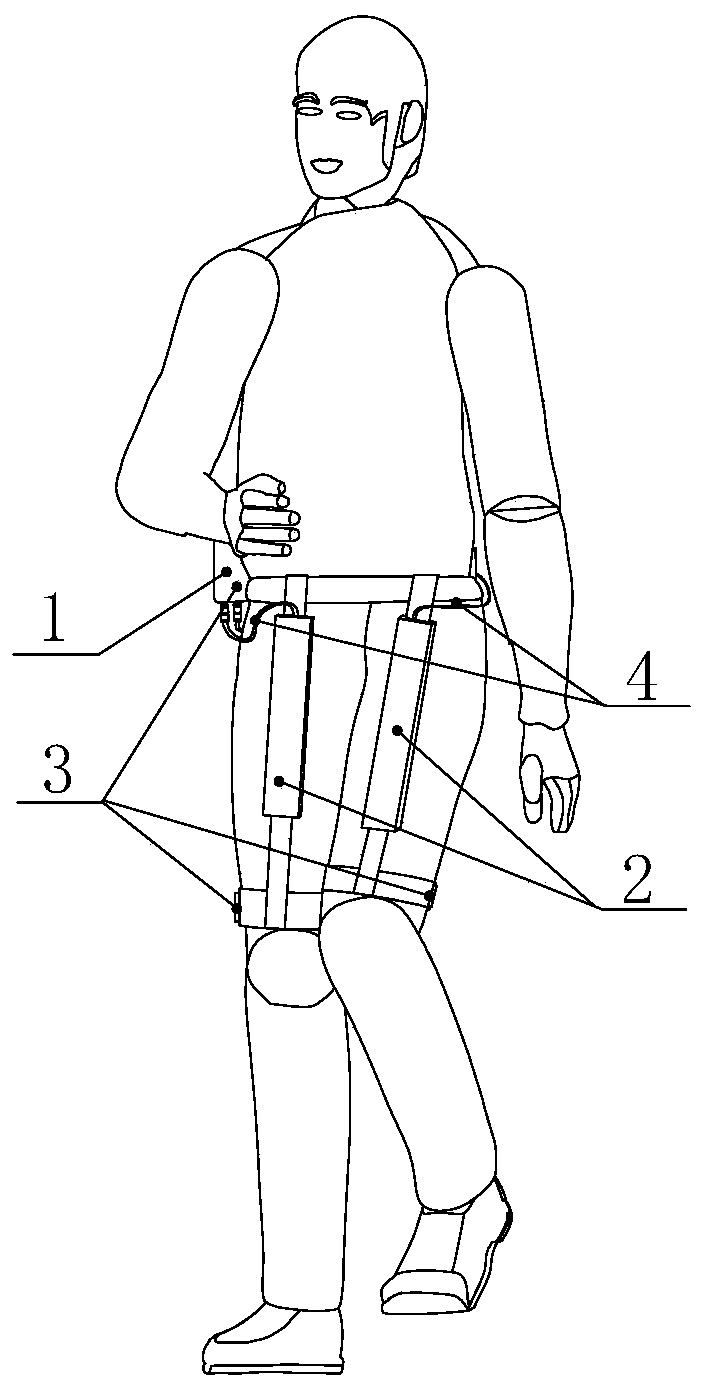
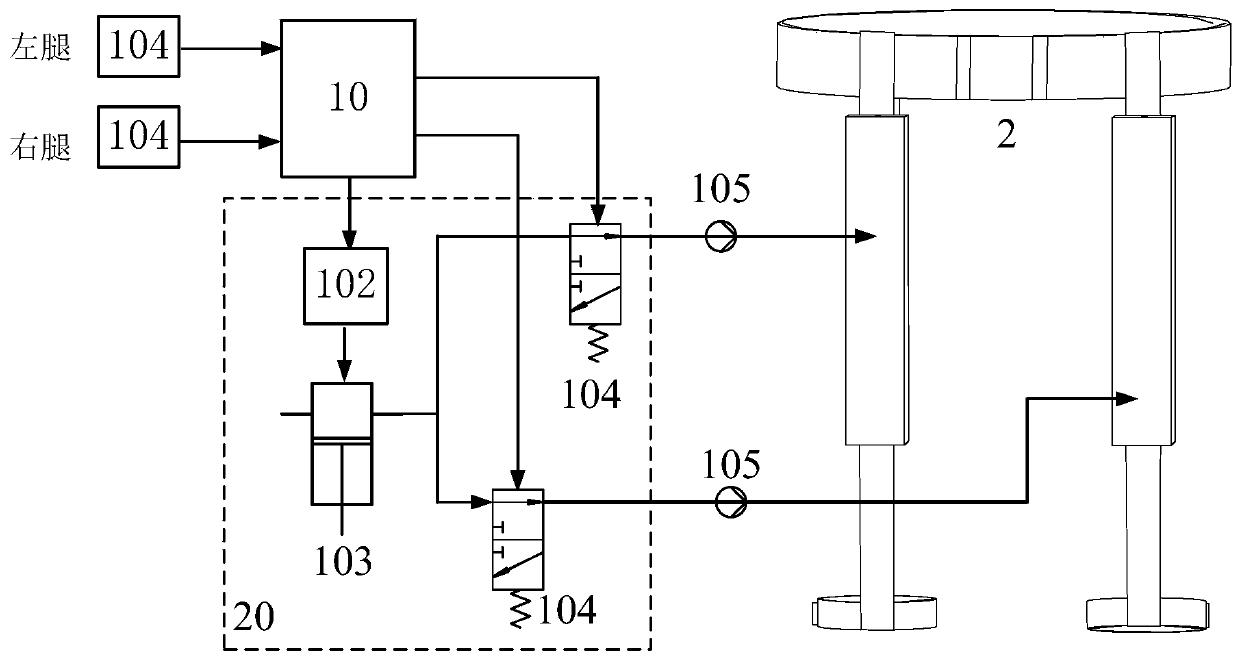
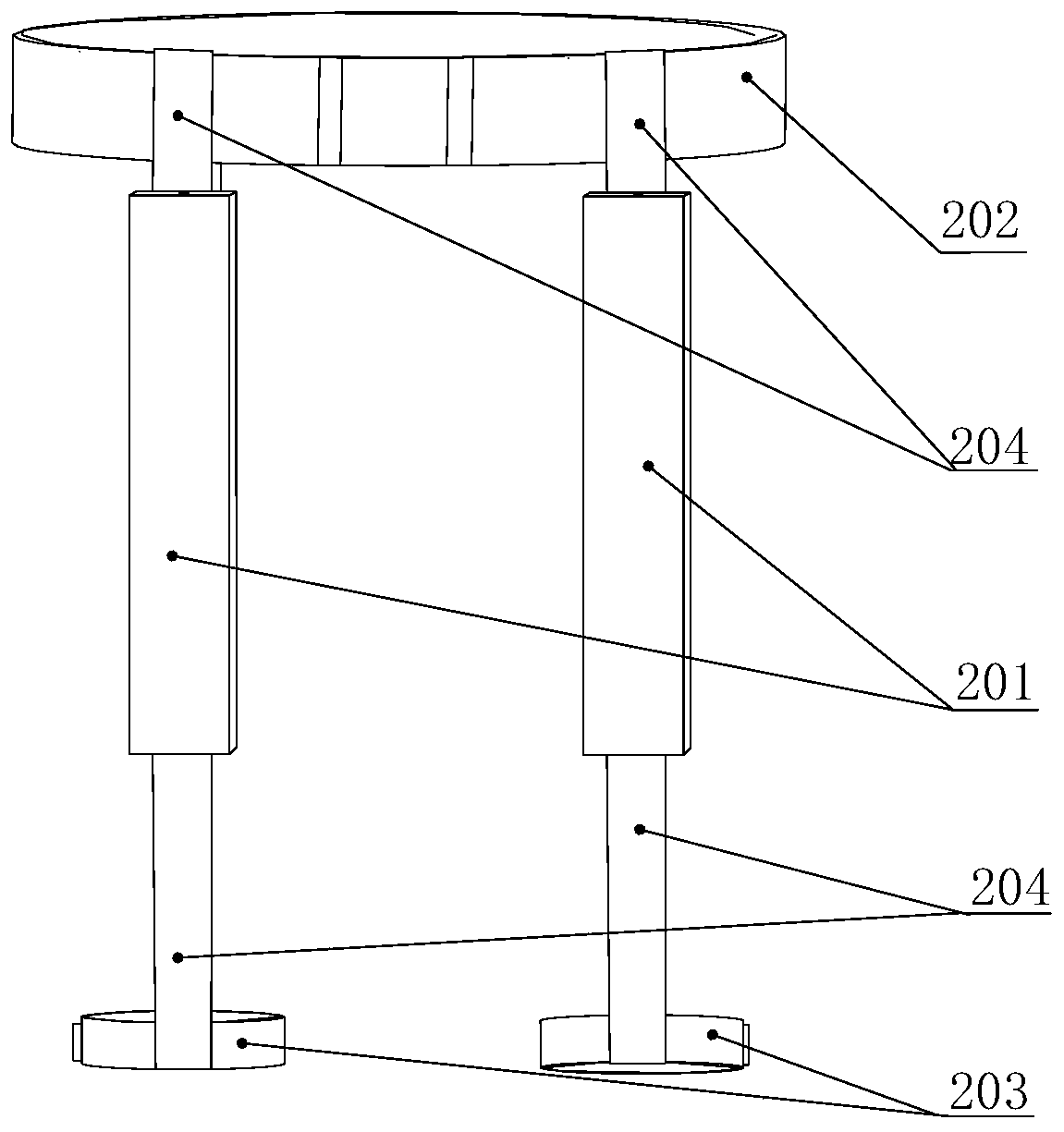
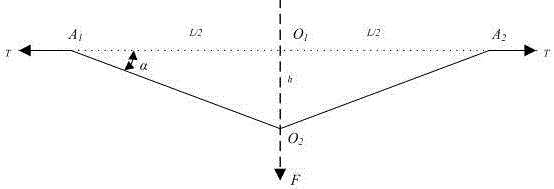
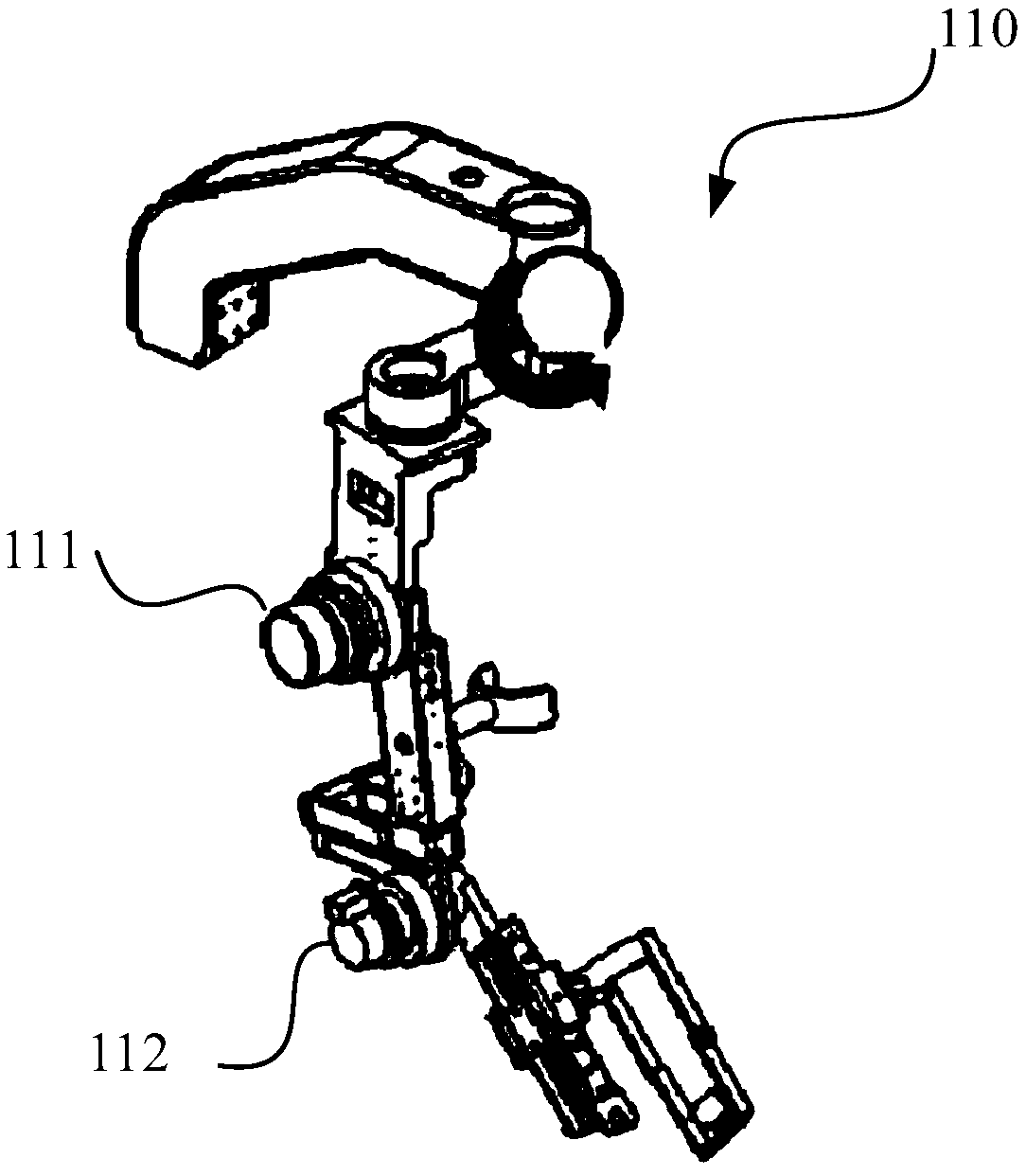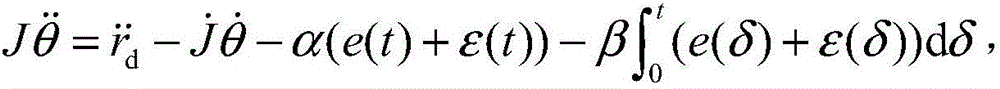Patents
Literature
52 results about "Joint moment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
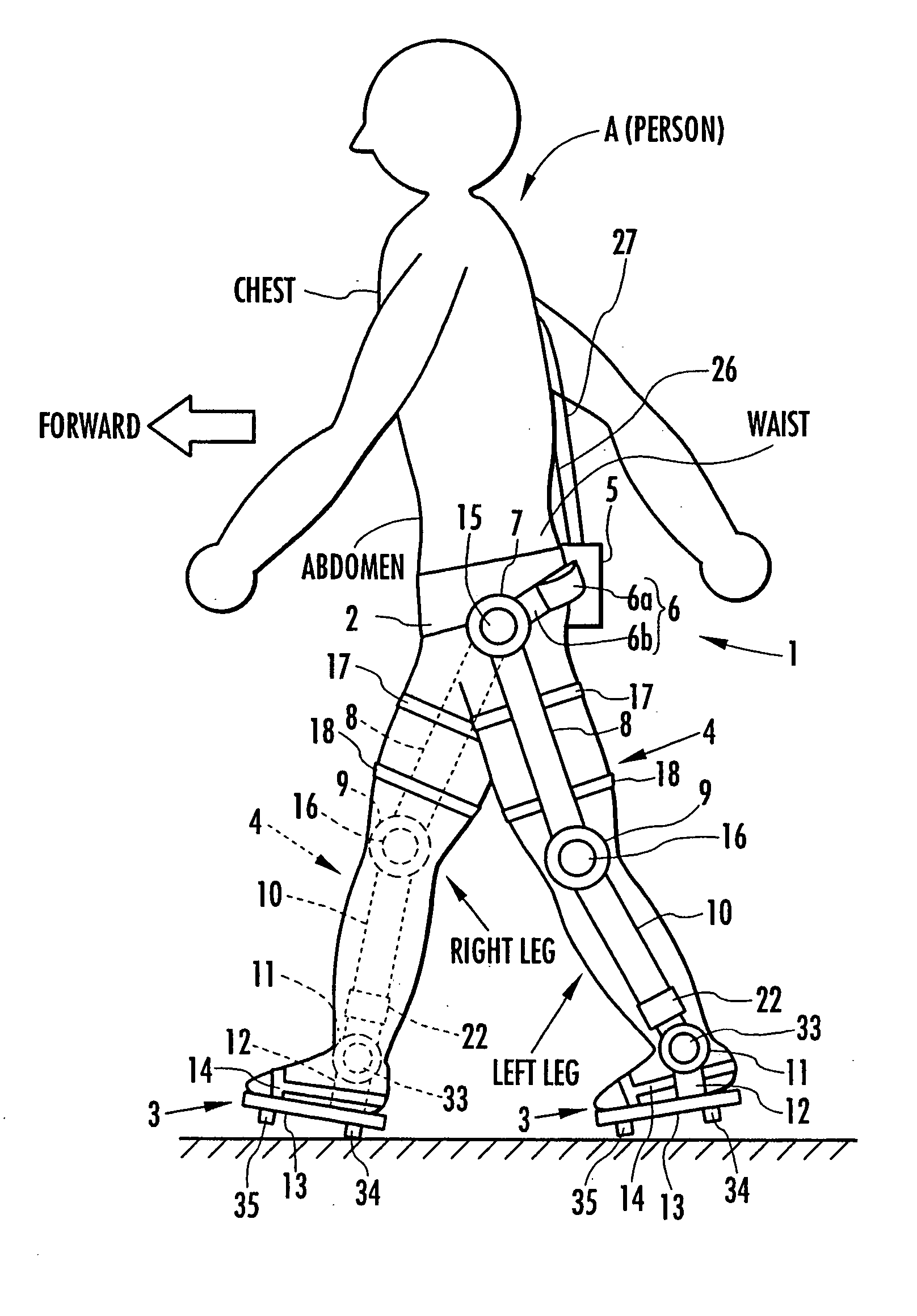
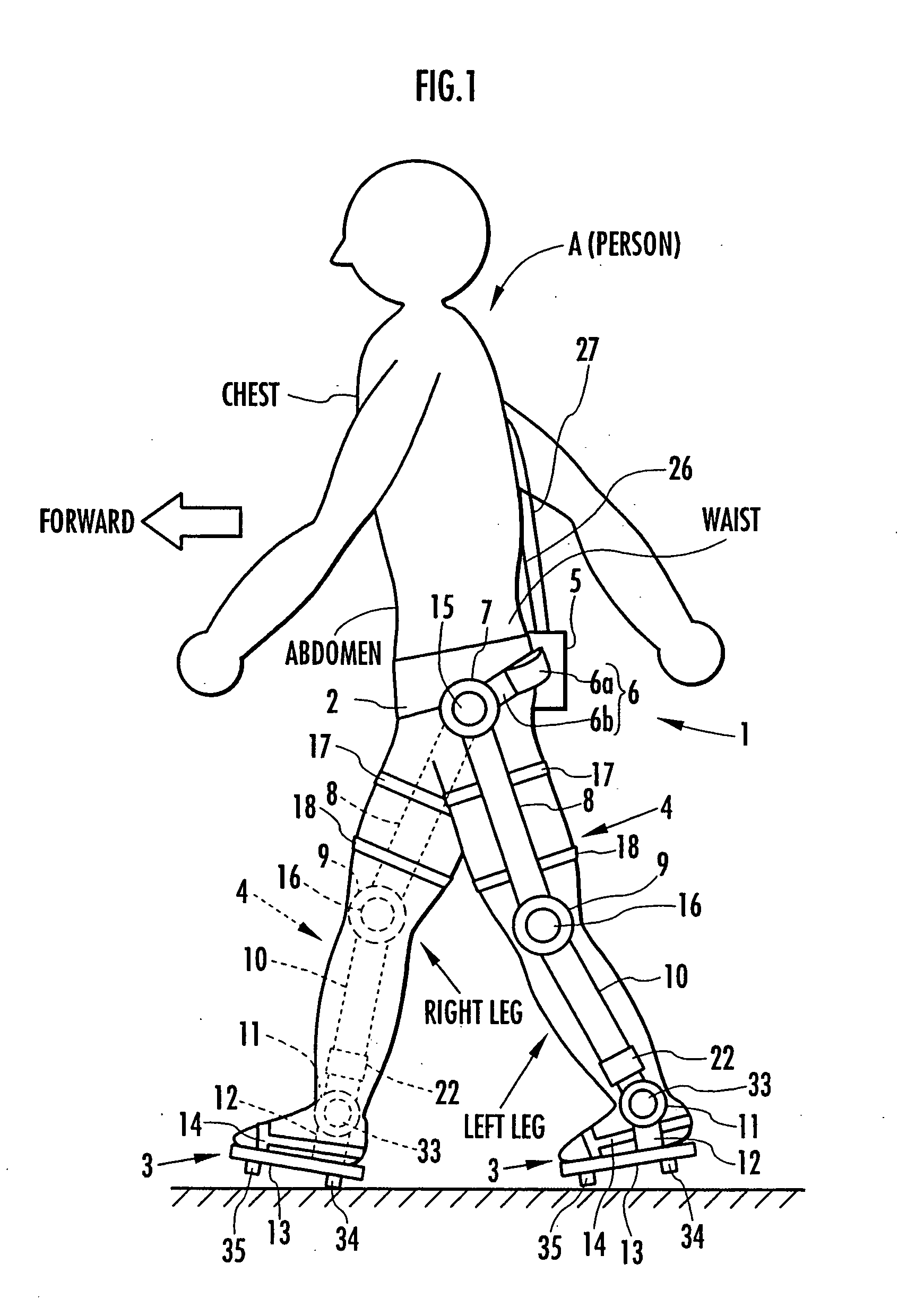
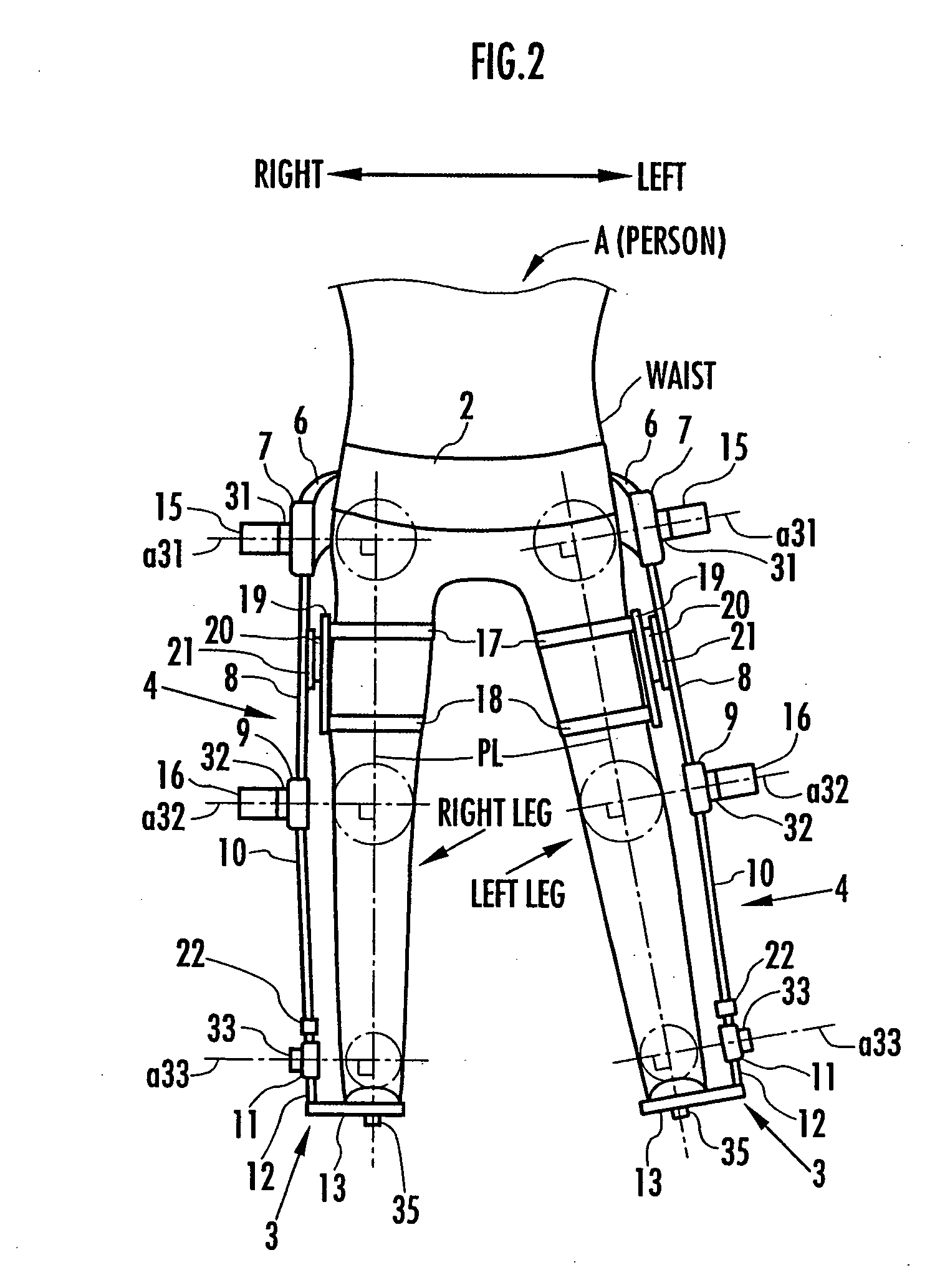
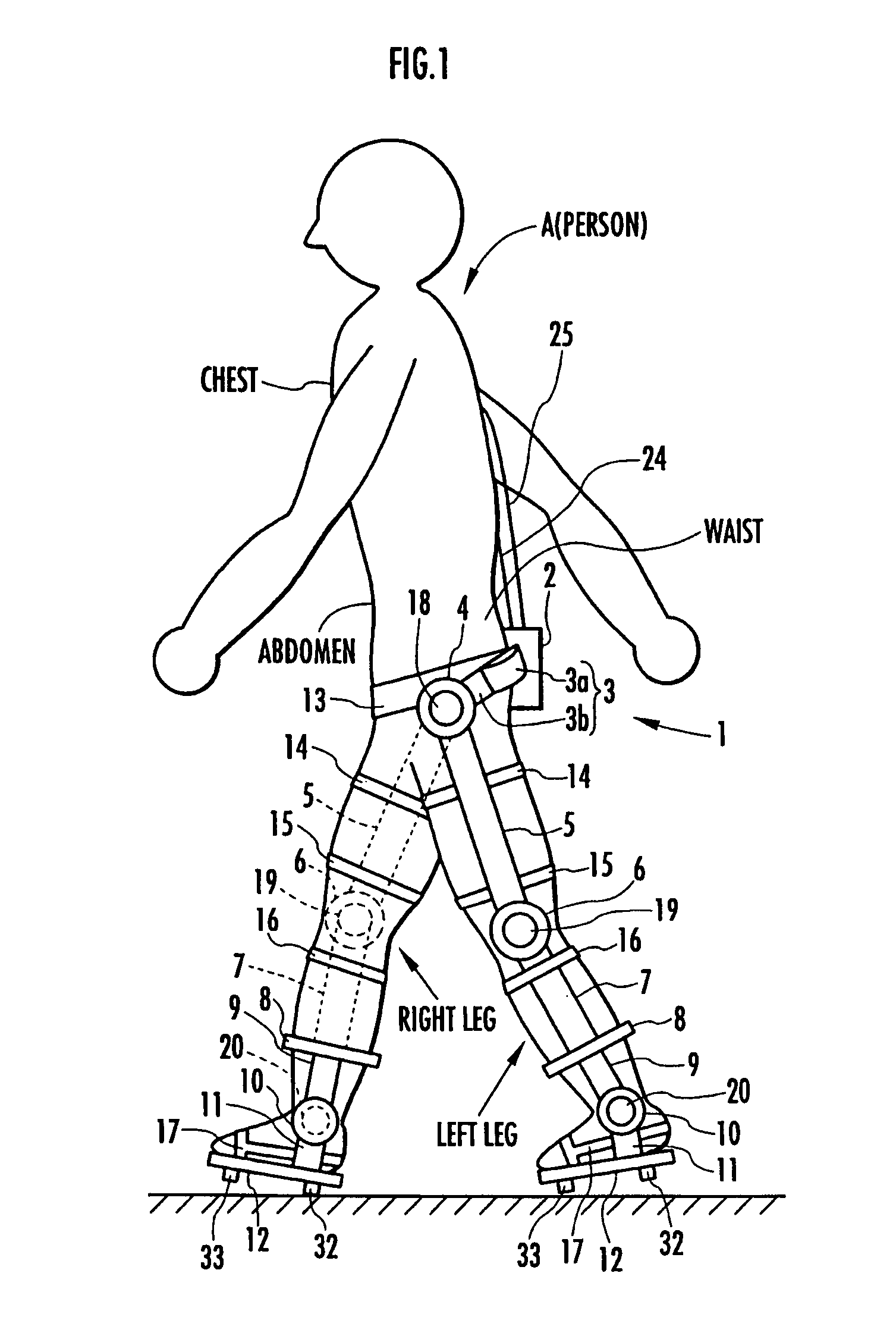
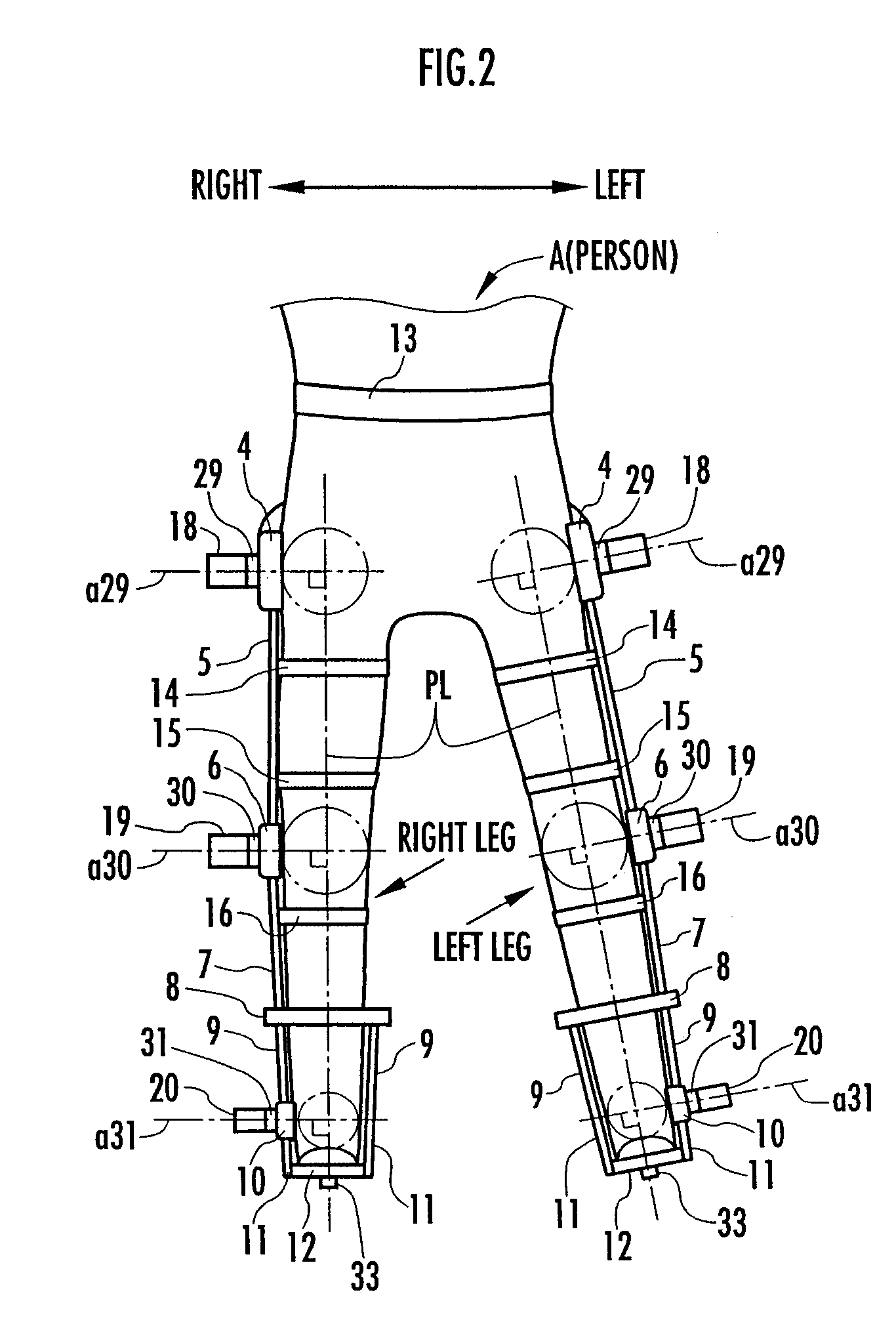
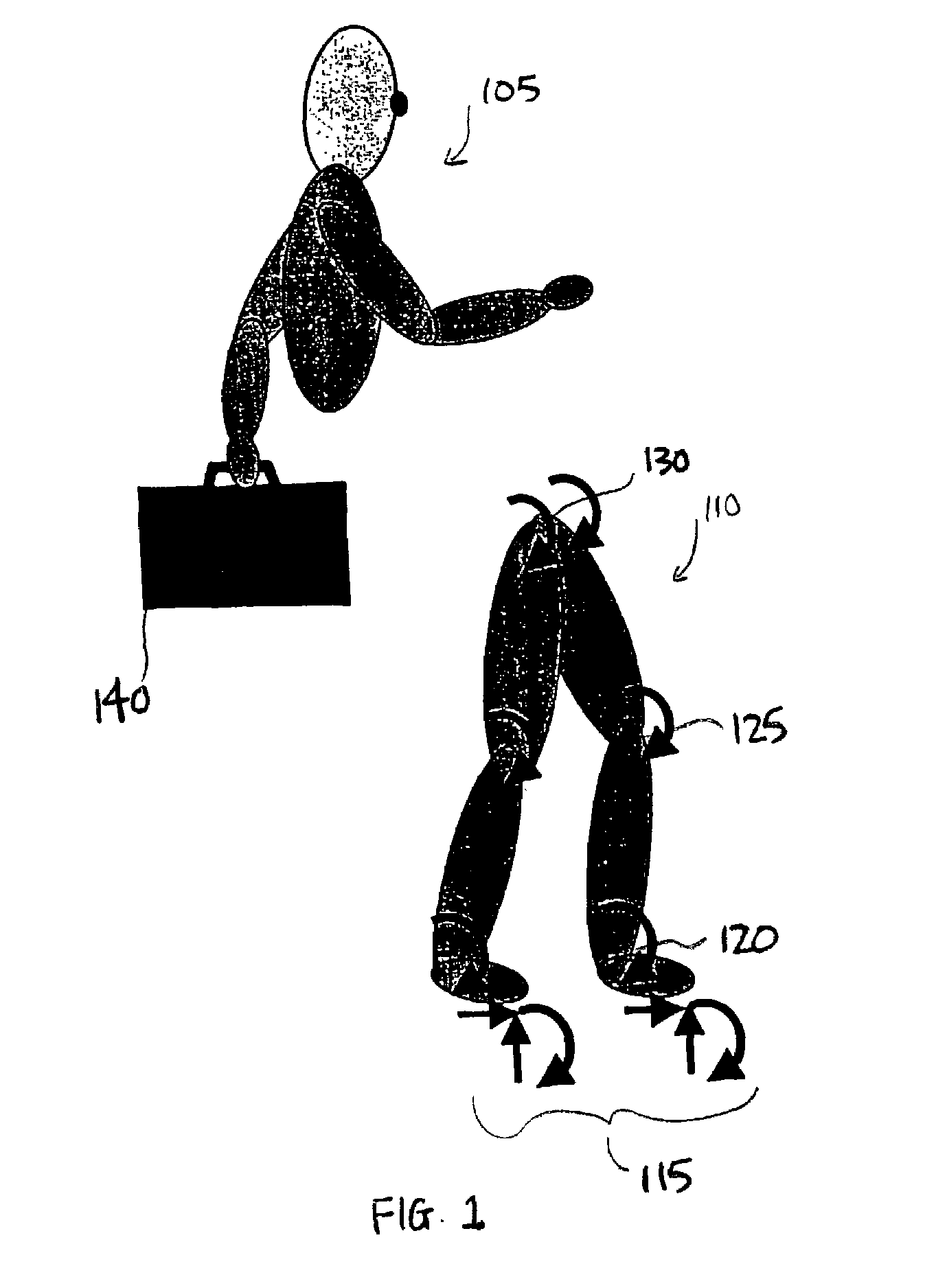
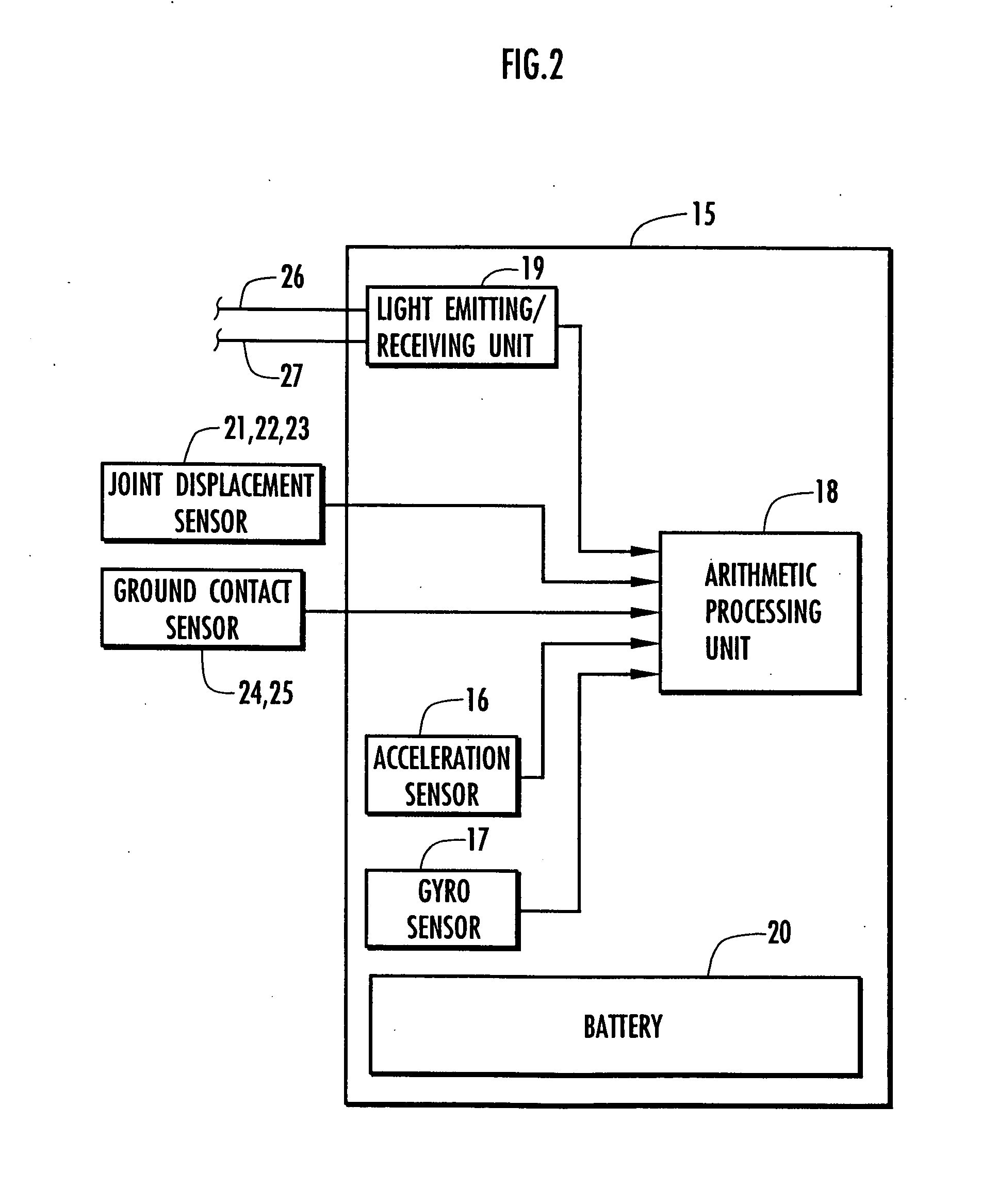
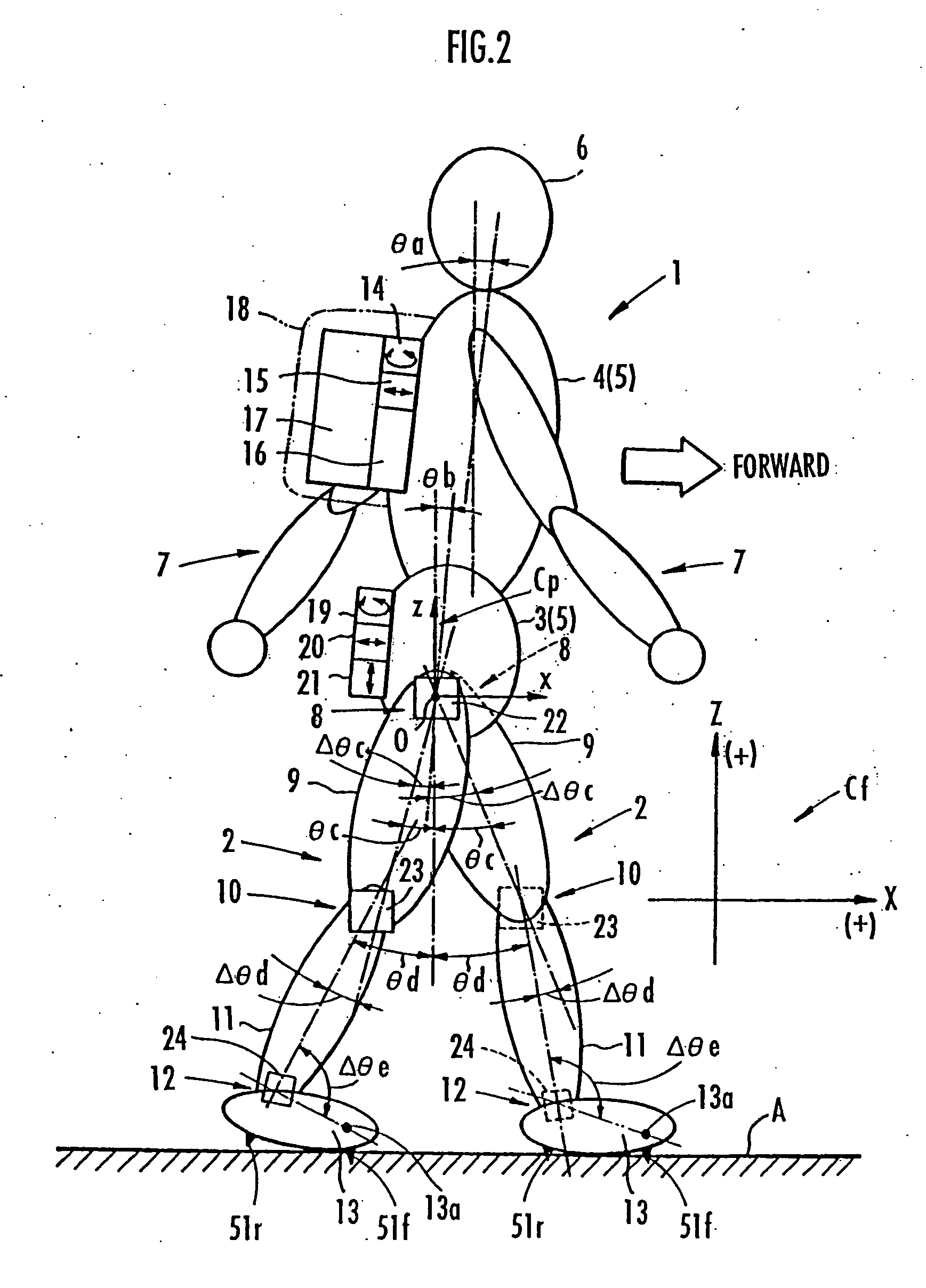
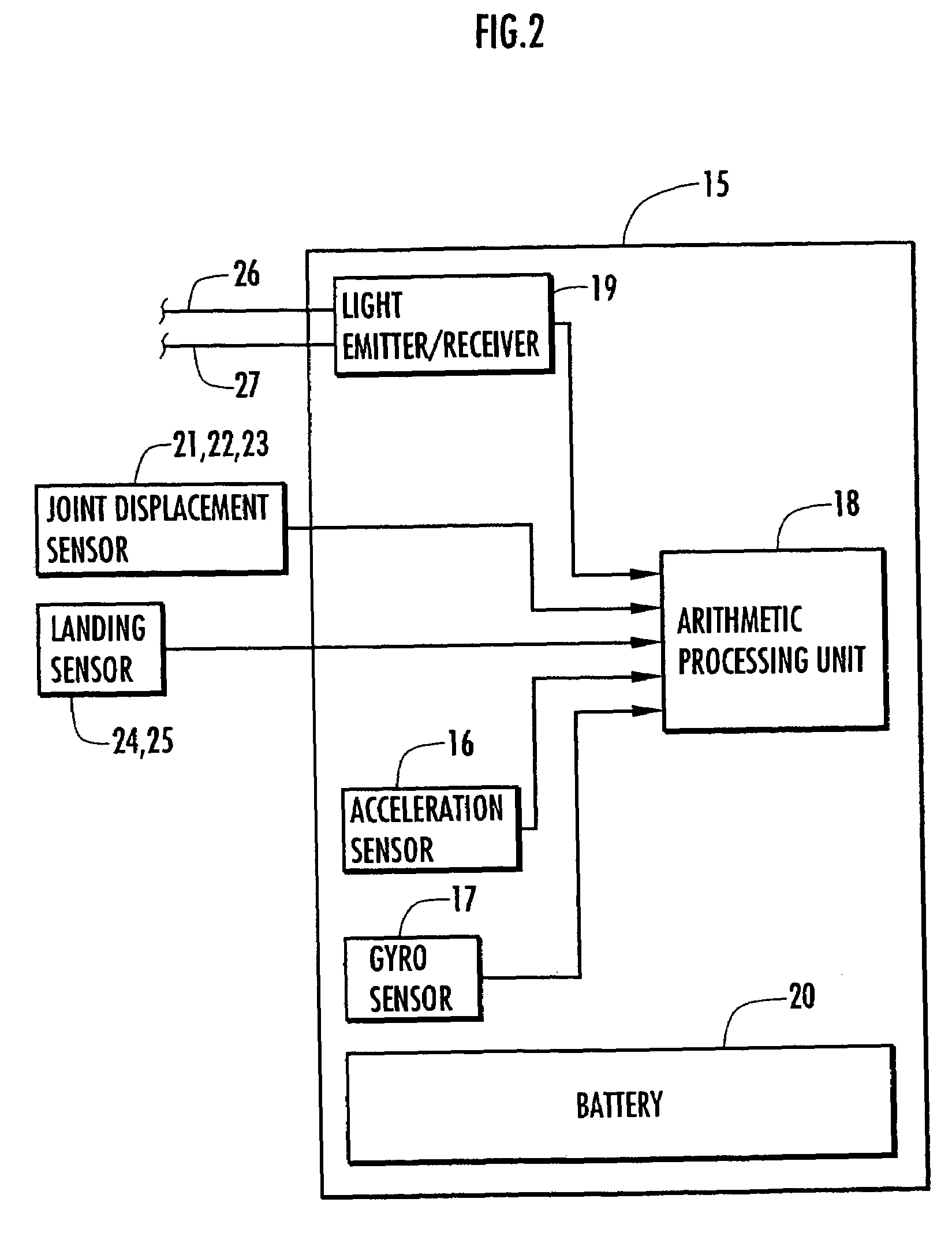
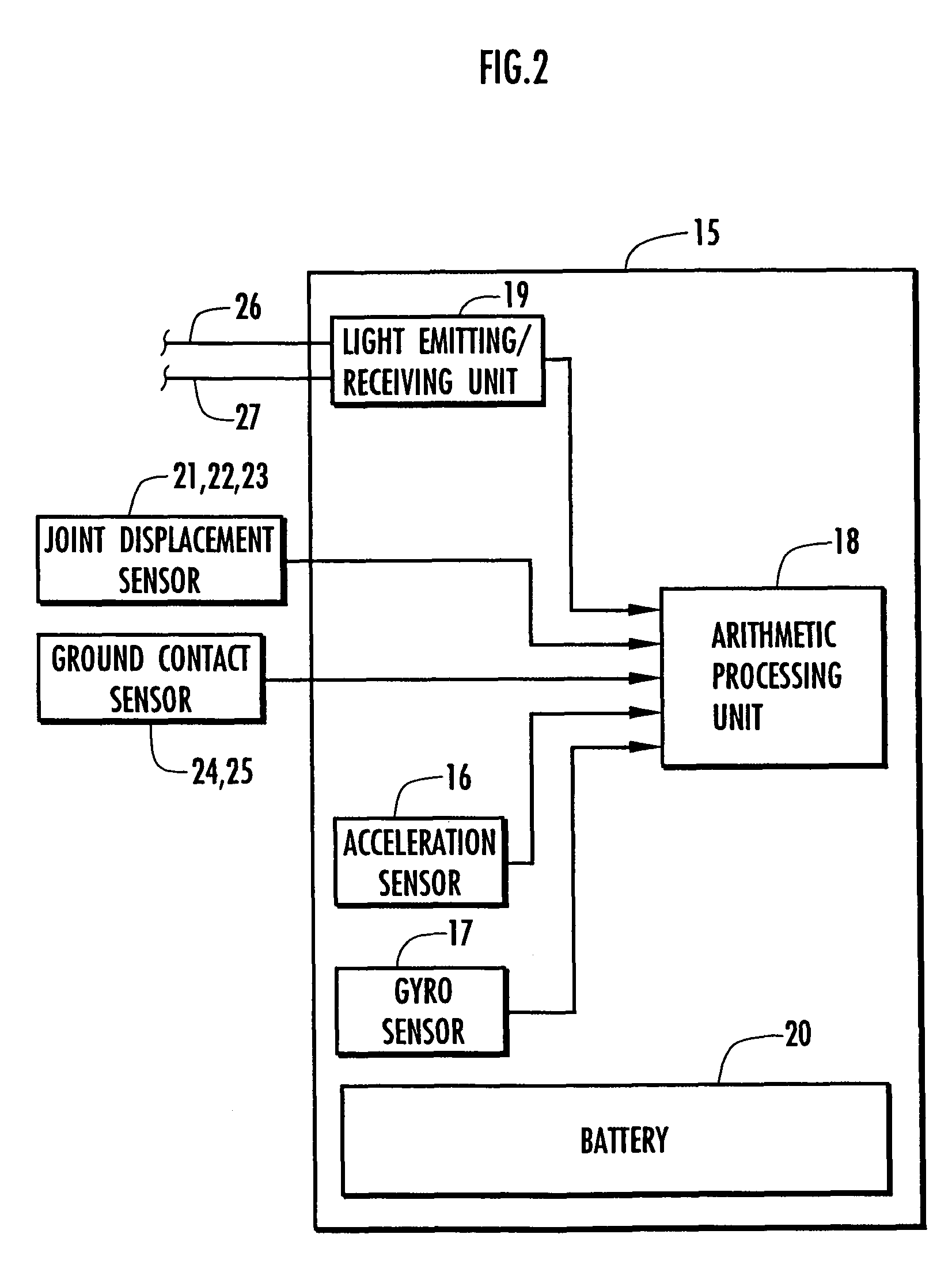
Support moment control method for leg motion support orthosis
InactiveUS20060130594A1Little strengthWork measurementNon-surgical orthopedic devicesIndependent motionEngineering
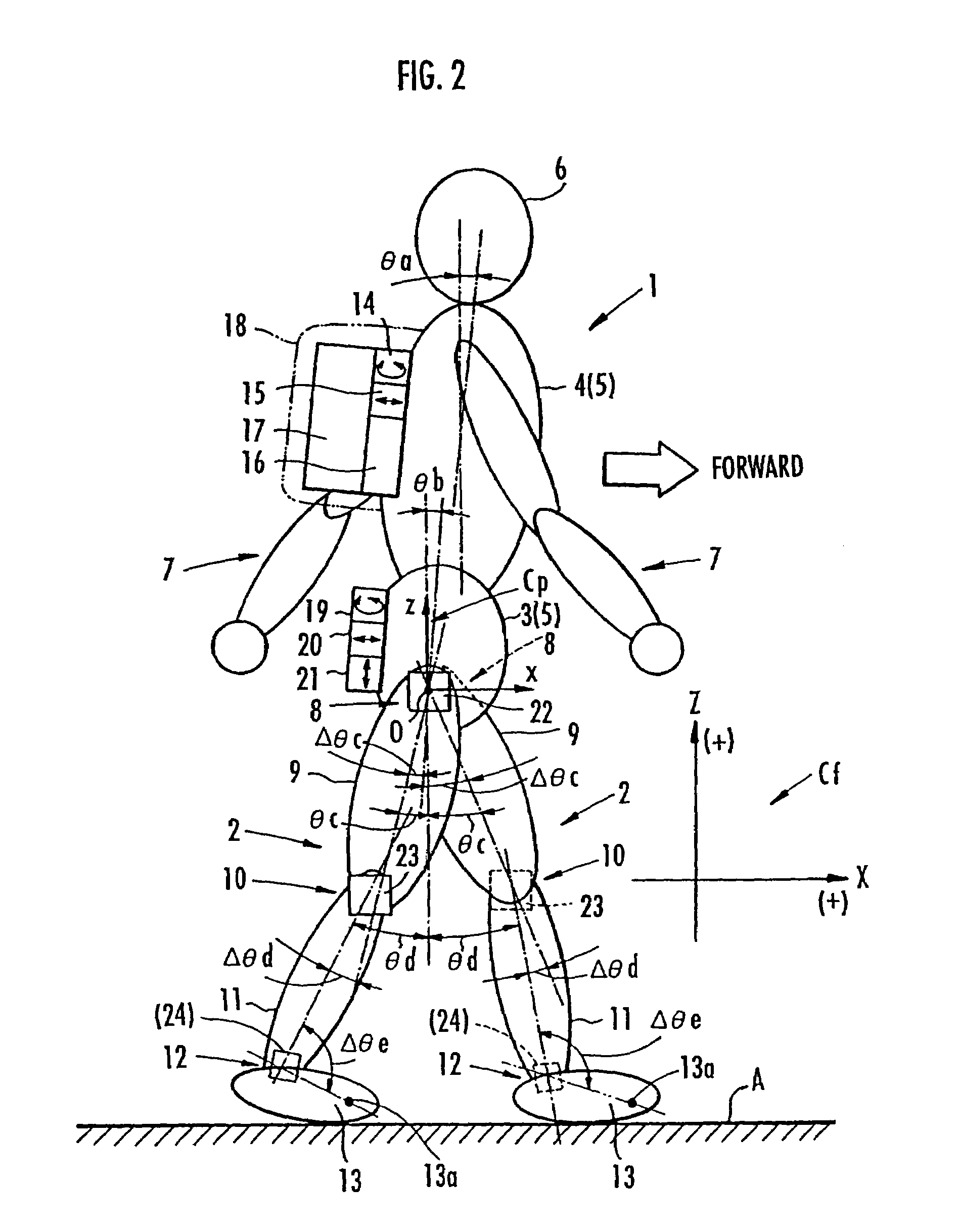
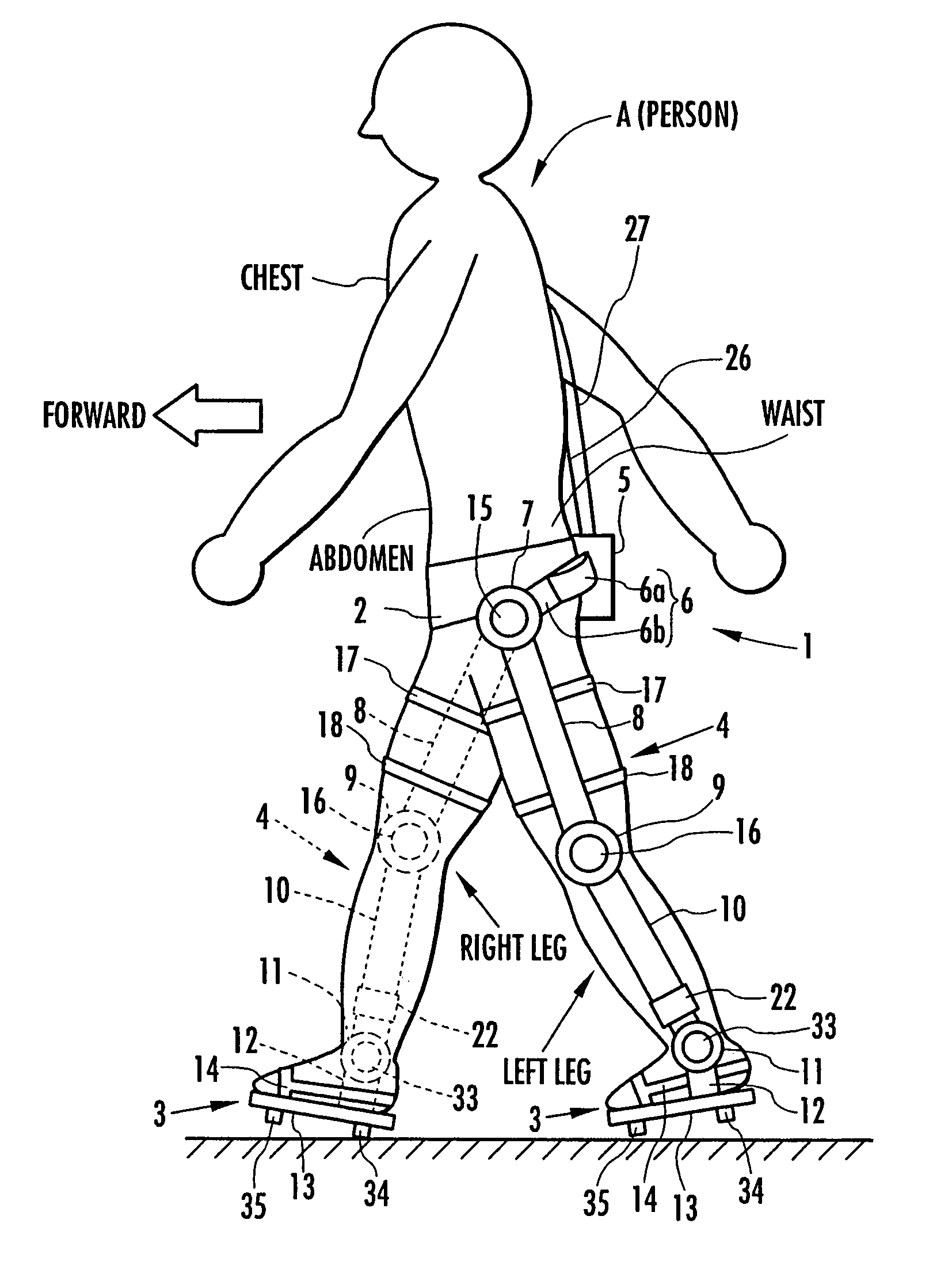
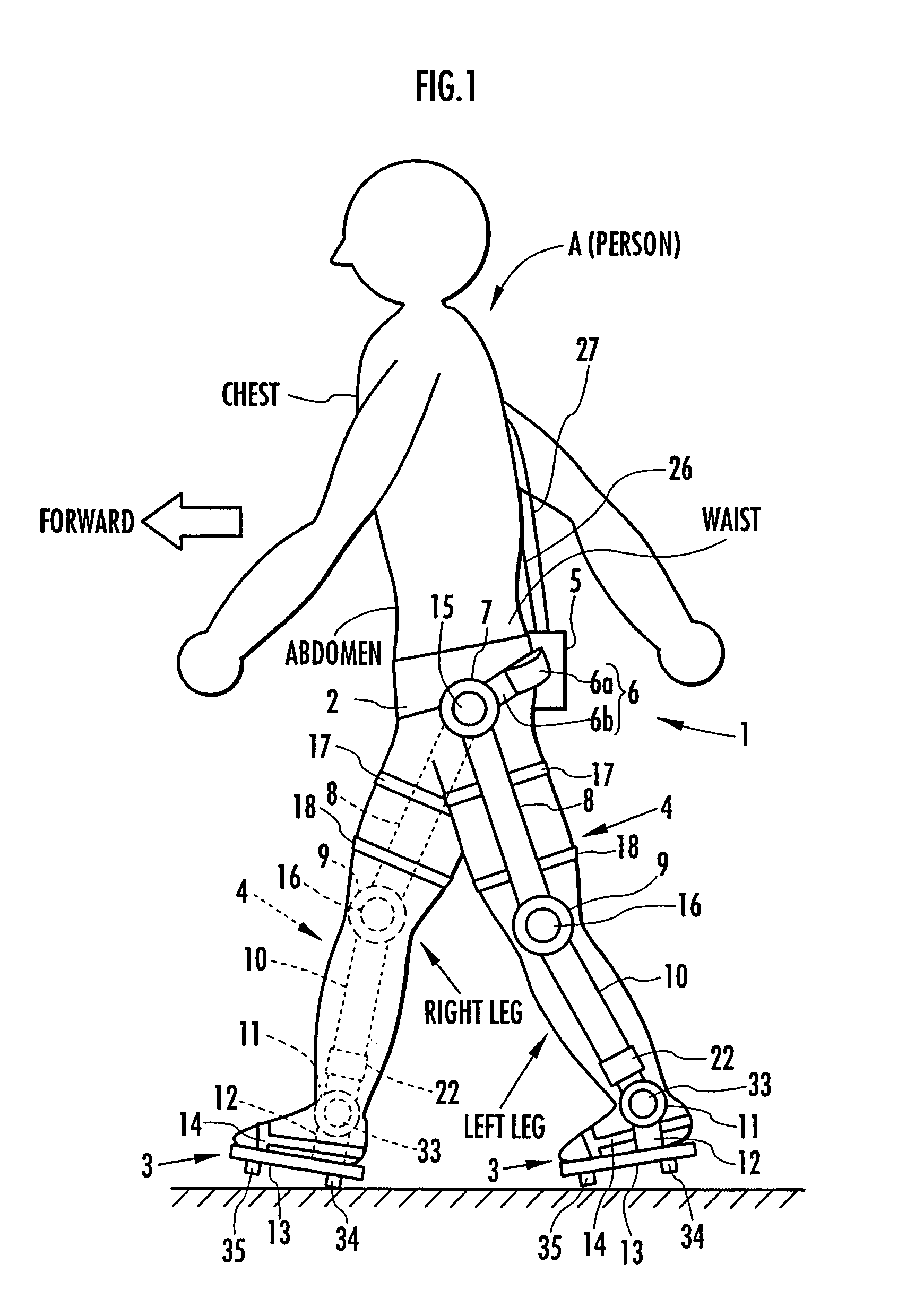
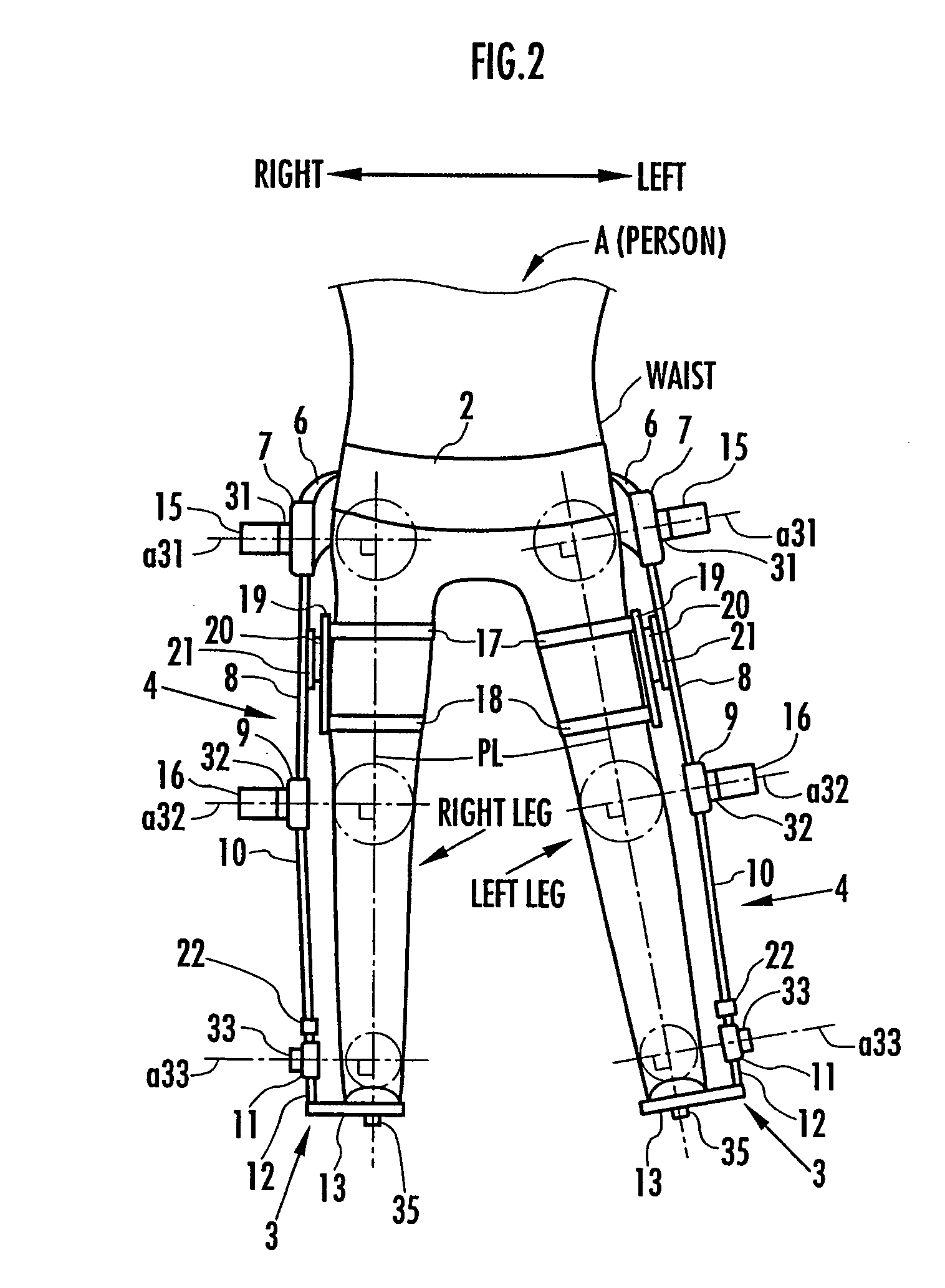
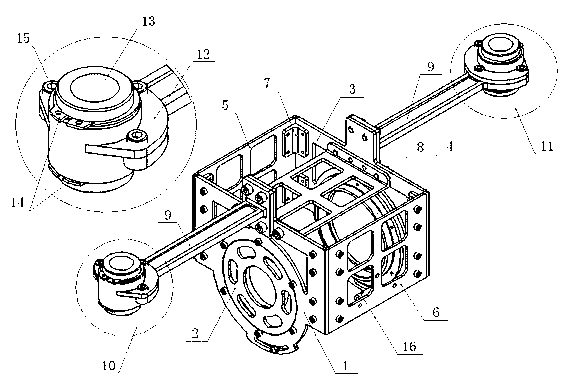
Target joint support moments of each leg are determined by estimating joint moments of the each leg necessary for the person A wearing a leg motion support orthosis (1) to make a motion independently and according to the estimated joint moments. Moreover, floor reaction forces for the support orthosis (1) to make a motion independently are estimated, and then estimated values of actual joint support moments actually applied from the support orthosis (1) to the joints of the each leg of the person (A) are found by using the estimated floor reaction forces and outputs of the force sensor (22) provided in a leg link portion (4) of the support orthosis (1). Torque generation units (15) and (16) of the support orthosis (1) are controlled in such a way that the estimated values of the actual joint support moments are coincident with