Method for recycling rare earth from waste nickel-hydride battery and conducting transformation
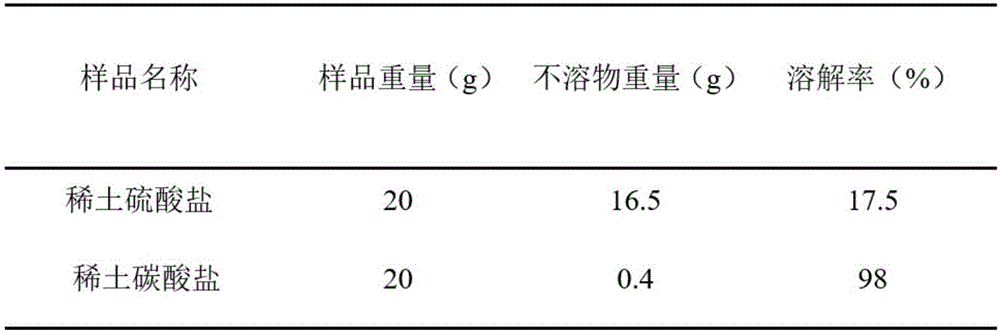
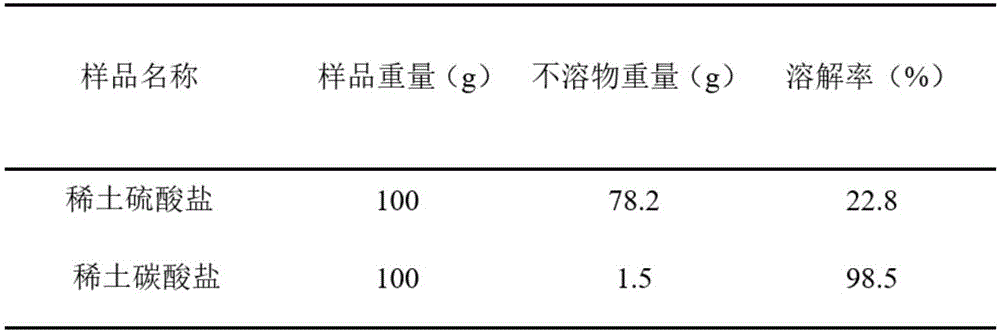
A nickel-metal hydride battery, waste technology, applied in battery recycling, waste collector recycling, recycling technology, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in returning to the rare earth production system, poor solubility of rare earth sulfate, and unfavorable deep processing, etc. Easy to break, easy to recycle, easy to dissolve
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
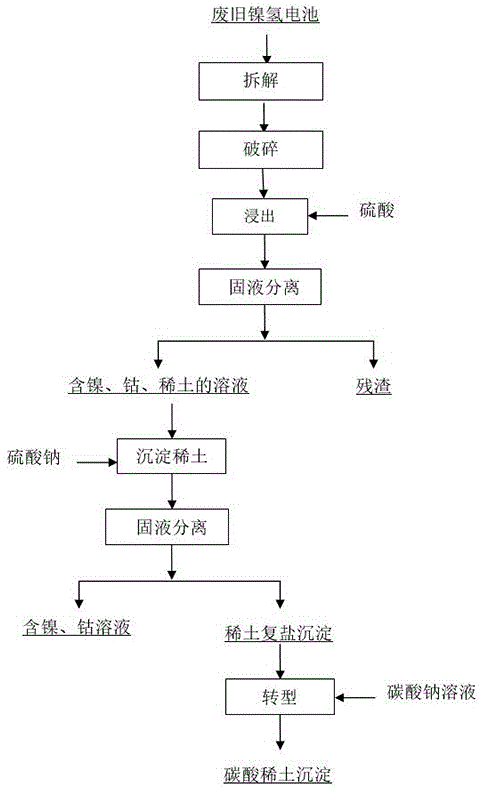
[0016] A crushing treatment: Take 95g of waste nickel-metal hydride batteries, in a dry state, cool the waste nickel-hydrogen batteries to 15 degrees Celsius, and then crush the waste nickel-metal hydride batteries with a temperature of 15 degrees Celsius. The temperature of the processed slag is lower than 18 degrees Celsius;
[0017] B acid leaching treatment: Slurry the slag with 1.5mol / L sulfuric acid at a liquid-solid ratio of 10.7:1, add 30% hydrogen peroxide and heat for a period of time (indicating the concentration of sulfuric acid), until the percentage of solid-liquid substances in the mixture No longer changes, when the pH value is 1.5;
[0018] C primary solid-liquid separation: the mixing after the acid leaching treatment carries out the solid-liquid separation treatment to obtain filtrate A and filter residue A, wherein filtrate A is nickel sulfate solution rich in impurities such as rare earth and cobalt, iron, manganese, and filter residue A is useless residue...
Embodiment 2
[0028] A crushing treatment: Take 2000g of waste nickel-metal hydride batteries, in a dry state, cool the waste nickel-hydrogen batteries to 15 degrees Celsius, and then crush the waste nickel-metal hydride batteries with a temperature of 15 degrees Celsius. 18 degrees Celsius;
[0029] B acid leaching treatment: Slurry the slag with 1.5mol / L sulfuric acid at a liquid-solid ratio of 10:1, add 30% hydrogen peroxide and heat for a period of time (indicating the concentration of sulfuric acid), until the percentage of solid-liquid substances in the mixture No longer changes, when the pH value is 2;
[0030] C primary solid-liquid separation: the mixing after the acid leaching treatment carries out the solid-liquid separation treatment to obtain filtrate A and filter residue A, wherein filtrate A is nickel sulfate solution rich in impurities such as rare earth and cobalt, iron, manganese, and filter residue A is useless residue;
[0031] D primary precipitation treatment: Add 200...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com