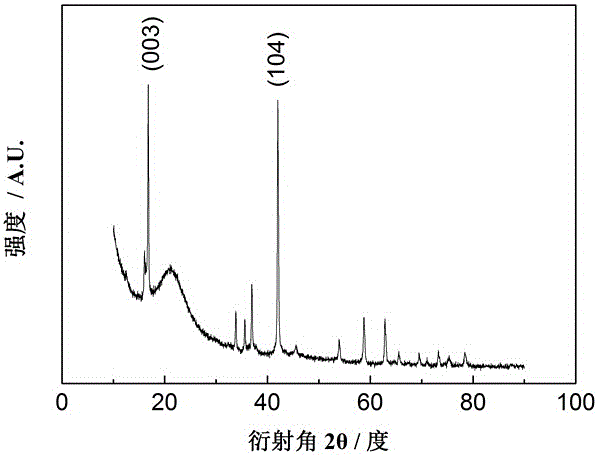
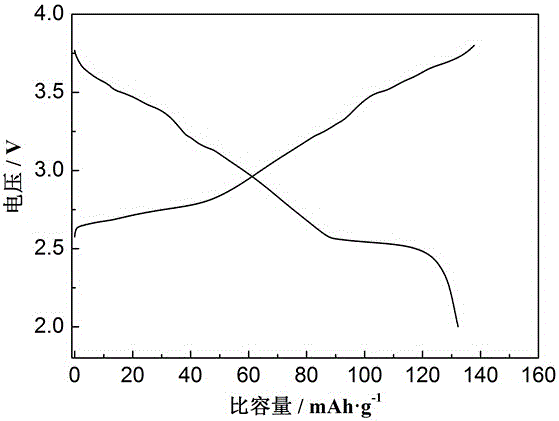
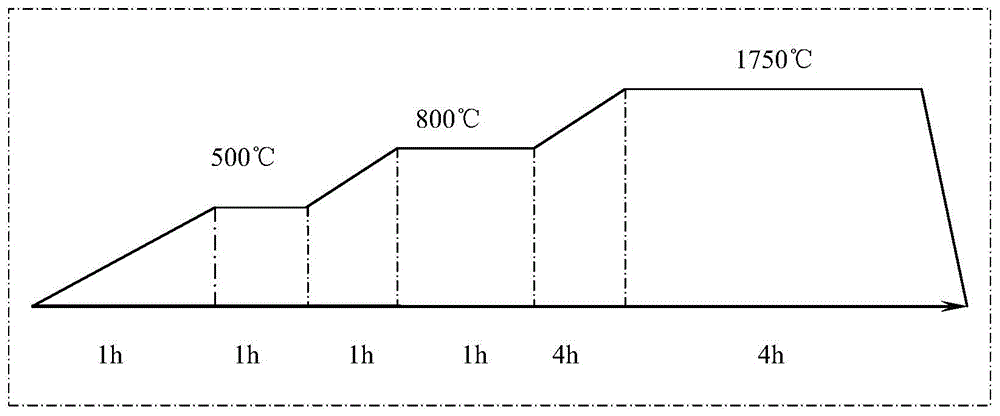
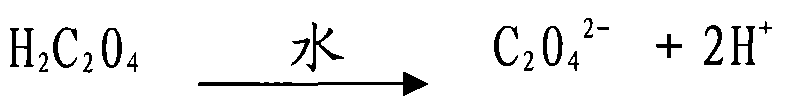
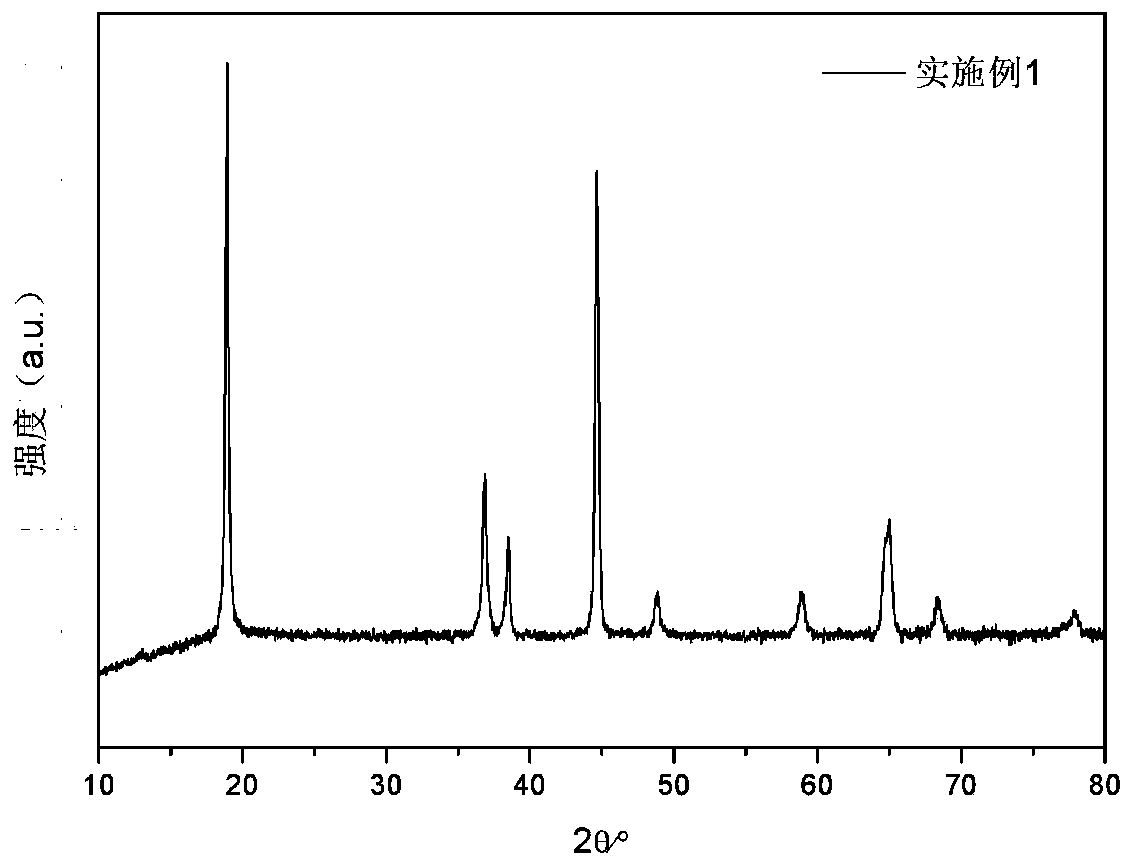
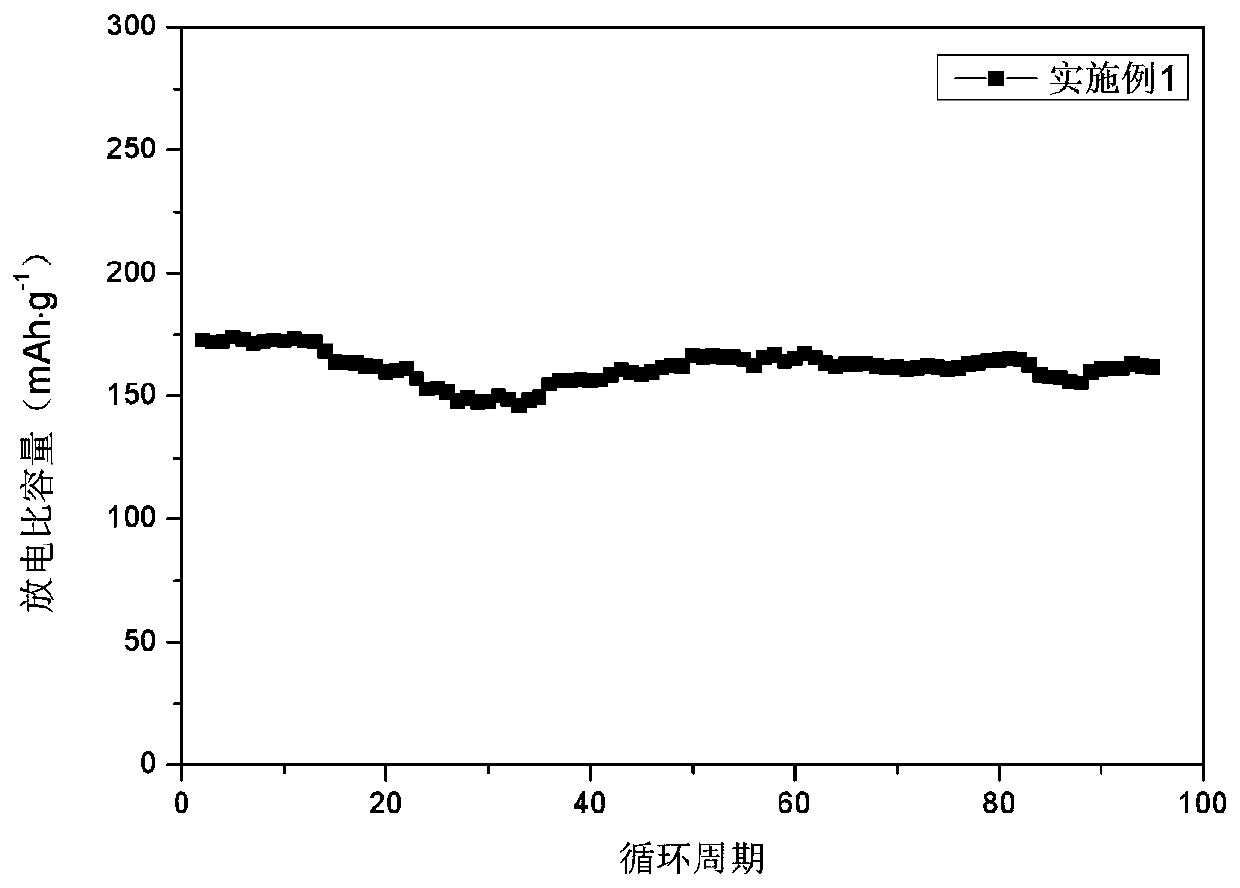
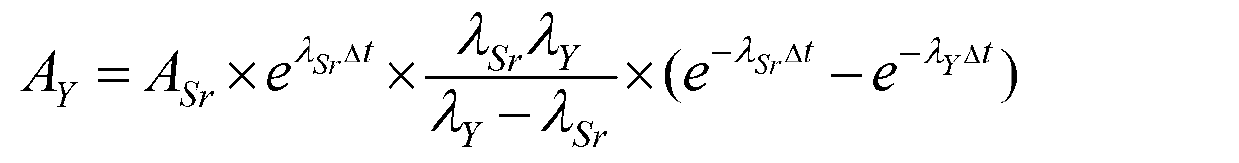Patents
Literature
80 results about "Oxalate precipitation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
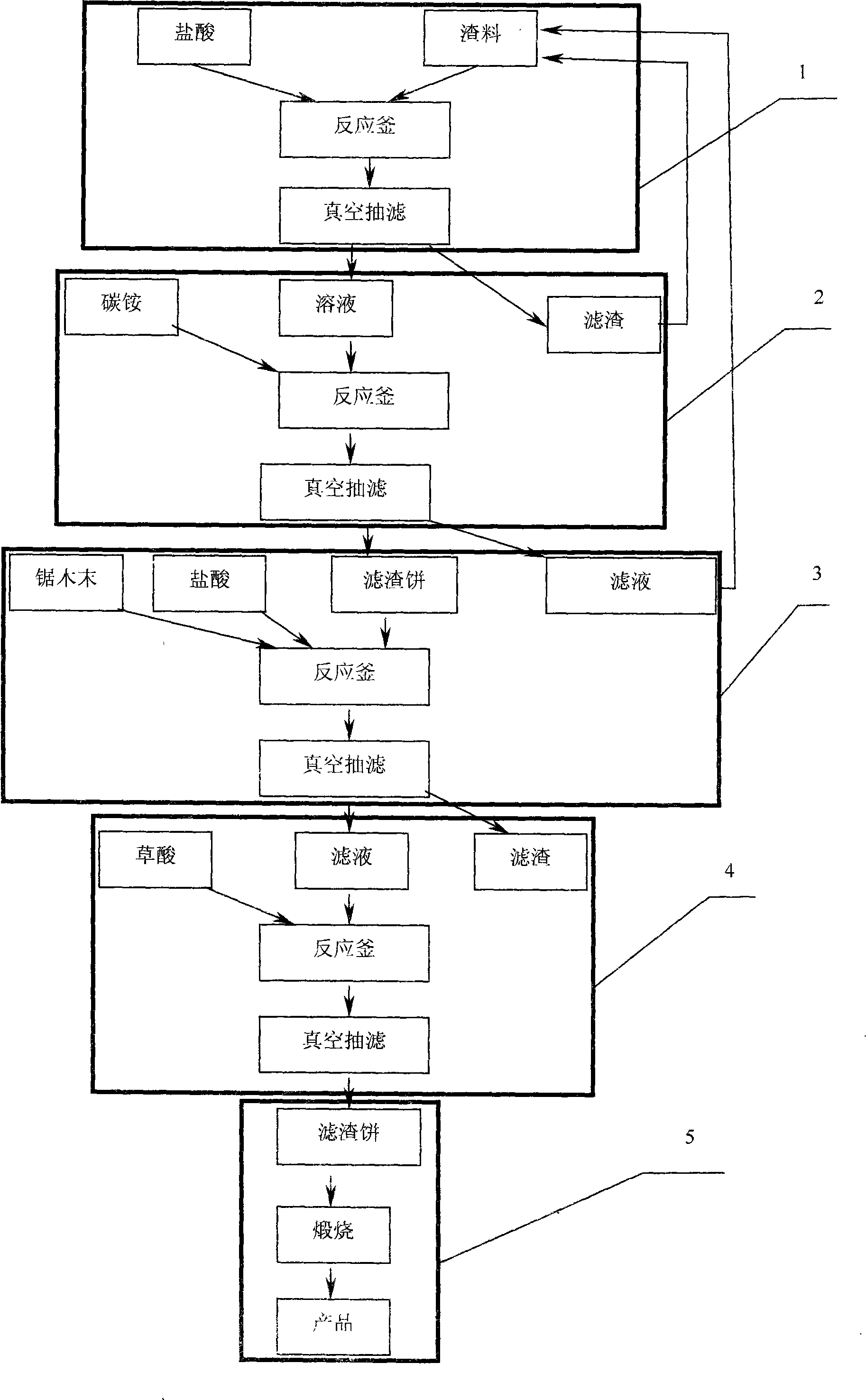
Method for recovering rare earth from rare earth-containing aluminum-silicon materials
ActiveCN101705380AAvoid enteringLess fixed investmentProcess efficiency improvementMolecular sieveSelective leaching
The invention relates to a method for recovering rare earth from rare earth-containing aluminum-silicon materials, which comprises the following steps: taking the rare earth-containing aluminum-silicon materials including rare earth-loaded molecular sieves, catalyst wastes, and the like as raw materials, conducting prioritized selective leaching by acid so as to lead the majority of the rare earth and a small amount of aluminum to be dissolved and separated from silicon and other impurities, leading the rare earth to form precipitates and be separated from the aluminum by adopting a double salt precipitation or oxalate precipitation method, and then recovering and purifying the rare earth. The method has the advantages of directly realizing the extraction of the rare earth from the aluminum-silicon materials including the molecular sieves and the like, with over 98% purity of the obtained rare earth, and avoiding impurities such as aluminum, silicon and the like entering the rare earth; and meanwhile, the technology also has the characteristics of little fixed investment, low production cost and easiness for realizing industrialized production.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Layered lithium-rich anode material clad by metal fluoride, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102496722AImprove electrochemical performanceAvoid corrosionCell electrodesWater bathsLithium
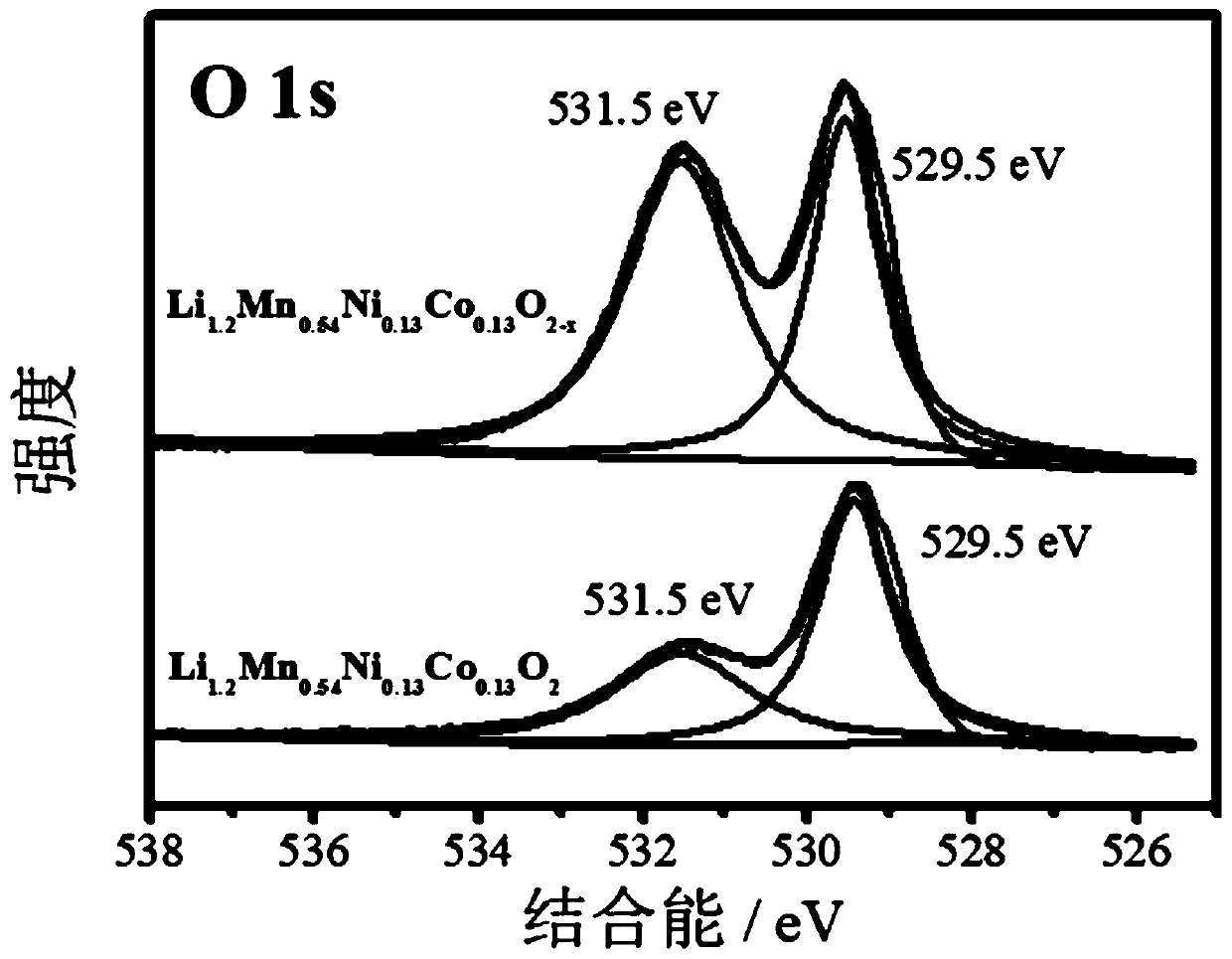
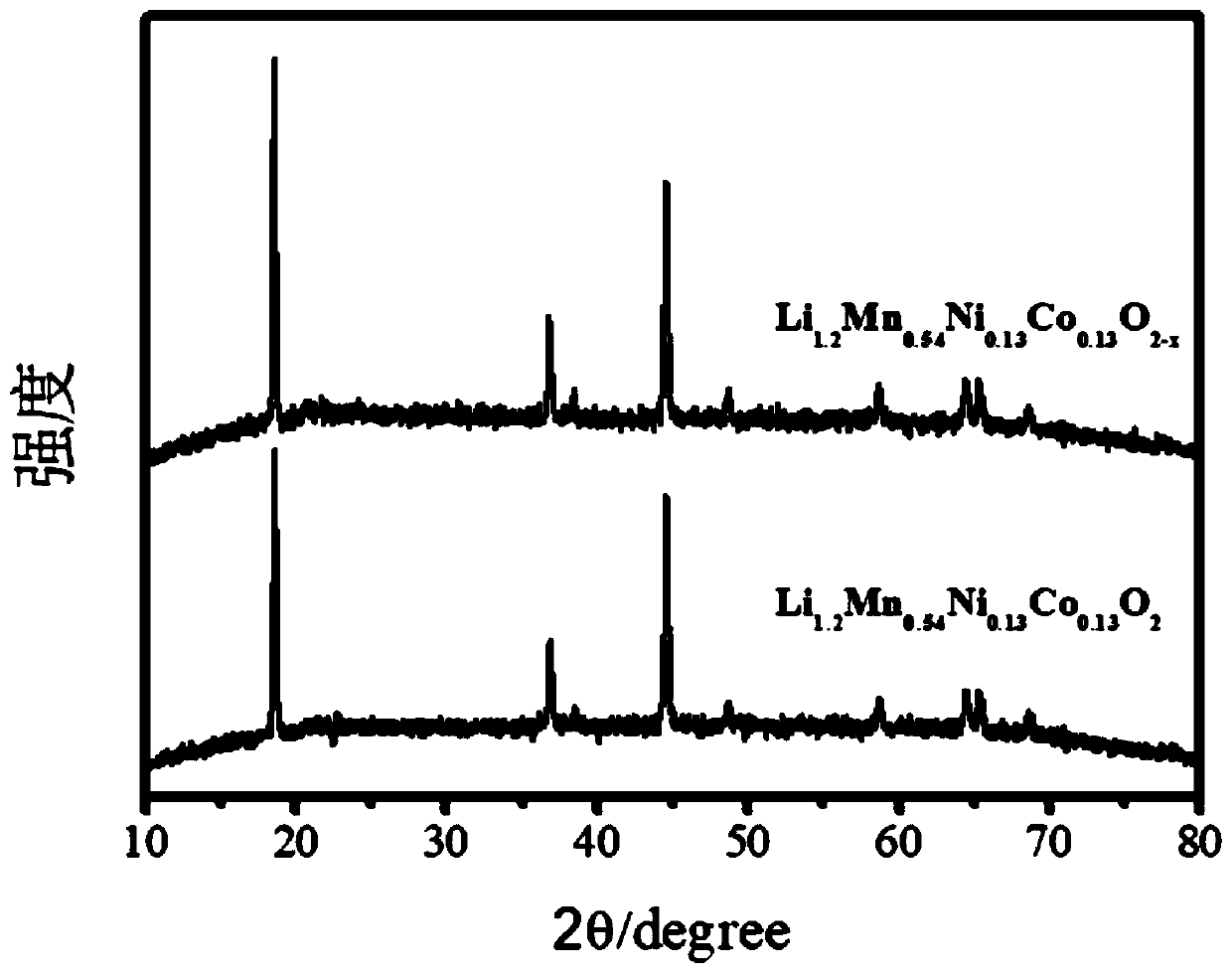
The invention relates to a layered lithium-rich anode material clad by metal fluoride, and a preparation method thereof. According to the invention, a layered lithium-rich material Li[Li(1-2x) / 3MxMn(2-x) / 3]O2 is prepared with a combined technology of a oxalate precipitation method and a hydro-thermal method, wherein M is Ni, Co, Cr or any two of them which coexist, and x=0 to 0.33. The lithium-rich material is impregnated in a solution of soluble salts of metals such as yttrium, magnesium and iron; a soluble fluoride solution is added to the mixture, wherein n(Me):n(F)=1:y; the solution is continuously stirred for 3-8h in a water bath with a temperature of 60-90 DEG C; the solution is subject to centrifugal washing, and is dried under a temperature of 60 DEG C in a vacuum thermostat; a