the target joint support moments. Thereby, the leg motion of the person can be supported. Moreover, it effectively prevents forces other than the necessary forces to support the leg motion of the person from acting on the person and enables the person to make a leg motion with feeling as if the person were not wearing the leg motion support orthosis as fully as possible.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
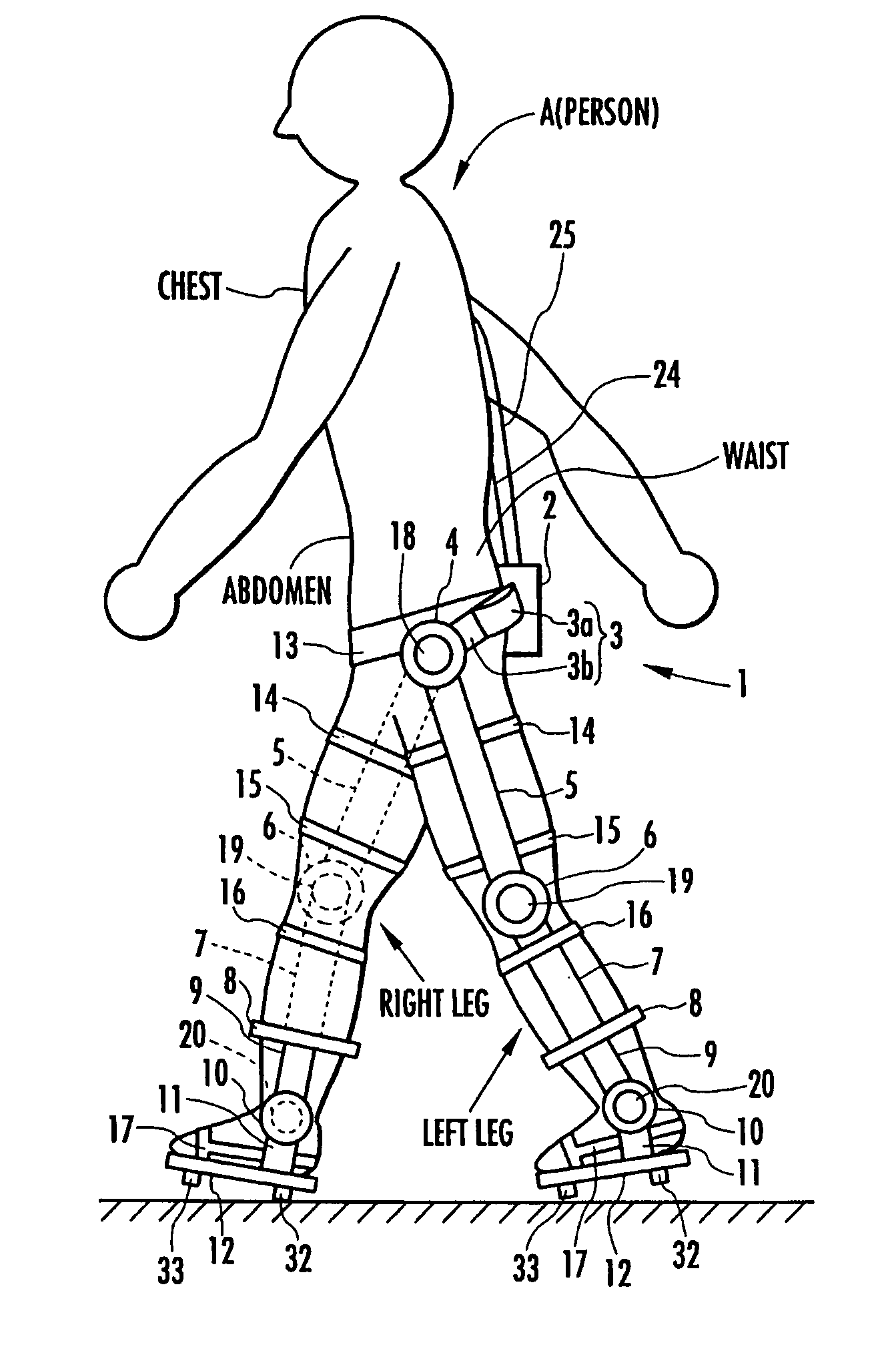
Generated torque control method for leg body exercise assistive apparatus
InactiveUS7278954B2Reduce weightReduce empty weightProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesEngineeringAssistive equipment
A generated torque control method for a leg body exercise assistive apparatus enabling a person to make a leg motion in such a feeling that the person is not wearing the leg body exercise assistive apparatus as much as possible by reducing the weight of the leg body exercise assistive apparatus attached to the person acting on the person. On the assumption that a person (A) not wearing the assistive apparatus (1) is making the same motion as a leg motion of the person (A) wearing the leg body exercise assistive apparatus (1) during the leg motion of the person (A), an estimation is made for a person-side joint moment to be generated in each joint of the leg of the person (A), and on the assumption that the assistive apparatus (1) is independently making the same motion as the leg motion, an estimation is made for an apparatus-side joint moment to be generated in the joint regions (4), (6), and (10) of the leg sections of the assistive apparatus (1). The estimated value of the apparatus-side joint moment is considered as a reference torque for torque generation means (18), (19), and (20), and a torque formed by adding a torque according to the estimated value of the person-side joint moment to the reference torque is generated in the torque generation means (18), (19), and (20).
