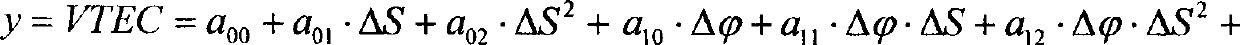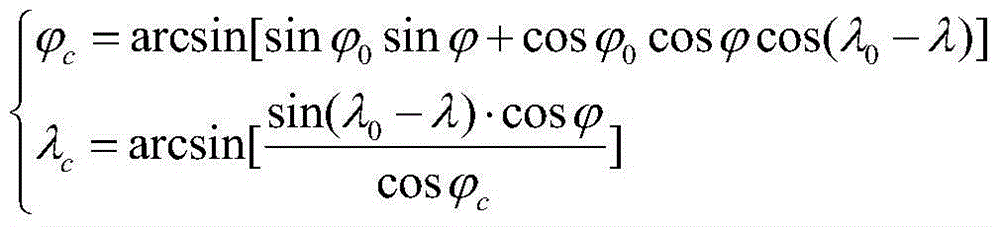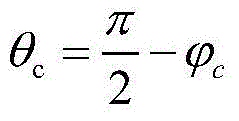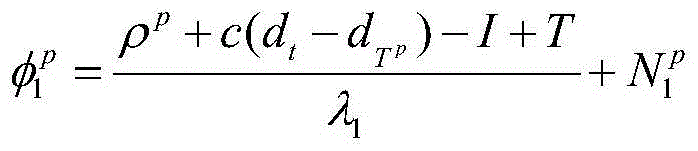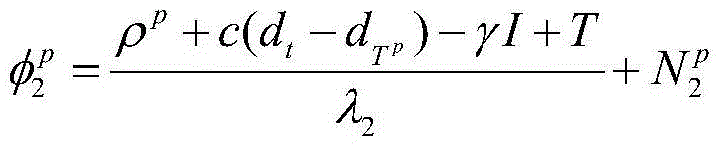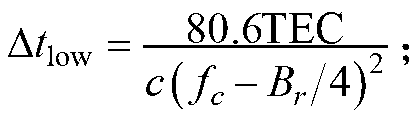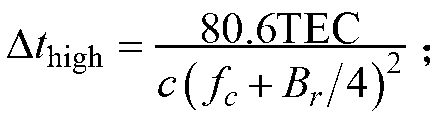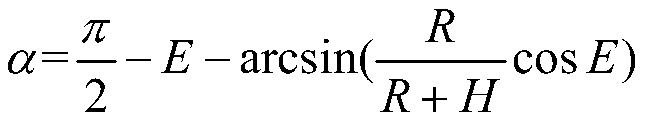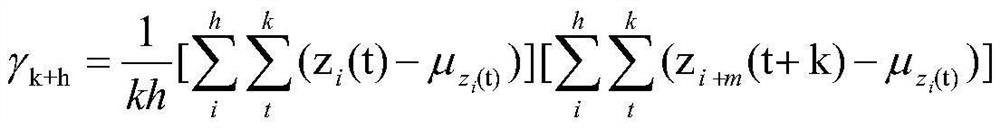Patents
Literature
75 results about "Total electron content" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
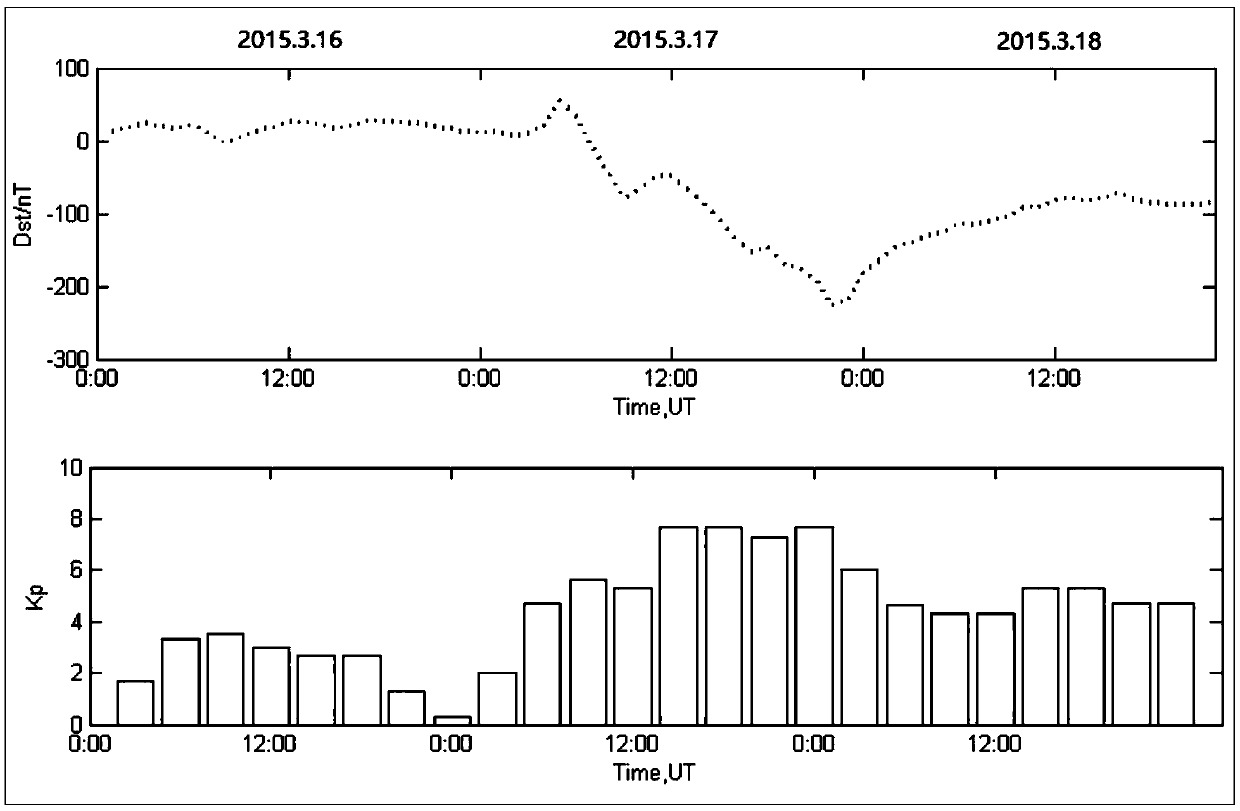
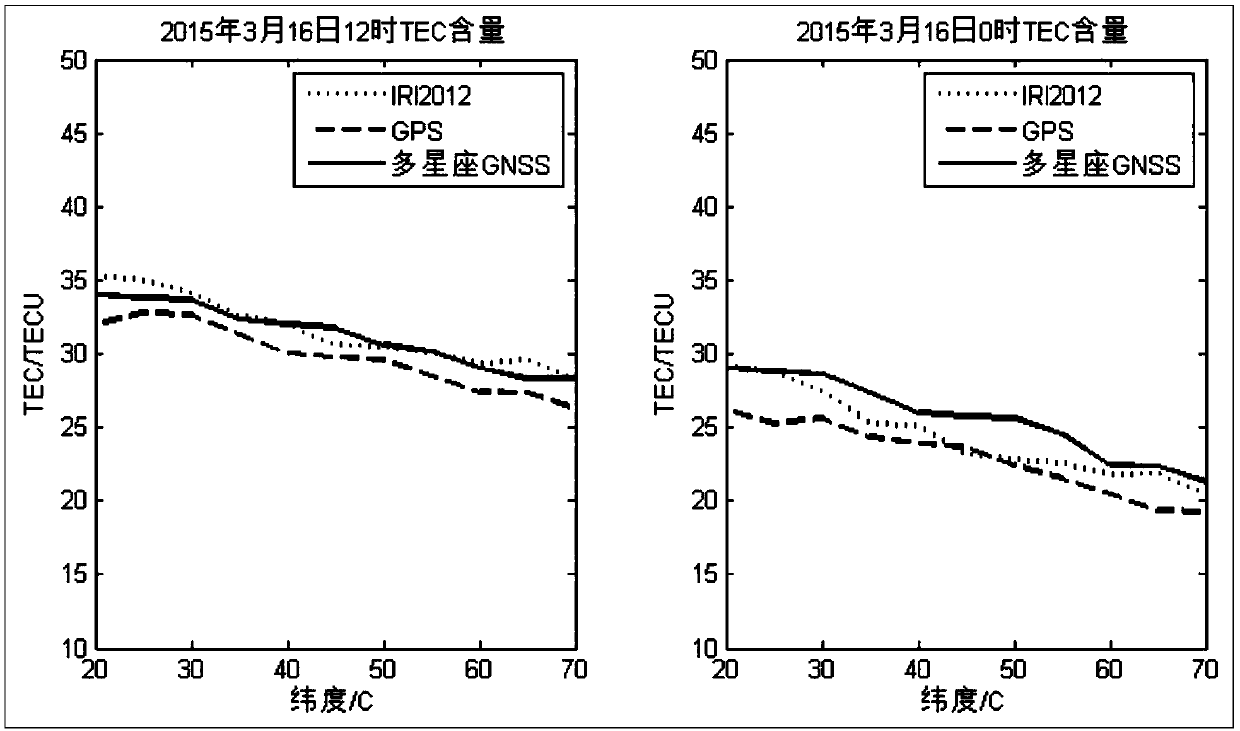
Total electron content (or TEC) is an important descriptive quantity for the ionosphere of the Earth. TEC is the total number of electrons integrated between two points, along a tube of one meter squared cross section, i.e., the electron columnar number density. It is often reported in multiples of the so-called TEC unit, defined as TECU=10¹⁶el/m².
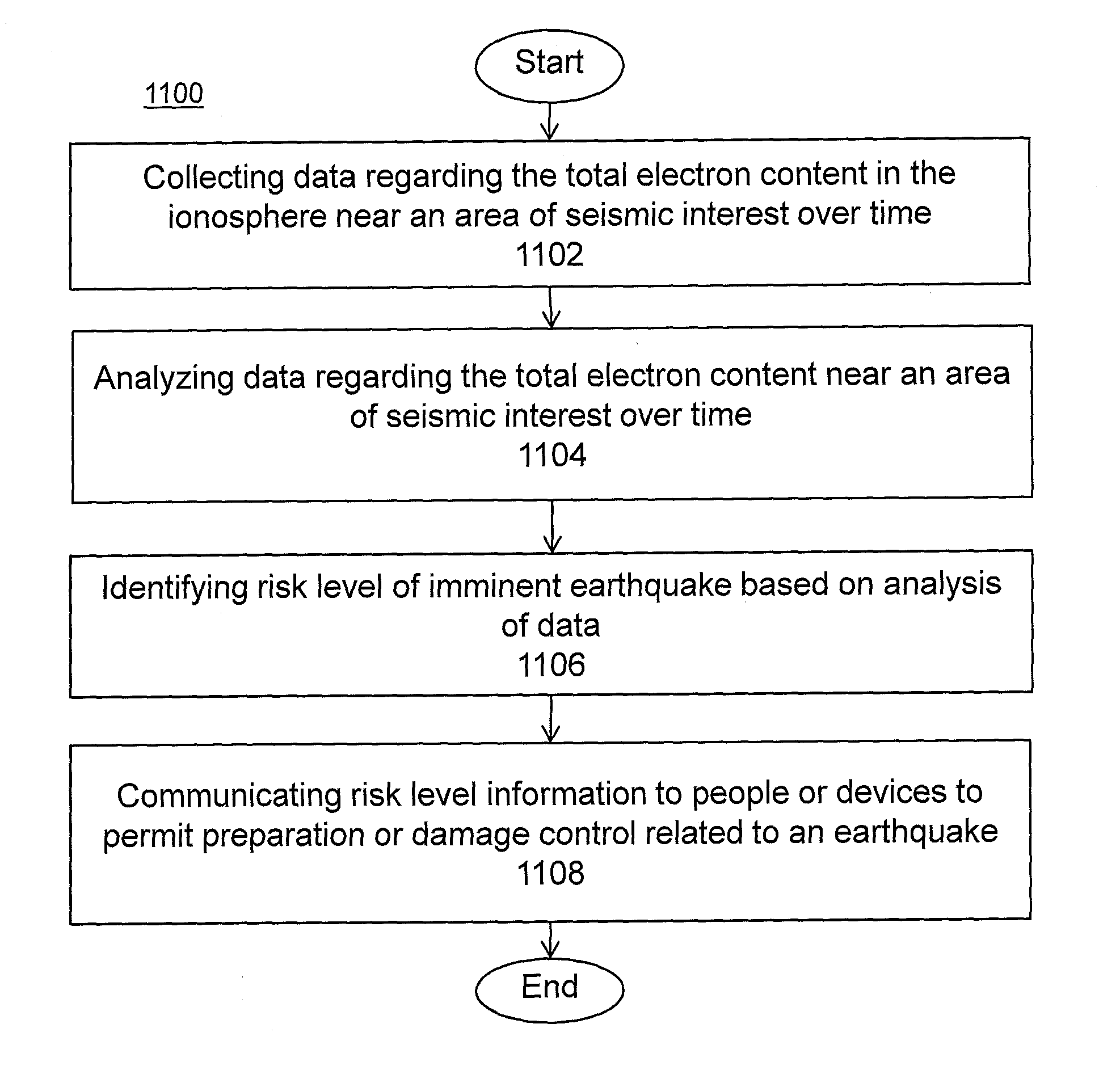
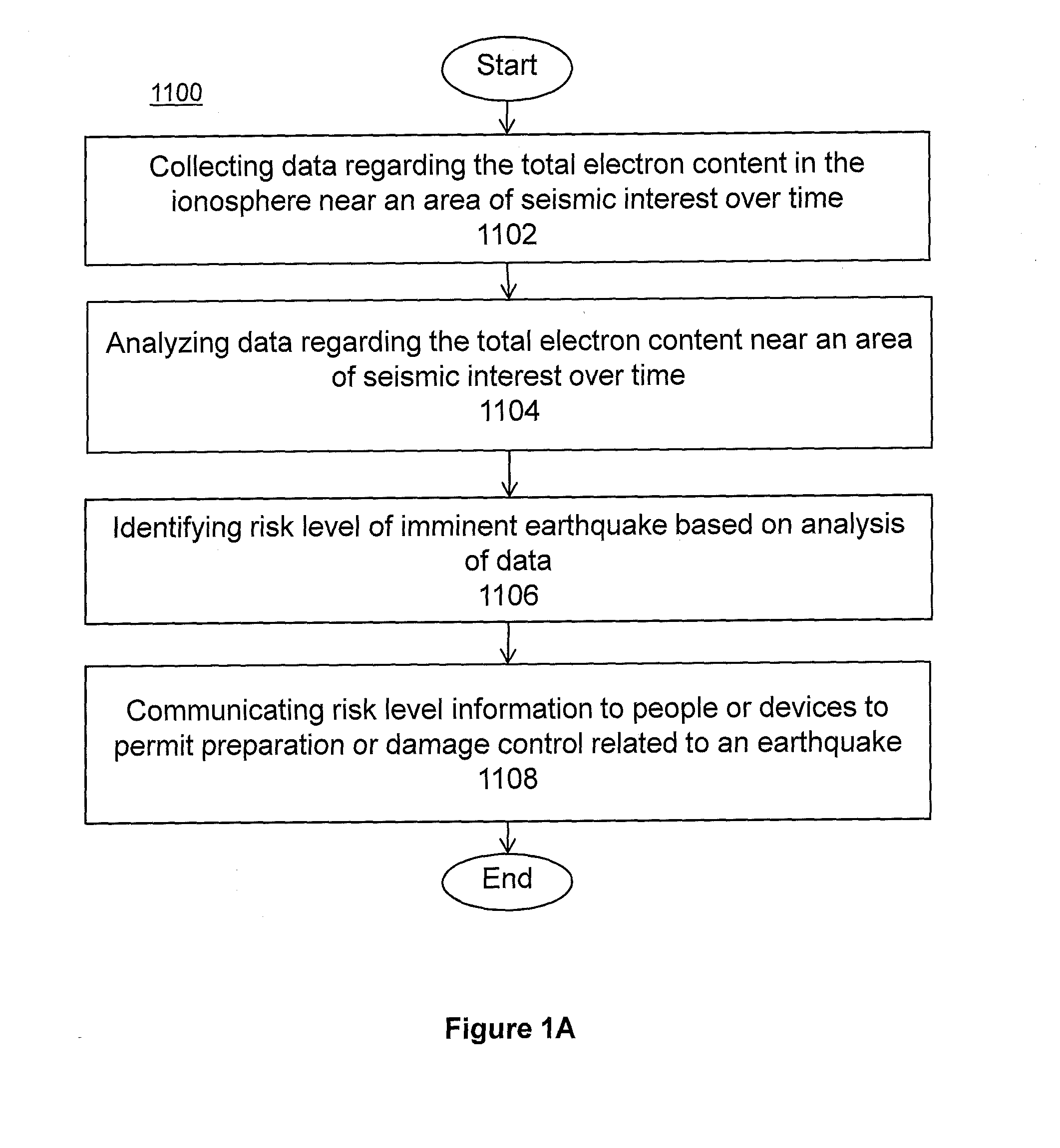
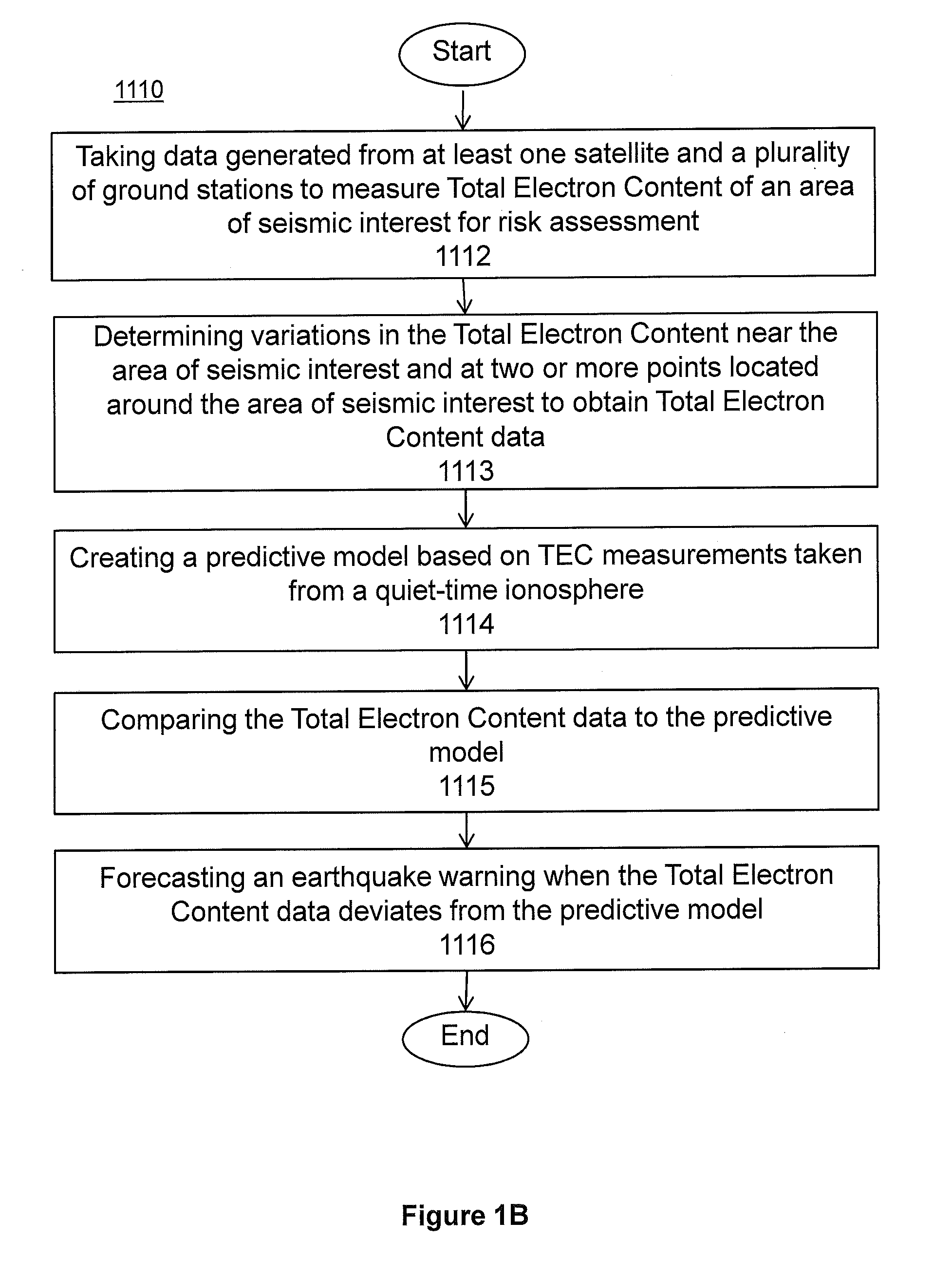
System and methods for risk prediction and assessment
InactiveUS20150051837A1Weather condition predictionEarthquake measurementIonosphereTotal electron content
A system and methods for predicting and assessing risk before an event occurs. More particularly, the present invention predicts and assesses risk such as the occurrence of an earthquake prior to the event by collecting and analyzing changes in Total Electron Content (“TEC”) in the ionosphere.
