Patents
Literature
74 results about "Zero moment point" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
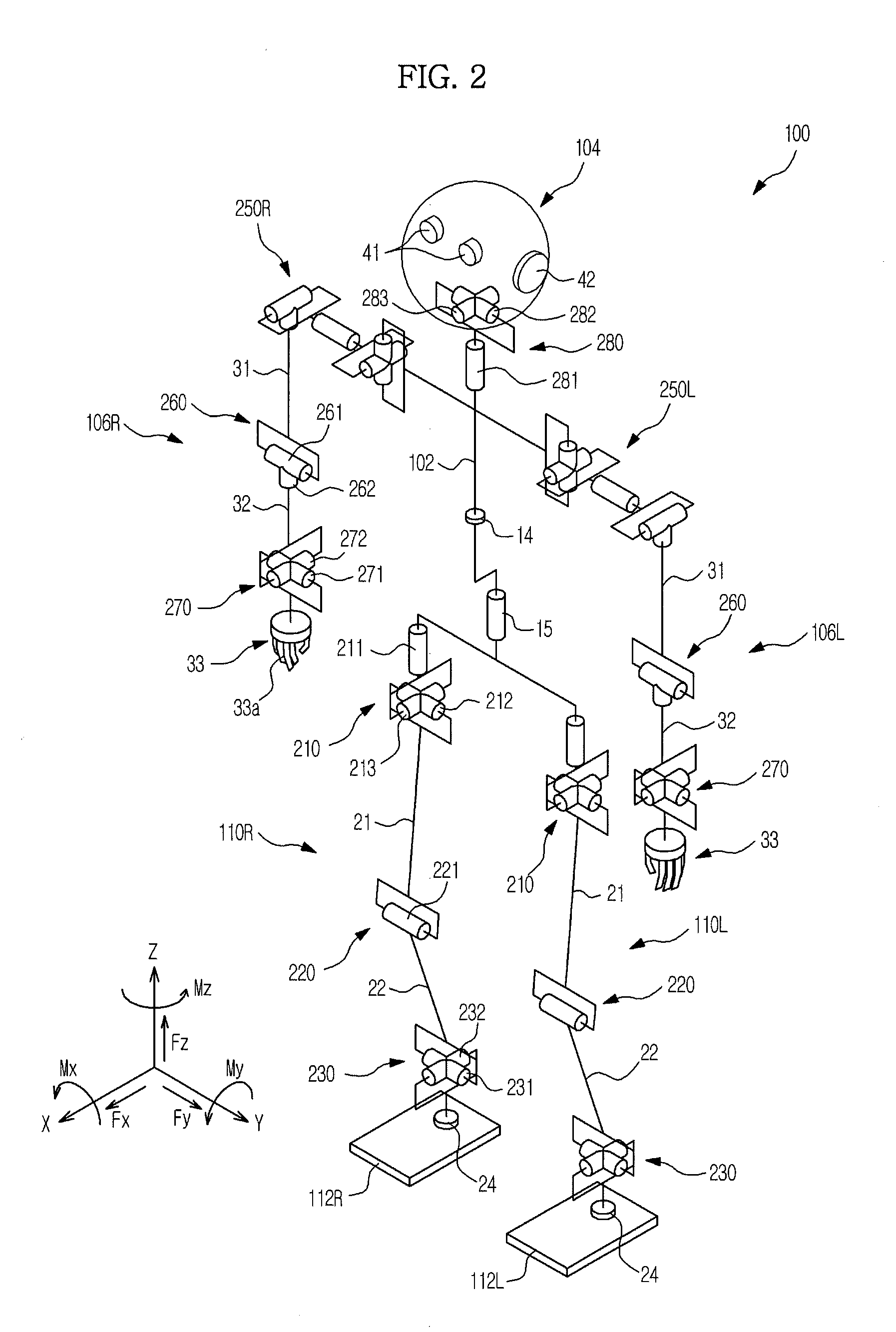
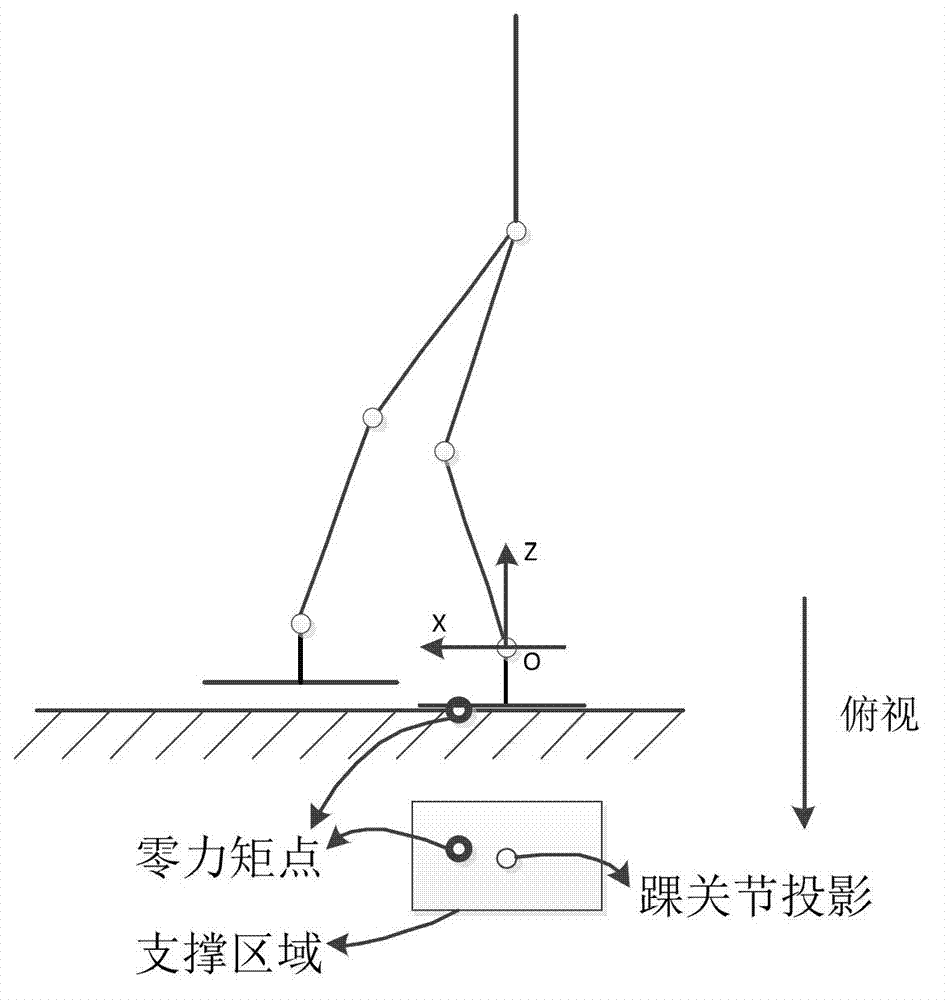
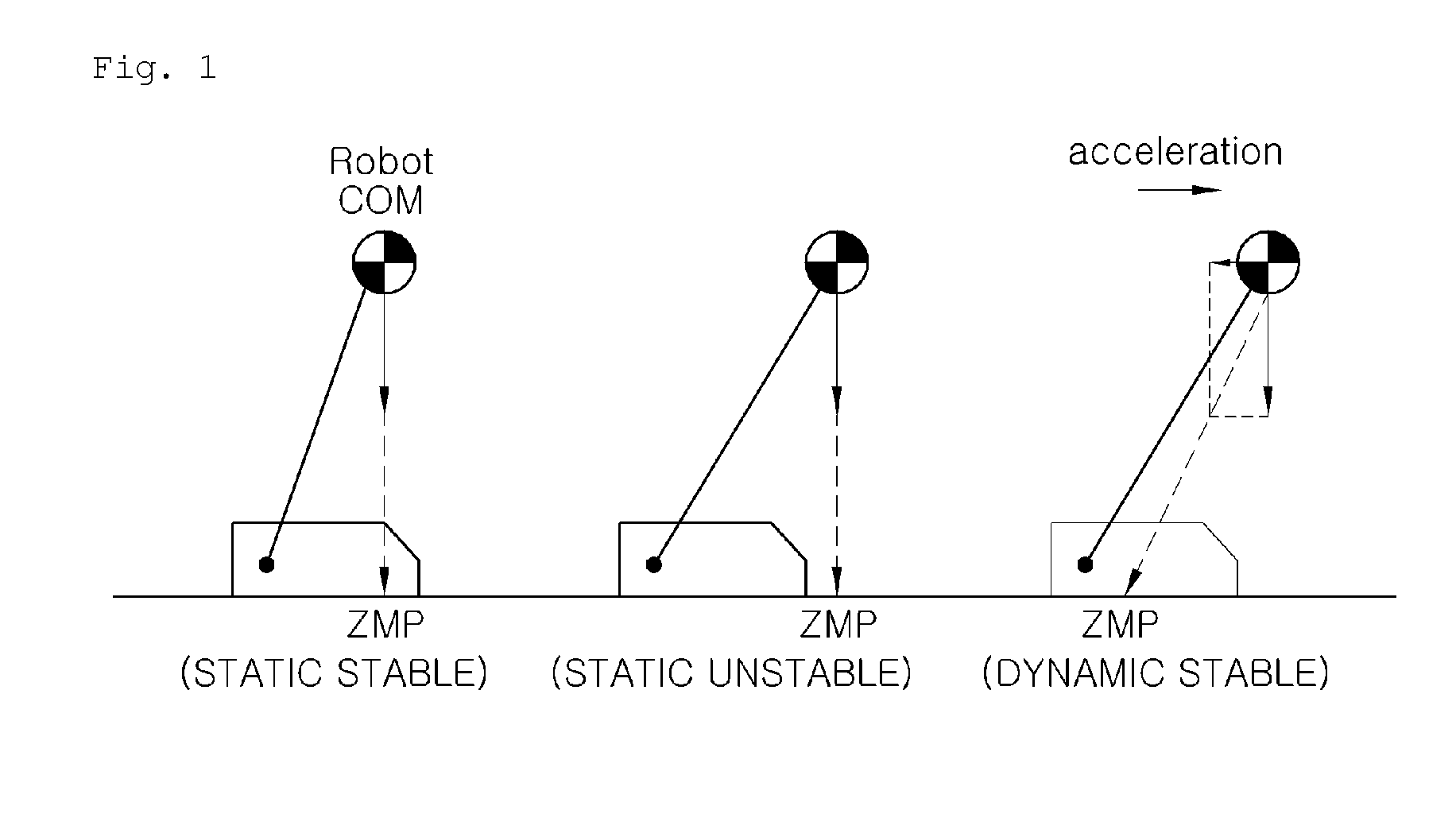
Zero moment point is a concept related with dynamics and control of legged locomotion, e.g., for humanoid robots. It specifies the point with respect to which dynamic reaction force at the contact of the foot with the ground does not produce any moment in the horizontal direction, i.e. the point where the total of horizontal inertia and gravity forces equals 0 (zero). The concept assumes the contact area is planar and has sufficiently high friction to keep the feet from sliding.
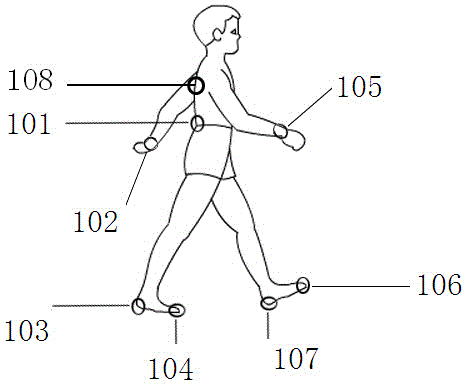
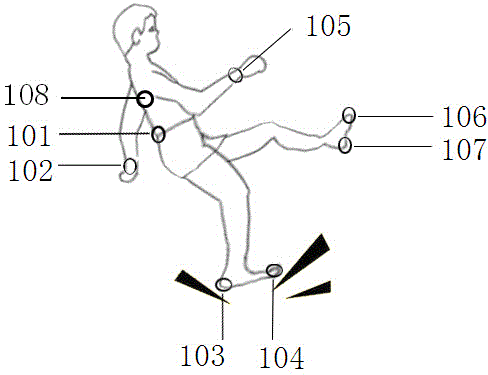
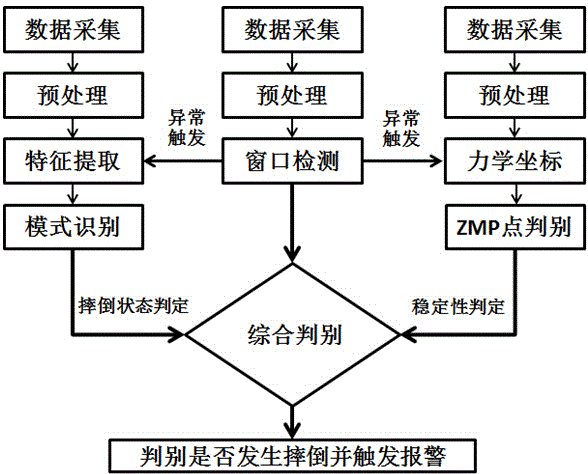
Wearing type dynamic real-time fall detection method and device
ActiveCN103976739AAchieve protectionHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringHuman bodyHardware structure
The invention discloses a wearing type dynamic real-time fall detection method and device. The wearing type detection device comprises a specific hardware structure consisting of a foot part, a waist part, a wrist part and a back part. According to the dynamic real-time fall detection method, real-time judgment of the fall of human body in any state can be finished. The core algorithm of the detection device comprises a threshold opening logic structure caused by sudden change of gait acceleration, a human body posture dynamic stability judgment algorithm based on zero moment point (ZMP), and a fall mode identification algorithm based on a human body motion database. A complete dynamic real-time detection system is constructed, and the aims of wide application field, low dependence on the application environment and real-time detection are fulfilled. Moreover, the detection method and the detection device are high in accuracy, and have the advantages of low system cost, small system size and good convenience in wearing.
