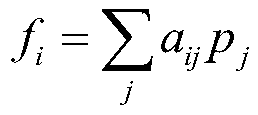Patents
Literature
128 results about "Scale size" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Scale Size 1:43 Scale is a model approximately 3 to 5 inches in length ... 1:18 scale is a model approximately 8 to 11 inches in length 1:12 scale is a model approximately 14 to 16 inches in length
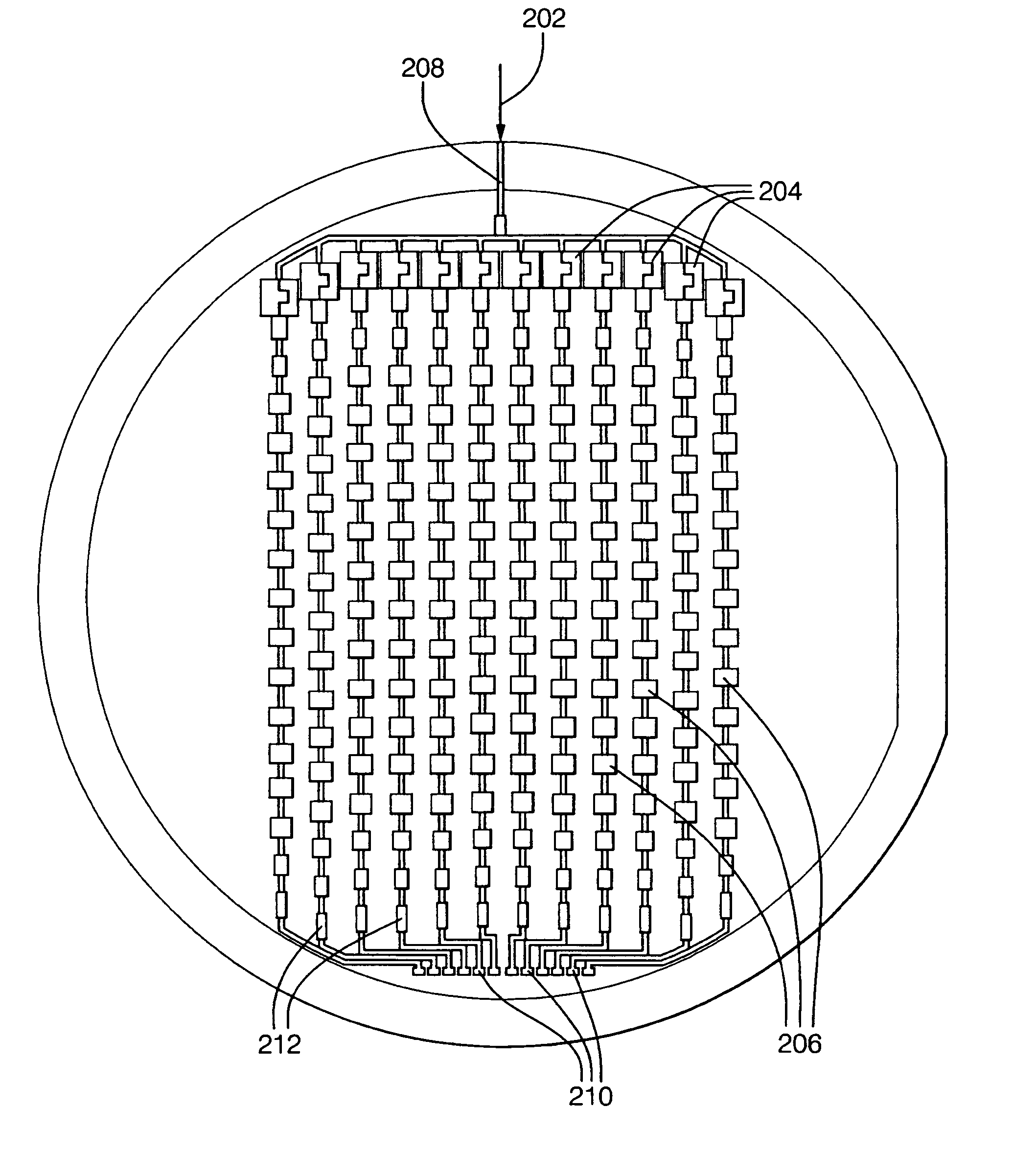
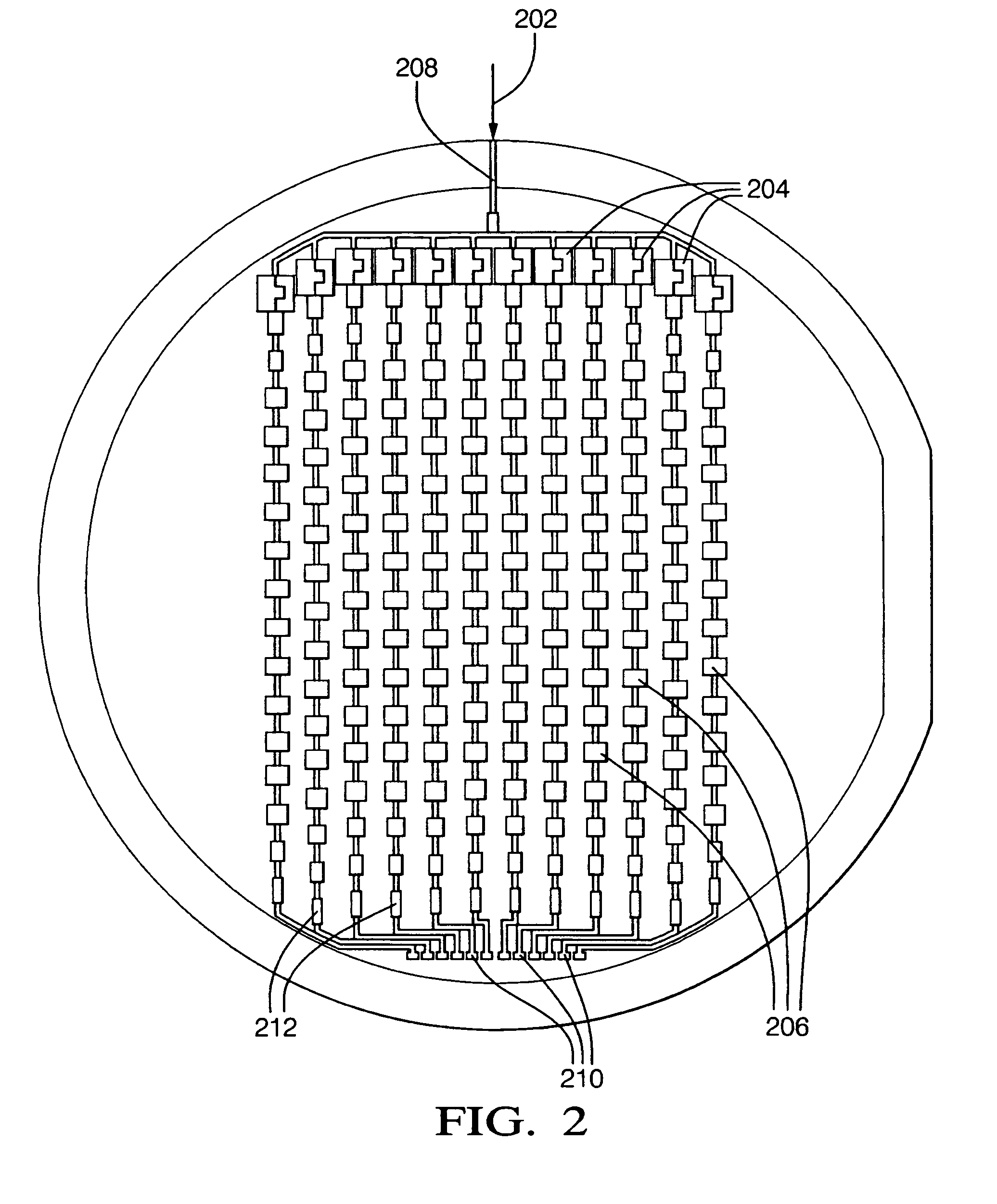
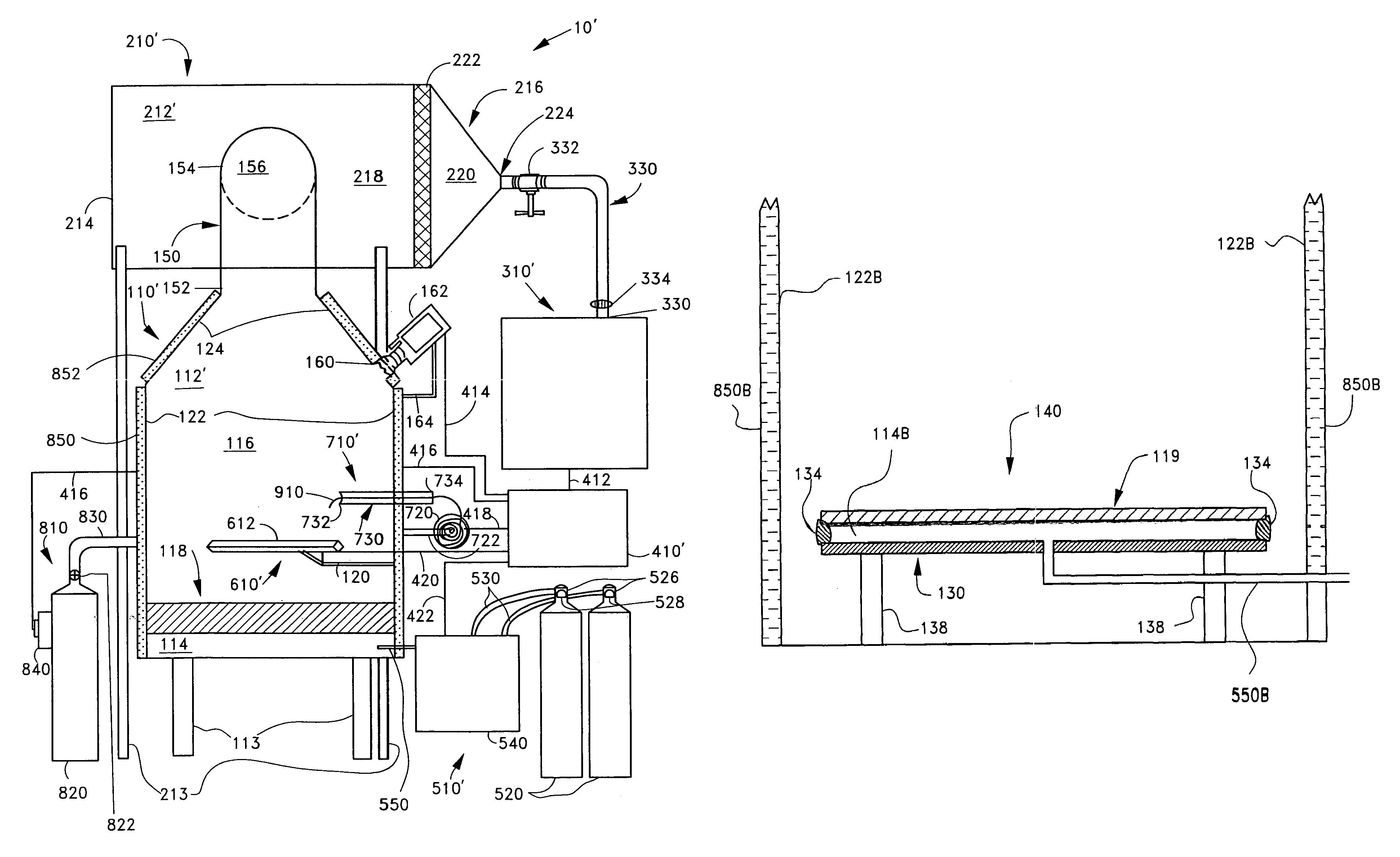
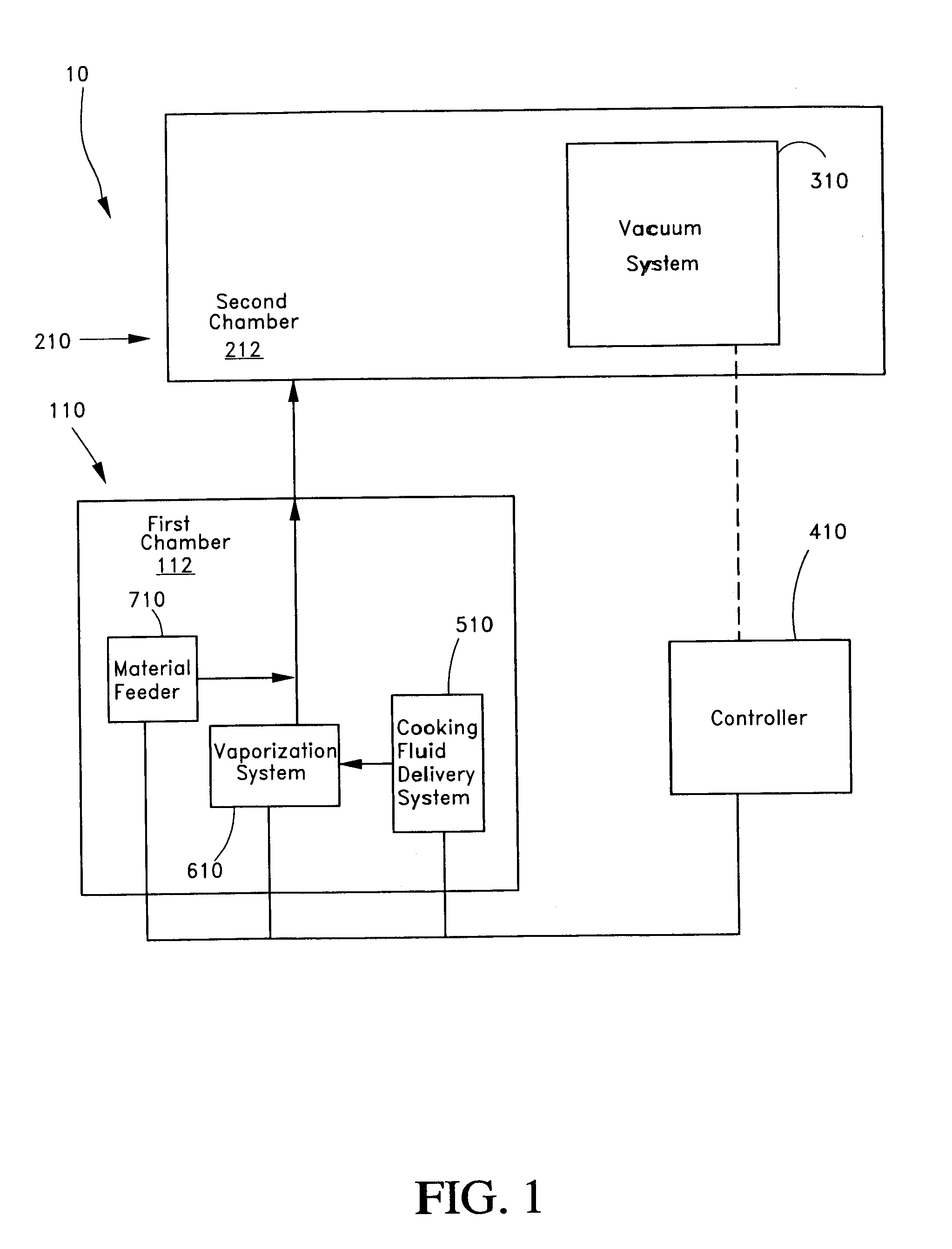
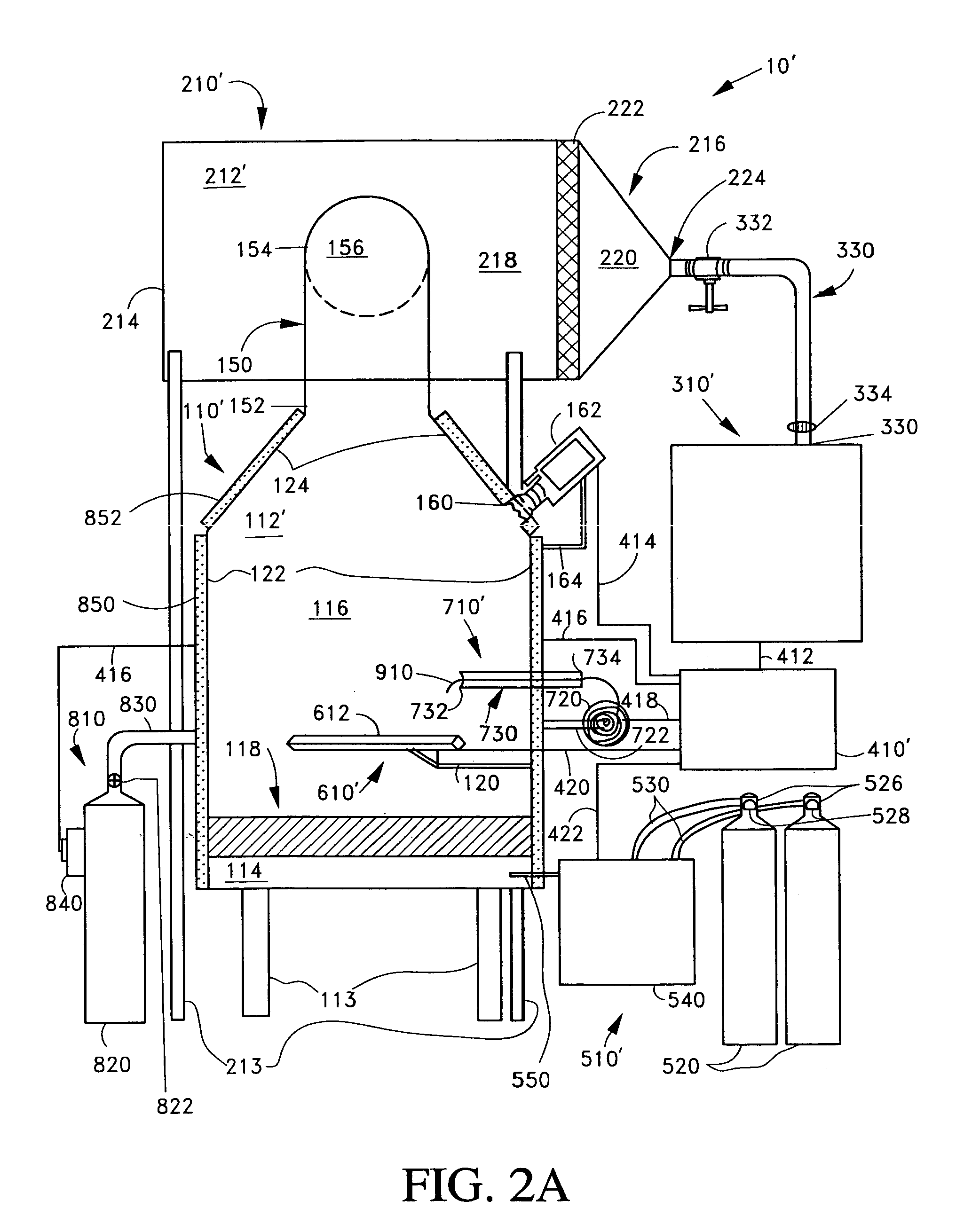
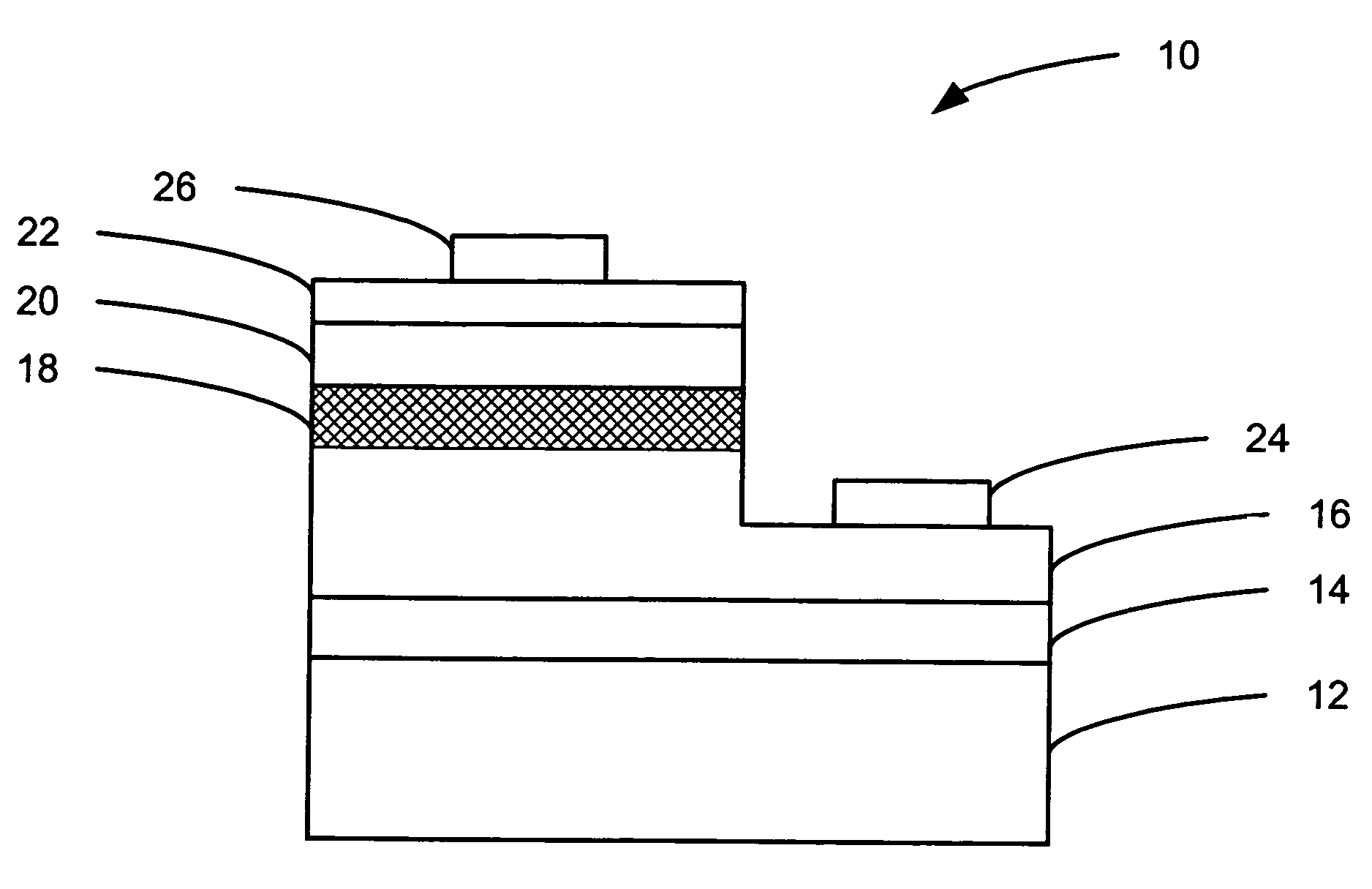
Phase shifters deposited en masse for an electronically scanned antenna
ActiveUS7324043B2Increase processing costPatterning of backsideSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectricEngineering
A system and method for an electronically scanned antenna is provided in which phase shifters are deposited en masse along with other electronically scanned antenna components on a wafer scale substrate using a thin film process. Alternative wafer scale sizes may be utilized to furnish a required antenna aperture area. Significant processing costs for radar and communication systems are saved utilizing the present invention as compared with contemporary discrete phase shifters that are individually mounted on an antenna. In an aspect, the phase shifter is made up of a base electrode, a barium strontanate titanate (BST) ferroelectric varactor and a top electrode. The BST ferroelectric material is a voltage variable dielectric, which generates a radiation phase. The radiation phase is regulated by a phase shifter control. The radiation phase generates an electromagnetic field about a radiating element and electromagnetic radio waves are radiated from the radiating element.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
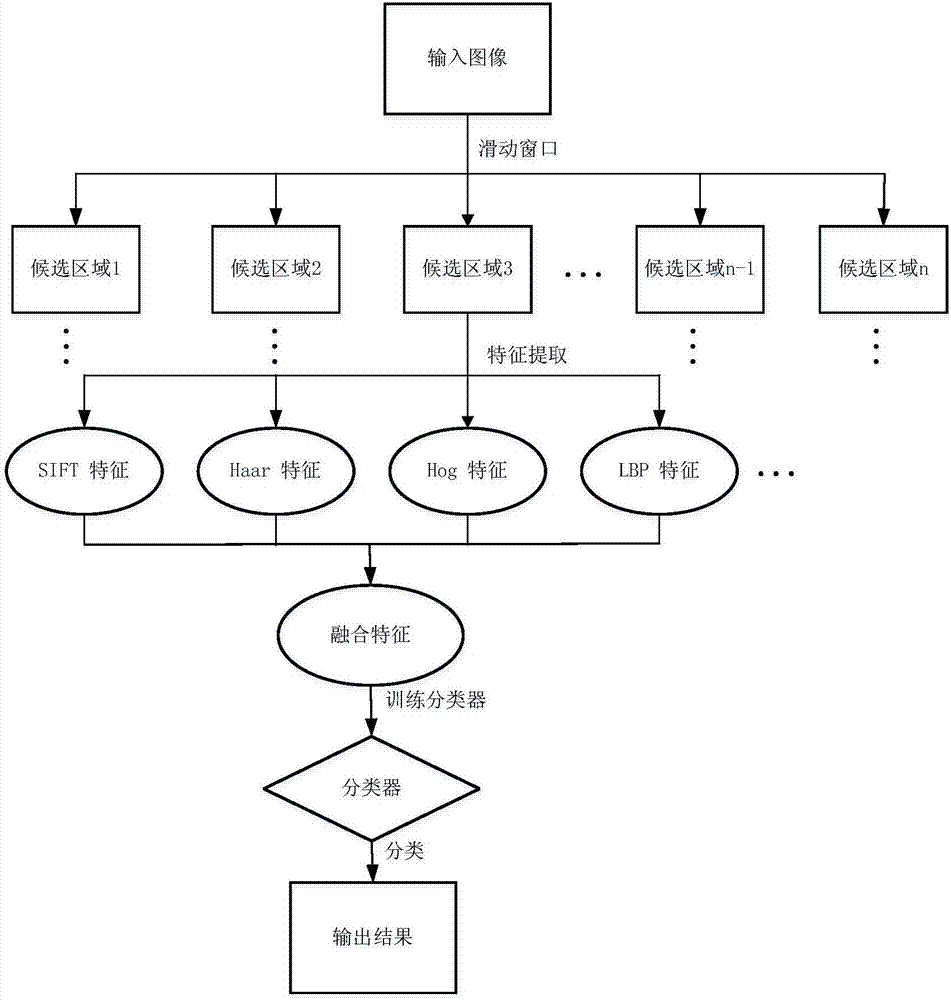
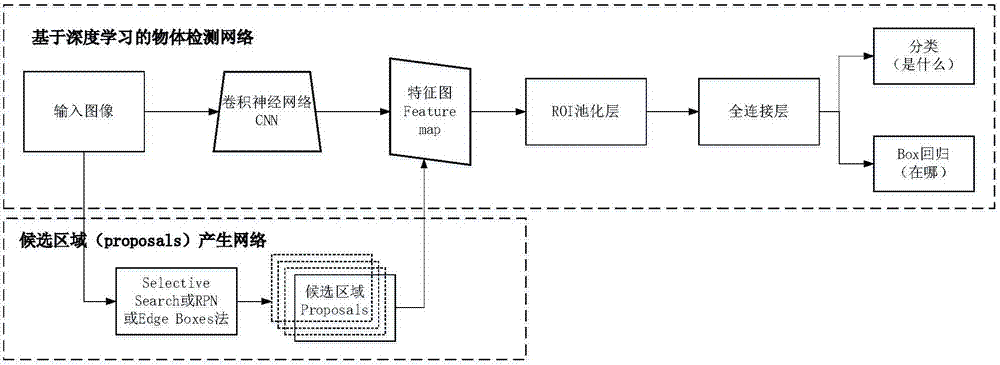
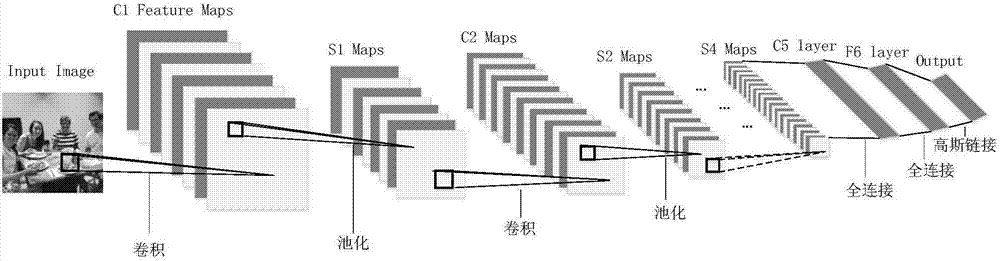
Multi-scale small object detection method based on deep-learning hierarchical feature fusion
ActiveCN107341517ARealize detectionEasy to identifyCharacter and pattern recognitionMachine visionResearch Object
The invention relates to the object verification technology in the machine vision field, and especially relates to a multi-scale small object detection method based on deep-learning hierarchical feature fusion; for solving the defects that the existing object detection is low in detection precision under real scene, constrained by scale size and different for small object detection, the invention puts forward a multi-scale small object detection method based on deep-learning hierarchical feature fusion. The detection method comprises the following steps: taking an image under the real scene as a research object, extracting the feature of the input image by constructing the convolution neural network, producing less candidate regions by using a