material obtained after drying is roasted for 4-8h under a temperature of 400 DEG C and under the protection of argon gas, such that Li[Li(1-2x) / 3NixMn(2-x) / 3]O2 clad by a fluoride MeFy is prepared. The electrode material provided by the invention is advantaged in high electrochemical capacity, good cyclical stability, excellent rate performance, and the like. The preparation process is simple, the cost is low, and the reproducibility is good.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for preparing anode material of lithium ion battery in series of phosphate of olivine type
InactiveCN101049922AAchieve hybridEvenly distributedCell electrodesPhosphorus compoundsAluminium-ion batteryPhosphate
This invention relates to a method for preparing olivine-type phosphate-series lithium ion battery anode material. The method comprises: mixing one or more of ferrous salt solution, cobalt salt solution and manganese salt solution with oxalic acid or oxalate (precipitating agent) aqueous solution to obtain composite oxalate precursor, uniformly mixing with lithium source and phosphorus source by ball milling, and reacting in inert or weak-reductive atmosphere to obtain olivine-type phosphate-series lithium ion battery anode material. The method utilizes co-precipitation method for metal ion doping, and realizes molecular level uniform mixing among different ions. The obtained olivine-type phosphate-series lithium ion battery anode material has uniform chemical and physical compositions. The average particle size can be controlled within 0.3-10 mu.m. The first charge and discharge cycle specific capacity can reach 150 mAh / g at 0.1 C rate and room temperature. The livine-type phosphate-series lithium ion battery anode material has such advantages as high cycle performance and high charge / discharge performance.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for preparing xylose and arabinose by hydrolyzing lignocellulose
InactiveCN101525355ALess side effectsLess corrosiveSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationHydrolysateBio engineering
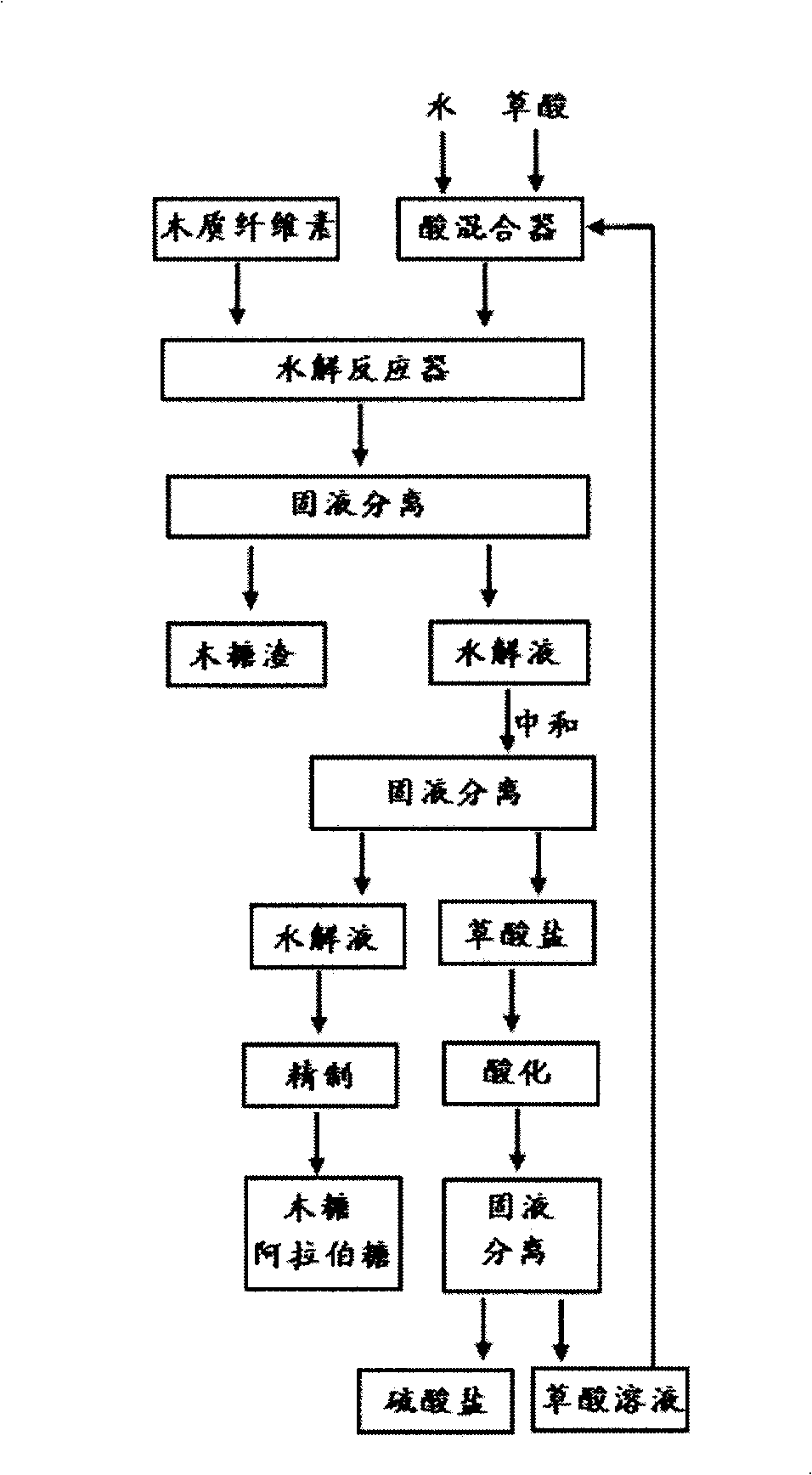
The invention discloses a method for preparing xylose and arabinose by hydrolyzing lignocelluloses in the technical field of biological engineering. In the method, aqueous oxalate solution is used for carrying out catalytic hydrolysis on crushed lignocelluloses; lignocelluloses hydrolysate solution and xylose resides are obtained by solid-liquid separation after the reaction; the hydrolysate solution is neutralized to obtain oxalate sediment and obtain solid oxalate by solid-liquid separation again; the oxalate reacts with sulfate in an acidizing tank for regeneration to obtain the aqueous oxalate solution; the oxalate solution is used repeatedly to catalyze next batch of lignocelluloses raw material. The invention uses oxalic acid as organic acid catalyst and has the advantages of high conversion rate, strong selectivity, less side reaction, being capable of recycling, and the like, the oxalic acid can replace regular inorganic acid catalyst, and the invention solves the problem thatthe traditional technology has equipment erosion, evaporating equipment scaling, serious pollution and the like and can be used for hydrolyzing the hemicellulose in lignocelluloses raw material and used for preparing the xylose and the arabinose.