Owner:CORNELL UNIV CORNELL CENT FOR TECH ENTERPRISE & COMMLIZATION CCTEC
Hyper-spectral estimation method of total nitrogen content of rice leaves and estimation model constructing method
InactiveCN106290197AClimate change adaptationColor/spectral properties measurementsEstimation methodsTotal nitrogen
An embodiment of the invention discloses a hyper-spectral estimation model constructing method of total nitrogen content of rice leaves. The method comprises steps as follows: multiple experimental plots are selected, and multiple sampling points are selected in each experimental plot; canopy spectral measurement is performed at the critical growing stage of rice; multiple sampling spectrums are recorded at each sampling point, and an average value is taken as a spectral measurement value of the sampling point; a hyper-spectral image of each experimental plot is acquired by an airborne imaging spectrometer; multiple function leaves at different parts are collected at each sampling point, and the total nitrogen content of the rice leaves is measured; the hyper-spectral estimation model of the total nitrogen content of the rice leaves is constructed with the adoption of spectral indexes or a partial least-squares regression method. The embodiment of the invention further discloses a hyper-spectral estimation method of the total nitrogen content of the rice leaves. The total nitrogen content of the rice leaves is estimated according to the model constructed with the method. The scientific and technical basis can be provided for space inversion of the nitrogen content of regional-scale rice and efficient implementation of precision agriculture.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
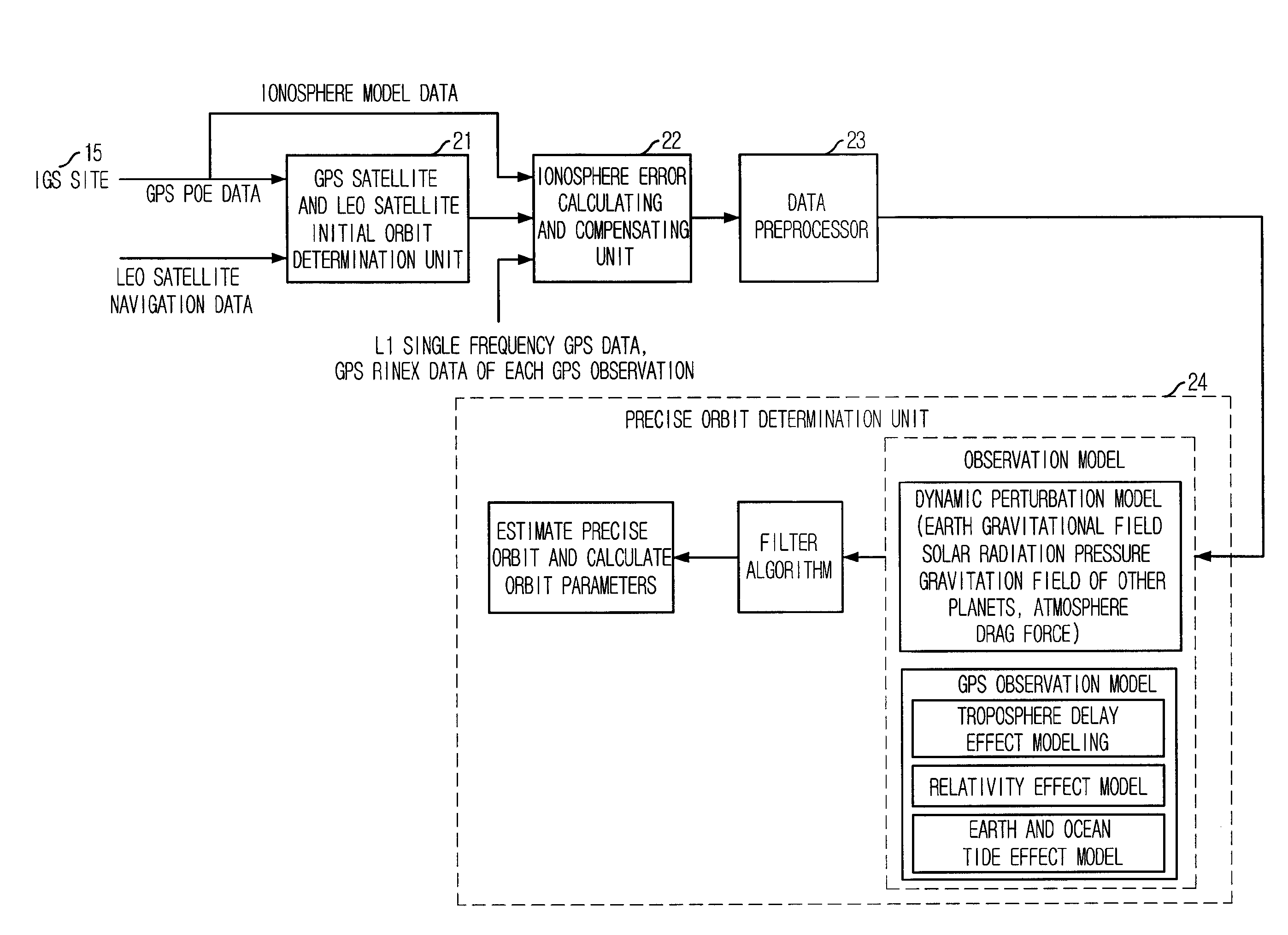
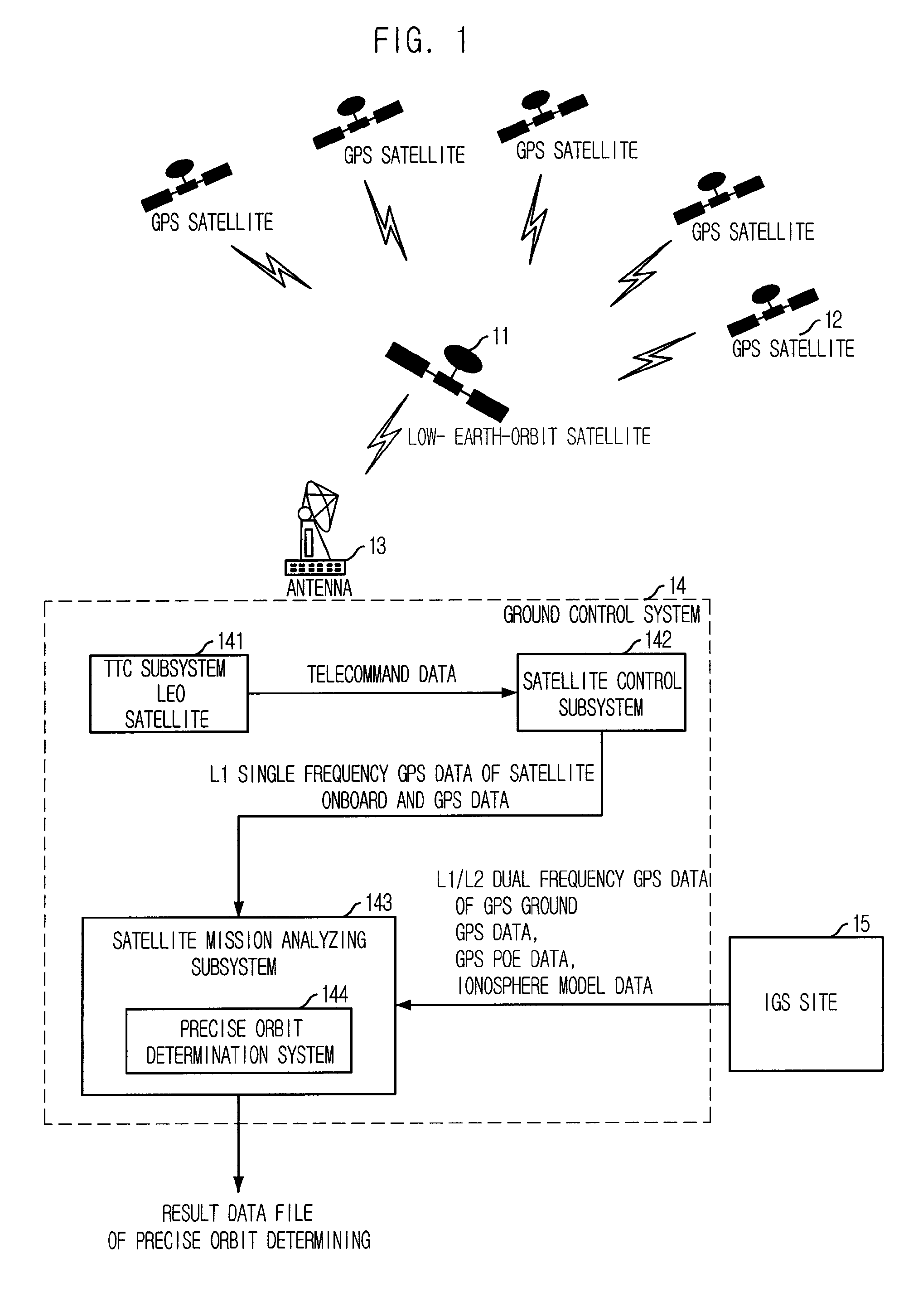
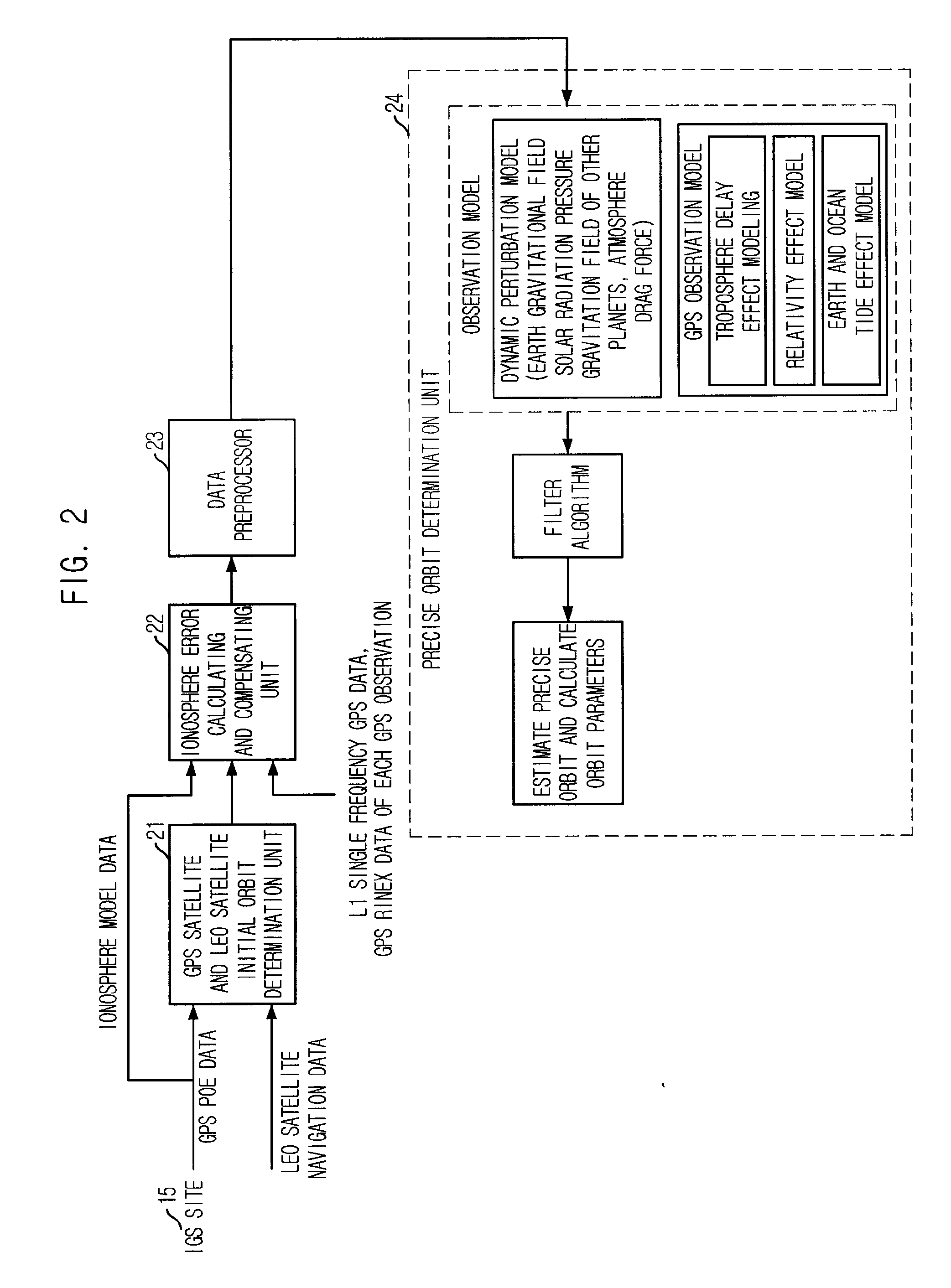
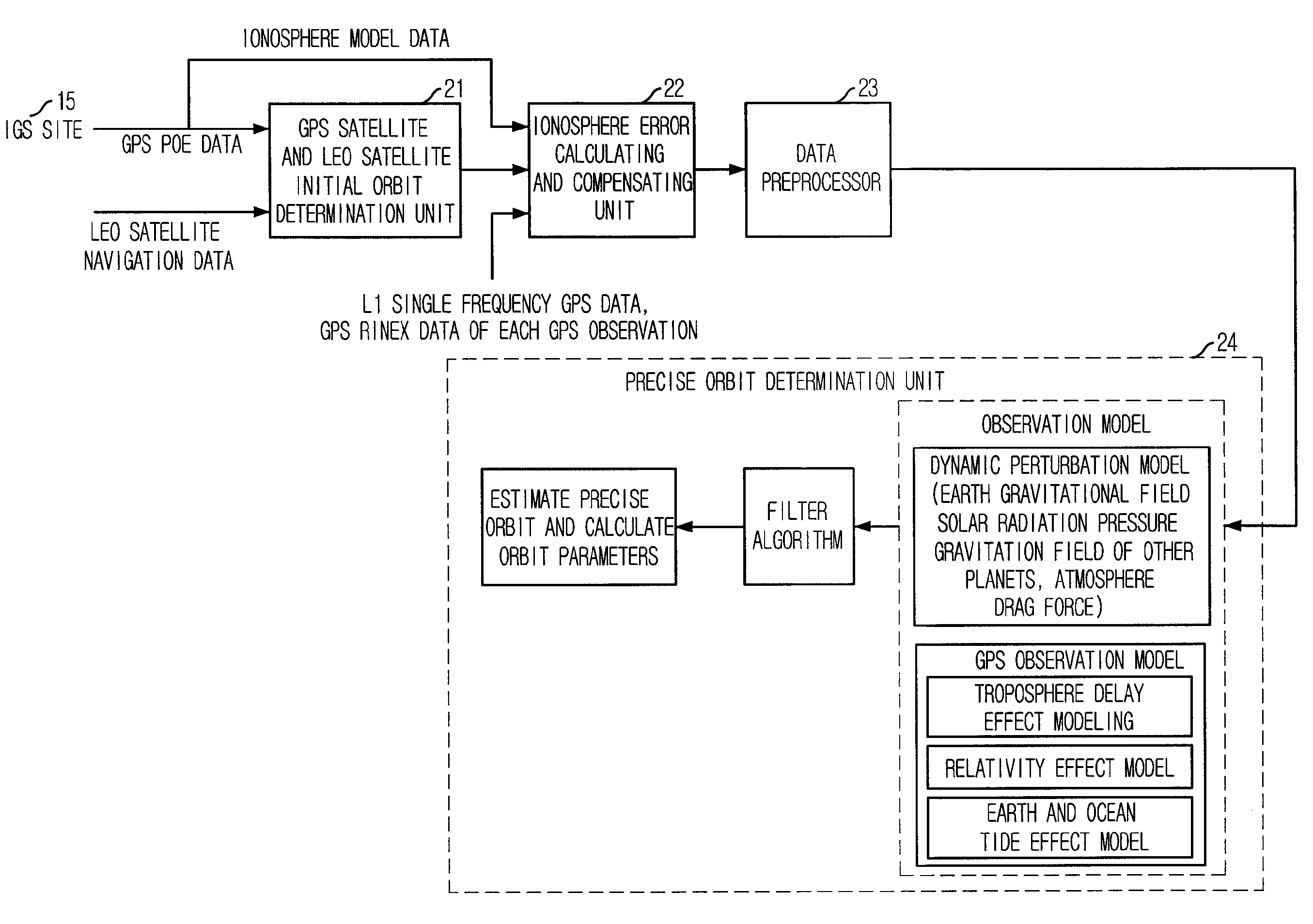
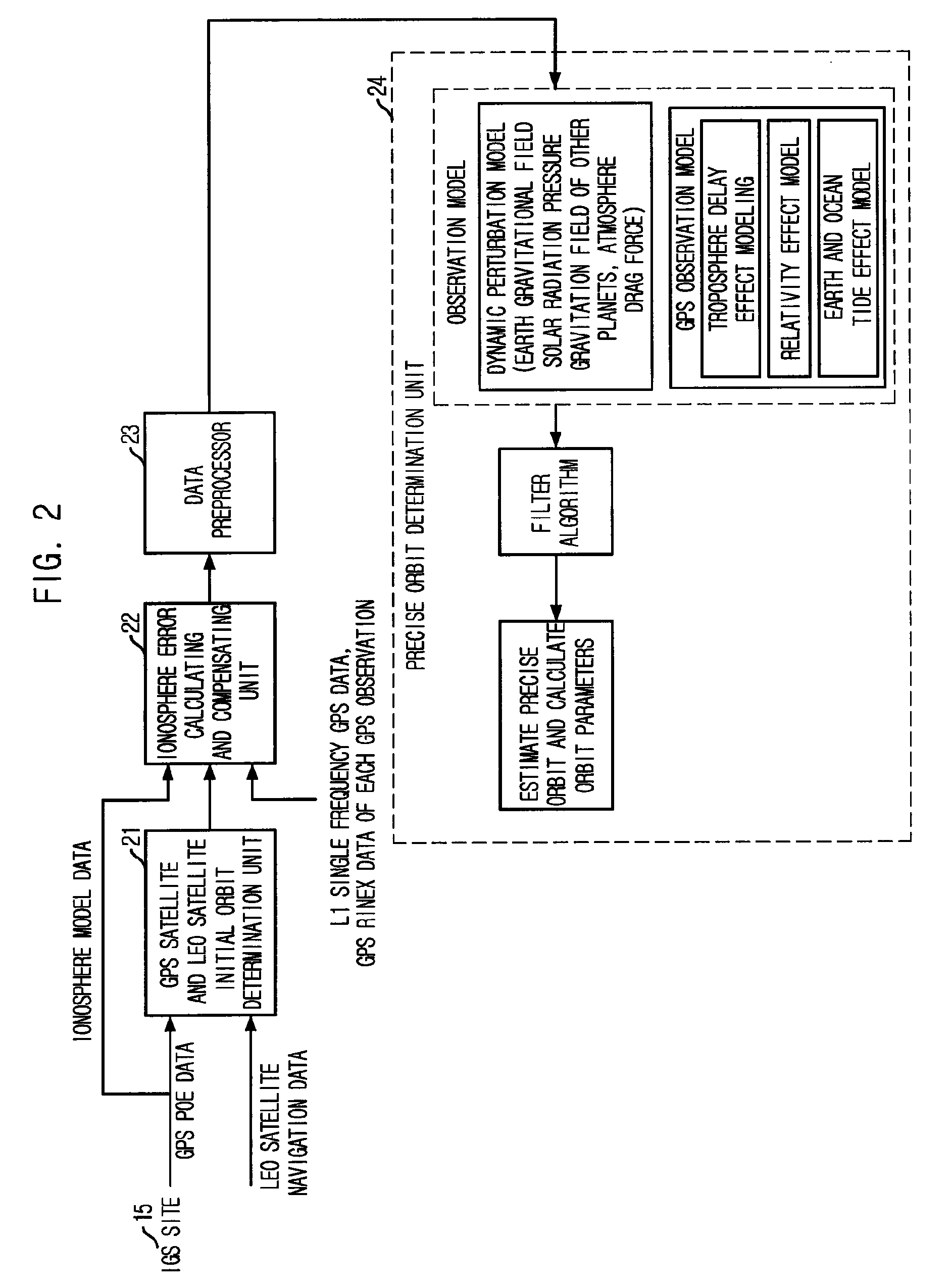
Method for correcting ionosphere error, and system and method for determining precision orbit using the same
InactiveUS20090091493A1Eliminate errorsAccurately determinePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingHigh elevationOne pass
Provided is a method of correcting an ionosphere error, a system of a precise orbit determination using the same and a method thereof. The method includes the steps of: a) determining a time of a highest elevation angle of a GPS satellite per one pass of each GPS satellite received at a LEO satellite or a receiver on a ground; b) determining a minimum total electron content found from an ionosphere model of the determined time per one pass of each GPS satellite; c) determining a total electron content directly calculated from the LEO satellite or a single frequency GPS data; d) determining an ionosphere error value of a single frequency GPS data by combining the minimum total electron content and the directly calculated total electron content; and e) correcting pseudorange data or carrier phase data based on the determined ionosphere error value.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Estimation method of total nitrogen content in crop canopy leaf
ActiveCN102313699AImprove acceleration performanceImprove stabilityColor/spectral properties measurementsNon destructiveEstimation methods
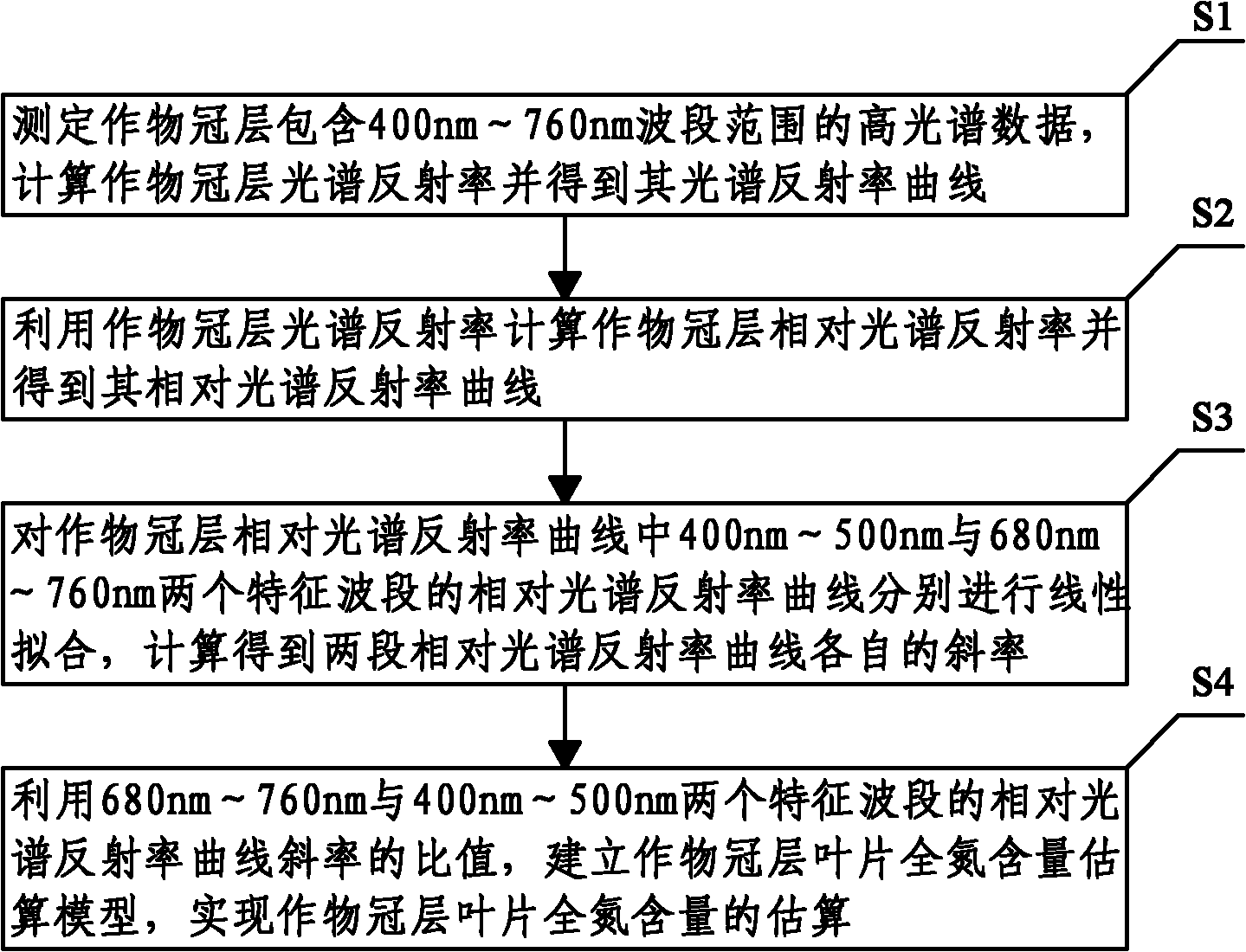
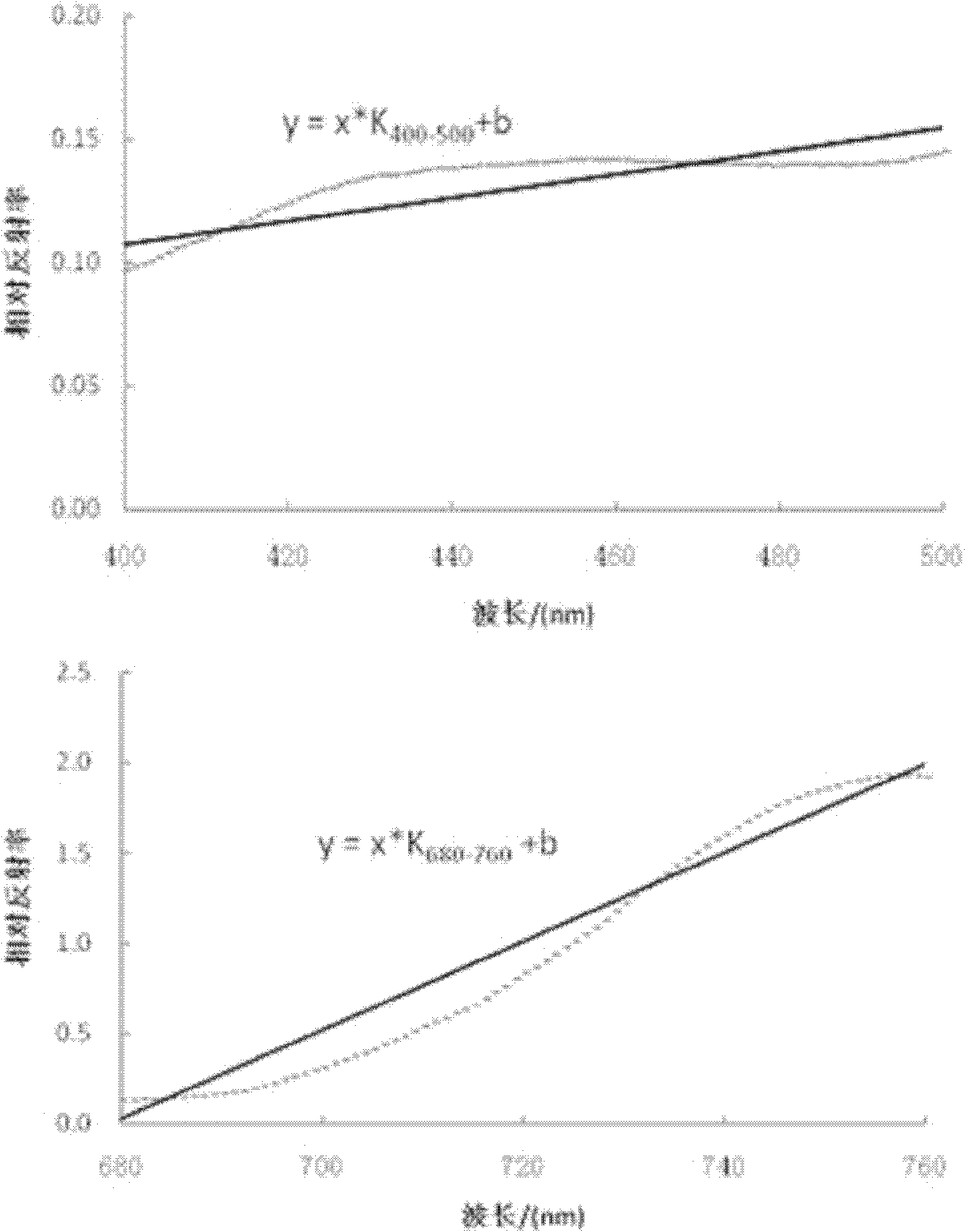
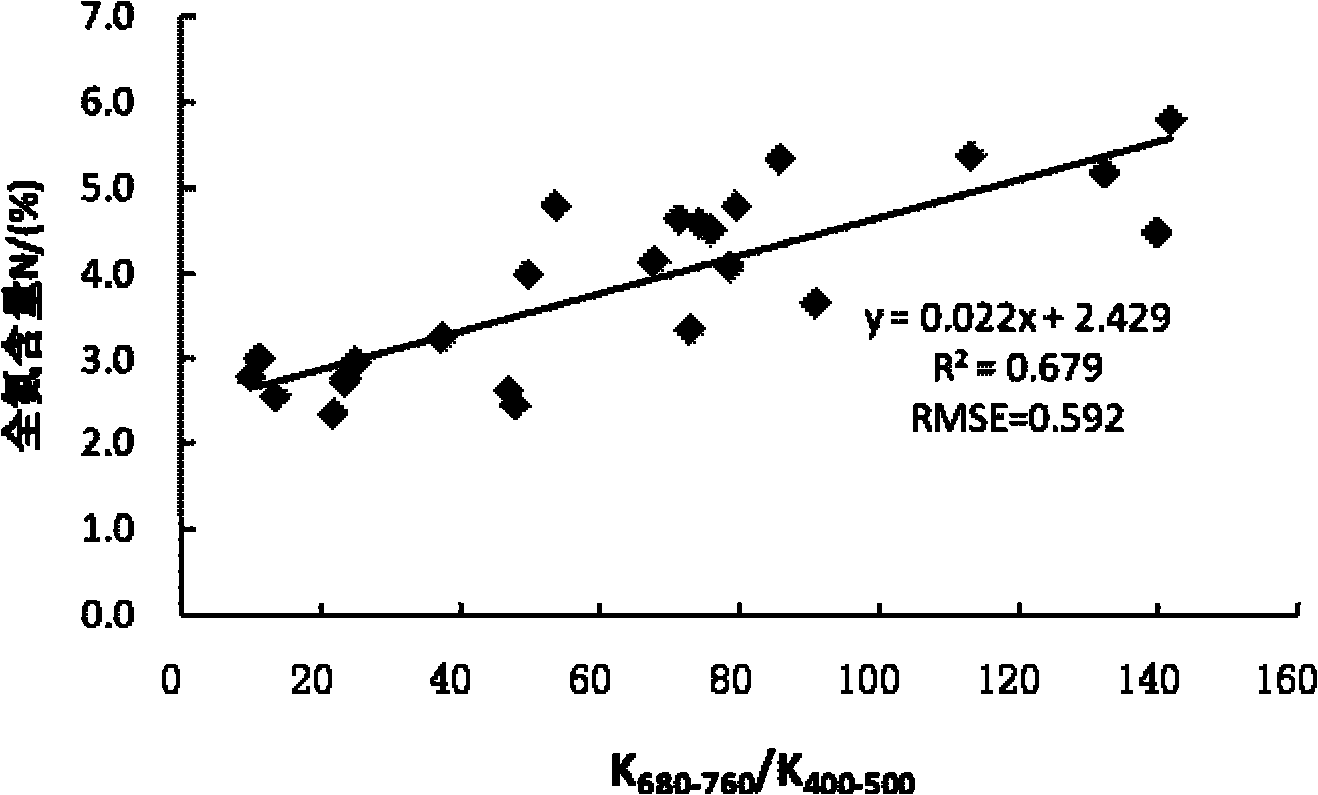
The invention discloses an estimation method of total nitrogen content in a crop canopy leaf, and relates to the technical field of spectrum non-destructive detection of biochemical components in a crop. The method comprises the following steps of: S1: determining hyperspectral data within the wave band range of 400nm-760nm of a crop canopy, calculating the spectral reflectance of the crop canopyand obtaining a spectral reflectance curve of the crop canopy; S2: calculating the relative spectral reflectance of the crop canopy by virtue of the spectral reflectance of the crop canopy and obtaining a relative spectral reflectance curve of the crop canopy; S3: respectively performing linear fitting on the relative spectral reflectance curves of two characteristic wave bands at 400nm-500nm and680nm-760nm in the relative spectral reflectance curve of the crop canopy and calculating the slopes of the two relative spectral reflectance curves; and S4: establishing an estimation model of the total nitrogen content in the crop canopy leaf by virtue of the ratio of the slopes of the relative spectral reflectance curves of the two characteristic wave bands at 680nm-760nm and 400nm-500nm so asto realize estimation of the total nitrogen content in the crop canopy leaf. By adopting the estimation method, the estimation model of the biochemical components in crop nitrogen can be established,and the model has strong expandability and high stability.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT FOR INFORMATION TECH & AGRI
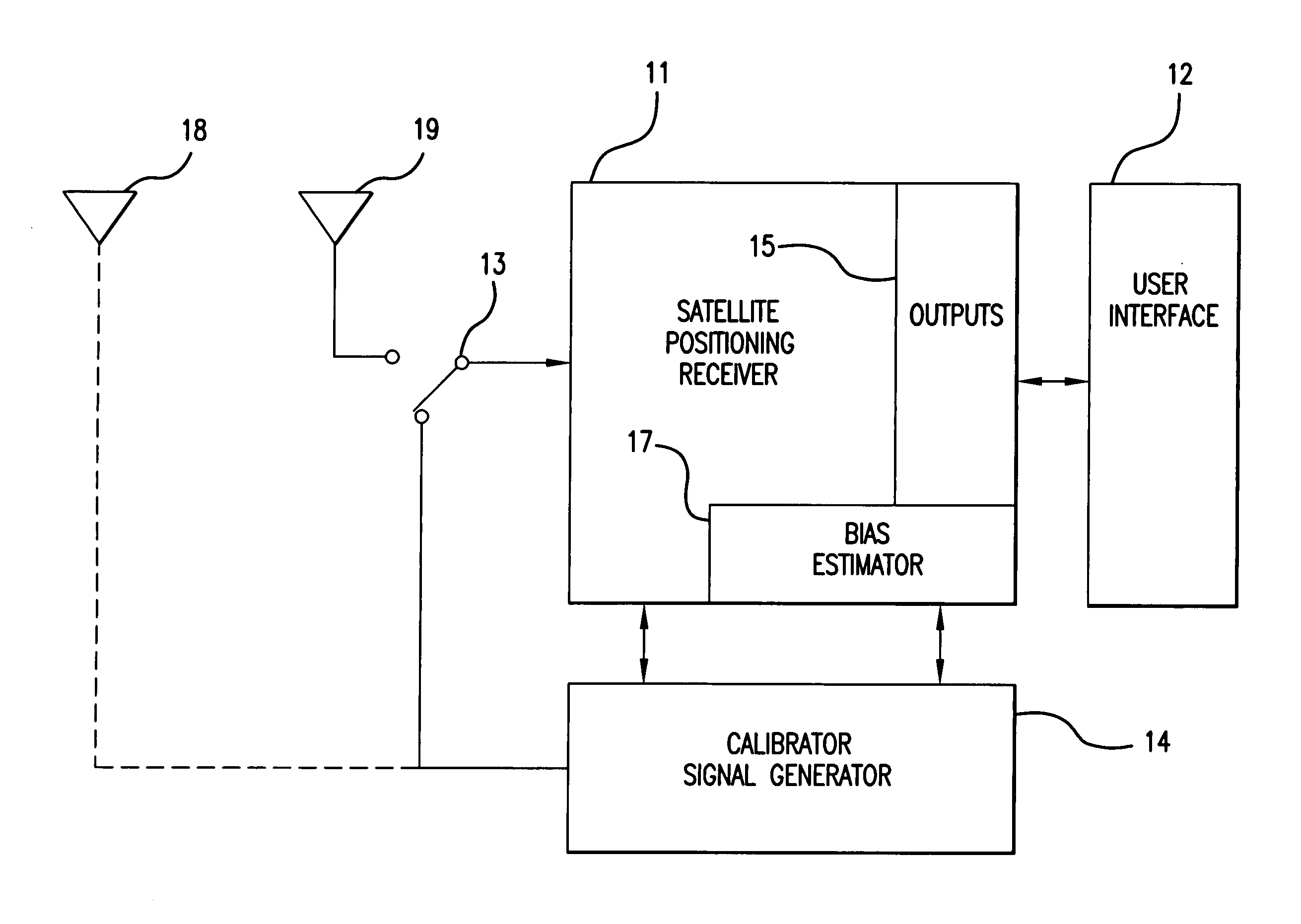
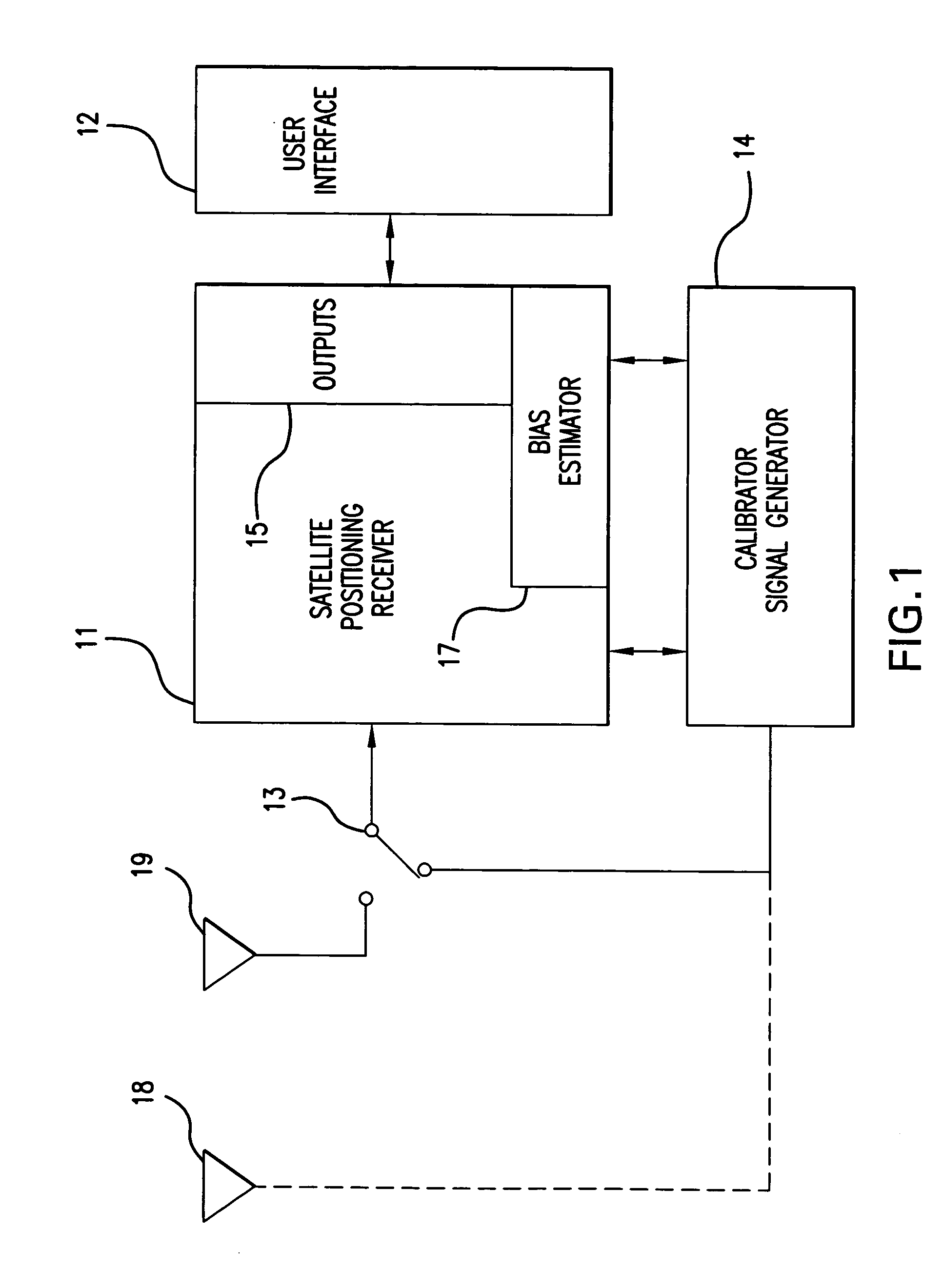
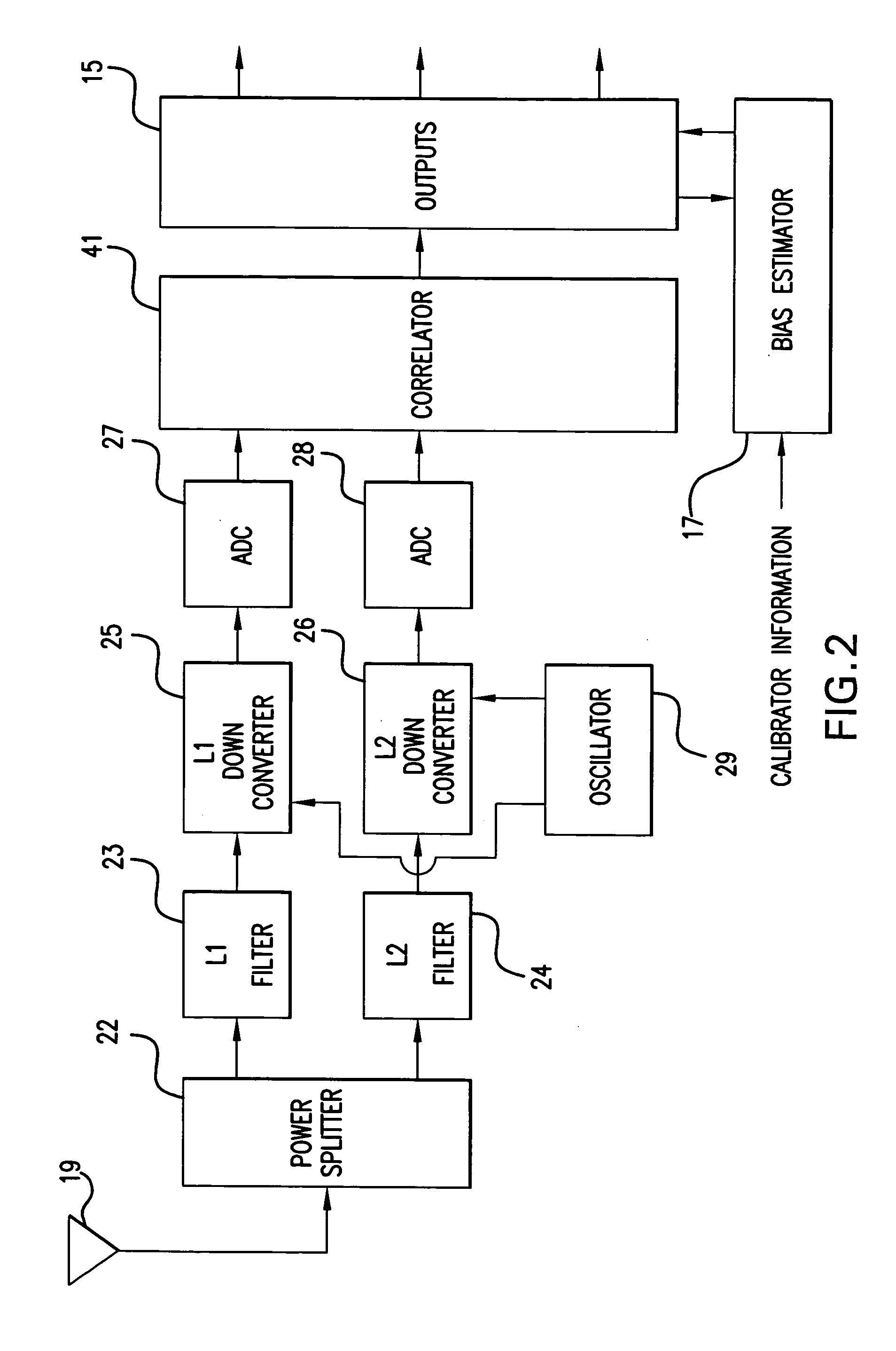
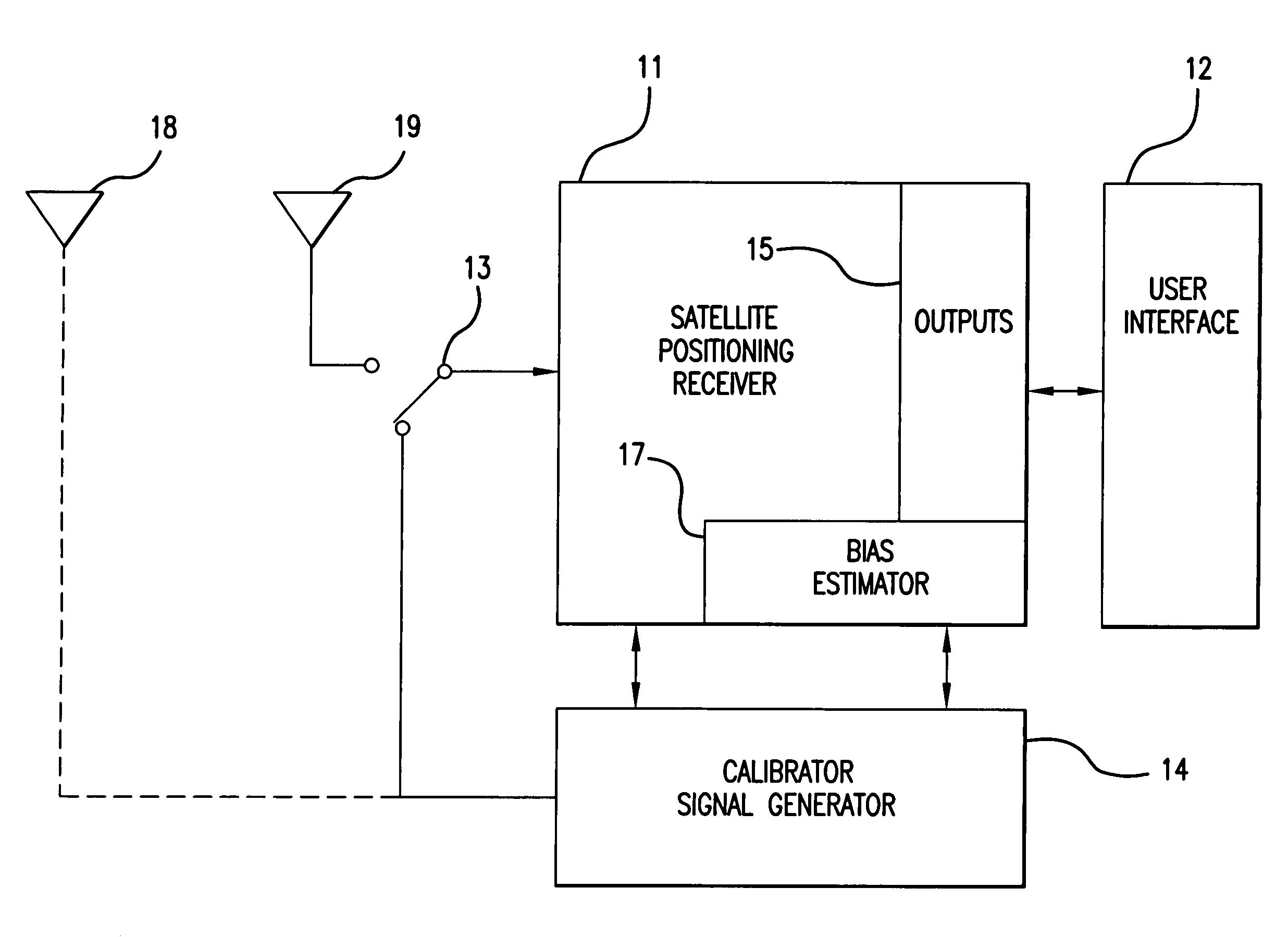
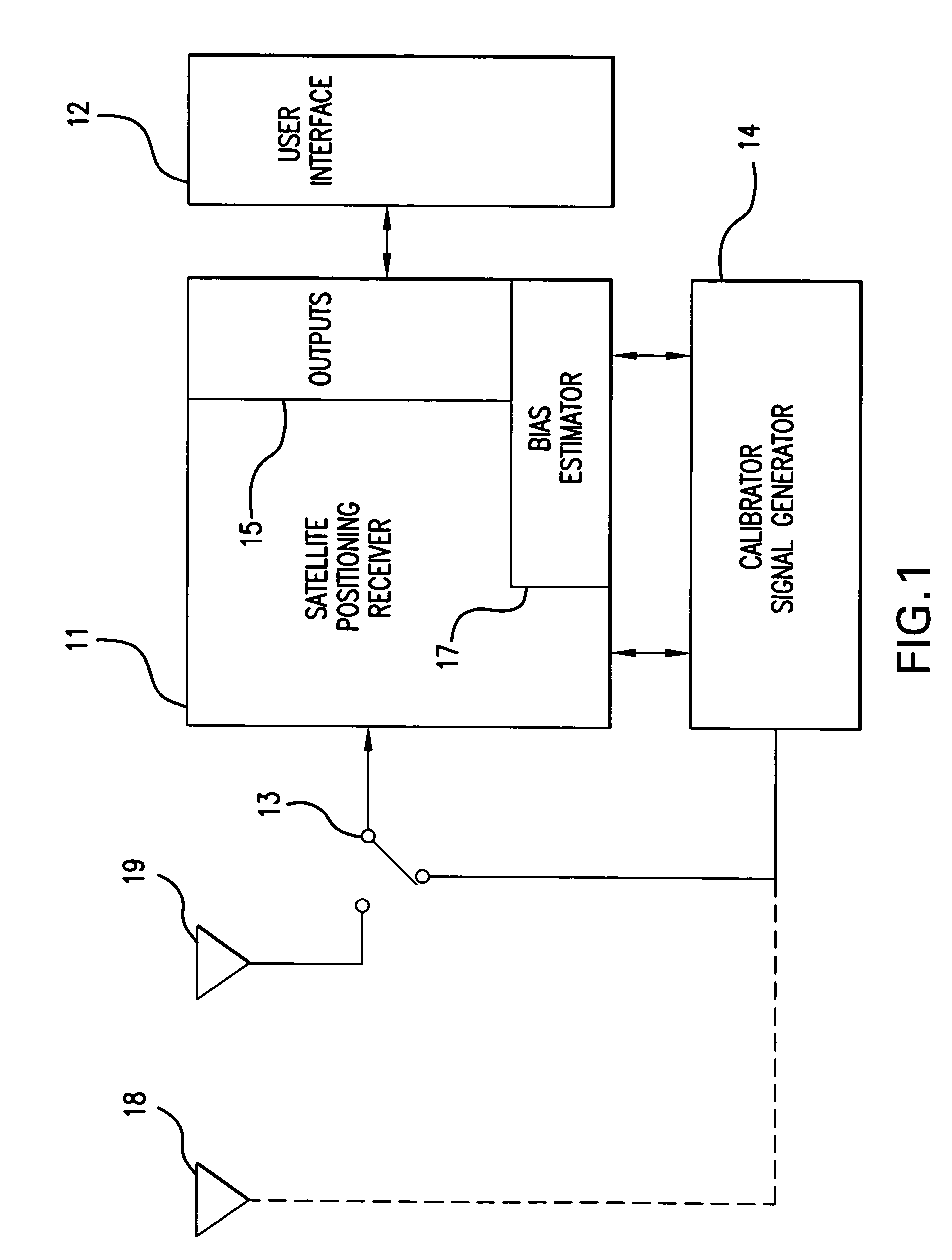
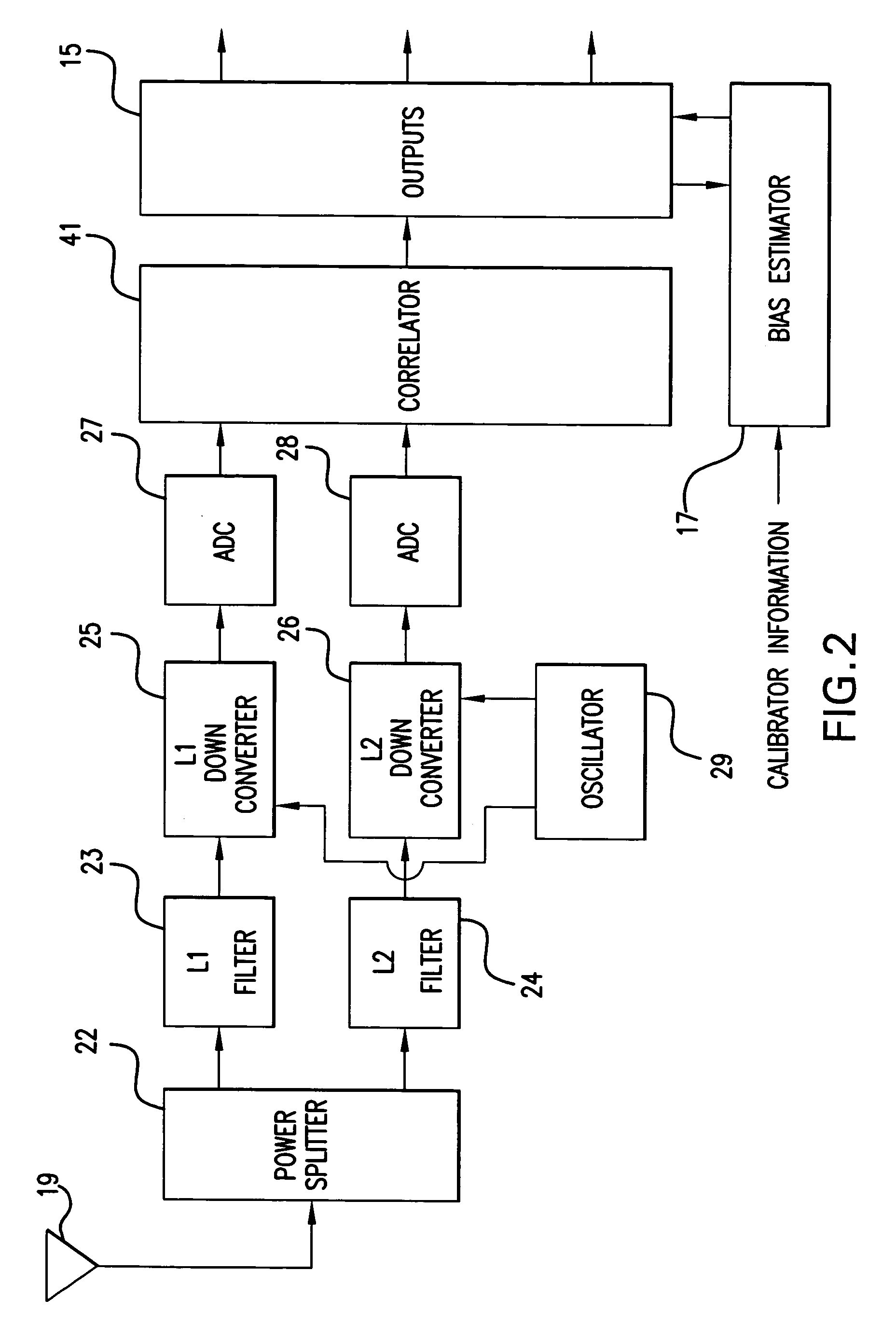
GPS receiver with calibrator
InactiveUS20070008216A1Improve accuracyGood estimatePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingTime delaysGps receiver