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
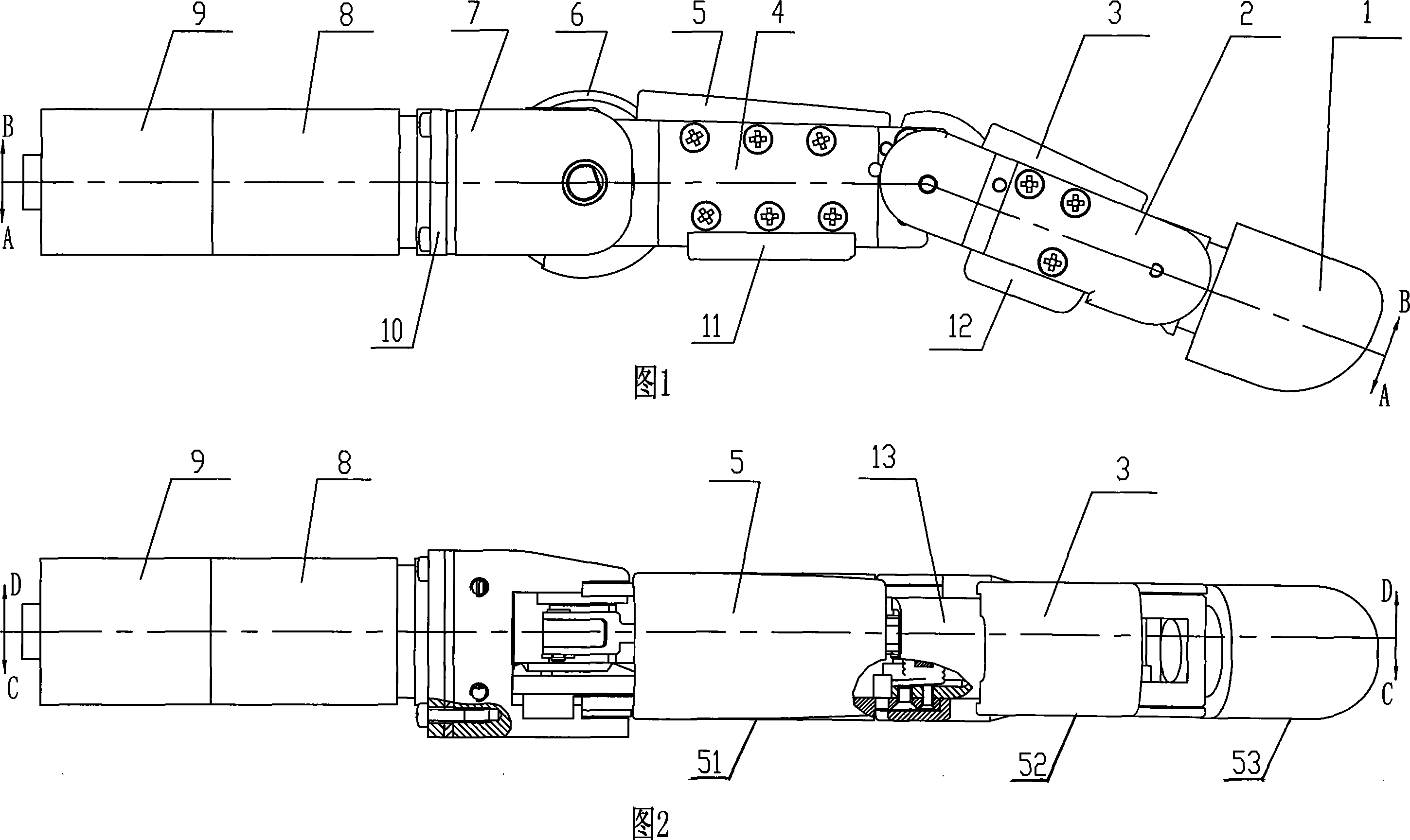
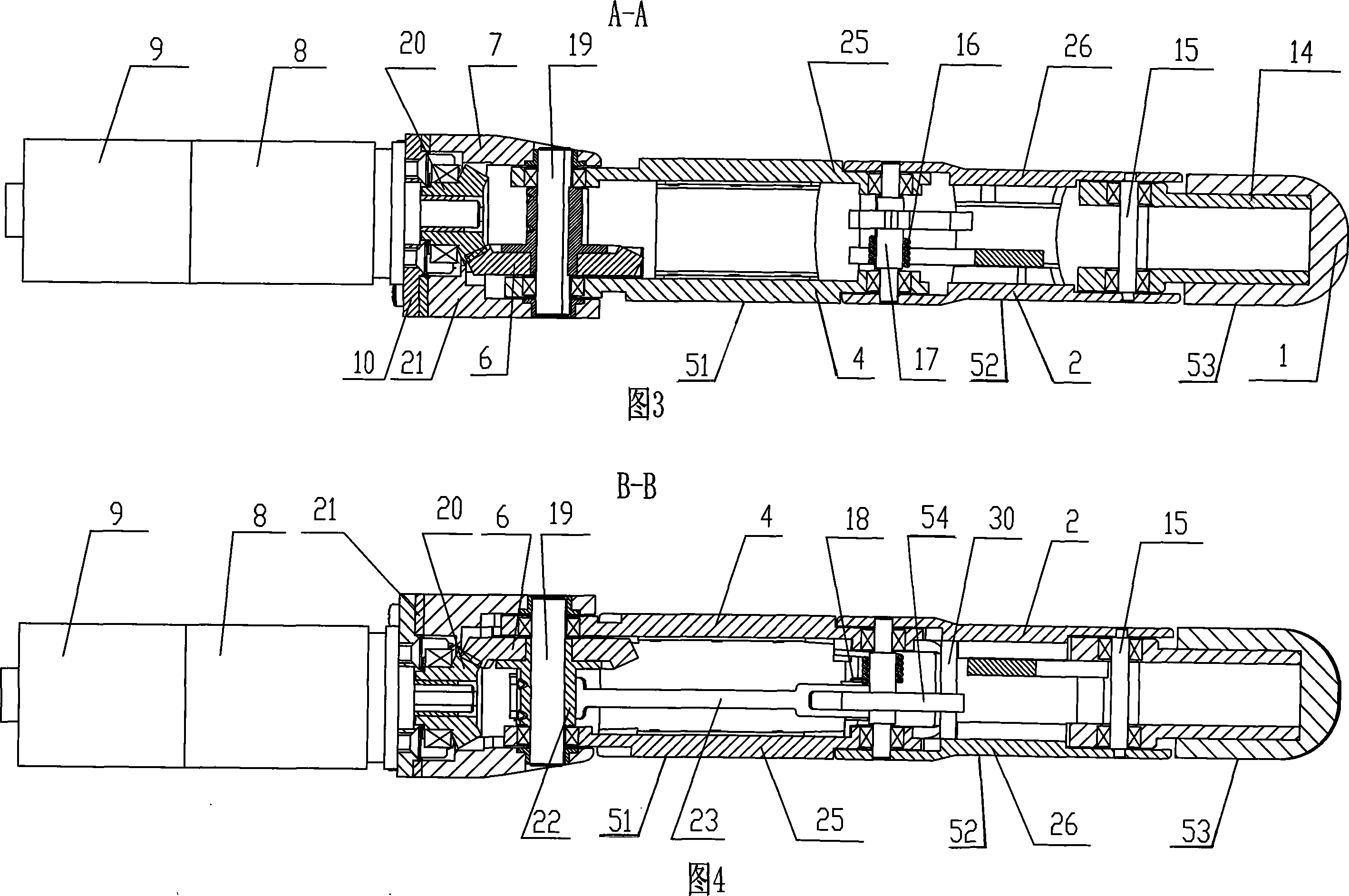
Under-actuated coupling transmission type imitation human finger mechanism
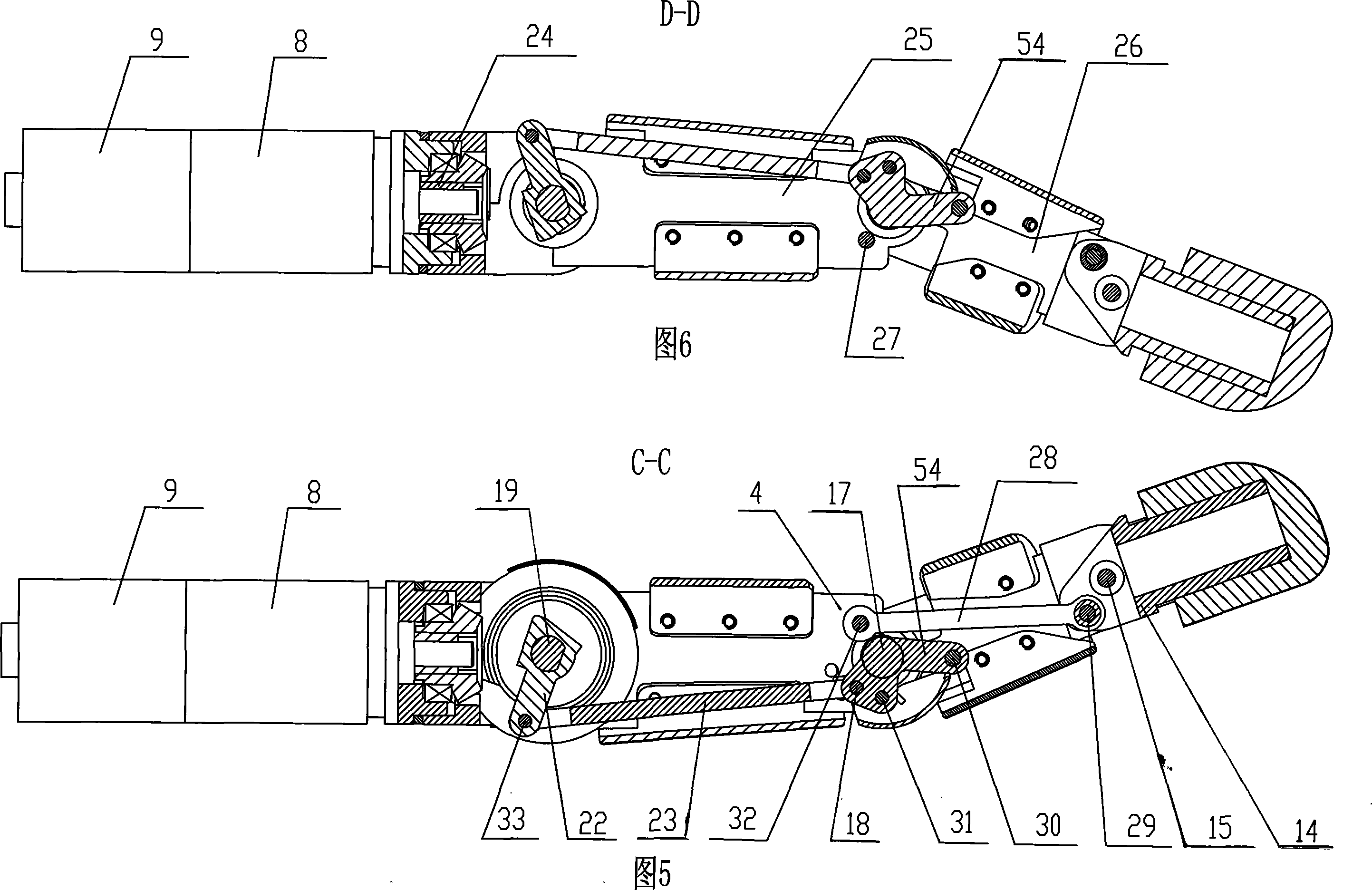
The invention provides an under-actuated coupling driving finger-imitating mechanism, in particular to a finger-imitating mechanism on the manipulator of a robot. The invention solves the problems of poor harmonization of all knuckles, being difficult to keep holding shape, slow speed when wrapping the article to be held, poor adaptability, etc. when the existing manipulator finger carries out a holding motion. One end of the invention, which is close to a knuckle connecting rod (23), is connected with a basic joint moment sensor (22); the other end close to the knuckle connecting rod (23) is connected with the shaft disc (54) of a central joint shaft; one end of a coupling connecting rod (28) is connected with a left plate (25) close to the knuckle and a right plate (4) close to the knuckle; the other end of the coupling connecting rod (28) is connected with a fingertip (14); a central knuckle left plate (26) and a central knuckle right plate (2) are connected with the shaft disc (54) of the central knuckle shaft by a coupling central knuckle shaft (30). By adopting the coupling transmission way, the central knuckle and the fingertip of the invention have the advantages of good motion harmony when the finger is bent, fast speed and convenient pre-tightening when the article to be held is wrapped.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Joint moment sensor providing torque and bending moment overload protection
InactiveCN101118194ARealization of torque overload protectionGuaranteed uptimeWork measurementTorque measurementEngineeringFlange
The present invention discloses a joint force moment sensor providing torque and bending moment overload protection, and relates to a joint force moment sensor, to solve the problems that the existing joint force moment sensor can only realize the overload protection on the force moment vertical to the ground. The present invention provides a blind hole (10) on each overload protection beam (5), four through holes (9) coaxial with the blind holes (10) are respectively arranged on the inner edge of an output connecting flange (2) along the radial direction, one end of each protection pin (6) respectively gets through the corresponding through holes (9) and arranged in the corresponding blind hole (10), and the other end of each protection pin (6) is fitted with the corresponding through hole (9) through a clearance. Under different operating modes of the sensor of the present invention, the variances of the overload protection annular clearances between the protection pins and the through holes are different, not only the joint force moment overload protection can be provided, but also the bending moment overload protection can be realized, thus making the system run more safely and reliably.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Industrial robot dragging teaching method without adopting torque sensor
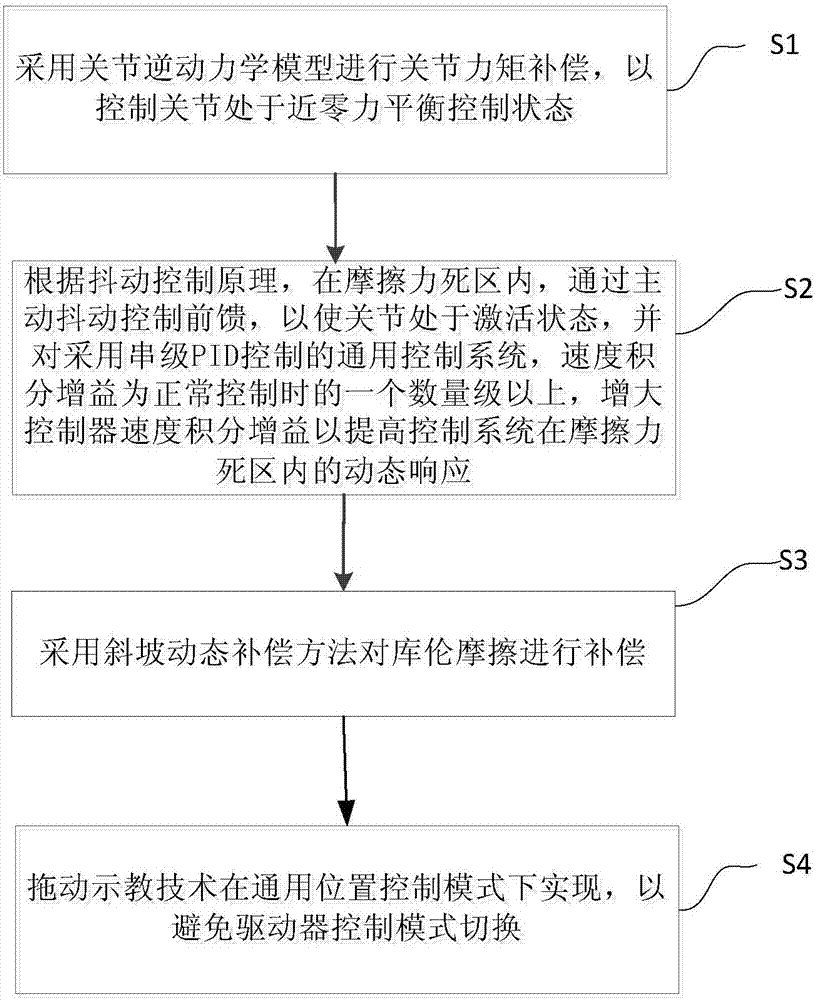
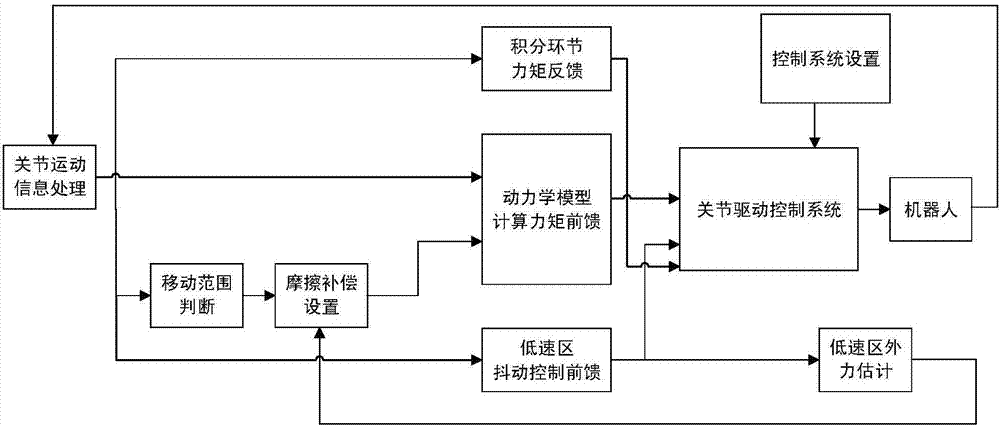
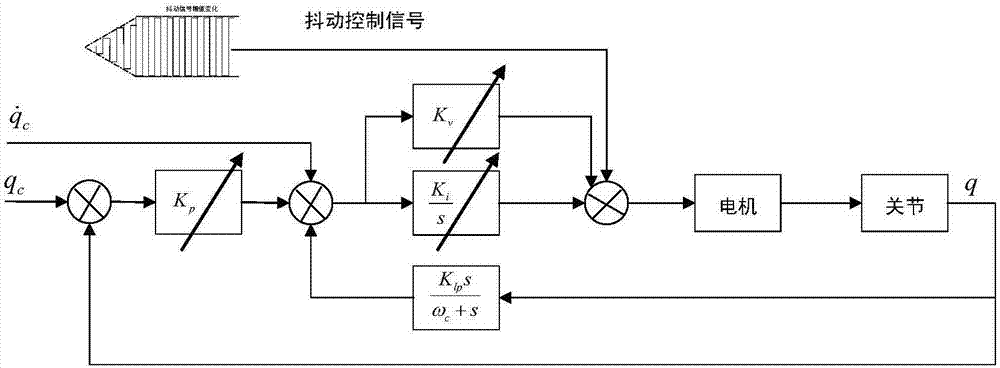
The invention provides an industrial robot dragging teaching method without adopting a torque sensor. The method comprises the steps that a joint inverse dynamic model is adopted for joint moment compensation, so that a joint is controlled to be in a near-zero force balanced control state; according to a jitter control principle, feedforward is controlled through drive jitter within a dead zone of friction force, so that the joint is in an activated state, velocity integral grain of a universal control system adopting serial PID control is one order of magnitudes that of a system adopting normal control, and the controller velocity integral gain is increased to improve the dynamic response of the control system in the dead zone of the friction force; a slope dynamic compensation method is adopted for compensating coulomb friction; and a dragging teaching technology is achieved in a universal position control mode, so that switching of a control mode of a driver is avoided. According to the dragging teaching method adopted in the invention, the torque sensor is not needed, and the cost is low.
