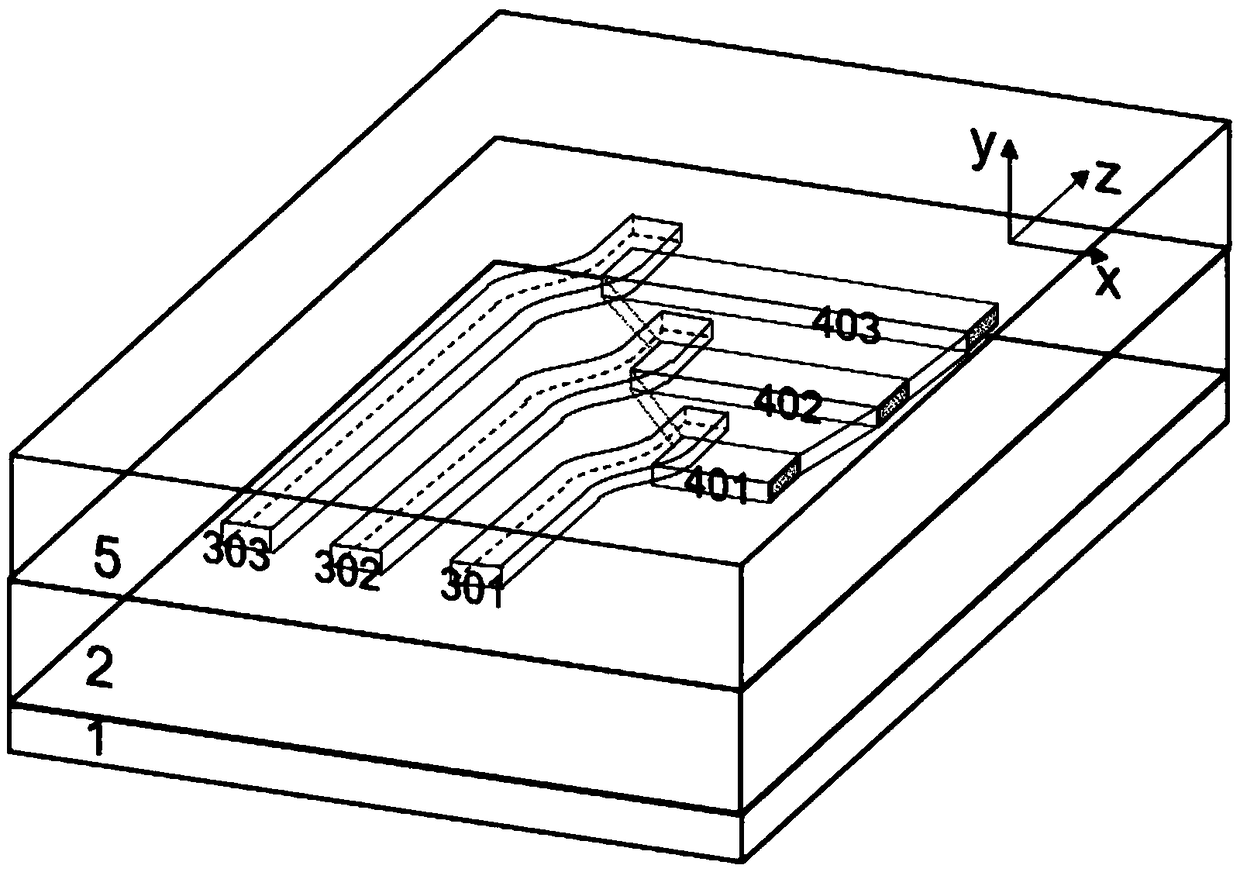
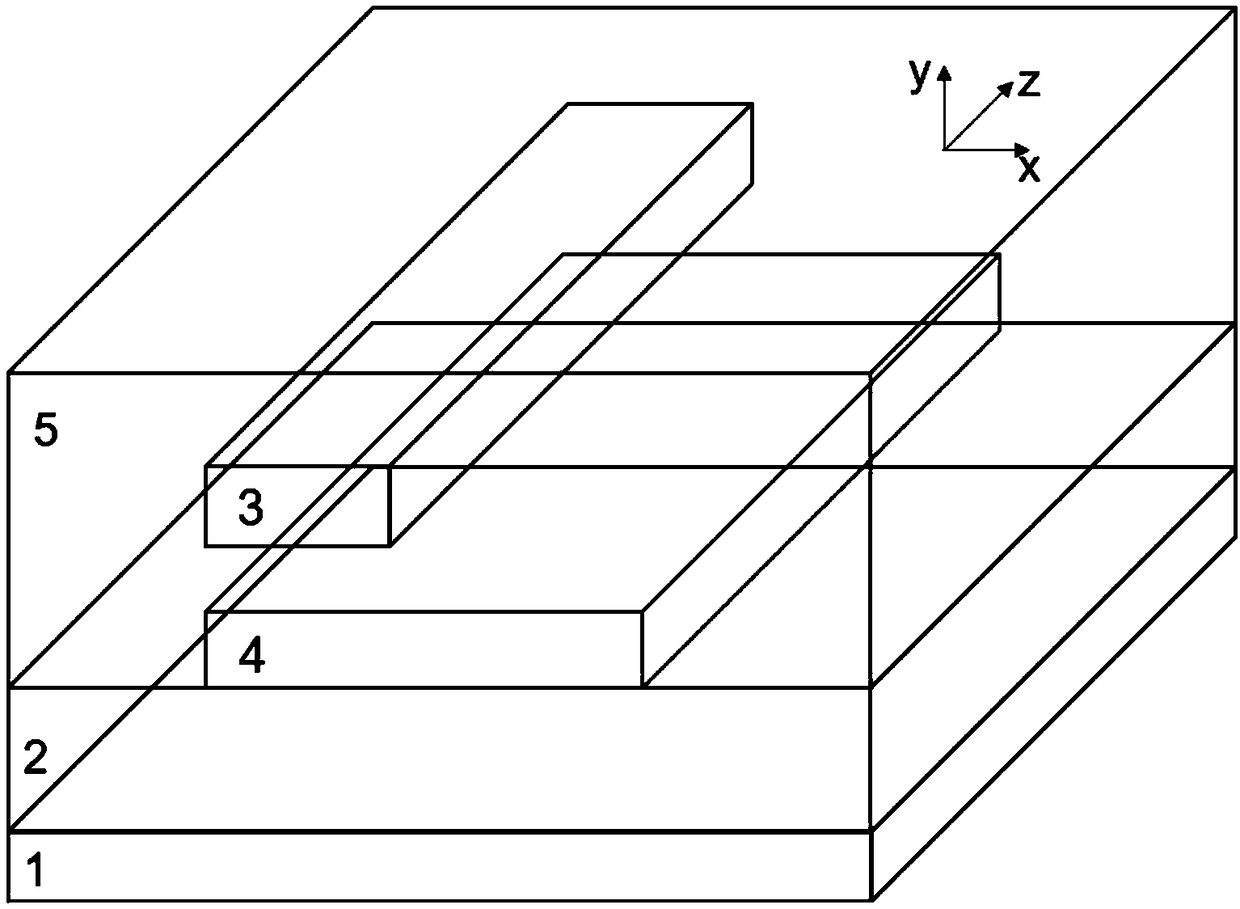
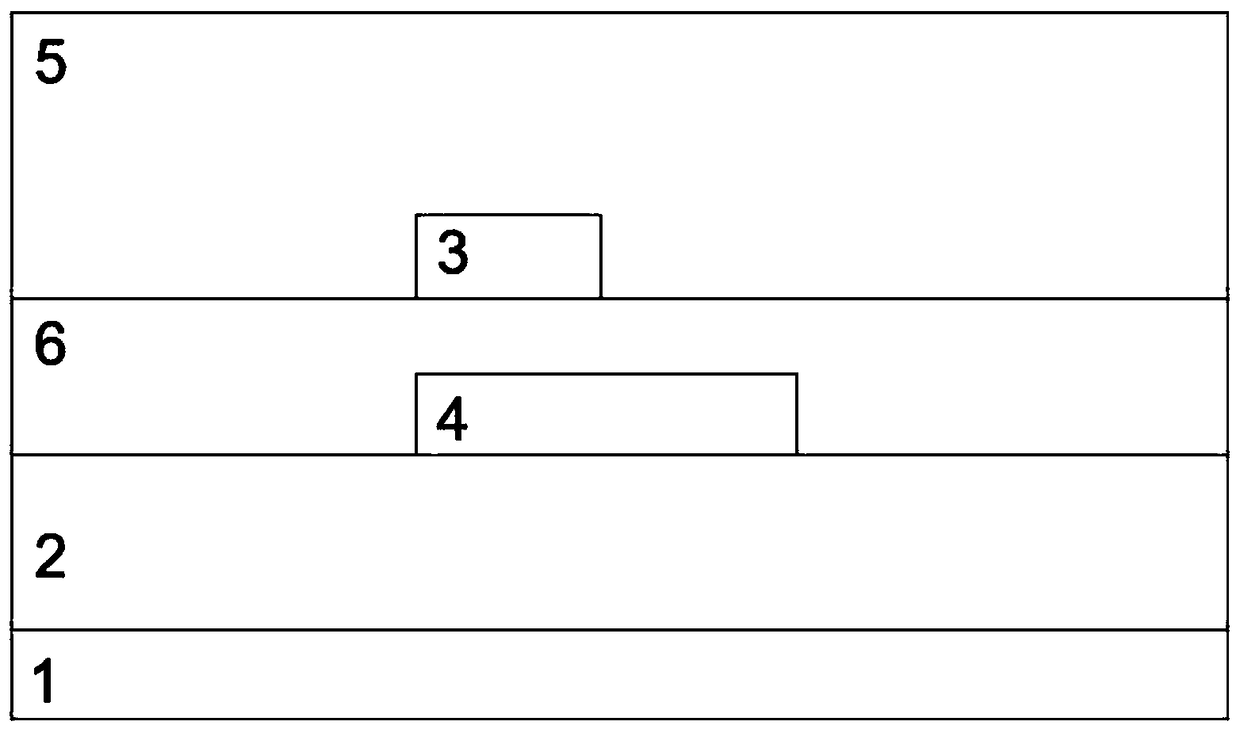
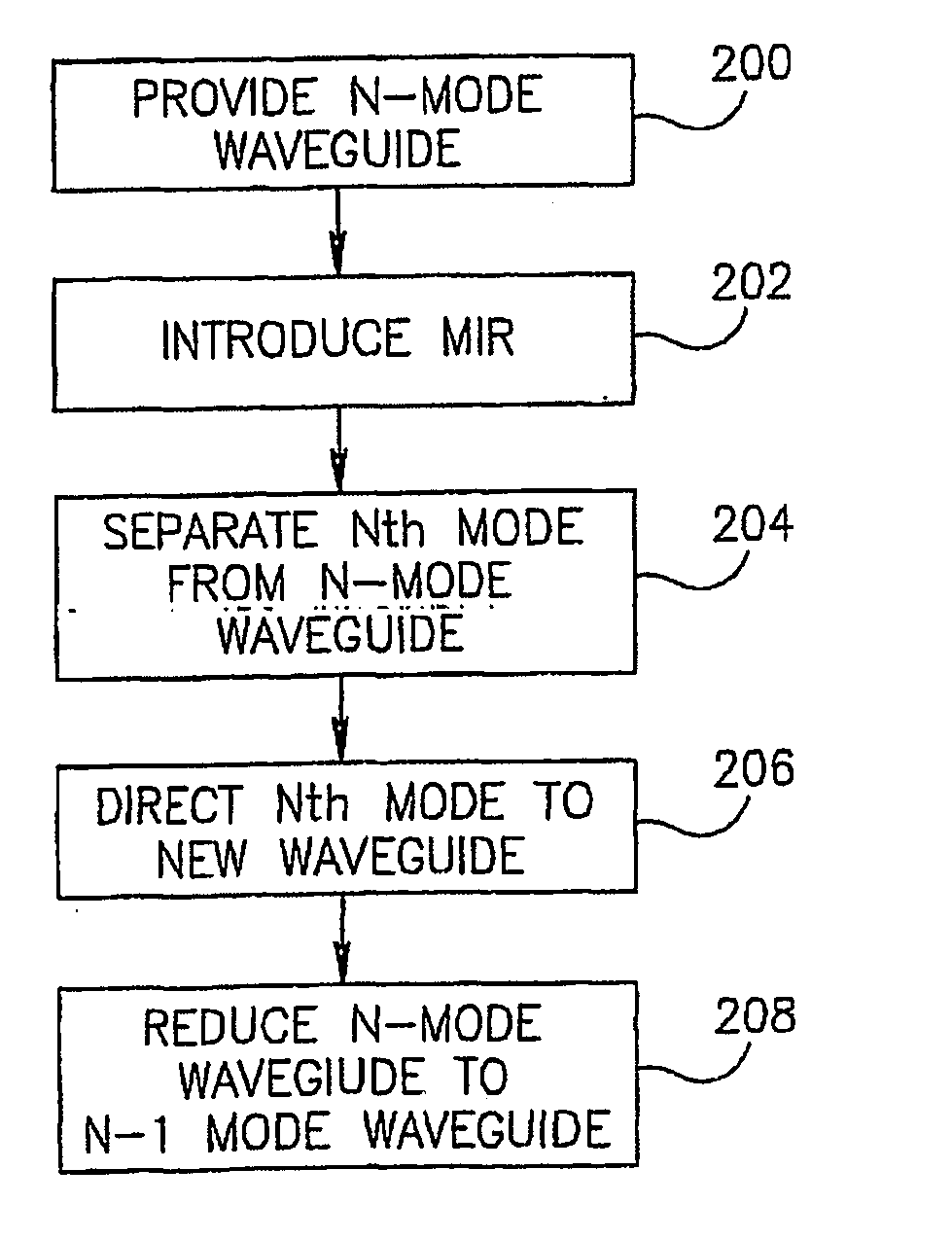
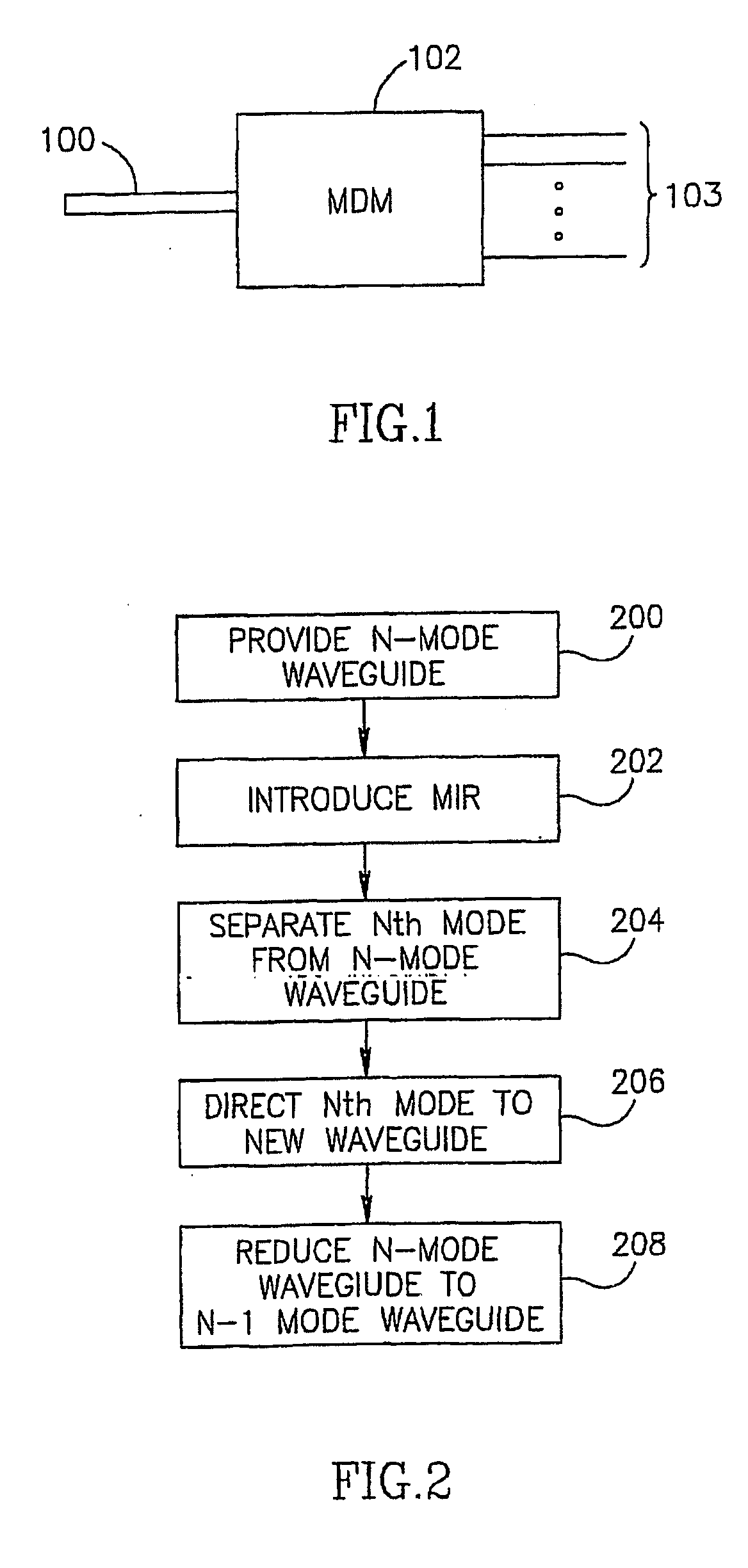
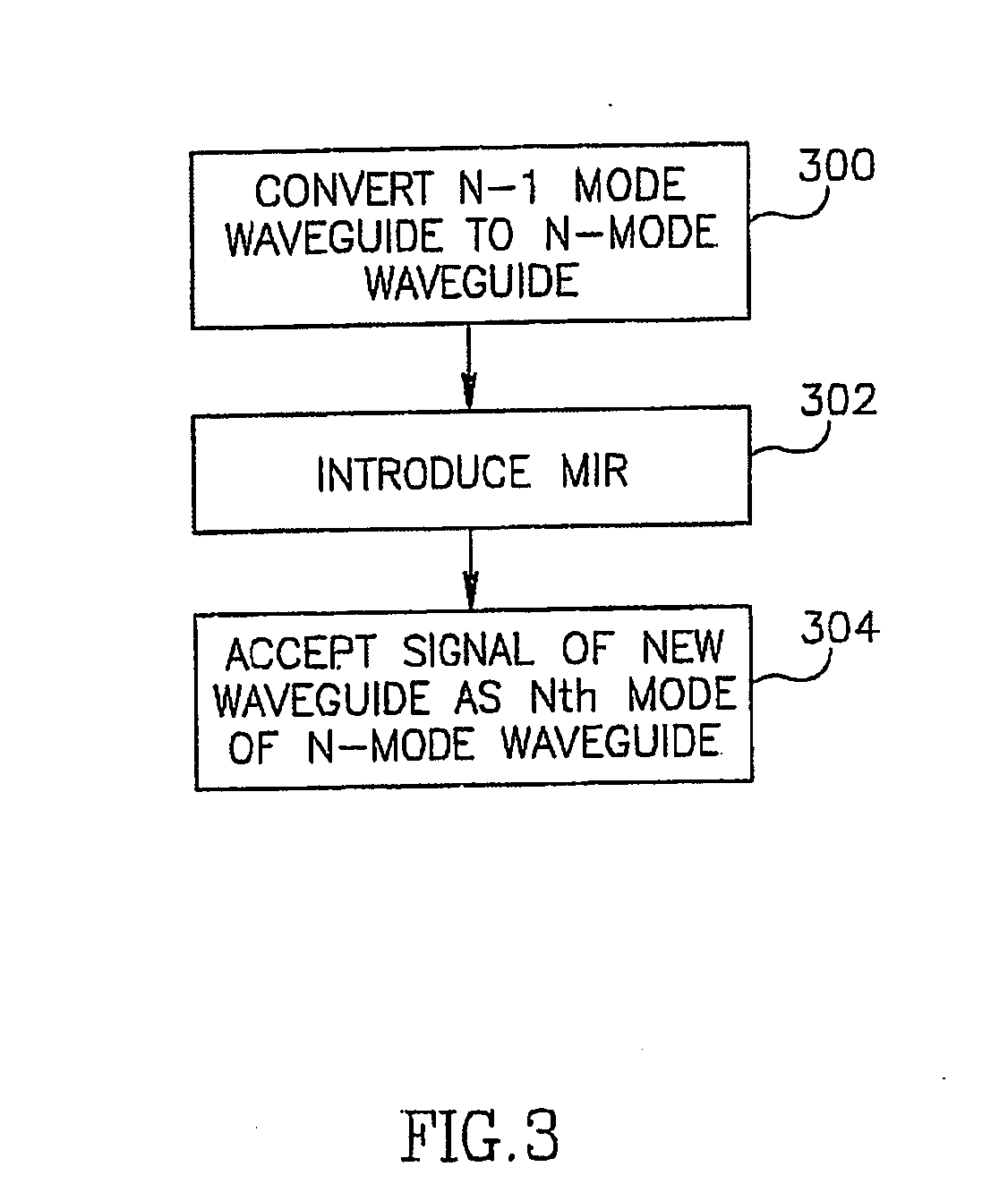
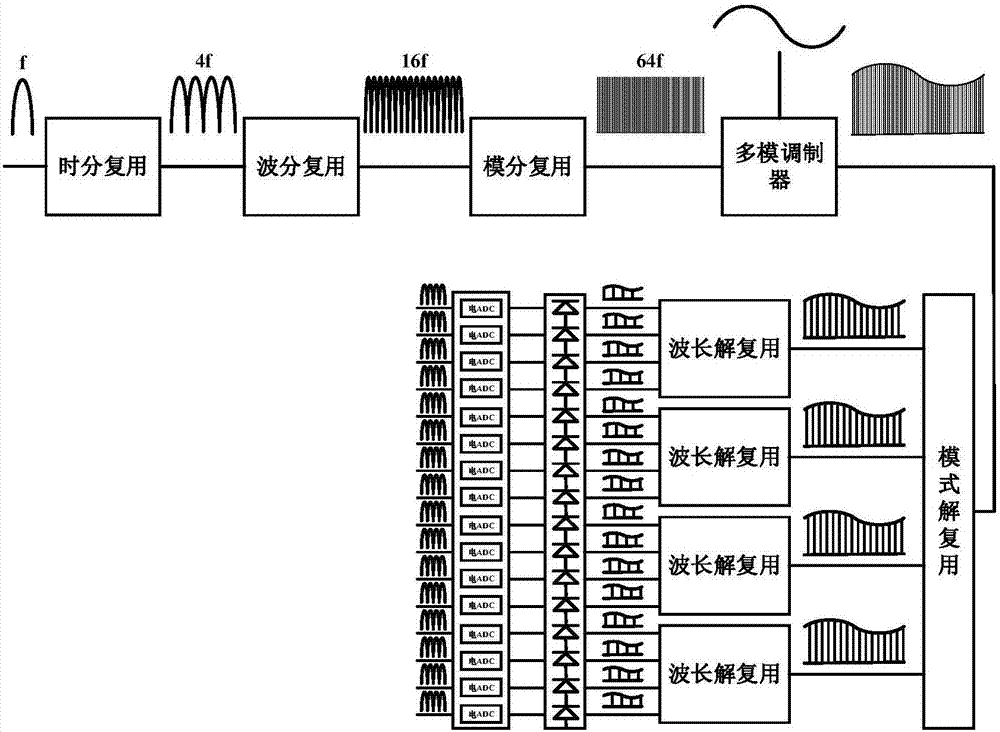
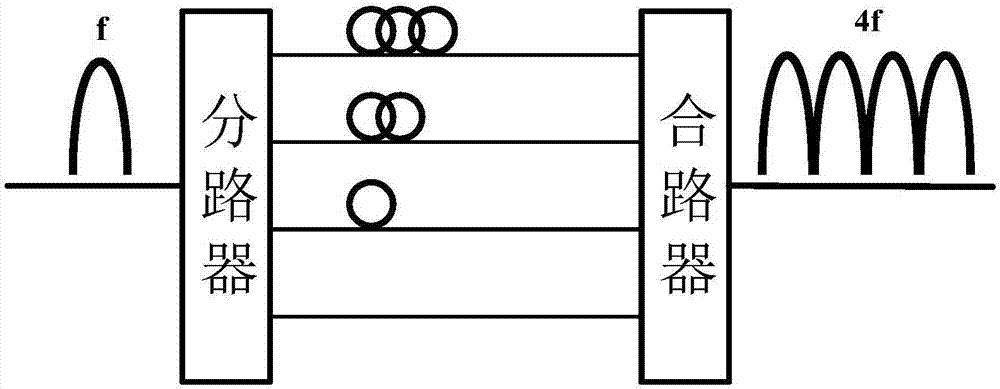
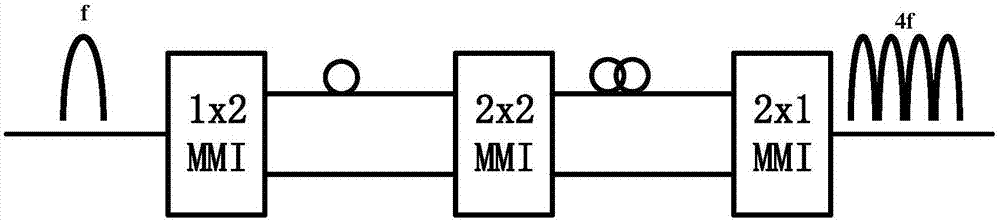
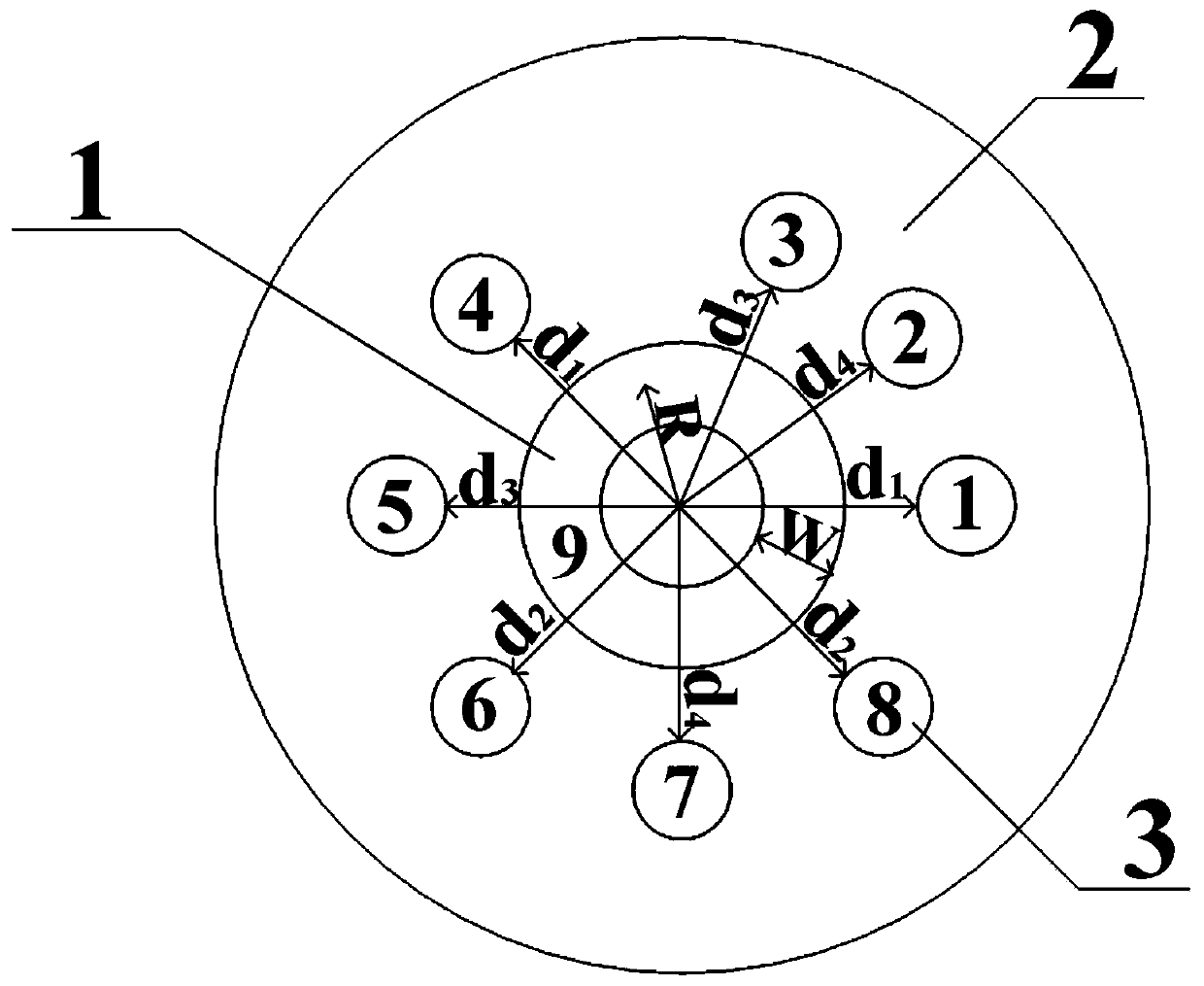
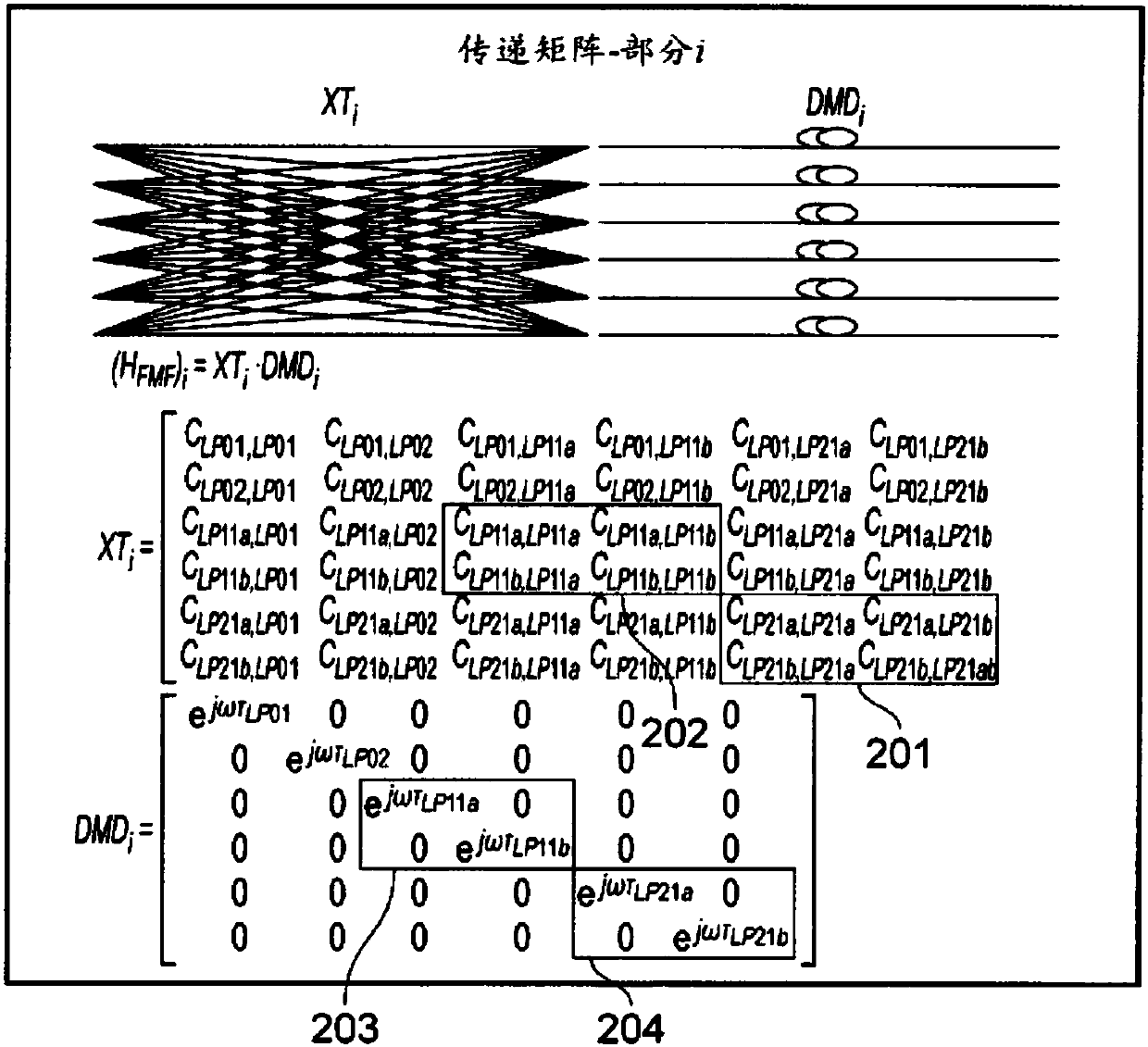
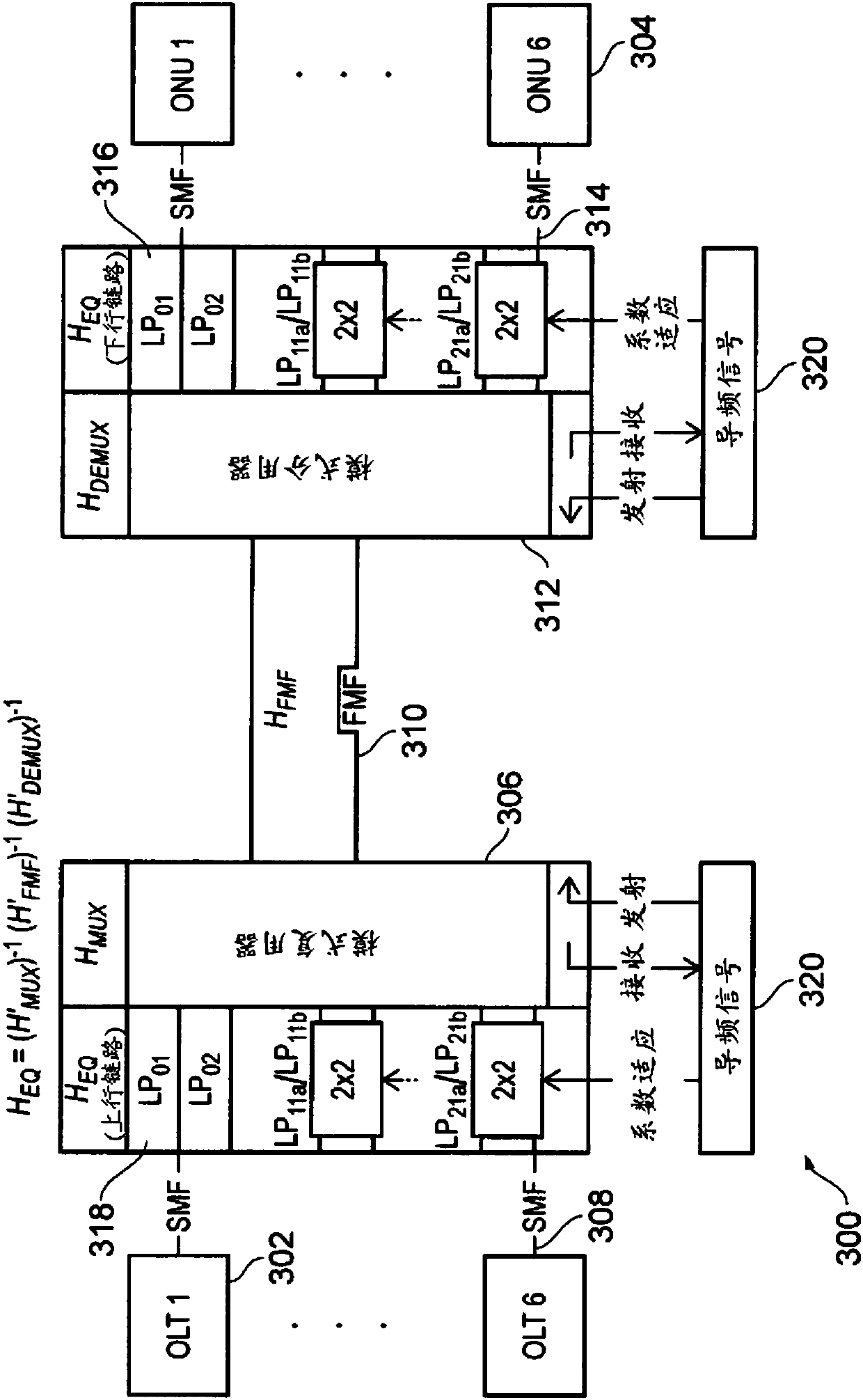
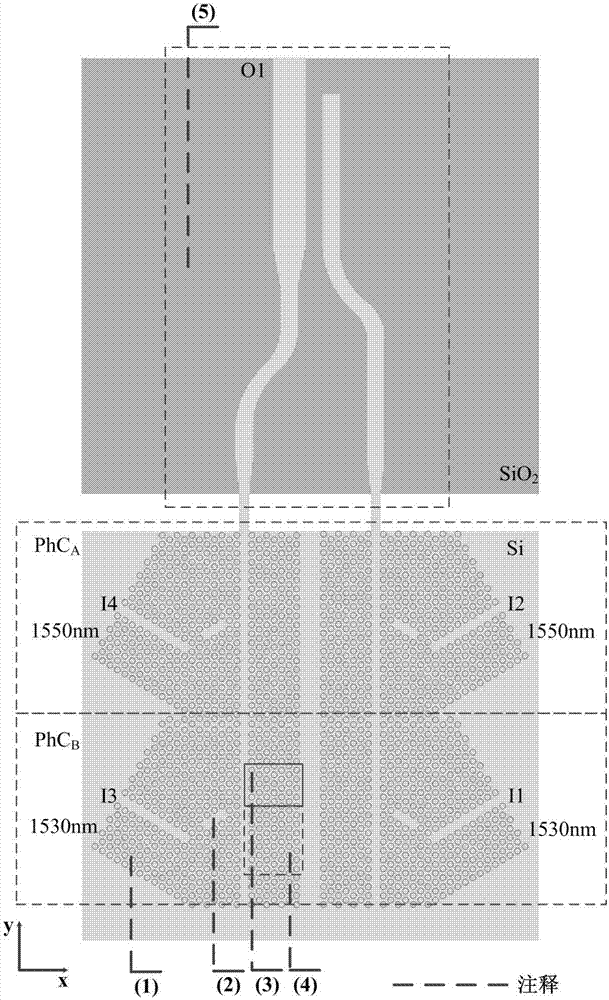
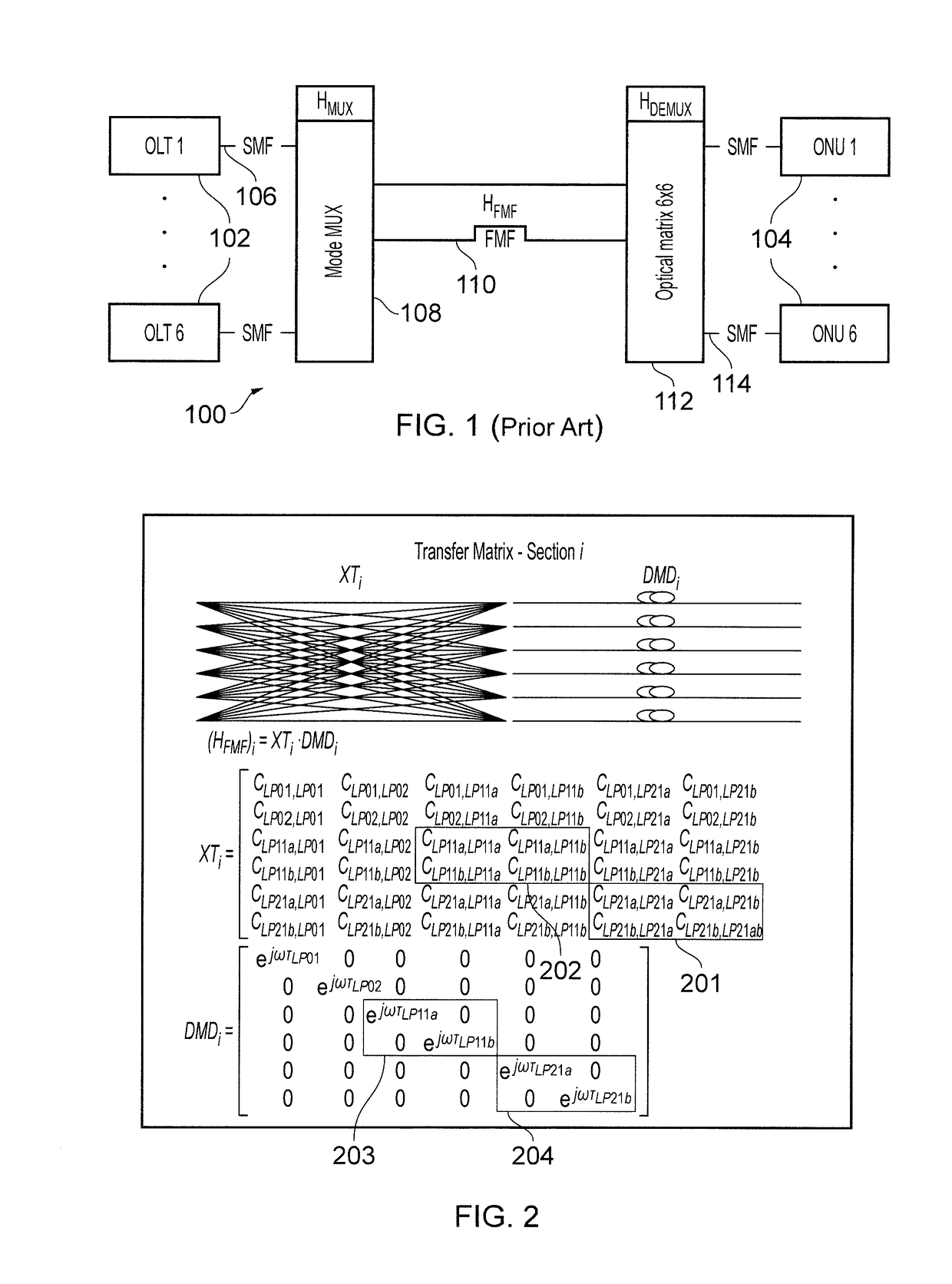
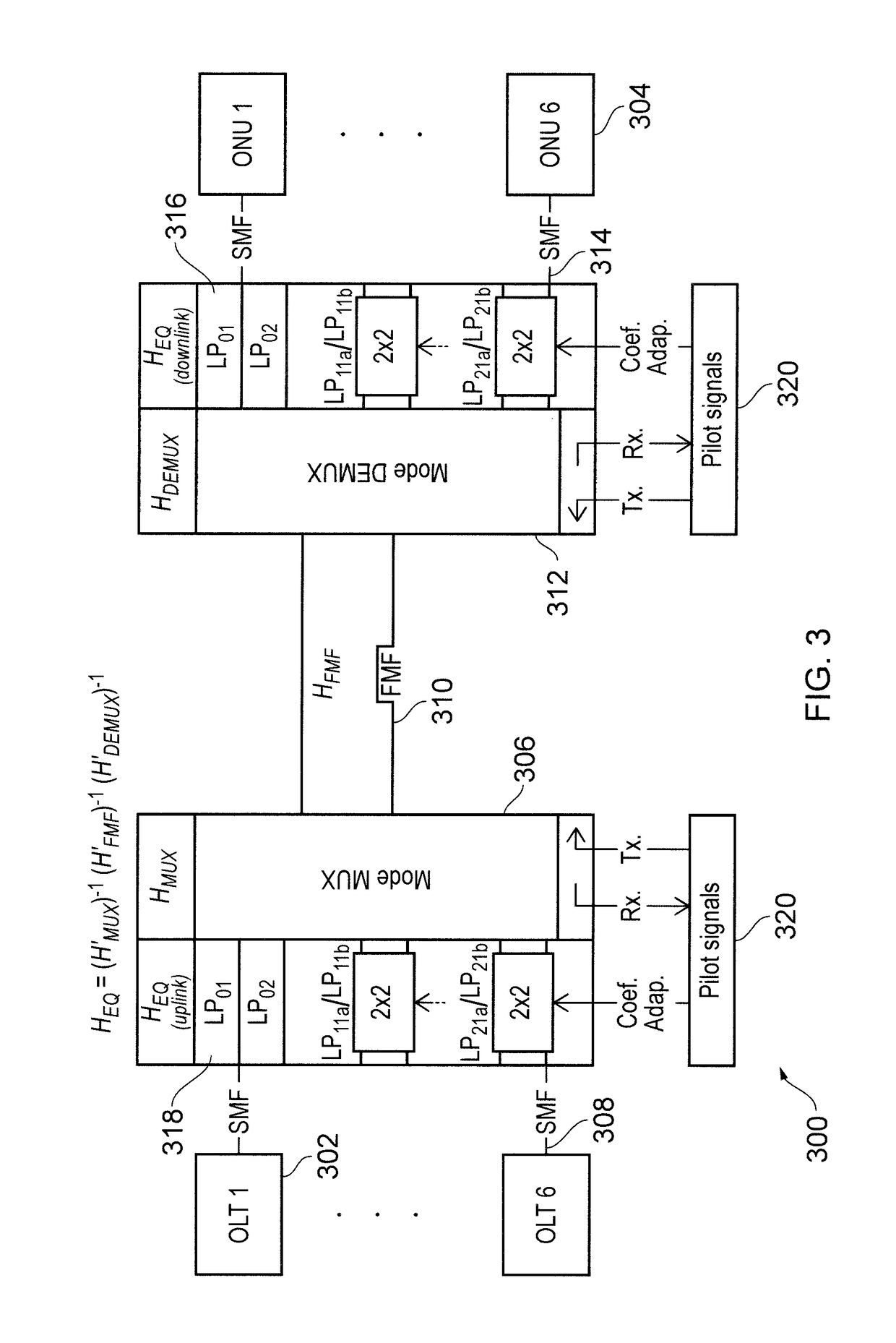
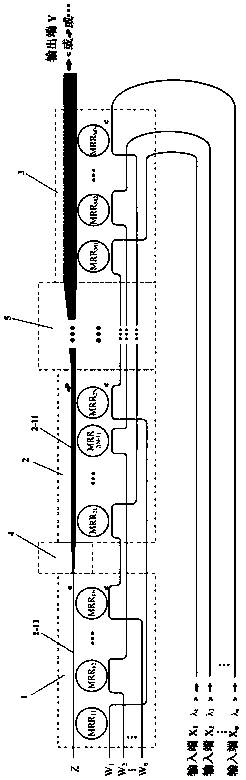
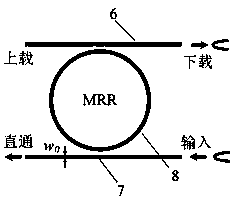
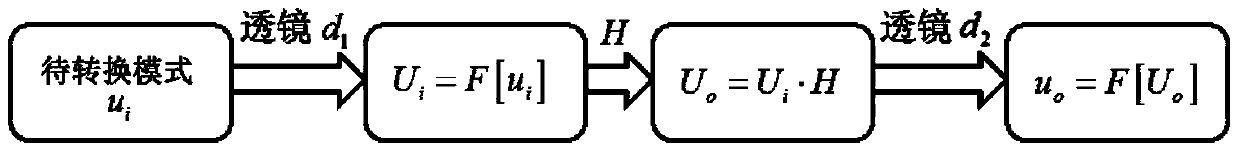Patents
Literature
172 results about "Mode division multiplexing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
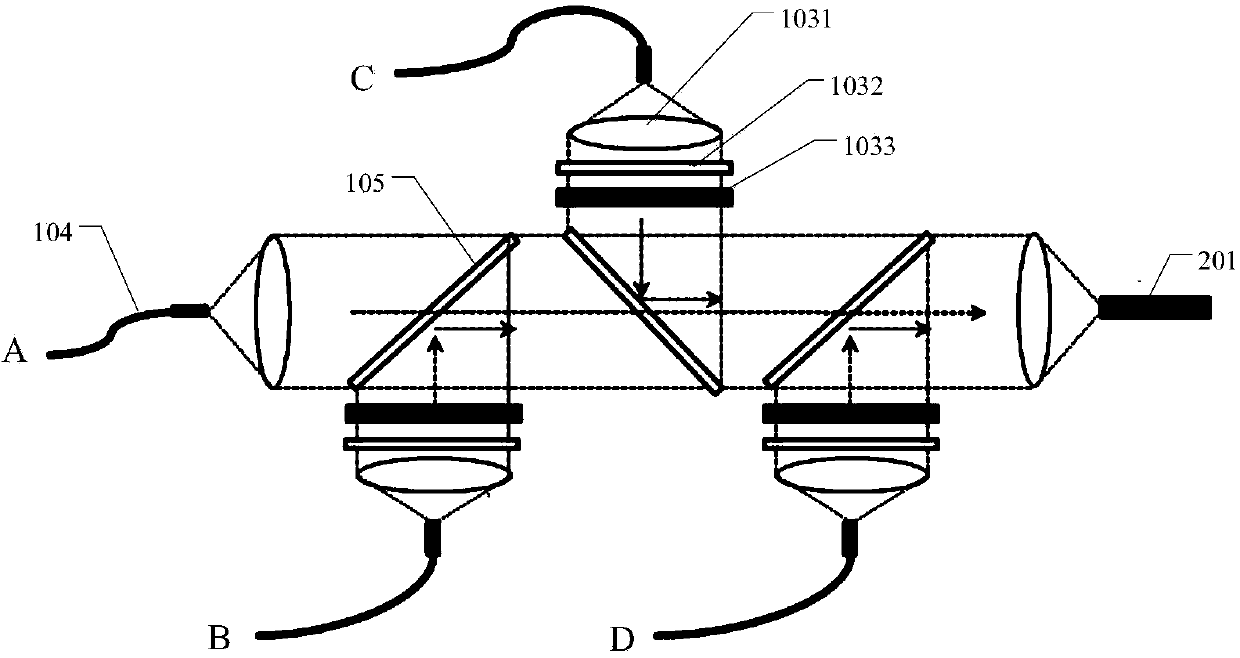
Self-correlation optical fiber communication system based on mode division multiplexing
ActiveCN103095373AImprove spectrum utilizationImprove nonlinear toleranceFibre transmissionElectromagnetic receiversFrequency spectrumLine width
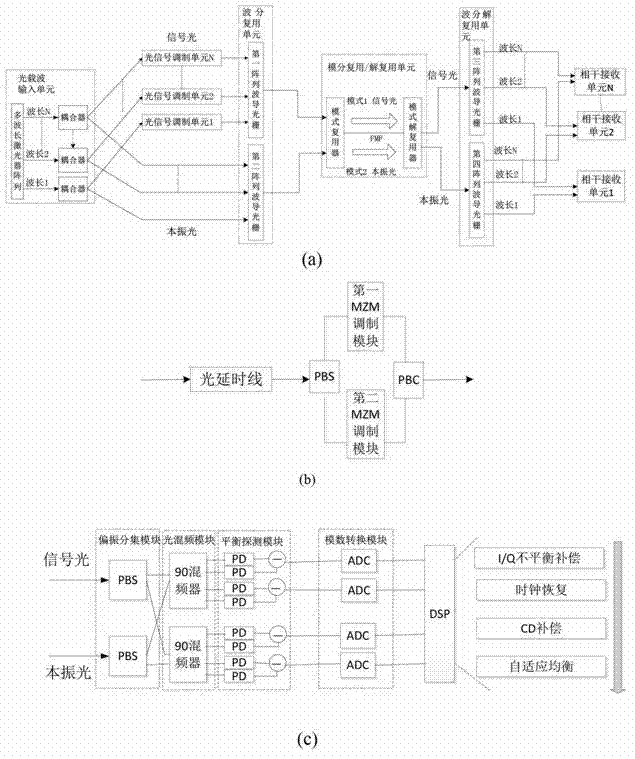
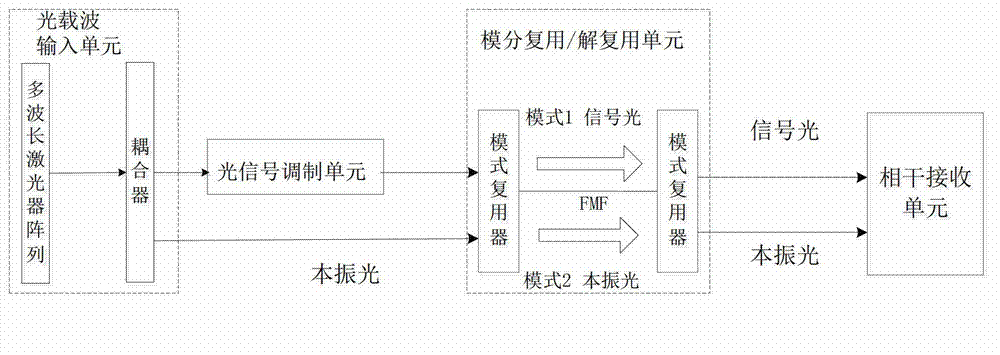
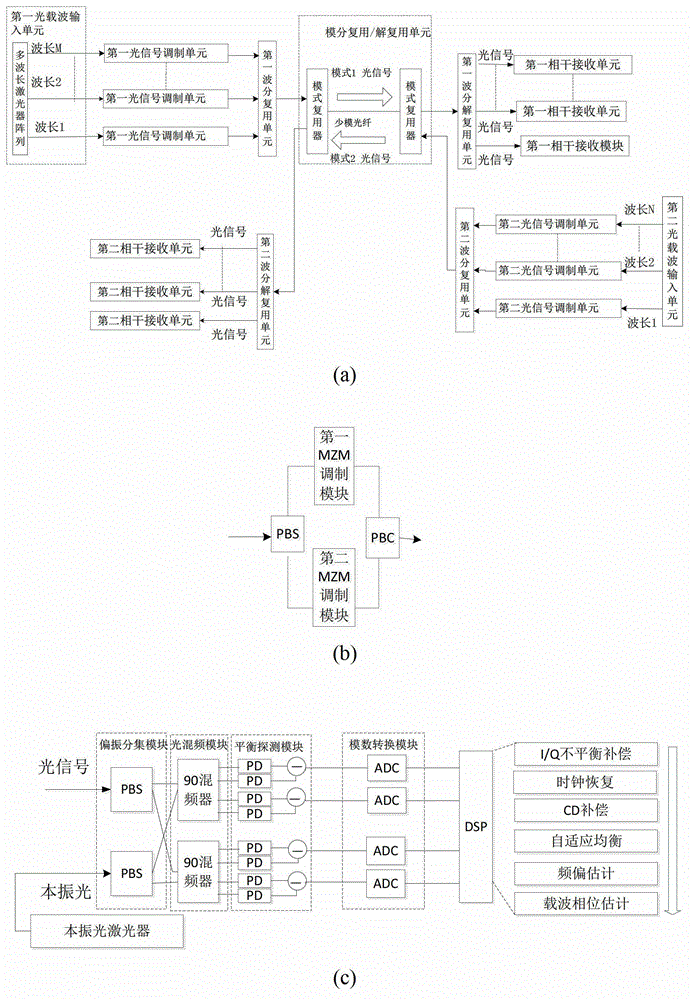
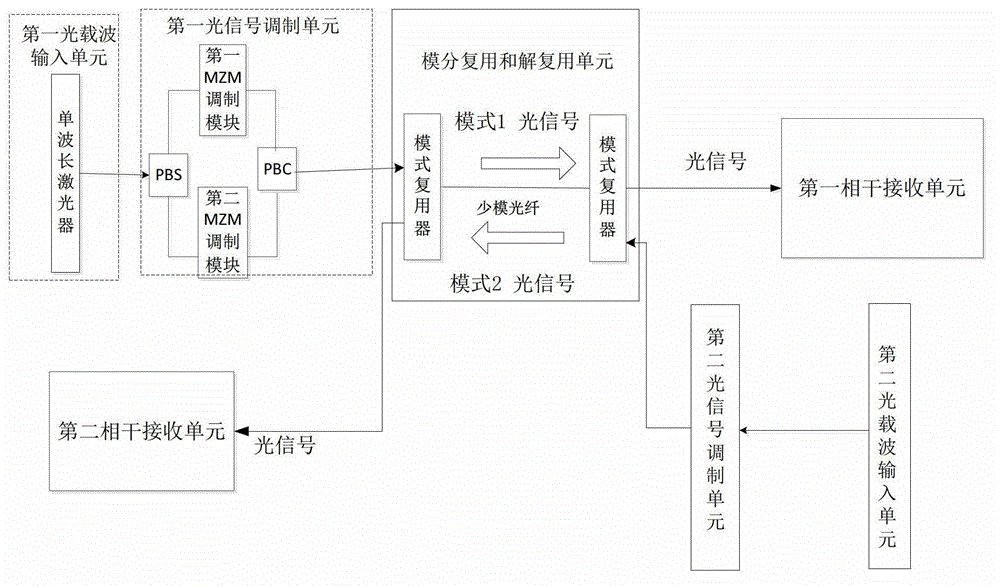
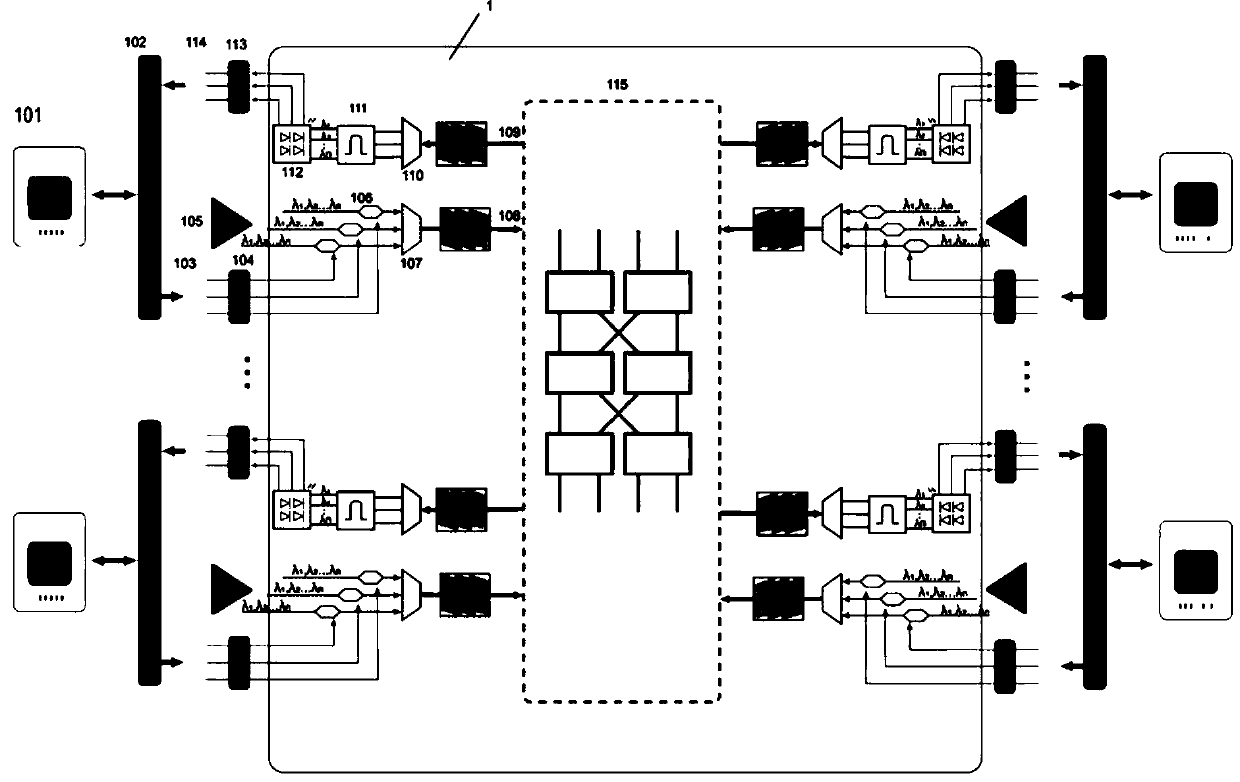
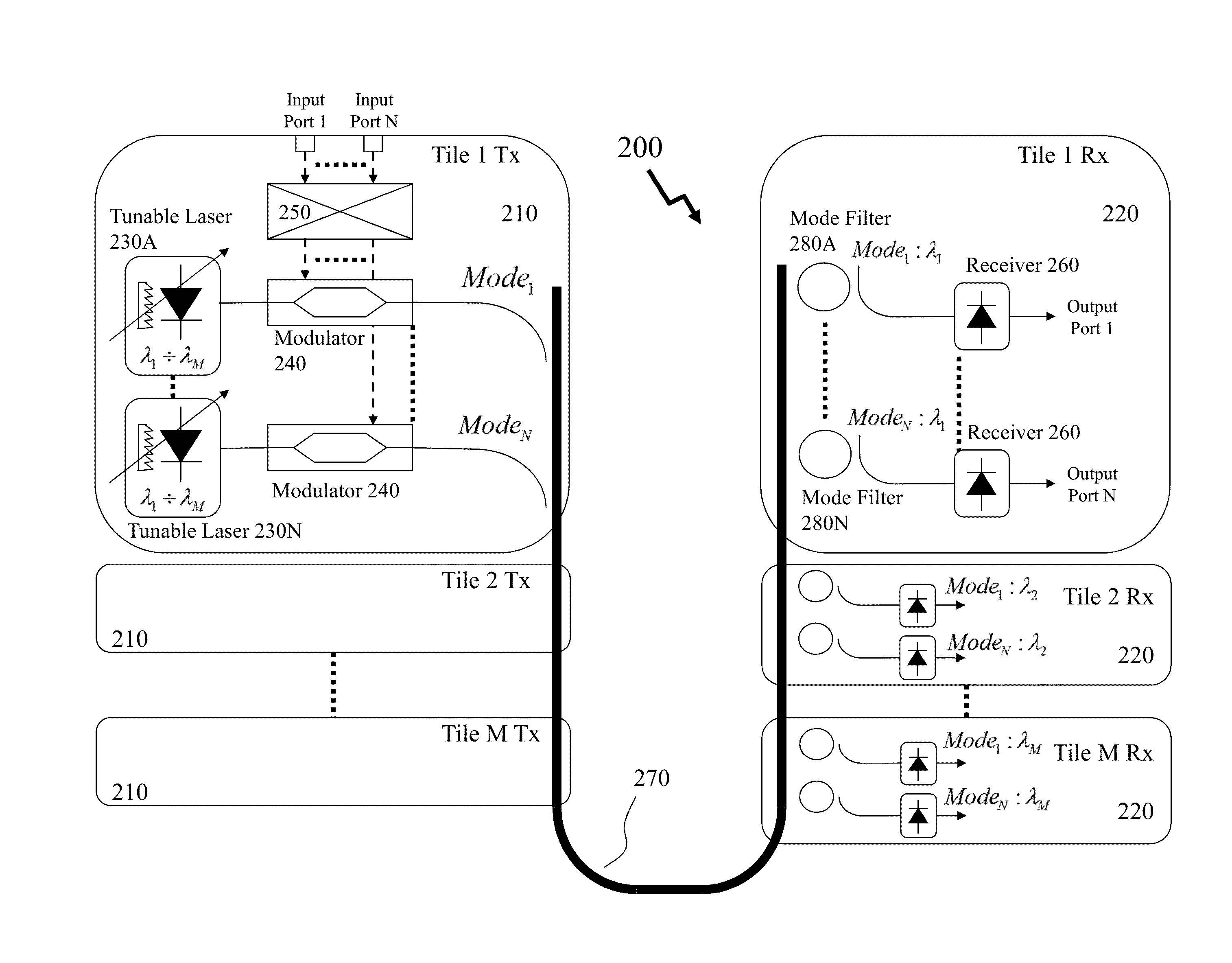
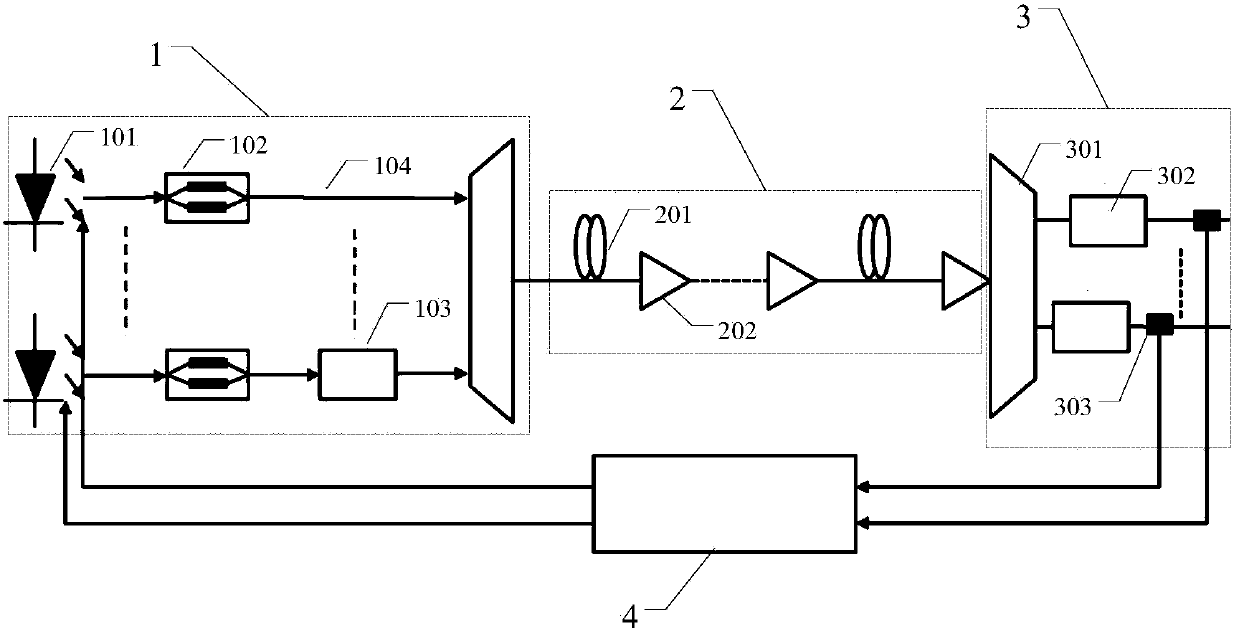
The invention discloses a self-correlation optical fiber communication system based on mode division multiplexing. The self-correlation optical fiber communication system based on mode division multiplexing comprises an optical carrier input unit, optical signal modulation units, a wavelength division multiplexing unit, a mode division multiplexing and demultiplexing unit, a wavelength division multiplexing unit and coherent reception units. The mode division