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for recovering organic acid and cobalt-manganese metal in terephthalic acid oxidized residues
ActiveCN102503813AOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsChemical recyclingMANGANESE ACETATEBenzoic acid
The invention belongs to the technology for recovering organic acid and catalyst from terephthalic acid oxidized residues, which includes the steps of firstly, discharging high-temperature oxidized residues from a pure terephthalic acid (PTA for short) production device, controlling the solid content within the range from 20% to 45% and implementing primary filtering separation within the temperature range from 55 DEG C to 90 DEG C, and directly vending separated solid for manufacturing resin or paint or returning the separated solid to an oxidation reactor for use, wherein primary filtrate is treated according to the process: (I) adding oxalic acid to obtain cobalt-manganese oxalate precipitation, obtaining cobalt-manganese oxalate by means of filtering separation, further cooling the filtrate by means of filtering separation, utilizing the separated solid for extracting benzoic acid and delivering the filtrate to a waste water treating device; or (II) directly cooling the primary filtrate for secondary filtering separation, utilizing the separated solid for extracting benzoic acid, adding oxalic acid into secondary filtrate to obtain cobalt-manganese oxalate precipitation, obtaining cobalt-manganese oxalate by means of filtering separation and delivering the filtrate to a waste water treating device; and secondly, carrying out reaction of the cobalt-manganese oxalate obtained from (I) or (II) with oxidant such as hydrogen peroxide, peroxyacetic acid, bromine, manganate, permanganic acid, manganese dioxide or / and hydrobromic acid, utilizing cobalt acetate aqueous liquor, cobalt bromide aqueous liquor, manganese acetate aqueous liquor, manganese bromide aqueous liquor, acetic acid or / and pure water as dissolvent, then carrying out reaction of the cobalt-manganese oxalate with metallic cobalt, metallic manganese or / and hydrobromic acid after the cobalt-manganese oxalate is completely dissolved, and obtaining homogeneous phase liquor containing cobalt-manganese bromide ions by means of purification and filtration, wherein the mixed liquor can be directly mixed with cobalt acetate, manganese acetate, cobalt bromide, manganese bromide, acetic acid or water to serve as oxidation catalyst for the terephthalic acid.