Owner:ROKAE SHANDONG INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
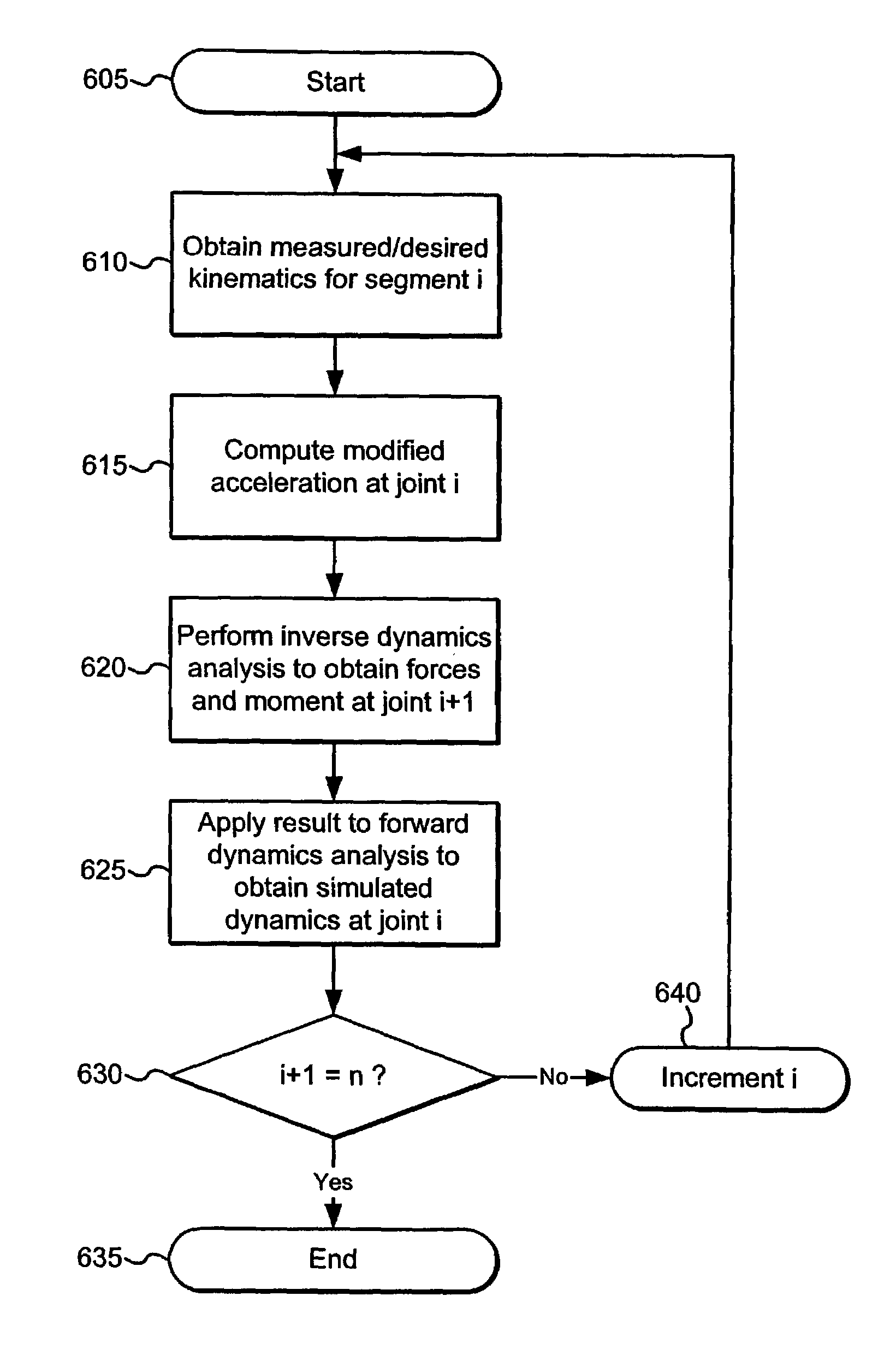
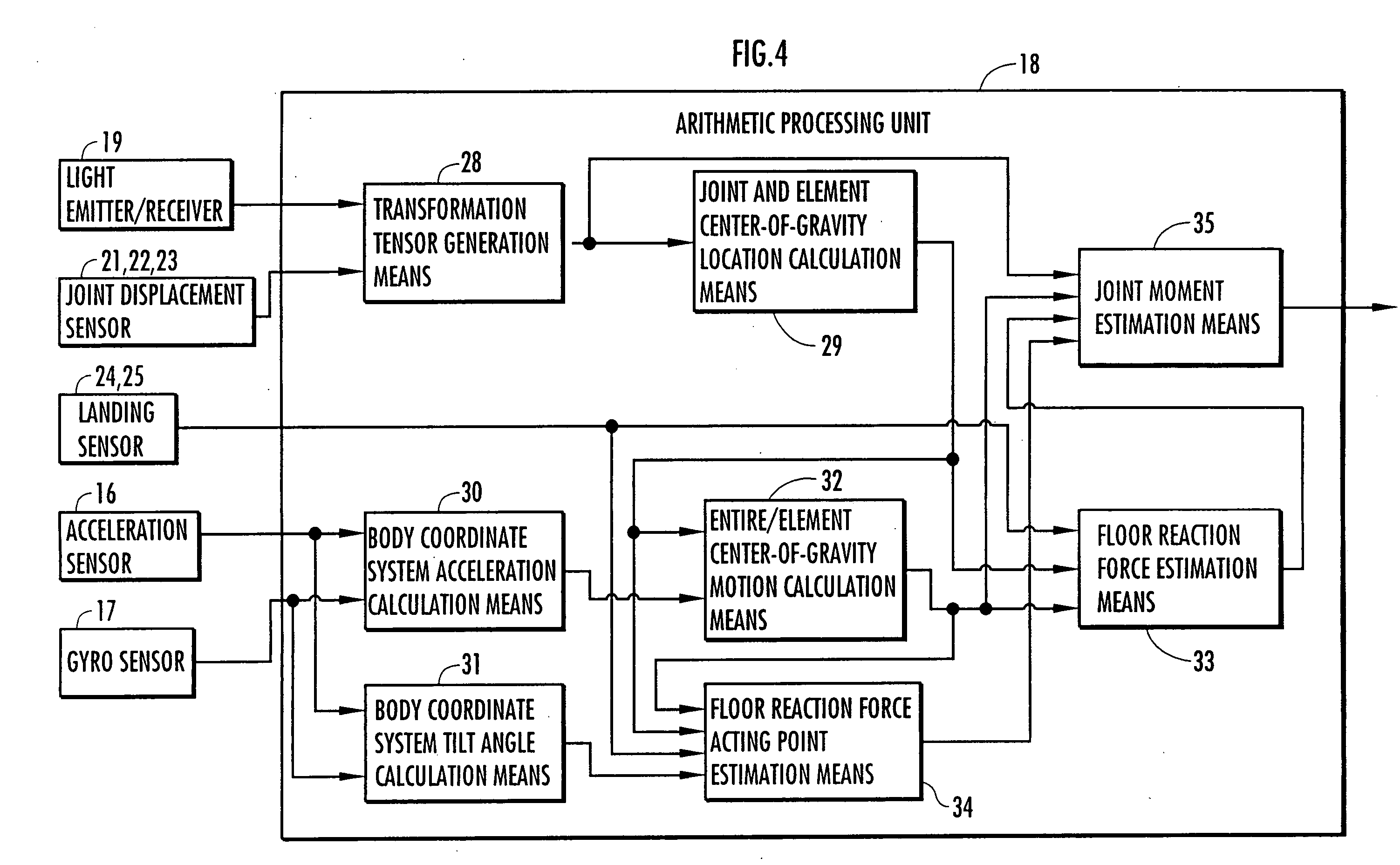
Feedback estimation of joint forces and joint moments
ActiveUS7135003B2Reduce sourceHigh precisionPerson identificationAnalogue computers for chemical processesInverse dynamicsControl theory
Apparatus and methods are provided for estimating joint forces and moments in human beings. A forward dynamics module determines simulated kinematic data. An error correction controller forces tracking error between the simulated kinematic data and measured (or desired) kinematic data to approach zero. The error correction controller generates a modified acceleration for input into an inverse dynamics module. The estimated joint forces and moments track the measured (or desired) kinematics without the errors associated with computing higher order derivatives of noisy kinematic data.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
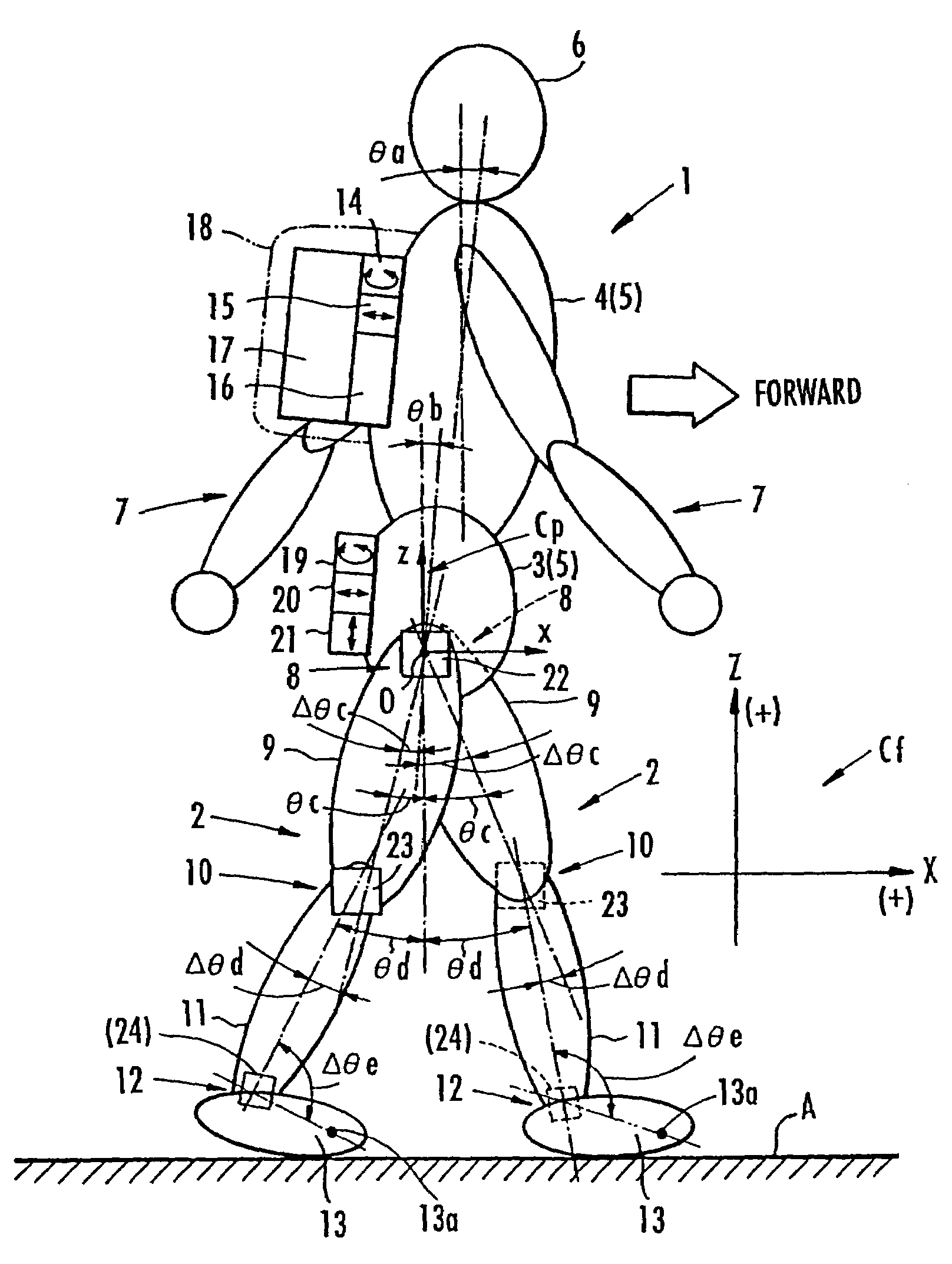
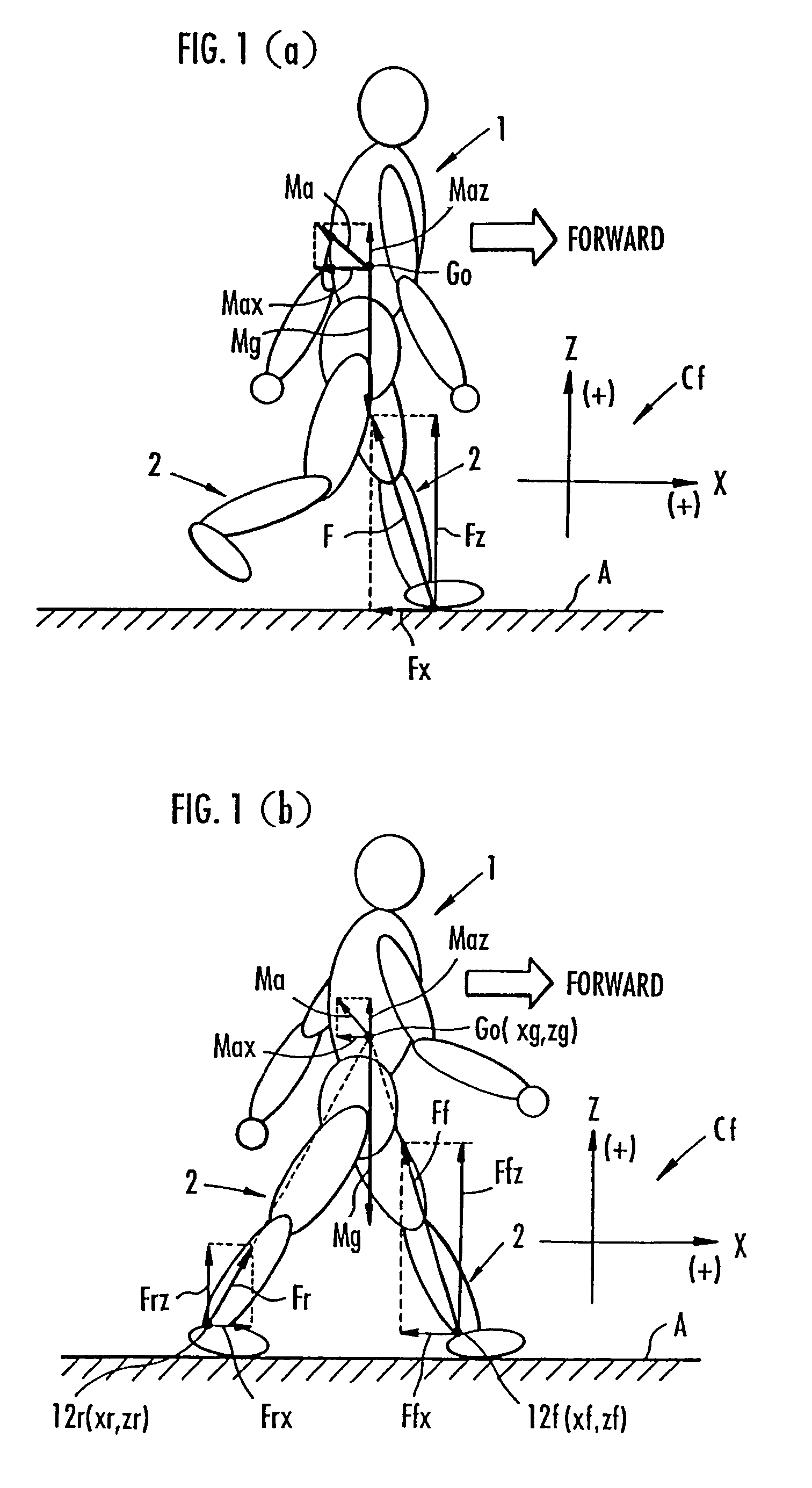
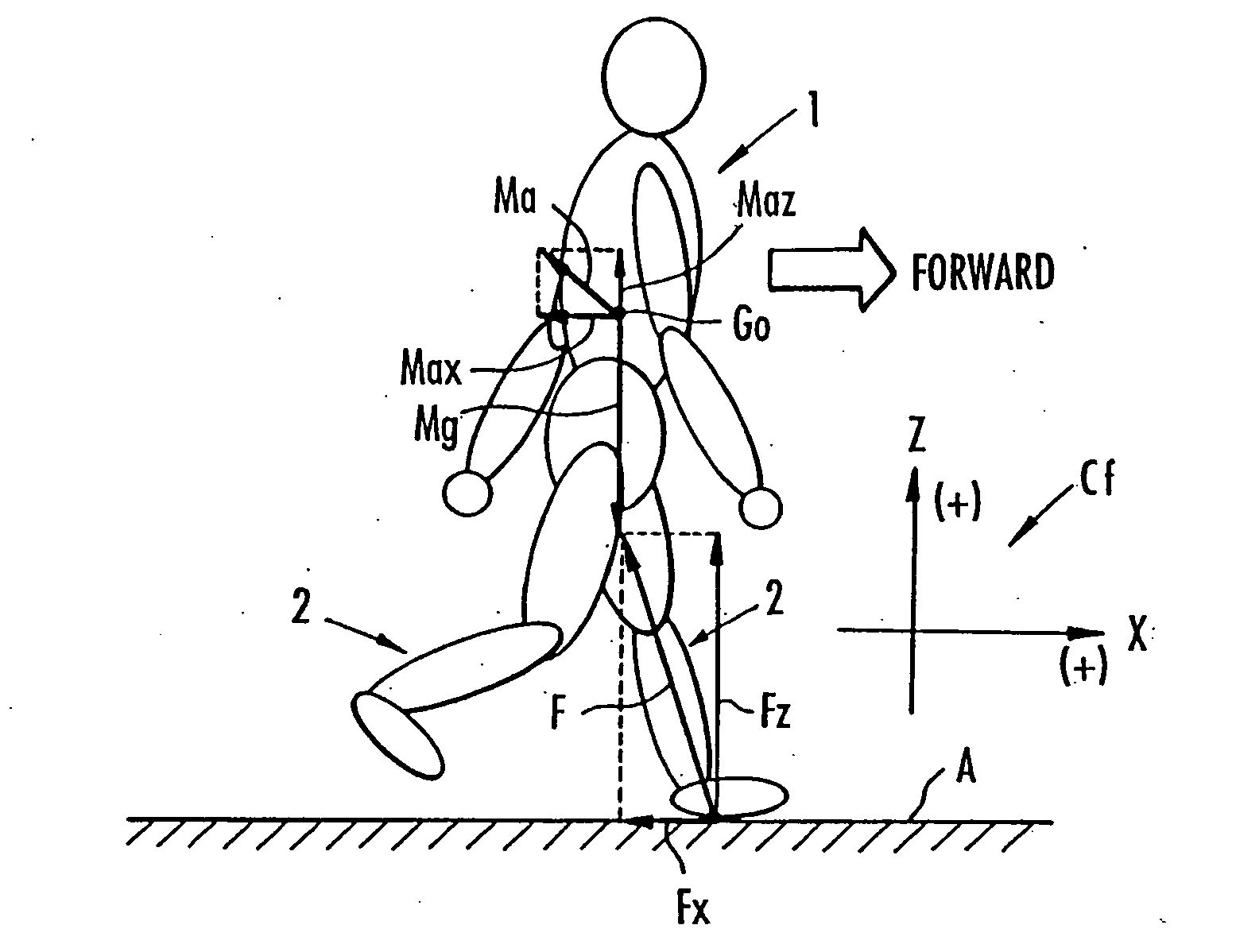
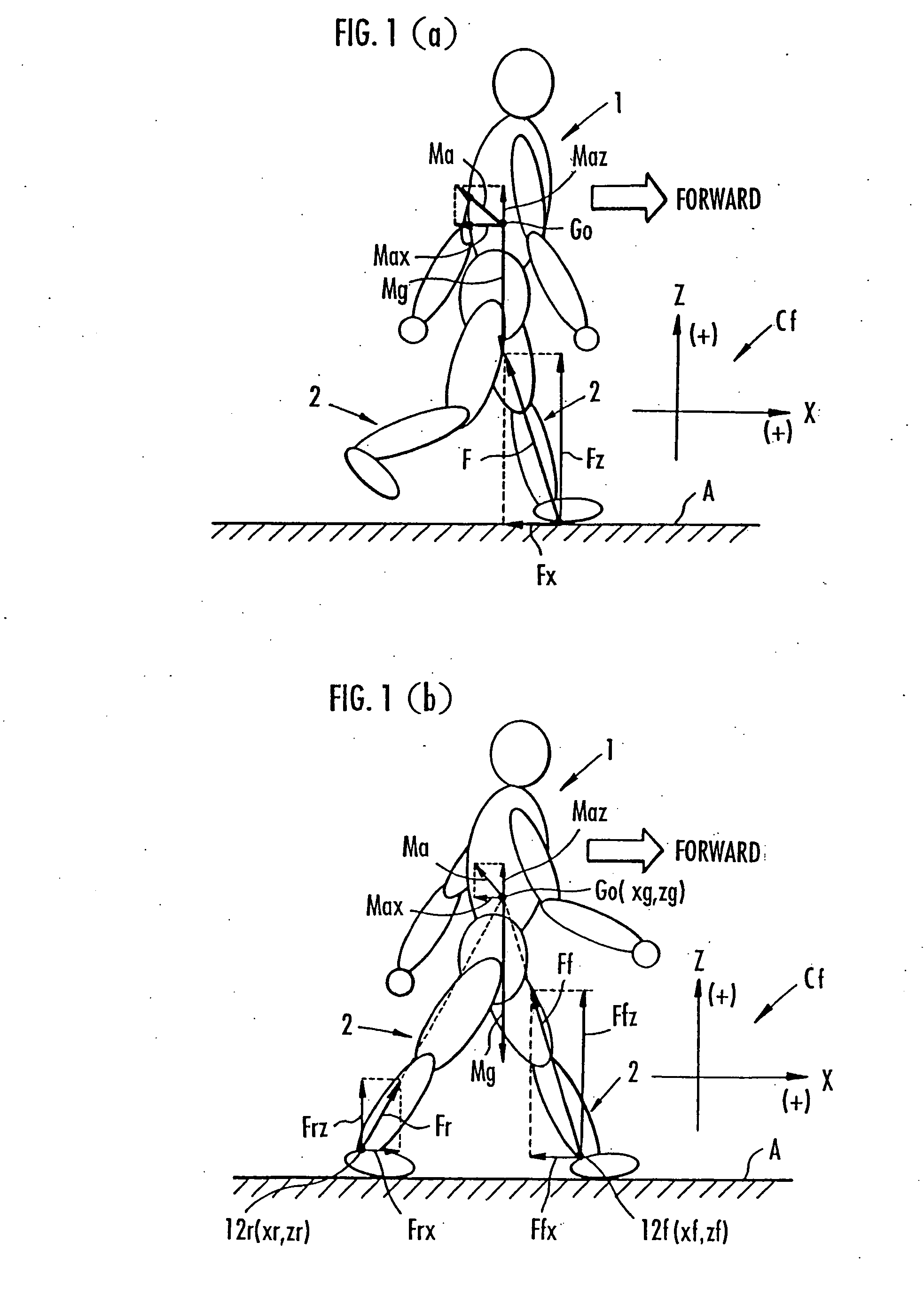
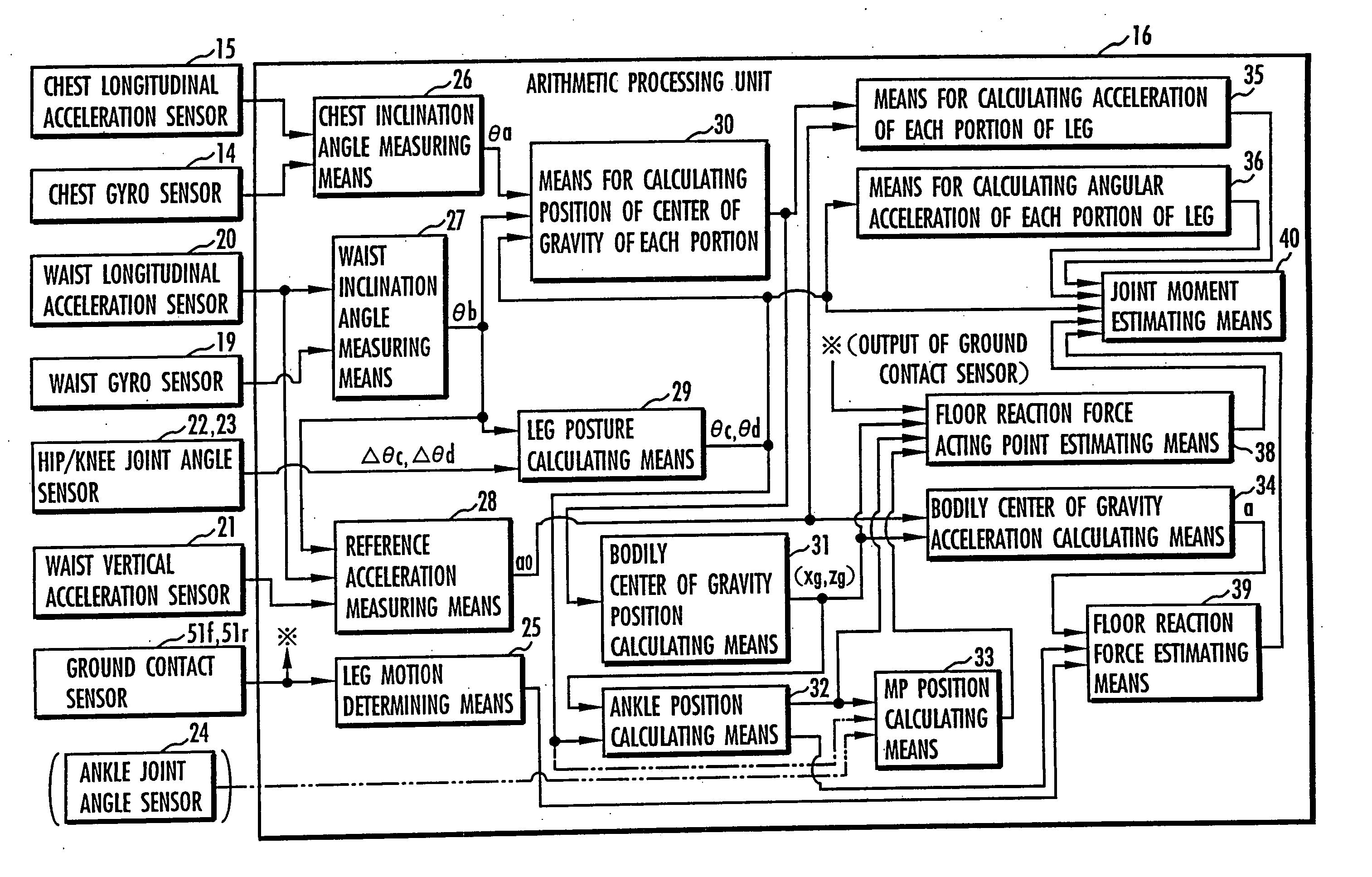
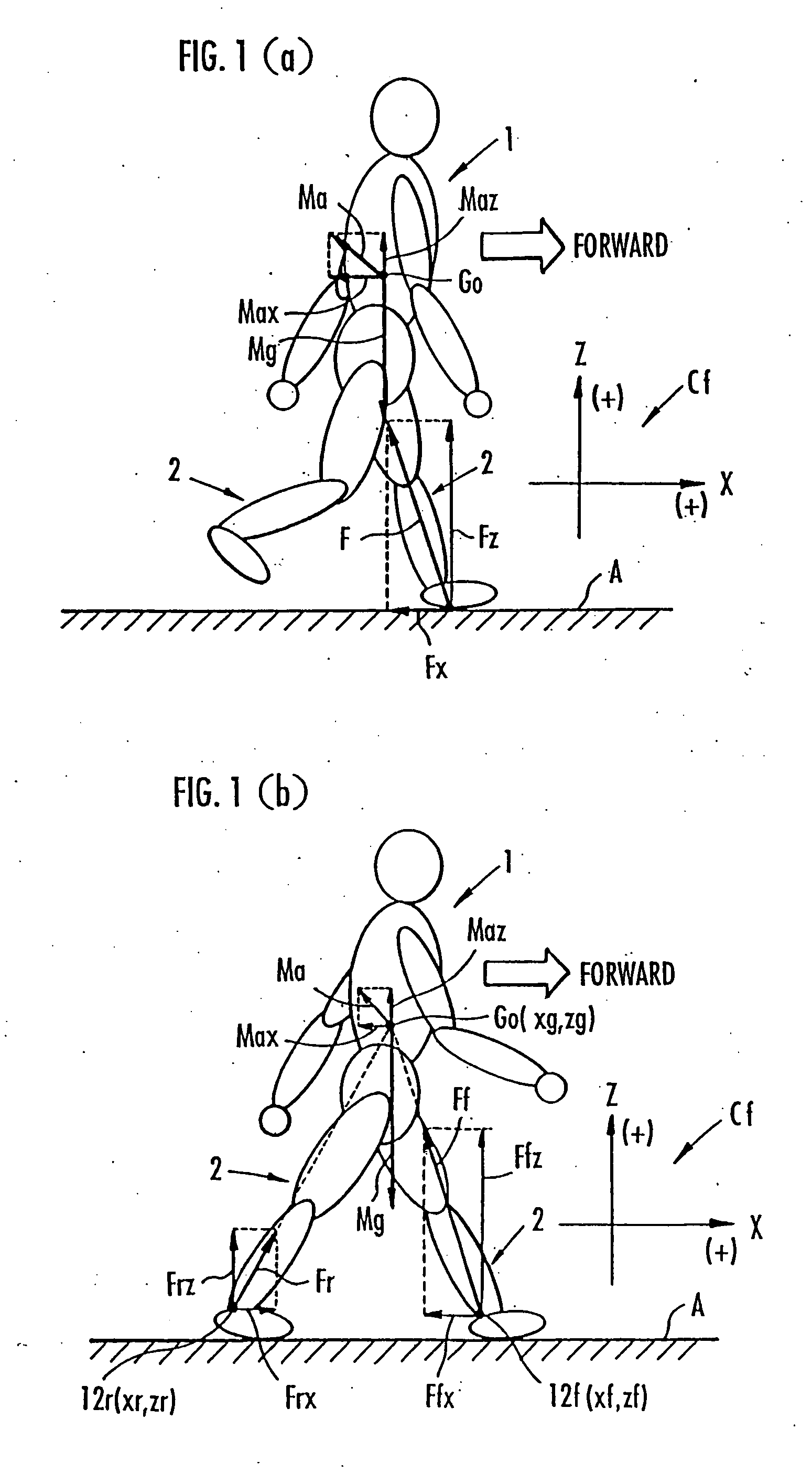
Method of assuming acting point of floor reaction force to biped walking mobile body and method of assuming joint moment of biped walking mobile body
InactiveUS7119510B2Good estimateHigh accuracy of estimated valueProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlGround contactEngineering
While a biped walking mobile body is in a motion, including level-ground walking, the position of the center of gravity (G0) of the biped walking mobile body, the position of an ankle joint (12) of each leg (2), and the position of a metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) of a foot (13) are successively grasped, and the horizontal position of a floor reaction force acting point of the leg (2) in contact with the ground is estimated on the basis of the relative positional relationship among the aforesaid positions. Depending on whether the center of gravity (G0) is behind the ankle joint (12), between the ankle joint (12) and the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a), or before the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) with respect to the advancing direction of the biped walking mobile body, the horizontal position of the ankle joint (12), the center of gravity (G0), or the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) is defined as the horizontal position of a floor reaction force acting point. The vertical position of the floor reaction force acting point is estimated on the basis of the vertical distance from the ankle joint (12) to a ground contact surface.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Support moment control method for leg motion support orthosis
Target joint support moments of each leg are determined by estimating joint moments of the each leg necessary for the person A wearing a leg motion support orthosis (1) to make a motion independently and according to the estimated joint moments. Moreover, floor reaction forces for the support orthosis (1) to make a motion independently are estimated, and then estimated values of actual joint support moments actually applied from the support orthosis (1) to the joints of the each leg of the person (A) are found by using the estimated floor reaction forces and outputs of the force sensor (22) provided in a leg link portion (4) of the support orthosis (1). Torque generation units (15) and (16) of the support orthosis (1) are controlled in such a way that the estimated values of the actual joint support moments are coincident with the target joint support moments. Thereby, the leg motion of the person can be supported. Moreover, it effectively prevents forces other than the necessary forces to support the leg motion of the person from acting on the person and enables the person to make a leg motion with feeling as if the person were not wearing the leg motion support orthosis as fully as possible.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
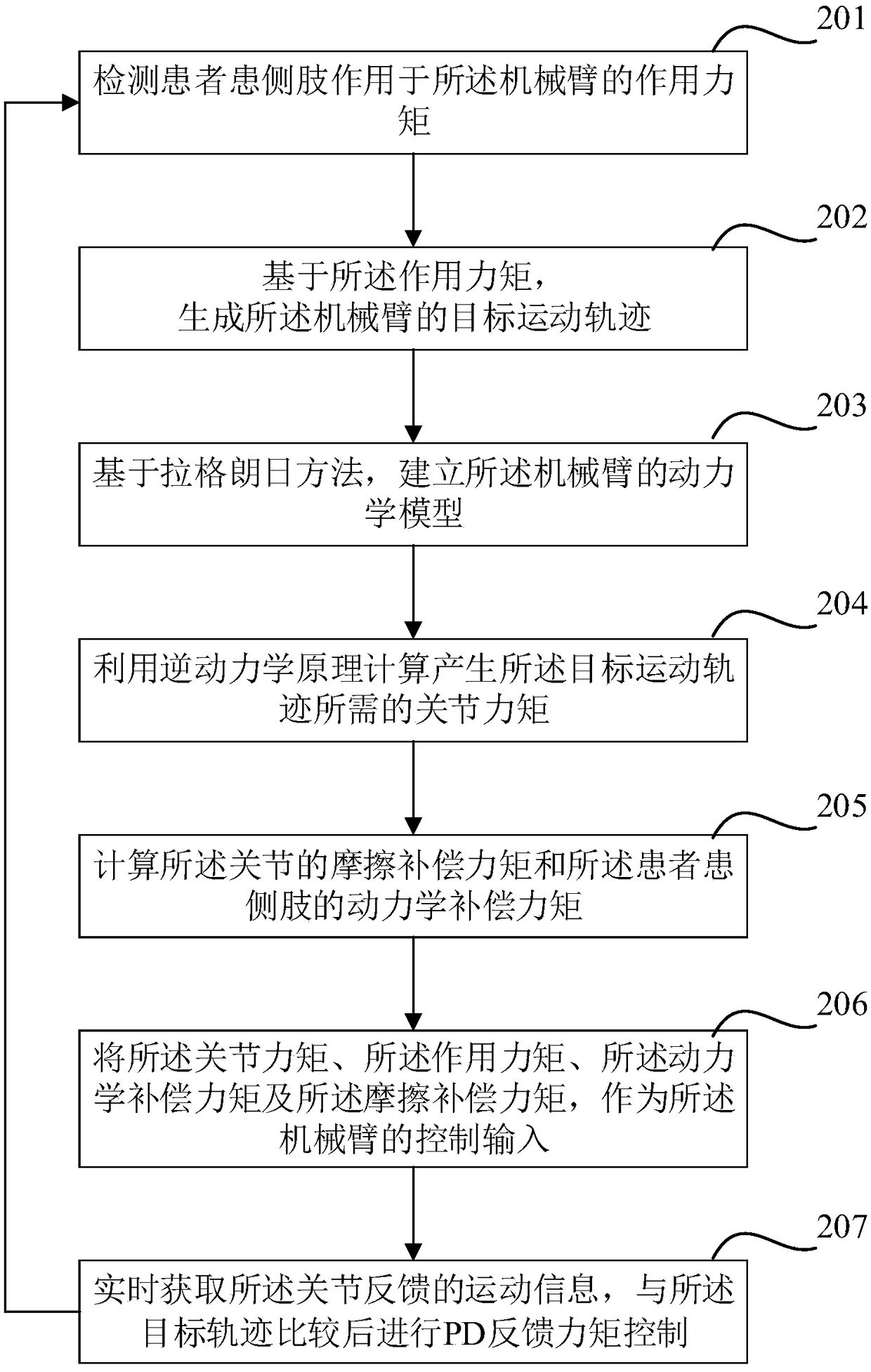
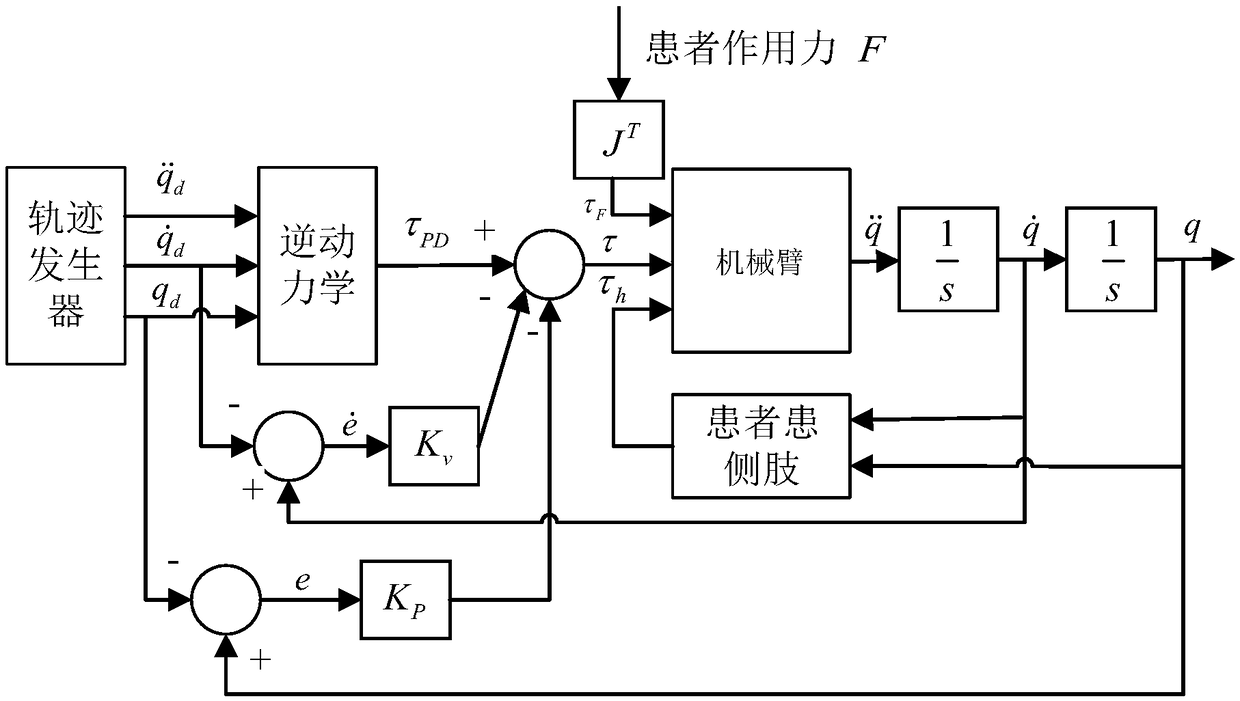
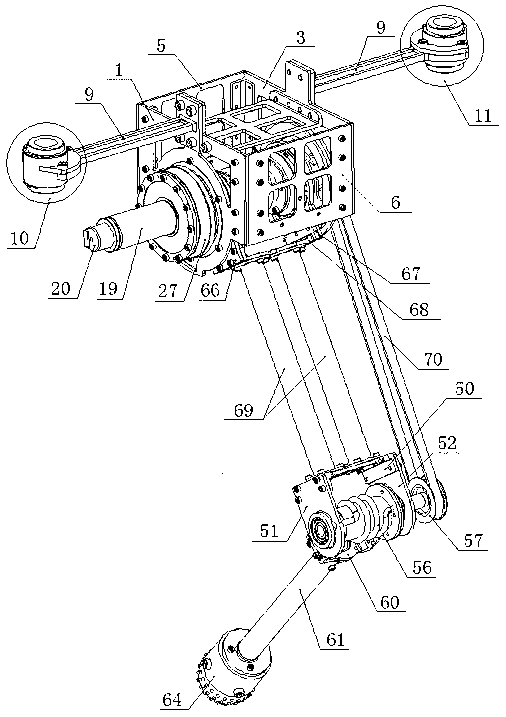
Rehabilitation robot and human-machine cooperative interaction force control method thereof
ActiveCN109223444AImprove movement flexibilityIncrease flexibilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesInverse dynamicsDynamic models
The invention discloses a rehabilitation robot and a human-machine cooperative interaction force control method thereof. The rehabilitation robot comprises a robot arm with at least one joint. The method for controlling the human-machine interaction force of the rehabilitation robot comprises the following steps: detecting an action moment of a patient's affected side limb acting on the robot arm;Generating a target motion trajectory of the manipulator; Establishing a dynamic model of the manipulator; Calculating a joint moment required for generating the target motion trajectory by using aninverse dynamics principle; Calculating a friction compensation torque of the joint and a dynamic compensation torque of the affected side limb of the patient; The joint torque, the action torque, thedynamics compensation torque, and the friction compensation torque are used as control inputs to the manipulator. The robot can provide the compliant force interactive control between the patient andthe rehabilitation robot arm, provides complete dynamic compensation, improves the equipment motion starting ability and flexibility, and is favorable for improving the experience degree of the patient to the auxiliary rehabilitation training. The invention can provide the compliant force interactive control between the patient and the rehabilitation robot arm, provides complete dynamic compensation, and improves the equipment motion starting ability and flexibility.
