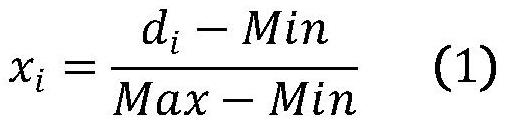Patents
Literature
57 results about "Space weather" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Space weather is a branch of space physics and aeronomy, or heliophysics, concerned with the time varying conditions within the Solar System, including the solar wind, emphasizing the space surrounding the Earth, including conditions in the magnetosphere, ionosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. Space weather is distinct from but conceptually related to the terrestrial weather of the atmosphere of Earth (troposphere and stratosphere). The term space weather was first used in the 1950s and came into common usage in the 1990s..
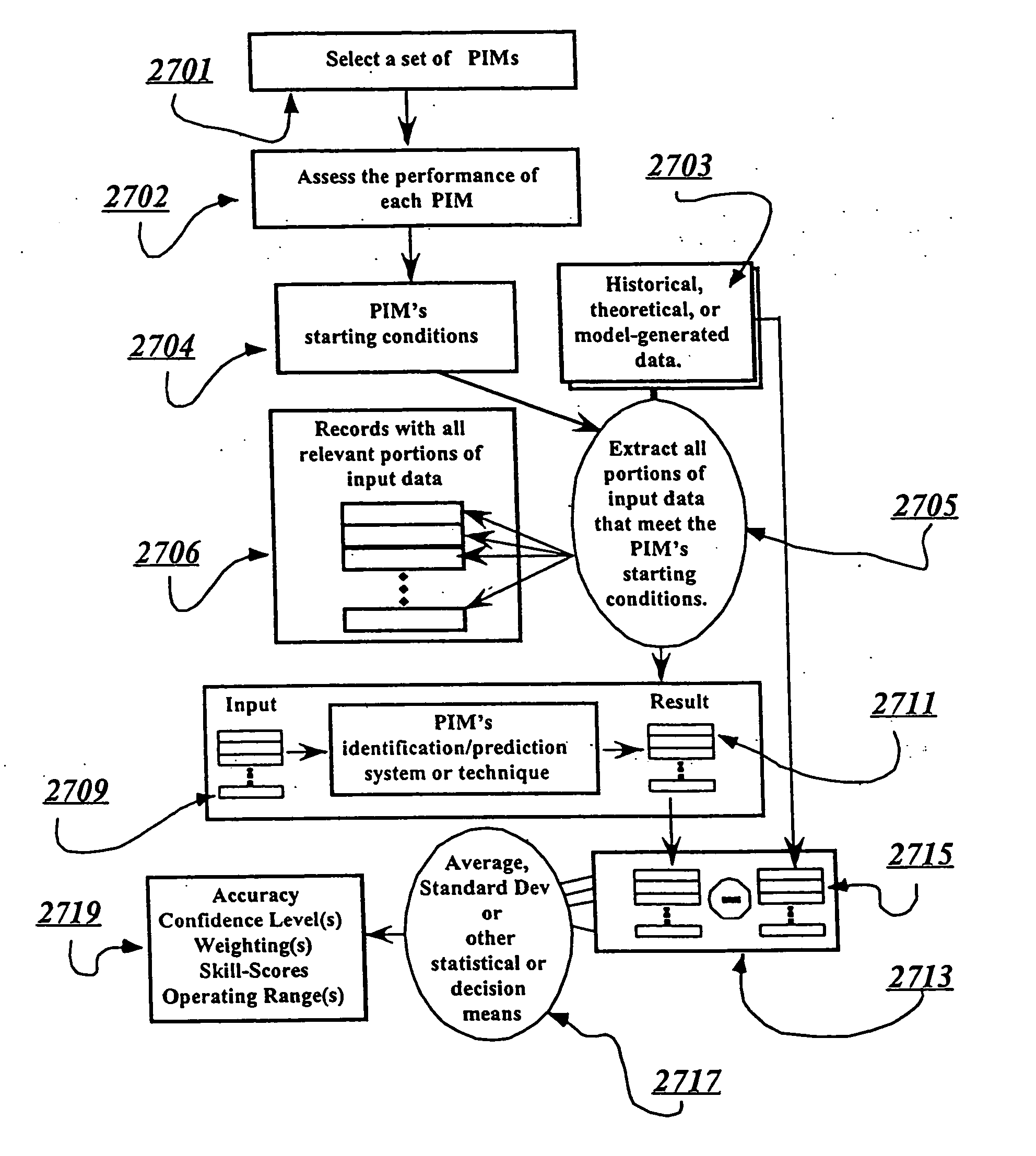
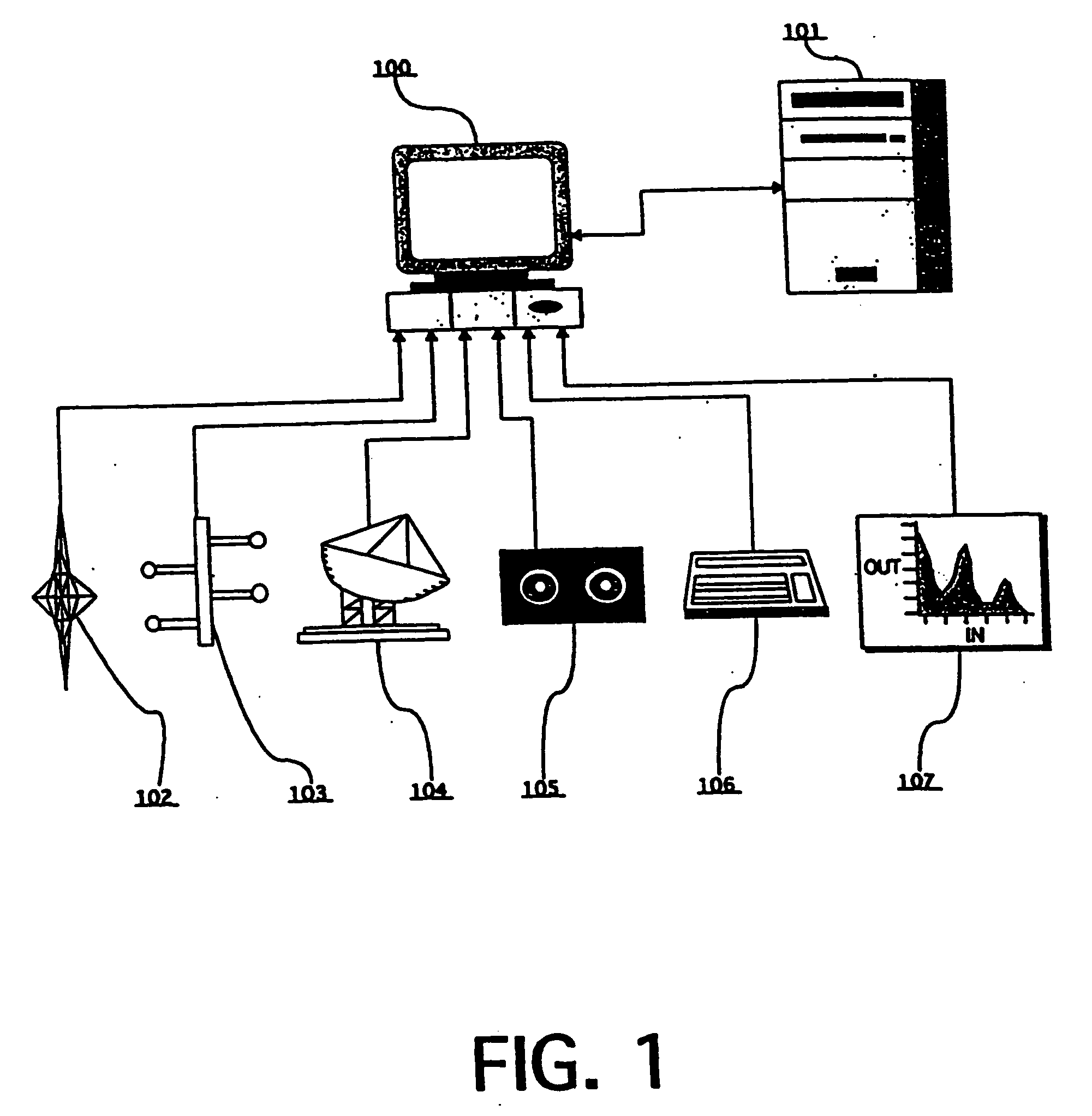
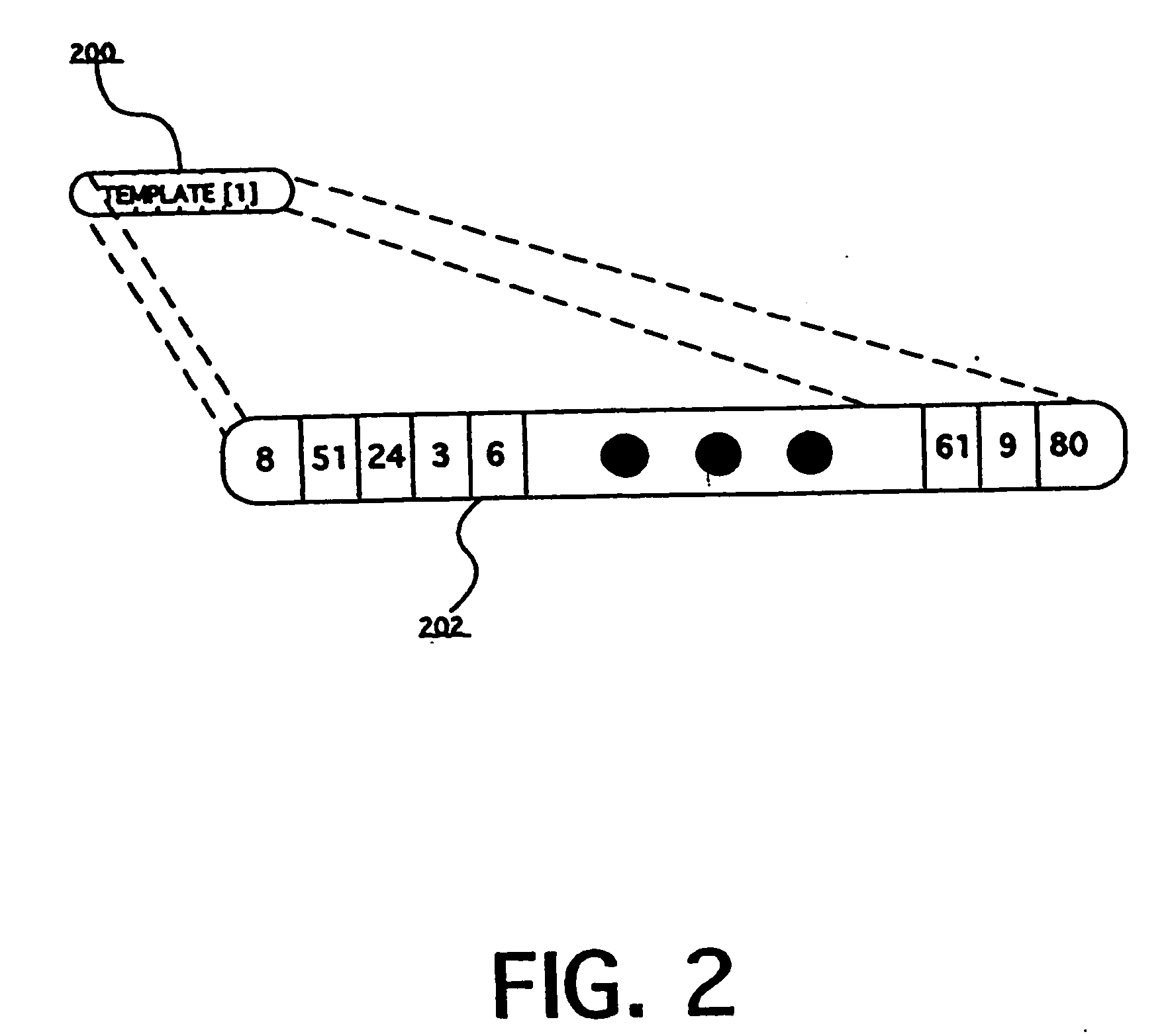
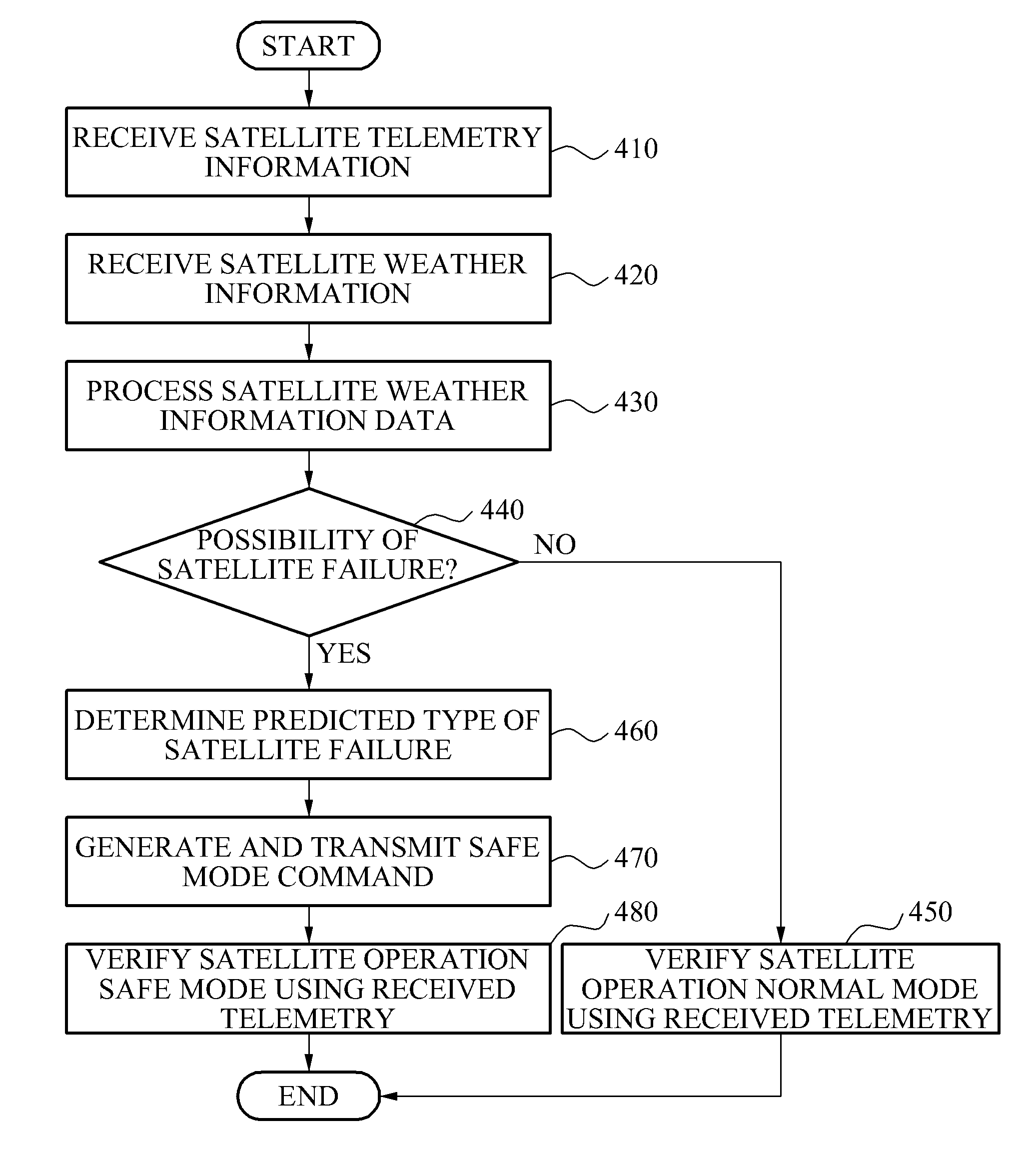
Space weather prediction system and method
InactiveUS20050159894A1Weather condition predictionSpecial data processing applicationsHybrid systemStart time
A system and method of forecasting space weather (at Earth or another location) based on identifying complex patterns in solar, interplanetary, or geophysical data. These data may include current or historical measurements and / or modeled data (predicted or simulated). Data patterns (both non-event and event-related) are identified (even when another event is occurring). Such patterns may vary with recent / cyclic variations in solar (e.g. solar max / min), interplanetary, or geophysical activity. Embodiments are built around: (1) templates, (2) expert systems, (3) neural networks, (4) hybrid systems comprising combinations of (1), (2) and / or (3), and multimodal intelligent systems. Forecasts are customized and / or updated as new data arise and as systems are dynamically modified (e.g. via feedback between system parts). Numerical or other indexes are generated representing: forecasts, associated confidence levels, etc. The invention predicts events / non-events and / or other values or parameters associated with space weather (e.g. Dst, event onset time, duration, etc.)
Owner:CARMEL SYST
Space weather prediction system and method
InactiveUS20050267685A1Weather condition predictionSpecial data processing applicationsHybrid systemStart time
A system and method of forecasting space weather (at Earth or another location) based on identifying complex patterns in solar, interplanetary, or geophysical data. These data may include current or historical measurements and / or modeled data (predicted or simulated). Data patterns (both non-event and event-related) are identified (even when another event is occurring). Such patterns may vary with recent / cyclic variations in solar (e.g. solar max / min), interplanetary, or geophysical activity. Embodiments are built around: (1) templates, (2) expert systems, (3) neural networks, (4) hybrid systems comprising combinations of (1), (2) and / or (3), and multimodal intelligent systems. Forecasts are customized and / or updated as new data arise and as systems are dynamically modified (e.g. via feedback between system parts). Numerical or other indexes are generated representing: forecasts, associated confidence levels, etc. The invention predicts events / non-events and / or other values or parameters associated with space weather (e.g. Dst, event onset time, duration, etc.)