candidate region generation network, and then mapping candidate region to a feature image generated by the convolution neural network to obtain the feature of each candidate region, obtaining the feature with fixed size and fixed dimension after passing a pooling layer to input to the full-connecting layer, wherein two branches behind the full-connecting layer respectively output the recognition type and the returned position. The method disclosed by the invention is suitable for the object verification in the machine vision field.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method of manufacturing an ultraviolet light emitting AlGaN composition and ultraviolet light emitting device containing same
InactiveUS7498182B1Laser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge carrierUltraviolet lights
An AlGaN composition is provided comprising a group III-Nitride active region layer, for use in an active region of a UV light emitting device, wherein light-generation occurs through radiative recombination of carriers in nanometer scale size, compositionally inhomogeneous regions having band-gap energy less than the surrounding material. Further, a semiconductor UV light emitting device having an active region layer comprised of the AlGaN composition above is provided, as well as a method of producing the AlGaN composition and semiconductor UV light emitting device, involving molecular beam epitaxy.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
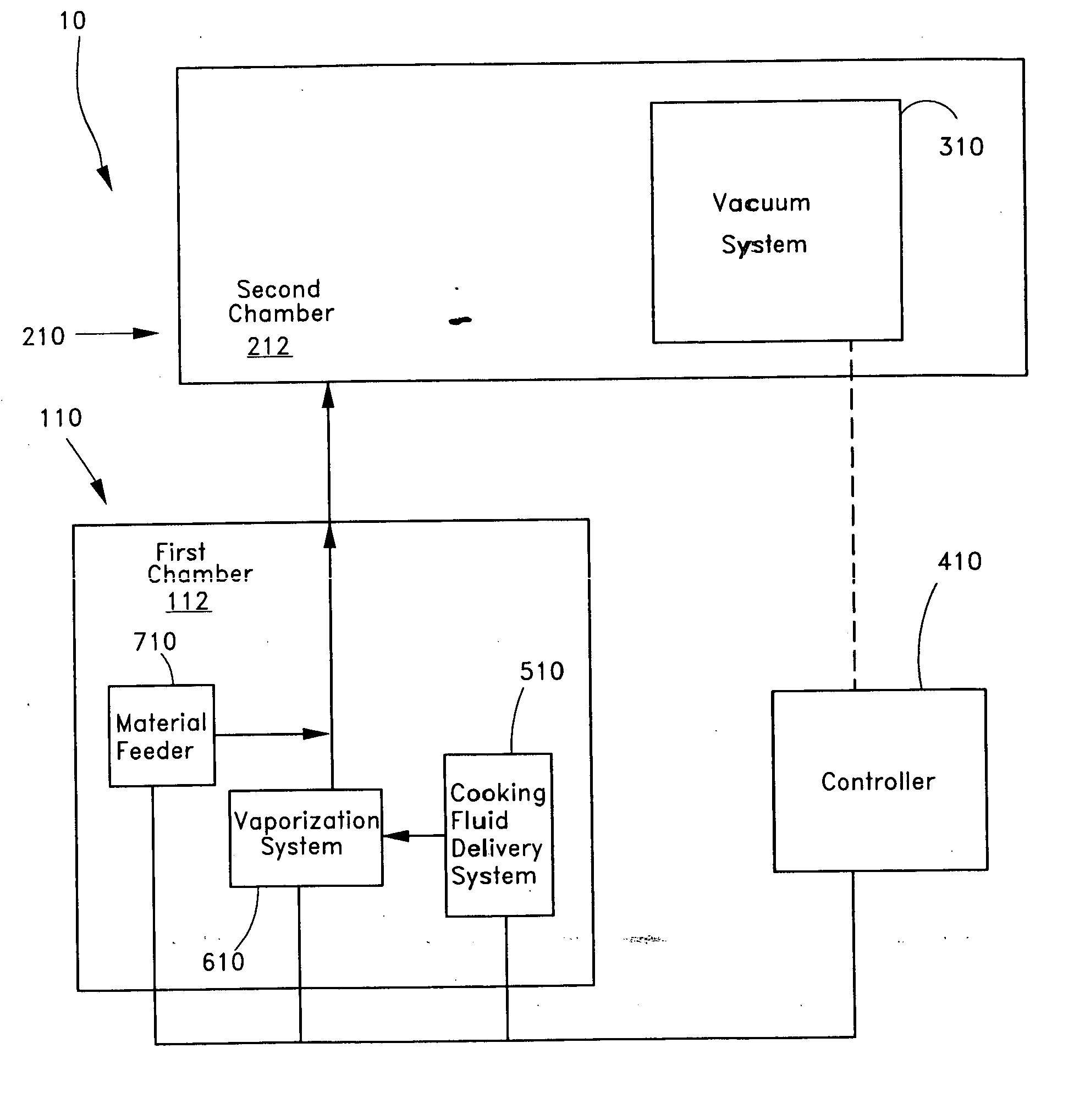
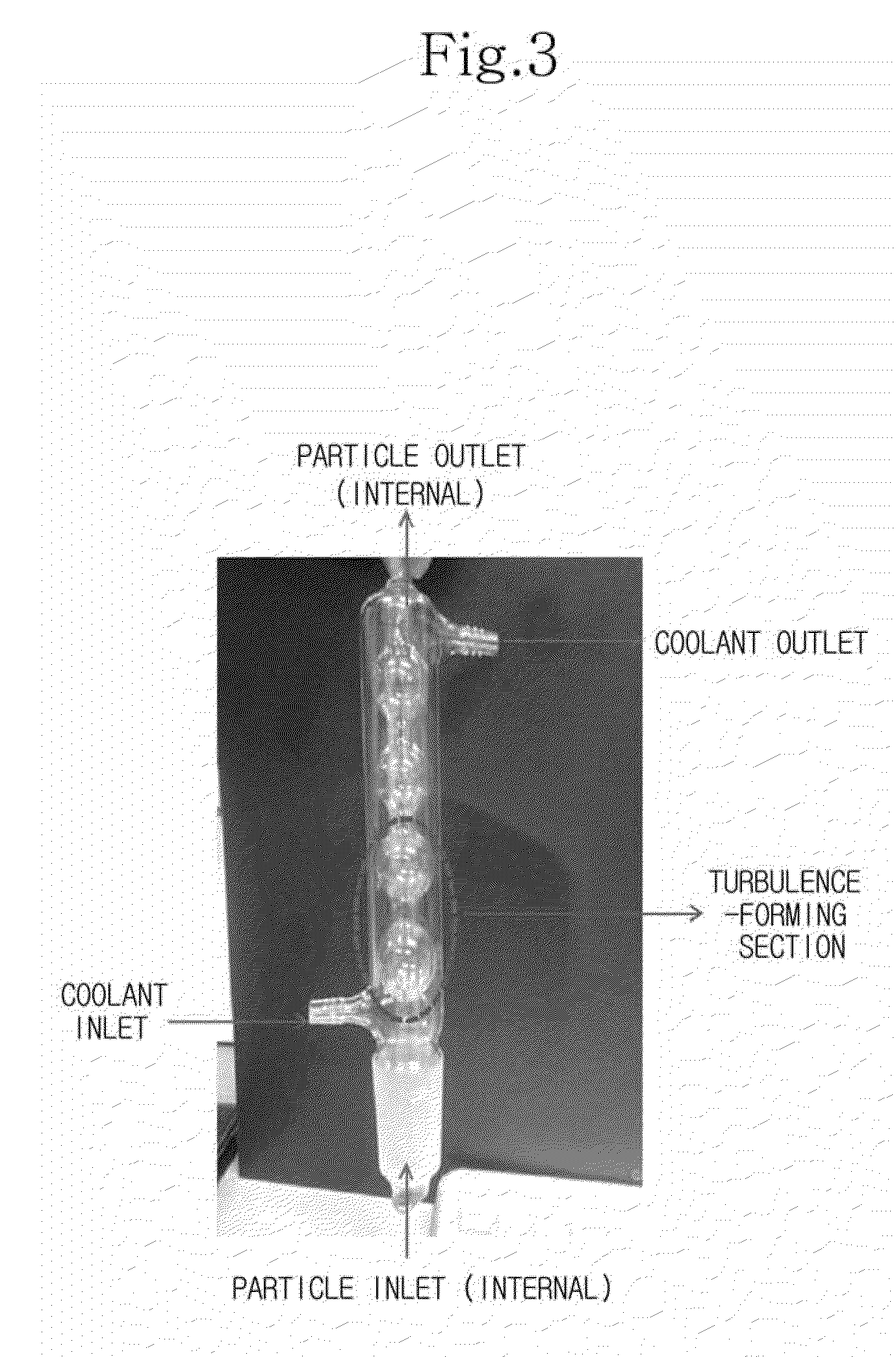
Method and apparatus for forming nano-particles
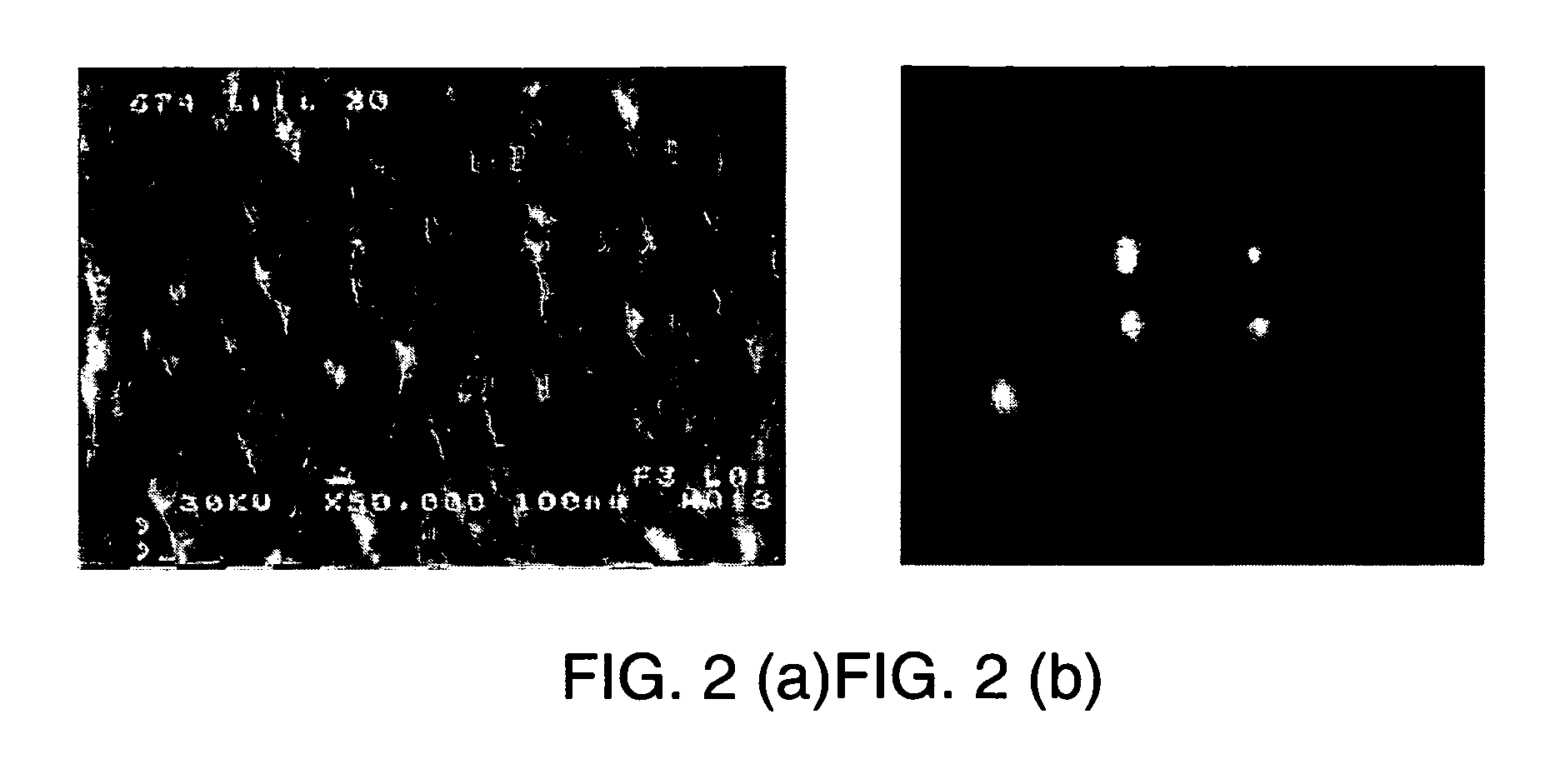
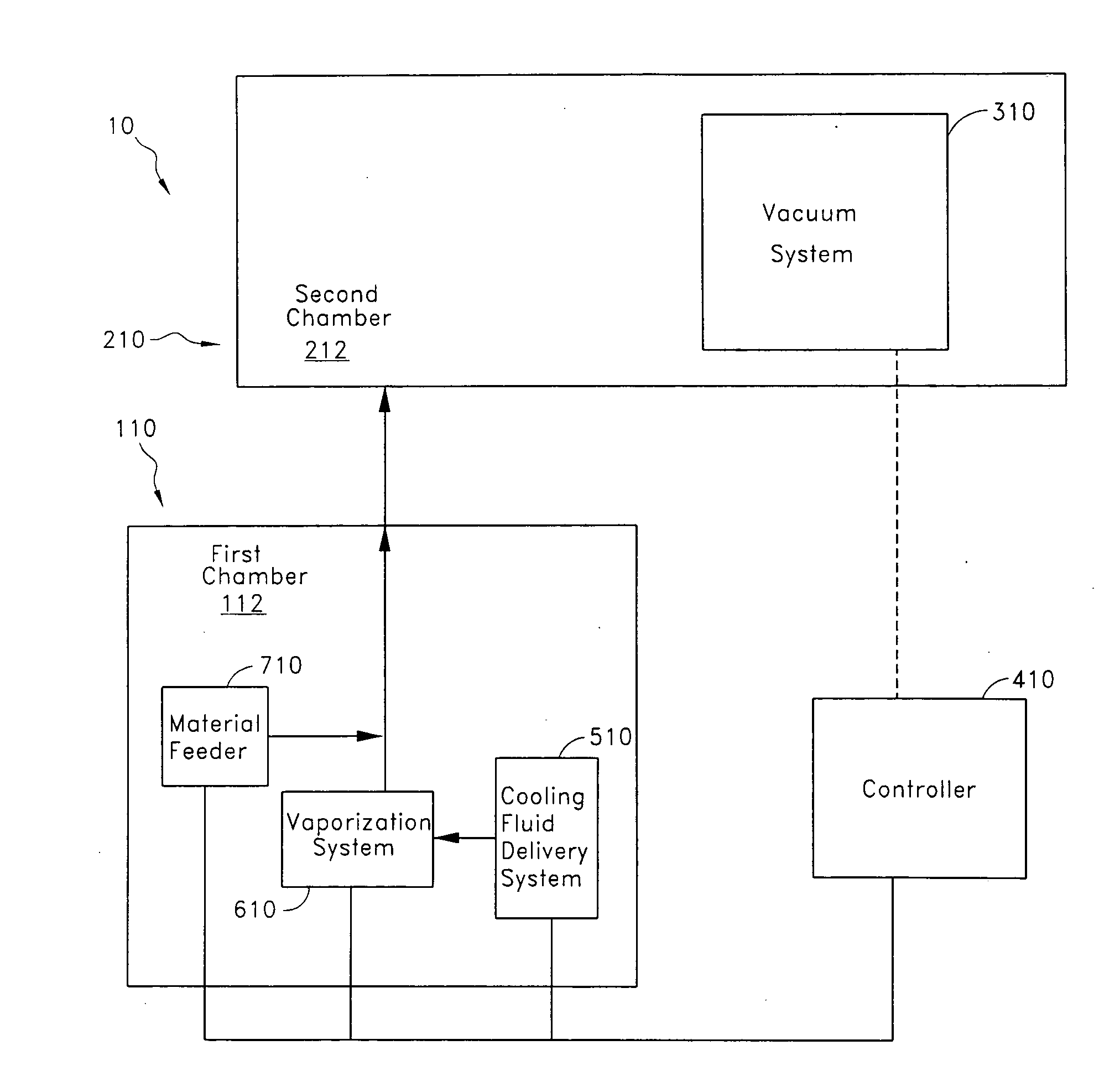
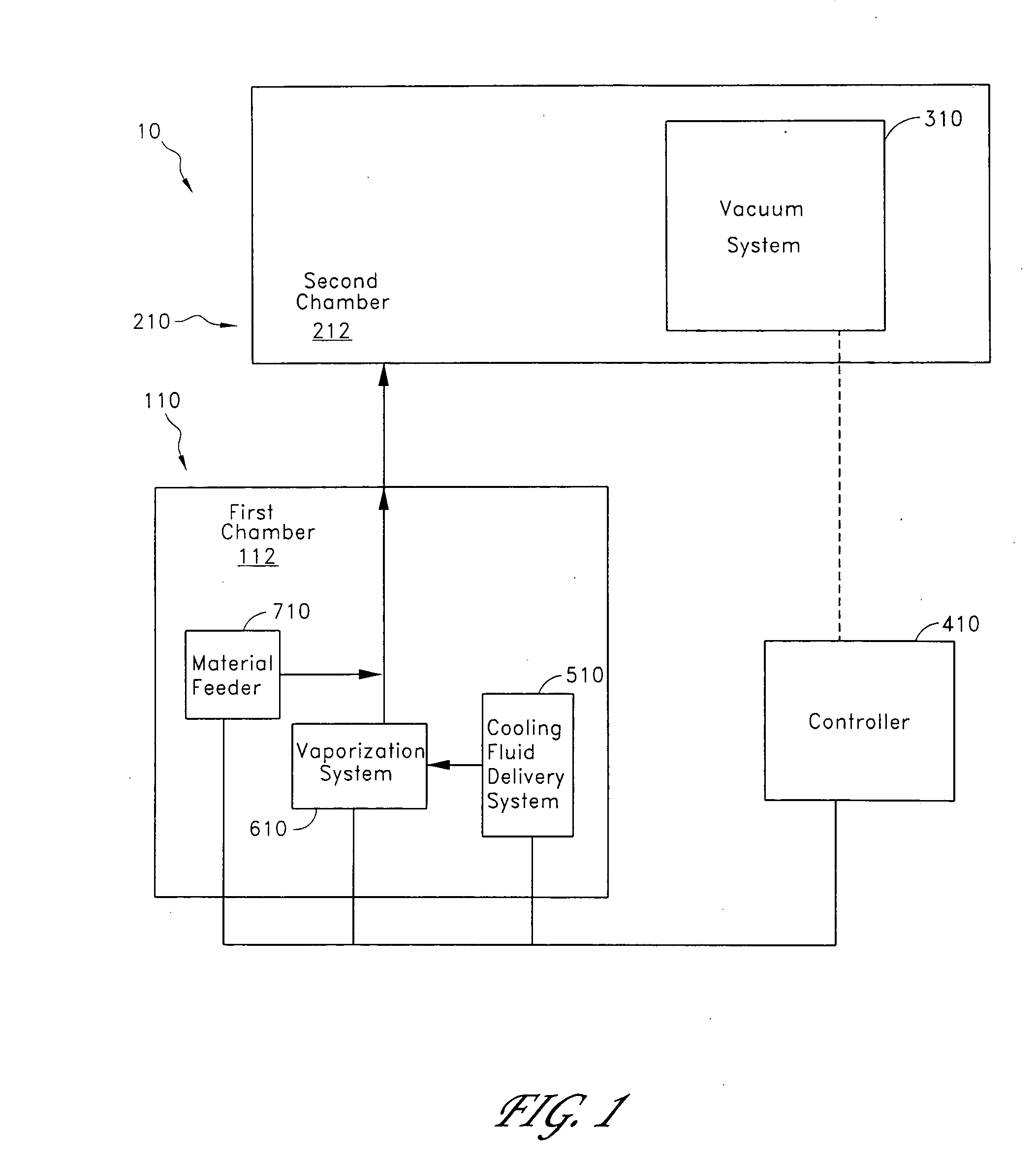
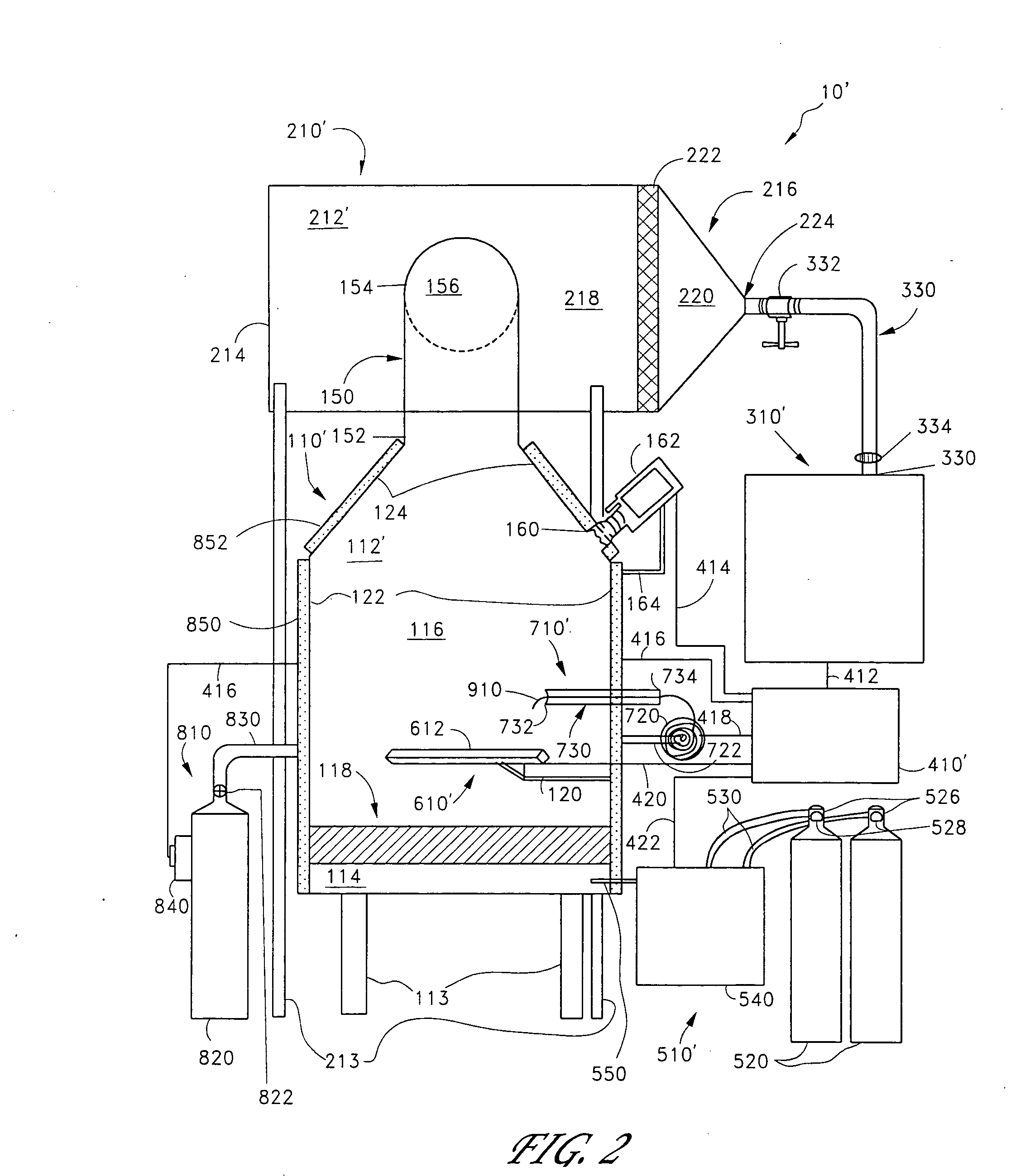
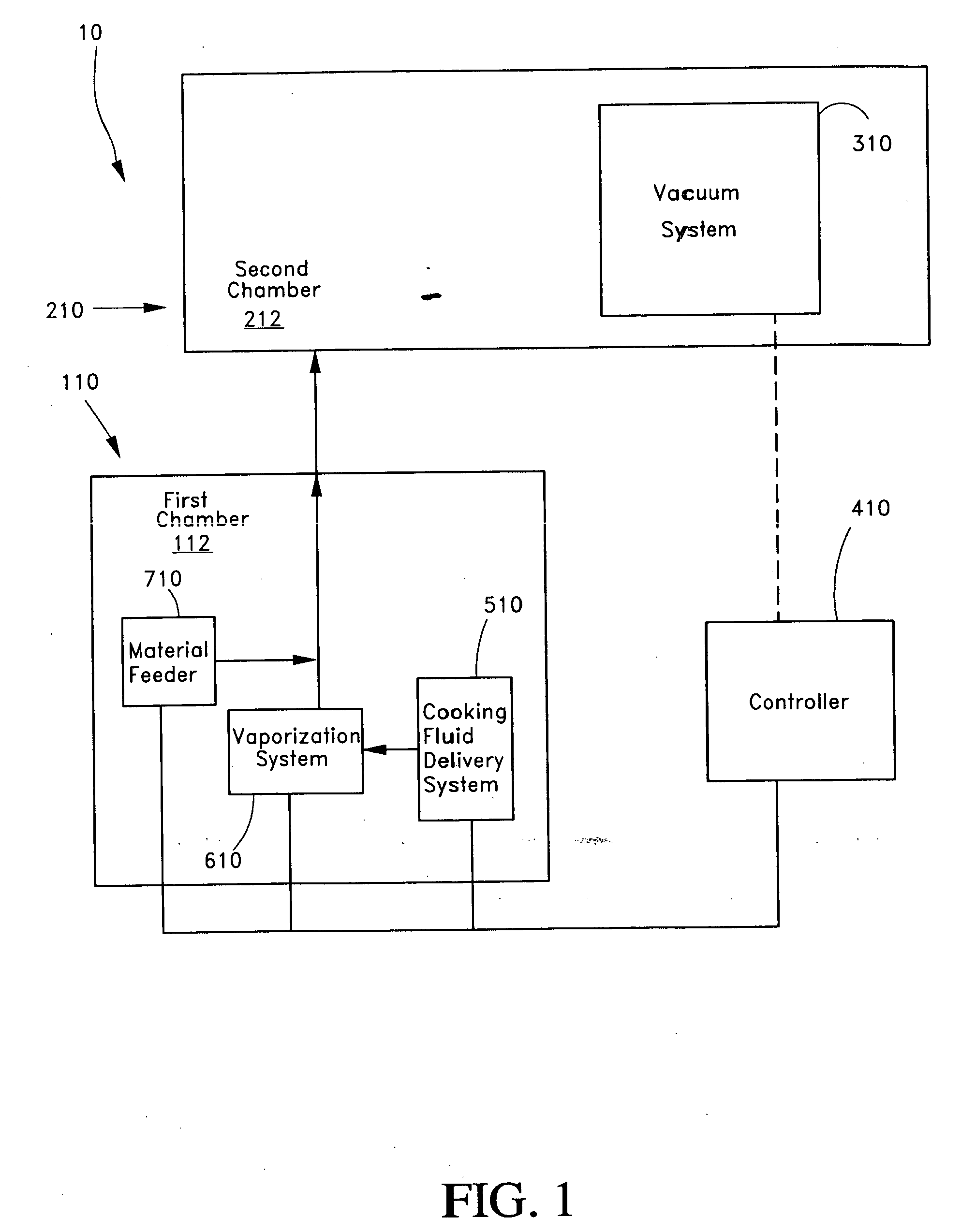
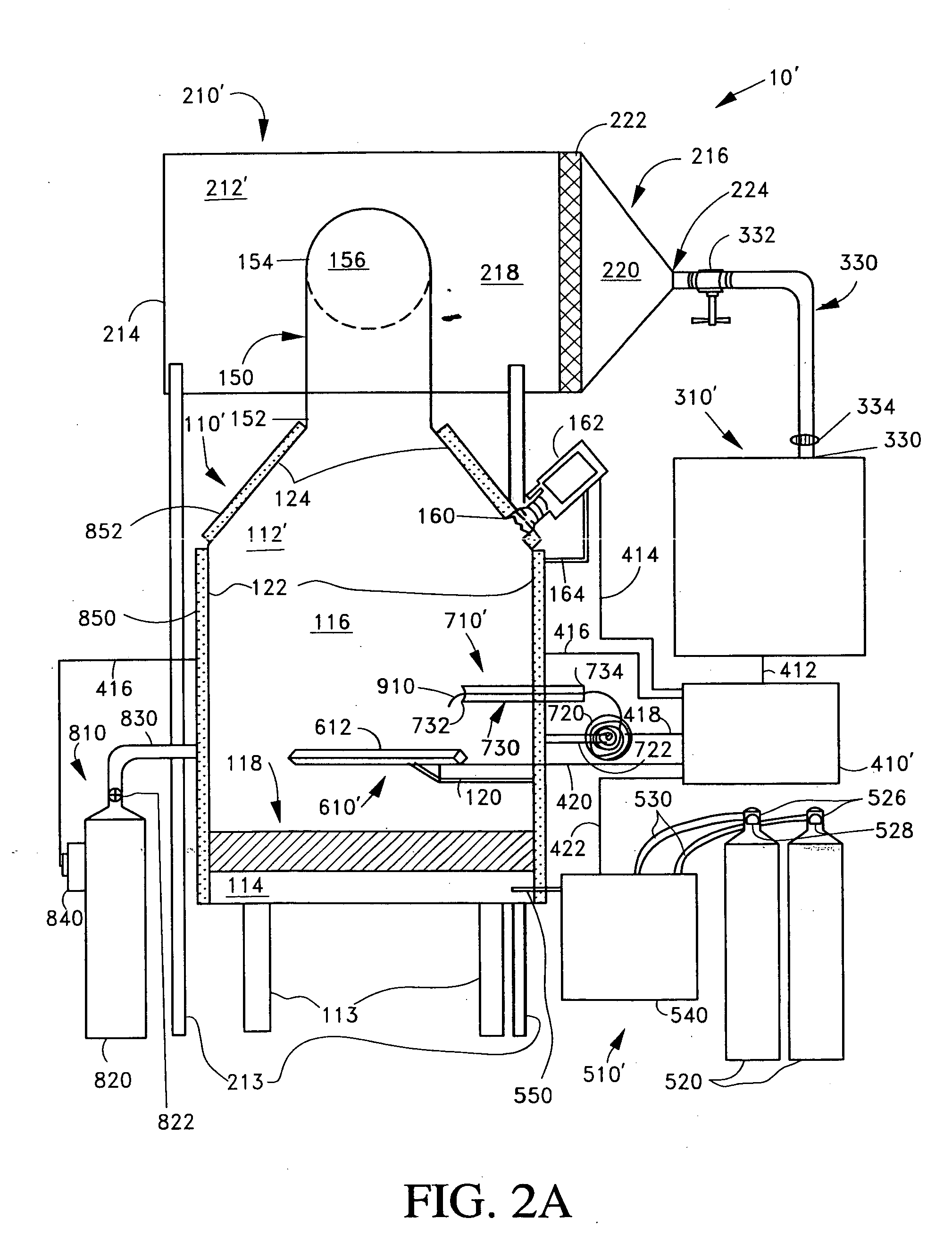
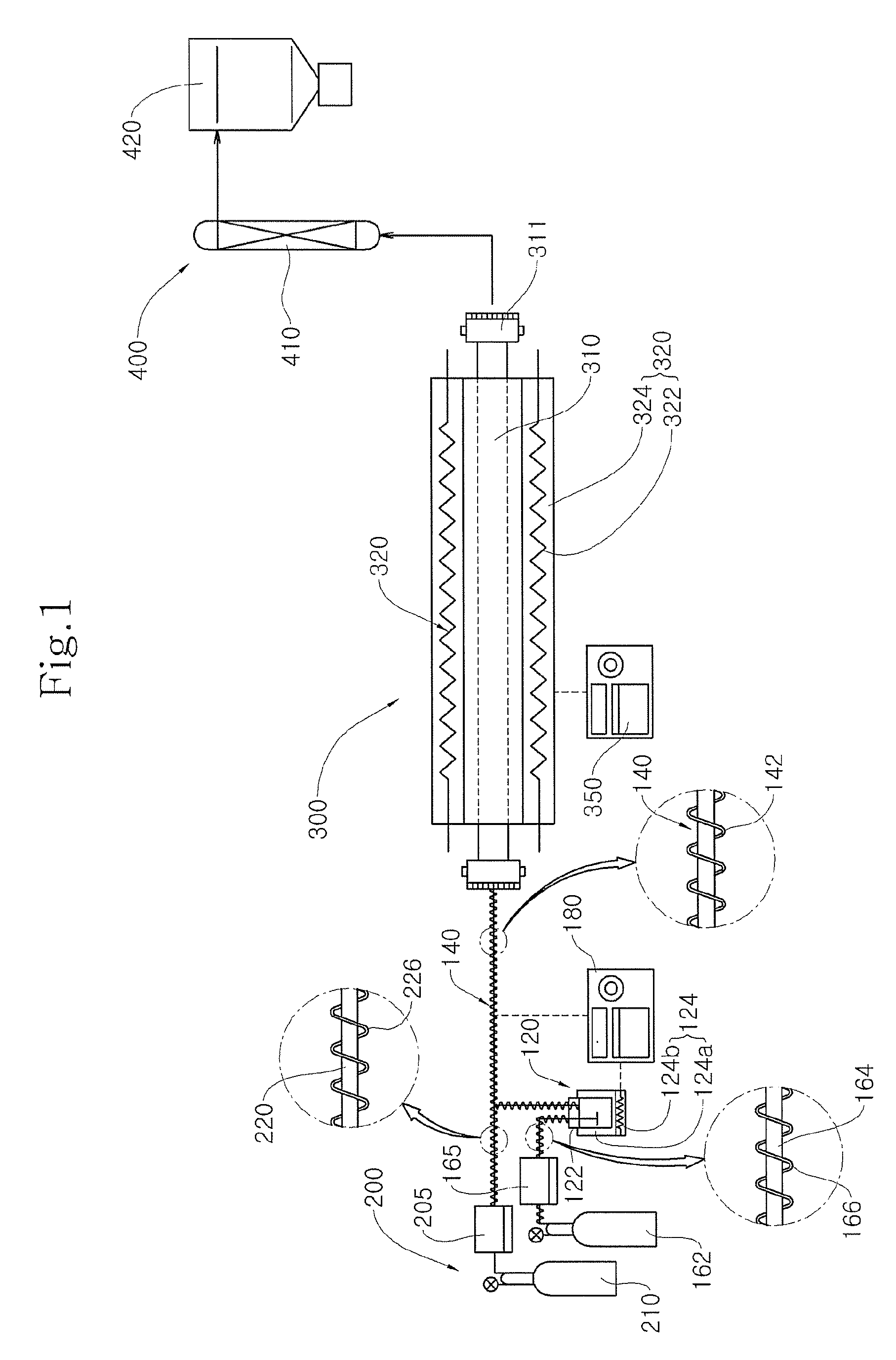
ActiveUS7282167B2Reduce flow turbulenceLarge particle sizeMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingMetallurgyCooling fluid
Nano-scale particles of materials can be produced by vaporizing the material and allowing the material to flow in a non-violently turbulent manner into thermal communication with a cooling fluid, thereby forming small particles of the material that can be in the nano-scale size range.
Owner:VIVAKOR INC +1
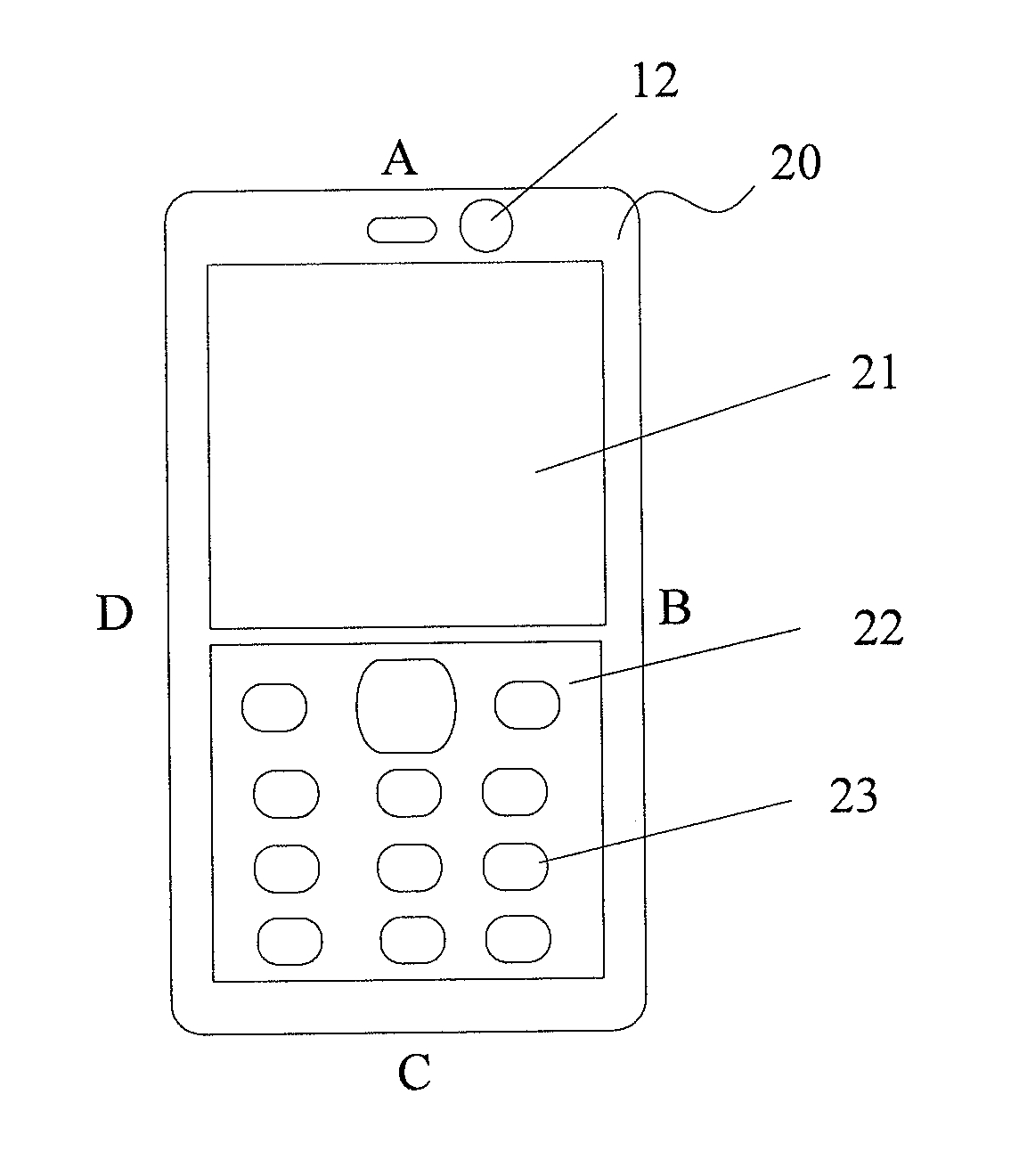
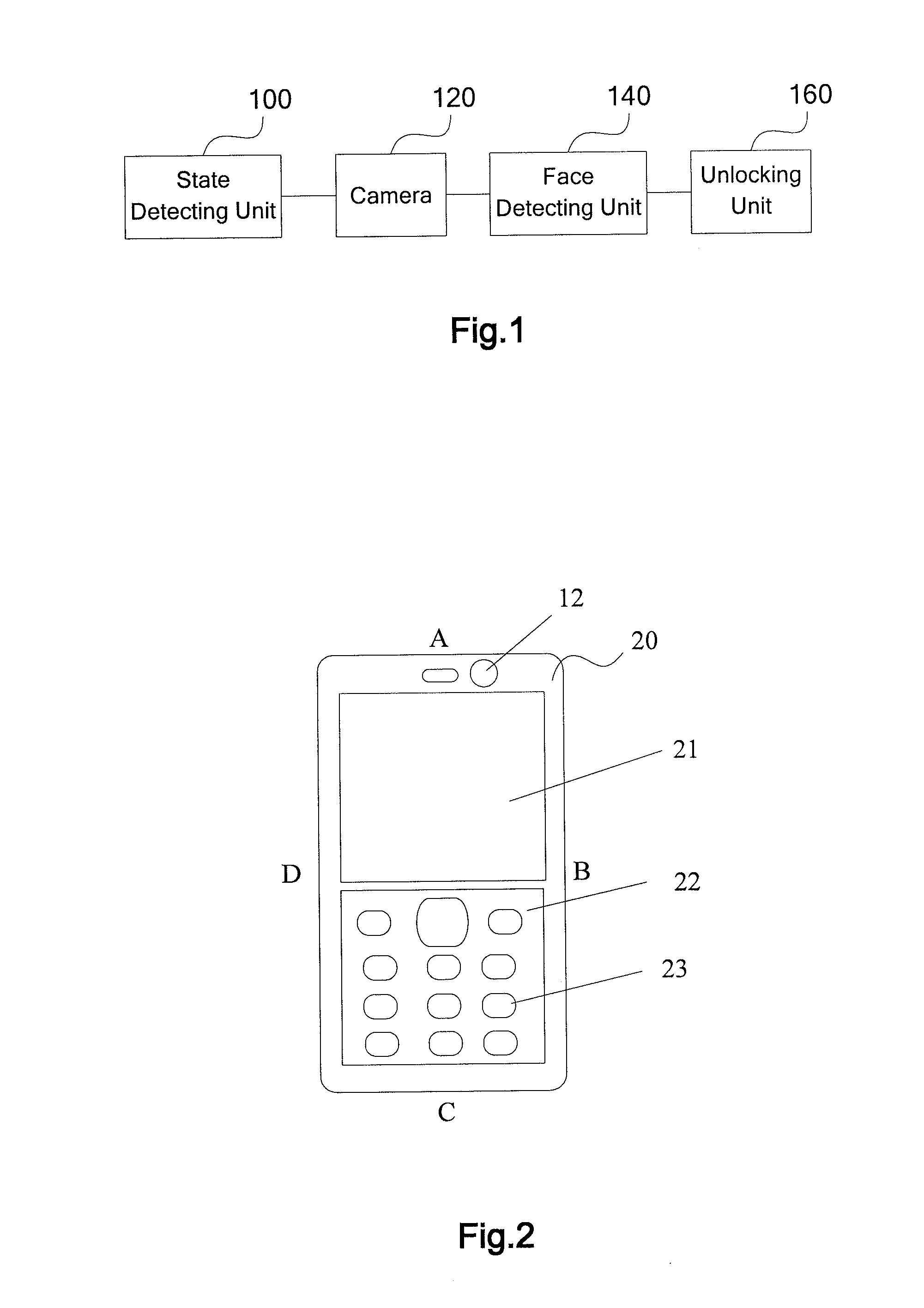
Automatic Keypad Unlocking Method and Apparatus for Mobile Terminal
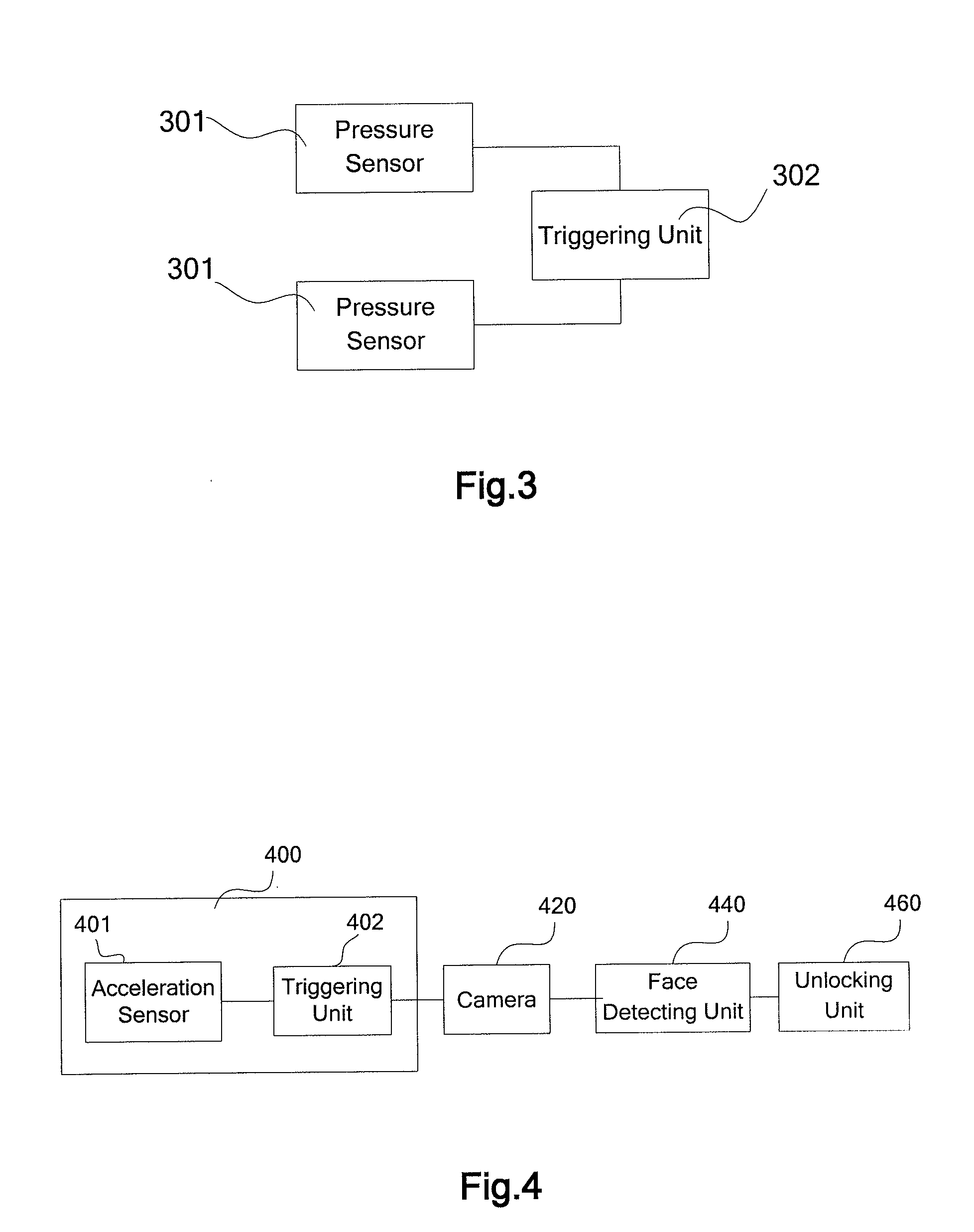
InactiveUS20110151934A1Easy to optimizeConvenient for userUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionDevices with sensorControl signalHand held