Owner:SHANGHAI ELECTRICGROUP CORP
Single-leg robot in-place jumping mechanism with power energy storage function
ActiveCN103264733AImprove the level of security protectionJump in placeVehiclesKnee JointEngineering
The invention discloses a single-leg robot in-place jumping mechanism with a power energy storage function and belongs to the technical field of robots. A robot is composed of five portions including a body, a hip joint, a knee joint, a pelma and a thigh and a shank, the body and the thigh are connected through the hip joint, the thigh and the shank are connected through the knee joint, the hip joint is composed of elements like a motor, a harmonic speed reducer, a coder and a hip spring, has a function of actively outputting joint moment and provides active moment output for the knee joint through a synchronous belt, a knee spring is mounted on a knee rotary shaft of the knee joint, the knee joint stores and complements energy for jumping of the robot by converting gravitational potential energy of the robot into elastic potential energy of the knee spring, and a force sensor is mounted on the pelma and used for detecting ground-touching information of the robot. By reasonably arranging the joints and combining an active and passive joint control technology to store and complement the energy for jumping of the robot, improving of quickness and efficiency in moving of the robot is facilitated.
Owner:HANGZHOU YUNSHENCHU TECH CO LTD
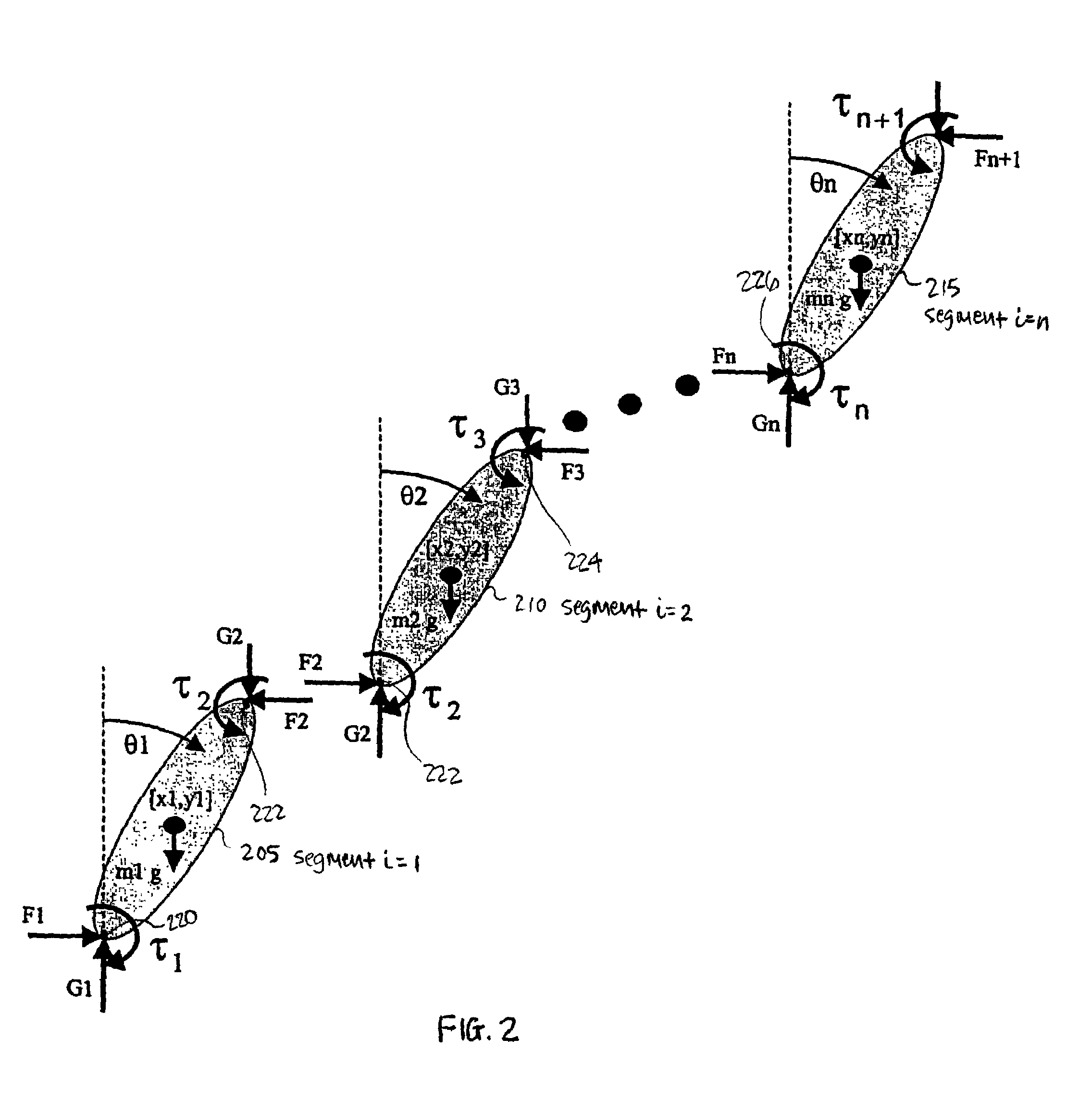
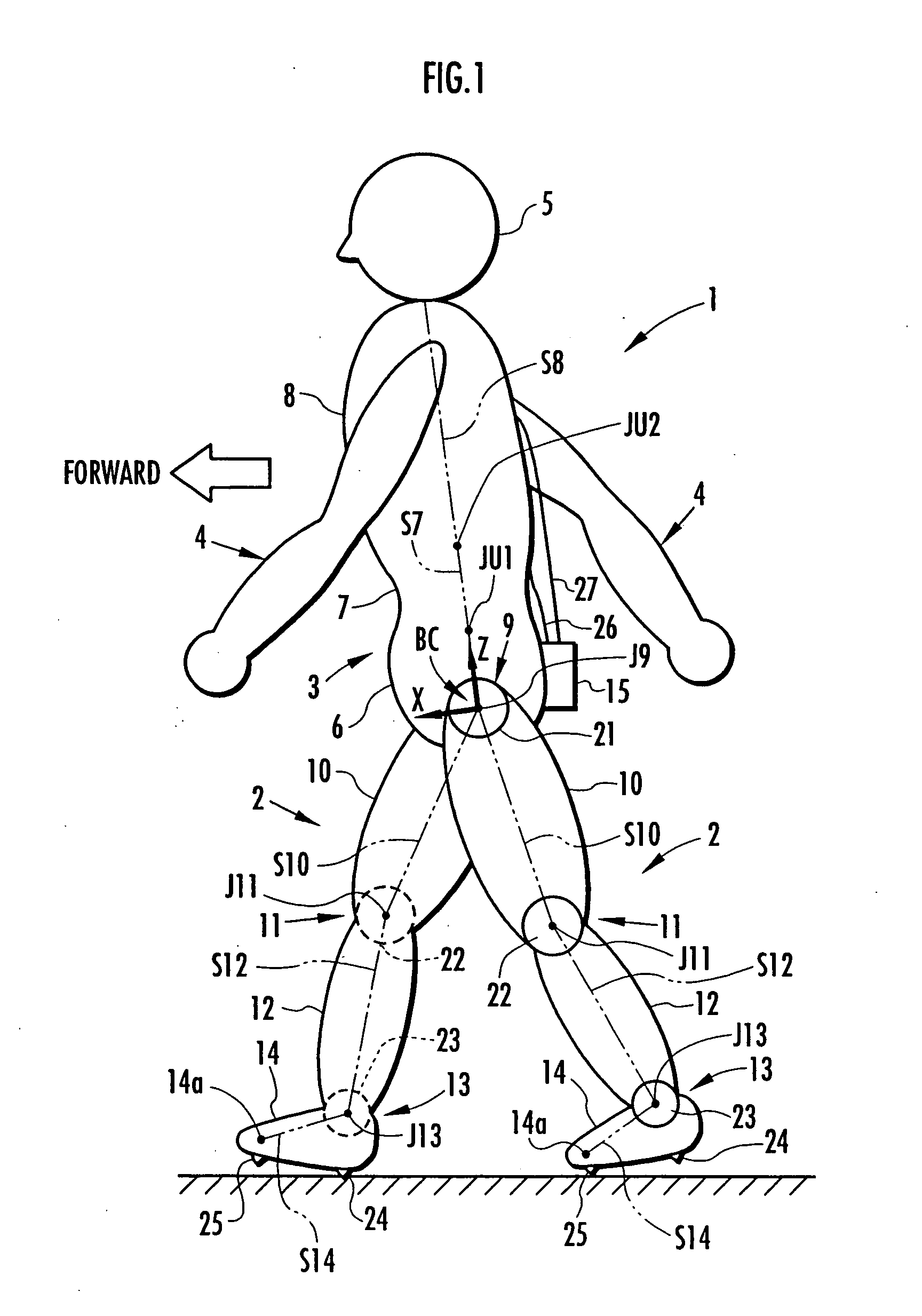
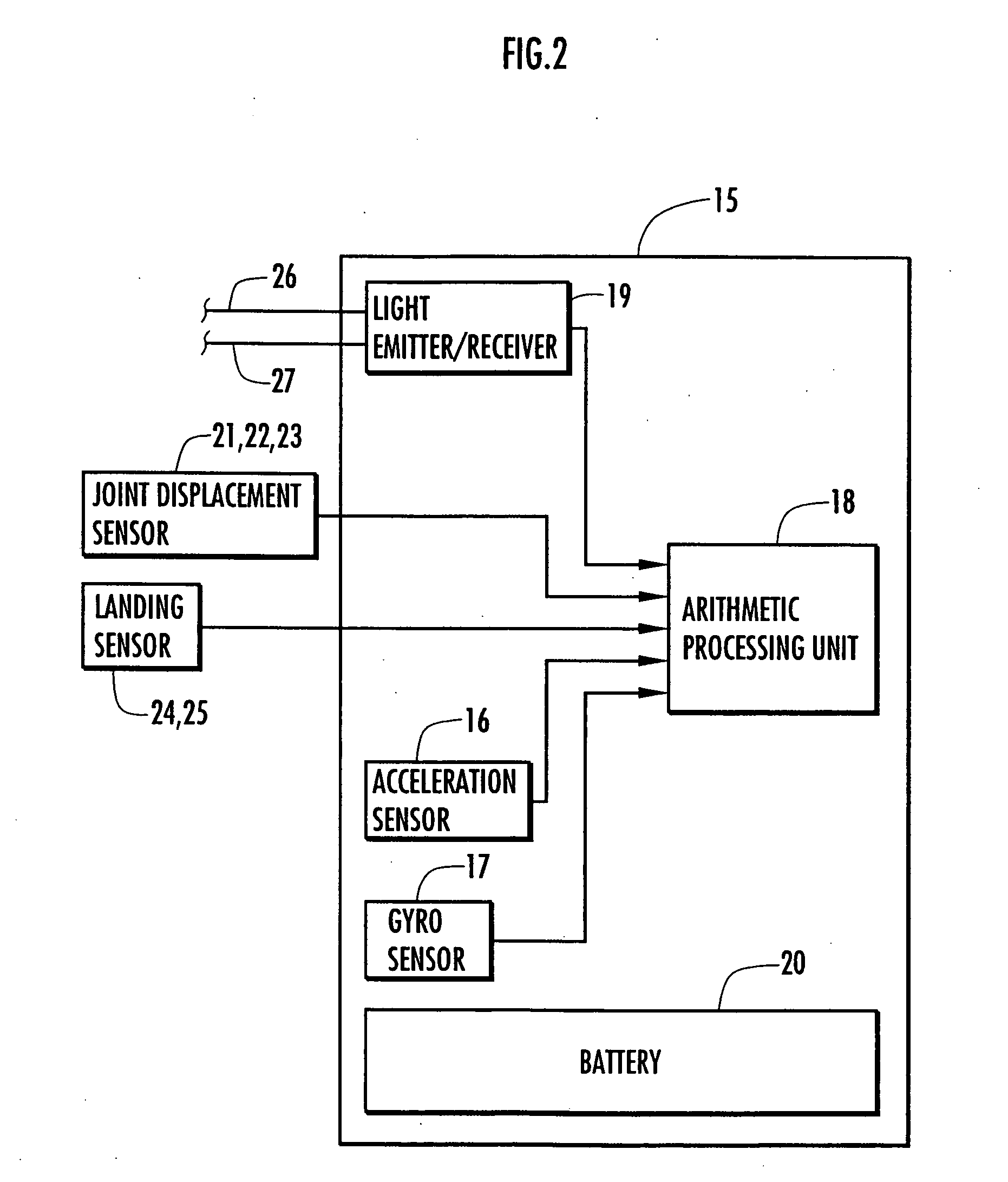
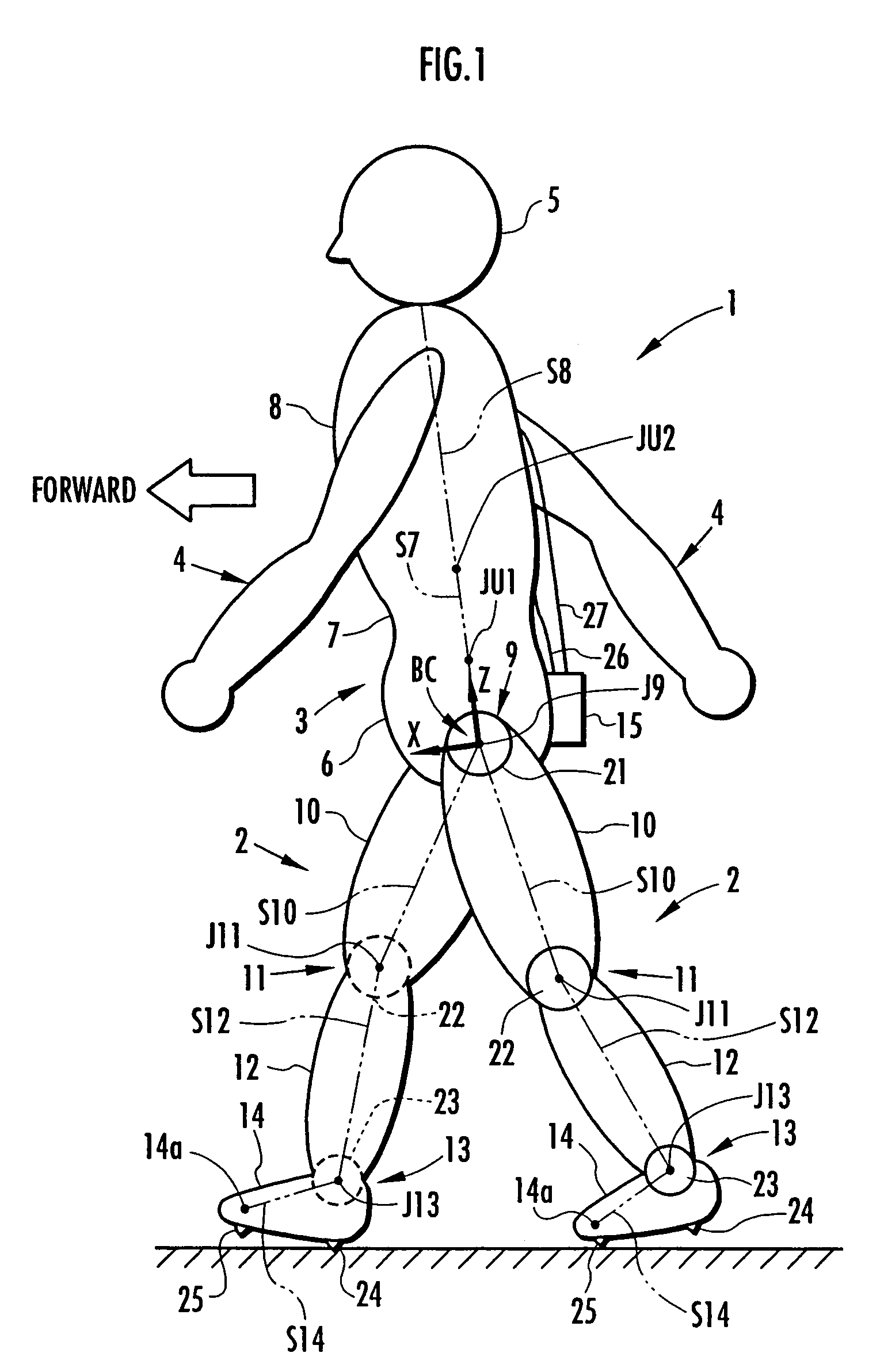
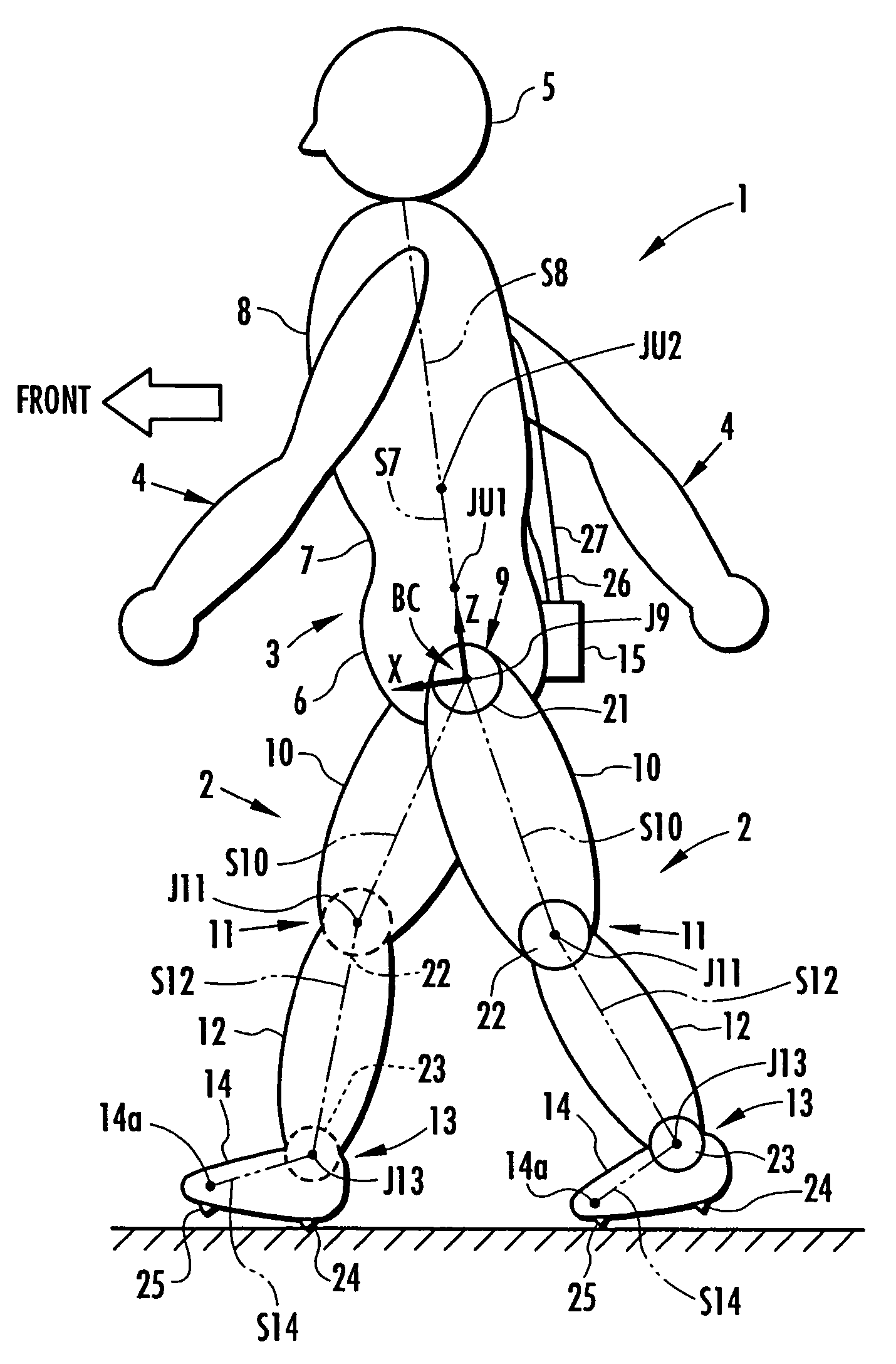
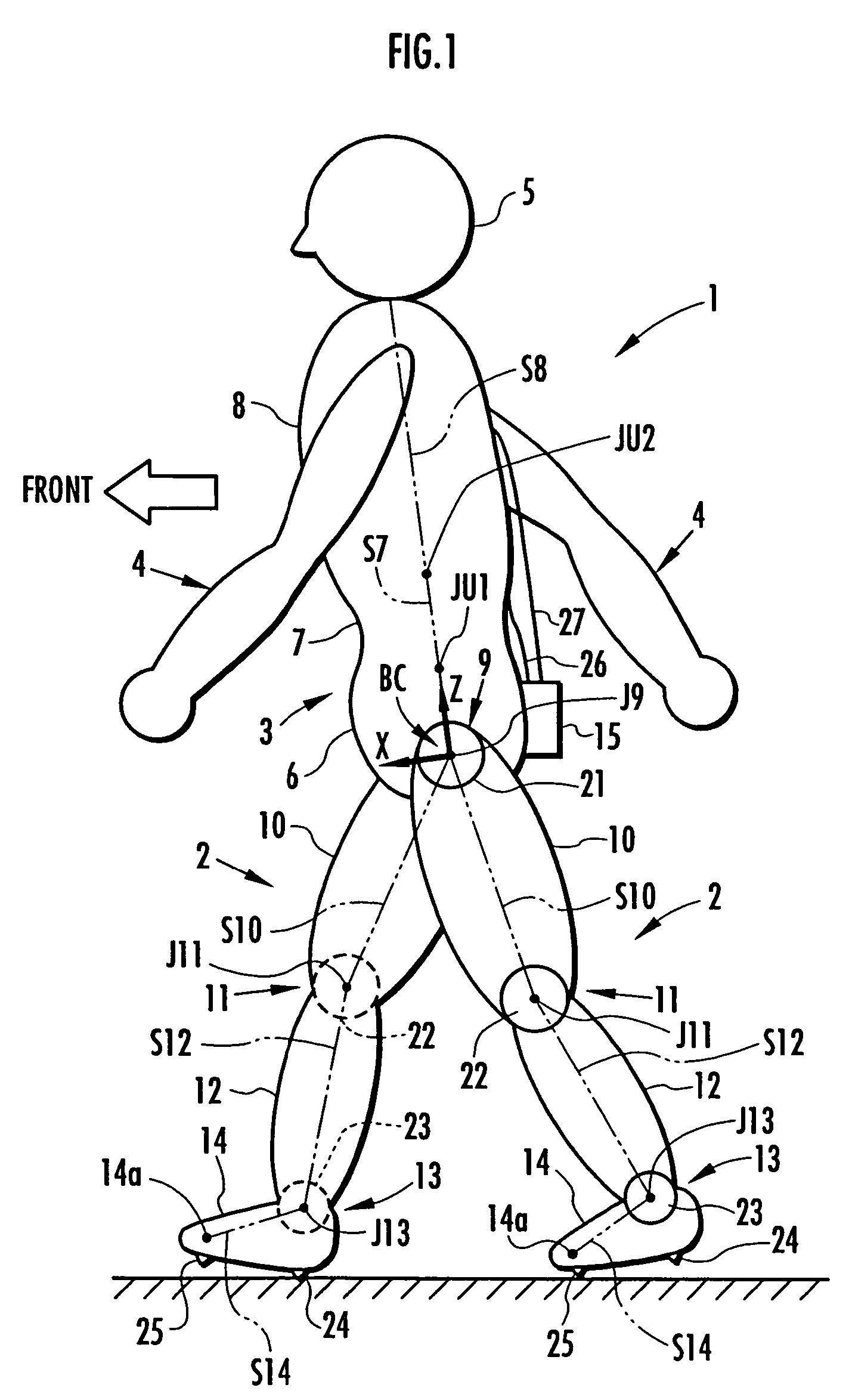
Method of estimating joint moment of bipedal walking body
InactiveUS20070084278A1Improve estimation accuracyImprove accuracyPerson identificationWalking aidsInverse dynamicsEngineering
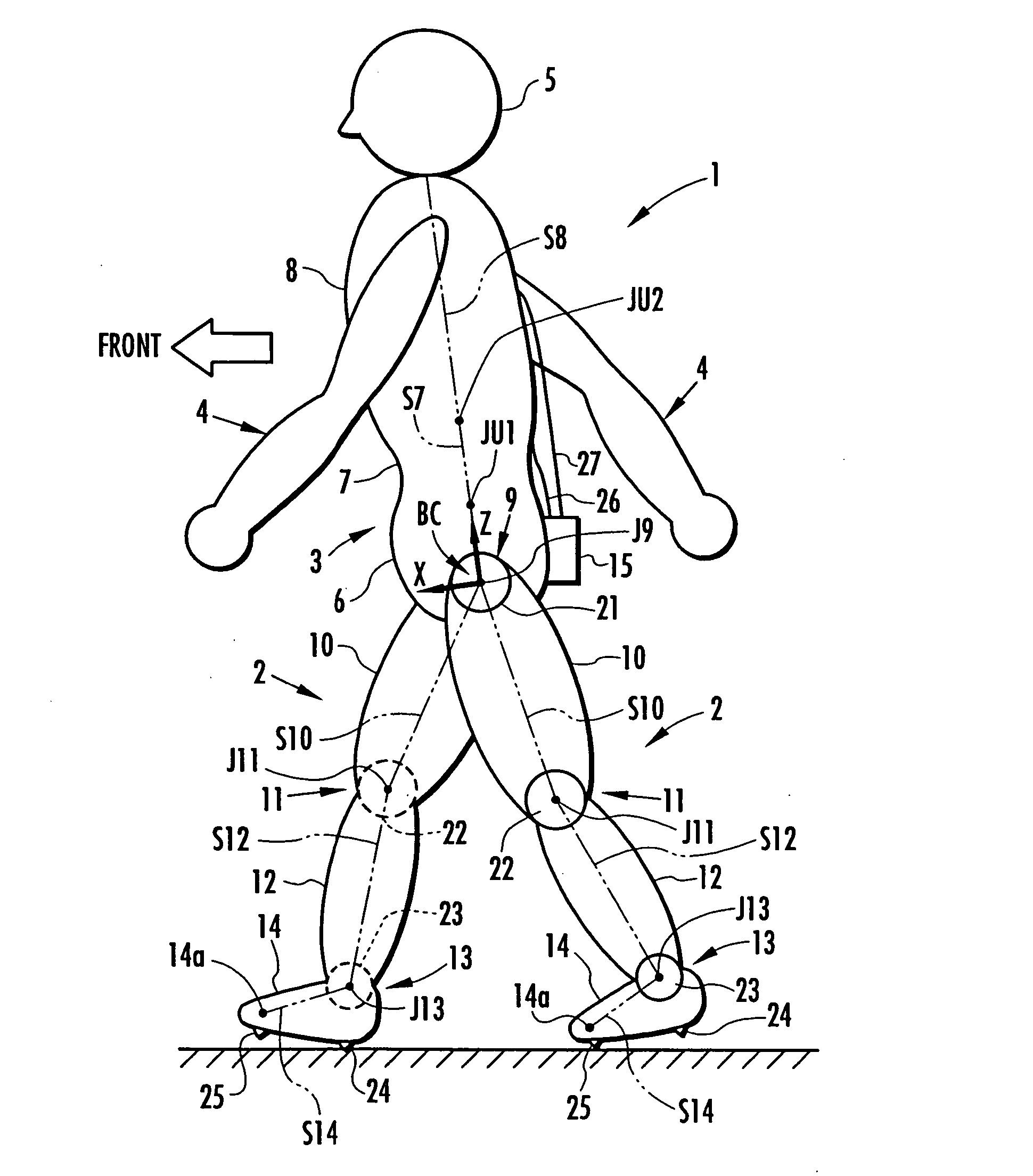
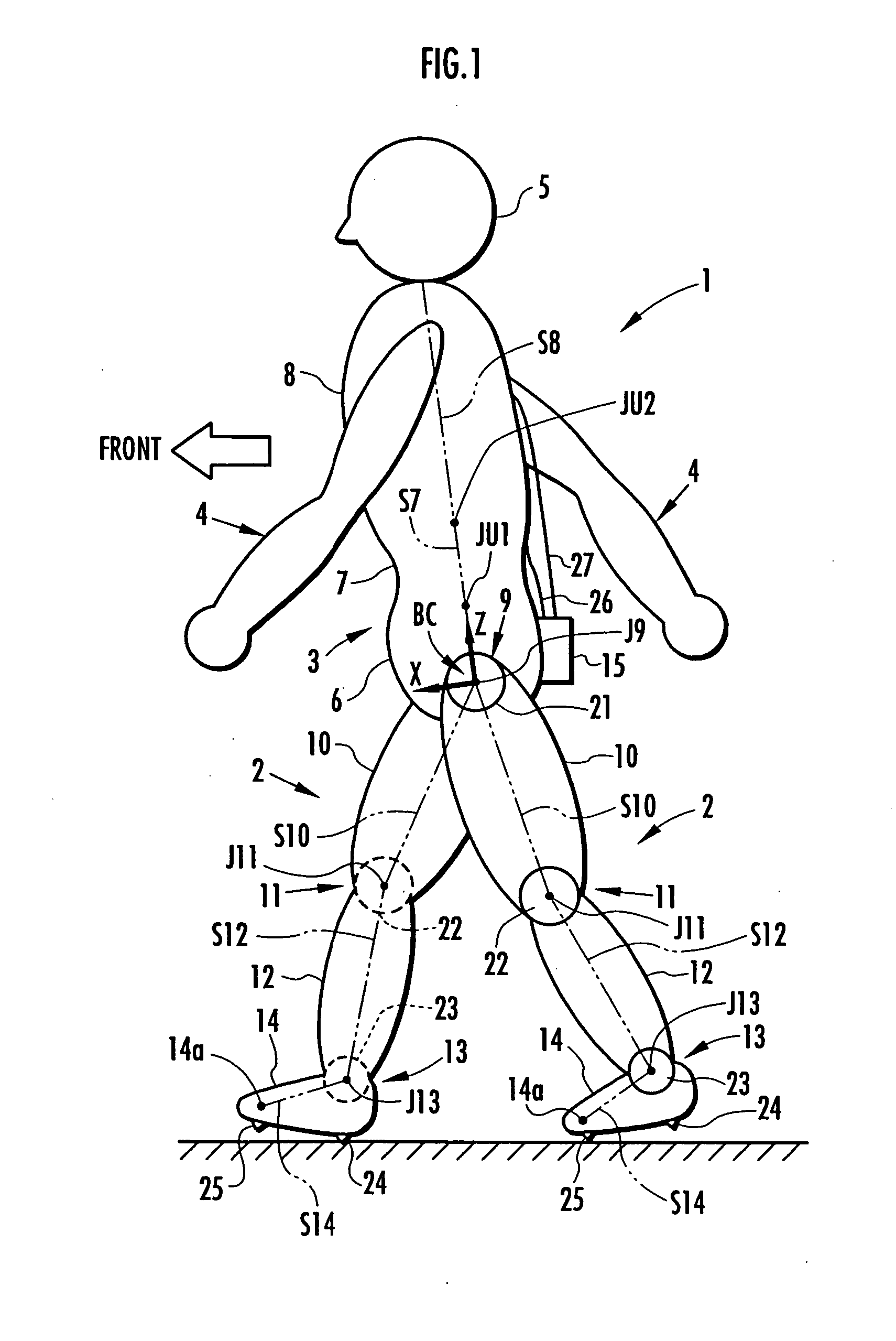
The joint rotational angles of joints 9, 11 and 13 of each leg 2 of a bipedal walking body 1 are detected to grasp the positions / postures of the corresponding rigid bodies 10, 12 and 14 of each leg 2 on a leg plane passing the joints 9, 11 and 13 of each leg 2. At the same time, the acceleration of a reference point (the origin of a body coordinate system BC) of the bipedal walking body 1, the floor reaction force acting on each leg 2 and the position of an acting point thereof are grasped in terms of three-dimensional amounts. Two-dimensional amounts obtained by projecting the acceleration, the floor reaction force and the position of the acting point thereof, and the positions / postures of the corresponding rigid bodies of each 2 onto the leg plane are used to estimate the moments acting on joints of each leg on the basis of an inverse dynamic model. The stability of the estimated values of joint moments can be improved while securing the accuracy of estimating the joint moments in the bending and stretching directions of each leg, considering three-dimensional motions of the bipedal walking body.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
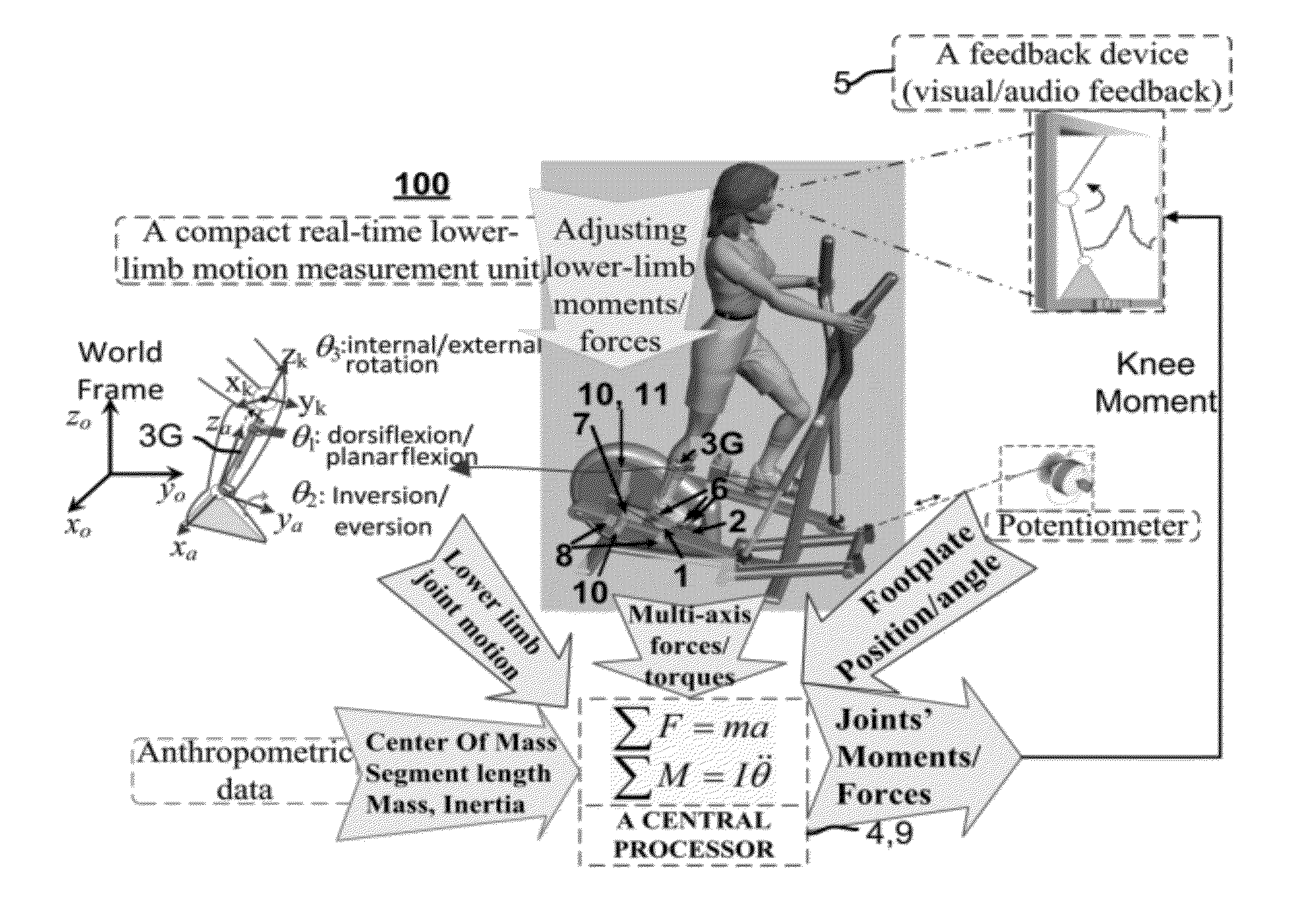
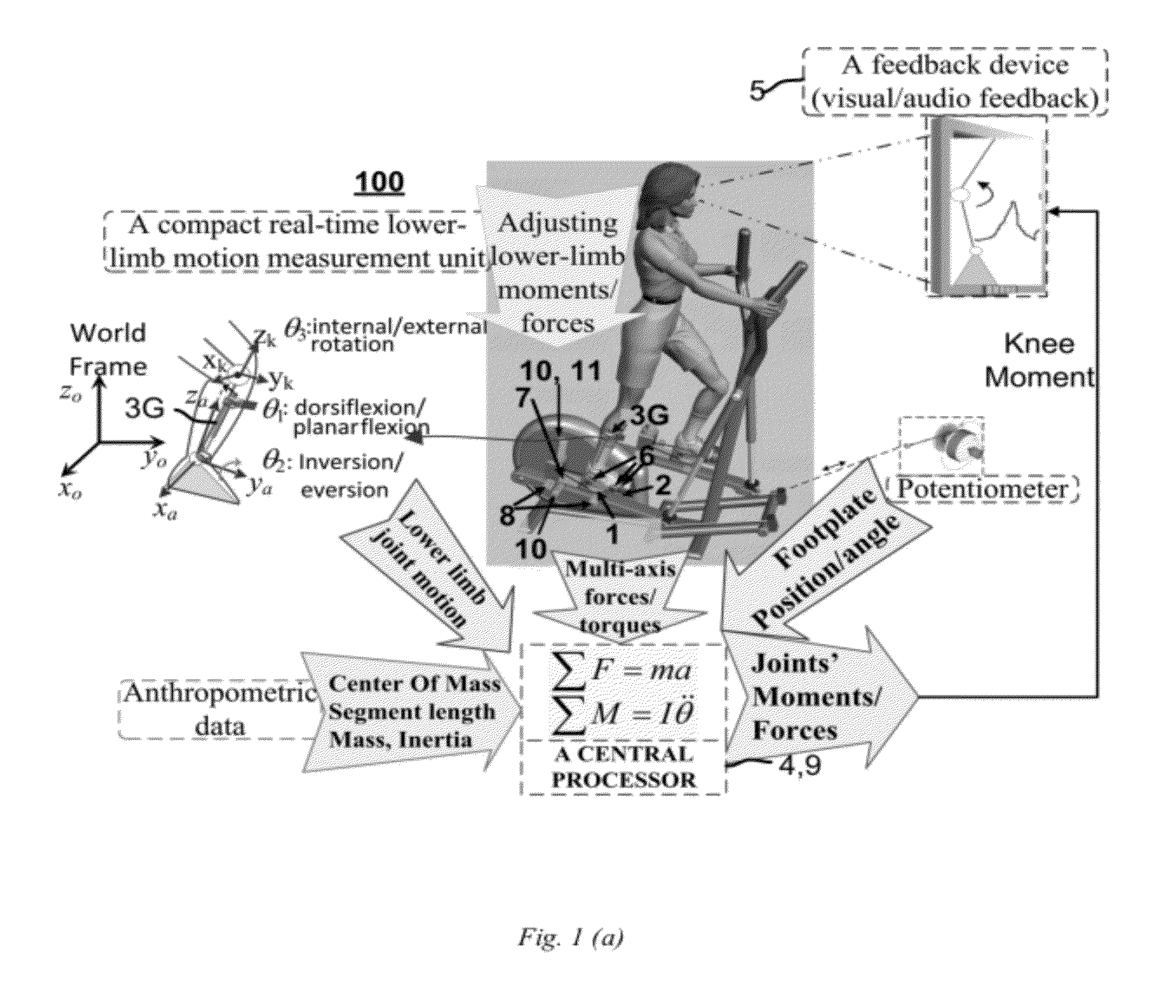
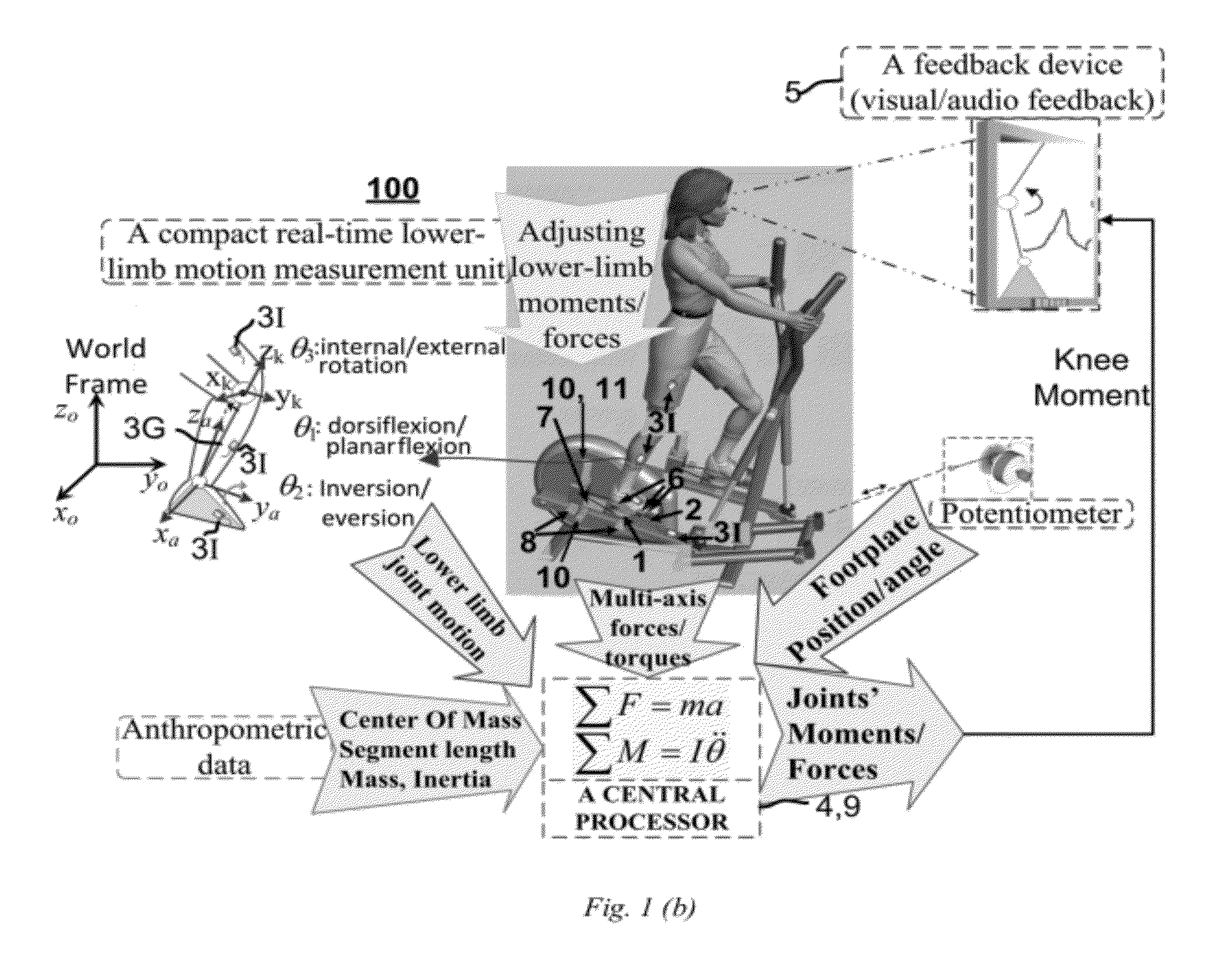
Apparatus and Method of Controlling Lower-Limb Joint Moments through Real-Time Feedback Training
InactiveUS20120277063A1Gymnastic exercisingDiagnostic recording/measuringClinical settingsEngineering