Owner:浙江上虞利星化工有限公司
Process for recovering and purifying neptunium from waste liquor discharged from 2AW+2DW in Purex flow
ActiveCN103305702AHigh recovery rateValence stableProcess efficiency improvementRadioactive decontaminationOxalate precipitationEngineering
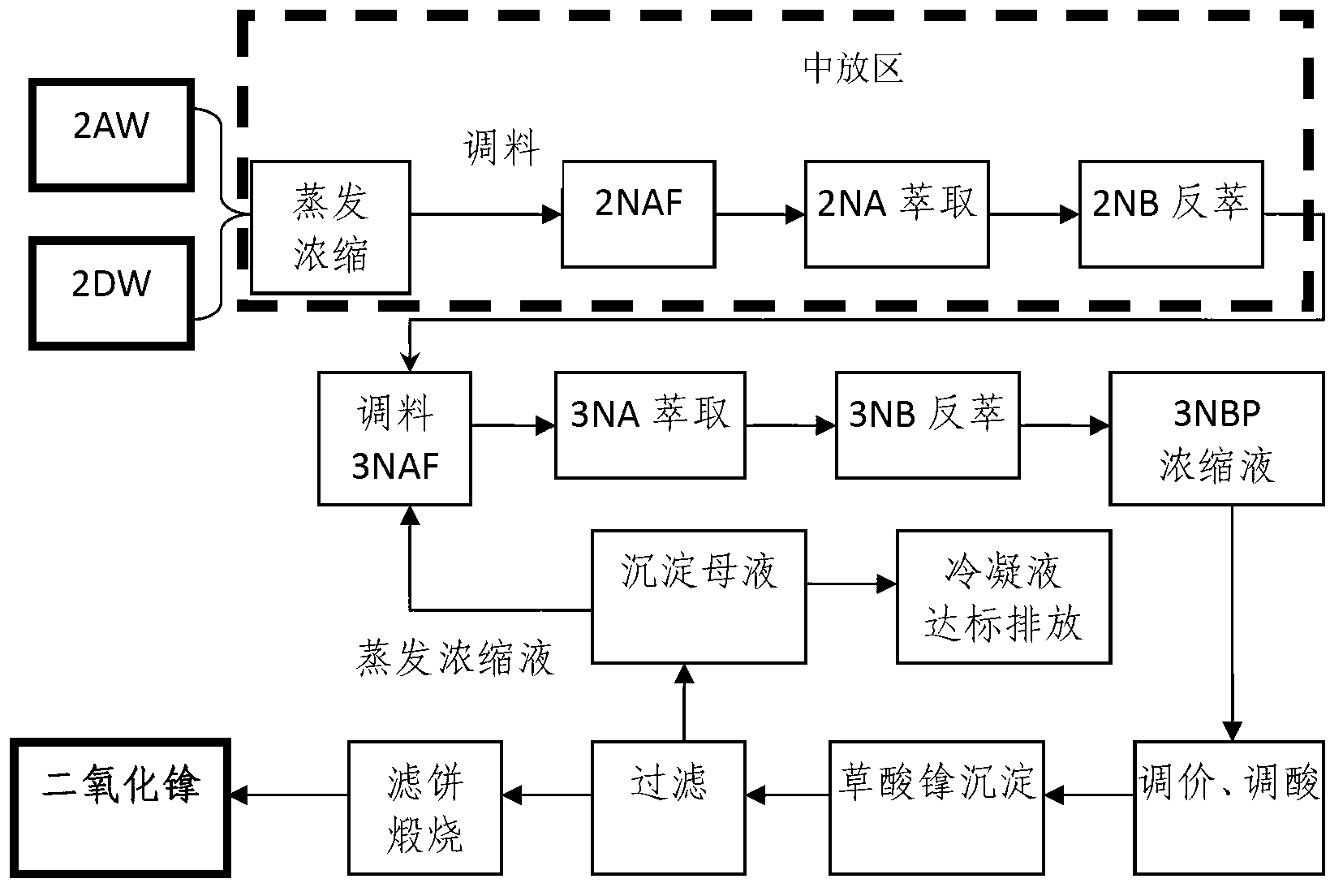
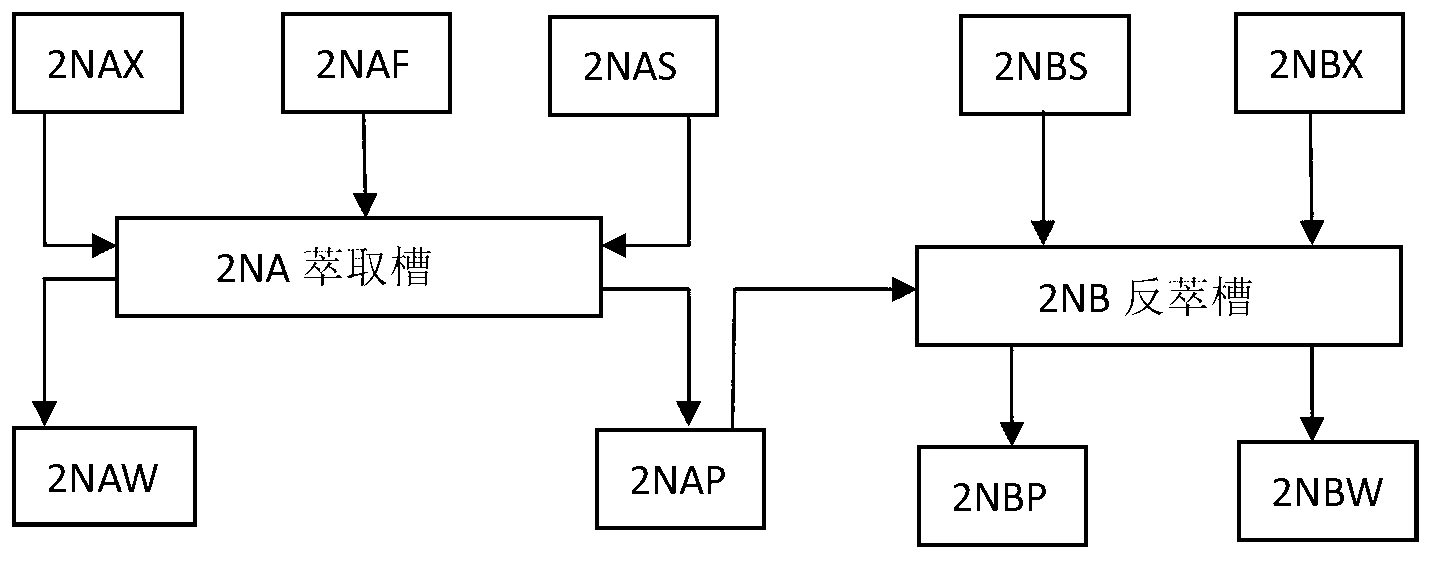
The invention belongs to the technical field of nuclear fuel reprocessing and discloses a process for recovering and purifying neptunium from waste liquor discharged from 2AW+2DW in Purex flow. The process comprises the primary neptunium purification process and the secondary neptunium purification process; the process comprises the following steps: by taking 30 volume percent of TBP-kerosene as an extraction agent, extracting Np, U and Pu to the organic phase, and allowing the fission fragments to enter the aqueous phase; adding a reducing agent and an extraction agent into the organic phase, reversely extracting the Np to the aqueous phase; further extracting uranium and plutonium, and performing oxalate precipitation, filtering and calcining on the obtained aqueous phase product to obtain the purified neptunium oxide solid. The process has the advantages that the neptunium recovery rate is over 98 percent, and the uranium and plutonium removal coefficient in neptunium is high.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
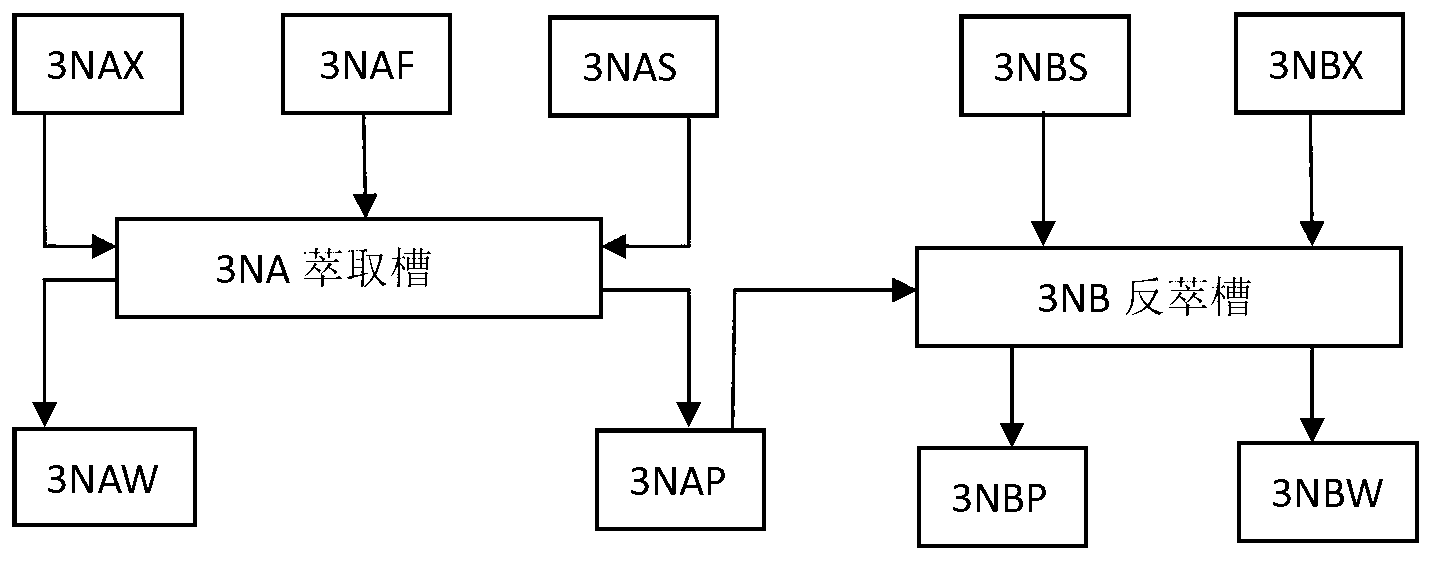
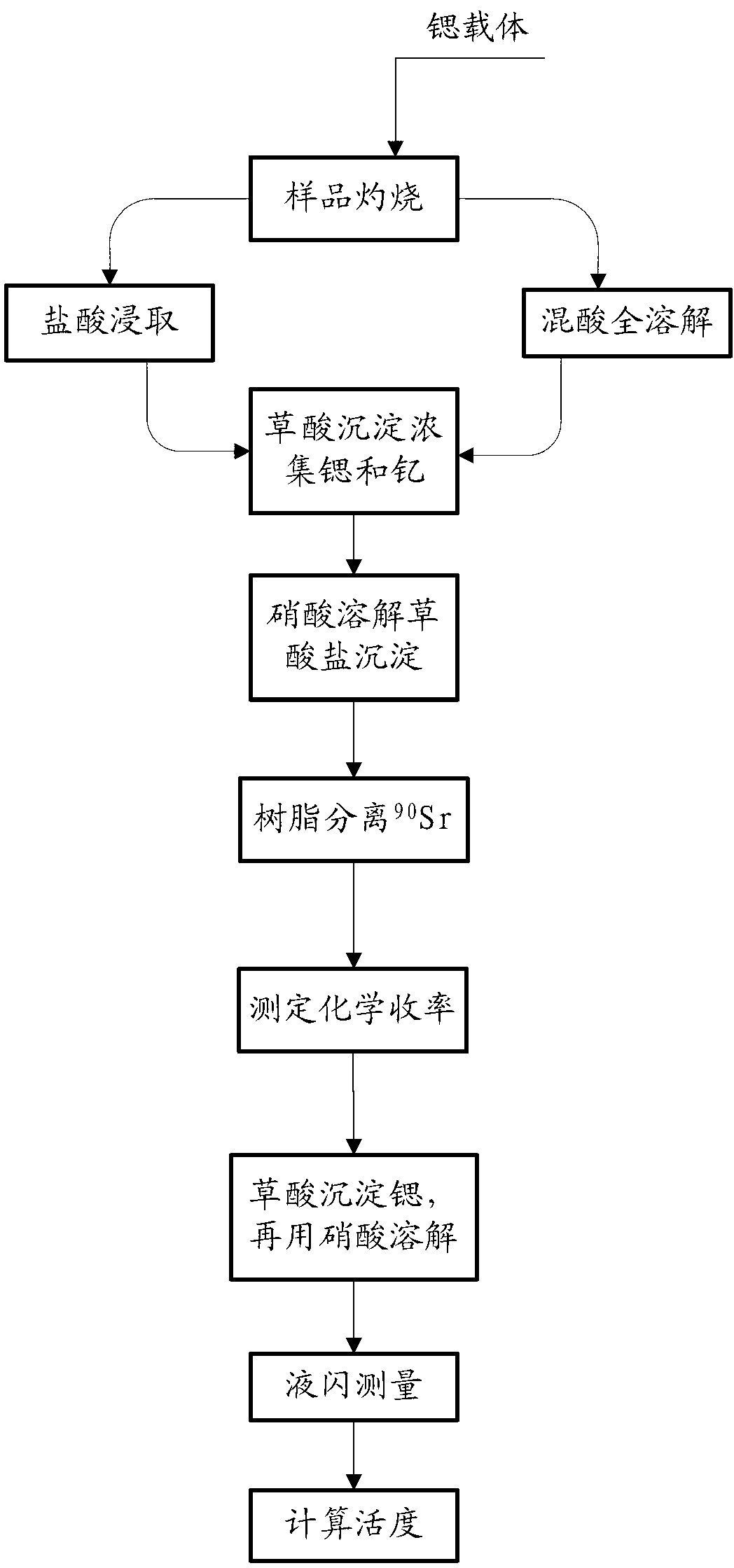
Radiochemical analyzing method of Sr-90 in soil
InactiveCN103344982AShort analysis timeX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEDesorption
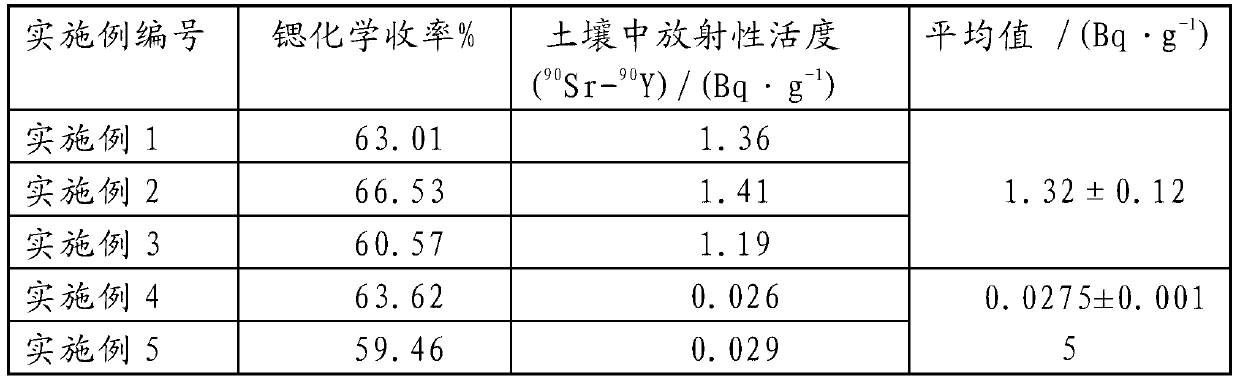
The invention relates to a radiochemical analyzing method of Sr-90 in soil. The radiochemical analyzing method of the Sr-90 in soil comprises the following steps that 1, pretreatment of soil samples is conducted; 2, sediment and concentration of strontium and yttrium are conducted by oxalic acid; 3, oxalate sediments are dissolved by nitric acid; 4, Sr-90 is separated by resin columns: strontium resin is soaked by distilled water and packed into columns in a wet-process mode, clear liquid obtained in step 3 flows through the resin columns, elution is conducted, desorption is conducted, and desorption solution is collected; 5, chemical yield measurement: sediment of strontium in the desorption solution is conducted by oxalic acid, and the strontium is washed and dried to achieve constant weight; 6, liquid flash measurement is conducted: the sediment is dissolved by nitric acid, liquid flash liquid is added to measure the belta factor; 7, radioactive activity of 90Sr-90Y in soil is calculated. The radiochemical analyzing method of the Sr-90 in soil can rapidly analyze the 90Sr content in soil samples in a radiochemical mode, the chemical yield of the 90Sr is about 60 percent during the whole process, analyzing time is less than 12 hours, the minimum detectable activity is 2 Bq / kg, and when the minimum detectable activity is compared with the industrial standard (EJ / T1035-1996) in the express method, and the minimum detectable activity and the industrial standard are consistent within the 5% error range.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Regeneration method of P507 organic-phase emulsified mixture for extracting and separating rare earth
InactiveCN104131163AHigh recovery rateLow priceProcess efficiency improvementOxalate precipitationEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses a regeneration method of a P507 organic-phase emulsified mixture for extracting and separating rare earth. The method concretely comprises the following steps: sequentially adding a P507 organic-phase emulsified mixture and a 4mol / L-8mol / L sodium hydroxide solution at 90-100 DEG C into a reaction pan; stirring and reacting for 5-10 minutes, and then standing and layering, wherein the upper layer is a clear organic phase, the middle layer is a transparent water phase, and the lower layer is a sediment containing rare earth hydrate, the water phase and the sediment are discharged from the bottom of the reaction pan, rare earth is recovered by an oxalate precipitation method after the water phase and the sediment are filtered, washed and dissolved by hydrochloric acid, the yield of the rare earth is about 95%, and the organic phase of the upper layer is a regenerated P507 organic phase, and can be directly applied to extraction and separation of the rare earth. The recovery rate of the P507 organic phase is high, and is up to 99-100%.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Sodium ion battery positive electrode material, and preparation method and application method thereof
ActiveCN105692721AUniform structureStoichiometric ratio is accurateCell electrodesSecondary cellsOxalate precipitationNickel compounds