Owner:INTRILIGATOR DEVRIE S +1
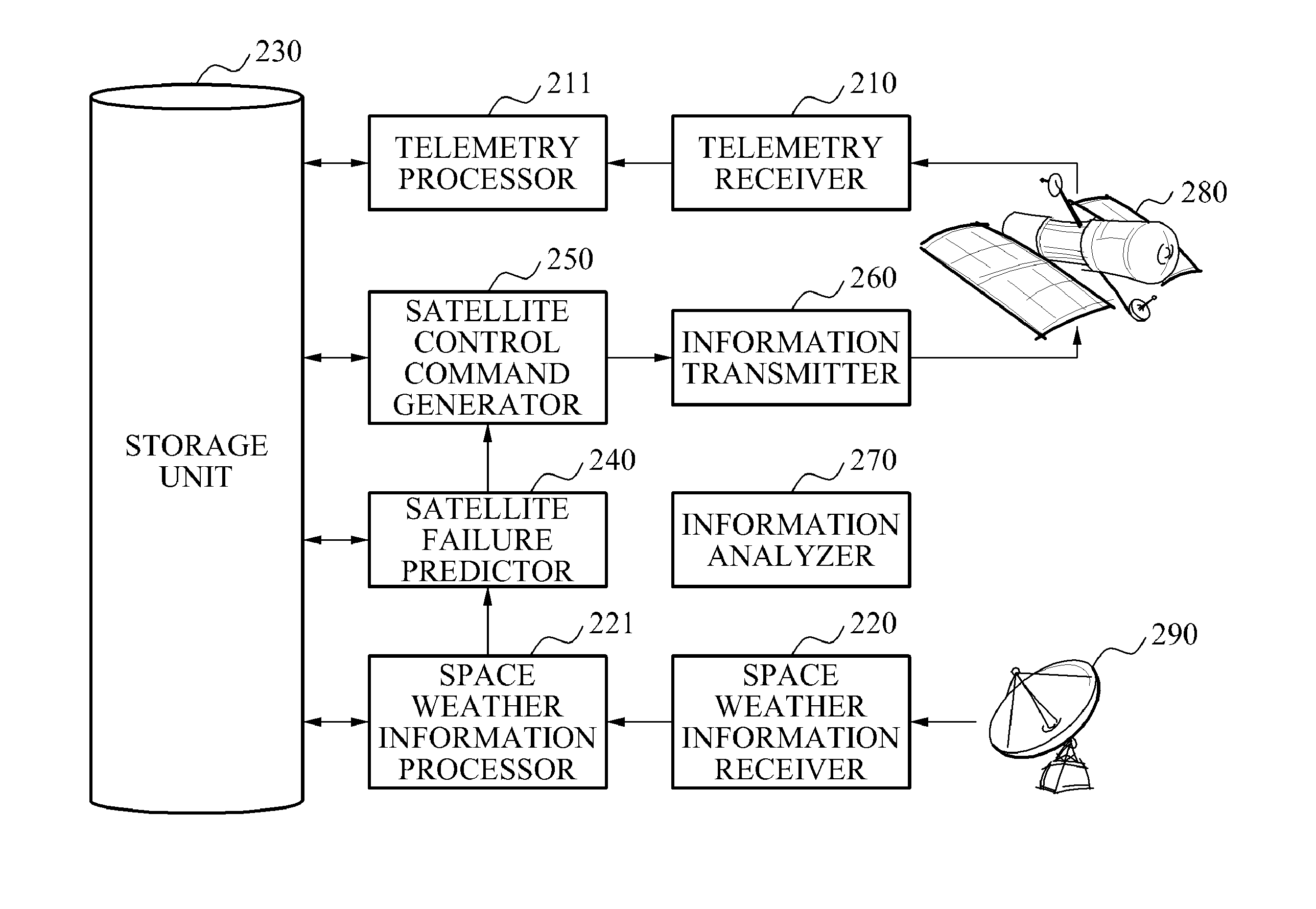
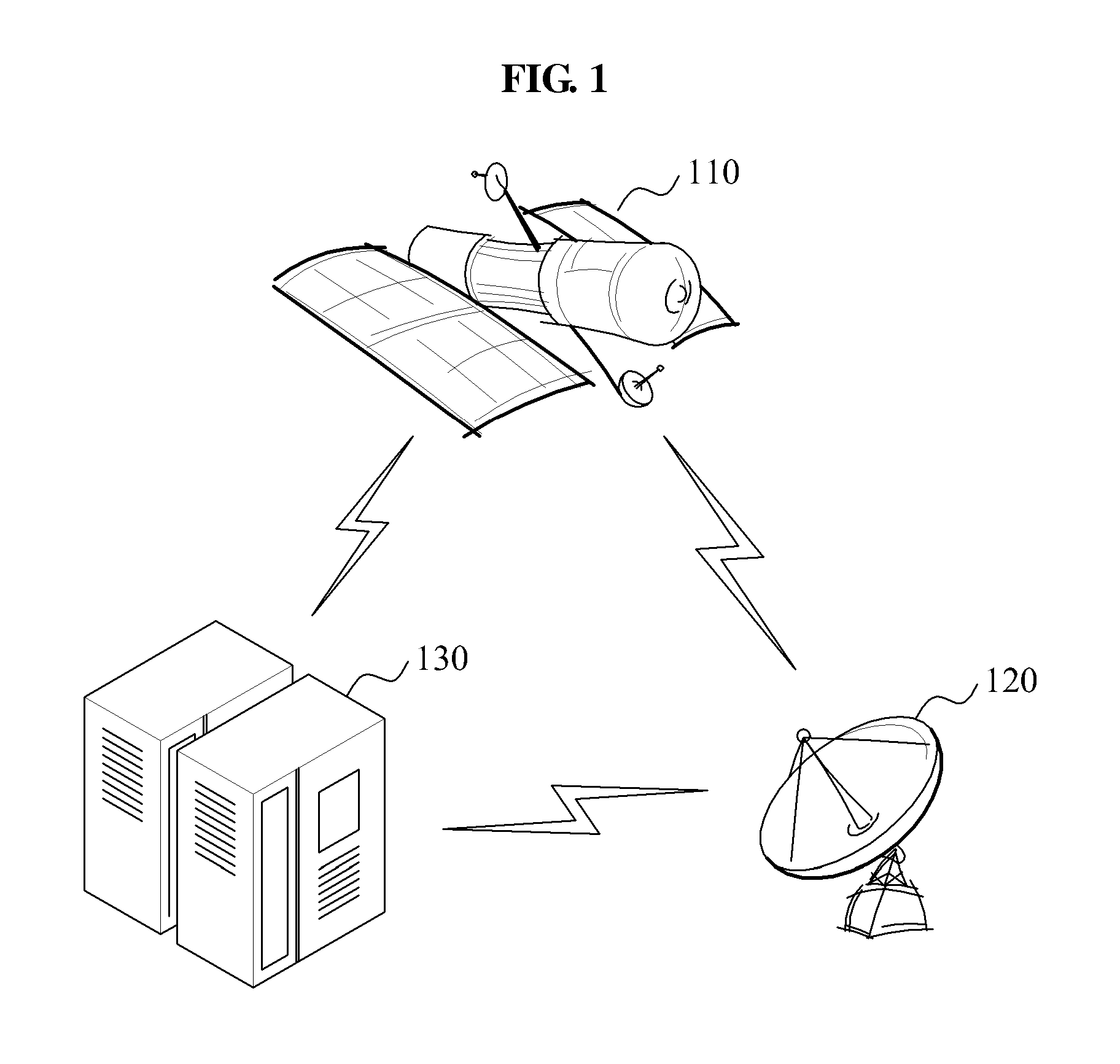
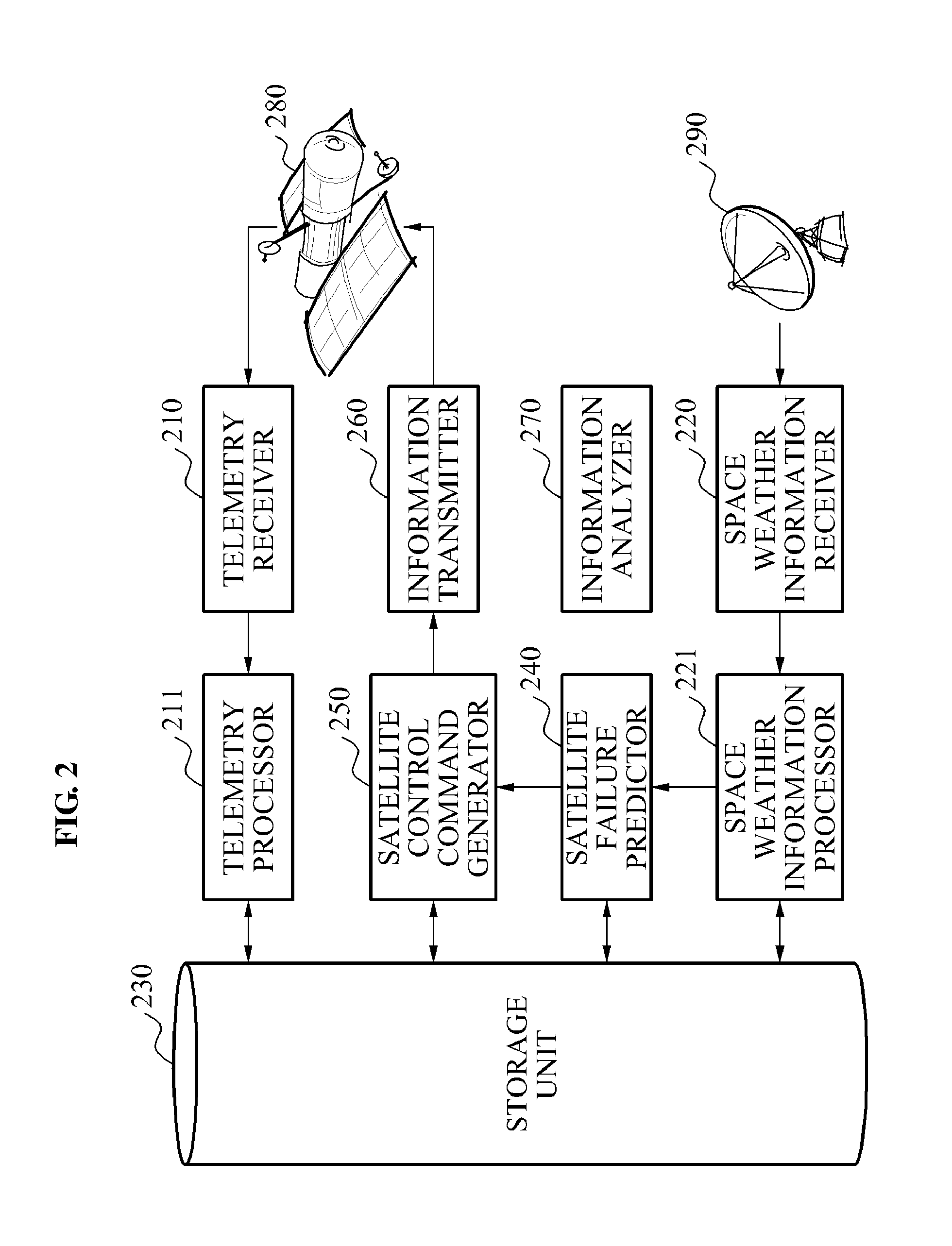
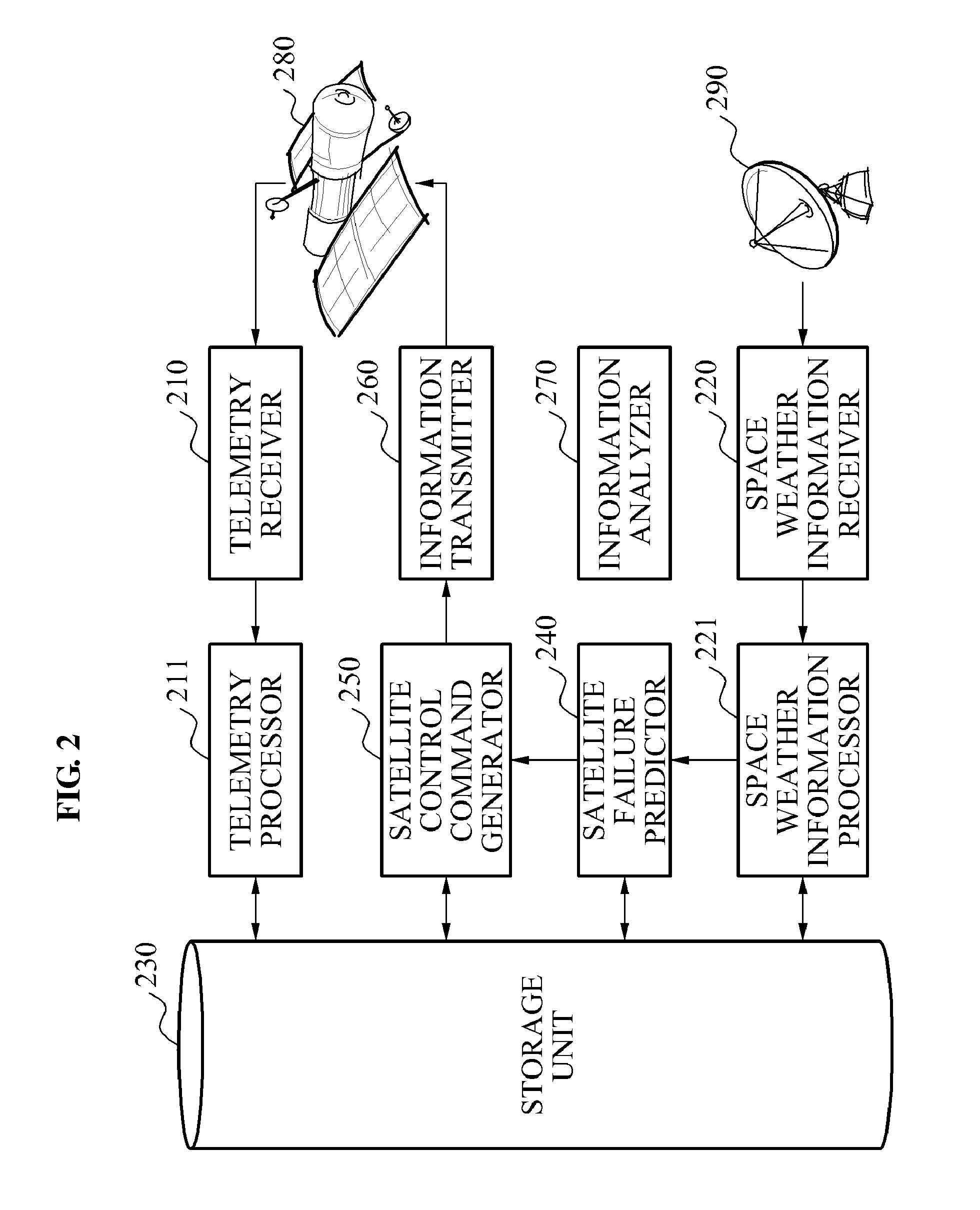
Apparatus and method for monitoring status of satellite
InactiveUS20140222255A1Data processing applicationsCosmonautic vehiclesMonitoring statusAtmospheric sciences
Provided is an apparatus and method for monitoring a status of a satellite, including classifying satellite telemetry information and space weather information and storing the information in a storage unit including respective databases, predicting whether a predetermined type of satellite failure occurs based on the space weather information, and generating satellite control command information to change a status of a predetermined satellite configuration when a satellite failure determining index used to determine a possibility of the satellite failure is beyond a predetermined critical alert range.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
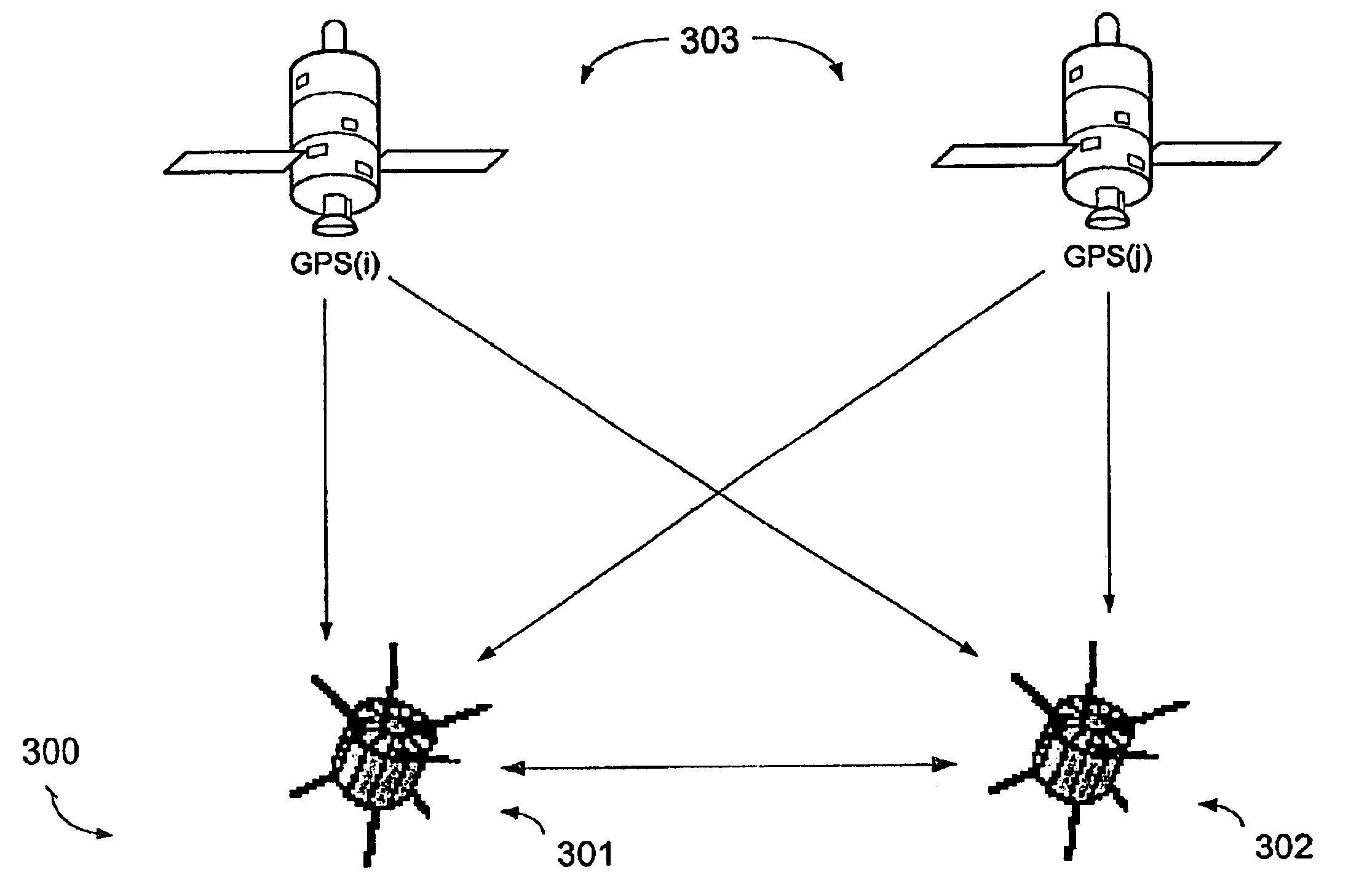
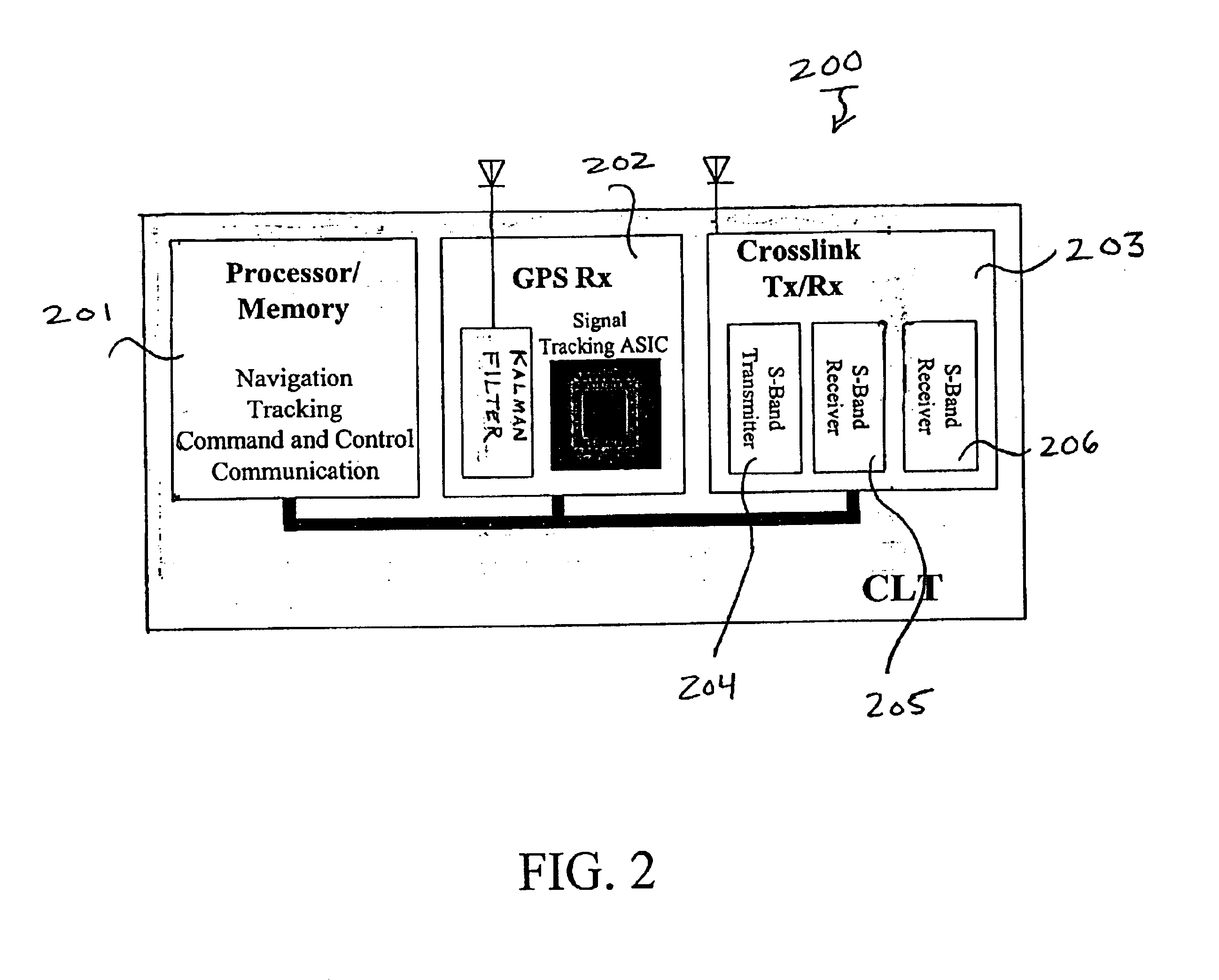
Method for using GPS and crosslink signals to correct ionospheric errors in space navigation solutions
ActiveUS6859690B2Correction errorCosmonautic vehiclesInstruments for comonautical navigationAmbiguityIonospheric heater
A method of correcting ionospheric delays induced in received signals by space systems is disclosed. The method takes advantage of received GPS signals and received crosslink signals among spacecraft to estimate the effect of ionospheric delays and correct for such delays in the computation of the range estimation between spacecraft. The method generates and initial estimate of the ionospheric delay by tracking pseudorandom codes on both GPS and crosslink signals at known frequencies to correct an initial relative range vector. Using the corrected range vector generated from the use of code, the method subsequently estimates a more precise correction by considering the carrier phase error as induced by ionospheric delay. This includes estimate the integer ambiguities on both the GPS signals and the crosslink signals iteratively and subsequently estimating a more precise ionospheric delay correction with is applied to the relative position vector using the carrier phase measurements. The method is also applicable to non-navigation applications including measuring dynamic ionospheric structure and variability over a wide range of scale sizes, thereby greatly improving operational models of navigation and communications, and improving interdependent models of atmospheric, ionospheric, magnetospheric, and space weather physics and prediction.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Active interference removing apparatus for buried pipeline
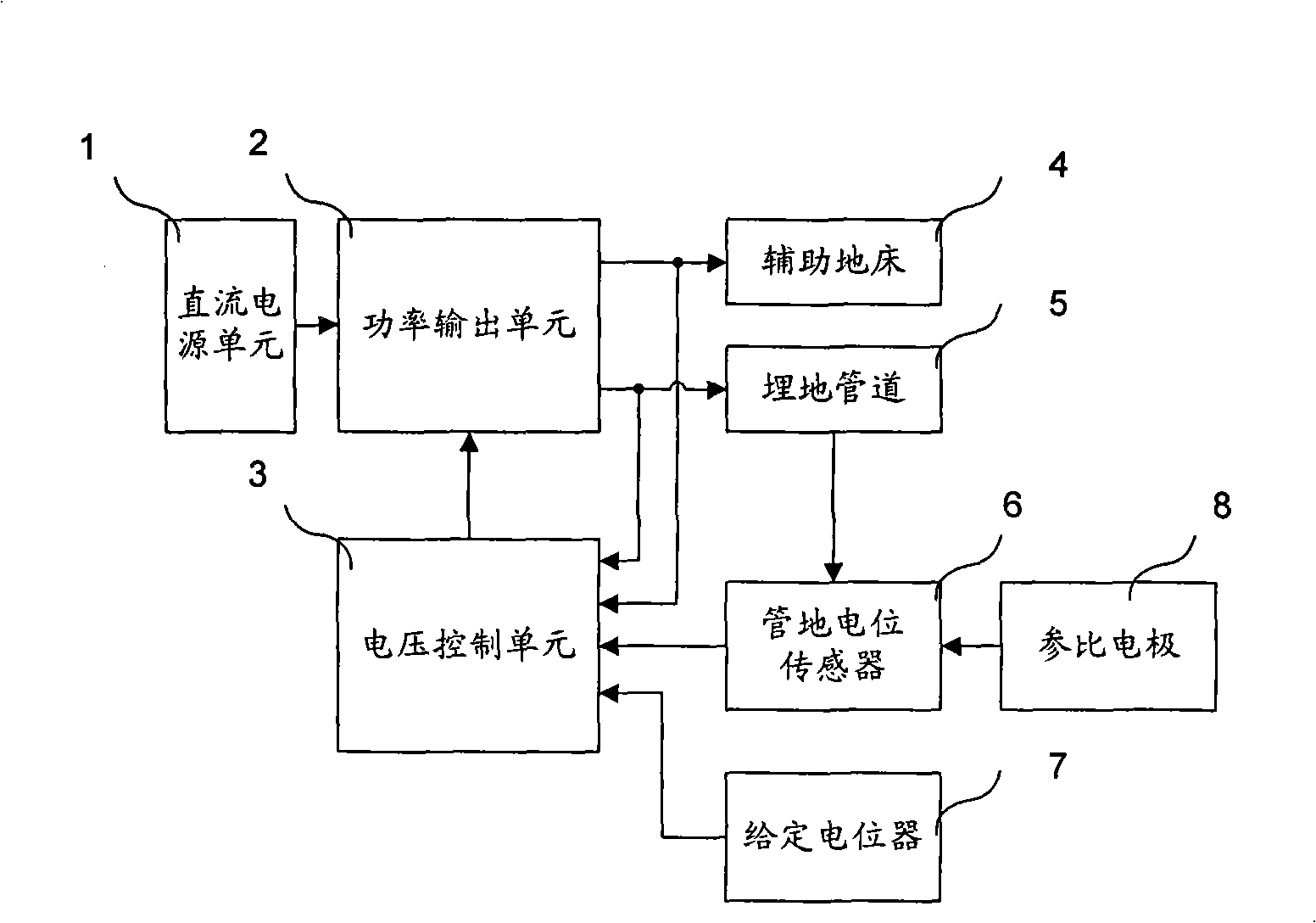
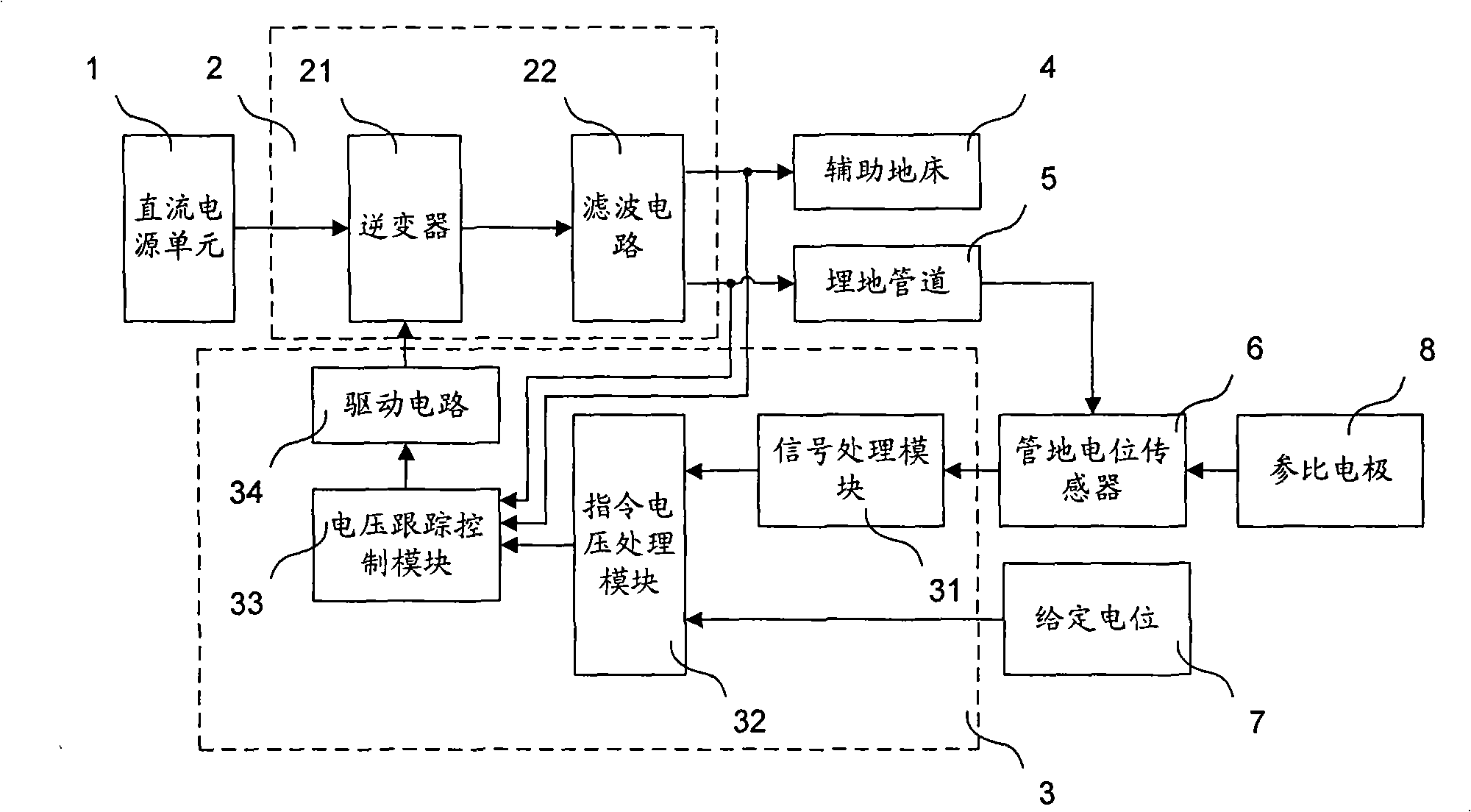
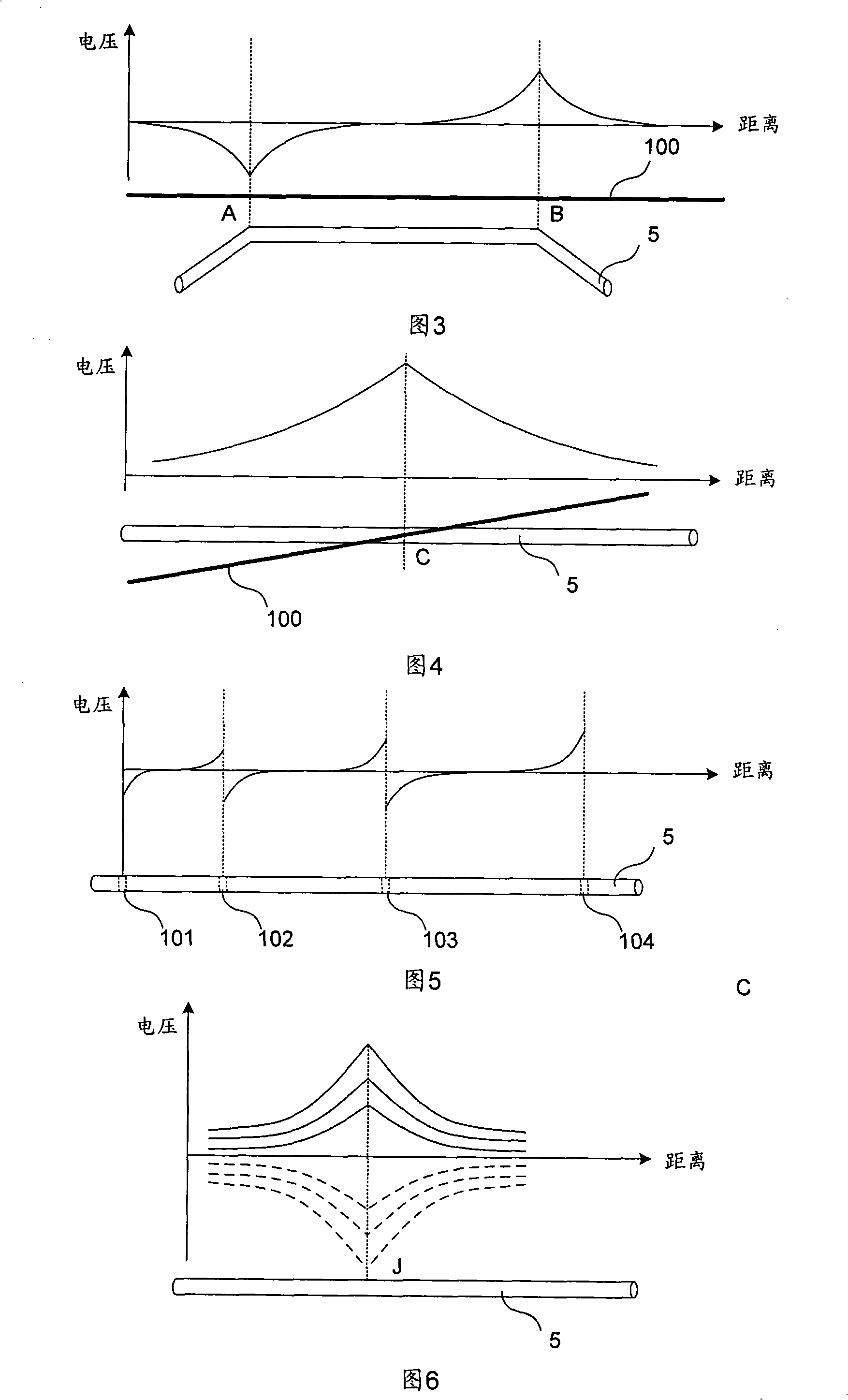
ActiveCN101343744AImprove output sensitivityEliminate distractionsCurrent/voltage measurementDisturbance voltageHigh pressure
The invention relates to a buried pipeline active disturbance removing device. The buried pipeline active disturbance removing device comprises a direct current power supply unit, a pipe-to-soil potential sensor, a given potentiometer, a voltage control unit and a power output unit, wherein the voltage control unit is used to generate the pulse width modulation (PWM) signal, and the power output unit is used to control the output of the internal invertor according to the pulse width modulation signal, and to output disturbance removing voltage which is performed with filtering treatment and which is equal to the pipe disturbance degree and