Owner:BEWIS TECH
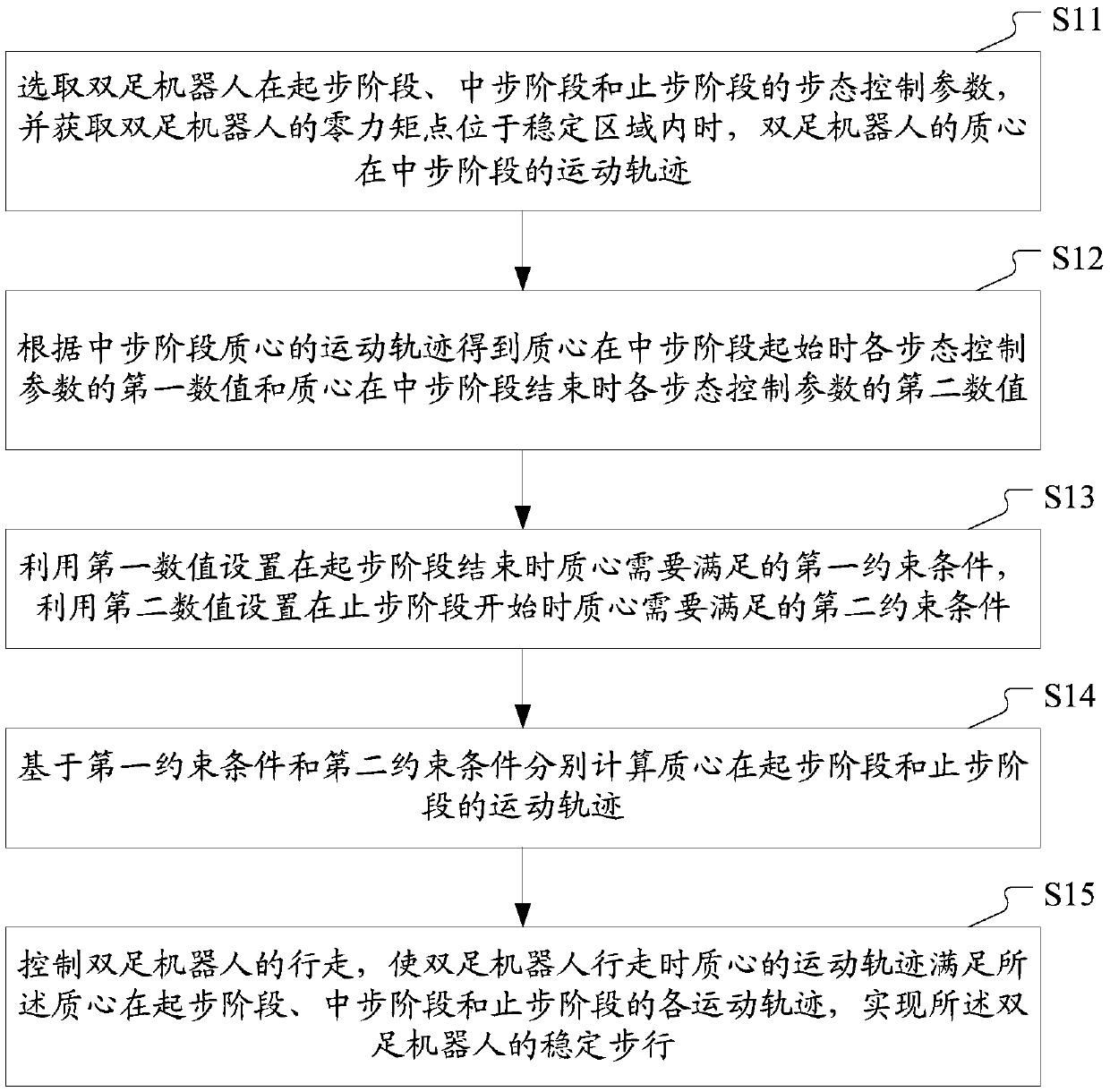
Gait control method and device for dual-foot robot
ActiveCN105511465AWalking smoothlyImprove stabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorNumerical controlEngineeringZero moment point
The invention discloses a gait control method and a device for a dual-foot robot. The method comprises the steps of selecting gait control parameters for a starting period, a walking period and a stopping period; acquiring the motion trajectory of the mass center of the dual-foot robot during the walking period when the zero moment point of the dual-foot robot is within a stable area; obtaining the first value of each gait control parameter when the mass center is at the initial moment of the walking period and the second value of the gait control parameter when the mass center is at the ending moment of the walking period; setting a first constraint condition at the ending moment of the starting period by utilizing the first value, and setting a second constraint condition at the starting moment of the stopping period by utilizing the second value; based on the first constraint condition and the second constraint condition, calculating the motion trajectory of the mass center during the starting period and during the stopping period respectively; controlling the walking of the dual-foot robot to enable the motion trajectory of the mass center of the dual-foot robot during walking to meet the motion trajectory of the mass center during the starting period, the walking period and the stopping period respectively. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the stable cohesion of the dual-foot robot during the starting period, the walking period and the stopping period and the walking stability of the dual-foot robot can be ensured.
Owner:GOERTEK INC
Robotic First Responder System and Method
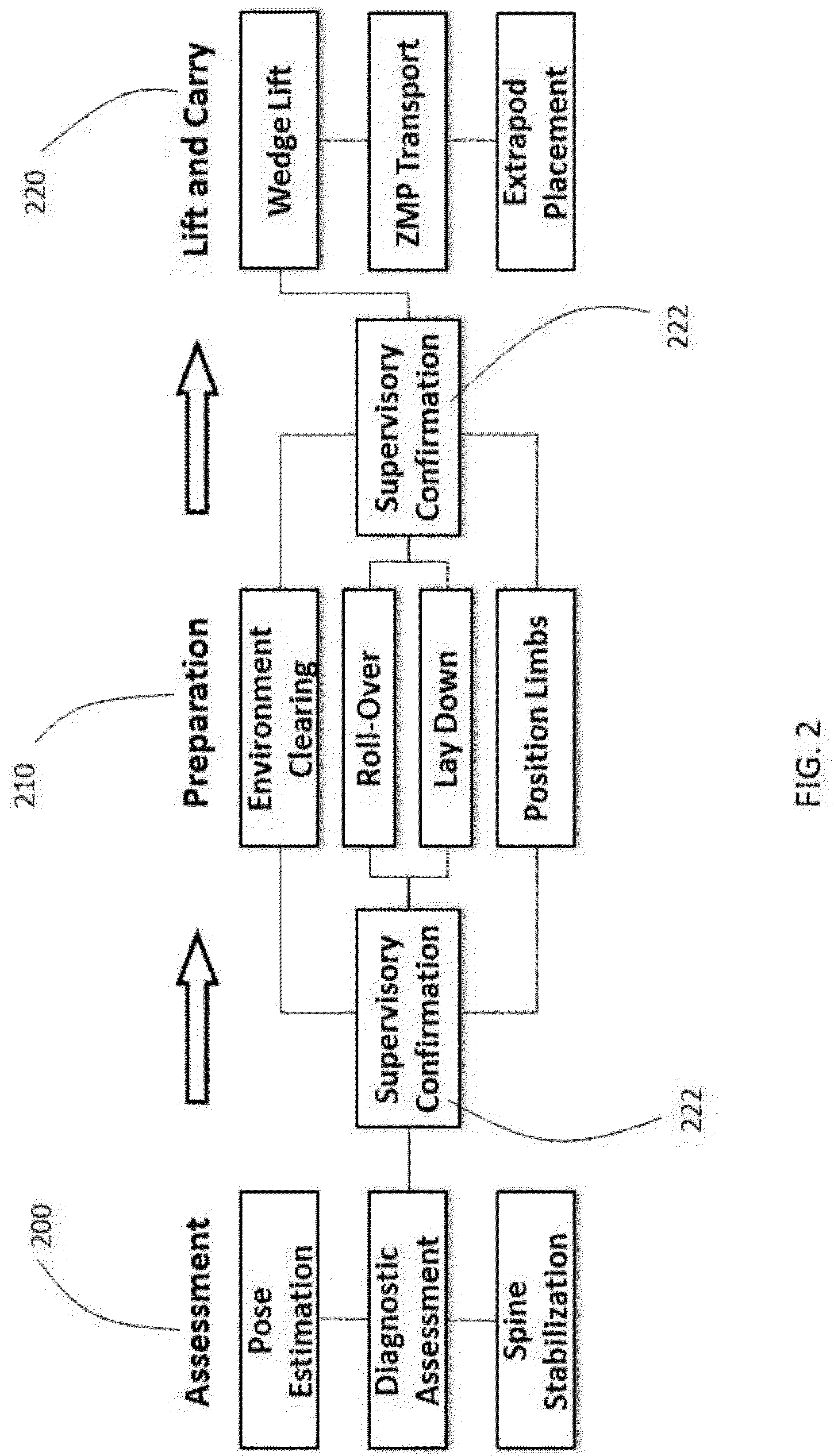
A robotic first responder system provides injured patients with first response medical care and extracts the injured patient from a dangerous or remote area. After assessing of the level of consciousness of an injured patient, the robotic unit utilizes an inflatable immobilization device for safe robotic rescue of injured patients. The robotic unit lifts and transfers an injured patient to an extraction vehicle, a secure, bullet-proof wheeled system that can be pulled by the robot to safe location. The extraction vehicle continues serving as the evacuation stretcher to a medical station. The robotic unit utilizes zero moment point control to maintain stability while lifting the patient. A robot first responder tows the extraction vehicle or the extraction vehicle self-navigates incorporating with power drive and autonomous navigation systems.