multiplexing and reconciliation multiplexing unit comprises a mode multiplexer and mode demultiplexer, and the mode multiplexer and the mode demultiplexer are connected through few-mode optical fibers. The optical carrier input unit is connected with each optical signal modulation unit, the wavelength division multiplexing unit and the mode multiplexer through single-mode optical fibers. The mode multiplexer is connected with the mode demultiplexer through few-mode optical fibers. The mode demultiplexer is connected with the wavelength division multiplexing unit and each coherent reception unit through single-mode optical fibers. The optical carrier input unit is further connected with the wavelength division multiplexing unit. The self-correlation optical fiber communication system based on mode division multiplexing eliminates an expensive narrow line width adjustable local oscillator light source which is arranged at a reception end, enables a laser to be conveniently managed and maintained, is free from using frequency offset estimation in a digital signal processor (DSP) and phase retrieval algorithm, reduces complexity of the DSP and has the advantages of being high in spectrum effectiveness and big in nonlinearity tolerance.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Single-fiber bidirectional transmission system based on mode division multiplexing
ActiveCN103152099AOvercome backscatterImprove spectrum utilizationDistortion/dispersion eliminationPolarization diversityPolarization multiplexed
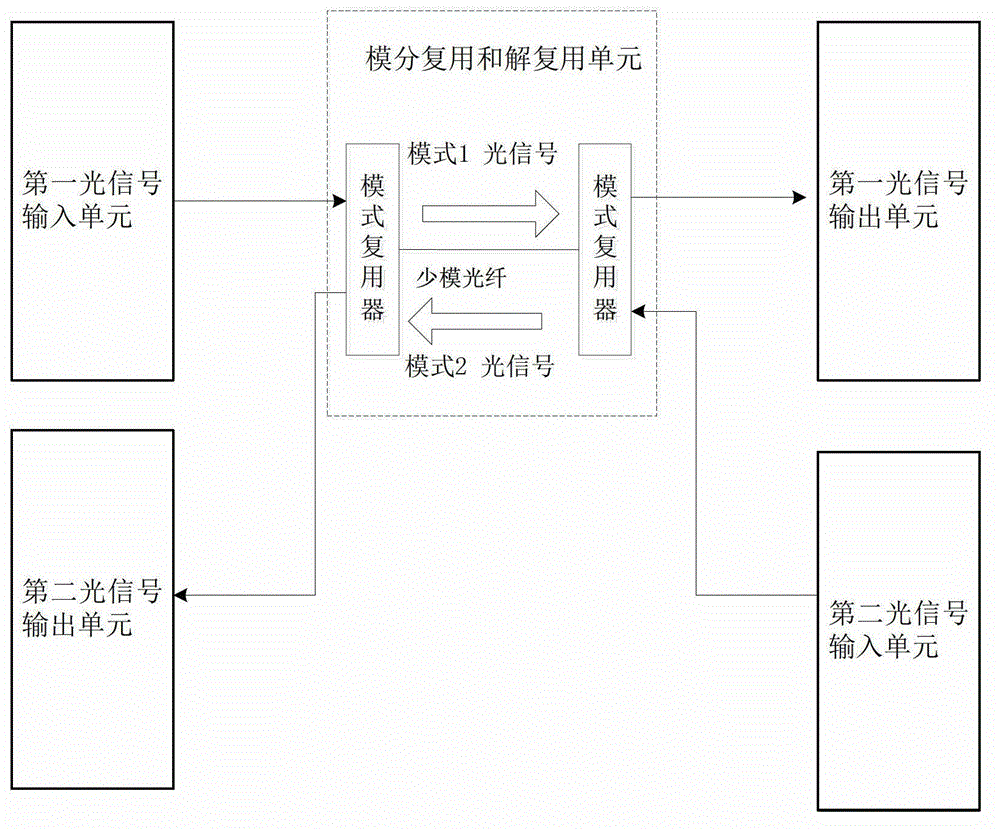
The invention discloses a single-fiber bidirectional transmission system based on mode division multiplexing. The single-fiber bidirectional transmission system based on the division multiplexing mainly comprises two optical signal input units, two optical signal output units and a mode division multiplexing and