is reverse to the direction to the auxiliary ground bed and the buried pipeline. Through adopting the tracking type PWM control method, the output of the buried pipeline active disturbance removing device of the invention can track the reference signal change of the directive voltage processing module in time, the buried pipeline active disturbance removing device has the advantages that the output sensitivity is high, the reaction speed is rapid, and the dynamic performance is good, and in particular the buried pipeline active disturbance removing device can be suitable for the eliminating of the disturbance caused by the high voltage transmission line and the space weather change.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING) +2
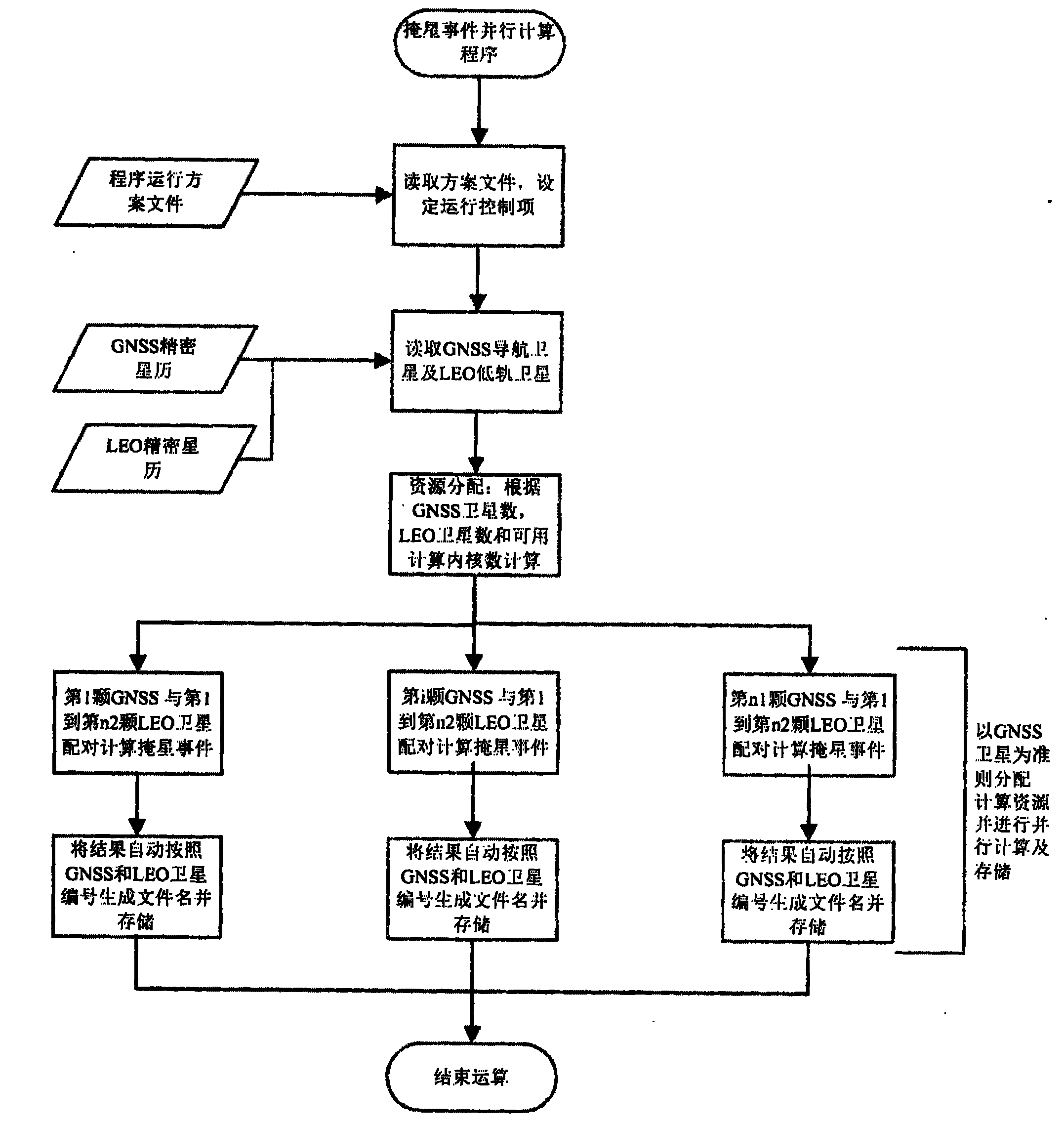
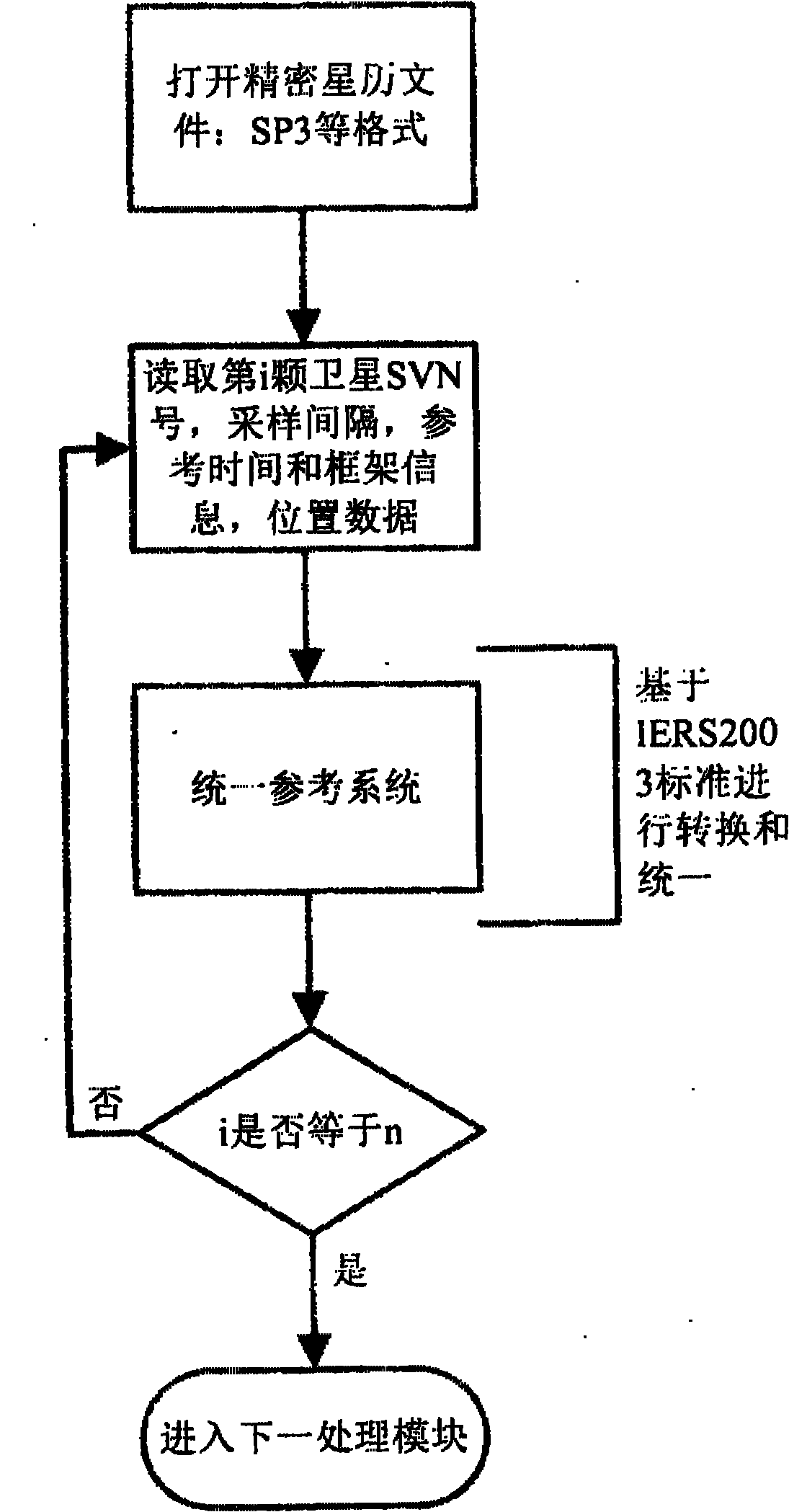
Quick data processing method of occultation event of parallel asterism
InactiveCN101872019AImprove efficiencyImprove work efficiencyMultiple digital computer combinationsSatellite radio beaconingData processing systemComputer science
The invention relates to the technical fields of the application and the parallel computation of a navigational satellite, in particular to a quick computation method of an occultation event of a parallel asterism. The method comprises the following steps of: navigating constellations, reading occultation asterism information, distributing satellite pairs according to an obtainable computation core, computing occultation event information accurately and finally, storing as an information file for subsequent occultation data processing. The method provided by the invention is applied to an occultation data processing system, is especially applied to the preprocessing process of a near-real-time (3 to 6h) occultation data processing system for computing the important part of the occultation event information, can enhance the computation efficiency of the process greatly and reduces the computation time greatly, thereby providing quicker data guarantee to the near-real-time application of occultation data applied to weather forecast and space weather forecast.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Real-time autonomous weather and space weather monitoring
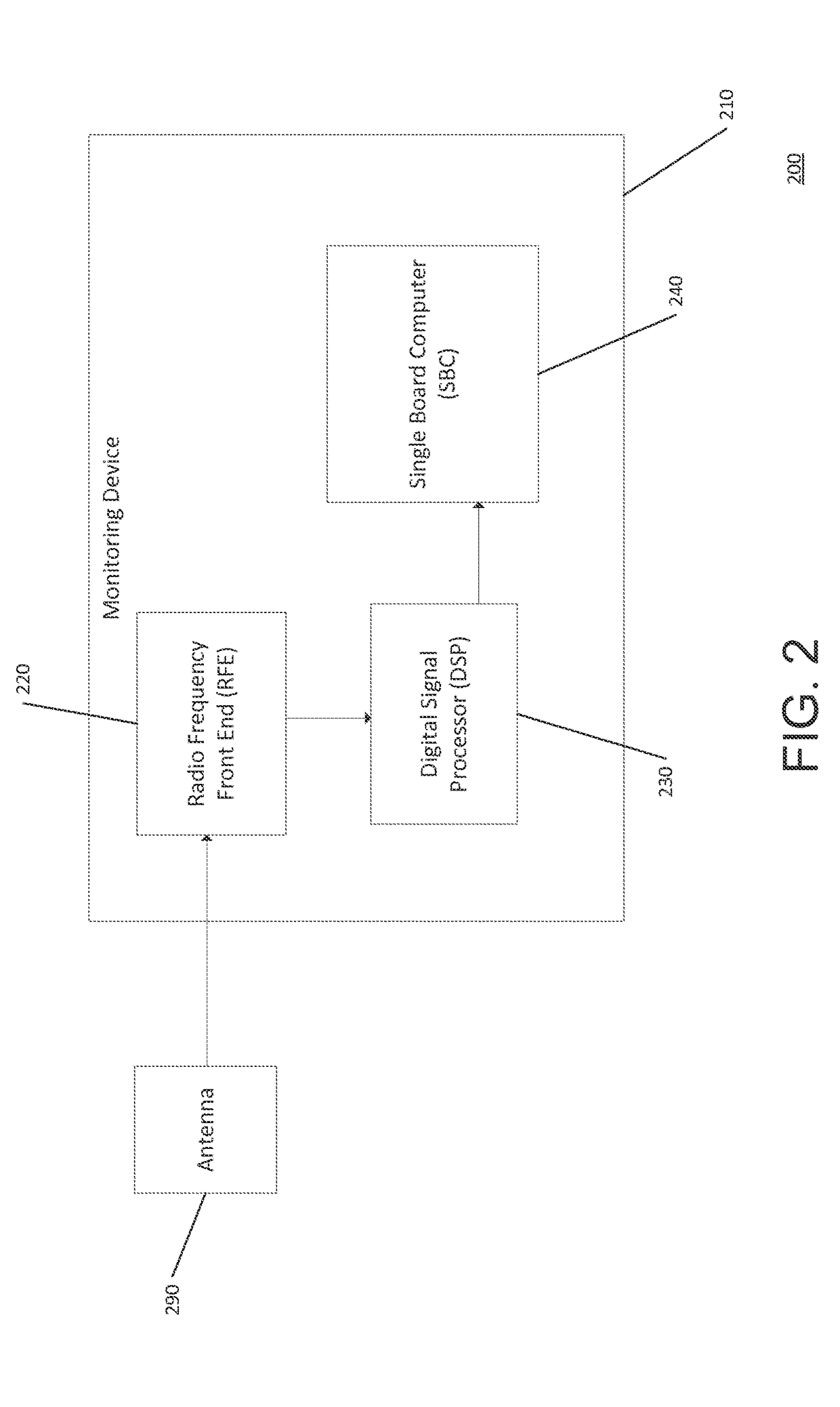
ActiveUS20170322303A1Eliminate relative motionIndication of weather conditions using multiple variablesSatellite radio beaconingHigh rateAntenna gain
A method of calculating ionospheric scintillation includes calculating a motion-corrected perturbation of a GNSS radio signal received by a monitoring device deployed in an oceanic environment. The method includes calculating the σφ using the high rate phase of the GNSS signal adjusted by removing the change in distance between the monitoring device and the GNSS satellite. The calculating the σo may further include passing the adjusted high rate phase through a high pass filter to remove a drift motion of the monitoring device. The method further includes calculating the S4 through calculating a tilt angle between the antenna of the monitoring device with the GNSS satellite and adjusting the antenna gain through known gain pattern of the antenna. The wave height of the oceanic environment may be calculated by detrending the antenna height to remove low frequency motion when a high rate position of the monitoring device is calculated.
Owner:ATMOSPHERIC & SPACE TECH RES ASSOCS
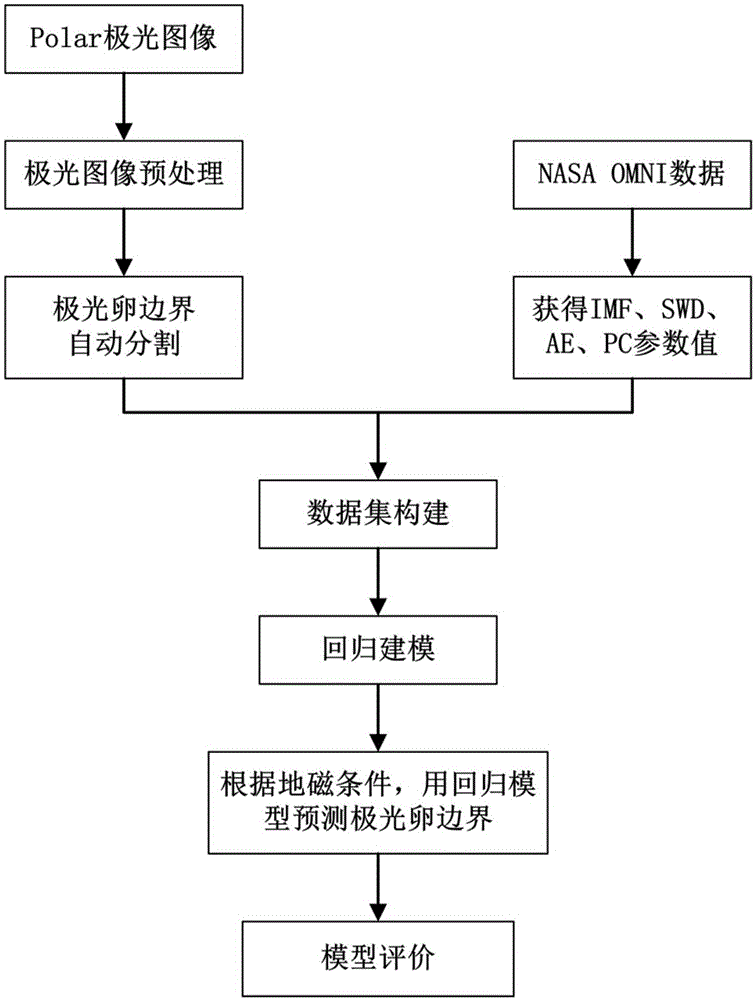
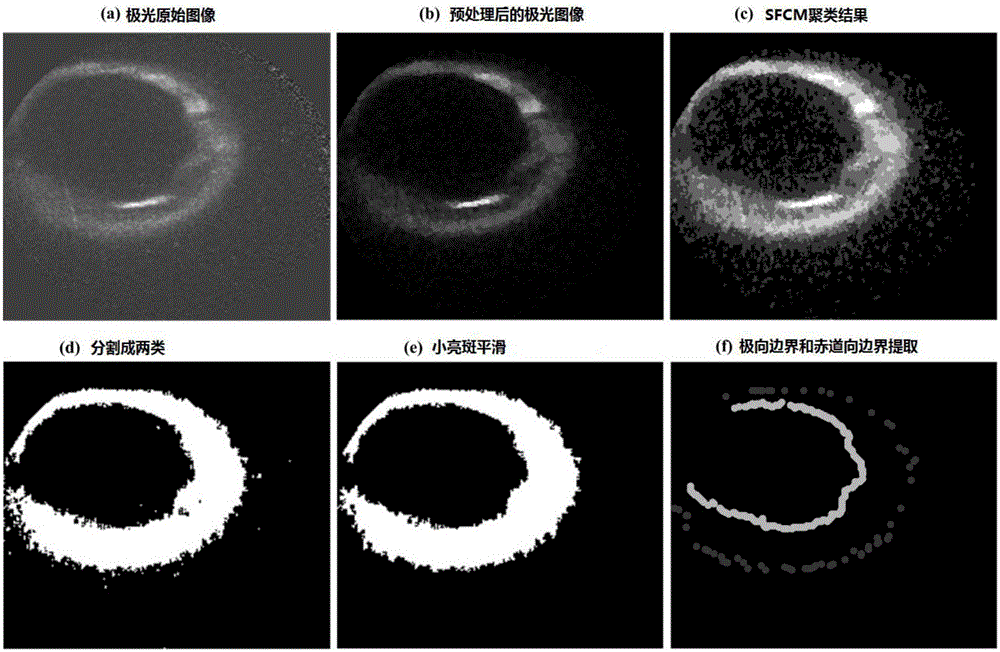
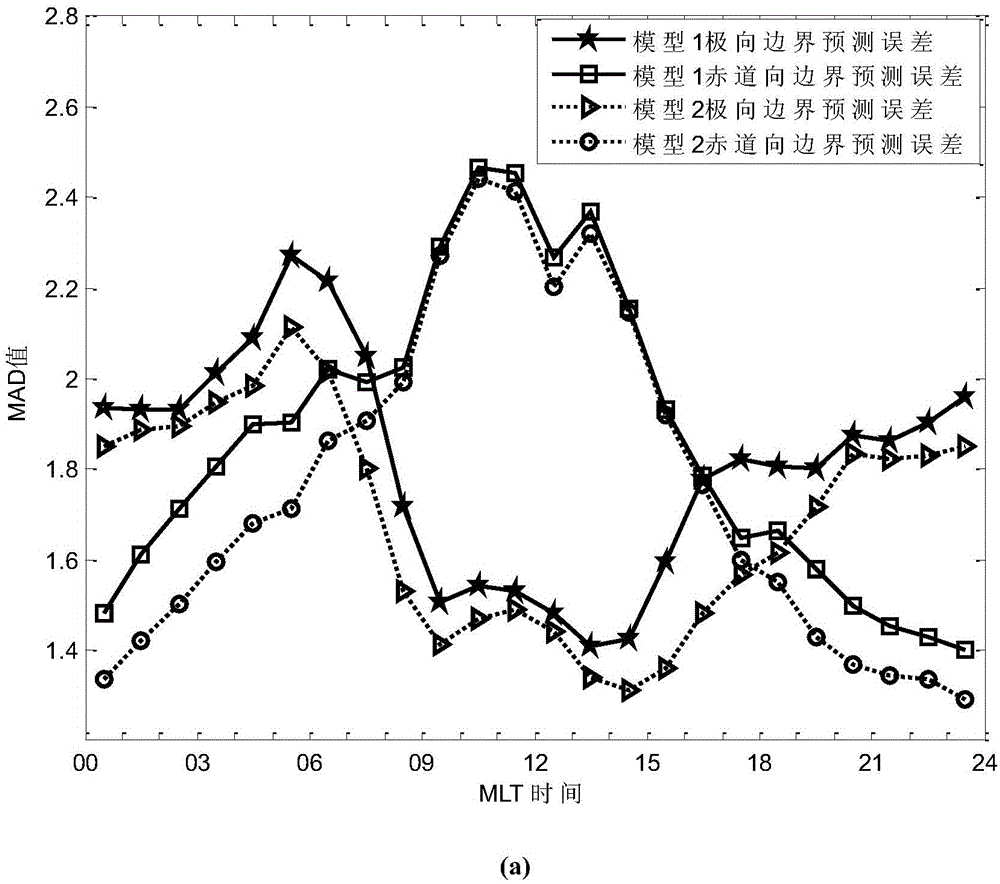
Auroral oval boundary position prediction method based on interplanetary and geomagnetic parameters