The present invention provides an automatic keypad unlocking method and apparatus for mobile terminal, so as to automatically unlock a keypad when the mobile terminal is to be used. The apparatus includes: a state detecting unit configured to detect a stress state or a motion state of the mobile terminal, to recognize whether the mobile terminal is in a hand-held state based on the stress state or the motion state, and to generate a triggering signal when the mobile terminal is recognized as in the hand-held state; a camera configured to receive the triggering signal, and to capture image based on the triggering signal; a face detecting unit configured to detect a facial image from the image captured by the camera, and to generate an unlock control signal if the face detecting unit determines that a facial image of predetermined scale size is contained in the captured image; and an unlocking unit configured to receive the unlock control signal, and to automatically unlock a locked keypad based on the unlock control signal. The present invention automatically unlocks the keypad by recognizing the hand-held state of the mobile terminal.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
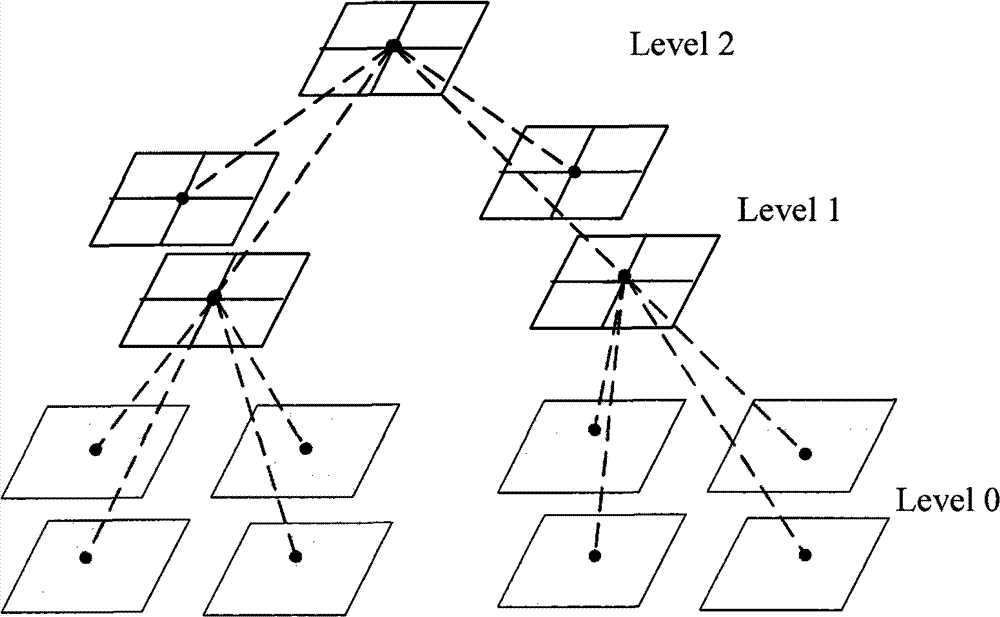
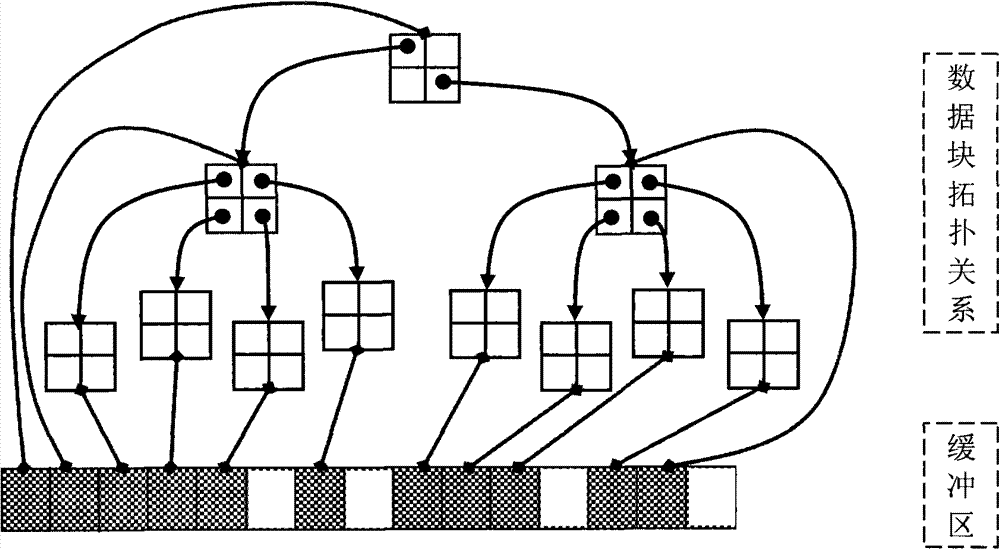
Three-dimensional vector real-time dynamic stacking technique based on LOD (Level of Detail) transparent textures
InactiveCN102737097AImprove display efficiencyThe display effect is delicateSpecial data processing applications3D modellingInternal memoryLevel of detail
The invention discloses a three-dimensional vector real-time dynamic stacking technique based on multiple LOD (Level of Detail) transparent textures. The three-dimensional vector real-time dynamic stacking technique comprises the following steps of: firstly, drawing various vector layers on the transparent textures of corresponding plotting scales respectively in an internal memory through data pre-processing, automatically carrying out block cutting on the vector layers, then saving the vector layers in a disk as an LOD pyramid data storage structure, and establishing a mapping relation with a same-level terrain and an image data block; and secondly, in a real-time terrain rendering and roaming stage, loading the transparent textures of vectors of the corresponding layers through dynamic selection, stacking the vector layers into the same level of image data block according to an established Alpha passage, and realizing the real-time stacking of the vector layers in the three-dimensional terrain based on an internal memory multi-passage texture blending technology. According to seamless visualization of high-resolution vector map data and a digital elevation model, the effect of the high-resolution vector map data and the digital elevation model in spatial information expression and analysis can be enhanced. According to the technique, the real time stacking of multilayer vector data in the rendering and roaming stage of a large-scale three-dimensional terrain scene is realized, and the dynamic interactive screening of the vector layers is supported.
