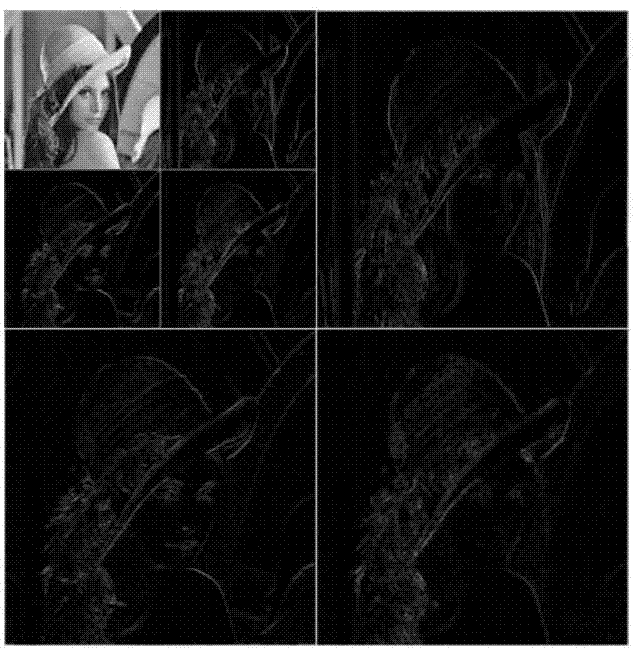
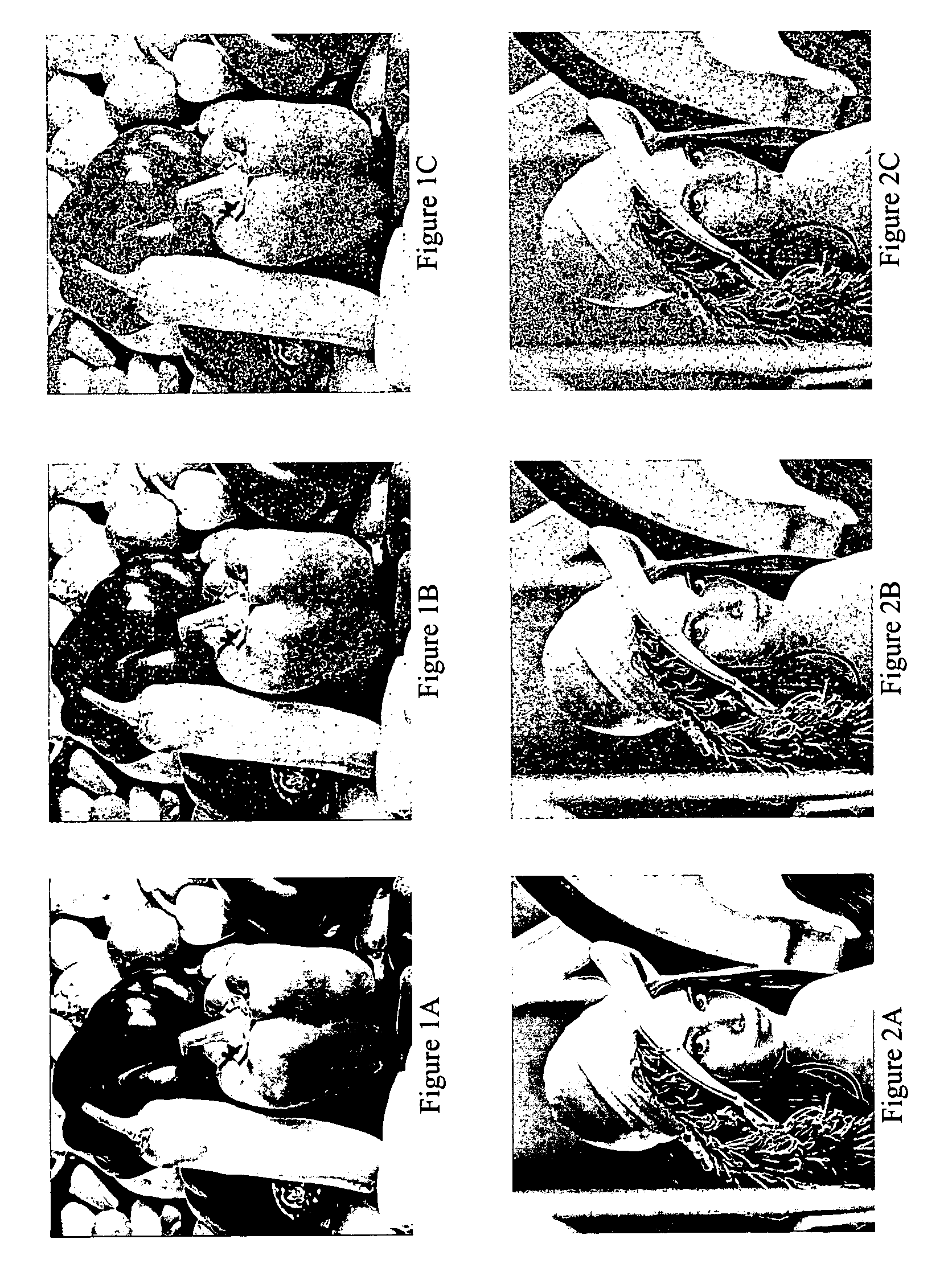
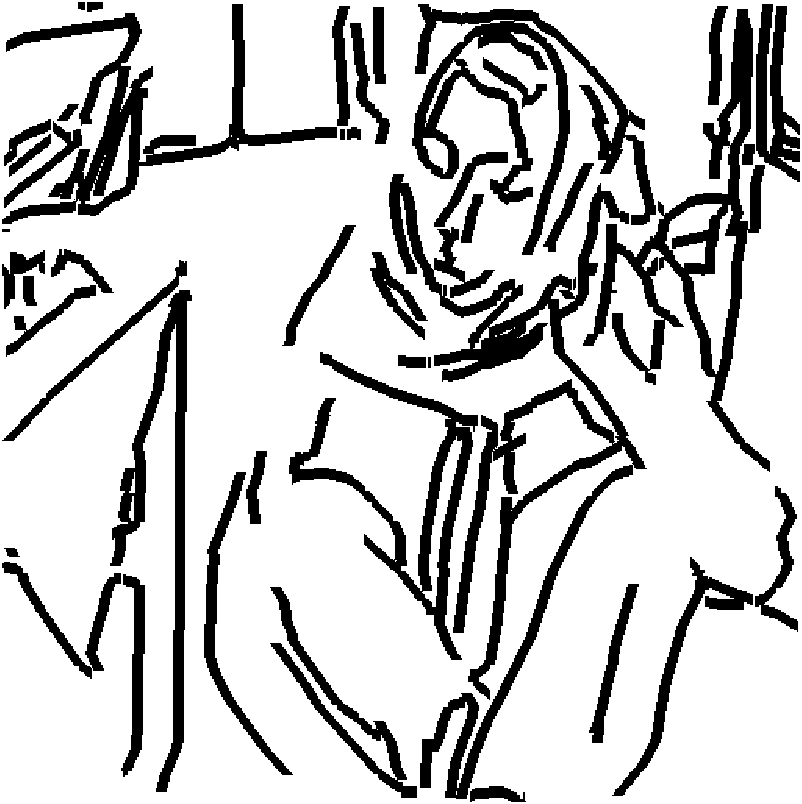
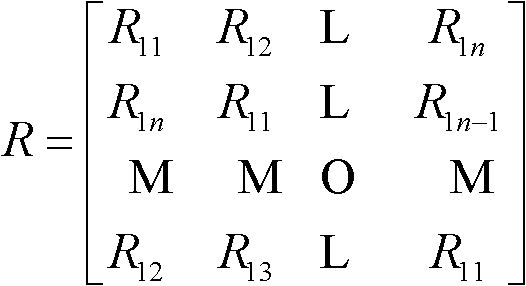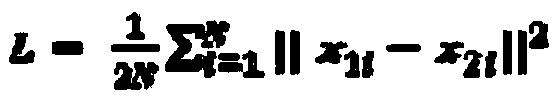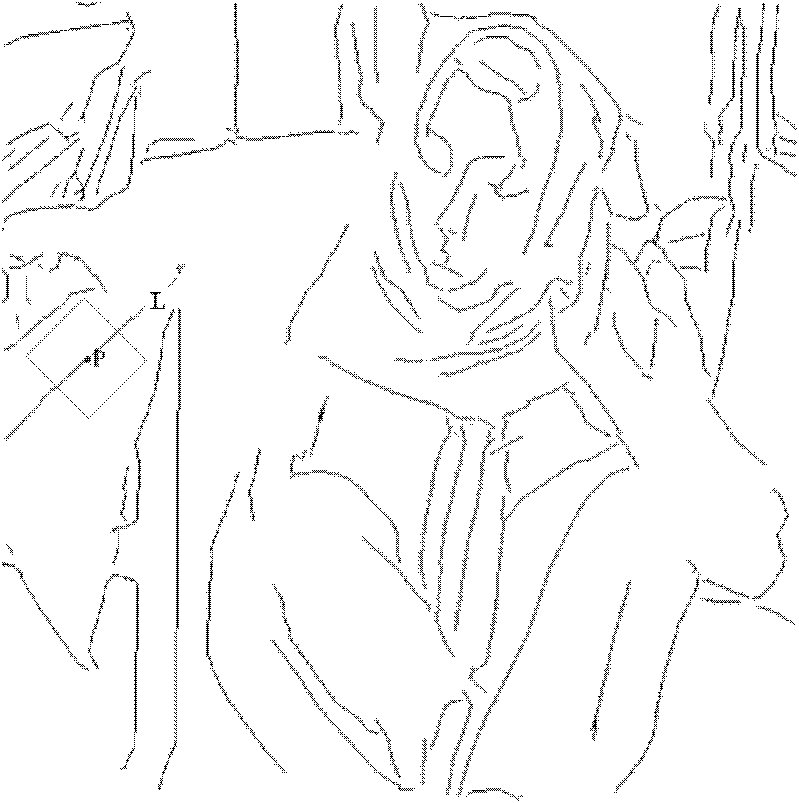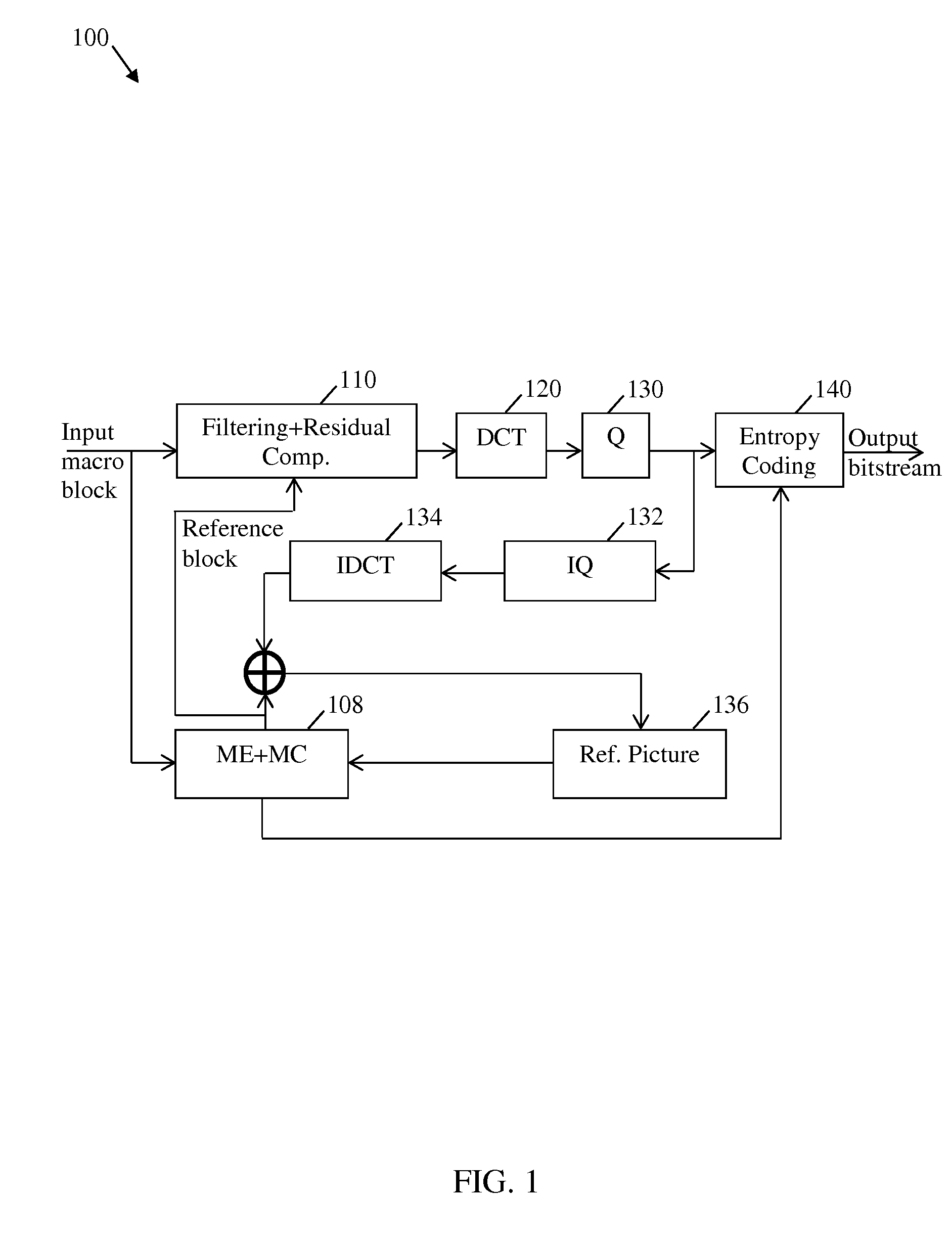Patents
Literature
310 results about "Denoising algorithm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
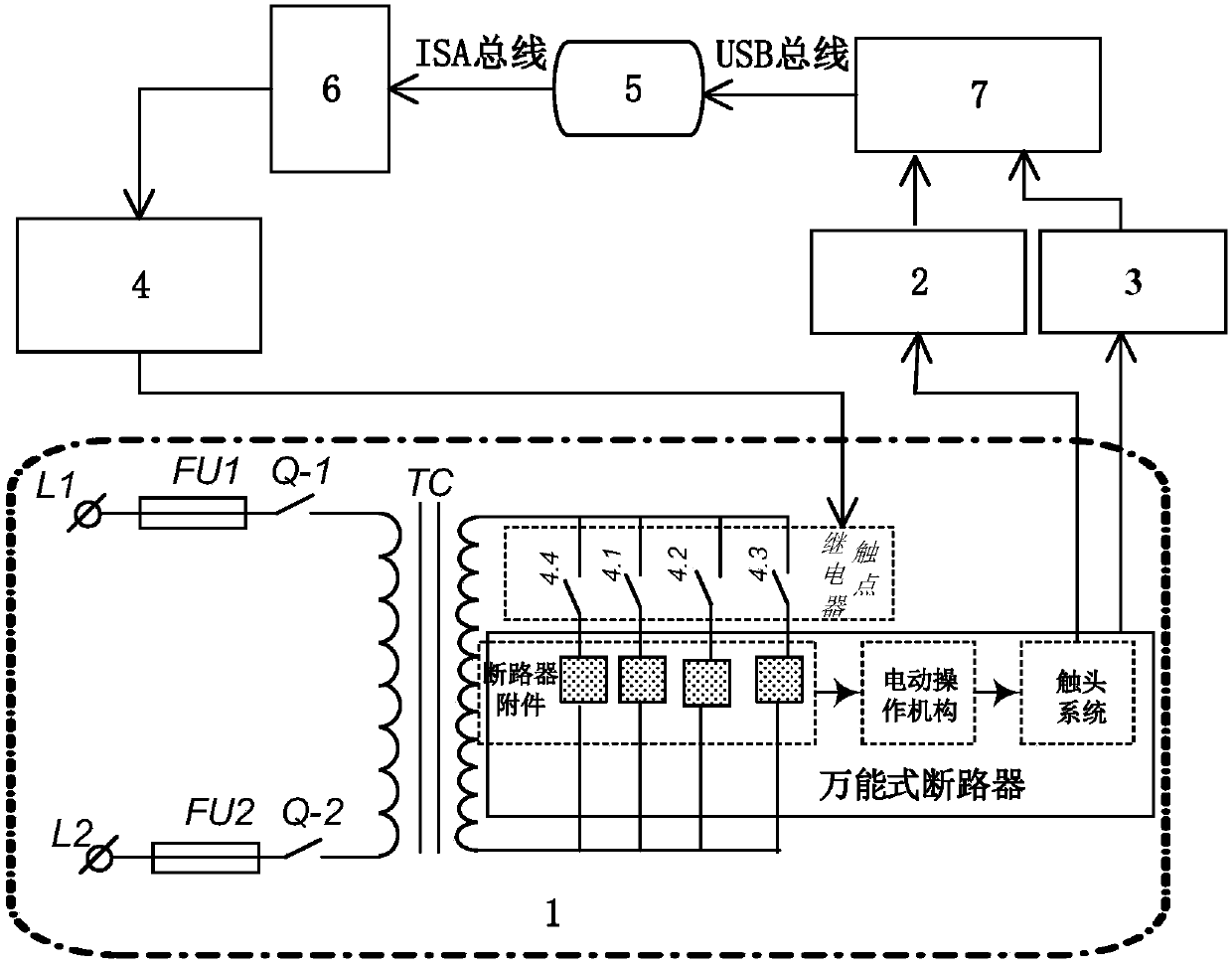
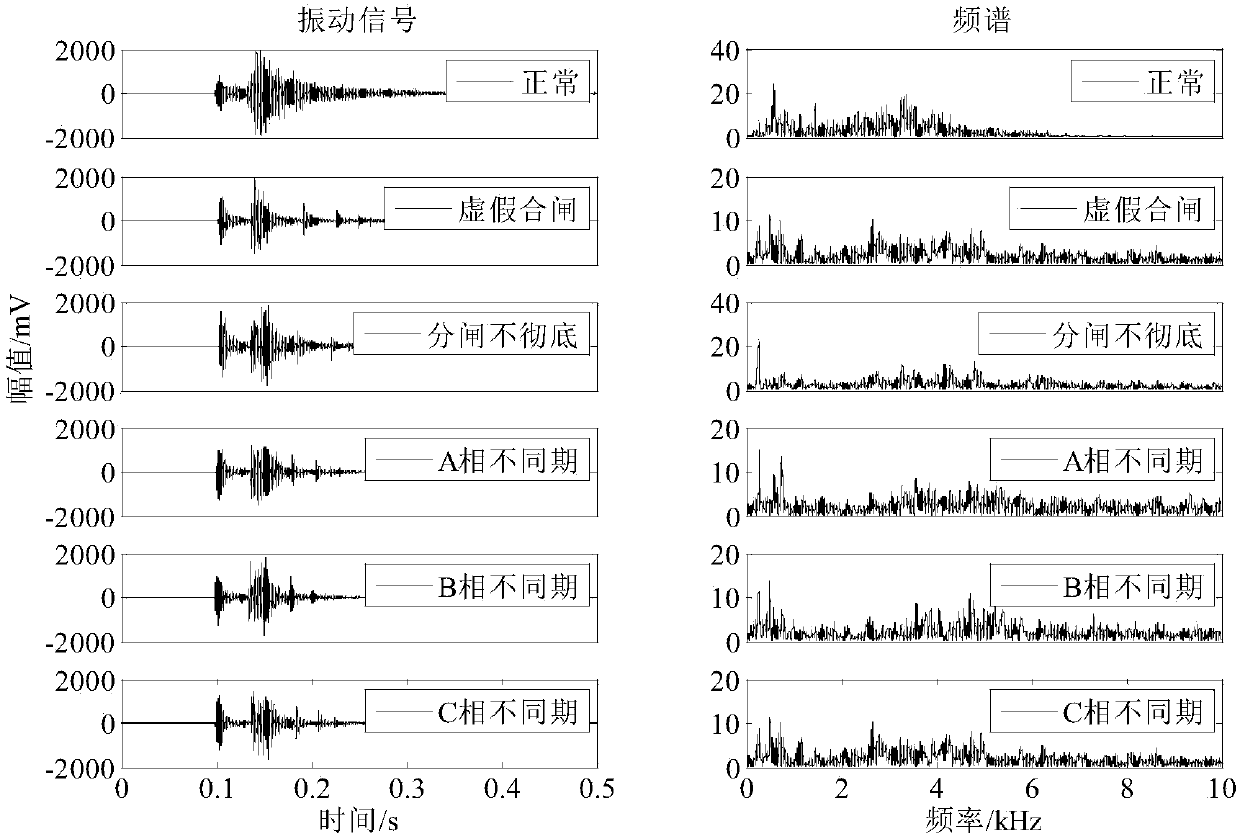
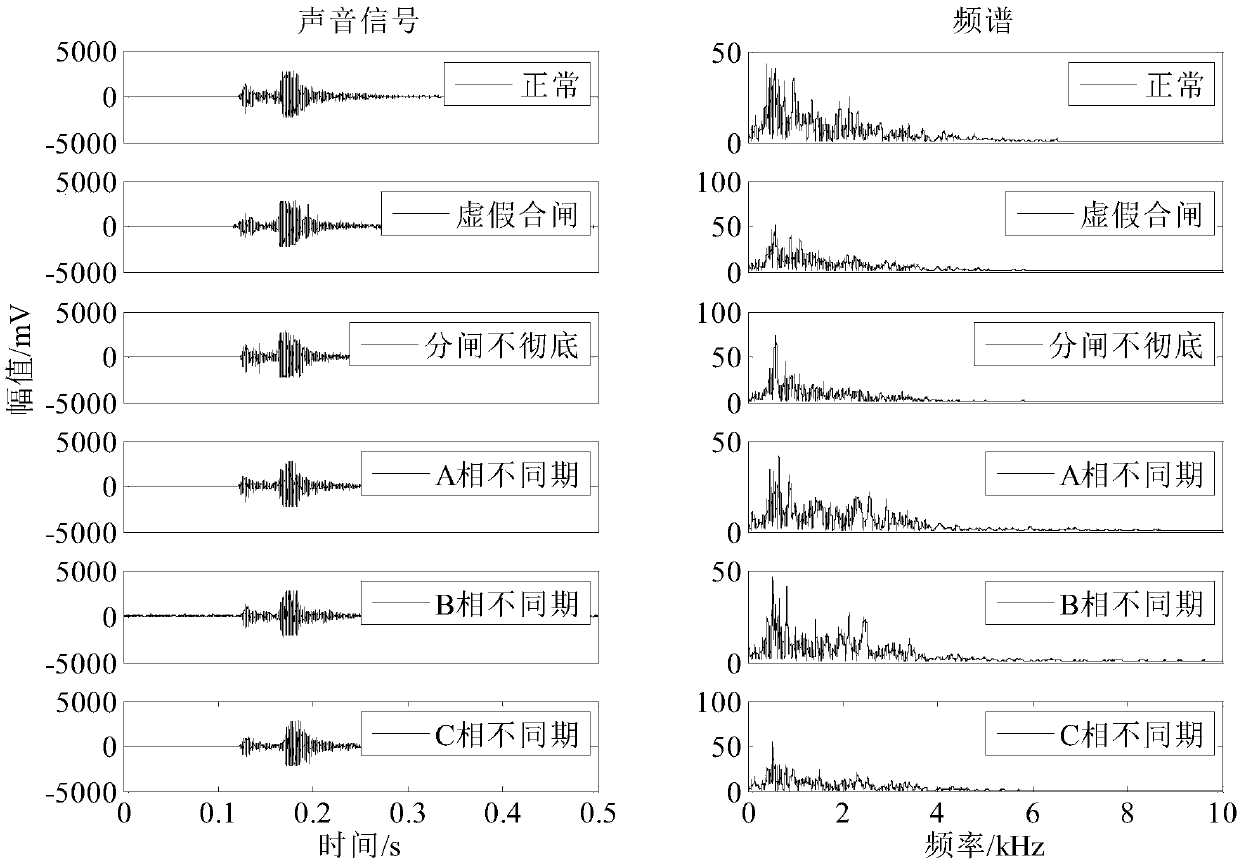
Universal circuit breaker mechanical fault diagnosis method based on feature fusion of vibration and sound signals
InactiveCN106017879AImprove reliabilityThe detection method is simpleMachine part testingCircuit interrupters testingDiagnostic Radiology ModalityMachining vibrations
The invention provides a universal circuit breaker mechanical fault diagnosis method based on feature fusion of vibration and sound signals. The method includes steps of 1, collecting machine vibration signals and machine sound signals during an engaging and disengaging process of a universal circuit breaker; 2, adopting an improved wavelet packet threshold value denoising algorithm for denoising; 3, adopting a complementary total average empirical mode decomposition algorithm for extracting a plurality of solid mode function components reflecting state information of engagement and disengagement actions of the circuit breaker from the denoising signals; 4, determining the number Z of the solid mode function components; 5, calculating the energy ratio, the sample ratio and the power spectrum entropy as three types of features; 6, adopting a combination core principal component analysis method for performing dimension reduction on a feature sample with unified three types of features of the vibration and the sound signals and obtaining M principle components; 7, establishing a related vector machine based sequence binary tree multiple classifier model.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Image denoising method based on self-adaptive wavelet threshold and two-sided filter
InactiveCN103700072AEfficient removalKeep detailsImage enhancementDenoising algorithmAdaptive wavelet
The invention provides an image denoising method based on a self-adaptive wavelet threshold and a two-sided filter and aims to improve the effect of a wavelet threshold denoising algorithm and better protect the edge and the detailed information of an image. The algorithm comprises the following steps of decomposing the image by adopting a discrete wavelet to obtain a plurality of sub-bands and the wavelet coefficients of the sub-bands; selecting a threshold which is self-adaptively changed along with the changes of wavelet-decomposing scales and the sub-bands, and carrying out quantitative threshold processing by adopting a soft threshold function; carrying out inverse wavelet transformation to obtain a reconstructed image; filtering the reconstructed image by adopting the two-sided filter so as to obtain the clear image. According to the image denoising method, wavelet threshold denoising is carried out by utilizing the threshold which is self-adapted to the wavelet-decomposing scales and the sub-bands, and filtering is carried out by combining the two-sided filter, so that through the designed denoising algorithm, not only can white gaussian noise be effectively removed, but also the edge and the detailed information of the image can be well reserved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Image denoising based on wavelets and multifractals for singularity detection and multiscale anisotropic diffusion
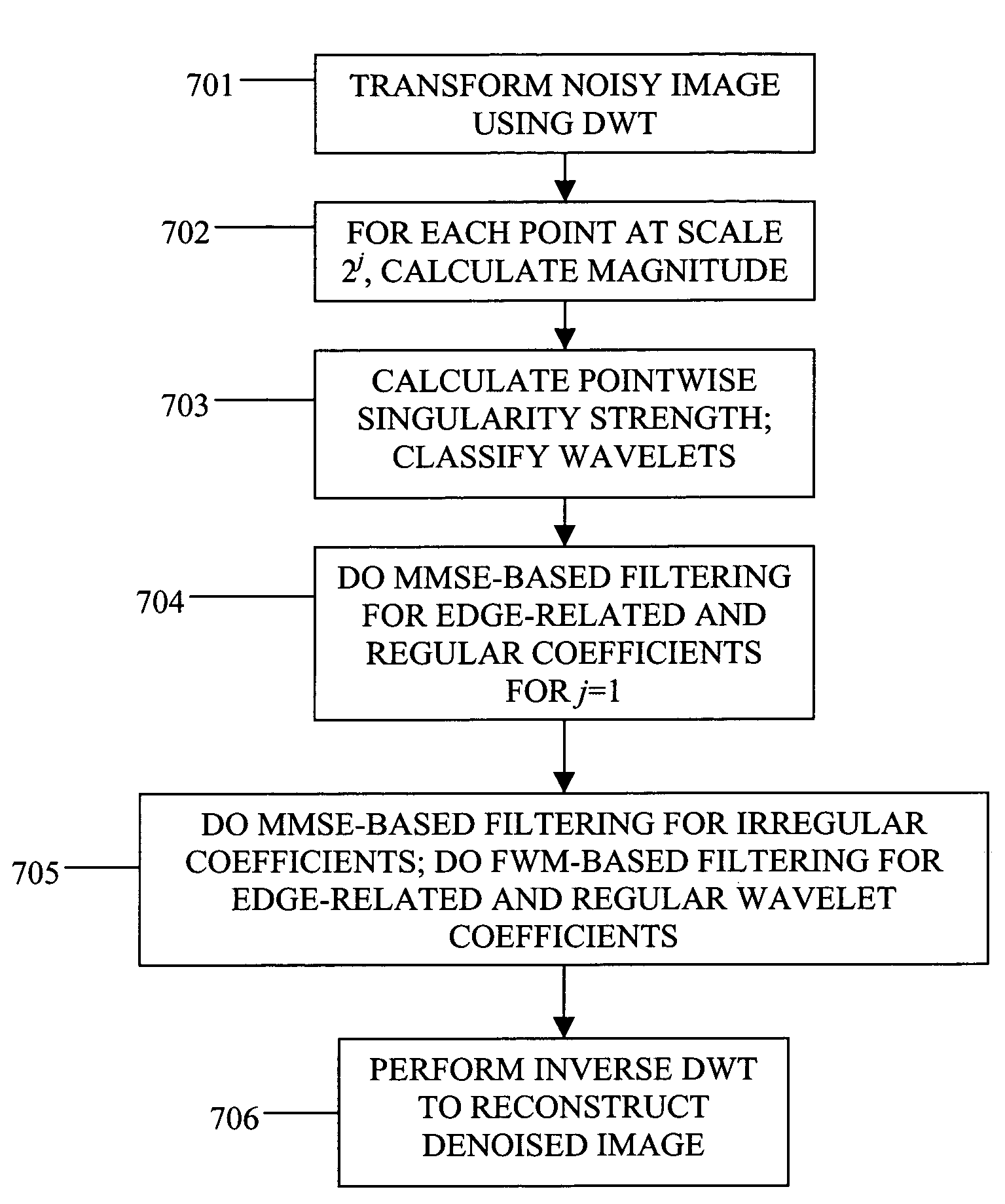
InactiveUS7515763B1Reduce noiseRestore signal componentImage enhancementImage analysisDenoising algorithmWavelet transform
A noisy image is transformed through a wavelet transform into multiple scales. The wavelet coefficients are classified at each scale into two categories corresponding to irregular coefficients, edge-related and regular coefficients. Different denoising algorithms are applied to different classes. Alternatively, a denoising technique is applied to the finest scale, and the wavelet coefficients at all scales are denoised through anisotropic diffusion.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift modeling method by optimizing dynamic recurrent neural network through genetic algorithm
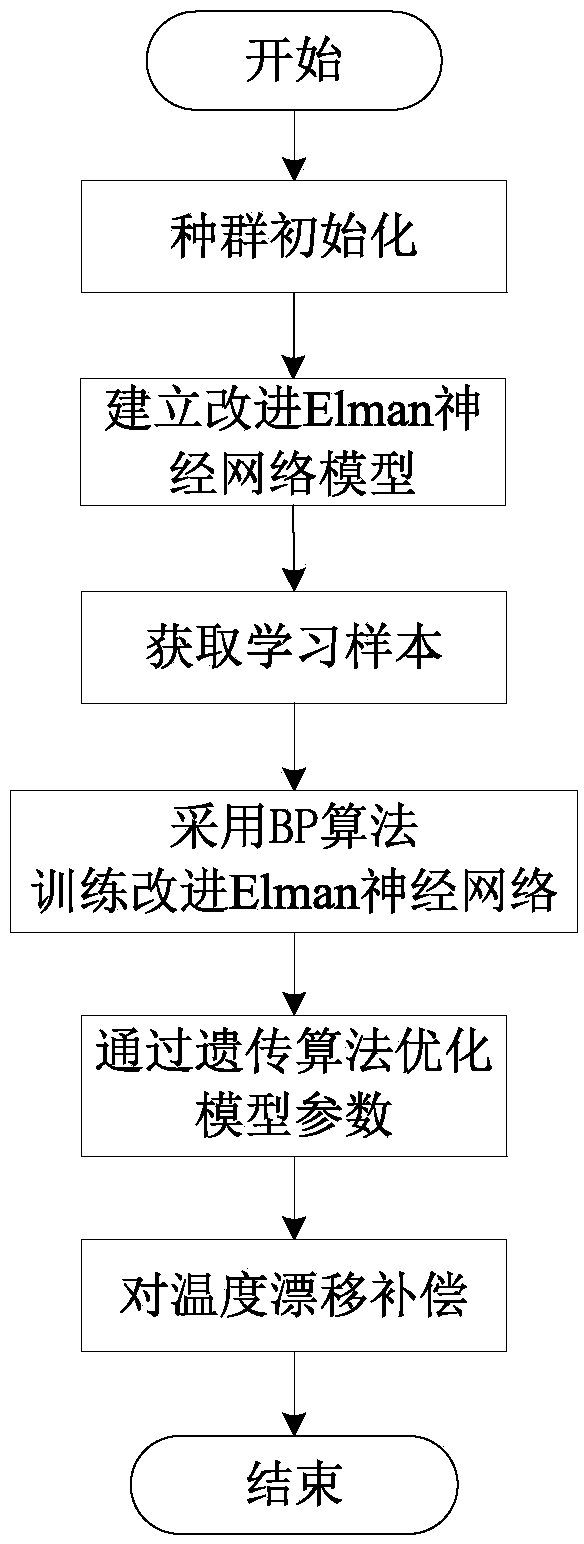
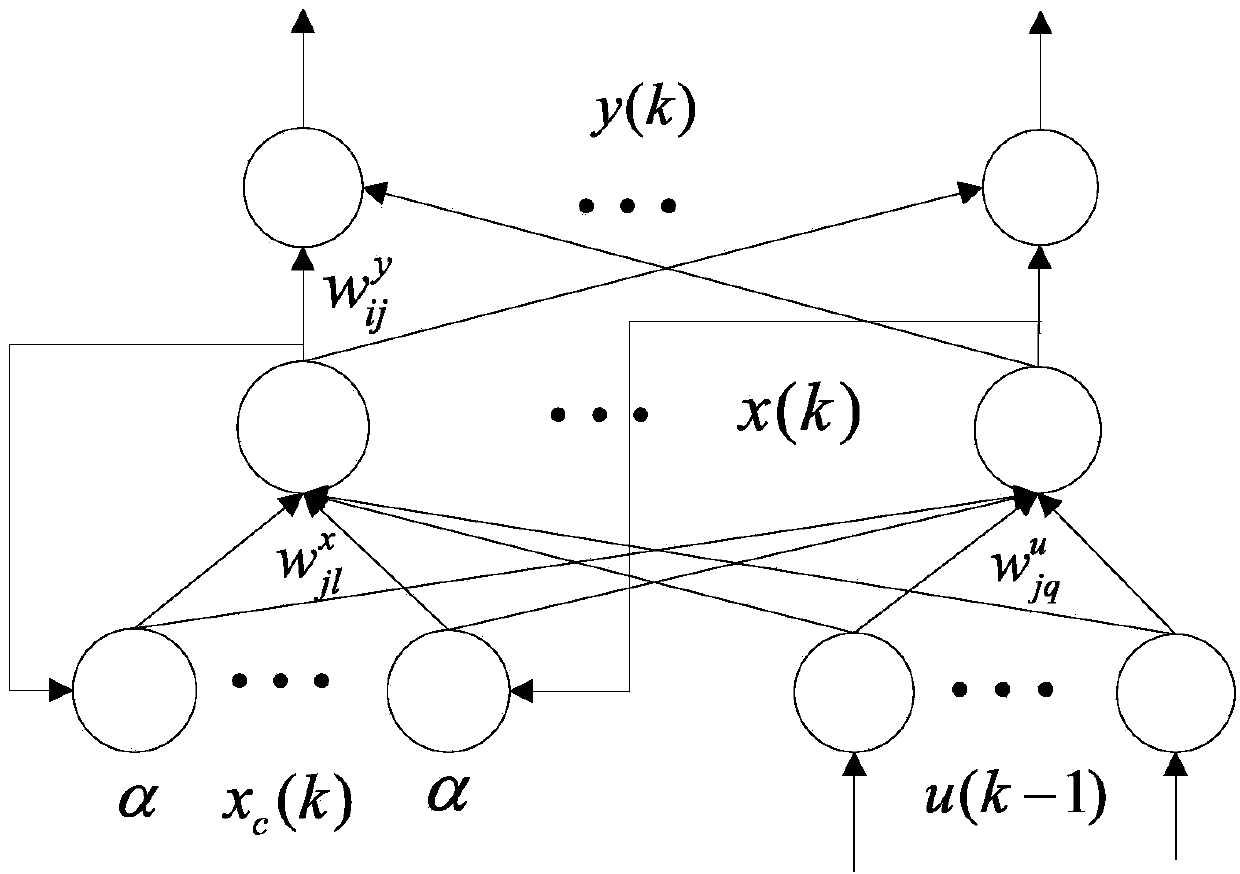
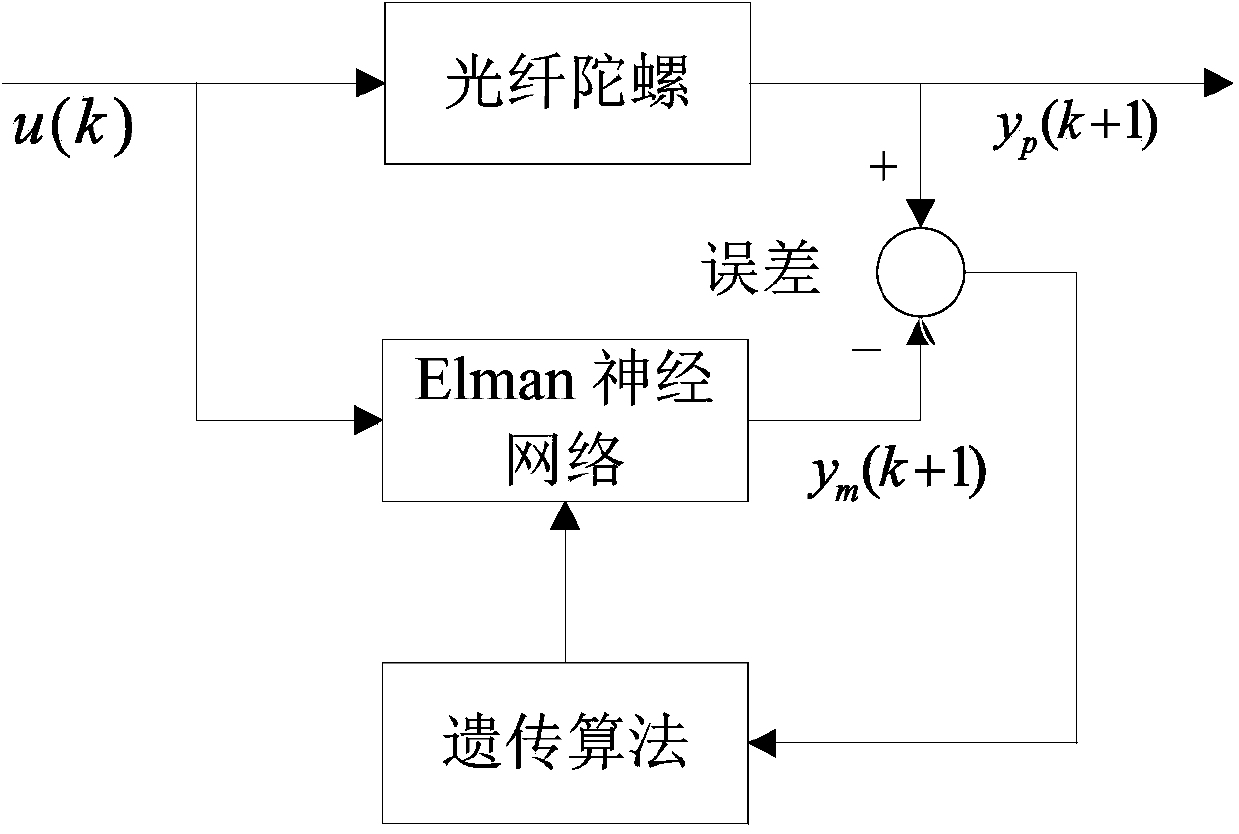