The invention discloses an auroral oval boundary position prediction method based on interplanetary and geomagnetic parameters. Estimation is performed on geomagnetic latitude of auroral oval boundaries in the equator direction and the pole direction at all magnetic places according to interplanetary and geomagnetic environment, and the method can be used in prediction for an auroral oval boundary position in space weather research. The method comprises the following achieving steps: (1) UVI image pre-processing, (2) automatic division of the auroral oval boundaries, (3) obtaining of the interplanetary and geomagnetic parameters, (4) construction of a data set, (5) regression modeling, (6) prediction of the auroral oval boundary position, and (7) evaluation of a prediction result. According to the experiment result, the method can predict the auroral oval boundary position at an about 1.7MLAT average absolute error in a relatively accurate manner, and the method has great practical value in the space weather prediction aspect.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
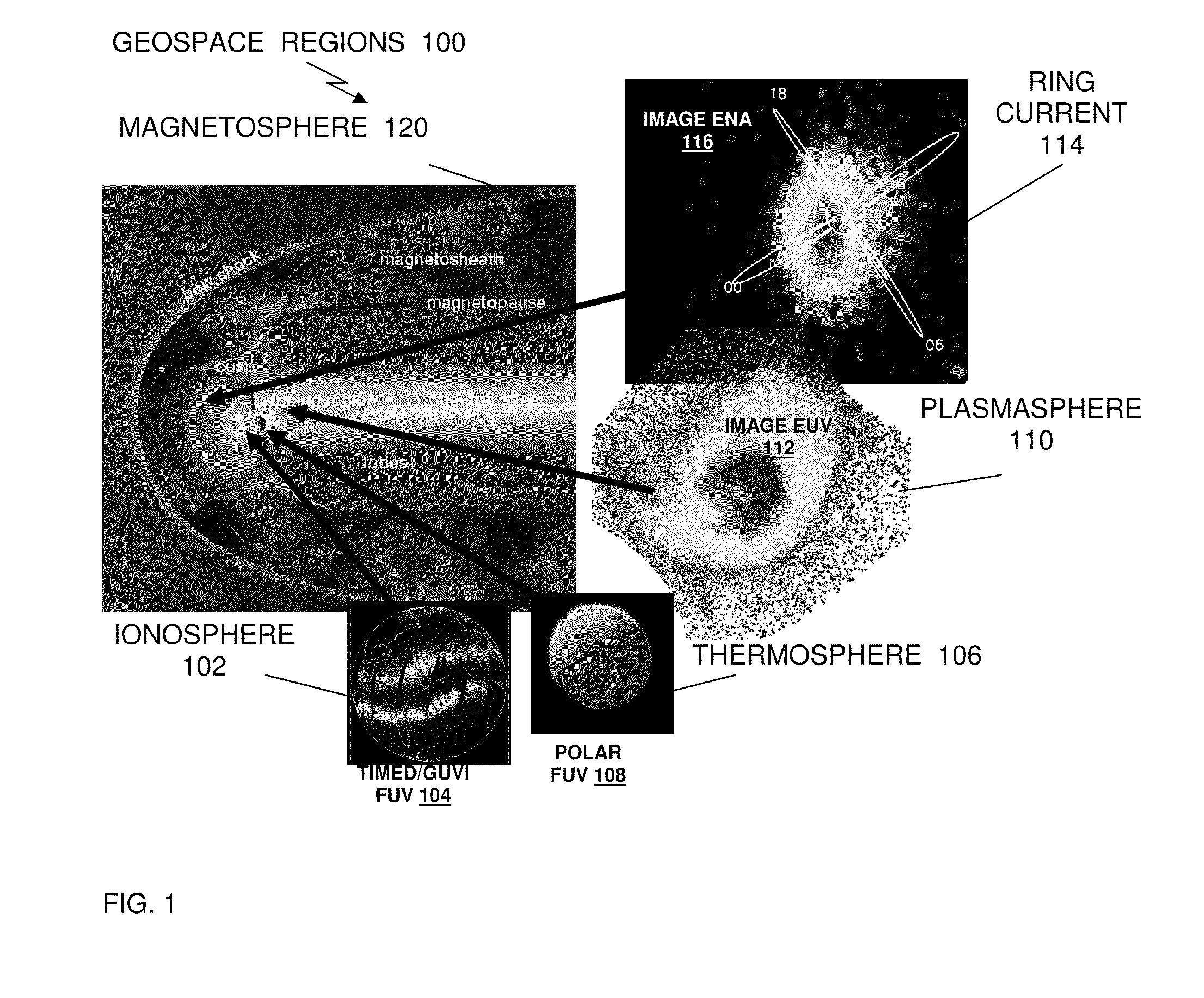
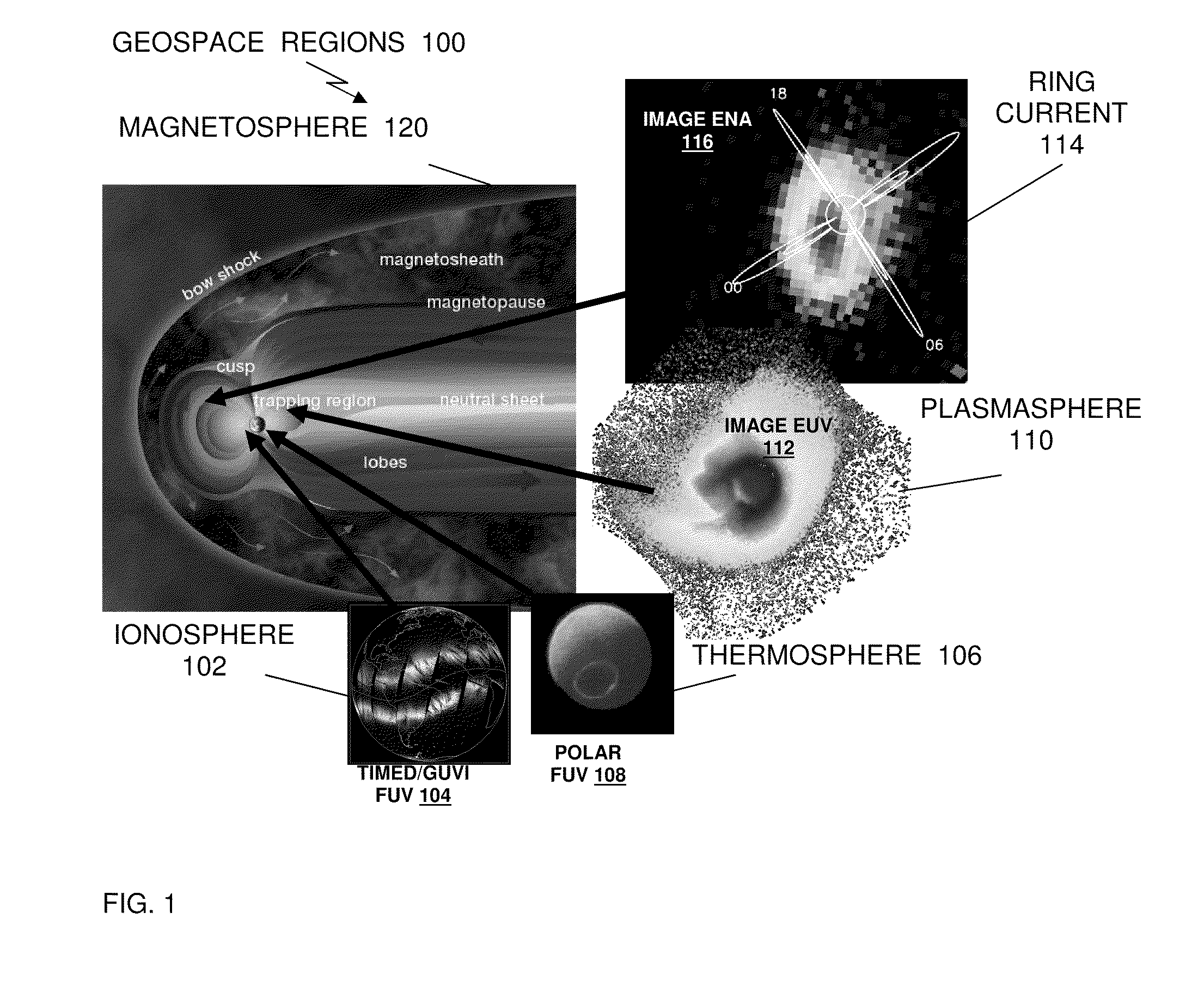
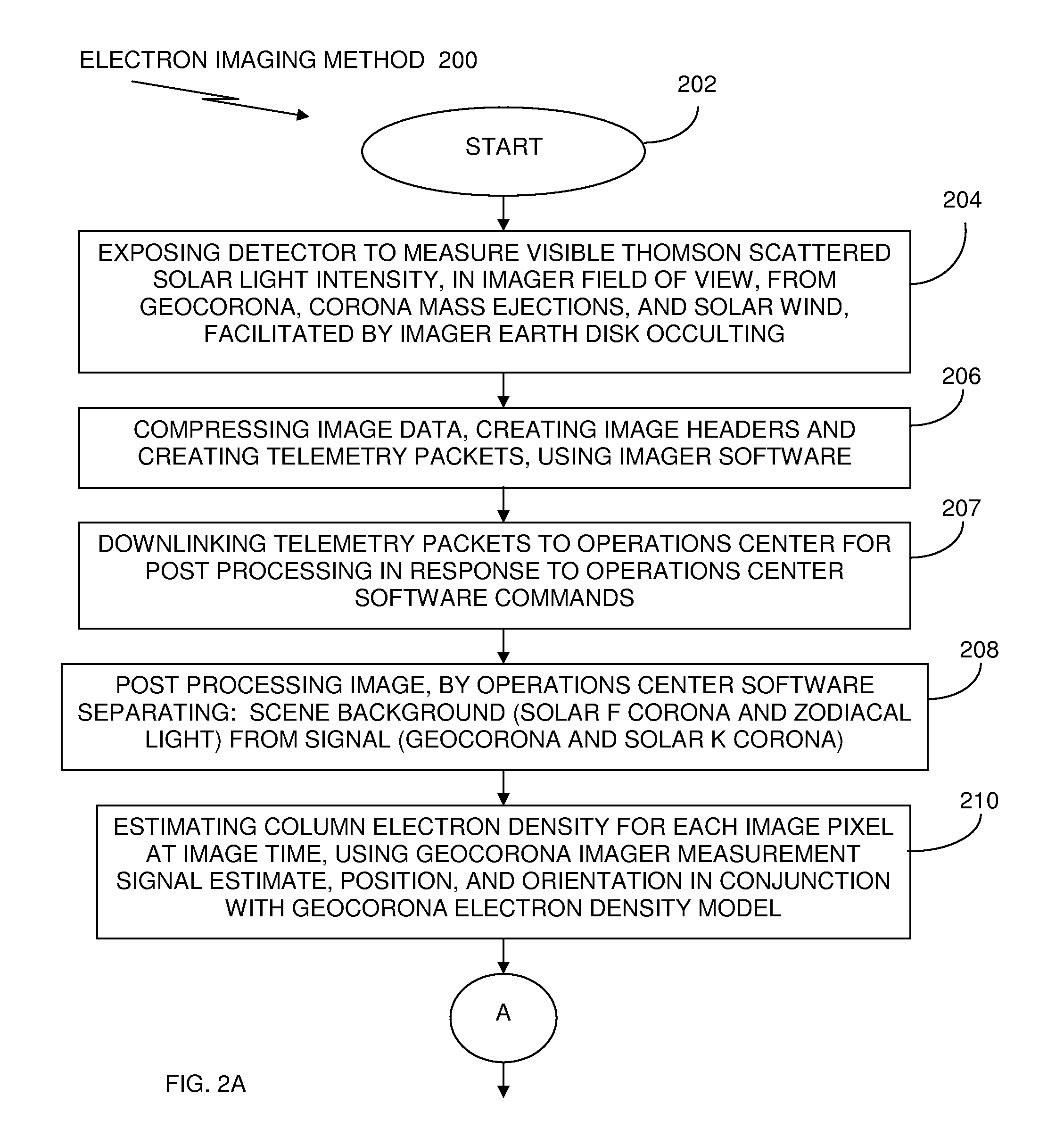
Method and system of imaging electrons in the near earth space environment
InactiveUS20100013645A1Electric/magnetic detectionSpecial data processing applicationsComputer scienceNear earth space
A method and system of globally monitoring space weather conditions, use an imager, including one or more telescopic instruments and one or more processors, containing computer program code. The imager is configured on a platform; and positioned in the near Earth space environment, where, based on the executed computer program code, the imager compiles information about space weather conditions, by directly detecting electron emissions on a global basis. Network interfaces coupled with the imager provide, over a communications network, a plurality of communications and information, about space weather conditions, between the imager and a plurality of operational space assets and operational Earth assets. The plurality of communications and information about space weather conditions includes signals and information which automatically alert the plurality of operational space assets and operational Earth assets of effects of a solar wind.
Owner:GOVT OF USA REPRESENTED BY SEC OF THE NAVY CHIEF NAVAL RES ONR NRL CODE OOCCIP
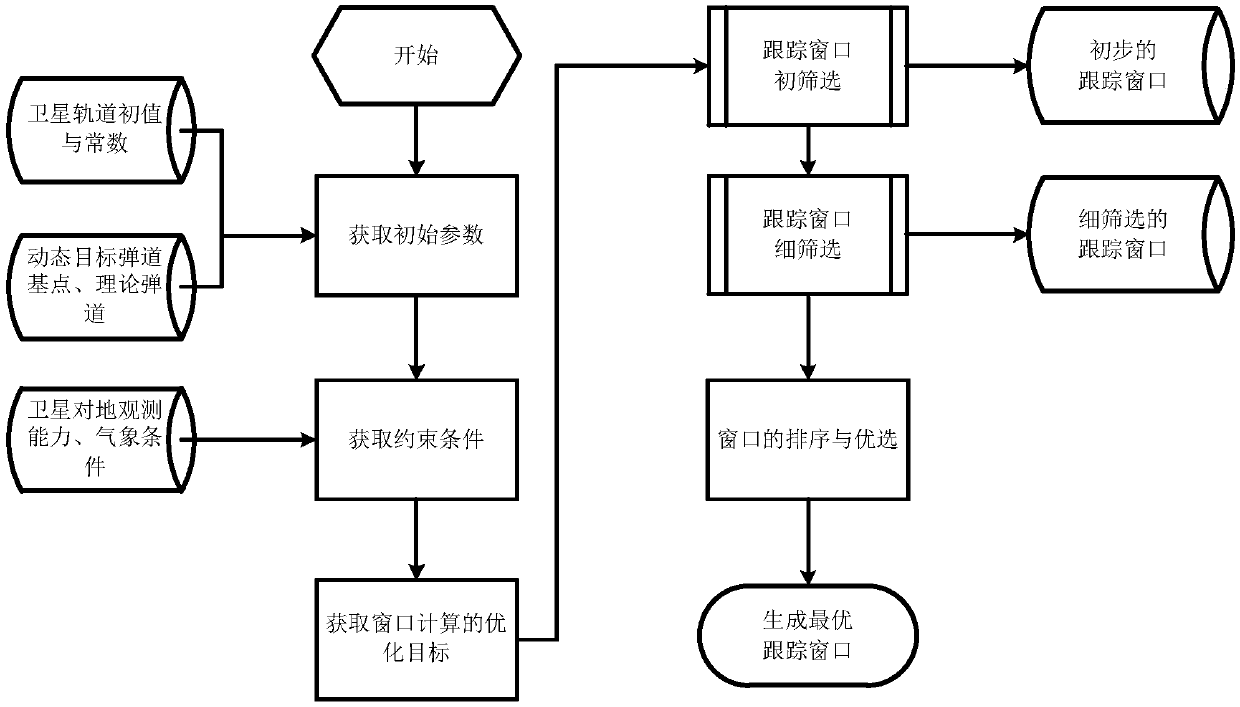
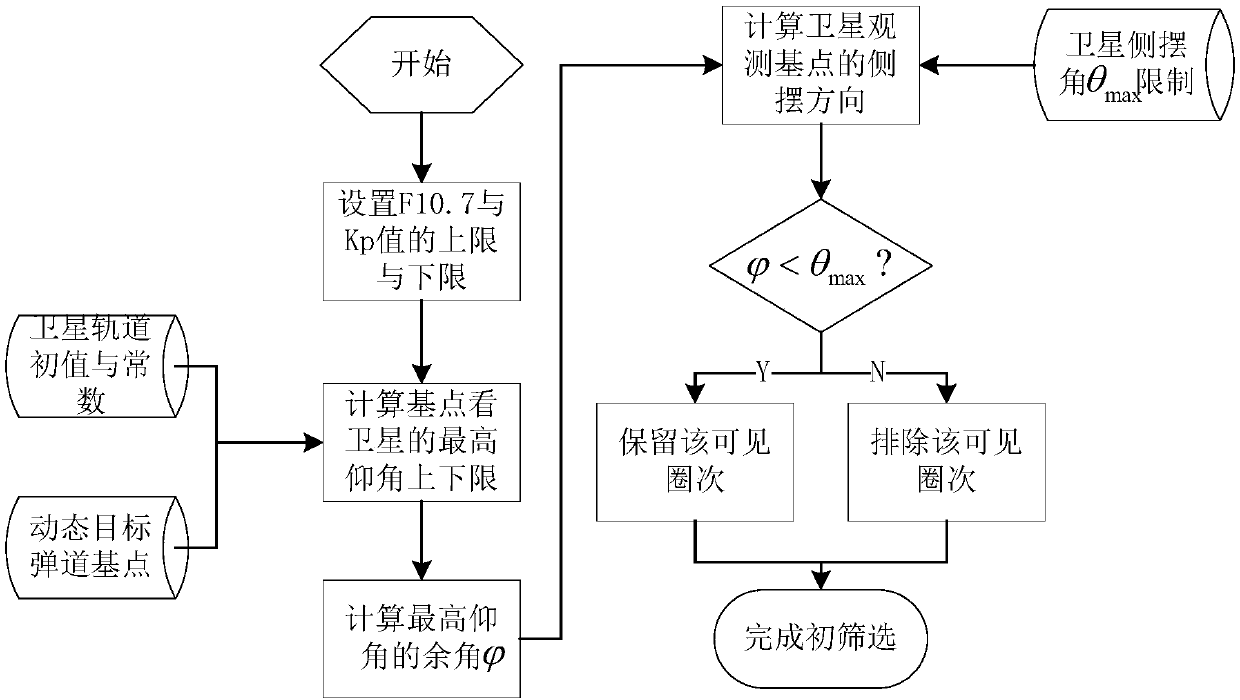
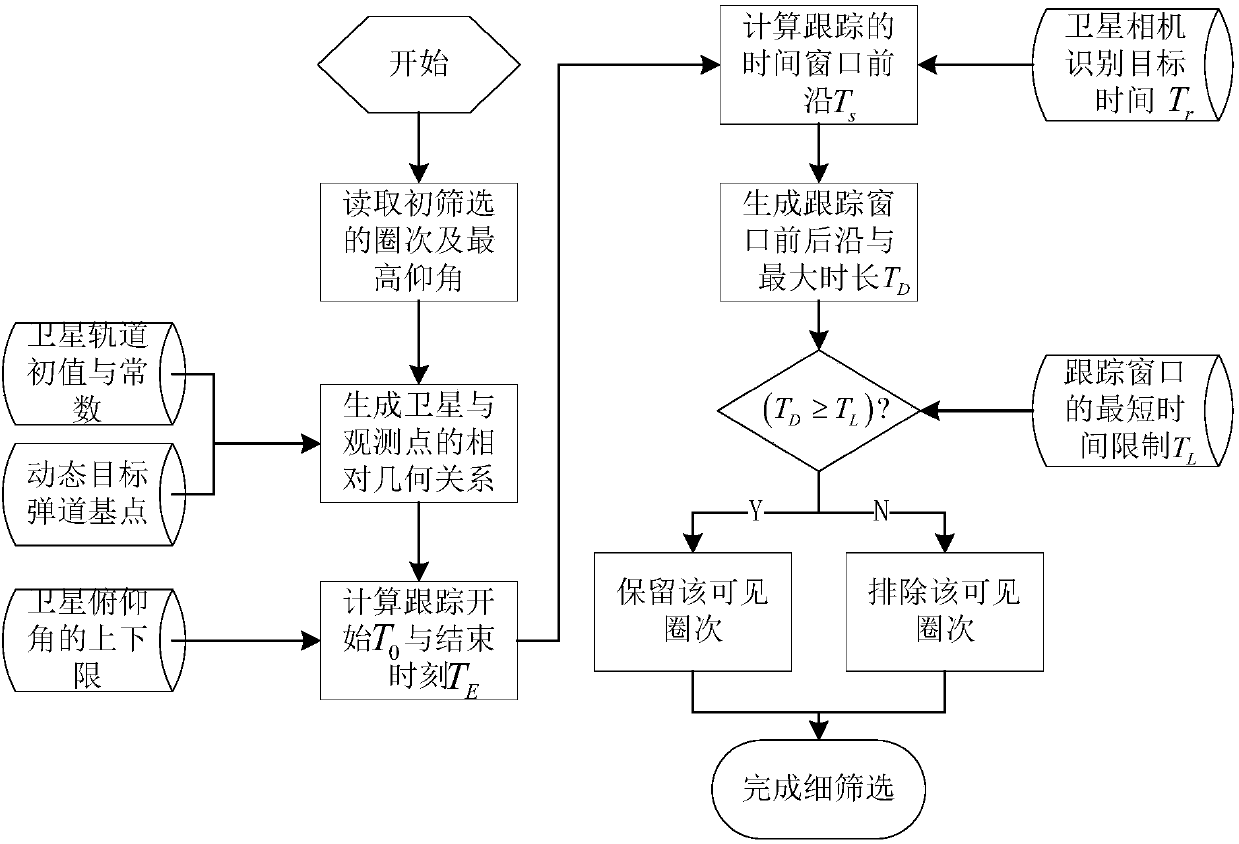
Window calculation method for low-orbit satellite tracking non-orbiting highly dynamic target
InactiveCN107831521ASolve the changeable windowSolve difficultyNavigation by astronomical meansSatellite radio beaconingGeometric relationsSatellite tracking
The invention provides a window calculation method for a low-orbit satellite tracking a non-orbiting highly dynamic target. Known conditions, constrained conditions and a calculation optimization target of a satellite tracking window are made clear; primary screening and fine screening are carried out; the window of the low-orbit satellite that tracks the highly dynamic target is calculated and optimized by taking a satellite orbit, a movement track of the highly dynamic target, the relative geometric relation between the satellite and the target, satellite visibility condition of a ground measurement and control station, space weather condition, and interference of the sun and moon on a satellite star sensor into consideration comprehensively; problems that the window of the satellite ischangeable and hard to determine are solved; and calculation is simple and the engineering availability is high.