Owner:北京峰盛博远科技股份有限公司
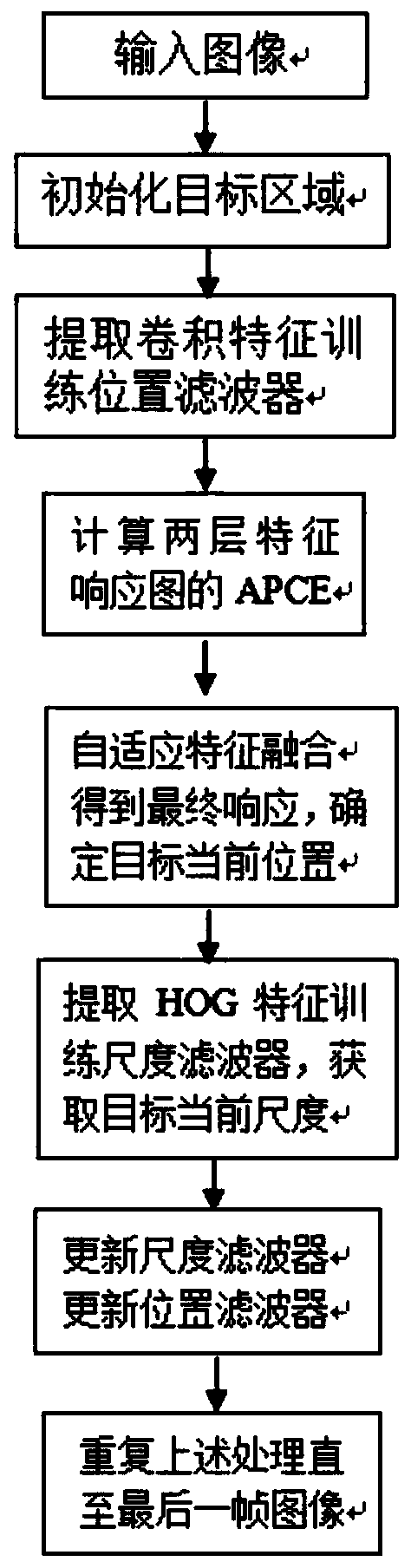
A multi-layer convolution feature self-adaptive fusion moving target tracking method
ActiveCN109816689AHigh expressionImprove adaptabilityImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionAdaptive weightingCorrelation filter
The invention relates to a multi-layer convolution feature self-adaptive fusion moving target tracking method, and belongs to the field of computer vision. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, initializing a target area in a first frame of image, and utilizing a trained deep network framework VGG-19 to extract first and fifth layers of convolution features of the target image block,and obtaining two templates through learning and training of a related filter; Secondly, extracting features of a detection sample from the prediction position and the scale size of the next frame andthe previous frame of target, and carrying out convolution on the features of the detection sample and the two templates of the previous frame to obtain a response graph of the two-layer features; calculating the weight of the obtained response graph according to an APCE measurement method, and adaptively weighting and fusing the response graph to determine the final position of the target; And after the position is determined, estimating the target optimal scale by extracting the directional gradient histogram features of the multiple scales of the target. According to the method, the targetis positioned more accurately, and the tracking precision is improved.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and apparatus for forming nano-particles
InactiveUS20080108005A1Low raw material costReduce manufacturing costMuffle furnacesTransportation and packagingProduct gasEngineering
Nano-scale particles of materials can be produced by vaporizing material and allowing the material to flow in a non-violently turbulent manner into thermal communication with a cooling fluid, thereby forming small particles of the material that can be in the nano-scale size range. A raw material feeder can be configured to feed raw material toward a heater which vaporizes the raw material. The feeder can include a metering device for controlling the flow of raw material toward the heater. A gas source can also be used to cause gas to flow through a portion of the raw material feeder along with the raw material.
Owner:BRICOLEUR PARTNERS LP
Distributed type multi-robot synchronous swarming control method
InactiveCN101901012AWork around size constraintsAvoid restrictionsVehicle position/course/altitude controlPosition/direction controlSimulationRobot position
The invention relates to a distributed type multi-robot synchronous swarming control method. The method comprises the steps of: identifying not more than six key neighbor robots in all the neighbor robots with the current position of a robot as a center, the detection distance of a sensor as a radius, and other robots in the circular area as neighbor robots, and designing a position control operator of the current robot by using an attraction-repulsion function among the current robot and the neighbor robots; designing a speed direction control operator of the current robot according to the linearization expression of a Vicsel model; and weighing and integrating the position control operator and the speed direction control operator to form a synchronous swarming control rate of the current robot. The invention visually demonstrates network topology and control action relations among robot positions, breaks the restriction on the scale size of robots, realizes purely distributed type extensible coordination control, guarantees communication of network topology structures in the process of group evolution, and can adjust parameters to avoid collision when the scale of the neighbor robots increases continuously and realize self-adapting to the change of the position relations of the robots.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
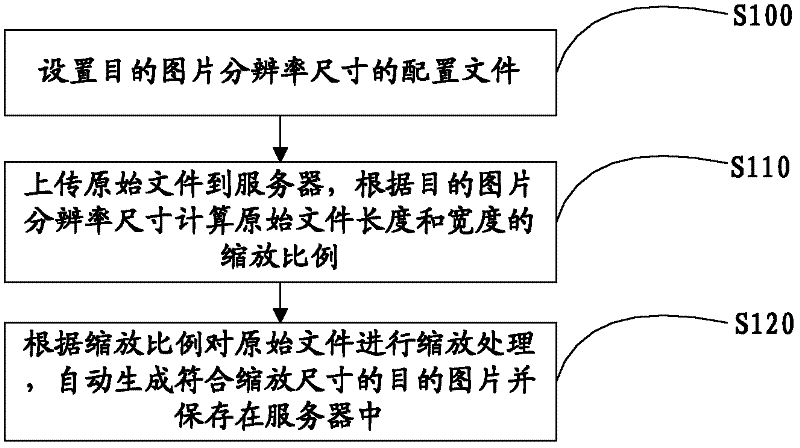
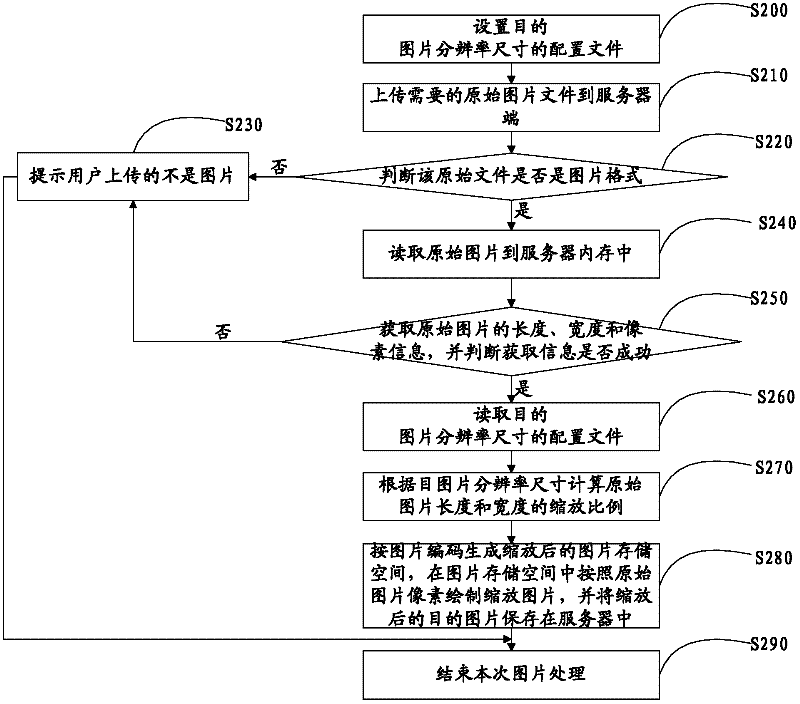
Image upload processing method and image upload processing system
InactiveCN102508851AImplement batch processingImprove processing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsImaging processingImage resolution
The invention belongs to the technical field of multimedia, and particularly relates to an image upload processing method and an image upload processing system. The image upload processing system includes: a, setting up configuration files of the resolution ratio size of a target image; b, uploading a source file to a server and calculating the scaling of the length and the width of the source file according to the resolution ratio size of the target image; and c, scaling the source file according to the scaling, automatically generating the target image according with the scaling size and storing the target image into the server. The image upload processing method and the image upload processing system have the advantages that by means of the scaling size of the target image arranged in advance, after the source image is uploaded to the server, the source image is automatically scaled by a program according to the resolution ratio size of the image, so that the new image according with the resolution ratio size is generated, complicated steps for uploading the image are simplified, processing processes are greatly saved, and image processing efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN WUJU SCI TECH
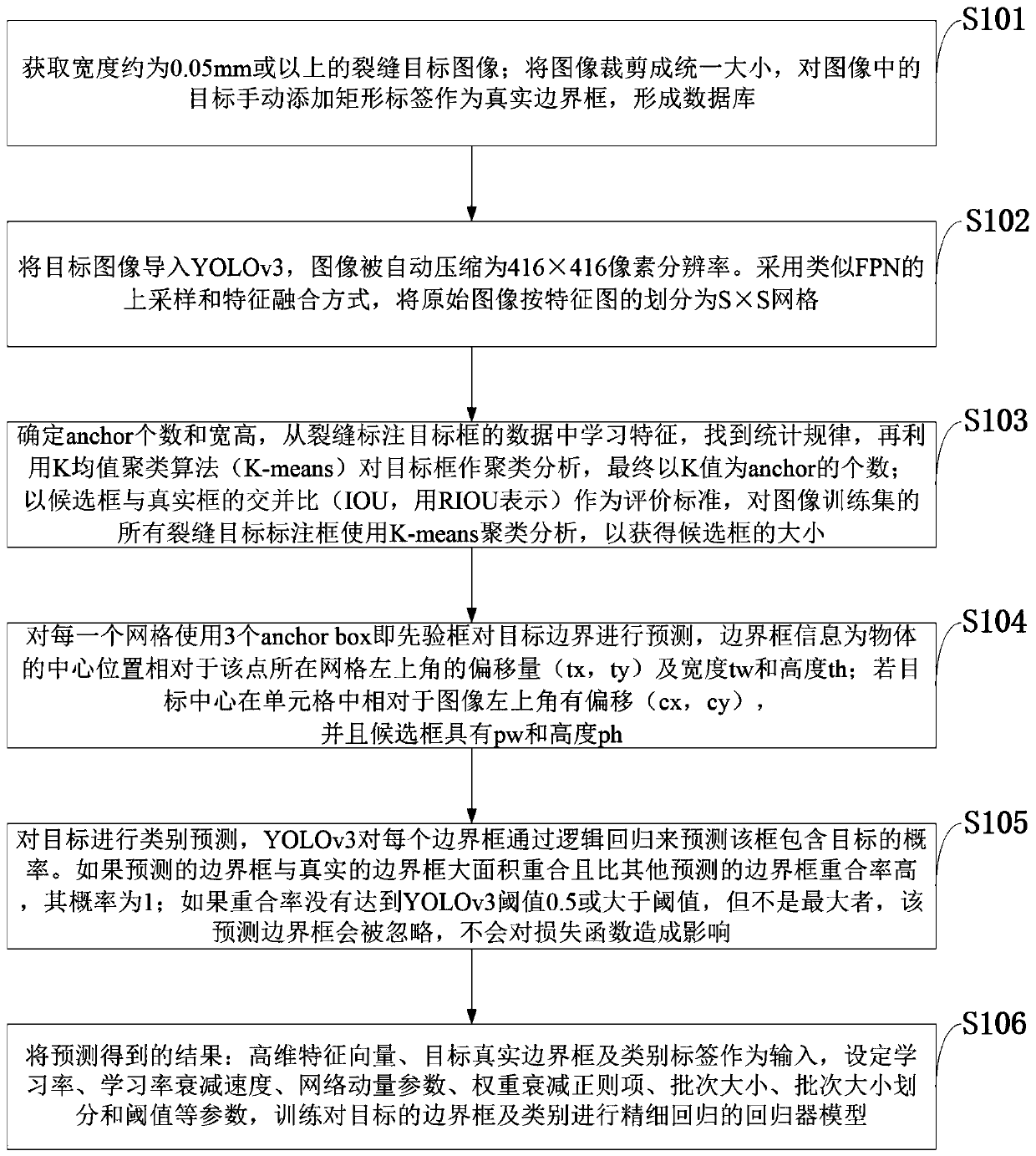
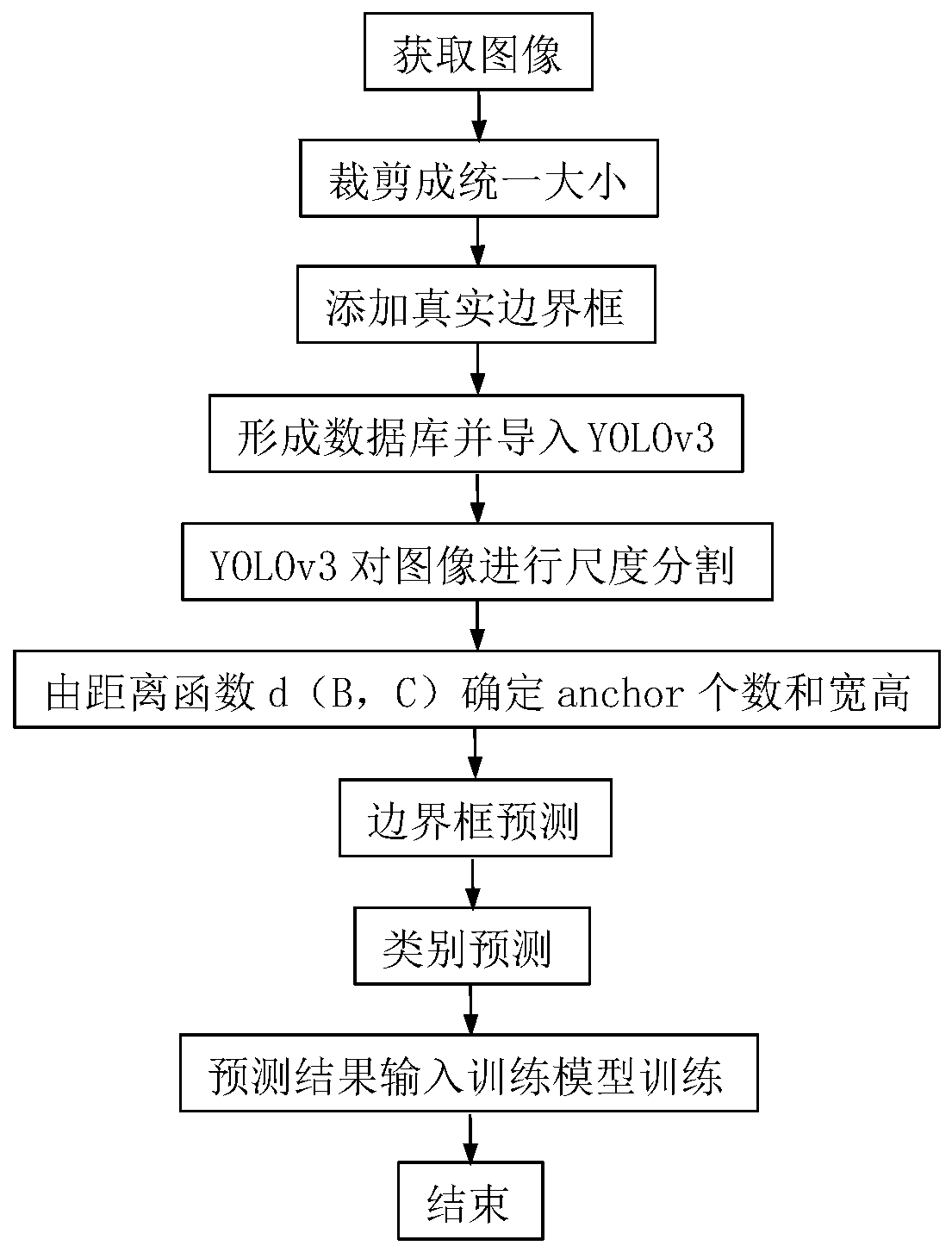
Concrete crack identification method based on YOLOv3 deep learning
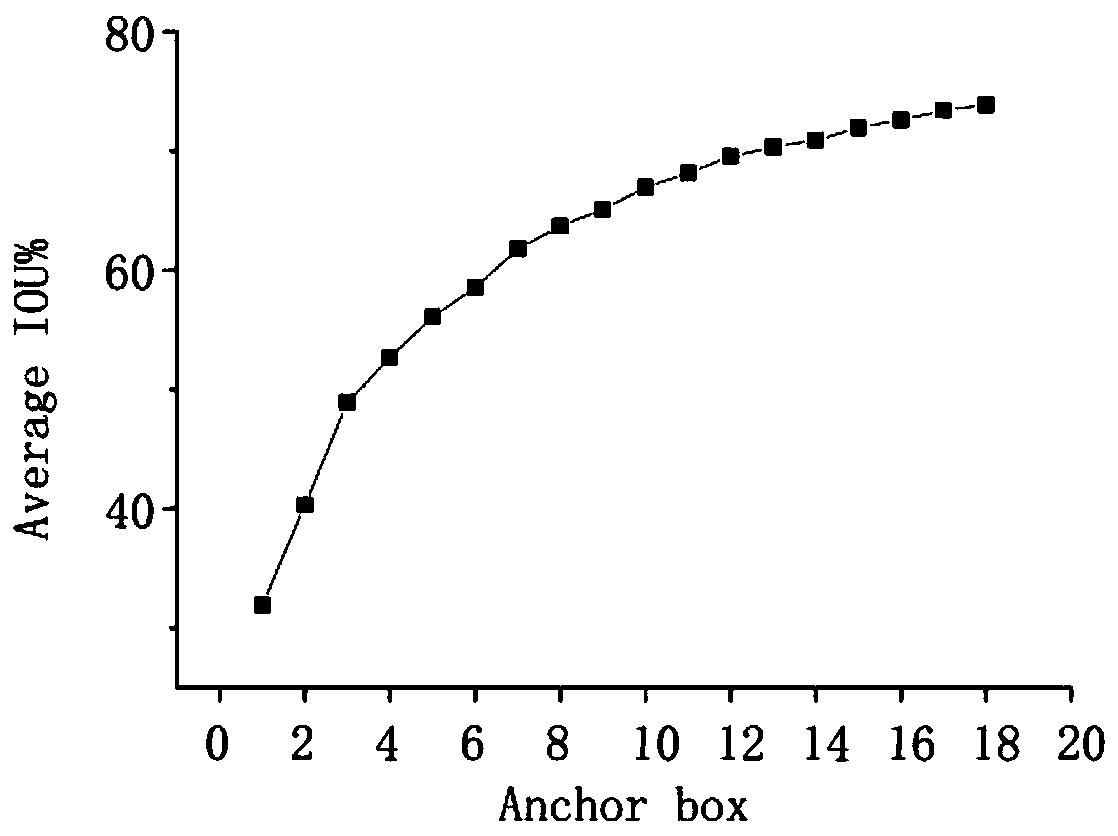
InactiveCN110175658ASimplify complexityReduce computing costCharacter and pattern recognitionOptically investigating flaws/contaminationRobustificationImage resolution
The invention belongs to the technical field of concrete structure damage detection, and discloses a multi-target crack recognition method based on a YOLOv3 deep learning algorithm, which comprises the following steps: importing a crack image into a YOLOv3 model, and automatically compressing the image into 416 * 416 pixel resolution; dividing the original image into S * S grids according to the scale size of the feature map by adopting an up-sampling and feature fusion mode similar to FPN; taking the cross-to-parallel ratio of the candidate box and the real box as an evaluation criterion, and; performing K-means clustering analysis on mark boxes for all crack target marking boxes of the image training set to obtain the size of a candidate box; and predicting the probability that the frame contains the target for each boundary frame through logistic regression. According to the method, the complexity of network training is simplified, and the operation cost is reduced; according to the method, the multiple targets are quickly and accurately identified, the accuracy far superior to that of other models is obtained while the target detection is quickly realized, and the method has higher robustness and generalization capability and is more suitable for an engineering application environment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
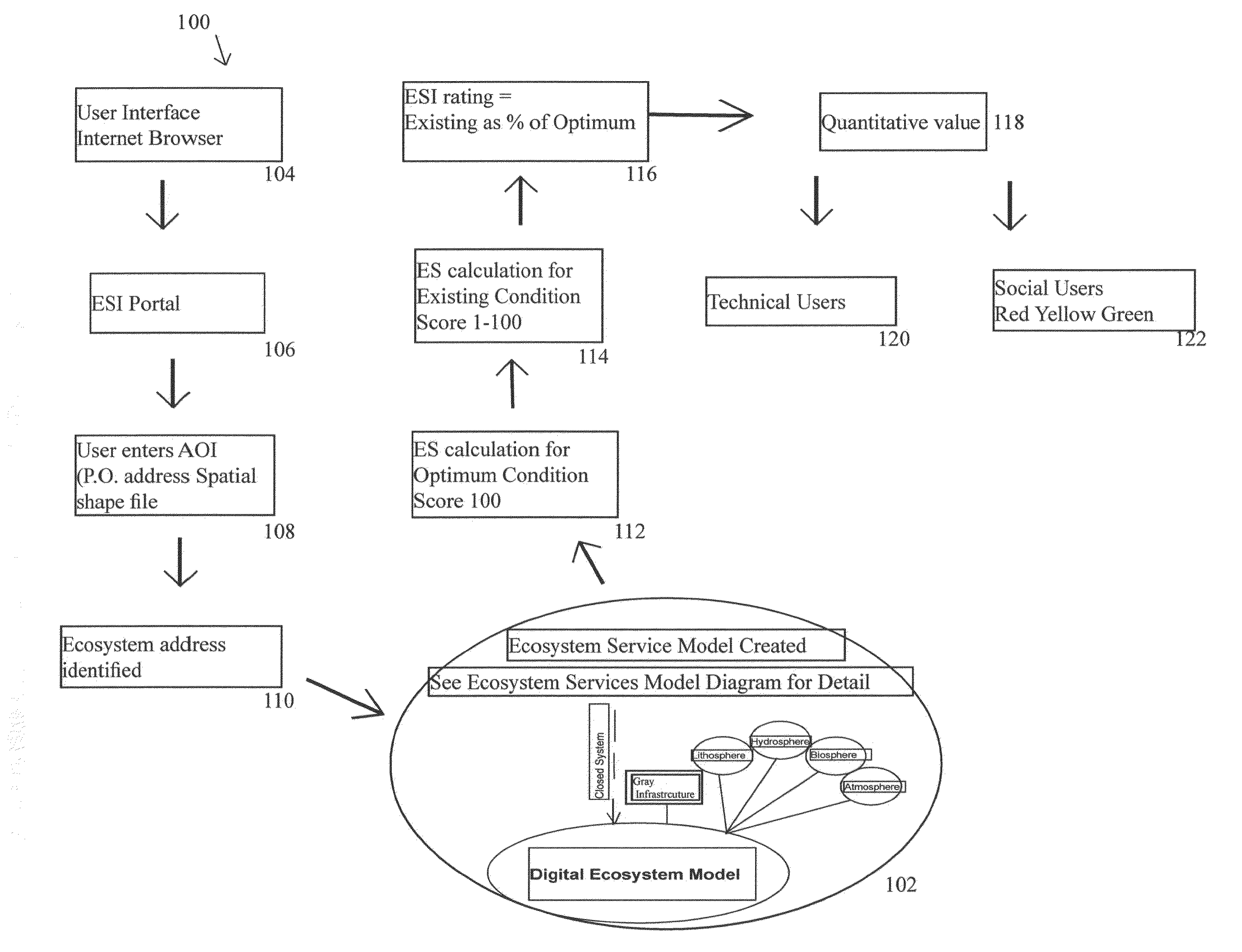
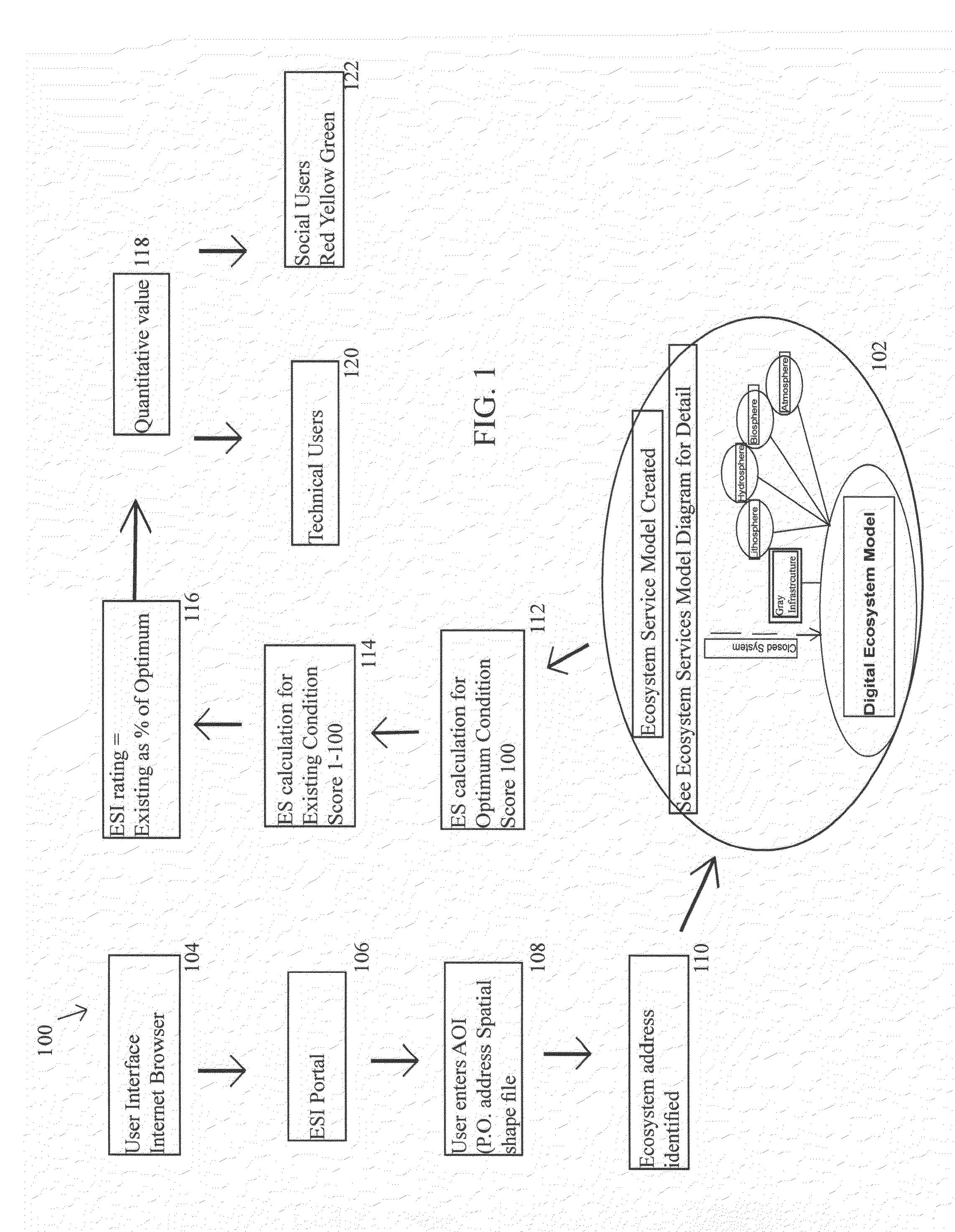
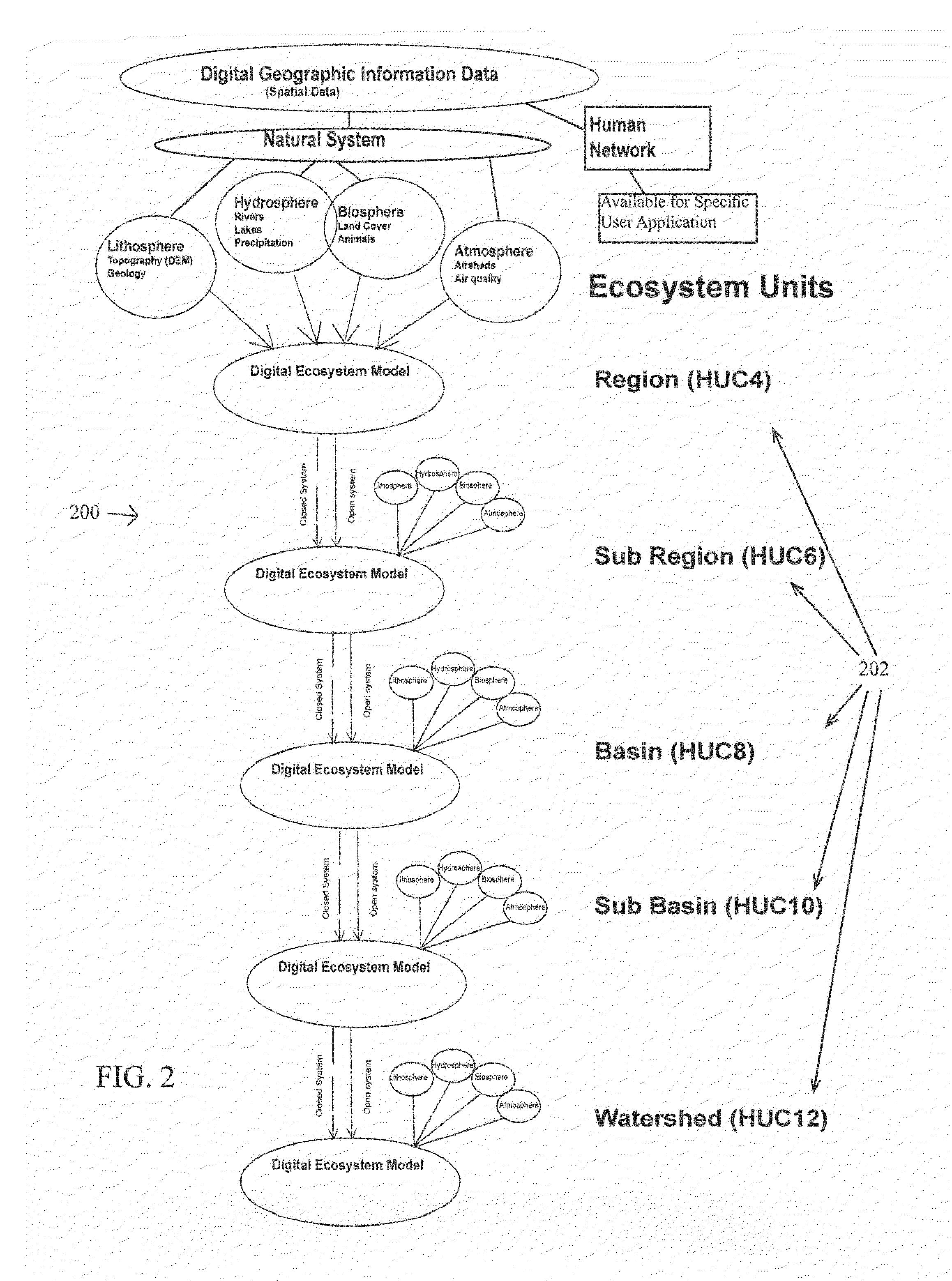
Ecosystem Services Index, Exchange and Marketplace and Methods of Using Same
InactiveUS20160203146A1Easy transferData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsService informationIndex score
A method of calculating an ecosystem services index score, comprising: receiving area of interest information from a user of an ecosystem services index calculating system; assigning an ecoaddress to the area of interest by a processor of the system; retrieving ecosystem services information about the area of interest from at least one database; retrieving ecosystem services information about the area of interest on at least one scale size larger or smaller than the area of interest from at least one database; and, deriving a multi-scale ecosystem services index score blending the retrieved ecosystem services information about the area of interest.
