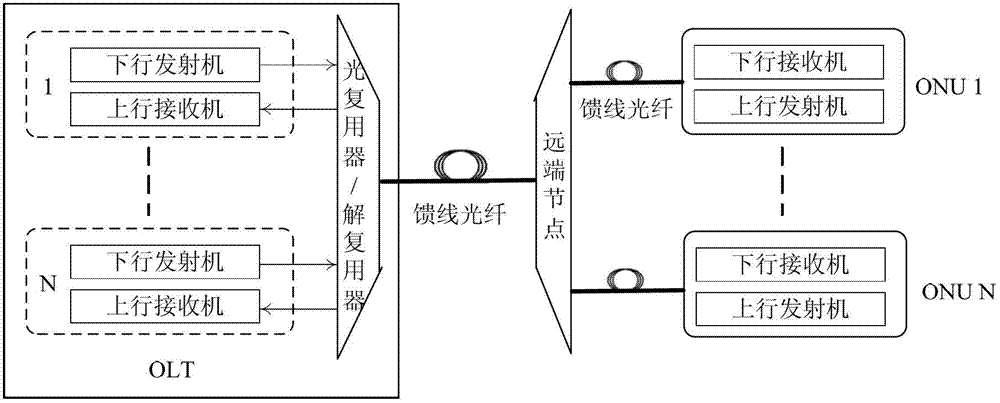
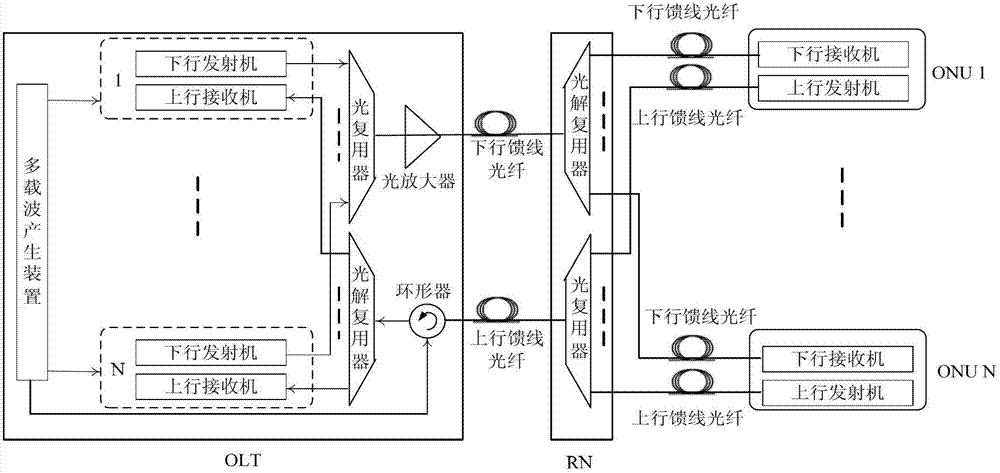
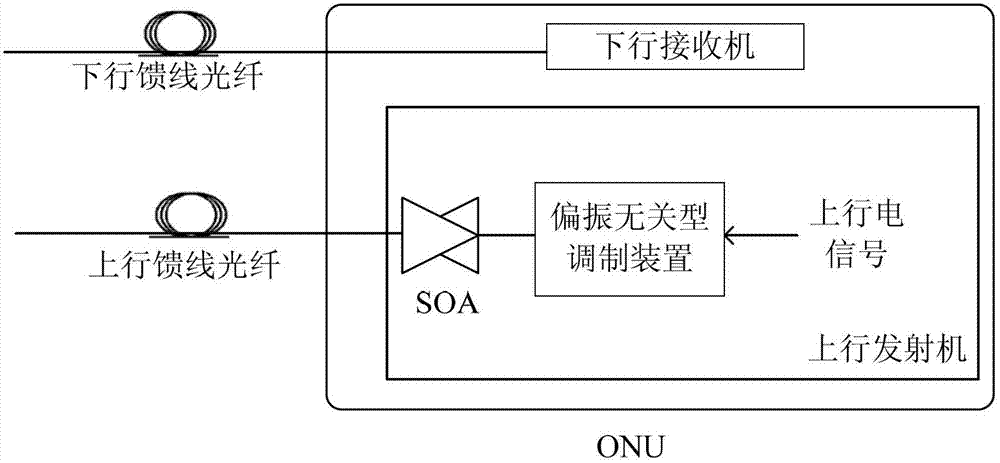
Patents
Literature
155 results about "Coarse wavelength division multiplexing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
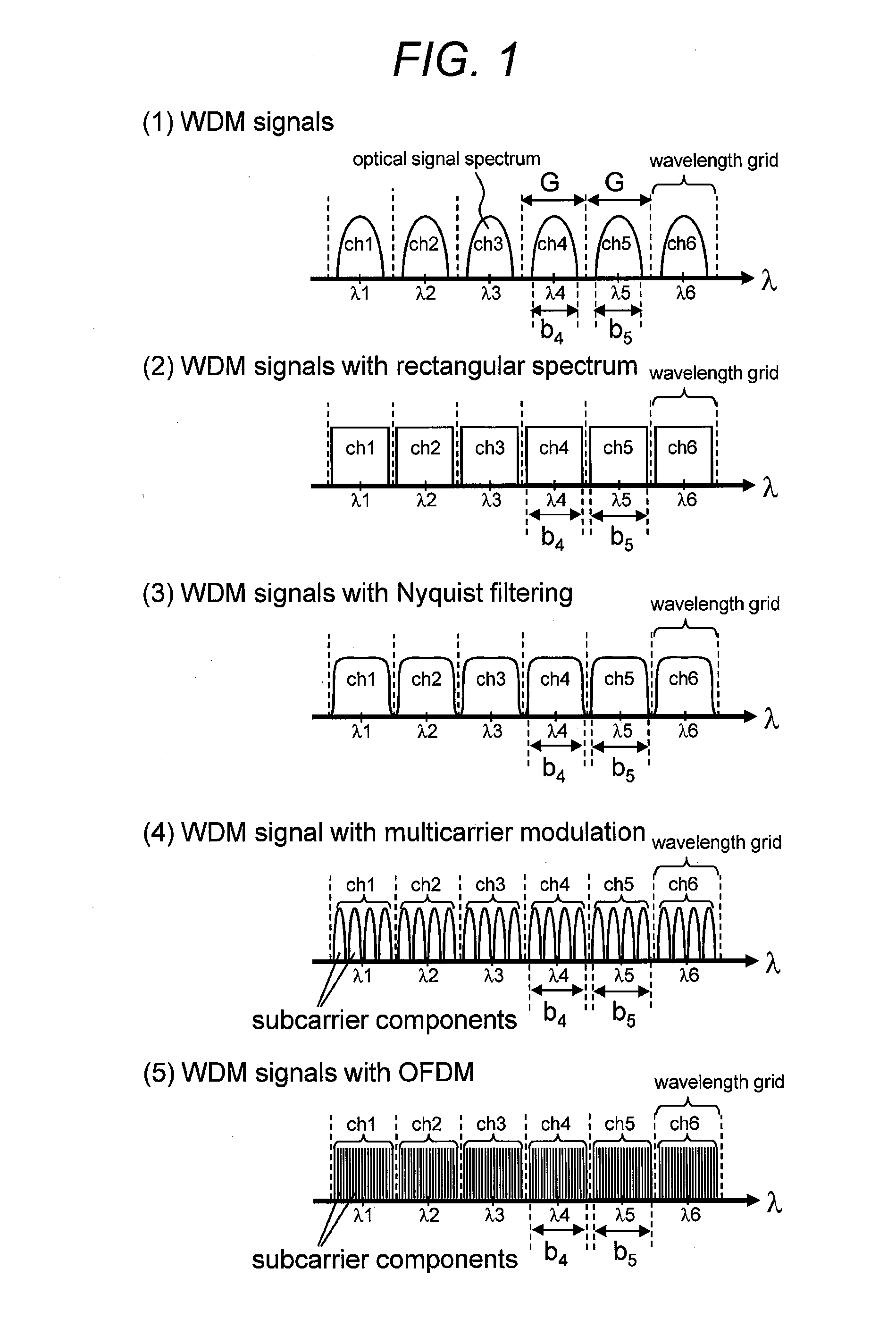
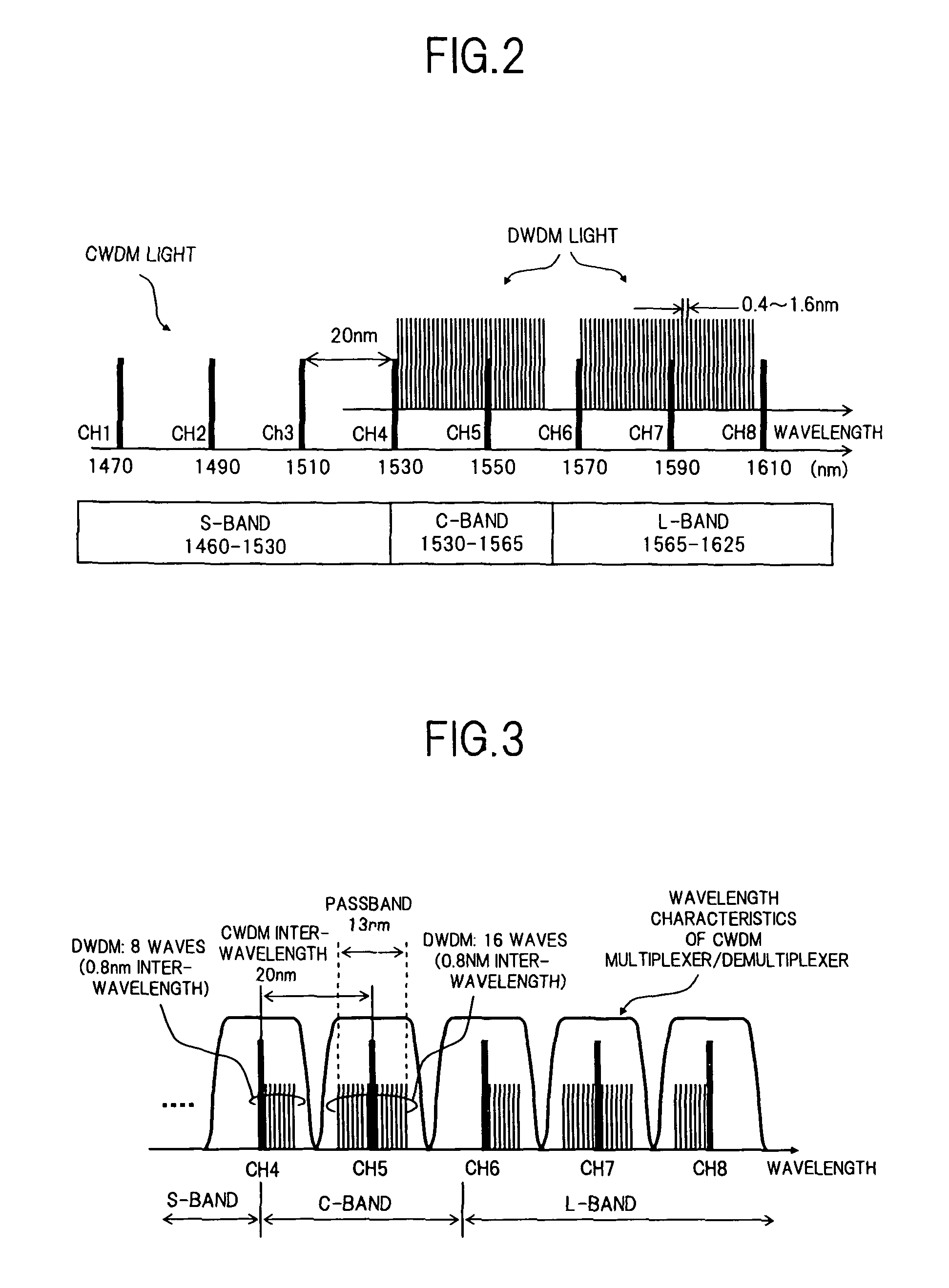
Coarse wavelength division multiplexing (CWDM), a variant of wavelength division multiplexing (WDM), is an optical transmission technique used for shorter distances as compared to dense WDM (DWDM).
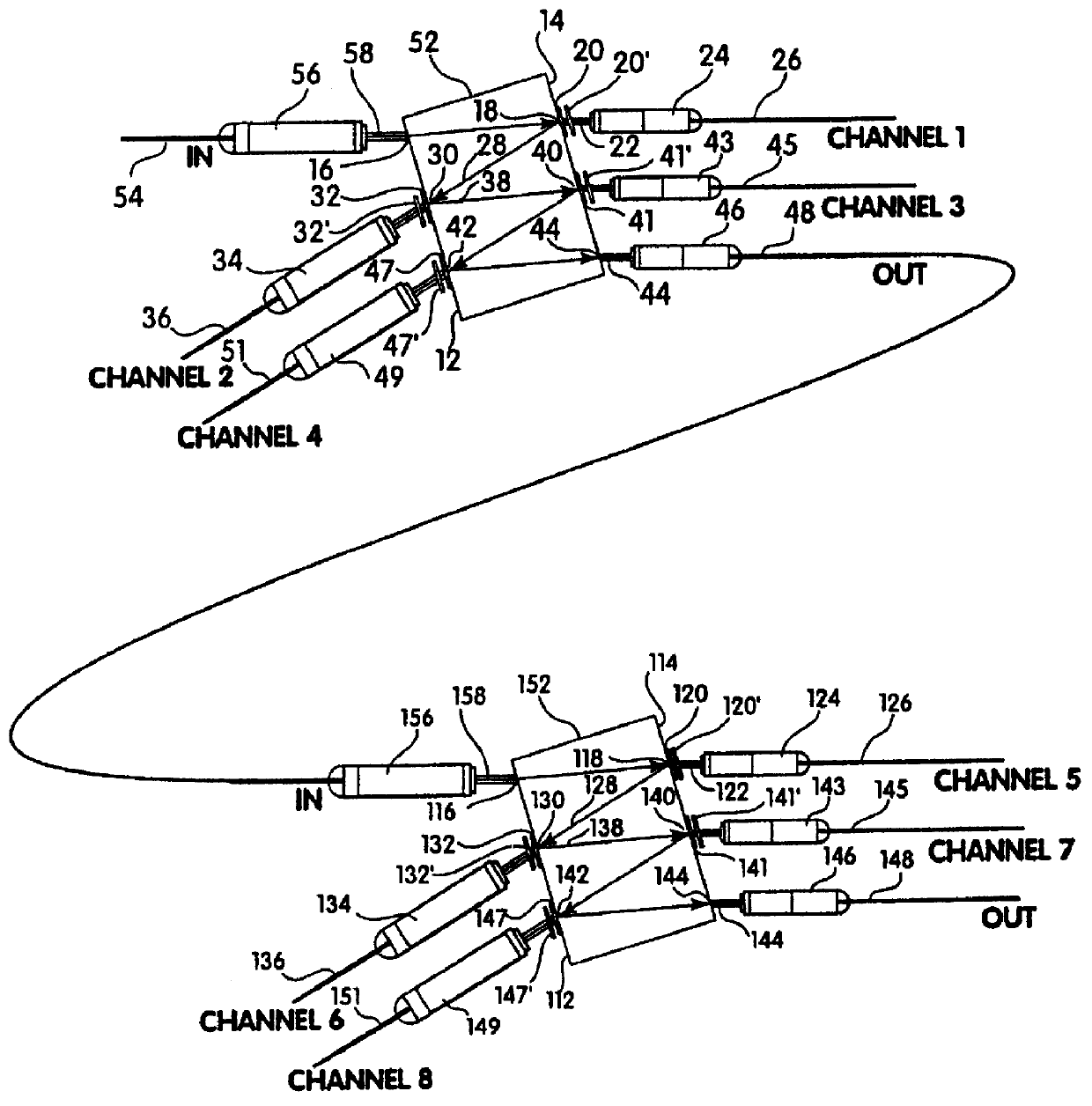
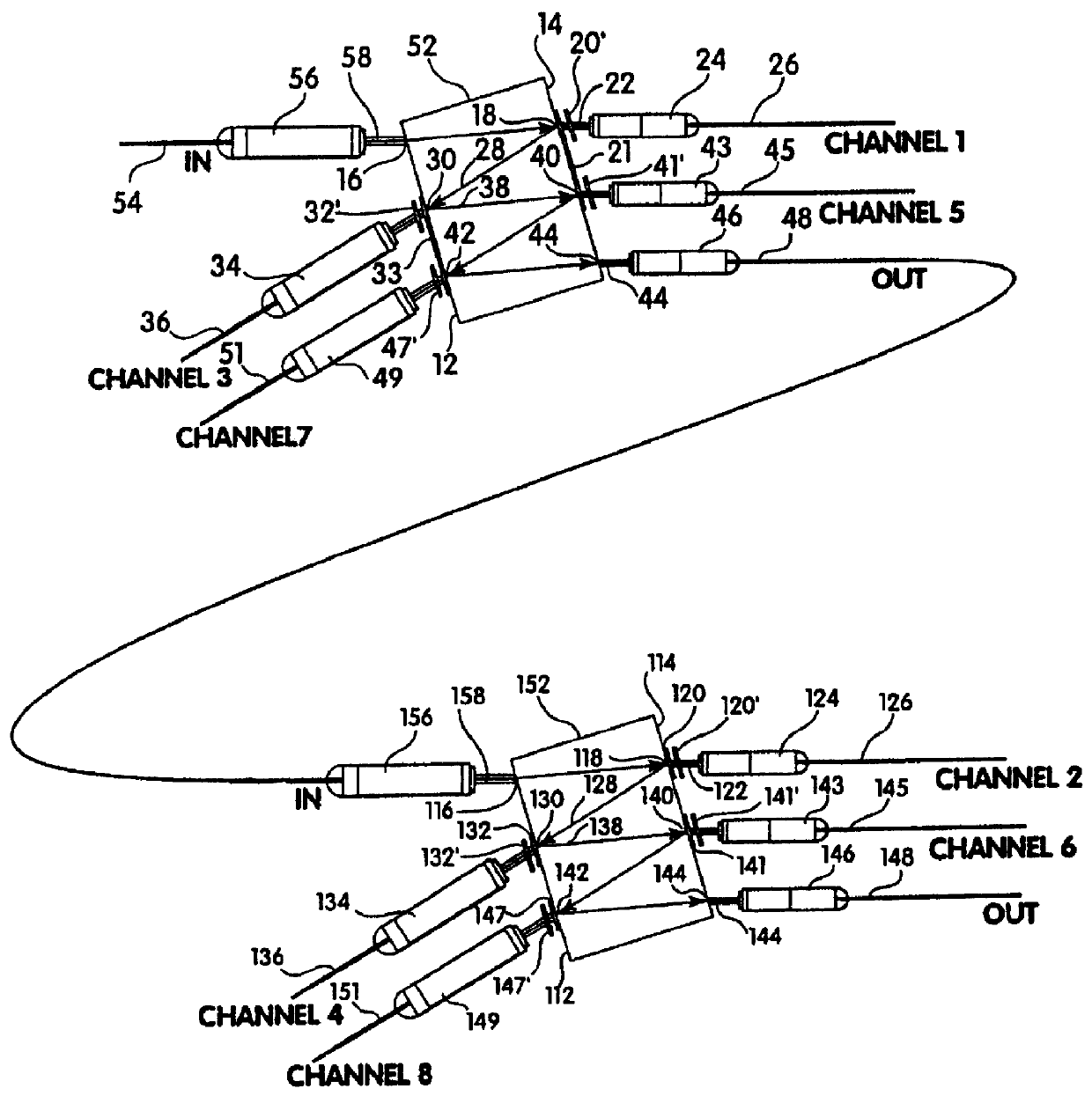
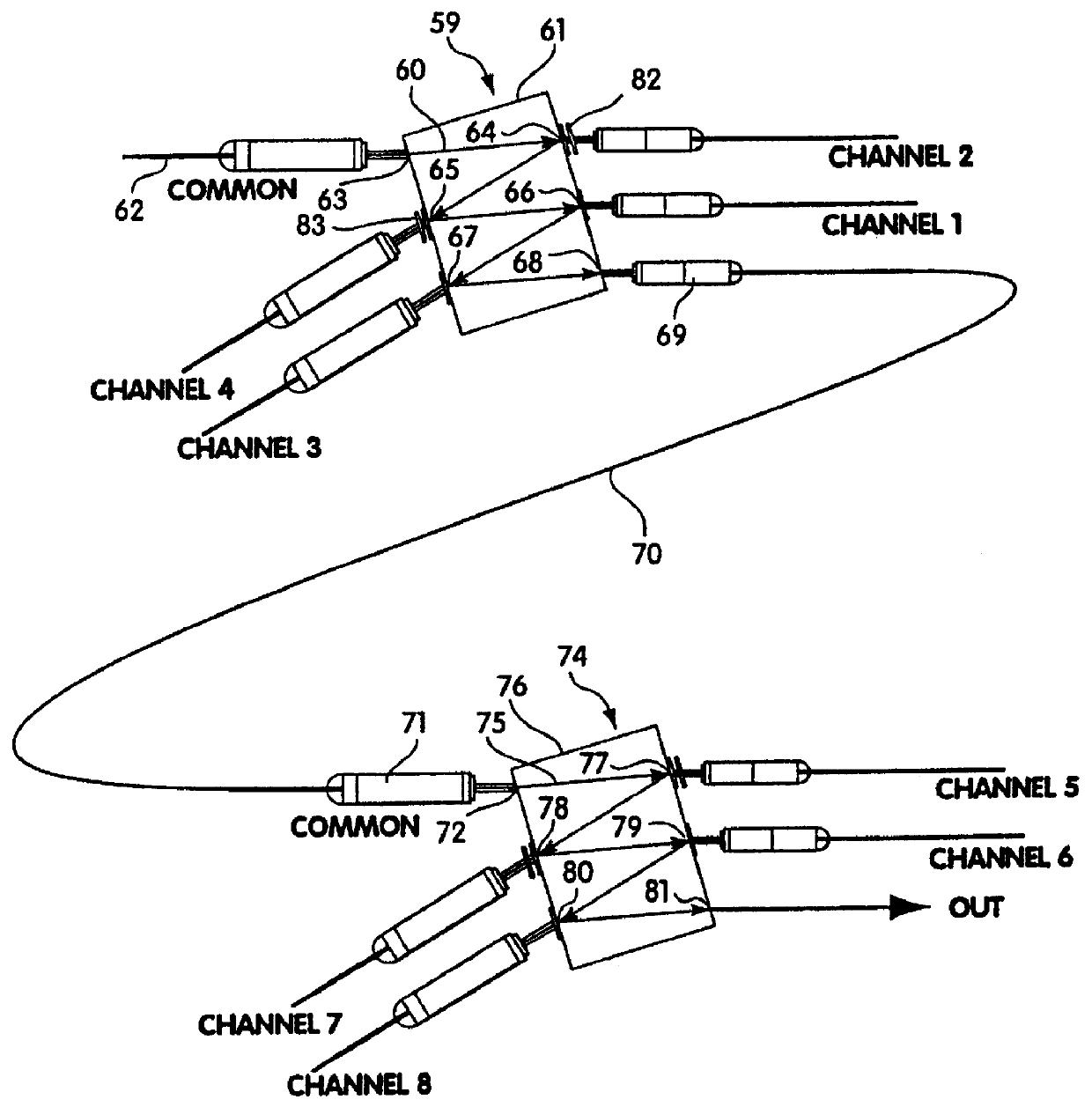
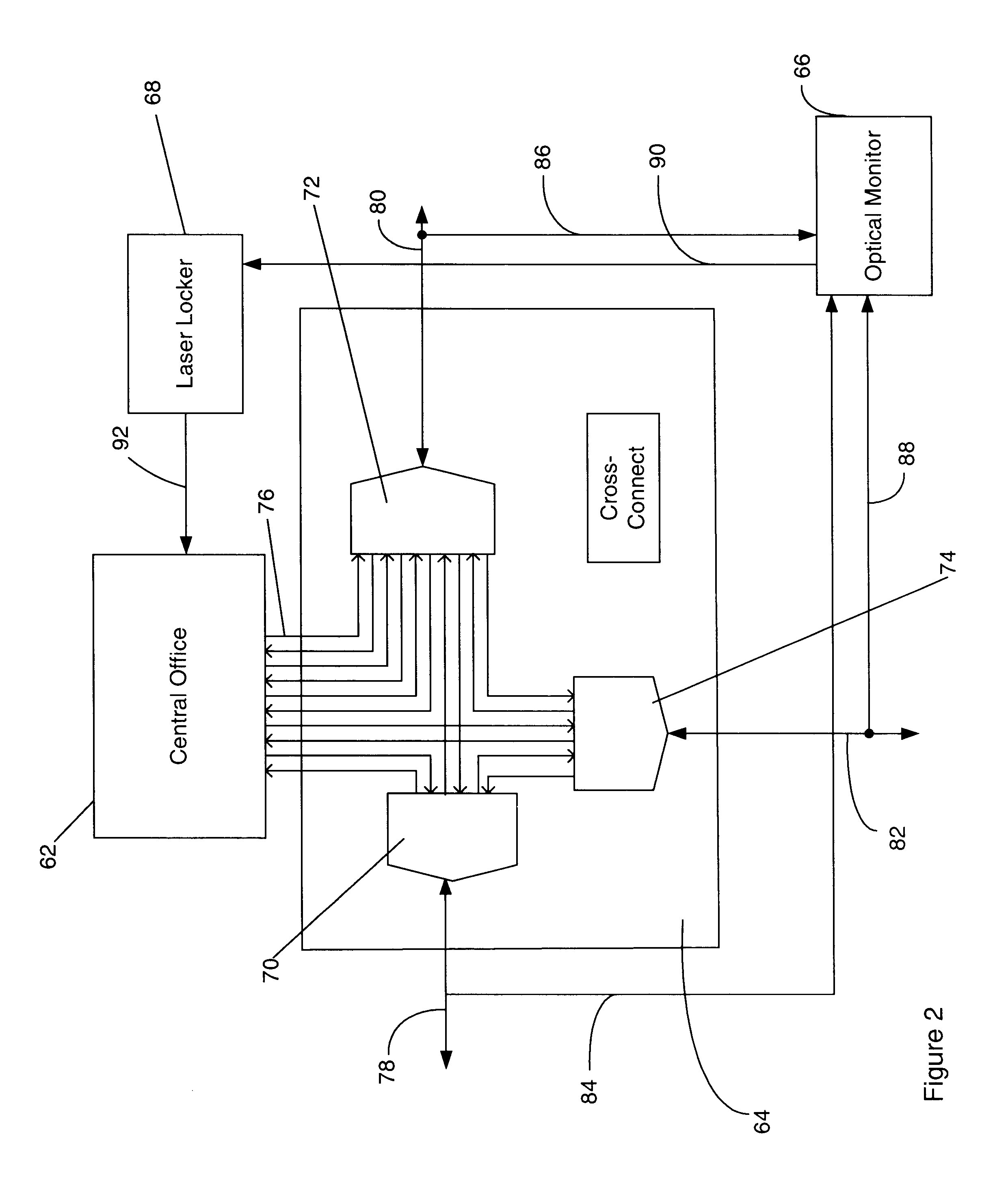
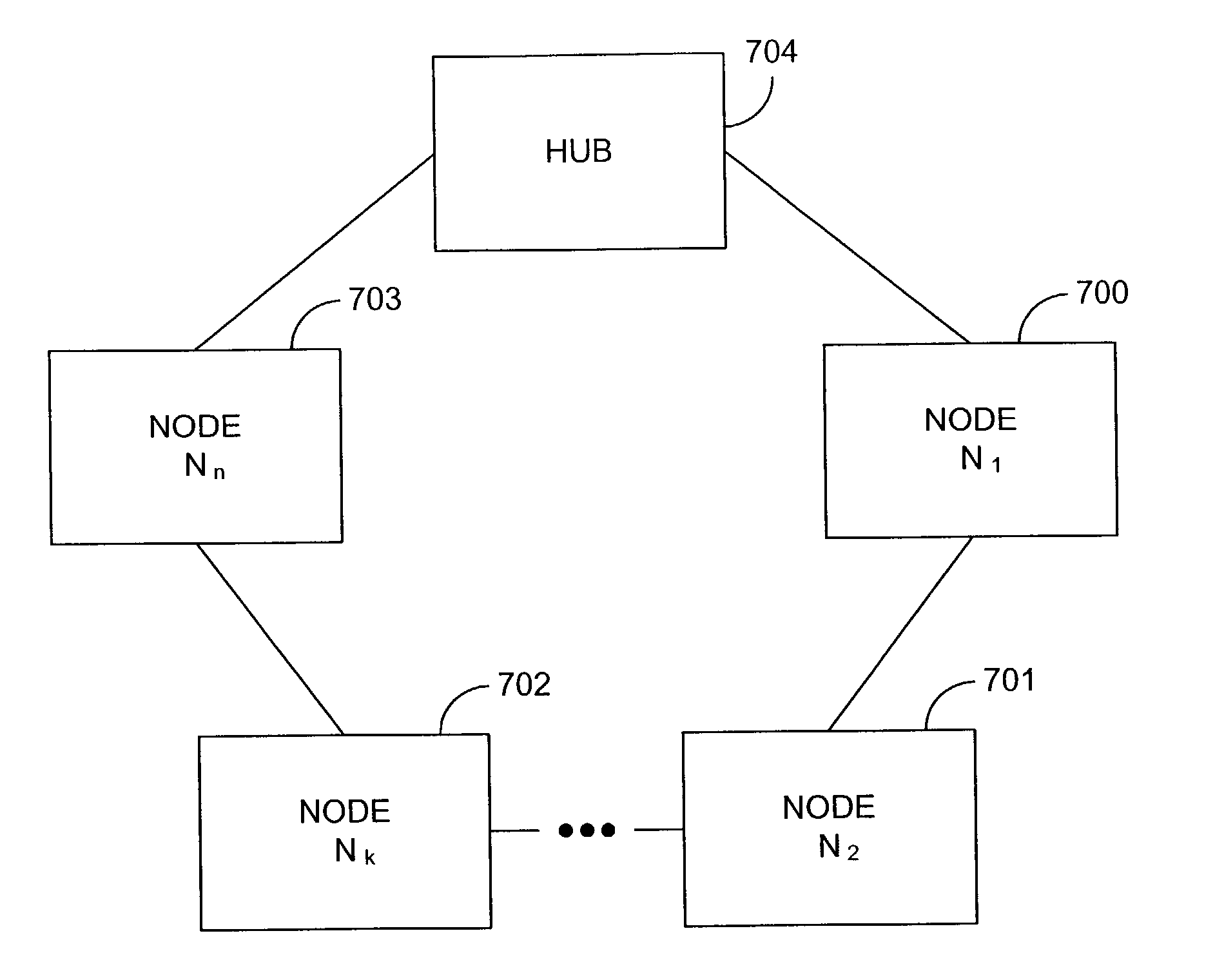
Optical fiber ring communication system
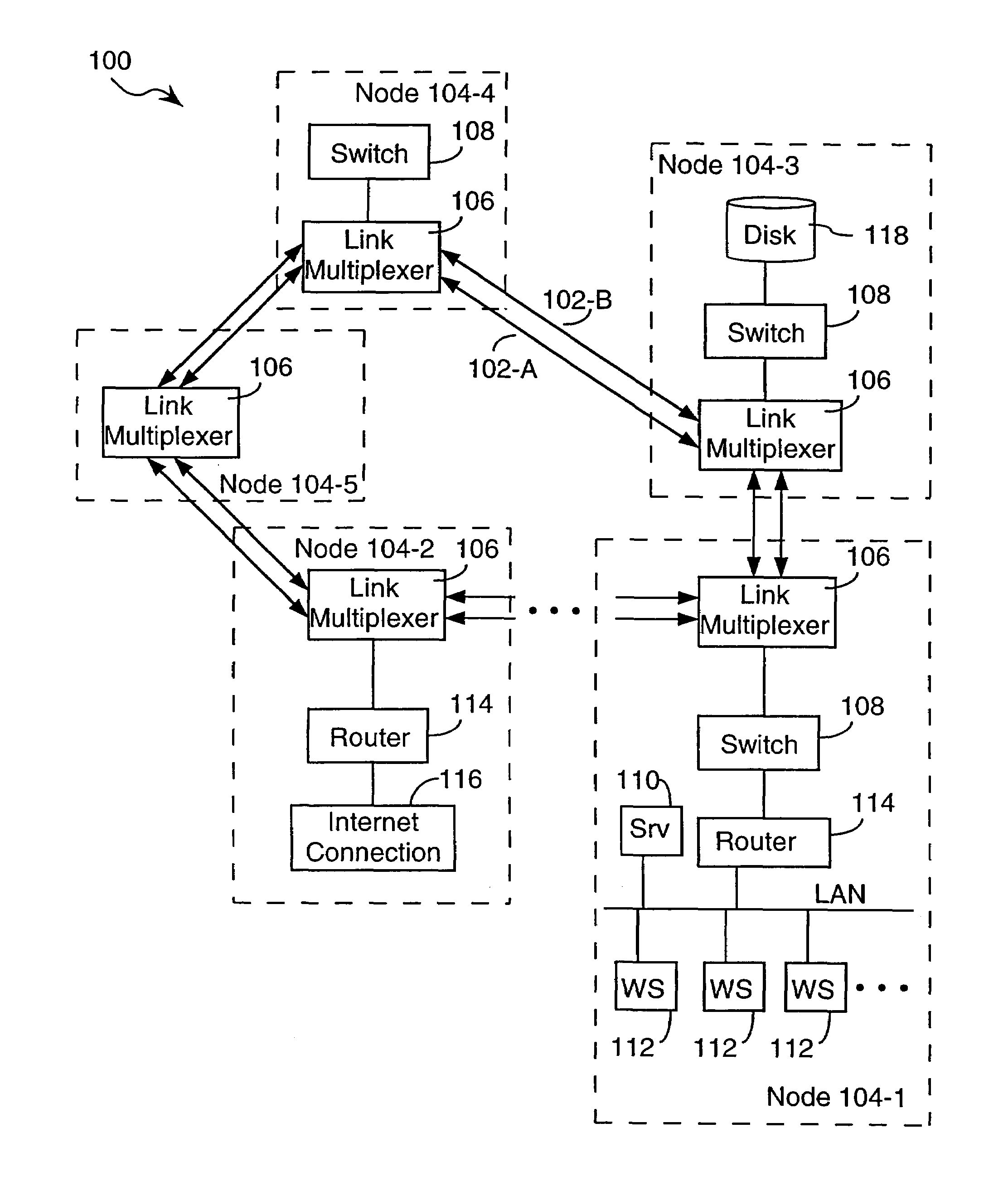
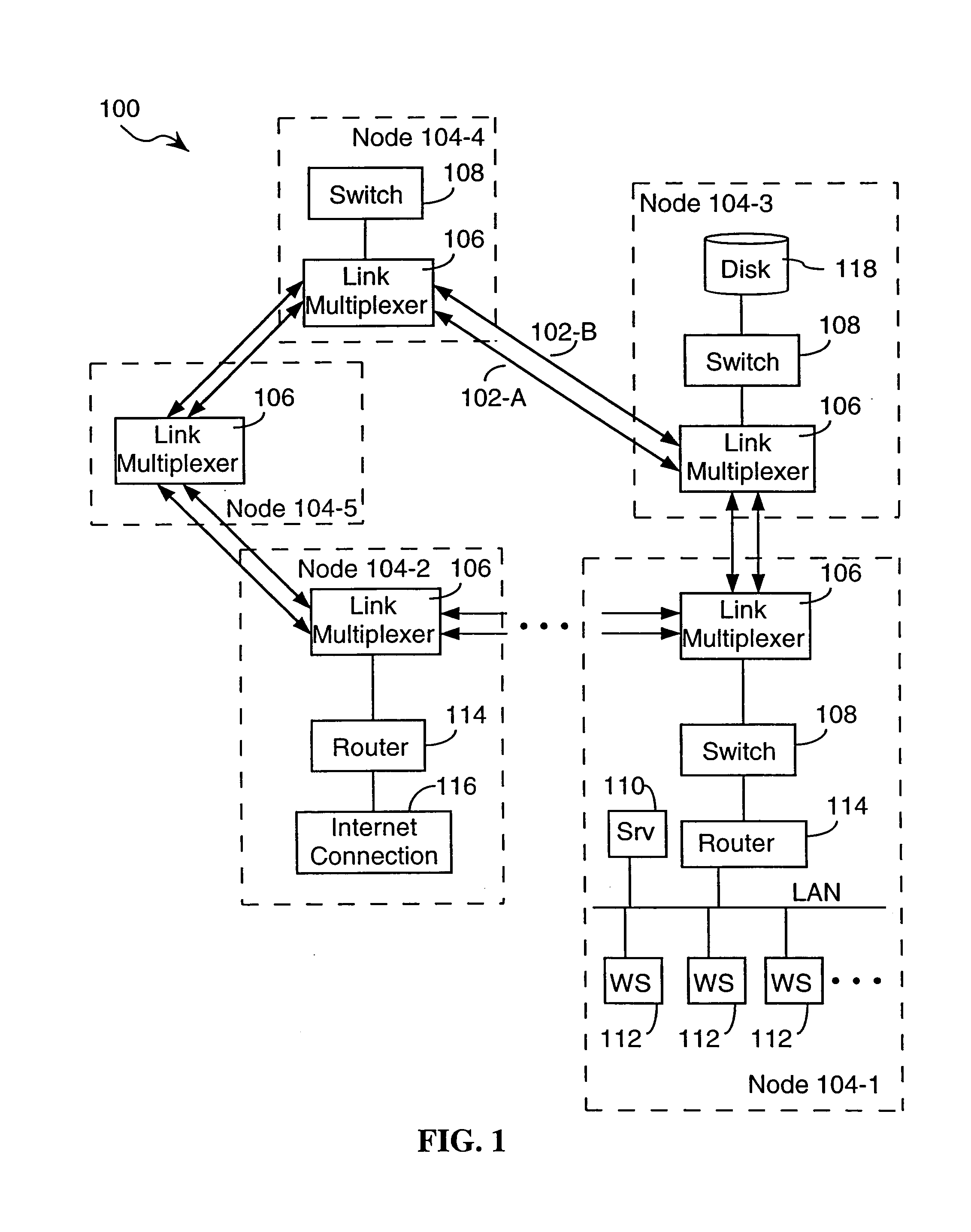
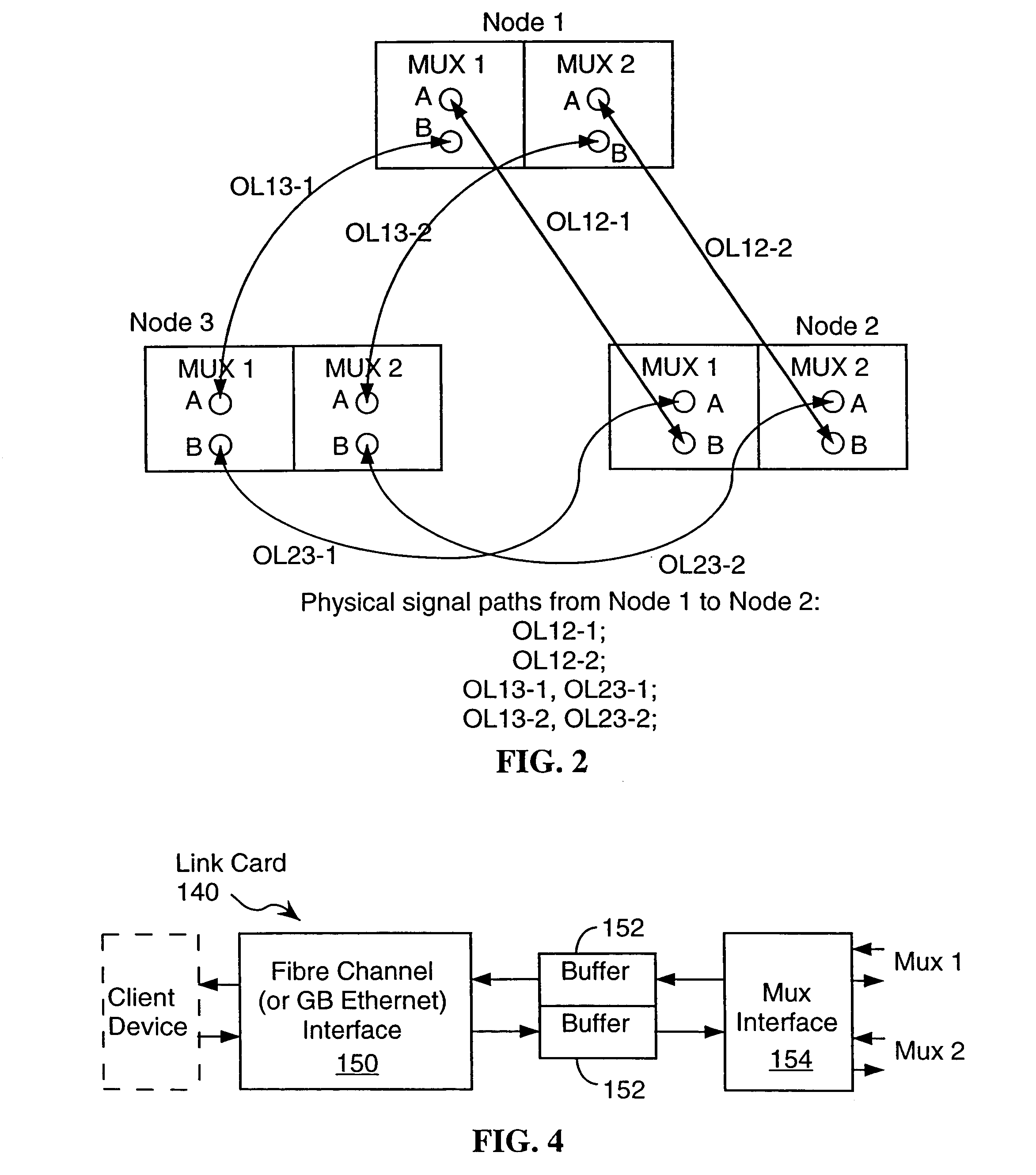
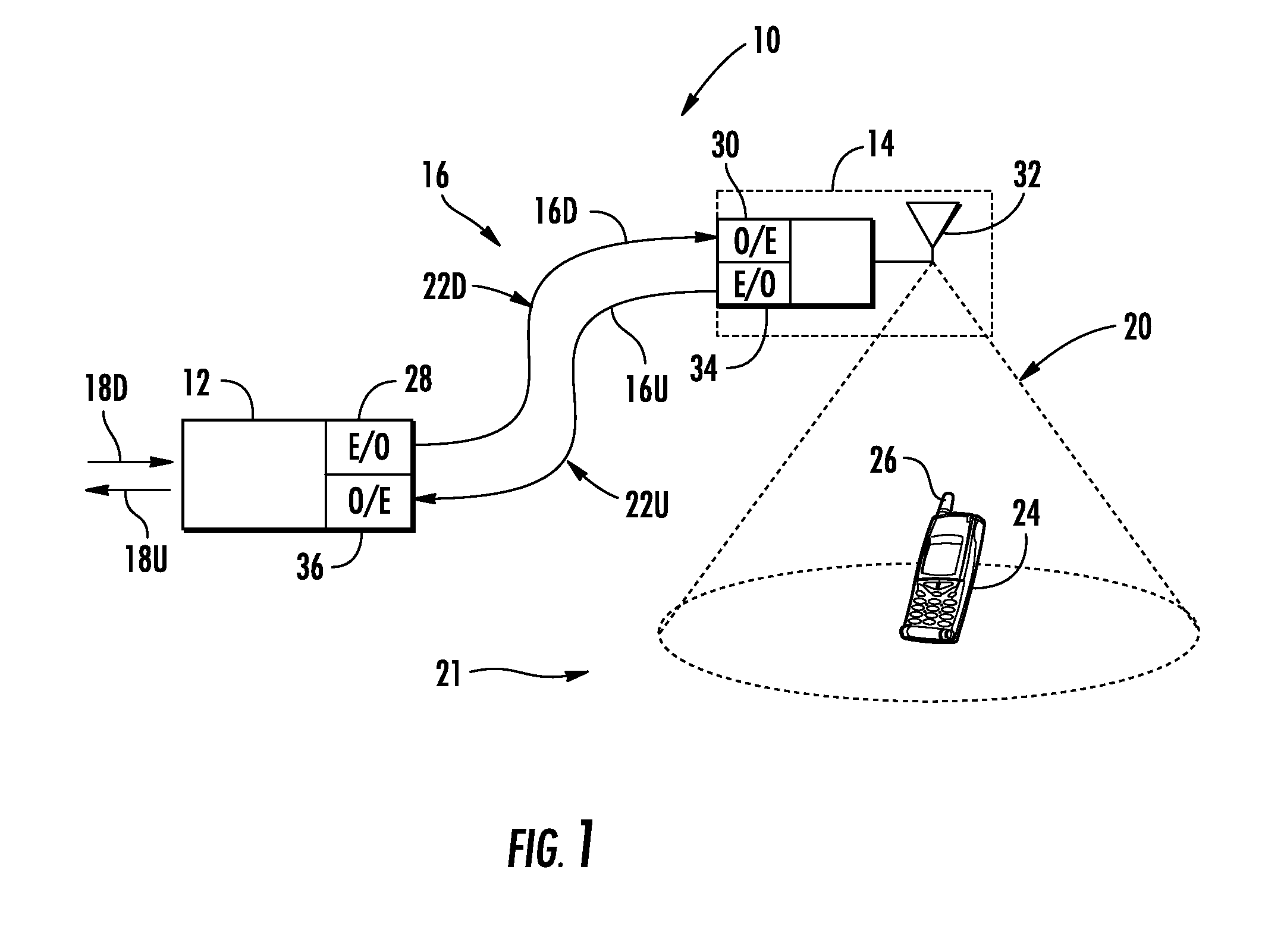
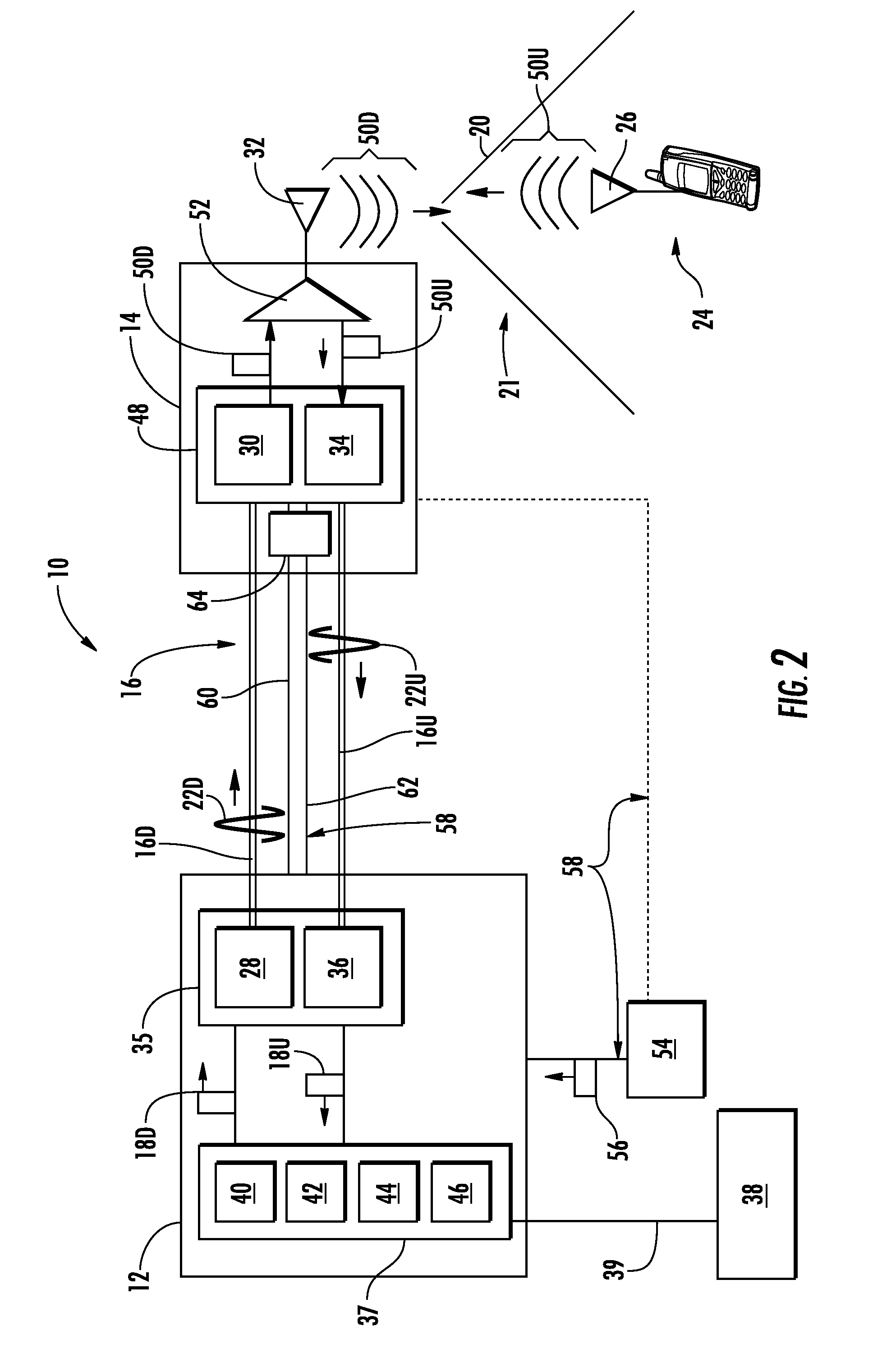
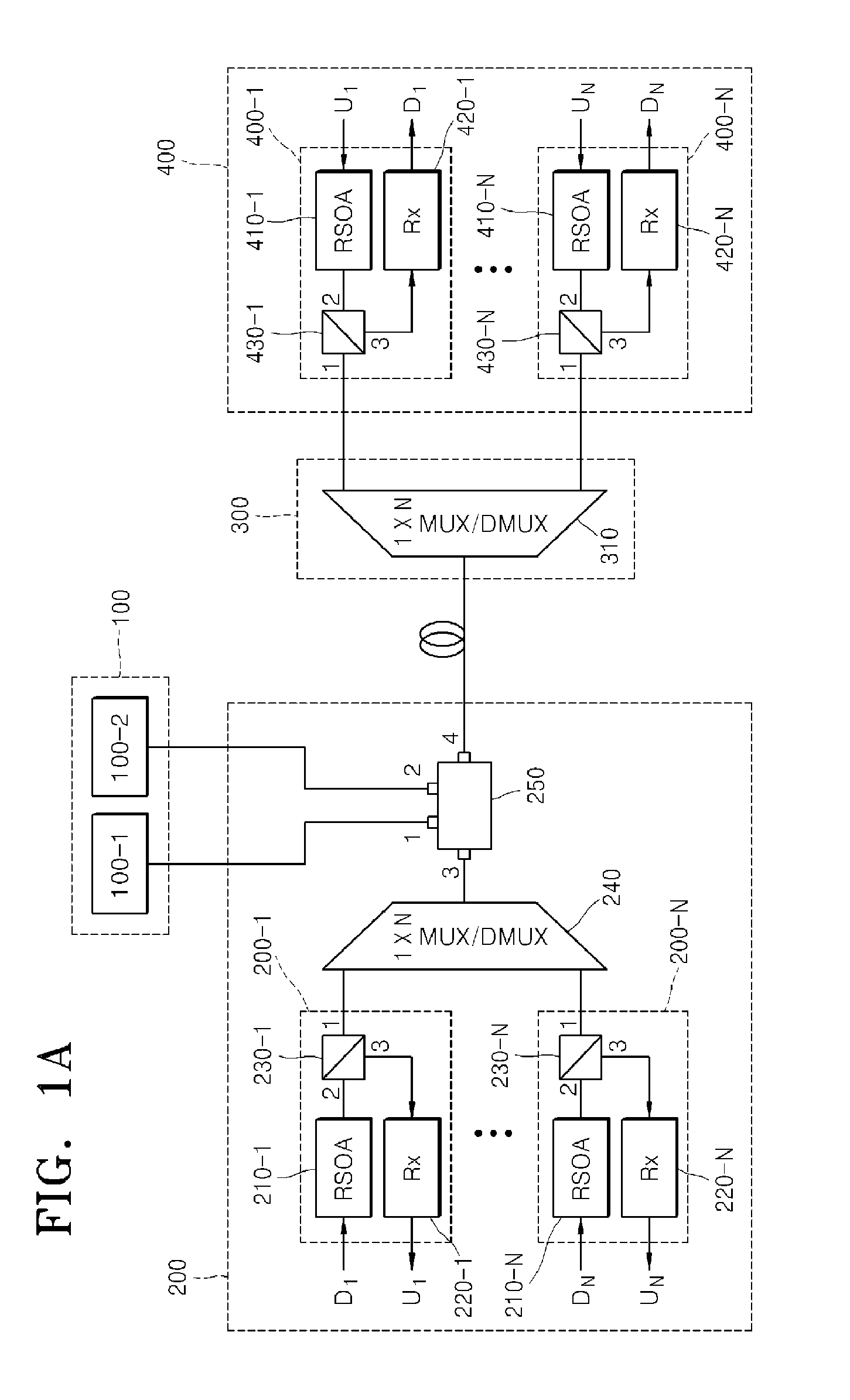
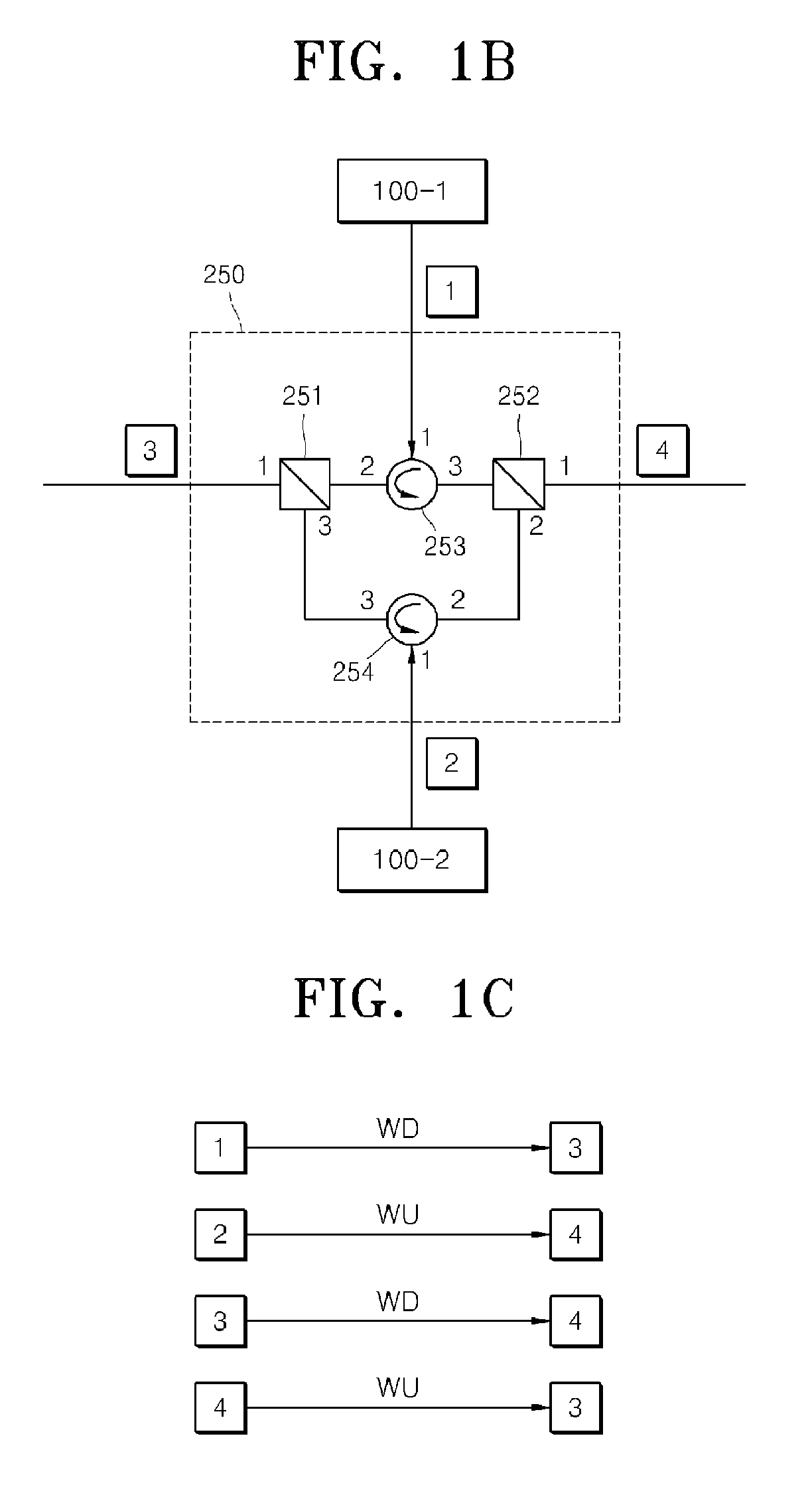
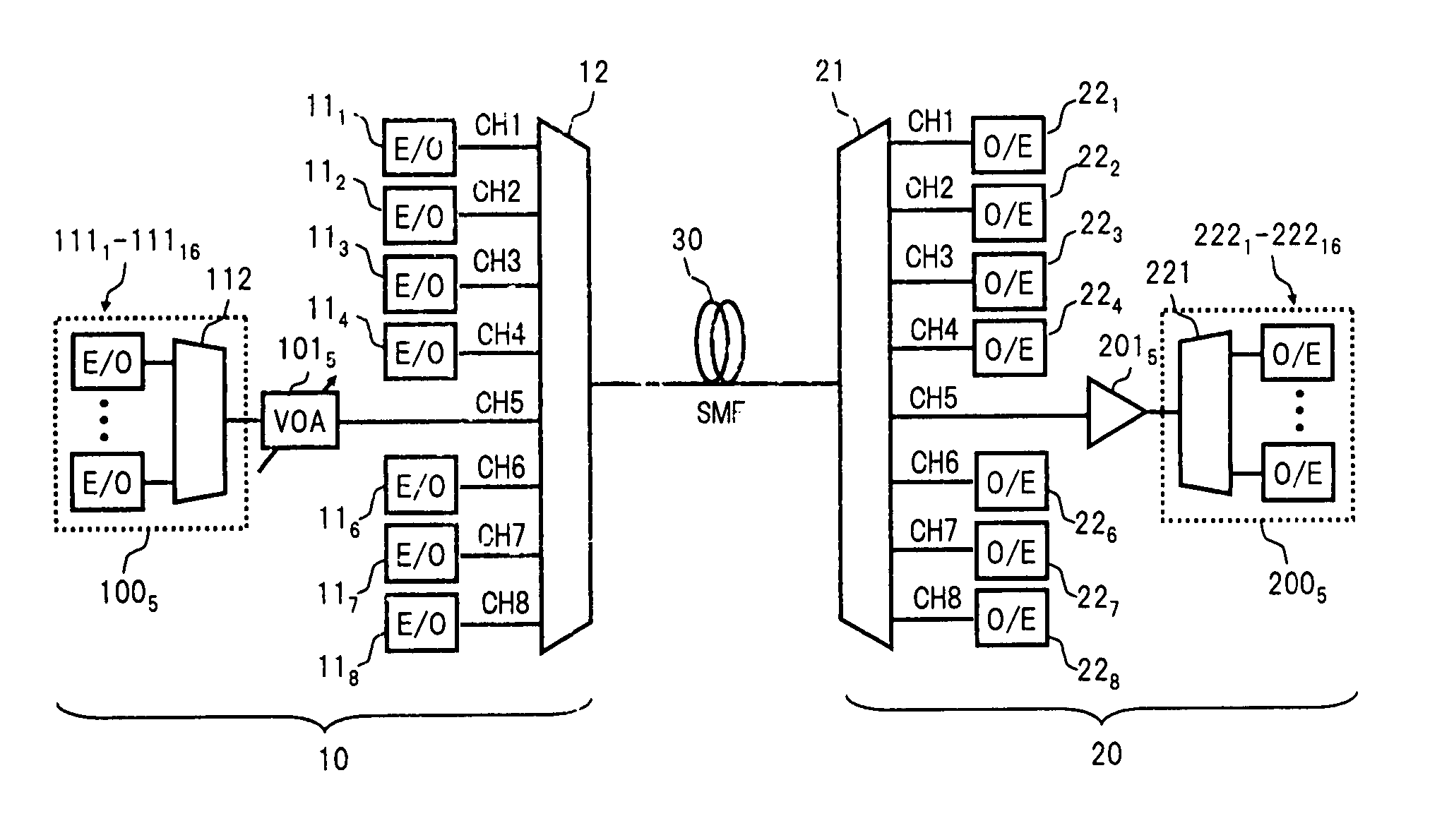
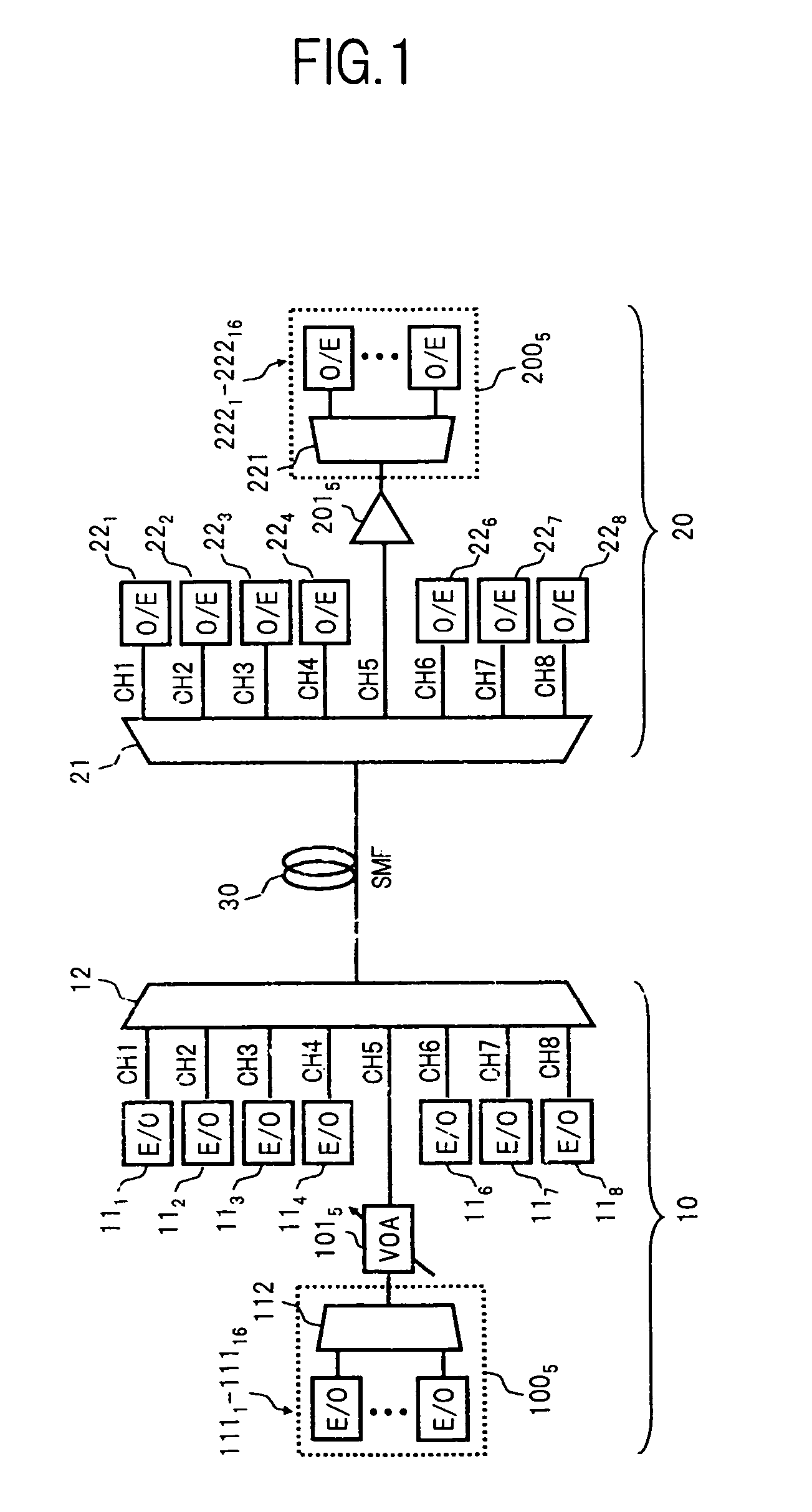
An optical fiber ring network includes a plurality of interconnected nodes, each pair of neighboring nodes being interconnected by a pair of optical links. Using coarse wavelength division multiplexing, data is transmitted in both directions over each link, using a first wavelength λ1 to transmit data in a first direction over the link and a second wavelength λ2 to transmit data in a second, opposite direction over the link. The two wavelengths λ1 and λ2 differ by at least 10 nm. Each of the data streams transmitted over the optical link has a bandwidth of at least 2.5 Gbps. Further, each data stream has at least two logical streams embedded therein. A link multiplexer at each node of the network includes one or more link cards for coupling the link multiplexer to client devices, and one or more multiplexer units for coupling the link multiplexer to the optical links. Each link card includes frame buffers capable of storing numerous Fiber Channel frames that are being transmitted to and from the client device(s) coupled to that link card. The link card also includes flow control logic for pre-filling the frame buffers with frames of data before the receiving client devices send flow control messages to request their transmission. The combined effect of the frame buffers and flow control logic is that the full bandwidth of the links can be utilized even when the network nodes are very far apart and the client devices have small input data buffers.