Owner:CHINA XIAN SATELLITE CONTROL CENT
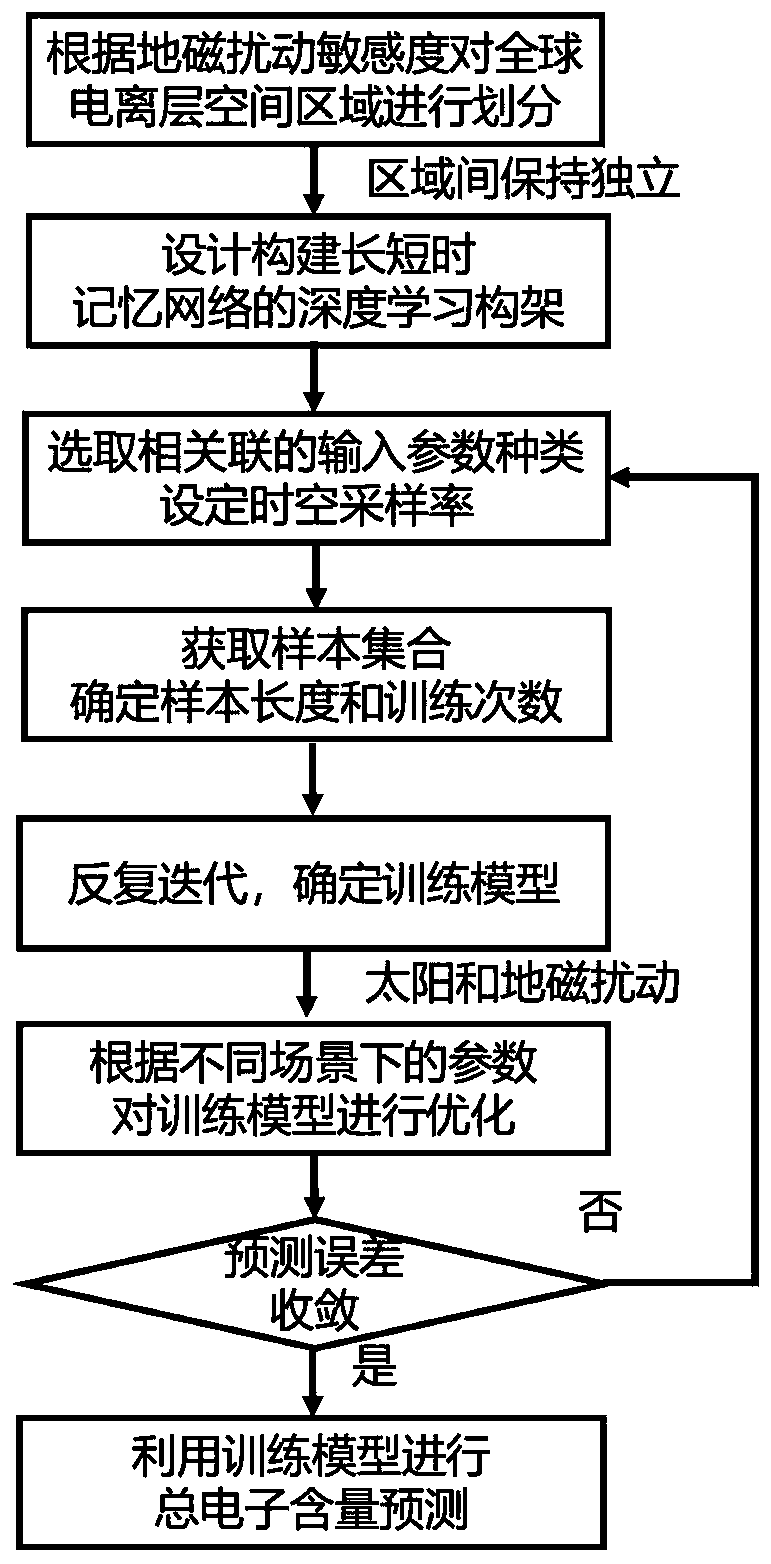
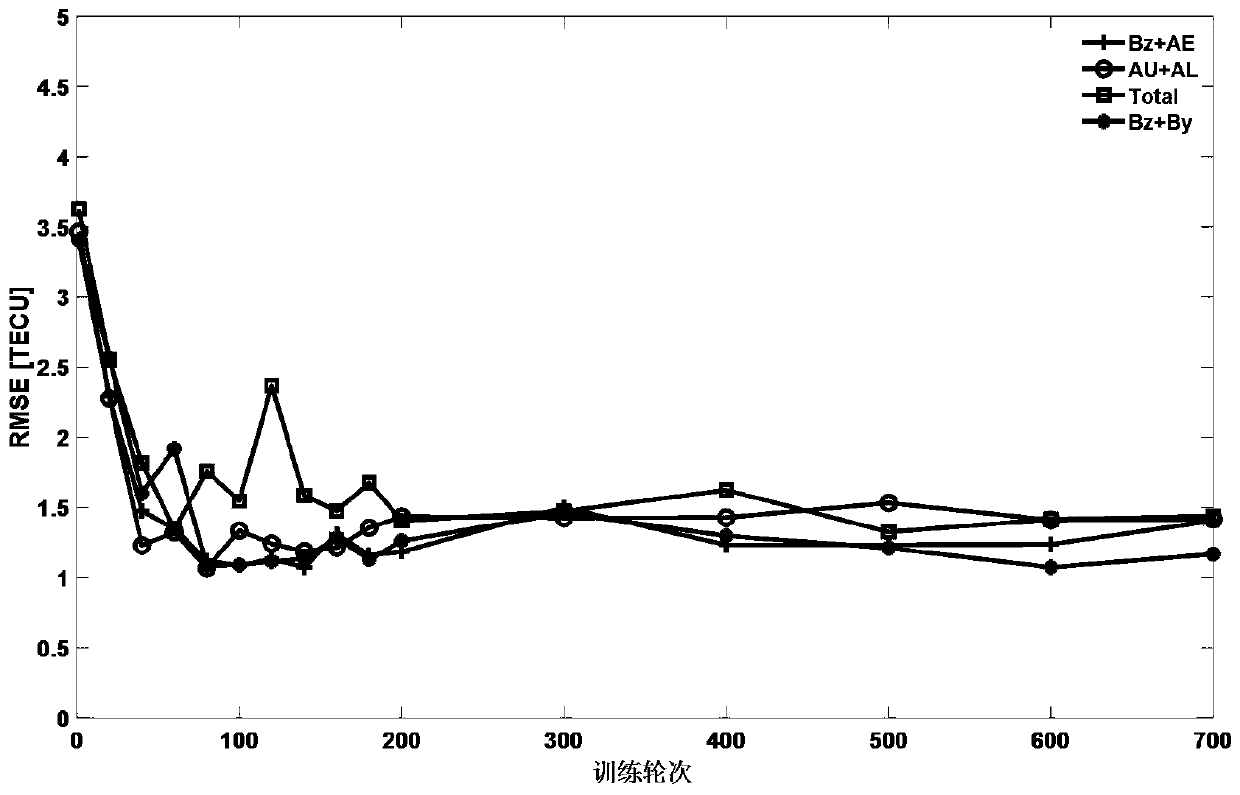
Total electron content prediction method for global ionosphere based on deep learning framework
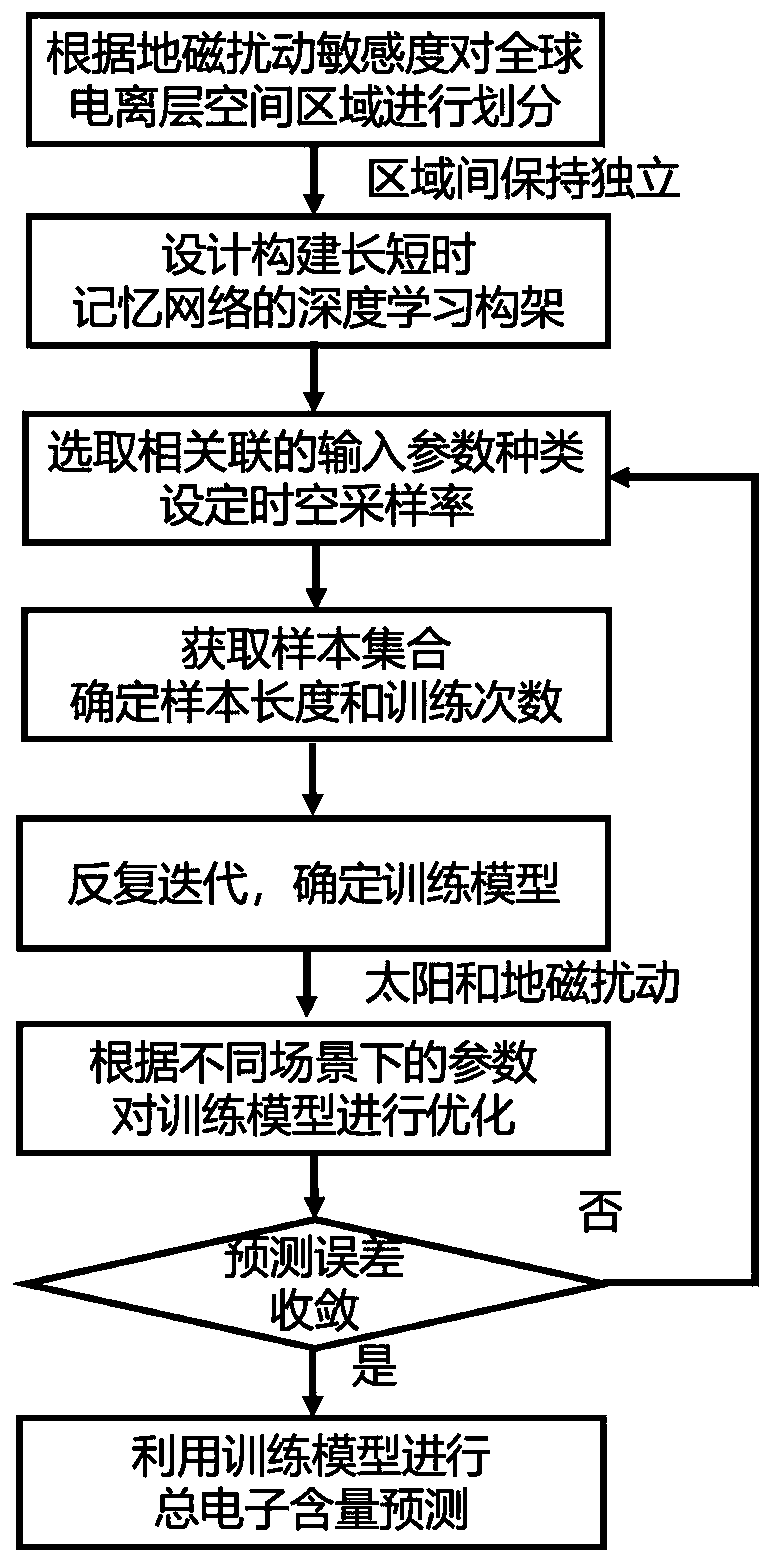
PendingCN111160646AHigh total electron content prediction accuracyEfficient extraction and utilization of associationsForecastingNeural architecturesSolar ActivitiesIonospheric total electron content
The invention relates to a total electron content prediction method for a global ionosphere based on a deep learning framework. The method comprises the steps: performing grid partitioning on a globaltotal electron content according to different response characteristics during geomagnetic disturbance, and on the basis, constructing a deep learning prediction model through an LSTM framework; setting the training sample length and the training frequency according to the periodic change characteristics of the global total electron content, and acquiring a pre-training model; analyzing the lengthof the training sample and the number of training times in combination with different sun activity and geomagnetic activity environments to obtain an optimal training model; finally, predicting the total electron content of the future global ionized layer by utilizing the training model, so a prediction error is within an expected range. The method can effectively predict the total electron content of the ionized layer in different regions of the world, so as to predict the total electron content of the global ionosphere, and provide better technical support for related applications such as space weather prediction and satellite navigation ionized layer error correction.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Satellite-borne very low frequency solar radio observation system
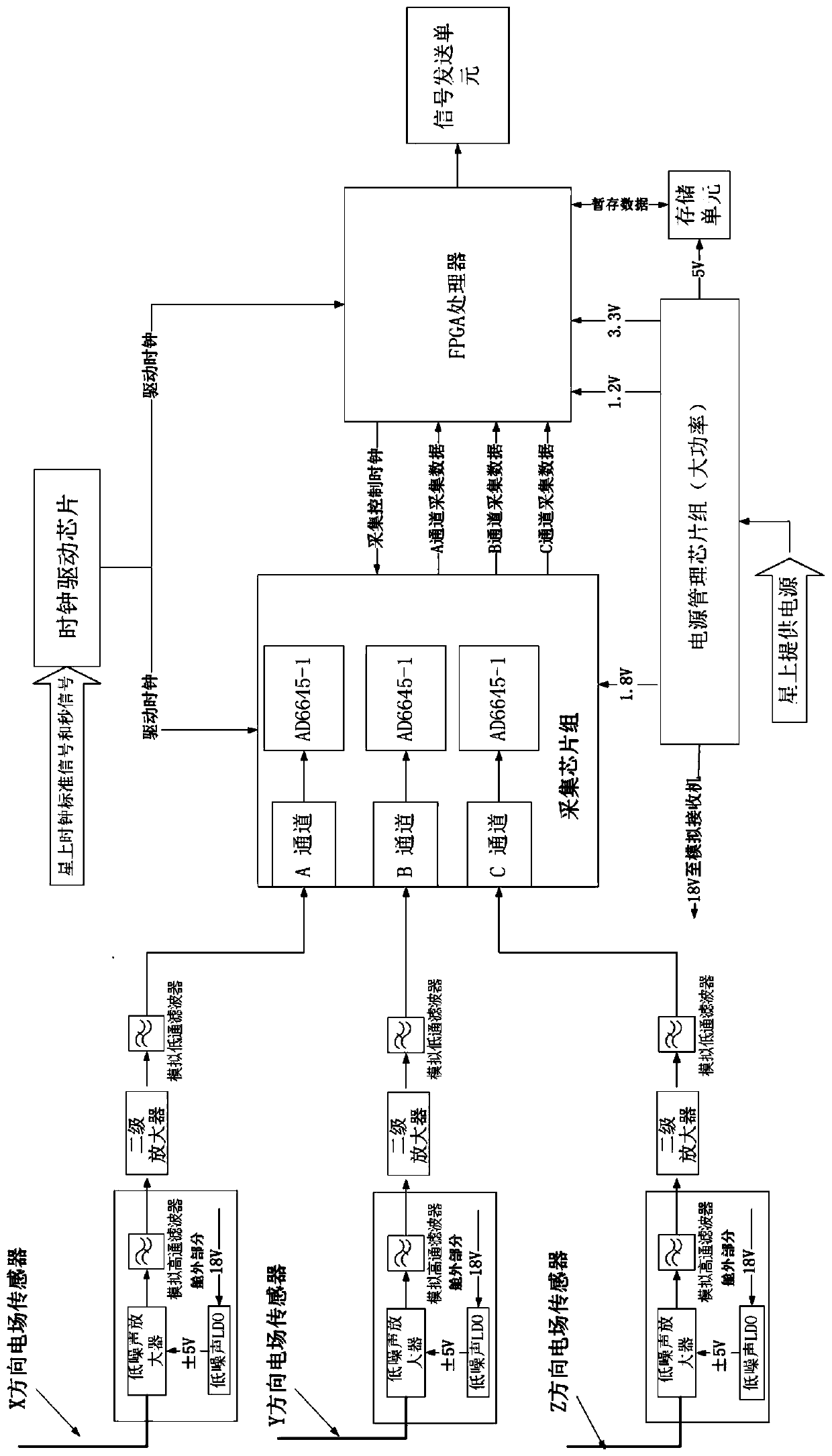
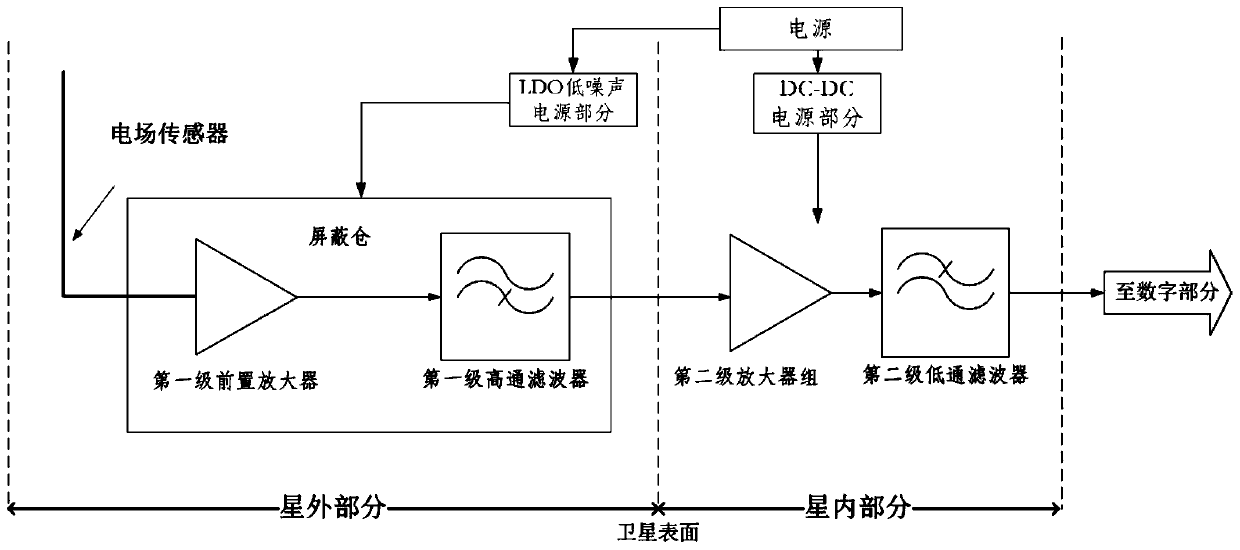
PendingCN109856464AReduce the impactReduce the effects of electromagnetic interferenceInstrument screening arrangementsElectrical testingElectric field sensorData acquisition
The invention discloses a satellite-borne very low frequency solar radio observation system. The system is used for observing a low frequency solar radio signal of 20-100 MHz. The system comprises three electric field sensors, three sets of analog receivers, a data acquisition and processing module,a time frequency module, a power module and a storage module, wherein the three electric field sensors are respectively connected with the three sets of analog receivers; the three sets of analog receivers and the time frequency module are respectively connected with the data acquisition and processing module; the data acquisition and processing module is connected with the storage module; and the data acquisition and processing module and the three sets of analog receivers are respectively connected with the power module. The system disclosed by the invention can judge the motion of coronal projectiles, predict and anticipate the future space weather event.
Owner:NAT SATELLITE METEOROLOGICAL CENT +1
Method for calculating geomagnetically induced current of grid in middle-low latitude region
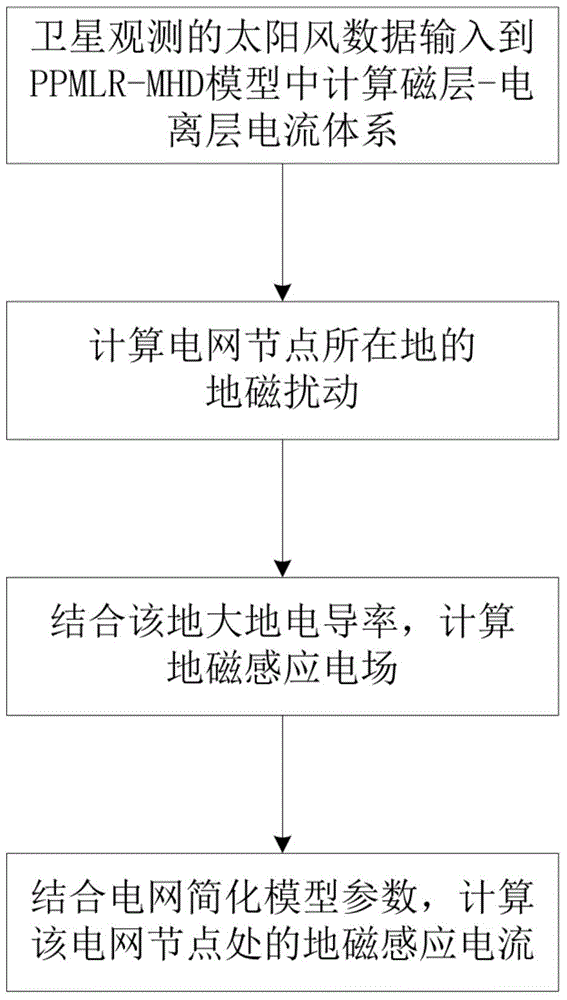
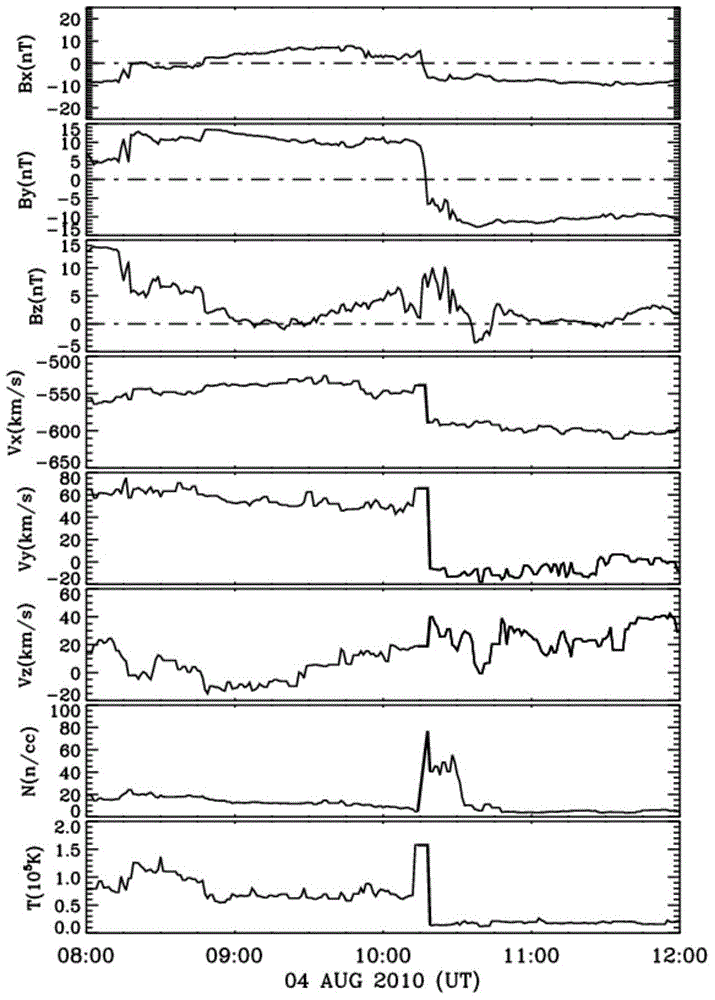
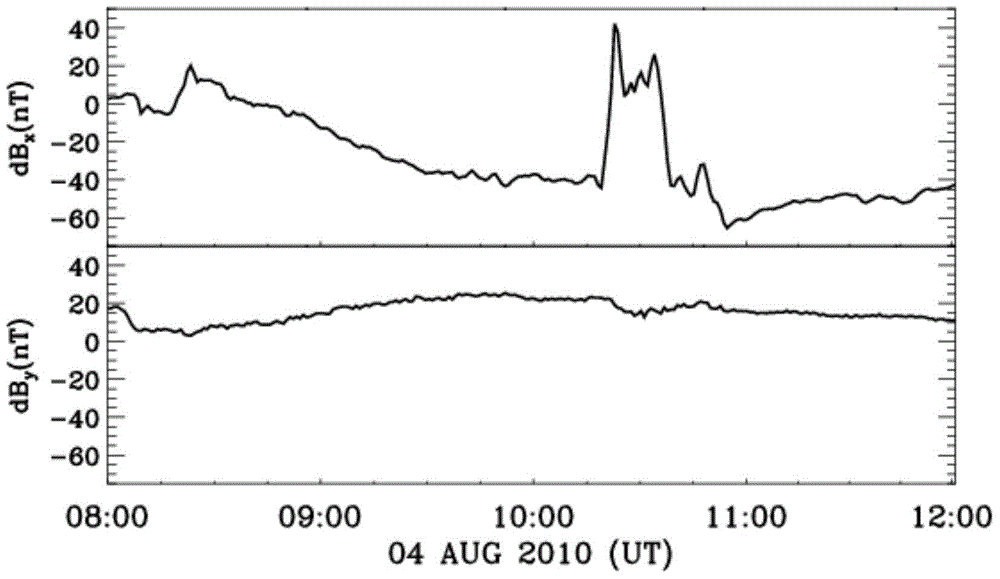
ActiveCN104635017AAvoid lostCurrent/voltage measurementSpecial data processing applicationsPredictive methodsMagnetohydrodynamics
The invention discloses a method for calculating geomagnetically induced current (GIC) of a grid in a middle-low latitude region. According to the method, on the basis of a global three-dimensional magnetosphere numerical model (a PPMLR-MHD (Lagrangian version of Piecewise Parabolic Method-Magnetohydrodynamic) model), solar wind parameters observed by a satellite serve as input conditions, geomagnetic disturbance generated by current is calculated by performing integration on a magnetic layer and an ionized layer current system, the geomagnetically induced current in the ground grid is calculated, the problem that the transitional predicting method is not suitable for calculating the GIC in the middle-low latitude region is solved, and the GIC of the grid in the middle-low latitude region calculated by the method can reflect the basic characteristic of the induced current which is actually monitored and is calculated by geomagnetic disturbance. By the method, people can timely calculate the GIC of the grid in the middle-low latitude region according to the solar wind parameters observed by an upstream satellite, whether the grid is invaded by a disastrous space weather event or not is estimated, and an active prevention measure is taken to prevent serious economic and social loss.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
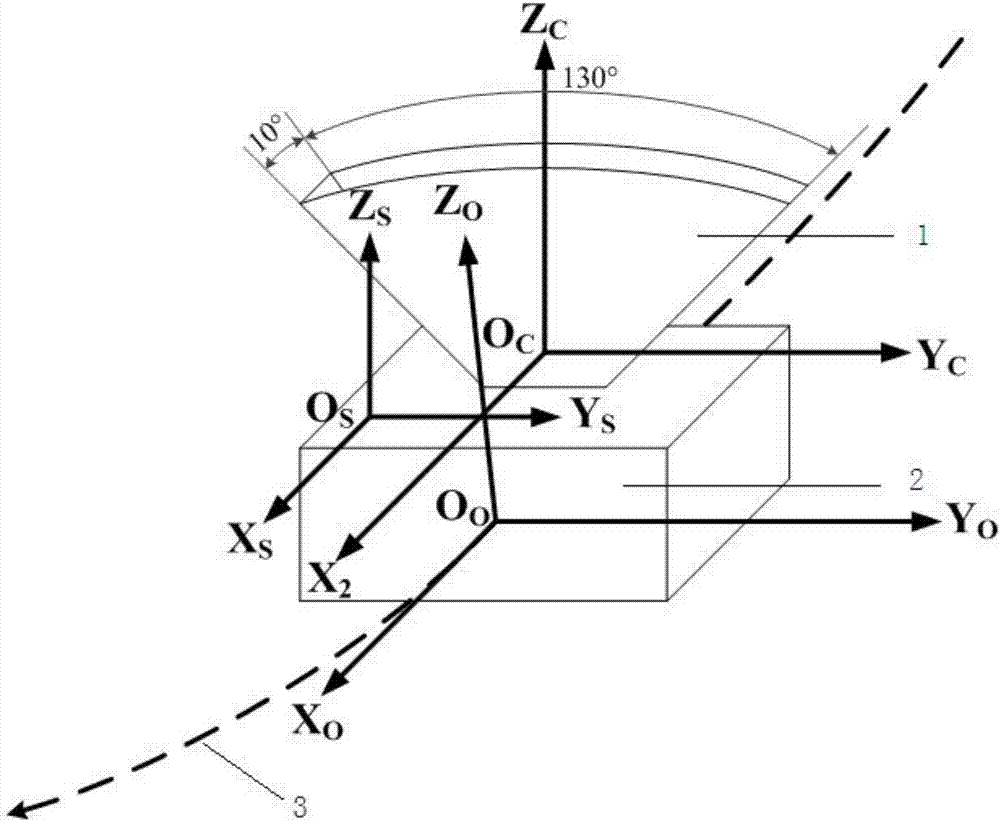
Automatic sunshine avoiding method for space to ground observation apparatus
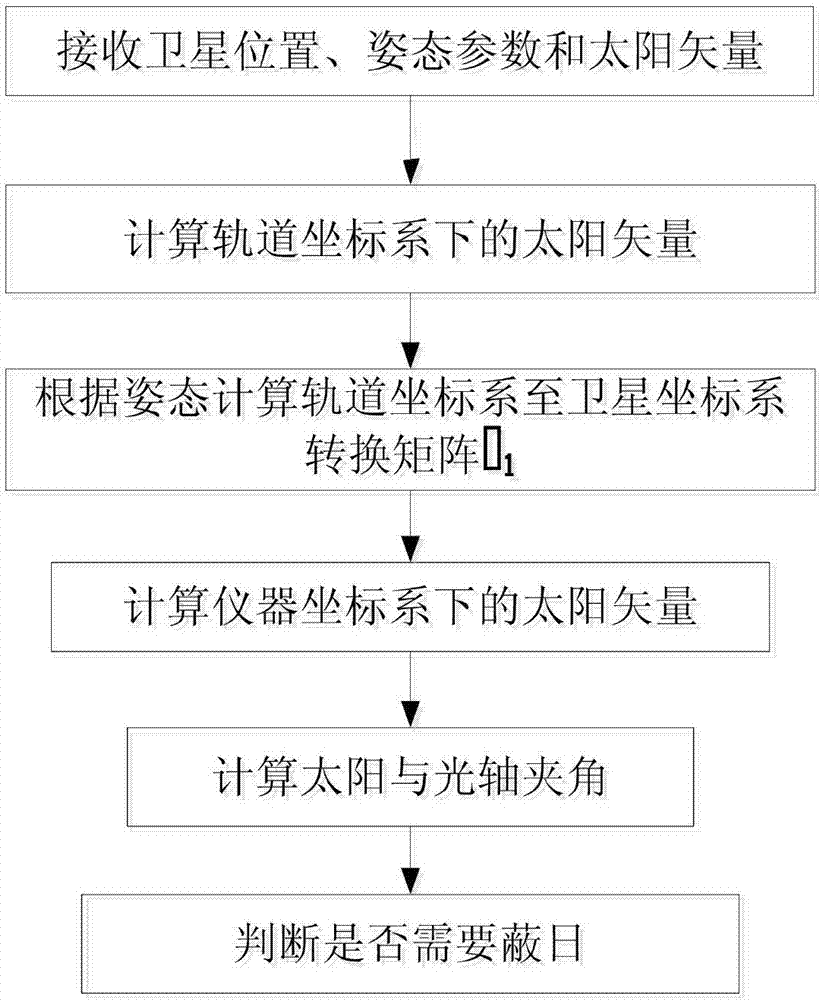
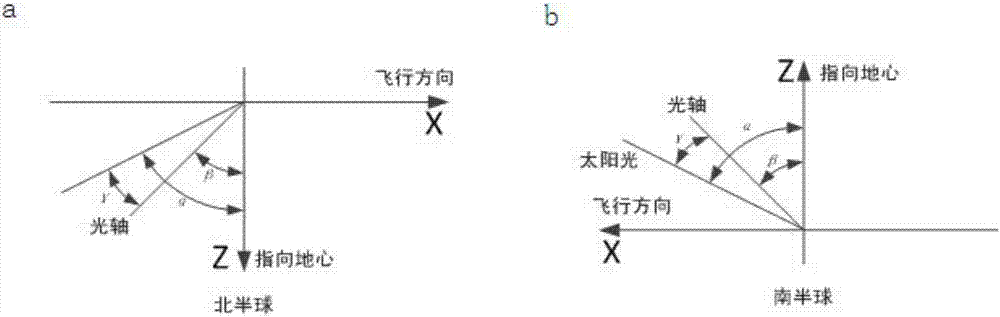
ActiveCN106896818ASolve the problem of automatic avoidanceImprove securityCosmonautic vehiclesNavigational calculation instrumentsOptical axisOrbit