Owner:MOLL GARY ALLISON +2
Method and apparatus for forming nano-particles
ActiveUS20060226564A1Improve particle size distributionReduce flow turbulenceMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingMetallurgyNanometre
Nano-scale particles of materials can be produced by vaporizing the material and allowing the material to flow in a non-violently turbulent manner into thermal communication with a cooling fluid, thereby forming small particles of the material that can be in the nano-scale size range.
Owner:VIVAKOR INC +1
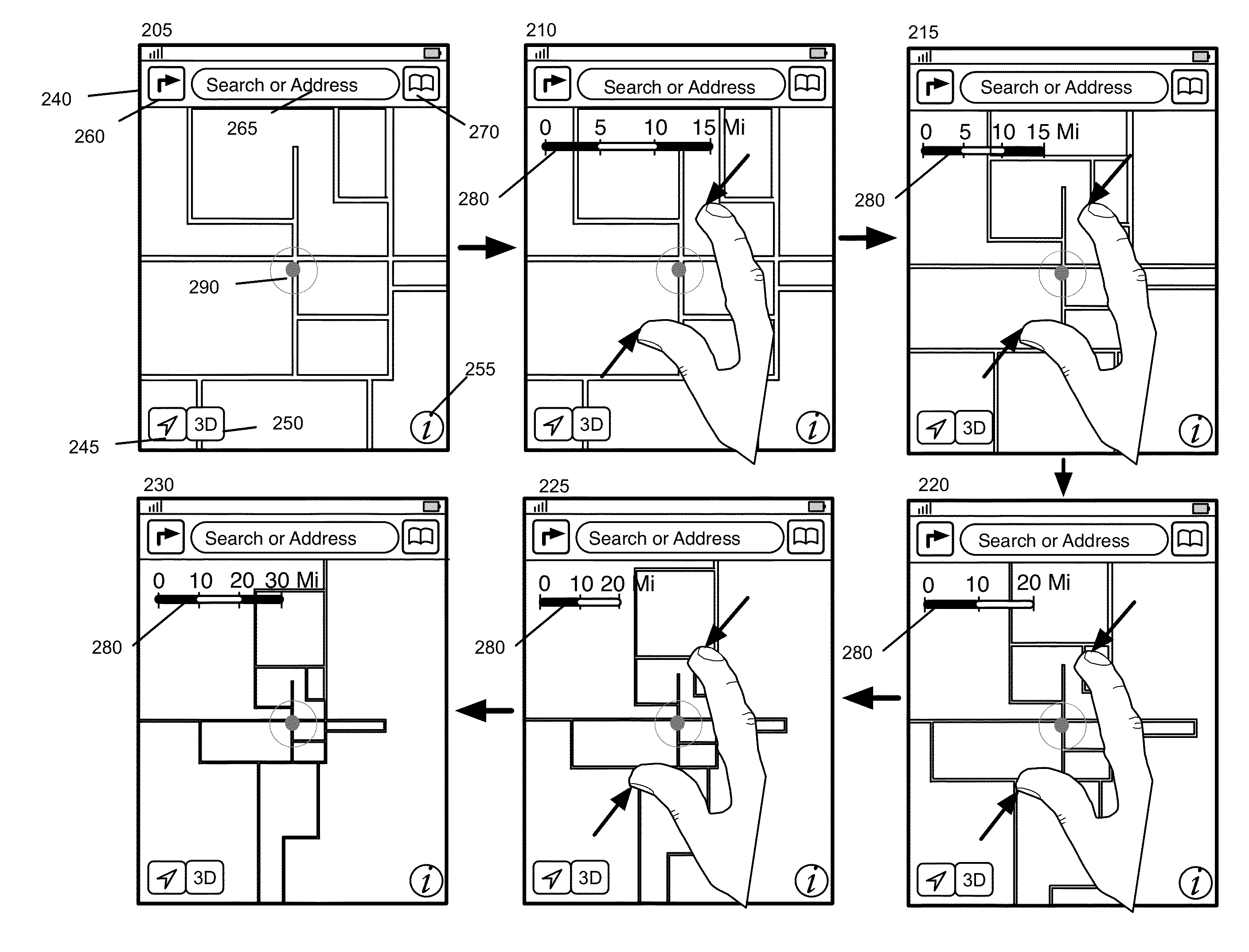
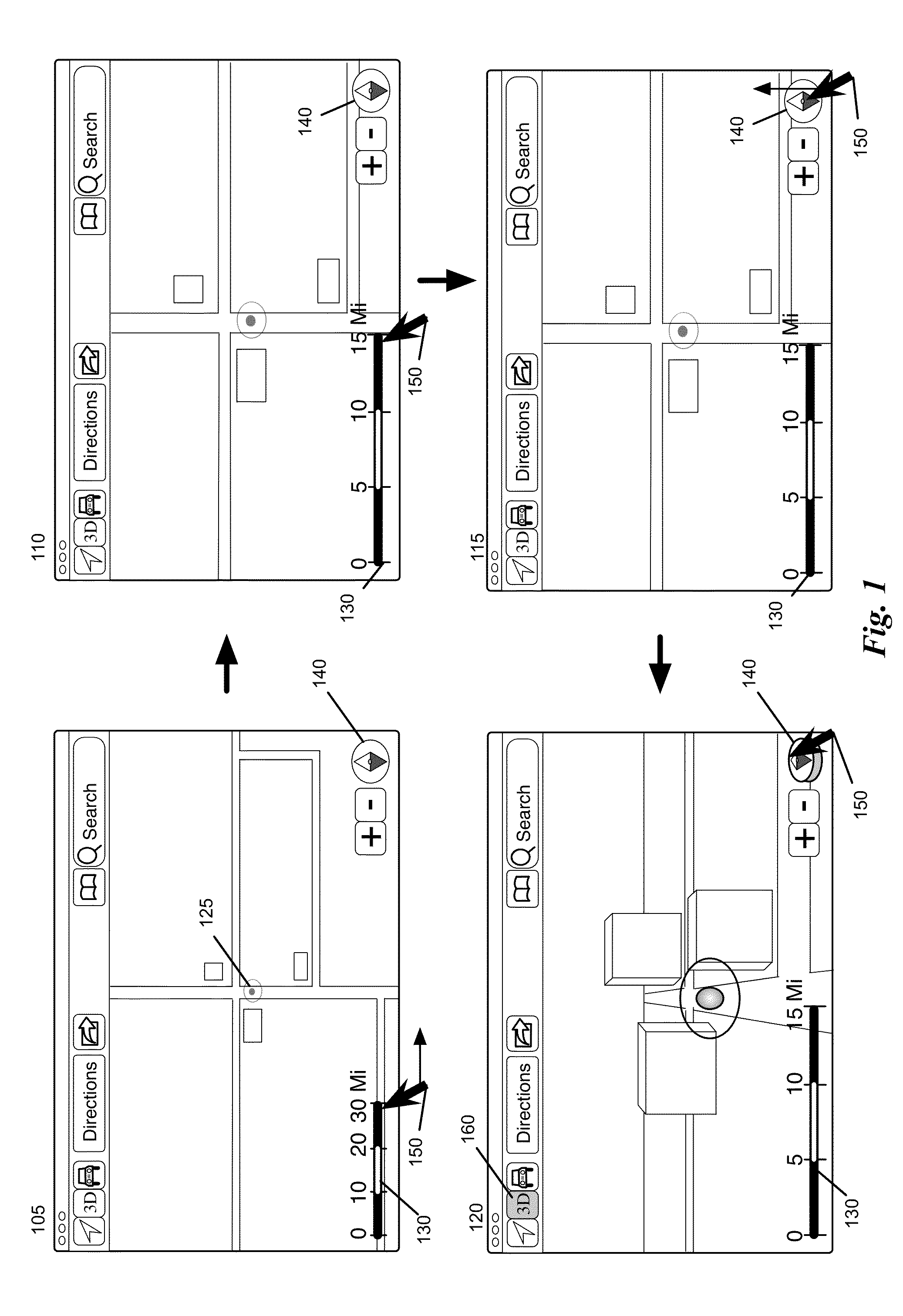
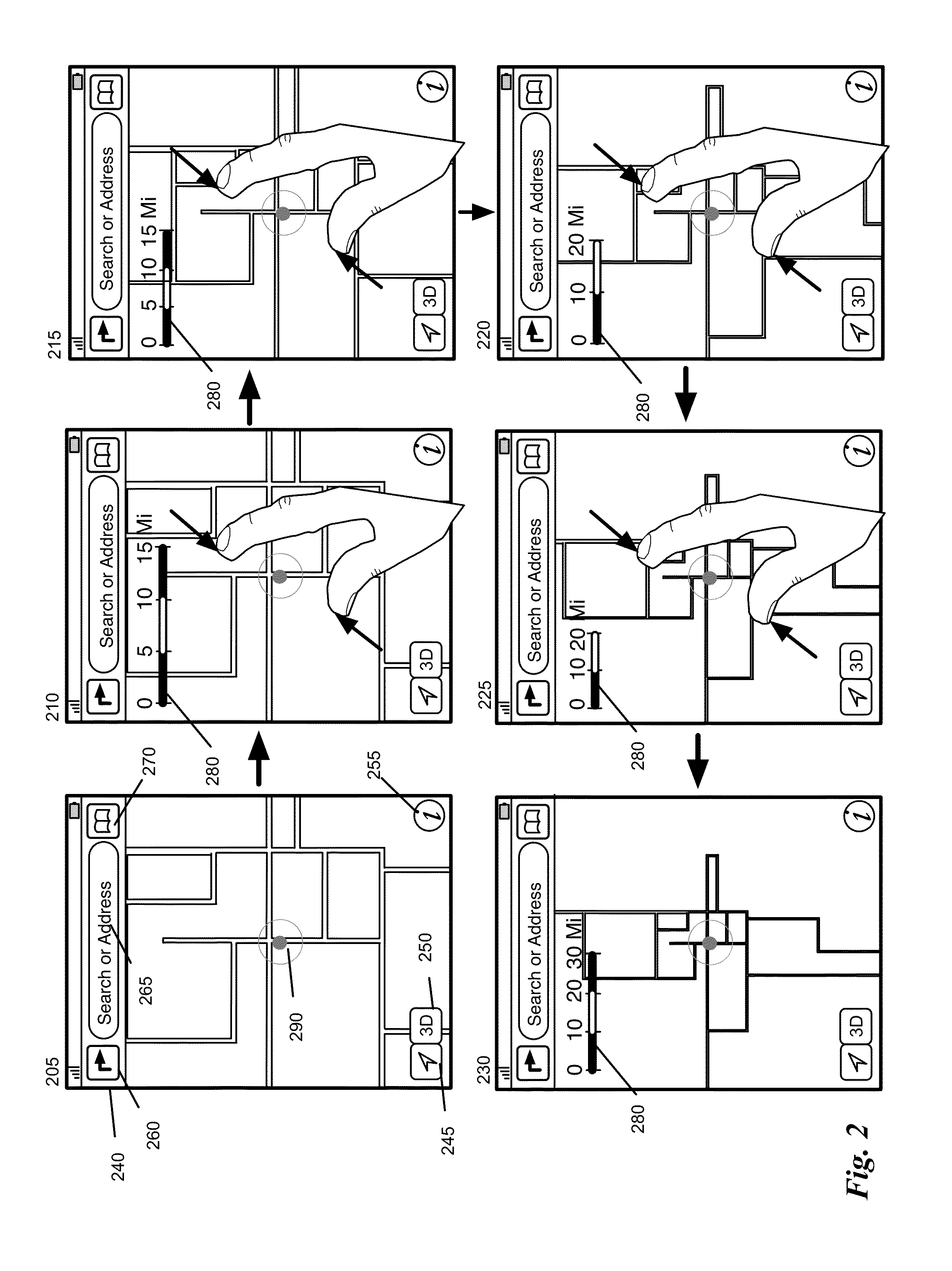
Mapping Application with Interactive Dynamic Scale and Smart Zoom
ActiveUS20140365934A1Avoid zoomInstruments for road network navigationInput/output processes for data processingScale sizeLine segment
Some embodiments provide a mapping application that includes a novel dynamic scale that can be used to perform different zoom operations. In some embodiments, the scale also serves as a distance measurement indicator for a corresponding zoom level. The application continuously adjusts several different attributes of the scale, including the scale size, the number of segments on the scale and the representative distance of a segment on the scale. In some embodiments, the mapping application provides a smart zoom feature that guides a user during a zoom to a location. In particular, the smart zoom detects that a location of a zoom is near a pin on the map, and if so, zooms to the pin on the map. Otherwise, if the location is near a cloud of pins, the application zooms to the cloud of pins. Otherwise the zoom is directed towards the user's selected location.
Owner:APPLE INC
Block zoom on a mobile electronic device
ActiveUS20130117658A1Unstructured textual data retrievalNatural language data processingDisplay deviceWeb page
A device, system and method are provided for processing structured documents, such as webpages, for display. Various elements within the structured document are parsed and rendered by an electronic device for outputting to an external or integrated display. In response to a detected scaling instruction, such as a zoom in instruction, a selected region of the displayed document indicated by the instruction is scaled to a first scaled size, including any text content therein. Any text content contained within the region may be reflowed according to the bounds of its containing element or a viewport. A dominant alignment is determined from the element or elements contained within the selected region, and the portion of the scaled region to be output to the display is determined based on the dominant alignment.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Ultraviolet light emitting AlGaN composition, and ultraviolet light emitting device containing same
InactiveUS7812366B1Improve efficiencyOvercome difficultiesLaser optical resonator constructionSolid-state devicesCharge carrierUltraviolet lights
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
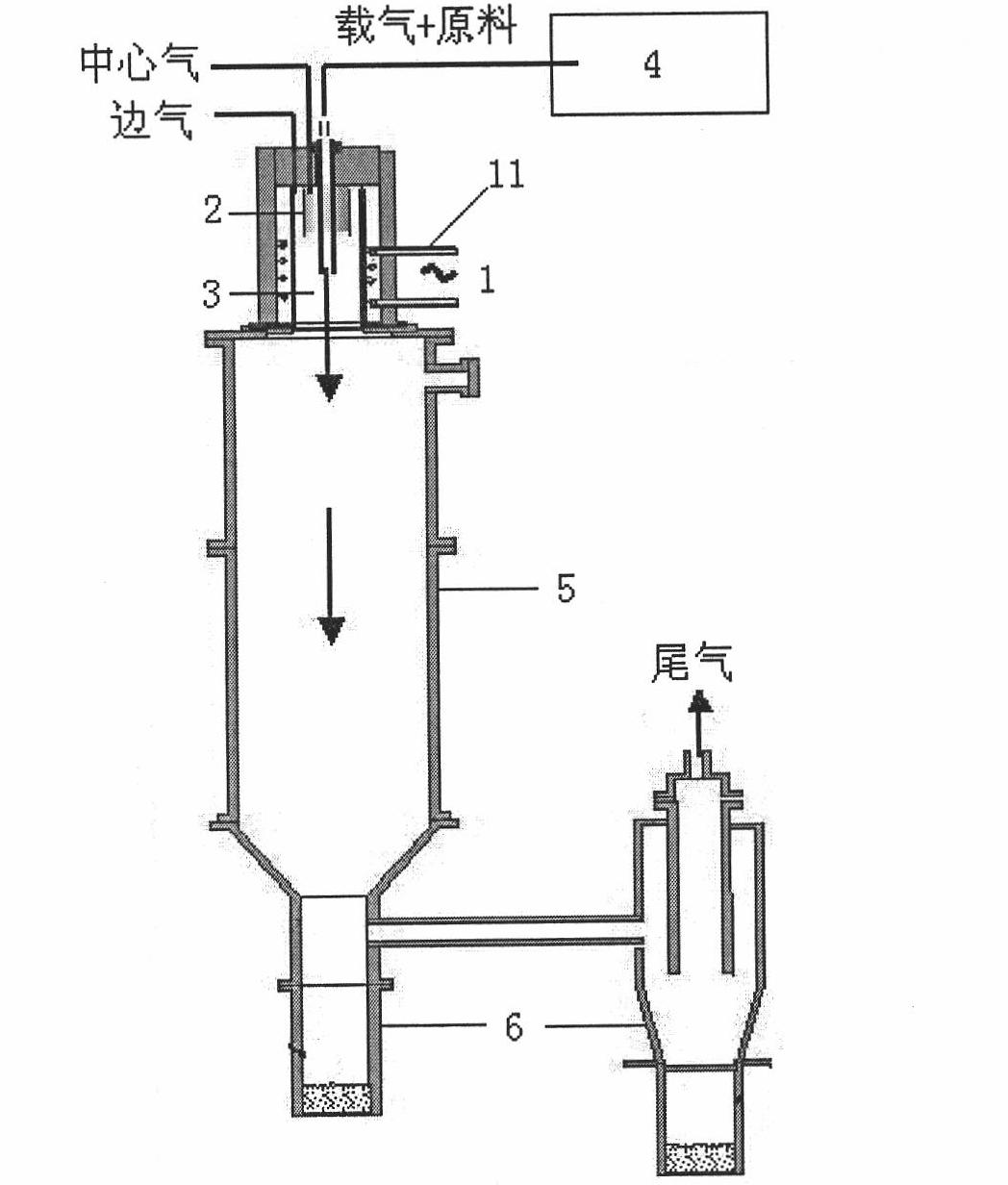
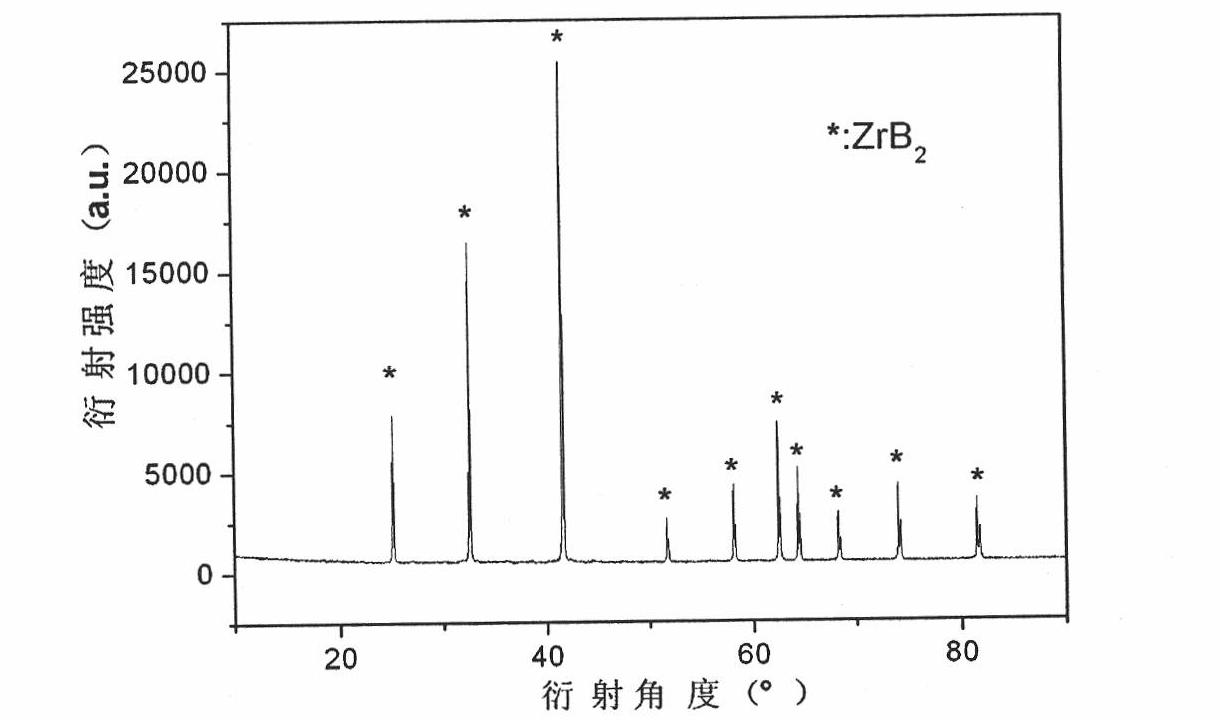
Method for preparing high-purity superfine zirconium boride powder by high-frequency plasma
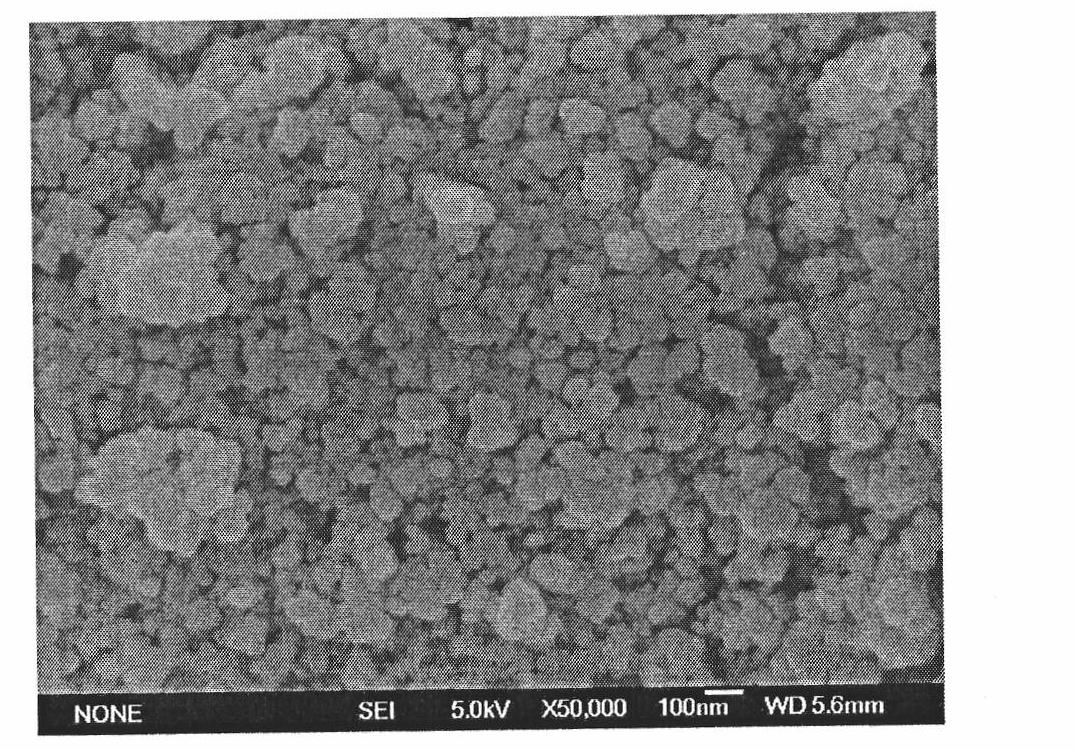
The invention relates to a method for preparing a high-purity superfine zirconium boride powder by high-frequency plasma. A superhigh temperature heat source provided by a high-frequency plasma arc provides enough high temperature and energy for synthetic reaction; the electrodeless heating characteristic of the high-frequency plasma guarantees the high-purity quality of the product; particles freely deposit and grow in an airflow to obtain superfine particles with good dispersibility; and a reactor is designed to achieve a purpose of regulating product particle size. The zirconium boride powder prepared by the method provided by the invention has the advantages of high purity, good dispersibility and nano-scale size and is suitable for preparing high-temperature ceramic and compound material. The high-frequency plasma technology has a short flow and is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
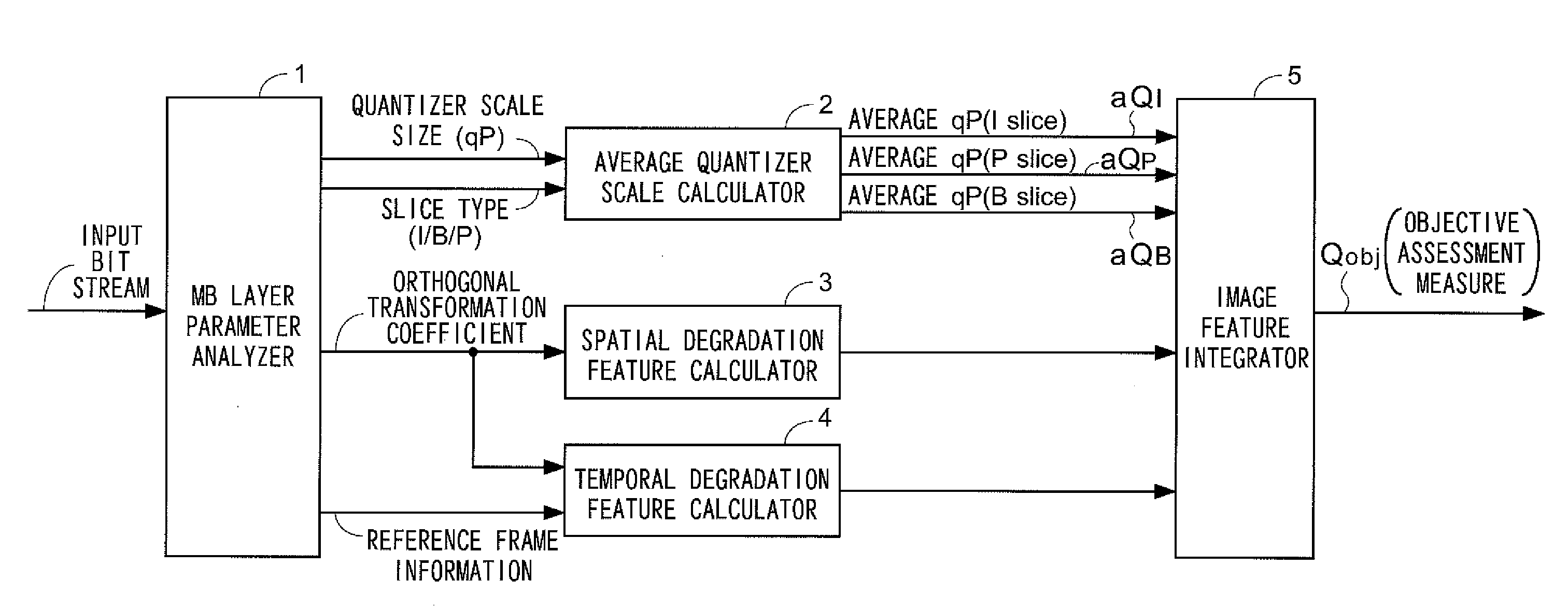
Objective image quality assessment device of video quality and automatic monitoring device
InactiveUS20110228859A1Saving amount of processColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionAcquired characteristic
An objective image quality assessment device of a video quality for estimating a subjective image quality from compressed bit stream is provided. The device includes a macro-block layer parameter analyzer for acquiring a quantizer scale size defined with respect to each macro-block and a coding type of a slice from a compressed bit stream, an orthogonal transformation coefficient in each macro-block, and a reference frame number in the macro-block applied with a motion compensating prediction, an average quantizer scale calculator for obtaining an average in a sequence of the quantizer scale size for every coding type of the slice, a spatial degradation feature calculator and a temporal degradation feature calculator for obtaining a spatial degradation feature and a temporal degradation feature, in each macro-block, and an image feature integrator for deriving the objective image quality based on the features obtained in the calculators.