Calibrating a receiver for a satellite positioning system. At preset intervals, a plurality of calibration signals are generated and applied to the receiver. The plurality of calibration signals correspond to a plurality of satellite signals, respectively, from the satellite positioning system. A relative time-delay bias from a delay estimation algorithm within the receiver. The time-delay bias is stored, preferably with the receiver. The receiver receives the plurality of satellite signals from the satellite positioning system. The plurality of satellite signals are processed with the time-delay bias. The processing reduces effects from the satellite receiver and improving estimate of the differential delay and total electron content (TEC).
Owner:CENT FOR REMOTE SENSING
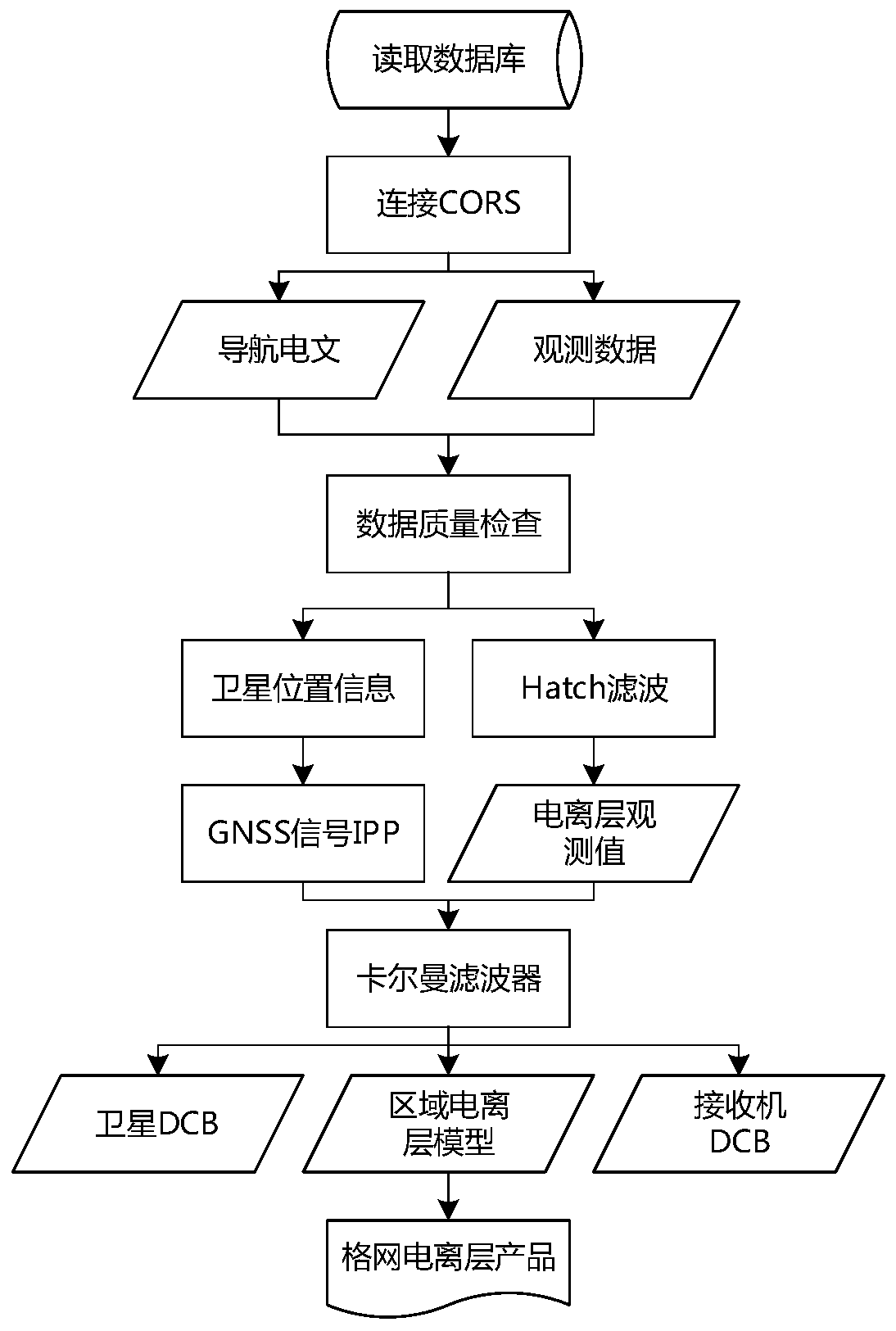
Real-time ionosphere modeling and monitoring method based on regional CORS
InactiveCN109828288AHigh positioning accuracyFaster convergence timeSatellite radio beaconingSimulationCarrier signal
The invention discloses a real-time ionosphere modeling and monitoring method based on a regional CORS (Continuous Operational Reference System). The method comprises the steps of: receiving originaldual-frequency observation data and a navigation message of a regional CORS station, rejecting a gross error, and then calculating a satellite position, an elevation angle and latitudes and longitudesof a puncture point; employing the Hatch filtering method and employing a carrier smooth pseudo-range observation value for differencing to obtain a TEC (Total Electron Contents) observation value without a geometric ionosphere; employing a spherical ion function to simulate the TEC distribution of the regional ionosphere, taking the model parameters and the satellite and the receiver differential code deviation as parameters to be estimated, constructing observation vectors by employing the observation data of all CORS stations of the single epoch to construct an observation equation; establishing a Kalman filter to perform real-time filtering processing for the parameters to be estimated, and separating from hardware delay to obtain an ionosphere TEC model; and finally, employing a model to calculate the grid point ionosphere delay, and storing and broadcasting the grid point ionosphere delay to regional users in a grid form. After an ionosphere product is obtained, a regional single-frequency PPP user location precision is obviously improved, and the dual-frequency PPP user convergence time is significantly improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for determining regional ionospheric layer delay
InactiveCN103455702AHigh precisionHigh degree of fitSpecial data processing applicationsNerve networkService provision
The invention discloses a method for determining regional ionospheric layer delay. The method includes: collecting data; firstly establishing a regional ionospheric second-order term model according to the collected regional ionospheric VTEC (vertical total electron content) data; establishing a VTEC second-order term model and a fusion model of a neural network; adopting the fusion model to calculate VTEC values of puncture points of other positions in this area. By the method, computed results of the regional ionospheric layer delay are high in precision, and CORS (continuous operational reference system) measured results are wide in application range. A large number of engineering example application result analysis shows that precision of the computed results by the method is improved by 40% as compared to that by the VTEC second-order term model. Ionospheric layer space activity rules are high in fitting degree and high in timeliness, and convenience in use is brought. The ionospheric layer space activity rules can be obtained through analyzing according to fitting results of the neutral network, the ionospheric layer delay in any point in the area can be rapidly corrected, transmission precision and stability of radio waves can be improved, and technical support for better service for CORS can be provided.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
GNSS ionization layer delay precise modeling method suitable for Chinese region
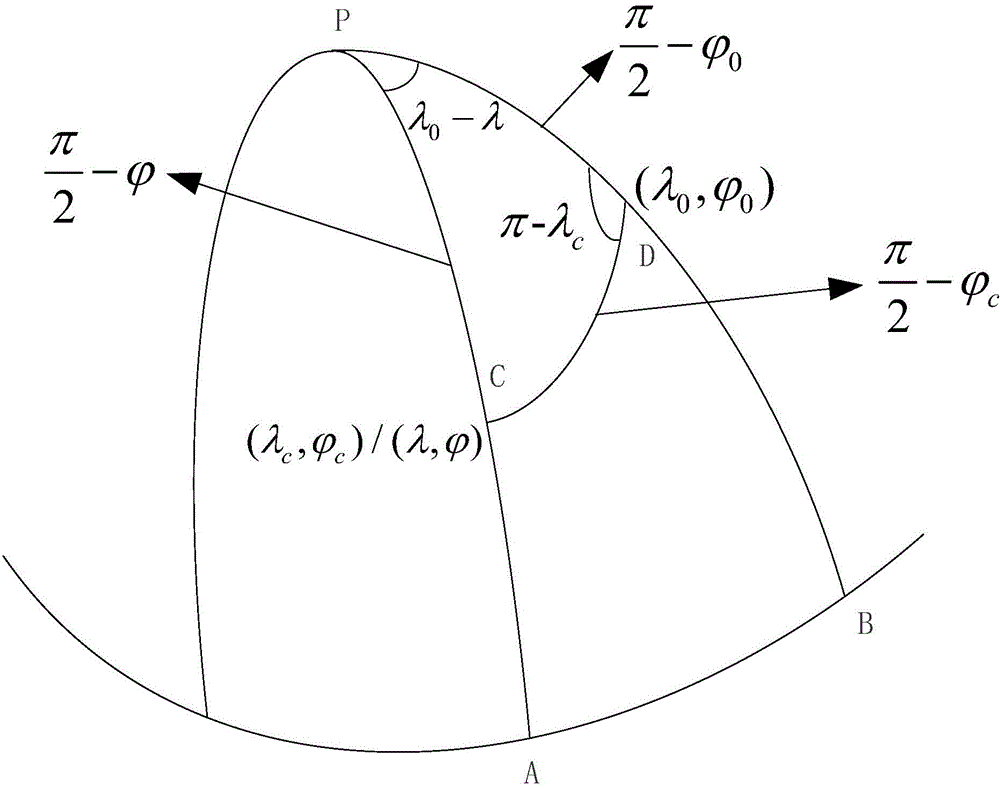
ActiveCN104101888APrevent morbidityAvoid non-integer orderSatellite radio beaconingLongitudeTotal electron content
The invention discloses a GNSS ionization layer delay precise modeling method suitable for a Chinese region. The geographical coordinates of the latitude and the longitude of a cross point are converted into coordinates under an established spherical crown coordinate system, so as to acquire the range of the latitude and the longitude of the cross point under the spherical crown coordinate system. The change range of the latitude and the longitude of the cross point is projected and converted into a global coordinate system. A spherical harmonic function is used to establish a regional ionization layer total electron content (TEC) model. The ionization layer delay precise modeling method suitable for the Chinese region is constructed. Compared with the existing method, the method provided by the invention has the advantages that through rotation projection and conversion, the distribution of the ionization layer cross point meets the requirement of the spherical harmonic function on physical quantity distribution in the form; ill-conditioned problems are solved when the spherical harmonic function is applied to regional modeling; the precise describing ability of the spherical harmonic function for global change physical quantity is effectively used; non-integral order in a spherical crown harmonic function is avoided; and the complexity of ionization layer TEC modeling calculation is reduced.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical module for wide temperature range and working temperature adjusting method thereof
