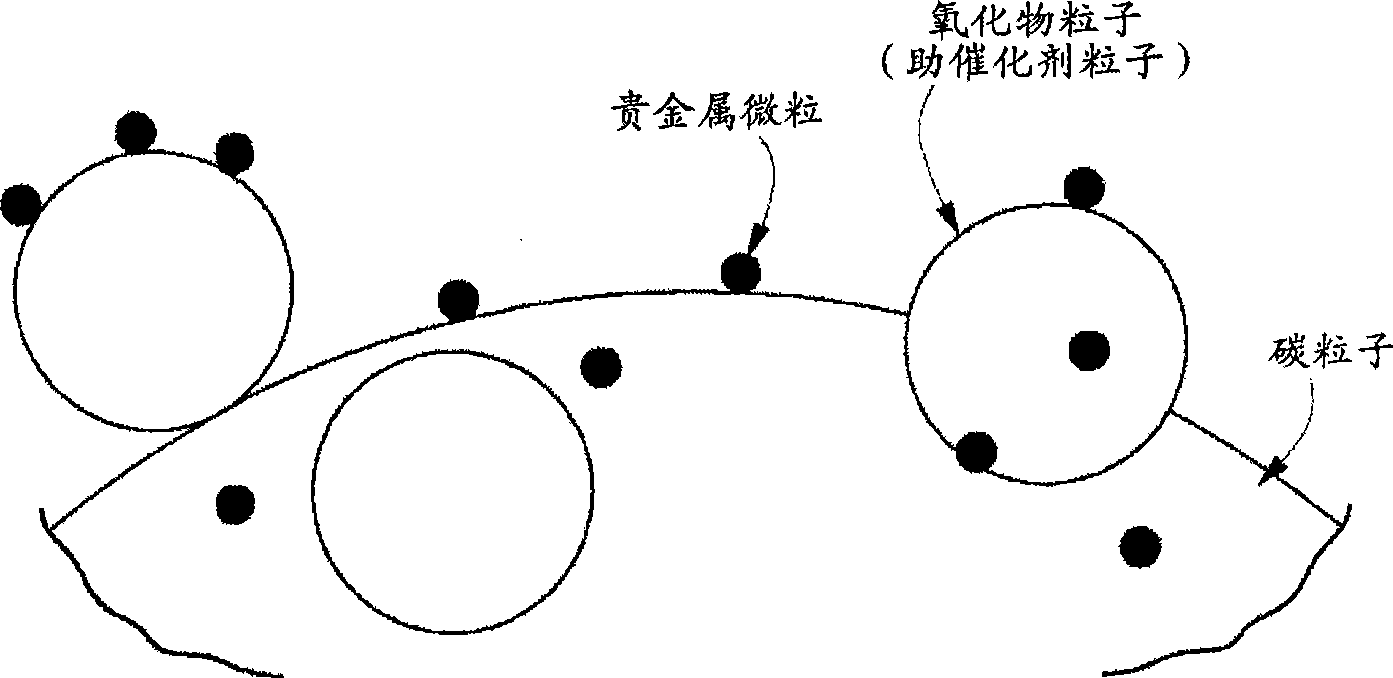
Carbon particle having deposited fine particles, process for producing the same, and electrode for fuel cell
InactiveUS20090202869A1Increased durabilityReduce usageMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsPt elementComposite oxide
Carbon particles having fine particles deposited thereon which can be used as a substitute for the carbon particles having platinum deposited thereon and metallic platinum particles which are presently in general use as, e.g., a catalyst for electrodes in fuel cells. Compared to the conventional carbon particles having platinum deposited thereon, etc., the carbon particles are effective in greatly reducing the amount of platinum to be used. The carbon particles are characterized by comprising carbon particles and, deposited on the surface of the carbon particles, fine particles of a perovskite type composite metal oxide in each of which fine noble-metal particles are present throughout the whole particle. Also provided is a process for producing the carbon particles.The carbon particles having deposited fine particles have a constitution in which fine particles of a perovskite type composite metal oxide each having fine noble-metal particles present throughout the whole perovskite type oxide particle and having a crystallite size of 1-20 nm are deposited on carbon particles. The process for producing such carbon particles having fine particles deposited thereon comprises preparing a solution containing fine perovskite type composite oxide particles and complex ions of a metal for constituting fine noble-metal particles, subsequently repeating the step of impregnating the solution into carbon particles and dried the particles to thereby adsorb complex ions of the metal onto the carbon particles, and then subjecting the resultant particles to heat treatment.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
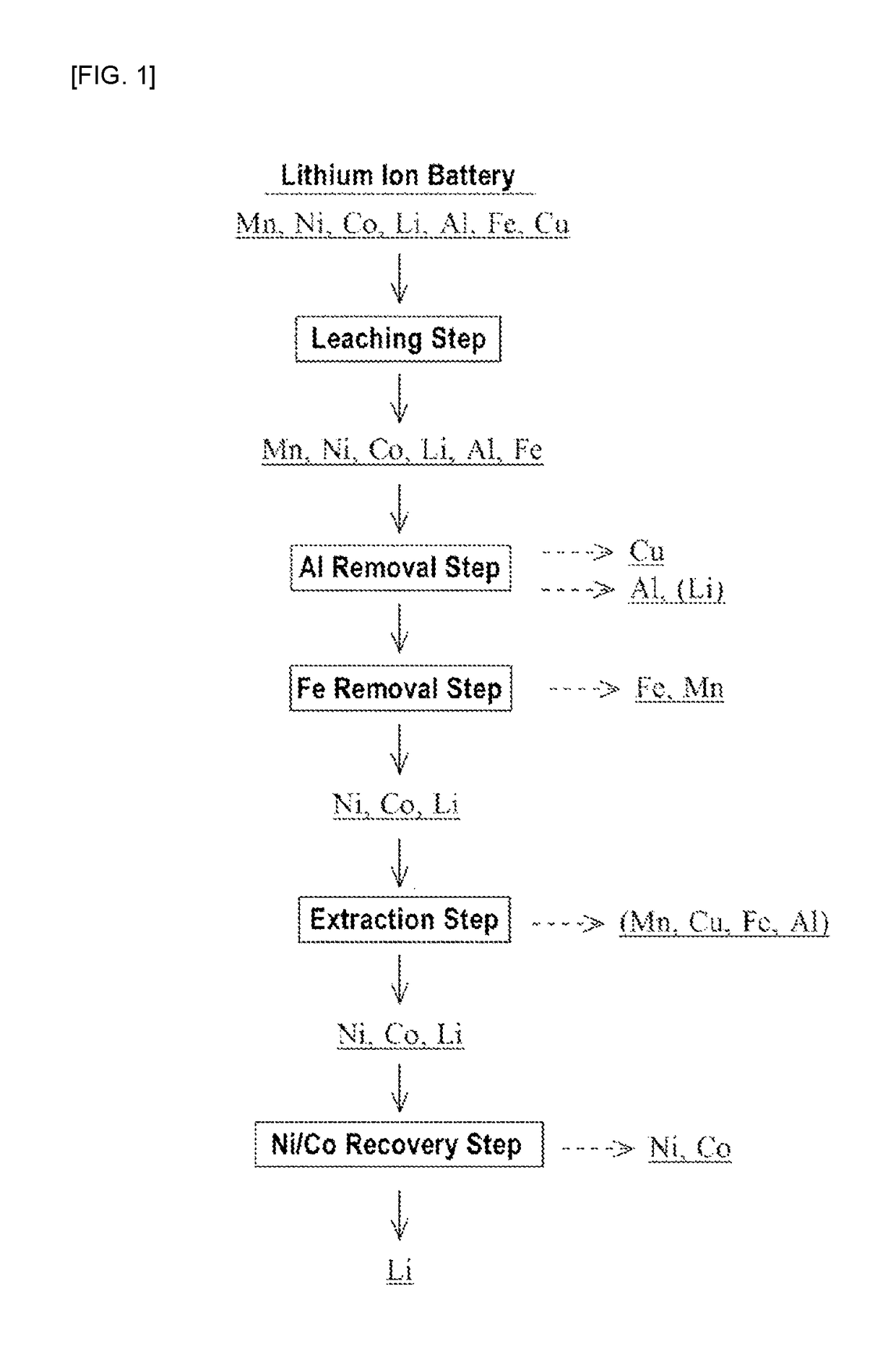
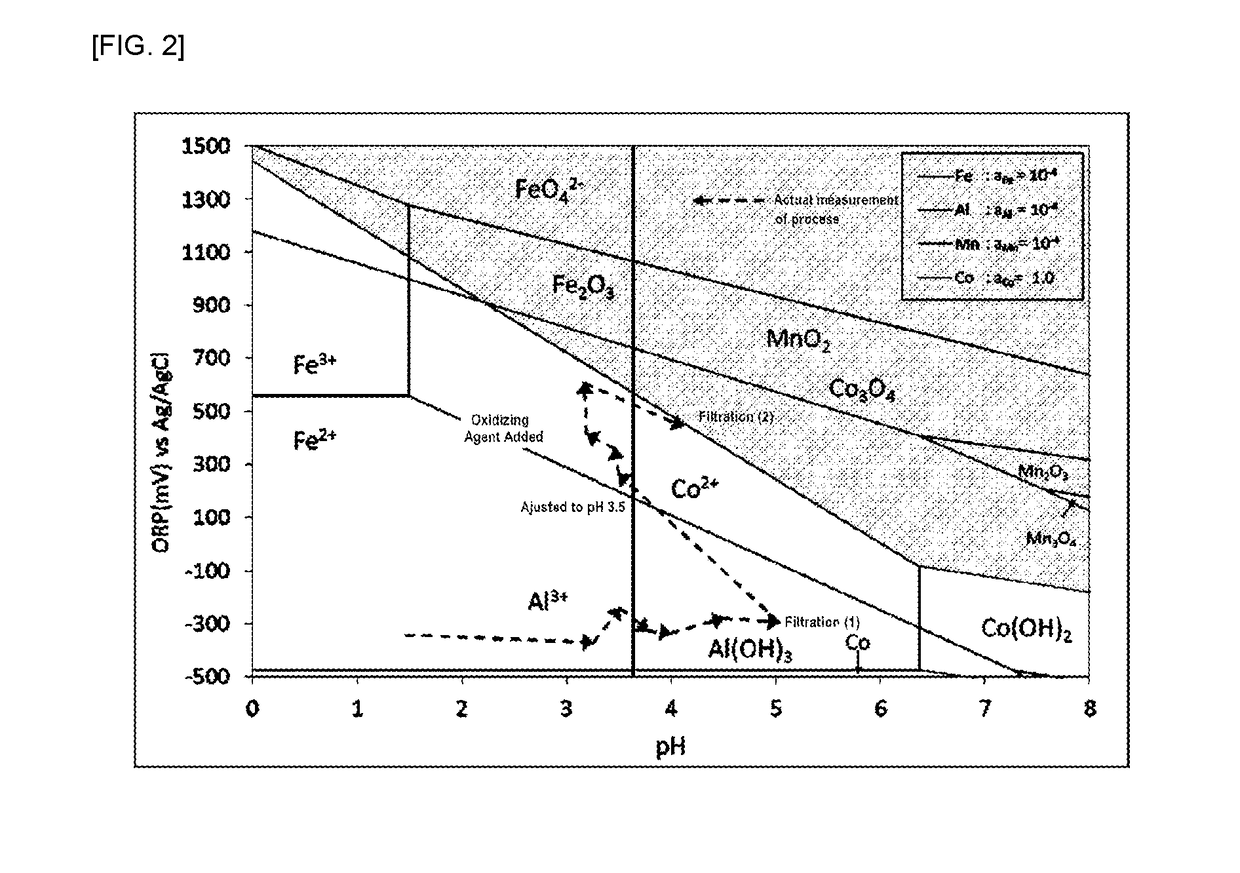
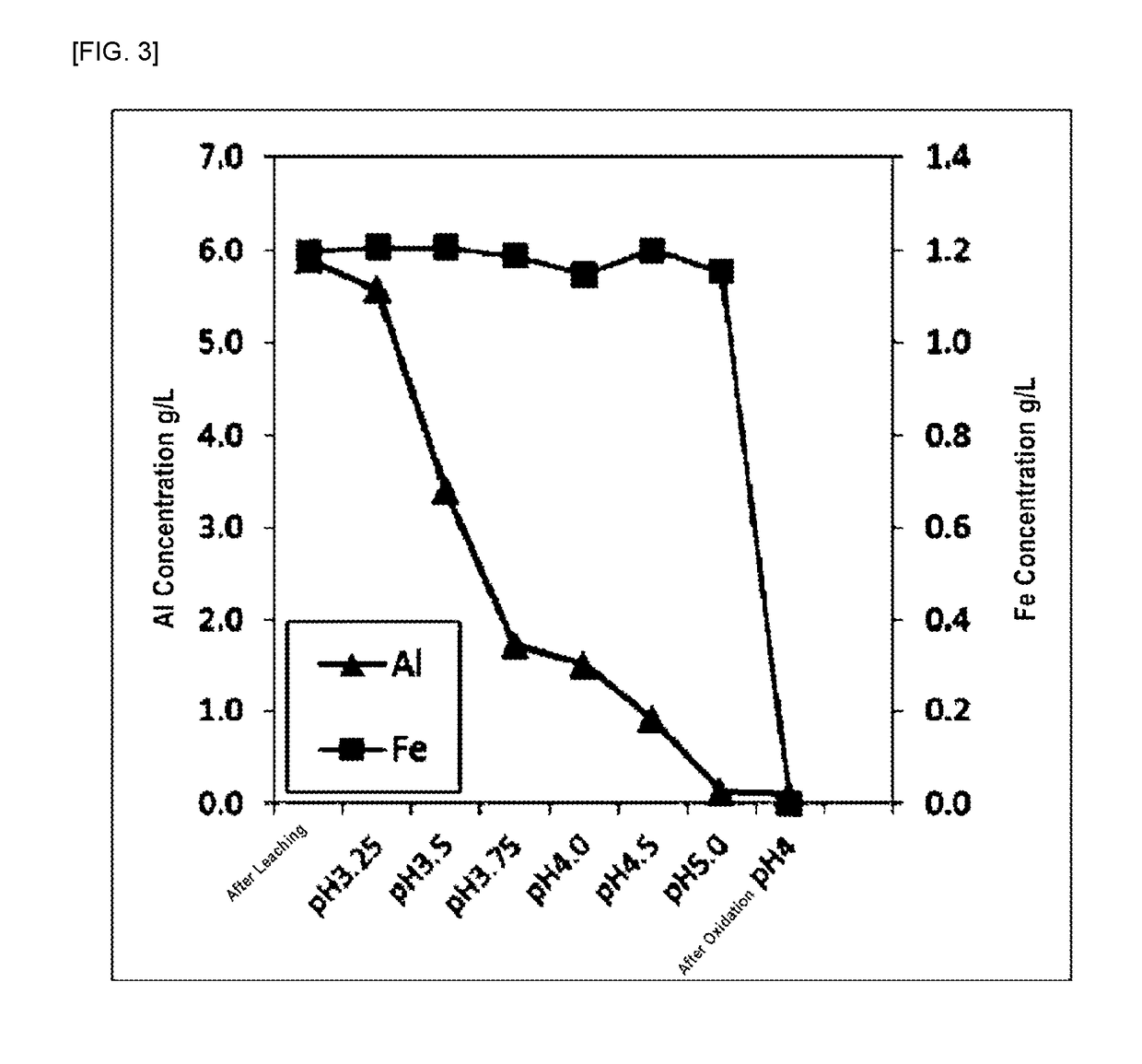
Processing method for lithium ion battery scrap
ActiveUS20190084839A1Transportation and packagingNickel compounds preparationElectrical batteryIron removal
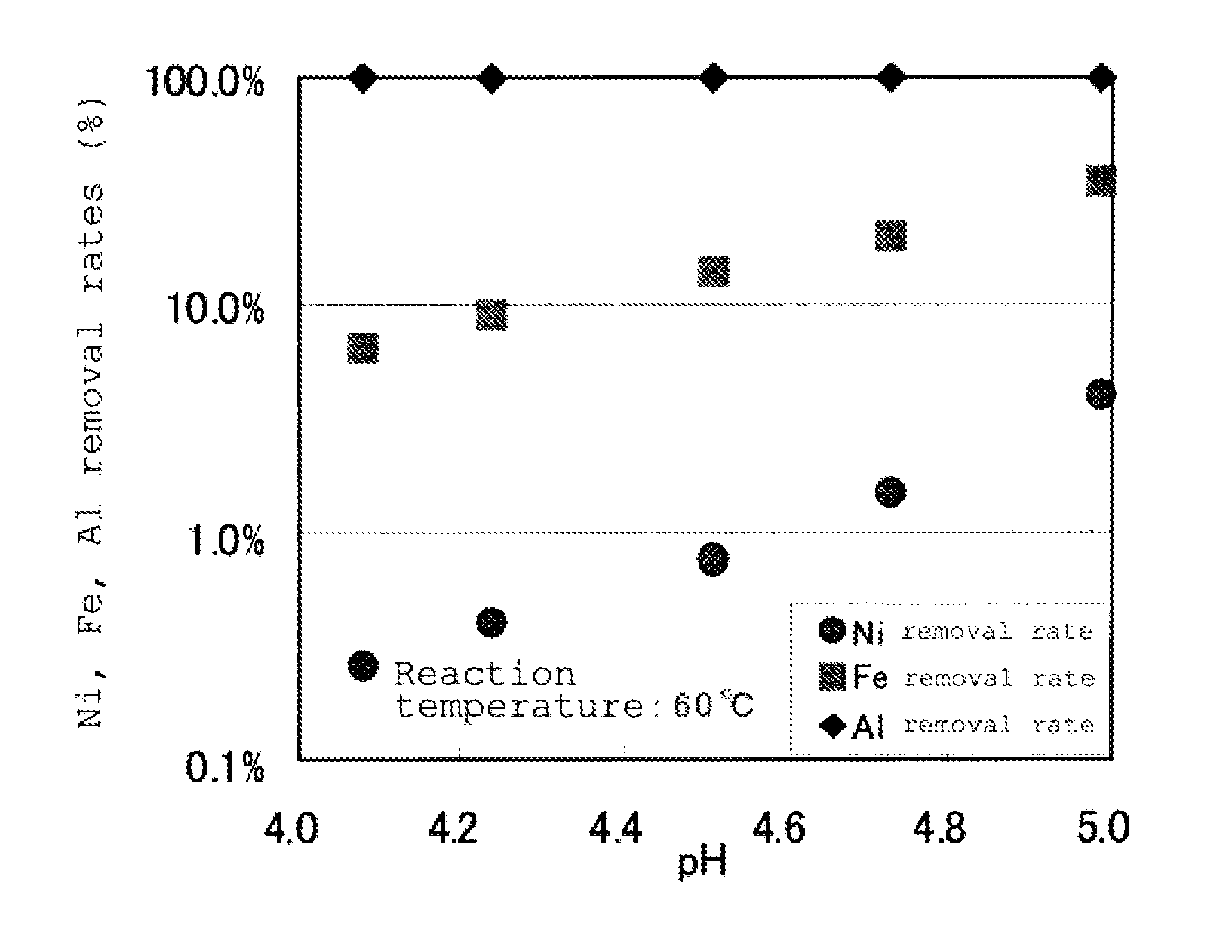
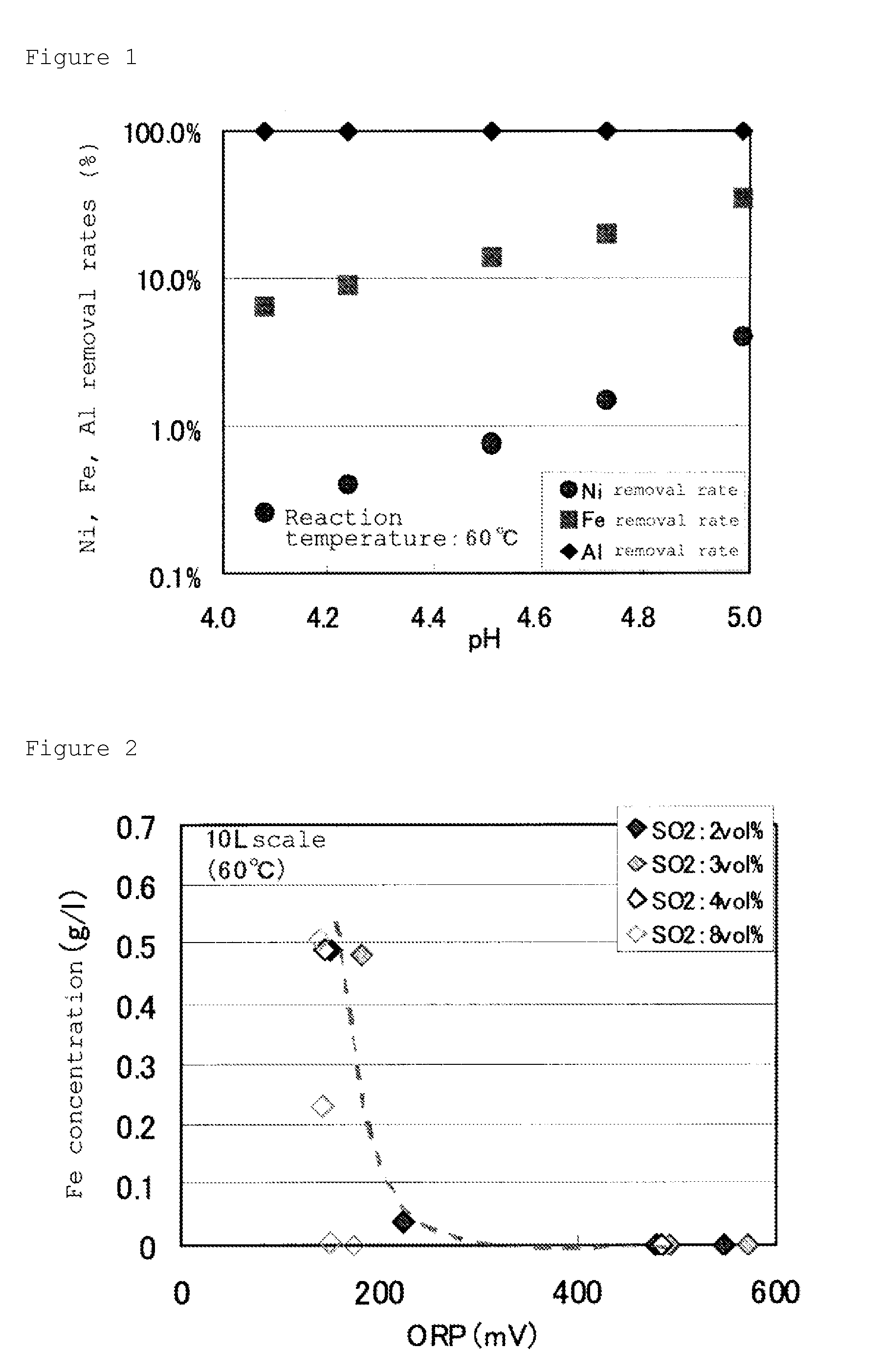
A method for processing lithium ion battery scrap according to this invention includes a leaching step of leaching lithium ion battery scrap to obtain a leached solution; an aluminum removal step of neutralizing the leached solution to a pH range of from 4.0 to 6.0, then performing solid-liquid separation and removing aluminum in the leached solution to obtain a first separated solution; and an iron removal step of adding an oxidizing agent to the first separated solution and adjusting the pH in a range of from 3.0 to 5.0, then performing solid-liquid separation and removing iron in the first separated solution to obtain a second separated solution.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Processes for treating red mud
ActiveUS9023301B2Simple and efficientLow costAluminium compoundsNickel compounds preparationRare-earth elementRed mud
There are provided processes for treating red mud. For example, the processes can comprise leaching red mud with HCl so as to obtain a leachate comprising ions of a first metal (for example aluminum) and a solid, and separating said solid from said leachate. Several other metals can be extracted from the leachate (Fe, Ni, Co, Mg, rare earth elements, rare metals, etc.). Various other components can be extracted from solid such as TiO2, SiO2 etc.
Owner:ORBITE ALUMINAE INC
Method for producing battery grade nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate by waste nickel cobalt alloy