Owner:HU JOHN +1
Closed-loop control-based humanoid robot omnidirectional walking method
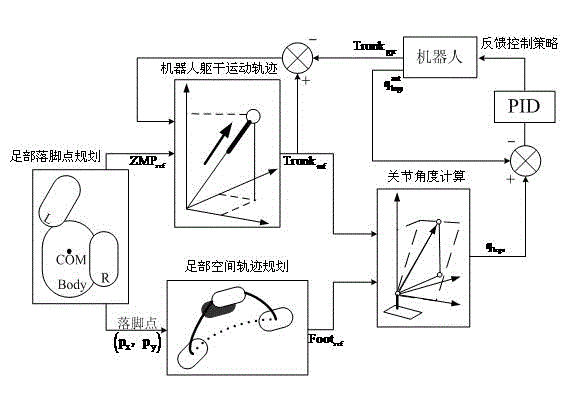
The invention provides a closed-loop control-based humanoid robot omnidirectional walking method, which comprises foot stance planning, robot body movement track, foot space track planning, joint angle calculation and feedback control policy. The method comprises the following steps of planning the stances of the feet of the robot in a two-dimensional space, and calculating a zero moment point (ZMP) value of the robot; establishing a bilinear inverted pendulum model with prediction control according to the ZMP value, and obtaining a reference pose of the robot body; performing cubic spline interpolation on the planned stances to obtain the best moving track of every two stances in a three-dimensional space so as to obtain a foot stance pose; and calculating angles of joints of the robot according to the reference poses of the body and the feet by using inverse kinematics knowledge. In the walking process of the humanoid robot, the omnidirectional walking of the robot is realized through closed-loop control. Compared with the prior art, the robot walking method has the advantages of high robustness and high stability.
Owner:DEEPBLUE ROBOTICS (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Whole-body humanoid control from upper-body task specifications