The invention relates to an automatic sunshine avoiding method for a space to ground observation apparatus, belongs to the space weather monitoring technology field and solves problems of complexity and poor timeliness existing in a ground intervention sunshine avoiding method in the prior art. The method comprises steps that a sun vector of a track coordinate system is converted to a sun vector S2 of an apparatus coordinate system through a conversion matrix T1 from the track coordinate system to a satellite coordinate system and a calibration conversion matrix T2 from the satellite coordinate system to the apparatus coordinate system, an included angle alpha=asin(s2x) of the sun vector S2 and a YcZc surface of the apparatus coordinate system is calculated, an included angle of the YcZc surface and an apparatus optical axis is made to be beta, an included angle of sunlight and the apparatus optical axis on an XcZc surface is gamma=alpha-beta(south pole) or gamma=beta-alpha(north pole), according to sunshine avoiding determination conditions, whether sunshine avoiding is needed is determined, if yes, an apparatus is controlled for rotation in an opposite direction, if not, the apparatus rotates in an original direction. The sunshine avoiding method is advantaged in that system safety is effectively improved, automatic in-orbit measurement is carried out, and the method further has properties of strong timeliness, low cost and easy realization.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
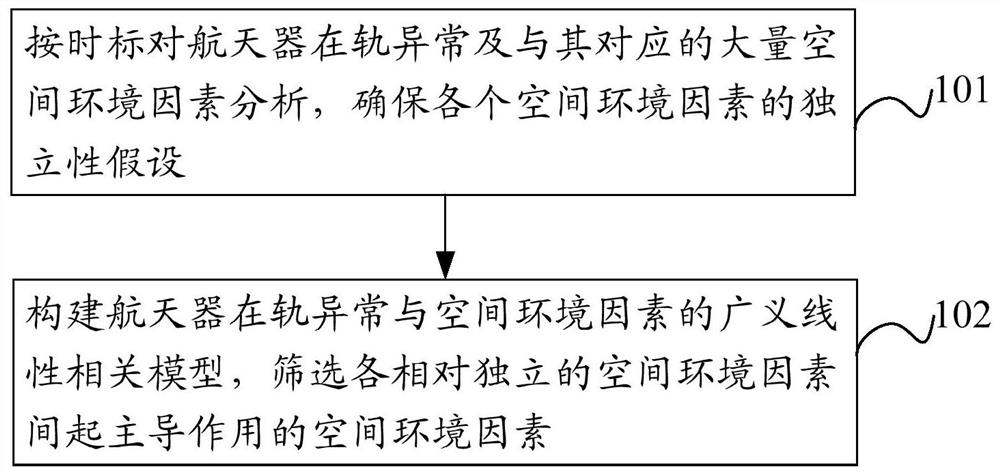
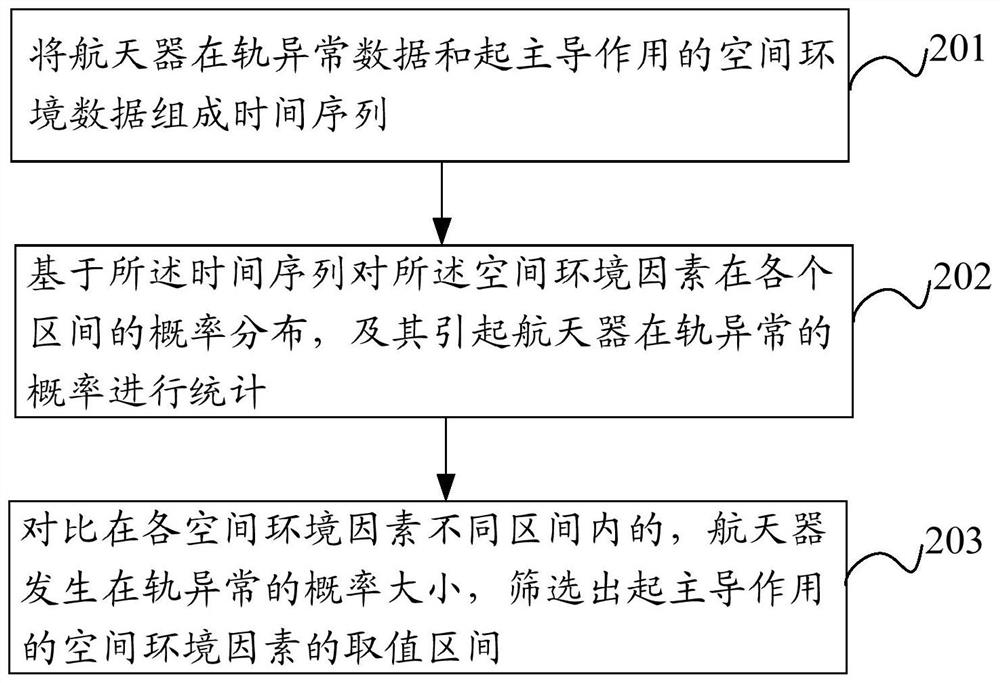
Spacecraft space environment abnormity and influence forecast method and system, storage medium, and server
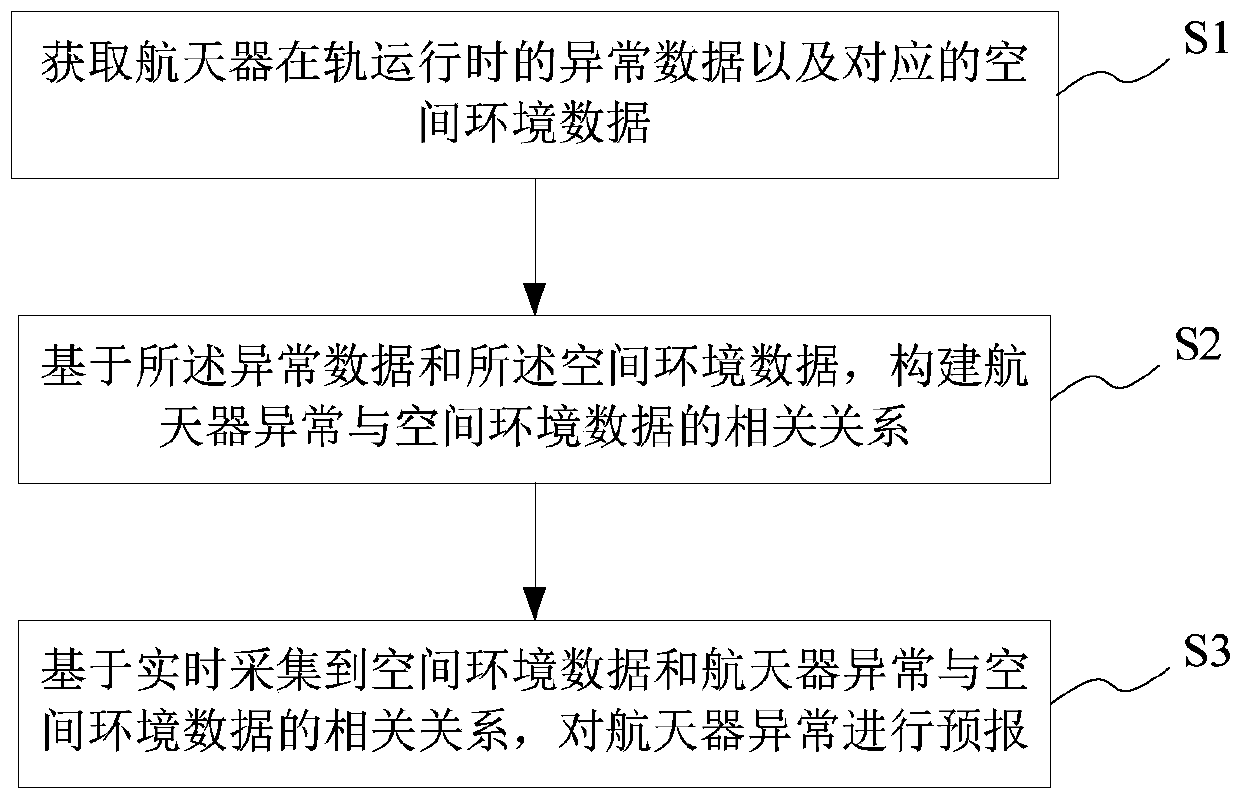
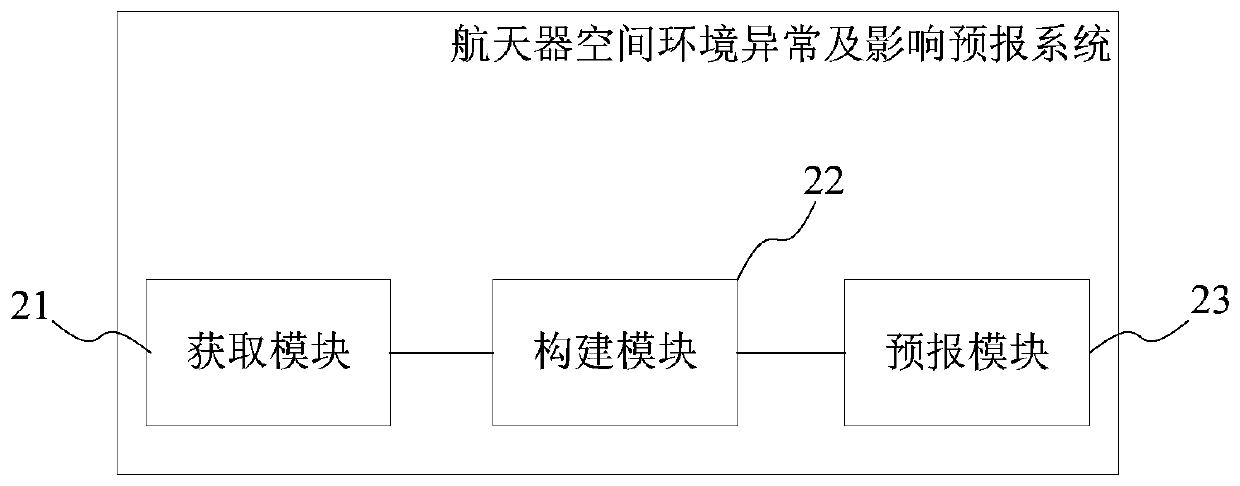
InactiveCN110017866APush for stabilityDrive reliabilityMeasurement devicesStructured data retrievalSpace environmentOrbit
The invention provides a spacecraft space environment abnormity and influence forecast method and system, a storage medium, and a server. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring abnormitydata of a spacecraft in in-orbit running and the corresponding space environment data; constructing correlativity of the spacecraft abnormity and space environment data based on the abnormity data andthe space environment data; and forecasting the spacecraft abnormity based on the real-time collected space environment data and the correlativity of the spacecraft abnormity and the space environment data. Through the spacecraft space environment abnormity and influence forecast method and system and the storage medium provided by the invention, the correlativity of the spacecraft in-orbit abnormity and the space environment is acquired through various abnormity data of the in-orbit spacecraft, thereby realizing the spacecraft abnormity and influence early-warning based on the space environment, and laying foundation for the space weather guarantee service of the spacecraft in the in-orbit running period.
Owner:NAT SATELLITE METEOROLOGICAL CENT +1
Full solar disk sun imager adopting two-channel atomic light filtering technology
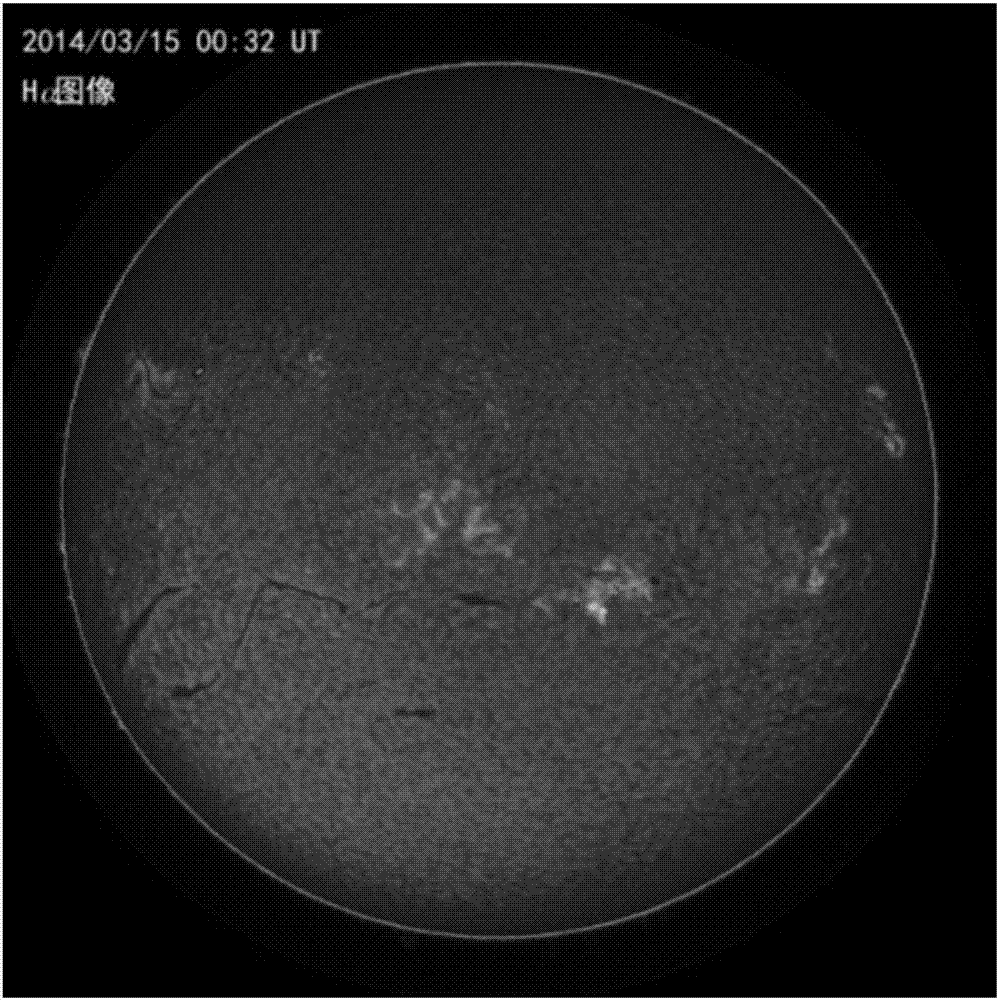
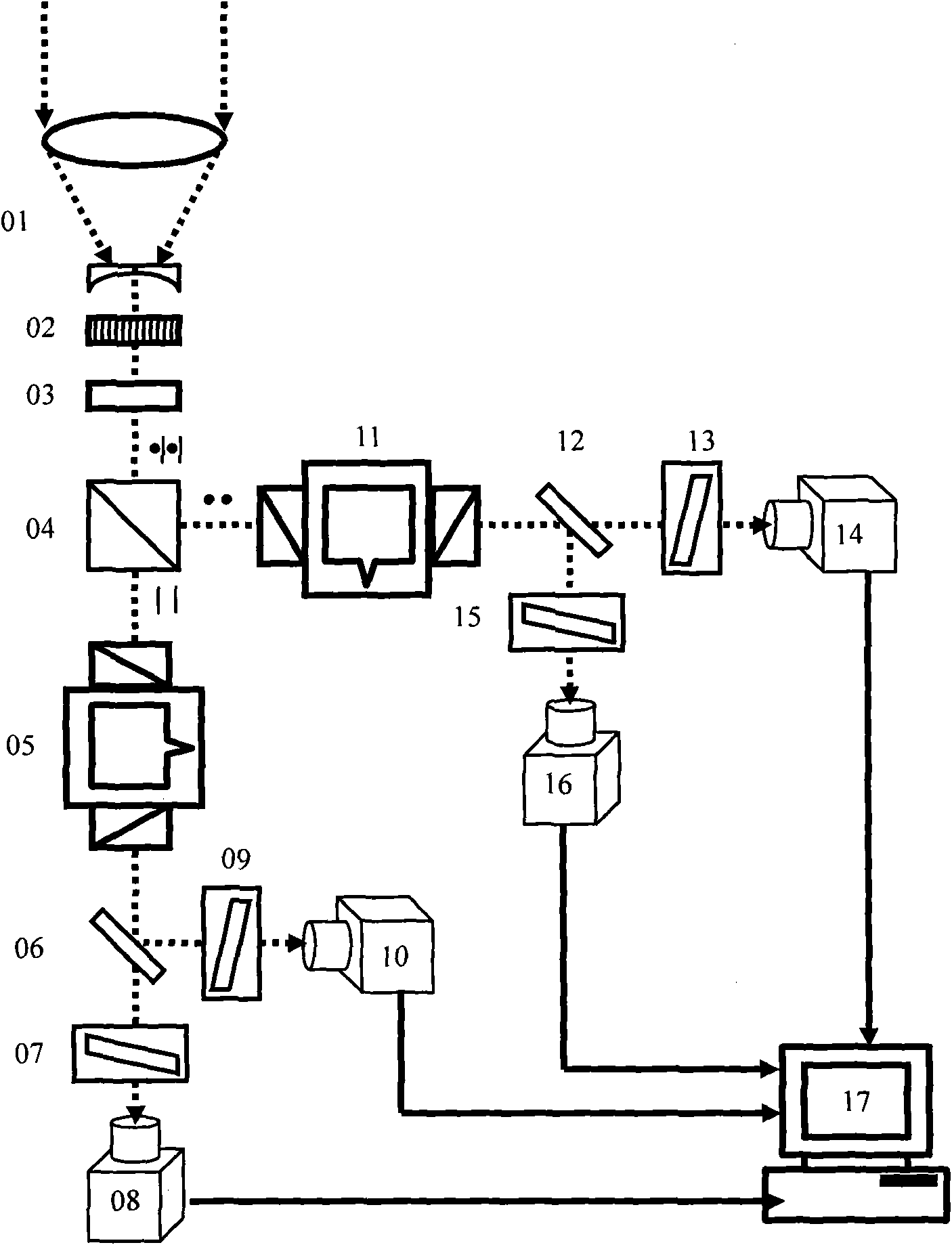
ActiveCN101620007AHigh precisionStandard is simple and convenientSpectrum investigationWeather condition predictionTelescopeSolar observation
The invention discloses a full solar disk sun imager adopting two-channel atomic light filtering technology, which comprises a telescope (01), a light filtering sheet (02), a lambda / 4 wave plate (03), a polarizing light splitter (4), an atomic light filter (05), an atomic light filter (11), a light splitter (06), a light splitter (12), an interferometer (07), an interferometer (09), an interferometer (13), an interferometer (15), a CCD (08), a CCD (10), a CCD (14), a CCD (16) and a computer (17). The polarizing light splitter, the atomic light filters, the four interferometers, the four CCDs and the like are fixedly connected without time sequence control, thus four high-resolution spectrum images of the sun can be obtained simultaneously, and the full solar disk brightness, the Doppler velocity and the magnetic field intensity can be obtained after treatment. The technical scheme has the characteristics of scientific scheme, stable and reliable system, convenient use and the like, improves the stability and the precision of measurement of the solar magnetic field, and provides a better detecting device for observing sun and monitoring and predicting space weather.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method and system of imaging electrons in the near earth space environment
InactiveUS8181511B2Special data processing applicationsElectric/magnetic detectionNear earth spaceComputer science
A method and system of globally monitoring space weather conditions, use an imager, including one or more telescopic instruments and one or more processors, containing computer program code. The imager is configured on a platform; and positioned in the near Earth space environment, where, based on the executed computer program code, the imager compiles information about space weather conditions, by directly detecting electron emissions on a global basis. Network interfaces coupled with the imager provide, over a communications network, a plurality of communications and information, about space weather conditions, between the imager and a plurality of operational space assets and operational Earth assets. The plurality of communications and information about space weather conditions includes signals and information which automatically alert the plurality of operational space assets and operational Earth assets of effects of a solar wind.