ActiveCN108622943AMild responseReduce pollutionCobalt sulfatesNickel compounds preparationNew energyEvaporation
The invention discloses a method for producing battery grade nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate by waste nickel cobalt alloy. The method comprises the following steps of performing pretreatment on nickel cobalt alloy waste materials; then, performing electrochemical dissolution; removing impurities such as iron, chromium and aluminum from the obtained solution step by step by a chemical method andan extraction method; firstly extracting cobalt from the solution subjected to impurity removal; then extracting nickel; thus respectively obtaining extraction liquid containing cobalt and nickel; after the reverse extraction, obtaining nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate solution; then, respectively performing evaporation, cooling crystallization, and centrifugal dewatering on the solution to obtain a product of the battery grade nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate. The problems of low nickel and cobalt leaching efficiency, low dissolution speed and the like in the waste nickel and cobalt alloy recovery process by a conventional wet process can be effectively solved; the battery grade nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate conforming to the product quality standard requirement can be produced, andcan be used as a new energy source battery raw material to be applied to the field of new energy source battery manufacturing. The process is simple; the environment pollution is low; the metal recovery rate is high; good practical values and economic values are realized.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Processes for treating red mud
ActiveUS20150275330A1Simple and efficientLow costAluminium compoundsNickel compounds preparationPregnant leach solutionRare-earth element
Owner:AEM TECH INC
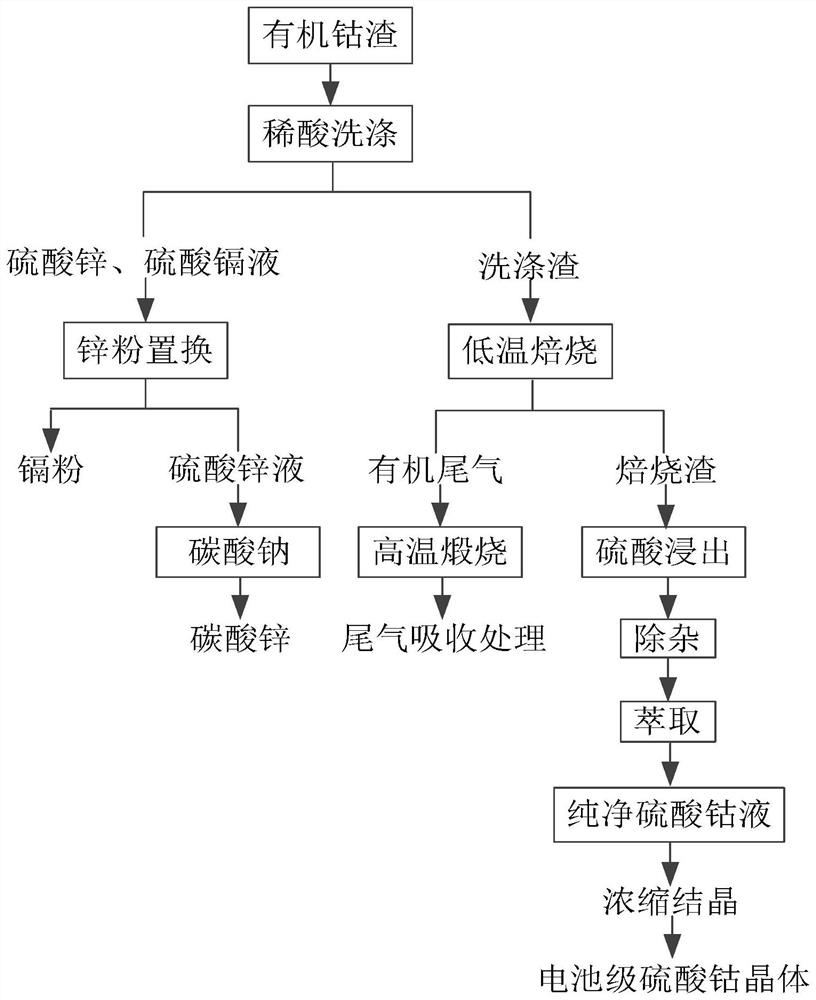
Method for producing cobalt sulfate by utilizing organic cobalt slag of zinc smelting plant
PendingCN112520790ADifficult to handleFully recycleCobalt sulfatesZinc compoundsSulfate zincZinc smelter
The invention discloses a method for producing cobalt sulfate by utilizing organic cobalt slag of a zinc smelting plant, and belongs to the field of non-ferrous metal hydrometallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, washing organic cobalt slag of a zinc smelting plant with dilute acid, enabling zinc and cadmium in the organic cobalt slag to react with dilute sulfuric acid to generate zinc sulfate and cadmium sulfate, enabling the zinc sulfate and cadmium sulfate to enter a solution, performing filtering, and recycling the solution to obtain cadmium powder and zinc carbonate;carrying out low-temperature roasting on the filter residues, carrying out high-temperature roasting on organic tail gas obtained by low-temperature roasting, carrying out high-temperature decomposition on the organic tail gas, carrying out cyclic absorption tail gas treatment through alkali liquor, carrying out low-temperature roasting to obtain cobalt oxide slag, performing leaching through sulfuric acid to obtain a solution containing cobalt sulfate, carrying out P204 extraction to deeply remove impurities, completely removing the impurities, extracting cobalt by using P507 to obtain a high-purity cobalt sulfate solution, and performing evaporation, concentration and crystallization to obtain a battery-grade cobalt sulfate crystal product. The application of the method develops a new cobalt raw material source for the field of non-ferrous metal hydrometallurgy, and the method has remarkable economic value and social value.