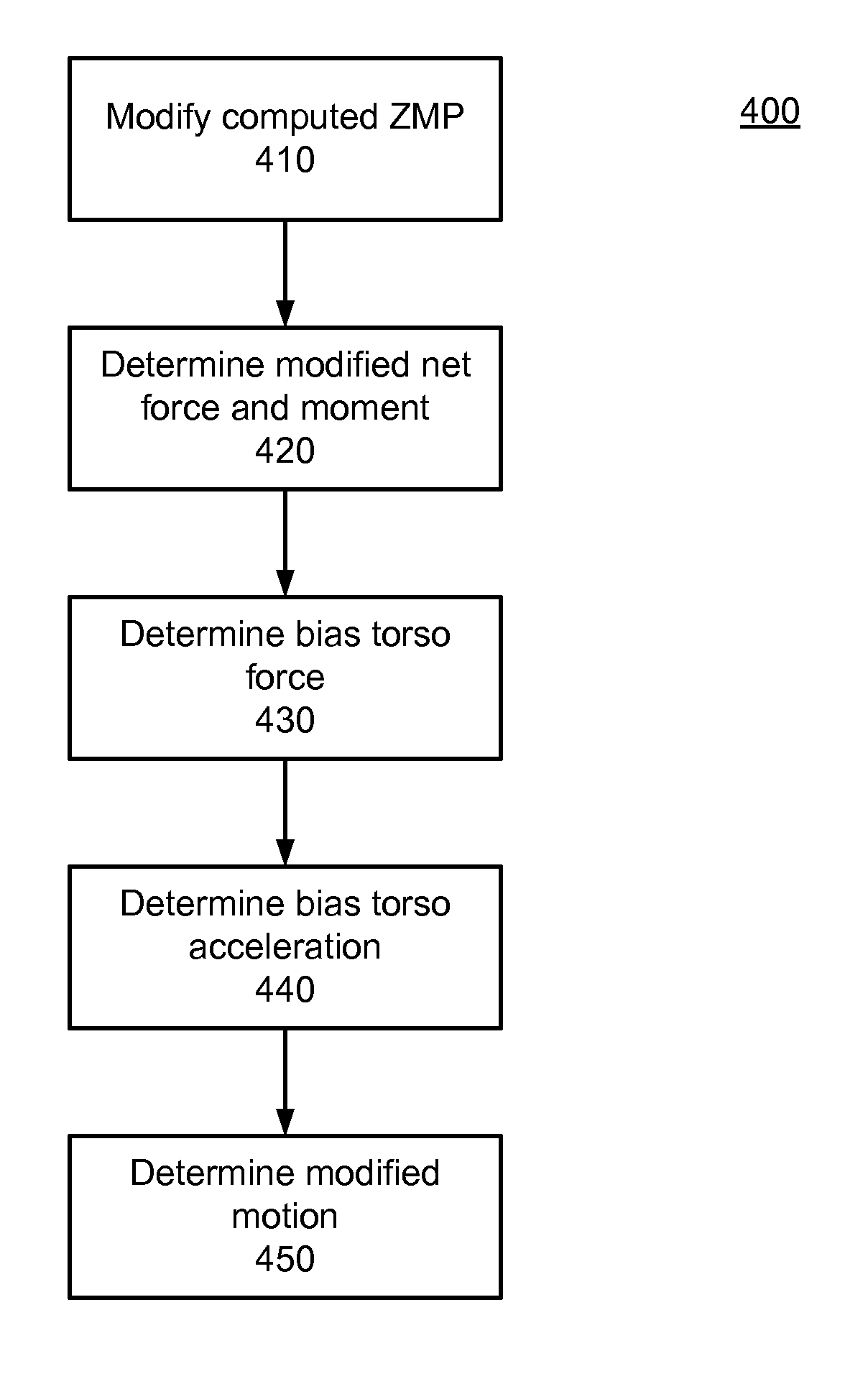
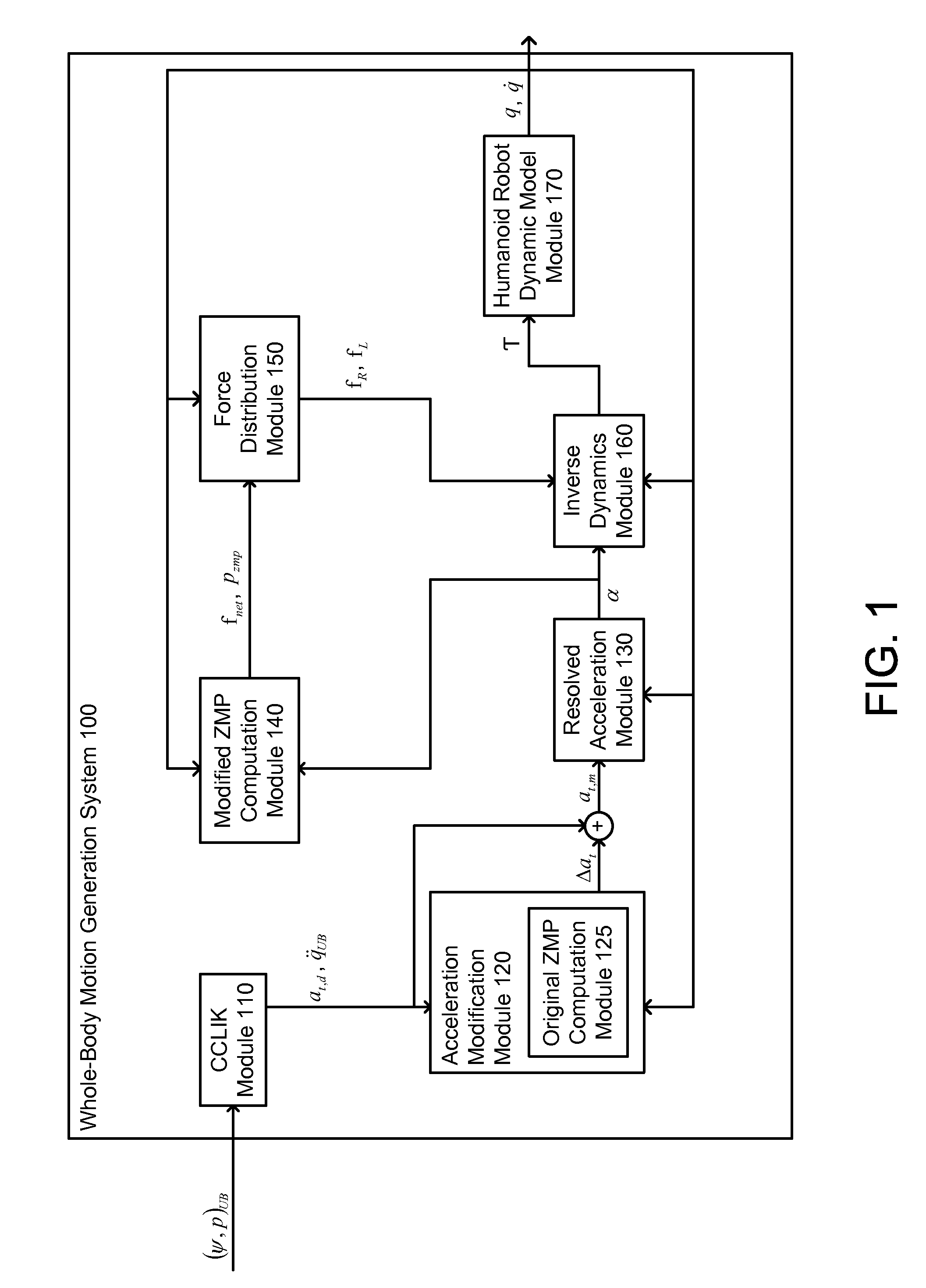
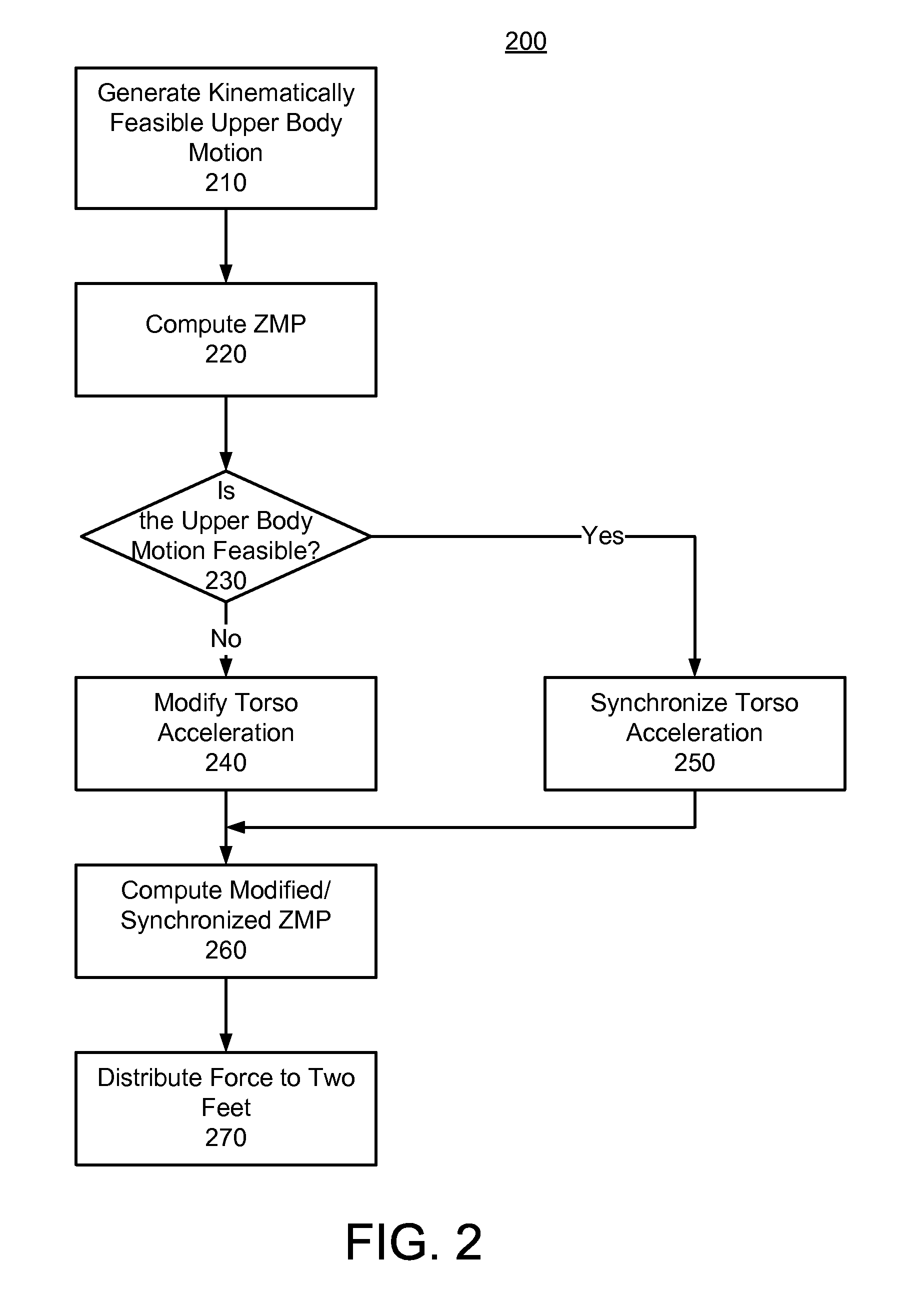
A system, method, and computer program product for generating dynamically feasible whole-body motion of a humanoid robot while realizing specified upper-body task motion are described. A kinematically feasible upper-body motion is generated based on the specified upper-body motion. A series of zero-moment points (ZMP) are computed for the generated motion and used to determine whether such motion is dynamically feasible. If the motion is not dynamically feasible, then the torso acceleration is modified to make the motion dynamically feasible, and otherwise synchronized as needed. A series of modified ZMP is determined based on the modified torso acceleration and used to distribute the resultant net ground reaction force and moment to the two feet.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Foot structure of humanoid robot based on modularized array sensor
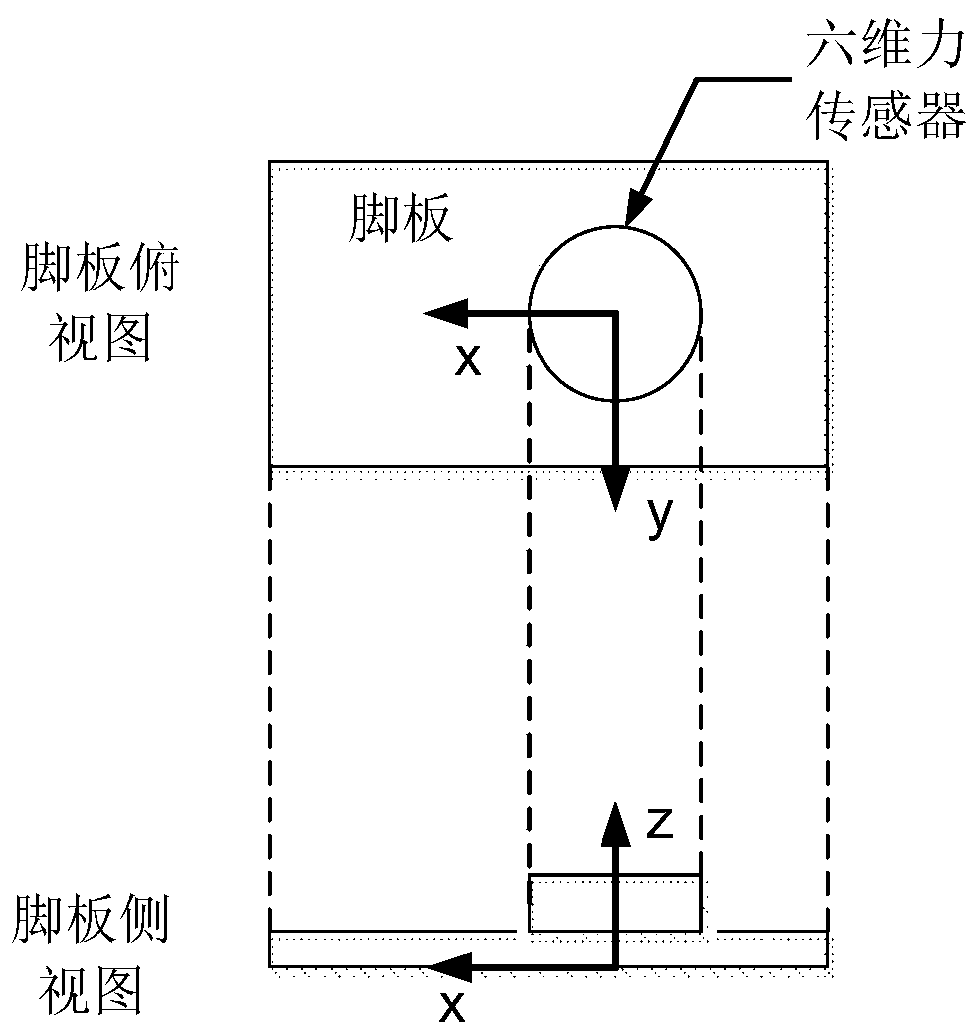
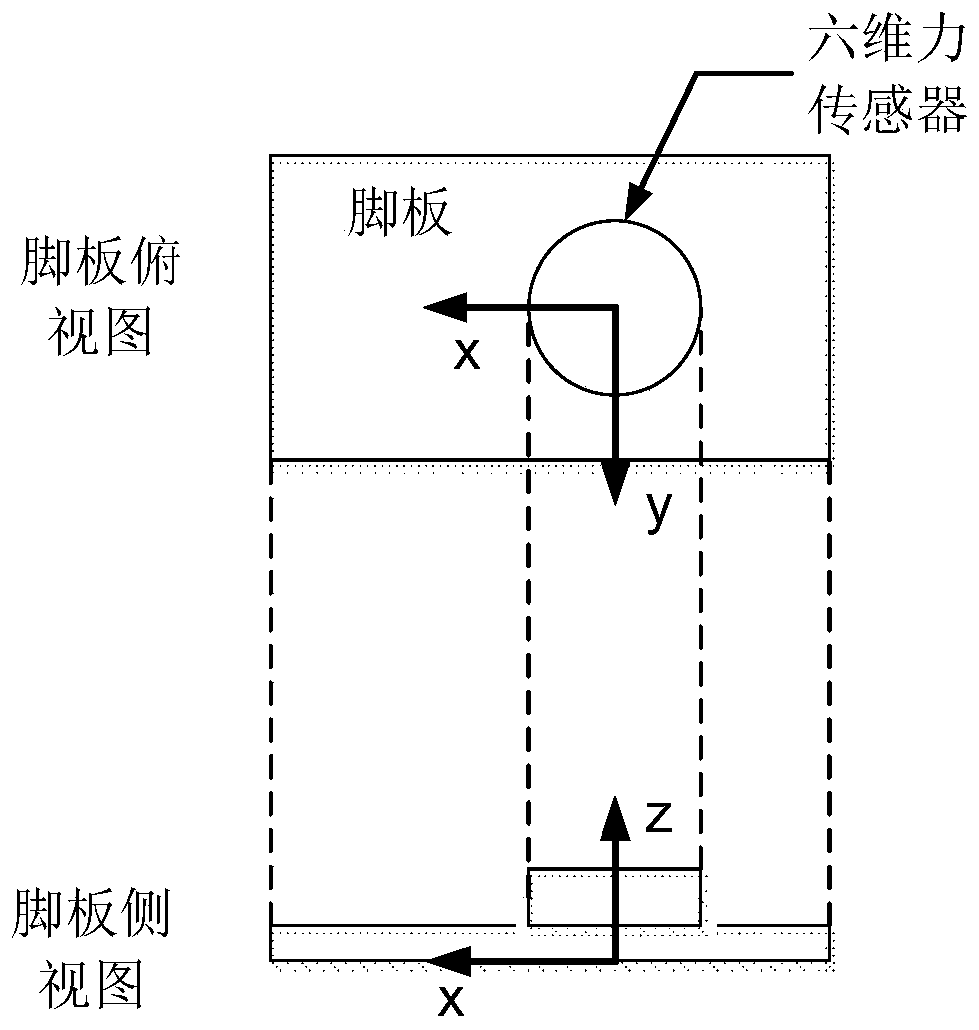
The invention relates to a foot structure of a humanoid robot based on a modularized array sensor. The foot structure comprises a foot plate, a rear foot sole fixed at the rear end of the foot plate, and a front foot sole connected with the foot plate through a foot sole connection piece and capable of