ActiveCN103593538AWith dynamic memorySimplify the scaleBiological neural network modelsSagnac effect gyrometersFiberGyroscope
The invention discloses a fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift modeling method by optimizing a dynamic recurrent neural network through a genetic algorithm. The fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift modeling method by optimizing the dynamic recurrent neural network through the genetic algorithm comprises the following steps of (1) initializing network parameters, and establishing an improved Elman neural network model; (2) obtaining a training and testing sample; (3) training an improved Elman neural network, and optimizing model parameters through the genetic algorithm; (4) outputting forecasts of an fiber optic gyroscope, and compensating errors. The output of the fiber optic gyroscope processed through a denoising algorithm is trained by introducing the improved Elman neural model with self-feedback connection weight, constant iterative optimization is carried out on the model parameters through the genetic algorithm, and the optimal model is obtained according to the magnitude of the errors of the model under different parameters. According to the fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift modeling method by optimizing the dynamic recurrent neural network through the genetic algorithm, the complexity of the algorithm is taken into consideration, the accuracy of the fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift model is improved, the application of the fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift model in engineering is expanded, and certain practical significance is achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
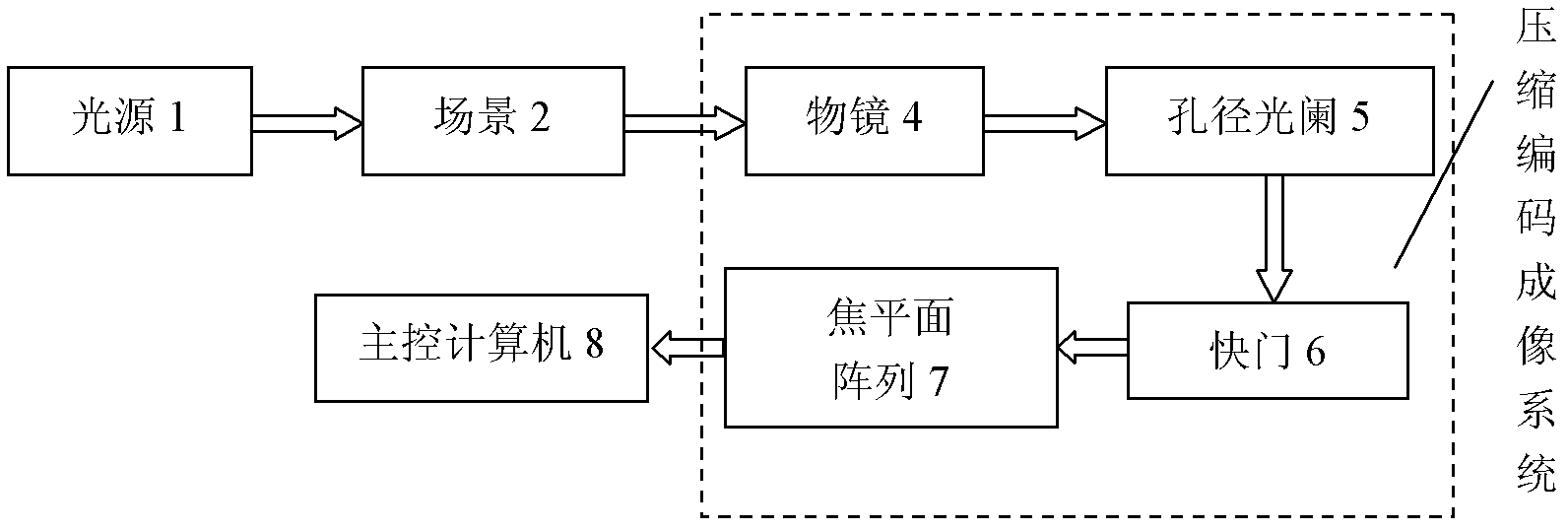
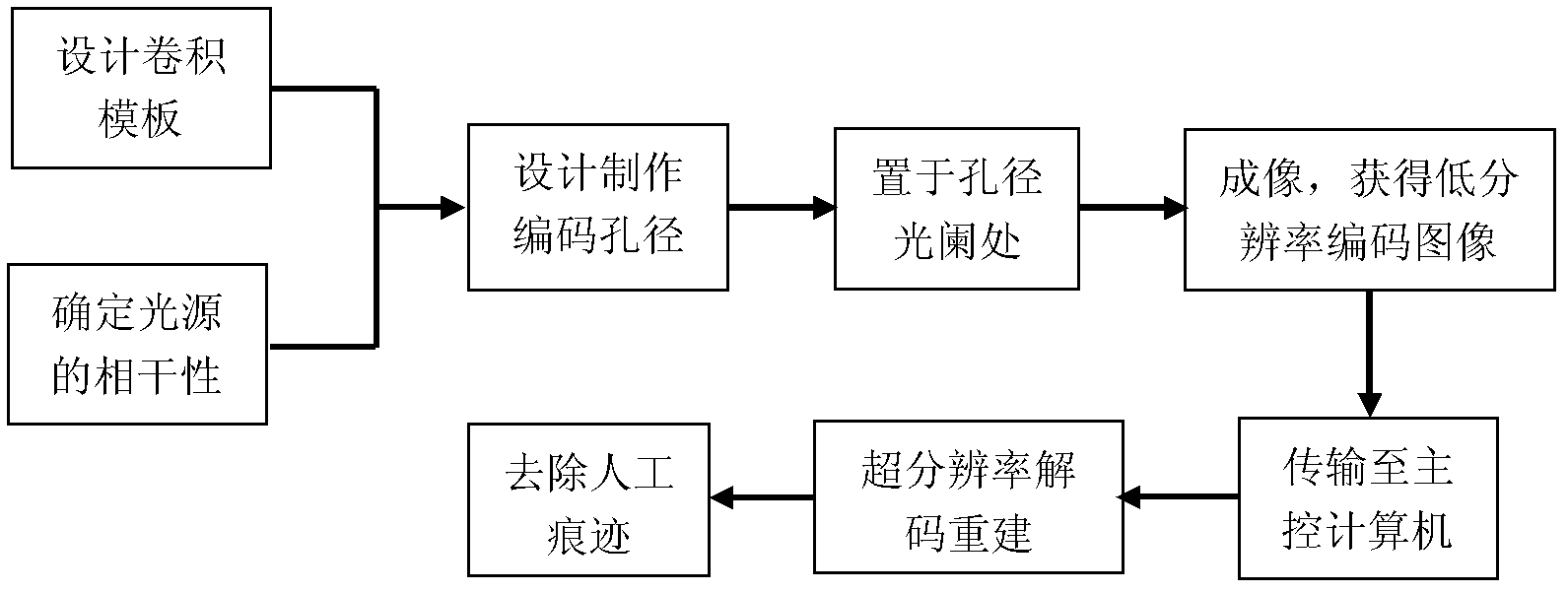
Super-resolution imaging system based on compression coding aperture and imaging method thereof
InactiveCN102438102ALow costReduce data volumeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDenoising algorithmHigh resolution image
The invention discloses a super-resolution imaging system based on a compression coding aperture and an imaging method thereof, mainly solving a problem of expensive imaging cost in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps: designing a convolution template, and making a coding aperture according to coherence of a light source; placing the prepared coding aperture at a position of aperture diaphragm in an optical system and pressing a shutter for imaging, and obtaining a low resolution coding image; transmitting the coding image to a master control computer, decoding super-resolution to reconstruct a high-resolution image, and using a denoising algorithm to remove an artificial trace in the high-resolution image. The system and the method are characterized in that: restriction of a Nyquist criterion is broken through, low frequency sampling is carried out on a scene, the high-resolution image is obtained through super-resolution reconstruction, data waste caused by first sampling and second compression of a traditional imaging system is overcome, in sampling, data volume is compressed, imaging cost, compression cost and transmission cost are reduced, and the system and the method can be used for infrared imaging and remote sensing imaging technology.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
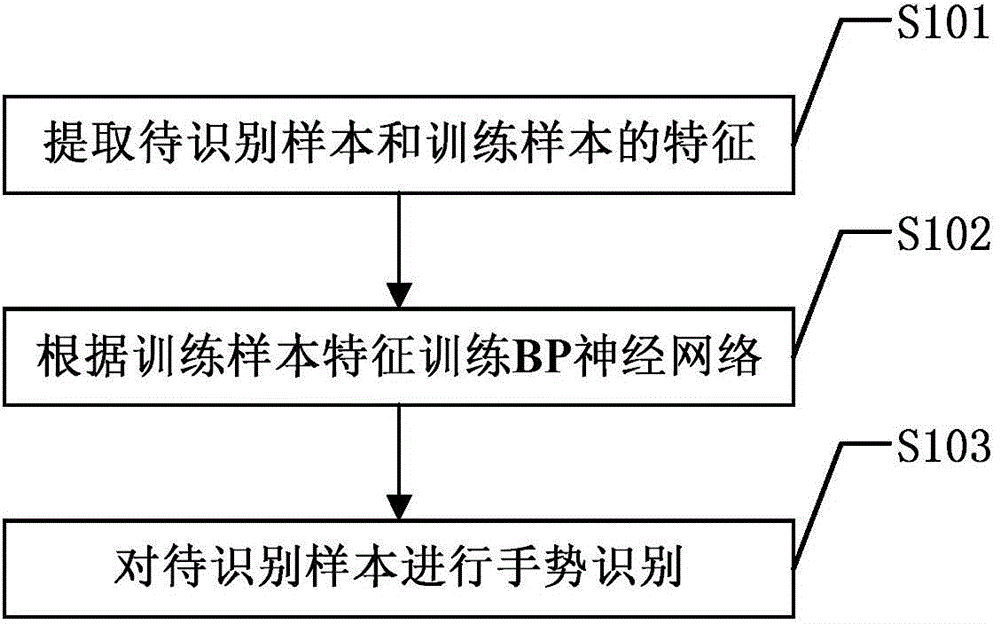
Hybrid neural network-based gesture recognition method
InactiveCN104834922AImprove denoising effectImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsFingertip detectionPattern recognition
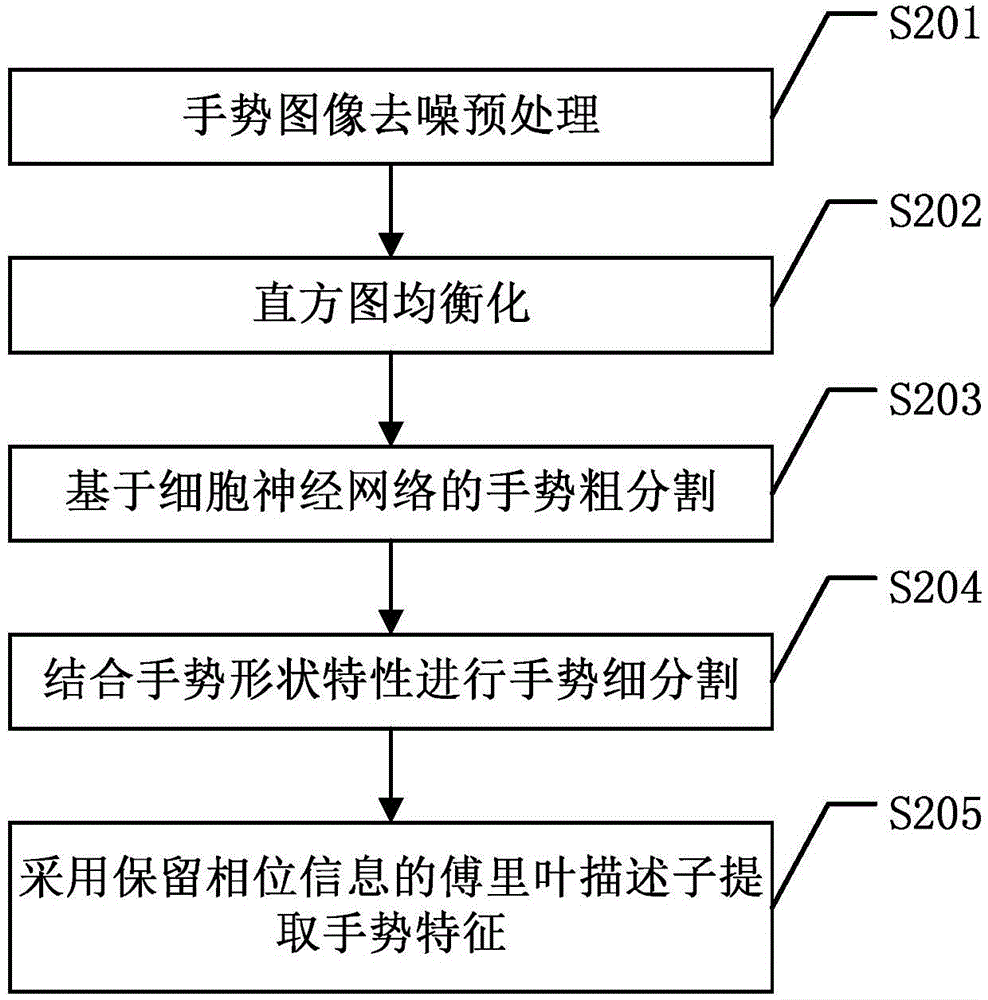
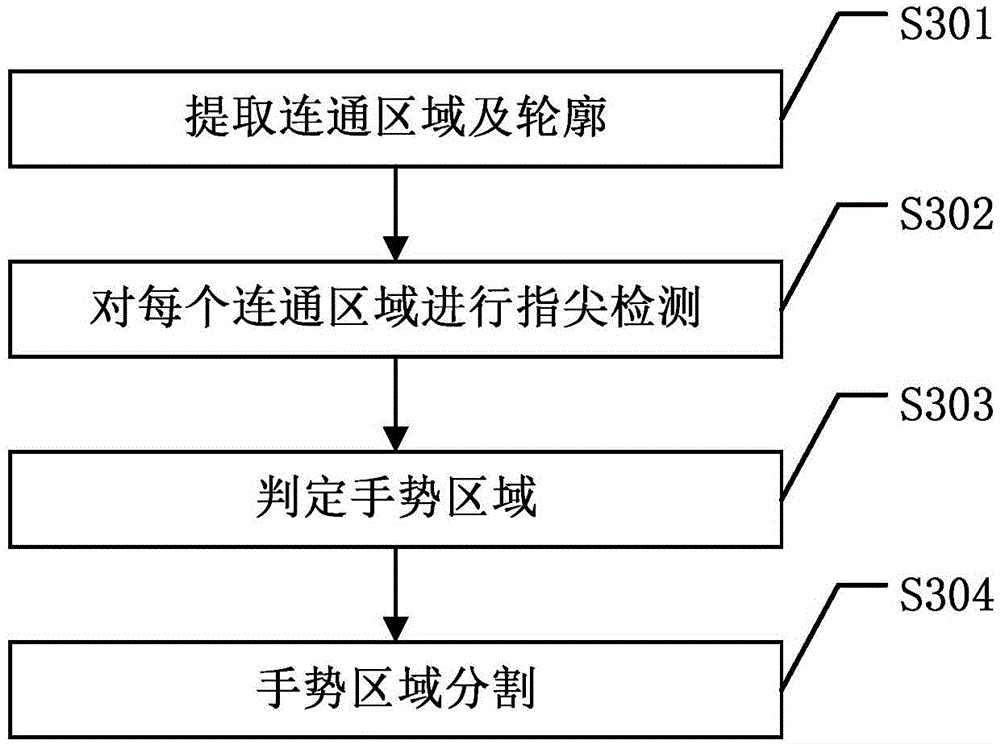
The invention discloses a hybrid neural network-based gesture recognition method. For a gesture image to be recognized and a gesture image training sample, first a pulse coupling neural network is used to detect to obtain noise points, then a composite denoising algorithm is used to process the noise points, then a cell neural network is used to extract edge points in the gesture image, connected regions are obtained according to the extracted edge points, curvature is used to perform fingertip detection on each connected region to obtain undetermined fingertip points, interference of a face part is eliminated to obtain a gesture region, then the gesture region is partitioned according to gesture shape features, Fourier descriptors which keep phase information are obtained according to contour points of the partitioned gesture region, and first multiple Fourier descriptors are selected as gesture features; and a BP neural network is trained according to gesture features of the gesture image training sample, and the gesture features of the gesture image to be recognized are input to the BP neural network for recognition. The hybrid neural network-based gesture recognition method provided by the invention improves the accuracy rate of gesture recognition through utilization of various neural networks.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Depth residual convolution neural network image denoising method based on PReLU