The invention discloses a sodium ion battery positive electrode material, and a preparation method and application method thereof, belonging to the field of electrochemistry. The component of the material is laminar sodium manganate nickelate of which the chemical general formula is NaxNi[0.5+y]Mn[0.5-y]O2, wherein x is 0.9-1.1, and y is 0-0.2. The preparation method comprises the following steps: precipitating a soluble manganese compound-nickel compound mixed solution through oxalates, carrying out hydrothermal reaction in a water-ethanol mixed solution, and finally, carrying out heat treatment to obtain the laminar sodium manganate nickelate product. The invention solves the problems of poor precursor composition control reproducibility, controllable product structure and shape and the like in the prior art. Since the precursor structure is uniform and the stoichiometric proportion is accurate, the structure is further optimized after the ethanol / hydrothermal treatment, thereby finally obtaining the material prepared by the obviously better traditional method.
Owner:浙江瓦司特钠科技有限公司
Method for preparing rare earth oxide with large particles
InactiveCN101780970AImprove liquiditySimple preparation processRare earth metal compoundsOxalate precipitationRare earth
The invention relates to a simple method for preparing a rare earth oxide with large particles, which is characterized by: a. preparing a rare earth salt solution; b. using oxalate as a precipitator, adding the prepared rare earth salt solution into an oxalate solution which is mixed to a certain acidity, carrying out precipitation through stirring, and obtaining rear earth oxalate precipitation; c. stopping stirring and standing and aging the precipitate; and d. filtering the aged precipitate, washing, firing, and obtaining the product of the rare earth oxide with large particles. The invention has the advantages that: since the process of oxalate precipitation is simplified, additive such as a dispersing agent or a surface active agent and the like is not added, the rare earth oxide powder with the particle size of 10-100 mum is prepared, the mobility of products is good, the preparation process is simple, the cost is low, and the invention is suitable for the industrial production.
Owner:BAOTOU RES INST OF RARE EARTHS +1
Method for preparing thorium dioxide pellets
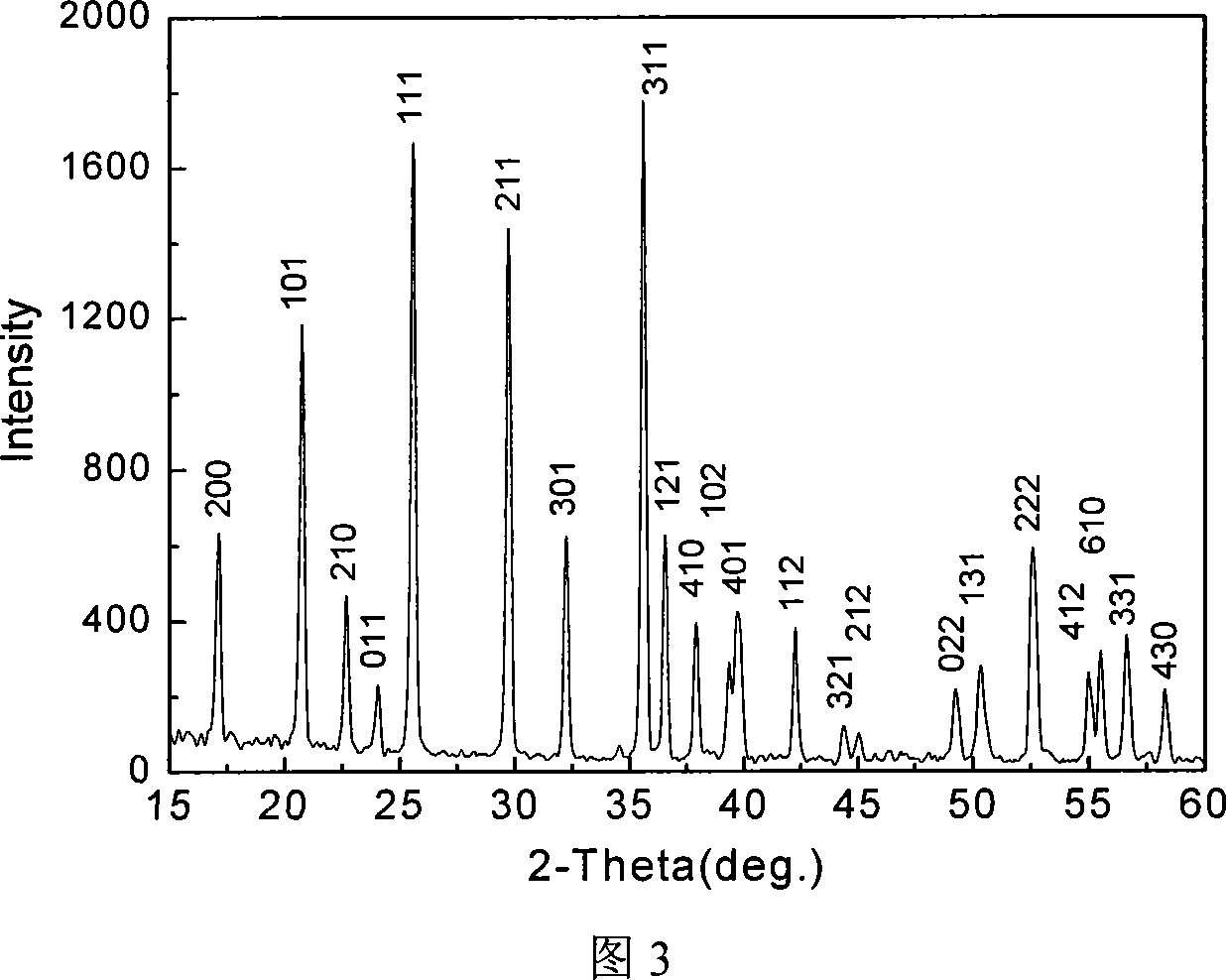
The invention belongs to the technical field of manufacturing of nuclear fuel elements, and specifically relates to a method for preparing thorium dioxide pellets. The method comprises a powder granulating process: pressing thorium dioxide powder prepared by adopting an oxalate precipitation method and serving as an original raw material into sheets by adopting a compression molding method, crushing in a granulator, screening by a granulator screen, and shaking in a top-knocked sieve shaker to obtain granules for forming the thorium dioxide pellets; a powder molding process: performing die pressing on the granules to obtain a green blank of the pellets; and a pellet sintering process: putting the green blank of the thorium dioxide pellets into a vacuum atmosphere sintering furnace, vacuumizing, washing the furnace, then introducing argon and sintering. The cobalt pellets are prepared by adopting a powder metallurgy process, so that the difficulty of low density of the green blank of the thorium dioxide powder is overcome; and the pellets prepared by the granulating, molding and sintering processes have high density and grain size meeting the index requirements of preparation of fuel elements.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR BAOTOU GUANGHUA CHEM IND
Method for treating and recycling rare earth oxalate precipitation mother solution
InactiveCN102976525ADoes not affect productionSimple methodMultistage water/sewage treatmentProcess efficiency improvementOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEOxalate precipitation
The invention discloses a method for treating and recycling a rare earth oxalate precipitation mother solution. The method comprises the steps of: adding a corresponding high-purity rare earth solution or high-purity rare earth carbonate into the precipitation mother solution to separate oxalic acid out in the form of rare earth oxalate precipitates, wherein the filtered mother solution can be directly used for preparing hydrochloric acid solutions of different concentrations to serve as refluxing acid or washing acid for extraction separation of rare earth elements, so that water and hydrochloric acid in the mother solution can be recycled totally; and returning the filtered rare earth oxalate precipitates to a rare earth precipitation process to serve as crystal seeds which can be added in a refined oxalic acid dissolution process or in a precipitation barrel before precipitation starts respectively, and ageing, washing, filtering and calcining the precipitates to obtain a high-purity rare earth product, thereby recycling originally non-precipitated rare earth and subsequently added rare earth completely. According to the invention, the comprehensive recycling problem of the rare earth oxalate precipitation mother solution of a rare earth separation plant is solved, and the method is simple and feasible, is suitable for recycling all rare earth oxalate precipitation mother solutions, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV +1
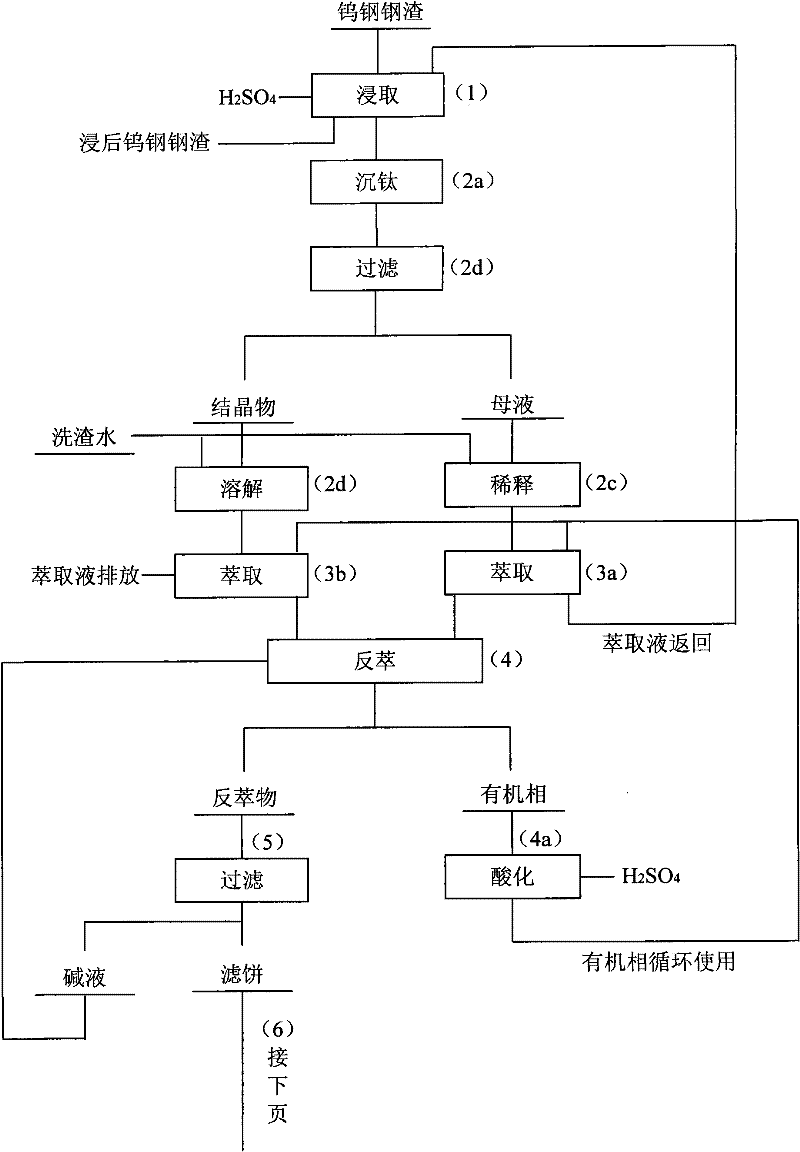