Owner:GOVT OF USA REPRESENTED BY SEC OF THE NAVY CHIEF NAVAL RES ONR NRL CODE OOCCIP
Earth plasmasphere dynamic tracking imager
InactiveCN103592807AImprove resolutionRealize multi-angle tracking imagingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPlasmasphereUltraviolet
The invention discloses an earth plasmasphere dynamic tracking imager, and belongs to the technical field of space weather monitoring. The earth plasmasphere dynamic tracking imager aims at solving the problem that in the prior art, earth plasmasphere overall-situation imaging can not be achieved, and comprises an optical system and a mechanical structure system, wherein the optical system comprises an annular optical entrance pupil, an image receiver and a spherical surface pole ultraviolet multi-film reflection mirror, and the optical imaging function of an earth plasmasphere at the 30.4nm wave band is mainly achieved. The mechanical structure system comprises an EUV camera imaging system and a two-dimensional rotary system, the EUV camera imaging system achieves the functions of installing, supporting and protecting the optical system and the like, and the two-dimensional rotary system achieves orientation and pitching adjustment on view angles of the EUV camera imaging system. After the earth plasmasphere dynamic tracking imager reaches an imaging track along with a spacecraft, image motion compensation to satellite motion and dynamic tracking imaging on an object during imaging are achieved through the two-dimensional rotary system, and multi-angle and high-quality overall-situation imaging on the object is achieved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
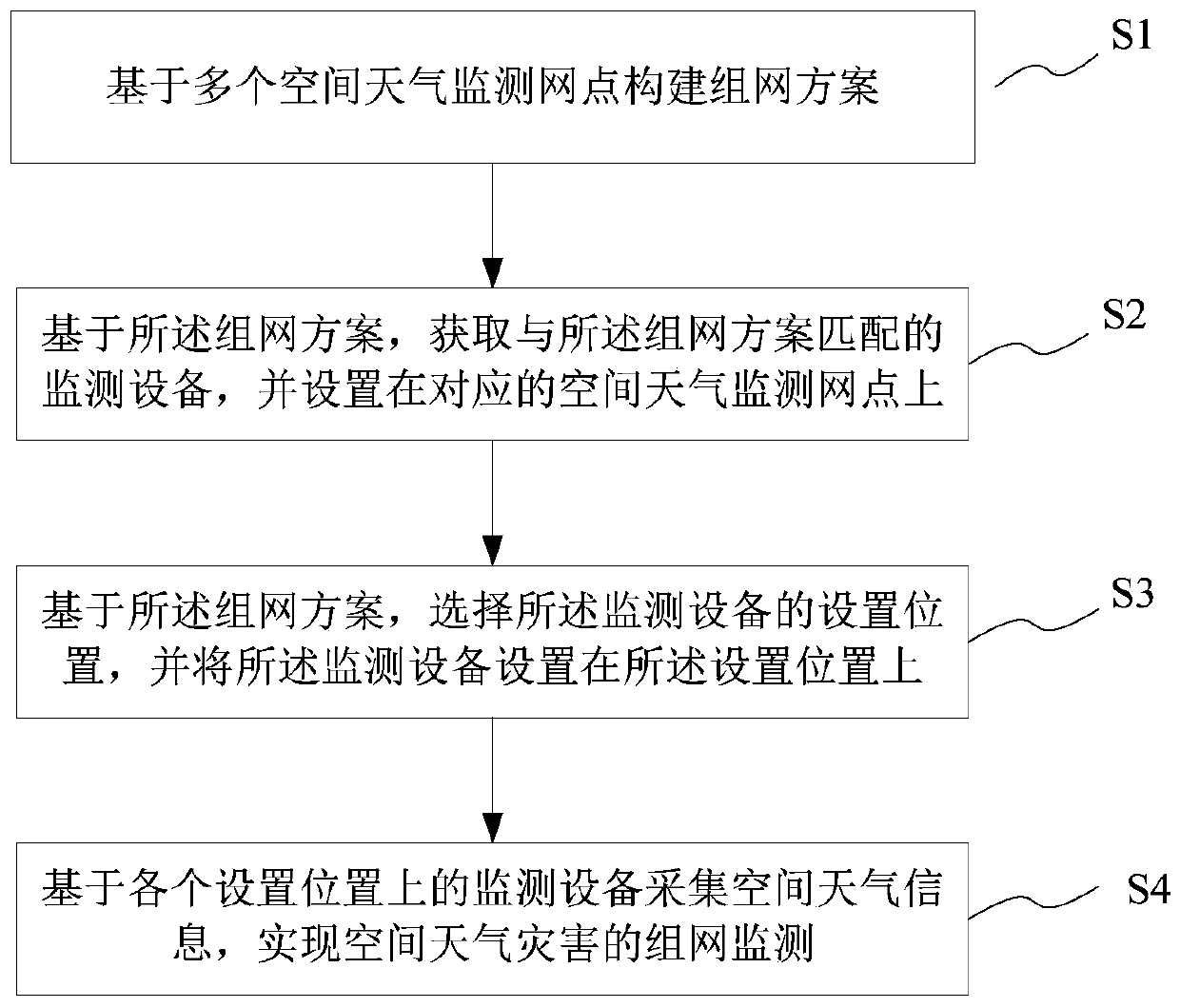
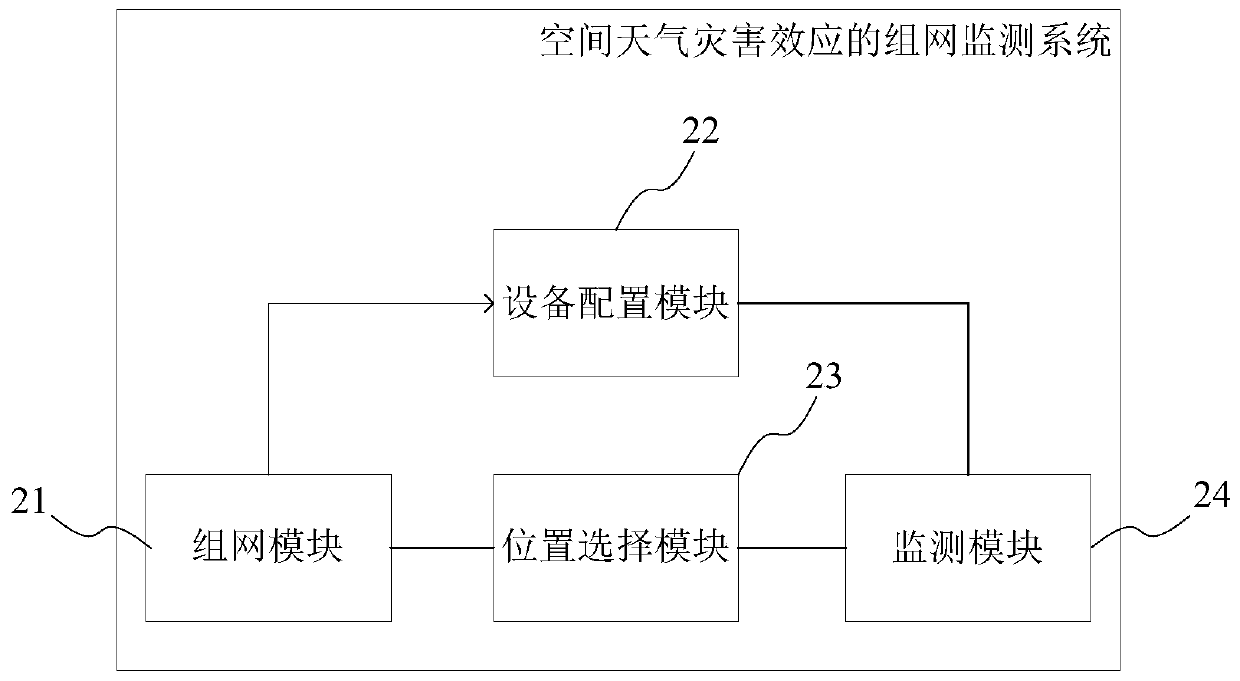
Networking monitoring method and system for space weather disaster effect
PendingCN109738968AEasy to monitorImprove early warning technology capabilitiesRadiation intensity measurementICT adaptationLow latitudePower grid
The invention provides a networking monitoring method and system for a space weather disaster effect. The method comprises the following steps that: on the basis of a plurality of space weather monitoring networks, constructing a networking scheme; on the basis of the networking scheme, obtaining monitoring equipment matched with the networking scheme, and arranging on the corresponding space weather monitoring network; on the basis of the networking scheme, selecting a monitoring equipment arrangement position, and arranging the monitoring equipment on the arrangement position; and on the basis of the monitoring equipment on each arrangement position, collecting space weather information, and realizing the networking monitoring of the space weather disaster. By use of the networking monitoring method and system for the space weather disaster effect, a plurality of space weather disaster effects are subjected to quasi real-time networking monitoring, and the quasi real-time monitoringwhich aims at various main space weather disaster effects, including short-wave communication, satellite-ground links, low-latitude region power grid geomagnetic induction current and the like, can berealized.
Owner:NAT SATELLITE METEOROLOGICAL CENT
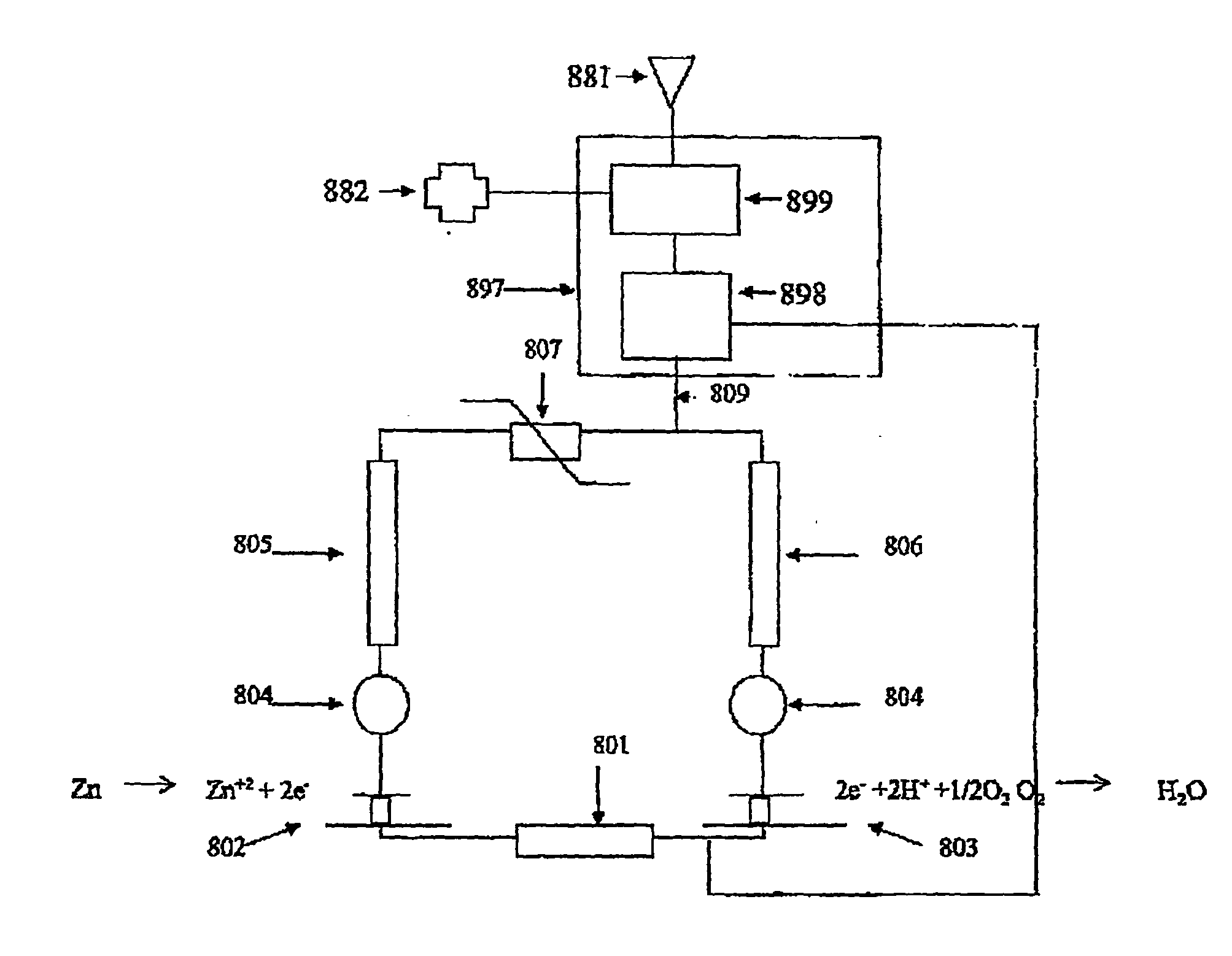
Control apparatus, system, and method for reduction and/or prevention of space weather induced corrosion
InactiveUS20100025261A1Minimize corrosive noiseReduce corrosionCellsWeather/light/corrosion resistanceConductive coatingControl electronics
An apparatus, system, method and computer program product directed to controlling corrosion, particularly space weather induced corrosion, of a conductive structure in contact with a corrosive environment and coated with a semiconductive coating, where the corrosion is controlled by a controllable filter and a corresponding electronic control unit configured to process and adjust the controllable filter in response to at least one measured parameter associated with space weather effects on the conductive structure.
Owner:APPLIED SEMICON INT
Space weather disaster monitoring and early warning method and system, storage medium and server
The invention provides a space weather disaster monitoring and early warning method and system, a storage medium and a server. The method comprises: collecting spatial weather monitoring data; carrying out preprocessing, including data extraction and format conversion of data in different formats, on the collected data; storing the data after preprocessing; according to a preset evaluation specification, evaluating the stored data; and carrying out early warning on a space weather disaster based on an evaluation result. According to the invention, various space weather disaster monitoring technologies such as communication and power are integrated to form a space weather disaster monitoring and early warning demonstration system embedded directly with a service system, so that the system serves as an important composition of the existing space weather service system.
Owner:NAT SATELLITE METEOROLOGICAL CENT
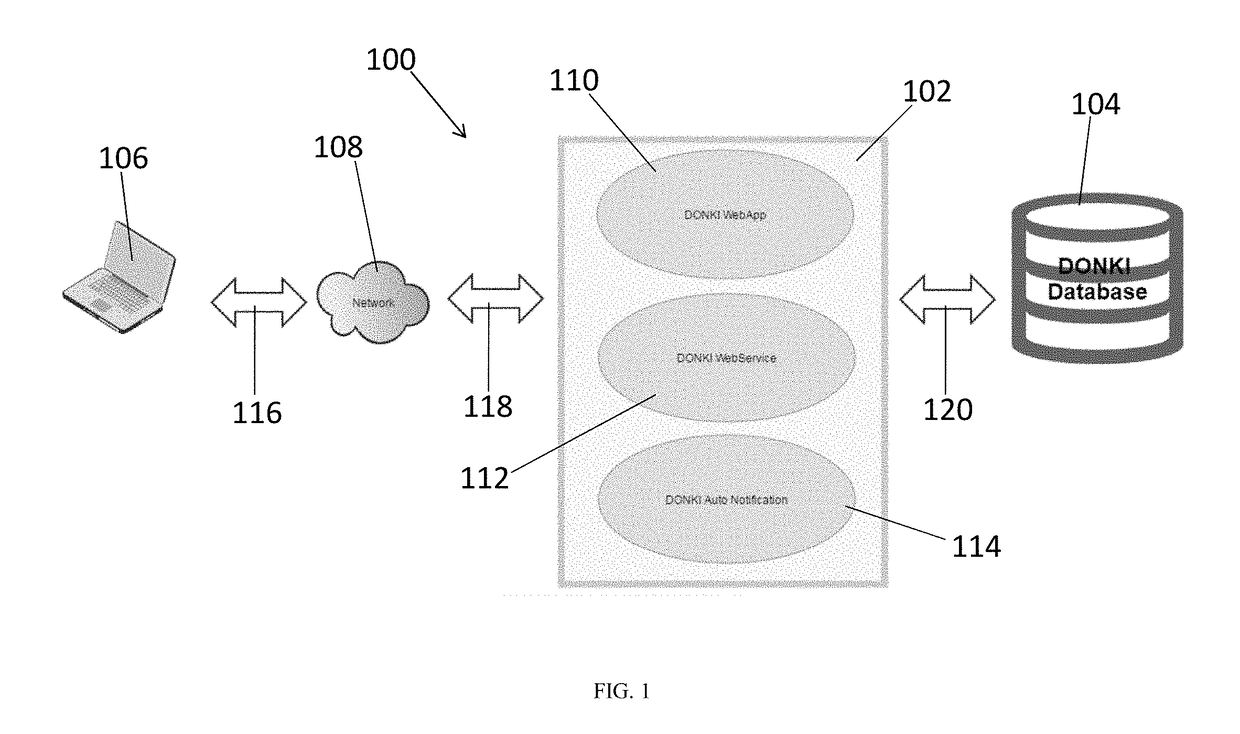
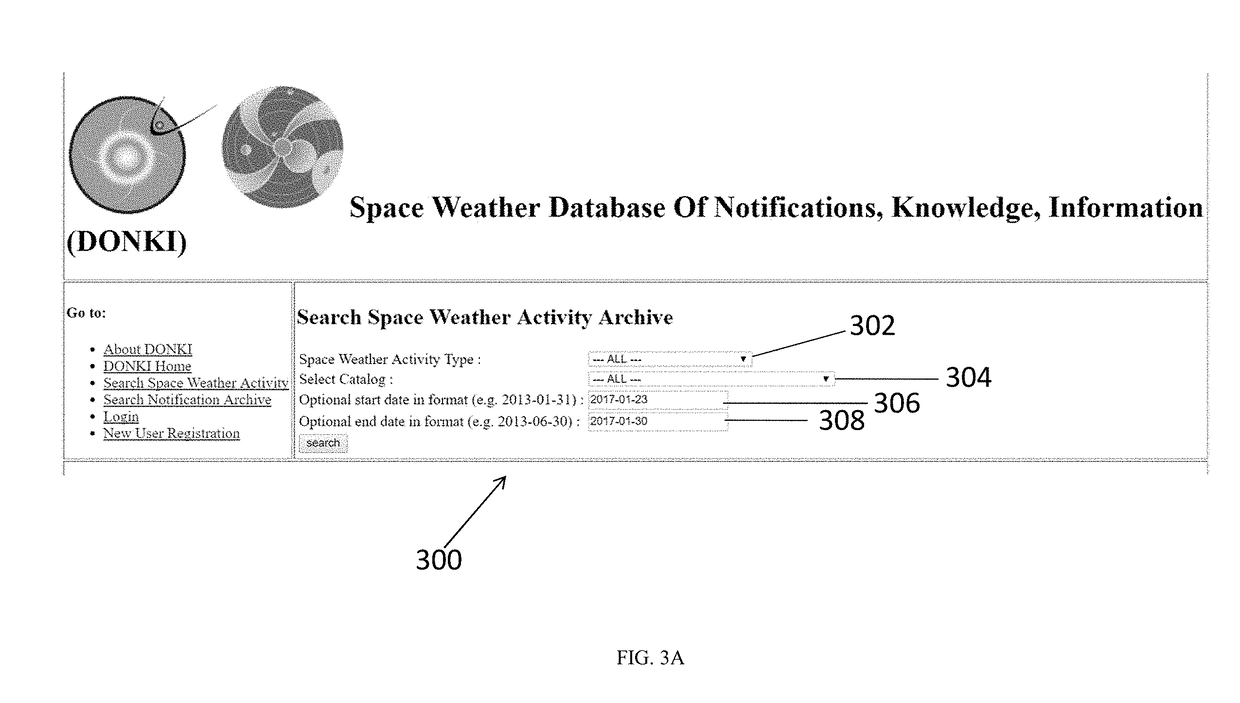
Space weather database
ActiveUS20190050485A1Weather condition predictionSpecial data processing applicationsSubject matterAtmospheric sciences
The disclosed subject matter relates to a database and systems associated therewith for space weather data (code name DONKI for Database of Notification, Knowledge, Information) relating to various space weather phenomena or phenomenon, such as, for example, solar flare, solar energetic particle, coronal mass ejection, interplanetary shock, magnetopause crossing, geomagnetic storm, radiation belt enhancement and high speed stream.
Owner:NASA
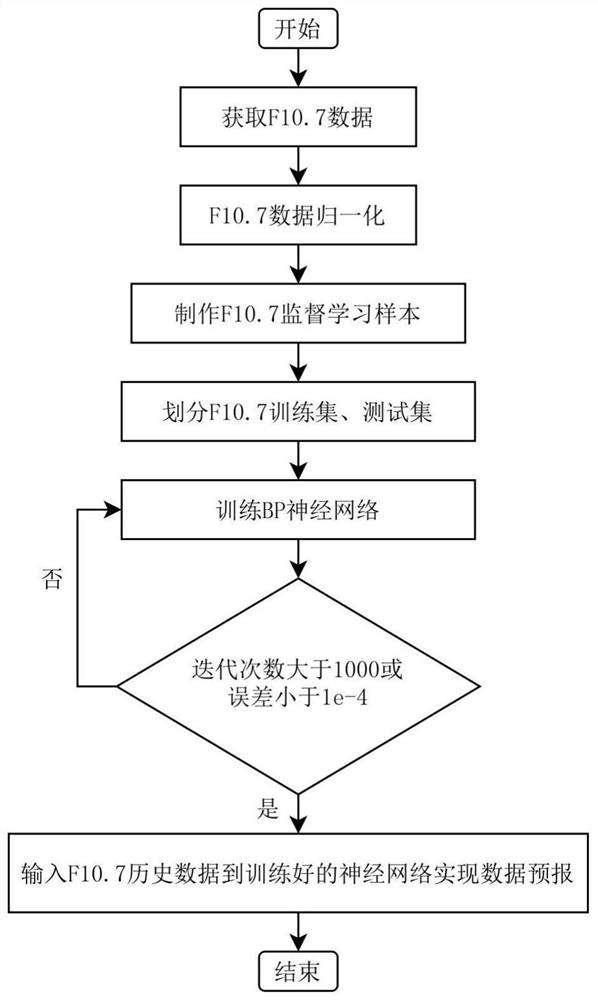
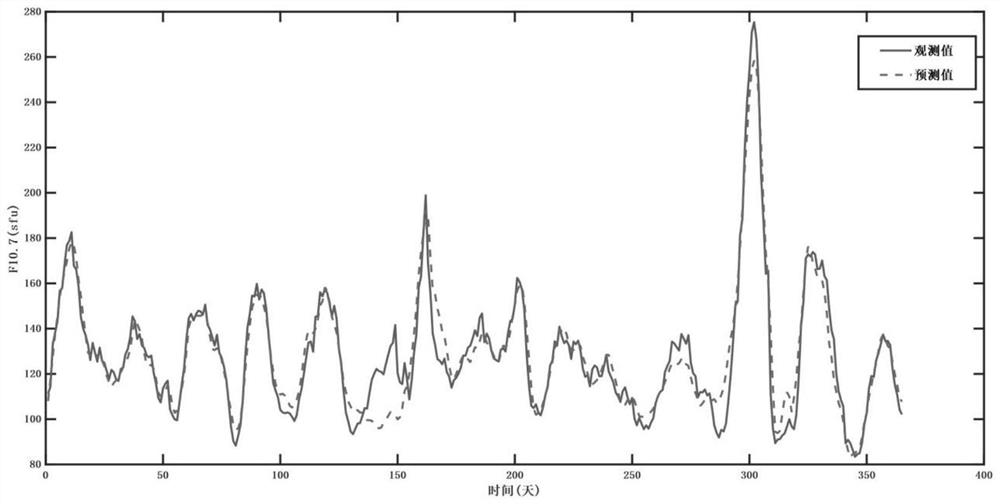
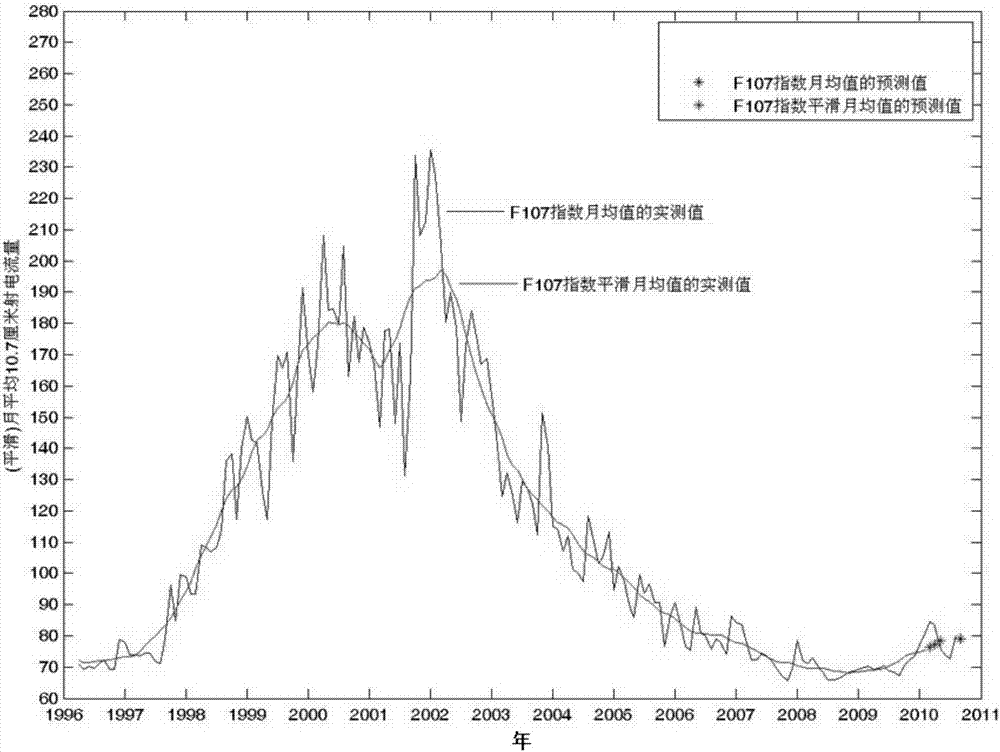
Solar 10.7 cm radio flow forecasting method based on BP neural network
PendingCN114091647AEasy to realize the forecast taskReduce modeling timeWeather condition predictionForecastingEngineeringSupervised learning
The invention belongs to the technical field of space weather prediction, and particularly relates to a solar 10.7 cm radio flow forecasting method based on a BP neural network, which comprises the following steps: acquiring observation value data of an F10.7 day and preprocessing the observation value data; converting the preprocessed data into supervised learning sample data capable of being trained by a BP neural network, and performing training set and test set division on the sample data; establishing a BP neural network according to the sample data; using the F10.7 training set to train a BP neural network; forecasting the trained BP neural network by using an input part of an F10.7 test set to obtain a forecast value, and performing error analysis on the forecast value and an output part of the test set to obtain forecast accuracy of the BP neural network; and inputting corresponding F10.7 historical data into the trained BP neural network to obtain prediction data. According to the method, the forecasting model of any period can be conveniently built, and the medium and short term forecasting precision of F10.7 can be effectively improved.