Owner:MEISHAN SHUNYING POWER BATTERY MATERIALS CO LTD
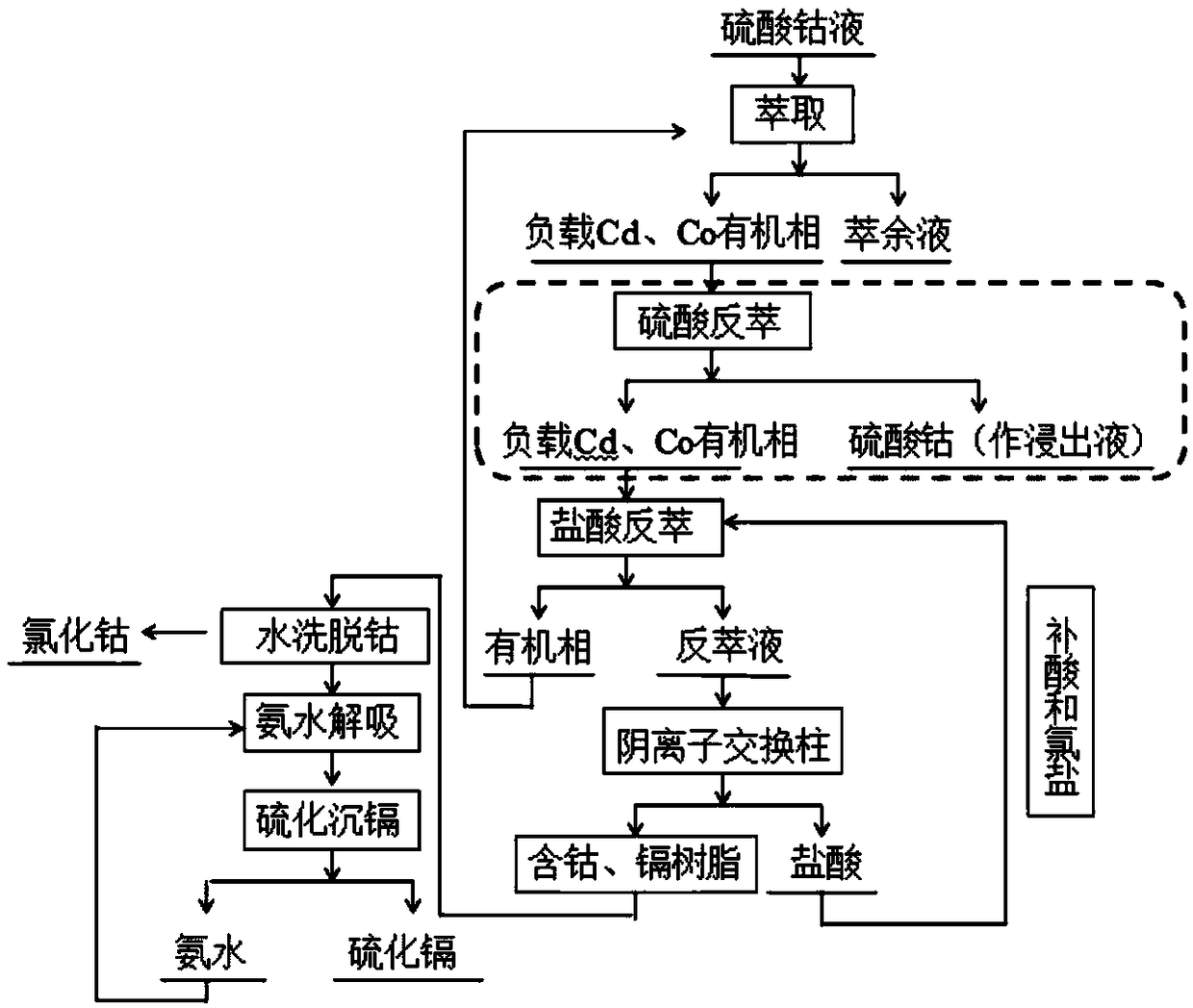
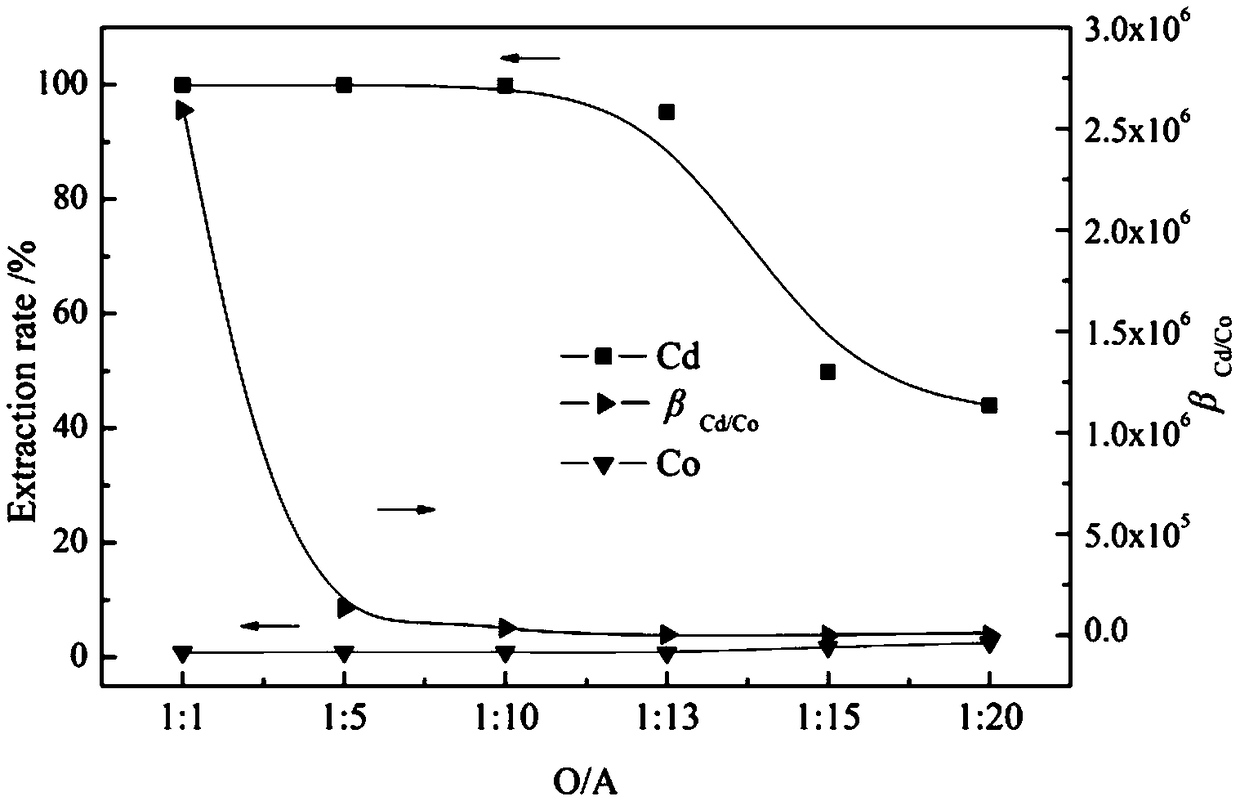
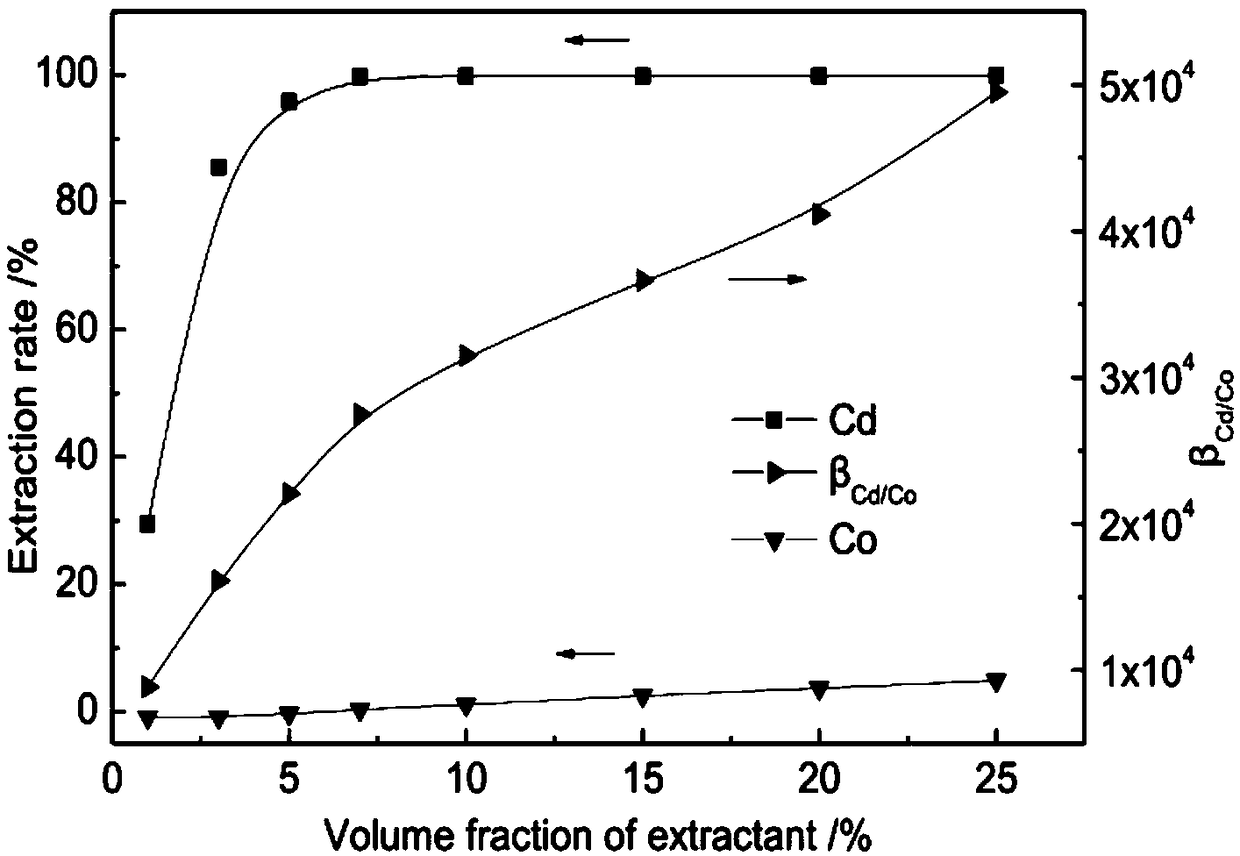
Method for deeply removing cadmium in high-concentration cobalt sulfate solution and recovering cadmium
ActiveCN108977669AAchieve deep extractionReduce concentrationCobalt sulfatesProcess efficiency improvementLoss rateHigh concentration
The invention discloses a method for deeply removing cadmium in a high-concentration cobalt sulfate solution and recovering the cadmium. According to the method, firstly, an extracted organic phase containing Cyanex301 is adopted to enable the concentration of the cadmium to be decreased to be 0.001 g / L or less; cobalt and the cadmium in the organic phase are reversely extracted through sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid, then resin is used for adsorbing metal complexing ions in stripping liquor, so that the cyclic utilization of the stripping liquor is realized; the resin is desorbed by using distilled water, so that separation of the cobalt and the cadmium on the resin is realized; and a desorption solution of the cadmium is subjected to vulcanization treatment, the cadmium is recycledin a form of a CdS product, and finally the ammonia desorption solution is returned for cadmium desorption, and the loss rate of the cobalt is almost zero in the whole technological process. The method has the advantages of being capable of efficiently removing the cadmium and cleaning and recovering the cadmium and capable of being widely applied to industrial production.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
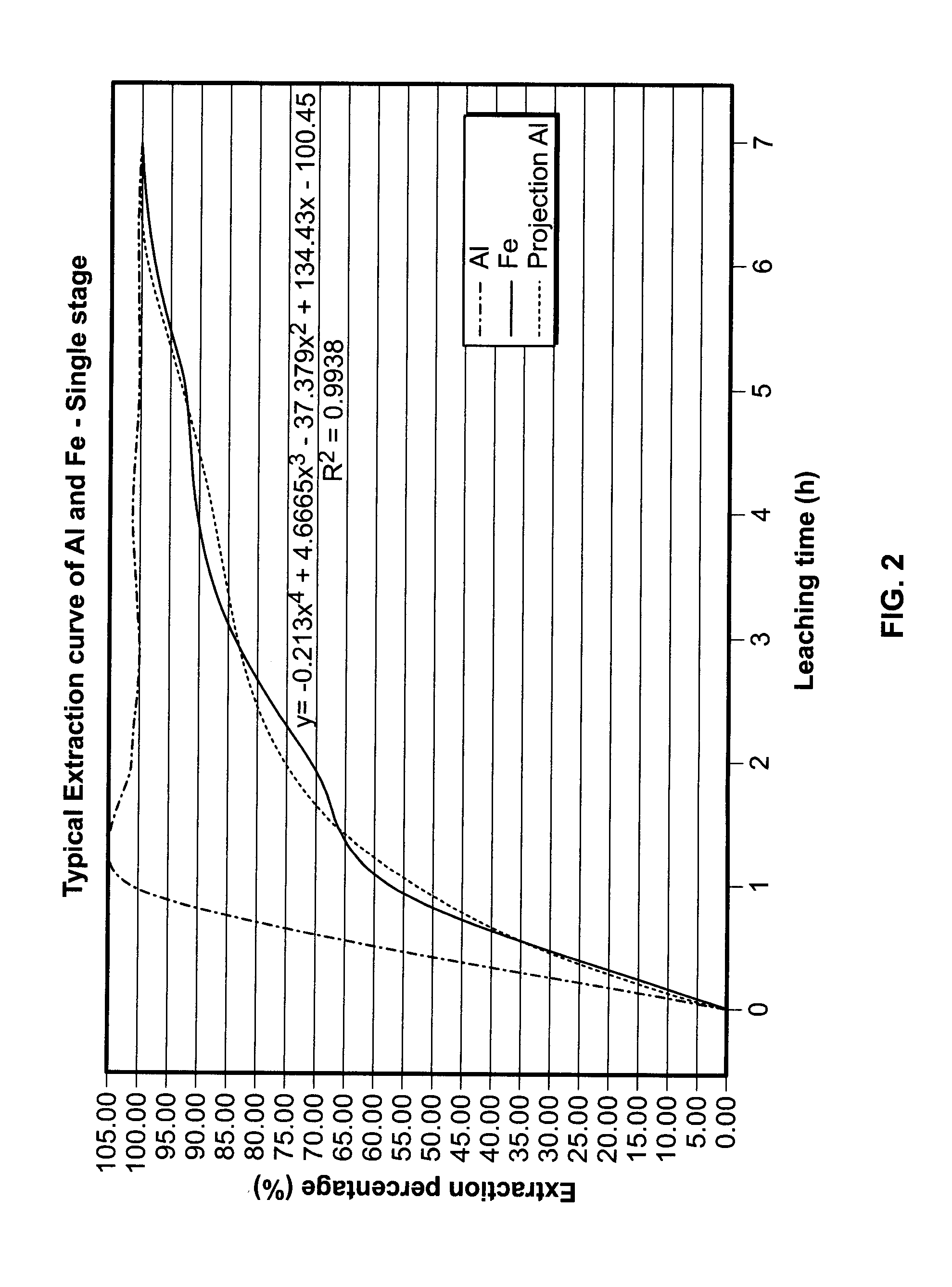
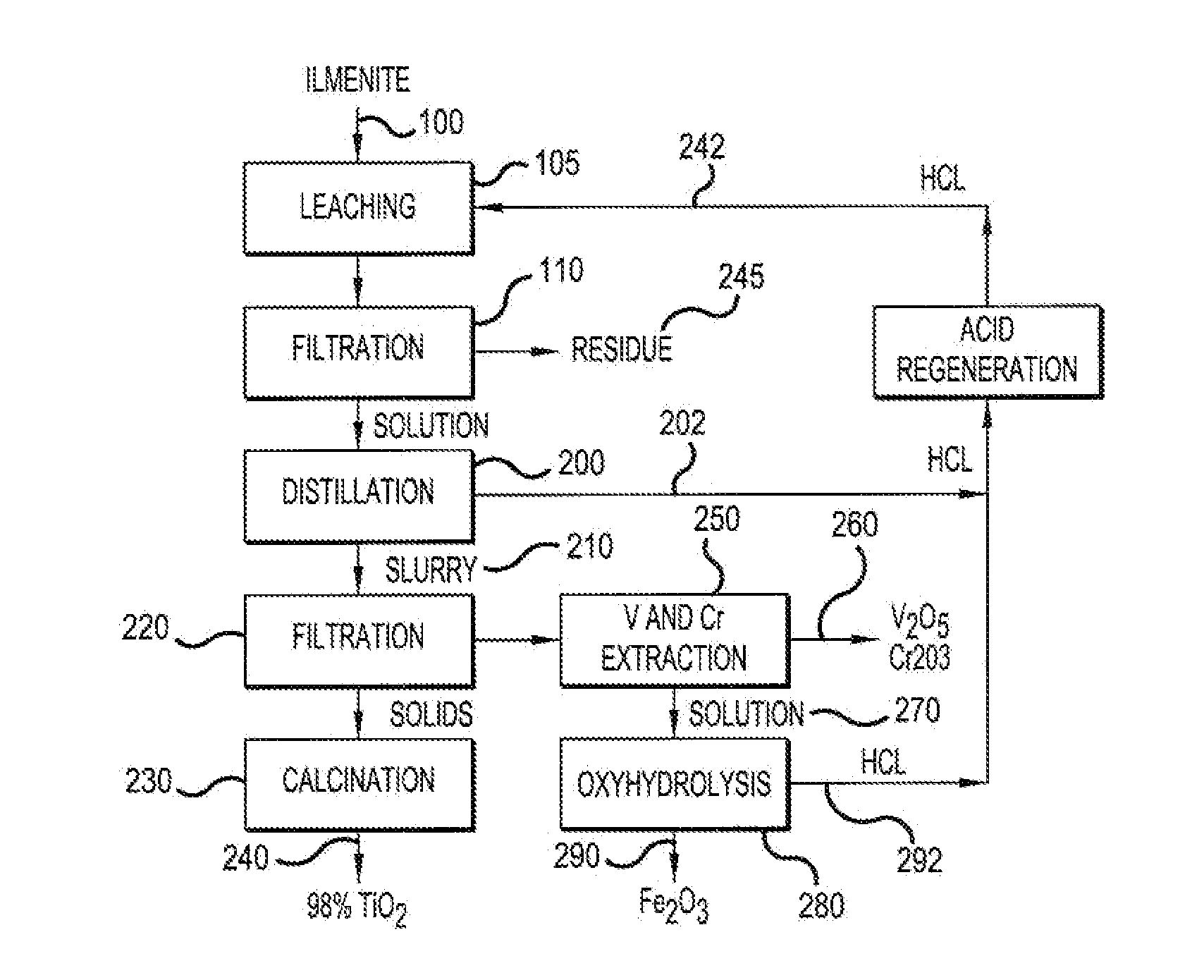
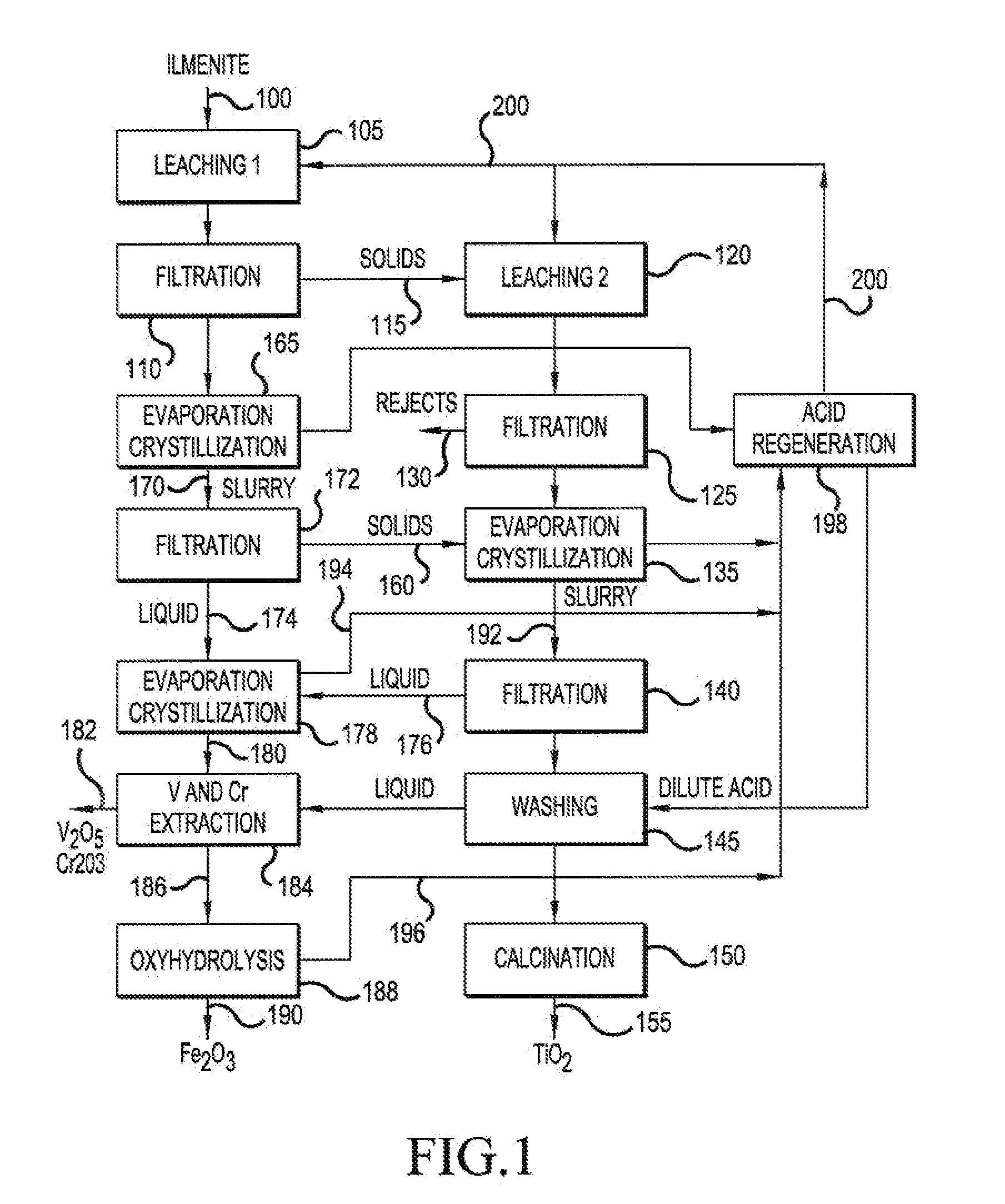
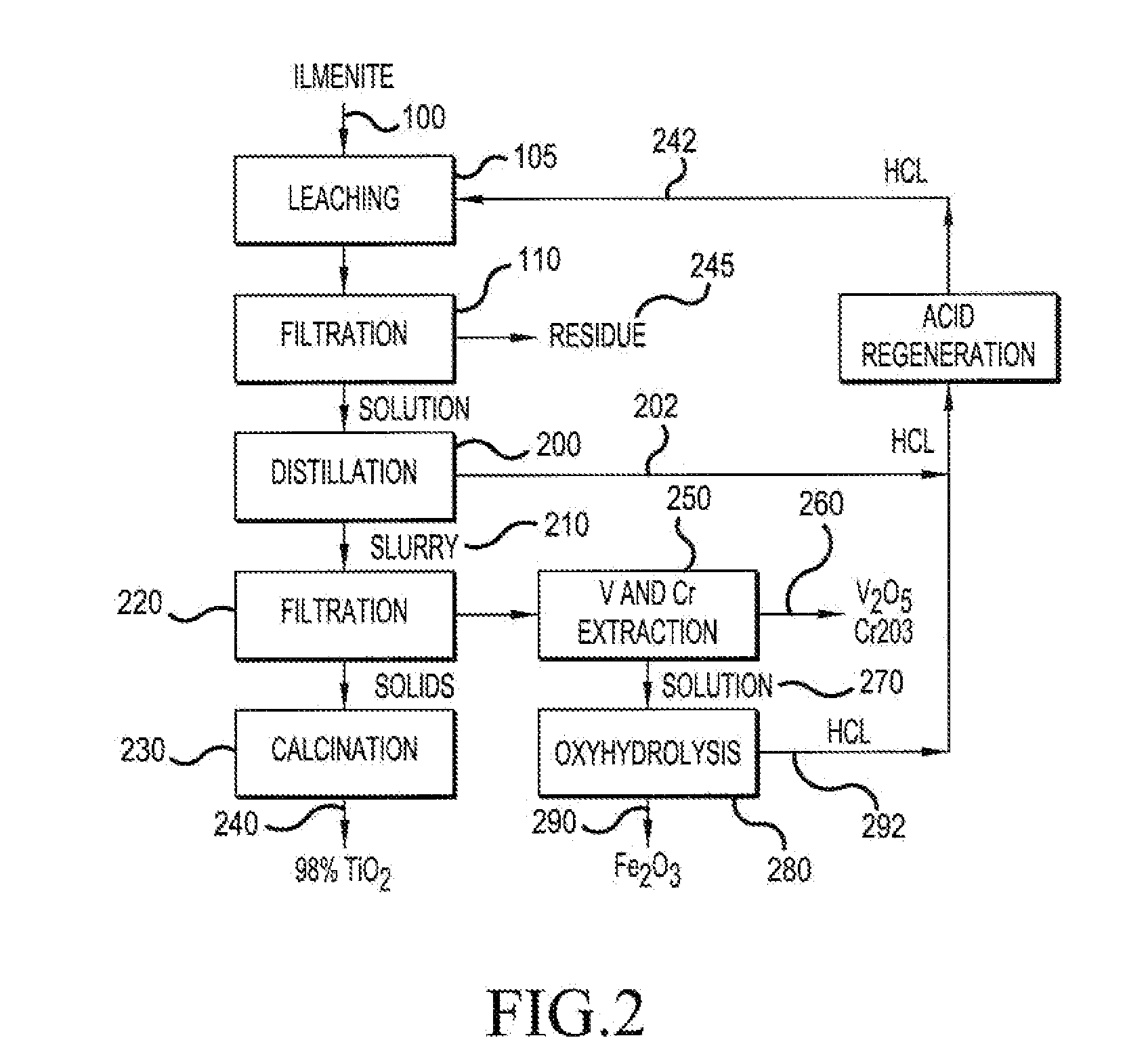
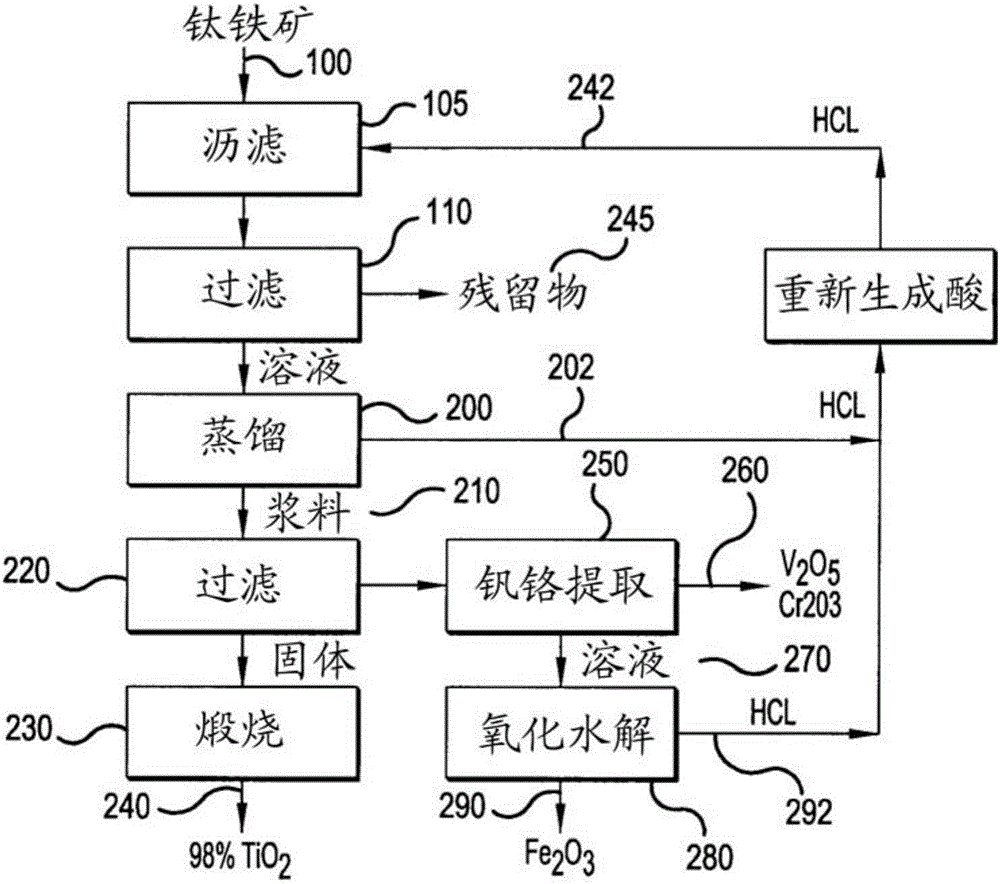
Production of high-grade synthetic rutile from low-grade titanium-bearing ores
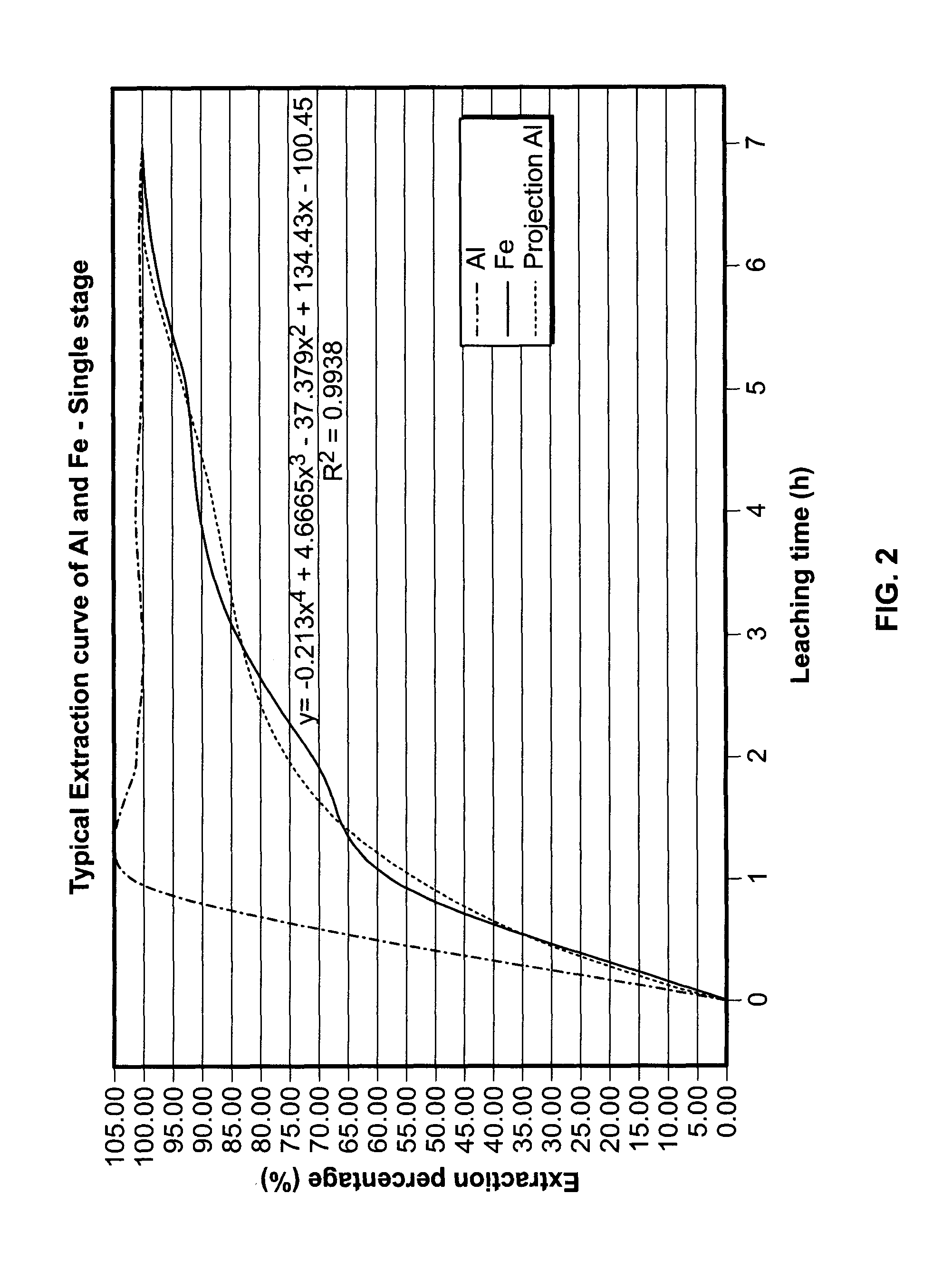
The present invention relates to a two-stage leaching process using concentrated hydrochloric acid that upgrades a variety of inferior quality titanium-iron ores into premium titanium concentrate and iron oxide products. The ground ore is leached with two separate quantities of hydrochloric acid after which the dissolved titanium is precipitated from the filtered liquor by hydrolysis. The still soluble iron chlorides are then optionally subjected to oxyhydrolysis to recover iron oxide and HCl. The process was developed for low-grade ores (under 12% TiO2), and can be naturally applied advantageously to higher grade titanium-bearing ores.
Owner:FFK TECH INC
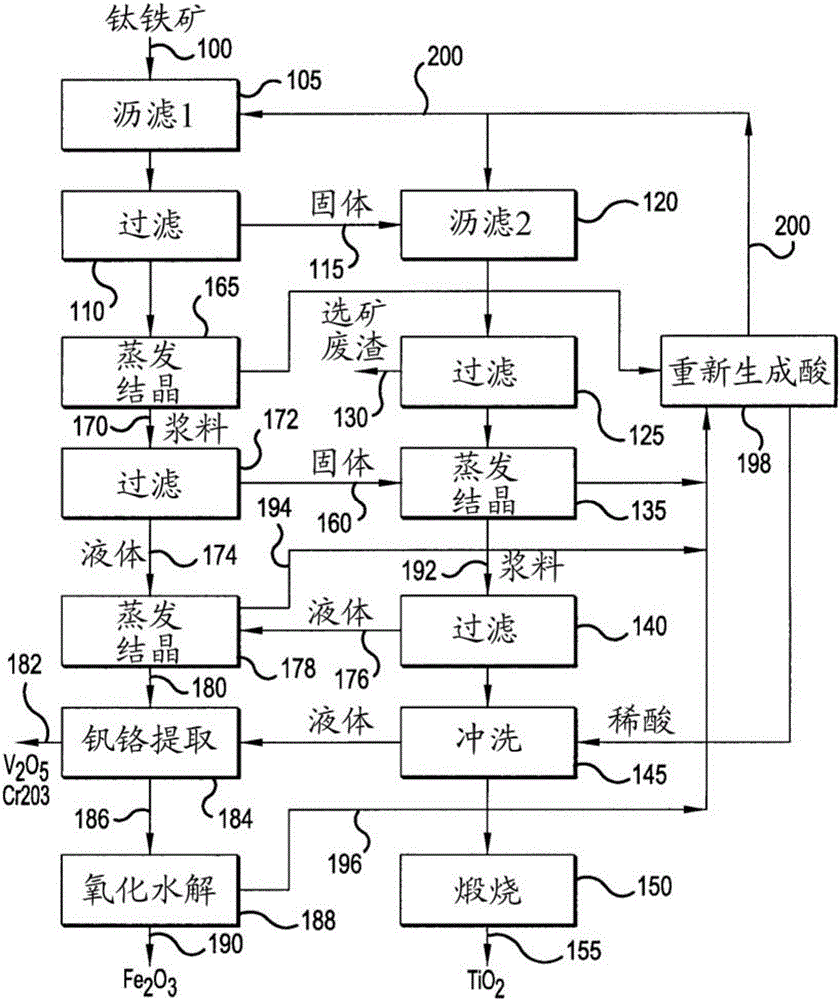
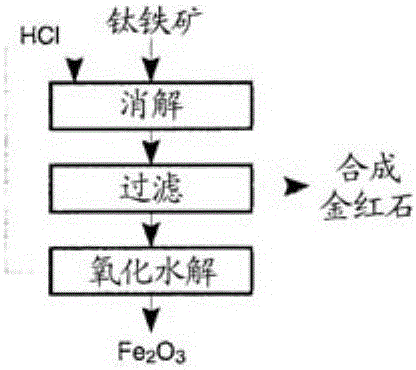
The production of high-grade synthetic rutile from low-grade titanium-bearing ores
InactiveCN106232840AWidely availableChlorine/hydrogen-chloride purificationFerric oxidesIronstoneHydrolysis
The present invention relates, first, to a two-stage leaching process using concentrated hydrochloric acid wherein ground ore is leached with two separate quantities of hydrochloric acid at different temperatures. Second, the invention relates to a one-step leaching process using concentrated HCl and a fixed acid to ore ratio to prevent hydrolysis of titanium. Afterwards the dissolved titanium is precipitated from the filter liquor by hydrolysis and the still soluble iron chlorides are then optionally subjected to oxyhydrolysis to recover iron oxide and HCl. The process was developed for low-grade ores (under 12% Ti02), and can naturally be applied advantageously to higher grade titanium-bearing ores, that upgrades a variety of inferior quality titanium-iron ores into premium titanium concentrate and iron oxide products.