rotating, wherein a sensor array comprising a plurality of sensors used for sensing ground counterforce information is arranged at the bottom of the foot plate; and a connection assembly used for being connected with robot legs is arranged on the foot plate. Therefore, the foot structure has the following advantages that the foot structure which is compact in structure, is provided with a ground self-adaption and energy absorption buffer device and can more accurately measure a zero moment point in the robot walking process is designed by a modularization method in an array arrangement way based on PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) piezoelectric film sensors; and the PVDF piezoelectric film sensors can be interchanged, so that a fault component can be dismounted and replaced when a fault occurs.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Robot control method and device, computer readable storage medium and robot
ActiveCN111015653AImprove stabilityImprove expressivenessProgramme-controlled manipulatorVehiclesSimulationRobot control
Owner:UBTECH ROBOTICS CORP LTD
Method and system for controlling apery robot stabilized walking based on effective stable domain
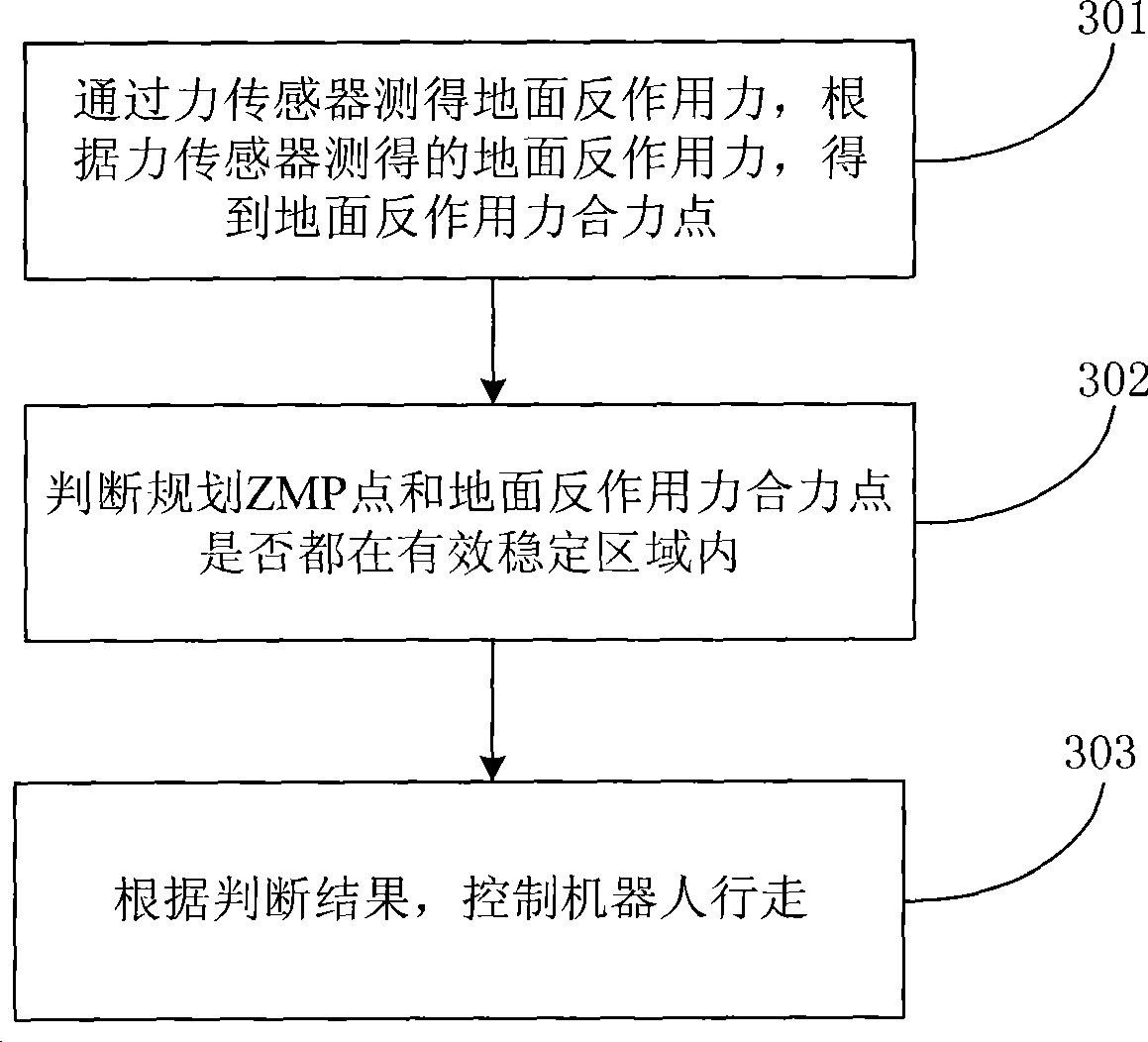
InactiveCN101414190AWalking smoothlyCorrected dynamic gaitVehicle position/course/altitude controlPosition/direction controlAnkleForce sensor
