Few mode optical fibers for mode division multiplexing
A technology of few-mode fiber and fiber core, which is applied in the field of few-mode fiber and can solve problems such as difficulty in demultiplexing optical signals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
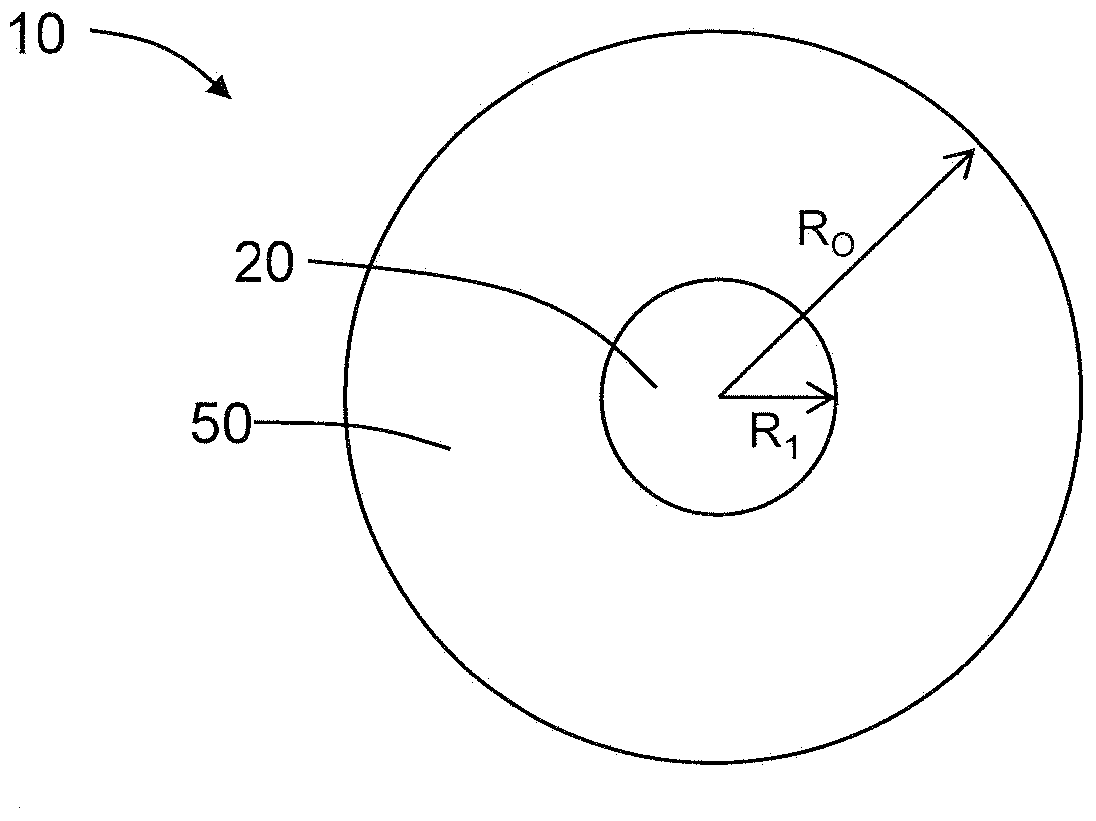
[0026] Reference will now be made in detail to various embodiments of optical fibers for use as long-distance transmission optical fibers, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings. Wherever possible, the same reference numbers will be used throughout the drawings to refer to the same or like parts.