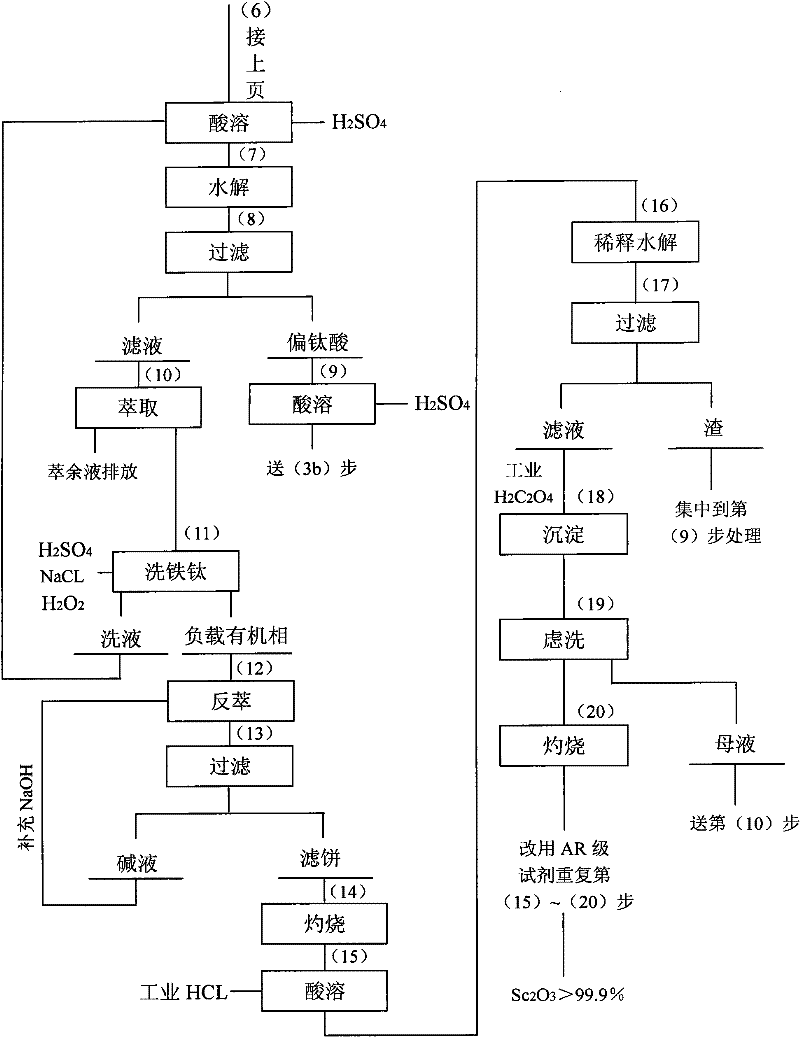
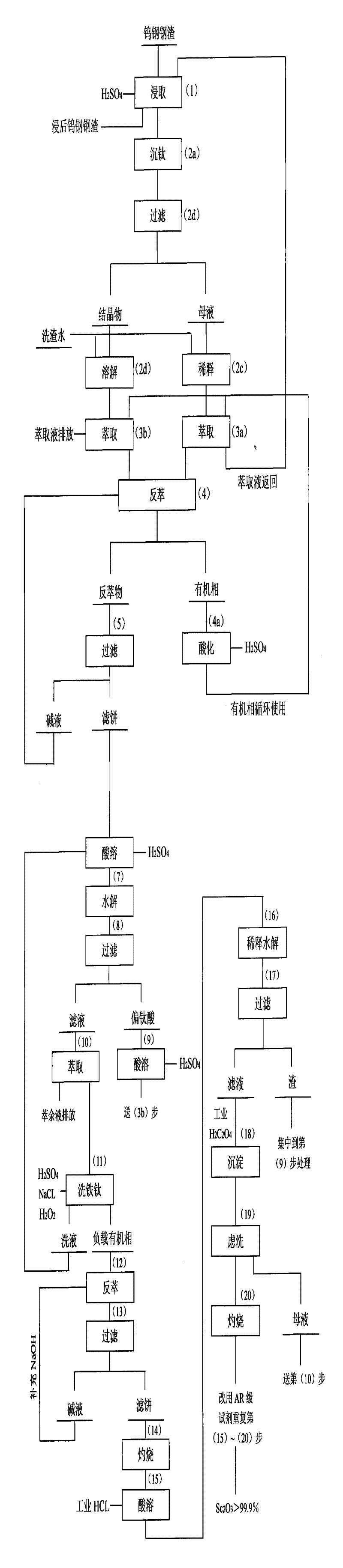
Method for extracting scandium oxide from tungsten steel slag
The invention relates to a method for extracting scandium oxide from tungsten steel slag. The method includes the steps: firstly, using a fine ball mill to crush the steel slag prior to performing main processes of inorganic acid leaching, organic solvent extraction, oxalate precipitation and the like, and enabling scandium in the tungsten steel slag to leach by the aid of sulfuric acid; secondly, allowing leaching liquor to stand to precipitate titanyl sulfate, filtering and removing titanyl sulfate, diluting mother liquor by slag washing water, and using the diluted mother liquor as feed liquor 1 of the extracted scandium; thirdly, dissolving the filtered titanyl sulfate solids by the slag washing water, and using filtrate with insoluble impurities as feed liquor 2 of the extracted scandium; fourthly, extracting the feed liquor 1 and the feed liquor 2, performing back extraction for a loaded organic phase by NaoH solution, and using sulfuric acid to dissolve hydroxide obtained after back extraction; fifthly, removing titanium by water, subjecting scandium-rich liquor with the titanium removed to secondary extraction according to conditions, washing the loaded organic phase by sulfuric acid solution containing Nacl and H2O2, then using NaoH solution for back extraction, and performing filtering, ignition and hydrochloric acid dissolving for scandium hydroxide obtained after back extraction; and finally, precipitating scandium oxalate from oxalate, and then converting the scandium oxalate to the scandium oxide by means of ignition.
Owner:龙颖
Method for extracting rare earth from phosphate rock by utilizing liquid membrane
InactiveCN102304628AImprove extraction efficiencyEfficient recyclingProcess efficiency improvementEmulsion liquid membraneKerosene
The invention belongs to the field of rare earth metallurgy, relates to an extraction of rare earth and provides a method for extracting rare earth from phosphate rock by utilizing a liquid membrane. The method comprises the following steps: mixing a neutral extracting agent with a surface active agent by the volume ratio of 5:1-1:5, mixing mixed liquid with kerosene by the volume ratio of 5:95-50:50 to prepare a mixed organic phase and mixing the mixed organic phase with a HNO3 solution by the volume ratio of 5:1-1:5 to finish the membrane preparation process; firstly adding phosphate decomposition liquid and an emulsion liquid membrane by the volume ratio of 500:15-200 into an extractor, then adding into a clarificator for demulsification after completion, and finally preparing rare earth oxide after precipitation and calcination by oxalic acid and oxalate. The purity of the rare earth oxide is more than 95 percent; and the total recovery rate of the rare earth oxide is more than 90 percent.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Recovery method of rare earth oxalate precipitation wastewater
ActiveCN103408091ASolve the emission problemWater/sewage treatment by extractionRecovery methodOxalate precipitation
The invention relates to a recovery method of rare earth oxalate precipitation wastewater. The method is characterized in that the rare earth oxalate precipitation wastewater and hydrochloric acid are prepared into a solution, wherein the concentration of oxalate is 0.01-10g / L, and the concentration of H<+> is 3.5-6mol / L. According to the method provided in the invention, the rare earth oxalate precipitation wastewater and hydrochloric acid are prepared into a solution for back extraction of rare earth from a rare earth loaded extraction solution. Therefore, the wastewater discharge problem is solved, and the acid needed by back extraction of rare earth and the oxalic acid required by final rare earth precipitation can also be saved.
Owner:INST OF RESOURCES UTILIZATION & RARE EARTH DEV GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of oxalate
ActiveCN102942471AEvenly distributedSmall particle sizeCarboxylic acid salt preparationOrganic solventOxalate precipitation
The invention discloses a preparation method of oxalate and relates to the technical field of preparation methods of the oxalate. The method includes the following steps: (1) adding one mole part of metal salt into a first organic solvent, stirring for 10-20min to mix evenly and obtain a metal salt organic solvent, adding 0.5-1.5 mole parts of oxalic acid into a second organic solvent, and stirring for 10-20min to mix evenly and obtain an oxalic acid organic solvent; (2) cooling the metal salt organic solvent and the oxalic acid organic solvent to a temperature ranging from-40DEG C to-80DEG C; (3) mixing the metal salt organic solvent and the oxalic acid organic solvent, stirring for 10-20min to obtain a mixed solution; and (4) stopping cooling, naturally warming the mixed solution, and evenly precipitating the oxalate precipitation. The method is simple in process, easy to operate, suitable for mass production and capable of preparing the oxalate with high purity, small particle diameters and even distribution.