A real-time estimation of 3D moments of lower-limb joints using a robotic multi-axis training system with a 6-axis force / torque (F / T) sensors and a 6-DOF goniometer is described. A joint moment such as the knee abduction moment (KAM) can be determined in real-time without using sophisticated optoelectronic motion tracking system. The system also does not require computation of the COP location. The knee adduction moment or any other lower-limb 3D joint moments can be determined conveniently during stepping movement on the training system for real-time biofeedback training on controlling the targeted joint moment(s). The 6-DOF goniometer is convenient to use with other analog signals including the 6-axis F / T and locomotion variables. As an example application, combined with the frontal plane movement on the robotic multi-axis elliptical trainer, it provides a useful tool suitable for clinical setting to help patients with knee OA to reduce potentially damaging peak knee adduction moment through real-time feedback training.
Owner:REHABTEK
Method of assuming acting point of floor reaction force to biped walking mobile body and method of assuming joint moment of biped walking mobile body
InactiveUS20060197485A1Simple arithmetic processingGood estimateProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlGround contactEngineering
While a biped walking mobile body is in a motion, including level-ground walking, the position of the center of gravity (G0) of the biped walking mobile body, the position of an ankle joint (12) of each leg (2), and the position of a metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) of a foot (13) are successively grasped, and the horizontal position of a floor reaction force acting point of the leg (2) in contact with the ground is estimated on the basis of the relative positional relationship among the aforesaid positions. Depending on whether the center of gravity (G0) is behind the ankle joint (12), between the ankle joint (12) and the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a), or before the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) with respect to the advancing direction of the biped walking mobile body, the horizontal position of the ankle joint (12), the center of gravity (G0), or the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) is defined as the horizontal position of a floor reaction force acting point. The vertical position of the floor reaction force acting point is estimated on the basis of the vertical distance from the ankle joint (12) to a ground contact surface.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
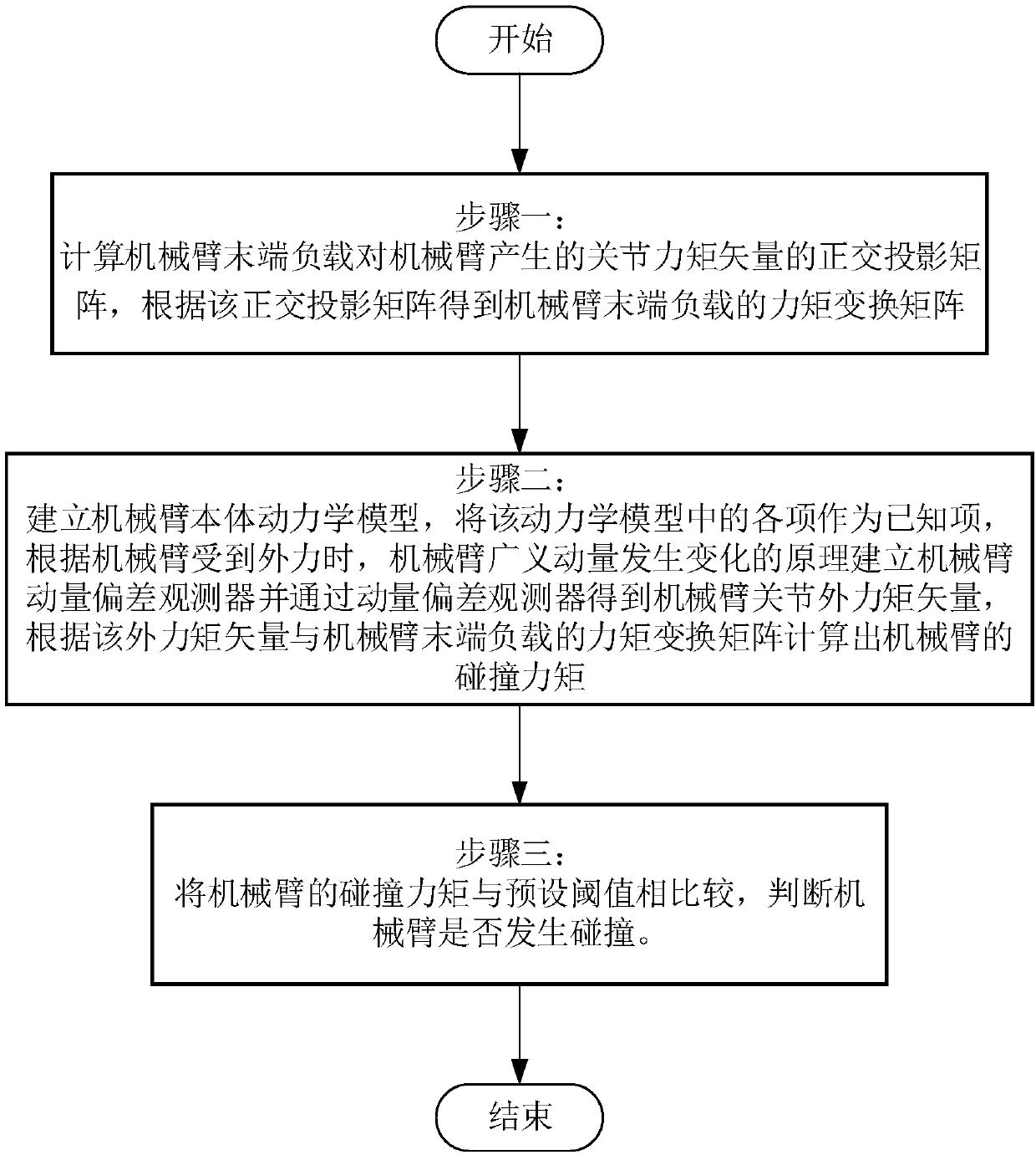
Sensorless mechanical arm collision detection method
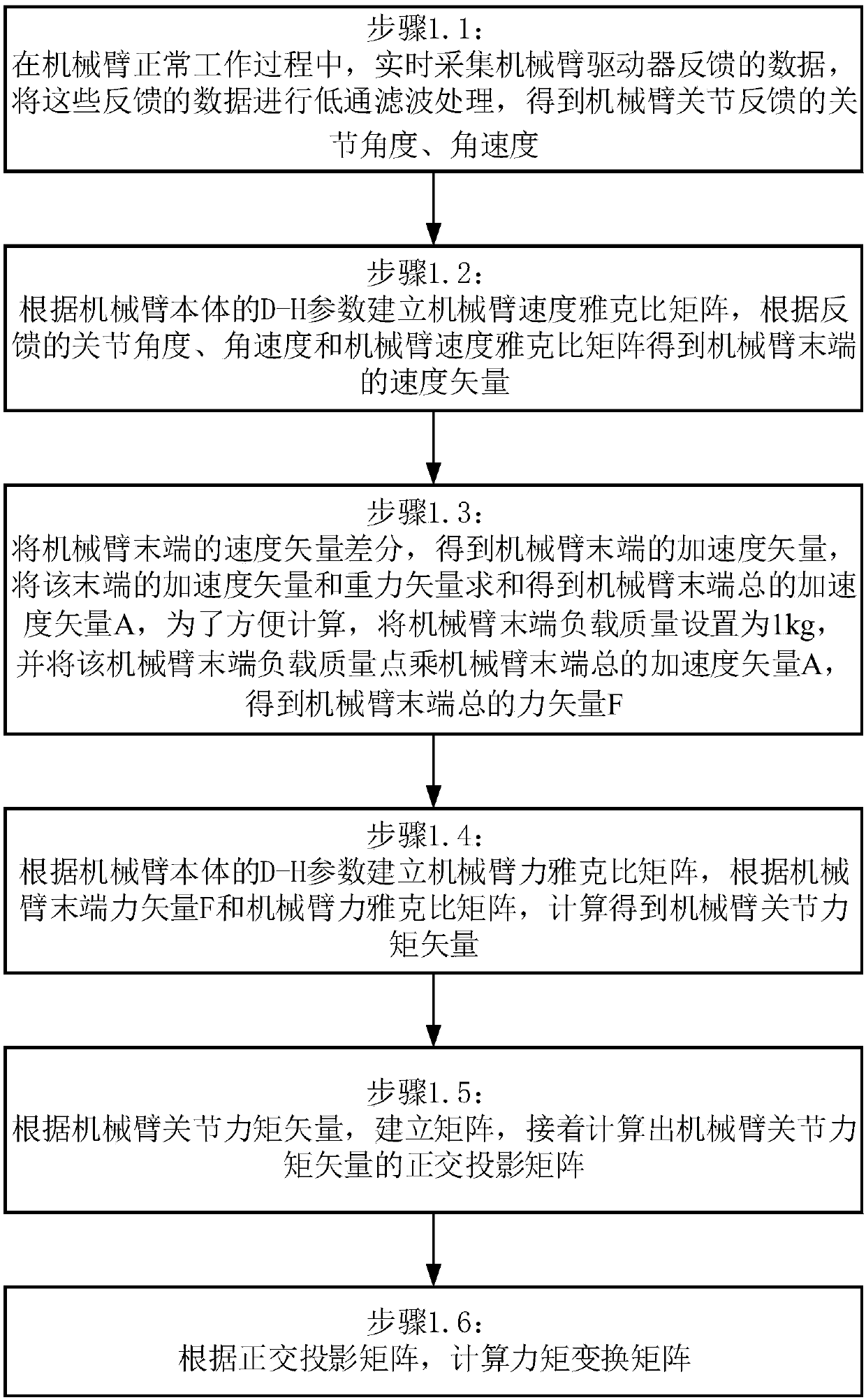
ActiveCN108015774AEliminate the effect of joint torqueAvoid misjudgmentProgramme-controlled manipulatorHat matrixMomentum
The invention discloses a sensorless mechanical arm collision detection method. The method comprises the steps that a rectangular projection matrix of the joint moment vector generated by the load ofthe tail end of a mechanical arm to the mechanical arm is calculated, and a moment transformation matrix of the load of the tail end of the mechanical arm is obtained according to the rectangular projection matrix; a mechanical arm body kinetic model is set up, a mechanical arm momentum deviation observer is set up according to various items in the kinetic model, the joint external moment vector of the mechanical arm is obtained through the momentum deviation observer, and the collision moment of the mechanical arm is calculated out according to the external moment vector and the moment transformation matrix of the load of the tail end of the mechanical arm; and the collision moment of the mechanical arm and a preset threshold value are compared, and whether a collision happens to the mechanical arm or not is judged. According to the collision detection method, collision detection of the mechanical arm with the load at the tail end can be achieved, and the method is simple, efficient and low in cost.