ActiveCN103281132ASave compensation power consumptionReduce BIAS currentFibre transmissionSemiconductor lasersOptical ModuleThermodynamics
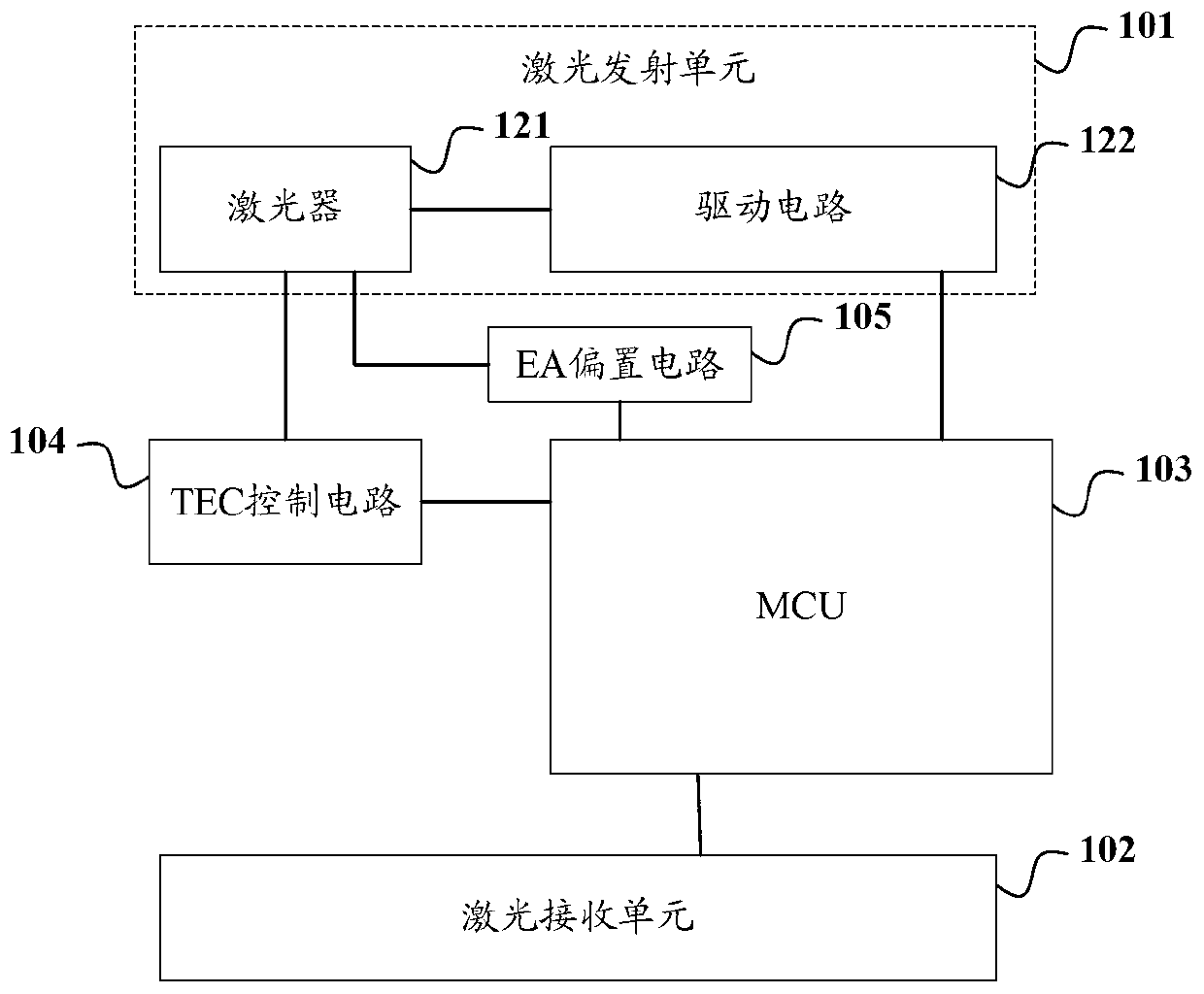
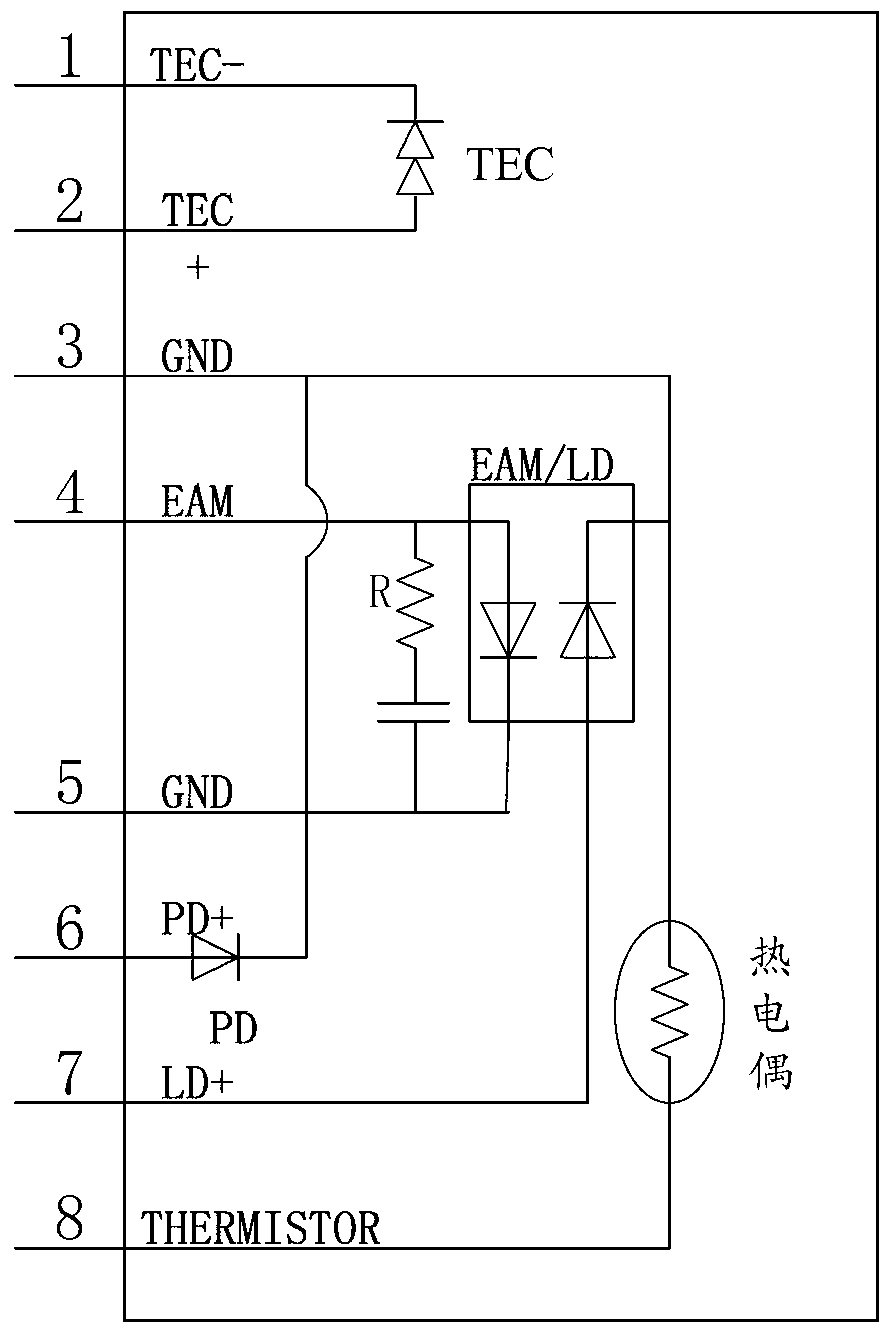
The invention discloses an optical module for a wide temperature range and a working temperature adjusting method thereof. The optical module comprises a laser transmitting unit, an MCU (microprogrammed control unit) and a TEC (total electron content) control circuit, wherein the laser transmitting unit comprises a laser and a drive circuit; the optical power of the laser is previously calibrated to the specific optical power range; the MCU is used for determining the working temperature setting value corresponding to the acquired temperature value after acquiring the temperature value detected by a temperature sensor; and the TEC control circuit is controlled to adjust the working temperature of the laser at the corresponding temperature according to the determined working temperature setting value. Since the working temperature of the laser is allowed to be changed along with the ambient temperature within a given temperature range, the heating or refrigerating power consumption can be reduced; and moreover, the optical power is previously calibrated to the appropriate range, so that the optical power can still meet the requirement within the variation range of the working temperature of the laser, the bias current is unnecessary to compensate, and the compensation power consumption can be further saved.
Owner:HISENSE BROADBAND MULTIMEDIA TECH
Ionosphere TEC (Total Electron Content) anomaly detection method
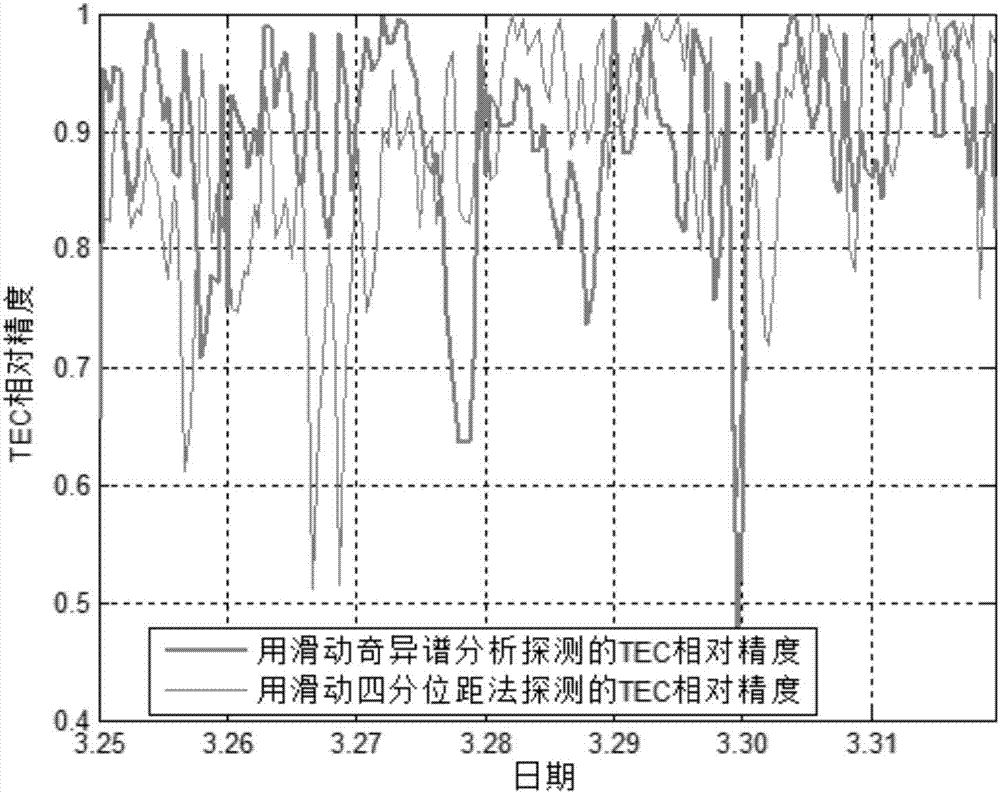
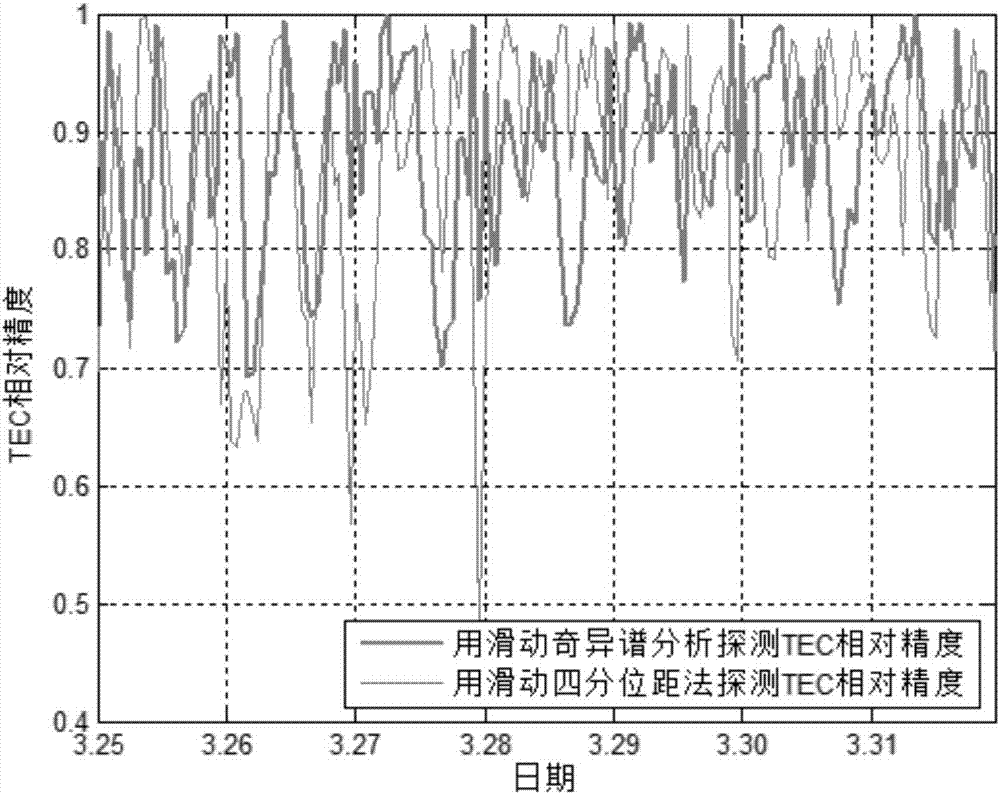
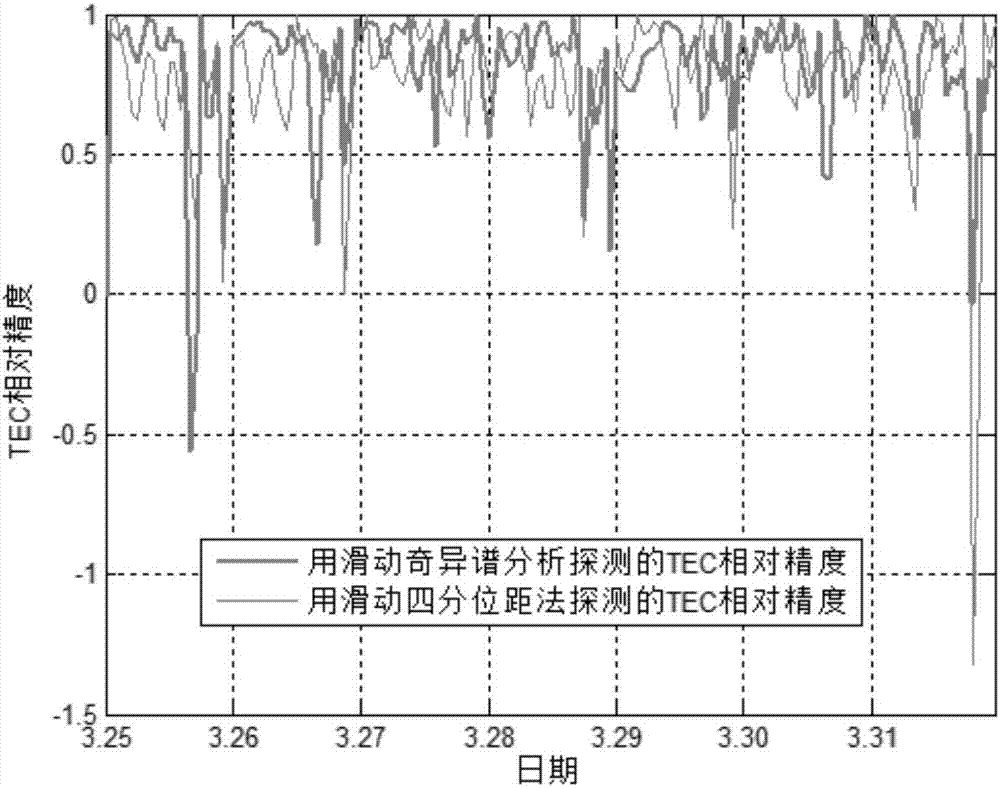
ActiveCN107356979ASimple and fast operationHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionElectric/magnetic detectionLower limitSingular spectrum analysis
The invention discloses an ionosphere TEC (Total Electron Content) anomaly detection method, which mainly comprises the steps of forming an ionosphere TEC time sequence, performing decomposition and reconstruction by using SSA calculate a background value, adopting a sliding quartile range method for an absolute value of the difference of the background value and an observed value to calculate a tolerance value at each moment of the detection day, and thus calculating an upper limit value and a lower limit value of the detection day. Singular spectrum analysis is adopted and slides day by day to calculate ionosphere TEC anomalies on the other days. The ionosphere TEC anomaly detection method performs ionosphere IEC anomaly detection based on a sliding singular spectrum analysis method, not only considers the background value of the ionosphere TEC at the detection moment, but also applies the traditional sliding quartile range method to the absolute value of the difference of the time sequence observed value and the background value to calculate the upper limit value and the lower limit value at each moment of the detection day, so that the accuracy and precision of an ionosphere TEC anomaly detection result are greatly improved by using robust statistical mathematical features of the sliding quartile range method, and the ionosphere TEC anomaly detection method has a characteristic of being universal.
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
Method for analyzing influences of background ionosphere on GEO SAR imaging
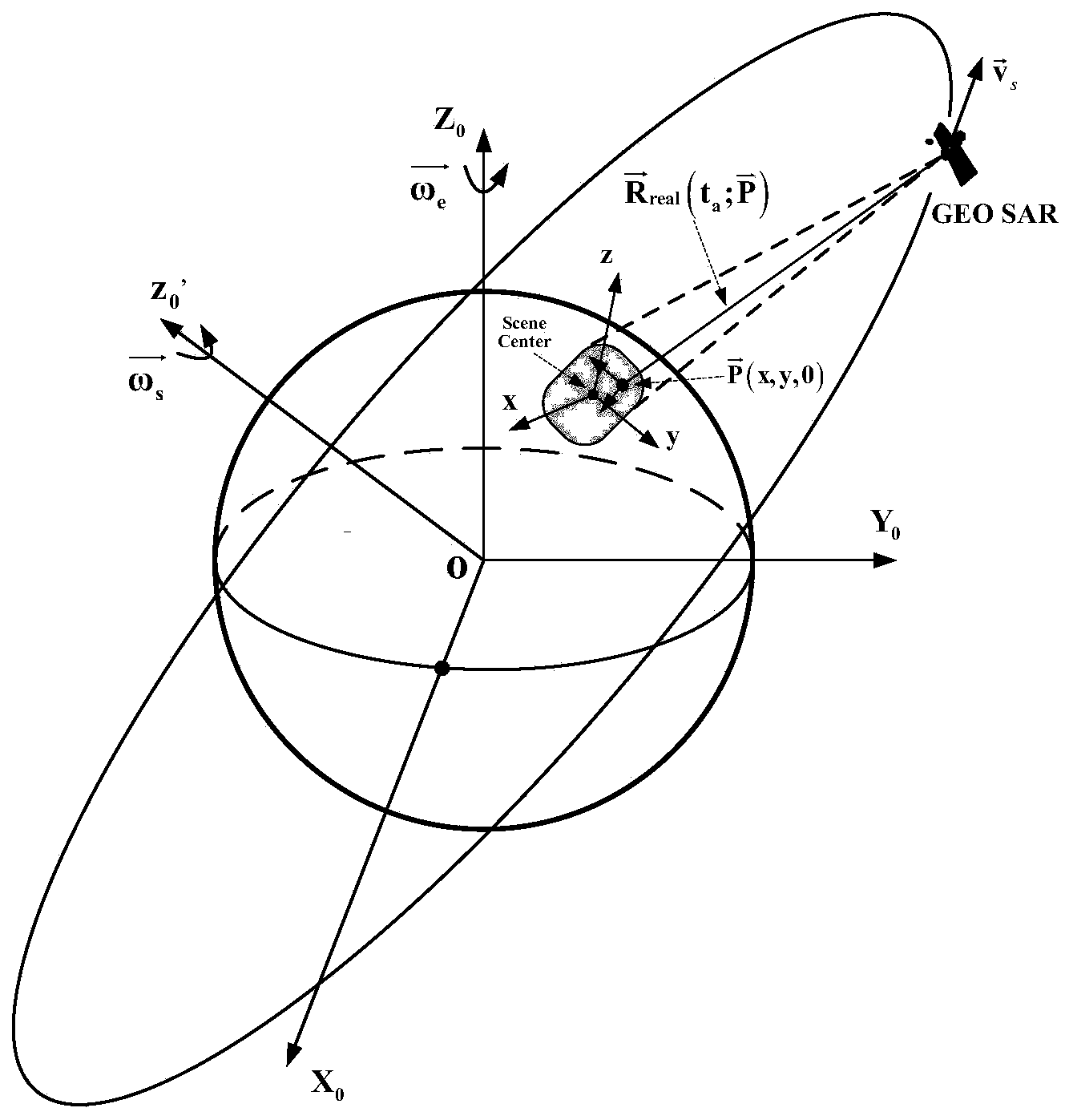
ActiveCN103675775AAccurate modelingImprove analytical accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImaging analysisIonosphere
The invention discloses a method for analyzing influences of a background ionosphere on GEO SAR imaging. The method includes the steps that a GEO SAR echo signal model influenced by a time-varying ionosphere is established, image offset and defocusing phase which are used for analyzing influences on imaging are derived on the basis of the model, and then judgment of the influences on imaging is performed; during analysis, GEO SAR echo signals influenced by the time-varying ionosphere and the measuring data of the ionosphere total electron content TEC on the propagation paths of the GEO SAR signals are obtained, polynomial fitting is performed on the TEC measuring data three times, a constant term and coefficients of first three items are obtained, echo signal parameters and TEC coefficients are substituted into a derived expression of the image offset and the defocusing phase, and compared with a threshold value, the influences of the background ionosphere on GEO SAR imaging are obtained. According to the method, modeling is performed specifically and is accurate, and imaging analysis is performed on the basis of the accurate model so that the analysis accuracy can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Ionospheric slant total electron content analysis using global positioning system based estimation
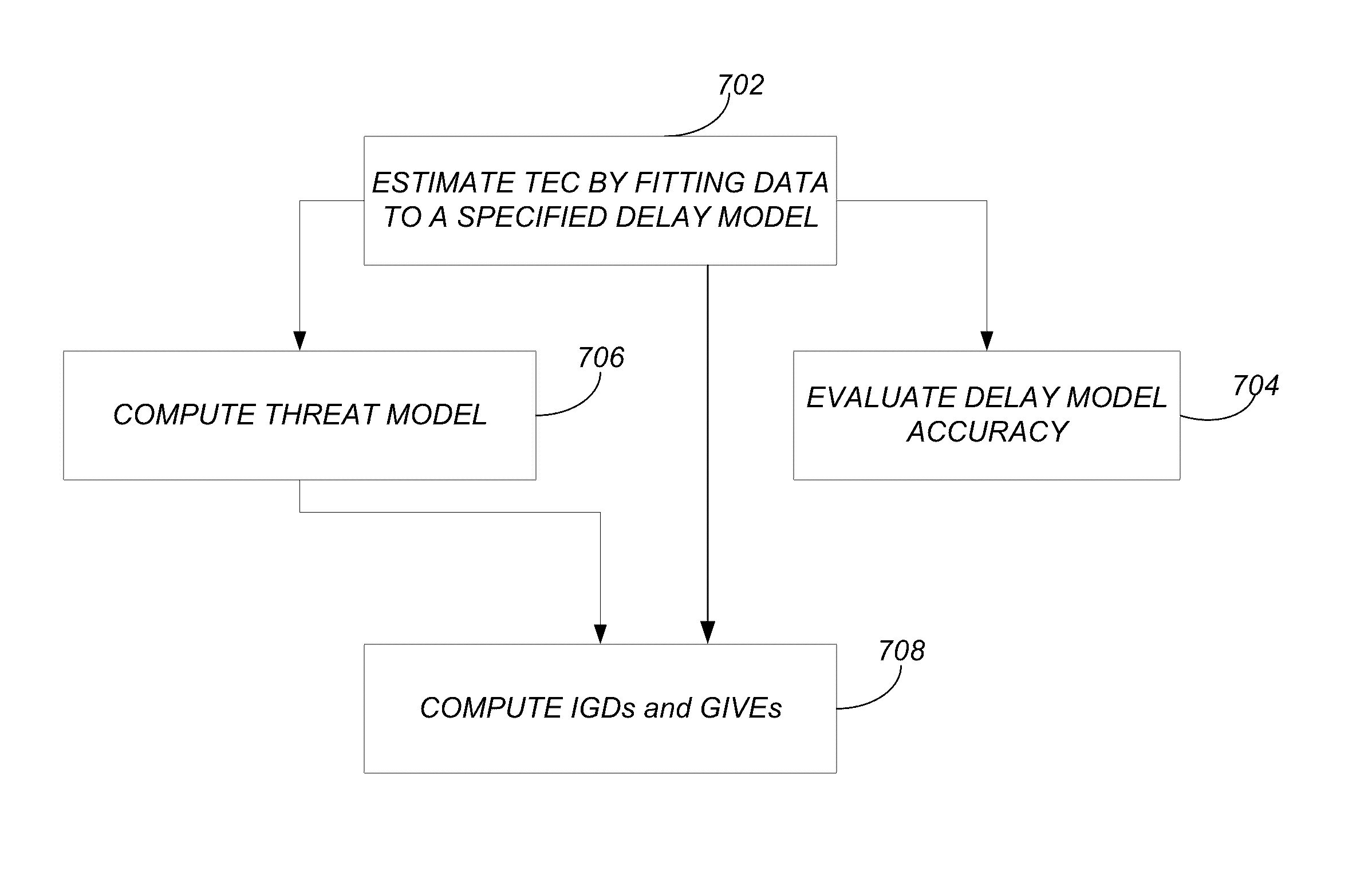