Owner:CIENA
Optical fiber-based distributed communications components, systems, and methods employing wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) for enhanced upgradability
InactiveUS20130089332A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionMultiplexingMultiplexer
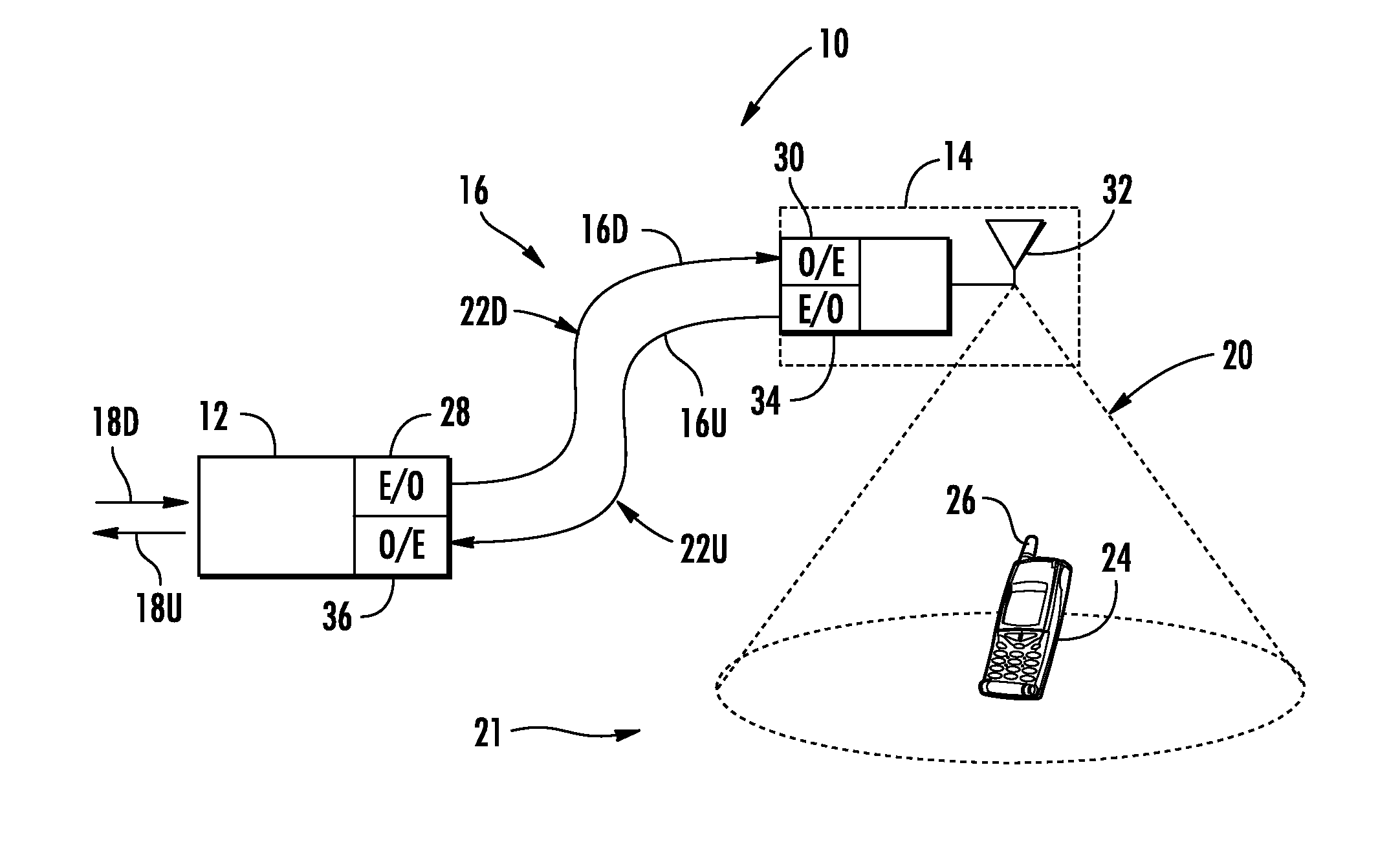
Optical fiber-based distributed communications components and systems employing wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) for enhanced upgradability. The system comprises a plurality of downlink optical transmitters configured to receive downlink electrical radio frequency (RF) signals from a plurality of RF sources and convert the downlink electrical RF signals into downlink optical RF signals. The system also has a wavelength division multiplexer configured to multiplex downlink optical RF signals into a plurality of downlink wavelengths over a common downlink optical fiber connected to a plurality of remote antenna units (RAUs). In this manner, additional downlink optical fibers are not required to support providing additional RAUs in the system. Wavelength-division de-multiplexing can avoid providing additional uplink optical fibers to distribute uplink signals to RAUs added in the system.
Owner:SAUER MICHAEL +1
Self-correlation optical fiber communication system based on mode division multiplexing
ActiveCN103095373AImprove spectrum utilizationImprove nonlinear toleranceFibre transmissionElectromagnetic receiversFrequency spectrumLine width
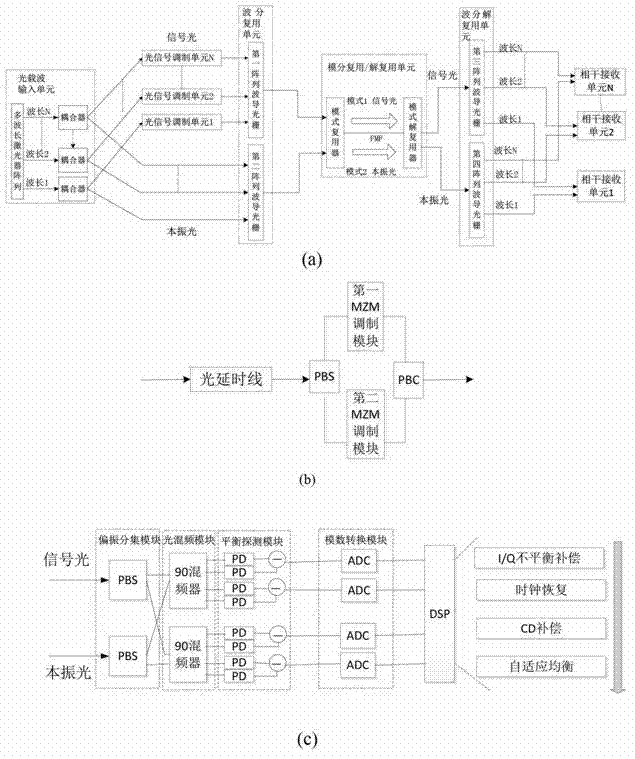
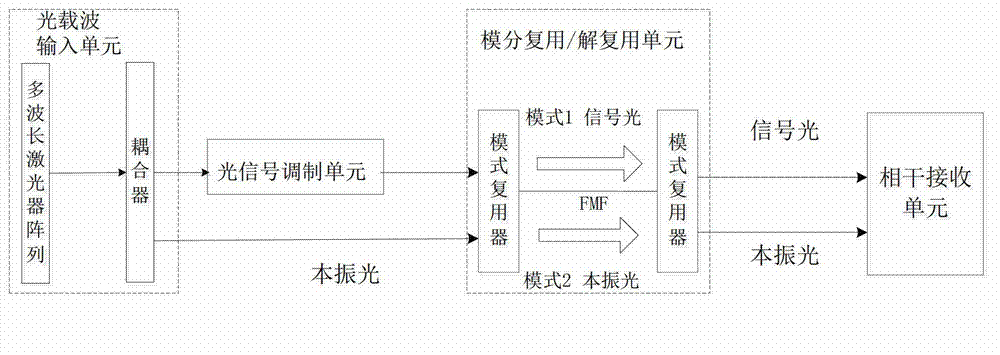
The invention discloses a self-correlation optical fiber communication system based on mode division multiplexing. The self-correlation optical fiber communication system based on mode division multiplexing comprises an optical carrier input unit, optical signal modulation units, a wavelength division multiplexing unit, a mode division multiplexing and demultiplexing unit, a wavelength division multiplexing unit and coherent reception units. The mode division multiplexing and reconciliation multiplexing unit comprises a mode multiplexer and mode demultiplexer, and the mode multiplexer and the mode demultiplexer are connected through few-mode optical fibers. The optical carrier input unit is connected with each optical signal modulation unit, the wavelength division multiplexing unit and the mode multiplexer through single-mode optical fibers. The mode multiplexer is connected with the mode demultiplexer through few-mode optical fibers. The mode demultiplexer is connected with the wavelength division multiplexing unit and each coherent reception unit through single-mode optical fibers. The optical carrier input unit is further connected with the wavelength division multiplexing unit. The self-correlation optical fiber communication system based on mode division multiplexing eliminates an expensive narrow line width adjustable local oscillator light source which is arranged at a reception end, enables a laser to be conveniently managed and maintained, is free from using frequency offset estimation in a digital signal processor (DSP) and phase retrieval algorithm, reduces complexity of the DSP and has the advantages of being high in spectrum effectiveness and big in nonlinearity tolerance.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cascading optical multiplexing device
InactiveUS6167171AReduce complexityLow costLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberMultiplexing
An optical multiplexing device is provided comprising multiple wavelength division multiplexers cascaded together. A first one of the wavelength division multiplexers has a common port and multiple optical ports which are optically coupled to the common port. The common port may be optically coupled to a trunk line of a system employing wavelength division multiplexing, for example, a fiber-optic telecommunication system employing 4, 8, 16 or other number of multiplexed channels. The optical ports include multiple channel ports, each of which is transparent to a corresponding wavelength sub-range and reflective of other wavelengths. The second wavelength division multiplexer has a common port optically coupled to one of the optical ports of the first wavelength division multiplexer. The second wavelength division multiplexer also has multiple optical ports which are optically coupled to its common port and include multiple wavelength-selective channel ports. A waveguide, such as a fiber-optic line, can optically connect the common port of the second wavelength division multiplexer to an optical port of the first wavelength division multiplexer. The cascaded WDMs each may be optically coupled to the output of a passive coupler and a housing may be provided defining an enclosed space in which the optical multiplexing device is mounted. Optionally, additional WDMs may be cascaded with the first two WDMs in a parallel or branched formation, an in-line formation or some combination. Preferably, the channels are interleaved, such that they are removed from the multiplexed signal in certain non-sequential order. The optical multiplexing device also may employ compound interleaving wherein adjacent channels are multiplexed by different ones of the cascaded WDMs. The optical multiplexing devices can operate to add signals, remove signals or a combination of both.