Owner:北京艾利特科技有限公司
Method and system for determining data associated with lower limb activity
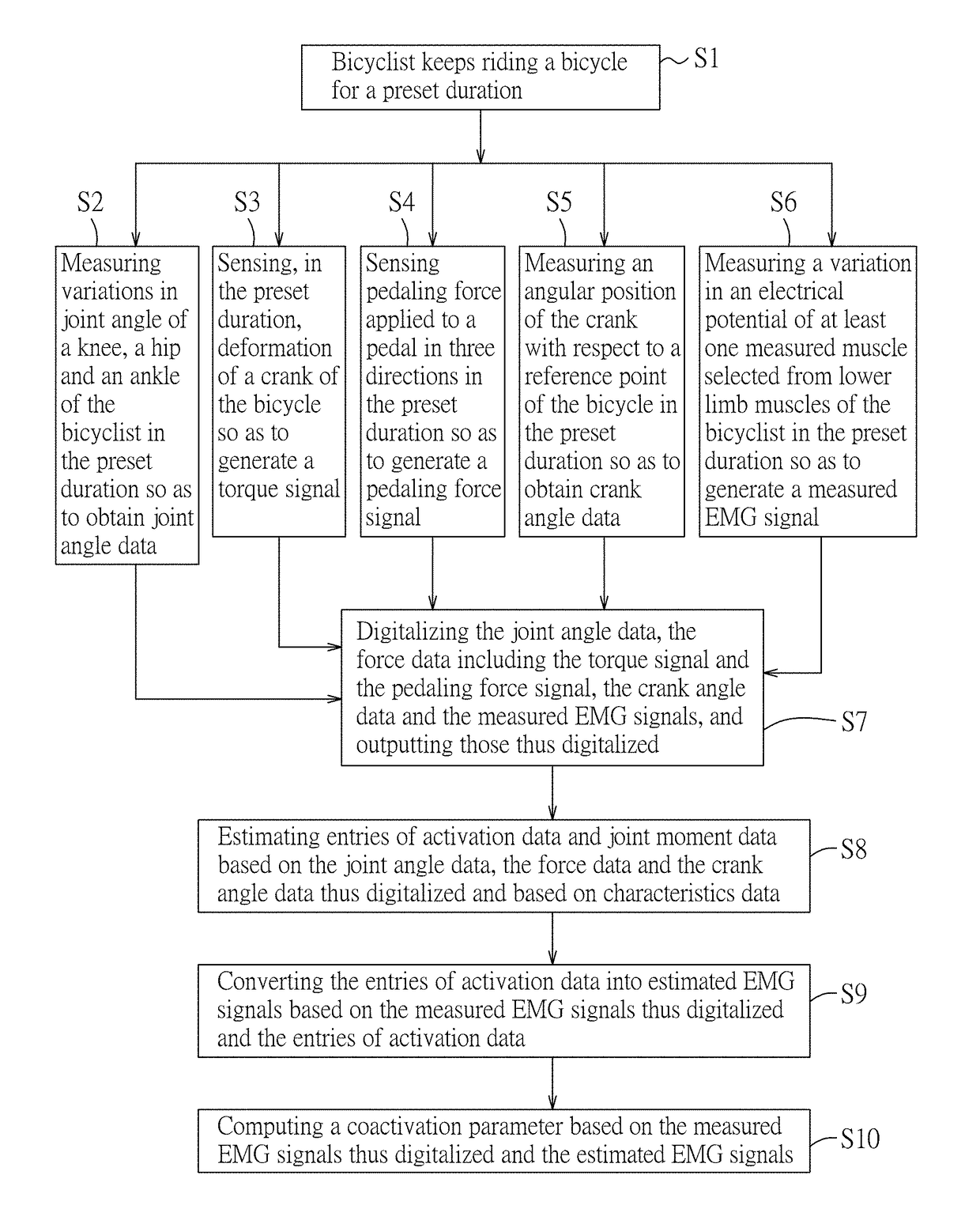
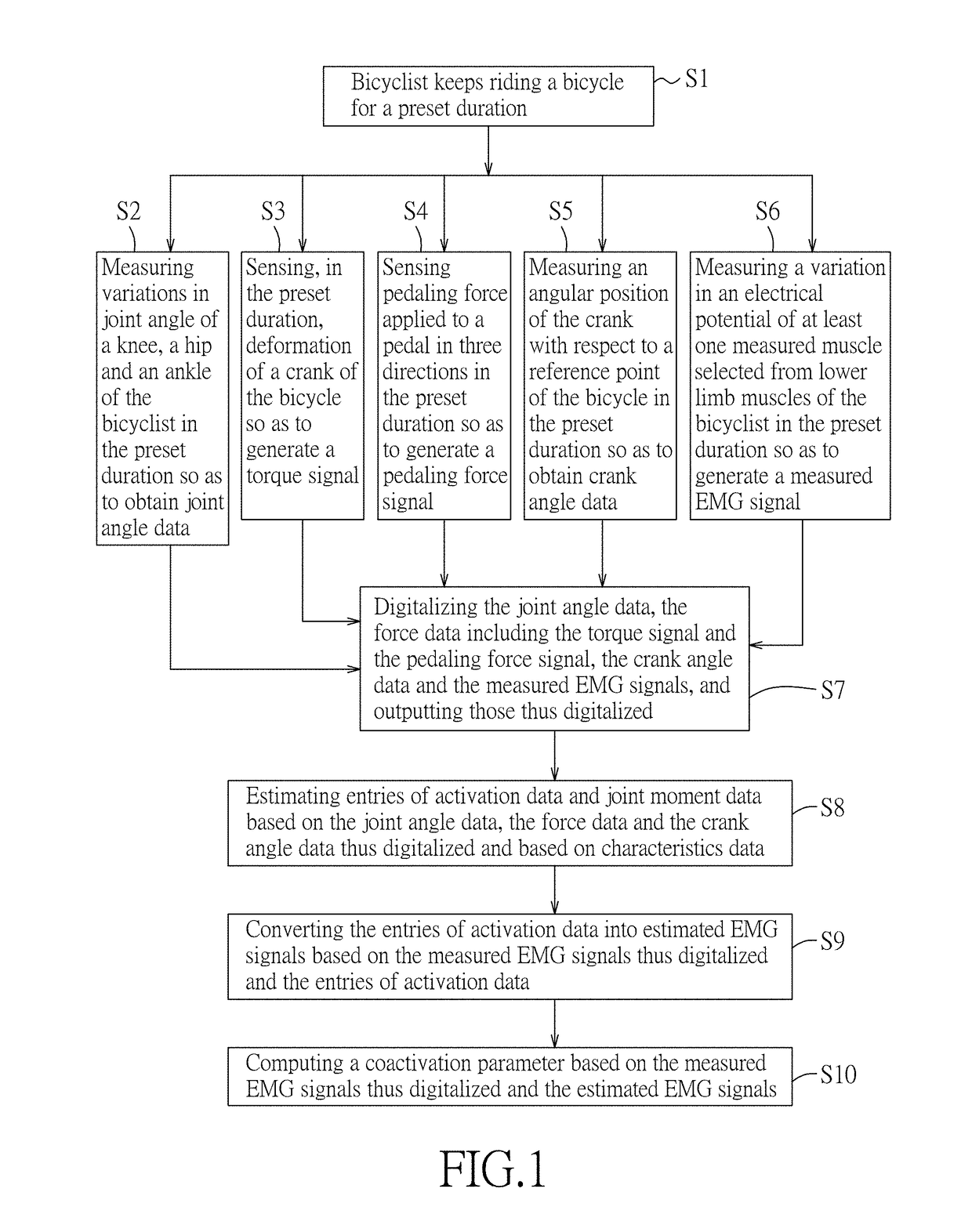
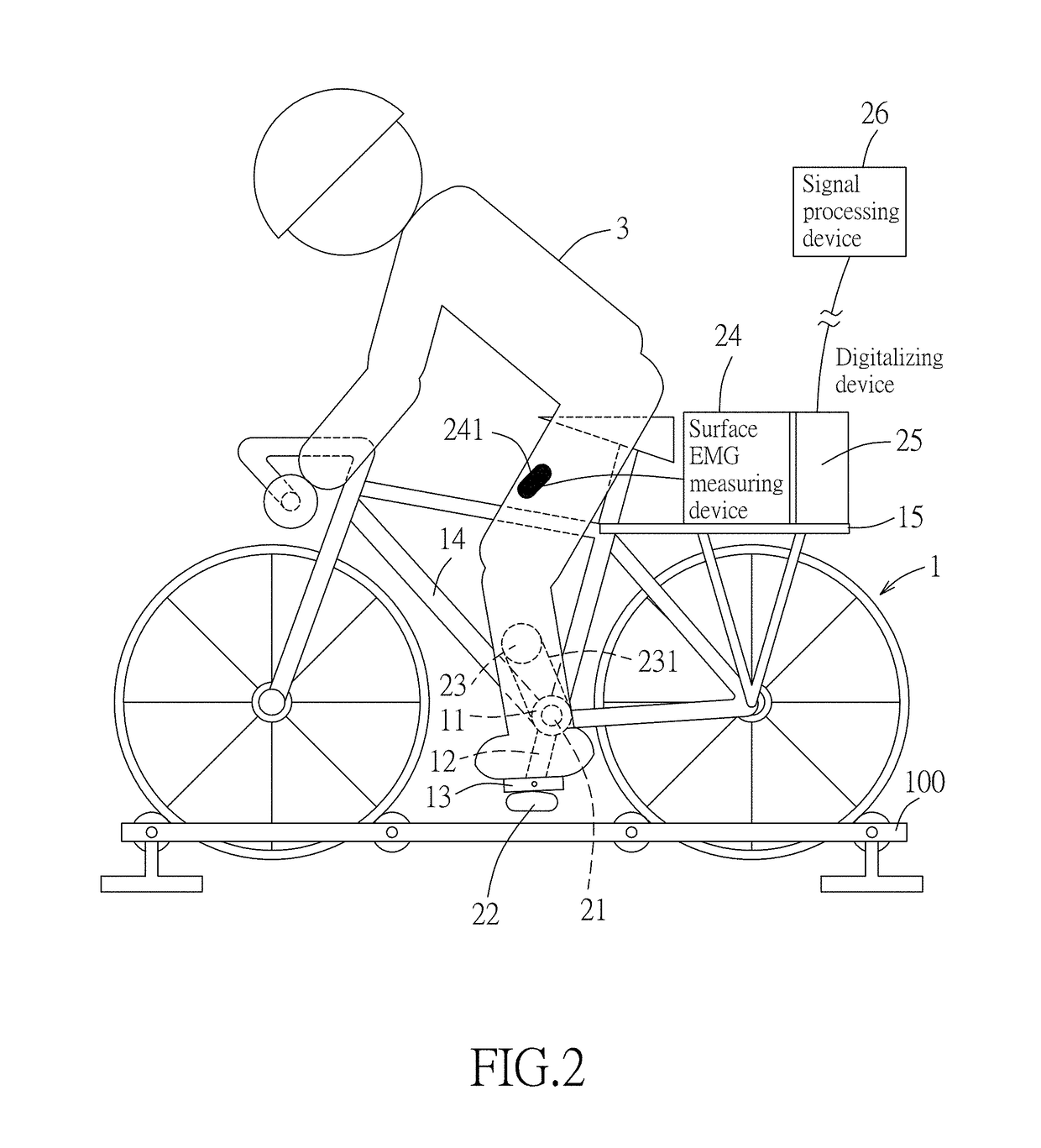
A method includes steps of: measuring a variation in joint angle of a knee of a cyclist to obtain joint angle data; sensing a torque applied on a crank of a cycle or pedaling force applied to a pedal of the cycle to obtain force data; measuring an angular position of the crank to obtain crank angle data; measuring an electrical potential variation of a measured muscle of the cyclist to generate a measured EMG signal; estimating activation data and joint moment data based on aforementioned data and characteristics data; converting the activation data into estimated EMG signals based on the measured EMG signal and the activation data; and computing a coactivation parameter based on the aforementioned EMG signals.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
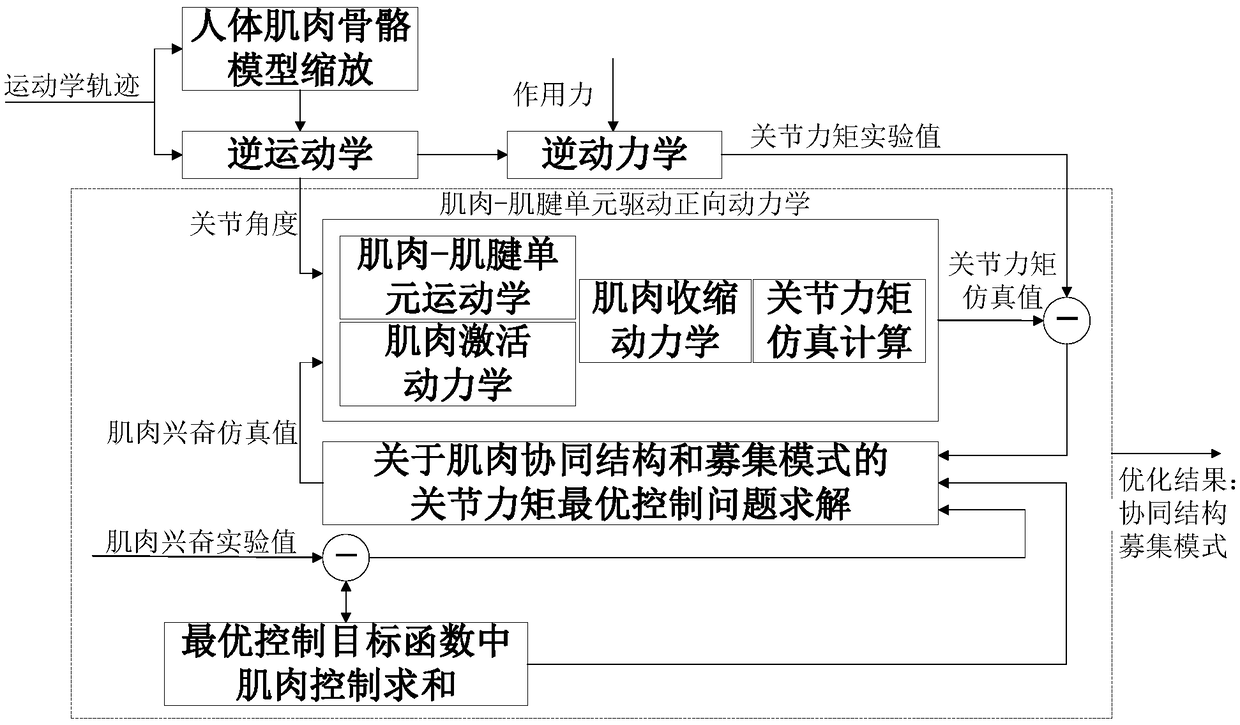
Muscle synergy analysis method based on human dynamics modeling and surface EMG signal correction
The invention discloses a muscle synergy analysis method based on human dynamics modeling and surface EMG signal correction. The method is characterized in that firstly, personalized human musculoskeletal model scaling of an experimental subject is performed; secondly, kinematics and dynamics data and EMG signals of the experimental subject in a moving state are collected, joint angles are solvedthrough inverse kinematics, physiological parameters are calculated through muscle and tendon kinematics, and joint moments are solved through inverse dynamics; an optimal control problem of joint moment distribution on the muscle synergy structure and a recruitment mode is solved according to the joint angles, the physiological parameters, the joint moments and the processed EMG signals, and themuscle synergy structure driving a human dynamics model and the recruitment mode are obtained. The method is advantaged in that the method is convenient to use, has high comfort level and security, iscompatible with joint moment and EMG signal errors and improves simulation model accuracy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Intelligent recovery device for lower limb spasm
ActiveCN103054690AIncrease proactive interventionSimple pan adjustmentChiropractic devicesEngineeringMuscle spasm
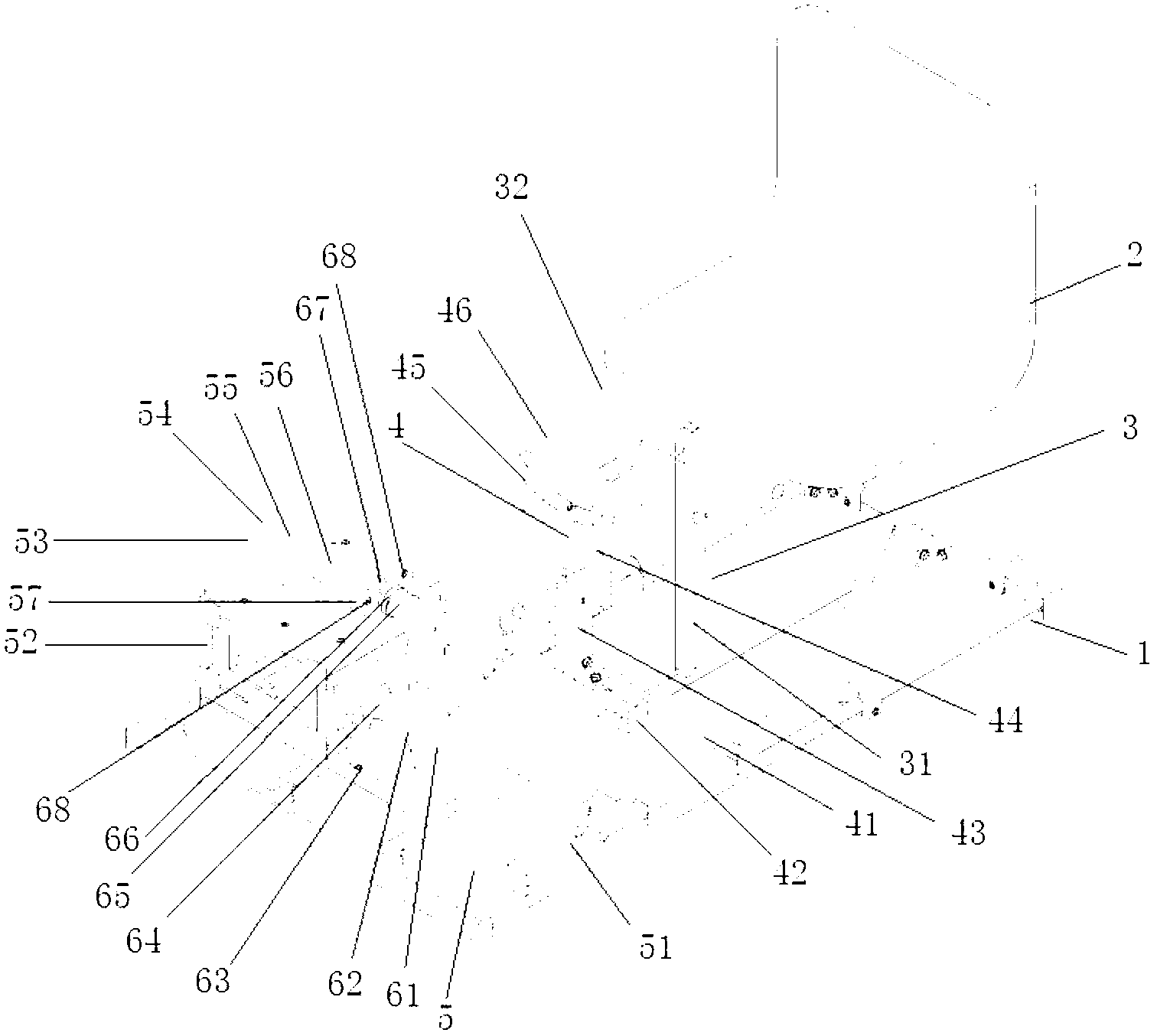
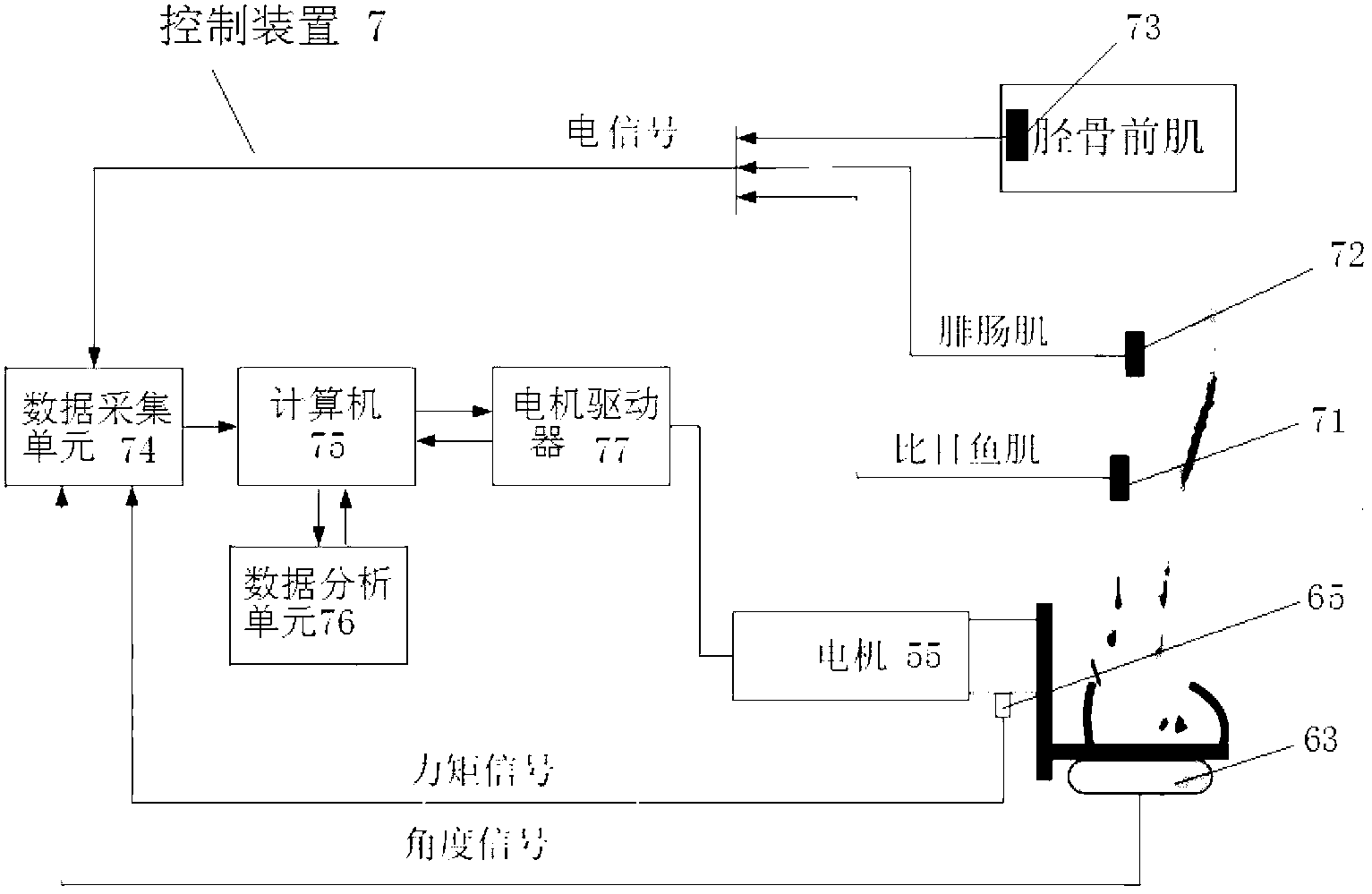
The invention relates to an intelligent recovery device for lower limb spasm. The intelligent recovery device comprises a chassis, a seat, a thigh supporting mechanism, a shank supporting mechanism, a motor driving mechanism, a foot plate fixing mechanism, a mechanical safety position-limit mechanism and a control module. The thigh supporting mechanism comprises a support rod and a T-shaped support, the shank supporting mechanism comprises a front-back translation rod, a left-right translation rod, a lower support rod, a vertical translation rod, an arc support and a bandage, and the motor driving mechanism comprises a front-back translation support, a motor support, a bearing seat and a motor external member. The foot plate fixing mechanism comprises a foot plate, a plurality of bandages, a tilt angle sensor, a foot lateral plate, a torsion sensor and a coupler, the control module comprises three electrode plates, a data acquisition unit, a motor driver and a data analysis unit arranged on a computer, and the data analysis unit comprises a calculation module and a circuit safety position-limit module. The intelligent recovery device enables a patient to participate in recovery control through feedback of electrical signals and joint moment on surfaces of muscles of the patient, increases initiative intervention of the patient, and accordingly promotes rehabilitation efficacy. The intelligent recovery device can be widely applied to recovery of the lower limb spasm.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
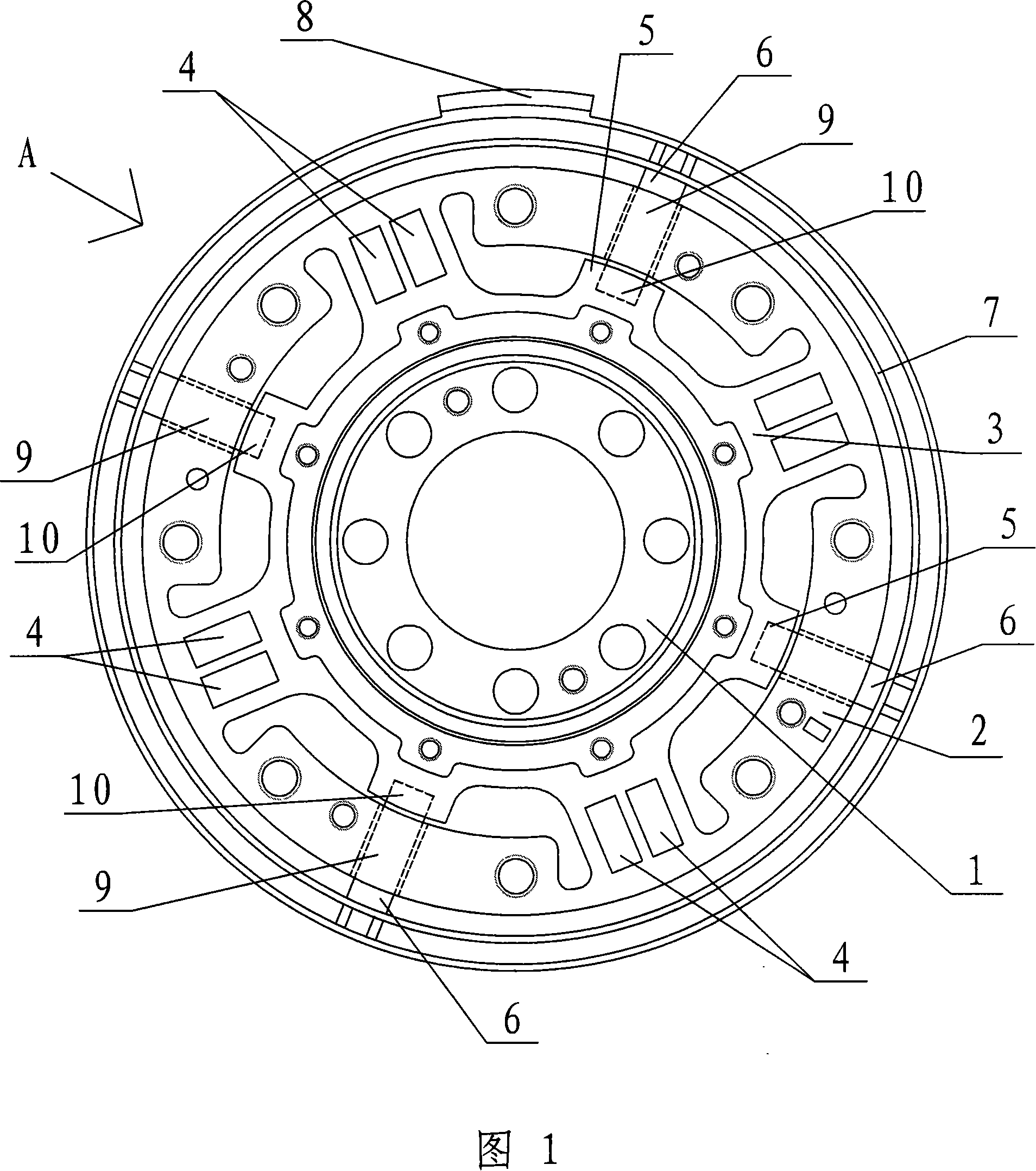
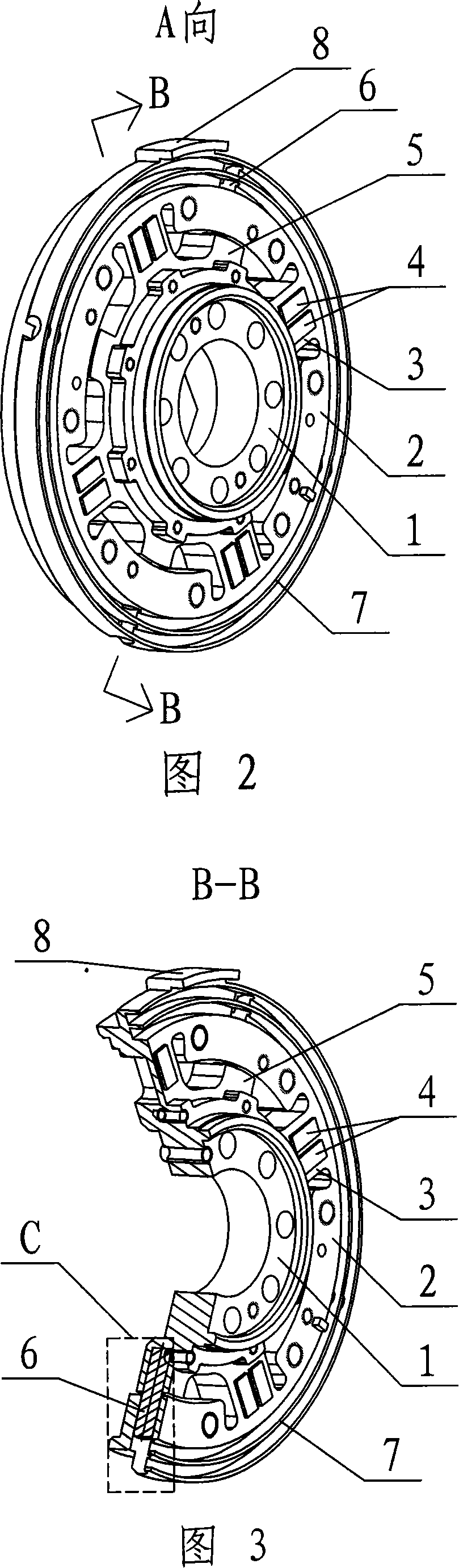
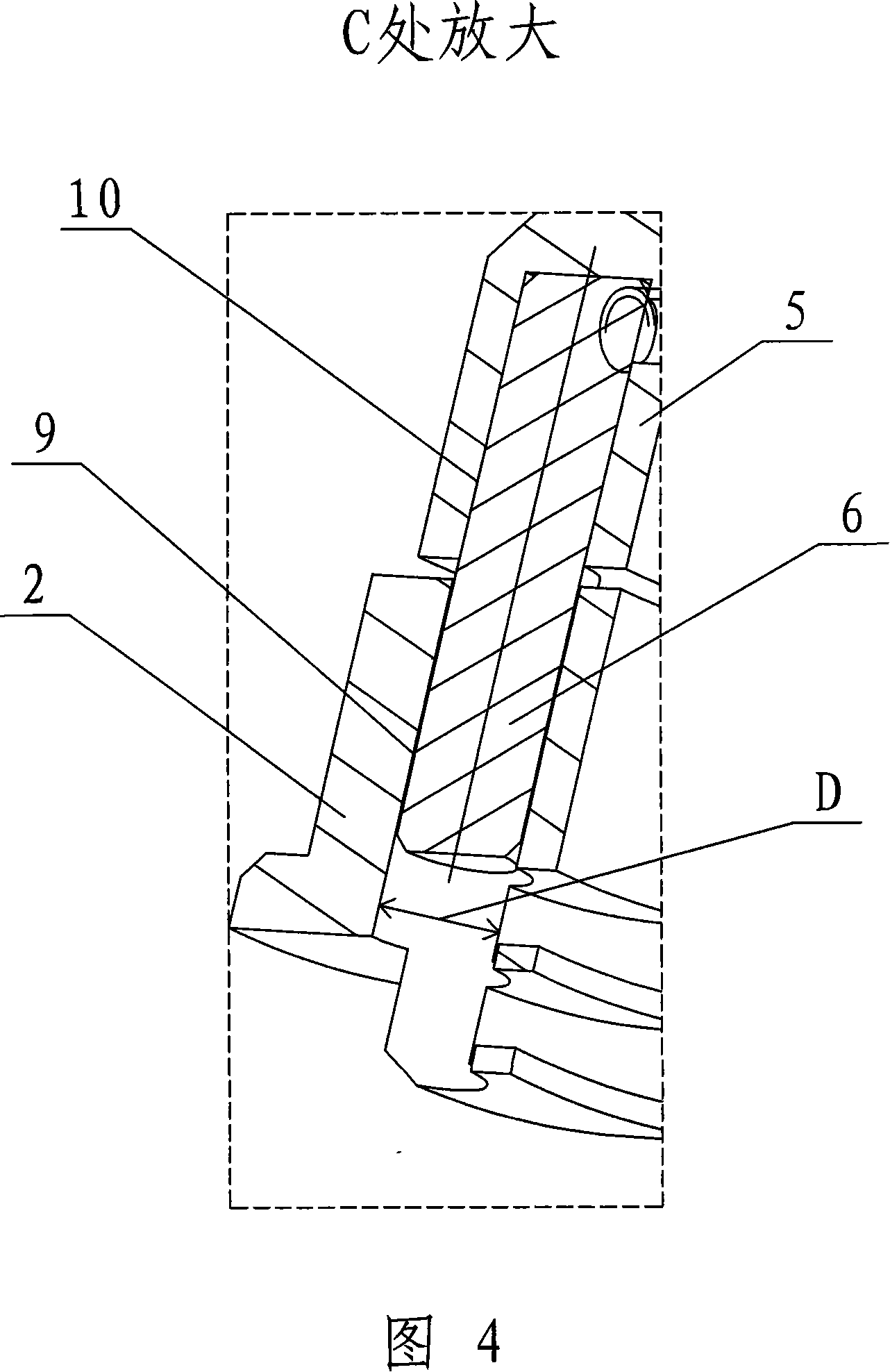
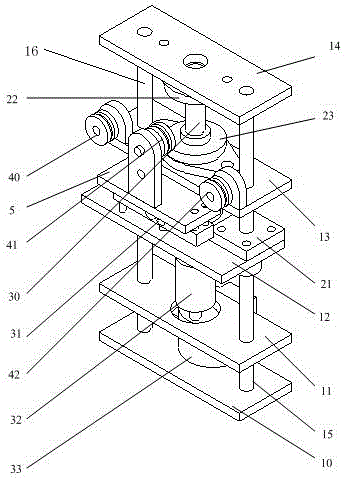
Joint torque sensor capable eliminating harmonic wave effect by itself
InactiveCN1815156ASolve problems where harmonic effects cannot be eliminatedInhibition effectWork measurementTorque measurementSignal qualityHarmonic
Present invention provides joint moment transducer capable of self eliminating harmonic influence. It includes moment inputting disk, moment outputting disk, four transducer straining beams, and eight strain gauges, wherein two ends of four beams integrally connected respectively with moment inputting disk outer edge and inner edge, and rectangular distribution along circumference, each straining beam respectively fixed with two strain gauges, eight strain gauges constituting two holotype full bridge. Said invented two full bridges present quadrature distribution, making output torque carried harmonic mutually counteracted. Said invention can effectively restrain influence to output signal of harmonic speed reducer output pulsation, improving transducer output signal quality raising robot behavioral control precision.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
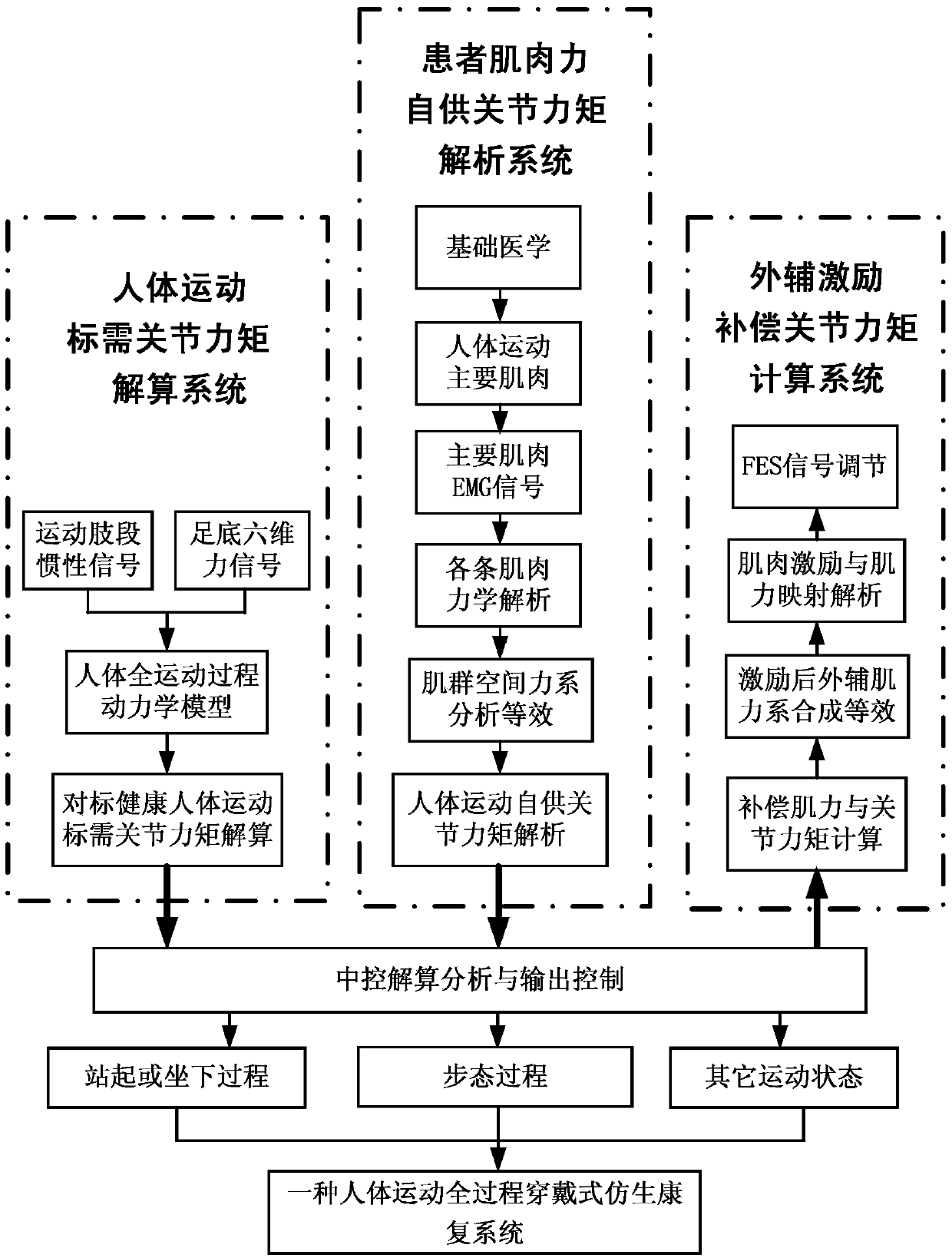
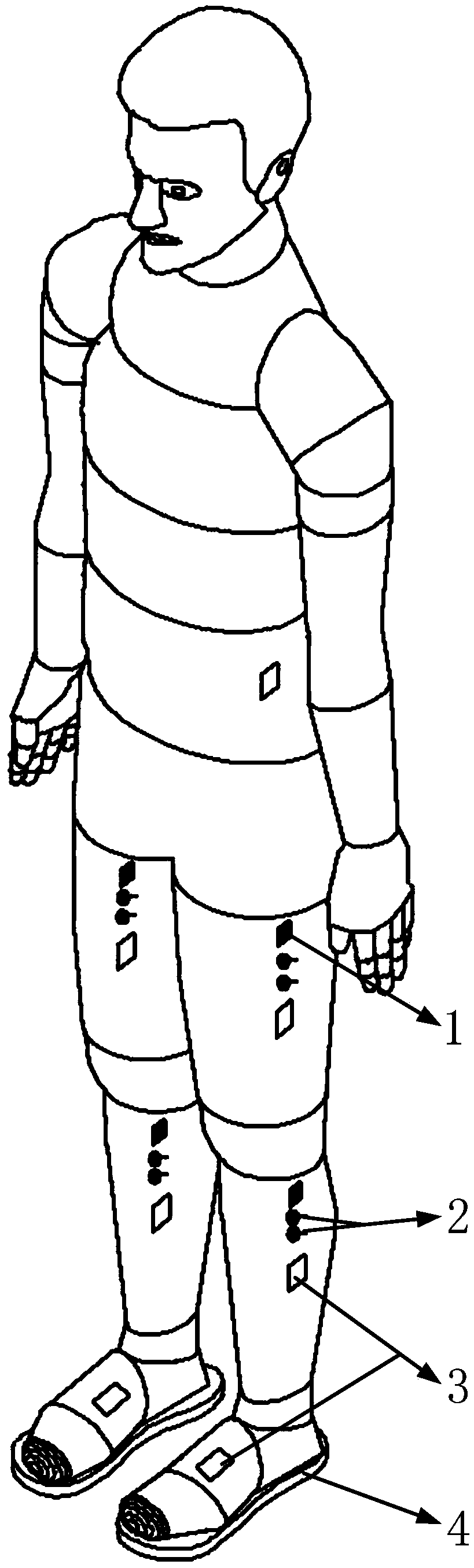
Bionic rehabilitation system worn in whole movement process of human body
ActiveCN109589496AProtect muscle exertion functionAid in RehabilitationElectrotherapySustainable transportationElectricityHuman body
The invention discloses a bionic rehabilitation system worn in the whole movement process of a human body. The bionic rehabilitation system mainly comprises a human body movement target joint moment resolving system, a patient muscle force self-supply joint moment resolving system and an external assistant excitation compensation moment calculation system. A mode that limbs of a patient are drivenby an external assistant mechanism of conventional rehabilitation equipment to achieve rehabilitation movement is changed. By adopting a lightened wearable use mode, in the situation that conventional muscle force functions of a patient are sufficiently protected, on the basis of bionics and a healthy body kinematic mechanics model, and by using multi-signal sensation fusion and resolving methodswith inertia signals, sole six-dimensional force signals, surface electromyogram signals, functional electrophotoluminescence signals and the like, space muscle force systems and self-supplied jointmoments of the patient the whole movement process of sitting, standing and walking are analyzed, compensation moments of different joints are calculated in real time, corresponding muscle is stimulated to exert force through the functional electrophotoluminescence signals, and rehabilitation movement assistance and training in the whole movement process of a human body can be achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method of assuming acting point of floor reaction force to biped walking mobile body and method of assuming joint moment of biped walking mobile body
ActiveUS20060200272A1Simple arithmetic processingImprove estimation accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlGround contactEngineering
While a biped walking mobile body is in a motion, such as level-ground walking, the position of the center of gravity (G0) of the biped walking mobile body, the position of an ankle joint (12) of each leg (2), and the position of a metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) of a foot (13) are successively grasped. The horizontal position of any one of the center of gravity (G0), the ankle joint (12), and the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) is estimated as the horizontal position of a floor reaction force acting point on the basis of the combination of the contact or no contact with the ground at a spot directly below the metatarsophalangeal joint 13a of the foot 13 and a spot directly below the ankle joint 12, which is detected by ground contact sensors 51f and 51r, respectively, provided on the sole of the foot 13. The vertical position of the floor reaction force acting point is estimated on the basis of the vertical distance from the ankle joint (12) to a ground contact surface.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
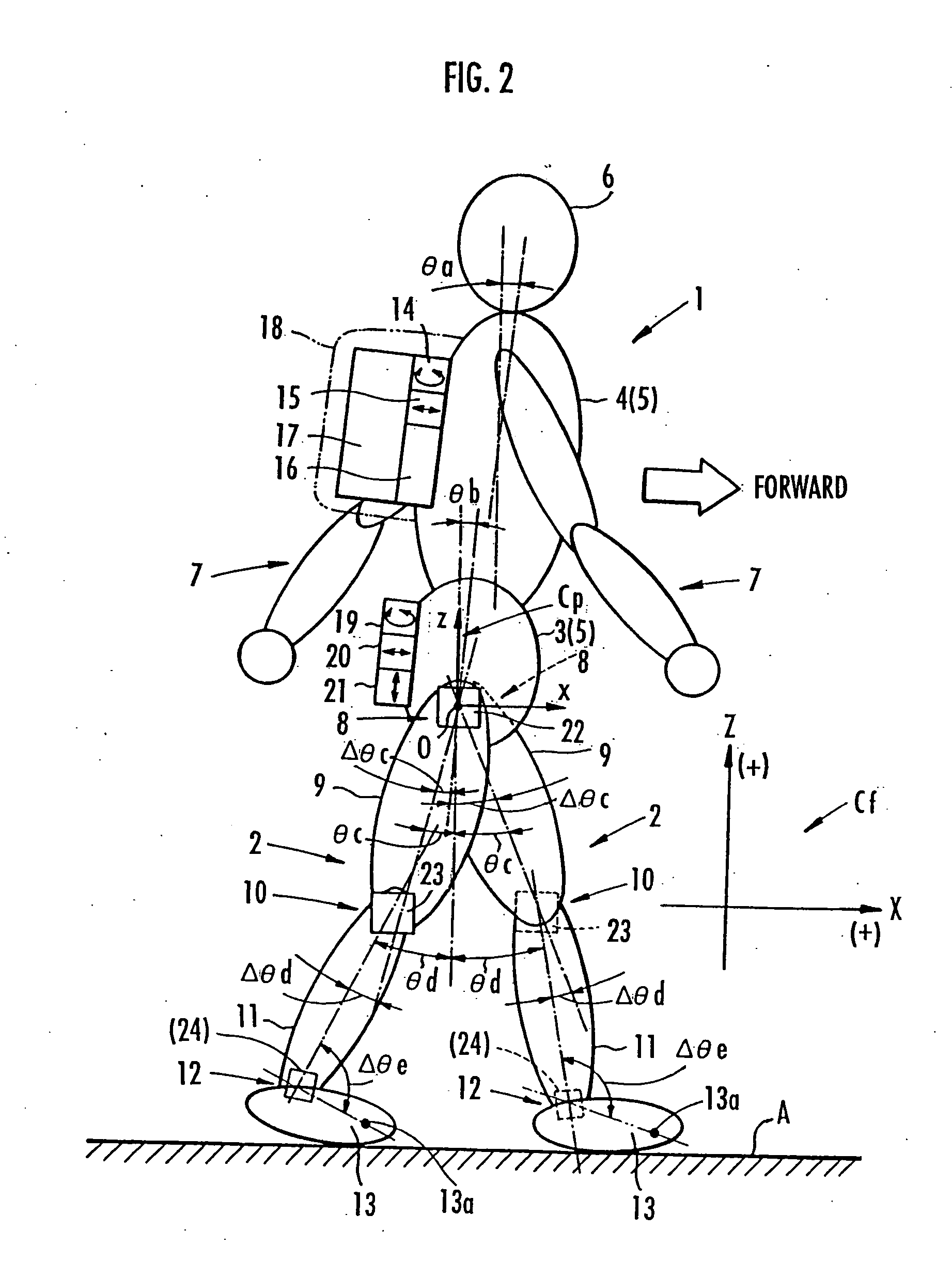
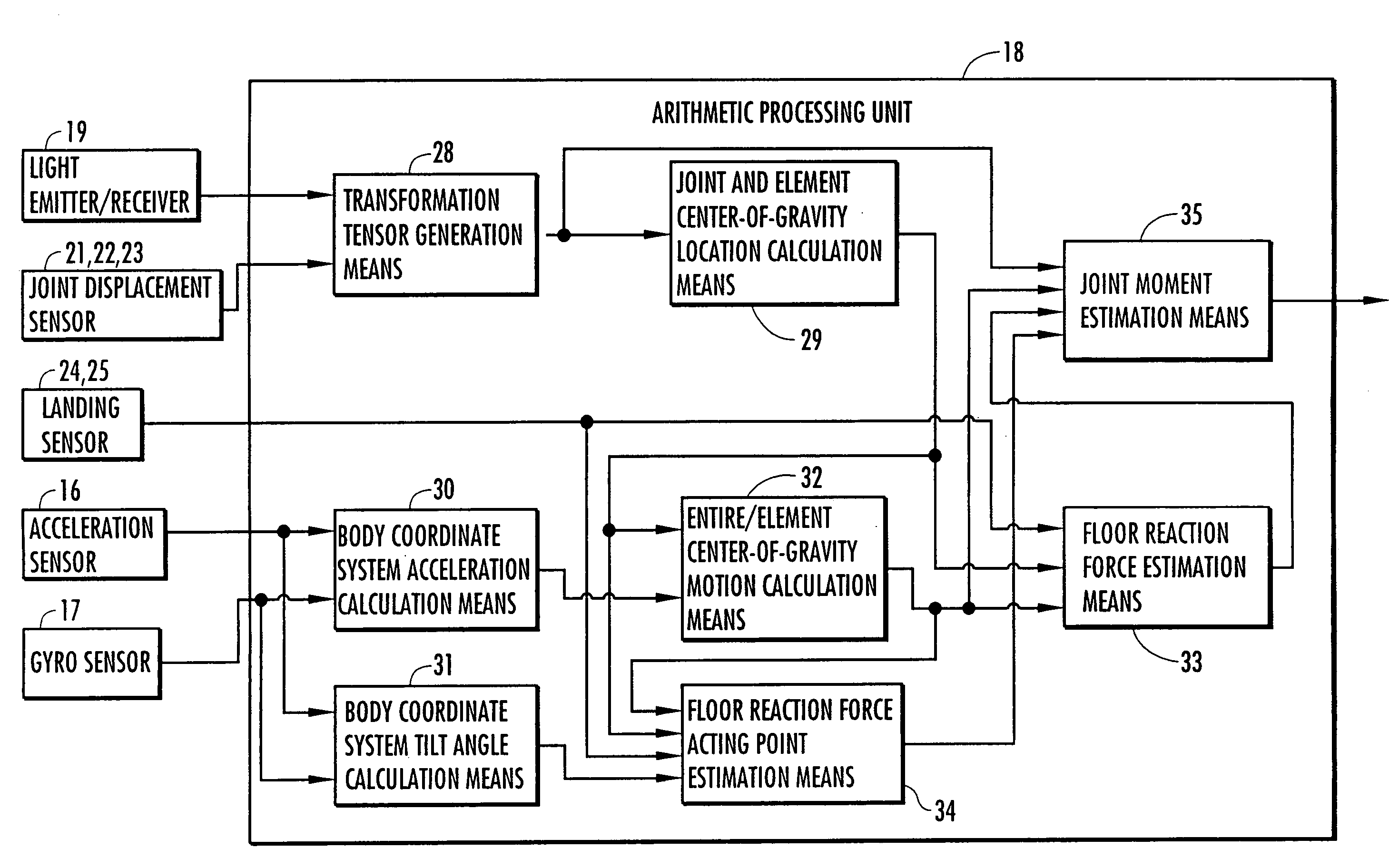
Method of estimating joint moment of two-legged walking mobile body
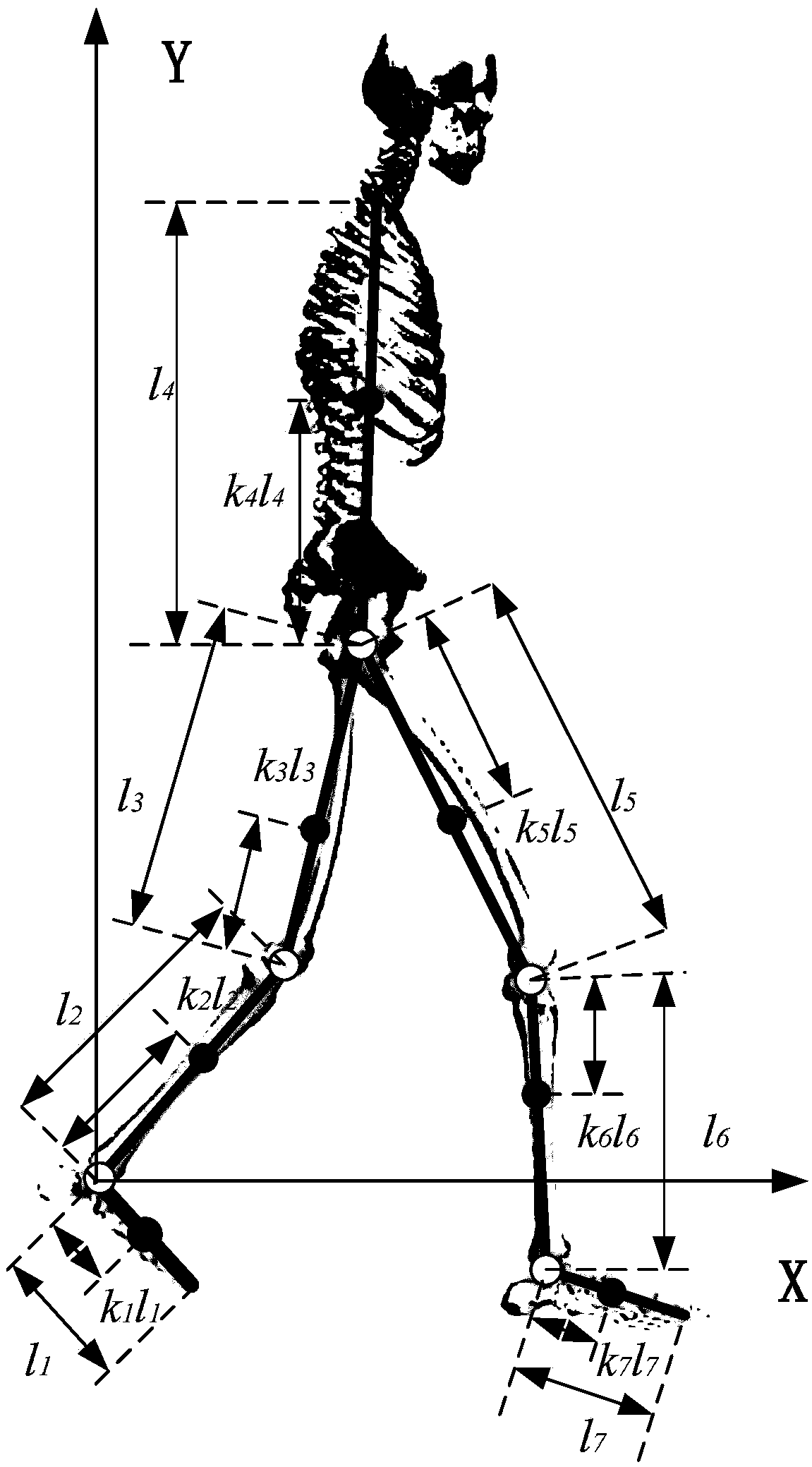
InactiveUS20060195223A1Improve estimation accuracyGood estimateProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlLink modelInverse dynamics
Displacements of respective joints corresponding to respective joint elements (J9 and the like) of a rigid link model (S1) representing a two-legged walking mobile body (1) are sequentially grasped. Also at the same time, values, in a body coordinate system (BC), of an acceleration vector of the origin of the body coordinate system (BC) fixed to a waist (6) as a rigid element, a floor reaction force vector acting on each leg (2), and a position vector of the point of application of the floor reaction force vector are sequentially grasped. With the use of the grasped values, joint moments respectively generated in an ankle joint (13), a knee joint (14), and a hip joint (9) of each leg (2) are sequentially estimated based on an inverse dynamics model using the body coordinate system. The estimation accuracy of the joint moments of the leg can be enhanced by reducing arithmetic processing using tilt information of the two-legged walking mobile body relative to the gravity direction as much as possible.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
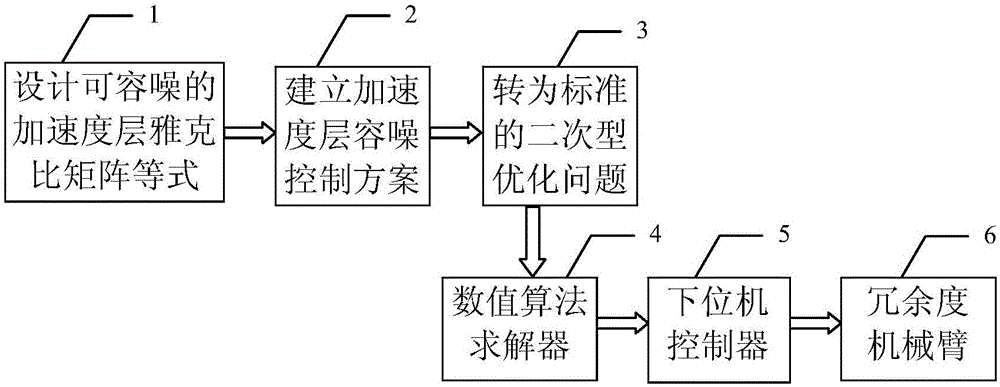
Redundant manipulator acceleration layer noise-tolerant control method
The invention provides a redundant manipulator acceleration layer noise-tolerant control method. The method comprises the following steps of: designing a noise-tolerant novel jacobian matrix equation by introducing position error and speed error feedback according to a manipulator acceleration layer jacobian matrix equation; and establishing an acceleration layer noise-tolerant control scheme in combination with a performance index needing to be optimized, wherein the control scheme is constrained in the novel jacobian matrix equation, the manipulator kinetic equation, the joint angle limit, the joint speed limit, the joint acceleration limit and the joint moment limit; the above mentioned control scheme is translated into a standard quadric form optimization problem, and a numerical algorithm solver is used for solving the standard quadric form optimization problem; a lower computer controller drives the manipulator to complete the given tail end task according to a solving result. The acceleration layer noise-tolerant control method disclosed by the invention not only can enable the manipulator to complete the given tail end task under the noise condition, but also can enable the final state speed of each joint of the manipulator to approach to zero.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting power assisting efficiency of load-bearing exoskeleton
ActiveCN110811553ASolve the mechanical propertiesReduce mistakesProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsHuman bodyKnee Joint