Owner:FFK TECH INC
Carbon particle having deposited fine particles, process forproducing the same, and electrode for fuel cell
InactiveCN101467285AIncreased durabilityAvoid corrosionMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesPtru catalystPerovskite (structure)
The present invention provides carbon particles with fine particles deposited thereon and a manufacturing method thereof. The carbon particles with fine particles deposited thereon is characterized in that the surface of carbon particle is loaded with perovskite type composite metal oxide particles. The entire body particle of the perovskite type composite metal oxide particle is provided with noble metal particle. The carbon particles with fine particles deposited thereon can replace the commonly used platinum-loaded carbon particle or metal platinum particle for being used as electrode catalyst of fuel cell, etc. Furthermore the use amount of platinum can be greatly reduced compared with the previous platinum-loaded carbon particle. The structure is that the perovskite type composite metal oxide particle is loaded on the carbon particle. The entire body of perovskite type composite metal oxide particle is provided with noble metal particles and the dimension of minicrystal is 1-20nm. For manufacturing the carbon particles with fine particles deposited thereon, the method comprising the following steps can be adopted: preparing a solution comprising the metal complexion forming the perovskite type composite metal oxide particles and noble metal particles, subsequently repeating the step of impregnating the solution into carbon particles and dried the particles thereby adsorbing complex ions of the metal onto the carbon particles, and then subjecting the resultant particles to heat treatment.
Owner:HITACHI MAXELL ENERGY LTD +1
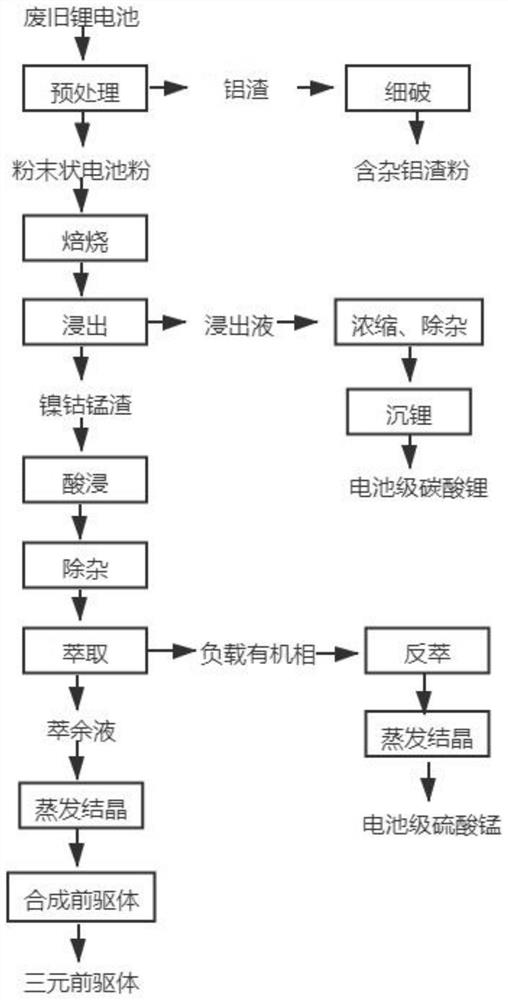
Method for recycling waste lithium battery and preparing ternary precursor
PendingCN113802003AHigh recovery rateAvoid the effects of extractionCobalt sulfatesNickel compounds preparationManganese sulphateMetal chloride
The invention discloses a method for recycling a waste lithium battery and preparing a ternary precursor. The method comprises the following steps of pretreating the waste lithium battery to obtain battery powder and aluminum slag, roasting the battery powder, adding water into the roasted battery powder to prepare slurry, adding metal chloride to carry out leaching reaction, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain nickel-cobalt-manganese slag and a lithium chloride solution; adding sulfuric acid into nickel-cobalt-manganese slag for acid leaching, adding aluminum slag into an acid leaching solution to remove copper, adjusting the pH value of the acid leaching solution to remove aluminum, mixing the aluminum-removed solution with a compound extraction agent, extracting to obtain a manganese-containing organic phase and a nickel-cobalt-containing raffinate, wherein the organic phase can be used for preparing manganese sulfate, and the raffinate can be used for preparing a high-purity nickel-cobalt sulfate mixed crystal through crystallization; and after the obtained battery-grade manganese sulfate and nickel-cobalt sulfate mixed crystal is dissolved in water, a certain amount of nickel-cobalt-manganese sulfate is supplemented to prepare a ternary precursor. The recovery process route provided by the invention has the advantages of simplicity in operation, low production cost, stability and reliability.