Owner:CORNING OCA CORPORATION
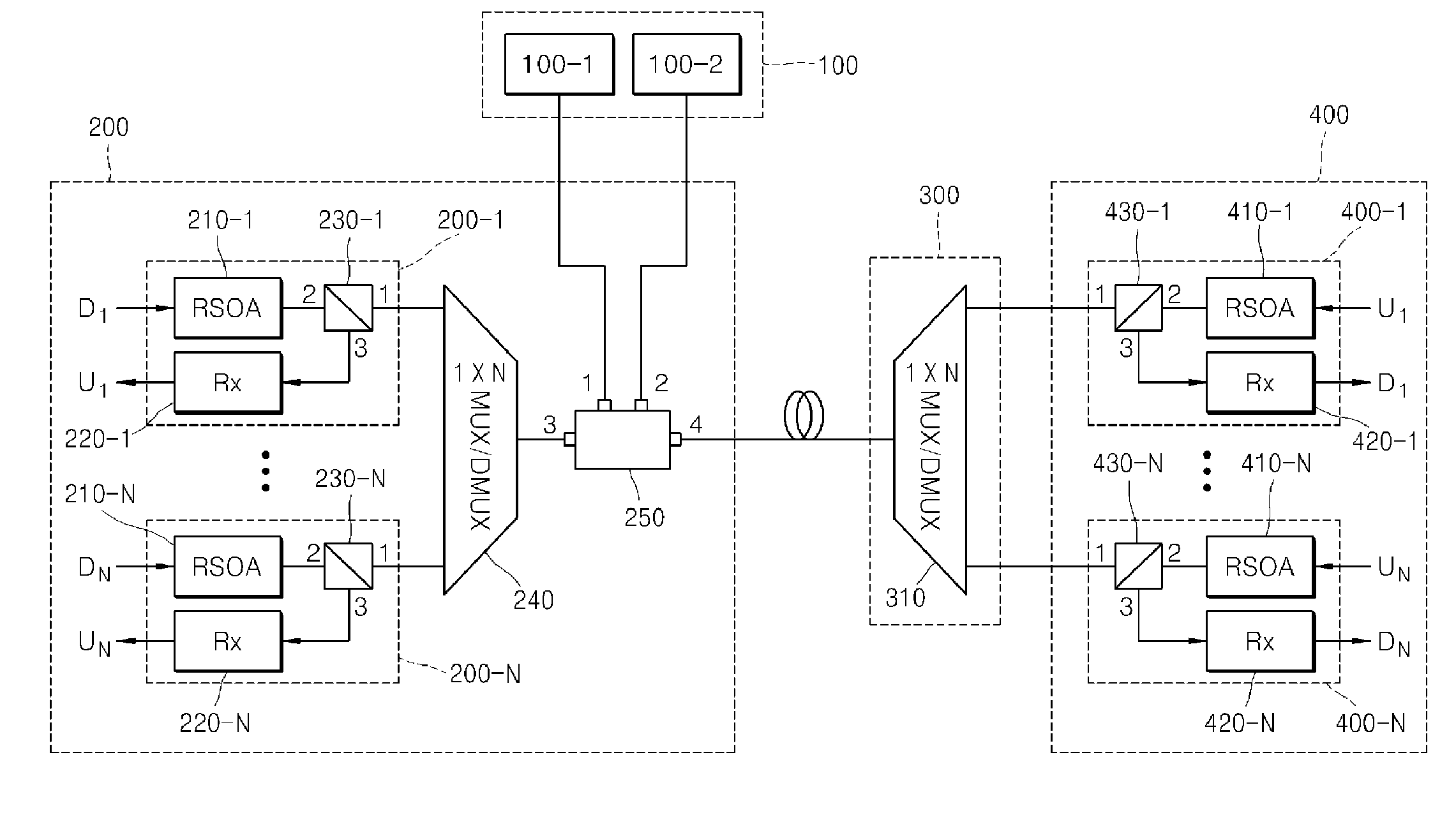
Wavelength division multiplexing-passive optical network using external seed light source
ActiveUS20100278535A1Quality improvementIncrease the number ofWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultimode transmissionFrequency spectrumCode division multiple access
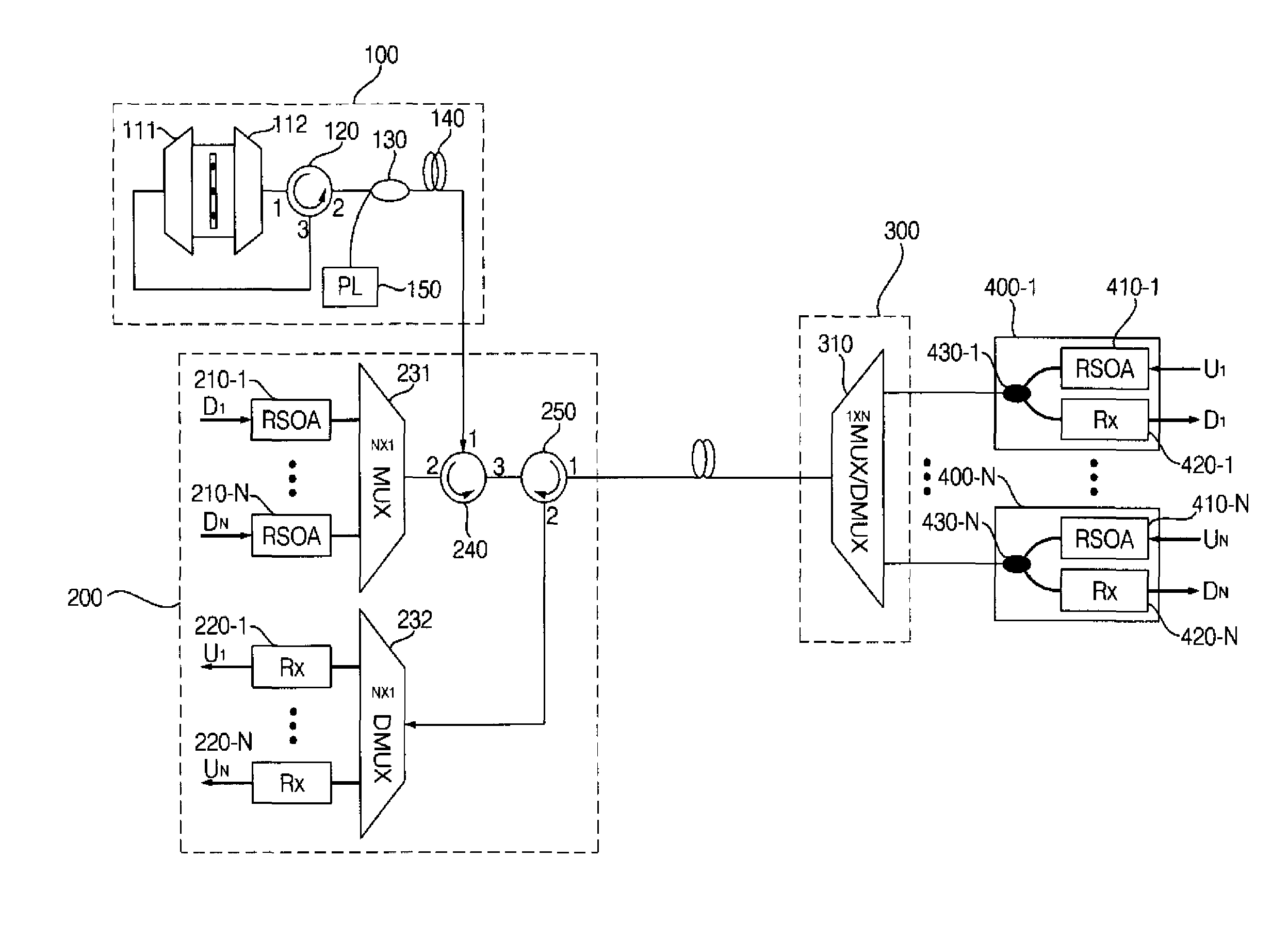
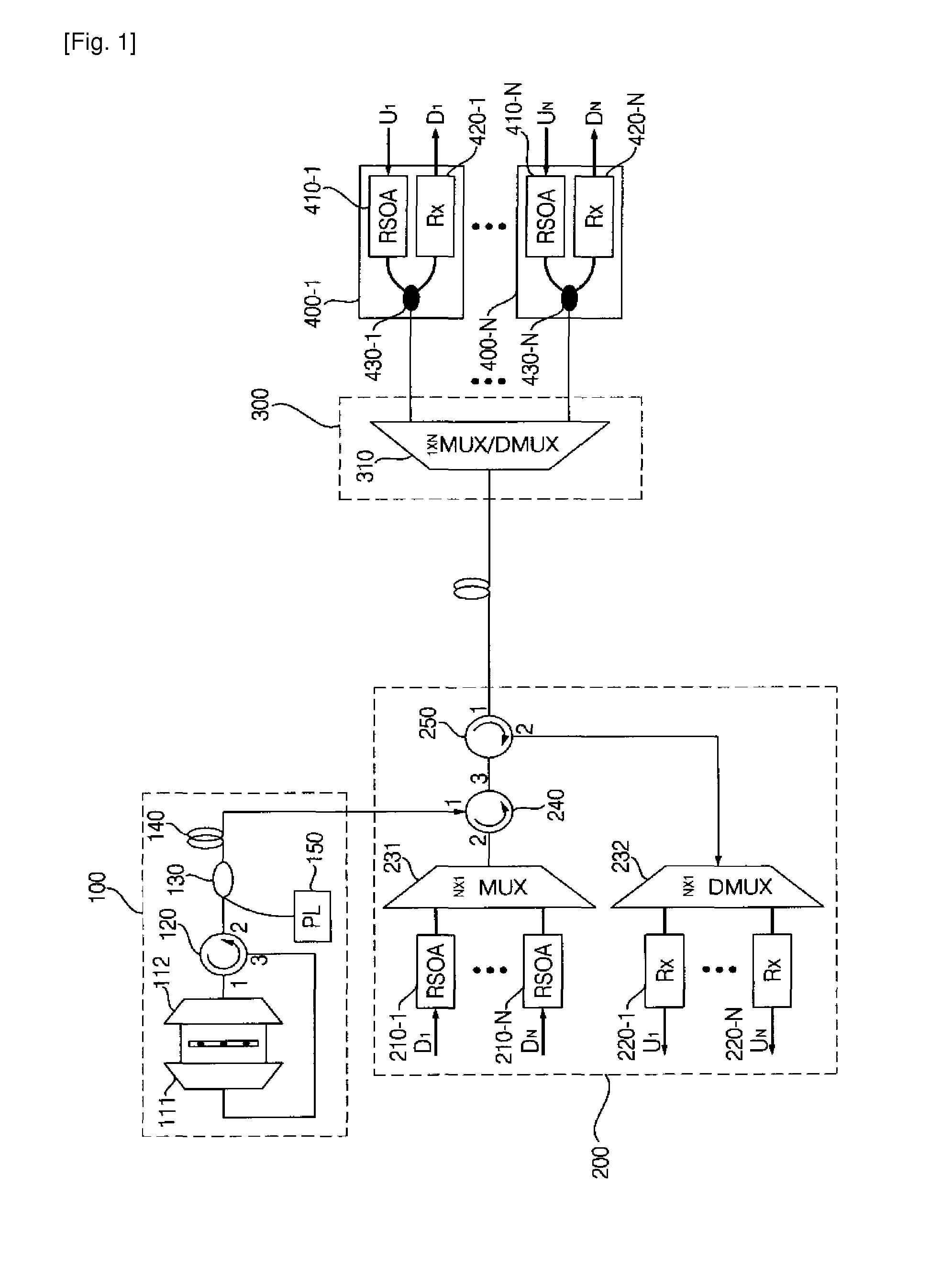
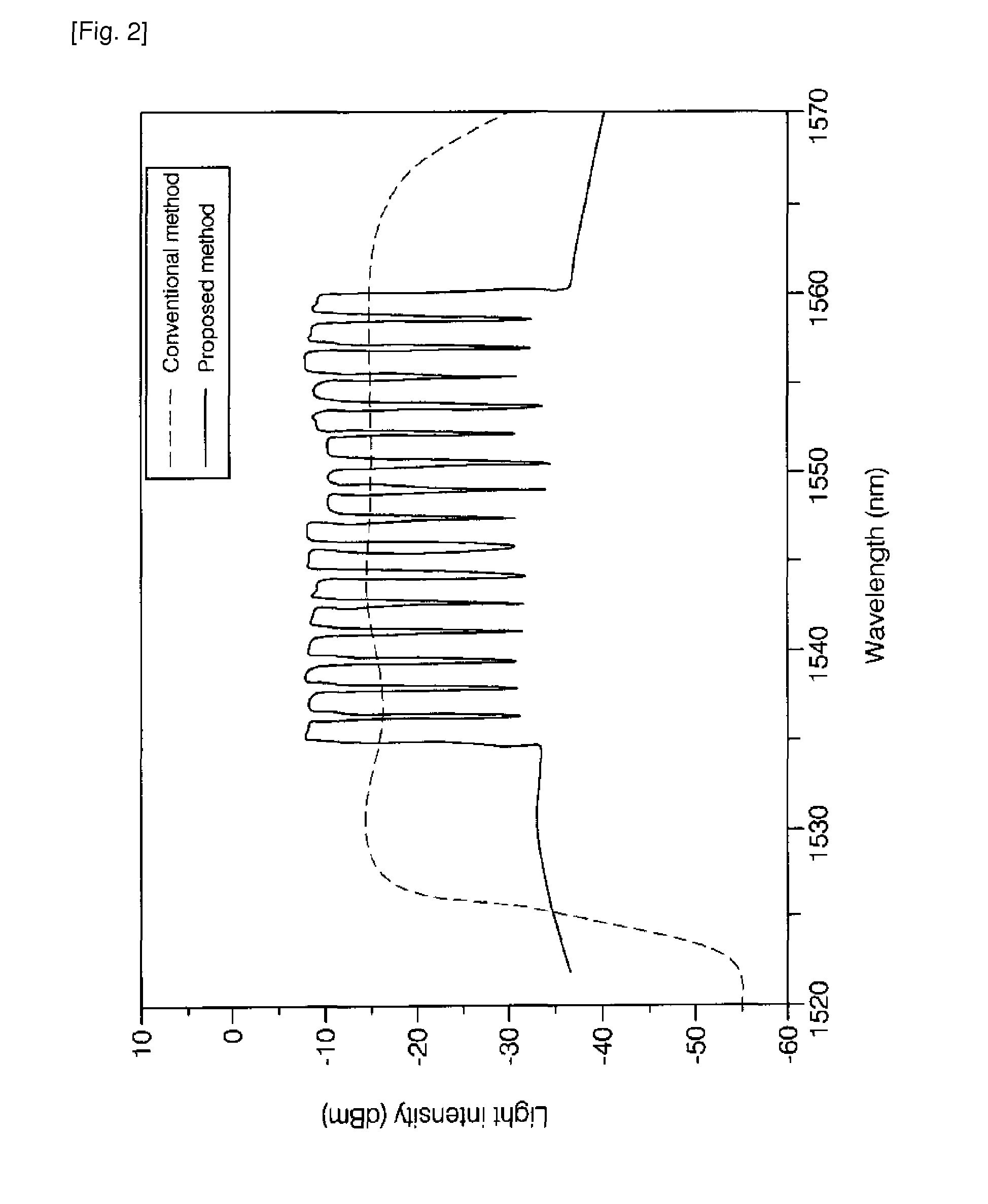
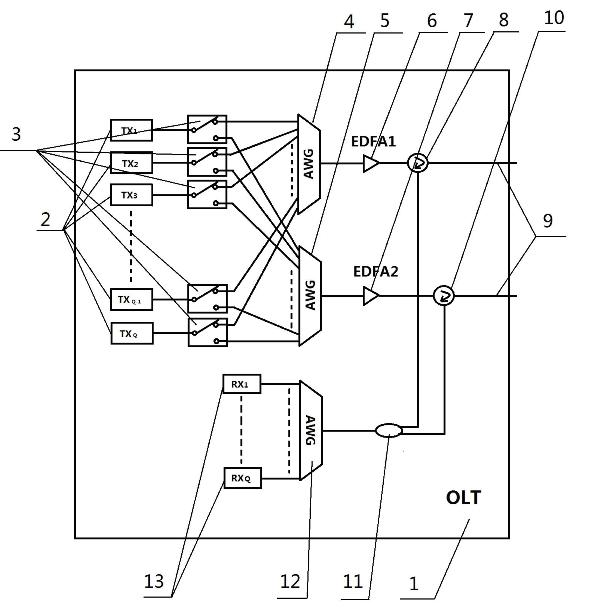
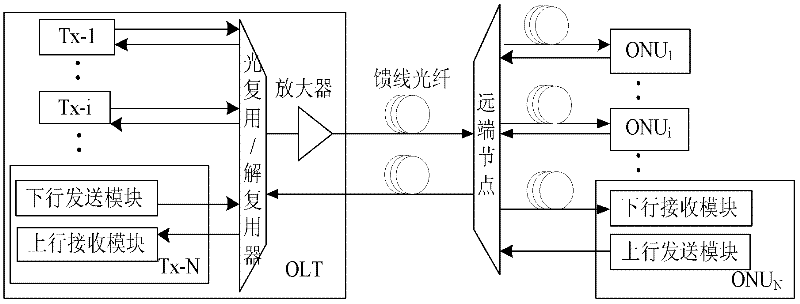
Provided are a wavelength division multiplexing-passive optical network (WDM-PON) in which a reflective semi-conductor optical amplifier (RSOA) is used as each optical transmitter of an optical line termination (OLT) and an optical network unit (ONU) and additional spectrum-sliced light is injected into RSOAs of each of the OLT and the ONU, and a WDM-PON that is combined with time division multiple access (TDMA) technology, by which the number of included ONUs increases and conventional TDMA ONUs can be used.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Restructurable optical add-drop multiplexer and wavelength cross connect
ActiveCN102696194ALow costEasy to implementWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical light guidesMultiplexerOptical add-drop multiplexer
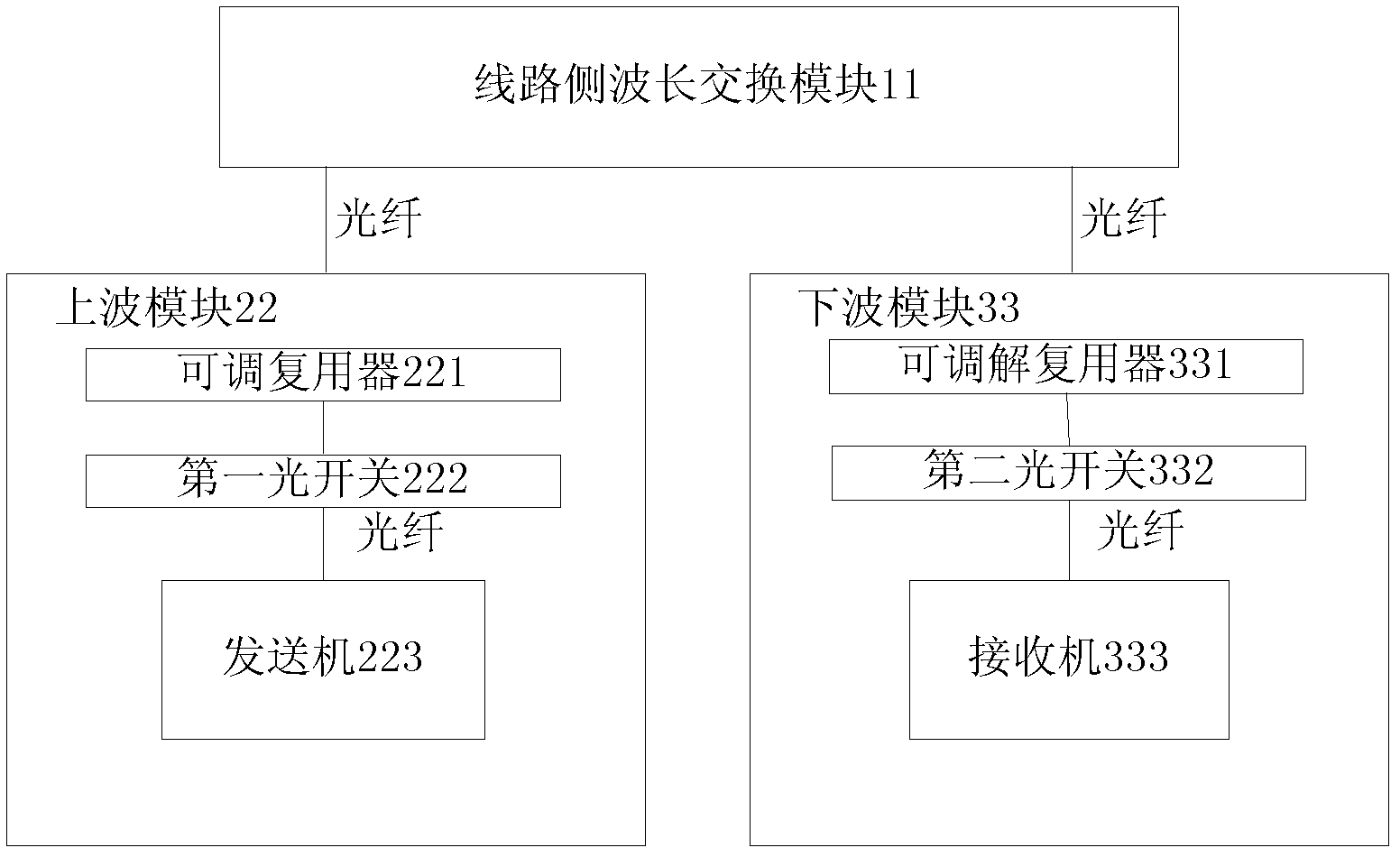
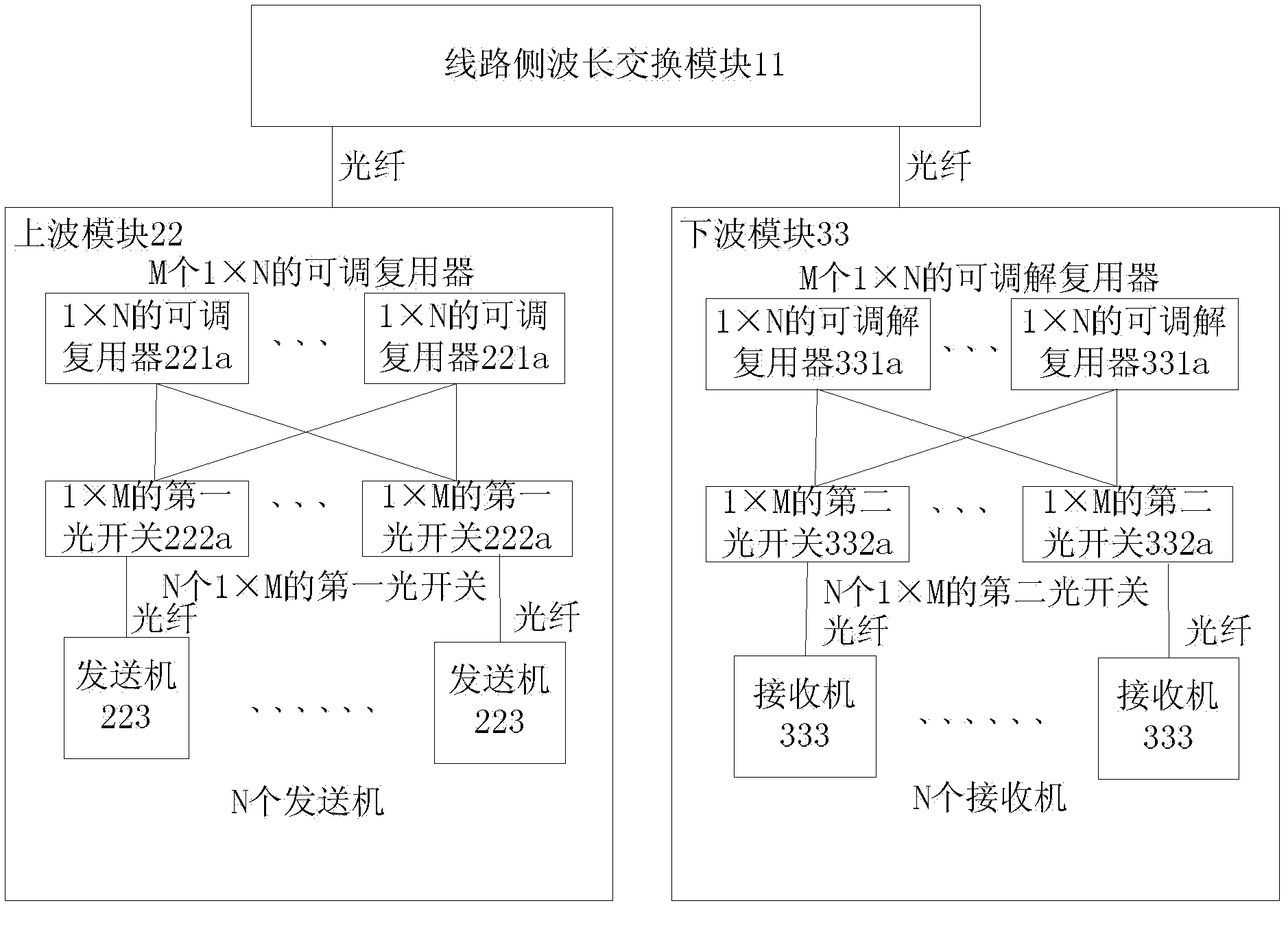
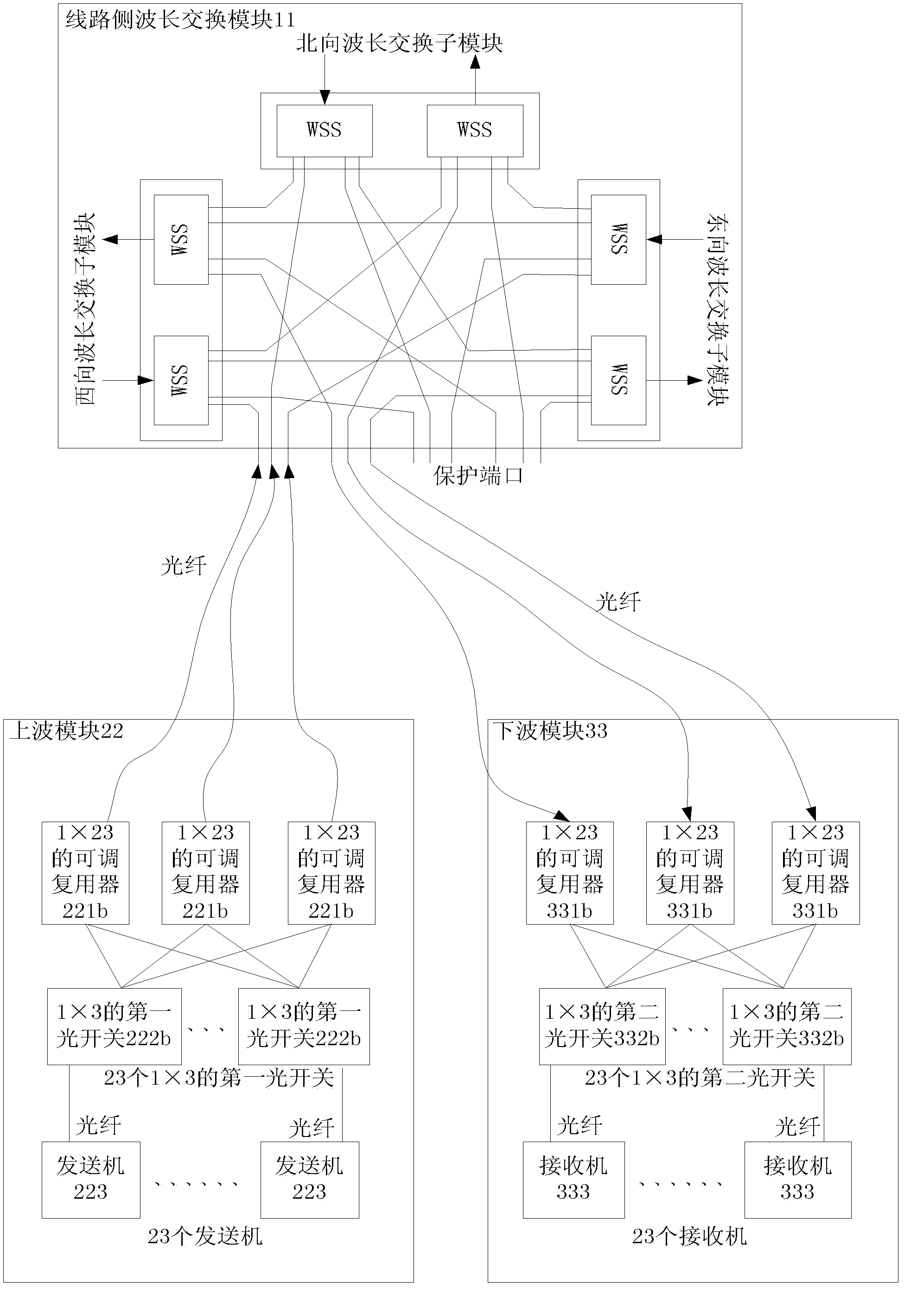
An embodiment of the invention provides a restructurable ROADM (optical add-drop multiplexer) and WXC (wavelength cross connect), and relatest to the field of communications, the ROADM comprises a line side wavelength switching module, an upper wave module, and a lower wave module; the upper wave module comprises a tunable multiplexer, a first optical switch and a transmitter; the first optical switch is used for connecting the fiber optical wavelength transmitted by the transmitter to the tunable multiplexer; the tunable multiplexer is used for multiplexing the received fiber optical wavelength, generating a WDM optical signal for wavelength division multiplexing, and outputting the WDM optical signal to the line side wavelength switching module; the lower wave module comprises a tunable demultiplexer, a second optical switch and a receiver, the tunable demultiplexer is used for demultiplexing the WDM optical signal from the line side wavelength switching module and outputting the signal through demultiplexing to the second optical switch, and the second optical switch is used for connecting the fiber optical wavelength through demultiplexing to the receiver. The embodiment of the invention reduces cost of ROADM.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Wavelength division multiplexing-passive optical network system
ActiveUS20110222855A1Preventing most of the lossIncrease distanceWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultimode transmissionOptical line terminationOptical transmitter
The present invention proposes a wavelength division multiplexing-passive optical network (WDM-PON) system which transmits downstream data to an optical network unit (ONU) as an optical line termination (OLT) receives seed light from a spectrum-sliced external light source module. One characteristic of the proposed WDM-PON system is that optical transmitters of the OLT and ONU are operated regardless of optical wavelength. Another characteristic of the proposed WDM-PON system is that a conventional TDMA-PON (E-PON or G-PON) ONU can be accommodated without a change.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Broad temperature WDM transmitters and receivers for coarse wavelength division multiplexed (CWDM) fiber communication systems
InactiveUS7412170B1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic receiversFiberPhotovoltaic detectors
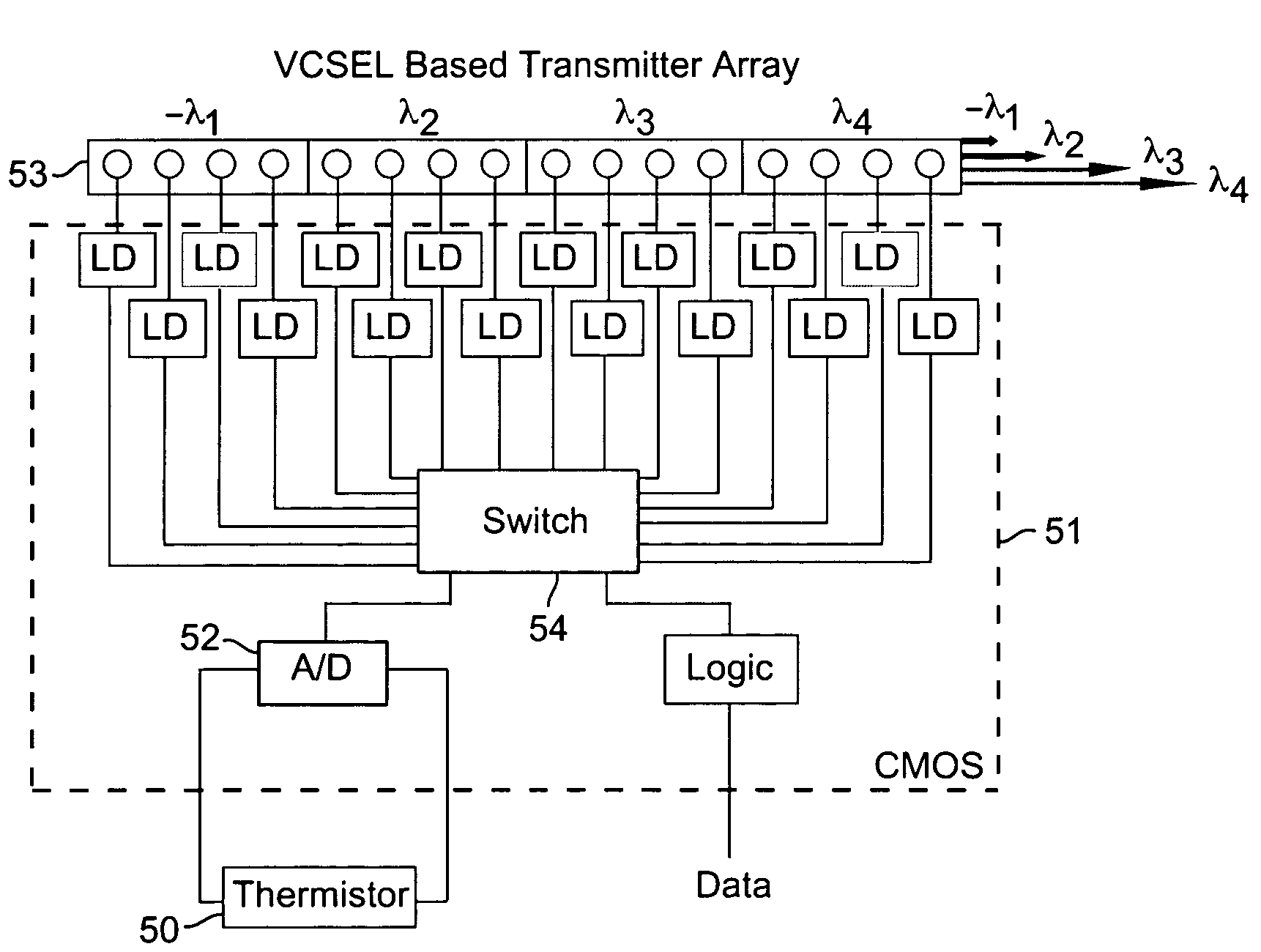
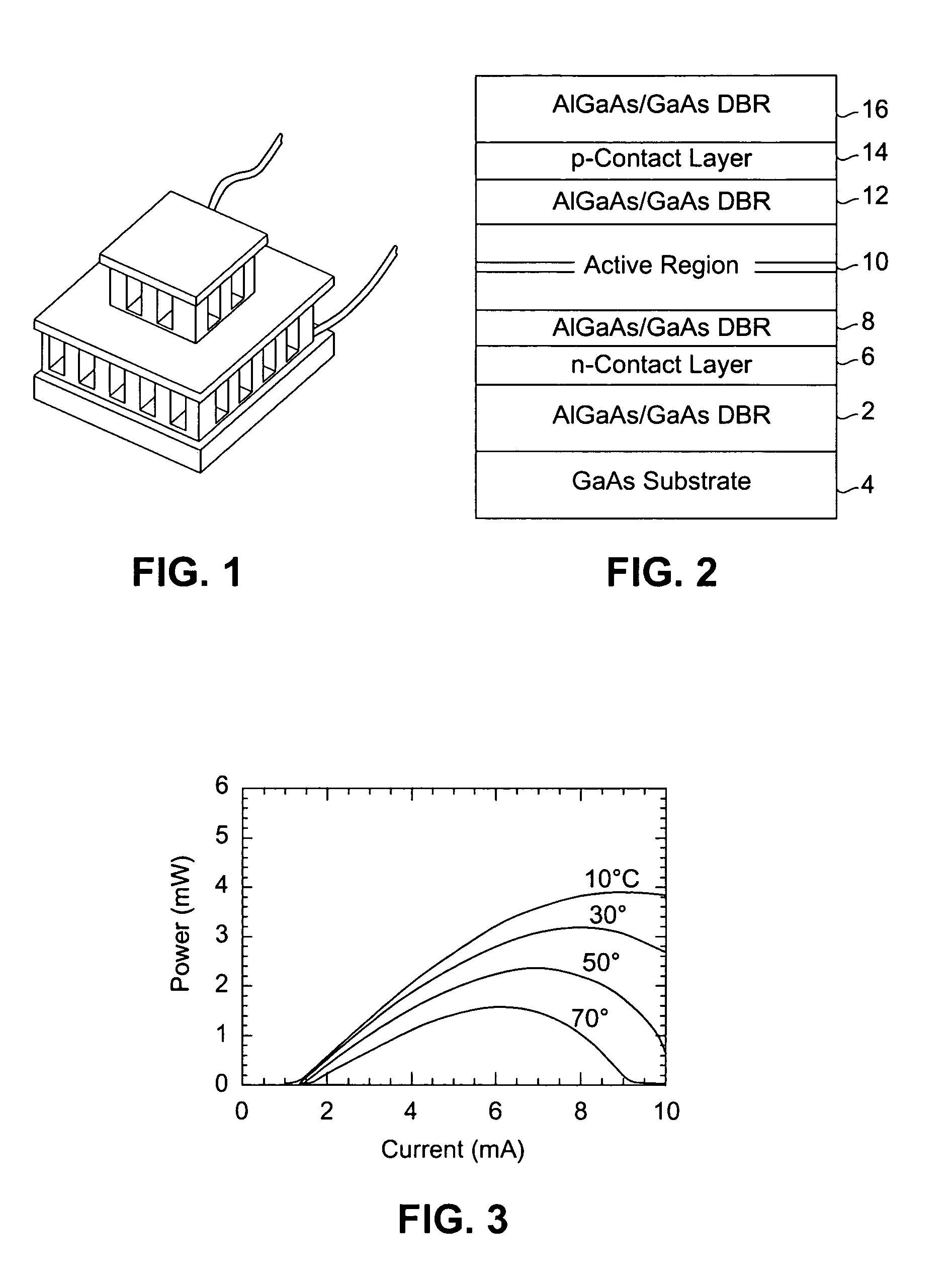
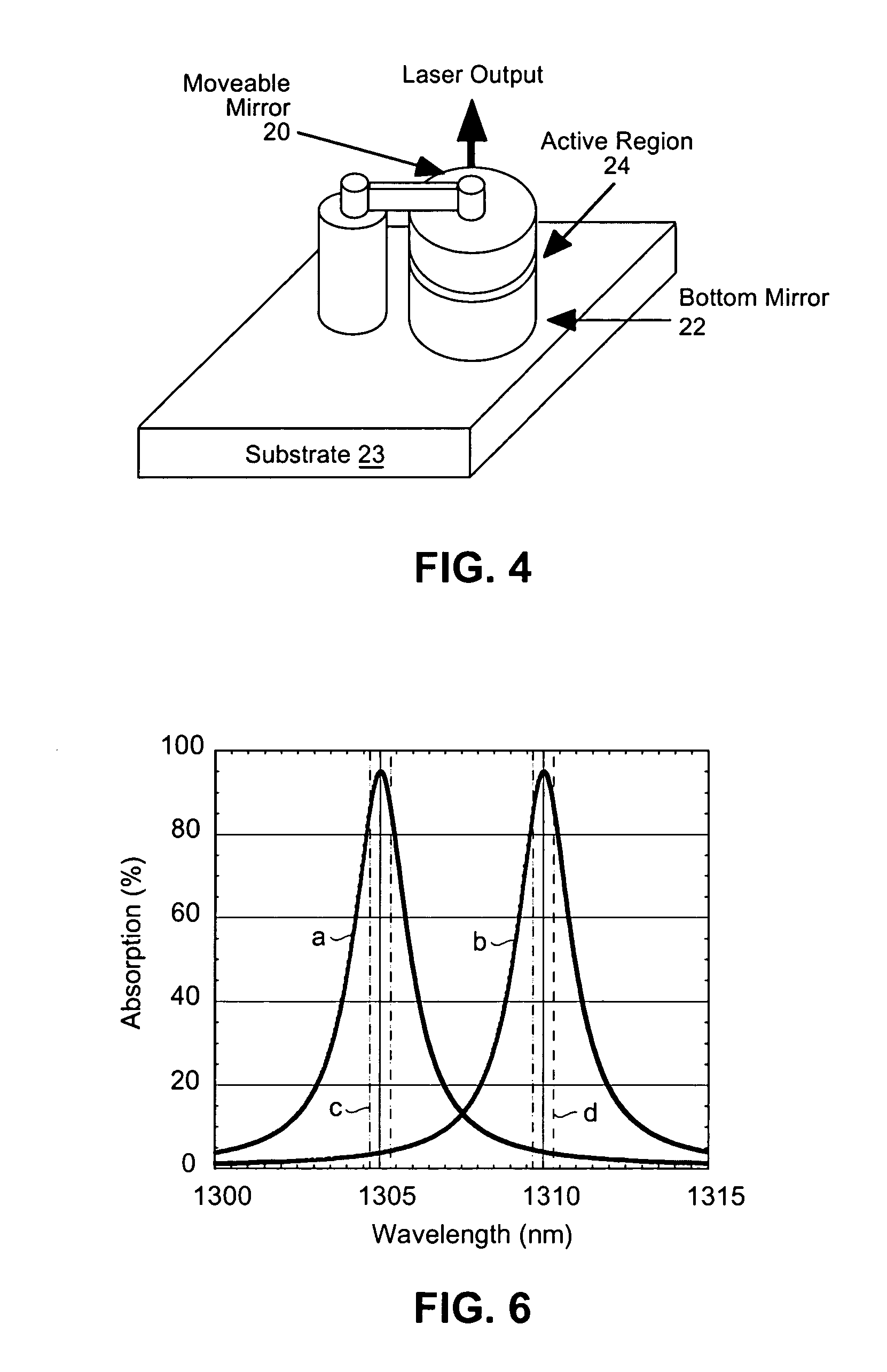
A wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) module for transmitting and / or receiving multiple signals simultaneously includes an array of vertical cavity surface emitting lasers (VCSELs) and / or photodetectors, respectively. In the transmitter case, different VCSELs are operated at different wavelengths that change depending on a value of a condition such as temperature and / or one or more other parameters. Multiple VCSELs are assigned to each channel of the WDM. The currently active VCSEL is switched to a different VCSEL assigned to a same channel and preferably having an operating wavelength that is closer to the signal wavelength at the current measured or estimated temperature and / or other parameter value. Multiple photodetectors are assigned to each channel of the WDM, and currently active detector is switched to the second detector within the same channel. A tuning layer and a resonant waveguide grating coupler are preferably integrated into the resonant structure of the VCSEL array and wavelength specific detector array.