Owner:SHANDONG MORIS TECH
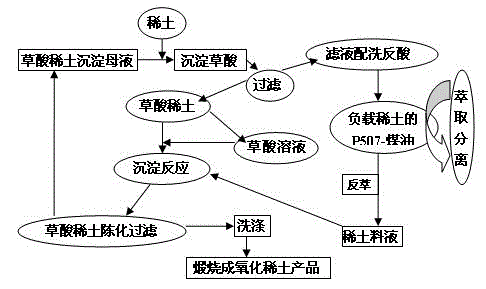
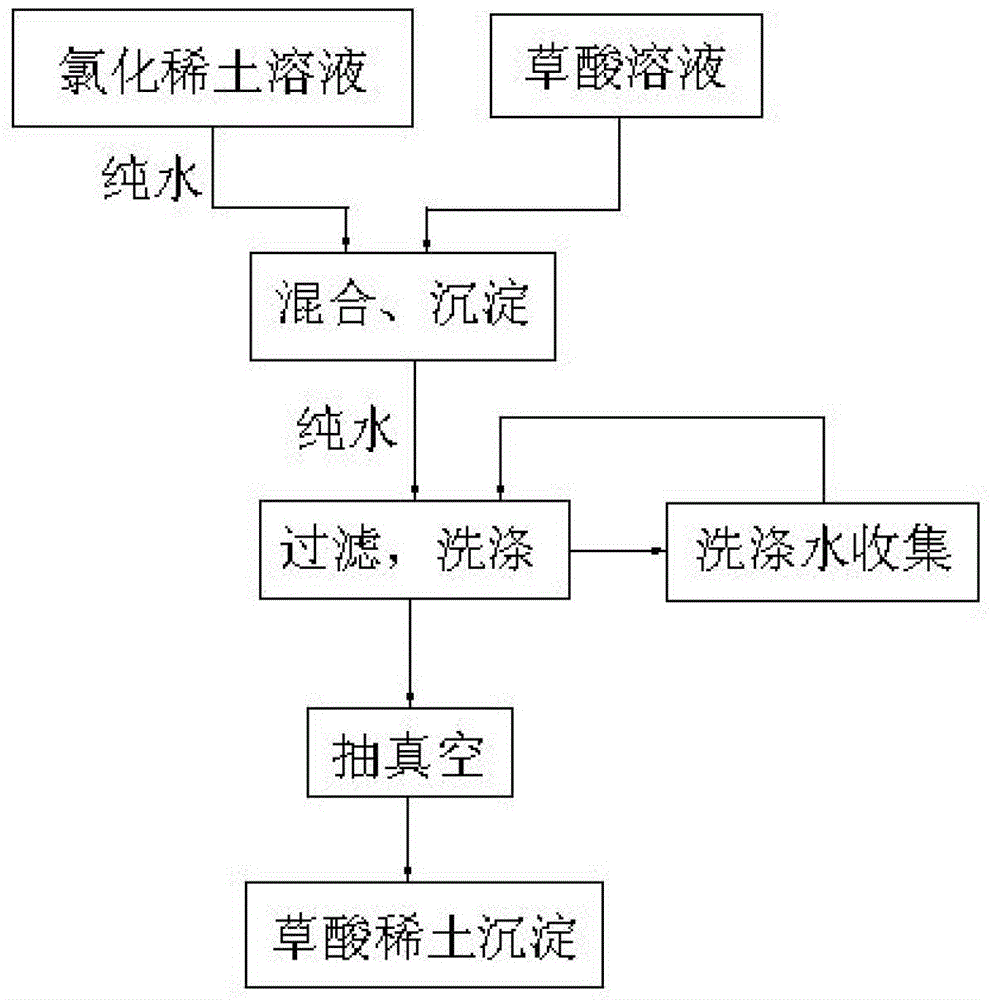
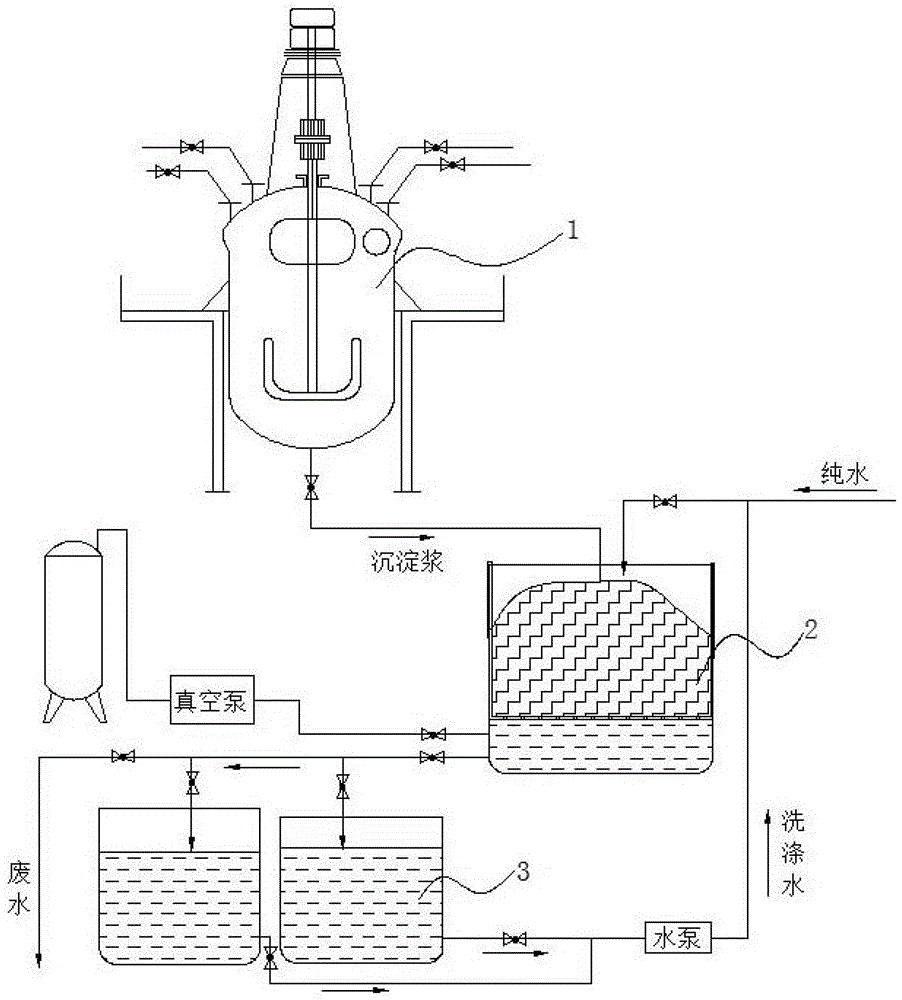
Method for preparing rare earth oxalate precipitation
The invention belongs to the field of rare earth preparation and especially relates to a method for preparing a rare earth oxalate precipitation. The method includes following steps: mixing a rare earth chloride and an oxalic acid solution; performing precipitation, filtering and washing the precipitation, collecting wash water and performing a vaccumizing process for removing water. The precipitation is filtered and washed in a self-made filter barrel, wherein the washing process is divided into a plurality of steps, wherein water, except in a first washing step, in the other steps are all collected for washing the follow-up precipitation while the water in the first washing step is discharged out, so that utilization rate of water resource can be greatly increased and waste water discharge is reduced. By means of a vacuumizing process after the washing process, moisture in the precipitations can be effectively removed for reducing volume of the rare earth oxalate precipitations, so that a subsequent burning time can be shortened, energy required in burning is saved, a production period of a rare earth oxide is reduced and a production cost is reduced. In addition, rare earth loss during spin-dry in a centrifugal machine, thereby increasing product yield.
Owner:中稀(常州)稀土新材料有限公司
Pre-reduction type high-temperature methanation catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105797785AEvenly dispersedLarge specific surface areaHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsGaseous fuelsOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEMethanation
The invention discloses a pre-reduction type high-temperature methanation catalyst. The catalyst comprises an active component, a carrier and an auxiliary, wherein the active component is reduction state nickel, the carrier is Al2O3, and the auxiliary is one or more of Mg oxide, Ca oxide, Ba oxide and La oxide. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the catalyst. The preparation method comprises the steps that nickel nitrate, aluminum nitrate and soluble salt of the auxiliary oxide are prepared into an aqueous solution, the prepared aqueous solution is added into a reaction kettle, oxalate precipitator is added for stirring and heating, and a semi-finished catalyst is obtained after washing and filtering; calcination is conducted after drying, cooling passivating is conducted, graphite and water are added, the mixture is mixed evenly, and then the catalyst is obtained through compression molding. The pre-reduction type high-temperature methanation catalyst is prepared through the method of oxalate precipitating and inert atmosphere calcination and has high specific surface area, CO produced through oxalic acid decomposing is used for reduction, the reduction type catalyst is directly obtained, the reduction degree of the passivated finished product is 80% or above, plenty of time is saved, and using is convenient.
Owner:XIAN SUNWARD AEROSPACE MATERIAL
Analysis method for trace oxalic acid root in mother liquor of plutonium oxalate precipitation
ActiveCN103760273AHigh sensitivityImprove accuracyComponent separationFuel reprocessingIon chromatography
The invention belongs to the technical field of spent fuel reprocessing, and discloses an analysis method for a trace oxalic acid root in a mother liquor of plutonium oxalate precipitation. The analysis method comprises the following steps that: (1) the mother liquor of plutonium oxalate precipitation is diluted by 10 to 20 times, and a reducing agent is added to destroy potassium permanganate in the mother liquor of plutonium oxalate precipitation; (2) the test solution prepared in the step (1) is placed on an IC - H column to remove the positive ions in the solution; (3) the solution collected in the step (2) is placed into a container and heated under a temperature condition of less than 60 DEG C, and a gas is used to purge the upper surface of the solution to full dry at the same time; (4) a beaker is washed with deionized water for many times, the washing liquor is collected for fixing a volume, and the content of the oxalic acid root in the solution is measured by an ion chromatography. The analysis method has the characteristics of small interference of matrix, high accuracy and simple device adopted.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Technique for producing 99% praseodymium-neodymium oxides by using Nd-Fe-B smelting slag
The invention relates to a production process of extracting Pr-Nd oxide by utilizing NdFB to smelt waste slag and magnetic slurry. The invention is characterized in that: according to chemical characteristics of rare metal ion, the valuable elements are separated and extracted by acid leaching, ammonium bicarbonate sedimentation, selective dissolution, oxalate sedimentation, and burning procedures, so as to produce high purity Pr-Nd oxide. The invention has the advantages of high purity (reaching 99%), high utilization ratio of raw materials (reaching 98%), simple process (two dissolutions and two sedimentations, and then burning are performed to obtain high purity products), no solid waste slag for polluting environment, and being suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:什邡市虹雨化工有限公司
Oxygen vacancy-containing layered lithium-rich cathode material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109935817AStable structureImprove performanceCell electrodesSecondary cellsChemical structureNickel salt
The invention provides an oxygen vacancy-containing layered lithium-rich cathode material preparation method. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: an oxalate precipitant is dissolved in a mixed solvent of ethanol and water to obtain a solution A; lithium salt, nickel salt, cobalt salt and manganese salt are dissolved in the mixed solvent of ethanol and water to obtain a solution B; the solution B is poured into the solution A, a precursor is obtained after stirring and drying, and a lithium-rich cathode material is obtained through staged calcination; and the lithium-rich cathode material is placed in a hydrogen-argon mixed gas for low-temperature calcinations, and after cooling, an oxygen vacancy-containing layered lithium-rich cathode material is obtained. The material synthesized in the invention has a stable chemical structure and excellent cycle performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Ultrafine lanthanum oxide and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105084407ASimple preparation processEvenly distributedRare earth metal compoundsOxalate precipitationFiltration
The invention belongs to the field of preparation of rare earth materials, and especially relates to an ultrafine lanthanum oxide and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the ultrafine lanthanum oxide comprises the following steps: 1, preparing a lanthanum salt solution A; 2, preparing an anionic surfactant solution B, and adding the solution B to the solution A to obtain a solution C; 3, preparing an oxalic acid solution, pouring the oxalic acid solution into a reaction container, adding the solution C to the oxalic acid solution in a dropwise manner while continuously stirring, and reacting the solution C with the oxalic acid solution to generate lanthanum oxalate precipitate; and 4, carrying out pumping filtration on the generated precipitate, washing with water, drying, calcining to obtain crude lanthanum oxide, crushing the crude lanthanum oxide, and sieving to obtain the ultrafine lanthanum oxide with uniformly distributed granularity. The preparation method of the ultrafine lanthanum oxide is simple, allows rare earth lanthanum oxide with small granularity and uniform particle distribution to be directly obtained through an oxalate precipitation technology, and can avoid particle fragmentation caused by a physical technology, and the ultrafine lanthanum oxide can be directly used in magnetic materials.