demultiplexing unit, wherein the mode division multiplexing and demultiplexing unit comprises two mode-type multiplexers which are connected through few-mode fiber. Polarization multiplexing optical signals are generated by the signal input units, the polarization multiplexing optical signals are enabled to be coupled into a mode field of the few-mode fiber by the mode-type multiplexer to finish the mode division multiplexing, the polarization multiplexing optical signals carried by the mode field are sent to the other mode-type multiplexer through the few-mode fiber, the received polarization multiplexing optical signals are enabled to be coupled into single-mode fiber by the other mode-type multiplexer and sent to the optical signal output units through the single-mode fiber, polarization diversity, mixing and balance detection are carried out on the received optical signals by the signal output units, then the received optical signals are changed into electric signals and then changed into digital signals. According to the single-fiber bidirectional transmission system based on the mode division multiplexing, the few-mode fiber is used for overcoming Rayleigh backward scattering effect, single-fiber bidirectional transmission is achieved, and use efficiency of optical fiber and wavelength resources is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Coupled system multi-core fiber, coupling mode multiplexer and demultiplexer, system for transmission using multi-core fiber and method for transmission using multi-core fiber
InactiveUS20110188855A1Optical mode multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesMultiplexerTransmission channel
The multi-core fiber of the present invention uses a multi-core fiber configuration, compatible with the “coupled” operation mode in which coupling between cores is positively utilized, to carry out mode division multiplexing transmission via a multi-core fiber that contains multiple single-mode cores in one optical fiber. The multi-core fiber of the present invention uses a configuration in which mode multiplexing transmission is carried out using a multi-core fiber that contains multiple single-mode cores in one optical fiber, wherein multiple cores are strongly coupled intentionally to form a coupled multi-core fiber that makes the coupled modes correspond, one to one, to the transmission channels.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP YOKOHAMA NAT UNIV +1
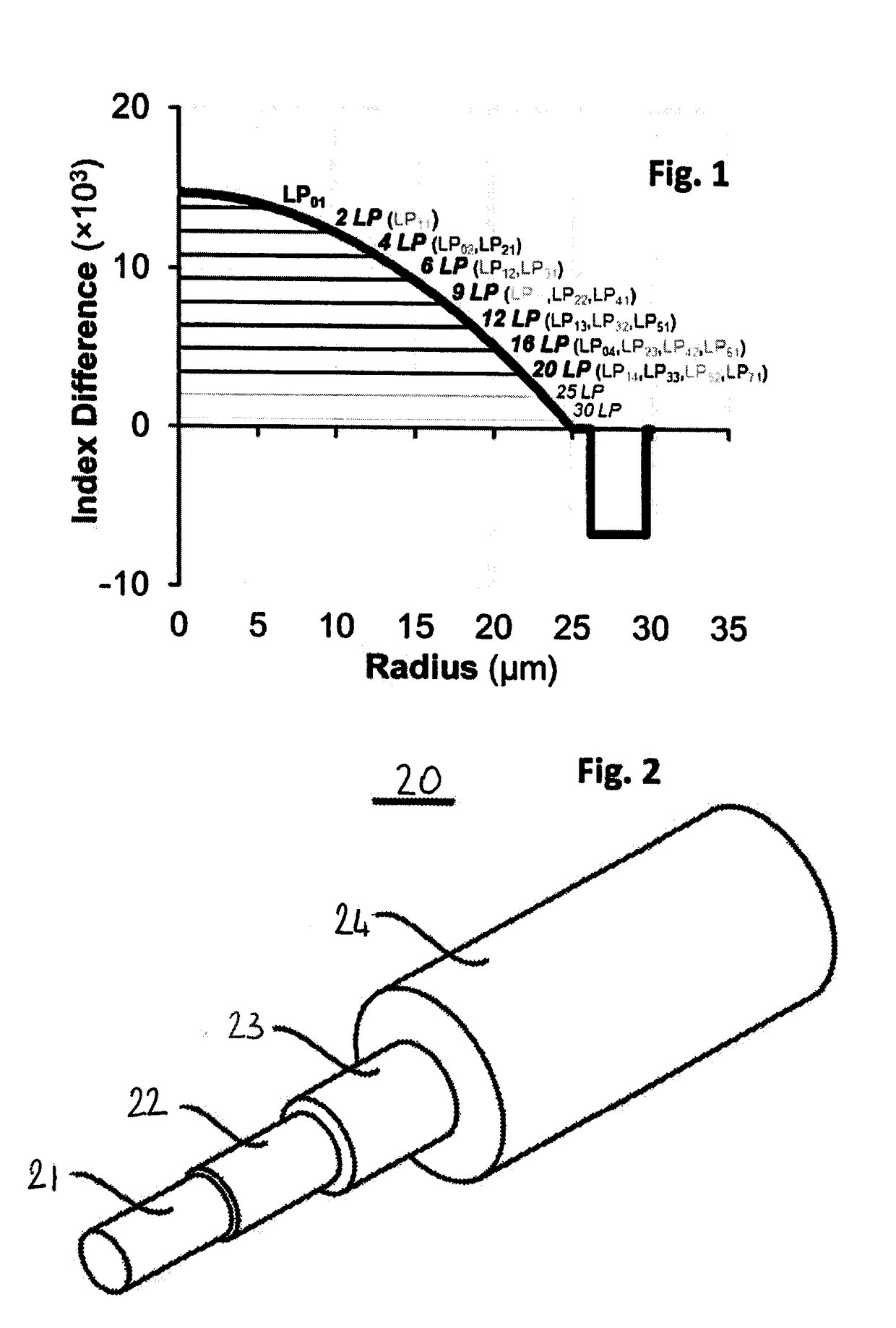
Few mode optical fibers for mode division multiplexing
ActiveCN104067152AOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideFew mode fiberRelative refractive index
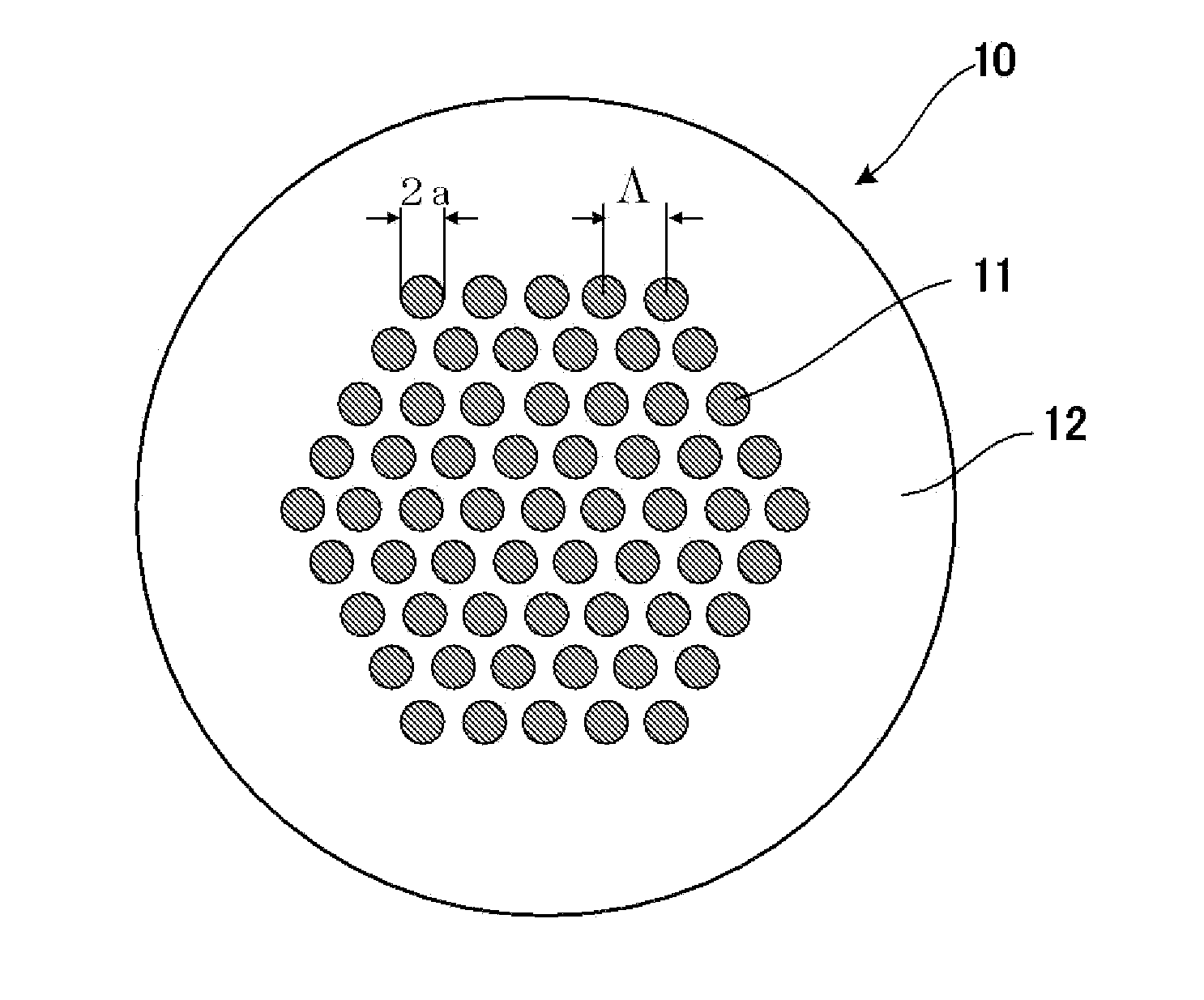
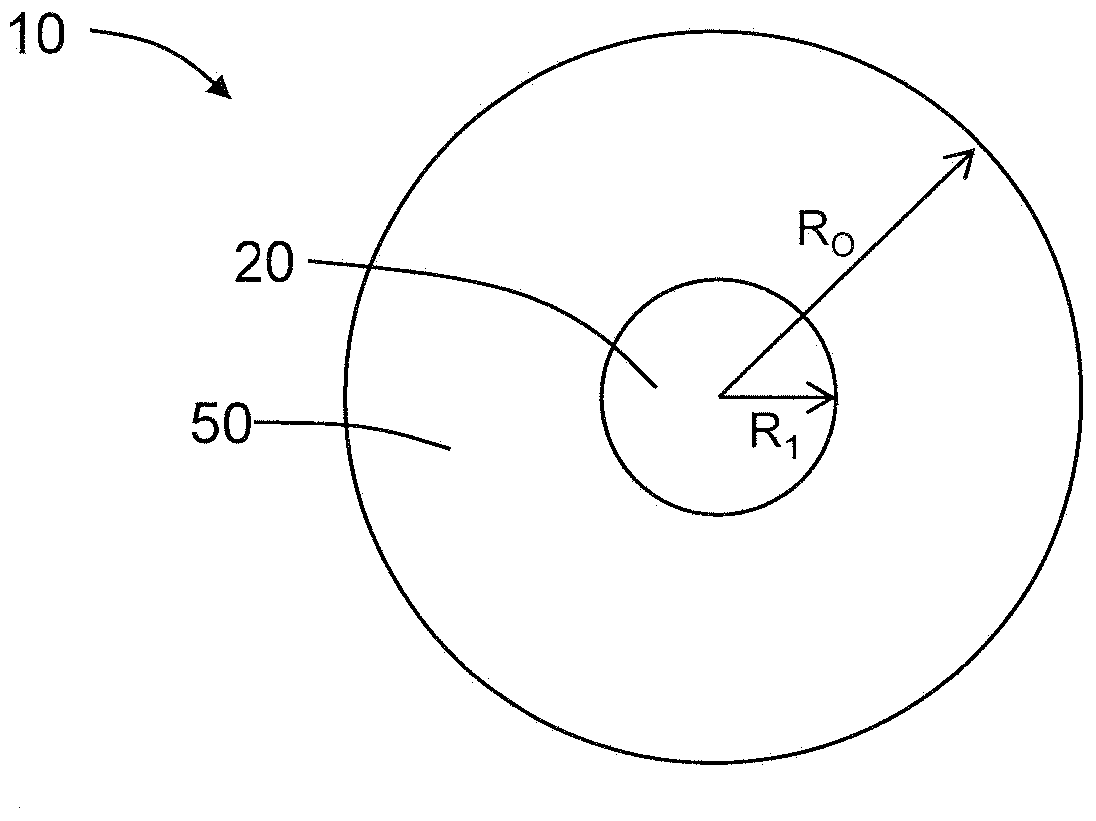
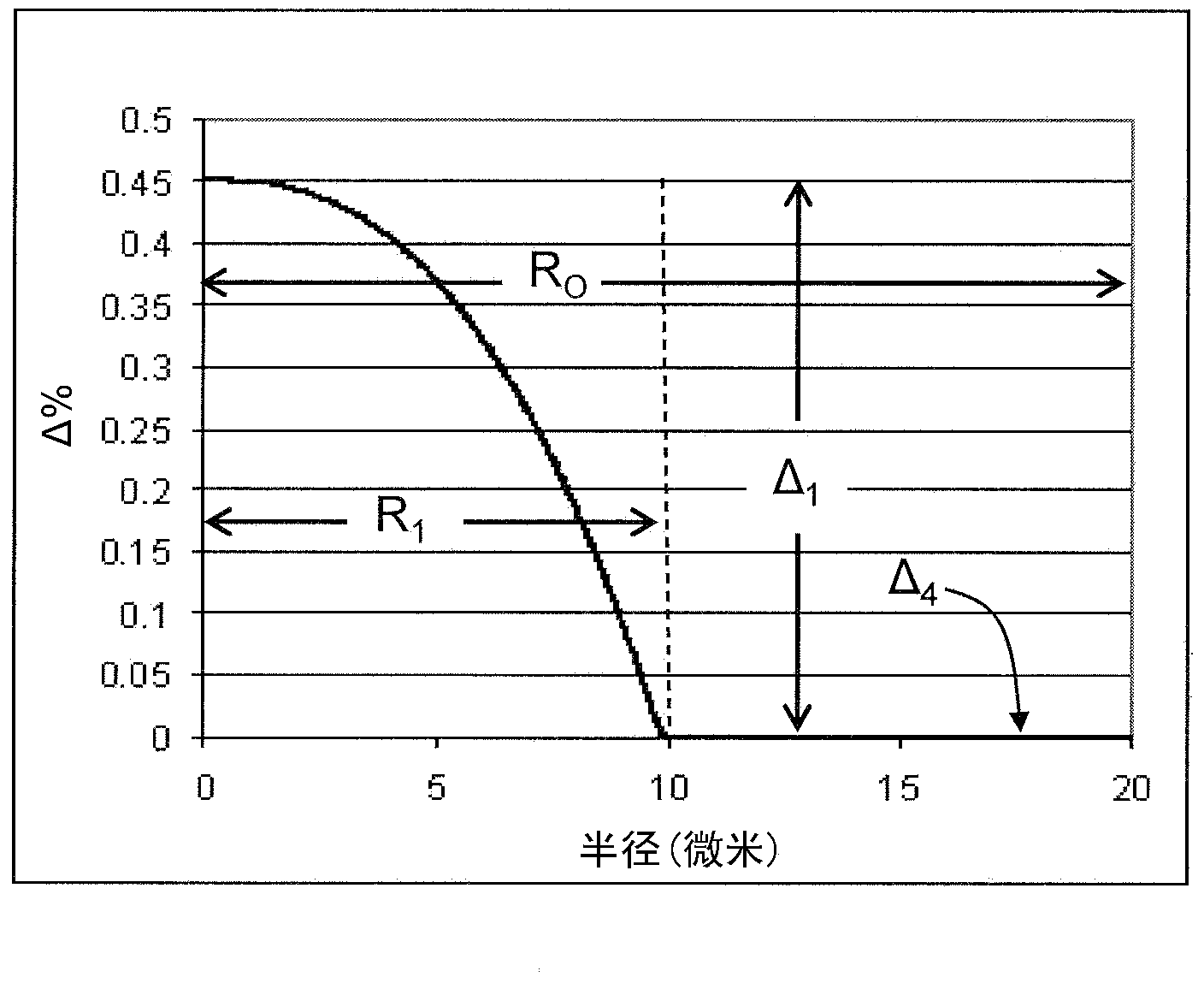
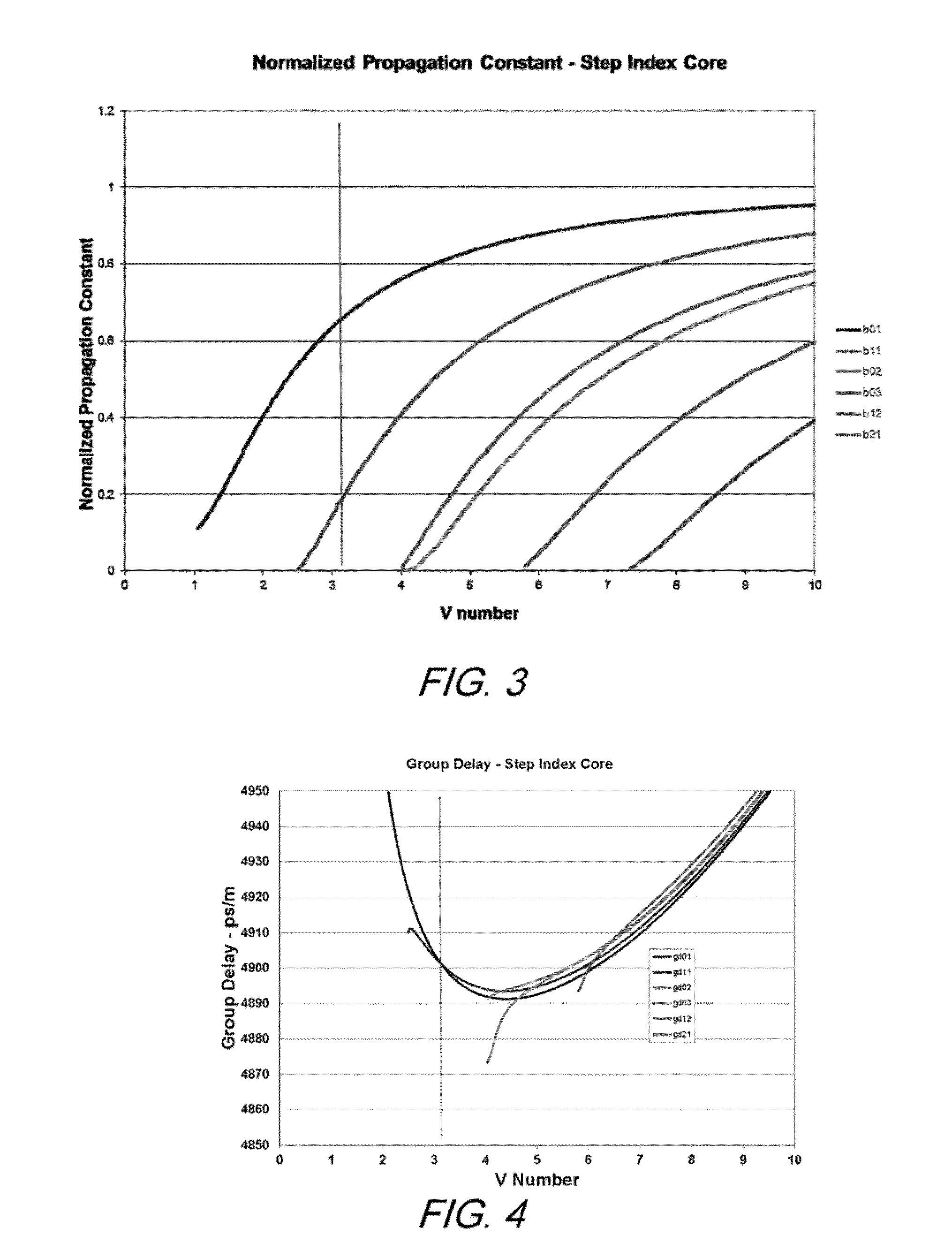
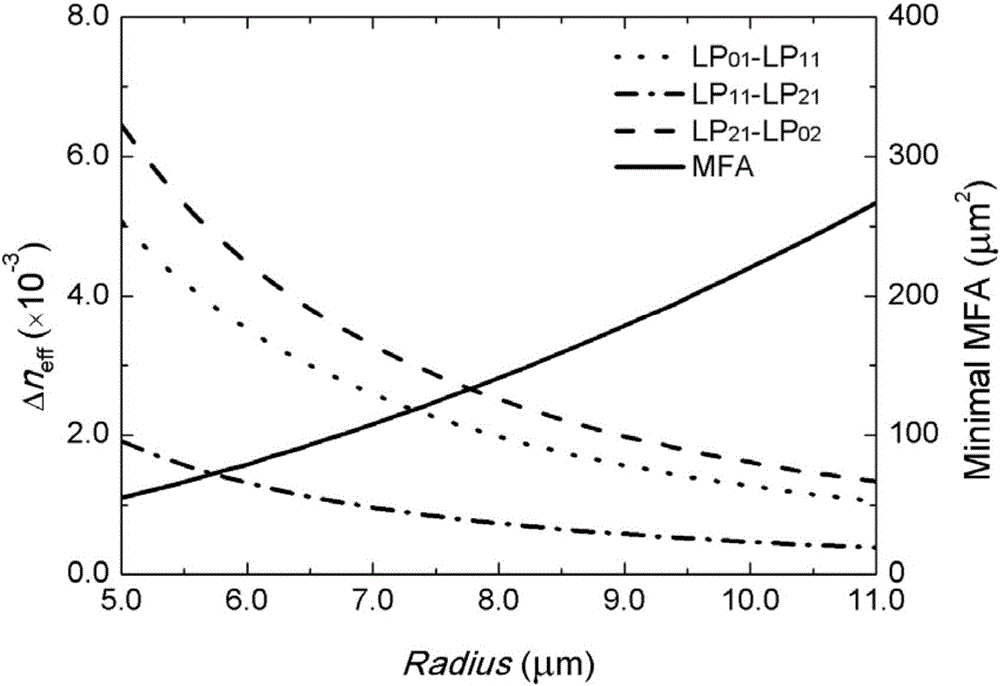
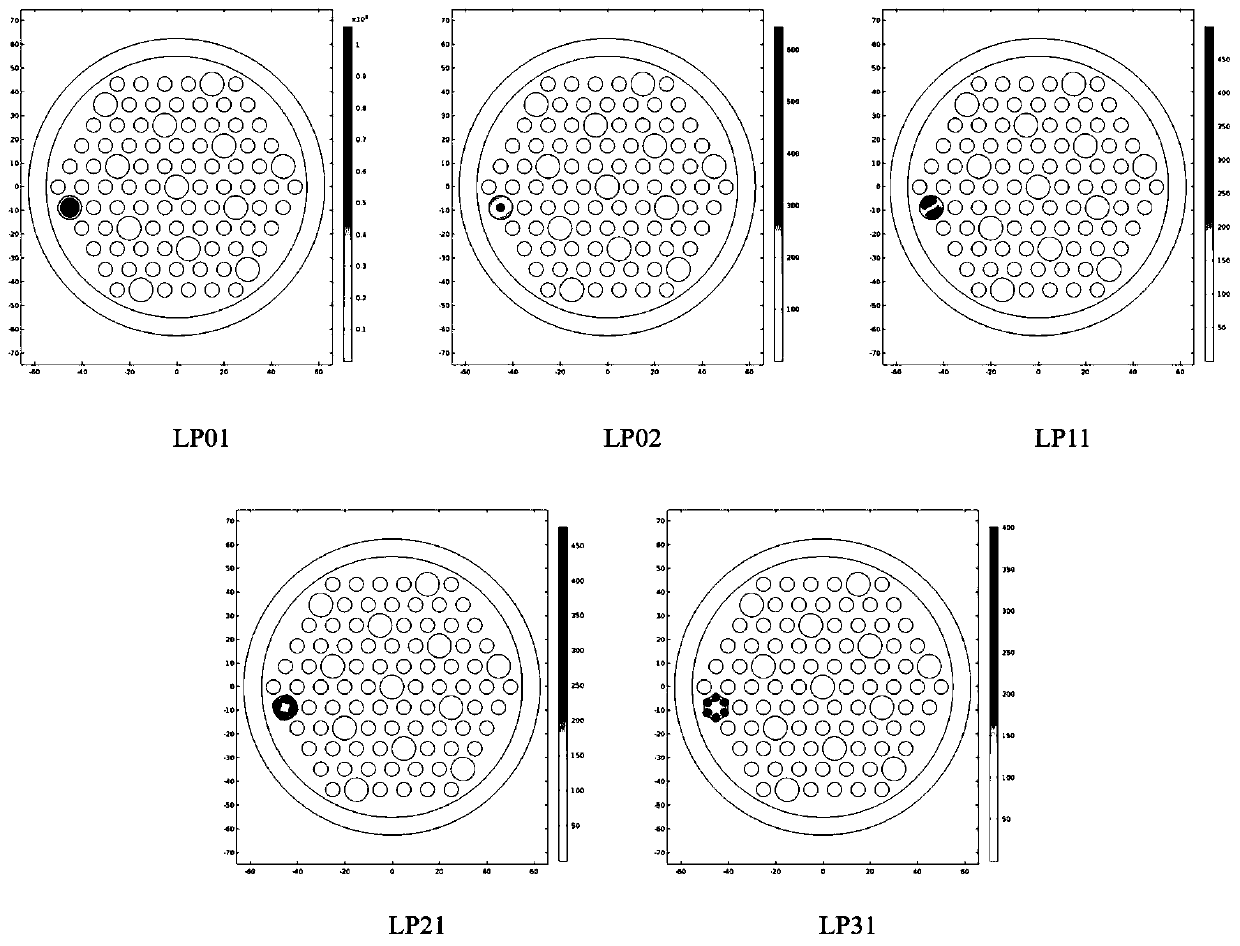
A few mode optical fiber suitable for use in a mode division multiplexing (MDM) optical transmission system is disclosed. The optical fiber has a graded-index core with a radius R1 in the range from 8 [mu]m to 14 [mu]m, an alpha value greater than or equal to about 2.3 and less than about 2.7 at a wavelength of 1550 nm, and a maximum relative refractive index Delta1MAX from about 0.3% to about 0.6% relative to the cladding. The optical fiber also has an effective area greater than about 90 [mu]m2 and less than about 160 [mu]m2. The core and cladding support only the LP01 and LP11 modes at wavelengths greater than 1500 nm. The cladding has a maximum relative refractive index Delta4MAX such that Delta1MAX>Delta4MAX, and the differential group delay between the LP01 and LP11 modes is less than about 0.5 ns / km at a wavelength of 1550 nm.