Owner:KDDI CORP
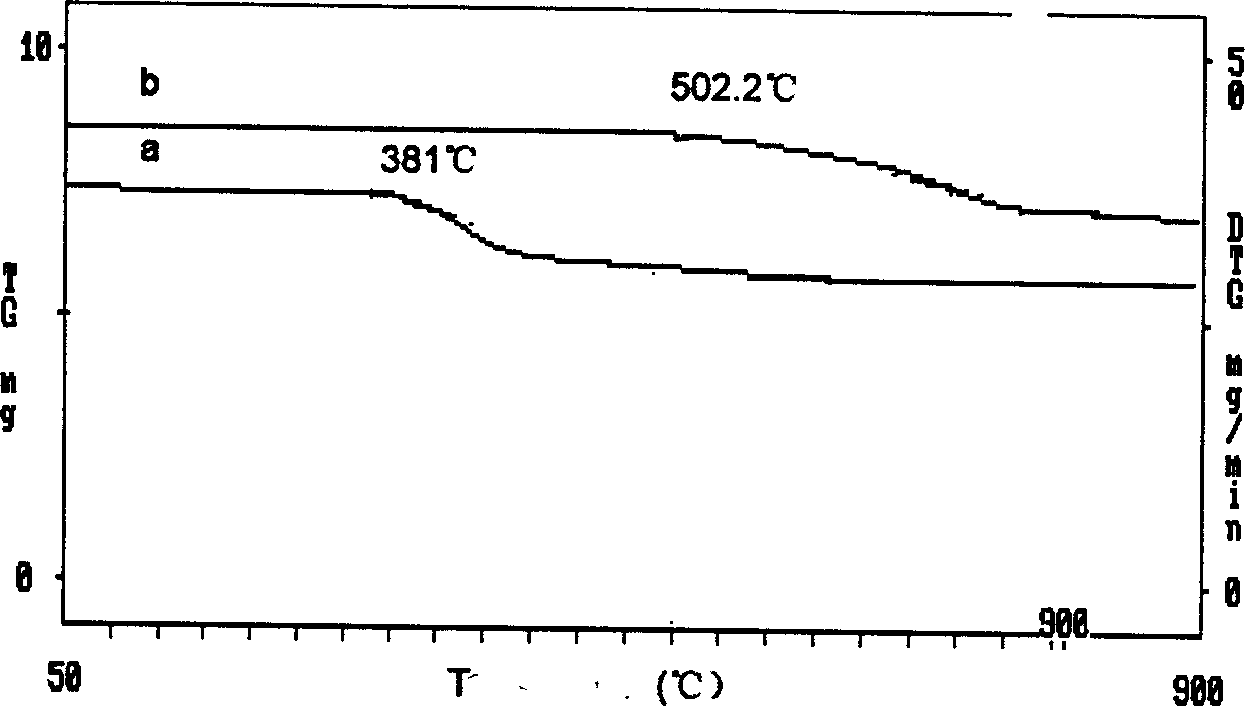
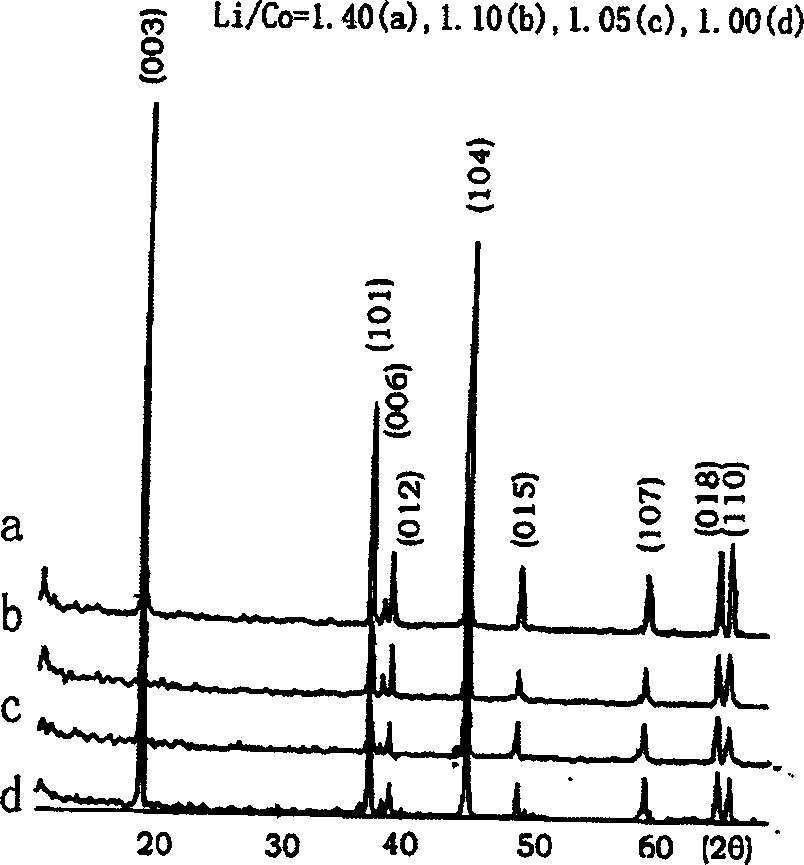
Preparation of lithium cobaltate as anode material of lithium ion cell from nano tricobalt tetroxide
InactiveCN1472829ASimple mixing processImprove performanceElectrode manufacturing processesActive material electrodesLithium carbonateReaction temperature
The method by which take nano-scale-size tricobalt tetroxide as raw material to prepare the battery's positive electrode material, the Lithium Cobalt Oxide; it belongs to the field of chemical materials. This invention takes the nano-scale-size tricobalt tetroxide Co3O4 powder and battery grade lithium carbonate as raw materials, adopts two stage solid phase synthesis for preparation, the potassium carbonate and nano-scale-size tricobalt tetroxide molar ratio Li / Co=1.03-1.05. This invention uses nano Co3O4 powder as raw materials to prepare LiCoO2, improves the property of products, simplifies the working procedure of materials mixing, reduces the temperature of reaction, shortens time of reaction, the products which is obtained has the equal shape the particle size varies in a small scale, the property of charging and discharging exceeds the same domestic and international products.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
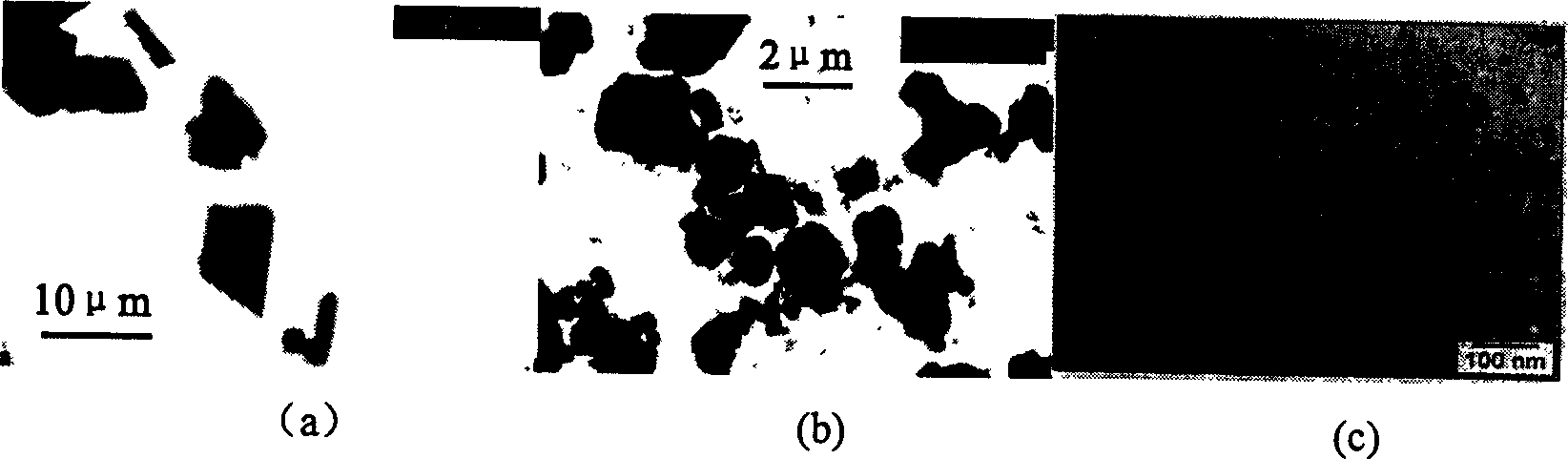
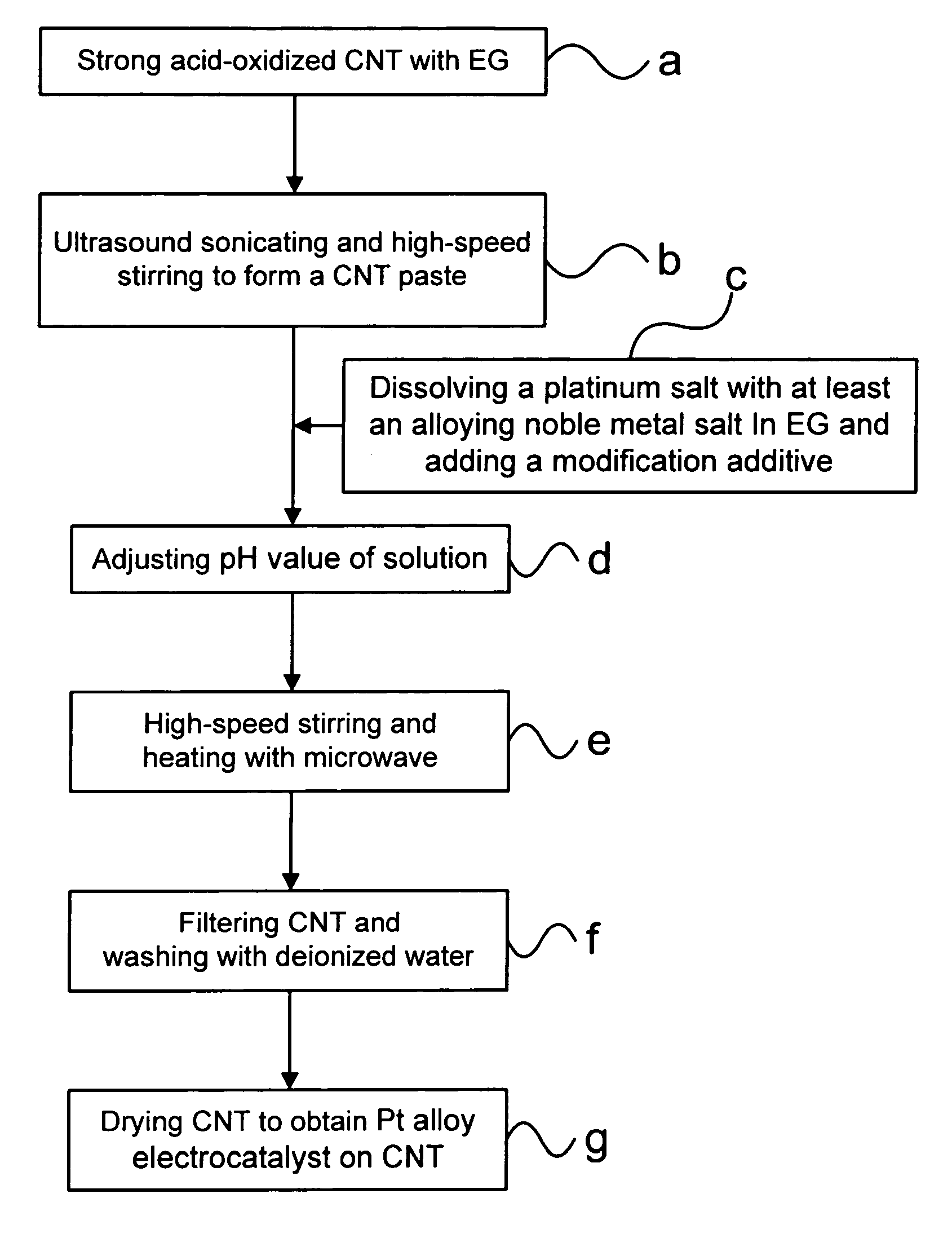
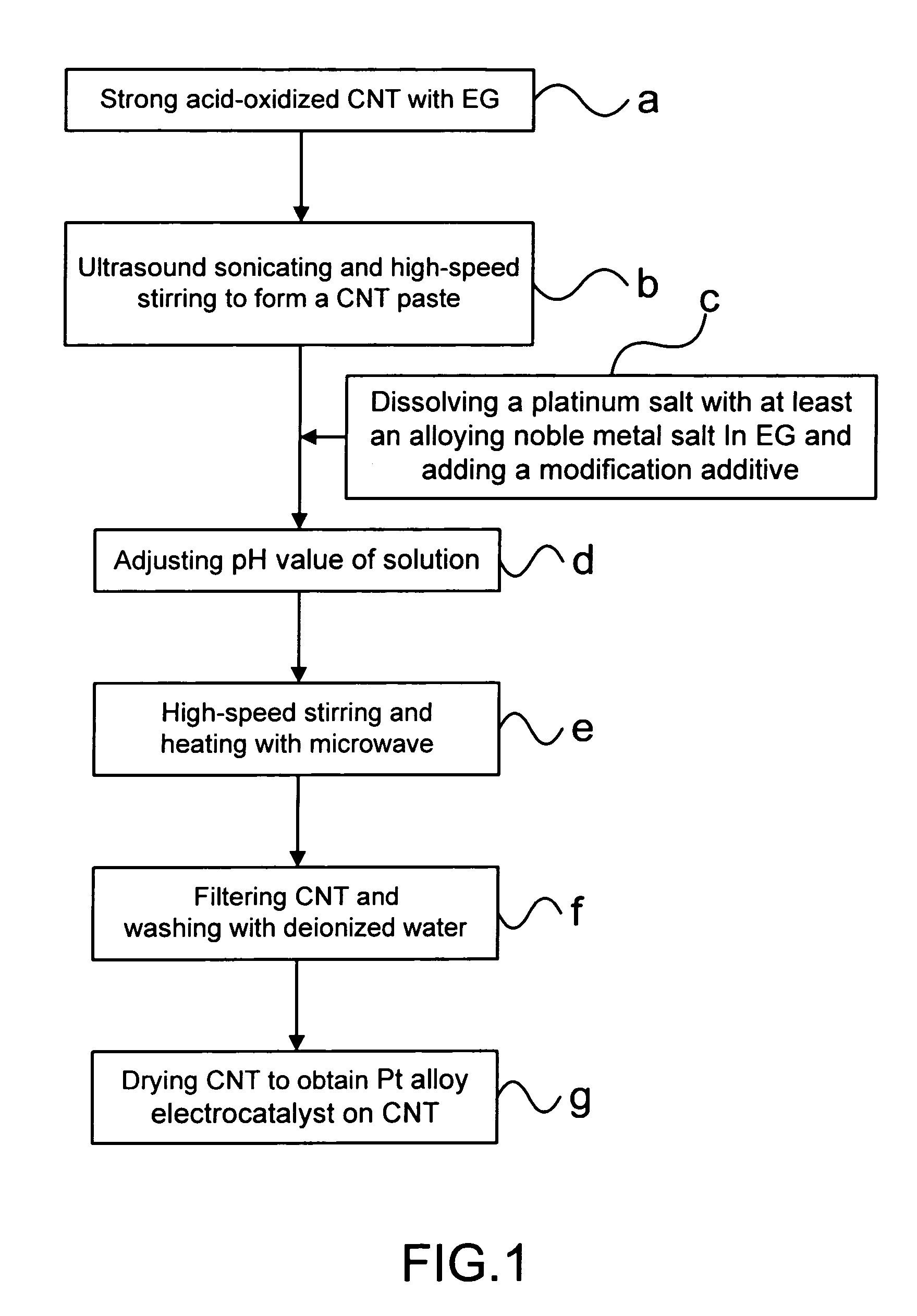
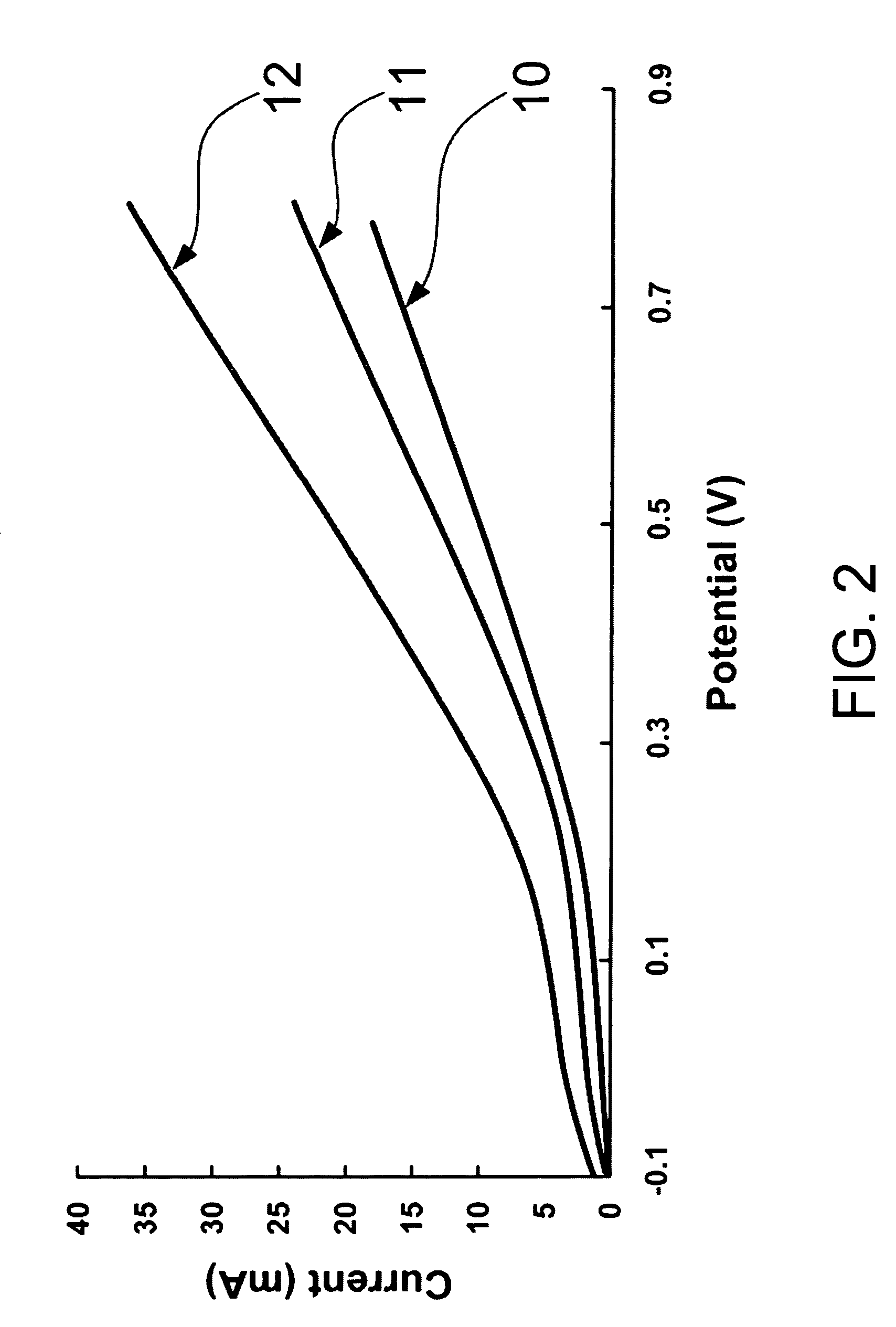
Method for making carbon nanotube-supported platinum alloy electrocatalysts
InactiveUS20070161501A1Improve uniformityEvenly dispersedFinal product manufactureCell electrodesPlatinumMetallurgy
In the present invention, platinum and alloying metal precursor ions are reduced to platinum alloy particles using specifically prepared reducing agents, under controlled reaction temperature and pH conditions, with uniform dispersion and high uniformity in nano-scale sizes adhered onto carbon nanotubes; besides, the compositions of prepared Pt alloy electrocatalysts can be put under control as desired.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
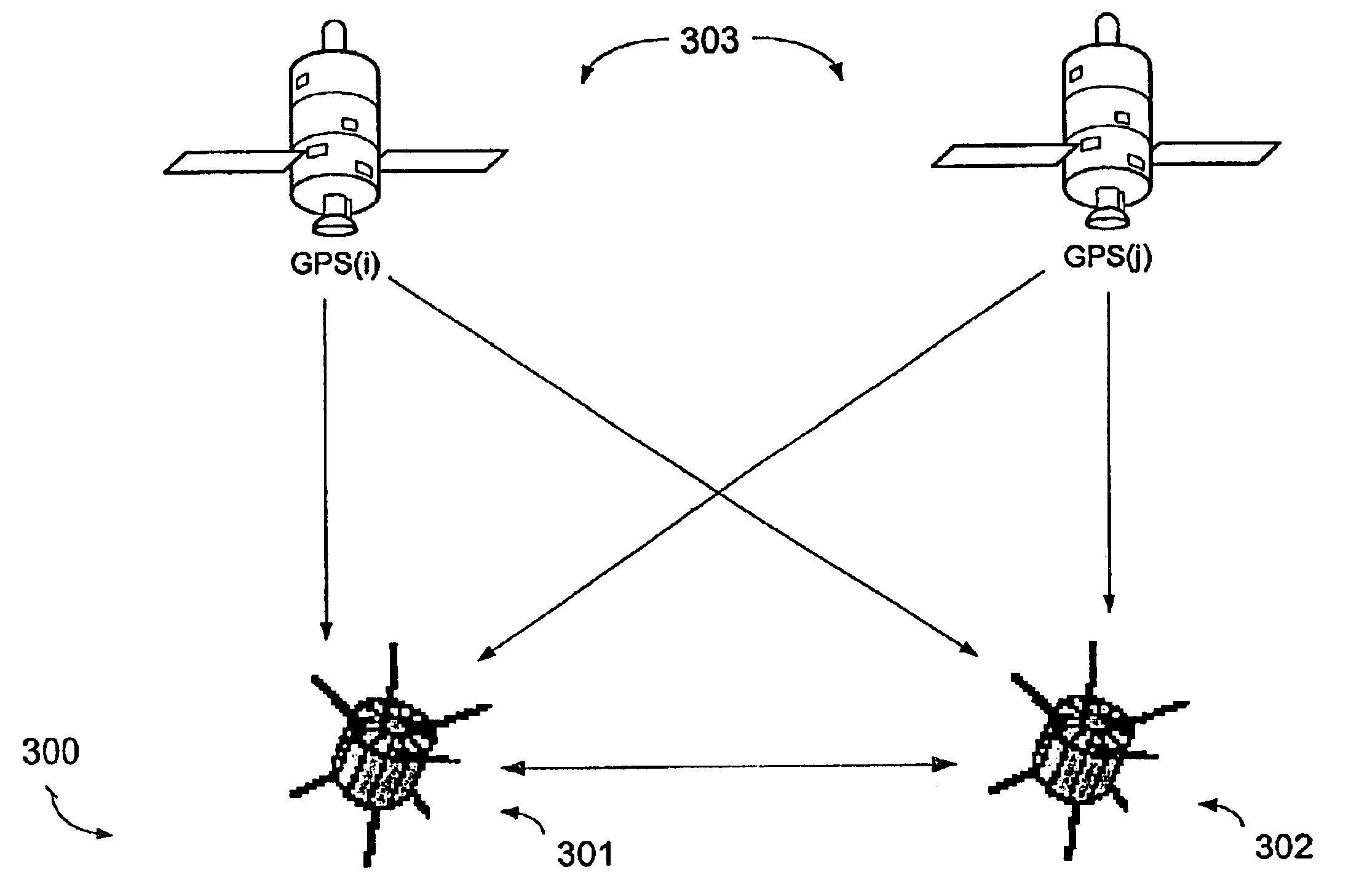
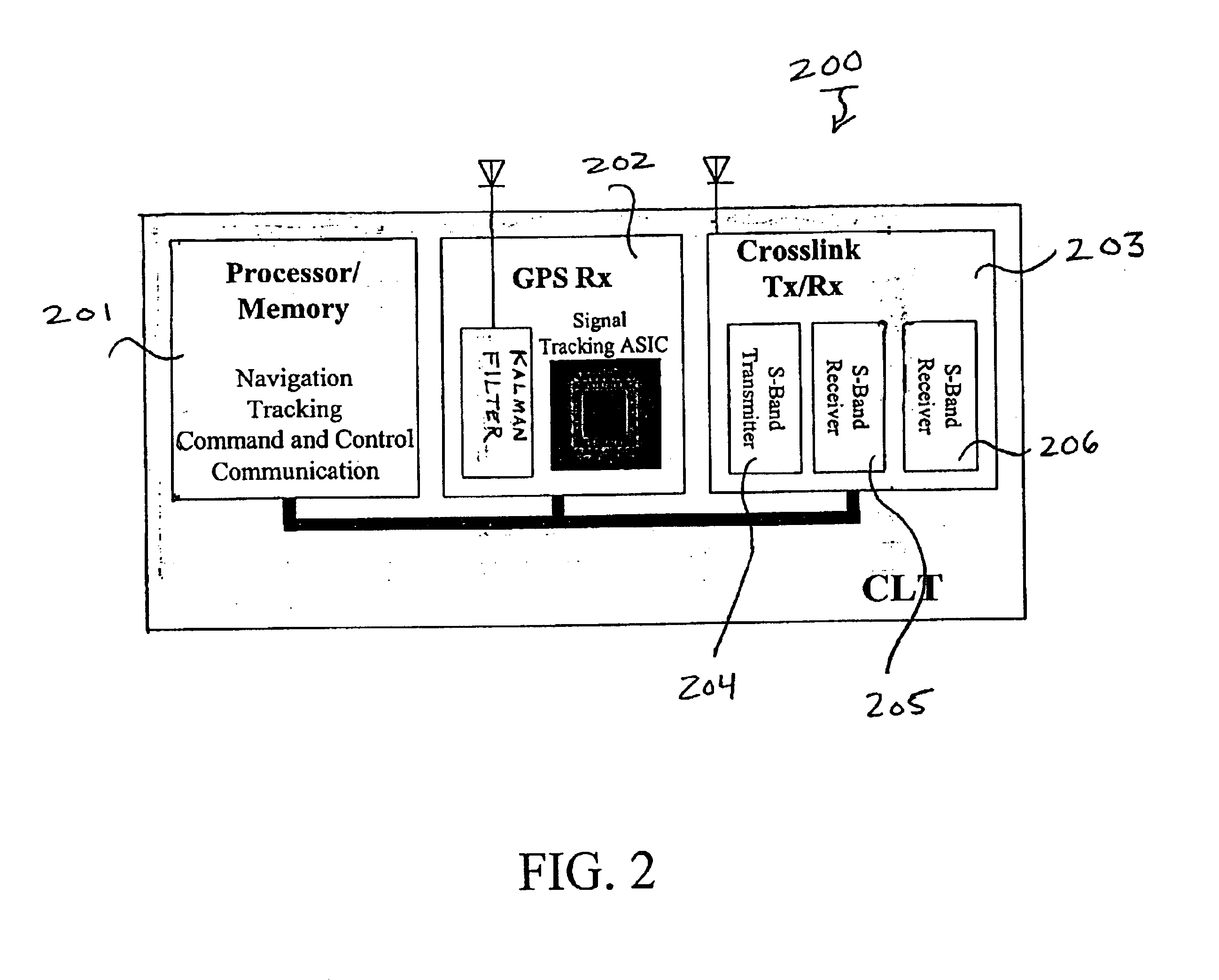
Method for using GPS and crosslink signals to correct ionospheric errors in space navigation solutions
ActiveUS6859690B2Correction errorCosmonautic vehiclesInstruments for comonautical navigationAmbiguityIonospheric heater
A method of correcting ionospheric delays induced in received signals by space systems is disclosed. The method takes advantage of received GPS signals and received crosslink signals among spacecraft to estimate the effect of ionospheric delays and correct for such delays in the computation of the range estimation between spacecraft. The method generates and initial estimate of the ionospheric delay by tracking pseudorandom codes on both GPS and crosslink signals at known frequencies to correct an initial relative range vector. Using the corrected range vector generated from the use of code, the method subsequently estimates a more precise correction by considering the carrier phase error as induced by ionospheric delay. This includes estimate the integer ambiguities on both the GPS signals and the crosslink signals iteratively and subsequently estimating a more precise ionospheric delay correction with is applied to the relative position vector using the carrier phase measurements. The method is also applicable to non-navigation applications including measuring dynamic ionospheric structure and variability over a wide range of scale sizes, thereby greatly improving operational models of navigation and communications, and improving interdependent models of atmospheric, ionospheric, magnetospheric, and space weather physics and prediction.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
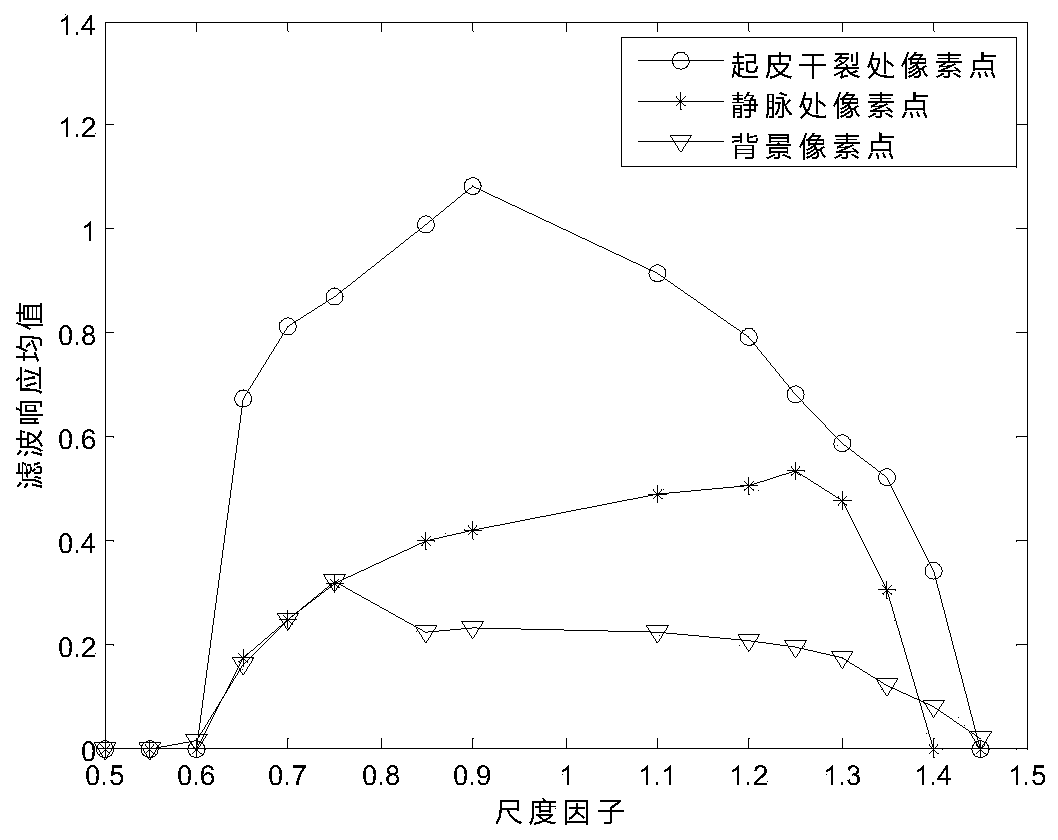
NLM filtering finger vein denoising method based on skin crack segmentation
ActiveCN110188614AAccurate detectionProtect vein informationImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionDenoising algorithm