InactiveCN109118435AOptimizationAvoid computational overheadImage enhancementImage analysisDenoising algorithmActivation function
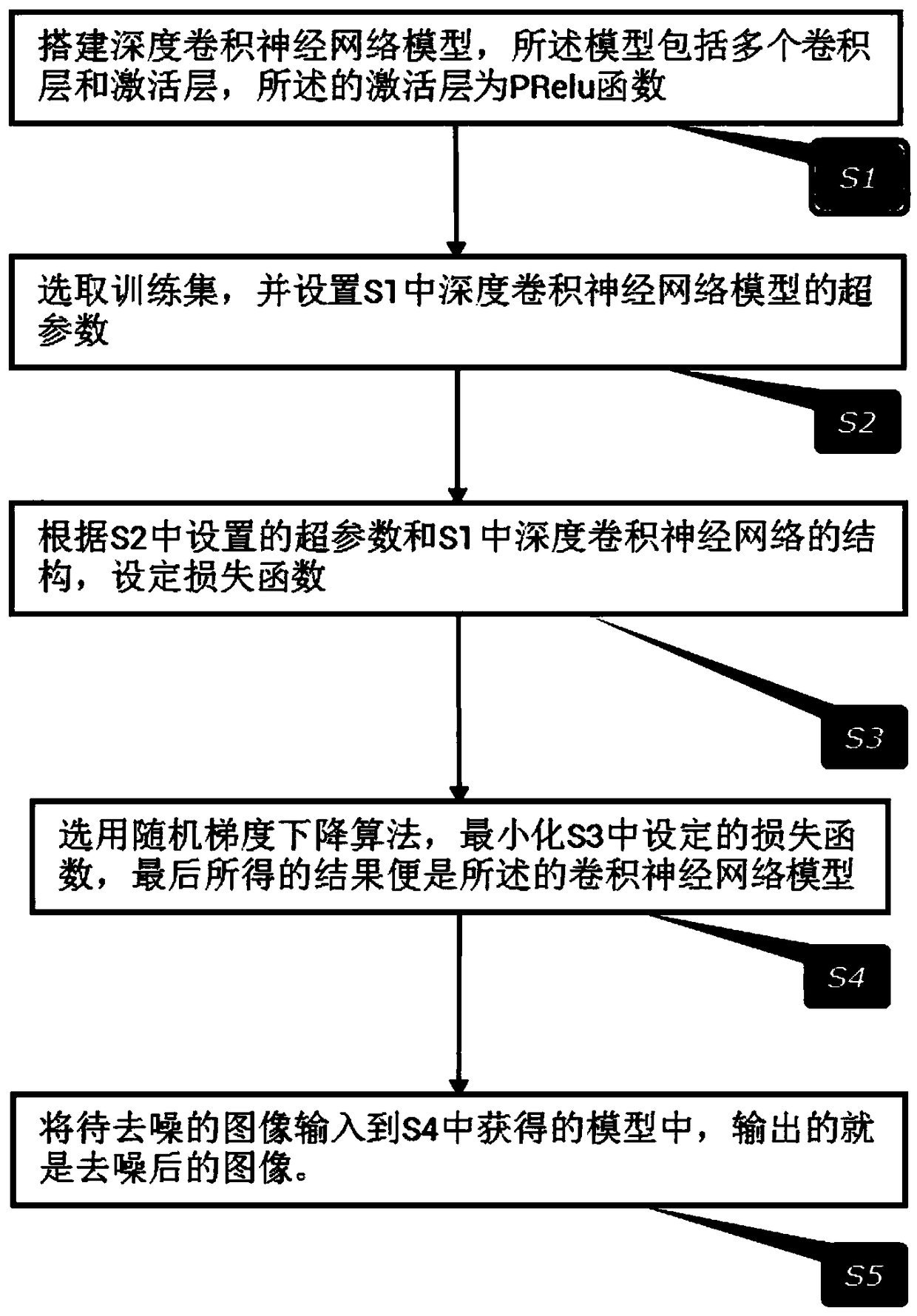
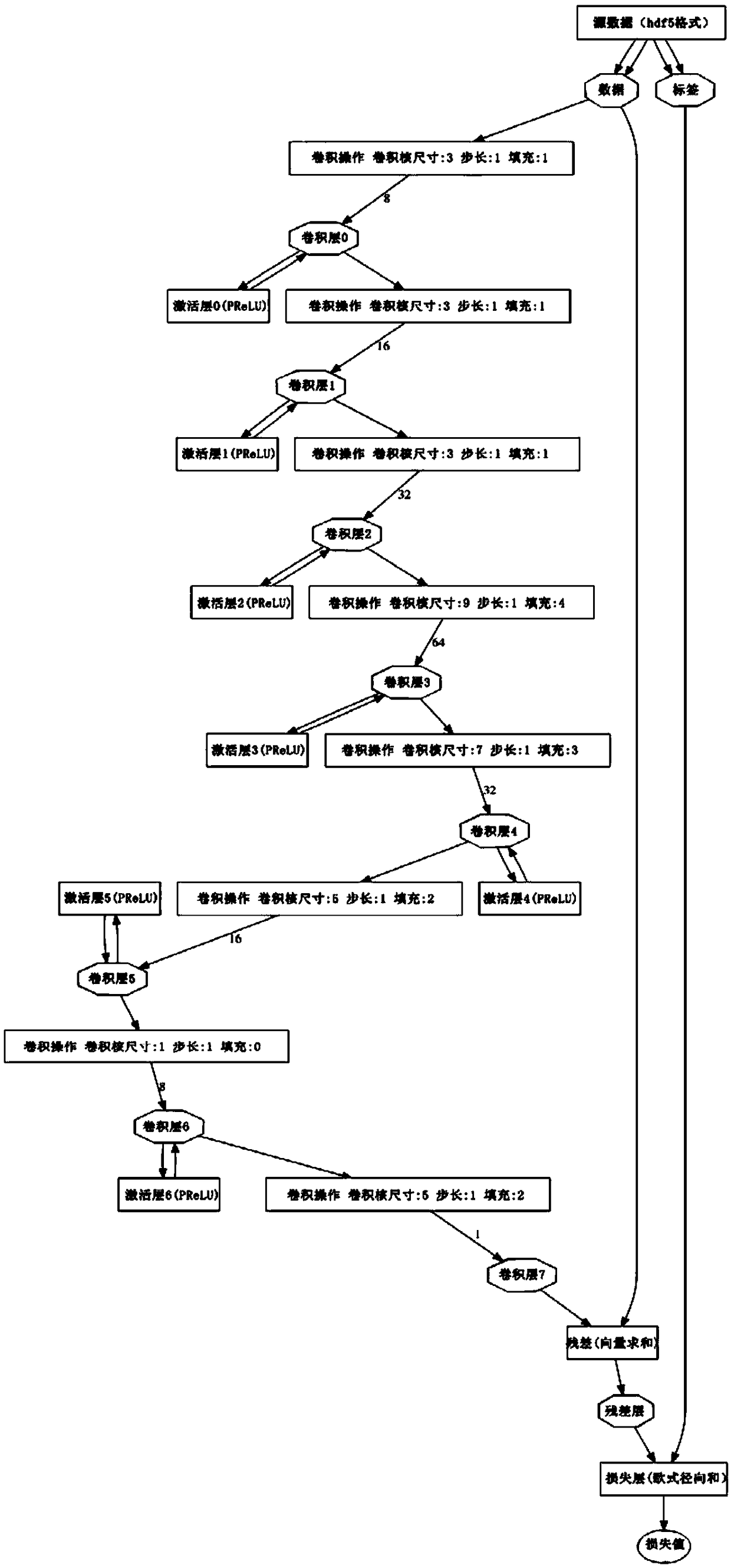
The invention relates to a depth residual convolution neural network image denoising method based on PReLU, based on deep convolution neural network, combined with Gaussian noise simulating unknown real noise image denoising task, in this paper, a deep convolution neural network for image denoising is proposed, which uses PReLU activation function instead of Sigmoid and ReLU function, increases residual learning and reduces mapping complexity, and adopts optimized network training techniques and network parameter settings to improve the denoising ability of the network. Compared with other existing denoising algorithms, the present invention performs very well under various Gaussian noise environments in which the standard variance is mixed, and the detailed information in the image can bewell preserved while the noise is eliminated.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
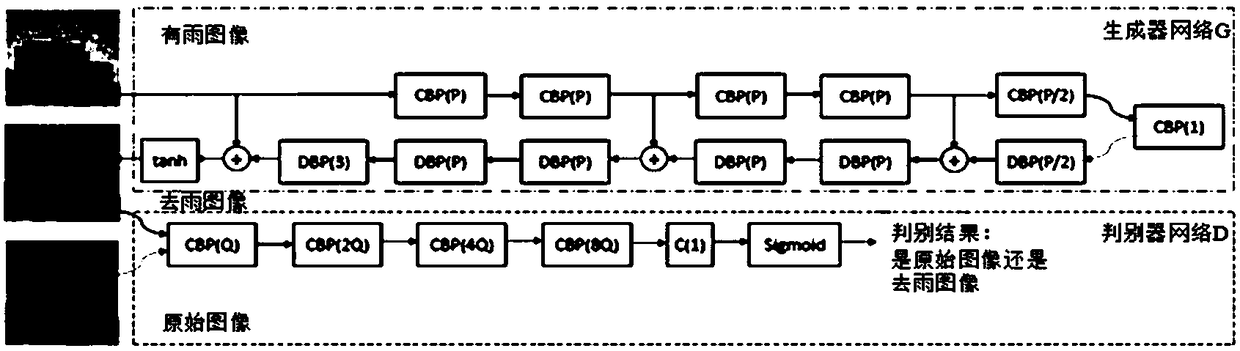
Single image rainfall removing method based on image partitioning of generating antagonistic network
The invention provides a single image rainfall removing method based on image partitioning of generating antagonistic network. By dividing images into image blocks with the same size and non-overlapping each other, each image block is used as a condition to generate input of antagonistic network, and the input dimension is reduced. A generate antagonism network is trained to realize the nonlinearmapping from rainless image block to rainless image block, which overcomes the problem that many details are neglected and can remove the rainline at every scale as much as possible. In order to maintain the consistency of the structure and color between the rainless image blocks, a new error function is constructed by using bilateral filter and non-mean local denoising algorithm, which is added to the total error function of the conditional generation countermeasure network. The invention does not need any prior knowledge, nor does it need to preprocess and post-process the image, thus ensuring the integrity of the whole structure. The results on the test set show that the invention is improved by 4-7dB compared with the classical algorithm.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
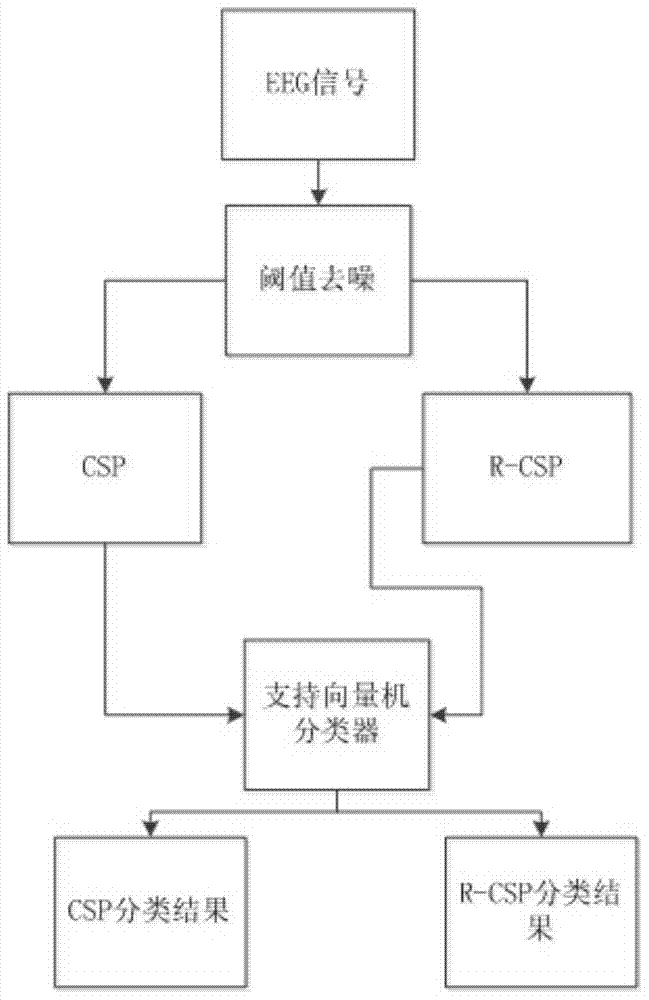
Electroencephalogram feature extraction method based on CSP and R-CSP algorithms
ActiveCN104771163AImprove classification resultsImprove adaptabilityDiagnostic signal processingSensorsElectroencephalogram featureSmall sample
The invention relates to an electroencephalogram feature extraction method based on CSP and R-CSP algorithms. According to the electroencephalogram feature extraction method, when a traditional CSP algorithm is used for extracting small sample electroencephalograms, covariance estimation of the traditional CSP algorithm will generate a larger error; according to the electroencephalogram feature extraction method, the traditional CSP algorithm is improved, and the regularization CSP algorithm R-CSP is put forward. Firstly, a small wave threshold denoising algorithm is used for conducting de-noising processing; secondly, covariance matrixes of five experimenters are solved, one target experimenter is selected, and the rest of the experimenters are auxiliary experimenters, an optimal spatial filter is constructed through selection of regularization parameters, and feature vectors are accordingly extracted; and finally, a genetic algorithm is used for optimizing a support vector machine classifier, and the correct rate of the classification result is further improved. The final classification result shows that the R-CSP algorithm is better in correct rate of the classification result compared with a traditional CSP algorithm.