Owner:CORNING INC
Multiple LP-mode fiber designs for mode-division multiplexing
ActiveUS20150168643A1Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideFew mode fiberCoupling
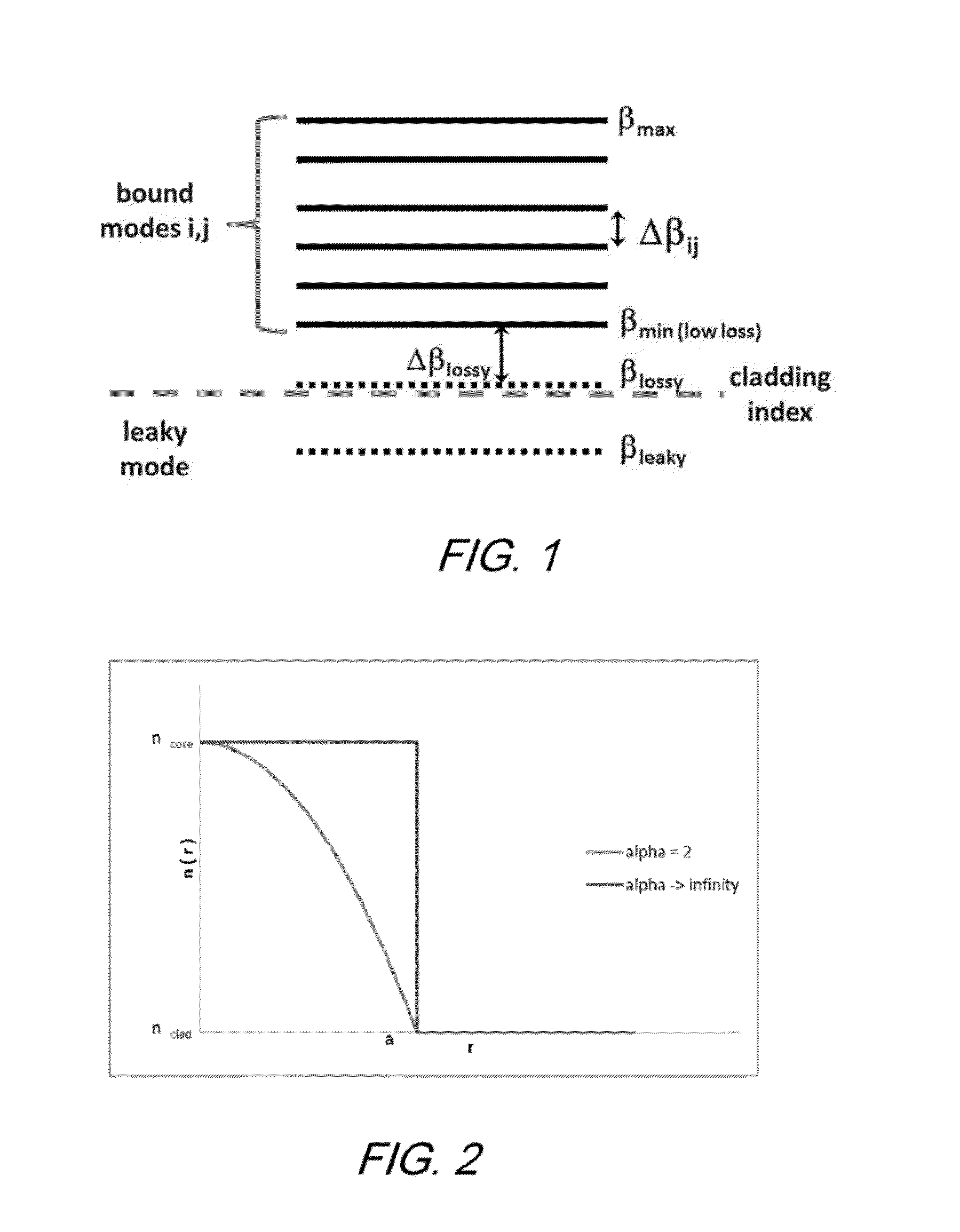
A few-mode fiber is described, having a graded-index core and a surrounding cladding comprising a ledge between the core and the trench, a down-doped trench abutting the ledge, and an undoped cladding region abutting the trench. The fiber's refractive index profile is configured to support 9 or more LP modes for transmission of a spatially-multiplexed optical signal. Undesired modes have respective effective indices that are close to, or less than, the cladding index so as to result in leakage of the undesired modes into the outer cladding. The index spacing between the desired mode having the lowest effective index and the leaky mode with the highest effective index is sufficiently large so as to substantially prevent coupling therebetween.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Silicon-based integrated on-chip multimode optical switching system compatible with wavelength division multiplexing signals
ActiveCN110012368AReduce power consumptionLower latencyMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical light guidesCarrier signalEngineering
A silicon-based integrated on-chip multimode optical switching system compatible with wavelength division multiplexing signals comprises a multimode optical switching array, N groups of wavelength division-mode division multiplexing optical signal transmitting and receiving systems, and a peripheral driving circuit system, an electrical serial-parallel conversion and parallel-serial conversion system and a high-speed data input and output electrical bus which are used for supporting the system on the chip. According to the system, high-speed serial electric signals generated by data processing nodes are converted into parallel multi-channel electric signals to be input; the optical signal is converted into an optical signal through a modulator array and is loaded on an optical carrier wave of which the wavelength and the mode are multiplexed together; the optical signals enter the multi-mode optical switching array through the multi-mode waveguide input port, are demultiplexed into optical signals of multiple channels after reaching the target port, are converted into parallel electric signals through the photoelectric detector, and are finally reduced into high-speed serial signals to be provided for a data node of the target port for use. The system has the characteristics of low energy consumption, high bandwidth and low delay. The data input interface and the data output interface are both electric domains and are compatible with data interfaces of various existing processors.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
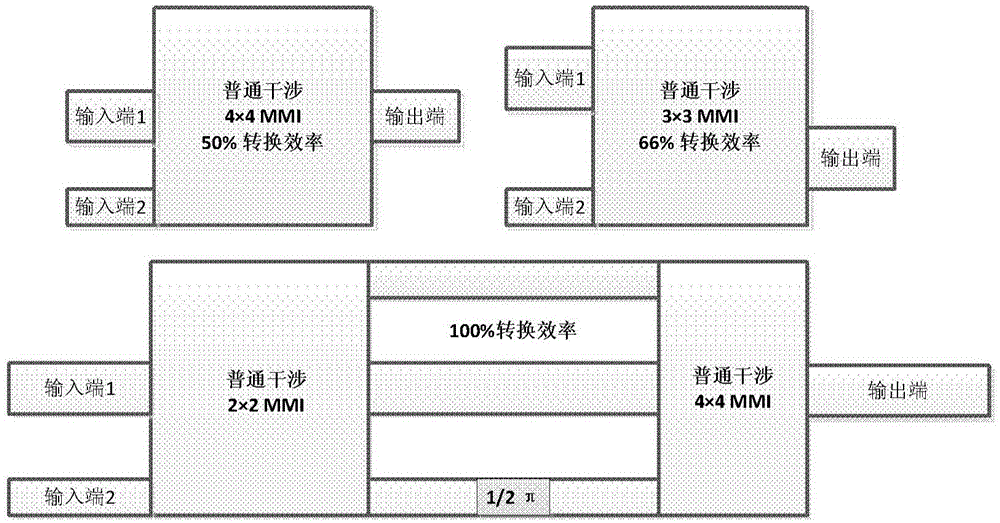
InP-based mode division multiplexer/demultiplexer structure based on multimode interference coupler
The invention relates to an InP-based mode division multiplexer / demultiplexer structure based on a multimode interference coupler. The structure mainly comprises three parts which are a multimode interference coupler based mode conversion and separation structure, Pi / 2 phase shift structure and a multimode interference coupler based 3dB coupler structure. In the Pi / 2 phase shift structure, a transmission mode in a waveguide is enabled to be changed in phase shift through tuning the thickness of a waveguide core layer, and the phase shift change reaches Pi / 2 when the length of the waveguide is a certain specific value. The mode multiplexer / demultiplexer structure has the advantages of compact structure, small device size, large channel bandwidth, low insertion loss and low channel crosstalk, and is simple in production process and high in production tolerance, thereby being very suitable for monolithic integration with devices such as a semiconductor laser, a modulator, an amplifier, a detector and the like, and being a key device for studying a mode division multiplexing technology based monolithic integration few-mode optical communication transmitting and receiving module.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical interconnection methods and systems exploiting mode multiplexing
ActiveUS20160094308A1Address limitationsMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical spaceMode division multiplexing
Optical solutions to address and overcome the issues of superseding / replacing electrical interconnection networks have generally exploited some form of optical space switching. Such optical space switching architectures required multiple switching elements, leading to increased power consumption and footprint issues. Accordingly, it would be beneficial for new optical, e.g. fiber optic or integrated optical, interconnection architectures to address the traditional hierarchal time-division multiplexed (TDM) space based routing and interconnection to provide reduced latency, increased flexibility, lower cost, and lower power consumption. Accordingly, it would be beneficial to exploit networks operating in multiple domains by overlaying mode division multiplexing to provide increased throughput in bus, point-to-point networks, and multi-cast networks, for example, discretely or in combination with wavelength division multiplexing.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV +1
Ring auxiliary type few-mode optical fiber for uncoupled mode-division multiplexing transmission and transmission method of ring auxiliary type few-mode optical fiber
ActiveCN105866881AIncrease the effective refractive index differenceReduced mode couplingOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingElectrical field strengthShortest distance
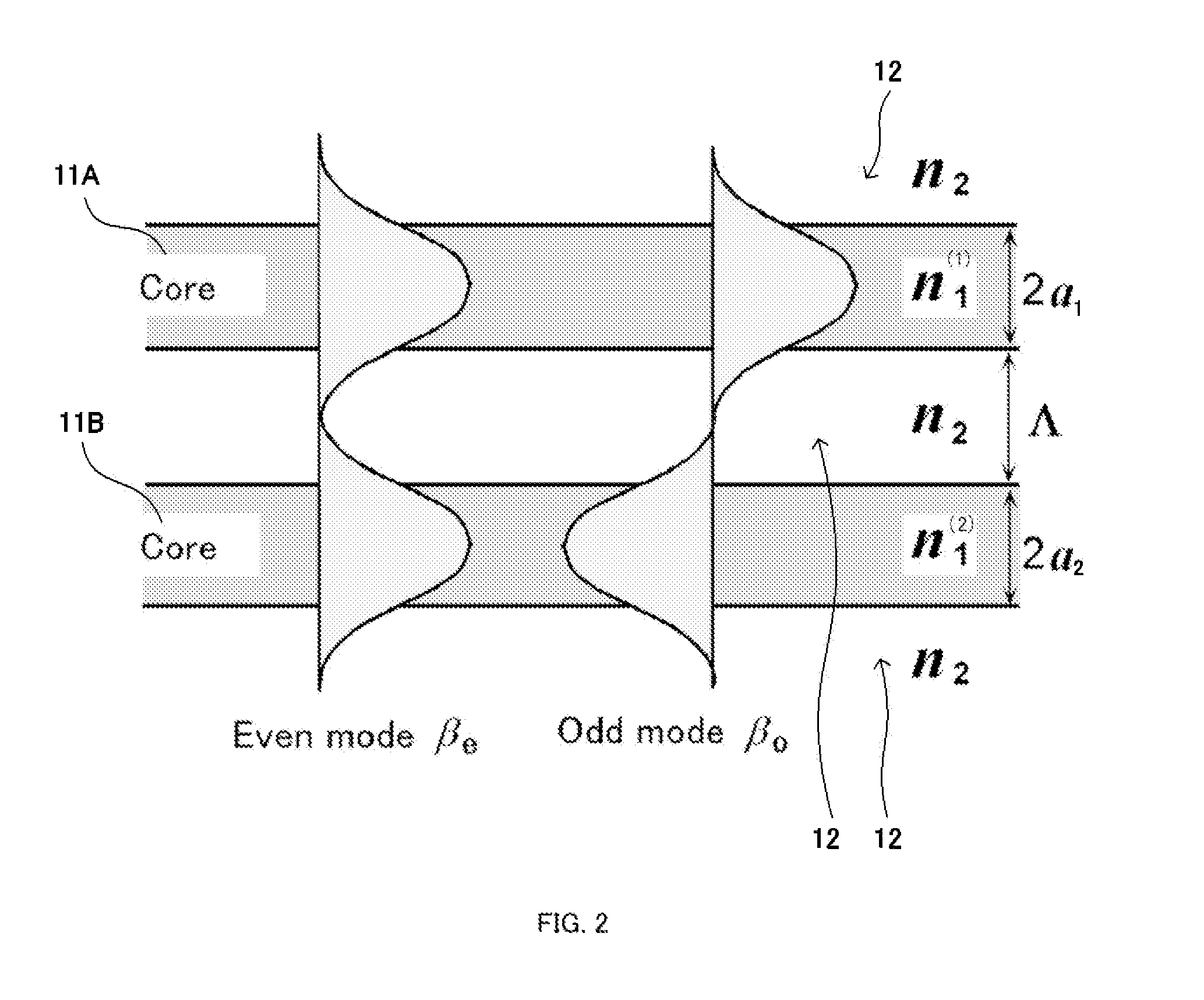
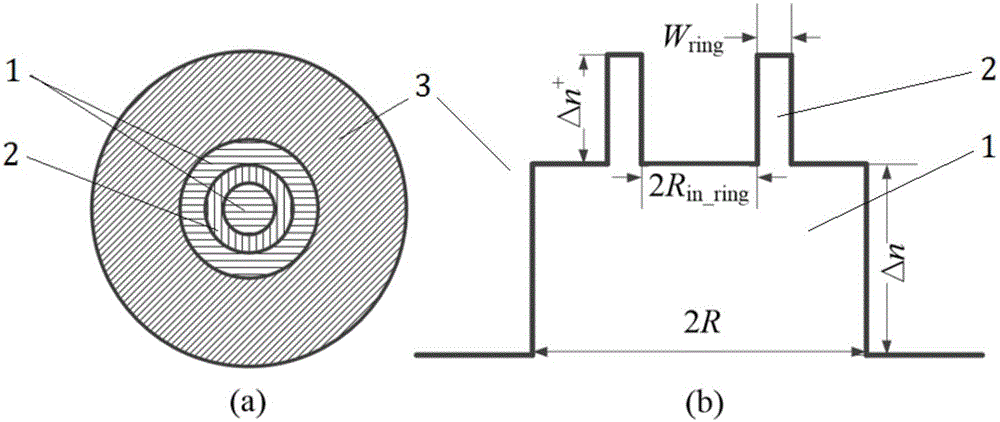
The invention relates to a ring auxiliary type few-mode optical fiber for uncoupled mode-division multiplexing transmission and a transmission method of the ring auxiliary type few-mode optical fiber. The ring auxiliary type few-mode optical fiber comprises a fiber core and a wrapping layer structure. A high refractive index ring is arranged in the fiber core, wherein the electric field intensity of an LP02 mode of the position where the high refractive index ring is located in the optical fiber is (0, 30%] of peak intensity, and the refractive indexes of the other parts, except the high refractive index ring, of the fiber core are the same. The ring auxiliary type few-mode optical fiber for uncoupled mode-division multiplexing transmission and the transmission method of the ring auxiliary type few-mode optical fiber effectively reduce mode coupling in the transmission process. By means of the technology, the minimum effective refractive index difference between modes can be increased by one time or above on the premise that the area of a mode field is basically unchanged, so that the uncoupled few-mode optical fiber with a large mode field area and low mode crosstalk is obtained, and great significance and application prospects are achieved on middle and short distance mode-division multiplexing transmission.
Owner:上海光织科技有限公司
Asymmetric directional coupler
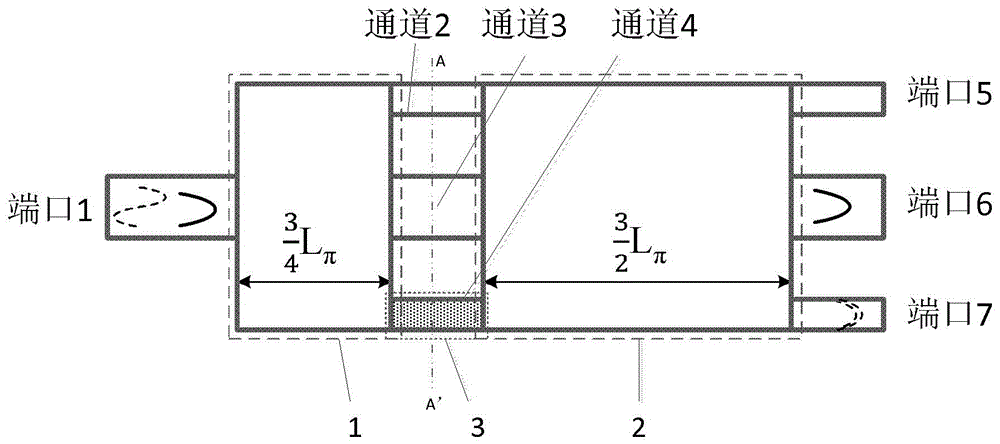
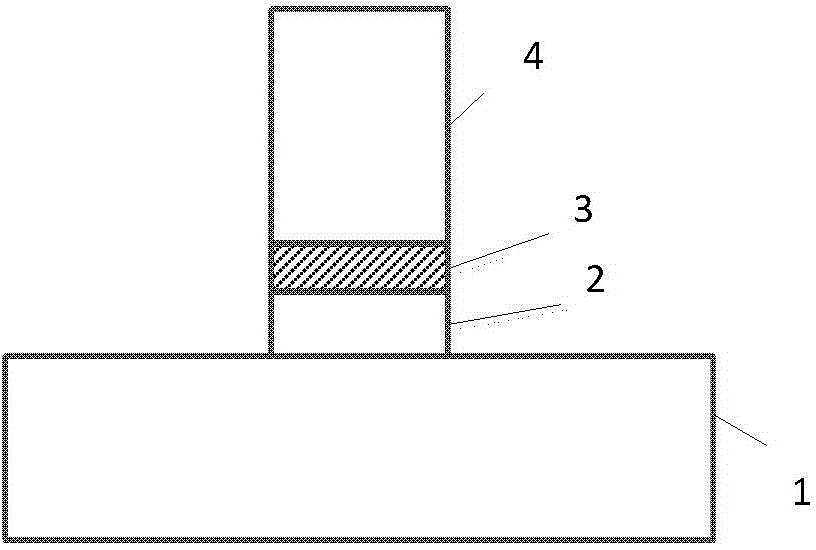
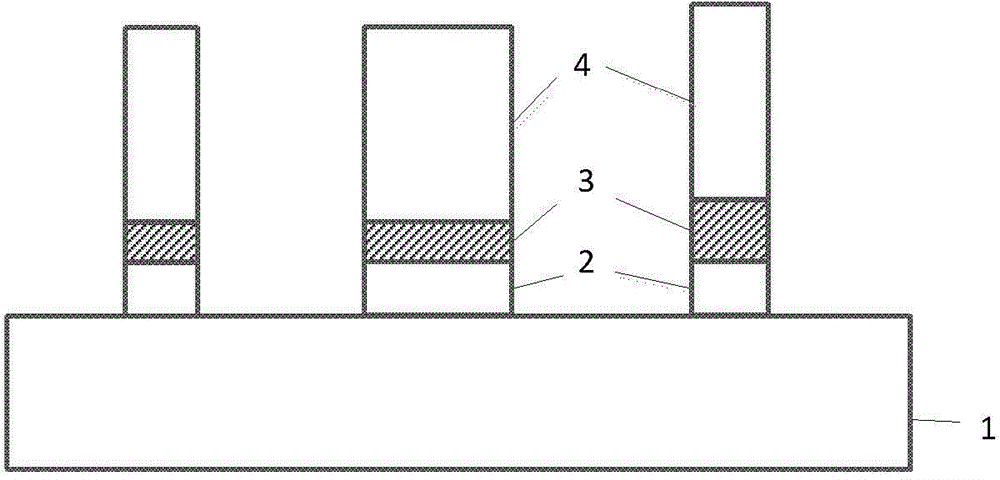
InactiveCN106842430ASimple designImprove coupling efficiencyCoupling light guidesCommunications systemMultiplexer
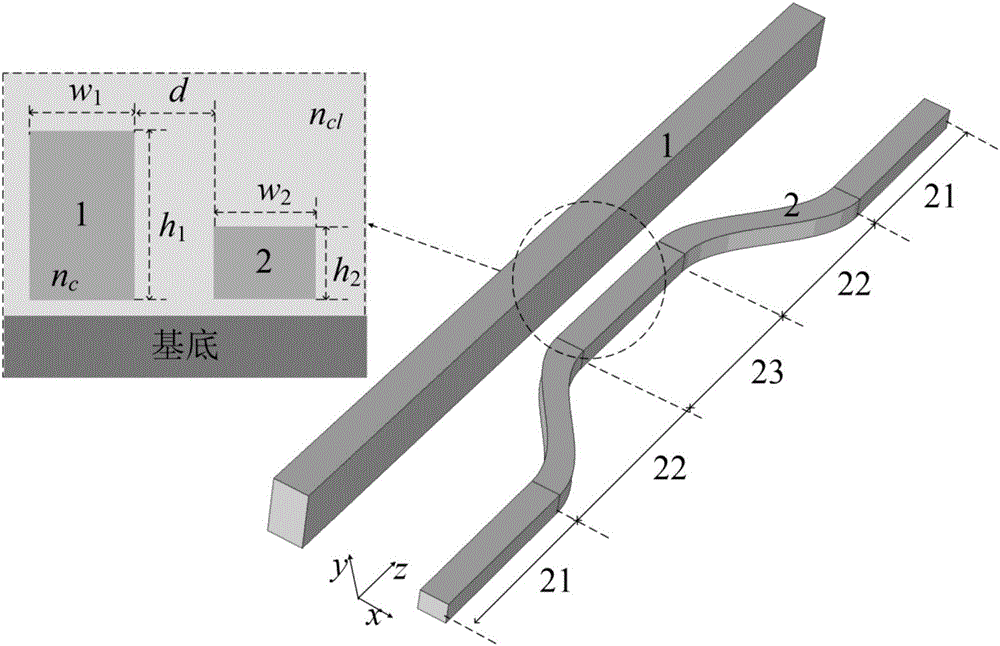