ActiveUS20140163938A1Irregularity may varyImproving WAAS availabilityComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationTotal electron contentIonospheric heater
A method, system, apparatus, and computer program product provide the ability to analyze ionospheric slant total electron content (TEC) using global navigation satellite systems (GNSS)-based estimation. Slant TEC is estimated for a given set of raypath geometries by fitting historical GNSS data to a specified delay model. The accuracy of the specified delay model is estimated by computing delay estimate residuals and plotting a behavior of the delay estimate residuals. An ionospheric threat model is computed based on the specified delay model. Ionospheric grid delays (IGDs) and grid ionospheric vertical errors (GIVEs) are computed based on the ionospheric threat model.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
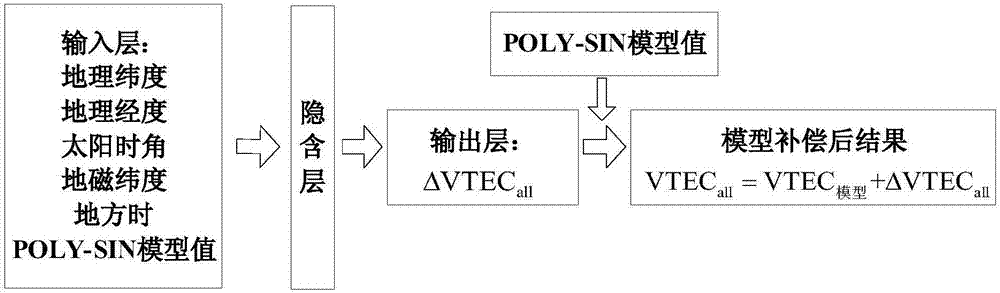
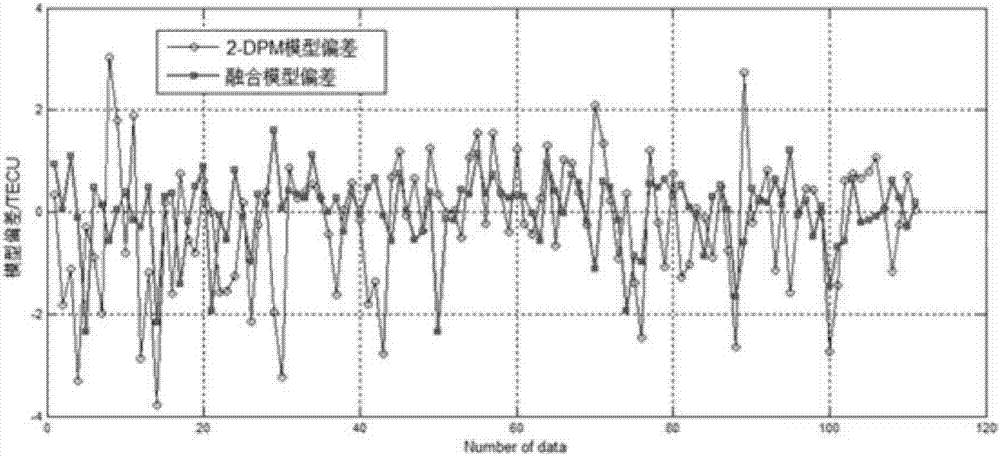
BP-polynomial model fusion-based regional ionized layer vertical total electron content modeling method
InactiveCN107085626AAvoid errorsHigh precisionBiological neural network modelsDesign optimisation/simulationObservation pointLongitude
The invention discloses a BP-polynomial model fusion-based regional ionized layer vertical total electron content modeling method. The method comprises the following steps of S1, obtaining puncture point geographic longitude and latitude information and ionized layer vertical total electron content information of a regional observation point, and converting obtained data to obtain a solar hour angle difference, geomagnetic latitude and local time information; S2, building a polynomial model and performing modeling on the ionized layer vertical total electron content information, thereby obtaining a polynomial model value and a corresponding model residual error value; S3, building a BP neural network error compensation model; and S4, forecasting ionized layer vertical total electron content residual errors fitted by the polynomial model by utilizing the BP neural network error compensation model, thereby compensating the polynomial model. According to the method, the problem of model errors in a conventional polynomial model can be solved; the precision of regional ionized layer vertical total electron content modeling can be improved; and the stability is high.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
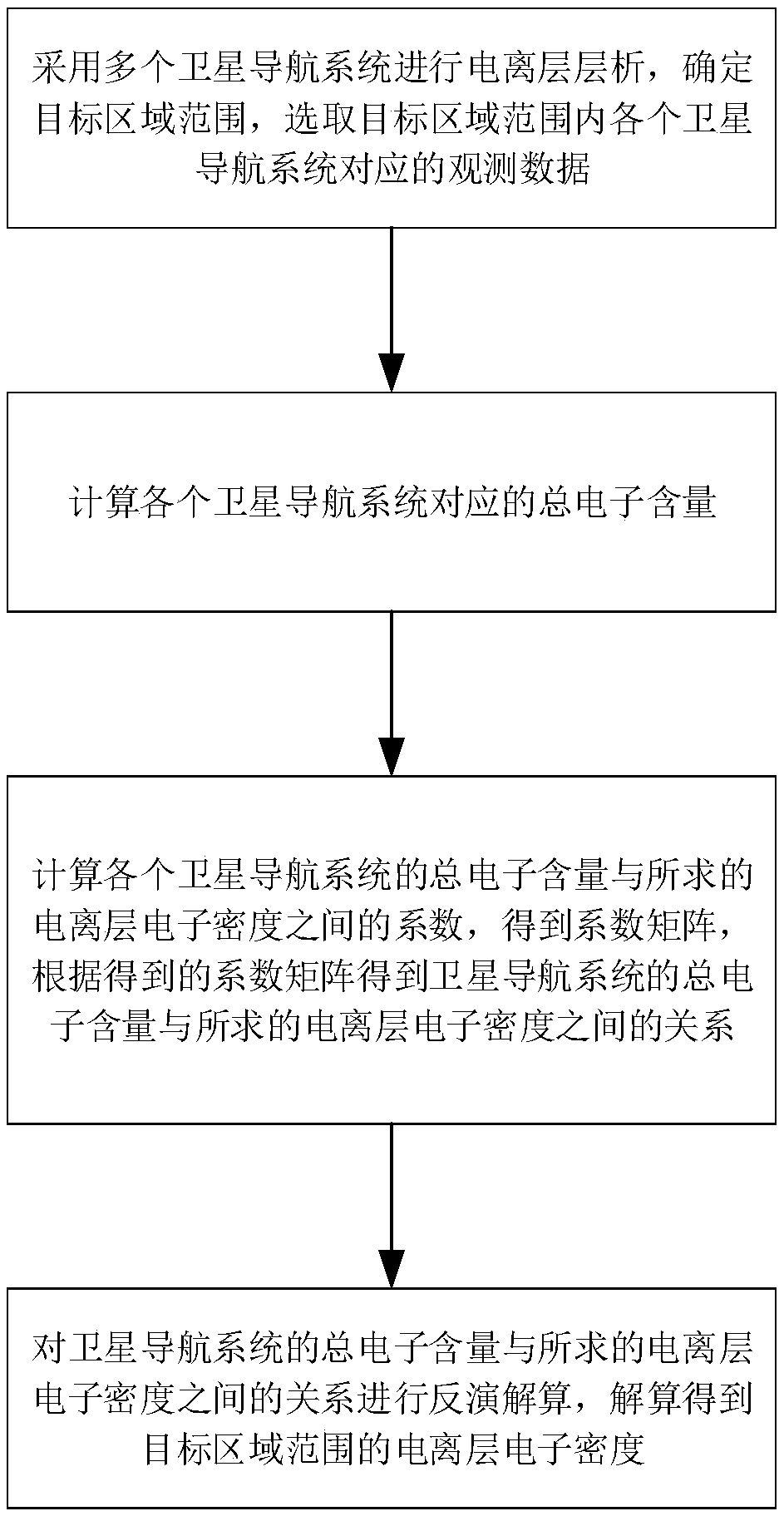
Ionized layer chromatography method and system based on multi-constellation GNSSs
InactiveCN109613565AImprove reliabilityHigh precisionSatellite radio beaconingObservation dataIonosphere
The invention relates to an ionized layer chromatography method and system based on multi-constellation GNSSs. The ionized layer chromatography method comprises the steps that multiple satellite navigation systems are adopted to carry out the ionized layer chromatography, firstly, an object region range is determined, observation data corresponding to all the satellite navigation systems within the object region range are selected; then total electron content corresponding to all the satellite navigation systems is calculated, and the relation between the total electron content of the satellite navigation systems and desired ionized layer electron density is obtained; and finally, the relation between the total electron content of the satellite navigation systems and the desired ionized layer electron density is subjected to inversion calculation, and the ionized layer electron density of the object region range is obtained by the calculation. The ionized layer chromatography operationis carried out through multiple different satellite navigation systems, and compared with an existing operation which is carried out only through one kind of satellite navigation systems, the accuracy of the ionized layer electron density obtained by the inversion is improved greatly, and the reliability of the ionized layer chromatography method is improved equally.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU
GPS receiver with calibrator
InactiveUS7221313B2Improve accuracyGood estimateBeacon systemsSatellite radio beaconingTime delaysGps receiver
Calibrating a receiver for a satellite positioning system. At preset intervals, a plurality of calibration signals are generated and applied to the receiver. The plurality of calibration signals correspond to a plurality of satellite signals, respectively, from the satellite positioning system. A relative time-delay bias from a delay estimation algorithm within the receiver. The time-delay bias is stored, preferably with the receiver. The receiver receives the plurality of satellite signals from the satellite positioning system. The plurality of satellite signals are processed with the time-delay bias. The processing reduces effects from the satellite receiver and improving estimate of the differential delay and total electron content (TEC).
Owner:CENT FOR REMOTE SENSING
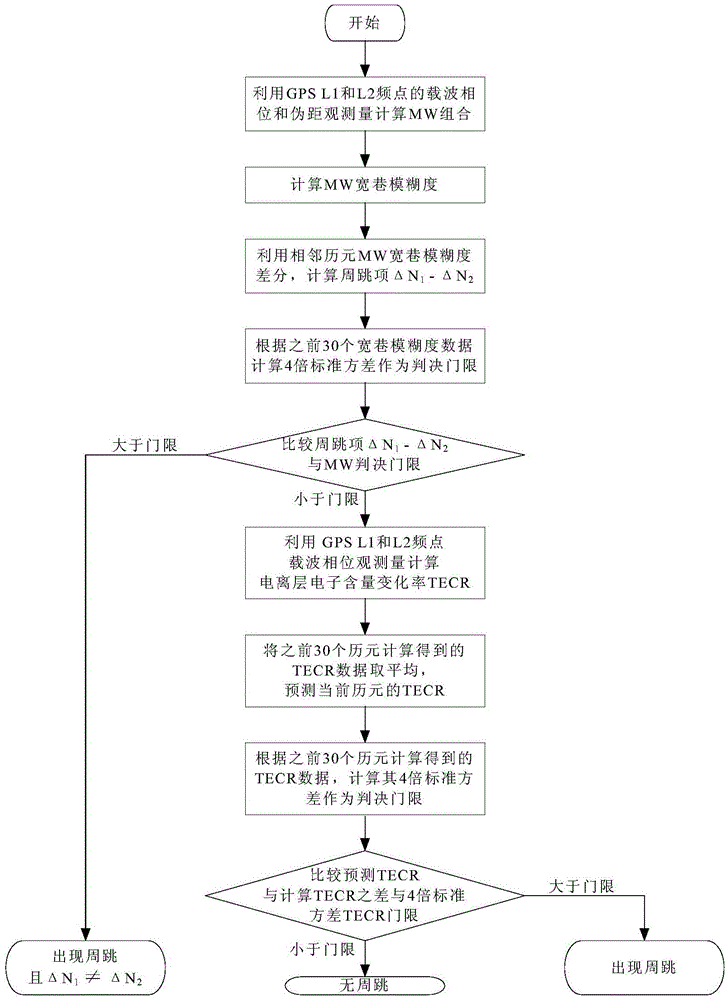
Detection method of real-time GPS (Global Position System) carrier phase cycle slip for frequency taming
InactiveCN104570013AReliable and convenient real-time dual-frequency carrier phase detectionImprove real-time performanceSatellite radio beaconingAmbiguityIonosphere