Owner:BEIBU GULF UNIV
Method of carrying out early warning on geomagnetic storm induction cardiovascular and cerebrovascular event through using multiple-space weather observation data
InactiveCN107390297AImprove developmentIncrease warning timeWeather condition predictionHigh energyConjoint analysis
The invention discloses a method for early warning of geomagnetic storm-induced cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events by using multiple space weather observation data. data, high-energy ray detection data, solar-terrestrial space environment parameters, and cosmic ray flow data; according to the time of observation data and the probability of affecting the geomagnetic field, the early warning probability of multi-band observation data is classified and graded, and used as a geomagnetic storm The early warning index for inducing cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events is used for early warning of the event; the method of the present invention has the advantages of early prediction time, large amount of observation data, reasonable scientific basis, long warning time, high efficiency and accuracy.
Owner:FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF KUNMING MEDICAL UNIV +1
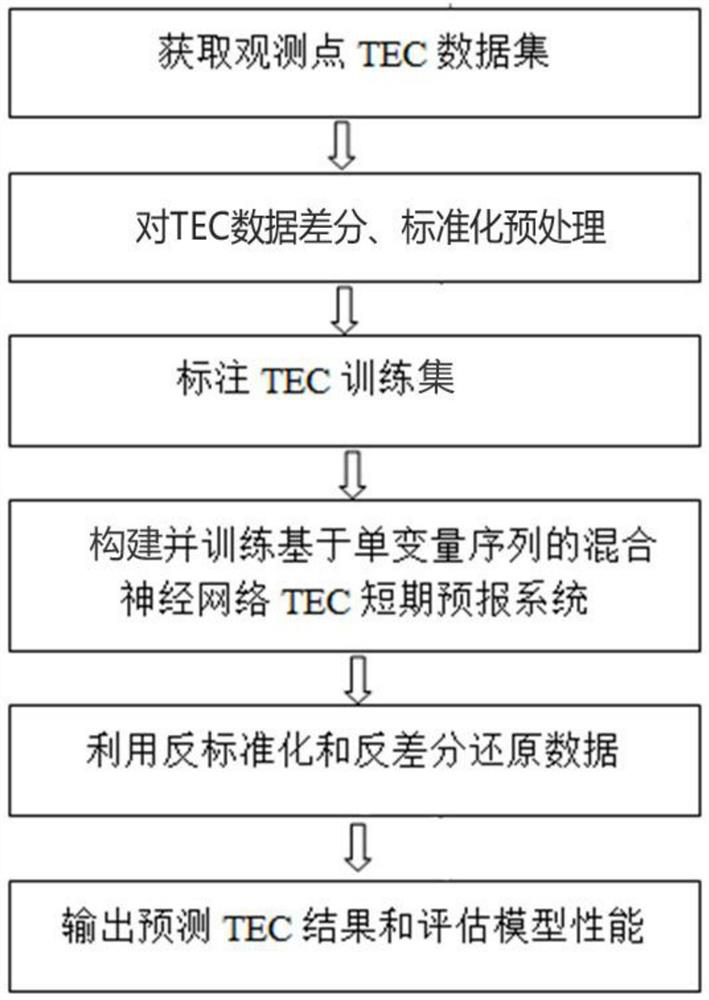
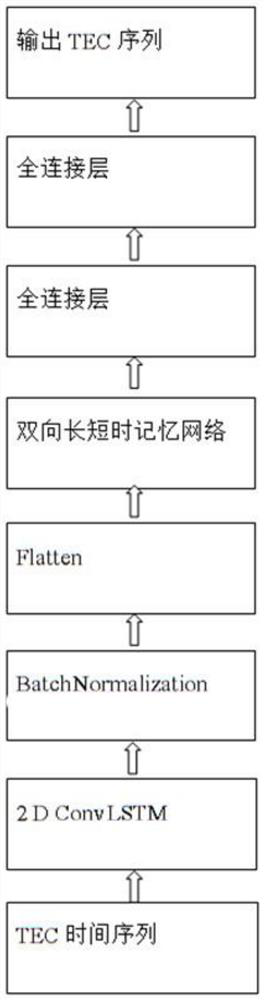
Short-term forecasting method suitable for single-station ionized layer TEC
PendingCN111932017AEffective spaceImprove service capabilitiesForecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionData setEngineering
The invention discloses a short-term forecasting method suitable for a single-station ionized layer TEC, and relates to the technical field of space weather and environment. The short-term forecastingmethod comprises the following steps: firstly, collecting a TEC data set of an observation point, and carrying out differential and standardized preprocessing on the data; secondly, marking a TEC training data set, and constructing and training a hybrid neural network TEC short-term forecasting system based on a univariate sequence; and finally, inputting a TEC data operation model, outputting asequence, restoring the data by adopting an anti-standardization and contrast technology, outputting a prediction TEC result and evaluating the model performance. According to the invention, a deep learning network ConvLSTM and a BiLSTM are combined; spatial-temporal features and periodic day-by-day change features of the sequence are effectively extracted; an accurate ionospheric refraction correction value can be provided for a space application system user taking radio as a propagation beacon, an effective space abnormal weather monitoring and early warning mechanism can be established, Meanwhile, data support is provided for morphological analysis of space weather and space environment.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Full-solar-surface multi-stage solar extreme-ultraviolet spectrum imaging method
InactiveCN108680253AReduce volumeRealize simultaneous observationSpectrum investigationGratingUv spectrum
The invention discloses a full-solar-surface multi-stage solar extreme-ultraviolet spectrum imaging method. Light at a light inlet is focused to a system focal plane by an off-axis parabolic reflecting mirror, wherein an extreme-ultraviolet variable-pitch grating is arranged at the focal plane of the system; focused solar extreme-ultraviolet radiation is dispersed by the extreme-ultraviolet variable-pitch grating and the dispersed light is received by five levels of detectors; images received by four detectors have chromatic dispersion phenomena and the image received by the intermediate detector has no chromatic dispersion, so that spatial information is obtained directly at the level without chromatic dispersion and the spectral information is obtained based on inversion results of the five levels of imaging. According to the invention, simultaneous observation of full-solar-surface space and spectral information is realized; the method is suitable for observing large-range dynamic solar activities like the CME; the solar burst speed information can be obtained; and a novel way is provided for researches of space weather and space environment.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
Apparatus and method for monitoring status of satellite
InactiveUS9162777B2Data processing applicationsCosmonautic vehiclesMonitoring statusAtmospheric sciences
Provided is an apparatus and method for monitoring a status of a satellite, including classifying satellite telemetry information and space weather information and storing the information in a storage unit including respective databases, predicting whether a predetermined type of satellite failure occurs based on the space weather information, and generating satellite control command information to change a status of a predetermined satellite configuration when a satellite failure determining index used to determine a possibility of the satellite failure is beyond a predetermined critical alert range.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
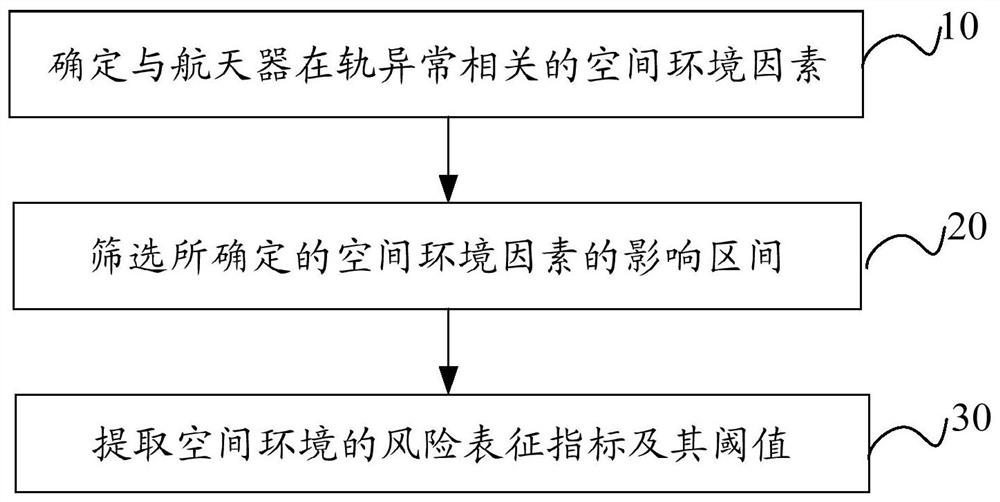
Space environment risk index construction method and device and storage medium
PendingCN111738604AMeet the needs of space weather risk forecastingForecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionSpace environmentSimulation
The invention discloses a space environment risk index construction method and device and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: firstly determining space environment factors related tothe on-orbit abnormality of a spacecraft; secondly, screening influence intervals of the determined space environment factors; and finally, extracting risk characterization indexes of the space environment and thresholds thereof. The risk characterization index and the threshold thereof obtained through the scheme can more effectively and accurately characterize the space radiation environment risk suffered by the spacecraft, thereby ensuring that the risk characterization index and the threshold thereof can meet the requirements of spacecraft anomaly and space environment correlation construction analysis and spacecraft space weather risk prediction.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
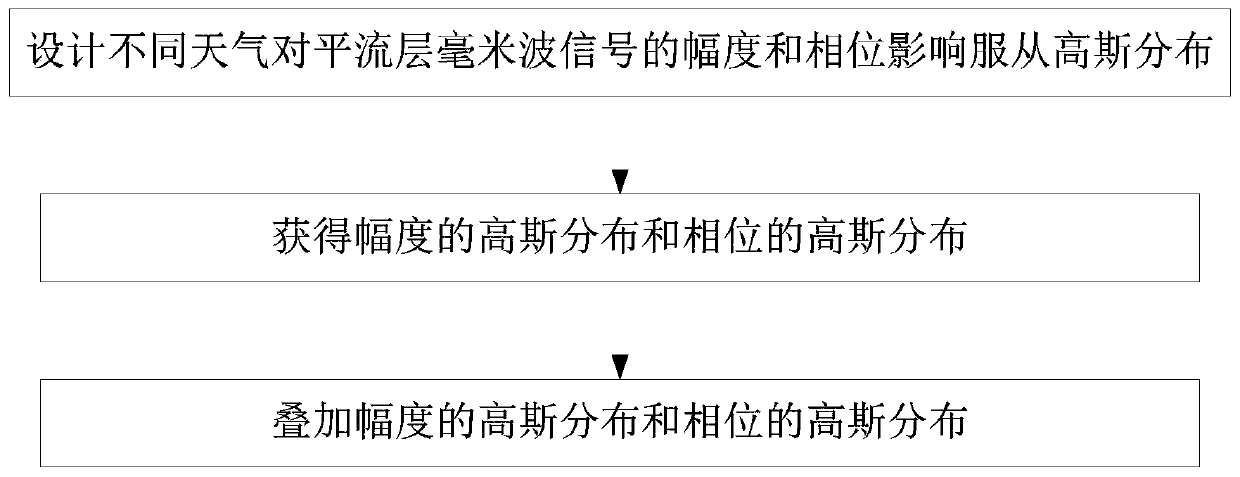
Stratospheric millimeter wave base station ground channel modeling method and modeling system thereof
ActiveCN110708130ASimulation is accurateTransmission monitoringMillimeter wave communication systemsSimulation
The invention discloses a stratospheric millimeter wave base station ground channel modeling method and a modeling system thereof. The method comprises the following steps: modeling the influence of the space weather condition of a space section on a stratospheric millimeter wave signal into a Gaussian distribution model by calculating the weather influence of the space section of base station communication on a user channel of a ground receiving end; modeling the influence of the ground environment of a ground section on a stratospheric millimeter wave signal into a three-state first-order Markov model by calculating the influence of the ground section on the ground environment of a user channel; through calculating the joint influence in a base station communication channel model, modeling on the channel by combining the weather condition and the influence of multipath fading and shadow fading caused by the ground environment where a receiving end is located on the channel. The basestation ground channel modeling method and modeling system can accurately simulate the influence of various factors on the stratospheric millimeter wave signal in the actual transmission process during ground communication, are suitable for modeling work under various weather and environment conditions, and can provide reference for stratospheric millimeter wave communication system simulation work and actual system deployment.
Owner:天地信息网络研究院(安徽)有限公司
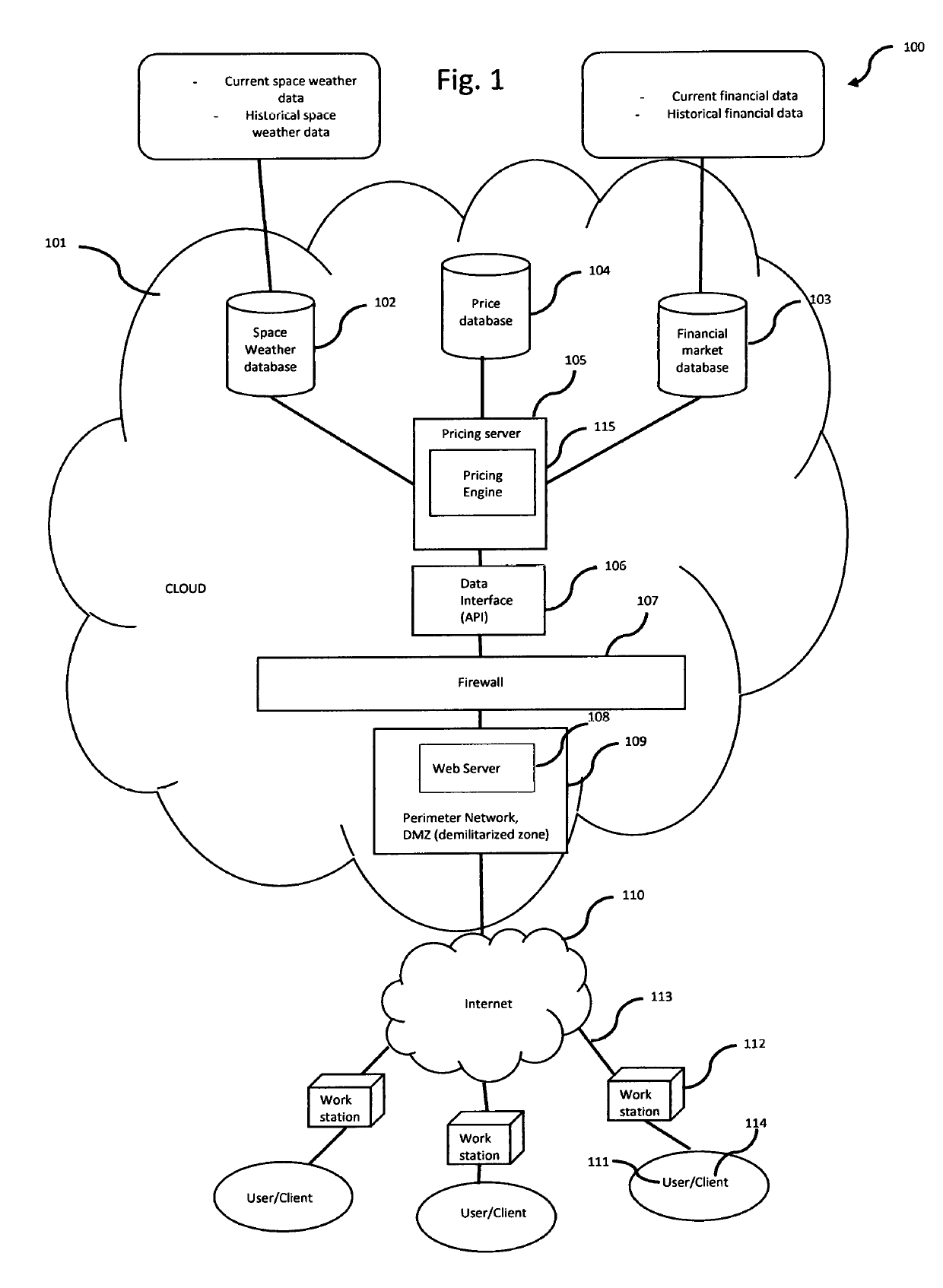
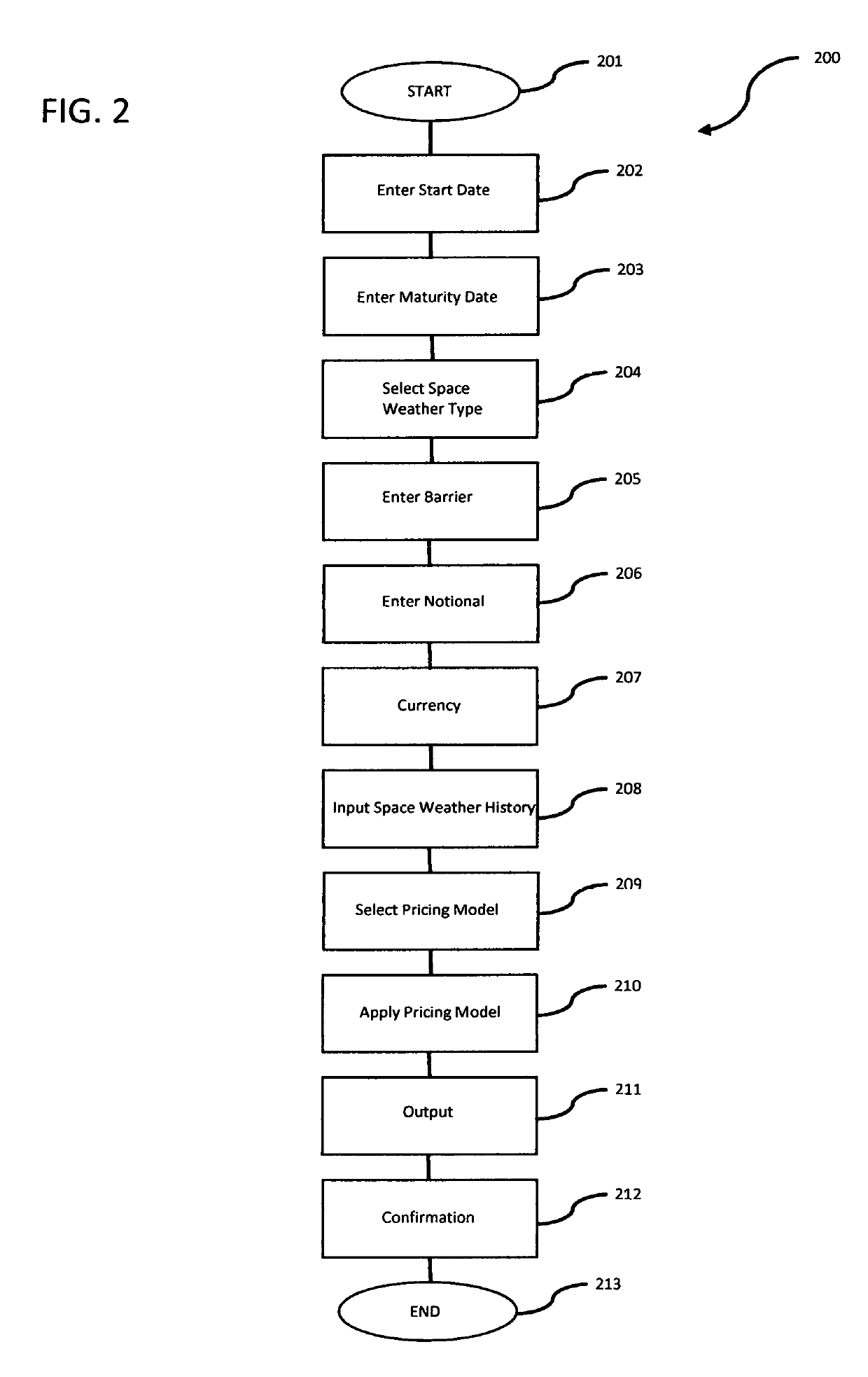
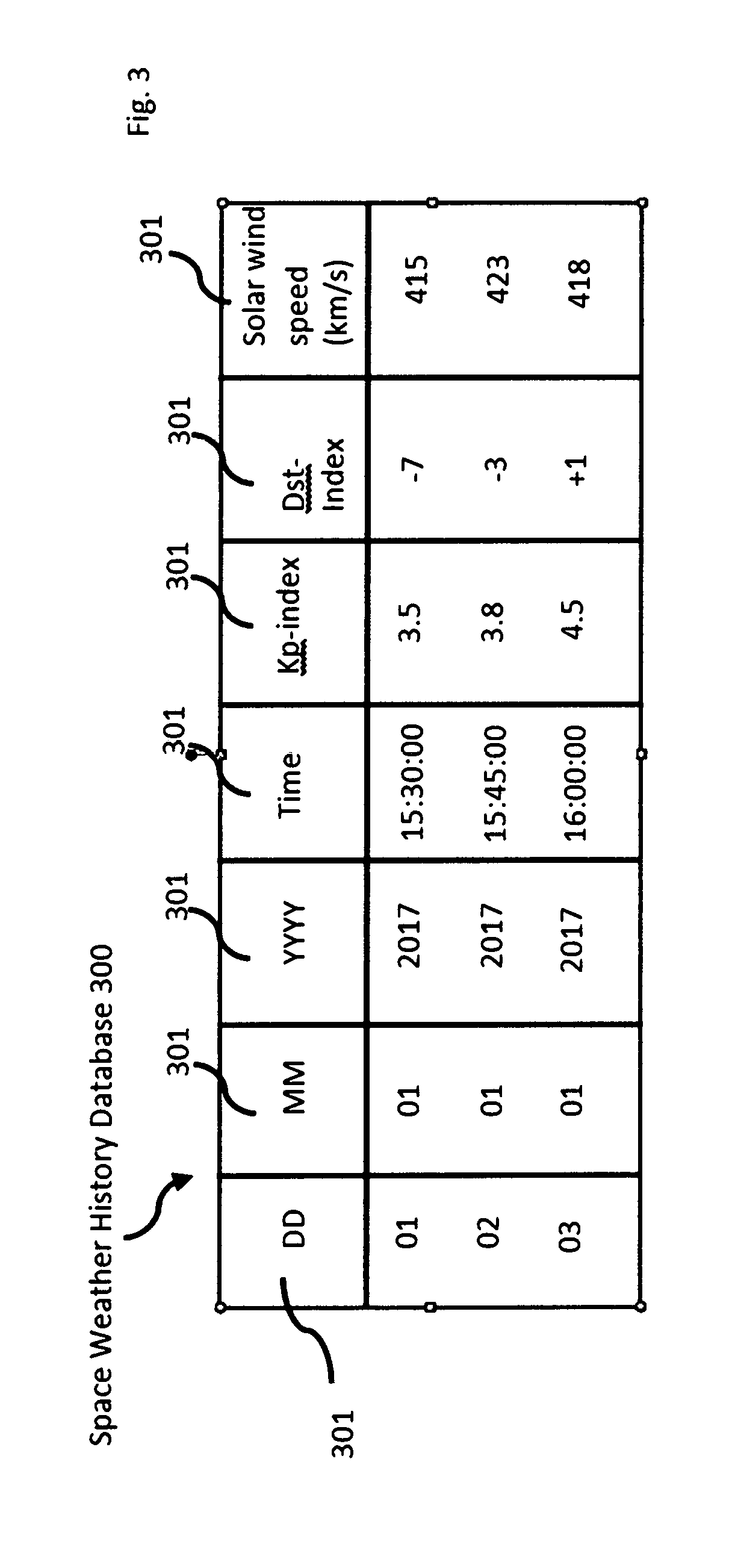
System, method, and computer program product for valuating space weather-based financial instruments
InactiveUS20190279304A1Easily and confidently be pricedMarket predictionsFinanceSolar ActivitiesFinancial transaction
A system and method for evaluating space weather-based derivatives, such as futures, options, swaps, and the like, with payout depending on solar activity. The system includes space weather data, financial databases and a central processing trading server that is accessible via a plurality of internal and external workstations.
Owner:UNGER STEPHAN +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com