Owner:GUANGDONG BRUNP RECYCLING TECH +2
Method for producing cobalt sulfate
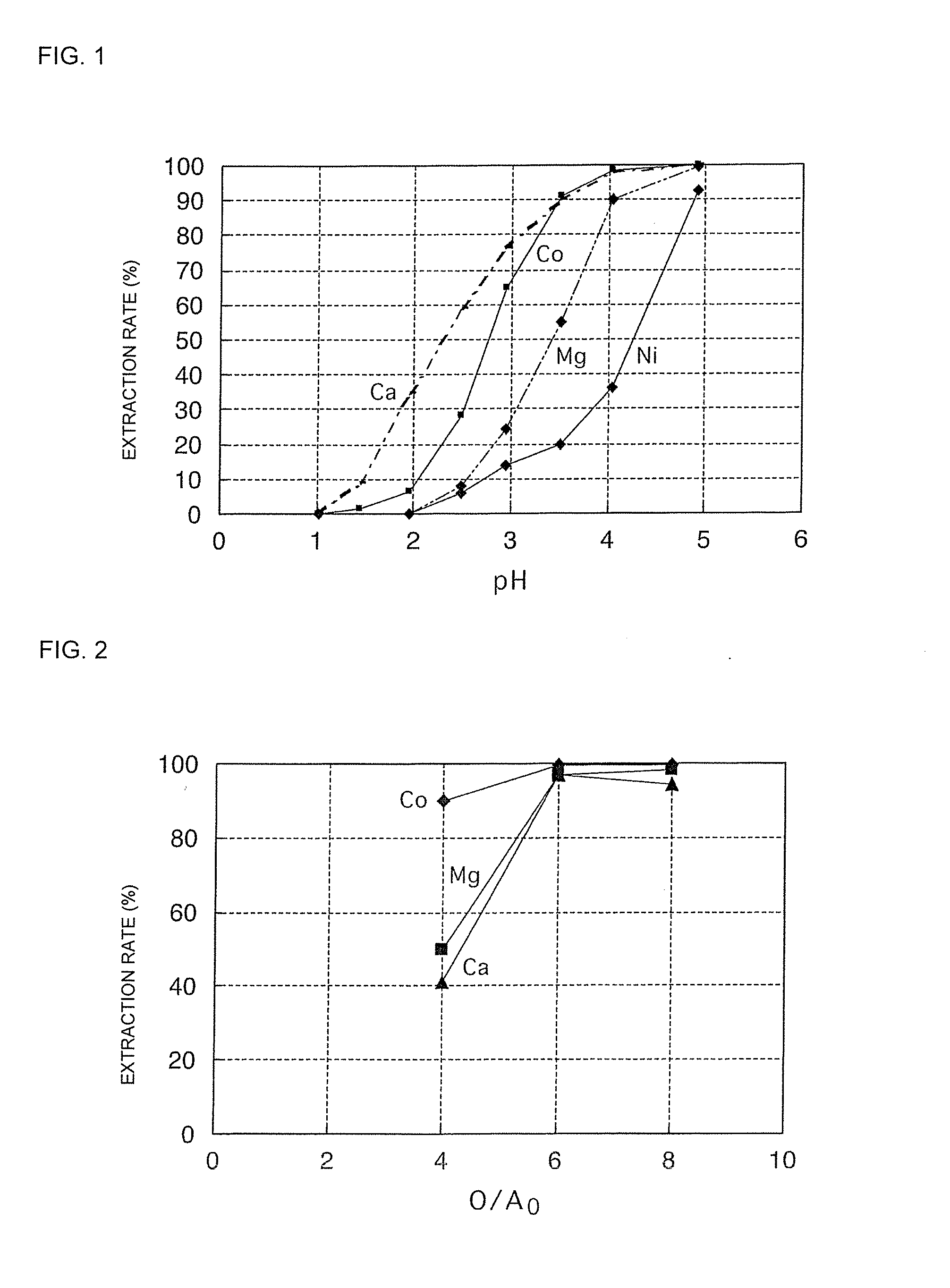
ActiveUS20140348731A1Reduce calcium concentrationHigh puritySolvent extractionIron compoundsDiluentSolvent
Provided is a method for producing cobalt sulfate, wherein, on the occasion of separating an acidic solution containing calcium, magnesium and sodium as impurities from a cobalt chloride solution by solvent extraction, when a diluent is added to the extractant to be used to dilute the extractant by 10% to 30% by volume; in Step 1, the operational pH is maintained in the range of 4.0 to 5.0 and the liquid volume ratio of organic phase / liquid phase is maintained in the range of 5.0 to 7.0; in Step 2, the operational pH is maintained in the range of 4.0 to 4.5 and the liquid volume ratio of organic phase / liquid phase is maintained in the range of 5.0 to 10.0; and in Step 3, the pH is maintained in the range of 0.5 to 1.0.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
Process for the extraction of specific transition metals with gaseous HCL
A process is disclosed for separation and recovery of vanadium, molybdenum, iron, tungsten, cobalt and nickel from alumina-based materials, mattes, ores, manufacturing by-products and waste. These elements are oxidized. The oxides are reacted with gaseous HCl to form volatile chloride-bearing compounds that subsequently sublimate. The volatile compounds are condensed in a downward-stepped thermal gradient that allows collection of moderate to high purity compounds of individual elements with exception of a nickel-cobalt co-condensate. Nickel is separated from cobalt by precipitation of nickel chloride from concentrated HCl pressurized with gaseous HCl.
Owner:METALS RECOVERY TECH
A method for producing battery-grade nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate from waste nickel-cobalt alloy
ActiveCN108622943BMild responseReduce pollutionCobalt sulfatesNickel compounds preparationNew energyEvaporation
The invention discloses a method for producing battery grade nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate by waste nickel cobalt alloy. The method comprises the following steps of performing pretreatment on nickel cobalt alloy waste materials; then, performing electrochemical dissolution; removing impurities such as iron, chromium and aluminum from the obtained solution step by step by a chemical method andan extraction method; firstly extracting cobalt from the solution subjected to impurity removal; then extracting nickel; thus respectively obtaining extraction liquid containing cobalt and nickel; after the reverse extraction, obtaining nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate solution; then, respectively performing evaporation, cooling crystallization, and centrifugal dewatering on the solution to obtain a product of the battery grade nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate. The problems of low nickel and cobalt leaching efficiency, low dissolution speed and the like in the waste nickel and cobalt alloy recovery process by a conventional wet process can be effectively solved; the battery grade nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate conforming to the product quality standard requirement can be produced, andcan be used as a new energy source battery raw material to be applied to the field of new energy source battery manufacturing. The process is simple; the environment pollution is low; the metal recovery rate is high; good practical values and economic values are realized.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
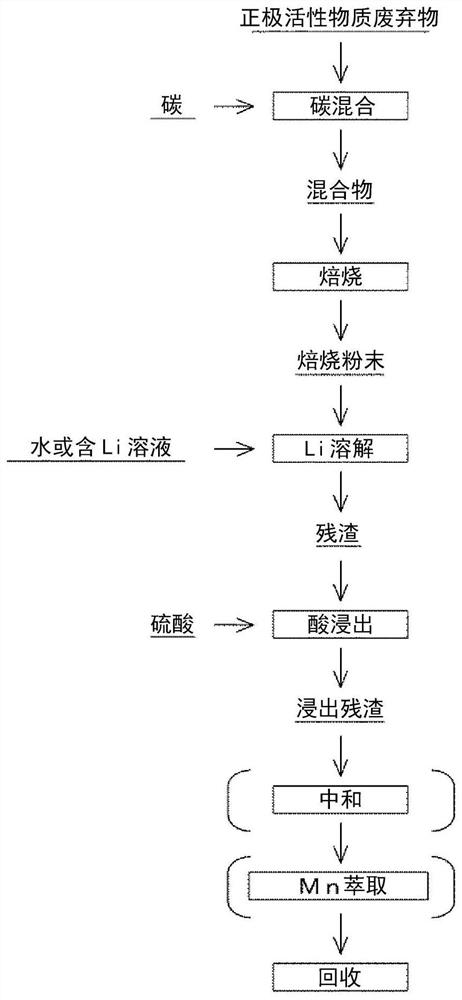
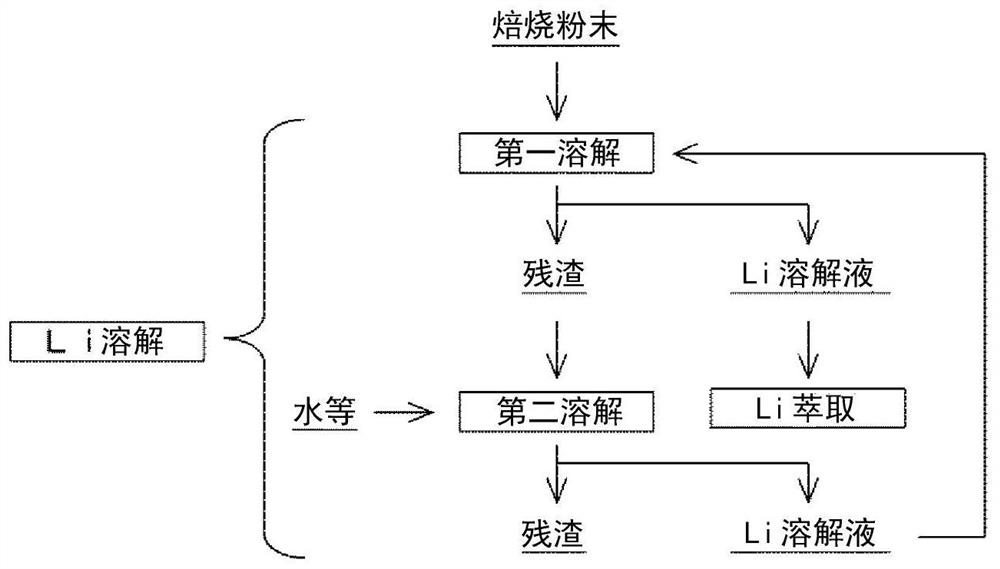
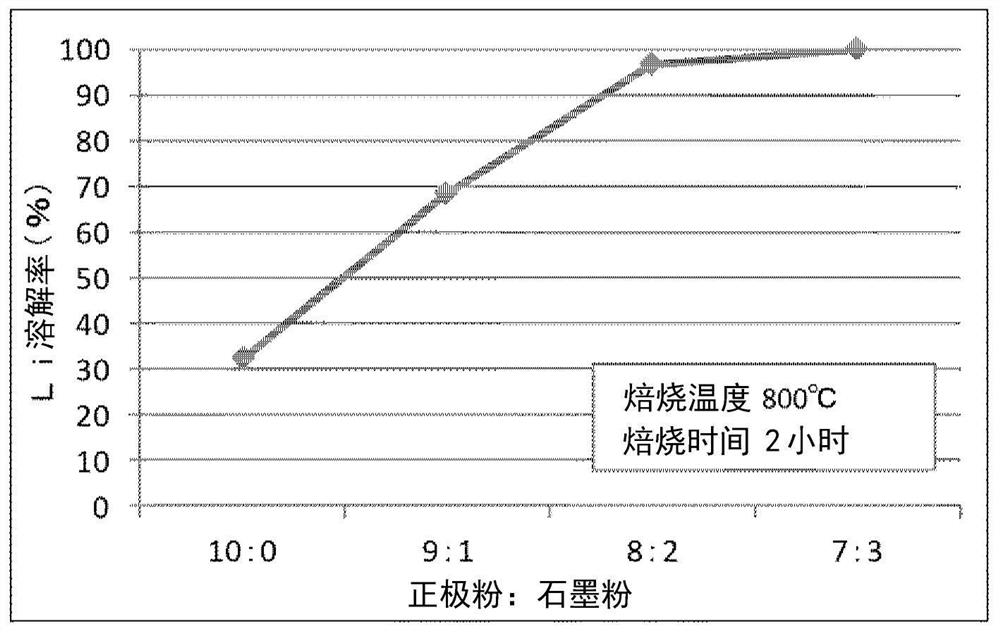
Treatment method of positive electrode active substance waste product of lithium ion secondary battery
PendingCN112930618AEfficient recyclingElectrode manufacturing processesTransportation and packagingManganeseBattery cell
A method is for treating a lithium ion secondary battery positive electrode active substance waste product that contains cobalt, nickel, manganese and lithium, and involves: a carbon mixing step in which a powder-form positive electrode active substance waste product is mixed with carbon to obtain a mixture in which the ratio of the mass of the carbon is 10-30% of the total mass of the positive electrode active substance waste product and the carbon; a roasting step for roasting the mixture at a temperature of 600-800 DEG C to obtain a roasted powder; a lithium dissolving step which involves a first dissolving process for dissolving the lithium in the roasted powder in water or a lithium-containing solution and a second dissolving process for dissolving the lithium in the residue obtained in the first dissolving process in water; and an acid leaching step in which the residue obtained in the lithium dissolving step is leached with acid.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CO LTD
Method for recovering nickel from sulfuric acid aqueous solution