Owner:OC ACQUISITION CORP
Wavelength-multiplexed optical transmission device, wavelength-multiplexed optical transmission system, wavelength-multiplexed optical transmission method
InactiveUS20140286637A1Suppress deficitMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingHigh density
Provided is a wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) optical transmission device which is suitable of performing splitting, wavelength multiplexing, switching, and routing on an optical WDM signal in which optical signals having a spectrum close to a rectangle are arranged with a high density, and efficiency of spectral usage is ultimately high in units of wavelengths. A WDM optical transmission device according to the present invention is configured to cause flat portions of adjacent transmission bands on a wavelength spectrum overlap each other.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Hybrid integrated planar waveguide detector chip based on coarse wave decomposing and multiplexing
ActiveCN102243340AImprove isolationMeet the requirements of four-wavelength demultiplexingOptical light guidesMultiplexingSingle fiber
The invention discloses a hybrid integrated planar waveguide detector chip based on coarse wave decomposing and multiplexing, which comprises an input port region and a detector array region, wherein a waveguide region is arranged between the input port region and the detector array region of the chip; the waveguide region comprises an input waveguide, three Mach-Zehnder interferometers and four output waveguides; the input port region is positioned at the input end of the chip and comprise an input optical fiber arranged in a V-shaped groove, a groove is arranged behind the V-shaped groove and connected with the input waveguide of the waveguide region; and the output waveguides of the waveguide region are connected with the detector array region. According to the invention, a hybrid integrated technology and a plane integration technology are combined, and multi-channel single fiber transmission and miniaturization of a CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) demultiplexing device are realized.
Owner:WUHAN TELECOMM DEVICES
Passive optical network system based on Nyquist wavelength division multiplexing and realization method
ActiveCN102820945AMaintain an advantageIncrease the number ofMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical circulatorOptical network unit
The invention discloses a passive optical network system based on Nyquist wavelength division multiplexing and a realization method. The system comprises an OLT (optical line terminal) and N ONUs(optical network unit), wherein the OLT is provided with a multi-carrier generation device and one three-port optical circulator; the multi-carrier generation device generates N paths of optical carriers with an equal frequency interval; N paths of downlink Nyquist wavelength division multiplexing signals are sent to the ONUs via a downlink feed line optical fiber; the three-port optical circulator transmits the N paths of optical carriers to the ONUs via an uplink feed line optical fiber for uplink modulation; and an uplink Nyquist wavelength division multiplexing signal from the ONUs is transmitted to the OLT via the uplink feed line optical fiber. According to the passive optical network system and the realization method., uplink and downlink both adopt the Nyquist wavelength division multiplexing technology, the advantage of WDM-PON (wavelength division multiplexing-passive optical network) is kept, the servable user amount is greatly increased by utilizing the high spectrum efficiency of the WDM-PON, and realization is simple.
Owner:WUHAN POST & TELECOMM RES INST CO LTD
Method and apparatus for reducing crosstalk and nonlinear distortions induced by raman interactions in a wavelength division mulitplexed (WDM) optical communication system
ActiveUS7271948B1Reduce distortion problemsReduce the Raman crosstalkLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsNonlinear distortionMultiplexing
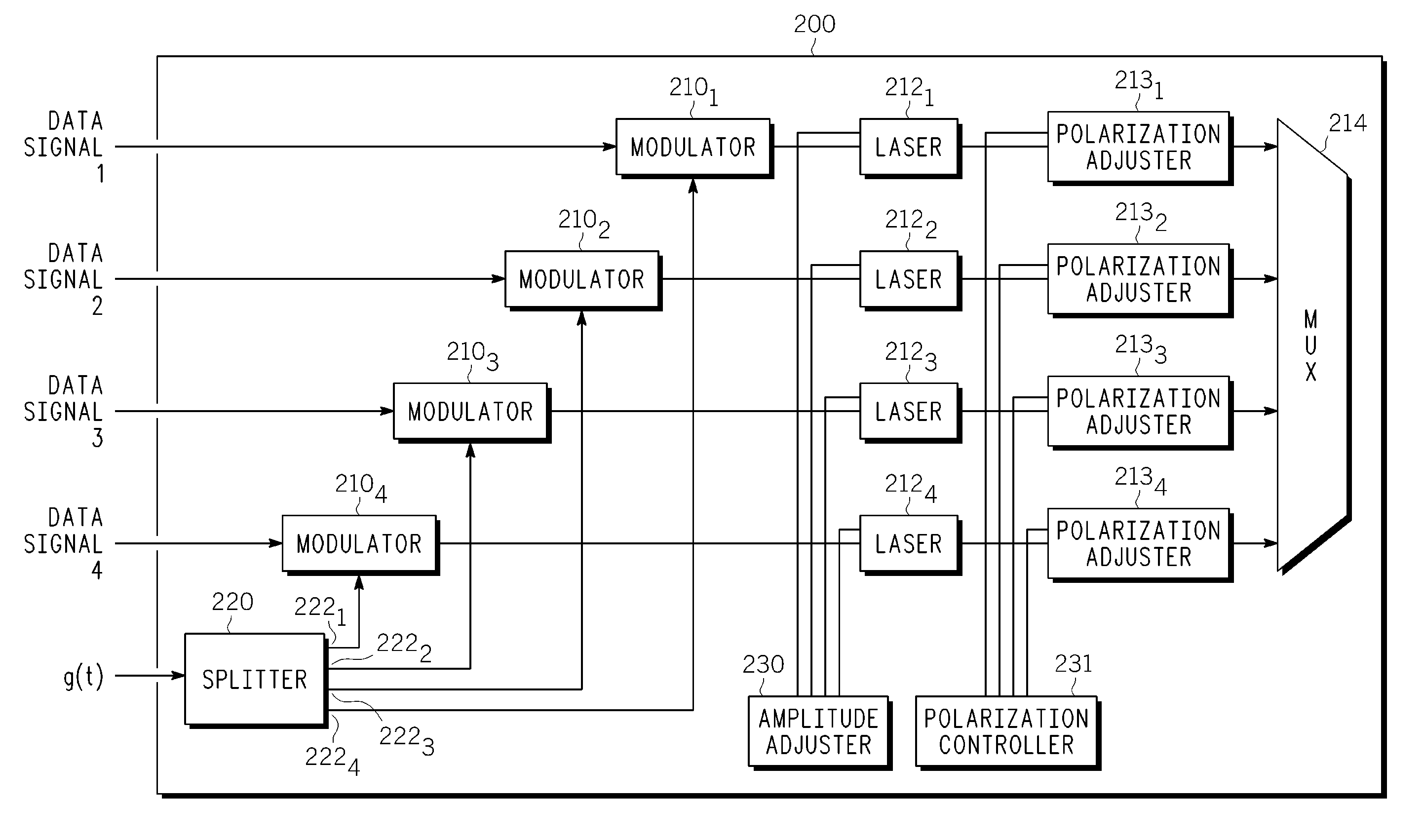
A method and apparatus is provided for transmitting a WDM optical signal. The method begins by modulating a plurality of optical channels that are each located at a different wavelength from one another with (1) a respective one of a plurality of information-bearing electrical signals that all embody the same broadcast information and (2) a respective one of a plurality of RF signals having a common functional broadcast waveform, at least one of the RF signals being out of phase with respect to remaining ones of the plurality of RF signals. Each of the modulated optical channels are multiplexed to form a WDM optical signal. The WDM optical signal is forwarded onto an optical transmission path.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
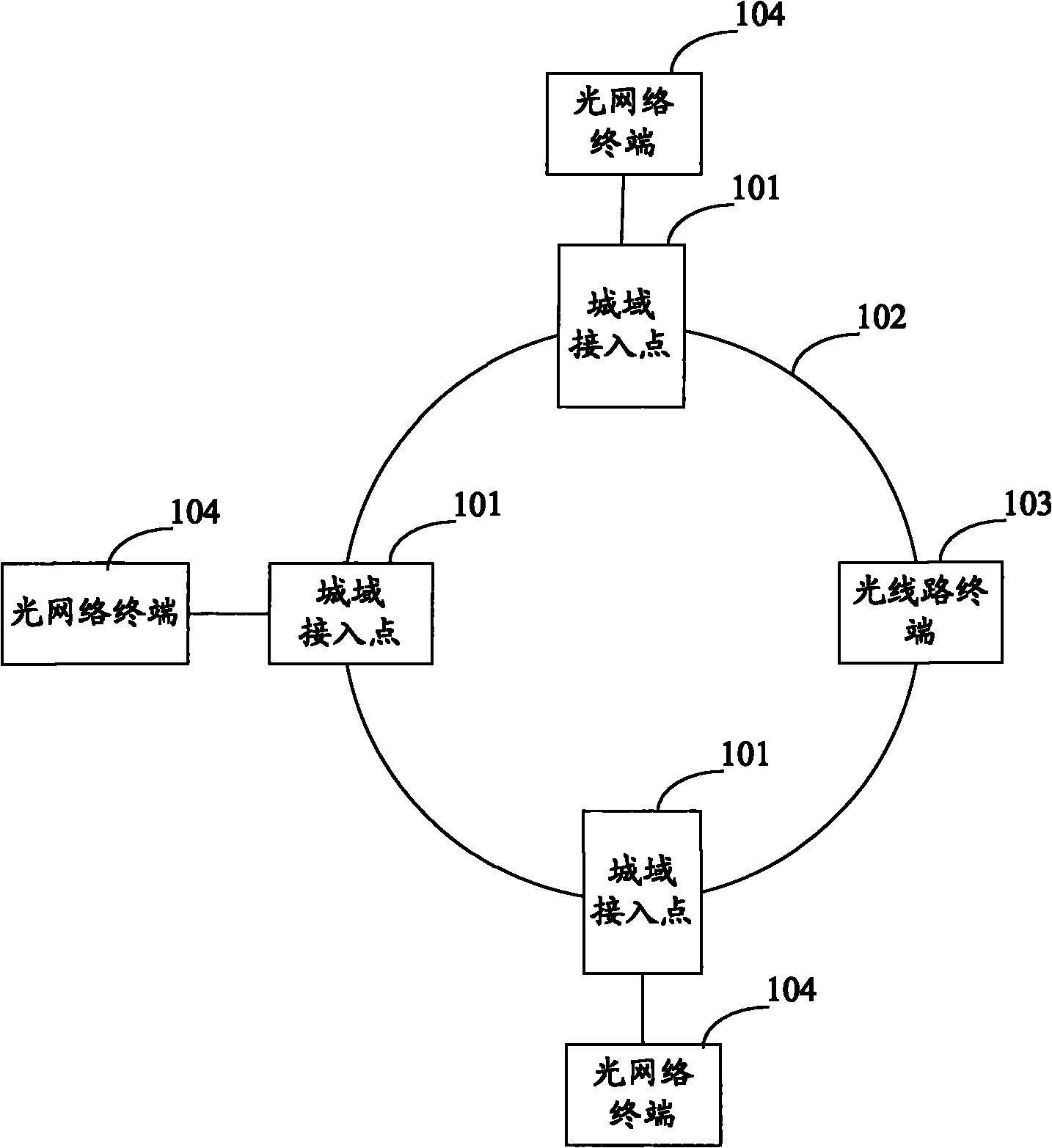
System for realizing network extension and protection functions with wave-division multiplexing annular optical access networks and method for realizing network extension and protection functions with wave-division multiplexing annular optical access networks
InactiveCN102523044AMultiplex system selection arrangementsRing-type electromagnetic networksGratingEngineering
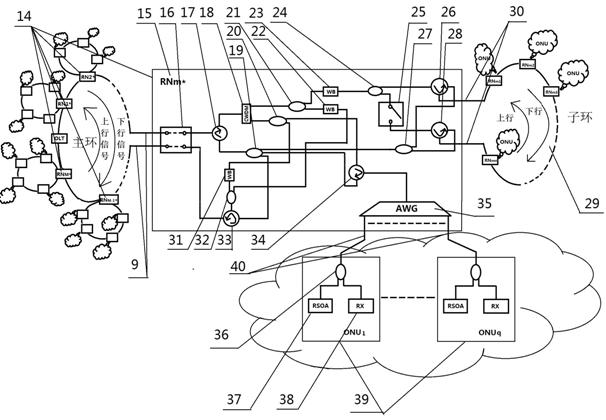
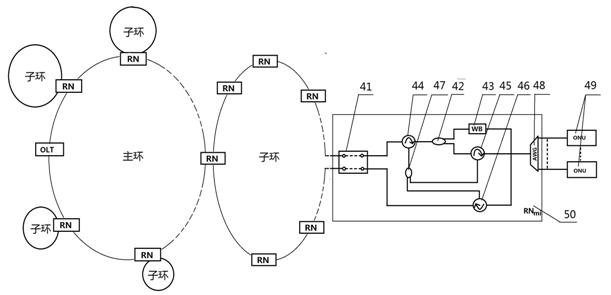
The invention relates to a system for realizing network extension and protection functions with wave-division multiplexing annular optical access networks and a method for realizing the network extension and protection functions with the wave-division multiplexing annular optical access networks. The system is characterized in that an OLT (optical link terminal) is connected with M RNs (remote nodes) through an optical fiber to form an annular network, and the remote nodes are connected with ONUs (optical network units) through a distributed optical fiber, wherein the optical link terminal mainly comprises Q=Mq (1+n) optical transmitters, Q receivers, Mq transmitting C wave-band wavelength, Mnq transmitting L wave-band wavelength, Q 1X2 optical switches, three AWGs (arrayed waveguide gratings) of an identical structure and with Q ports, two EDFAs (erbium-doped fiber amplifiers), two optical circulators and a 2X1 coupler; and each remote node on a main ring mainly comprises a 2X2 optical switch, a 1X2 optical switch, two WBs (wavelength blockers), a CWDM (coarse wavelength division multiplexing), four common circulators, a closed circulator, six couplers and an arrayed waveguide grating. A feeder optical fiber is protected by the aid of use of the optical switches at the OLT end and designs of the annular structures and RN structures. By means of effective arrangement of the RN nodes, network scale extension can be realized, typical annular tangent topological structures are realized, network coverage area is greatly widened, and the quantity of users is greatly increased. The system realizes dynamic dispatching of the wavelength by adjusting the wavelength blockers and changing operating ports of the arrayed waveguide gratings, and achieves balance between the cost and the performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
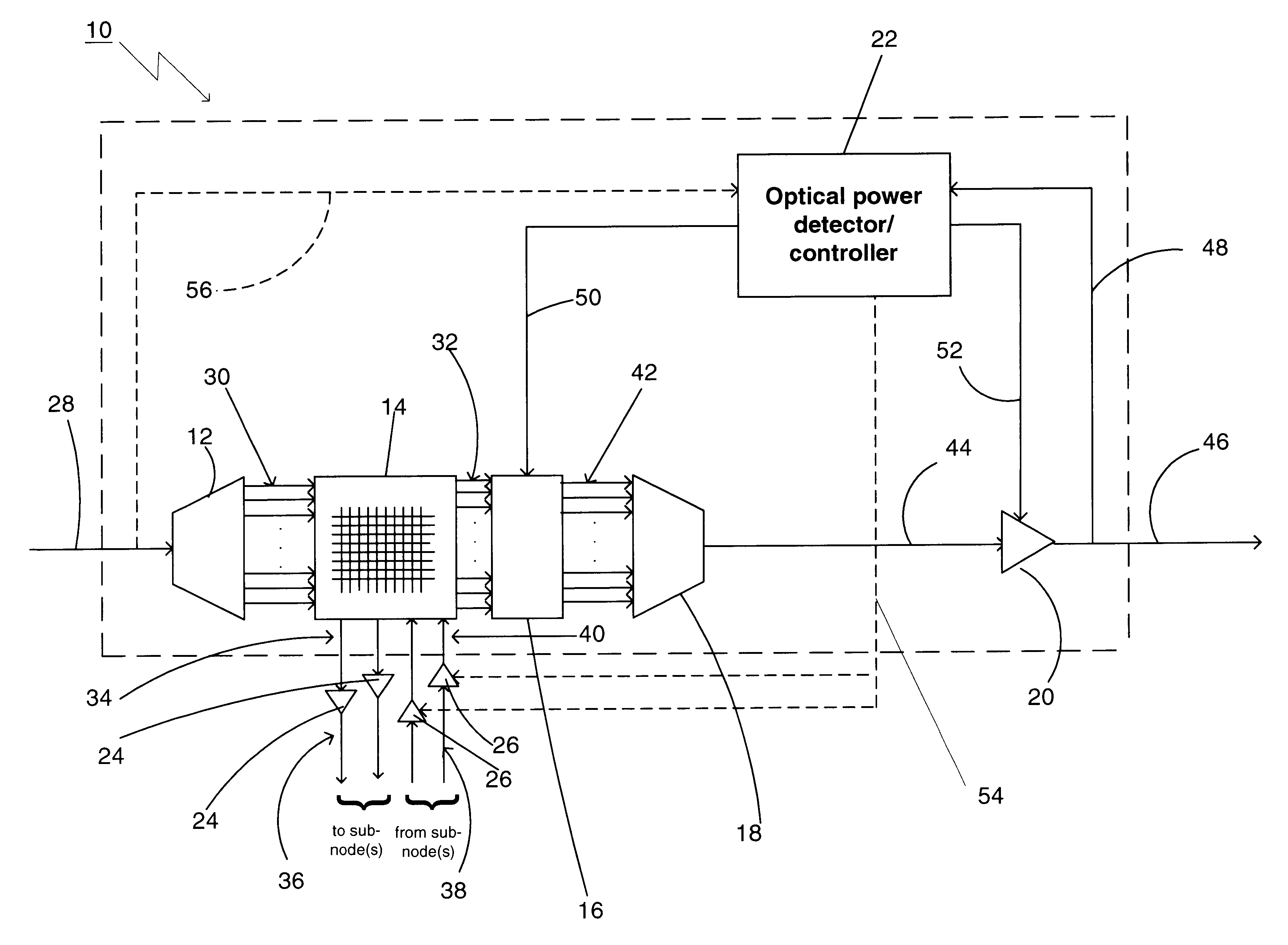
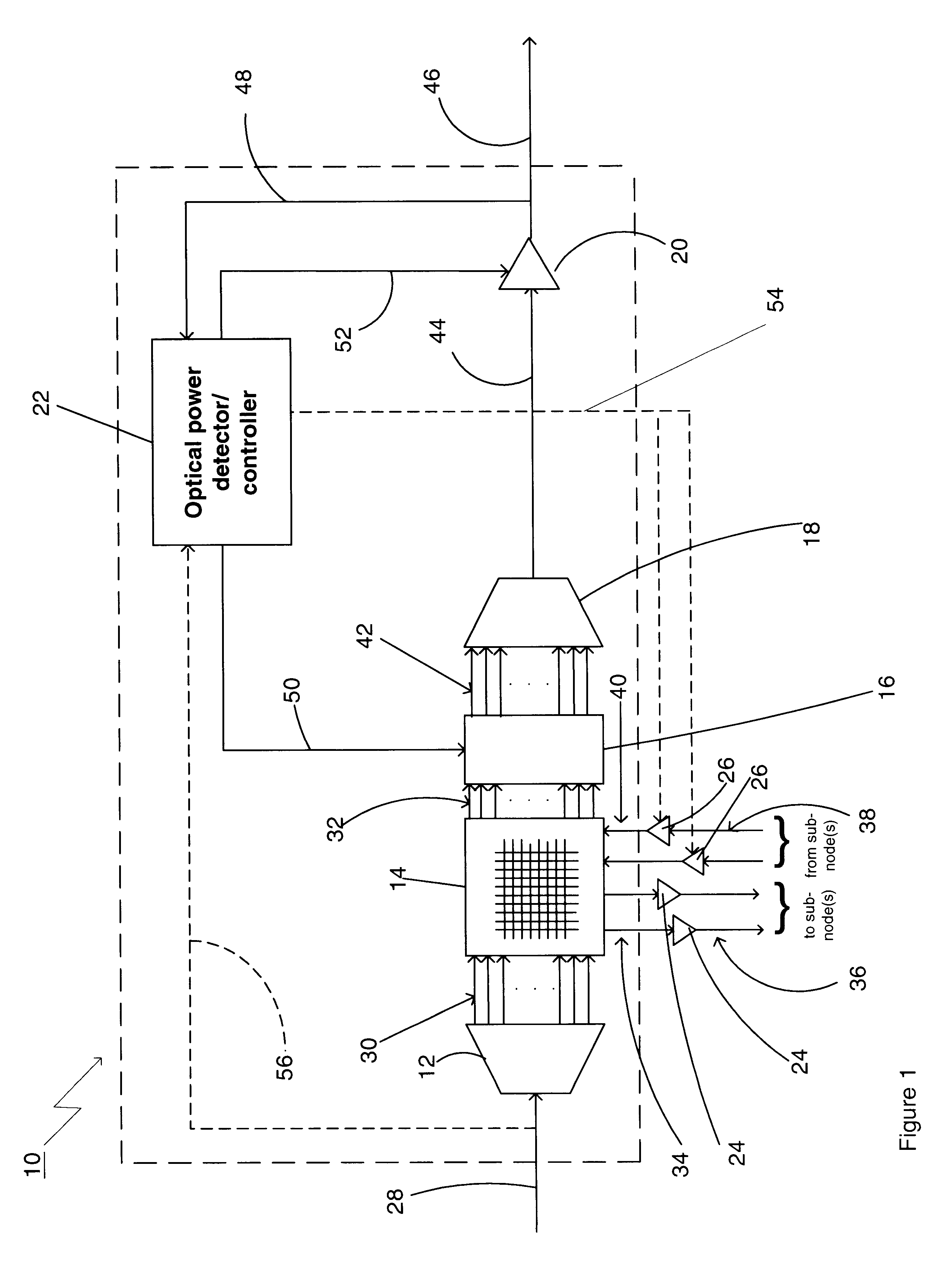
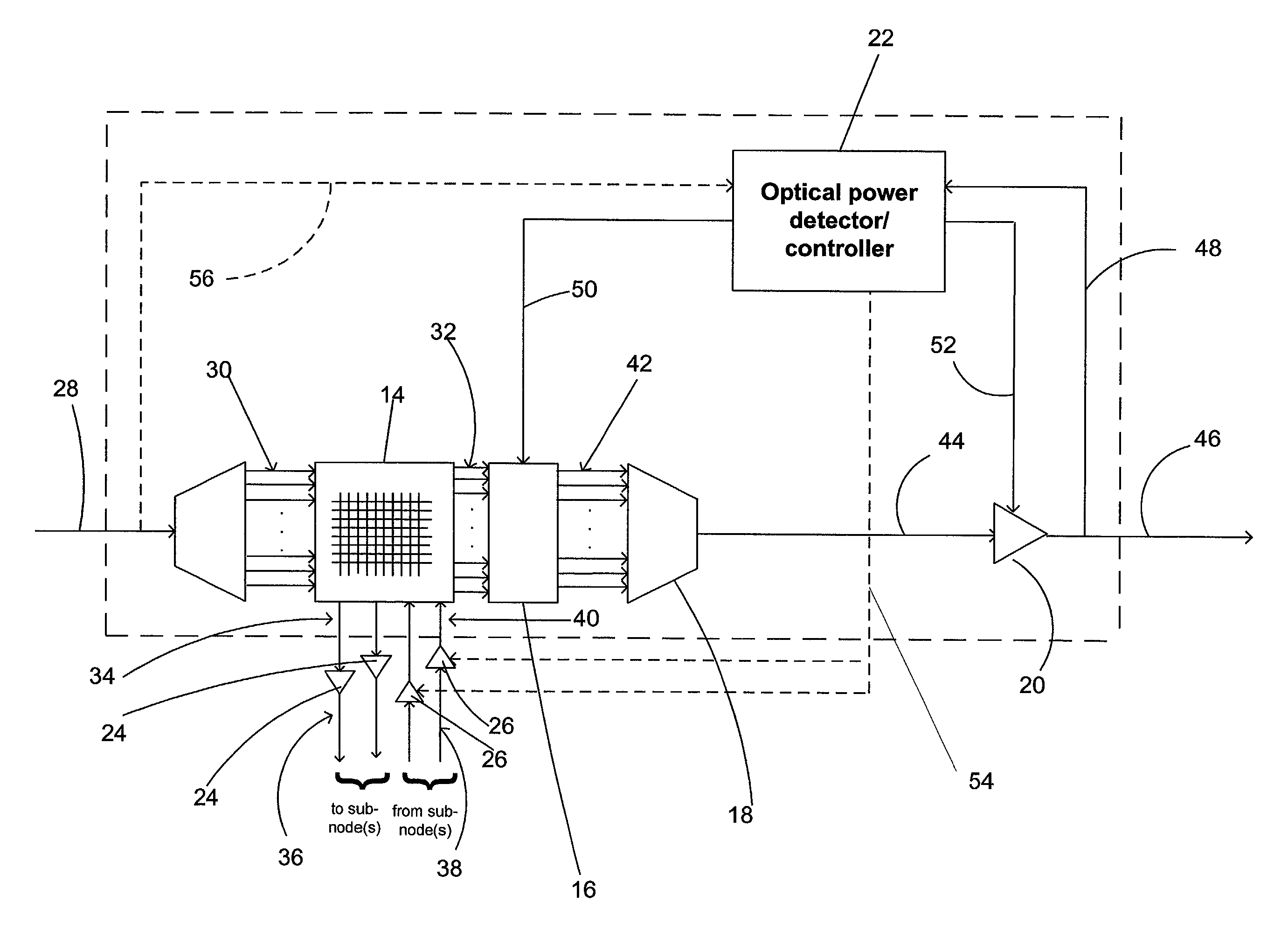
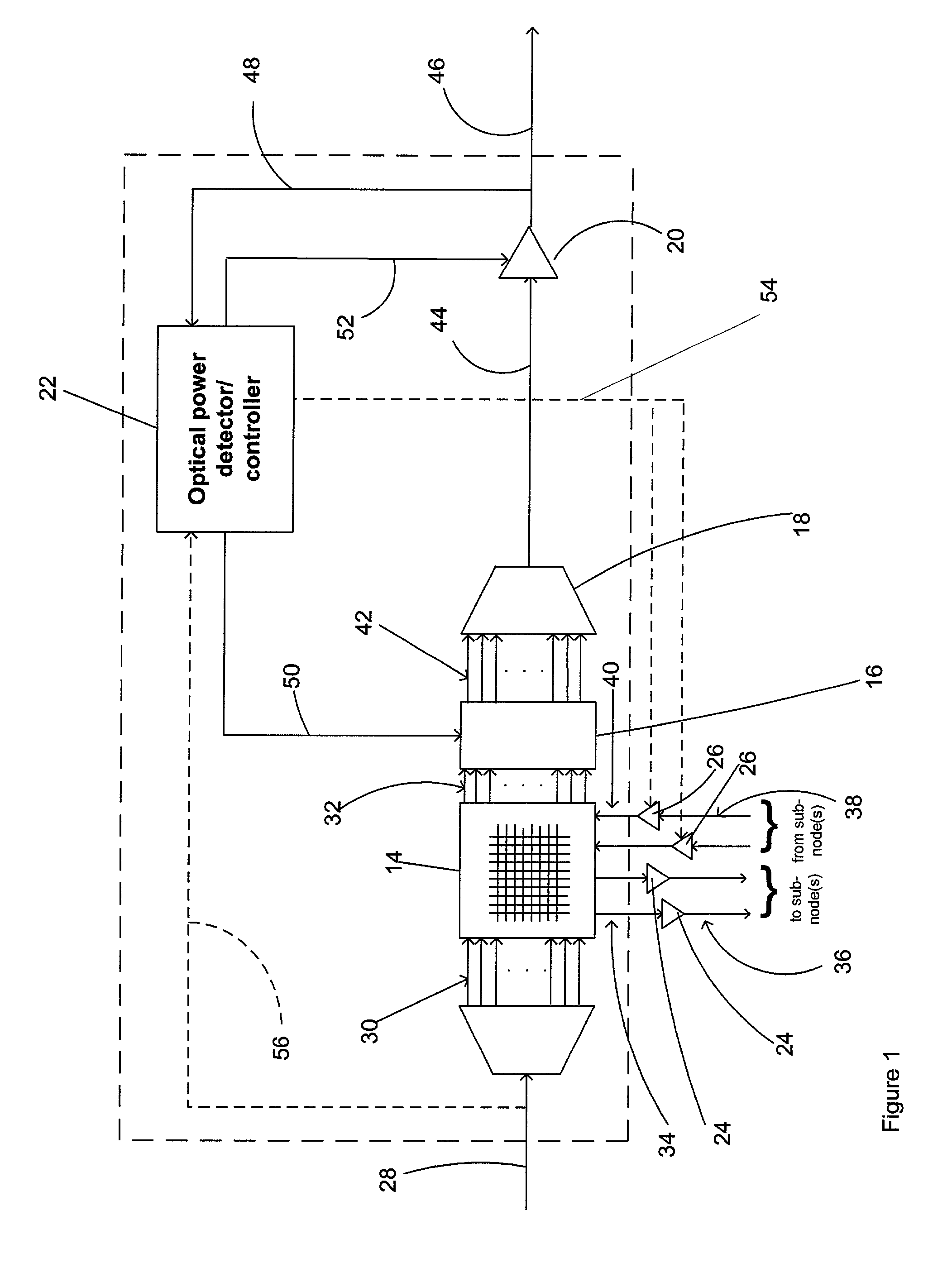
Optical power managed network node for processing dense wavelength division multiplexed optical signals
InactiveUS6449068B1Efficient and cost-effectiveMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsPower detectorOptical power
A technique for processing dense wavelength division multiplexed optical signals in a network node is disclosed. In one embodiment, the technique is realized as an optical power managed network node comprising a dense wavelength division multiplexing device for combining a plurality of narrowband optical signals into a multiplexed polychromatic optical signal. The optical power managed network node also comprises a wavelength-selective optical power detector for detecting the power of each of the plurality of narrowband optical signals combined into the multiplexed polychromatic optical signal. The optical power managed network node further comprises a plurality of attenuators for attenuating the power of at least one of the plurality of narrowband optical signals based upon the detected power of each of the plurality of narrowband optical signals.
