System for realizing network extension and protection functions with wave-division multiplexing annular optical access networks and method for realizing network extension and protection functions with wave-division multiplexing annular optical access networks
A technology of wavelength division multiplexing and network expansion, applied in the field of optical communication, which can solve the problems of inability to dynamically schedule the system and inconvenient scheduling of system wavelengths.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
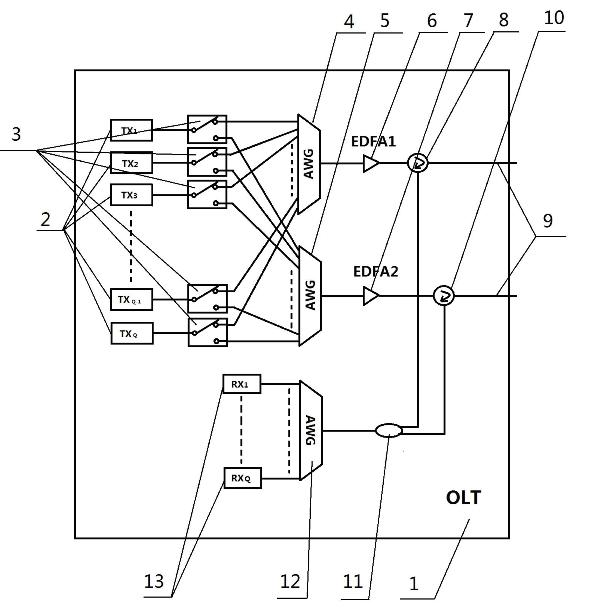
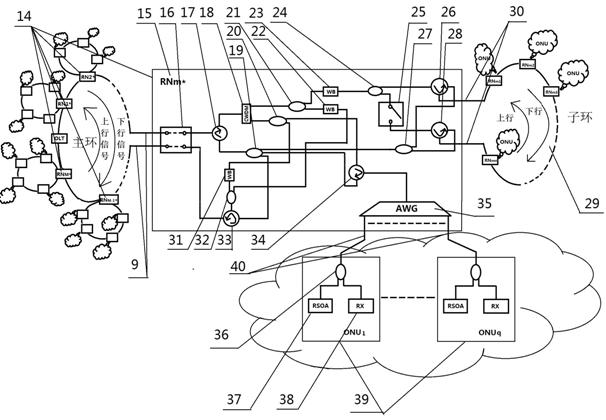
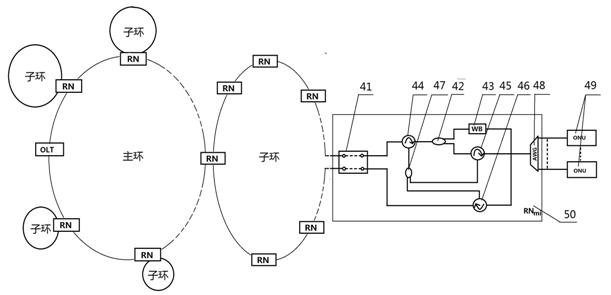
[0035] see Figure 1~Figure 4 , this wavelength division multiplexing ring wavelength division multiplexing ring optical access network realizes the system of network expansion and protection function, the optical link terminal OLT (1) connects M A main ring remote node RN (14) forms a ring structure, which is called a main ring here. Each remote node RN of the main ring a (14) Each sub-ring (29) is connected to each sub-ring (29) by connecting the optical fiber (15), and each sub-ring (29) is connected to n remote nodes RNb (5) Connected, the remote node RN of the main ring a and the remote node RN on each sub-ring b (15,16) respectively connect q optical network units ONU through distribution optical fiber (55) b (49); and, the main ring (1) passes each main ring remote node RN a (14) Directly connect q optical network units ONU a It is characterized by:
[0036] 1) The optical link terminal OLT (1) has Q optical transmitters (2) respectively connected to two arrayed w...
Embodiment 2
[0042] This WDM ring optical access network realizes network expansion and protection function method, adopts the system of embodiment 1 to operate as follows:
[0043] 1) There are Q wavelengths belonging to C-band and L-band, among which the wavelengths of C-band are supplied to each remote node RN on the main ring (1) a (14) Directly connected optical network unit ONU a (39) use, the L-band wavelength is for the remote node RN of each sub-ring b Optical Network Unit ONU under (50) b (49) USED. where in normal mode, such as Figure 5 As shown, in the downlink, the optical link terminal OLT (1) Q optical transmitters (2) send signals through Q optical switches (3) and then transmit them to the first arrayed waveguide grating AWG (4) for multiplexing, and then Through the first EDFA1 (6) and the optical circulator 1 (8), the output from its right port enters the main ring feeder fiber (9). Such as Image 6 As shown, the downlink signal is transmitted clockwise in the mai...
Embodiment 3
[0048] The wavelength division multiplexing ring optical access network realizes the network expansion and protection function method, adopts the system of embodiment 1 to operate as follows:
[0049] 1) if Figure 8 , Figure 9 As shown in , when the sub-ring feeder fiber fails, the corresponding main ring remote node RN a (14) When working in protection mode: here to convert the remote node RN m* (15) and its connected sub-ring (29) as an example, when the feeder fiber fails, the remote node RN m* The optical switch (25) receives the control signaling from the optical link terminal OLT (1), and is in the closed state. At this time, for Figure 9 , sub-ring remote node RN m1 The downlink and uplink transmissions are still transmitted in the above way; for RN m2 ...RN mn The downlink signal λ m21 ...λ m2q ...λ mmq ...λ mnq From remote node RN m* The optical switch (25) reaches the third optical circulator (28), is input from its left port, and the output from the lo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com