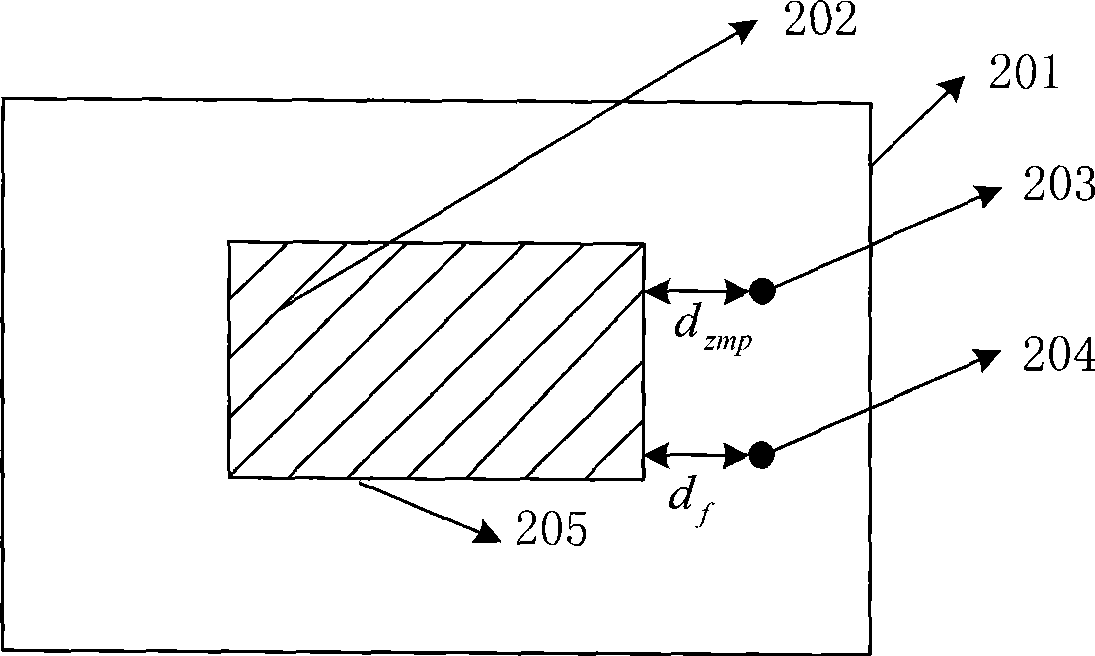
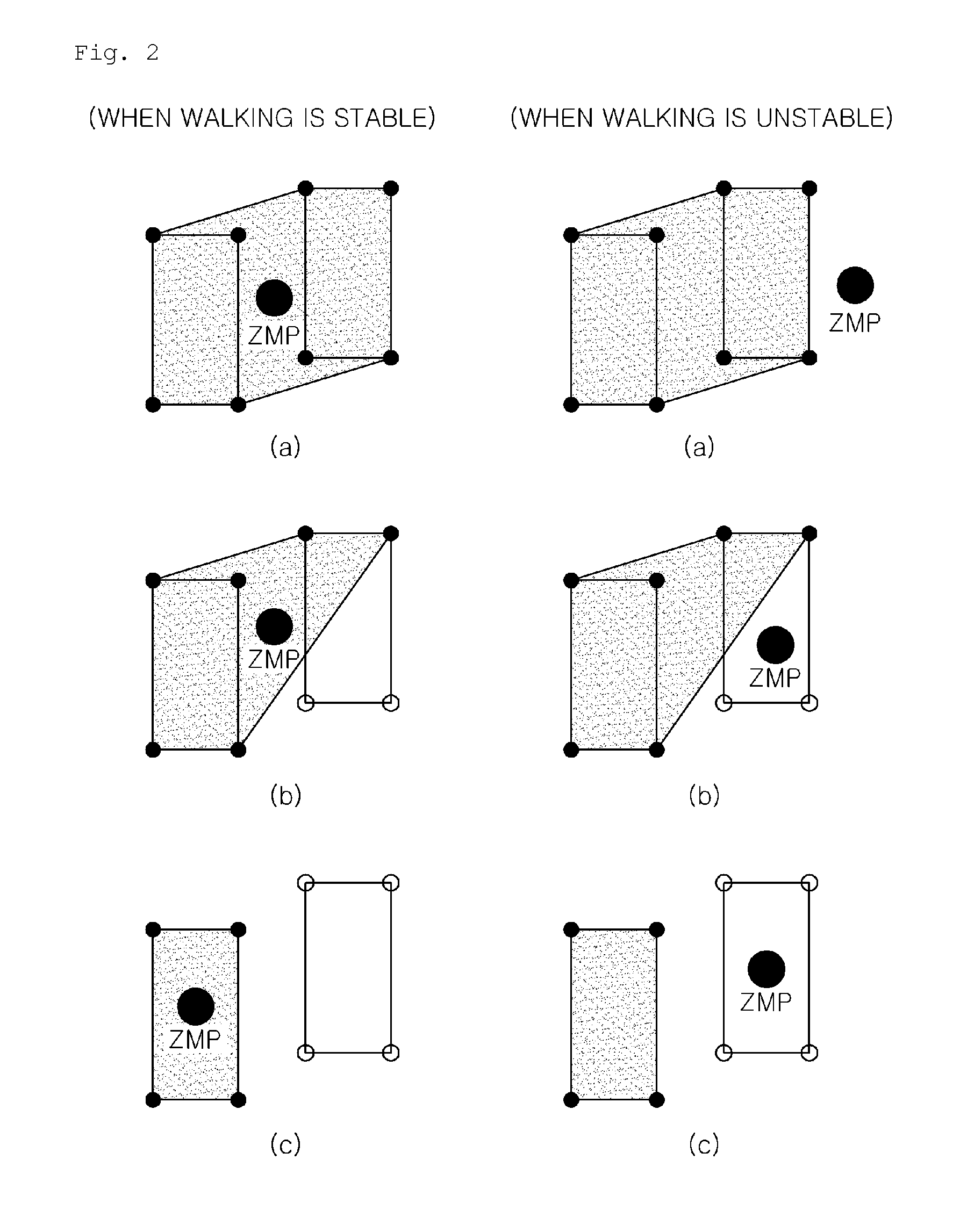
The invention discloses a method for controlling steady walking of a humanoid robot based on an effective stable region, and belongs to the automation control field. The method comprises the following steps: measuring a ground reaction force of the robot by a force sensor; obtaining a resultant force point of the ground reaction force of the robot according to the ground reaction force; judging whether a planned zero moment point (ZMP) and the resultant force point of the ground reaction force are within the effective stable region; and controlling the robot to walk according to a judgment result. The device comprises the force sensor, a processing module, a judgment module and a control module. The system comprises a forward feeder, a real-time corrector and a servo driver. The system causes the planned ZMP and the resultant force point of the ground reaction force to be in the effective stable region by the real-time correction of an angle of ankle joints of the robot, thus achieving the aim of the steady walking of the robot.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for performing zero moment point (ZMP) calibration autonomously by robot
ActiveCN101950176AHigh degree of automationHigh precisionAttitude controlPosition/direction controlStable fixationEngineering