[0027] the term
[0028] The following terminology will be used herein to describe optical fibers, some of which parameters are introduced and defined in conjunction with various exemplary embodiments as follows:
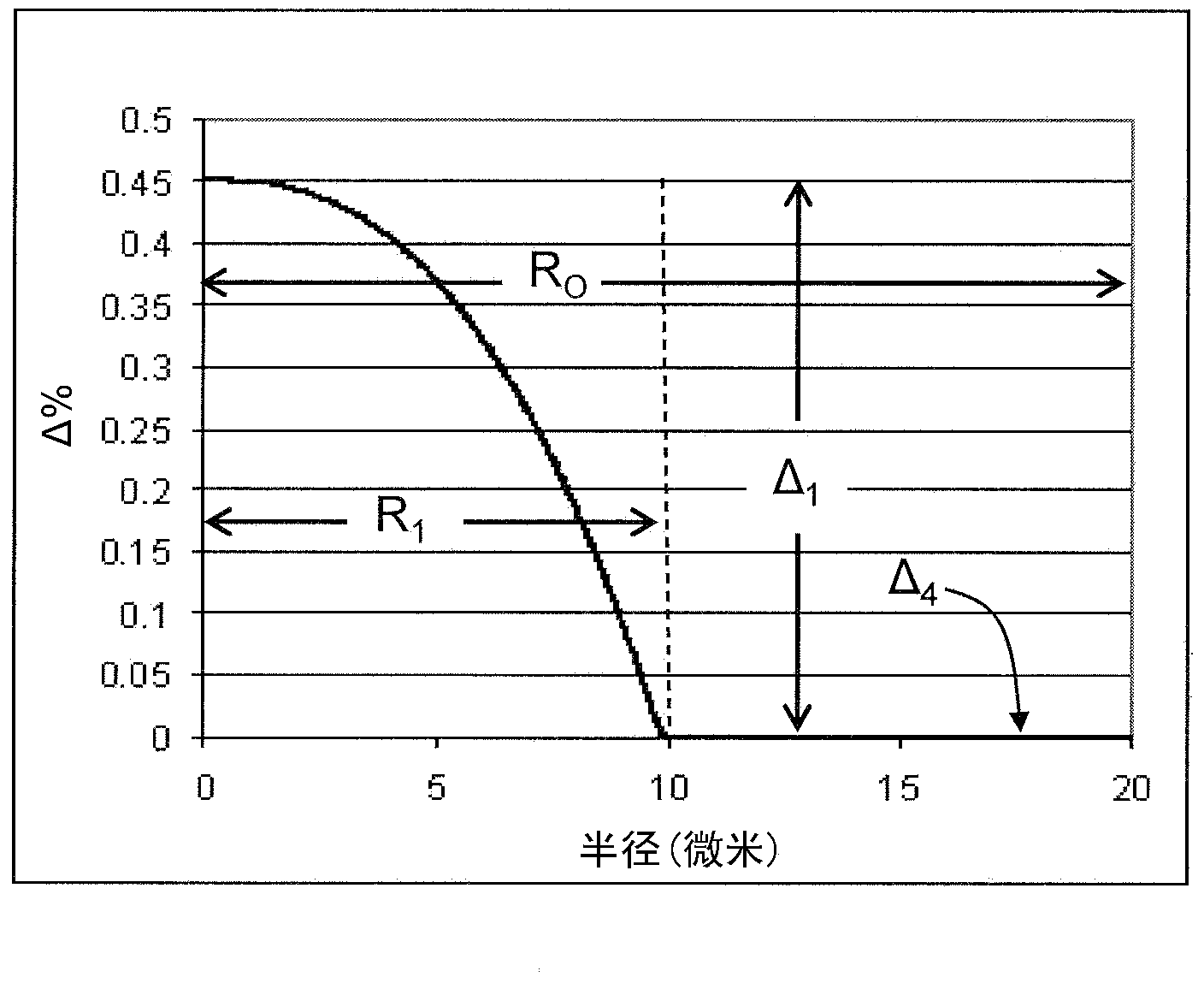
[0029] Herein, the term "refractive index profile" refers to the relationship between the refractive index or the relative refractive index and the radius of the optical fiber.
[0030] The term "relative refractive index", as used herein, is defined as:
[0031] △(r)%=100x[n(r) 2 –n REF 2 )] / 2n(r) 2 ,
[0032] Unless otherwise indicated, n(r) is the refractive index at radius r. Relative refractive indices are defined at 1550 nm unless oth...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Radial thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Radial thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Radius | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com