ActiveUS8580213B2Easy to useImprove economySolvent extractionNickel compounds preparationPhosphateManganese
A method for recovering nickel from sulfuric acid aqueous solution, for recovering nickel in an effectively utilizable form as a raw material of nickel industry material, by separating efficiently impurity elements of iron, aluminum, manganese, etc., from the sulfuric acid aqueous solution containing nickel and cobalt, and the impurity elements, iron, aluminum, manganese, etc. The method comprises the following steps: subject the sulfuric acid aqueous solution to oxidation neutralization treatment; then subject the solution to neutralization treatment, and separate and recover mixed hydroxides containing nickel and cobalt; subject the mixed hydroxides to dissolution treatment in a sulfuric acid solution having a concentration of equal to or higher than 50% by mass; subject the concentrated solution to solvent extraction treatment, using a phosphate ester-based acidic extraction agent; add a neutralizing agent to the resultant extraction residual liquid; subject the solution to the neutralization treatment, and separate and recover nickel hydroxide generated.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
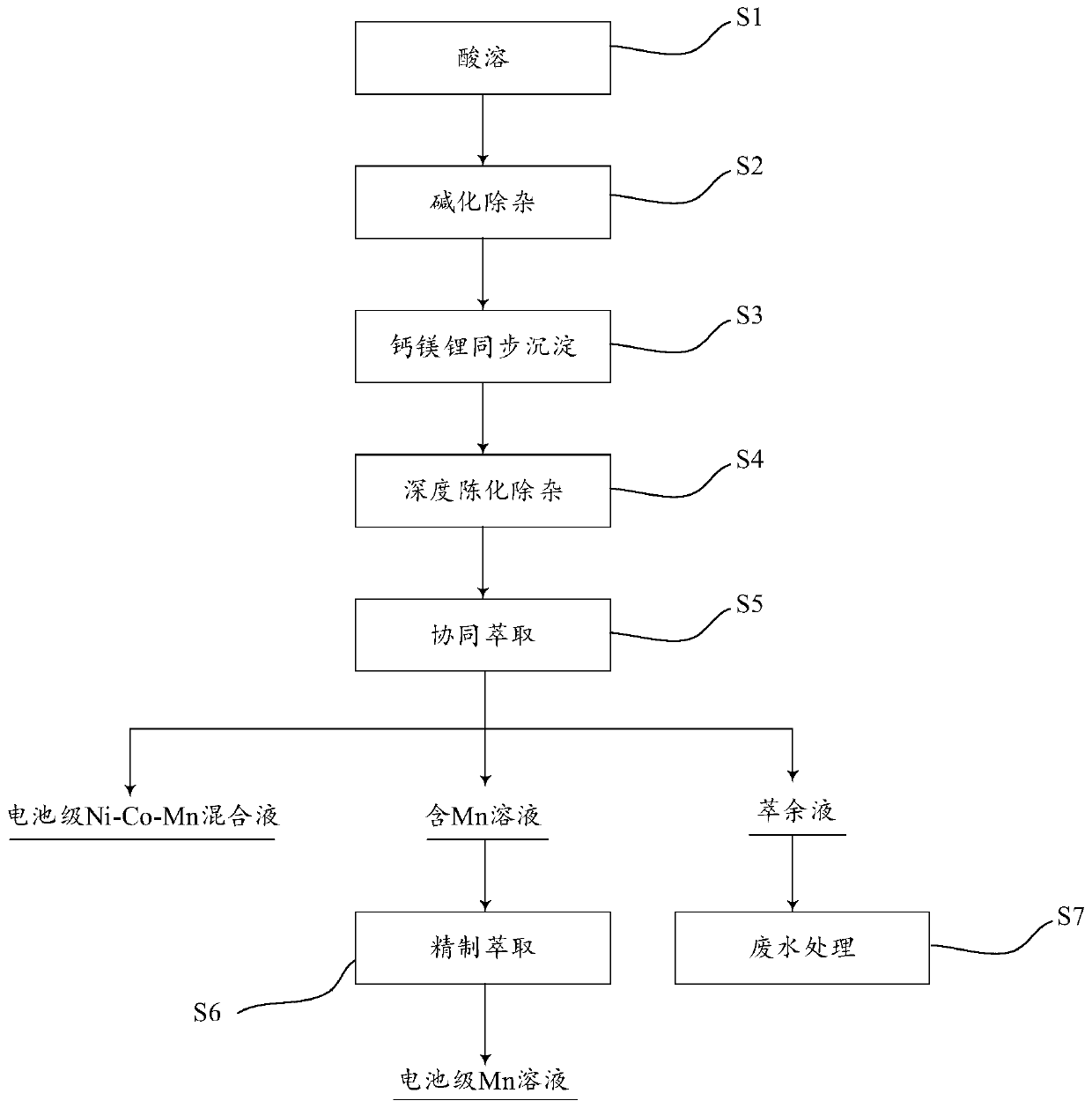
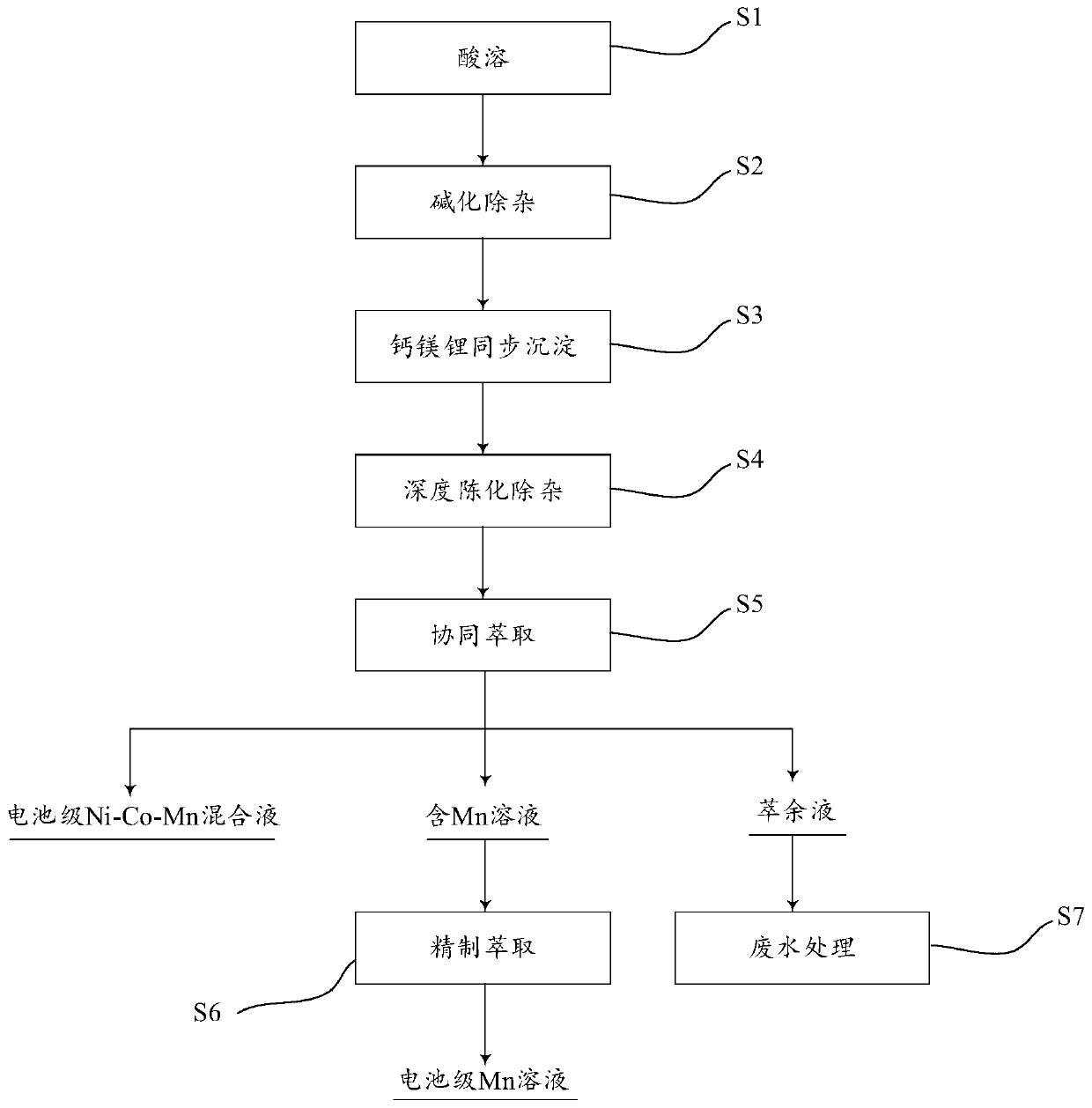
Preparation method of battery-grade Ni-Co-Mn mixed solution and battery-grade Mn solution
ActiveCN111180819ALow impurity contentHigh recovery rateMagnesium fluoridesCell electrodesPhysical chemistryAcid dissolution
The invention discloses a preparation method of a battery-grade Ni-Co-Mn mixed solution and a battery-grade Mn solution. The preparation method comprises the following steps: acid dissolution, alkalization and impurity removal, calcium-magnesium-lithium synchronous precipitation, deep aging and impurity removal, collaborative extraction and refined extraction. The deep aging impurity removal and synergistic extraction step comprises the following steps: carrying out deep aging on filtrate obtained after the calcium-magnesium-lithium synchronous precipitation step, and performing filtering to remove impurities, so as to obtain aged filtrate; and extracting the aged filtrate by using P204 to obtain a loaded organic phase, and carrying out graded reverse extraction on the loaded organic phaseto obtain a battery-grade Ni-Co-Mn mixed solution and a Mn-containing solution. Through cooperation of multiple process steps of calcium-magnesium-lithium synchronous precipitation, deep aging impurity removal and synergistic extraction, the impurity content of the obtained battery-grade Ni-Co-Mn mixed solution is remarkably reduced, and the battery-grade Ni-Co-Mn mixed solution can be directly applied to preparation of a lithium battery ternary precursor material; and meanwhile, a battery-grade Mn solution can be obtained, large-scale application of the process is facilitated, and economic benefits are improved.
Owner:JINGMEN GEM NEW MATERIAL +1
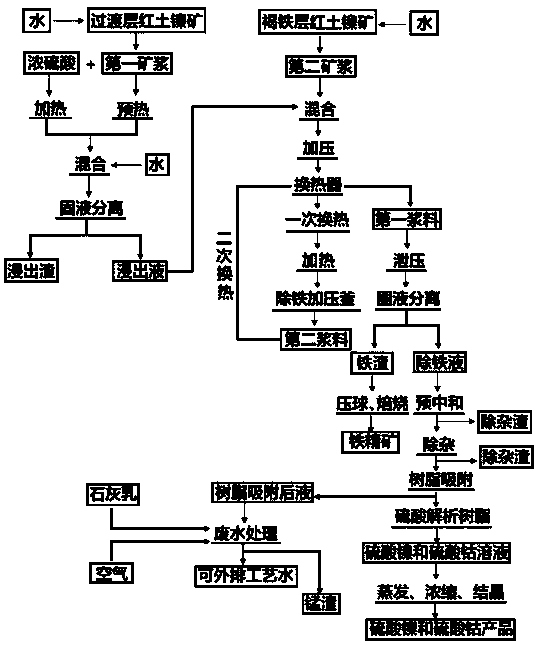
Method for extracting nickel, cobalt and iron from low-grade laterite nickel ore
InactiveCN111004915AImprove iron gradeAchieve recyclingCobalt sulfatesNickel compounds preparationSmelting processElectrical battery
The invention provides a method for extracting nickel, cobalt and iron from low-grade laterite nickel ore. Laterite nickel ore on a transition layer and laterite nickel ore on a limonite layer are processed respectively, and the iron grade of produced iron concentrate reaches 60-65%; and meanwhile, after a resin adsorption technology is adopted and evaporation, concentrating and crystallizing areperformed, a nickel sulfate product containing 20-23% of nickel and a cobalt sulfate product containing 1-2.2% of cobalt are produced and can be used as raw materials for battery production. Accordingto the method, the economic benefit of a laterite nickel ore wet smelting process technology is greatly increased, it is achieved that a cold material before reacting exchanges heat with a hot material after reacting through a heat exchanger, energy consumption is reduced, and in addition, the technological process is simplified.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
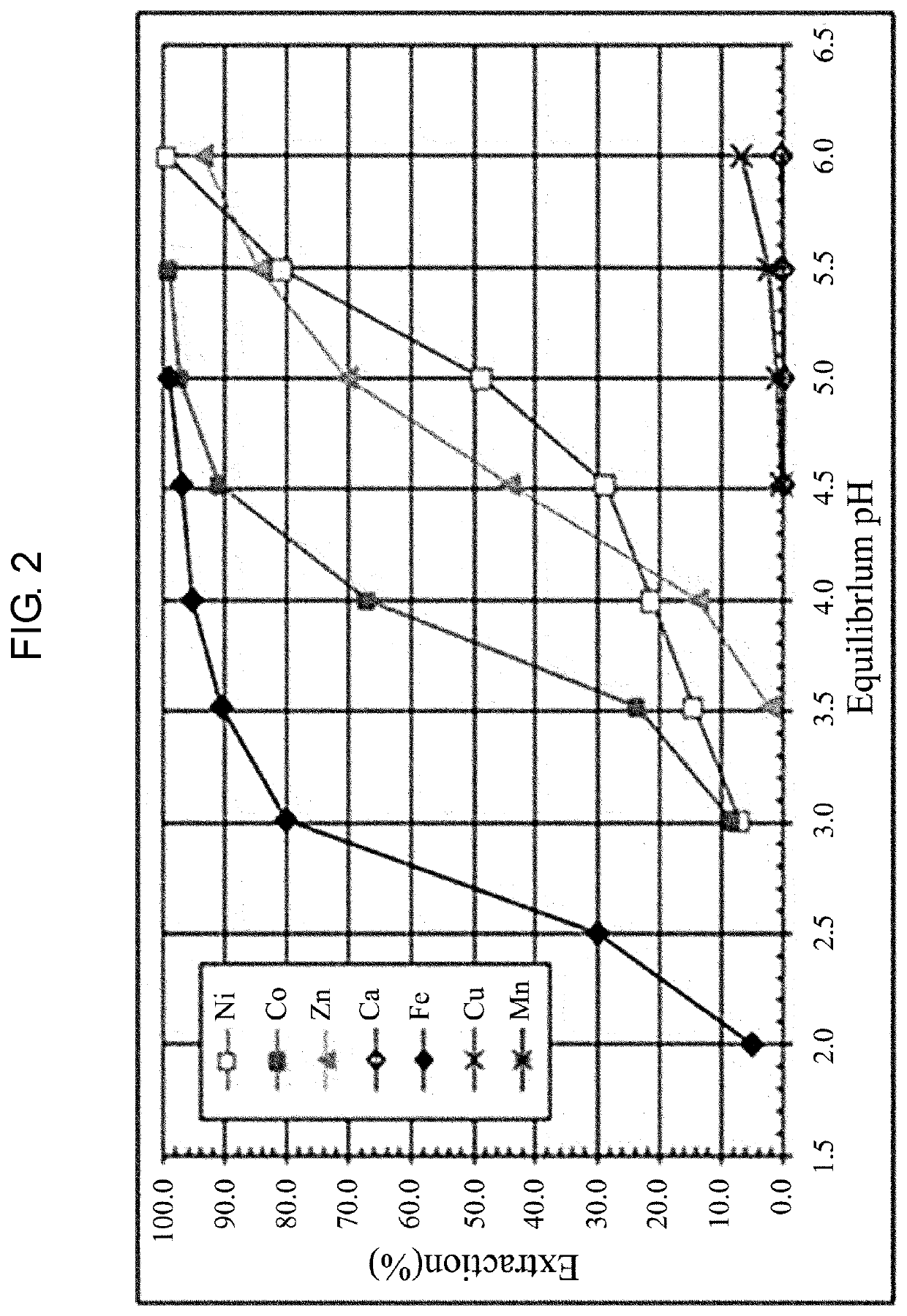
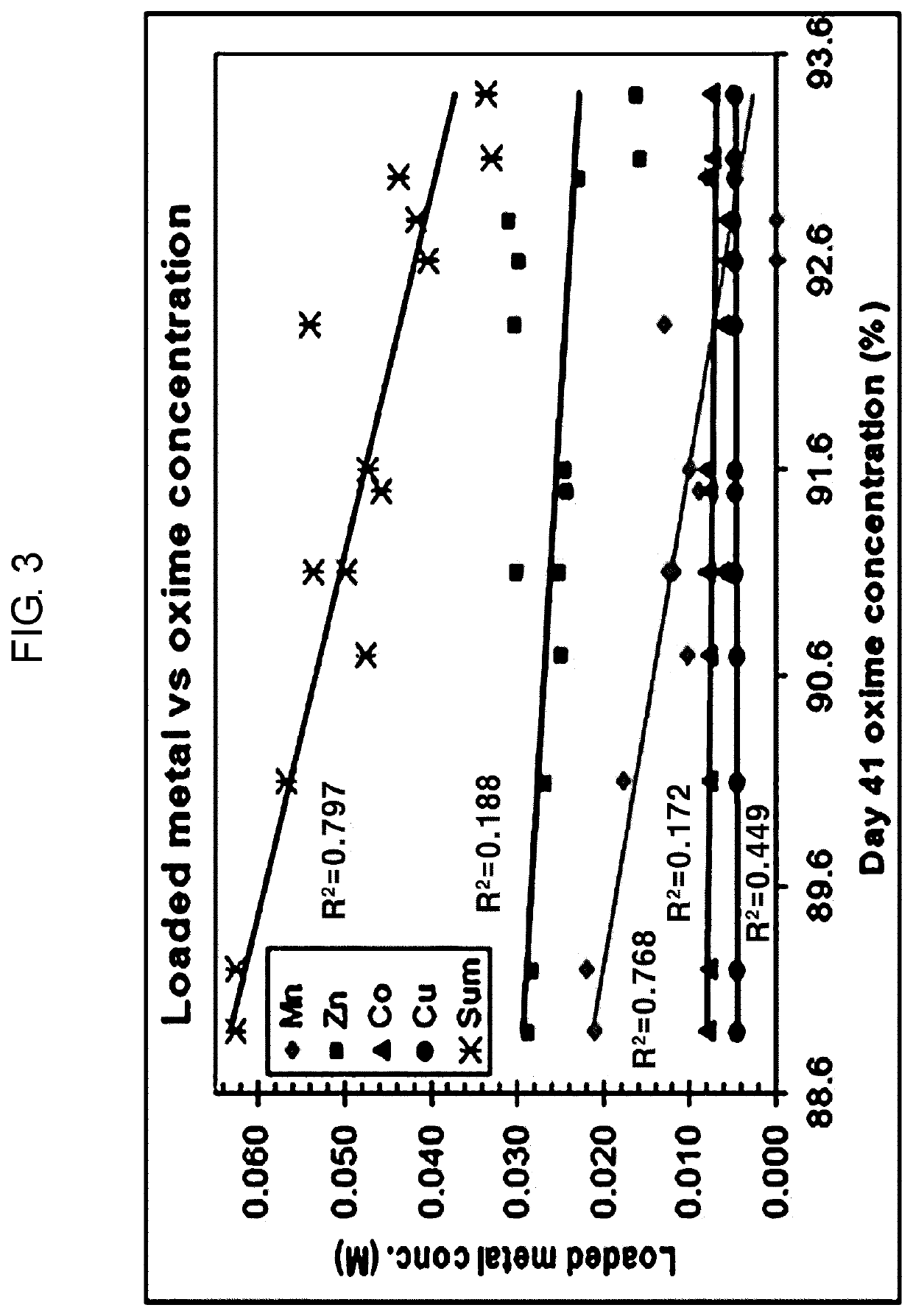
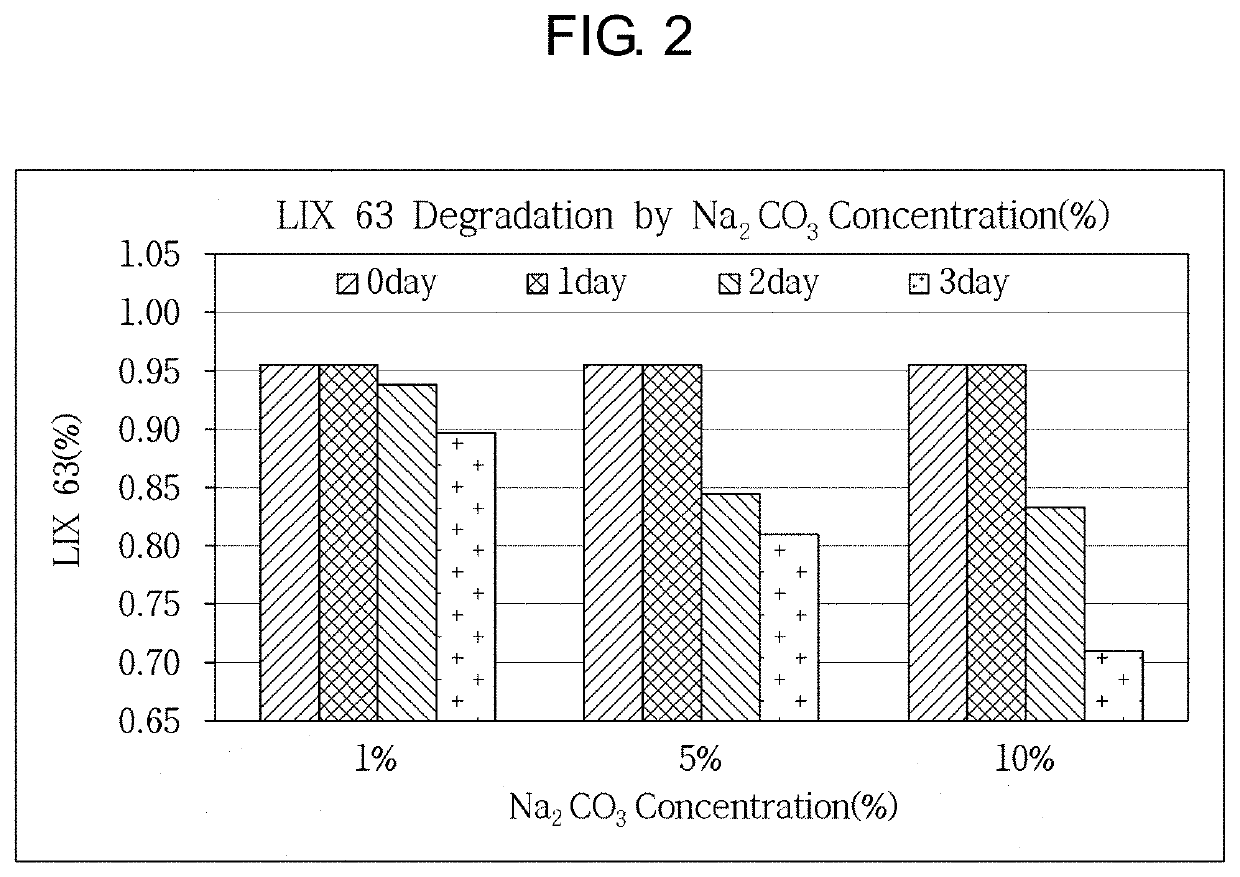
Method for inhibiting extractant degradation of dsx process through manganese extraction control
ActiveUS20210024366A1Minimizing extractionPrevent degradationZinc compounds preparationProcess efficiency improvementManganeseSolvent
Provided is a method for inhibiting extractant degradation in the DSX process through the manganese extraction control, the method comprising: (a) stirring DSX solvent and DSX feed solution, which is a solution containing a valuable metal from which iron has been removed in an agitator, in which soda ash (Na2CO3) is further added to maintain a constant pH; and (b) scrubbing the manganese from the DSX solvent, extracted in step (a).