Owner:西安慧脑智能科技有限公司
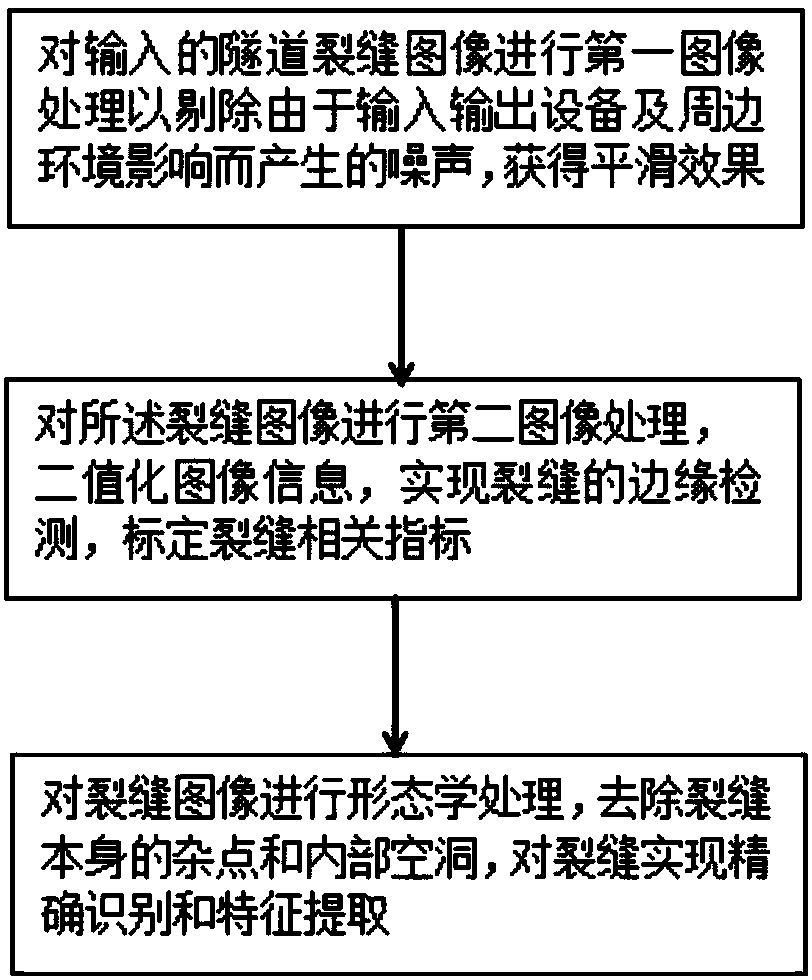
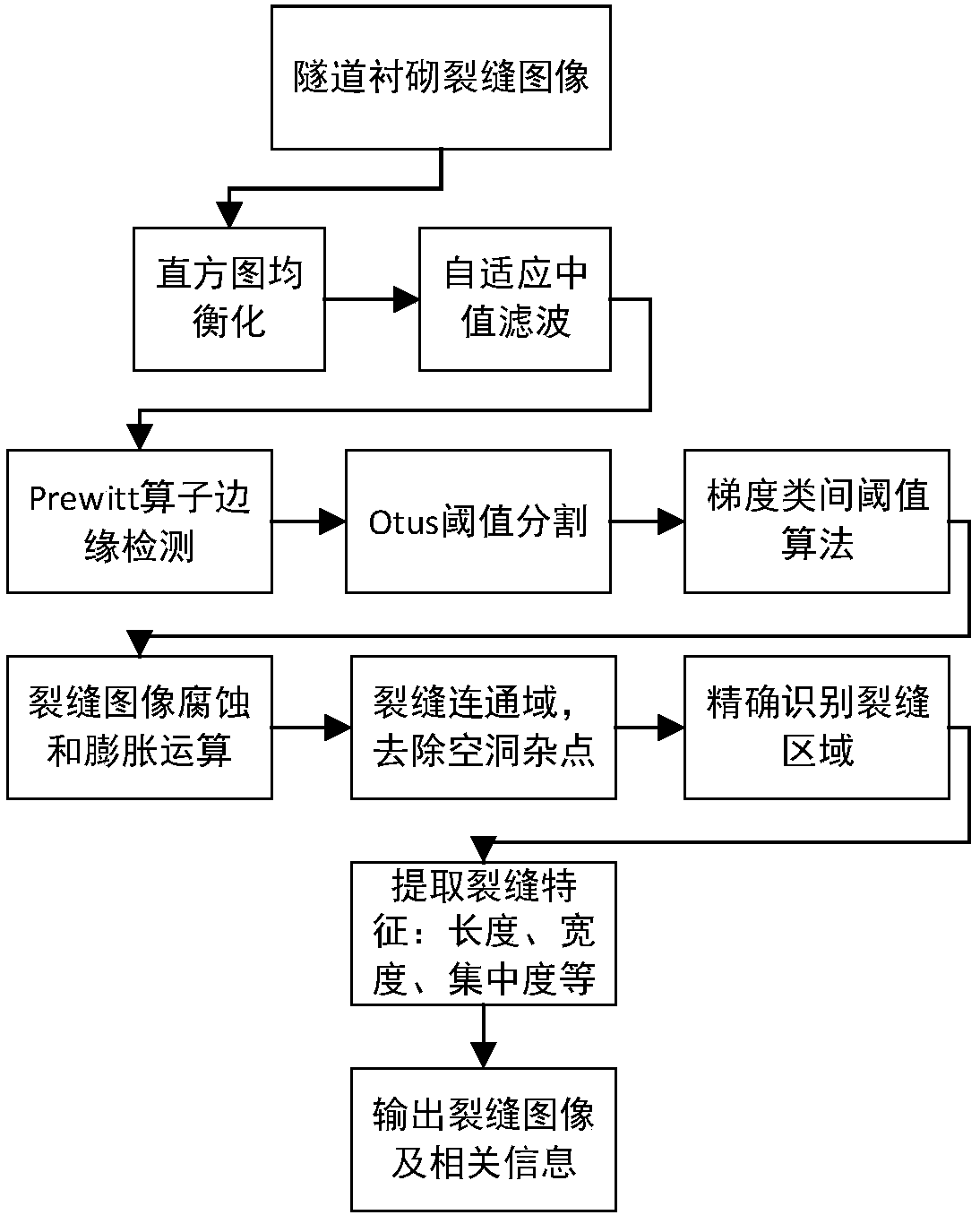
Tunnel lining crack recognition method and system based on gradient inter-class threshold algorithm
InactiveCN107862677AEasy to storeEasy to filterImage enhancementImage analysisRailway tunnelPattern recognition
The present invention discloses a tunnel lining crack recognition method and system based on a gradient inter-class threshold algorithm. The method comprises: (1) denoising a tunnel crack image; (2) using a gradient inter-class threshold algorithm to carry out binarization processing on the denoised image, carrying out edge detection on the obtained binarized image, and calibrating the fracture index; and (3) carrying out morphological processing on the binarized image to remove the noise of the crack itself and fill the internal void, and carrying out crack index extraction on the filled image. The system comprises an image enhancement module, an edge detection module, and a crack recognition extraction module that are connected in sequence. The tunnel lining crack recognition method andsystem based on the gradient inter-class threshold algorithm provided by the present invention has a good recognition effect for the tunnel lining crack images with huge processing amount and multi-interference, and is applicable to the automatic detection of the lining of the high-speed railway tunnel skylight period.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY SIYUAN SURVEY & DESIGN GRP
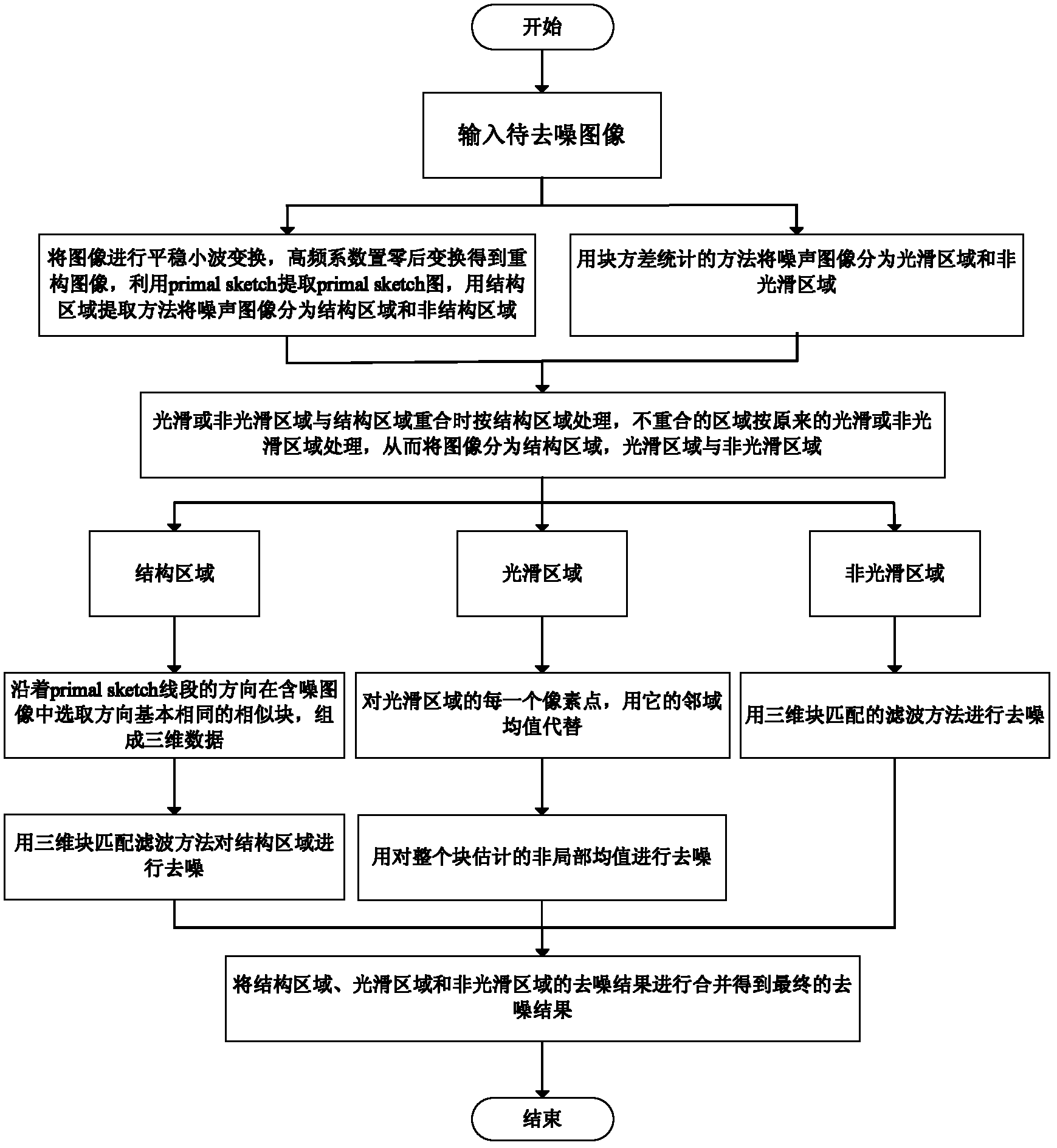
Natural image denoising method based on regional division
ActiveCN102663702AGood removal effectImprove smoothnessImage enhancementDenoising algorithmBlock match
The invention discloses a natural image denoising method based on the regional division, which mainly solves the problem that patches exist in an image after an image is donoised through the existing three-dimensional block matching denoising algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing two-dimensional stationary wavelet transform on an input image to be denoised, and performing inverse transform on a high frequency coefficient subjected to zero setting, so as to obtain a reconstructed image; secondly, exacting the structural information of the reconstructed image, so as to obtain an image structure sketch; thirdly, dividing the noisy original image into a structure region, a smooth region and a non-smooth region through statistic features of an image block and the image structure sketch; fourthly, performing denoising on the smooth region with an improved non-local mean method, performing denoising on the non-smooth region with a BM3D (Block matching 3D) method, and performing denoising on the structure region with a directional feature-based BM3D method; and fifthly, combining estimated results of the structure region, the smooth region and the non-smooth region, so as to obtain the final denoised image. The method can be used for preprocessing natural images.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
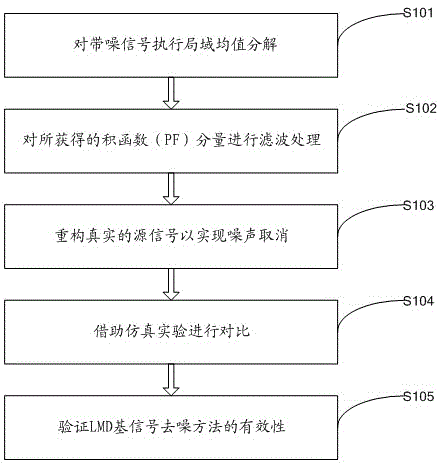
Signal denoising method based on local mean value decomposition
InactiveCN103984866AEliminate noise interferenceVerify validitySpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionDenoising algorithm
The invention discloses a signal denoising method based on local mean value decomposition. The method comprises the steps that the local mean value decomposition is carried out on a noisy signal, amplitude thresholding filtering processing is carried out on the obtained product function (PF) component, and a real source signal is reconstructed, so that noises are omitted, comparison is carried out by means of a simulation experiment, and the effectiveness of an LMD-based signal denoising method is verified by a practical signal noise elimination experiment. According to the method, the noise jamming in observed signals is eliminated, the effectiveness of the LMD-based signal denoising method is verified by virtue of a series of simulation and experiments and through the comparison with the existing wavelet transform (WT)-based denoising method and an empirical mode decomposition (EMD)-based denoising method which appears in recent years, the method is simple, the advantages of the denoising effect which utilizes an LMD-based denoising algorithm are obvious, the combination property is better, the secondary exquisite denoising of the noisy signal is realized, and the noise elimination effect is good.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
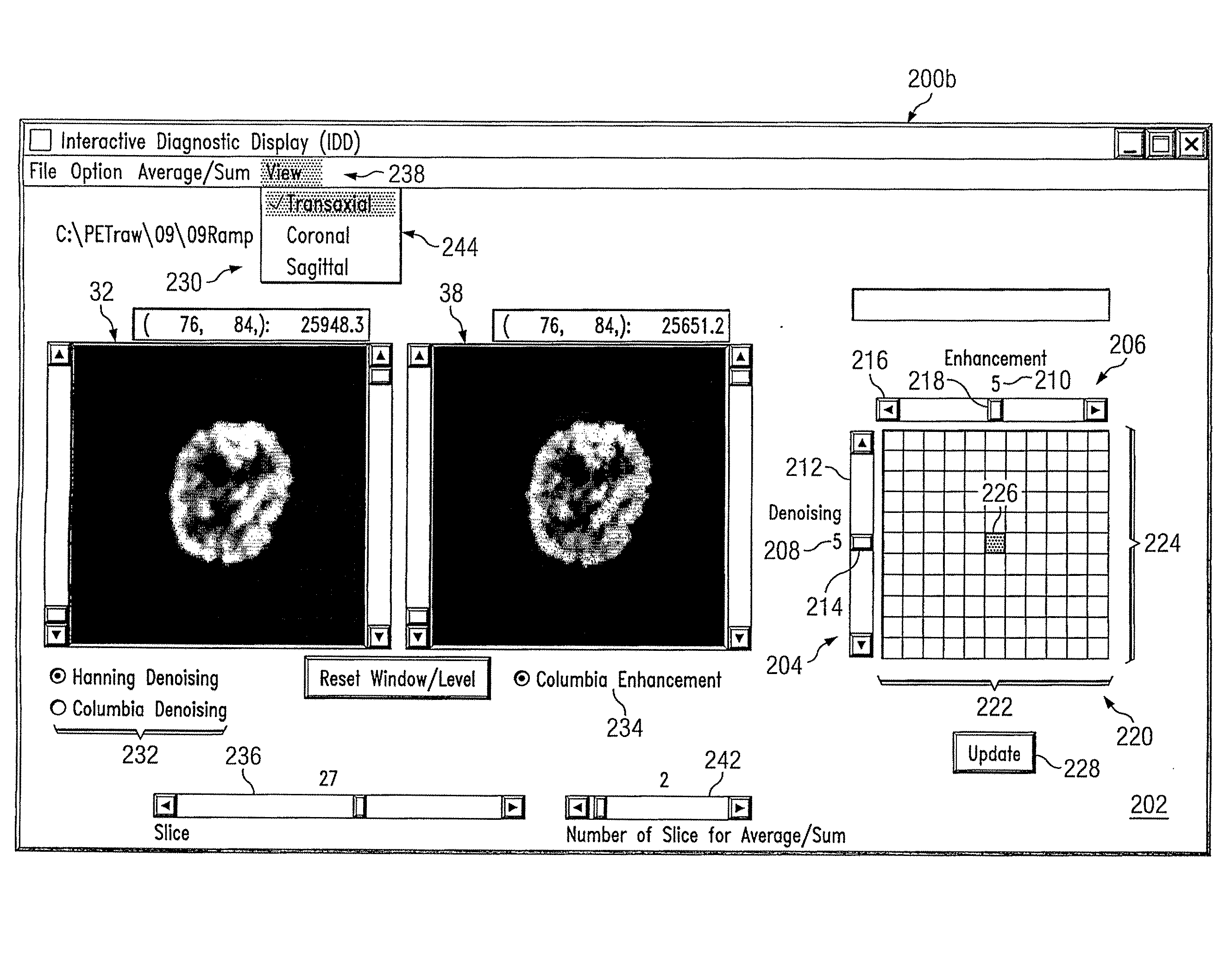
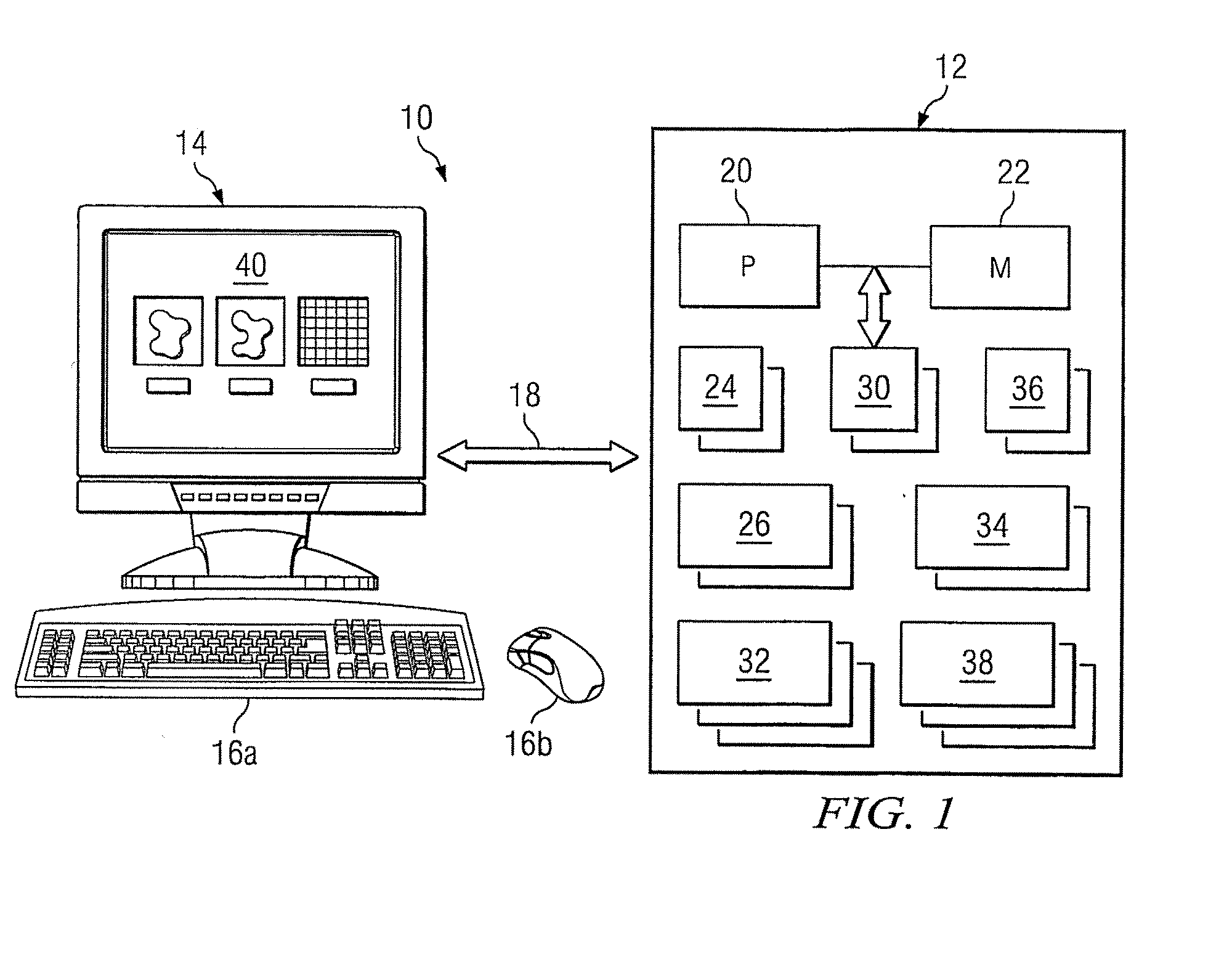
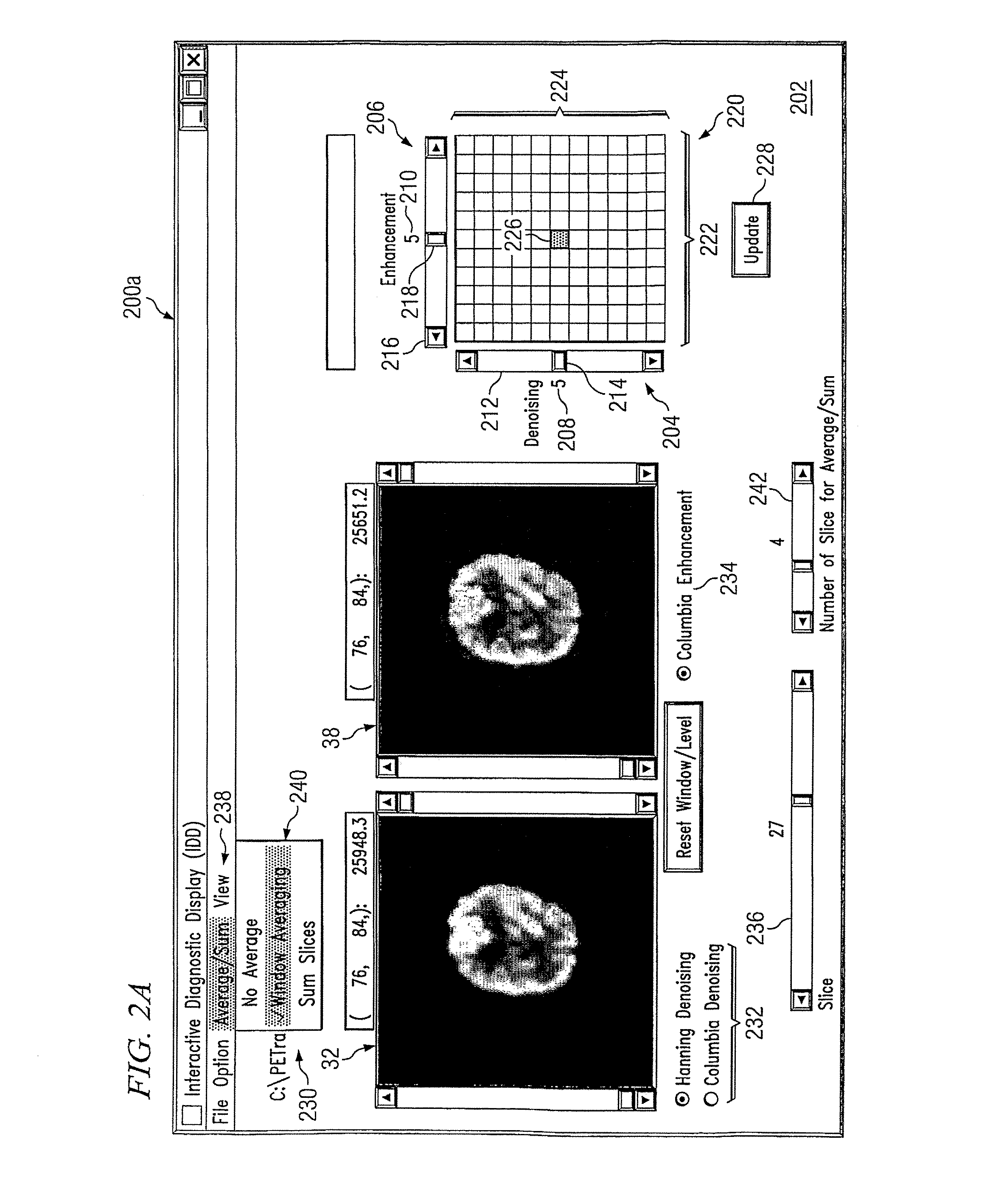
Interactive diagnostic display system
InactiveUS20080247618A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedEnhance the imageImage enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic dataDenoising algorithm
In certain embodiments, an interactive diagnostic display system comprises a database, a digital data processing device, and a display. The database includes: (1) diagnostic data based on measurements of one or more characteristics of a patient's body; (2) denoising algorithms, each corresponding to a value of a denoising parameter; and (3) enhancement algorithms, each corresponding to a value of an enhancement parameter. The digital data processing device is operatively coupled to the database and configured to: (1) receive a denoising value and an enhancement value from a client input device; (2) based on the denoising value, apply the corresponding one of the denoising algorithms to the diagnostic data to generate denoised diagnostic data; (3) based on the enhancement value, apply the corresponding one of the enhancement algorithms to the denoised diagnostic data to generate enhanced denoised data; and (4) generate denoised and enhanced denoised images based on the respective denoised diagnostic data and the enhanced denoised diagnostic data. The display is operatively coupled to the digital data processing device and configured to simultaneously display the denoised diagnostic data and the enhanced denoised diagnostic data.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
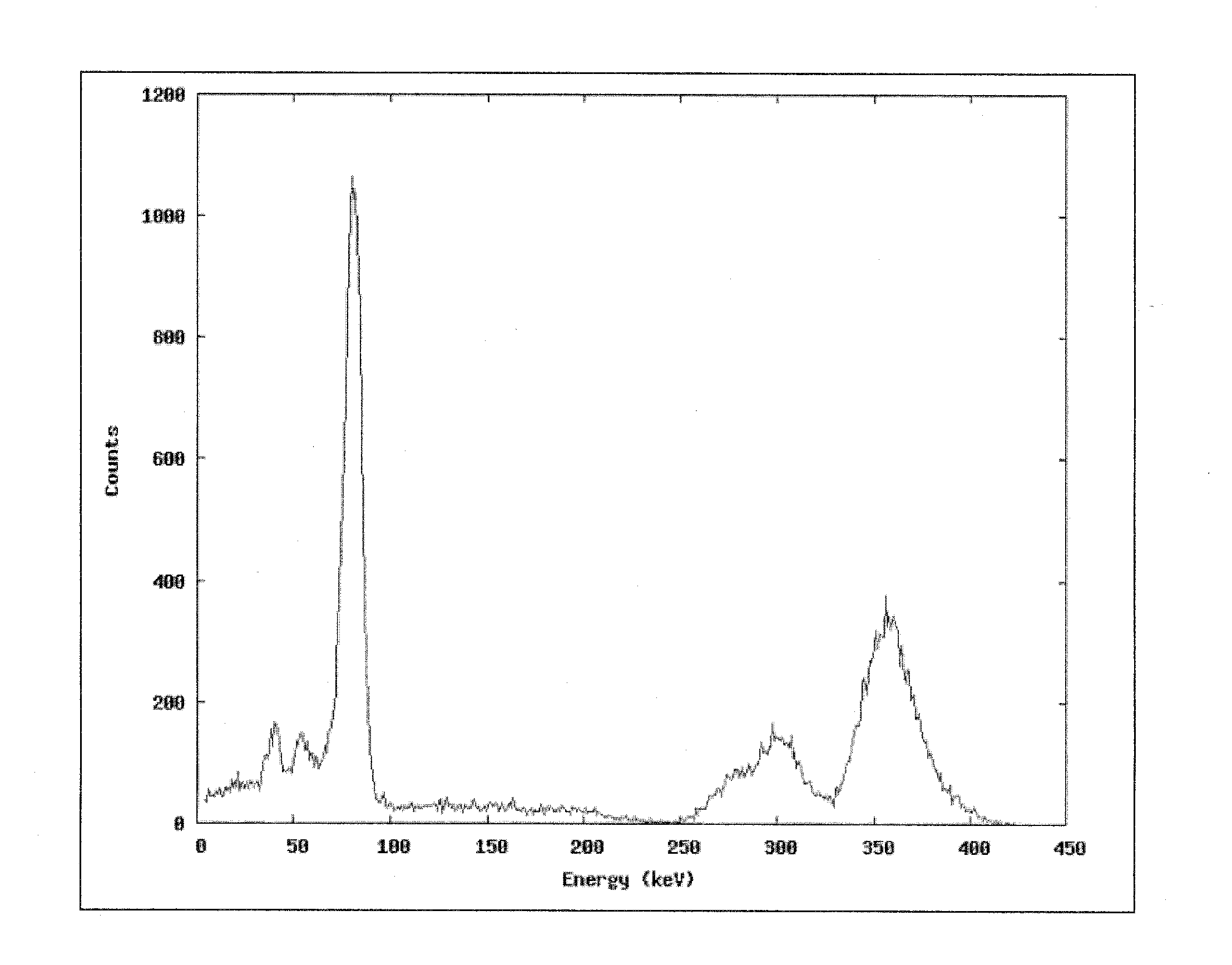
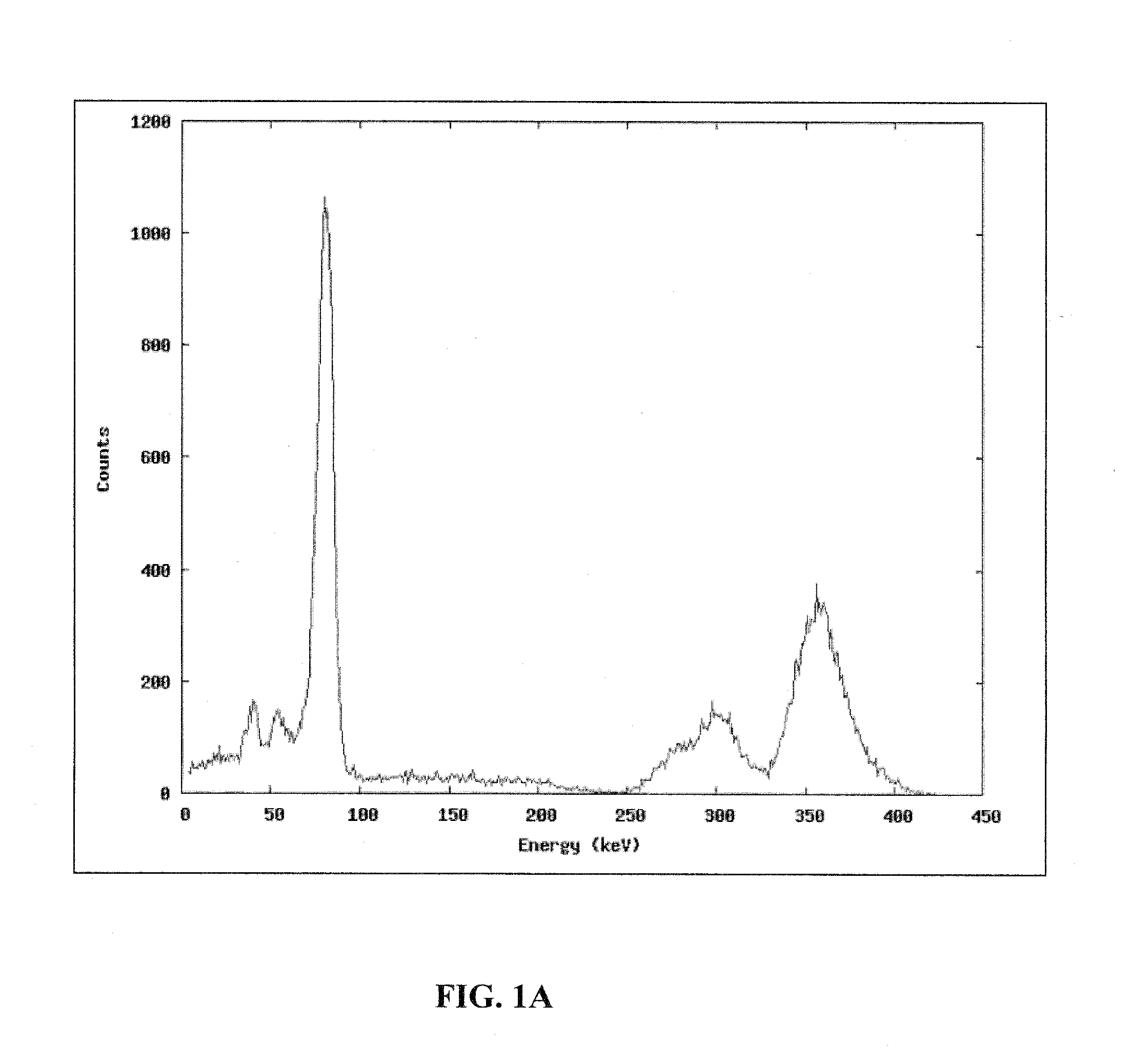