Owner:DIGITAL LIGHTWAVE +1
Single-optical-port wavelength division multiplexing/demultiplexing photoelectric transceiver device
ActiveCN103744145AReduce usageReduce volumeWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesTransceiverMultiplexer
The invention discloses a single-optical-port wavelength division multiplexing / demultiplexing photoelectric transceiver device. A pin and a glass carrier are respectively arranged above and below a collimating lens of the device. A total reflector plate and a band-pass optical filter array are respectively bonded on the upper surface and the lower surface of the glass carrier. A glass partition is arranged below the glass carrier. An optical circulator is arranged above the glass carrier or on one side surface of the glass partition. A laser transmitting module and a detector receiving module are respectively arranged on the two side surfaces of the glass partition. The single-optical-port wavelength division multiplexing / demultiplexing photoelectric transceiver device has the advantages that since the laser module and the detector module share the same multiplexer / demultiplexer and one public optical port, the input and the output of downlink detector signals and uplink laser signals from the same optical port can be realized, the used device cases and the size of a module can be effectively reduced, the miniaturization and the integration of the device and the module are facilitated and the working wavelength of the device can be applied to the situation of simultaneous working of multi-channel wavelength of CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) and LWDM (LAN Wavelength Division Multiplexing).
Owner:WUHAN TELECOMM DEVICES
Four-channel coarse wavelength division multiplexing QSFP optical module
ActiveCN107479150AAvoid failureHigh sensitivityWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesPigtailSingle mode fiber coupling
Owner:LINKTEL TECH CO LTD
Hybrid passive optical network system
ActiveCN101197638ALow costExpand the scope of the networkWavelength-division multiplex systemsNetworked systemEngineering
The invention relates to a mixed type passive optical network system which comprises a plurality of optical line terminals, a coarse wavelength division multiplexing and demultiplexing device, an optical branching device, and a plurality of optical network units, wherein, each optical line terminal occupies two different wavelengths of coarse wavelength division multiplexing standards, and the two different wavelengths are respectively used for transmitting optical signals of a transmitting end and a receiving end of the optical line terminal; the optical branching device is provided with a plurality of ports and connected with the coarse wavelength division multiplexing and demultiplexing device through an optical fiber; the network units are connected with corresponding ports of the optical branching device through optical communication. The invention adopts mature coarse wavelength division technologies to make a plurality of mutually independent EPON systems enter into a single optical fiber through simultaneous superposition of different CWDM optical wavelengths and simultaneously be shared by each ONU through the optical branching device. By adoption of the topological structure, the invention has the advantages of great conversation of optical fiber resources connected between metropolitan area networks and cells, simultaneous further exertion of EPON advantages, capability of flexibly increasing user number, reduction of cost of each line, and acceleration of promotion of an EPON network.
Owner:SHANGHAI BROADBAND TECH
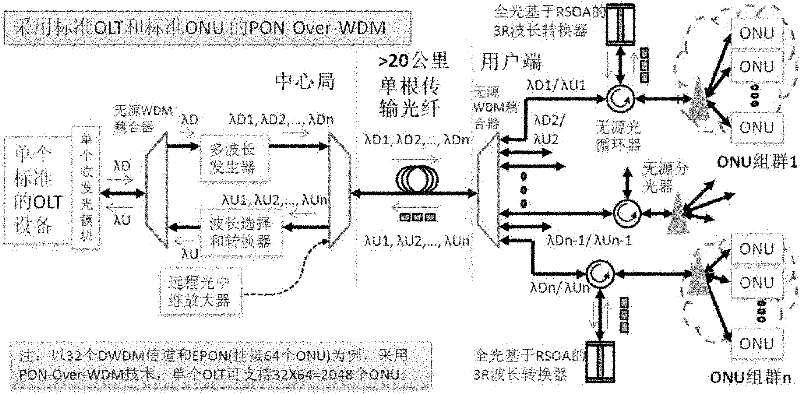
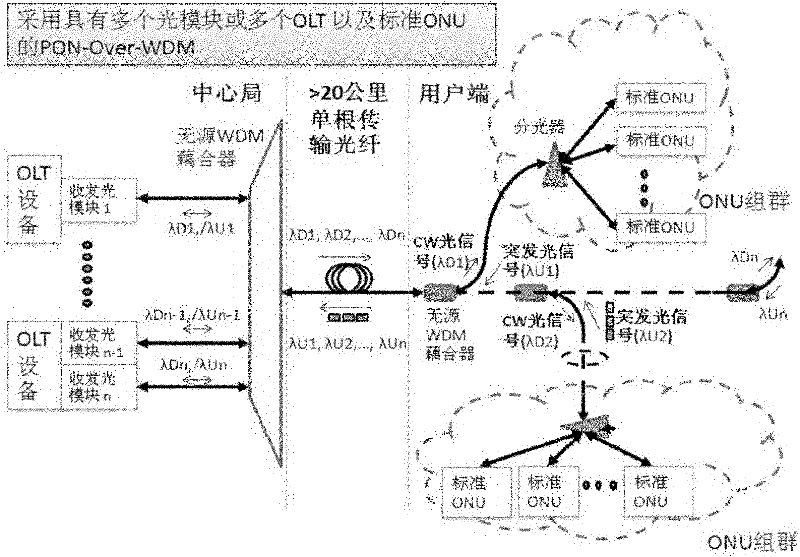
Passive optical network over wavelength division multiplexing
ActiveCN102695101ALow costIncrease costMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransverterCoarse wavelength division multiplexing
The invention relates to a passive optical network over wavelength division multiplexing (PON-Over-WDM). The network includes a first WDM coupler, an ONU terminal, a light circulator and a first wavelength converter, wherein the light circulator directs a burst optical signal transmitted by the ONU terminal to the first wavelength converter, and the first wavelength converter is used for performing wavelength conversion of the optical signal and transmitting the wavelength-converted optical signal to the first WDM coupler for coupling after which the optical signal is transmitted through a single optical fiber. The network of the invention is low in cost and flexible in expansion. The network can be accessed by high-capacity ONU equipments or terminal users and is compatible for different equipment suppliers and service providers. The network can be applied to optical communication networks.
Owner:SUZHOU CREALIGHTS TECH
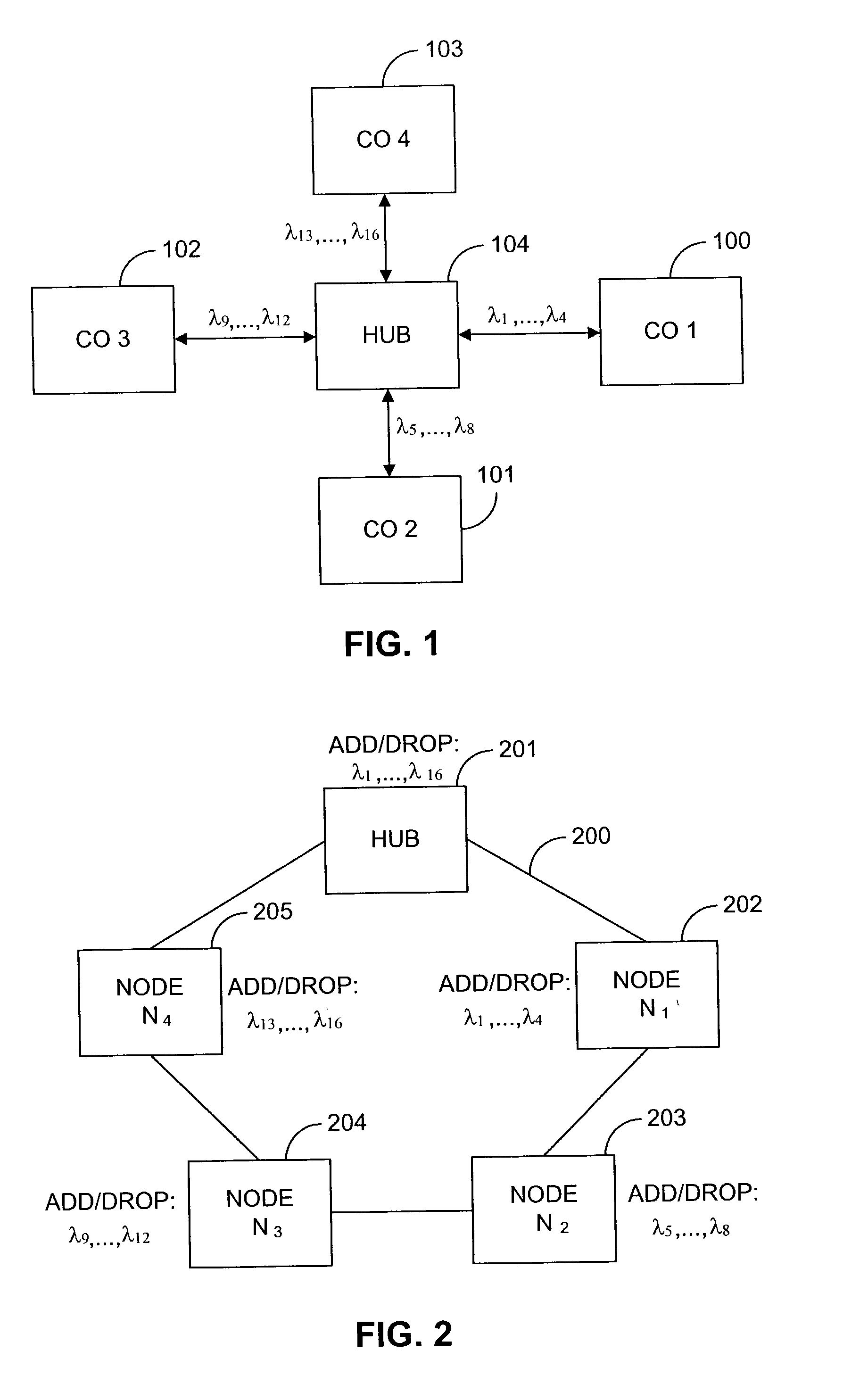
Coarse wavelength division multiplexing system
ActiveUS7149429B2Maximize coverageWavelength-division multiplex systemsGlass fiberAudio power amplifier
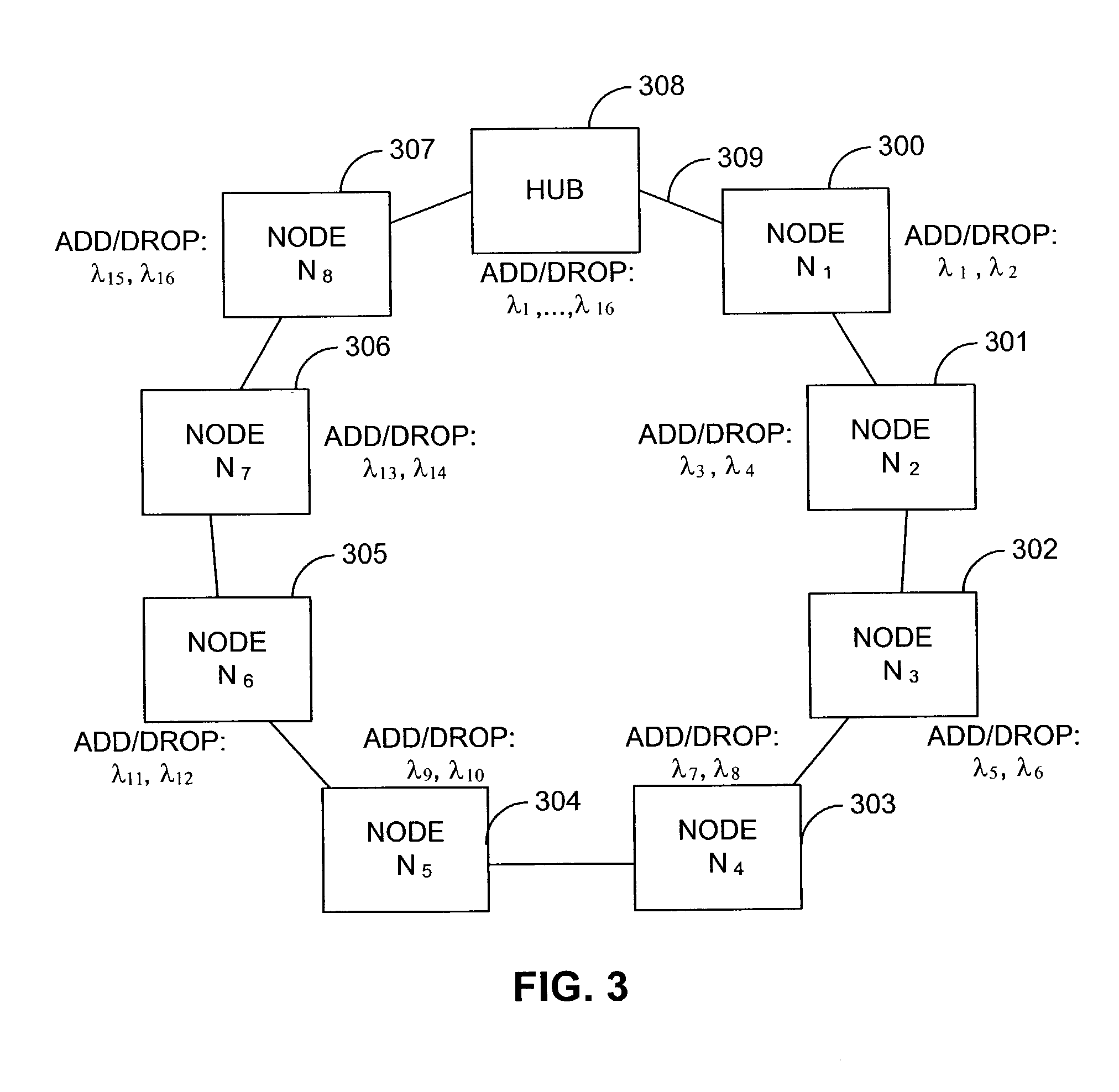
In a ring network comprising a plurality of nodes and a 16 channel coarse wavelength-division multiplexing (CWDM) plan, a technique is disclosed for adding and dropping channels that reduces the maximum attenuation loss that any channel encounters—thereby enabling longer rings to be constructed without using optical amplifiers in the ring. The 16 channels are typically distributed between the wavelengths 1310–1610 nm with 20 nm separation between channels. It is obscured that glass fibers have gradually decreasing loss at longer wavelengths in this band. The network includes a hub and several nodes that are interconnected by optical fibers in a ring configuration, where distance from the hub is the minimum value measure in either the clockwise or counterclockwise direction. Channels are assigned to the various nodes based on their wavelength. The channels whose wavelengths are near 1310 nm are assigned to nodes that are progressively closer to the hub.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
PON system mixing TDMA and WDM having function of local area network
ActiveCN101309191AIncrease profitQuick switchMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringLength wave
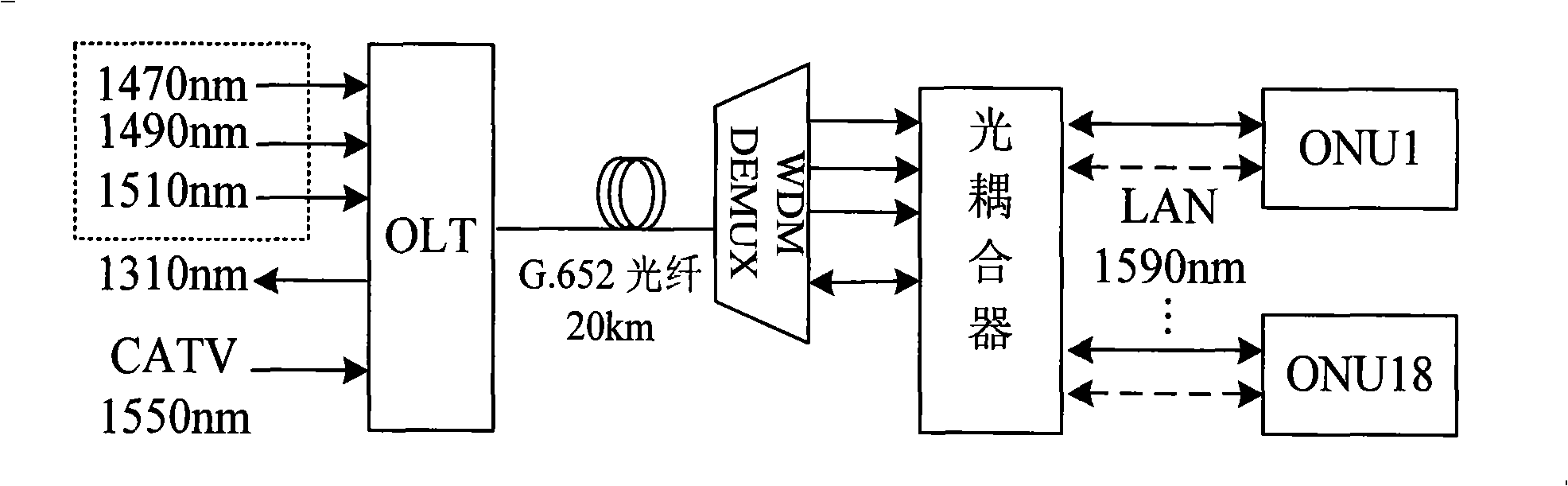
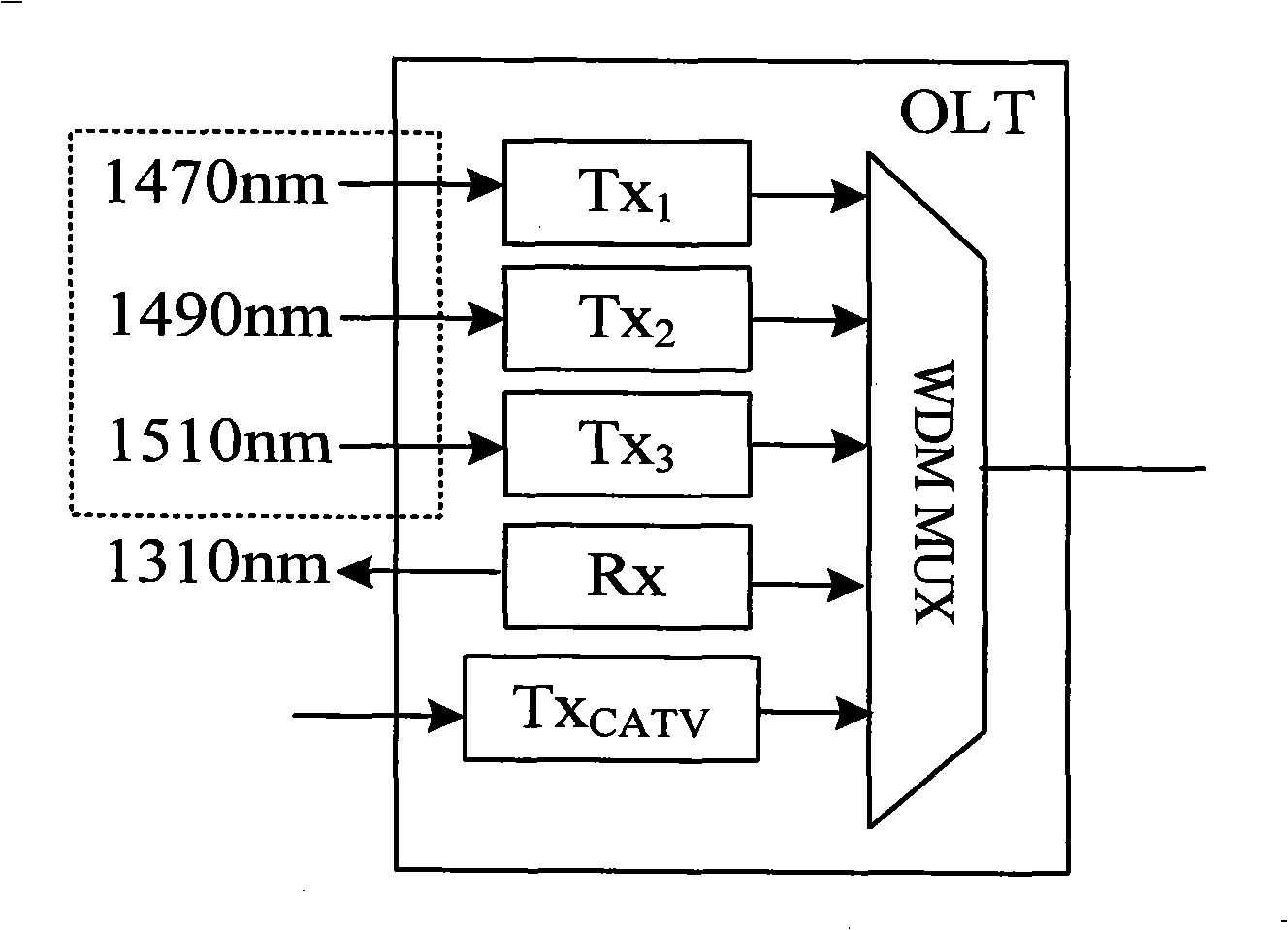
The invention discloses a PON system with the combination of TDMA and WDM and the LAN function. An OLT is connected with N ONU through an optical coupler; the OLT end includes M transmitter modules Tx with different wavelengths, a receiver module Rx with single wavelength and a CATV RF signal transmitter module Tx; each ONU includes a transmitter module and a receiver module with the function of high speed wavelength switching. The PON system adopts the coarse wavelength division multiplexing technique to realize the multi wavelength downstream data transmission; each wavelength is distributed to a plurality of ONU for sharing through the current TDMA technology so that the system bandwidth is extended; the LAN mode is separated from the PON system by the receiver-transmitter module with the wavelength switching function in the ONU end so that the rapid switching between the PON mode and the LAN mode is realized and the problem of low channel utilization rate found in the traditional access mode is solved.