Owner:KOREA MINE REHABILITATION & MINERAL RESOURCES CORP
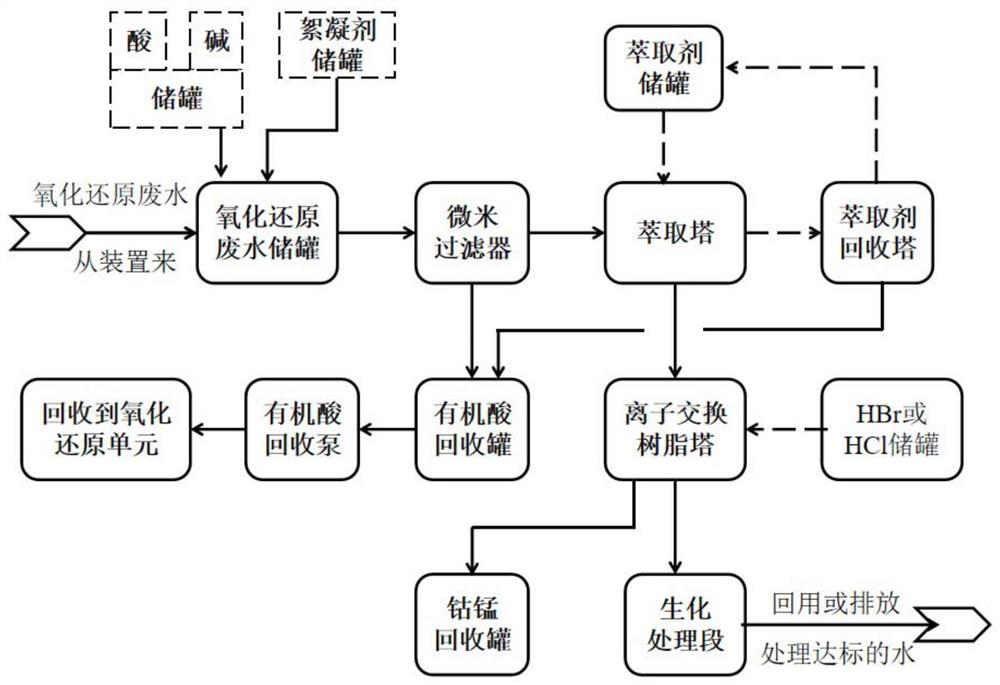
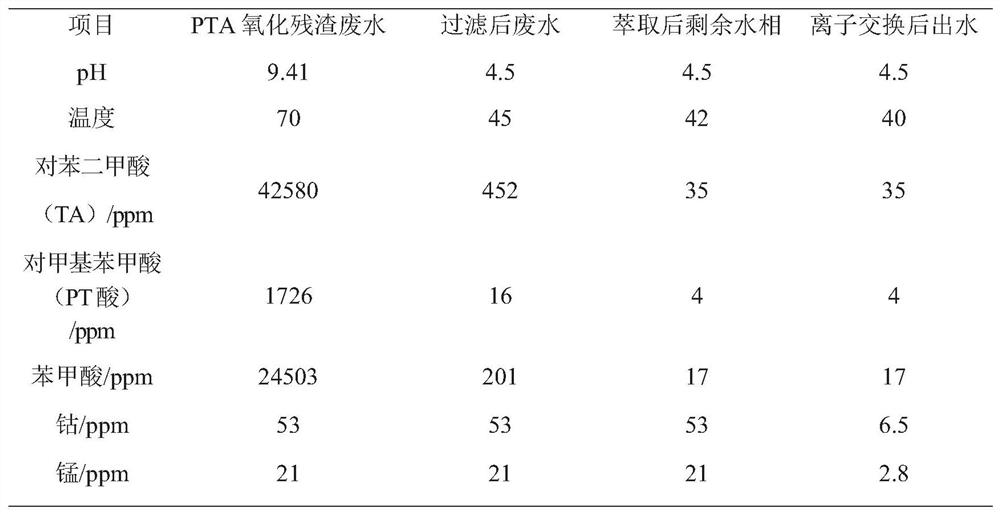
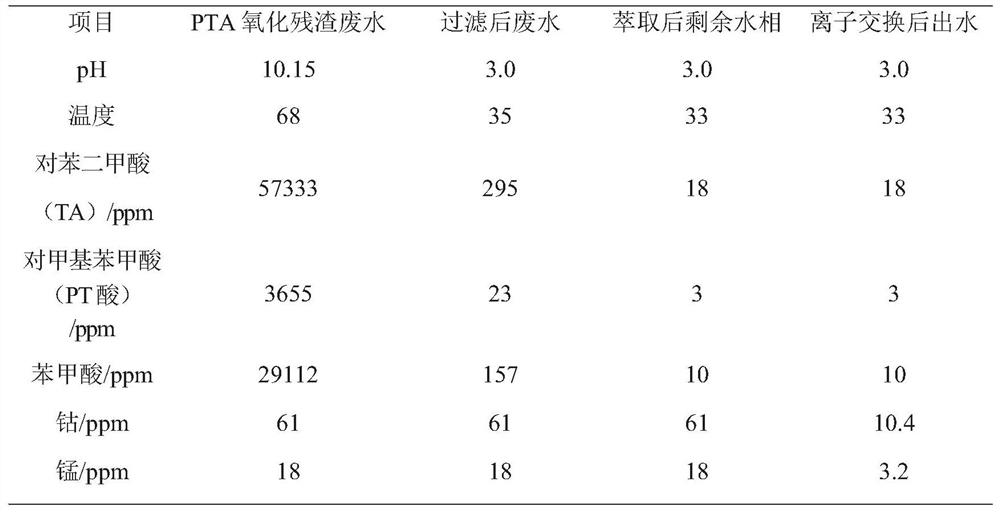
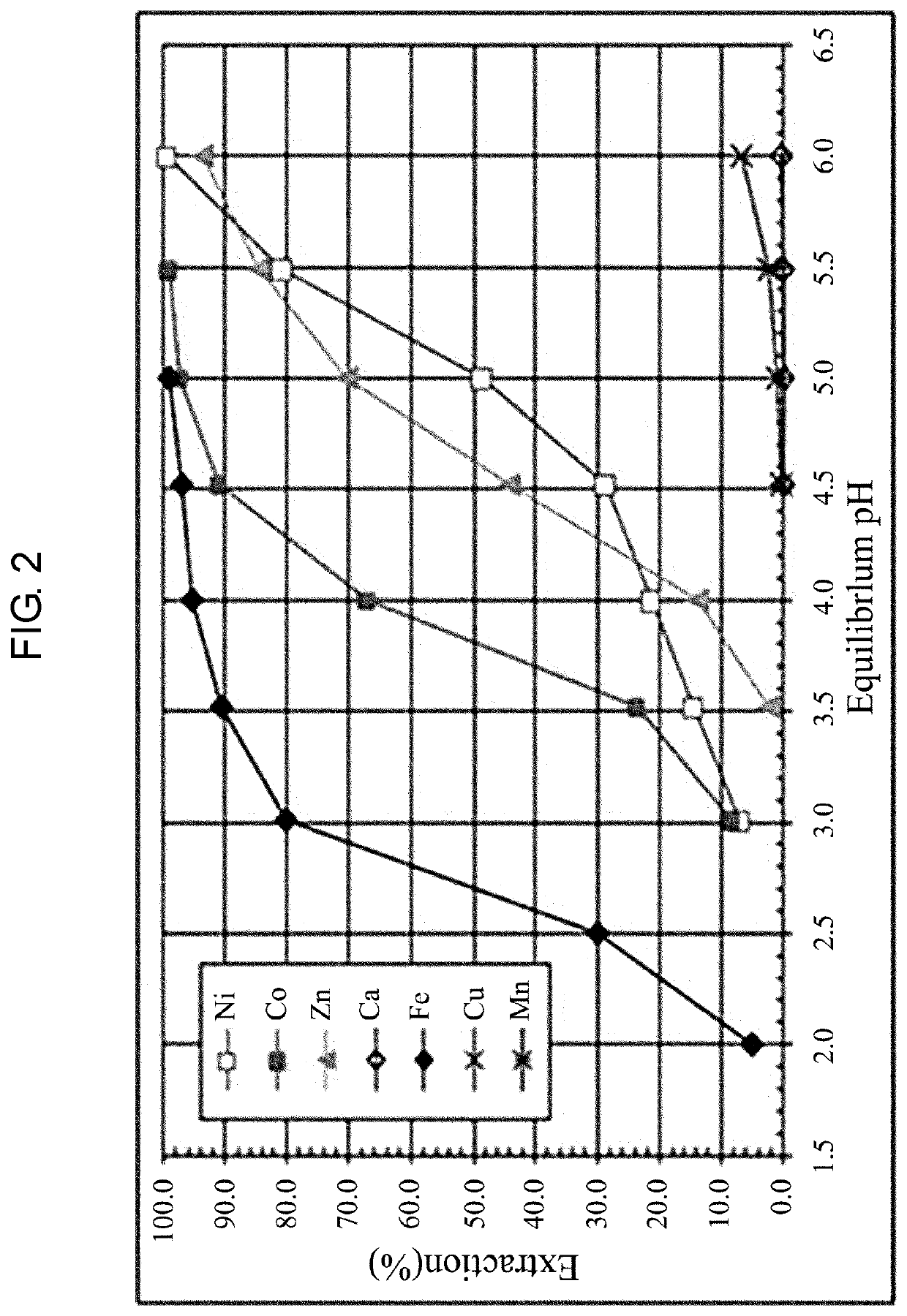
Method for recycling purified terephthalic acid wastewater
PendingCN113105056AReduce processing loadThe logic of the operation process is clearWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsIon exchangeCarboxylic acid
The invention discloses a method for recycling purified terephthalic acid wastewater. The method comprises the following steps: providing purified terephthalic acid wastewater, adjusting the temperature of the purified terephthalic acid wastewater to 30-45 DEG C, adjusting the pH value of the purified terephthalic acid wastewater to 2.5-4.5, and filtering the purified terephthalic acid wastewater to obtain a filtrate and a first solid which contains aromatic carboxylic acid; feeding the filtrate into an extraction system for extraction treatment to obtain an extraction phase and a raffinate phase; feeding the extraction phase into a rectifying tower, performing regeneration treatment to obtain a second solid matter containing aromatic carboxylic acid, feeding the raffinate phase into an ion exchange system, and performing ion exchange treatment; and carrying out desorption treatment on ion exchange resin in the ion exchange system to obtain cobalt and manganese ions. According to the method provided by the invention, recovery treatment of organic carboxylic acid and metal ions in the PTA wastewater is comprehensively considered, and the treatment load of a downstream section is remarkably reduced while effective recycling of resources is realized.
Owner:新疆中泰创新技术研究院有限责任公司
Method for inhibiting extractant degradation of DSX process through manganese extraction control
ActiveUS11203531B2Minimizing extractionPrevent degradationZinc compounds preparationProcess efficiency improvementManganeseSolvent
Provided is a method for inhibiting extractant degradation in the DSX process through the manganese extraction control, the method comprising: (a) stirring DSX solvent and DSX feed solution, which is a solution containing a valuable metal from which iron has been removed in an agitator, in which soda ash (Na2CO3) is further added to maintain a constant pH; and (b) scrubbing the manganese from the DSX solvent, extracted in step (a).