Method and Apparatus for Spectral Deconvolution of Detector Spectra
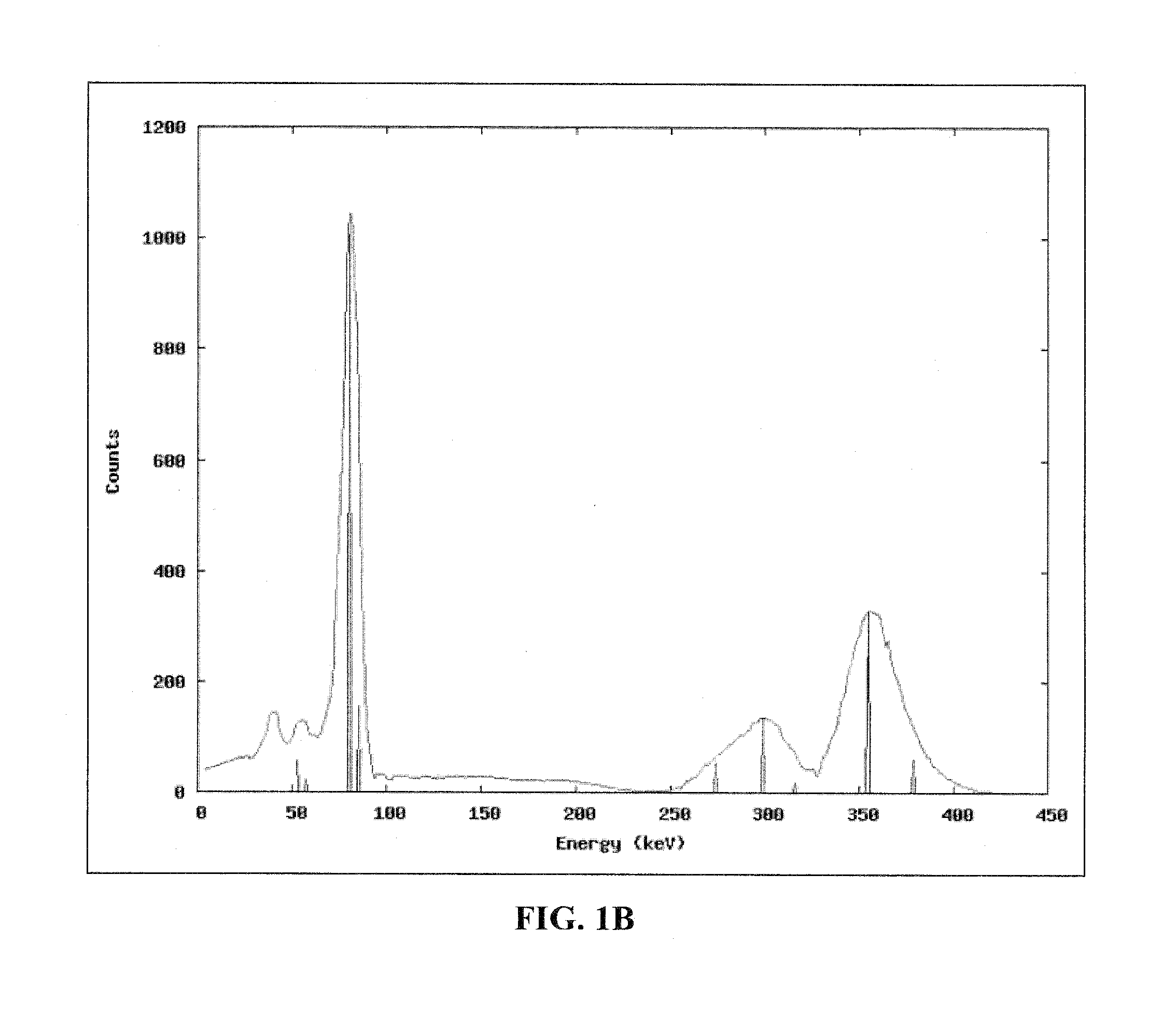
InactiveUS20100305873A1Generate accuratelyAccurate methodMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSolid-state devicesHigh energySodium iodide
Embodiments of the invention pertain to a method and apparatus for spectral deconvolution of detector spectra. In a specific embodiment, the method can be applied to sodium iodide scintillation detector spectra. An adaptive chi-processed (ACHIP) denoising technique can be used to remove the results of stochastic noise from low-count detector spectra. Embodiments of the ACHIP denoising algorithm can be used as a stand alone tool for rapid processing of one dimensional data with a Poisson noise component. In a specific embodiment, the denoising technique can be combined with the spectral deconvolution method. Embodiments of the denoising technique and embodiments of the deconvolution method can be applied to any detector material that provides a radiation spectrum. Specific embodiments can incorporate one or more of the following for spectral deconvolution: denoising, background subtraction, detector response function generation, and subtraction of detector response functions. Photopeaks can be rapidly identified, starting at the high-energy end of the spectrum. The detector response functions can be estimated for photopeaks with a combination of Monte Carlo simulations and simple transformations.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
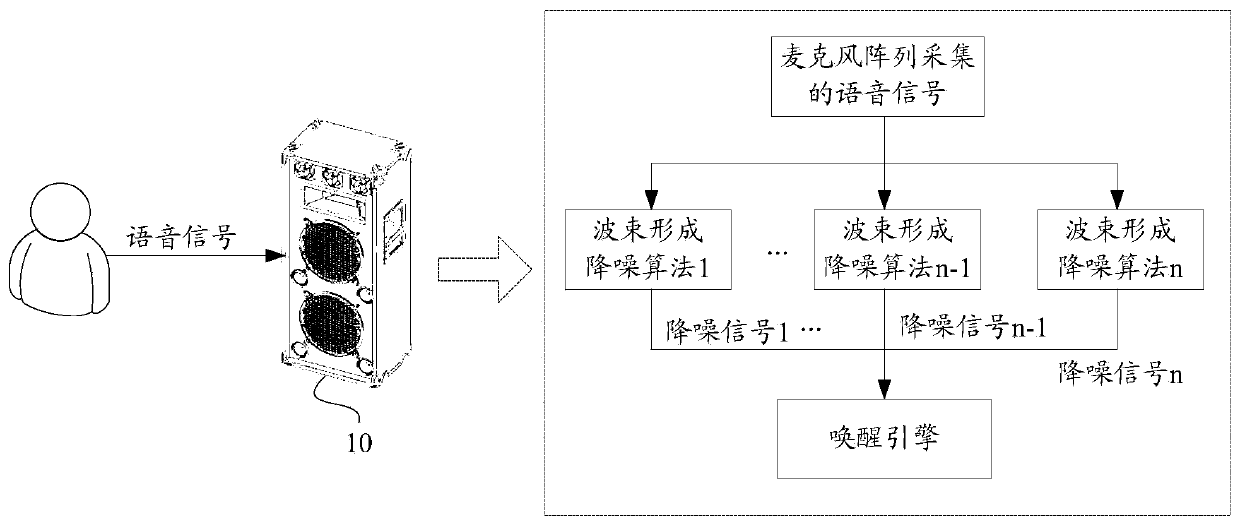
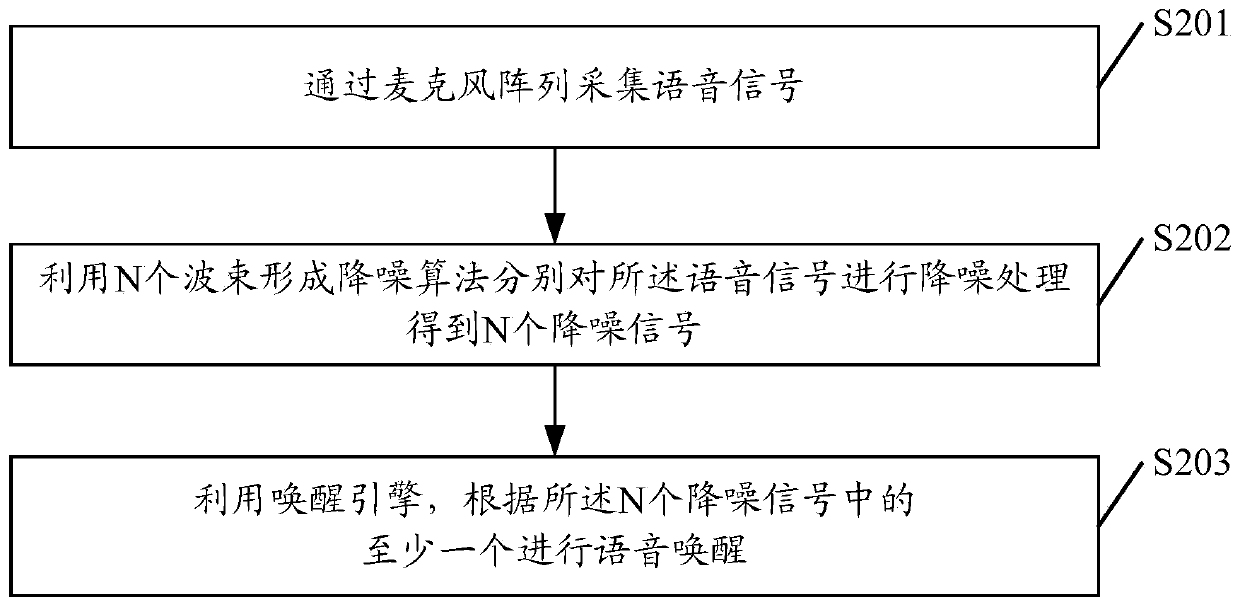
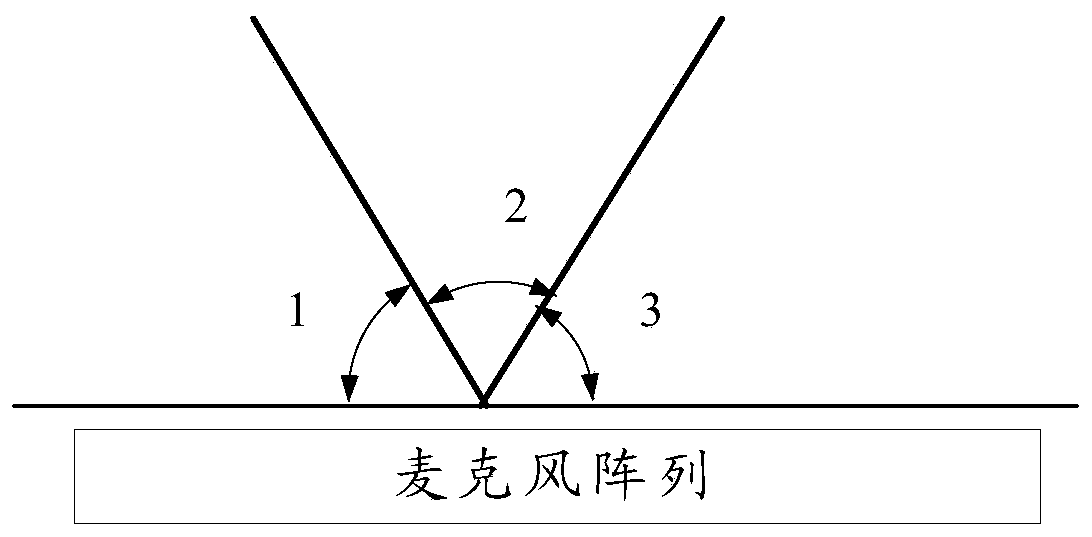
Voice awakening method and device, equipment and medium
ActiveCN109949810AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove the success rate of awakeningSpeech recognitionDenoising algorithmComputer science
The invention discloses a voice awakening method. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a voice signal through a microphone array; respectively carrying out denoising processing on the voice signal by utilizing N beam forming denoising algorithms so as to obtain N denoising signals, wherein each beam forming denoising algorithm corresponds to one area in N areas, the areas corresponding to the different beam forming denoising algorithms are different, the union set of the N areas cover a signal acquisition area of the microphone array, and N is a positive integer greater than 1;and carrying out voice awakening according to at least one of the N denoising signals by utilizing an awakening engine. The method is capable of playing the denoising performance of the denoising algorithms to the greatest extent, and eliminating the echoes outside the beams so as to enhance the echo elimination performance, has a relatively high awakening rate and recognition rate, and is simpleto realize and easy to popularize. The invention further discloses a corresponding device, equipment and a medium.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
Framework for wavelet-based analysis and processing of color filter array images with applications to denoising and demosaicing
InactiveUS20100092082A1Reduce computational complexityReduce computing costGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionComputation complexityDenoising algorithm
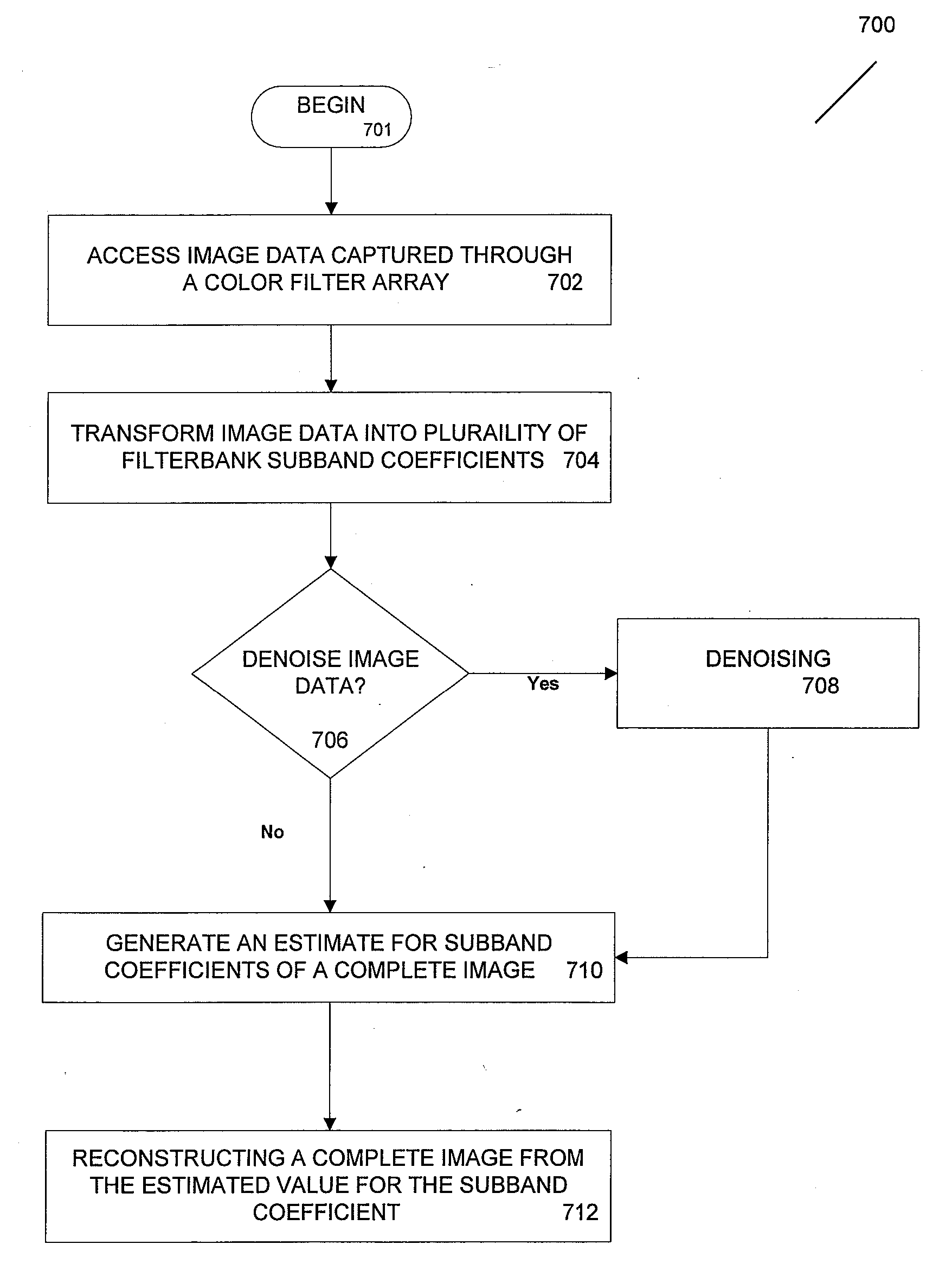
One aspect of the present invention relates to a new approach to the demosaicing of spatially sampled image data observed through a color filter array. In one embodiment properties of Smith-Barnwell filterbanks may be employed to exploit the correlation of color components in order to reconstruct a sub-sampled image. In other embodiments, the approach is amenable to wavelet-domain denoising prior to demosaicing. One aspect of the present invention relates to a framework for applying existing image denoising algorithms to color filter array data. In addition to yielding new algorithms for denoising and demosaicing, in some embodiments, this framework enables the application of other wavelet-based denoising algorithms directly to the CFA image data. Demosaicing and denoising according to some embodiments of the present invention may perform on a par with the state of the art for far lower computational cost, and provide a versatile, effective, and low-complexity solution to the problem of interpolating color filter array data observed in noise. According to one aspect, a method for processing an image is provided. In one embodiment, image data captured though a color filter array is trans-formed into a series of filterbank subband coefficients, by estimating the filterbank transform for a complete image (which estimation can be shown to be accurate in some embodiments) computation complexity associated with regenerating the complete image can be reduced. In another embodiment, denoising of the CFA image data can occur prior to demosaicing, alternatively denoising can occur in conjunction with demosaicing, or in another alternative, after demosaicing.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
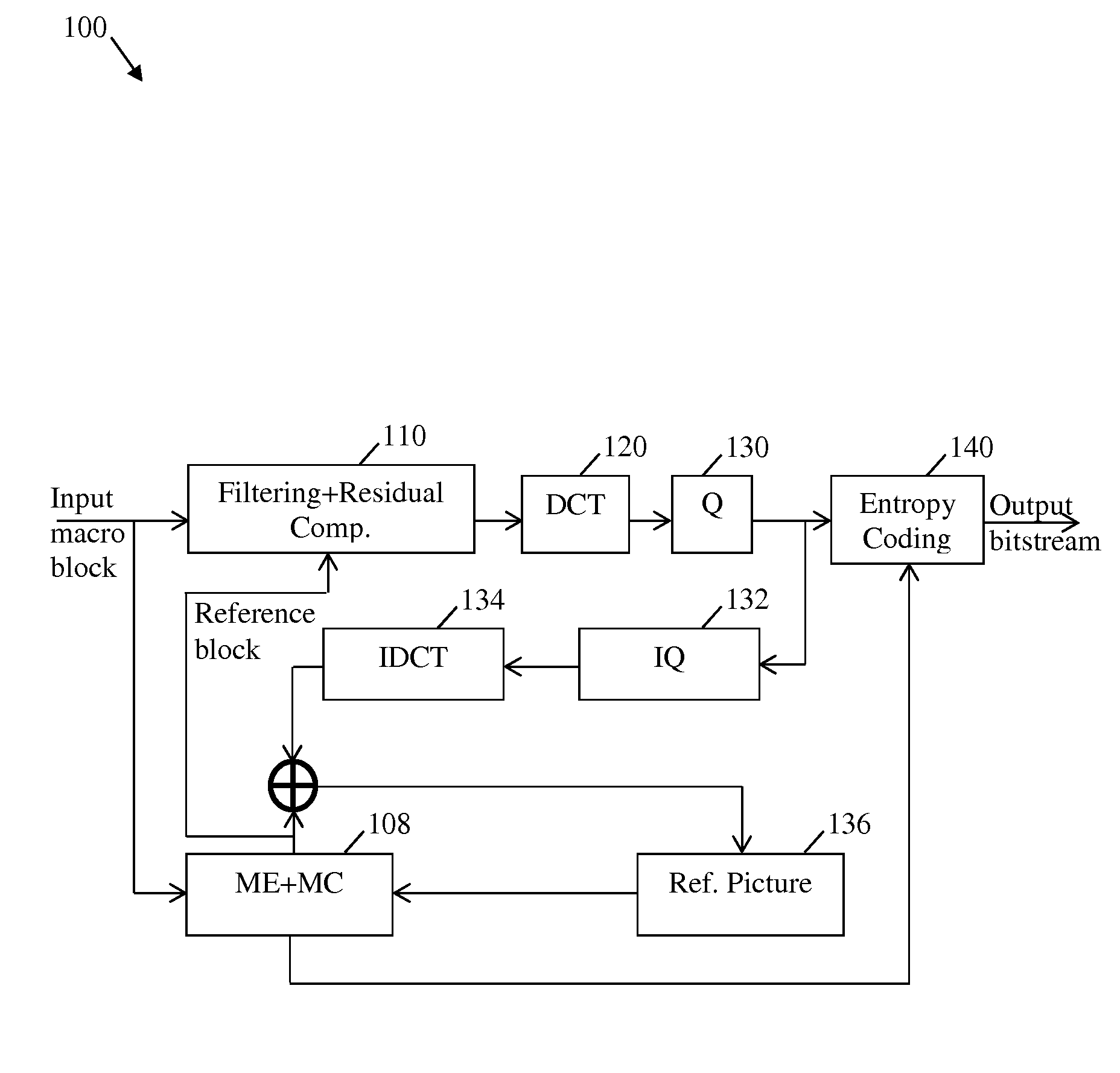
System and Method for Encoder-Integrated Media Denoising
ActiveUS20130286288A1Cancel noiseTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPattern recognitionDenoising algorithm
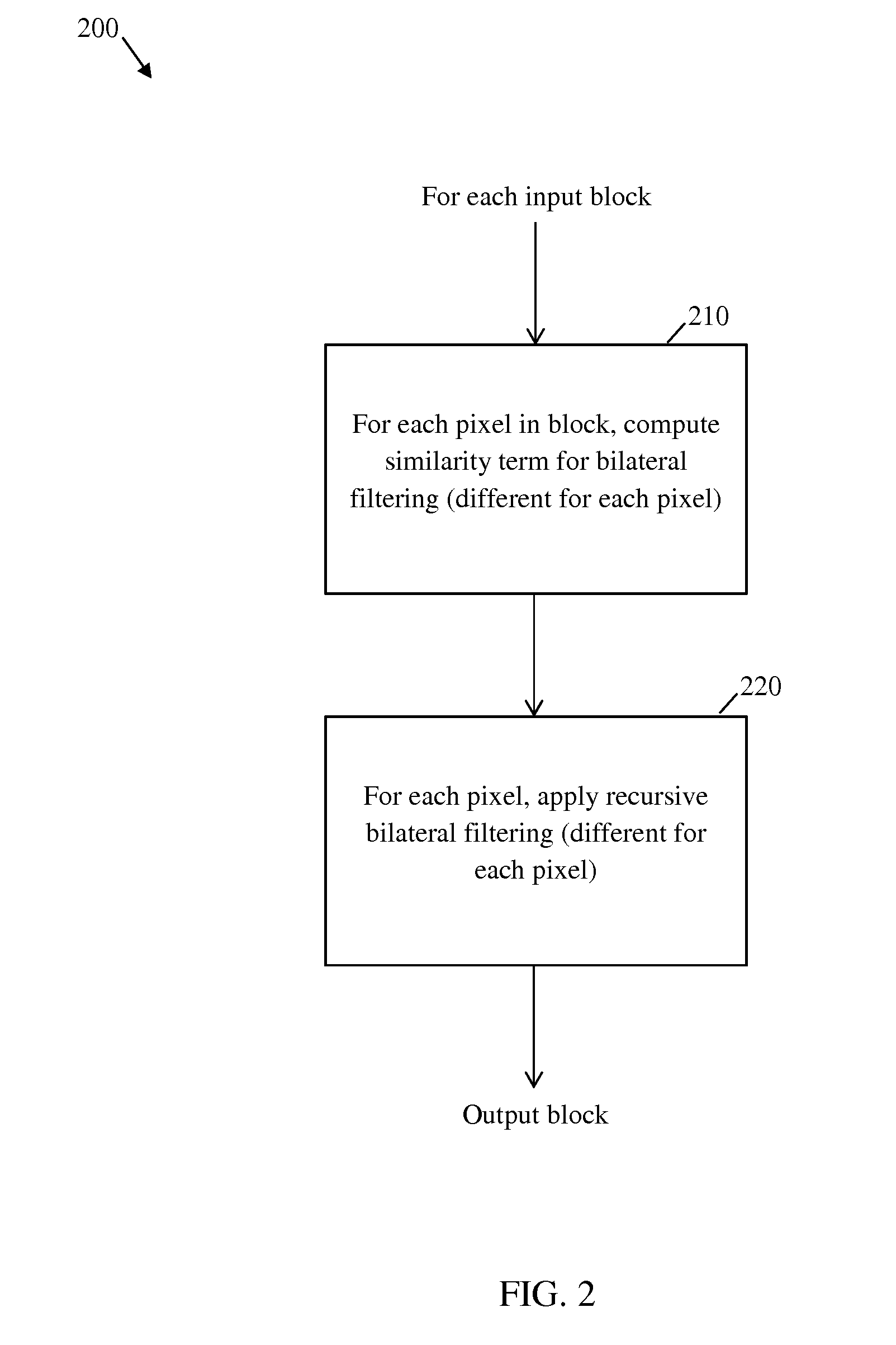
Embodiments are provided herein to achieve video or image sequence encoding with an improved denoising algorithm that is both efficient computationally and has acceptable overhead cost in comparison to other denoising schemes for video encoding. The embodiments include using recursive bilateral filtering as part of the denoising algorithm, which is integrated into a video encoder to overcome limitations of other encoder-integrated denoising algorithms. An embodiment method includes receiving, at a filtering and residual computation function at the encoder, a macro block comprising a plurality of pixels. The filtering and residual computation function also receives, from a motion estimation function at the encoder, a reference block. The reference block comprises a plurality of reference pixels corresponding to the macro block. The filtering and residual computation function further applies a recursive bilateral filter function to each of the pixels of the macro block using the reference pixels of the reference block.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Low frequency oscillation online identification method based on cross-correlation function denoising algorithm