The invention discloses an asymmetric directional coupler. The asymmetric directional coupler comprises a multi-mode waveguide (1) and a single-mode waveguide (2), wherein the height and width of the cross section of the multi-mode waveguide (1) are different from those of the single-mode waveguide (2). A traditional directional coupler can be used for easily implementing coupling of two odd-modes or two even-modes in an optical fiber, but cannot be used for converting odd-modes and even-modes in the horizontal direction since the coupling coefficient determined by electric field distribution characteristics of the odd-modes and even-modes is zero. In the asymmetric directional coupler, widths and heights of two waveguides are not equal, so that the symmetricity of a device in the vertical direction is destroyed, conversion between odd-modes and even-modes in the optical fiber can be especially realized. The asymmetric directional coupler can be used as a mode converter, a mode multiplexer / demultiplexer, and can be applied to mode division multiplexing optical fiber communication systems.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and device for controlling mode light power
InactiveCN104202094AImprove transmission performanceElectromagnetic transmissionEngineeringFeedback control
The invention discloses a method and a device for controlling a mode light power, and relates to the technical field of mode division multiplexing transmission. The device comprises a sending end, a transmission link, a receiving end and a feedback control unit, wherein the sending end, the transmission link and the receiving end are sequentially connected; the feedback control unit is connected with the sending end and the receiving end respectively; the transmission link further comprises a few-mode optical fibre and an optical fibre amplifier. According to the method and the device disclosed by the invention, the receiving power or the light signal-to-noise ratio of the light beam of each mode are acquired through the receiving end, an input power ratio is determined by the feedback control unit according to the receiving power or the light signal-to-noise ratio, the input power of the light beam is adjusted by the sending end according to the input power ratio, thus realizing control on the input power of each mode, and improving the overall transmission performance of the system.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
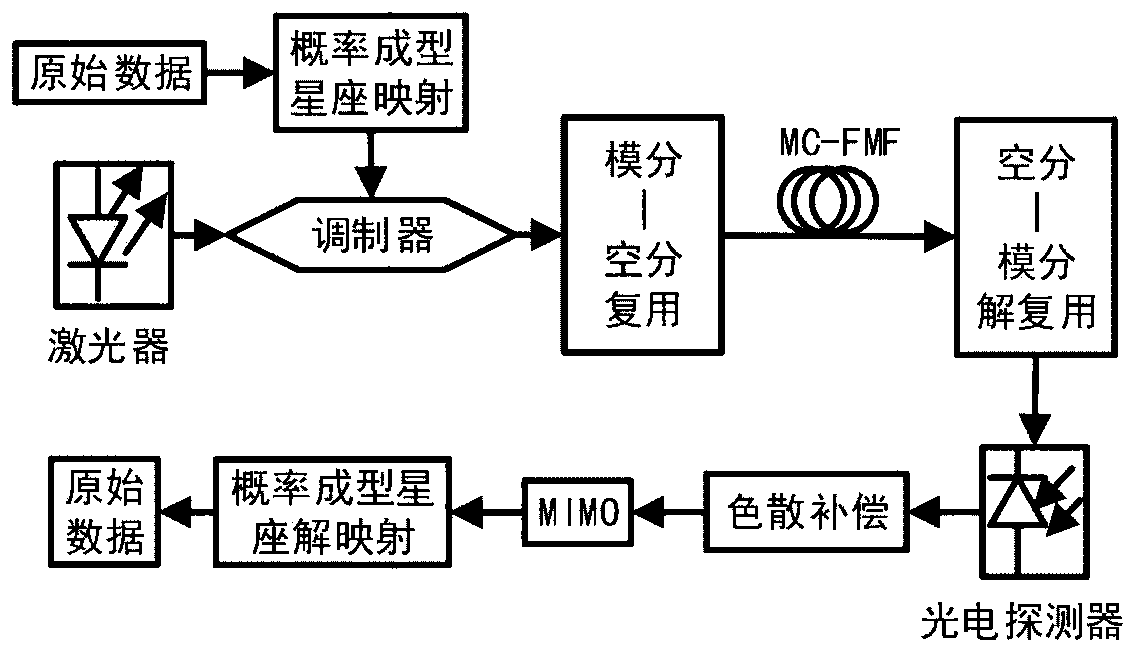
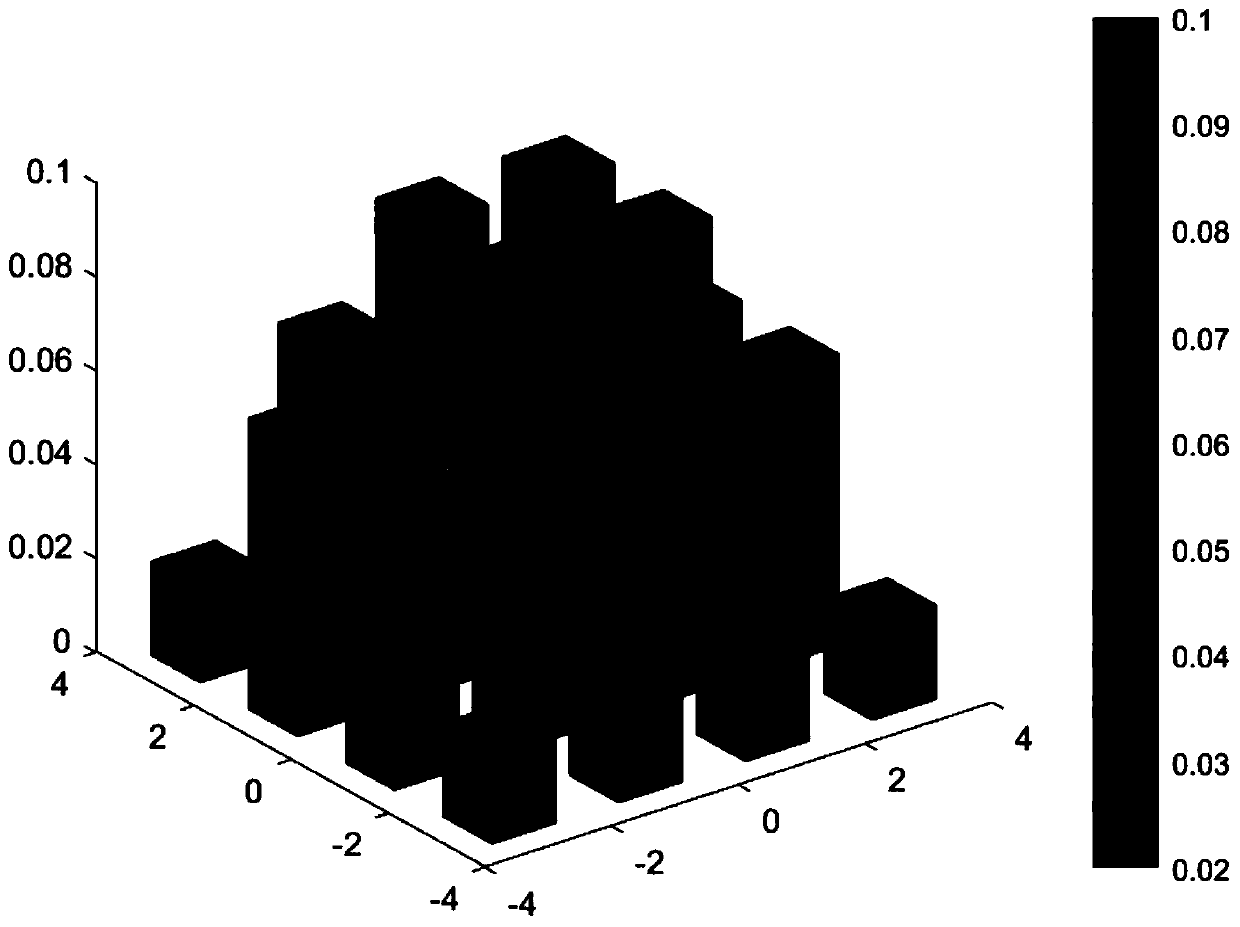
Photon probability shaping signal transmission method based on few-mode multi-core optical fiber
ActiveCN111064514AImprove transmission capacityFlexible transfer rateFibre transmissionElectromagnetic receiversData streamEqualization
The invention discloses a photon probability shaping signal transmission method based on a few-mode multi-core optical fiber. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out probability shapingconstellation mapping on multiple paths of parallel bit data streams to obtain a 16QAM signal; enabling a modulator to modulate a 16QAM signal to laser, and then converting the 16QAM signal into a signal in a high-order mode after mode conversion; enabling a few-mode multi-core optical fiber entry mode multiplexer to realize different-mode transmission and space division multiplexing of differentprobability signals; enabling a receiving end to carry out demultiplexing through a space division mode division multiplexer, decomposing the optical signal into multiple signals, sending the signalsto a photoelectric detector for detection, converting the optical signal into an electric signal to obtain multiple 16QAM signals, and carrying out dispersion compensation on the converted 16QAM signals; carrying out MIMO equalization processing on the 16QAM signal symbol in an MIMO equalizer by applying an adaptive step length equalization algorithm so as to carry out compensation mode couplingand modal delay; and finally, performing corresponding probability shaping constellation de-mapping and digital signal processor processing to obtain initial bit data.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Multi-core few-mode microstructure optical fiber for field of space division-mode division multiplexing
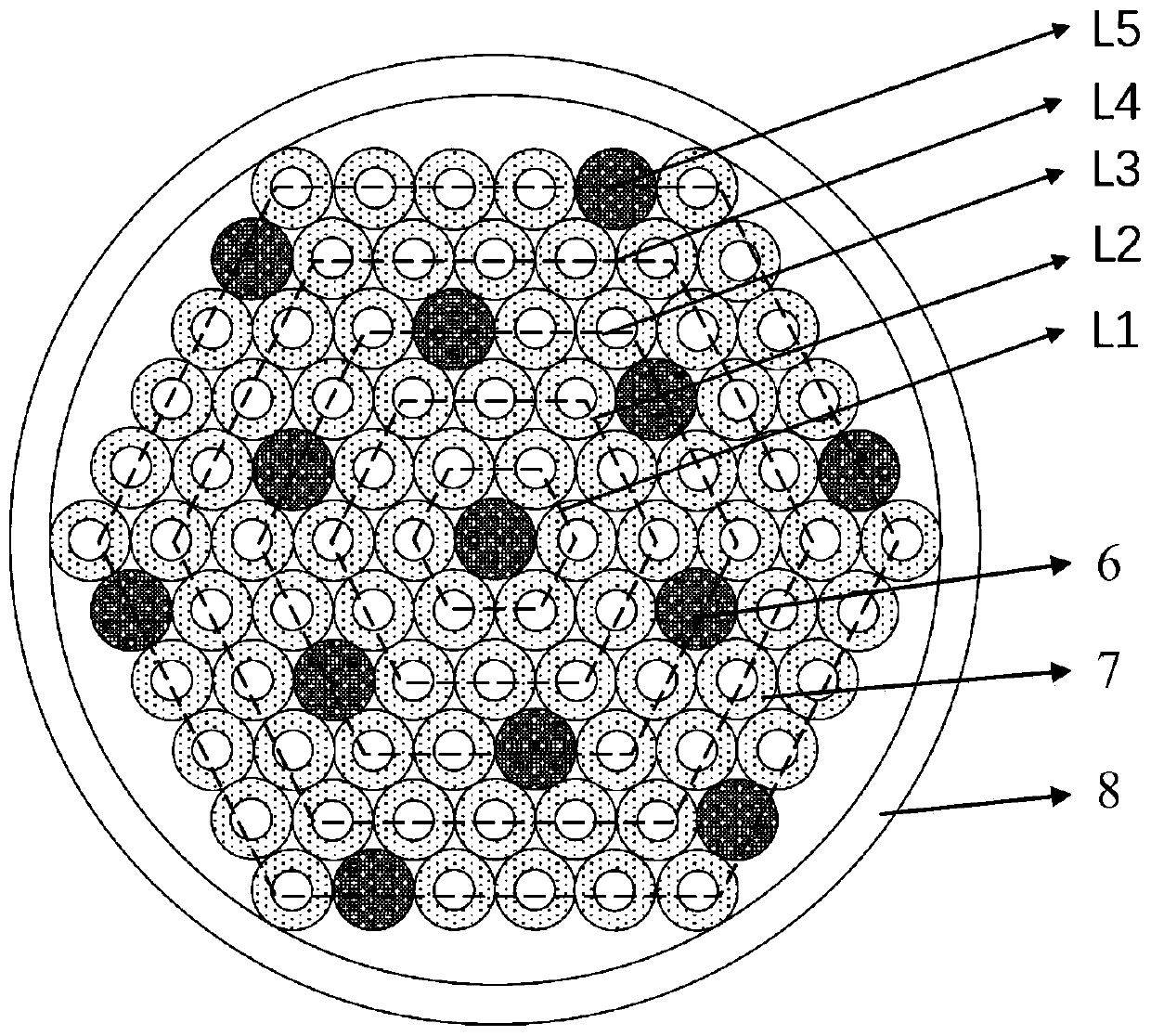
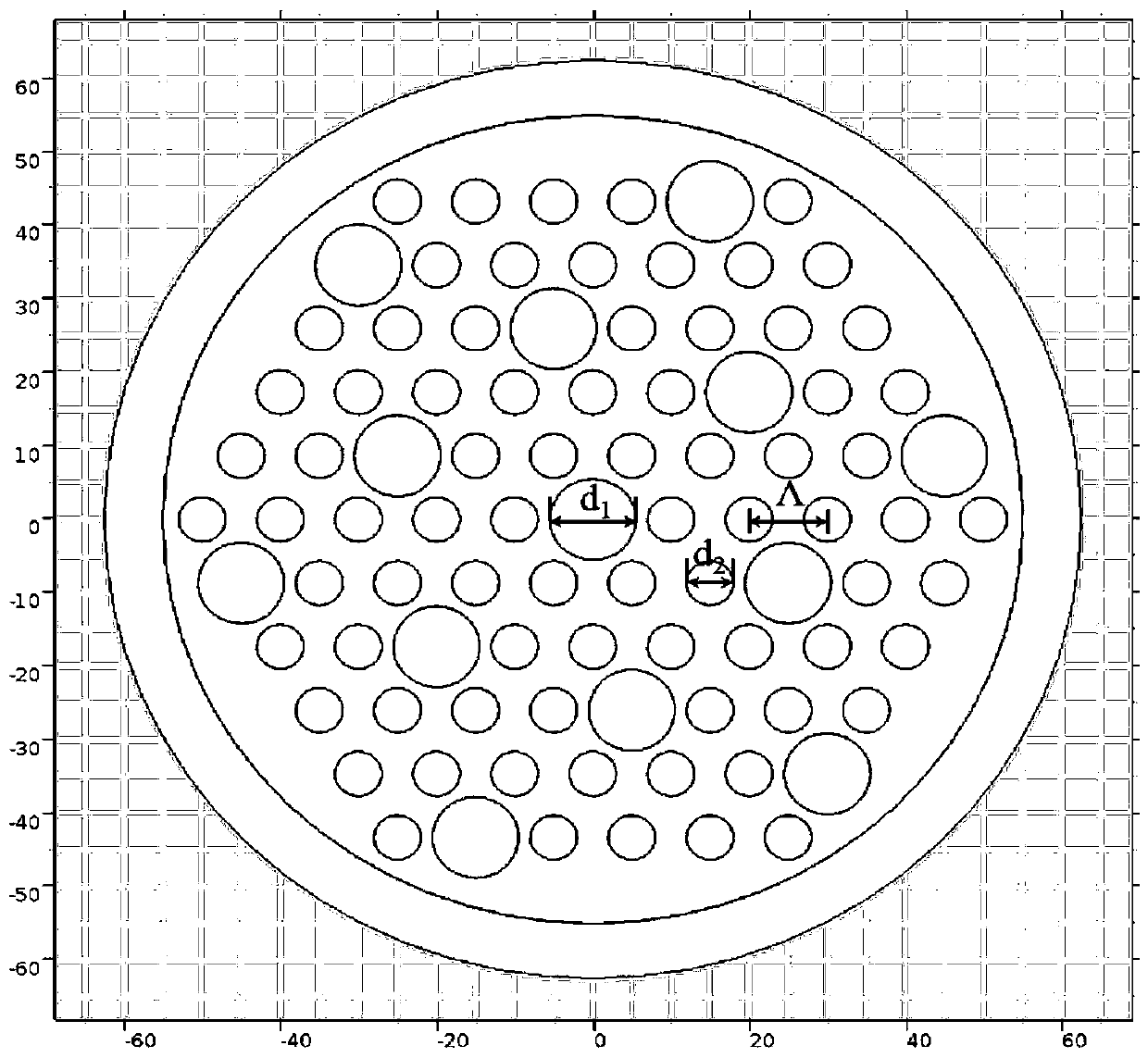
ActiveCN110927863ASmall sizeControl the refractive index differenceCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideRefractive indexEngineering
A multi-core few-mode microstructure optical fiber for the field of space division-mode division multiplexing comprises a central area and an outer cladding area, and the outer cladding area is arranged on the periphery of the central area. The central area comprises few-mode fiber cores and an air hole inner cladding, and a plurality of few-mode fiber cores are arranged in the central area. The number of degenerate transmission modes of a single few-mode fiber core is greater than or equal to 2. One few-mode fiber core is arranged in the center of the central area, the other few-mode fiber cores are uniformly distributed around the few-mode fiber core in the center, any three adjacent few-mode fiber cores are equidistant, and an air hole inner cladding is arranged between the periphery ofeach few-mode fiber core and the two adjacent few-mode fiber cores. According to the optical fiber, the number of degenerate transmission modes of each fiber core can be ensured to be more than two by designing and adjusting the diameters of the air holes and the distances between the holes and controlling the refractive index difference of materials, the size of the optical fiber is reduced as much as possible, inter-core / inter-mode crosstalk and differential mode group delay are controlled on the basis to meet the communication requirement, and the communication capacity is improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Three-dimensional multilayer waveguide mode multiplexing and de-multiplexing device and preparation method thereof
PendingCN108761637AIncrease the dimension of integrationHighly integratedOptical waveguide light guideMultiplexerDirect coupling
The invention relates to a three-dimensional multilayer waveguide mode multiplexing and de-multiplexing device and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the optical communication device technical field, in particular, a mode division multiplexing system. According to the three-dimensional multilayer waveguide mode multiplexing and de-multiplexing device and the preparation method thereof ofthe invention, a three-dimensional multilayer waveguide integrated structure is adopted, and therefore, the limitations of a traditional two-dimensional planar waveguide structure can be eliminated, the integration dimensions of the device can be increased, the integration and flexibility of the device can be enhanced, and the communication capacity of a system can be improved. The boundary of anyone side of the upper-layer waveguide of the three-dimensional waveguide is aligned with the boundary of any one side of the lower-layer waveguide of the three-dimensional waveguide, so that the direct three-dimensional coupling of a fundamental mode and a high-order mode is realized, and therefore, a defect that a traditional three-dimensional mode multiplexer fails to realize direct coupling ofmodes can be eliminated, and the structure and complexity of the device can be simplified. The device of the invention is prepared based on a mature CMOS process, so that high efficiency, low cost and mass production of the device can be realized. With the three-dimensional multilayer waveguide mode multiplexing and de-multiplexing device and the preparation method thereof of the invention adopted, the flexible three-dimensional coupling of the modes can be realized, a solid foundation is laid for on-chip mode multiplexing technology. The three-dimensional multilayer waveguide mode multiplexing and de-multiplexing device and the preparation method thereof can be further applied to the flexible mode routing of a mode division multiplexing network.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
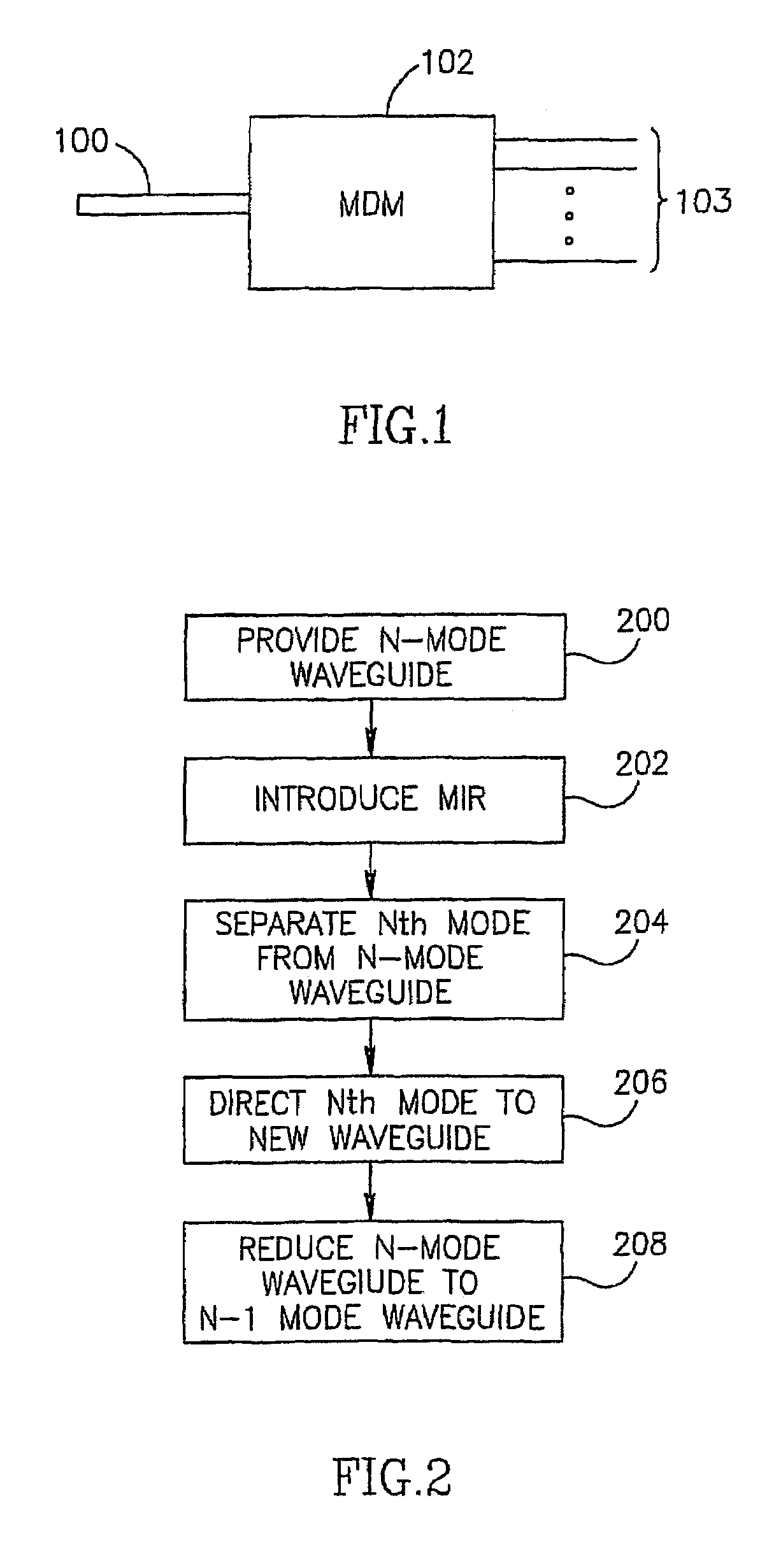
Method and apparatus for optical mode division multiplexing and demultiplexing
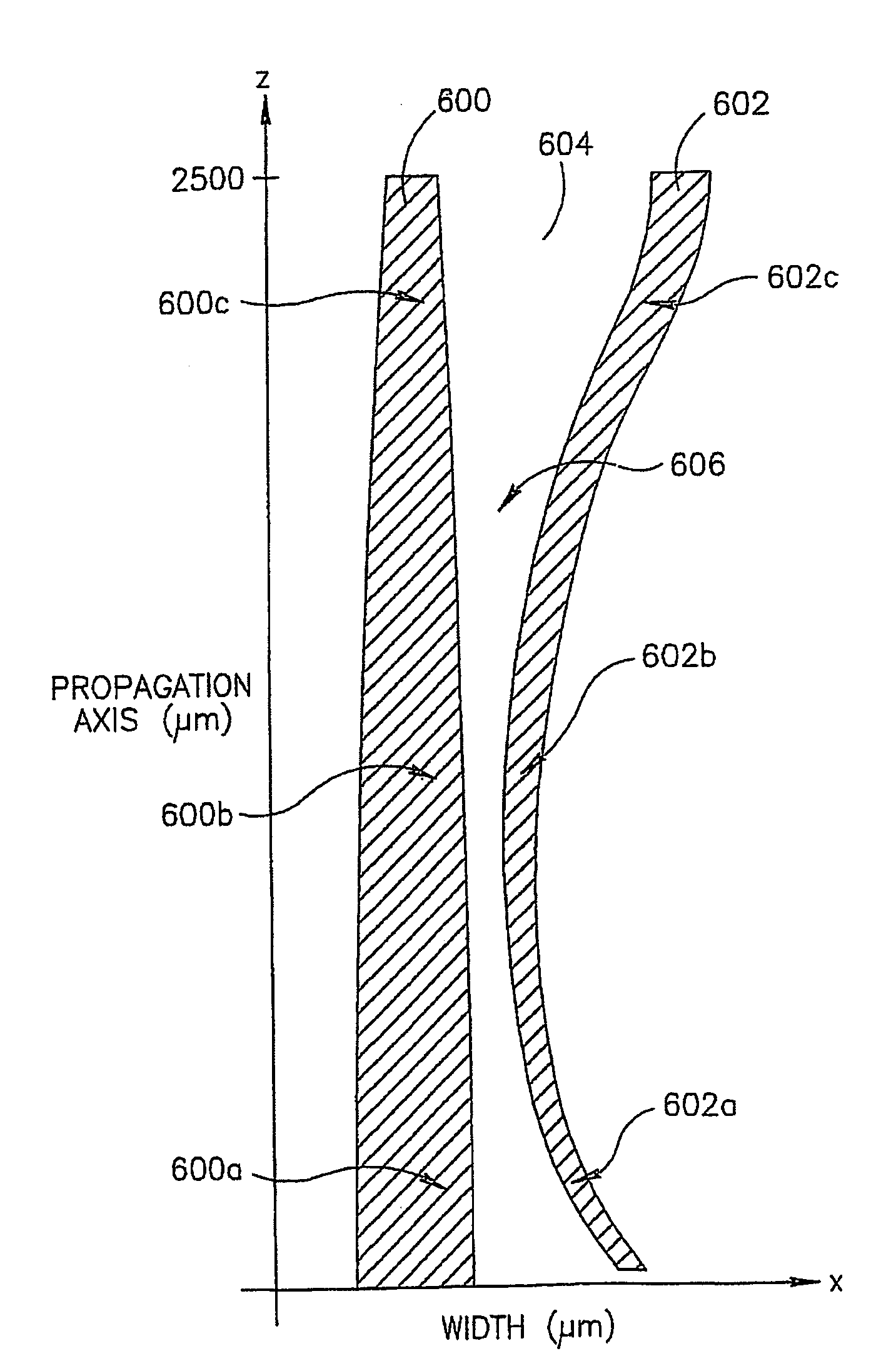
A method of mode selective coupling or mode multiplexing between integrated multimode (600) and single mode (602) waveguides. Evanescent coupling and tapering is used so that the signal may be transferred adiabatically from a first region of a first waveguide to a second, proximal, region of a second waveguide.