The invention discloses an NLM filtering finger vein denoising method based on skin crack segmentation. The method comprises: firstly, using a multi-scale Frangi filtering algorithm for carrying out filtering response analysis on a finger vein image with skin crack characteristics caused by finger ecdysis, and selecting the spatial scale size and a segmentation threshold value; performing NLM filtering denoising on the detected area interfered by the skin cracks according to the skin crack binary image, and not performing denoising processing on the non-interfered area. The finger vein denoising algorithm based on switch type non-local mean filtering performs denoising specifically aimed at the exuvial skin crack area, pseudo vein interference is reduced, loss of information of a normal vein area is avoided, redundant information of other areas on the image can be fully utilized when the method is applied to the finger vein image, a certain restoration effect can be achieved, and the denoising effect is better. Therefore, the method is a finger vein denoising algorithm which is good in finger ecdysis type finger vein image denoising effect.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
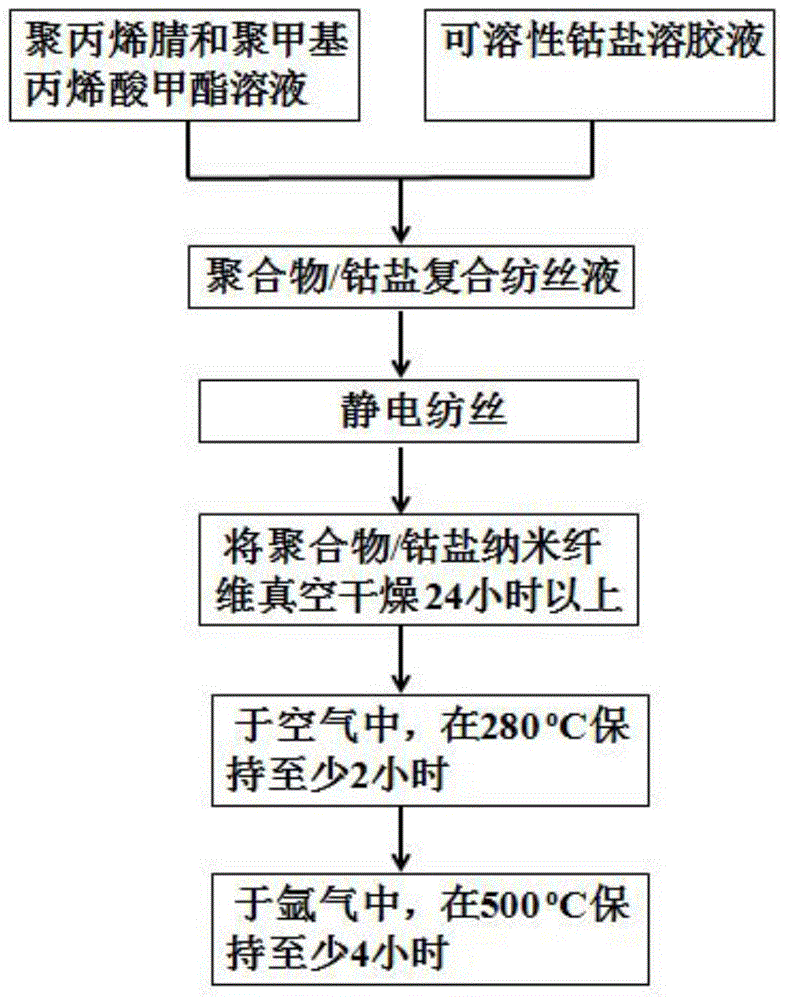
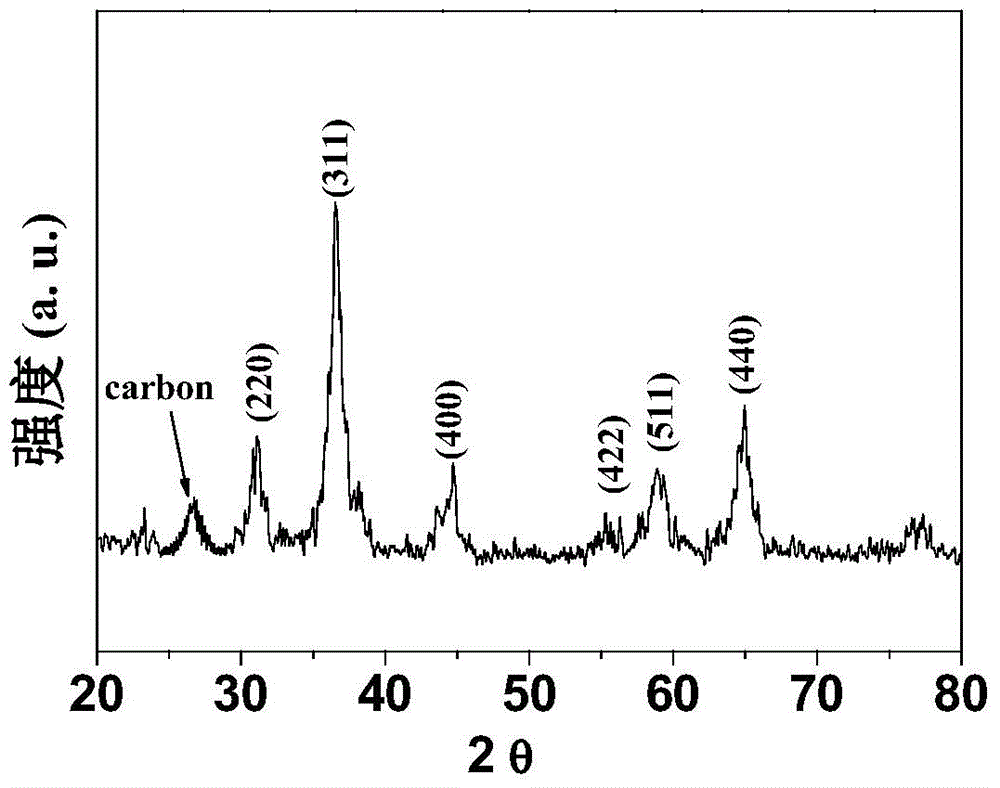
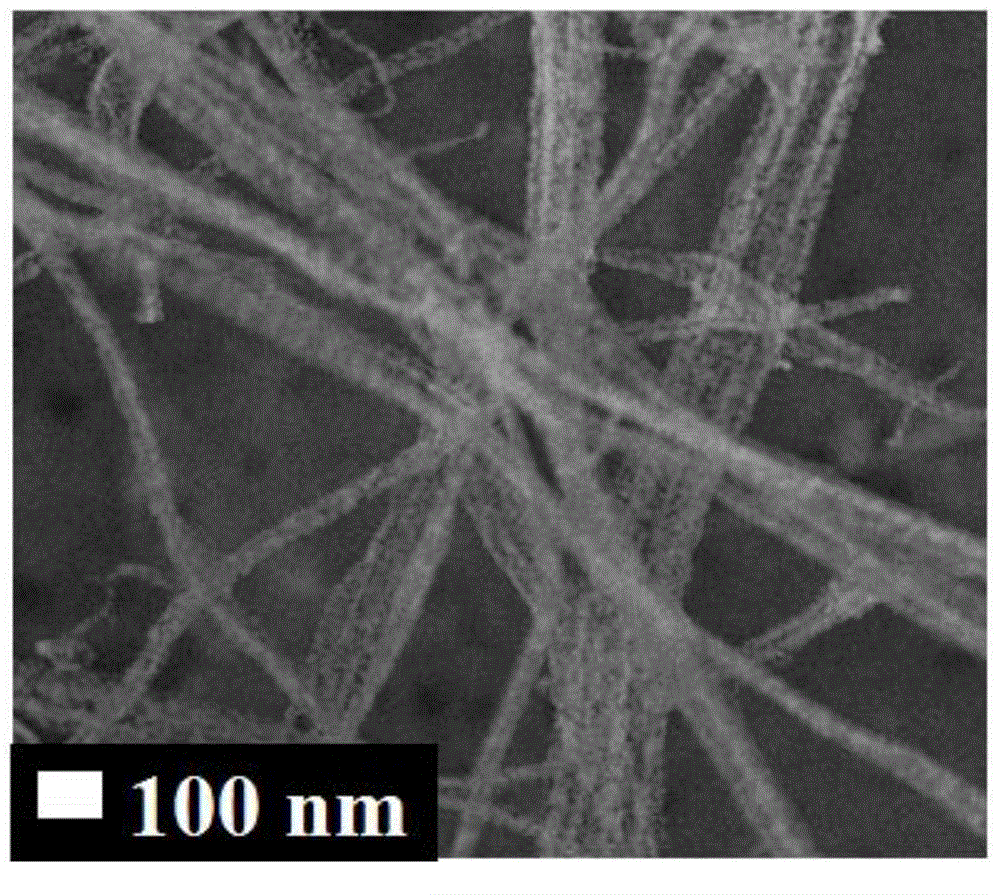
Preparation method of cobaltosic oxide-carbon porous nanofiber and application of cobaltosic oxide-carbon porous nanofiber to preparation of lithium ion battery
InactiveCN104466168AImprove cycle lifeImproved magnification performanceMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesPolymethyl methacrylateCarbon nanofiber
The invention discloses a preparation method of a cobaltosic oxide-carbon porous nanofiber and application of the cobaltosic oxide-carbon porous nanofiber to preparation of a lithium ion battery. The preparation method comprises the steps of dropwise adding a sol solution of soluble cobalt salt into a dimethylformamide solution of polyacrylonitrile and polymethyl methacrylate, continuously stirring, and keeping at the temperature of 80-100 DEG C for 24 hours; preparing a polymer / cobalt salt composite fiber supported on aluminum foil by using an electrostatic spinning process; heating the polymer / cobalt salt composite fiber to 280 DEG C at the rate of 2-4 DEG C / min in air, and keeping heating for 2 hours; and then, heating to 500 DEG C in the presence of inert atmosphere, keeping heating for 4 hours, and then, cooling to obtain the cobaltosic oxide-carbon porous nanofiber. The composite material has nano-scale size and high conductivity; when the cobaltosic oxide-carbon porous nanofiber is used as a negative electrode material of a lithium battery, the cycle life of the lithium battery can be prolonged, and the rate capability of the lithium battery can be improved; in addition, the preparation method is simple in process, good in repeatability, easy to implement and beneficial to industrial production.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
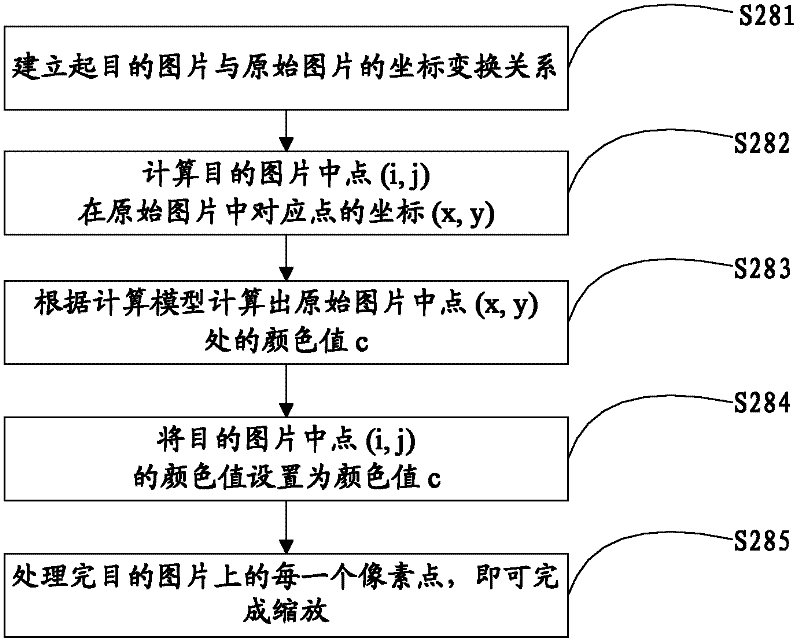
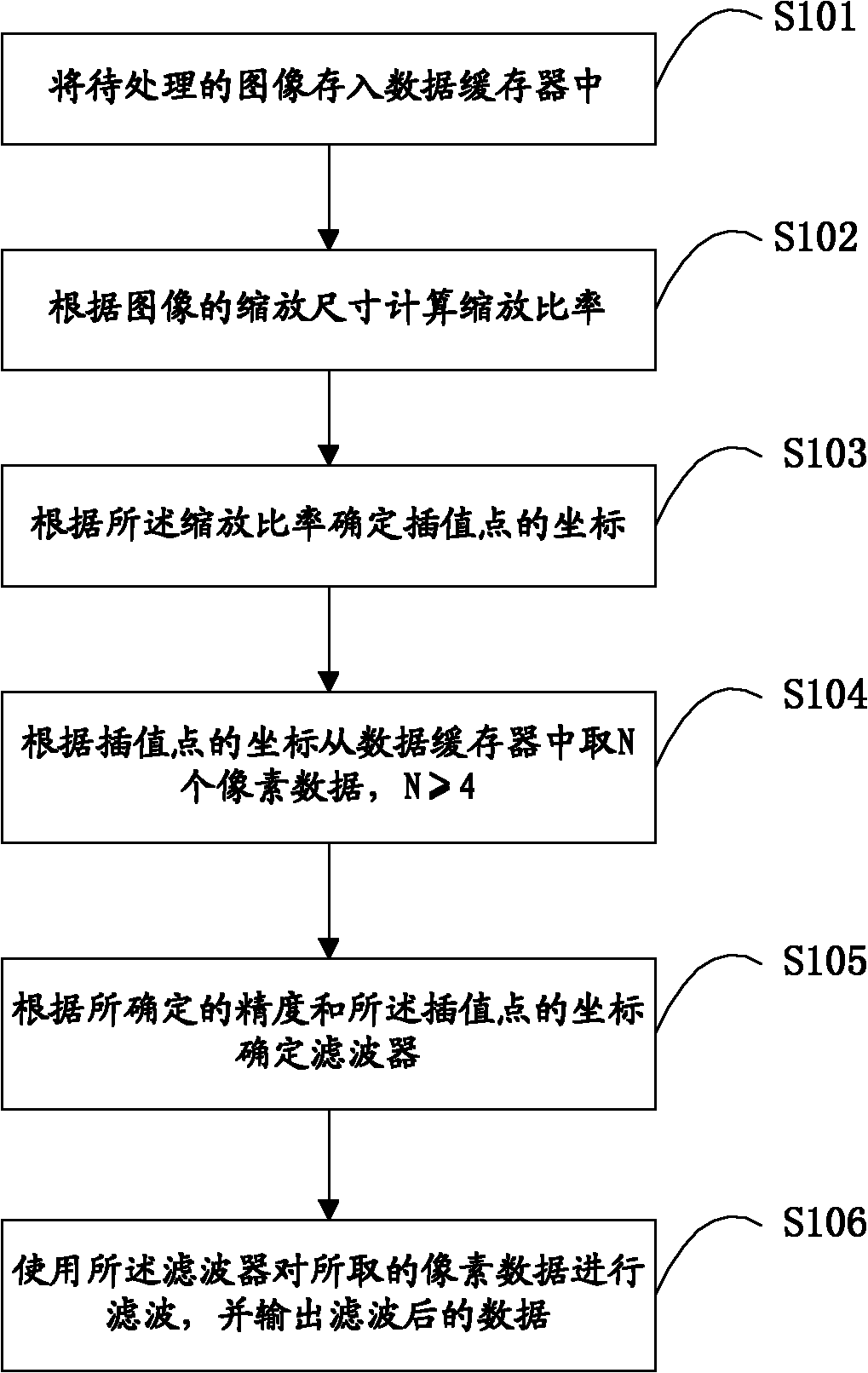
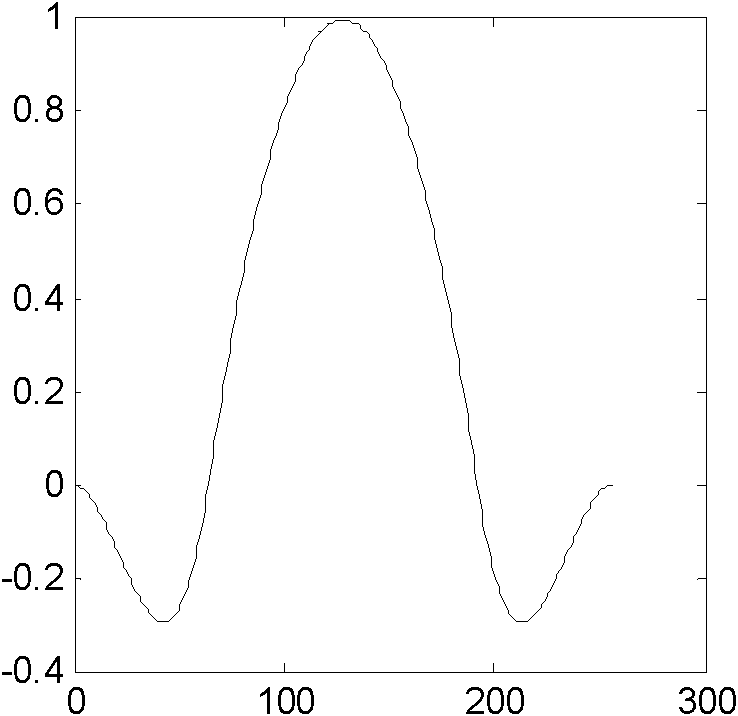
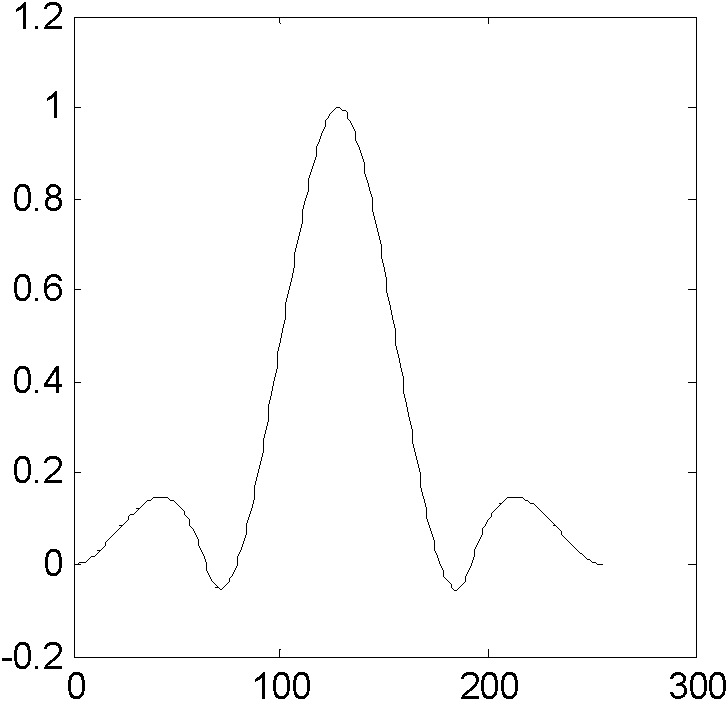
Image scaling method and system
InactiveCN102222317AFlexible designReduce computational complexityGeometric image transformationImaging qualityImage scale
The invention discloses an image scaling method and a system. The method comprises the steps of: A, storing images to be processed in a data register; B, calculating the scaling rate according the scaling size of the images; C, determining a coordinate of interpolation points according to the scaling rate; D, taking N pixel data from the data register according to the coordinate of the interpolation points, wherein N is more than or equal to 4; E, determining a filter according to the determined accuracy and the coordinate of the interpolation points; and F, using the filter to carry out filtering on the taken pixel data, and outputting the filtered data. By implementation of the technical scheme in the invention, 1, the function of scaling at any proportion is realized; 2, the complexity of scaling operation is greatly reduced; and 3, the scaling is realized and simultaneously the image quality is improved.