Owner:WUHAN HONGXIN TELECOMM TECH CO LTD
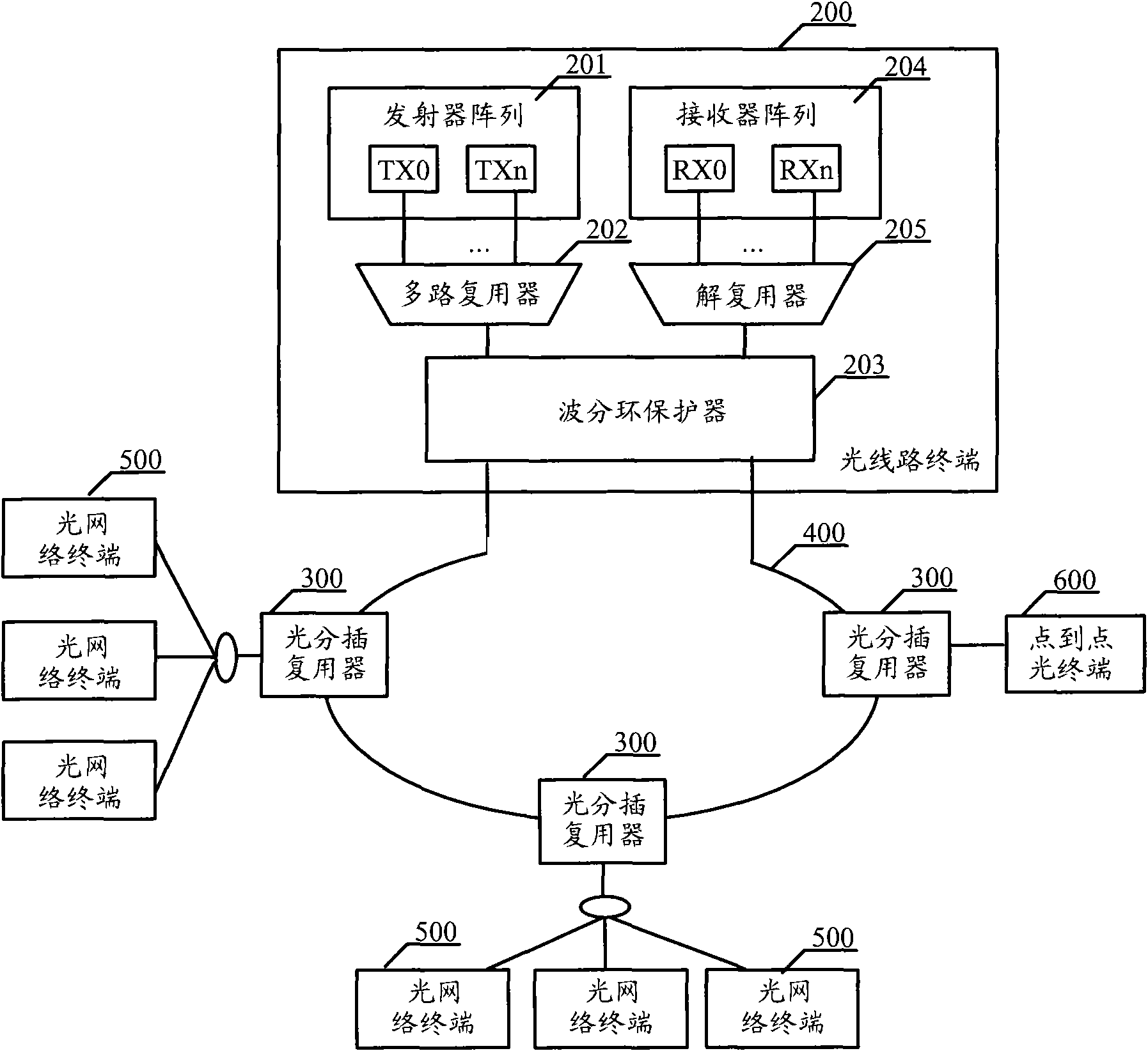
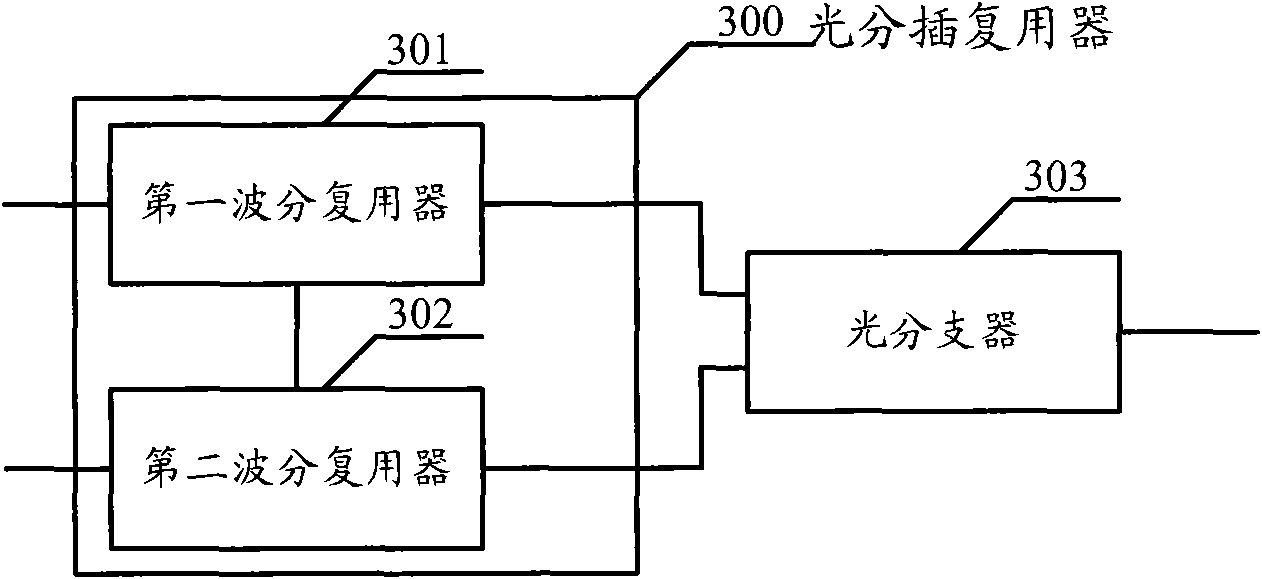
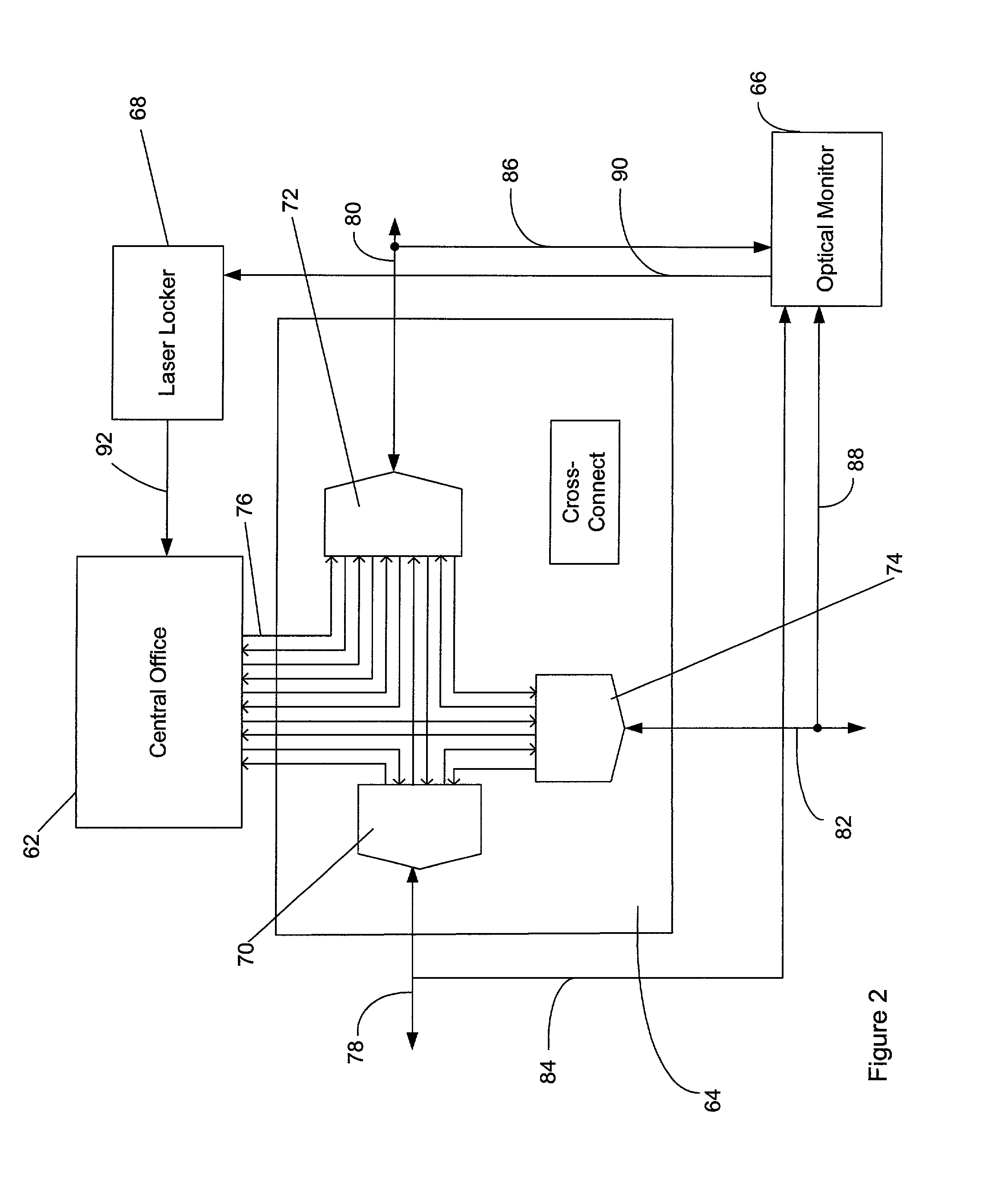
Optical line terminal, optical add-drop multiplexer and optical access system
ActiveCN101902665AImplement backup protectionMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical add-drop multiplexerMultiplexer
The embodiment of the invention discloses an optical access system comprising one or more optical add-drop multiplexers sequentially connected through optical fibers in series to form a wavelength division multiplexing ring, wherein both ends of the wavelength division multiplexing ring are connected with one optical line terminal. The optical line terminal comprises a transmitter array, a multiplexer, a wavelength division ring protector, a receiver array and a demultiplexer, wherein the wavelength division ring protector is used for detecting whether the wavelength division multiplexing ring is broken or not; when the wavelength division multiplexing ring is normal, multiplexed downstream optical signals are transmitted to the wavelength division multiplexing ring from one end; when the wavelength division multiplexing ring is broken, the downstream optical signals are transmitted to the wavelength division multiplexing ring from both ends; and when the wavelength division multiplexing ring is normal, upstream optical signals are received from one end of the wavelength division multiplexing ring, and when the wavelength division multiplexing ring is broken, the upstream optical signals are received from both ends of the wavelength division multiplexing ring, and then the received upstream optical signals are transmitted to the demultiplexer.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Optical power managed network node for processing dense wavelength division multiplexed optical signals
InactiveUS20020021463A1Efficient and cost-effectiveMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical powerPower detector
A technique for processing dense wavelength division multiplexed optical signals in a network node is disclosed. In one embodiment, the technique is realized as an optical power managed network node comprising a dense wavelength division multiplexing device for combining a plurality of narrowband optical signals into a multiplexed polychromatic optical signal. The optical power managed network node also comprises a wavelength-selective optical power detector for detecting the power of each of the plurality of narrowband optical signals combined into the multiplexed polychromatic optical signal. The optical power managed network node further comprises a plurality of attenuators for attenuating the power of at least one of the plurality of narrowband optical signals based upon the detected power of each of the plurality of narrowband optical signals.
Owner:DIGITAL LIGHTWAVE +1
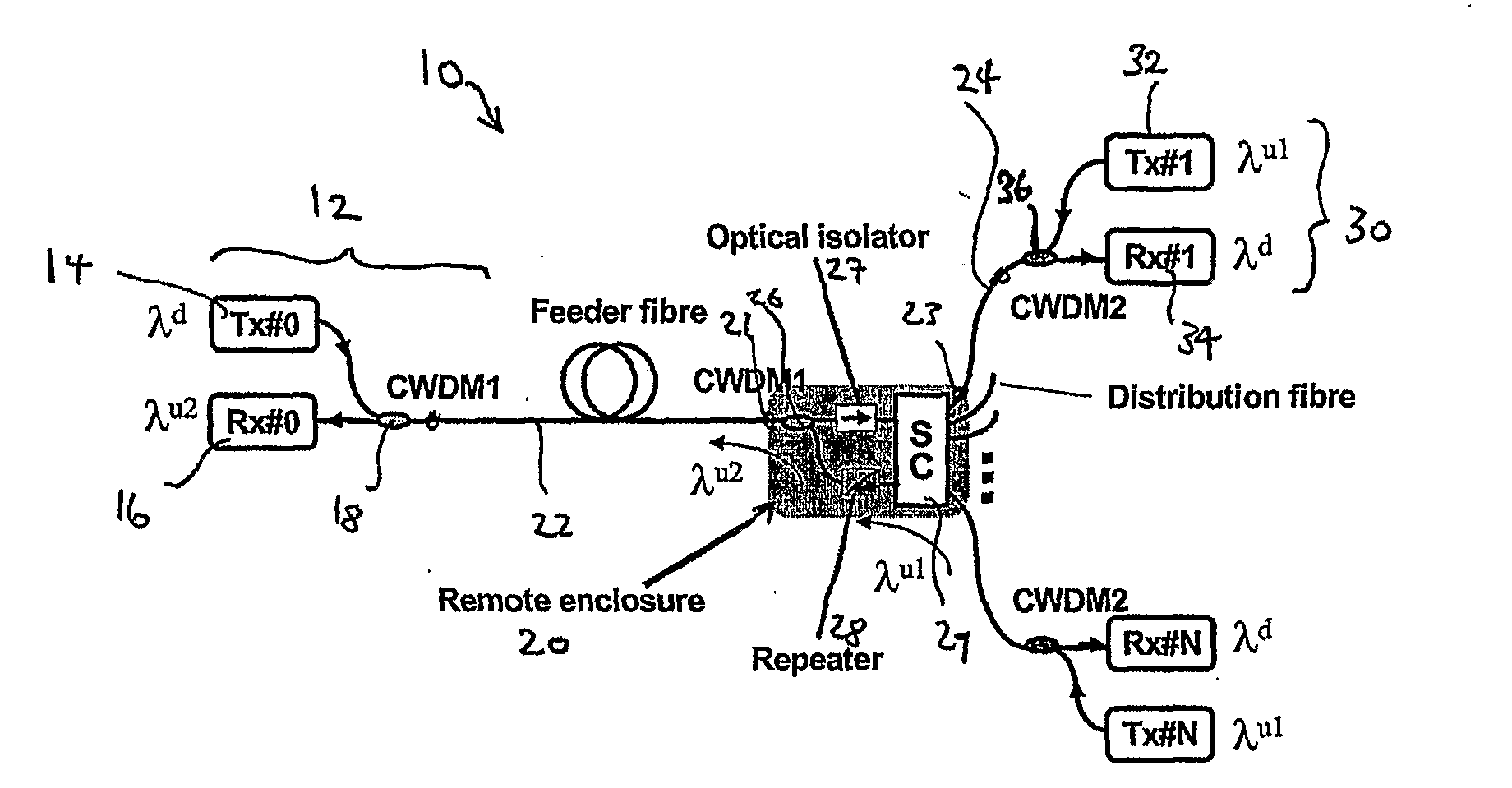
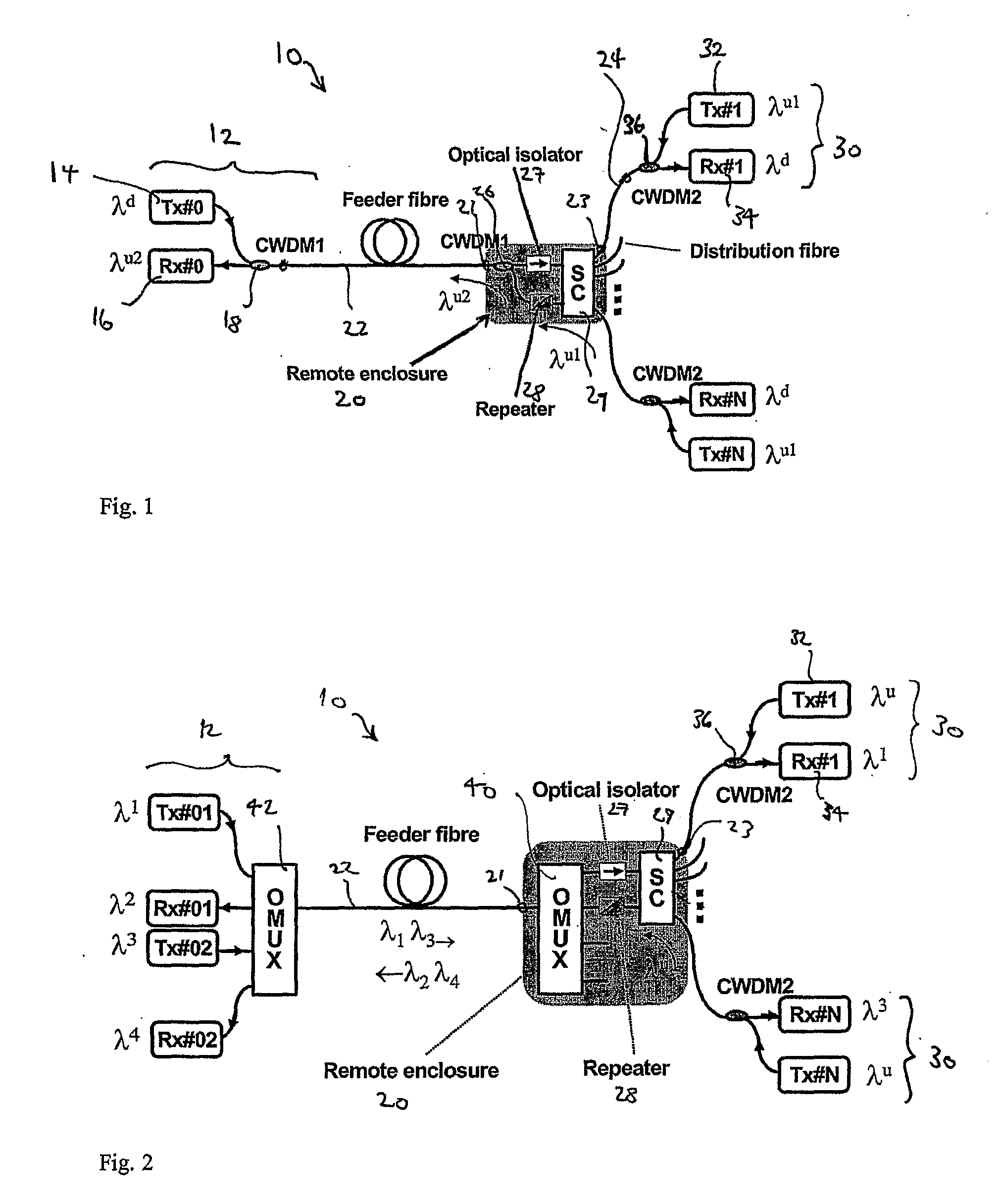
Pon System With a Remote Upstream Repeater
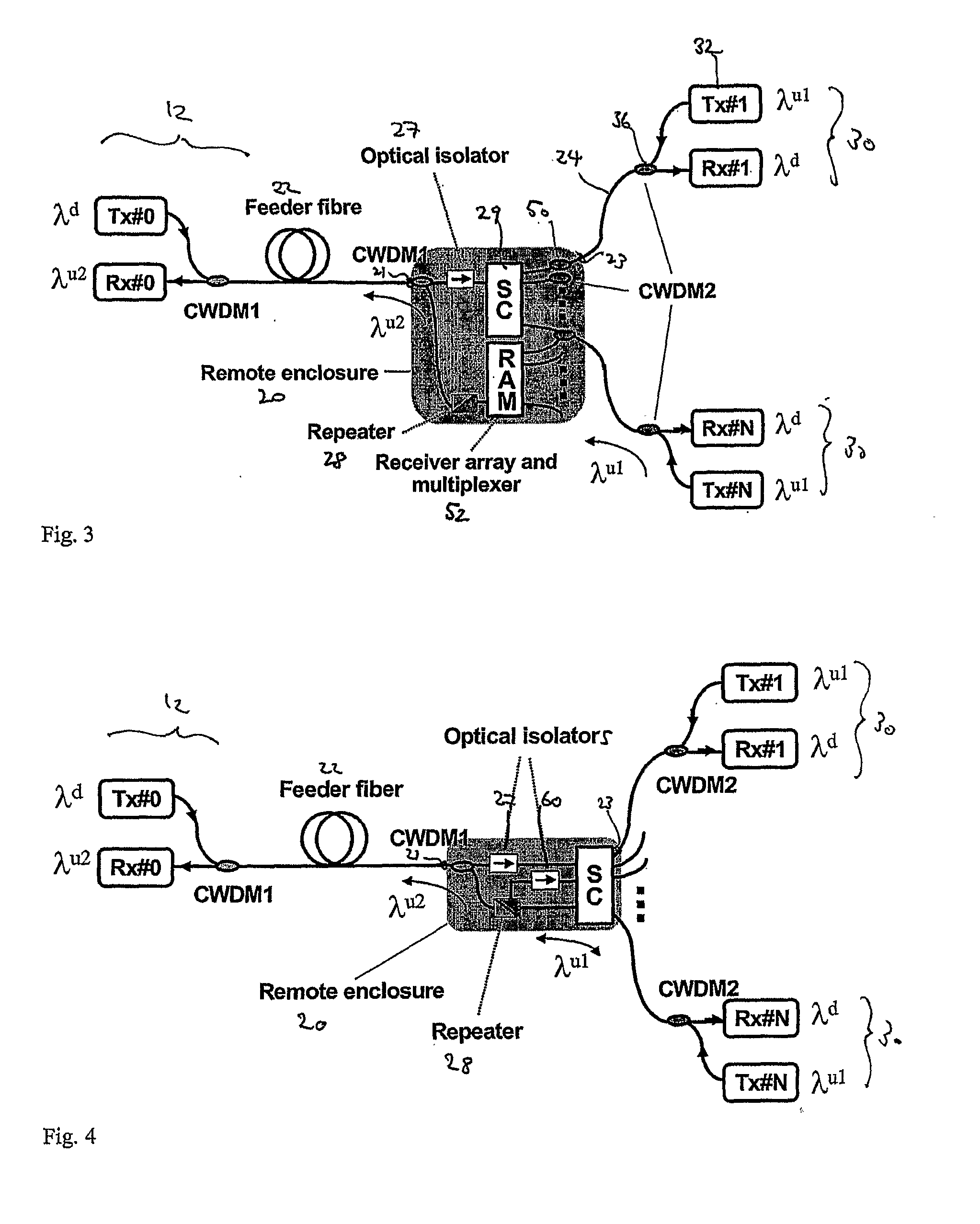
InactiveUS20080193130A1Access speedReduce lossWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesMultiplexerEngineering
A signal coupler (20) for a passive optical network (PON) system is disclosed. The coupler (20) includes a first port for two-way feeder side communication with a PON terminal (12), a star coupler (29), other ports (23) for two-way distribution side communication with each of plural remote optical network units (ONUs) (30), and a repeater (28) installed on the upstream signal path from the ONUs (30) to the PON terminal (12). Upstream signals from ONUs (30) are received by the repeater (28) without passing through the star coupler (29) by using a coarse wavelength division multiplexer (50) on each distribution fibre and taking out the upstream light before arrival at the star coupler (29) and redirecting it to a receiver array and multiplexer (52). The repeater (28) regenerates each upstream signal and changes its wavelength.