Owner:CHANGZHOU GEOQUIN NANO NEW MATERIALS
Etching bath composition for transparent conductive film
The invention relates to an etching bath composition for transparent conductive film, which has few indium oxalate precipitation in the corrosion processing for transparent conductive film of ITO film used in liquid crystal display device and the like. The indium oxalate precipitation can be effectively prevented even if the concentration of indium is high in the etching bath in the transparent conductive film corrosion process, through the etching bath composition for transparent conductive film containing oxalic acid and alkaline compounds (except triethanolamine).
Owner:KANTO CHEM CO INC
Manufacturing Method of Black Vinegar and Black Vinegar Manufactured by the Method
InactiveUS20090047383A1Small contentVinegar preparationFood preparationAcetic acidOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATE
An object of the present invention is to provide a manufacturing method of black vinegar which contains sugar derived from rice and barley abundantly, and is free from precipitation, and black vinegar manufactured by the method.The present invention provide a manufacturing method of black vinegar having the sugar content of 8-50 weight / volume % derived from rice and / or barley, wherein acetic acid fermentation is performed by mixing a saccharified solution and an alcoholic fermented broth of rice and / or barley, and the final concentration of oxalic acid in black vinegar is 36 ppm or less, and preferably 30 ppm or less.In addition, as a decreasing method of oxalic acid in black vinegar, storing with stirring a saccharified solution of rice and / or barley or a fermented broth after completion of acetic acid fermentation is effective. And the present invention provides black vinegar manufactured by these methods in which oxalate precipitation is hardly to occur, and which is suitable for drinking.
Owner:MIZKAN GRP & MIZKAN
Method for recovering oxalate and acid liquor from acidic etching waste liquor
InactiveCN102070436AExemption from the procedureCost-freeWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatmentLiquid wasteHigh concentration
The invention discloses a method for recovering oxalate and acid liquor from acidic etching waste liquor. The method comprises the following steps of: mixing a proper amount of oxalic acid and the acidic etching waste liquor; performing hydrolysis reaction to form oxalic acid radicals; combining the oxalic acid radicals and bivalent metal ions in the acidic etching waste liquor to form water-insoluble oxalate precipitates; and separating the oxalate precipitates out from the acidic etching waste liquor by a filter method or a precipitate clarification method and the like to obtain solid-state oxalate, wherein the acidic etching waste liquor from which the metal ions are extracted becomes the acidic liquor with higher concentration and can be used for preparing etching liquor or can be used as a raw material for other industries. By the method, the cost of raw materials is greatly reduced, and a reprocessing procedure and the expenditure cost are saved; and the method has great significance to energy conservation and effective pollution prevention.
Owner:苏州超联光电有限公司
Preparation method and application of potassium ion battery positive electrode material
InactiveCN109713295AImprove cycle stabilityUniversalCell electrodesSecondary cellsMANGANESE ACETATENew energy
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a potassium ion battery positive electrode material and belongs to the technical field of electrochemical new energy, and the problem ofunstable cycling performance of the potassium ion battery positive electrode material can be solved. The chemical formula of the material is KtNixCoyMnzO2, t is larger than 0.5 and smaller than 0.9, xis larger than 0.15 and smaller than 0.4, y is larger than 0.15 and smaller than 0.4, and z is larger than 0.2 and smaller than 0.7. According to a synthetic route, three soluble acetates of nickel acetate, cobalt acetate and manganese acetate are used and are dissolved in deionized water in proportion to obtain a mixed metal ion salt solution, the mixed metal ion salt solution is slowly droppedinto an oxalic acid solution to obtain an oxalate precipitate, after processes of washing, drying and pre-sintering, a potassium source is added, high-temperature sintering is performed, and cooling with a furnace is carried out obtain the material. The method has the advantages of simple operation, low cost and universality, and the prepared material is used for a new potassium ion battery test and has good cycle stability and rate performance.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Process for preparing bifunctional catalyst for preparing dimethyl ether directly with synthesis gas
InactiveCN101314134ALow reaction temperatureReduce adverse effectsMolecular sieve catalystsEther preparationAlcoholOxalate precipitation
The invention discloses two methods for directly preparing a bifunctional catalyst of dimethyl ether by synthesis gas. The core principle is to add an active component for methanol synthesis to a methanol dehydration component in an oxalate precipitation mode, for example, the following steps are adopted: a. the active component which can be used as a methanol synthesis catalyst is dissolved into alcohol in a soluble salt mode to prepare a mixed solution A; b. an active component which can be used as a methanol dehydration catalyst is added into the mixed solution A to be stirred to prepare suspension B; and c. an alcoholic solution of oxalic acid is added into the suspension B during the stirring, and a generated oxalate coprecipitate is aged, filtered, dried and finally roasted at a temperature of between 250 and 550 DEG C to prepare the bifunctional catalyst. The methods have simple preparation process, and the prepared bifunctional catalyst has low reaction temperature, high transformation rate of carbon monoxide, and good selectivity of the dimethyl ether.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Method and device for directly recovering oxalate precipitate of waste acid
InactiveCN102115438AReduce pollutionReduce consumptionPreparation from carboxylic acid saltsCarboxylic acid salt preparationDistillationOxalate precipitation
The invention relates to a method and a device for directly recovering the oxalate precipitate of waste acid. The method is characterized in that a soluble metal salt solution and oxalic acid are added in a precipitation-distillation kettle and sufficiently mixed to generate an oxalate precipitate and waste acid, and then the waste acid in the precipitation-distillation kettle is distilled and recovered; and water is added in the precipitation-distillation kettle, the oxalate precipitate is stirred into slurry, and then the slurry is discharged, filtered, washed and dried to obtain an oxalate product. The method can not only greatly reduce the evaporation capacity of waste acid as well as the energy loss and material damage in the prior precipitation process, but also greatly save the consumption of oxalic acid. In addition, the adopted device has the advantages of long service life, low maintenance cost, energy conservation and the like. The method and the device have the characteristics of simple process, less consumption of chemical raw materials, high efficiency, energy conservation, environmental protection and low running cost, and not only solve the problems of waste acid recovery and environmental pollution in the oxalate precipitation process, but also realize better economic benefit.
Owner:GANZHOU RECYCLE NEW TECH
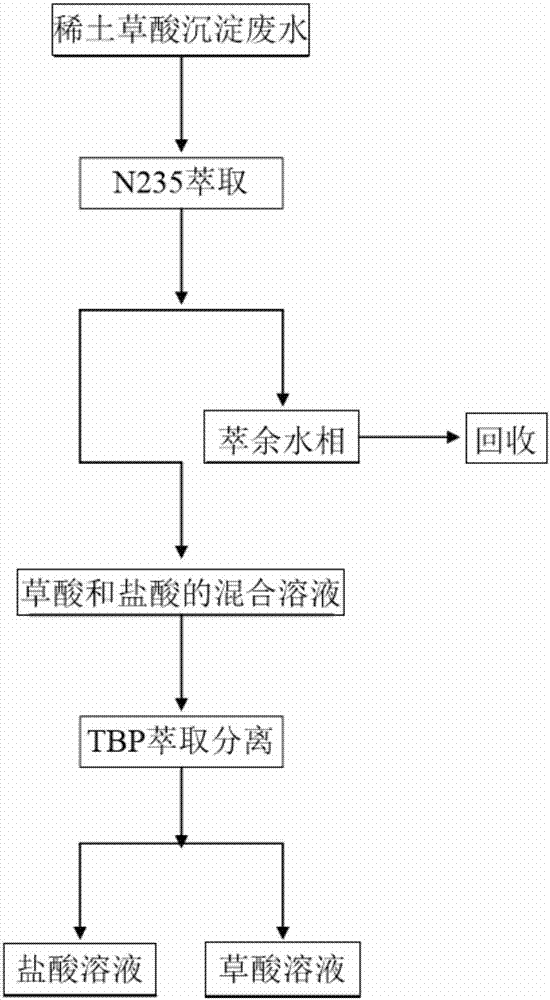
Method for recycling oxalic acid and hydrochloric acid from rare earth oxalate precipitation wastewater
ActiveCN106892479AReduce volumeChlorine/hydrogen-chloride purificationWater contaminantsResource recoveryOxalate precipitation
The invention relates to the field of treatment of industrial rare earth wastewater and resource recycling, in particular to a method for recycling oxalic acid and hydrochloric acid from rare earth oxalate precipitation wastewater. The method comprises the following steps: extracting the oxalic acid and the hydrochloric acid from the rare earth oxalate precipitation wastewater through an extraction method, thus obtaining an oxalic acid and hydrochloric acid mixing solution, and recycling the wastewater; and separating the oxalic acid from the hydrochloric acid through the extraction method, thus respectively obtaining an oxalic acid solution and a hydrochloric acid solution. By the use of the method, no rare earth oxalate precipitation wastewater is discharged, and the oxalic acid and the hydrochloric acid are recycled. Valuable resources in the rare earth oxalate precipitation wastewater are recycled, so that the production cost is reduced, and the environmental pollution is relieved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
811NCM ternary cathode material of three-dimensional nanowire array structure and preparation method thereof
PendingCN110867577AEasy reunionGood lookingSecondary cellsPositive electrodesElectrolytic agentNickel salt
An 811NCM ternary cathode material of three-dimensional nanowire array structure and a preparation method thereof are disclosed. The micromorphology of the ternary positive electrode material is characterized in that primary spherical single-crystal particles are self-assembled into a nanowire, and then the nanowires are self-assembled into a strip-shaped array structure, wherein the particle hasa length of 10[mu]m to 50[mu]m, and a width of 1[mu]m to 3[mu]m. The preparation method comprises: dissolving a nickel salt, a cobalt salt and a manganese salt in a solvent by a solvothermal method; adding ammonia water or sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH value; performing a solvothermal reaction at a certain temperature for 10-24 hours; after the synthesized oxalate precipitate containing nickel-cobalt-manganese is mixed with a lithium source uniformly, calcining the mixture at high temperature to obtain the 811NCM ternary cathode material. The preparation process is simple in operation andlow in cost. In the synthesis process, ethylene glycol or glycerol is used as both a solvent and a dispersant. Compared with a co-precipitation method, the method improves particle agglomeration. Thecrystal structure of a final product is layered structure with a large specific area, thereby helping an electrolyte to further wet the material and further improving the electrochemical performanceof a battery.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com