Owner:王洪剑
Vanadia—titania catalyst for removing nitrogen oxides and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS9101908B2Large specific surface areaGood dispersionHeat treatmentsDispersed particle separationVanadium dioxideTitanium
Provided is a method for preparing a vanadia-titania catalyst, comprising: vaporizing a titanium precursor; conveying the vaporized titanium precursor to a reaction unit together with an oxygen supplying source; reacting the vaporized titanium precursor conveyed to the reaction unit with the oxygen supplying source to produce titania particles; condensing the titania particles, collecting and recovering them; mixing the recovered titania particles with a vanadium precursor solution; drying the mixture of the titania particles with the vanadium precursor solution; and calcining the dried mixture under oxygen atmosphere or air. Provided also is a vanadia-titania catalyst obtained by the method. The vanadia-titania catalyst has a large specific surface area, uniform and fine nano-scaled size, and high dispersibility, thereby providing excellent nitrogen oxide removal efficiency, particularly in a low temperature range of 200° C.-250° C.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
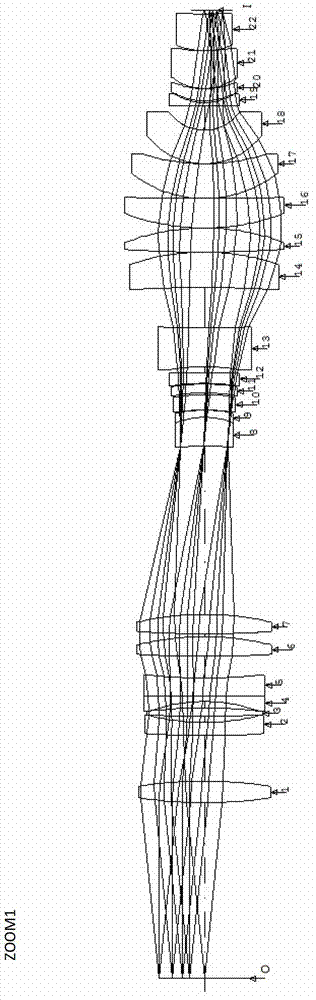
Aspherical focal length-variable photoetching objective lens system
ActiveCN102789044AOptical total lengthSmall aperturePhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusNegative powerPositive power
The invention provides an aspherical focal length-variable photoetching objective lens system, belonging to the technical field of optics, and aiming at solving the problem that the existing photoetching objective lens can not expose mask plate exposure patterns with different scale sizes by the same photoetching objective lens. The system provided by the invention from an object plane to an image plane sequentially comprises: the object plane, a first lens set, a second lens set, a third lens set, a fourth lens set, a fifth lens set and the image plane; the object plane is the plane where a mask plate is arranged; the first lens set is used for fixing the distance between the object plane and the first lens set of a focal length-variable system; the second lens set is used for changing the focal length of the photoetching objective lens and the size of the image plane; the third lens ser is used for compensating the movement of the image plane when a zooming group moves, so that the position of the image plane is invariably kept in the whole process of zooming; the fourth lens set has the negative power, the fifth lens set has the positive power, and a back fixed set consists of the fourth lens and the fifth lens, so that the invariable distance between the final lens of the photoetching objective lens which is near to one side of the image plane and the image plane can be guaranteed; and the image plane is the plane where an etching substrate is arranged.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
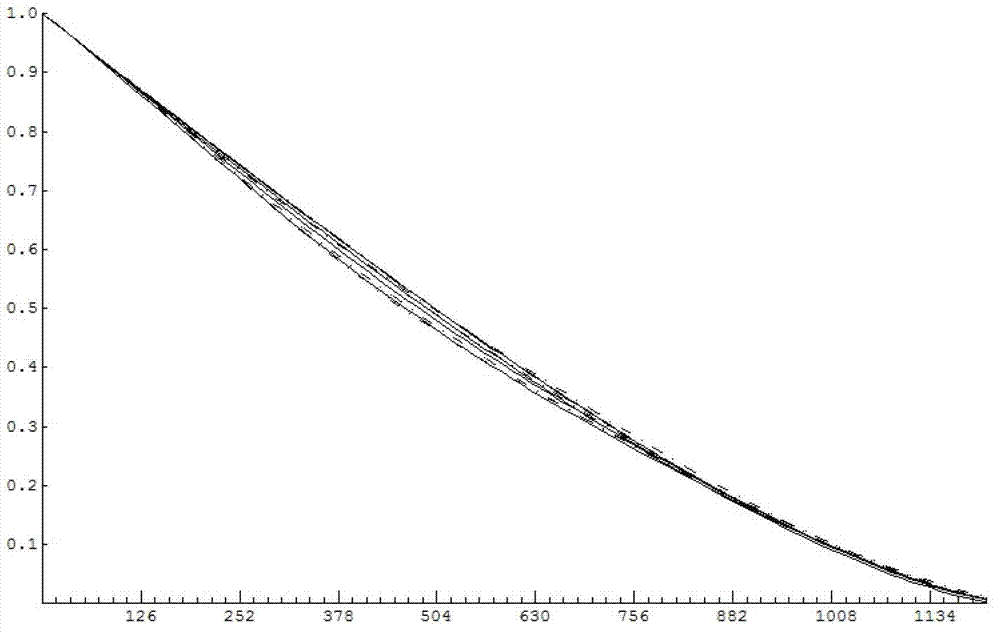
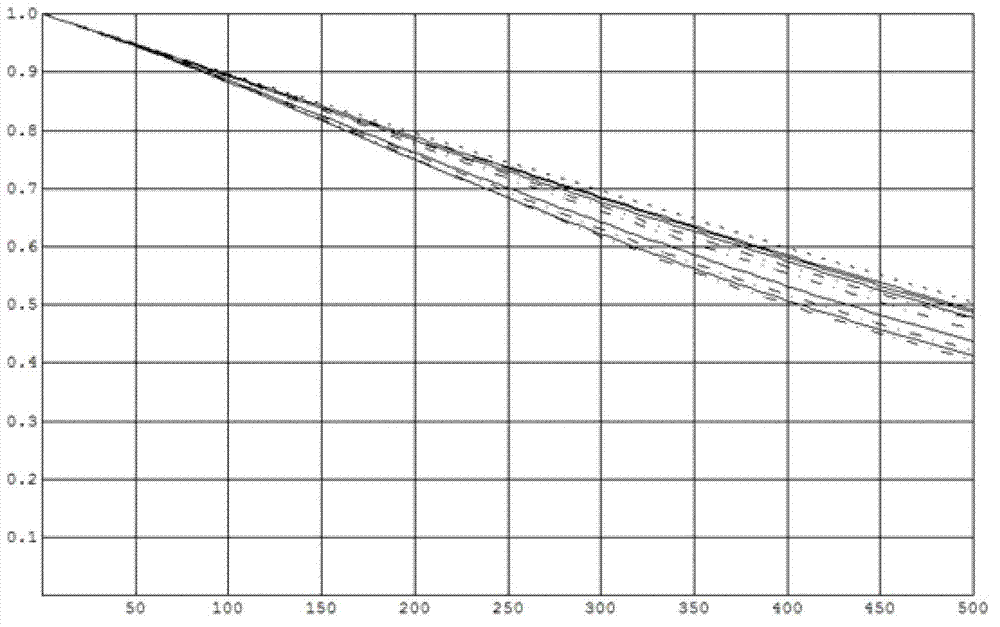
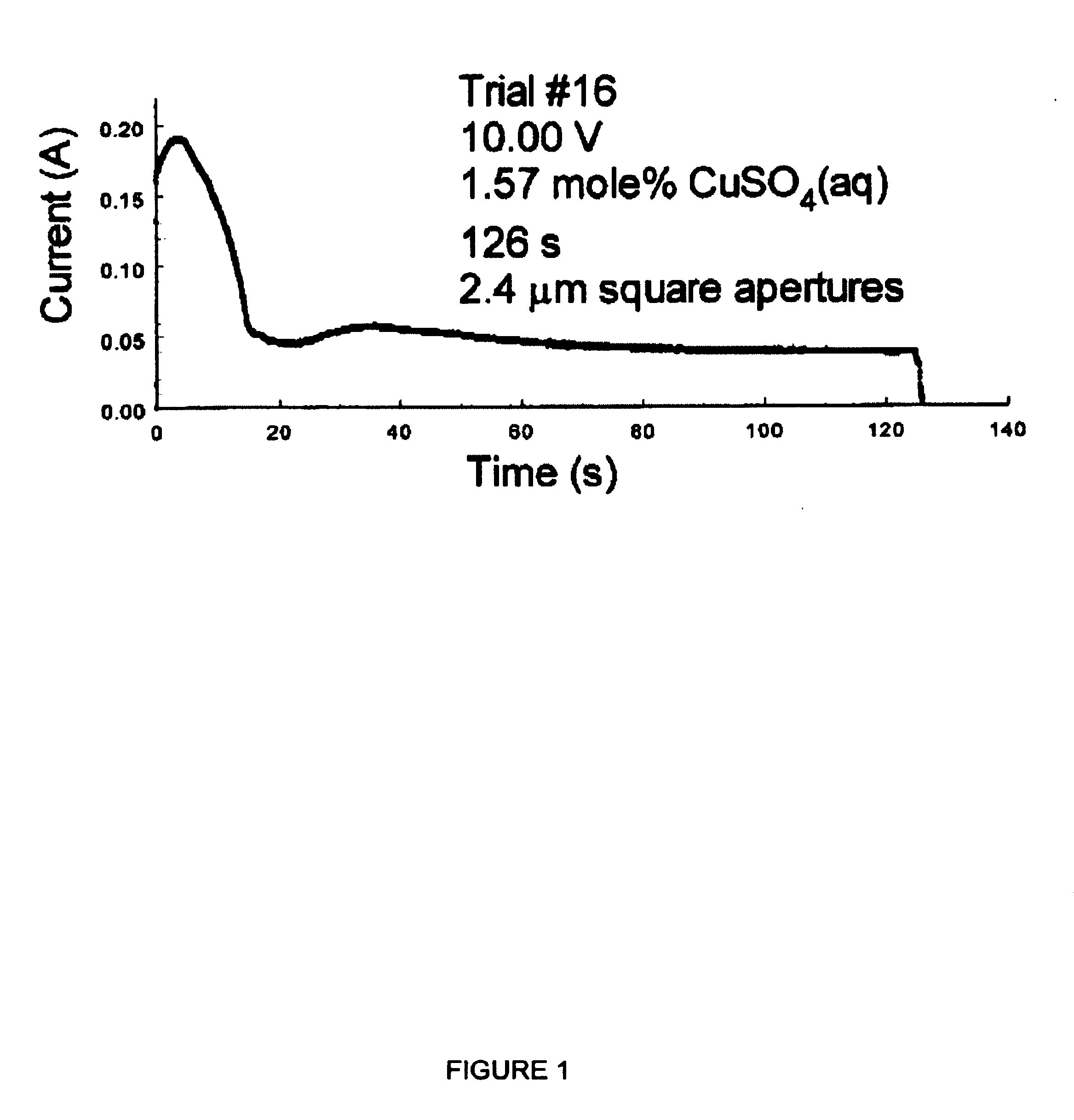
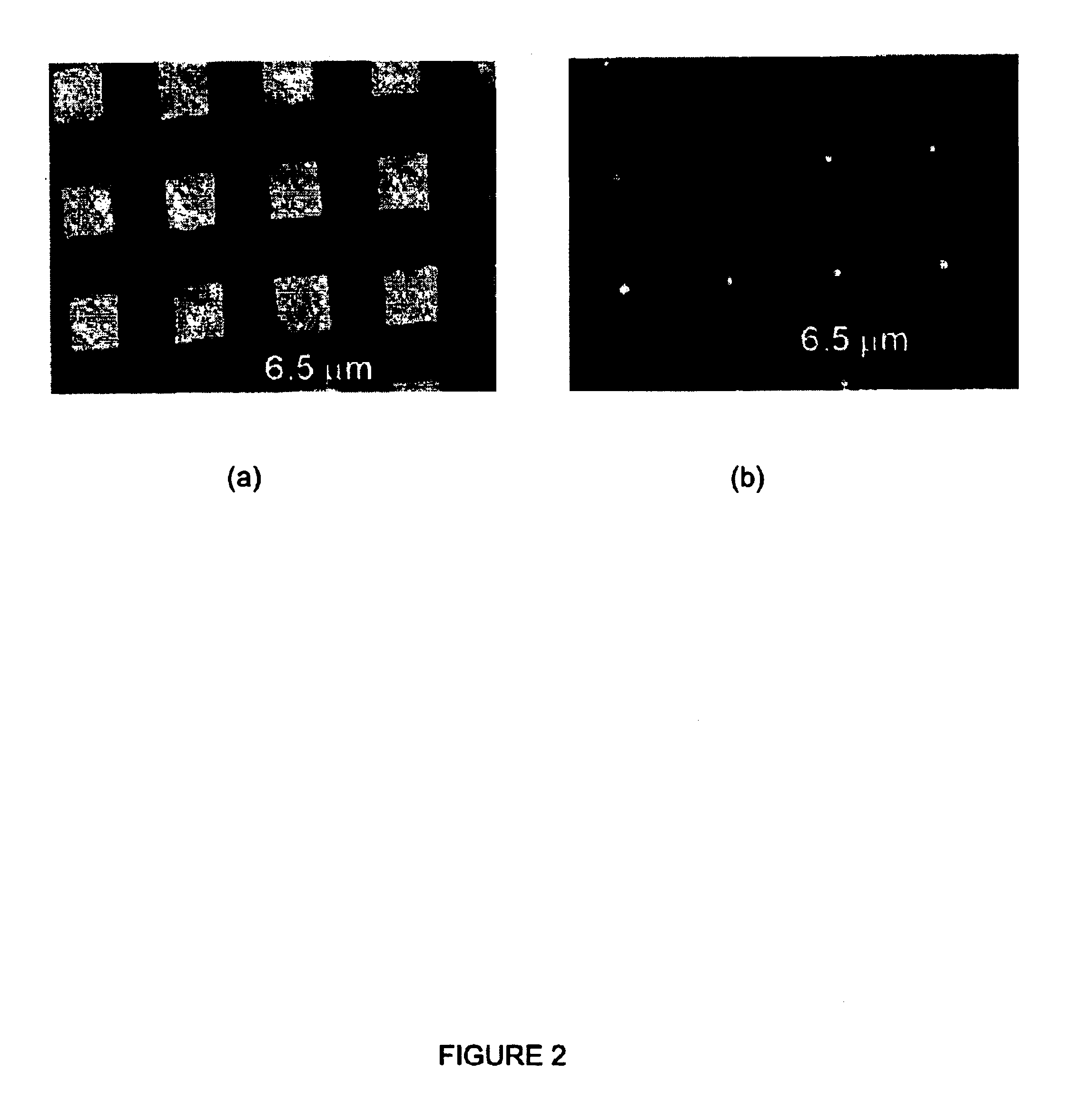
Method for uniform electrochemical reduction of apertures to micron and submicron dimensions using commercial biperiodic metallic mesh arrays and devices derived therefrom
InactiveUS6797405B1Rapid depositionReduced dimensionMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsElectricitySpectral filtering
A method for electrodepositing a uniformly thick coating on a metallic mesh is provided, the method comprises the steps of: (1) providing a metallic mesh having a plurality of apertures having at least one dimension greater than nanometer scale sizes; (2) subjecting the metal mesh to a relatively fast deposition of an electrodeposited material so as to substantially uniformly coat said mesh with electrodeposited material; and (3) subjecting the product of the relatively fast deposition step to a relatively slow deposition of an electrodeposited material so as to reduce at least one dimension greater than nanometer scale size to a size of nanometer scale. Also provided are metallic meshes so prepared and spectral filters.
Owner:OHIO STATE INNOVATION FOUND
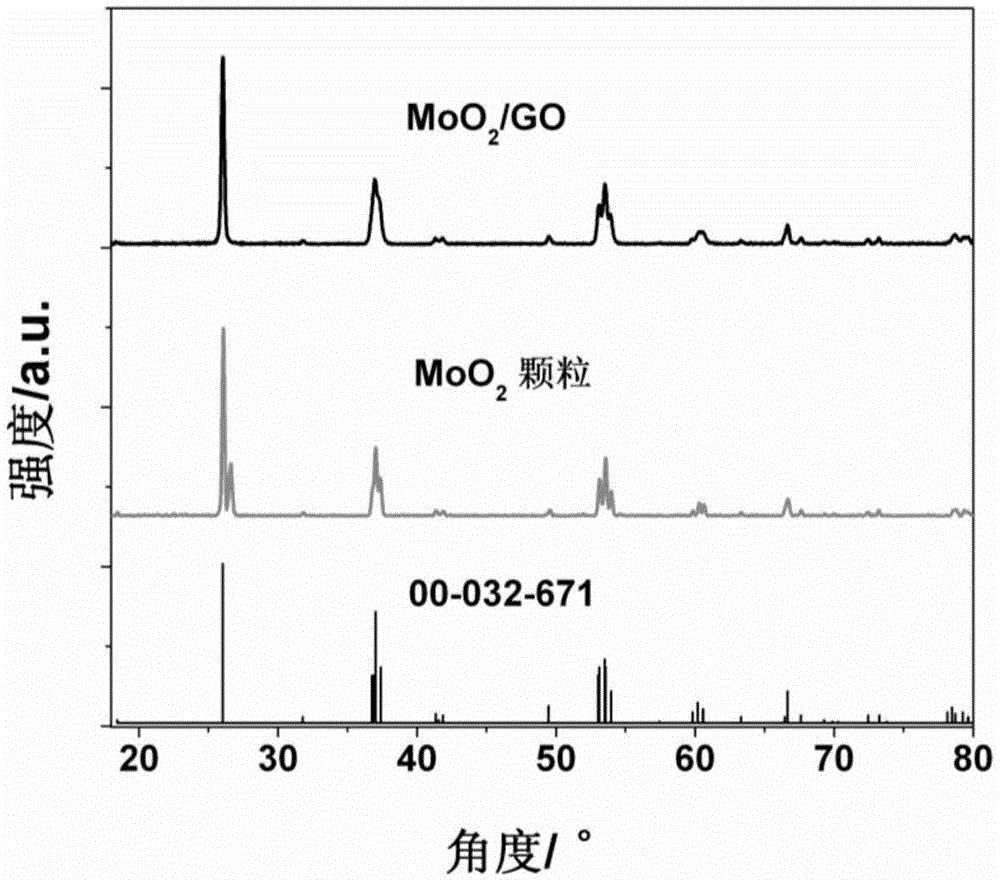
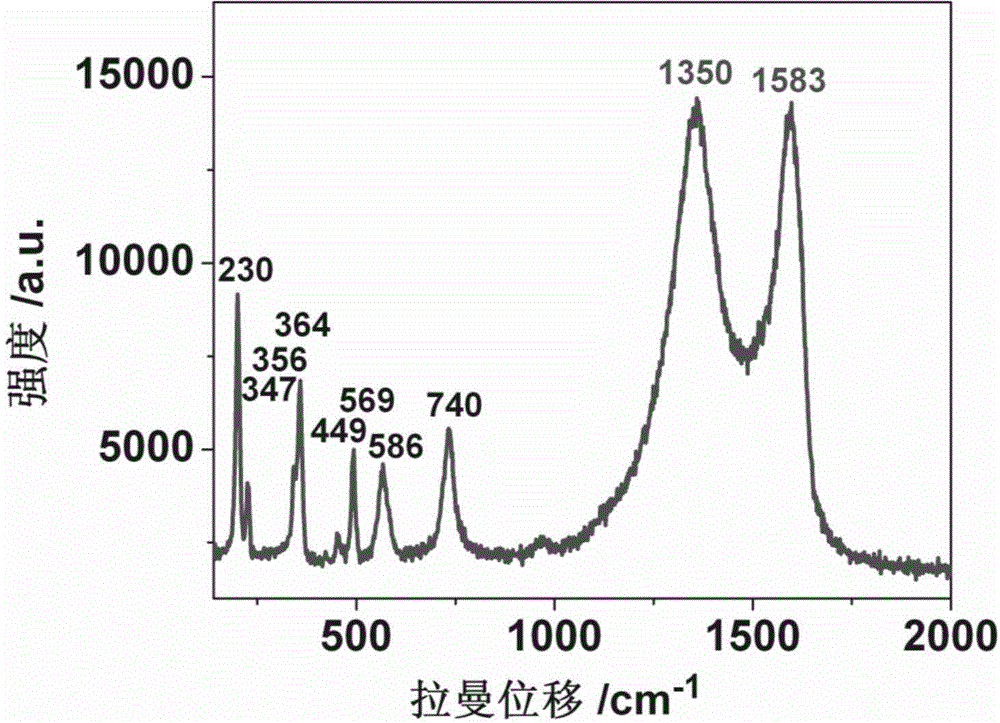
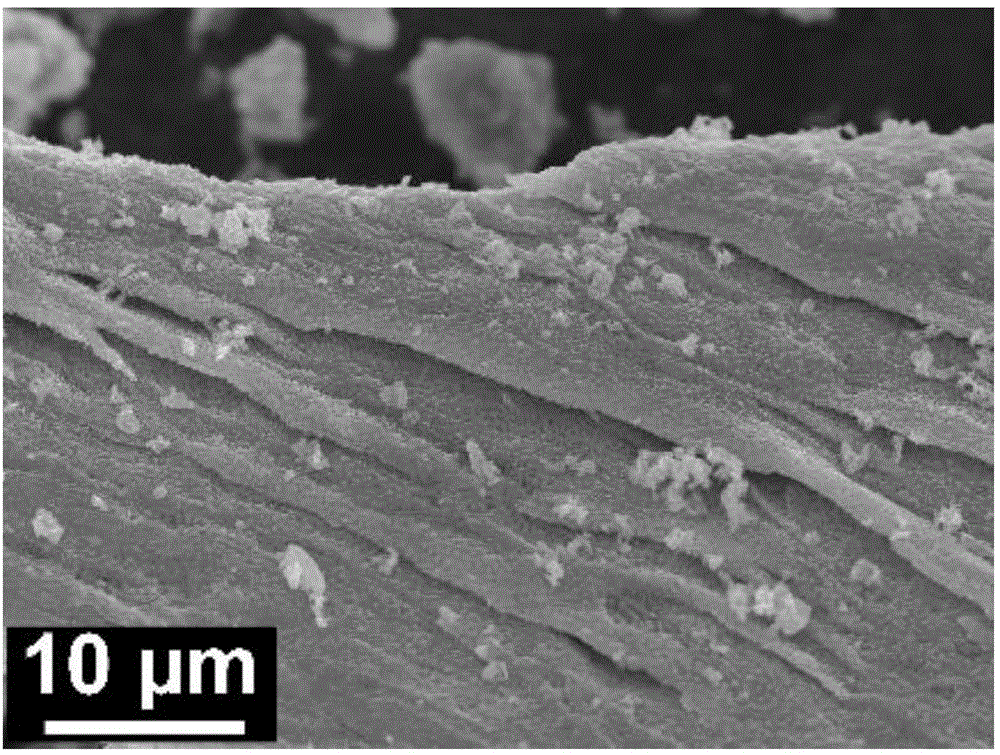
Preparation method of graphene-oxide-based MoO2 high-performance electrode material of lithium/sodium ion battery
The invention discloses a preparation method of a graphene-oxide-based MoO2 high-performance electrode material of a lithium / sodium ion battery and belongs to the technical field of preparation of the electrode material of the lithium / sodium ion battery. The technical scheme is as follows: the preparation method comprises the following steps: dropwise adding (NH4)Mo7O24 aqueous solution into a graphene-oxide water dispersing system, fully stirring, dispersing to be uniform, and then evaporating water in the dispersing system to form molybdenum amino acid and derivative / graphene-oxide layered preform; then carrying out heat treatment on the molybdenum amino acid and derivative / graphene-oxide layered preform, and thus preparing the graphene-oxide-based MoO2 high-performance electrode material of the lithium / sodium ion battery. The preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the operation is simple, the reaction time is short, the repeatability is high, the cost is lower, the yield is large, and the structure of a product is easily controlled; and the prepared negative material of the battery reaches the nano-scale size, and has the characteristics of large specific capacity, good conductivity, low resistivity and high circulating times and the like.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Multi-illumination face recognition method based on morphologic quotient images
InactiveCN101539992ARealize identificationSolve the problem of face recognitionCharacter and pattern recognitionNear neighborOperational approach
The invention provides a multi-illumination face recognition method based on morphologic quotient images. The method comprises the following steps that: illumination intensity of each position of a face is estimated, including light-source intensity and normal vector information; a quotient value of an original illumination image and an illumination estimation image is evaluated so as to obtain the reflectivity information of the face surface, namely face texture features unrelated to illumination conditions; because dividing operation can produce noise points which are unrelated to the face texture features in the prior shadow region, the original image is preprocessed before illumination estimation; illumination estimation adopts a morphologic closed operation method and uses the simplest and most convenient rectangular mean template; the scale size of the template adopts a dynamic principle; according to the characteristics of different local regions, the size of the template is chosen through self-adaptation; a quotient image result obtained through division is subjected to nearest neighbor classification; and a distance criterion adopts normalized correlation. The method has the advantage of improving the security of automatic face recognition systems, and has important application value in the field of biometrics recognition.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Adhesives comprising linear isotactic polymers
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com