InactiveCN103944174AImprove operation accuracyFast convergenceElectrical testingPower oscillations reduction/preventionDiagnostic Radiology ModalityPattern recognition
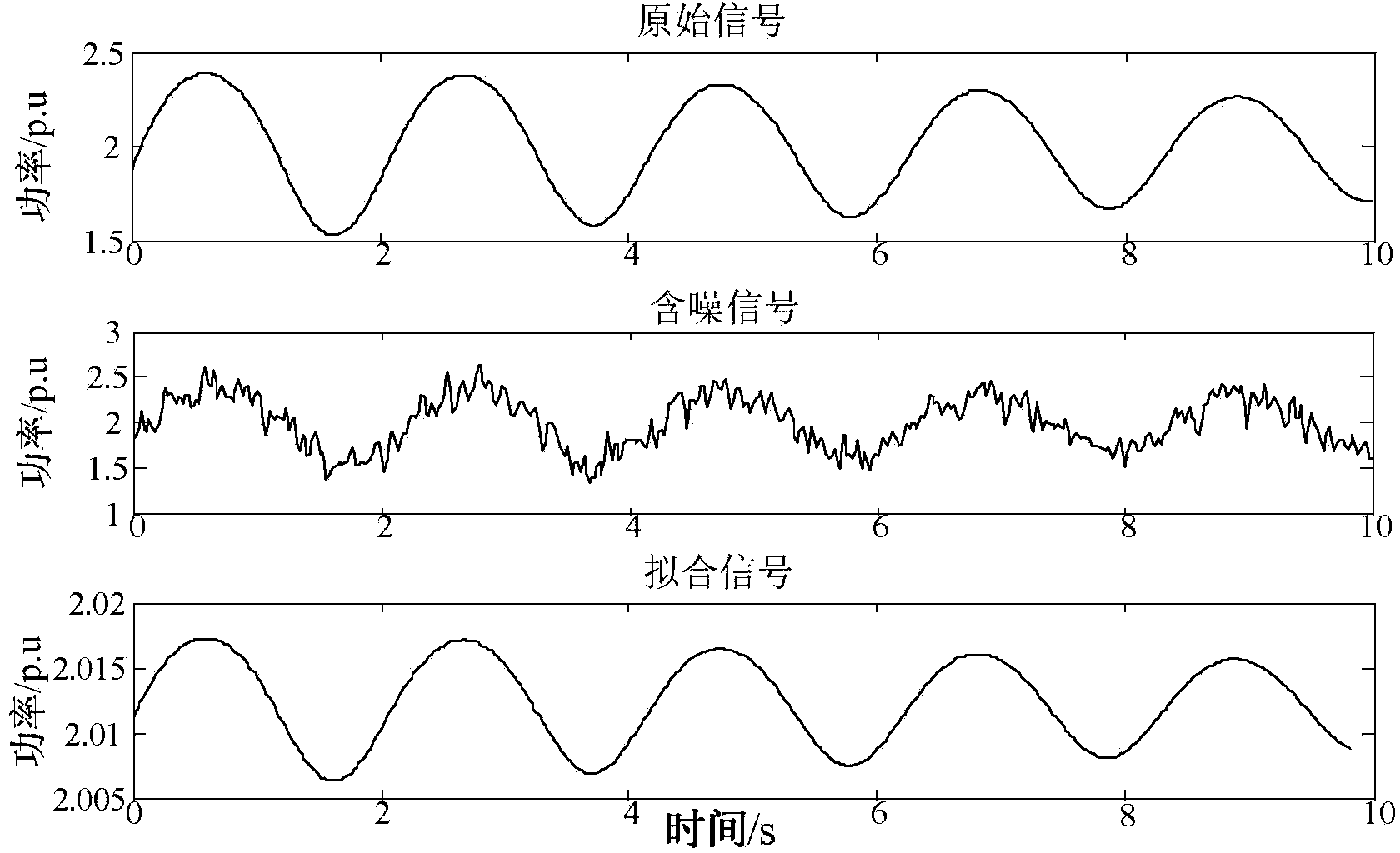
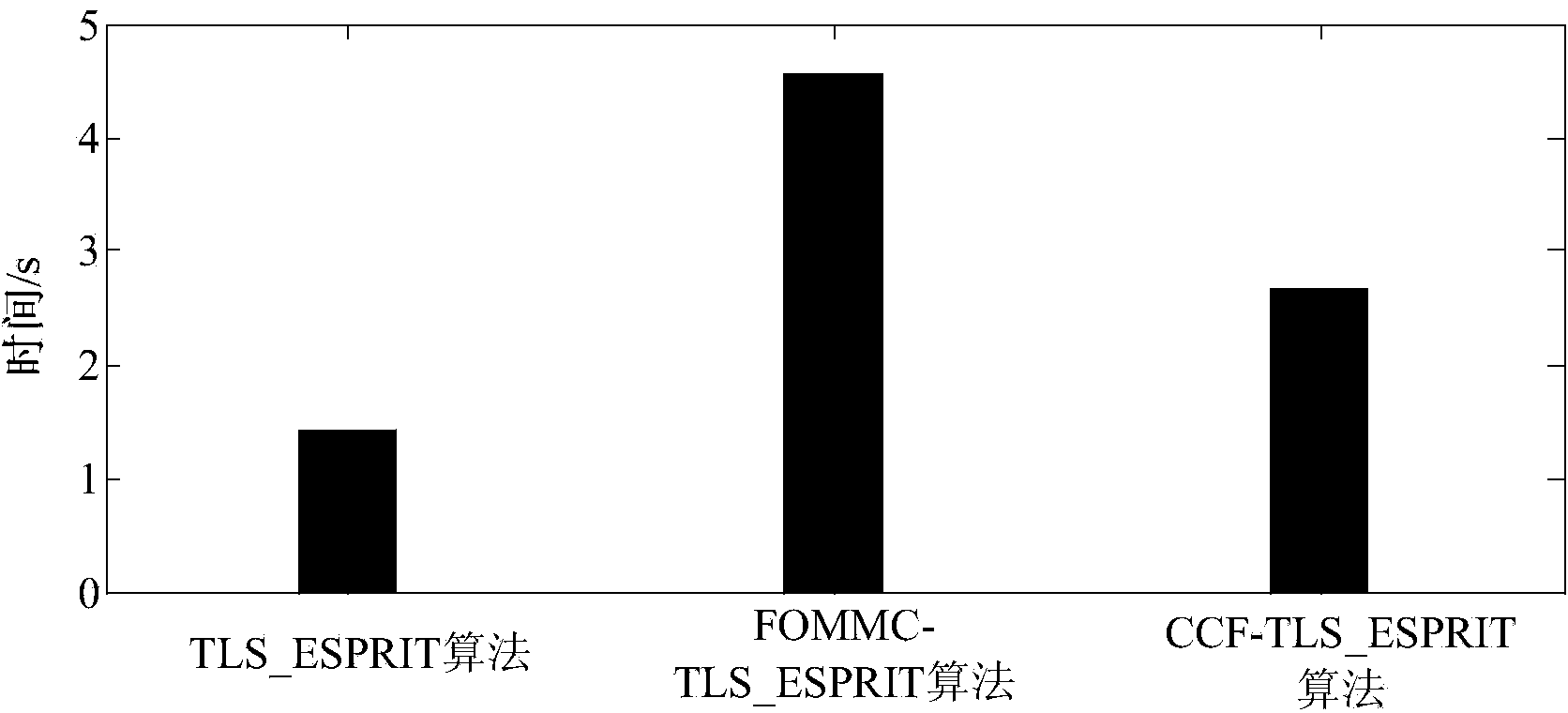
The invention discloses a low frequency oscillation online identification method based on a cross-correlation function denoising algorithm. The low frequency oscillation online identification method based on the cross-correlation function denoising algorithm is characterized in that cross-correlation functions are used for replacing actual measured signals to restrain color noise, and modal identification of low frequency oscillation is carried out by combining a total least square-rotation invariant technology parameter estimation (TLS-ESPRIT) algorithm. The algorithm can identify the modality of the low frequency oscillation of a power system under a color noise environment quickly and accurately, and an effective basis is provided for security and stability analysis and restraining measures of a system.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +3
Electrocardio image recognition method under weak supervision
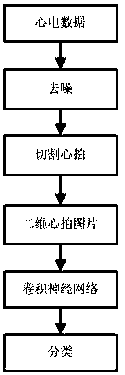
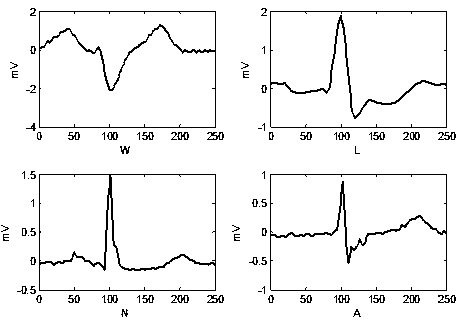
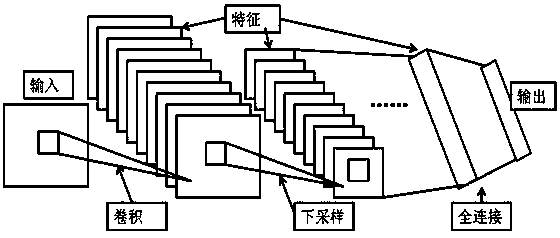
InactiveCN108464827AHigh precisionImprove recognition accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalDenoising algorithm
The invention discloses an electrocardio image recognition method under weak supervision, and belongs to the field of image recognition. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of 1) using a denoising algorithm to remove electrocardio signal noise; 2) locating each heart beat in an electrocardio signal through a locating algorithm, then cutting the electrocardio signal into single heart beats, wherein it is ensured that each heart beat includes all information of one heartbeat; 3) converting the one-dimensional heart beats into heart beat pictures, and then dividing the heart beat pictures into three parts including training pictures, verification pictures and test pictures; 4) inputting the heart beat training pictures into a convolutional neural network for training, and constructing a heart beat picture recognition model; 5) inputting the heart beat verification pictures into the recognition model in step 4 for verifying the heart beat picture recognition accuracy of the model and adjusting various key parameter values; 6) finally, inputting the heart beat test pictures into the heart beat picture recognition model after parameter adjustment in step 5, andconducting classification. By means of the method, the accuracy of classifying the heart beat pictures is high, only a small amount of picture data is needed for model construction, and the method hasgreat significance for the accurate identification of the electrocardio signal.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
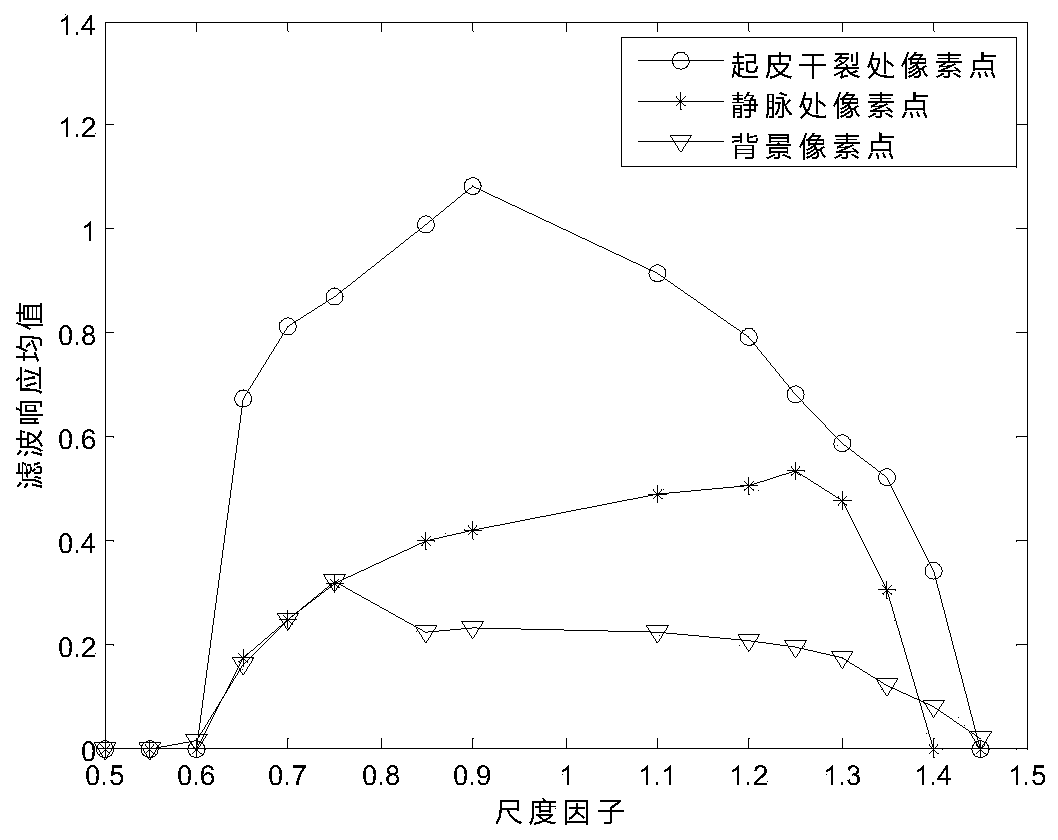
NLM filtering finger vein denoising method based on skin crack segmentation
ActiveCN110188614AAccurate detectionProtect vein informationImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionDenoising algorithm
The invention discloses an NLM filtering finger vein denoising method based on skin crack segmentation. The method comprises: firstly, using a multi-scale Frangi filtering algorithm for carrying out filtering response analysis on a finger vein image with skin crack characteristics caused by finger ecdysis, and selecting the spatial scale size and a segmentation threshold value; performing NLM filtering denoising on the detected area interfered by the skin cracks according to the skin crack binary image, and not performing denoising processing on the non-interfered area. The finger vein denoising algorithm based on switch type non-local mean filtering performs denoising specifically aimed at the exuvial skin crack area, pseudo vein interference is reduced, loss of information of a normal vein area is avoided, redundant information of other areas on the image can be fully utilized when the method is applied to the finger vein image, a certain restoration effect can be achieved, and the denoising effect is better. Therefore, the method is a finger vein denoising algorithm which is good in finger ecdysis type finger vein image denoising effect.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
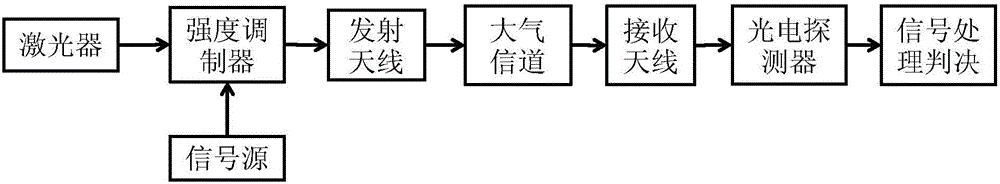
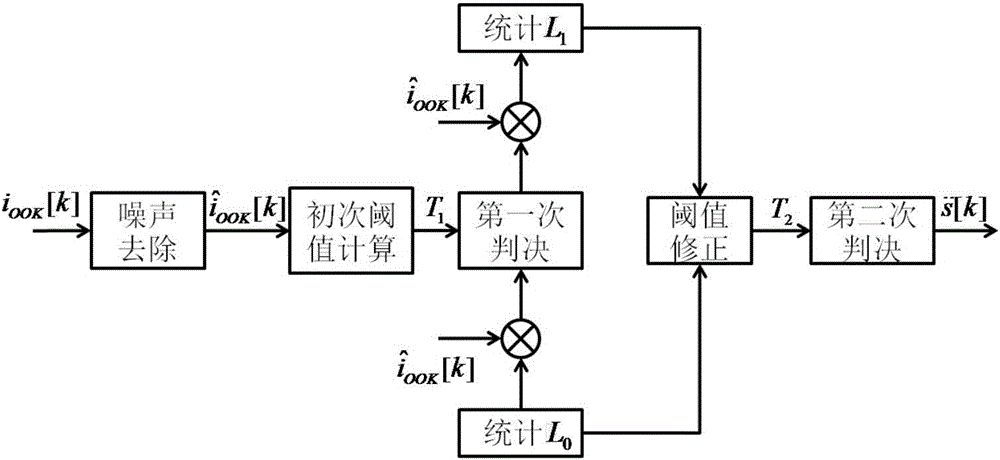
Method for blind detection of receiver according to wireless optical communication
InactiveCN106130660AReduce complexityImprove denoising effectReceivers monitoringElectromagnetic receiversCommunications systemDenoising algorithm
The invention discloses a method for blind detection of a receiver according to wireless optical communication. A wireless optical communication system adopts an intensity-modulation direct detection system; a transmitter of the system transmits signals; and the signals are output to the receiver of the system after signal denoising and twice threshold judgment, so that blind detection of the receiver is realized. The process of signal denoising and twice threshold judgment comprises the following steps: conducting denoising treatment on the received signals according to a modified wavelet transform threshold denoising algorithm; and recovering the digital signals through twice threshold judgment, so that the whole signal detection process is fulfilled. According to the method disclosed by the invention, noise introduced in the signal transmission process can be suppressed to a great extent, so that the bit-error-rate performance can be better, and blind detection can be realized under an unknown channel state condition; and the method has better noise performance and lower algorithm complexity, and can reduce impact of an atmospheric channel and noises on an optical signal, and improve the sensitivity of the detection system.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method and system for removing raindrops in videos