The invention relates to a method for detecting the power assisting efficiency of a load-bearing exoskeleton. The method comprises the following steps of (1) when a person does not wear the exoskeleton and does not bear a heavy load, obtaining kinematic and dynamic information by using a three-dimensional motion acquisition system and a force measuring treadmill; and verifying a human body joint moment positive test model based on surface electromyogram signals by using the human body joint moment calculated by inverse dynamics as a reference; (2) when the person wears the exoskeleton and bearing a load G1, obtaining the relationship between the time and the moment of the hip joint, the knee joint and the ankle joint by a method based on the surface electromyogram signals; (3) when the person does not wear the exoskeleton and carries out a load bearing test of 0 to 40 kg, testing the relationship between the time and the moment of the hip joint, the knee joint and the ankle joint of the human body under different loads in the time period; and (4) obtaining the ratio of the effective load to the total load according to data, measured in experiments, between the load of the human body and the driving moment of the total joint of the human body when the exoskeleton is not worn under the condition of different loads. The invention provides a novel method for testing the lower limbjoint moment of the exoskeleton.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
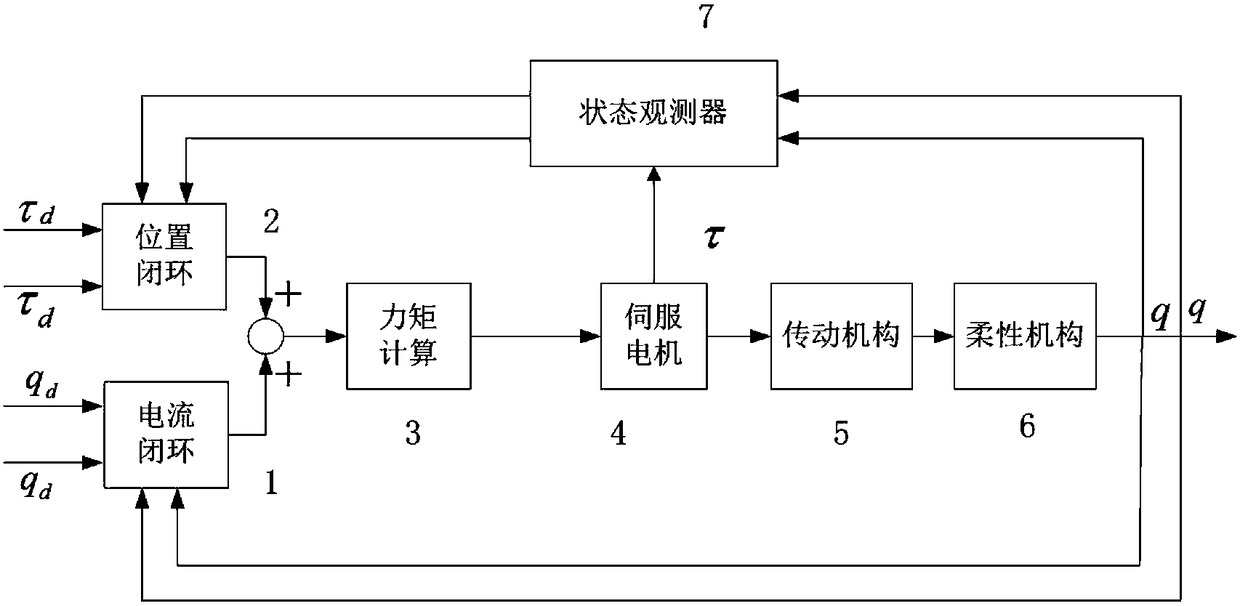
Control method of semiflexible mechanical arm system
The invention discloses a control method of a semiflexible mechanical arm system. The semiflexible mechanical arm system consists of a rigid mechanical arm and an additional flexible connecting rod, wherein the rigid mechanical arm consists of a series of rigid connecting rods and joints; each joint is a rotating joint or a moving joint. The method comprises the following steps that the rigid mechanical arm is totally provided with (n+1) rigid connecting rods; the additional flexible connecting rod is R; a fixed connection coordinate system of the (n+1) rigid connecting rods is built and obtained by an improved DH parameter method via the rigid mechanical arm; the connecting rod parameters of the (n+1) rigid connecting rods are obtained through calculation; the length of the flexible connecting rod R in the flexible connecting rod parameters is regarded as a variable value, and other parameters are invariable; a coordinate system transformation formula of the adjacent connecting rods between the rigid connecting rods and the flexible connecting rod R is determined according to the connecting rod parameters; then, the relationship between the joint moment, and the joint angle, the joint speed and the joint acceleration speed is built to serve as a kinetic equation; the semiflexible mechanical arm system is controlled according to a set control method in accordance with the kinetic equation.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
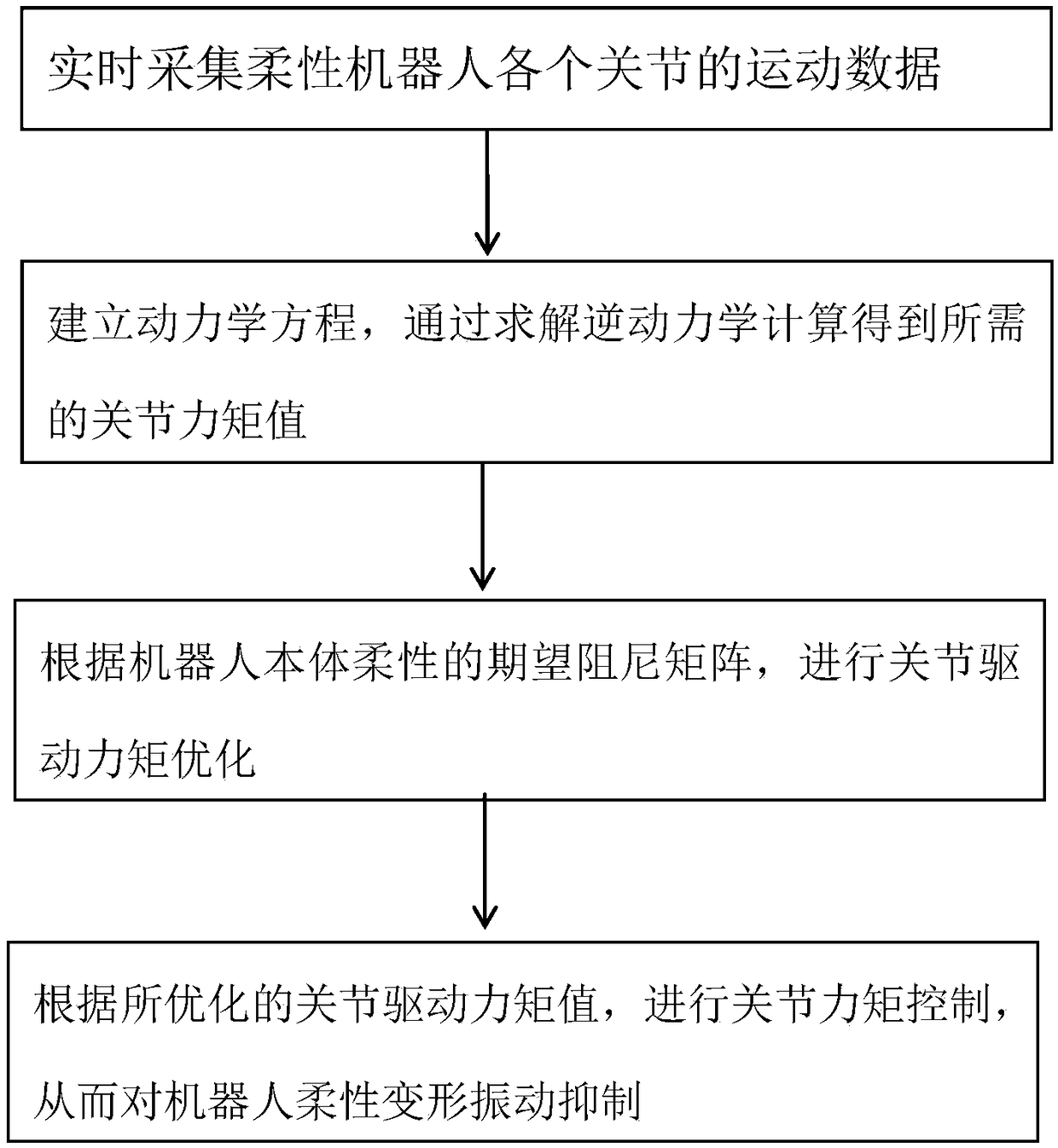
Vibration suppression method of flexible multi-joint robot and vibration control system of flexible multi-joint robot
InactiveCN109202884ALow costSuppression of flexible vibrationProgramme-controlled manipulatorControl systemDynamic equation
The invention relates to the technical field of robots, in particular to a vibration suppression method of a flexible multi-joint robot. The vibration suppression method of the flexible multi-joint robot comprises the following steps that motion data of joints of the flexible robot are collected in time; according to the collected motion data of the joints, a dynamic equation of the rigid body andjoint deformation of the robot and a dynamic equation of an expected trajectory of the robot tail end are established, and a required joint moment value is obtained by solving the inverse dynamic calculation; according to a flexible expected damping matrix of a robot body, joint driving moment is optimized to obtain an optimized joint moment value; and according to the optimized joint driving moment value, joint moment control is carried out so as to suppress the flexible deformation vibration of the robot. The vibration suppression method of the flexible multi-joint robot has the beneficialeffects of suppressing the flexible vibration of the robot body and improving the trajectory tracking precision of the robot.
Owner:SHENYANG SIASUN ROBOT & AUTOMATION
Method of estimating joint moment of two-legged walking mobile body
InactiveUS7698020B2Reduce processImprove estimation accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlLink modelInverse dynamics
Displacements of respective joints corresponding to respective joint elements (J9 and the like) of a rigid link model (S1) representing a two-legged walking mobile body (1) are sequentially grasped. Also at the same time, values, in a body coordinate system (BC), of an acceleration vector of the origin of the body coordinate system (BC) fixed to a waist (6) as a rigid element, a floor reaction force vector acting on each leg (2), and a position vector of the point of application of the floor reaction force vector are sequentially grasped. With the use of the grasped values, joint moments respectively generated in an ankle joint (13), a knee joint (14), and a hip joint (9) of each leg (2) are sequentially estimated based on an inverse dynamics model using the body coordinate system. The estimation accuracy of the joint moments of the leg can be enhanced by reducing arithmetic processing using tilt information of the two-legged walking mobile body relative to the gravity direction as much as possible.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Functional rehabilitation robot based on flexible cable-driven hand movement
ActiveCN105881519AReduce weightAssurance controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsHand movementsEngineering
The invention provides a functional rehabilitation robot based on flexible cable-driven hand movement. The functional rehabilitation robot is composed of a driving unit and an execution unit connected with the driving unit; the execution unit comprises a metacarpophalangeal joint unit module for driving the finger root joints to move, a proximal interphalangeal joint unit module for driving the finger middle joints to move and a distal interphalangeal joint unit module for driving the finger end joints to move, and the driving unit comprises three sets of driving modules which work independently, have the completely same structure and correspondingly drive the metacarpophalangeal joint unit module, the proximal interphalangeal joint unit module and the distal interphalangeal joint unit module. According to the functional rehabilitation robot, not only can the three freedom degrees of the fingers except for the thumb and the movement angles of all the joints be met, but also a serial elastic driver is introduced, and therefore precise control over the joint moment is guaranteed; in addition, most parts are made through 3D printing, the weight of the acting fingers is greatly decreased on the premise that the strength is guaranteed; furthermore, the robot adapts to the individual difference of the finger length within a certain range.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF TECH & EDUCATION TEACHER DEV CENT OF CHINA VOCATIONAL TRAINING & GUIDANCE
Walking assisting flexible exoskeleton and control method thereof
ActiveCN110303478AOvercome securityOvercome comfortProgramme-controlled manipulatorControl systemControl engineering
The invention discloses walking assisting flexible exoskeleton and a control method thereof. The flexible exoskeleton is mainly composed of a control system, a detection system, a pneumatic flexible execution system and an air pipe assembly. The control system analyzes user movement information and pressure information of the flexible assistance execution system acquired by the detection system, and realizes identifying and understanding of movement intention of lower limbs on the basis of a gait estimation model; and calculating is conducted to obtain corresponding instructions of aerodynamicforce opening and closing, pressure, flow rate and the like based on a hip joint moment model, corresponding actions are executed, real-time control is conducted on the negative pressure input and unloading processes of the pneumatic flexible execution system, the pneumatic flexible execution system can convert air pressure provided by the control system into mechanical energy capable of realizing linear movement in real time, assisting moment required by buckling and stretching of a hip joint is provided in real time according to the walking posture of a user, and the purpose of walking assisting is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Online detection method for moment of artificial muscle group driven robot joint
ActiveCN106153235AReduce string inSimple structureApparatus for force/torque/work measurementElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
The invention relates to an online detection method for the moment of an artificial muscle group driven robot joint, belonging to the technical field of moment detection. According to the online detection method, a strain gauge is adhered to a stress-sensitive elastic element by virtue of a double-hole cantilever parallel girder strain type sensor according to a force triangle relation in mechanics and a principle that a force is unchangeably transferred on a flexible rope, and when the elastic element is stressed to be deformed, the strain gauge generates a corresponding strain, the strain is converted into resistance variation and is converted into voltage variation of a measurement circuit, a certain numerical value can be measured at a proper position where the elastic element is clamped to a stay cord by measuring a numerical value of an output voltage under the condition that the tension of the stay cord is released, and an actual tension and a joint moment of the stay cord can be converted through certain arithmetical operation, and therefore, the stringing of a force measurement into an artificial muscle group driven robot joint system can be reduced. The online detection method is suitable for popularization and application, the structure is simple, and the testing is convenient.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method of estimating joint moment of bipedal walking body
InactiveUS7860607B2Avoid componentsImprove accuracyPerson identificationWalking aidsInverse dynamicsEngineering
The joint rotational angles of joints 9, 11 and 13 of each leg 2 of a bipedal walking body 1 are detected to grasp the positions / postures of the corresponding rigid bodies 10, 12 and 14 of each leg 2 on a leg plane passing the joints 9, 11 and 13 of each leg 2. At the same time, the acceleration of a reference point (the origin of a body coordinate system BC) of the bipedal walking body 1, the floor reaction force acting on each leg 2 and the position of an acting point thereof are grasped in terms of three-dimensional amounts. Two-dimensional amounts obtained by projecting the acceleration, the floor reaction force and the position of the acting point thereof, and the positions / postures of the corresponding rigid bodies of each 2 onto the leg plane are used to estimate the moments acting on joints of each leg on the basis of an inverse dynamic model. The stability of the estimated values of joint moments can be improved while securing the accuracy of estimating the joint moments in the bending and stretching directions of each leg, considering three-dimensional motions of the bipedal walking body.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com