Owner:NEOPHOTONICS CORP
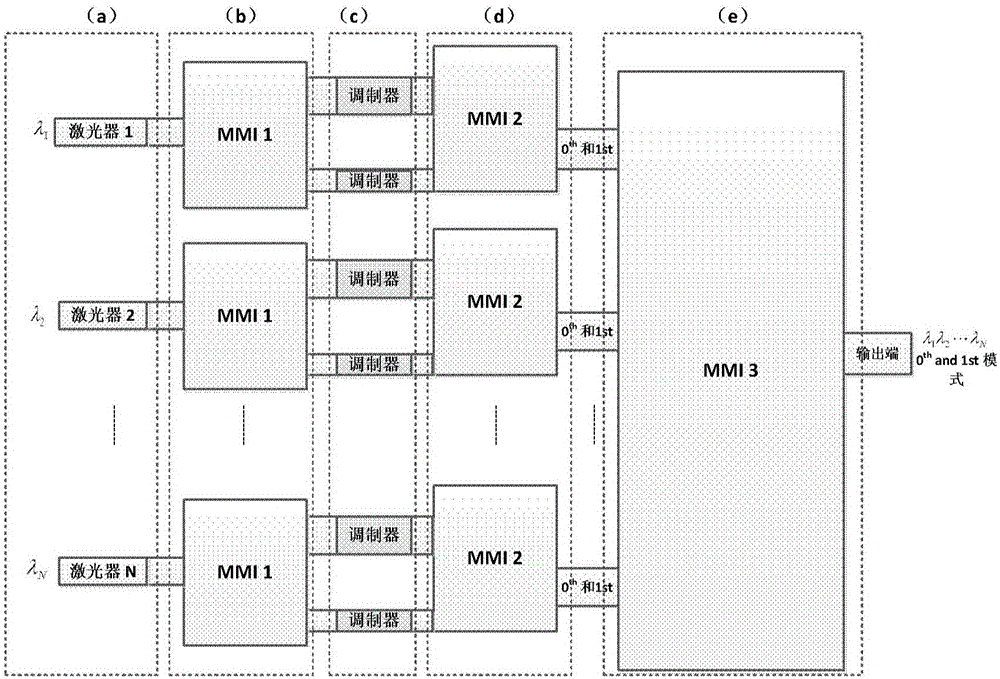
InP-based wavelength division-mode division multiplexing few-mode communication photon integrated emission chip
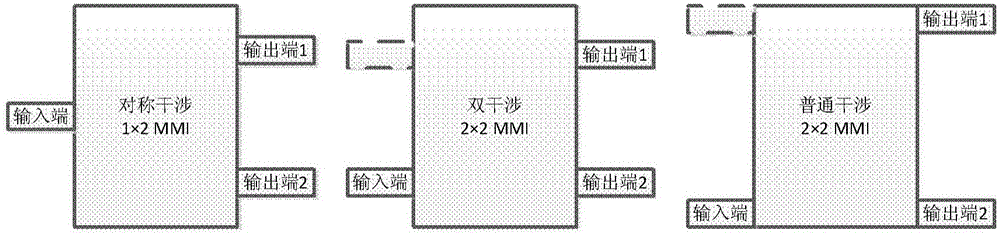
An InP-based wavelength division-mode division multiplexing few-mode communication photon integrated emission chip includes: multiple single-mode semiconductor lasers with different wavelengths, the semiconductor lasers serving as light sources; multiple multimode interference couplers (MMI) having different functions and used for optical power distribution, mode conversion and multi-wavelength multimode multiplexing; and multiple modulator structures for modulation of basic mode signals. The above parts are connected through straight waveguides or bent waveguides. The excellent characteristics of the multiple multimode interference couplers are that the couplers exhibit great design and technical tolerance, have great optical bandwidth, are insensitive to polarization, are small in size, etc. The multimode interference couplers are utilized to serve as multi-wavelength multimode couplers for the first time, wavelength division multiplexing and mode division multiplexing are combined, and thus the fiber transmission capacity is further improved.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
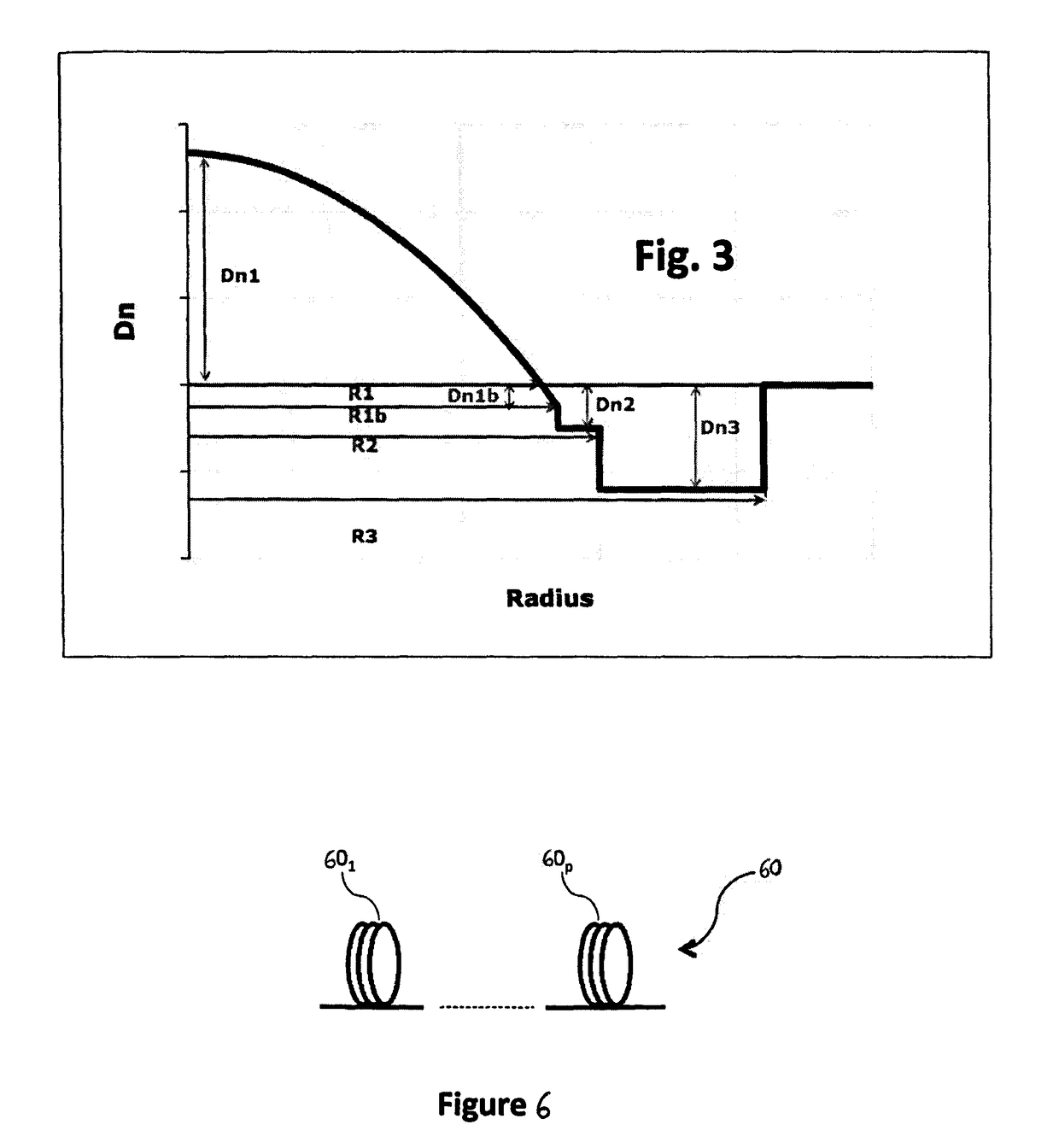
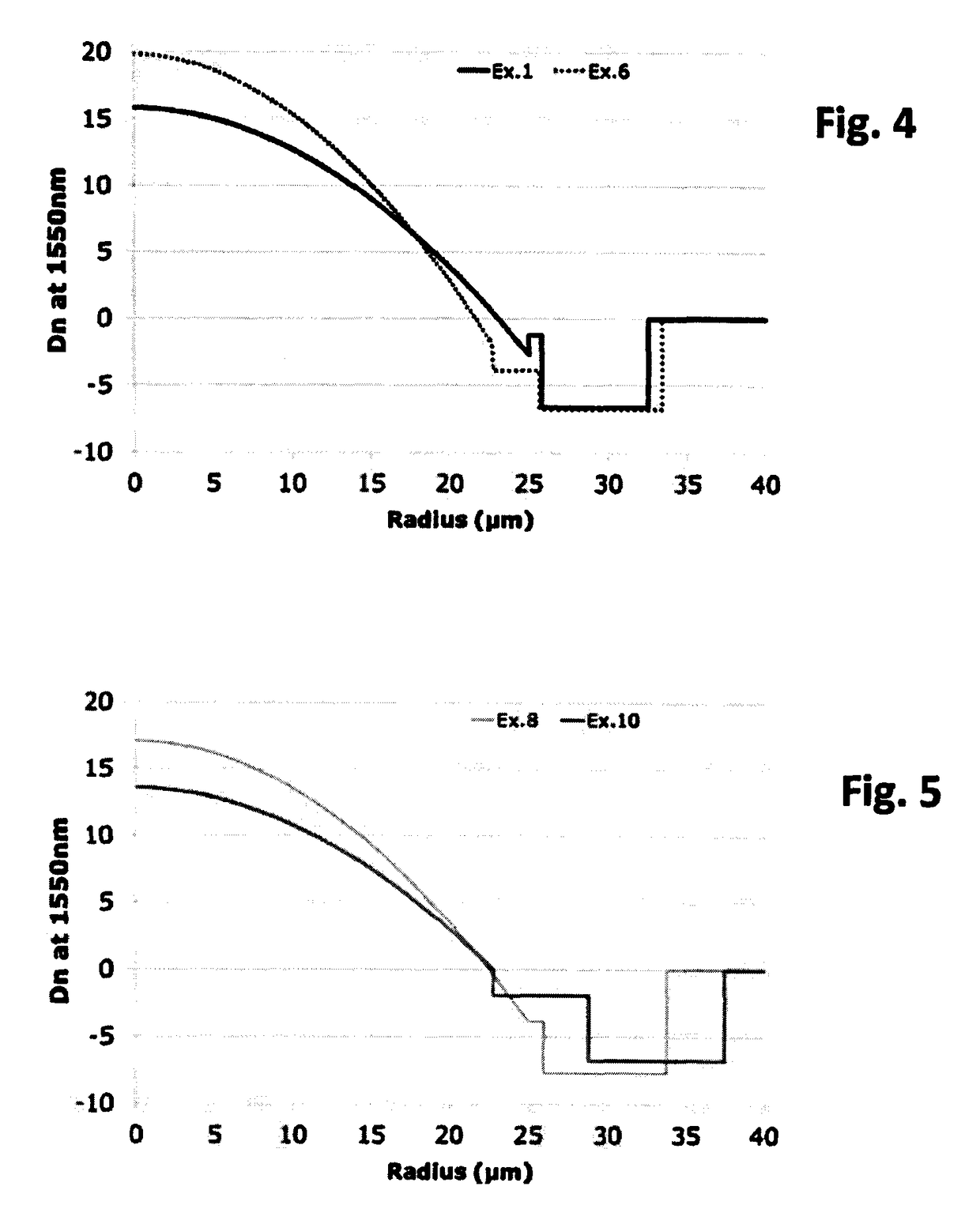
Few mode optical fibers for mode division multiplexing
ActiveUS20190033515A1Improve propertiesIncrease the number ofOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFew mode fiberRefractive index
Few mode optical fibers for mode division multiplexing. The Few Mode Fiber supporting 25 or 30 LP guided modes and includes a graded index core with a α-profile, a radius R1 (at 0 refractive index difference) between 21.5 and 27 μm and a maximum refractive index difference Dn1 between 12.5×10−3 and 20×10−3, and an end of the α- profile at a radius R1b, with index difference Dn1b; a trench surrounding the core with radius R3 between 30 and 42 μm and refractive index difference Dn3 between −15.10−3 and −6.10−3, an intermediate depressed trench with a radius R2, with R1b<R2<R3 and a refractive index difference Dn2, with Dn3<Dn2<0, wherein: for |Dn1b−Dn2|>=0.5×10−3, Min(Dn1b, Dn2)≤−1.5×10−3, and for |Dn1b−Dn2|<0.5×10−3, Dn2 is between −5×10−3 and −3.5×10−3.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Silicon optical integration-based photon analog-to-digital conversion chip
ActiveCN106933001ASmall sizeReduce power consumptionOptical analogue/digital convertersOptical integrationWaveguide mode
The invention discloses a silicon optical integration-based photon analog-to-digital conversion chip, which comprises a time-division multiplexing unit, a wavelength-division multiplexing unit, a mode-division multiplexing unit, a multi-mode modulator, a mode demultiplexing unit, a wavelength demultiplexing unit and a photoelectric detection unit, wherein various components are monolithically integrated on the same silicon chip. The repetition frequency of an input light pulse of a light wave is further improved through different polarization modes and different waveguide modes, thereby more easily achieving optical analog-to-digital conversion with a high sampling rate.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Orbital angular momentum mode multiplexing and demultiplexing coupler based on microstructure optical fiber
ActiveCN110673264ASimple structureFlexible design of structural parametersCoupling light guidesRefractive indexEngineering
The invention discloses an orbital angular momentum mode multiplexing and demultiplexing coupler based on a microstructure optical fiber. The orbital angular momentum mode multiplexing and demultiplexing coupler comprises a middle annular fiber core which supports N orbital angular momentum mode transmission in a waveband with a given central wavelength lambda, a background material, and n single-mode fiber cores which only support fundamental mode transmission and are distributed around the annular fiber core, n=2N, and the single-mode fiber cores are divided into N pairs. The refractive indexes of the single-mode fiber cores and the annular fiber core are higher than that of the background material. The radiuses of the two single-mode fiber cores in each pair of single-mode fiber cores,refractive index differences between the two single-mode fiber cores and the background material and distances between the two single-mode fiber cores and the annular fiber core are equal, included angles between the two single-mode fiber cores and a center of the coupler is (2m + 1) pi / 2l, m = 0, 1, 2...(l1), and l is orders of orbital angular momentum modes of the single-mode fiber cores coupledto middle annular fiber core. According to the orbital angular momentum mode multiplexing and demultiplexing coupler, N pairs of single-mode signals in the single-mode fiber cores are multiplexed toN orbital angular momentum modes in the middle annular fiber core, the mode division multiplexing is realized, and so the transmission capacity of an optical fiber communication system is increased.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Mode coupler with wavelength-division multiplexing function, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109031531AEasy to operateHigh precisionCoupling light guidesThermal isolationFew mode fiber
The invention provides a mode coupler with a wavelength-division multiplexing function, and a preparation method thereof. The coupler is manufactured by a plurality of optical fibers through a thermalisolation biconical taper and a fused biconical taper so as to realize the simultaneous multiplexing of multiple wavelengths and multiple modes. The thermal isolation fused biconical taper is performed on the optical fiber, the phase matching is realized between the fine-drawn optical fiber cladding, and the wavelength multiplexing is realized by adjusting stretching distance. The mode coupler issimple in operation and high in accuracy. The simultaneous multiplexing of the wavelength and mode is small in loss, high in mode purity, small in inter-mode cross-talking, large in work bandwidth, and stable in performance, and has extensive application prospect in the field of the high-order mode production, the mode conversion, the mode-division multiplexing, the wavelength-division multiplexing, the few-mode optical fiber laser and like fields.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
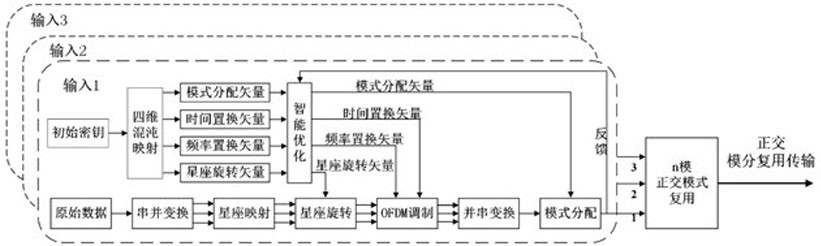
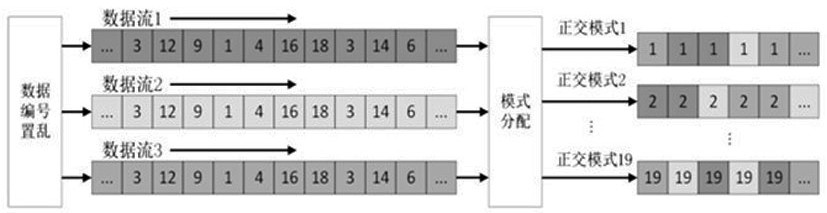
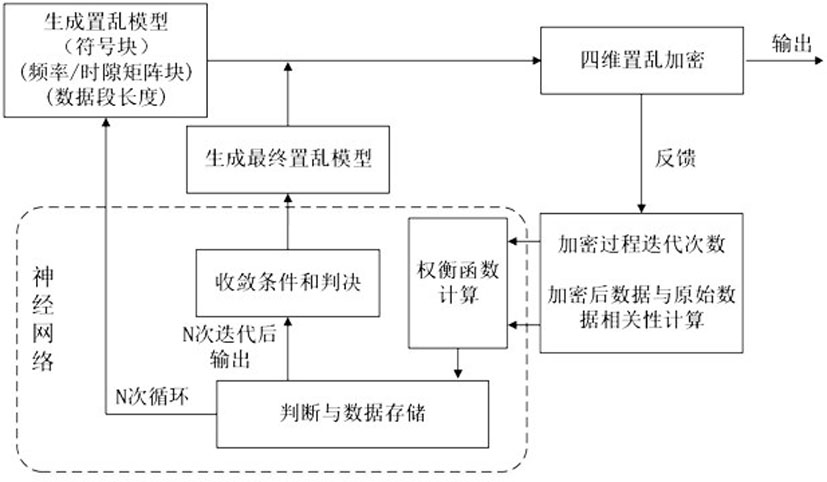
Intelligent optimization four-dimensional chaotic vector encryption orthogonal transmission method
ActiveCN111934848AAchieve coordinated optimizationReduce negative efficiencyOptical mode multiplex systemsFree-space transmissionDigital signal processingCommunications security
The invention discloses an intelligent optimization four-dimensional chaotic vector encryption orthogonal transmission method. The invention belongs to the technical field of information transmission,the method is based on an orthogonal mode division multiplexing transmission system. A communication system is encrypted from four dimensions of communication constellation, OFDM subcarrier frequency, the time and the mode; enough key space can be provided by multi-dimensional hyper-chaotic encryption to provide powerful guarantee for communication security, innovatively utilize machine learningto multi-dimensional encryption optimization, and realize coordination optimization between dimensions, thereby effectively reducing the time of an encryption processing process, and reducing the negative efficiency of the communication system with encryption steps in the digital signal processing module. Compared with a traditional encryption transmission scheme, the scheme provided by the invention has more powerful security guarantee, and the encryption cost is lower.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
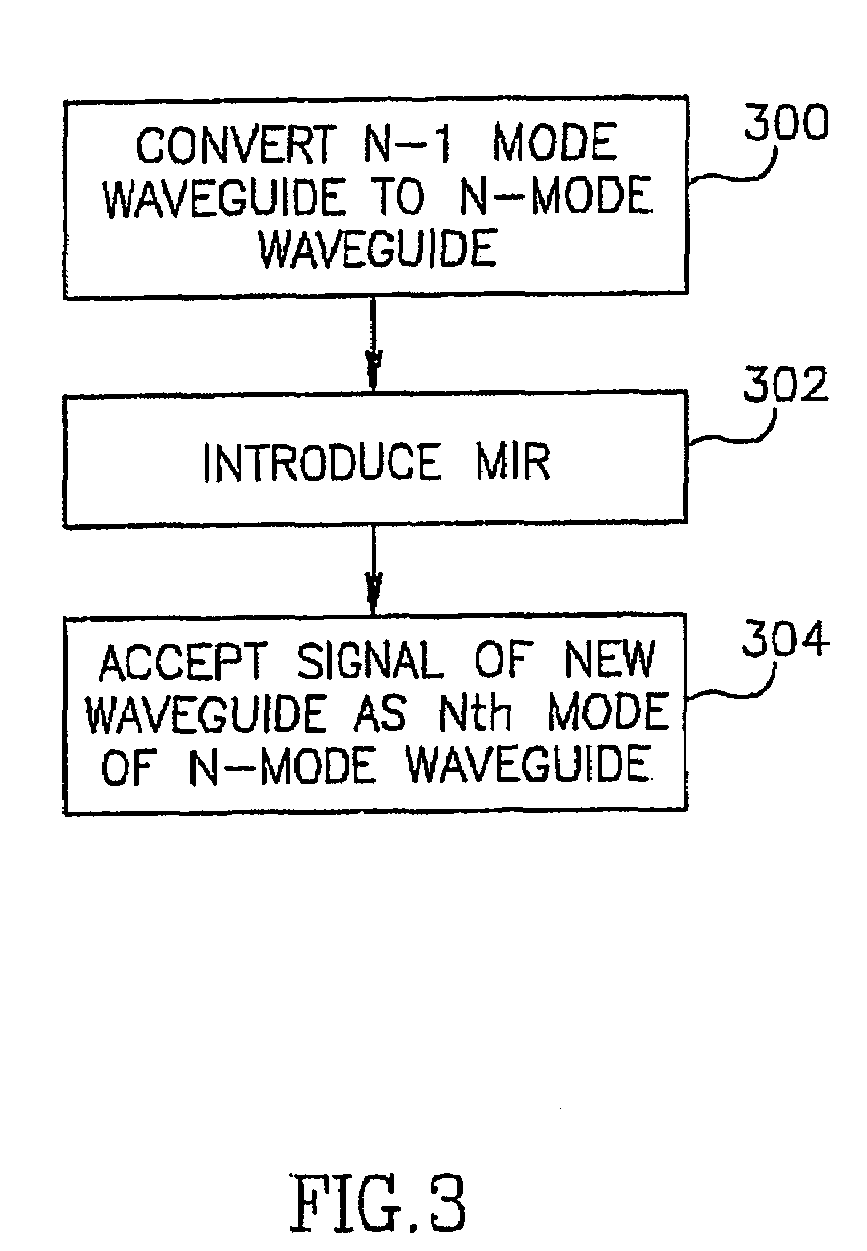
Method and apparatus for optical mode division multiplexing and demultiplexing
A method of mode selective coupling or mode multiplexing between integrated multimode (600) and single mode (602) waveguides. Evanescent coupling and tapering is used so that the signal may be transferred adiabatically from a first region of a first waveguide to a second, proximal, region of a second waveguide.
Owner:NEOPHOTONICS CORP
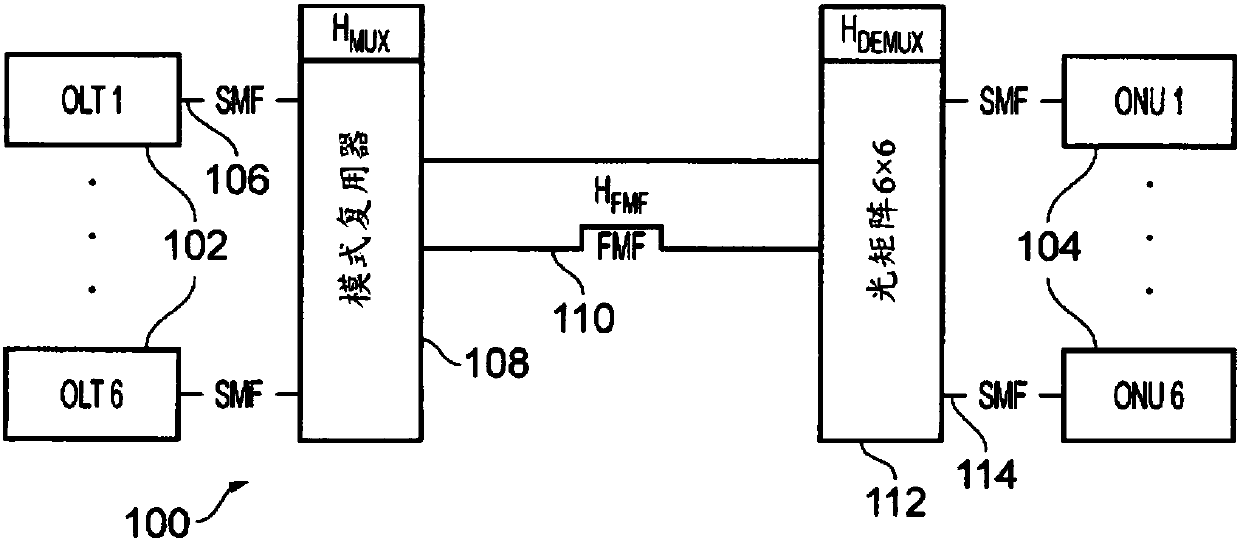
Mode division multiplexed passive optical network
InactiveCN108028718ALow costOptical mode multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationMultiplexerEngineering
A mode division multiplexing passive optical network (PON) in which channel estimation / inversion is performed in the optical domain. The PON comprises a plurality of input channels; a multiplexer having a plurality of input ports connected to a respective one of the input channels; an optical fiber having an uplink end connected to an output port of the multiplexer, whereby the multiplexer outputsa mode multiplexed signal corresponding to the optical signals from the plurality of input channels. The PON includes an optical equalizer arranged to transfer power between optical signals having different modes to compensate for crosstalk between the different modes. In this system, compensation for crosstalk occurs in the optical domain, e.g. by using the optical equalizer to adapt the opticalsignals where necessary.