ActiveCN105046653AShorten the timeQuality improvementImage enhancementPattern recognitionDenoising algorithm
The present invention belongs to the technical field of video raindrop removal, and especially relates to a method and a system for removing raindrops in videos. The method comprises: a step a of reading video frames and performing color space conversion for the video frames; a step b of performing raindrop initial detection through photometric characteristics of static raindrops, performing image edge part identification through a guide filter, and subtracting an edge part from an initial detection result, so as to obtain optimized candidate raindrops; and a step c of obtaining final detection raindrops through a denoising algorithm and raindrop area constraint, and removing the raindrops through a defogging equation and photometric characteristics of dynamic raindrops, so as to obtain a final raindrop removing result. The method of the present invention greatly shortens time required for removing the raindrops, improves raindrop removing efficiency, reduces false detection of raindrop pixels, and avoids introducing of artificial noise, in addition, the method combines the defogging equation and the photometric characteristics of dynamic raindrops to perform raindrop removal processing for images, thereby effectively improving image quality and achieving a good raindrop removal effect.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
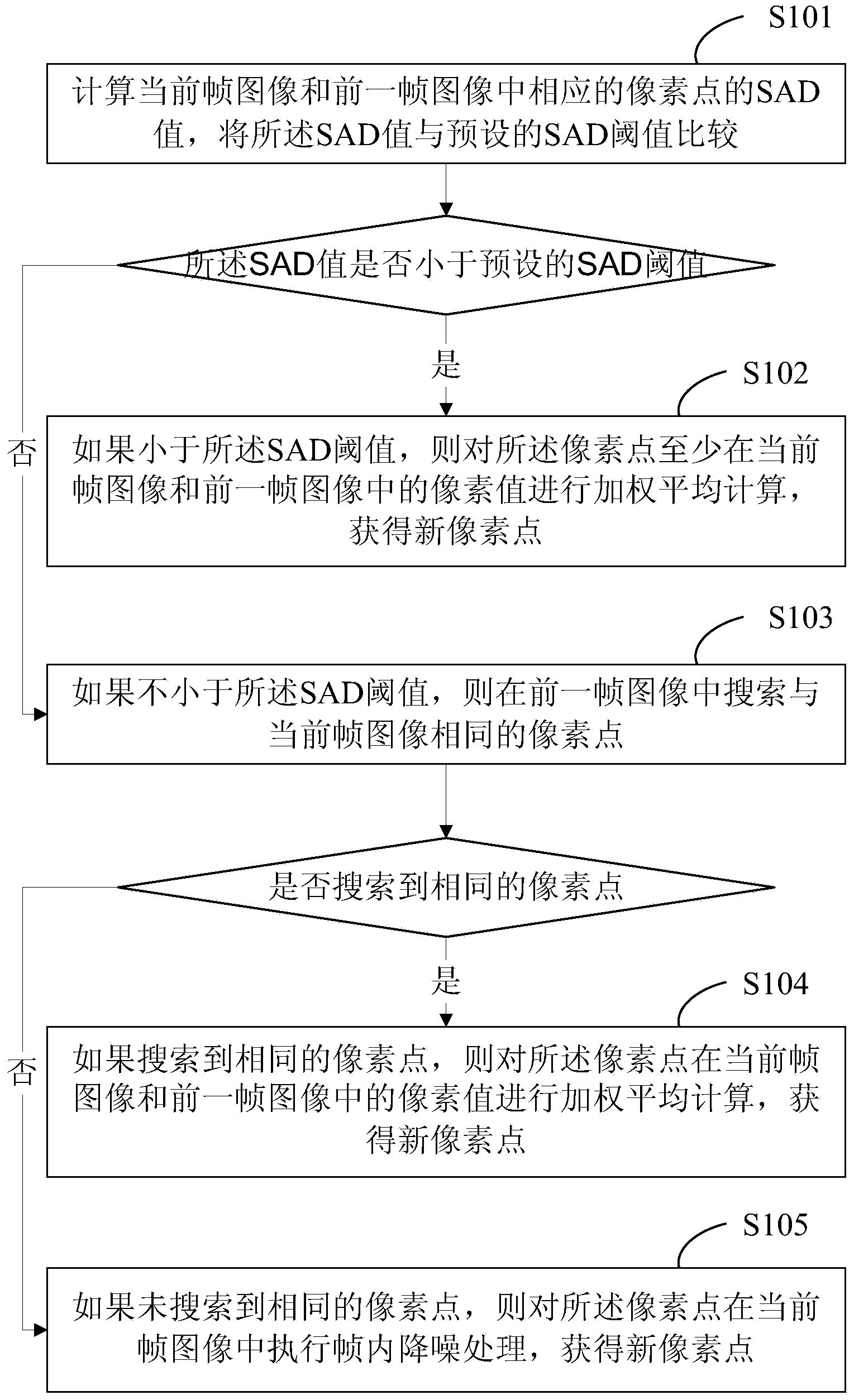
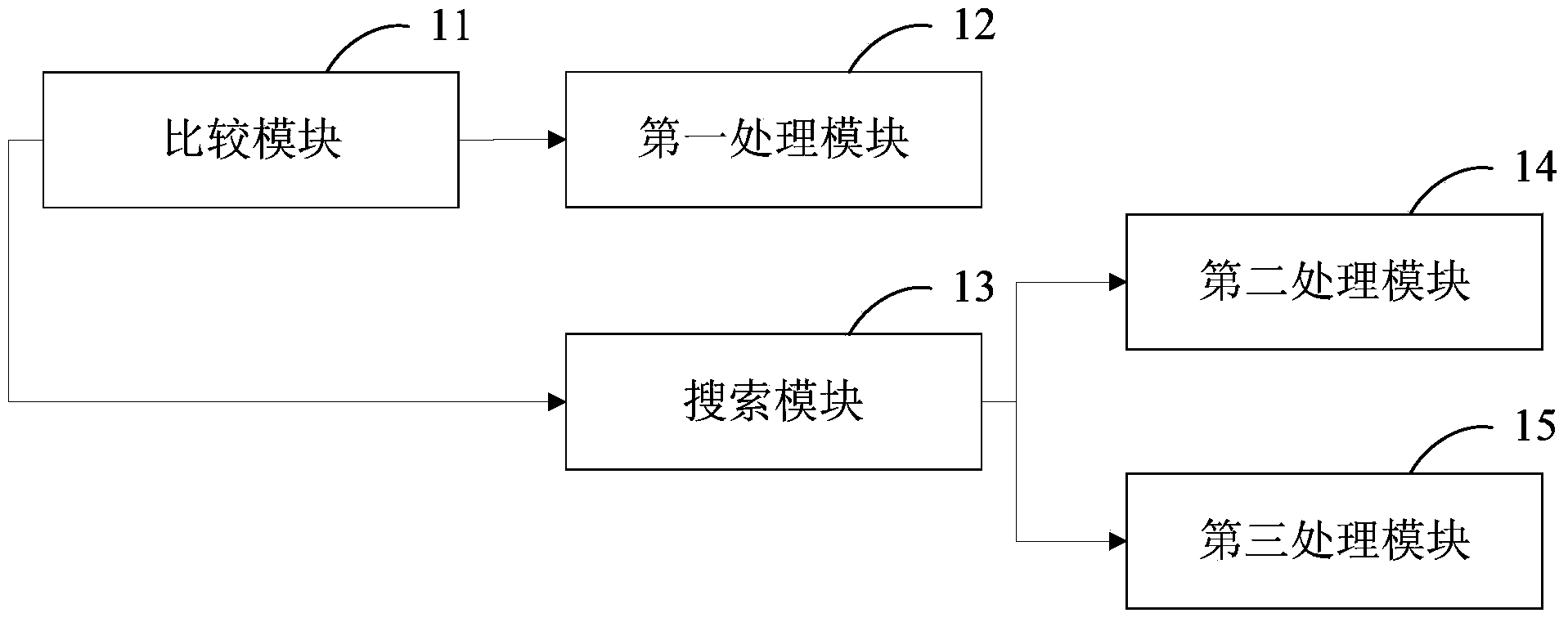
Video denoising method and video denoising system
ActiveCN104253929AImprove noise reductionReduce occupancyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDenoising algorithmComputer graphics (images)
The invention provides a video denoising method and a video denoising system. According to the method, SAD values of corresponding pixels in a current frame image and a previous frame image are computed so as to judge whether the pixels in the current frame image and the previous frame image are moved or not through the SAD values, the corresponding pixels of the current frame and at least one previous frame image are searched, and pixel values of the corresponding pixels at least in the current frame image and the previous frame image are subjected to weighted averaging so as to achieve the purpose of denoising the current frame image by the aid of the previous frame images. Moreover, newly-presented pixels in the current frame are subjected to intra-frame denoising, all the pixels in each frame video image can be denoised, and denoising effect is good. A complicated denoising algorithm is omitted in execution in the whole video denoising method, the video denoising method is simple, video denoising is fast, occupancy on processing resources of a CPU (central processing unit) is less, and the requirement on real-time performance of the network video technology is met.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HUADUO NETWORK TECH
A method and system for underwater image target detection
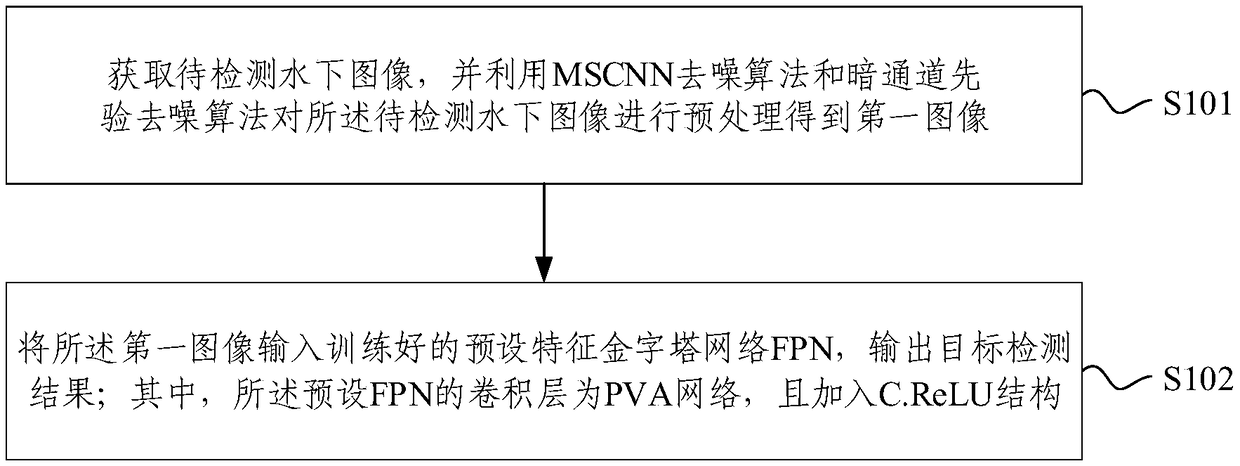
InactiveCN109214319AImprove accuracyDetection time is shortCharacter and pattern recognitionDenoising algorithmComputer vision
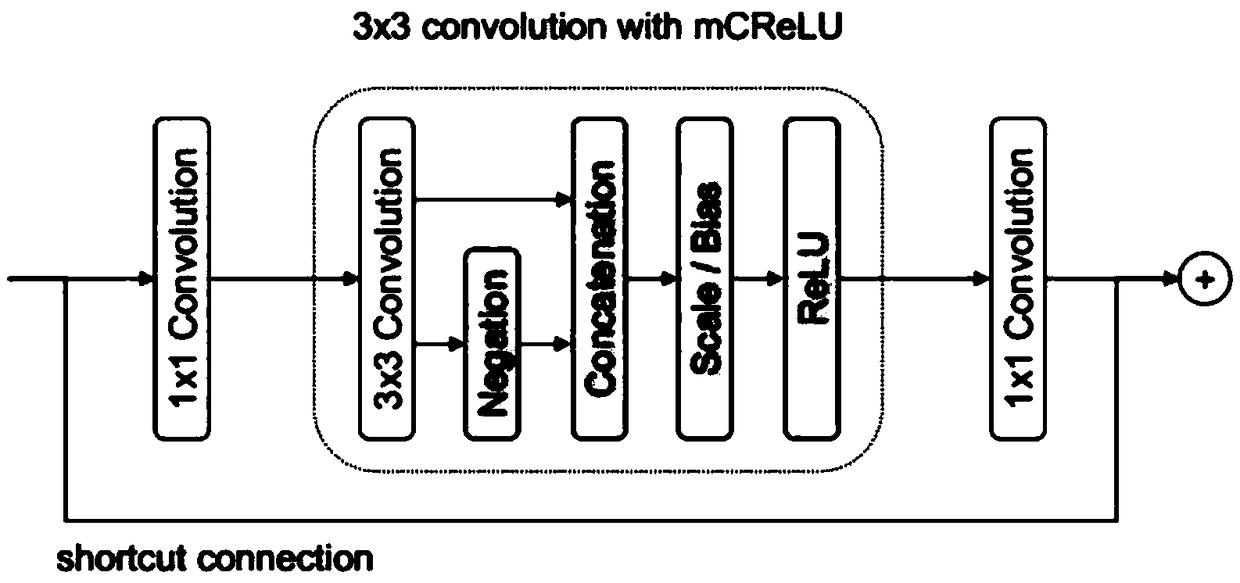
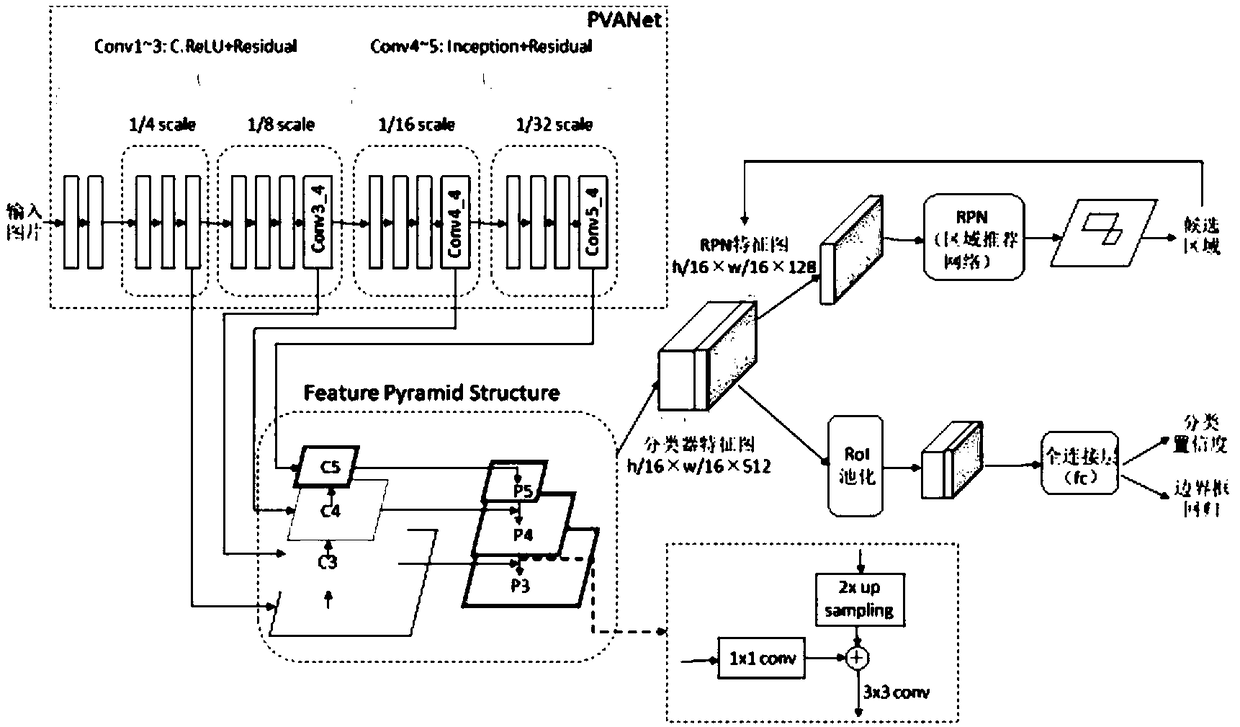
The embodiment of the invention provides an underwater image target detection method and system, comprising the following steps: obtaining an underwater image to be detected, and utilizing MS-CNN denoise algorithm and dark channel prior denoising algorithm preprocess that underwater image to be detected to obtain a first image; inputting the first image into the trained preset feature pyramid network FPN, and outputting a target detection result; wherein the convolution layer of the preset FPN is a PVA network and a C. ReLU structure is added. As the underwater image to be detected is preprocessed, the improved FPN is used to detect the target from the preprocessed underwater image and output the target detection results without manual feature design. The detection process is time-consuming and the detection results have high accuracy. It can be well adapted to the practical application requirements such as automatic detection and automatic fishing.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
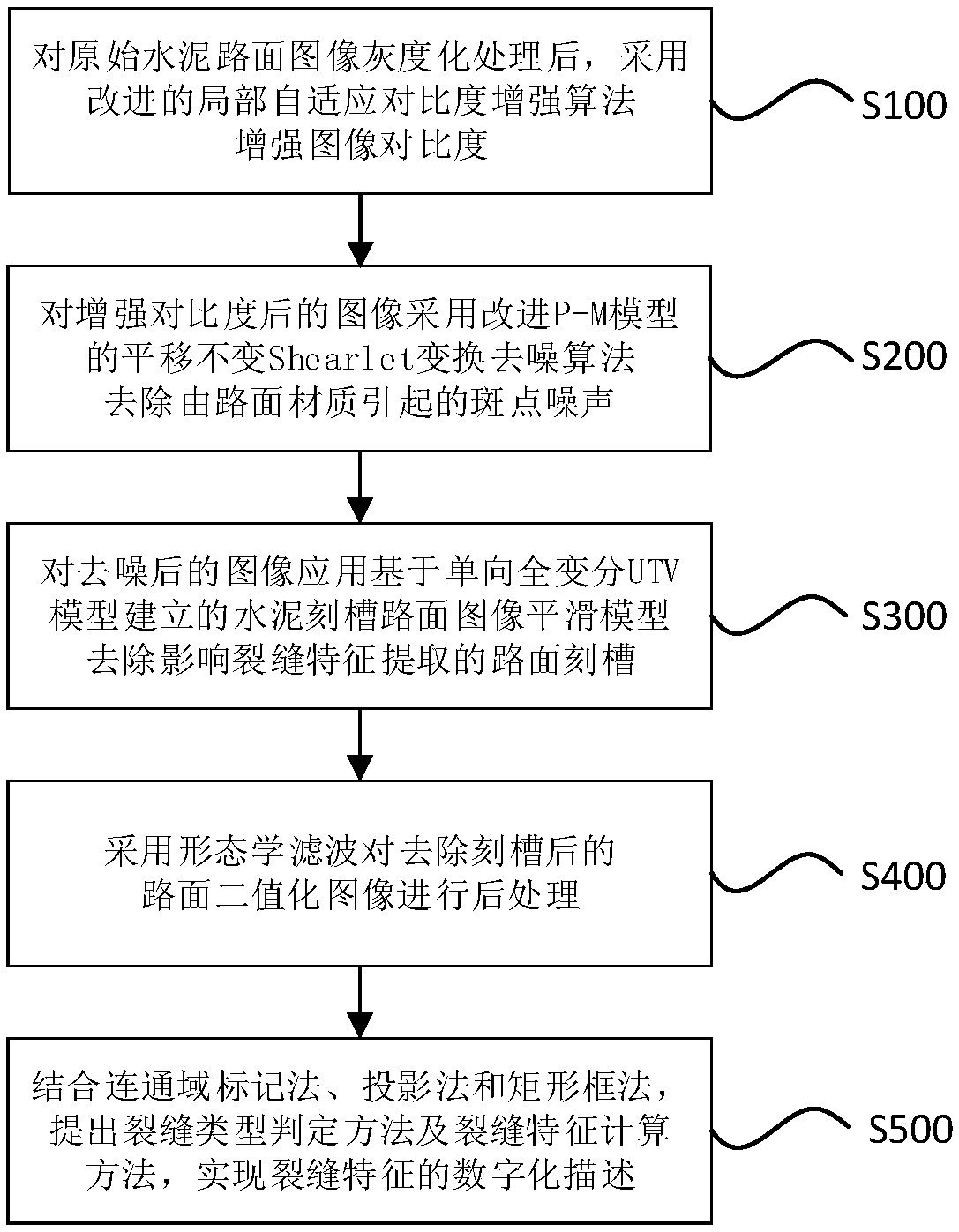
Cement notch groove pavement image noise reduction enhancement and crack feature extraction method
ActiveCN108460744AImprove claritySmall distortionImage enhancementImage analysisImage noise reductionRoad surface
The present invention discloses a cement notch groove pavement image noise reduction enhancement and crack feature extraction method aiming at the problems that the pavement contrast is too low causedby external factors and the payment spots and notch groove autointerference caused by pavement materials. The method comprises the following steps of: employing an improved local adaptive contrast enhancement algorithm to enhance image contrast after graying processing of an original cement pavement image; employing translation invariance Shearlet transform denoising algorithm of an improved P-Mmodel to remove speckle noise caused by pavement materials; employing a cement notch groove pavement image smoothing model established based on an unidirectional total variation UTV model to the imageafter denoising to remove a pavement notch groove influencing feature extraction; and combining a connected domain mark method, a projection method and a rectangular frame method to extract a crack type determination method and a crack feature calculation method to achieve digital description of crack features. The cement notch groove pavement image noise reduction enhancement and crack feature extraction method is systematic and comprehensive, small in calculated amount and easy to apply.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
A sign language recognition method based on multi-source information fusion
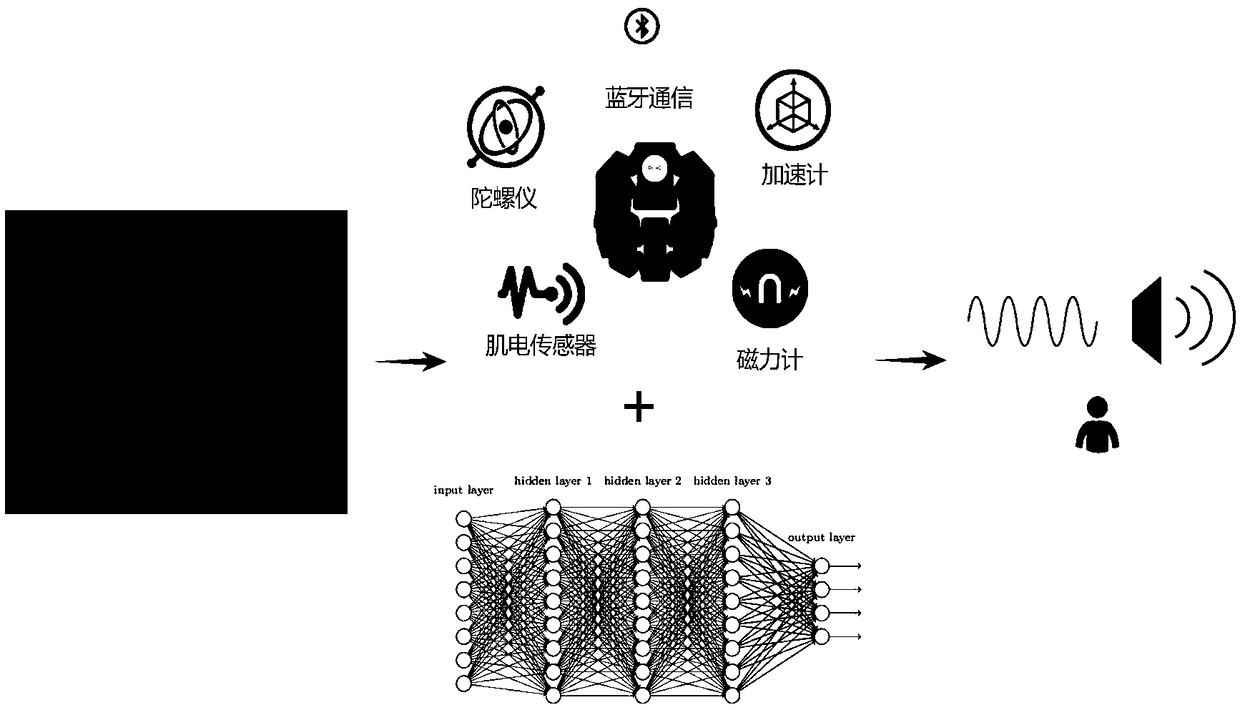
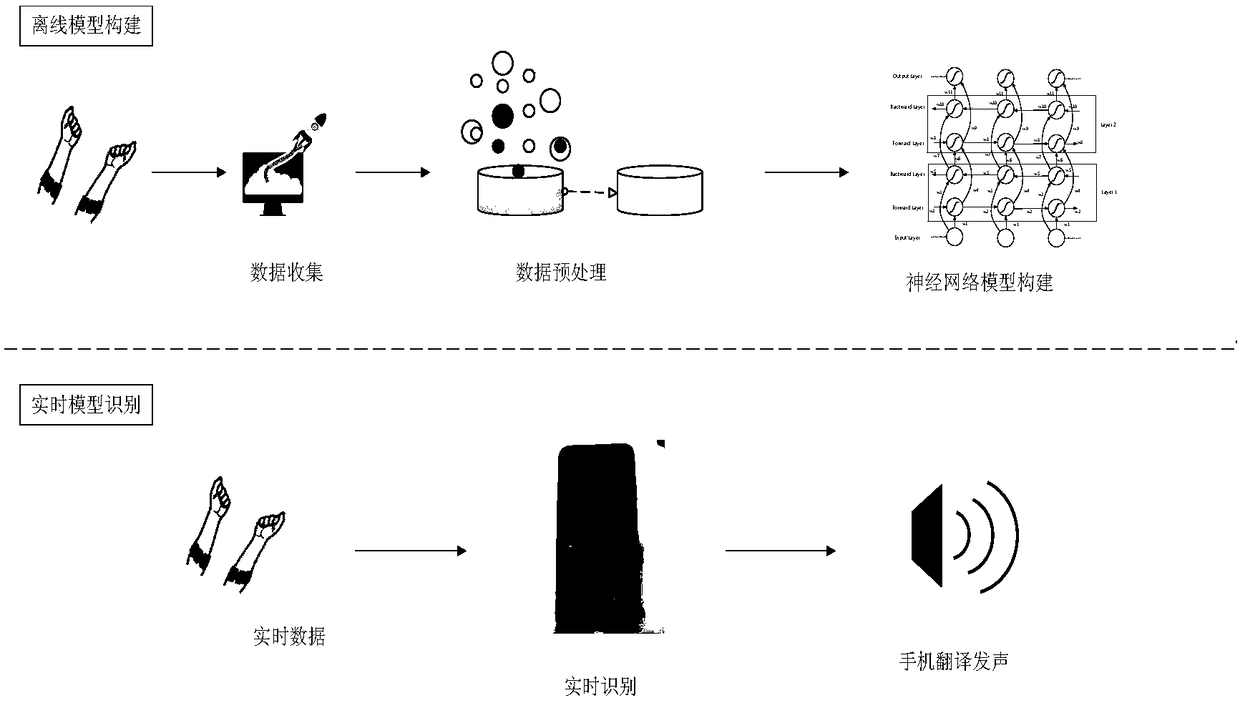
InactiveCN109271901AGuaranteed accuracyIntegrity guaranteedCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesNetwork modelBluetooth