The invention discloses a detection method of real-time GPS (Global Position System) carrier phase cycle slip for frequency taming. The detection method comprises the following steps: S1, calculating an observed value of an MW (Melbourne-Wubbena) wide lane combination, S2, estimating ambiguity of an MW wide lane, S3, calculating a cycle slip decision item, S4, calculating a cycle slip decision threshold, judging whether the cycle slip decision item exceeds the cycle slip decision threshold, and moving to Step S5 if not, S5, calculating an electron content change rate of an ionized layer of an epoch (k), S6, predicting TECR (Total Electron Content Change Rate) value of the epoch (k) according to history data, and S7, calculating a detection threshold of a TECR method, calculating the difference between a calculated value and a predicted value of the epoch (k), and judging whether the detection threshold of the TECR method is exceeded. The method is combined with a constraint condition limitation that the total electron content change rate of the ionized layer is limited in a short period, shows the same cycle slip on L1 and L2 frequency points via linear combination of a carrier phase observation equation, and covers the shortage of an MW method.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF RADIO METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT
Method for correcting ionosphere error, and system and method for determining precision orbit using the same
InactiveUS7840351B2Eliminate errorsAccurately determinePosition fixationNavigation instrumentsOne passHigh elevation
Provided is a method of correcting an ionosphere error, a system of a precise orbit determination using the same and a method thereof. The method includes the steps of: a) determining a time of a highest elevation angle of a GPS satellite per one pass of each GPS satellite received at a LEO satellite or a receiver on a ground; b) determining a minimum total electron content found from an ionosphere model of the determined time per one pass of each GPS satellite; c) determining a total electron content directly calculated from the LEO satellite or a single frequency GPS data; d) determining an ionosphere error value of a single frequency GPS data by combining the minimum total electron content and the directly calculated total electron content; and e) correcting pseudorange data or carrier phase data based on the determined ionosphere error value.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method for calibrating long-wavelength satellite-borne CTLR-mode compact-polarized SAR
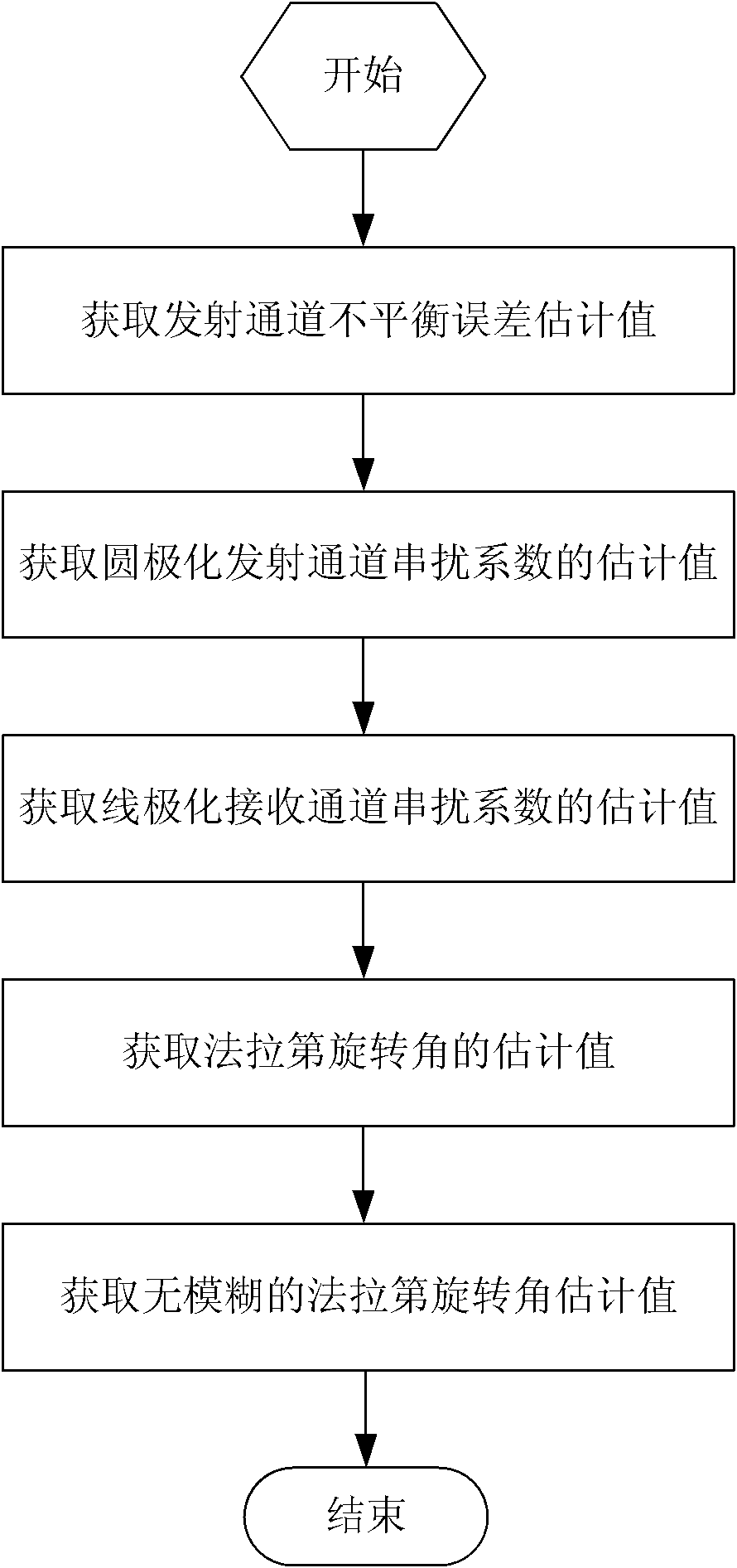
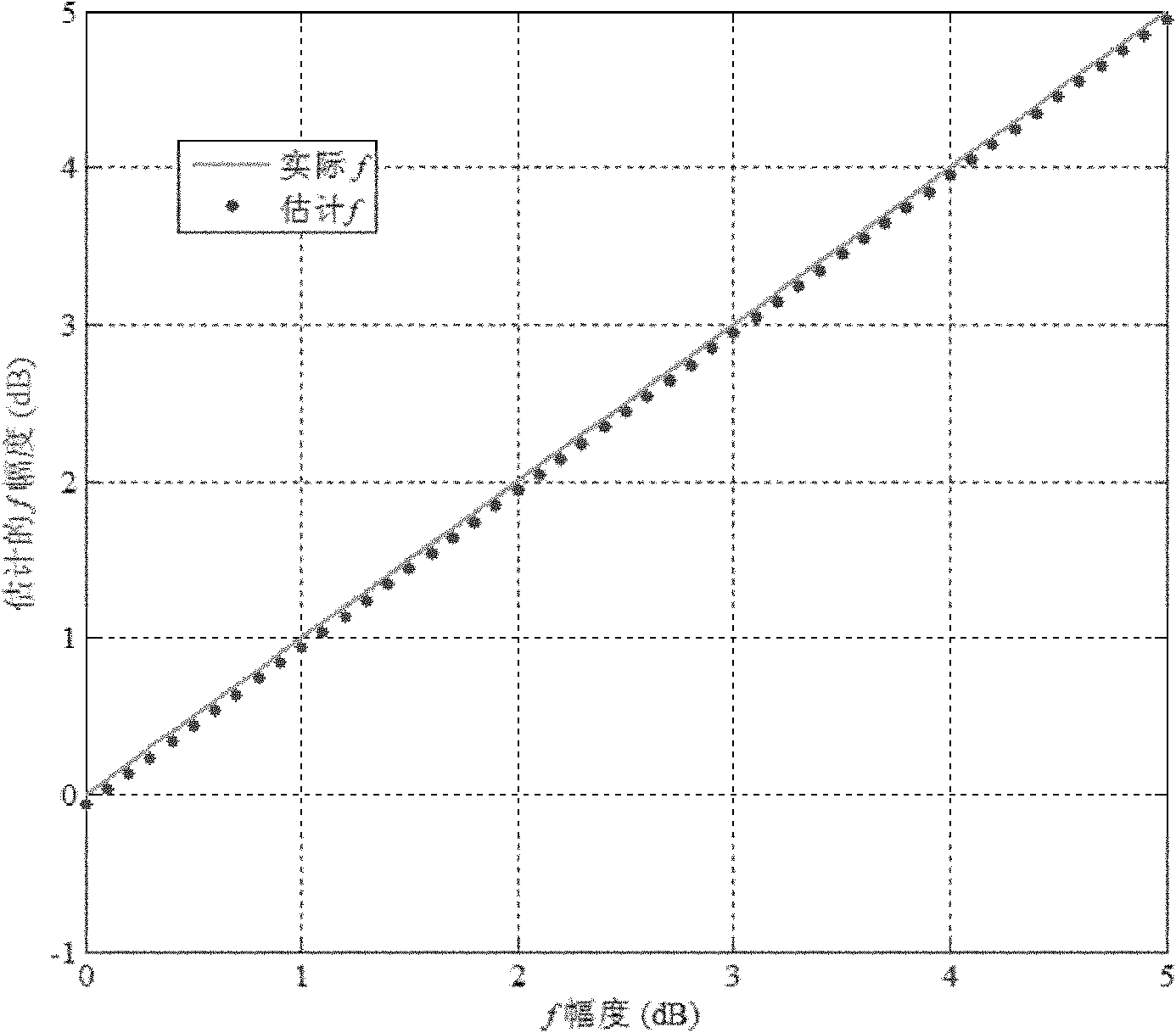
InactiveCN102183743AEasy to handleHigh precisionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTotal electron contentComputer science
The invention discloses a method for calibrating long-wavelength satellite-borne CTLR-mode compact-polarized SAR. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, acquiring an estimated value of an unbalanced error of a receiving channel; 2, acquiring an estimated value of a crosstalk coefficient of a circular-polarized transmitting channel; 3, acquiring an estimated value of a crosstalk coefficient of a linear-polarized receiving channel; 4, acquiring an estimated value of a Faraday rotation angle; and 5, acquiring an unambiguous estimated value of the Faraday rotation angle by using total electron content (TEC) data of a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) to finish SAR calibration. By the method, the processing process is simple and the processing precision is high; and the application of the method in processing of the long-wavelength satellite-borne CTLR-mode compact-polarized SAR data represented by a P wave band is very important.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for forecasting ionospheric vertical total electron content based on time-series two-dimensionalization
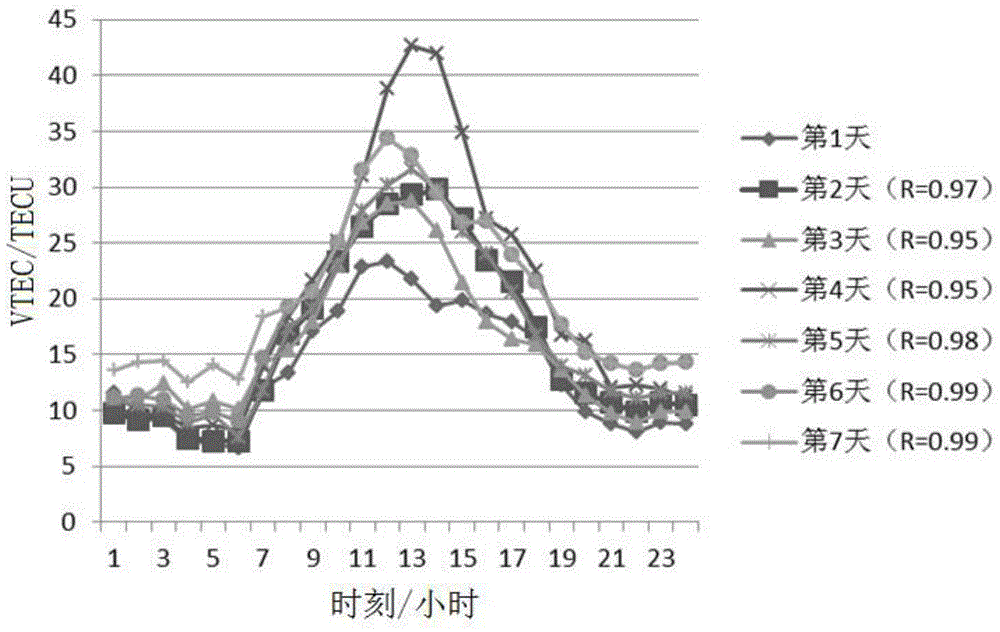
ActiveCN104992054AExcellent forecast effectFully excavatedBiological neural network modelsSpecial data processing applicationsIonosphereNetwork model
The present invention discloses a method for forecasting an ionospheric vertical total electron content based on time-series two-dimensionalization. The method comprises four steps: step S1, by means of known ionospheric vertical total electron content data, analyzing variation characteristics of the ionospheric vertical total electron content over time; step S2, establishing a time-series two-dimensionalization plane, determining a weight value between an ionospheric vertical total electron content to be forecast and the known ionospheric vertical total electron content, and according to the weight value, performing weighting processing on the known ionospheric vertical total electron content data that is to be used as an input layer; step S3, establishing a neural network model; and step S4, by using the neural network model, forecasting the ionospheric vertical total electron content. According to the invention, by performing time-series two-dimensionalization processing on the ionospheric vertical total electron content and by setting different weight values, a good forecast of ionospheric vertical total electron content can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
GNSS base band signal processing method for monitoring total electron content of ionized layer
ActiveCN103592672AEliminate DynamicsReduce signal noiseX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentDiscriminatorIonosphere
The invention provides a GNSS base band signal processing method for monitoring the total electron content of the ionized layer. The method for monitoring the TEC of the ionized layer through GNSS double-frequency carrier signals is based on the application characteristics of the GNSS in the field of monitoring the TEC of the ionized layer, addition and subtraction are performed on carrier tracking loop phase discriminators of the GNSS double-frequency signals, and tracking loops of the double-frequency carrier signals are coupled, so that mutual assistance between the double-frequency signal carrier tracking loops is achieved; moreover, code loops are smoothed through differential loop output conversion values of the tracking loops to output the calculated TEC of the ionized layer, and thus the high-precision and high-accuracy value of the TEC of the ionized layer can be obtained. With the GNSS base band signal processing method for monitoring the total electron content of the ionized layer, the precision for monitoring the TECA of the ionized layer can be effectively improved, and effects of cycle slip on the monitored value of the TEC of the ionized layer can be avoided due to the mutual assistance between the double-frequency signals; due to the mutual assistance between the double-frequency signal carrier tracking loops, the double-frequency carrier tracking loops can be assisted mutually by loop tracking information of each other, and thus the tracking sensitivity of the double-frequency signals can be improved.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
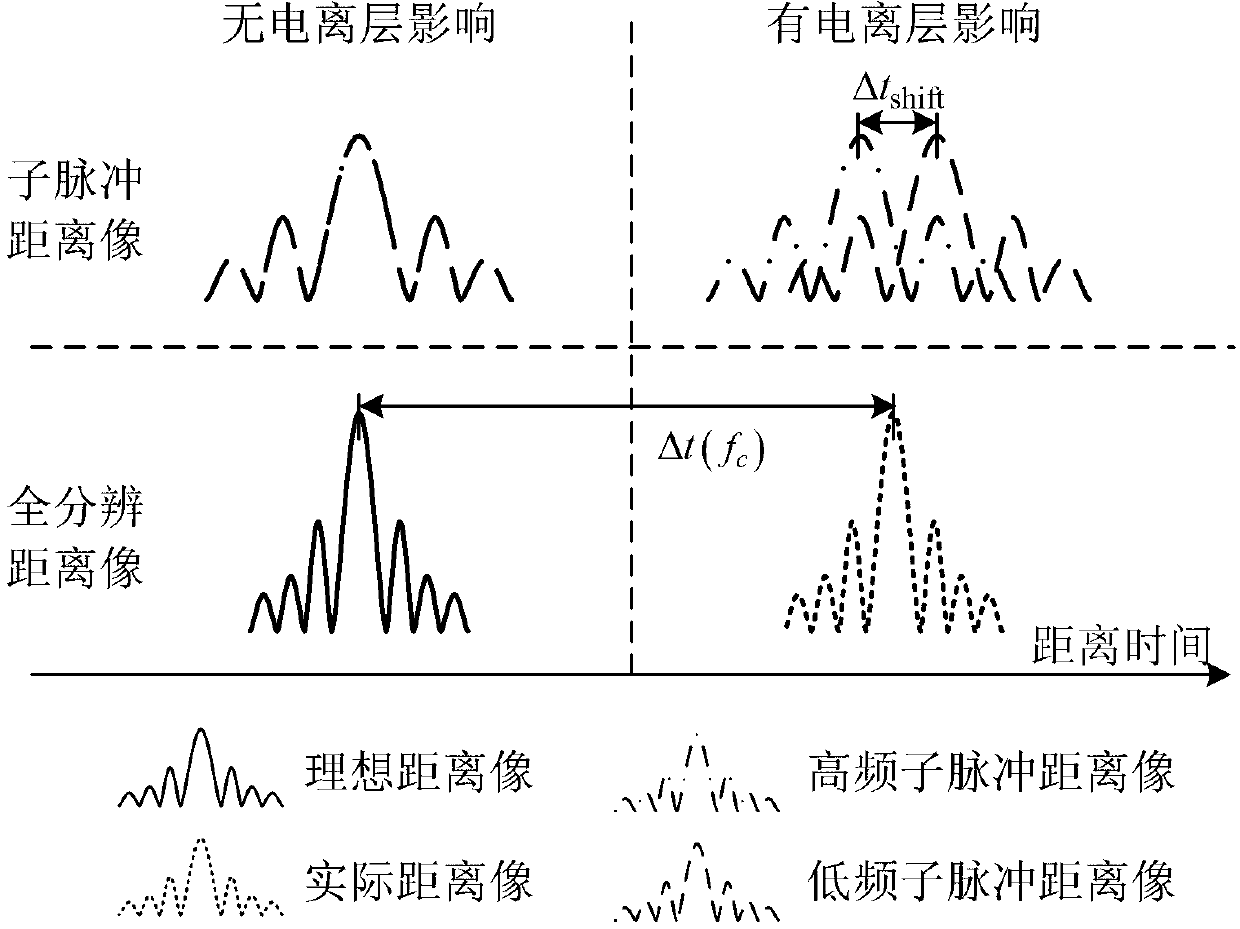
Sub-range profile offset deviation-based satellite borne SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) ionosphere calibration method
ActiveCN103217669AImprove signal-to-noise ratioReduce noiseRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarMutual correlation
The invention provides a sub-range profile offset deviation-based satellite borne SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) ionosphere calibration method, which eliminates the limitation to a sampling rate while eliminating the influence of a non-ideal matrix envelope and improves the robustness of ionosphere TEC (Total Electron Content) measuring accuracy. The method comprises the following steps: 1, decomposing a strong scattering point target signal or an active calibrator signal into two upper and lower sub-band pulse signals by using a low-pass filter and a high-pass filter; 2, compressing distance of the upper and lower sub-band pulse signals; 3, mutually correlating upper and lower sub-range profile envelopes to obtain a normalized mutual correlation energy spectrum; and 4, extracting a phase spectrum of the normalized mutual correlation energy spectrum in the third step, obtaining an estimated value of delta t shift by estimating the slope for change of the phase along with frequency f, and further obtaining an estimated value of the ionosphere TEC, wherein the sub-range profile offset deviation generated by ionosphere is at a sub-pixel level, i.e., the delta t shift is less than 1 / fs, fs represents a radar sampling rate, and the phase wrapping of the normalized mutual correlation energy spectrum is avoided.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
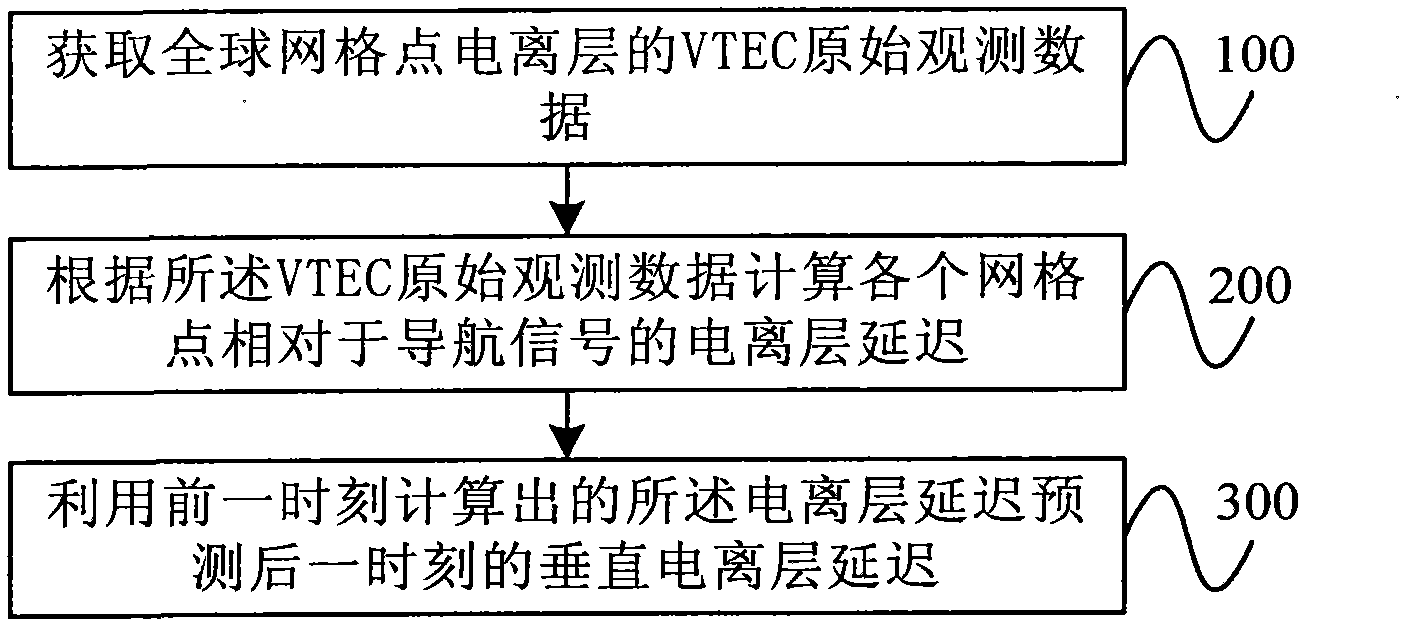
Forecasting method and device of ionospheric delay of satellite navigation
InactiveCN102520417AAchieve forecastGood forecastSatellite radio beaconingGlobal gridObservation data
The invention provides a forecasting method and a device of ionospheric delay of satellite navigation. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining VTEC (Vertical Total Electron Content) original observation data of ionospheres of global grid points; according to the VTEC original observation data, calculating ionospheric delay of each grid point relative to a navigation signal; and utilizing the calculated ionospheric delay in a former moment to forecast vertical ionospheric delay in a later moment. According to the method, forecast for the ionospheric delay is effectively realized, and a better forecasting effect is obtained. The calculation process is simple and is easily realized, and the method provides a new idea for forecasting the ionospheric delay.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Micro-flow method for measuring total nitrogen content of tobacco
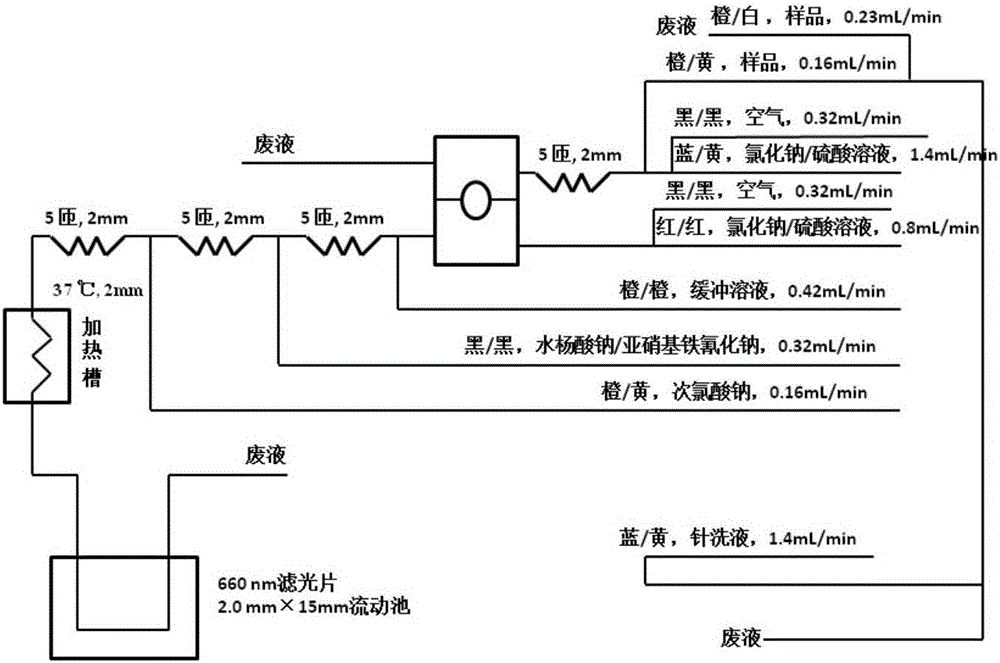
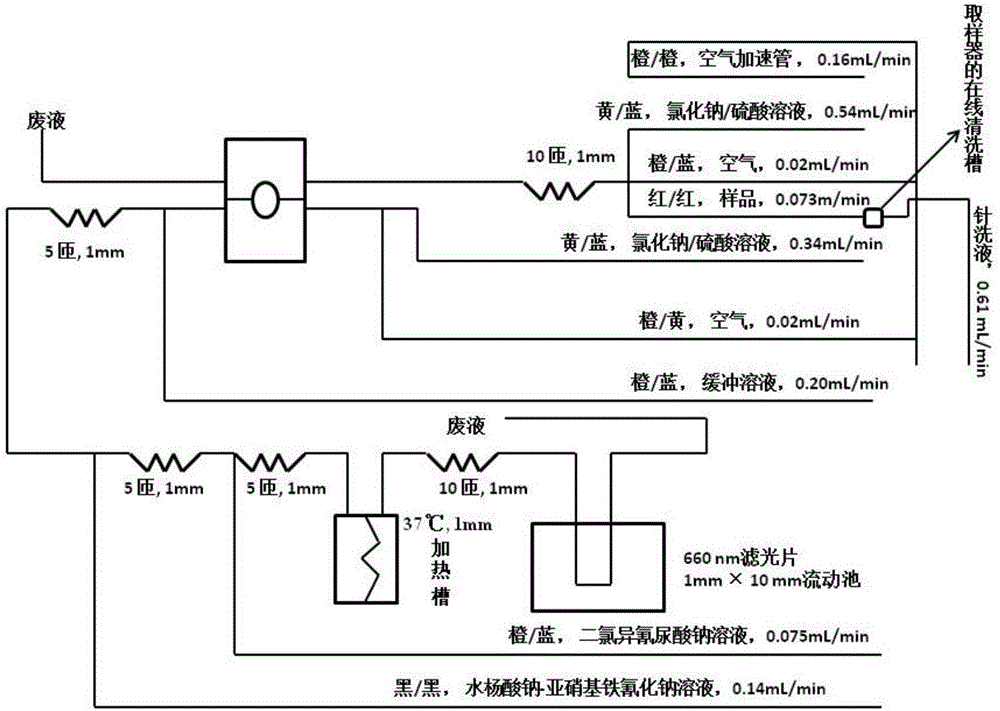
ActiveCN107179416AReduce dosageImprove performanceMaterial analysisContinuous flowTotal electron content
The invention discloses a micro-flow method for measuring total nitrogen content of tobacco. The flow path structure and process parameters of a conventional continuous flow analyzer are modified, including: arranging an air accelerating pipe, changing the inner diameter of a glass coil, changing the inner diameter and flow rate of a pump pipe and adopting a novel reagent preparation method, so that performance optimization is realized, and the using amount of the reagent is saved to the maximum extent. The method runs stably, and the problems of baseline raising, peak pattern drifting and the like do not occur after 60 cups of samples are fed at one time. The micro-flow method has the advantages of high analysis speed (60 samples per hour), high accuracy and high precision, contributes to reduction of reagent consumption, and is suitable for measuring total nitrogen in tobacco and tobacco products on a large scale.