Owner:NAT ICT AUSTRALIA
Wave-division frequency division multiplex system of optics fiber fabry-perot sensor
InactiveCN1694387ARealize WDMSignal-to-noise ratio has little effectWavelength-division multiplex systemsBroadband light sourceBroadband
A WDFDM system of a fiber Fabry-Perot sensor includes a broadband light source, a rough WDM device, fibers, a coupler, an index of refraction matching solution, sensors and splitter and a spectrometer, among which, the fiber is an ordinary single-mode one, the sensor is a fiber Fabry-Perot sensor. The rough WDM device is used to divide broadband light into light in multiple channels to realize WDM. The splitter cuts in sensor of different cavity lengths on each channel to realize WDM. Sensor number capable of multiplexing in the WDFDM system is the product of the number of WDM and FDM independently so as to increase the multiplex efficiency greatly and obtain accurate test value.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
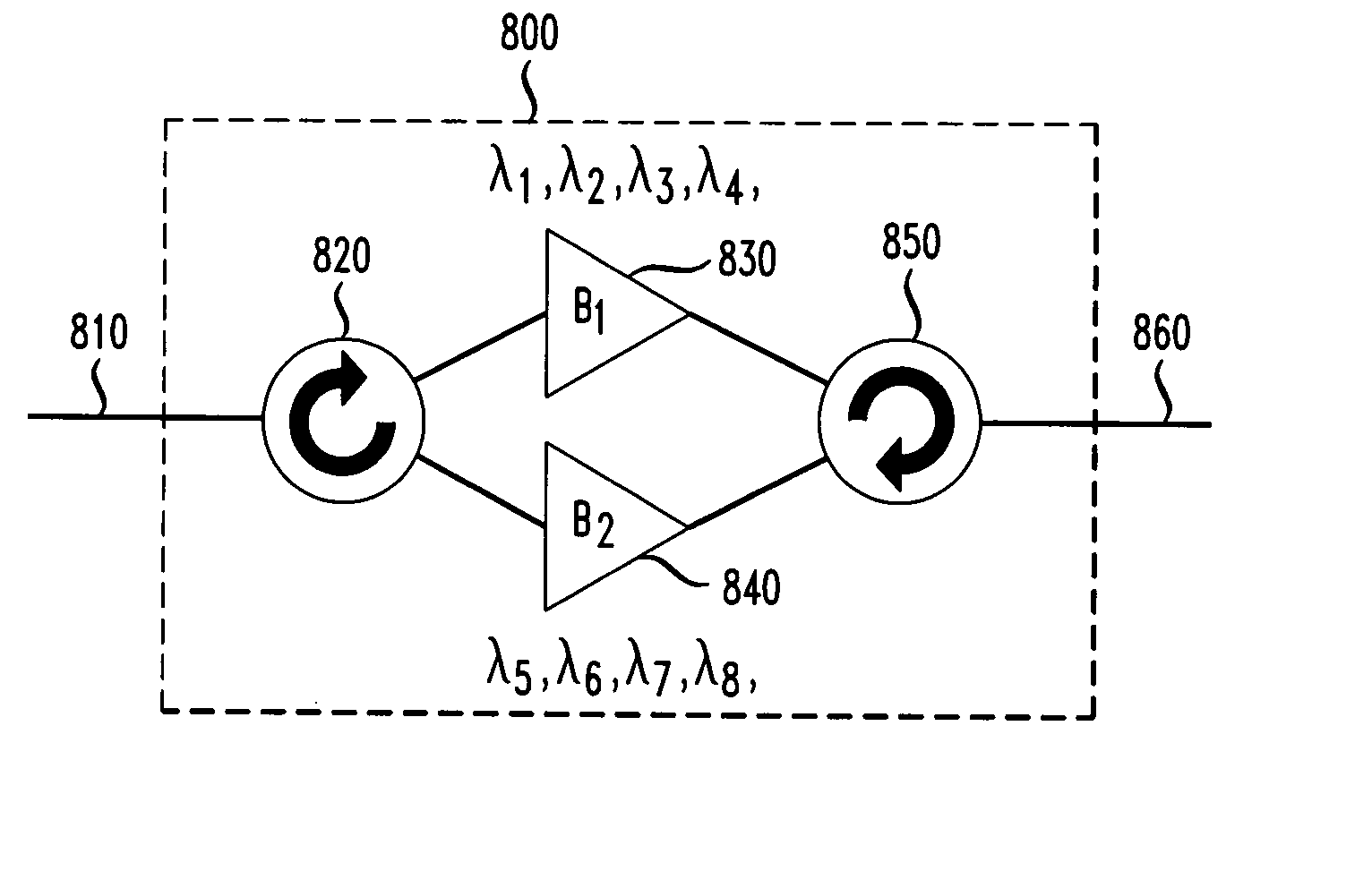
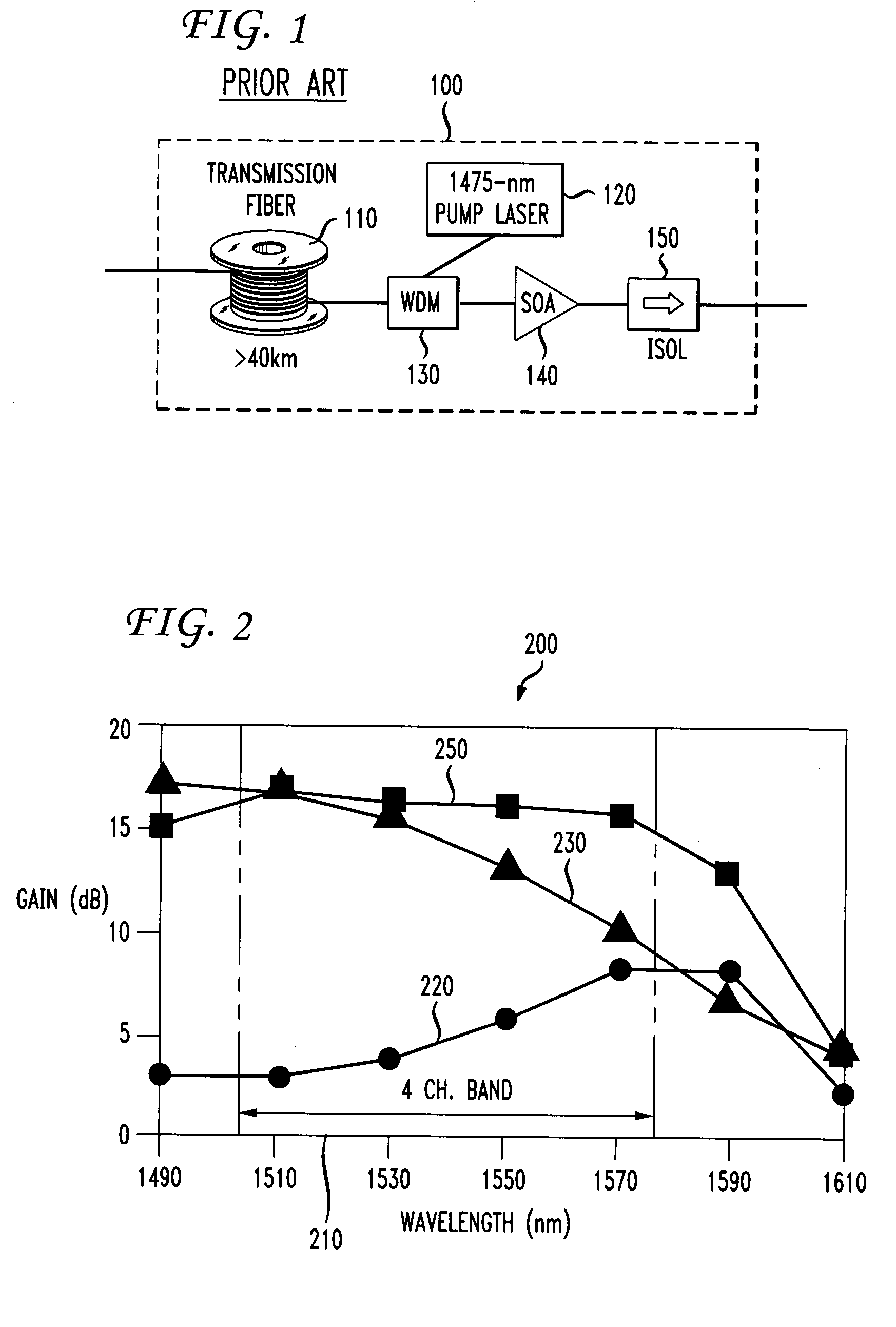
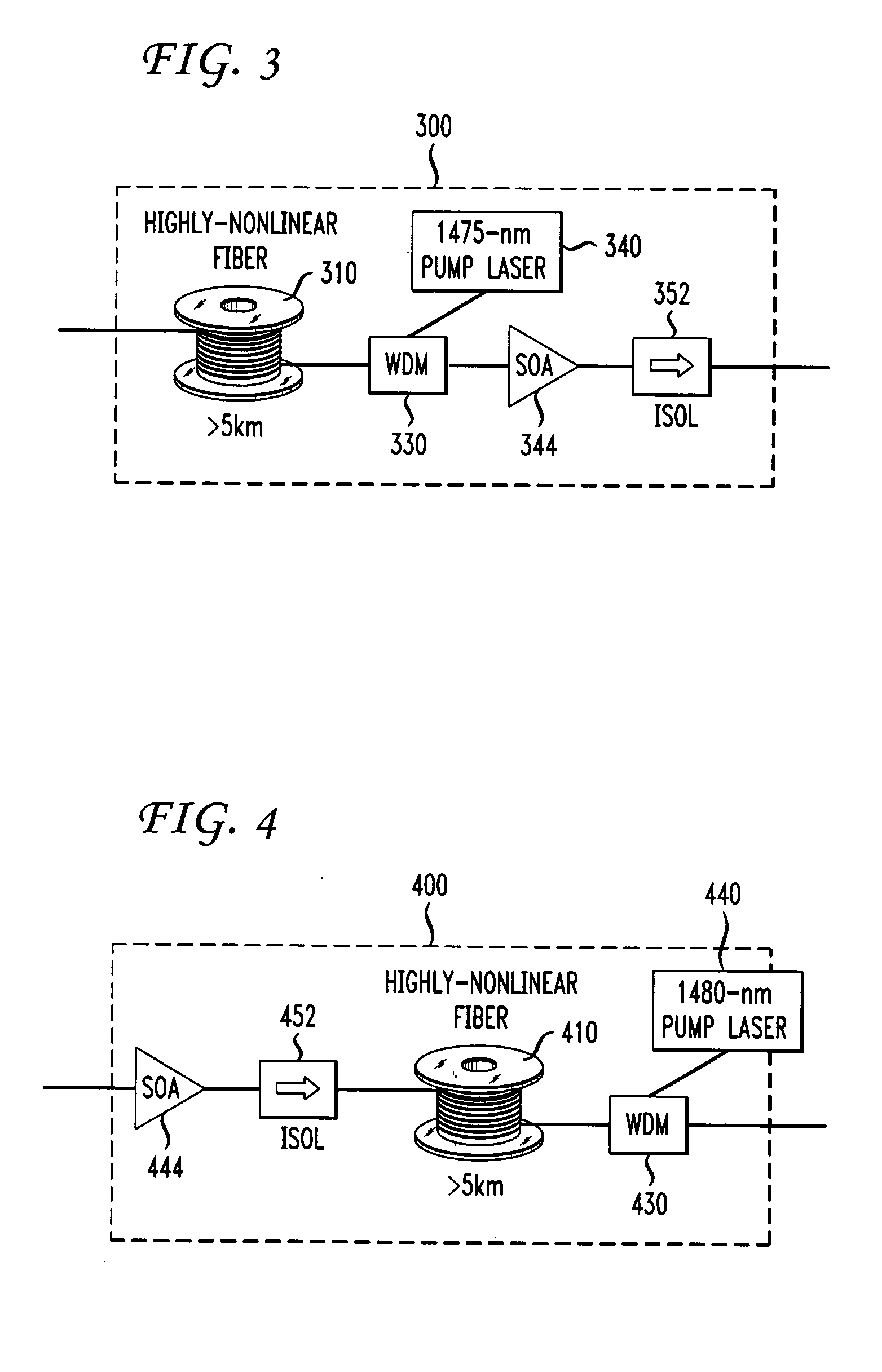
Multiband amplifier based on discrete SOA-Raman amplifiers
Several discrete hybrid amplifiers are used in parallel for amplifying an optical signal in an optical fiber system. An optical signal is first split into two or more separate signals each with a separate wavelength band. Each wavelength band is then amplified by a Raman pump utilizing a length of highly non-linear fiber as the gain medium, and by an SOA amplifier. The combination of the Raman amplifier and the SOA yields a level gain over the wavelength band. The amplified wavelength band signals are then recombined. The disclosed amplifier is especially useful in coarse wavelength division multiplexing (CWDM) systems and in local access portions of the network.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
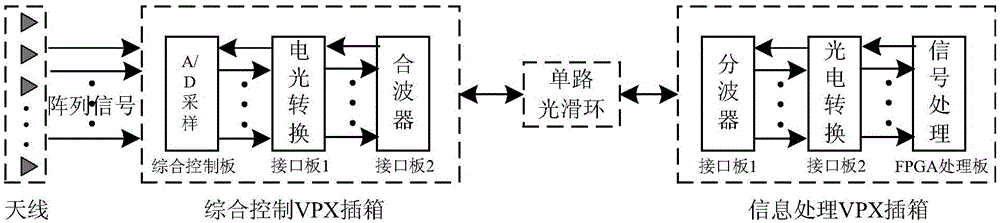
Radar signal wavelength division multiplexing module design method based on VPX platform
InactiveCN105119681AImprove isolationIncrease optical powerWavelength-division multiplex systemsInformation processingCoarse wavelength division multiplexing
The invention relates to a radar signal wavelength division multiplexing module design method based on a VPX platform. The method comprises steps: multiple digital signals generated by a phase array radar are received, multiple coarse wavelength division single-mode optical signals are outputted through an electric light conversion circuit, electromagnetic interference and crosstalk between channels are inhibited through a shielding module, a single-channel coarse wavelength division multiplexing optical signal is formed through a combiner, is transferred through an optical slip ring and enters a signal processing cabinet, the single-channel multiplexing optical signal is converted into multiple single-mode optical signals with different wavelengths through a wave separator first, then the optical powder is raised through a relay and an amplification circuit, multiple CML level signals are outputted through a photovoltaic conversion circuit and transmitted to a signal processing module, and therefore miniaturization and light-weight application of the wavelength division multiplexing function can be achieved on a VPX general information processing platform.
Owner:THE 724TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
Wavelength division multiplexed light source and passive optical network using the same
InactiveUS20060233550A1Increase the number ofWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultimode transmissionMultiplexerOptoelectronics
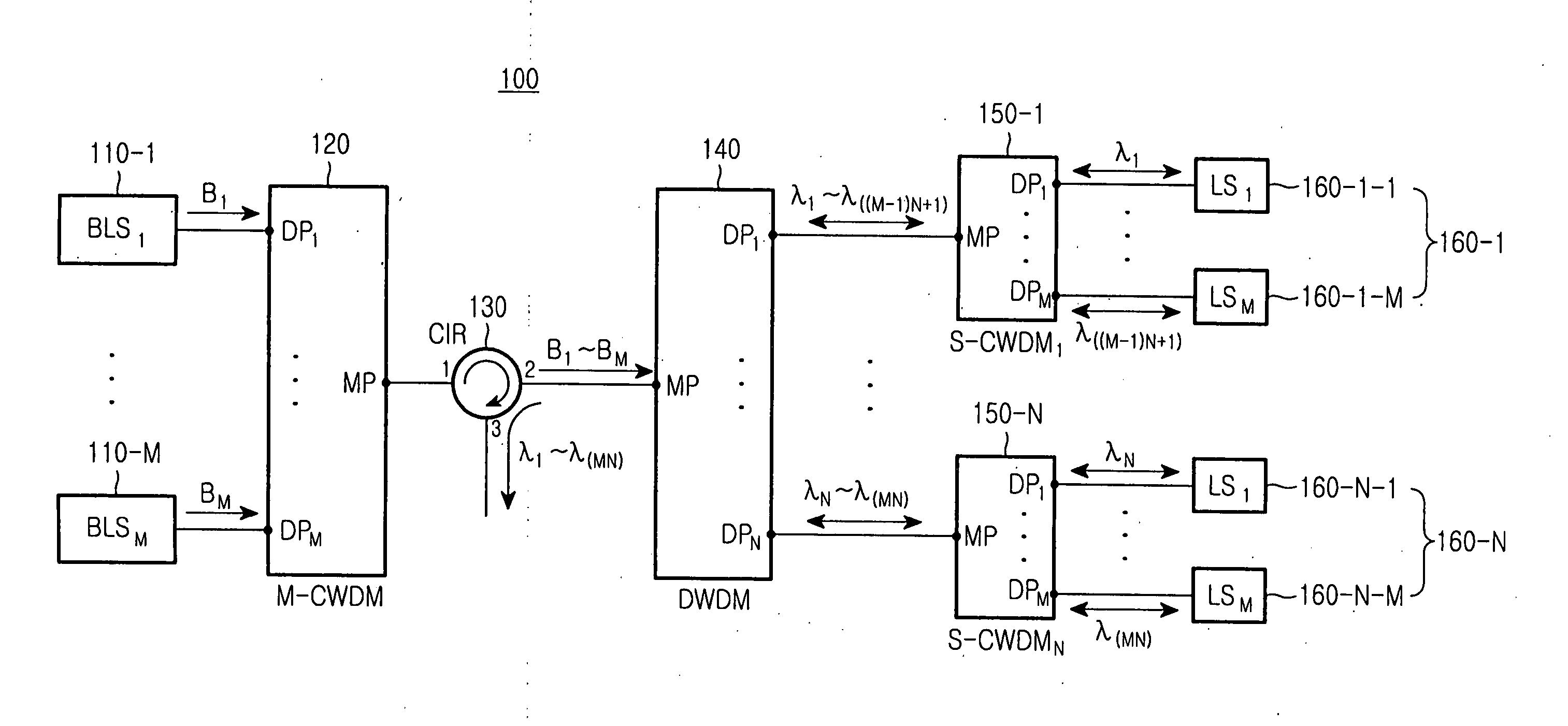
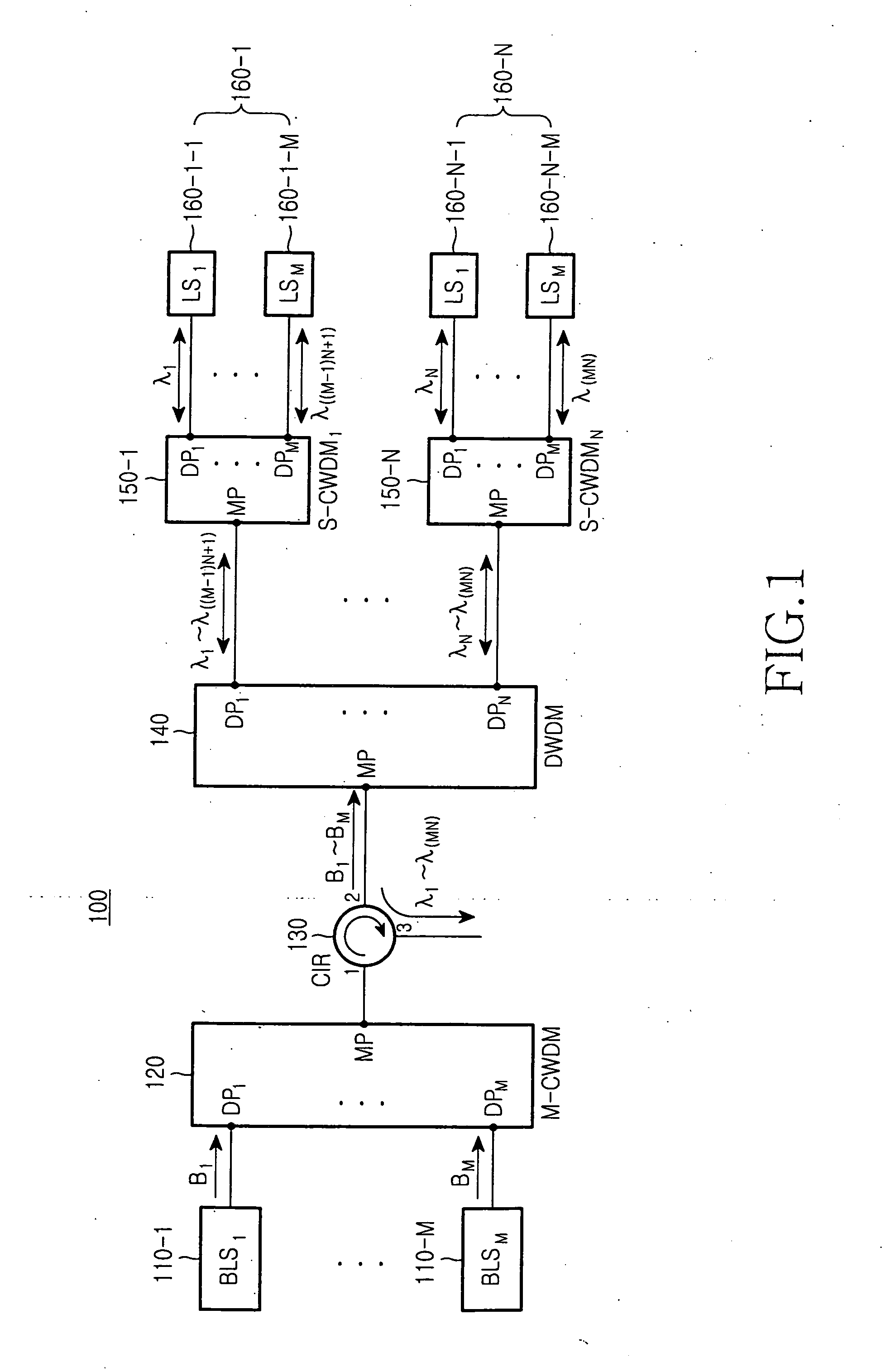
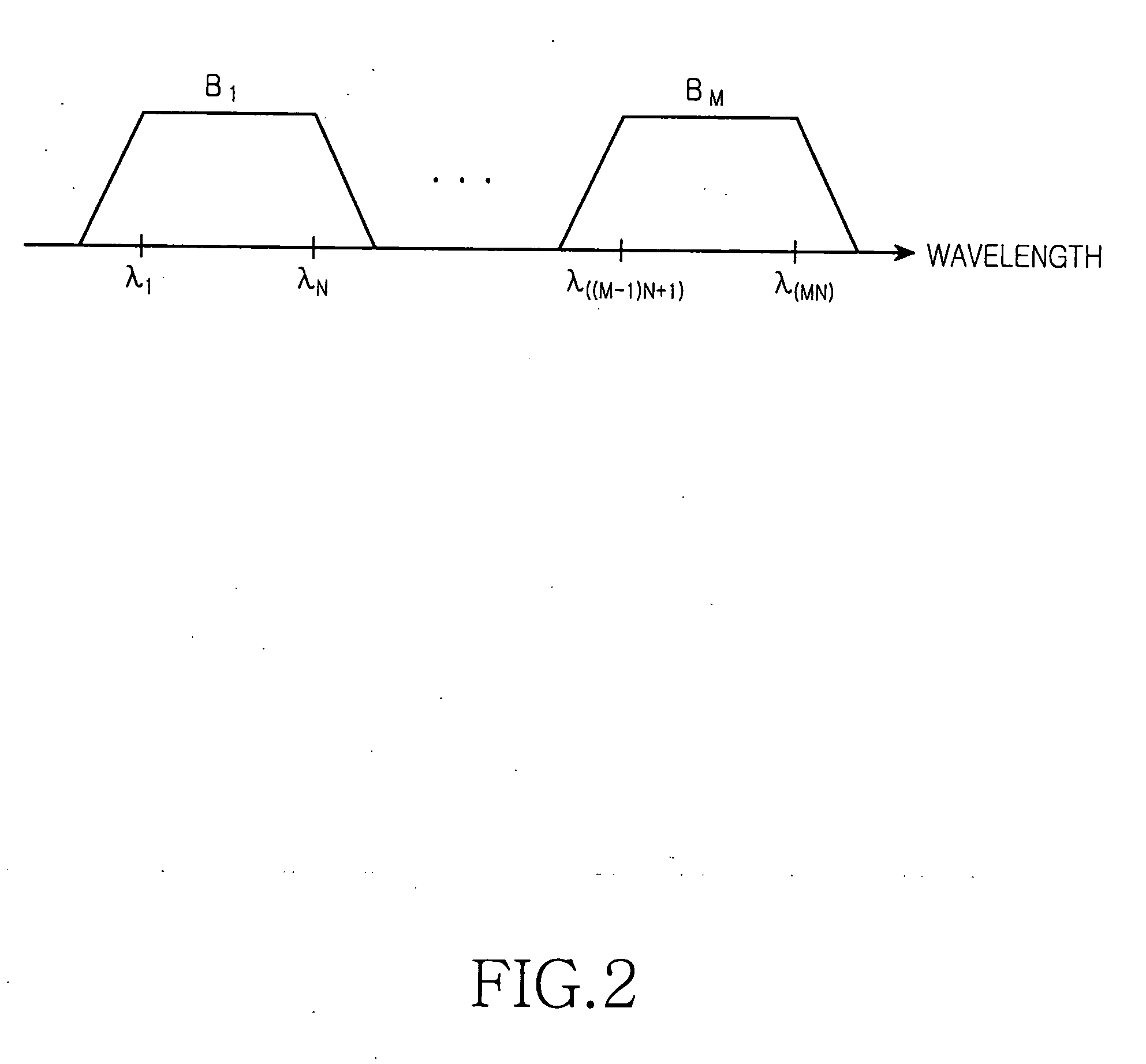
A wavelength division multiplexed light source for a passive optical network using the same includes broadband light sources arranged at a desired interval on a wavelength axis, so as to output wavelength bands each having a plurality of structural wavelengths. Further included is a main coarse wavelength division multiplexer (M-CWDM) for multiplexing the lights and a dense wavelength division multiplexer (DWDM) for spectrally dividing the multiplexed light into the channels corresponding to structural wavelengths of the multiplexed light. Groups are consequently generated each of which has a plurality of channels spaced at wavelength period.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
OFDM (orthogonal frequency division multiplexing)-based WDM (wavelength division multiplexing)-PON (positive optical network) system and downlink data transmission method
InactiveCN102238130AImprove transmission distanceGuaranteed communication qualityWavelength-division multiplex systemsMulti-frequency code systemsData streamEngineering
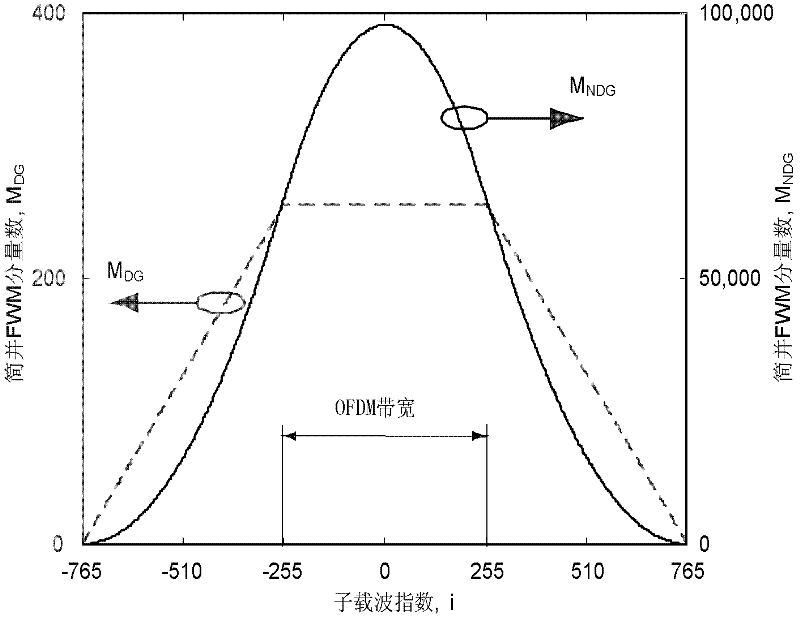
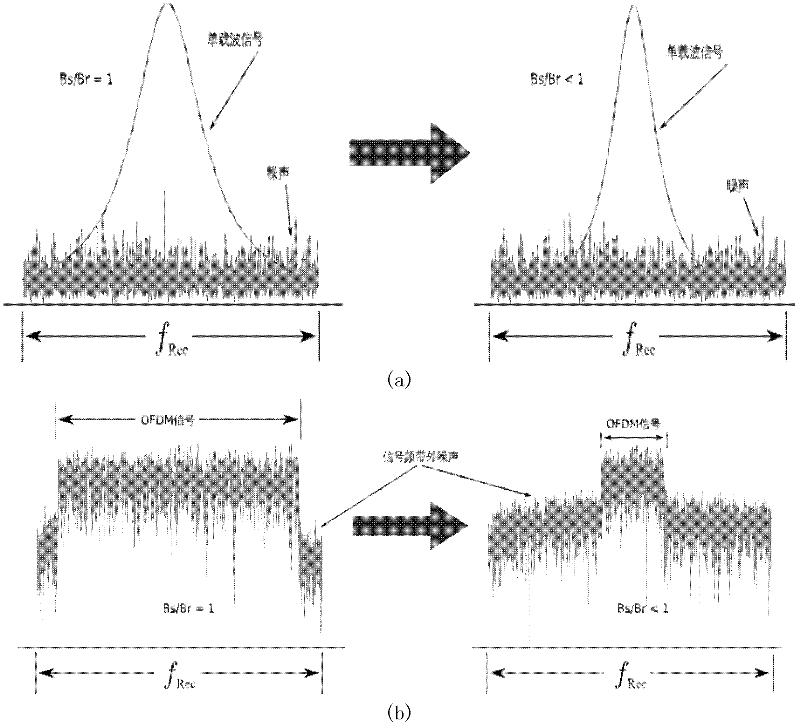
The invention provides an OFDM (orthogonal frequency division multiplexing)-based downlink data transmission method of a WDM (wavelength division multiplexing)-PON (passive optical network), and a system for implementing the method, wherein the method has longer transmission range and can effectively restrain an FWM (four wave mixing) effect. Each downlink sending module of an optical line terminal performs OFDM modulation on a downlink data stream, and converts generated base band OFDM signals up to an optical domain so as to form downlink optical signals; the downlink optical signals output by the downlink sending module of the optical line terminal have different wavelengths, an optical multiplexer / demultiplexer multiplexes the downlink optical signals output by each downlink sending module into one path of optical signals; and the downlink sending module keeps subcarriers at the central part of an OFDM frequency band vacant while performing the OFDM modulation. The downlink sending module keeps a central frequency band with serious FWM component vacant while performing the OFDM modulation, and the central frequency band is no longer used for carrying valid data, so that the downlink data transmission is less influenced by the FWM effect, and power for generating component of the FWM is greatly reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Coarse wavelength division multiplexing optical transmission system, and coarse wavelength division multiplexing optical transmission method
ActiveUS7831118B2Increase the number ofAvoiding reduction in transmission qualityWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesMultiplexerLength wave
In a CWDM optical transmission system of the present invention, in place of an optical signal of at least one wave among a plurality of optical signals corresponding to a CWDM system, a DWDM light output from an additional light transmission unit of a DWDM system is given to a multiplexer via a variable optical attenuator, and multiplexed with the optical signals corresponding to CWDM, to be sent out to a transmission path. At this time, the total power of the DWDM light sent out to the transmission path, is attenuated by the variable optical attenuator, so as to be approximately equal to the power per one wavelength of the CWDM light. On an optical reception terminal, the light propagated through the transmission path is demultiplexed by a demultiplexer, and the DWDM light corresponding to the additional wavelengths is amplified by an optical amplifier and thereafter, received by an additional light reception unit. As a result, the addition of optical signals in the CWDM system can be realized at low-cost, while avoiding the reduction in transmission quality.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Mixed integral single fibre three-way device
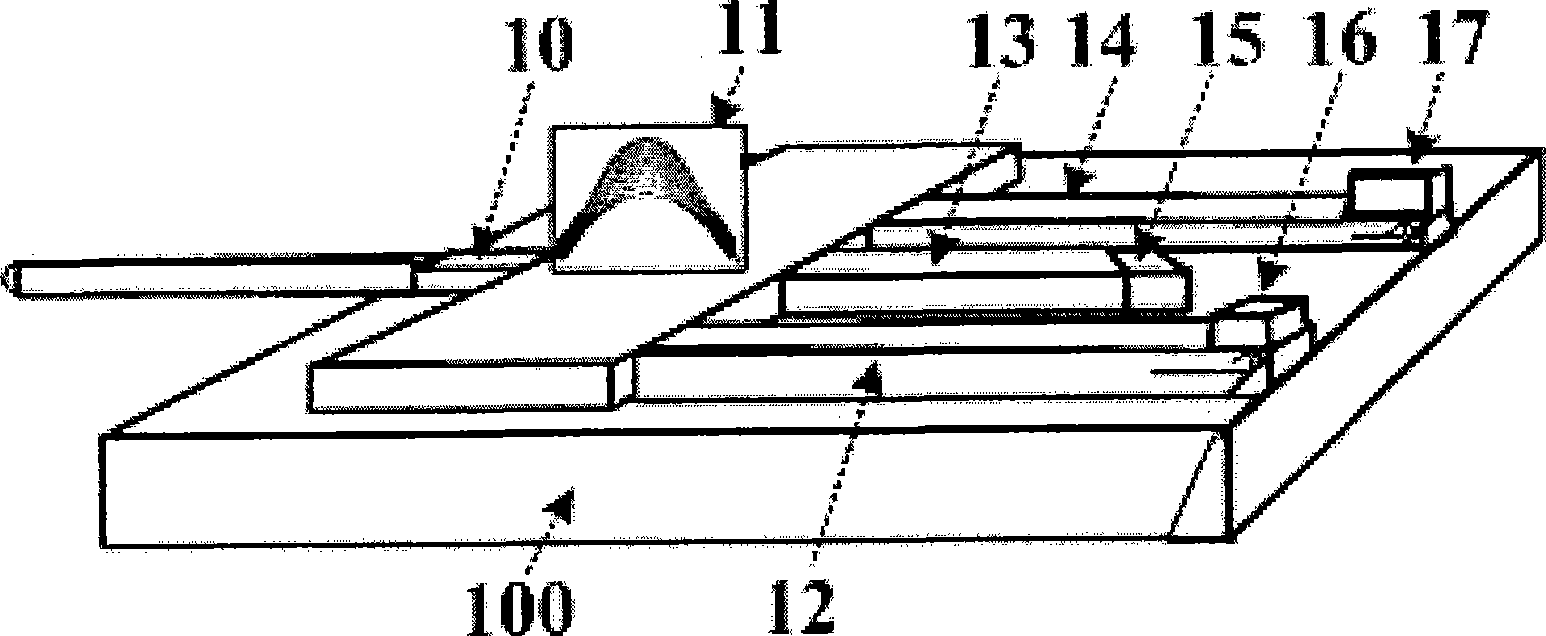
InactiveCN101464540ALow costReduce the difficulty of hybrid integration processCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionSingle fibreCoarse wavelength division multiplexing
The invention provides a hybrid integrated single-fiber three-direction device which comprises a substrate (100), a coarse wavelength division multiplexing array wave-guide optical grate (11), a first input wave guide (10), a first output wave guide (12), a second output wave guide (14), a second input wave guide (13), a laser (15), a first monitoring surface detector (16) and a second monitoring surface detector (17). The hybrid integrated single-fiber three-direction device simplifies the manufacture process, saves the cost, and can be used in low-cost EPON or GPON optical networks.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com