The invention discloses a sign language recognition method based on multi-source information fusion, in which a data collection model, a data preprocessing model, a neural network model and a real-time identification model are used. The invention adopts the multi-sensor fusion technology and the depth learning method to recognize the sign language, and sends out the sound corresponding to the signlanguage action through the loudspeaker. The process is as follows: 1. collecting sign language motion information through surface electromyography (sEMG) sensor and inertial measurement unit (IMU),and transmitting data through Bluetooth; 2, cleaning the collected data by feature extraction and denoising algorithm, and processing the data into a data format that can be input into a neural network; 3, constructing a bi-directional double-layer LSTM neural network and training a preservation model; 4, transplantting the model to a mobile phone, cutting the real-time motion data, inputting theprocessed motion data into the model to obtain a label correspond to the sign language motion, and using the open source language library to send out the speech corresponding to the motion label.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
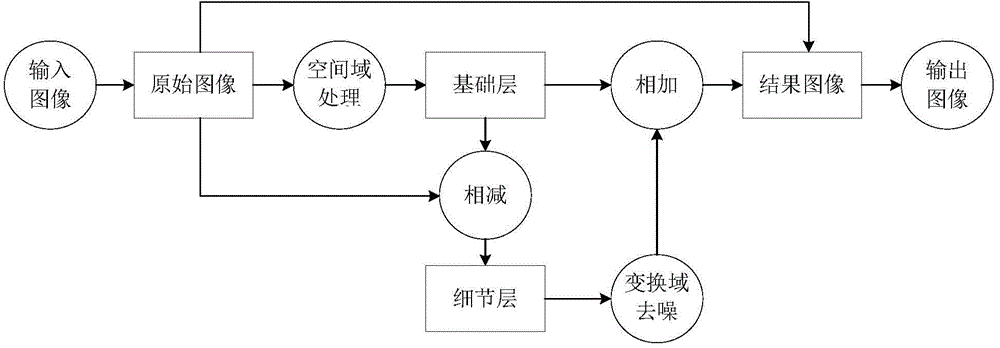
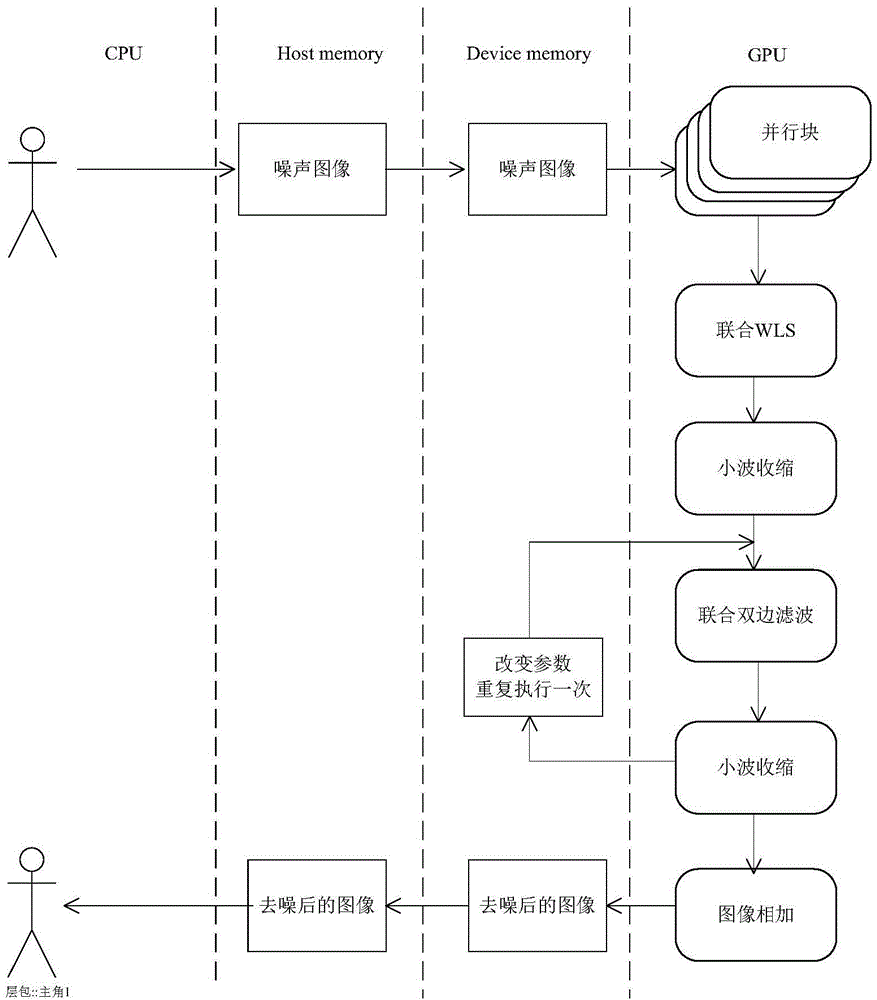
OpenCL-based parallel optimization method of image de-noising algorithm
The invention discloses an openCL-based parallel optimization method of an image de-noising algorithm. According to an idea of image layering, an image is divided into a high-contrast base layer and a low-contrast detail layer by using a combined dual-side filtering algorithm and a combined WLS algorithm; de-noising processing is carried out on the detail layer by using stockham FF; and then image restoring is carried out by changing frequency spectrum contraction and image adding methods, thereby realizing the de-noising effect. According to the invention, on the basis of characteristics of large execution function processing data volume and high data parallelism of the base layer obtaining and detail layer de-noising processing, the openCL platform model is used and parallel calculation of the image de-noising algorithm is realized on GPU; and then details of the calculation process are modified, wherein the modification processing contains local internal memory usage, proper working team size selection, and parallel reduction usage and the like. The speed-up ratio of the de-noising algorithm that is realized finally can reach over 30 times; and thus the practicability of the algorithm can be substantially improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Preprocessing method based on inspection image
InactiveCN110400267AEliminate mistCancel noiseImage enhancementImage analysisWeather factorPretreatment method
The invention discloses a preprocessing method based on an inspection image, and the method comprises: an image defogging algorithm which removes the impact on the image quality from a weather factor,and guarantees the original features of an image; an image segmentation algorithm which is used to obtain a condition area satisfying uniformity and connectivity, and extract an interested target ora meaningful area; an image denoising algorithm for removing a large amount of noise introduced in the imaging process and ensuring the original characteristics of the target object; an image enhancement algorithm, in whch image enhancement processing is used for optimizing the image quality, emphasizing the region of interest in the image and improving the readability of the image; and an image restoration algorithm which is used for processing the image which is degraded due to distortion, blurring, distortion or noise mixing to obtain a source image which is restored as much as possible. The technical scheme of the embodiment of the invention is used for preprocessing the inspection image, improving the quality of the inspection image, highlighting the characteristics of the target object, facilitating the later intelligent recognition and classification, and greatly reducing the cost compared with a mode of processing only depending on manual discrimination.
Owner:ANHUI JIYUAN SOFTWARE CO LTD +3
Pseudo-Zernike moment-based image denoising algorithm
The invention discloses a pseudo-Zernike moment-based image denoising algorithm, which is realized by a non-local mean denoising algorithm and pseudo-Zernike moment calculation. The pseudo-Zernike moment-based image denoising algorithm disclosed by the invention aims to remove noise better and obtain an image with clear details; and simulation tests indicate that the algorithm not only can effectively remove noise, but also can maintain the edge information of the image, thus obtaining a better denoising effect than that of the traditional non-local mean denoising algorithm.
Owner:LIAONING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Digital X-ray imaging system
InactiveCN104574316ASolve the problem of artifactsImprove denoising effectImage enhancementPersonalizationX-ray
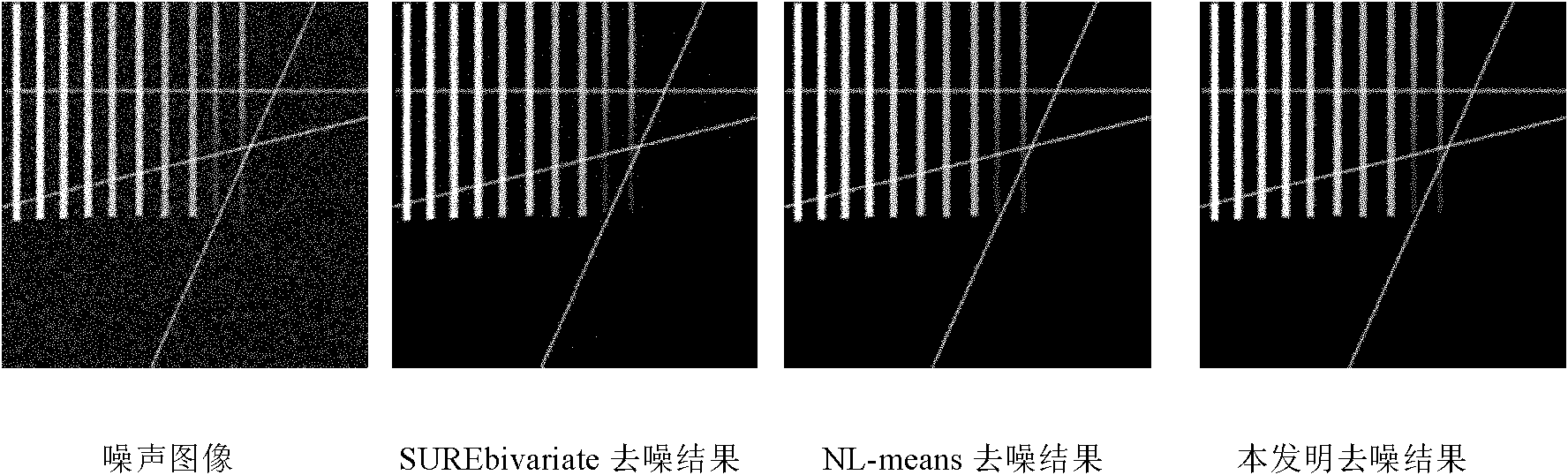
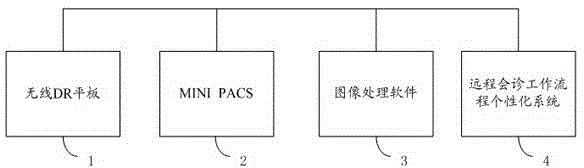
The invention discloses a digital X-ray imaging system. The system comprises a wireless DR panel, a MINI PACS, image processing software and a remote consultation working process personalization system, wherein the MINI PACS serves as the image storing, transmitting and managing system and is capable of achieving domestic and abroad remote consultation and telemedicine, and the image processing software comprises a fully-automatic imaging denoising algorithm package and an intelligent image contrast enhancing algorithm package. According to the system, direct digital radiograph, image processing and image management, storage and transmission are integrated, resolution ratio is reserved to the maximum and image detail contrast is enhanced to the maximum by means of the fully-automatic imaging denoising algorithm, intelligent images in different areas are enhanced by means of the intelligent image contrast enhancing algorithm so that the content of each detail can be displayed clearly, zero-operation diagnosis of a radiologist is achieved, remote consultation is achieved through the PACS, and software and hardware integration is achieved.
Owner:NANJING BAINENGWEI MEDICAL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com