Owner:YUNNAN TOBACCO QUALITY SUPERVISION MONITORING STATION
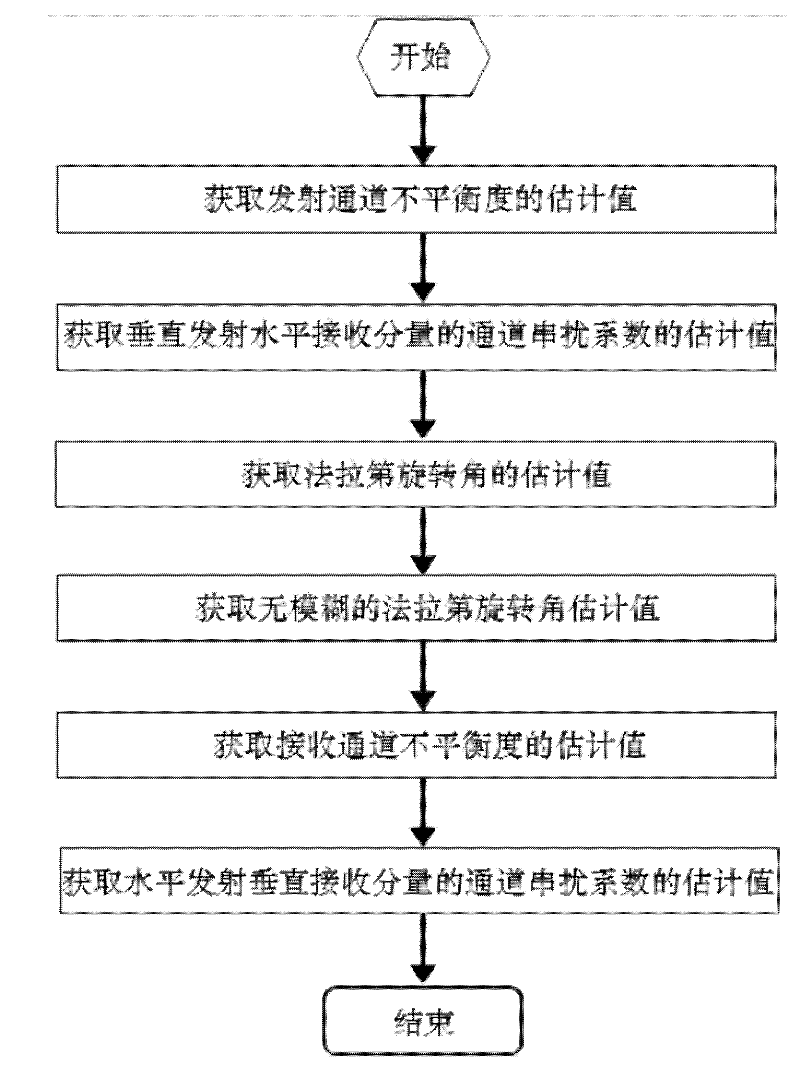
Method for calibrating compact polarimetric SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) in long wave-length spaceborne pi/4 mode
InactiveCN102253374AEasy to handleRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarTransmission channel
The invention discloses a method for calibrating a compact polarimetric SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) in a long wave-length spaceborne pi / 4 mode. The method comprises the following steps: 1, acquiring an estimation value of the degree of unbalancedness of a transmission channel; 2, acquiring an estimation value of a channel crosstalk coefficient of a vertical-launching horizontal-receiving component; 3, acquiring an estimation value of a Faraday rotation angle; 4, acquiring an estimation value of an unambiguous Faraday rotation angle by utilizing TEC (Total Electron Content) data provided bya global navigation satellite system; 5, acquiring an estimation value of the degree of unbalancedness of a receiving channel; and 6, acquiring an estimation value of a channel crosstalk coefficient of a horizontal-launching vertical-receiving component. By utilizing the method, accurate calibration still can be performed without scaler errors or system noise, and high-precision calibration can still be performed when the scaler errors and system noise exist. The method provided by the invention has important application value in processing the compact polarimetric SAR data in the long wave-length spaceborne pi / 4 mode represented by a P wave band.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
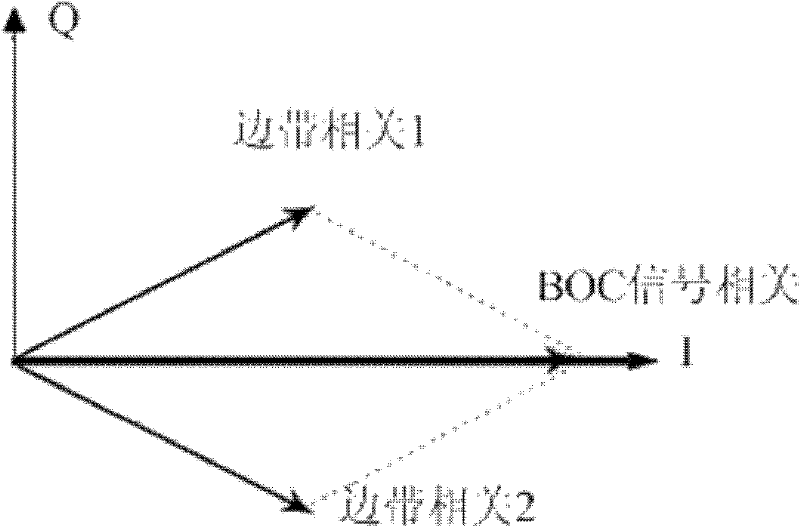
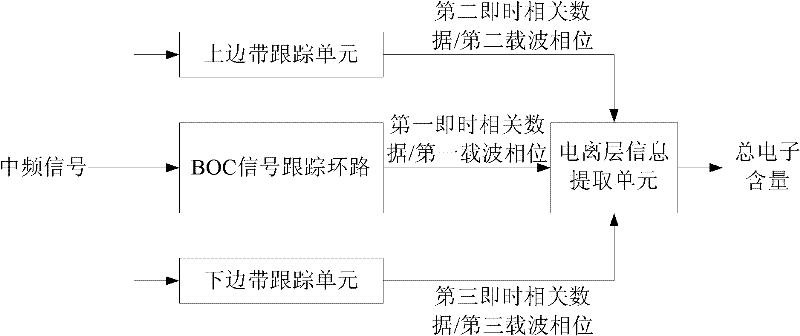
Ionized layer error estimation method and system for binary offset carrier (BOC) signal
ActiveCN102540215ARealize Error EstimationThe influence of multipath effect is smallSatellite radio beaconingIntermediate frequencyCarrier signal
The invention discloses an ionized layer error estimation method and an ionized layer error estimation system for a binary offset carrier (BOC) signal. The method comprises the following steps of: tracking pseudo-random noise codes, BOC subcarriers and carrier phases of an intermediate-frequency signal by using a BOC signal tracking ring to obtain a first carrier phase; tracking an upper sidebandsignal of the intermediate-frequency signal to obtain a second carrier phase; tracking a lower sideband signal of the intermediate-frequency signal to obtain a third carrier phase; obtaining a total electron content (TEC) according to the difference between the first carrier phase and the second carrier phase, difference between the first carrier phase and the third carrier phase, the center frequency of a BOC modulating signal, and frequencies of the upper sideband signal and the lower sideband signal; and calculating errors introduced by ionospheric refraction to the carrier phase and pseudorange observation quantity according to the TEC. The BOC signal can be subjected to signal-frequency ionized layer error estimation; and the TEC is calculated by the carrier phases, so the method andthe system are slightly influenced by a multi-path effect and measurement noise.
Owner:UNICORE COMM INC
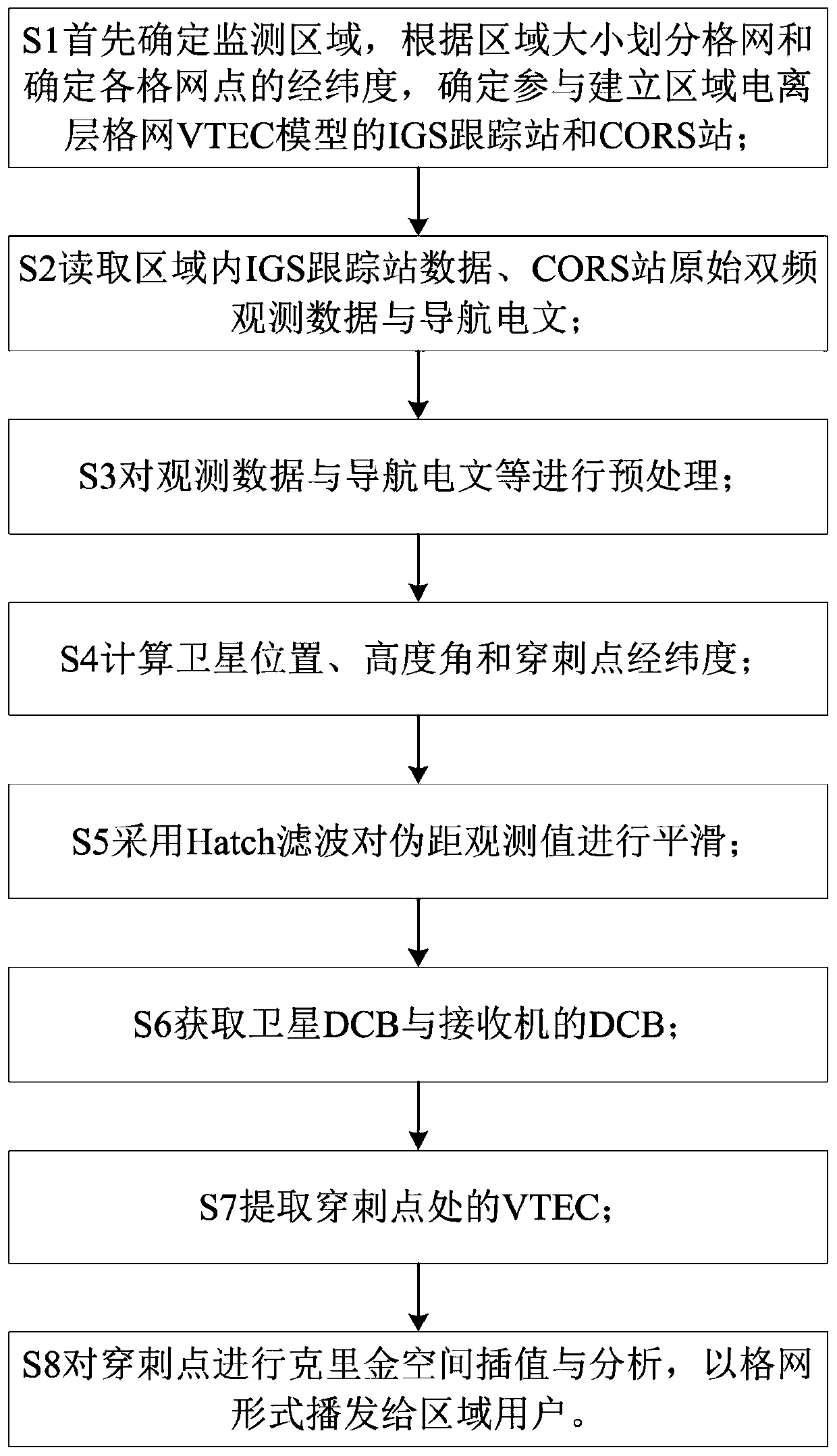
Regional ionospheric TEC real-time monitoring method based on IGS and CORS
ActiveCN110568459AHigh precisionImprove reliabilitySatellite radio beaconingElevation angleObservation data
The invention provides a regional ionospheric TEC (Total Electron Content) real-time monitoring method based on IGS (Internal GNSS Service) and CORSs (Continuously Operating Reference Station), whichcomprises the steps as follows: determining a monitoring region, and dividing the monitoring region into grids according to the size of the monitoring region; determining the longitude and latitude ofeach grid, and determining IGS tracking stations and CORSs participating in establishment of a regional ionospheric grid VTEC (Vertical Total Electron Content) model; reading the data of the IGS tracking stations, the original double-frequency observation data of the CORSs and a navigation message; preprocessing the observation data and the navigation message; calculating the position and elevation angle of a satellite and the longitude and latitude of a puncture point; smoothing a pseudo-range observation value; acquiring the DCB (Difference Code Bias) of the satellite and the DCB of a receiver; extracting the VTEC at the puncture point; carrying out Kriging spatial interpolation and analysis on the puncture point, and broadcasting the result to regional users in a grid form. According to the method, a regional ionospheric grid VTEC model is established by combining IGS and CORS data, the problems of precision reduction and the like caused by insufficiency of the IGS tracking stations are solved, the range of a monitoring region is expanded, and the precision and reliability of the ionospheric grid VTEC model in areas such as the equator are improved.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Ionosphere vertical-total-electron content modeling method based on ellipsoidal-harmonic-function theory
ActiveCN108491616ADescribe nonlinear vibration characteristicsHigh precisionSatellite radio beaconingSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionObservation point
The invention discloses an ionosphere vertical-total-electron content modeling method based on ellipsoidal-harmonic-function theory. The method comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring geographiclongitude of a puncture point of region observation points, geographic latitude of the puncture point and an electron content of a vertical direction of the puncture point; S2, carrying out reductioncalculation on geocentric latitude; S3, selecting the order of an ellipsoidal harmonic function, and adopting the ellipsoidal harmonic function to establish a region ionosphere vertical-total-electroncontent model; and S4, calculating parameters of the region ionosphere vertical-total-electron content model through a least square method, and correcting the region ionosphere vertical-total-electron content model. Compared with the prior art, the method more accurately describes nonlinear vibration characteristics of ionosphere delay information over time, better simulates spatiotemporal variation features of a region ionosphere, and effectively improves model accuracy.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Algorithm for predicting total electron content of global ionized layer
ActiveCN111651941AHigh precisionAccurate extractionWeather condition predictionDesign optimisation/simulationPrediction algorithmsIonosphere
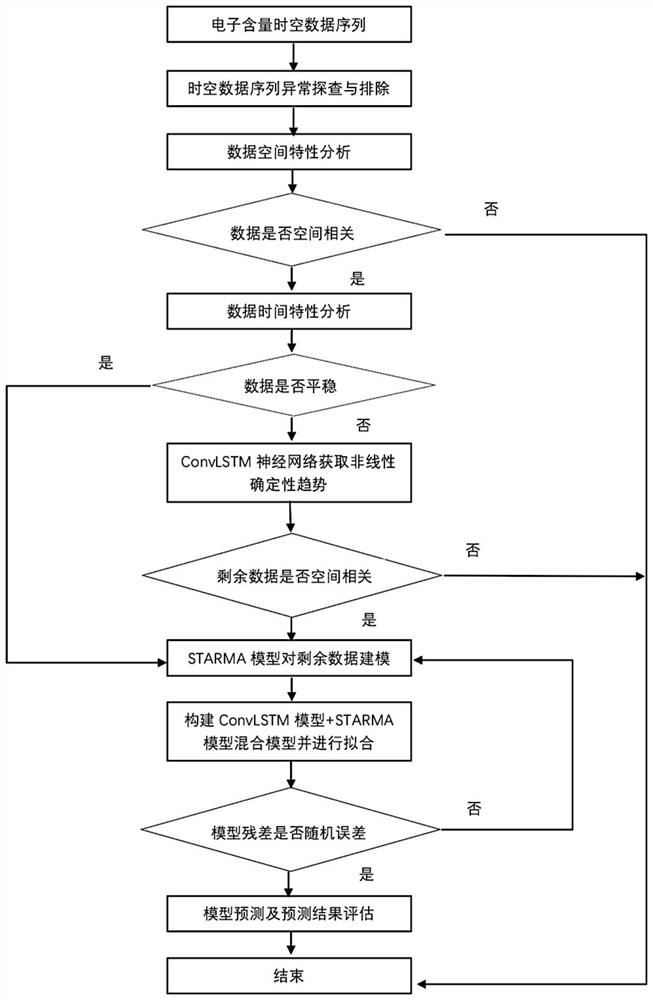
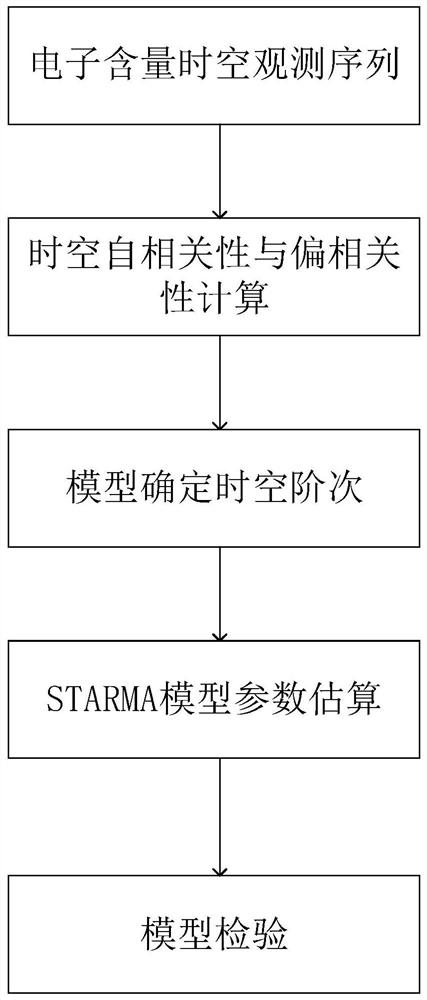
The invention provides a global ionized layer electron total content prediction method based on a space-time sequence hybrid framework. According to a prediction method, calculation is made on two types of space-time sequences. For a stabilized spatial sequence, an STARMA model prediction method is constructed. For a non-stationary spatio-temporal sequence, the method comprises the following steps: firstly, extracting a nonlinear space-time trend in a non-stationary space-time sequence by adopting a ConvLSTM method; until the extracted residual error passes the stability test; the calculation efficiency can be greatly improved and the calculation time can be saved by using the parallel calculation method, and meanwhile, the global ionospheric electron content distribution characteristicis fully considered, so that the ionospheric prediction algorithm better conforms to the spatial weather law, and the prediction precision is higher.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Ionospheric slant total electron content analysis using global positioning system based estimation
ActiveUS9576082B2Design optimisation/simulationSatellite radio beaconingTotal electron contentIonospheric heater
A method, system, apparatus, and computer program product provide the ability to analyze ionospheric slant total electron content (TEC) using global navigation satellite systems (GNSS)-based estimation. Slant TEC is estimated for a given set of raypath geometries by fitting historical GNSS data to a specified delay model. The accuracy of the specified delay model is estimated by computing delay estimate residuals and plotting a behavior of the delay estimate residuals. An ionospheric threat model is computed based on the specified delay model. Ionospheric grid delays (IGDs) and grid ionospheric vertical errors (GIVEs) are computed based on the ionospheric threat model.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
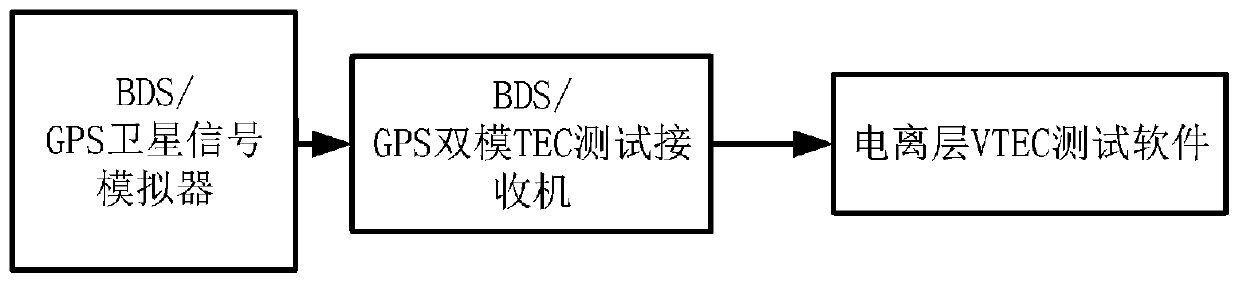
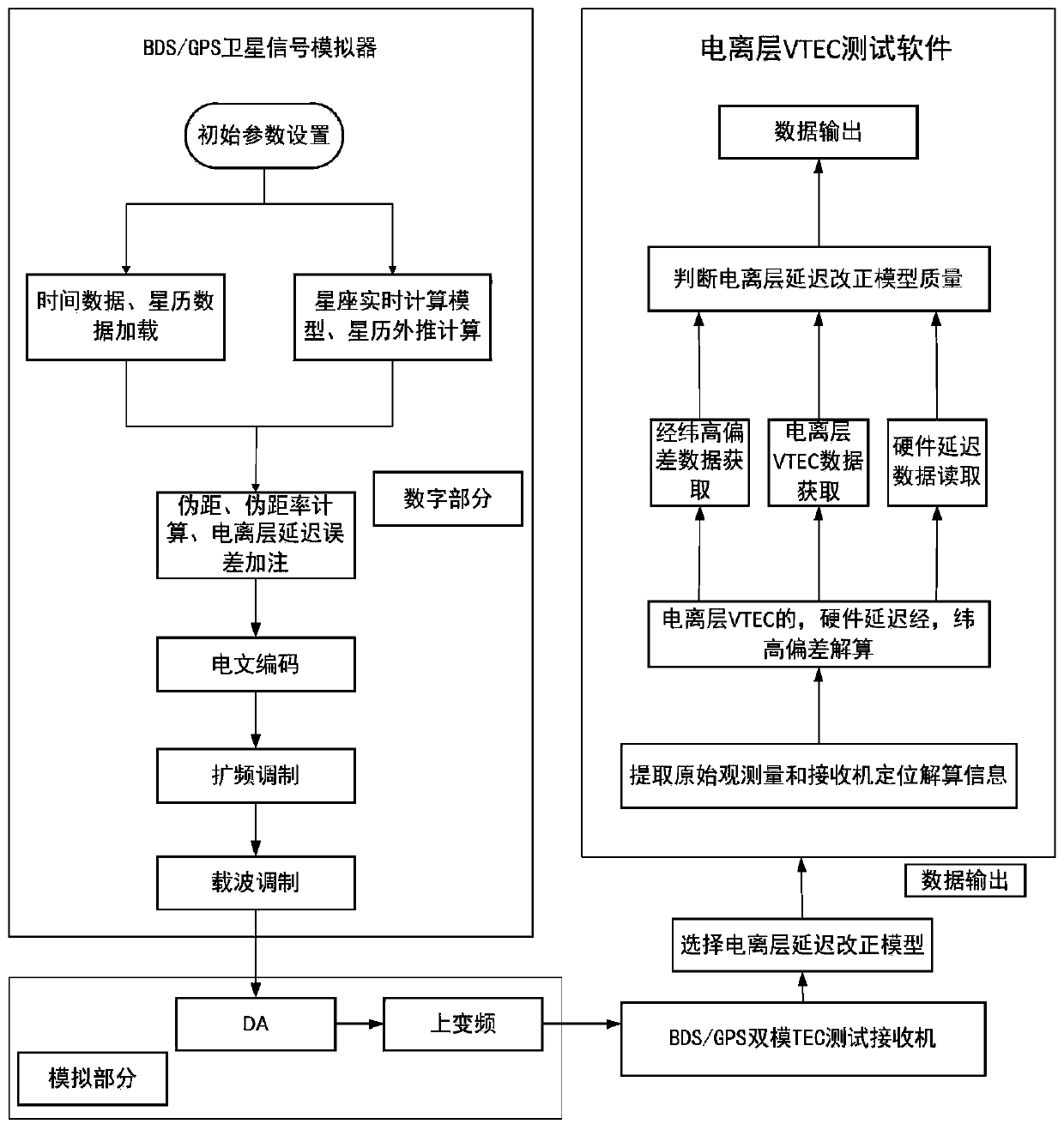
GNSS-based ionospheric VTEC closed-loop test system
ActiveCN110568458AAccurate calculationHigh precisionSatellite radio beaconingReal-time simulationClosed loop
The invention provides a GNSS-based ionospheric VTEC (Vertical Total Electron Content) closed-loop test system, which comprises a BDS / GPS satellite signal simulator used for generating a satellite downlink navigation signal, loading a tropospheric model and an ionospheric model and realizing real-time simulation of tropospheric delay and ionospheric delay of a satellite signal, a BDS / GPS dual-modeTEC test receiver used for receiving the satellite signal and generating an ionospheric delay correction model, and an ionospheric VTEC test upper computer software used for obtaining the original observed quantity of a tracking loop and the positioning calculation information of the receiver according to the ionospheric delay correction model, acquiring the hardware delay, ionospheric VTEC data,longitude and latitude deviation and height deviation of the receiver and the satellite and judging the quality of the ionospheric delay correction model according to the hardware delay, ionosphericVTEC data, latitude and longitude deviation and height deviation of the receiver and the satellite.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com