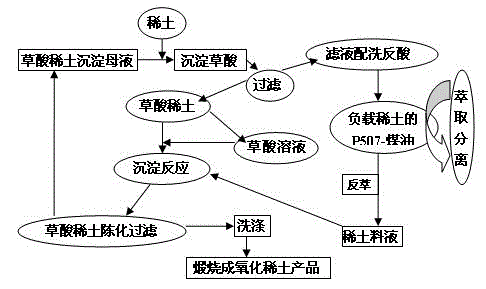
Method for treating and recycling rare earth oxalate precipitation mother solution
A recovery method and technology for precipitating mother liquor, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of complex process, low oxalic acid extraction efficiency, and high equipment requirements. Simple method, significant economic and social benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0009] Get the supernatant after the precipitation of 100ml high-purity yttrium oxalic acid respectively, add different volumes of high-purity yttrium feed liquid (Y 2 o 3 / REO≥99.999%, 5NY), there is obvious white precipitate, stir and age for a certain period of time, filter, take the filtrate for analysis, and calculate the residual rate or removal rate of oxalate according to the oxalate content in the solution before and after precipitation. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0010] It can be seen from the results in Table 1 that with the increase of the amount of 5NY feed solution, the precipitation of yttrium oxalate increases, the content of oxalate in the solution decreases correspondingly, and the removal rate of oxalate increases. At the beginning, the removal rate of oxalic acid caused by the addition of each milliliter of feed liquid increased rapidly, and the increase after 6 milliliters was small, and the removal rate was above 70%. When feeding, the ...
Embodiment 2
[0016] Prepare stripping acid (5 mol / l hydrochloric acid solution) with the above-mentioned solutions with different oxalic acid contents (concentration from 0.027-0.16mol / l) obtained through different degrees of treatment, and carry out stripping with P507-kerosene organic phase loaded with high-purity yttrium Experiment, compared to O / W=1:4. The results show that although the hydrochloric acid prepared from the untreated oxalic acid precipitation mother liquor is directly used for stripping the yttrium in the organic phase of P507-kerosene, no obvious white precipitate will be produced, but the rare earth analysis in the solution will be affected, and the end point will be delayed when titrated with EDTA. The tail is serious, and the concentration of oxalic acid in the water phase is also significantly reduced, generally below 0.04mol / l. It is proved that the presence of oxalic acid will affect the stripping of rare earths, and a part of oxalic acid will enter the organi...
Embodiment 3
[0018] Get the supernatant after the precipitation of 100ml high-purity yttrium oxalic acid respectively, add different weights of high-purity yttrium carbonate solid (Y 2 o 3 / REO≥99.999%, containing about 40% yttrium oxide, reacted with 5NY feed liquid and sodium bicarbonate to form yttrium carbonate precipitate, filtered after aging and crystallization, and dried at 50°C). Carbon dioxide gas is produced, and as the dissolved amount increases, the solution begins to appear turbid, and yttrium oxalate precipitates are formed. After aging for a certain period of time, filter and analyze the filtrate. Calculate the residual rate or removal rate of oxalate according to the oxalate content in the solution before and after precipitation, and the results are shown in Table 2. As the amount of yttrium carbonate increases, the precipitation of yttrium oxalate increases, the content of oxalate in the solution decreases accordingly, and the acidity also decreases. However, the decre...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Median particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Median particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Median particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com