Owner:ASTON UNIV
Wavelength division and mode division hybrid multiplexer based on photonic crystal and nanowire waveguide
ActiveCN107976738AApplicable wavelength range is largeSmall sizeOptical waveguide light guideNanowireWaveguide mode
The invention is a wavelength division and mode division hybrid multiplexer based on photonic crystal and nanowire waveguide. A two-dimensional triangular lattice photonic crystal filter (1) is an air-hole photonic crystal plate structure periodically distributed along an X-Y plane, and uses silicon as a host material. An L3-type resonant cavity (2) is formed by removing three air holes. Narrow waveguide structural regions I and II are formed by integrally translating the air holes on a side of the photonic crystal waveguide. A nanowire mode division multiplexer (5) uses silicon as a host material, uses silicon dioxide as a substrate material, and uses asymmetrical directional coupling structure. By using the coupling effect of the microcavity and the waveguide, a download filtering function for a specific-frequency light wave is realized. On this basis, in combination with the nanowire waveguide mode division multiplexing structure, a hybrid multiplexing structure is formed. The wavelength division and mode division hybrid multiplexer can be further cascaded and expanded, can be applied to a C + L band coarse wavelength division (channel spacing of 20 nm) multi-mode (>2) multiplexing system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
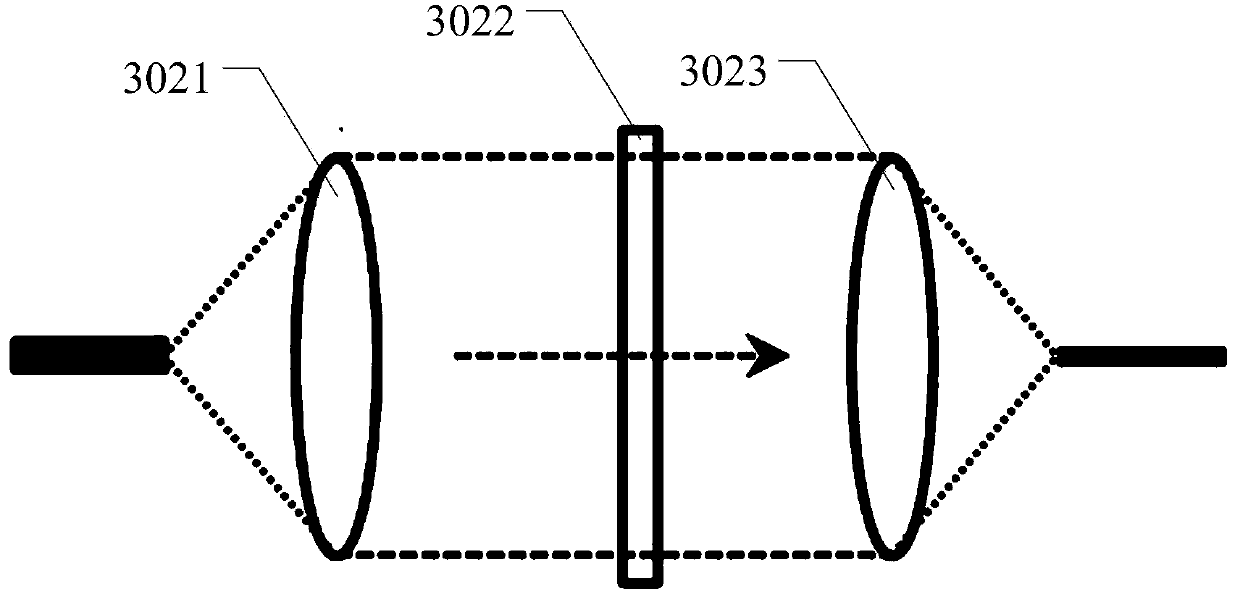
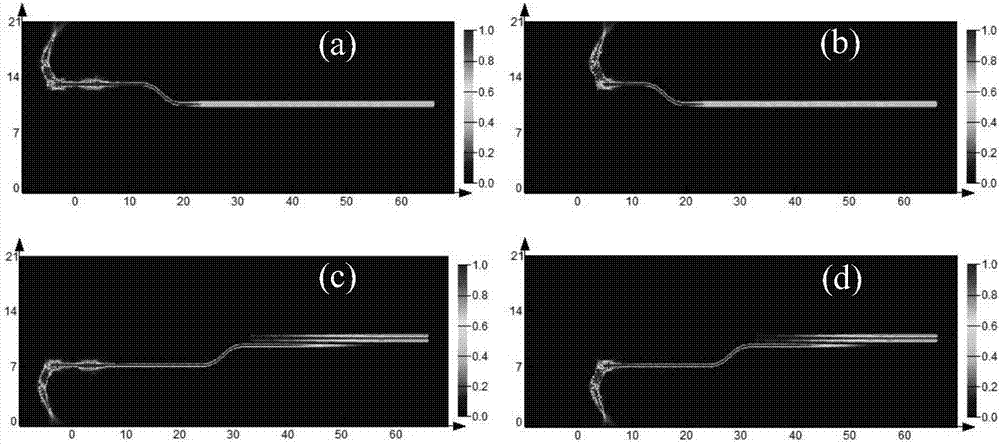
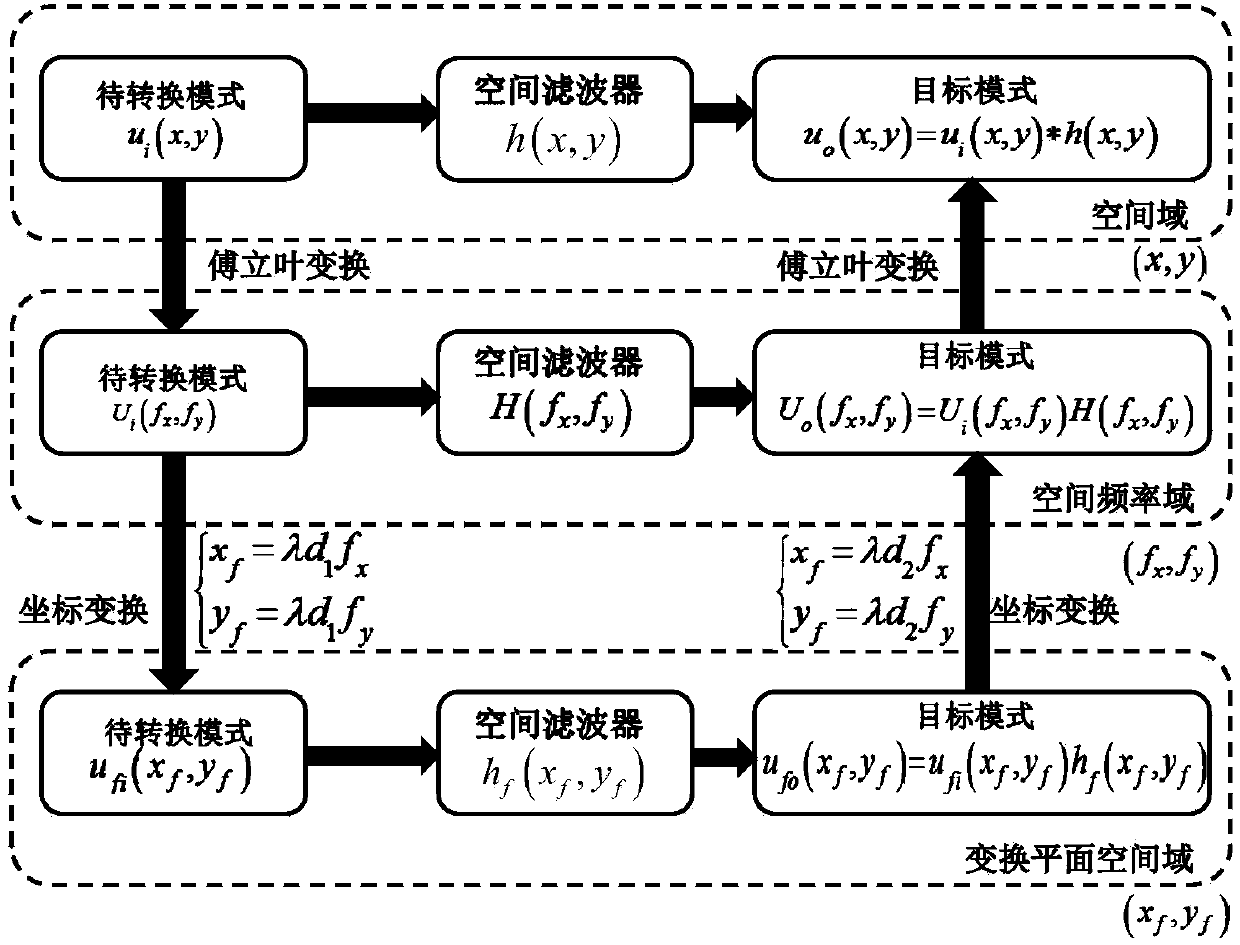
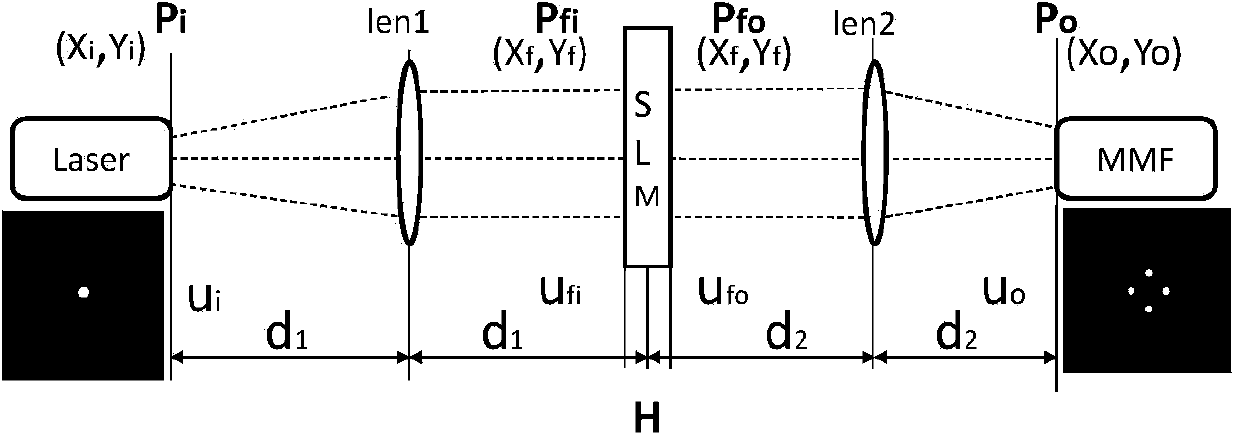
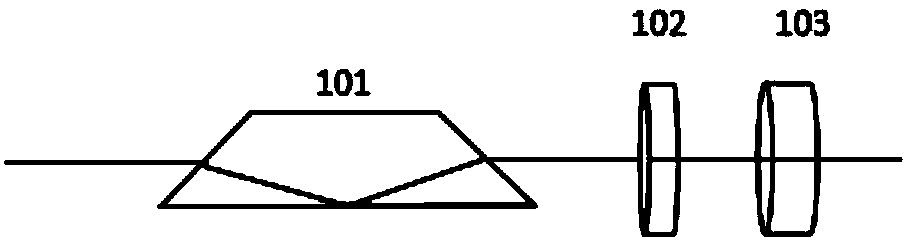
Frequency spectrum mode field radius matching method in mode conversion based on spatial frequency spectrum filtering
ActiveCN103812598AImplement schema conversionOptical mode multiplex systemsFrequency spectrumSpatial light modulator
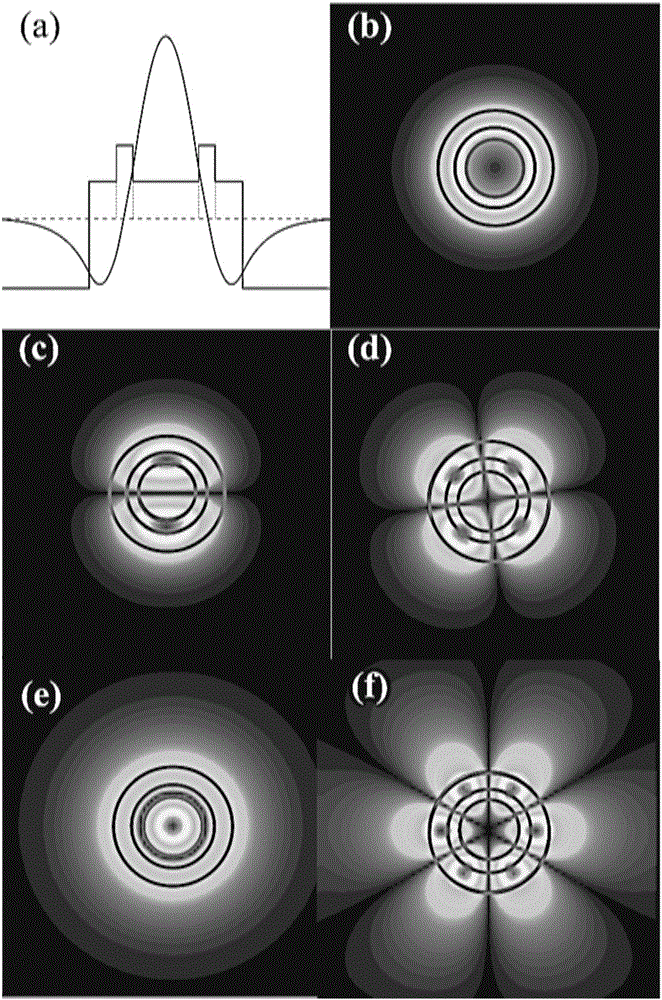
Mode conversion is a key technology of a mode division multiplexing optical fiber communication system, and a conversion method between two arbitrary modes is under study at present. The invention provides a method for achieving conversion among arbitrary modes. The method includes firstly, analyzing mode field distribution characteristics of a mode to be converted and a target mode from a space domain, a spatial frequency domain and a conversion plane space domain, then theoretically establishing a transfer function model of the conversion among the arbitrary modes based on spatial frequency spectrum filtering, and finally using a phase position type space light modulator to build a mode conversion optics system. According to the mode conversion optics system, a conversion plane space domain mode field distribution matching principle is obtained by adapting the mode field beam waist radius of the conversion plane space domain to radiuses of mode fields of different modes, and a matching condition between the mode field beam waist radius of the conversion plane space domain and distribution of the mode fields of the different modes, and a mode field radius matching parsing method of the mode to be converted and the target mode are provided.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Optical fiber for maintaining vortex beam transmission, and manufacturing method of optical fiber
InactiveCN109100827ASimple structureReduce lossOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideOptical communicationMode division multiplexing
The invention relates to an optical fiber for maintaining vortex beam transmission, and a manufacturing method of the optical fiber. The refractive indexes of all cladding layers inside the optical fiber are reasonably configured, and in combination with a rotary wire drawing technology, a spun optical fiber having distributed refractive indexes and applied to a ring structure for maintaining transmission of vortex beam with orbital angular momentum is provided; and the optical fiber has the characteristics of low loss, low bending loss, relatively low chromatic dispersion, relatively large effective area, simple structure, low price, easy for industrial production and the like, is suitable for mode division multiplexing and space division multiplexing systems in optical communication, canbe applied to optical fiber laser devices and optical fiber sensors to perform vortex beam transmission and generation, and has good popularization and application values.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Mode division multiplexed passive optical network
InactiveUS20180234185A1Differential time delayOptical mode multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationMultiplexerEngineering
A mode division multiplexing passive optical network (PON) in which channel estimation / inversion is performed in the optical domain. The PON comprises a plurality of input channels; a multiplexer having a plurality of input ports connected to a respective one of the input channels; an optical fibre having an uplink end connected to an output port of the multiplexer, whereby the multiplexer outputs a mode multiplexed signal corresponding to the optical signals from the plurality of input channels. The PON includes an optical equalizer arranged to transfer power between optical signals having different modes to compensate for crosstalk between the different modes. In this system, compensation for crosstalk occurs in the optical domain, e.g. by using the optical equalizer to adapt the optical signals where necessary.
Owner:ASTON UNIV
Integrated optical mode switch compatible with wavelength division multiplexing function and mode division multiplexing function
The invention relates to an integrated optical mode switch compatible with a wavelength division multiplexing function and a mode division multiplexing function. The integrated optical mode switch comprises a plurality of multiplexing units arranged sequentially; every two adjacent multiplexing units are connected together through an adiabatic cone; the multiplexing unit is composed of a pluralityof micro-ring resonators which are connected with one another sequentially; the micro-ring resonator comprises a first straight waveguide and a second straight waveguide which are arranged in parallel; a nano-silicon-based nanowire micro-ring is arranged between the two straight waveguides; the first straight waveguides of two adjacent micro-ring resonators in the same multiplexing unit are connected with one another; all the first straight waveguides in the same multiplexing unit are connected with one another so as to form a first output waveguide; and the first output waveguide of one multiplexing unit is connected with an output waveguide in a multiplexing unit adjacent to the multiplexing unit. With the optical mode switch adopted, the multiplexing of M modes and N wavelengths can berealized, and the mode of each input end, which is multiplexed into a trunk waveguide, can be freely selected and dynamically switched, so that the number of input ends and output ends in a mode division multiplexing system can be freely allocated, and the paths of the mode division multiplexing system can be selected freely.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Mode division multiplexer, mode division multiplexing system, demultiplexing system and communication system
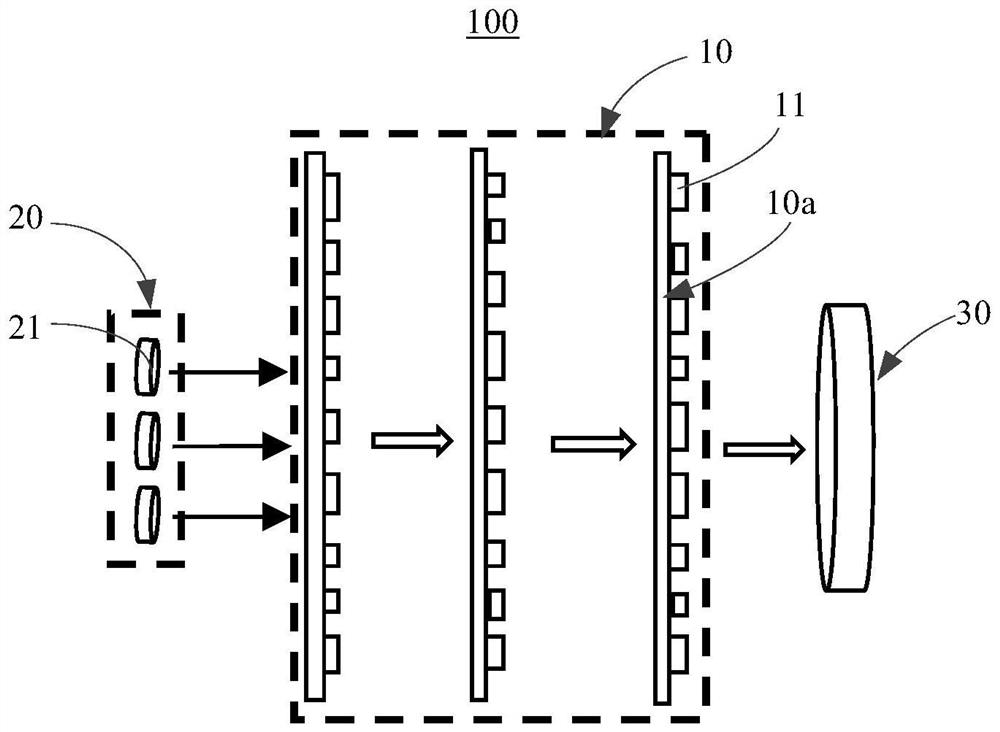
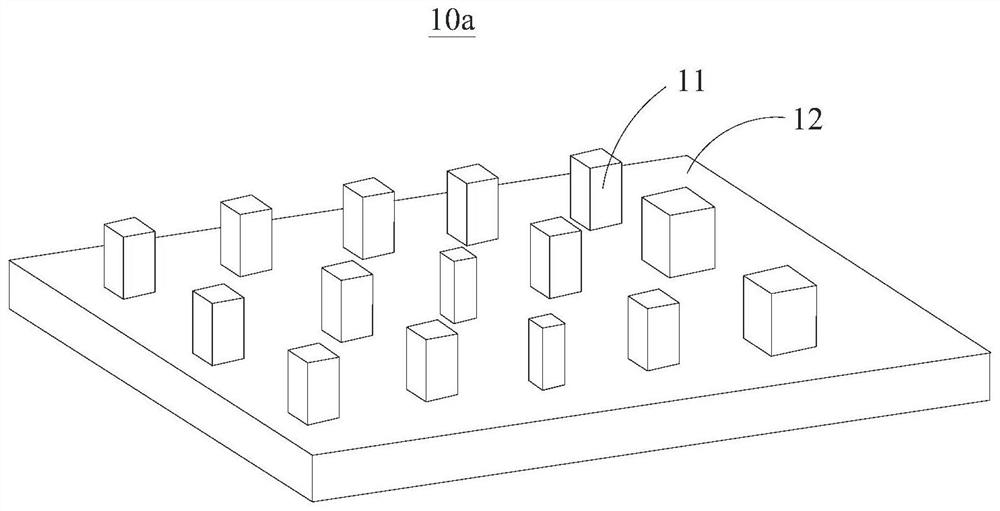
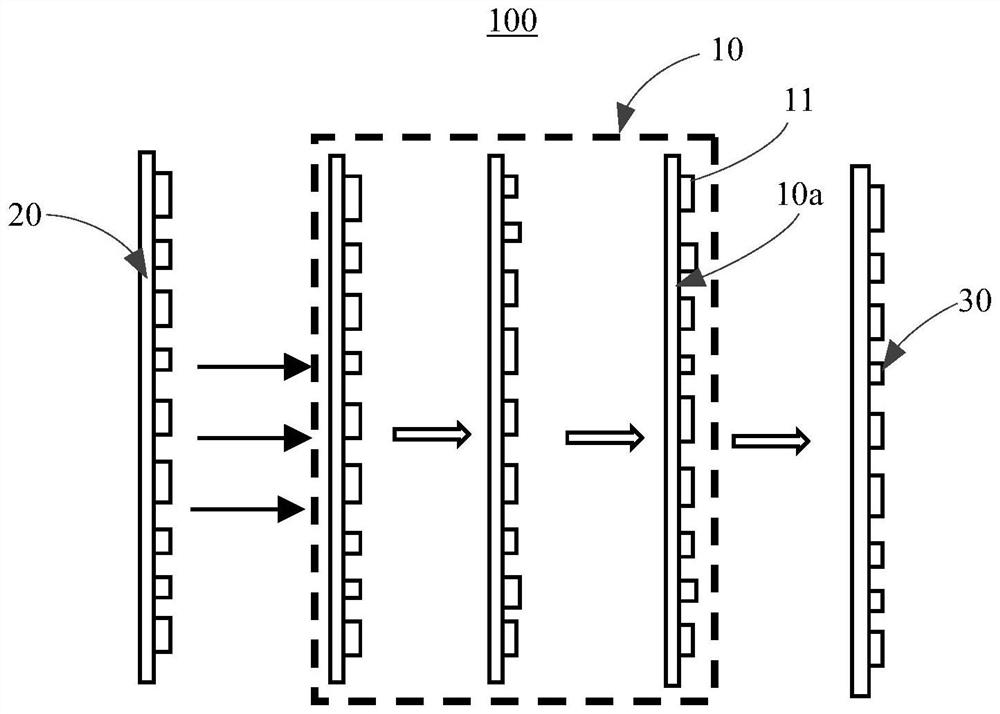
ActiveCN111722320ASmall pixel sizeReduce crosstalkPolarisation multiplex systemsOptical mode multiplex systemsSpatial light modulatorSoftware engineering
The invention provides a mode division multiplexer, a mode division multiplexing system comprising the mode division multiplexer, a demultiplexing system comprising the mode division multiplexer, anda communication system comprising the mode division multiplexing system and the demultiplexing system. The mode division multiplexer includes a metasurface having a plurality of sub-wavelength electromagnetic resonance units arranged in an array. Each electromagnetic resonance unit is used for carrying out phase modulation on the light beam transmitted to the electromagnetic resonance unit so as to convert the spatial mode order of the light beam. Since the size of the electromagnetic resonance units is sub-wavelength, the size of the electromagnetic resonance units is smaller than the pixel size of a spatial light modulator in the prior art, crosstalk of different spatial modes after phase modulation of the mode division multiplexer is low, and crosstalk is low when light beams of different spatial modes are multiplexed in at least mode / multimode optical fibers. Meanwhile, compared with the polarization dependence problem of the spatial light modulator in the prior art, the mode division multiplexer provided by the invention can realize polarization-independent phase modulation.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Quantum key distribution network system and method based on orbital angular momentum multiplexing
ActiveCN107634831ASmooth transmissionRealize long-distance communicationKey distribution for secure communicationMomentumAngular momentum
The invention discloses a quantum key distribution network system and method based on orbital angular momentum multiplexing. The system comprises an Alice control side, an orbital angular momentum mode division multiplexing unit and a Bob user side. The Alice control side comprises a signal modulation unit and an orbital angular momentum multiplexing unit. The orbital angular momentum mode division multiplexing unit comprises a Galileo telescope assembly and an orbital angular momentum separation device. The Bob user side comprises N Bob users. Each Bob user comprises a polarization controllerand a detection device. A light signal generated by the signal modulation unit enters the orbital angular momentum multiplexing unit, the Galileo telescope assembly and the orbital angular momentum separation device in sequence, then is transmitted to the polarization controller of the corresponding Bob user side and finally enters the detection device for detection. According to the system and method, one-to-many communication of quantum network communication is realized, each user is relatively independent, the number of the users can be increased as the orbital angular momentum multiplexing is increased, and the system and the method have high expandability and relatively high practicability.
Owner:NAT QUANTUM COMM GUANGDONG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com