Owner:KOREA MINE REHABILITATION & MINERAL RESOURCES CORP
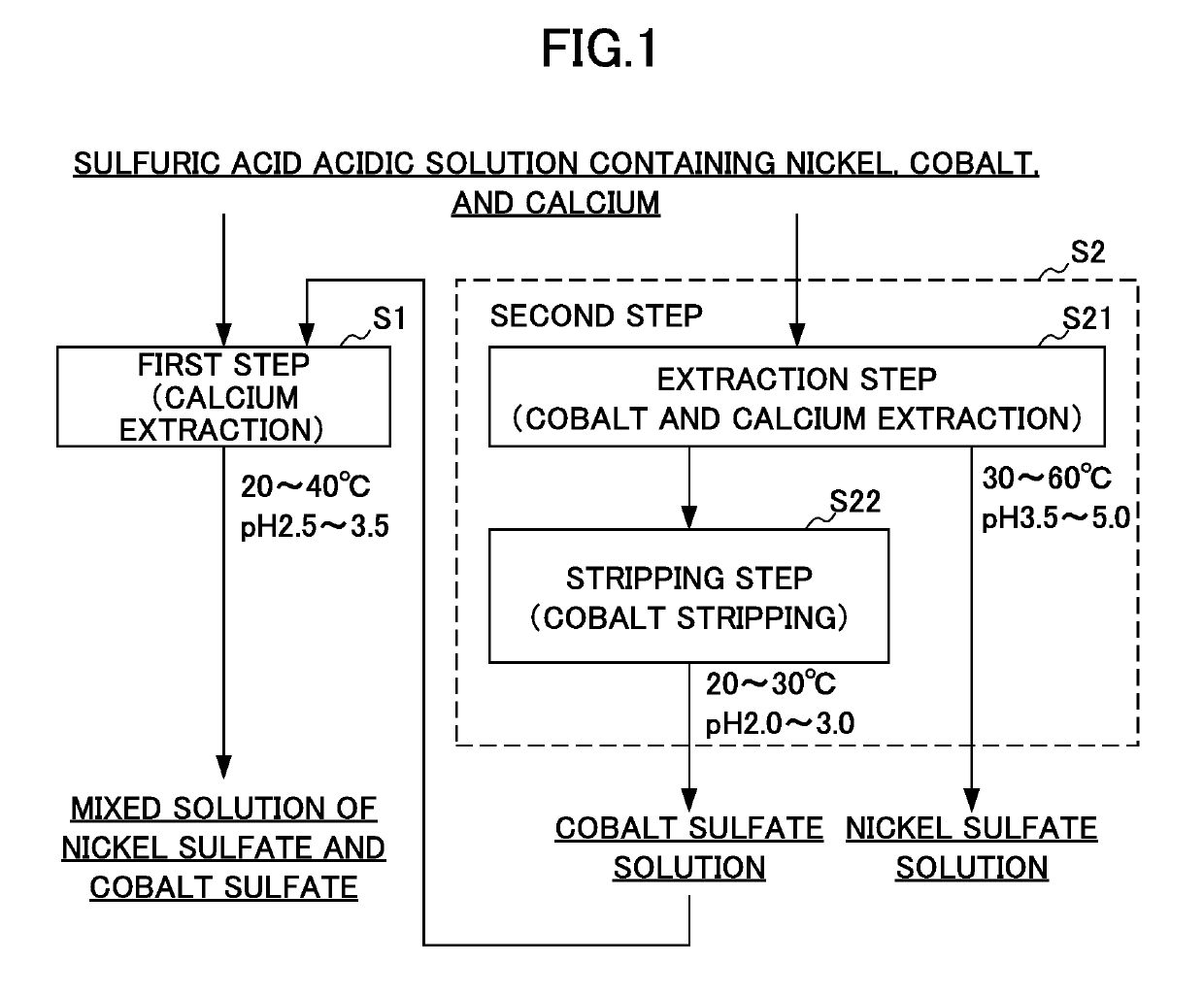
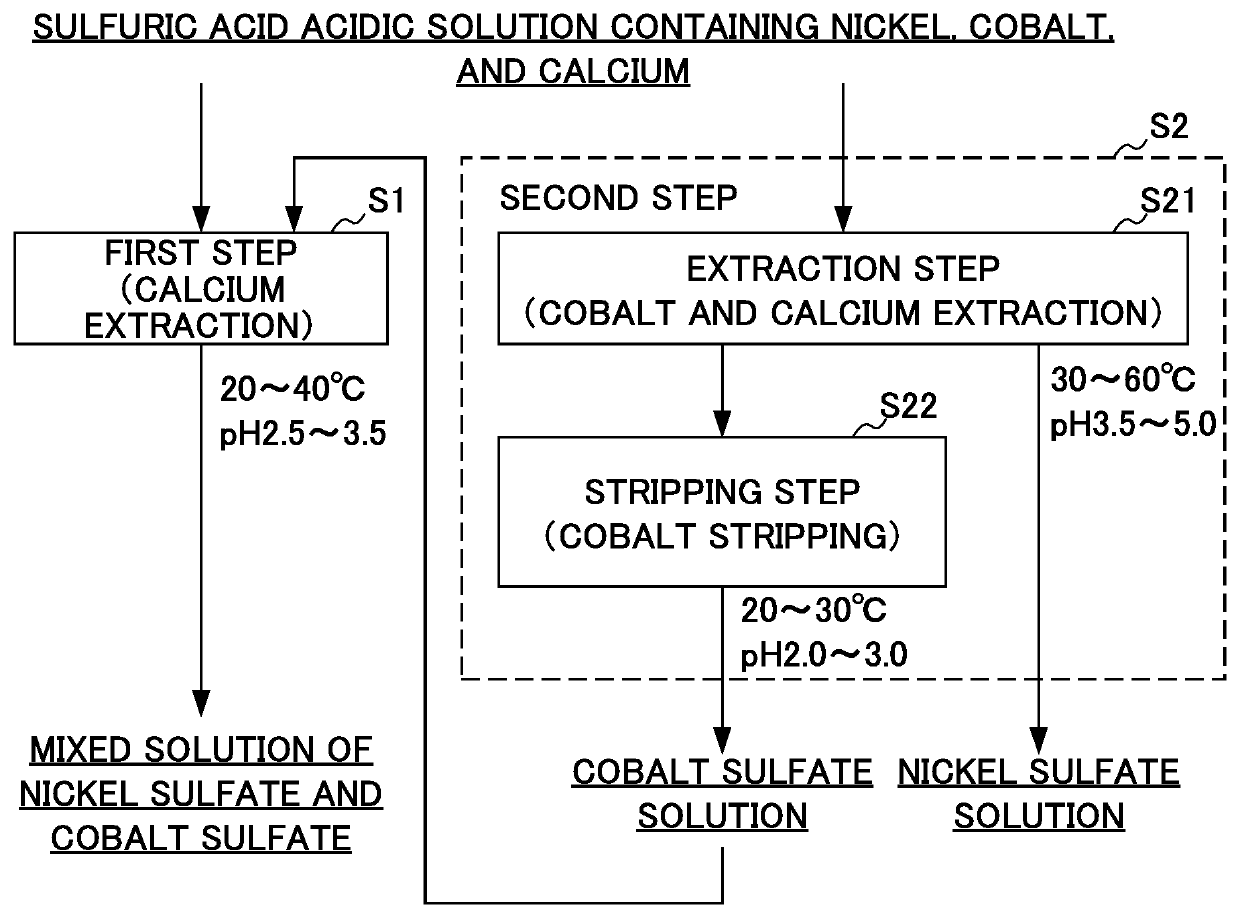
Method for producing solutions containing nickel or cobalt
ActiveUS20190194031A1Efficiently obtainedCobalt sulfatesNickel compounds preparationOrganic solventSolvent
Provided is a method for producing solutions, by which two solutions, namely a high-purity nickel sulfate solution and a mixed solution of nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate are able to be obtained at the same time from a sulfuric acid solution containing nickel, cobalt and calcium. A method for producing solutions according to the present invention uses a sulfuric acid solution containing nickel, cobalt and calcium and performs a first step S1 for producing a mixed solution of nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate from the sulfuric acid solution and a second step S2 for producing a solution of nickel sulfate from the sulfuric acid solution in parallel. In the first step, the sulfuric acid solution is subjected to solvent extraction by an extractant, thereby obtaining a first organic solvent after extraction In the second step, the sulfuric acid solution is subjected to solvent extraction by means of an extractant.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
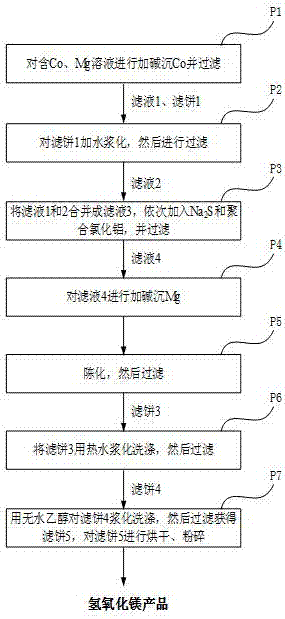
The method that reclaims magnesium and prepares magnesium hydroxide from cobalt-nickel industry cobalt-containing magnesium solution
ActiveCN106276989BEmission reductionReduced enrichmentMagnesium hydroxideCobalt compounds preparationAluminium chlorohydrateCobalt
The invention provides a method for recovering magnesium from a cobalt and magnesium contained solution in cobalt-nickel industry for preparation of magnesium hydroxide. The method comprises following working procedures: working procedure one: the cobalt and magnesium contained solution is taken, the pH value is regulated through addition of 3-6 mol / L of sodium hydroxide, a mixed solution is subjected to temperature control and stirred, and cobalt is enabled to be precipitated sufficiently; working procedure two: the mixed solution is filtered, first filtrate and a first filter cake are obtained, the first filter cake is pulpified through addition of water, filtering is performed again, and second filtrate is obtained; working procedure three: the second filtrate and the first filtrate are mixed, third filtrate is obtained, a sodium sulfide solution is added, a mixed solution is subjected to temperature control and stirred, then polyaluminum chloride is added, filtering is performed again, and fourth filtrate is obtained; working procedure four: the fourth filtrate is added to an alkaline solution, the pH value is regulated, and temperature control and stirring are performed; working procedure five: aging and filtering are performed sequentially, and a third filtrate cake is obtained; working procedure six: the third filtrate cake is pulpified, washed and filtered, and a fourth filter cake is obtained; working procedure seven: the fourth filter cake is pulpified, washed, filtered, dried and smashed, and a finished product is obtained. With the adoption of the method, magnesium can be recovered in a cobalt-nickel production process simply and efficiently for preparation of magnesium hydroxide.
Owner:JINGMEN GEM NEW MATERIAL
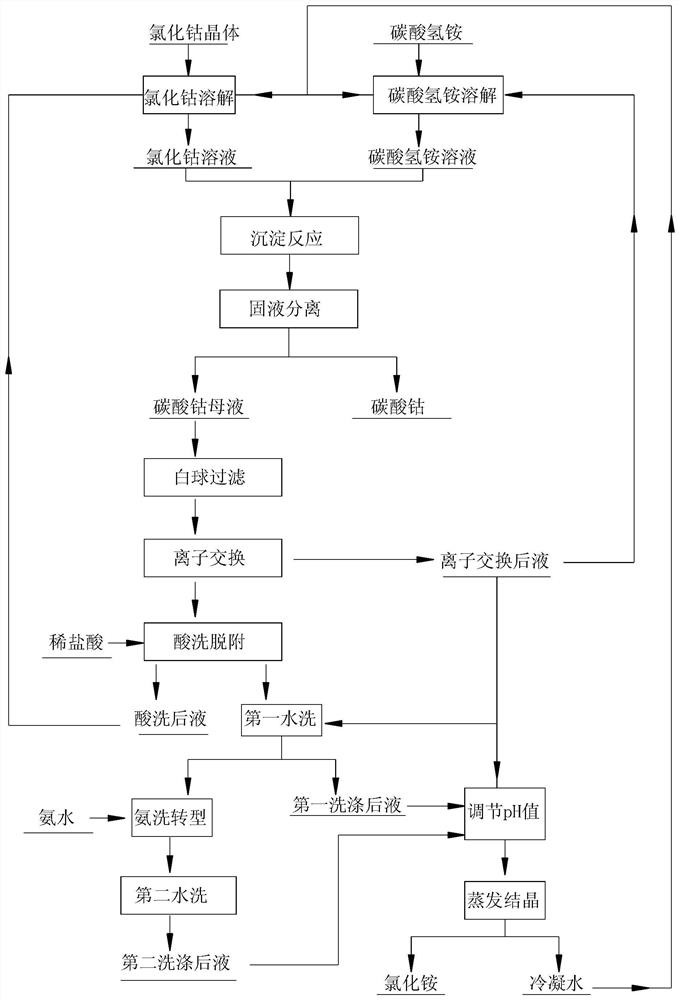
Method for treating cobalt carbonate mother liquor in preparation process of spherical cobalt carbonate
ActiveCN113355523AReduce usageReduce evaporationProcess efficiency improvementCobalt carbonatesIon exchangeIon-exchange resin
The invention discloses a method for treating cobalt carbonate mother liquor in the preparation process of spherical cobalt carbonate. The method comprises the following steps that (1) ion exchange resin adsorption is carried out on the cobalt carbonate mother liquor filtered by white balls to obtain ion adsorption post-liquor and supported resin, the supported resin is desorbed by diluted hydrochloric acid to obtain hydrogen-type resin and acidic post-liquor, the hydrogen-type resin is transformed by ammonia water to obtain ammonium-type resin, the ammonium-type resin obtained after transformation continues to be used for treating the cobalt carbonate mother liquor, and the cobalt carbonate mother liquor is recycled; and (2) after evaporative crystallization is carried out on one part of the ion adsorption post-liquor in the step (1), ammonium chloride crystals and condensed water are obtained, the other part of the ion adsorption post-liquor is used for washing the ammonium-type resin, and only the ion adsorption post-liquor is adopted for washing the ammonium-type resin for the second time. By means of the method, the water treatment capacity can be reduced, the cobalt recovery rate can be improved, and the wastewater treatment difficulty can be reduced.
Owner:安徽寒锐新材料有限公司
Method for inhibiting extractant degradation of dsx process through metal extraction control
ActiveUS20210024367A1Minimizing extractionPrevent degradationIron compounds preparationZinc compounds preparationPhysical chemistrySlurry
Provided is a method for inhibiting extractant degradation in the DSX process through the metal extraction control, the method comprising steps of: (a) adding limestone to a copper solvent extraction-raffinate to precipitate iron (Fe) and aluminum (Al) as a slurry, recovering a clarifying liquid; and (b) adding sulfuric acid to the recovered clarifying liquid to adjust the pH thereof.
Owner:KOREA MINE REHABILITATION & MINERAL RESOURCES CORP
Method for preparing nano cobalt tungstate and recovering crude titanium slag
ActiveCN112939094AIncrease valueImprove economyMaterial nanotechnologyTitanium dioxidePtru catalystNonferrous metal
The invention relates to a method for preparing nano cobalt tungstate and recovering crude titanium slag, and belongs to the field of non-ferrous metal recovery. According to the recovery method, high-purity nanometer cobalt tungstate and high-quality coarse titanium slag are obtained through recovery through the steps of pretreatment, element separation, titanium element recycling, tungsten element purification, tungsten element recycling and the like, the recovery process is simple and easy to implement, the element recovery rate is high, the product can be directly applied industrially, and reasonable and efficient treatment of the waste SCR denitration catalyst is achieved.
Owner:华电光大(宜昌)环保技术有限公司
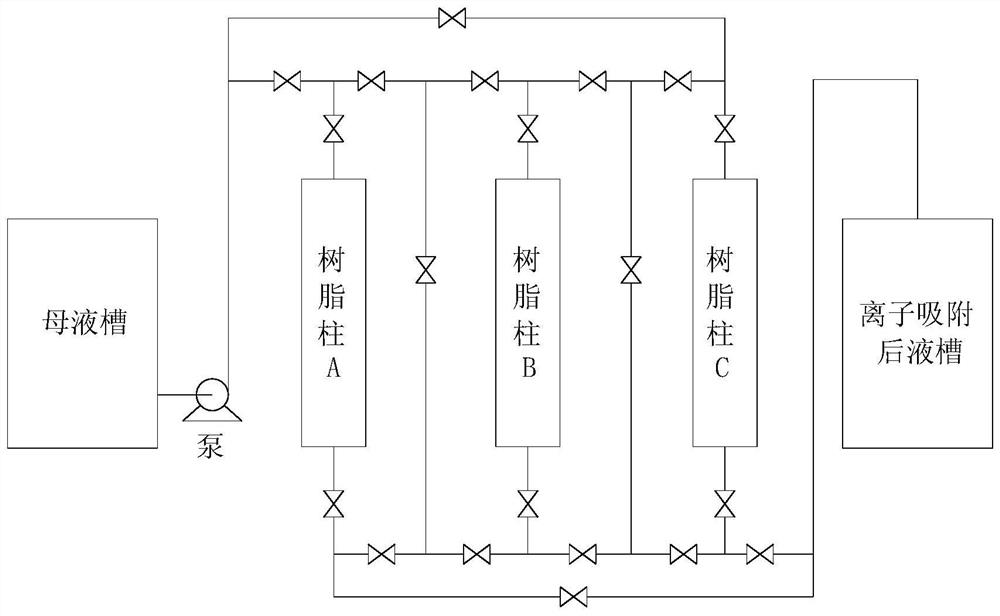
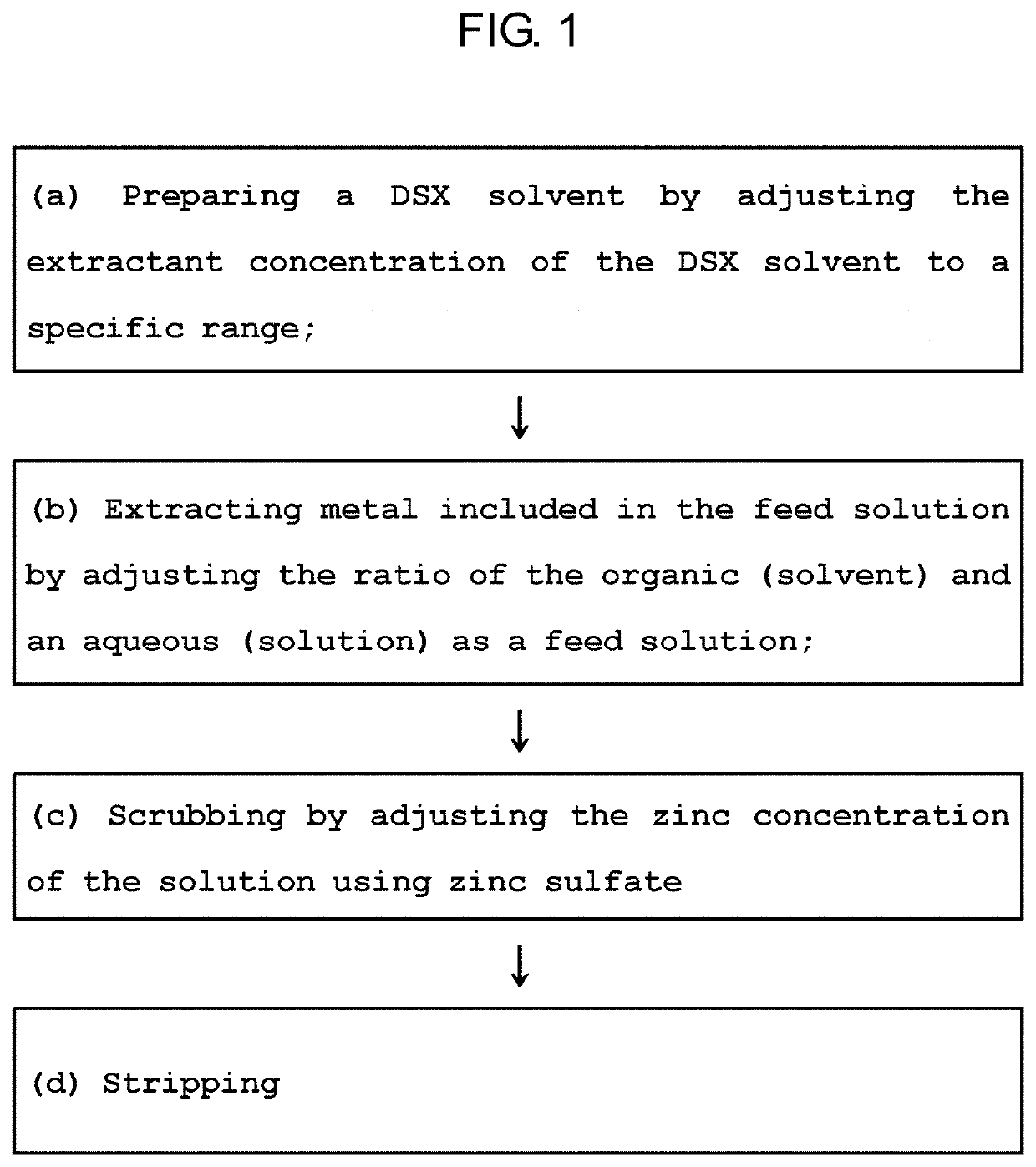
Method of inhibiting extractant degradation by controlling extractive capacity and preventing direct degradation
ActiveUS20210024369A1Inhibits extractant degradationImprove extraction efficiencyZinc compounds preparationProcess efficiency improvementSulfate zincSolvent
Provided is a method for inhibiting extractant degradation comprising preparing step, extracting step and scrubbing step, the method including: (a) the preparing step of a DSX solvent by adjusting the extractant concentration of the DSX solvent to a specific range; (b) the extracting step of metal included in the feed solution by adjusting the ratio of the organic (solvent) and an aqueous (solution) as a feed solution; (c) the scrubbing step of adjusting the zinc concentration of the solution using zinc sulfate; and (d) stripping step.
Owner:KOREA MINE REHABILITATION & MINERAL RESOURCES CORP
Method for producing solutions containing nickel or cobalt
ActiveUS10577255B2Efficiently obtainedCobalt sulfatesNickel compounds preparationOrganic solventProcess engineering
Provided is a method for producing solutions, by which two solutions, namely a high-purity nickel sulfate solution and a mixed solution of nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate are able to be obtained at the same time from a sulfuric acid solution containing nickel, cobalt and calcium. A method for producing solutions according to the present invention uses a sulfuric acid solution containing nickel, cobalt and calcium and performs a first step S1 for producing a mixed solution of nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate from the sulfuric acid solution and a second step S2 for producing a solution of nickel sulfate from the sulfuric acid solution in parallel. In the first step, the sulfuric acid solution is subjected to solvent extraction by an extractant, thereby obtaining a first organic solvent after extraction. In the second step, the sulfuric acid solution is subjected to solvent extraction by means of an extractant.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com