The invention provides a method for performing zero moment point (ZMP) calibration autonomously by a robot. The robot has at least two legs and feet, wherein the at least two legs can drive the robot to walk; the feet are connected with the legs through ankle joints respectively; and the feet are provided with force sensors. The method comprises the following steps of: calculating the projection of a barycenter of the robot on the ground according to each part and the position thereof of the robot, wherein the robot is supported by a single foot to maintain a certain stable fixed posture and the part above the ankle joint of the supporting foot of the robot is seen as a mass point; adjusting the ankle joint of the supporting foot of the robot so as to make the projection of the barycenter spread over the surface of the supporting foot; and obtaining a table by sampling, wherein in the table, a true ZMP corresponds to the ZMP measured by the force sensors. The robot can perform the ZMP calibration according to the projection of the barycenter of the robot and the movement of the ankle joints, so the method has the advantages of no need of human intervention, high efficiency, a large number of sampling points, high precision and low requirement on a mounting environment.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Humanoid robot gait planning and synthesizing method
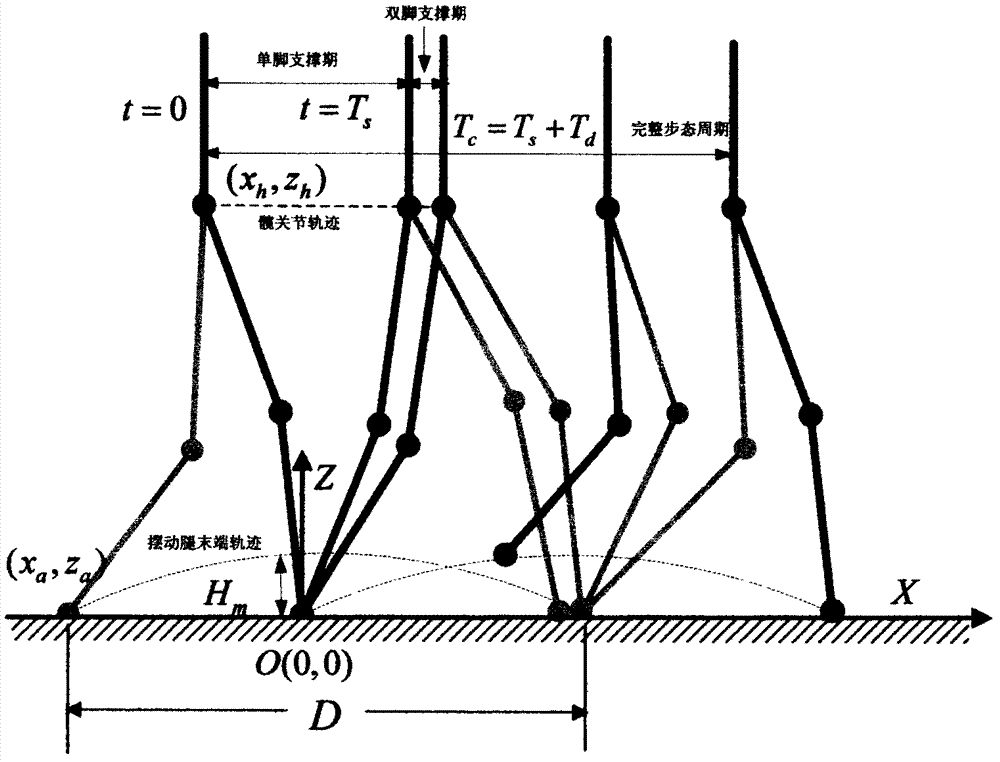
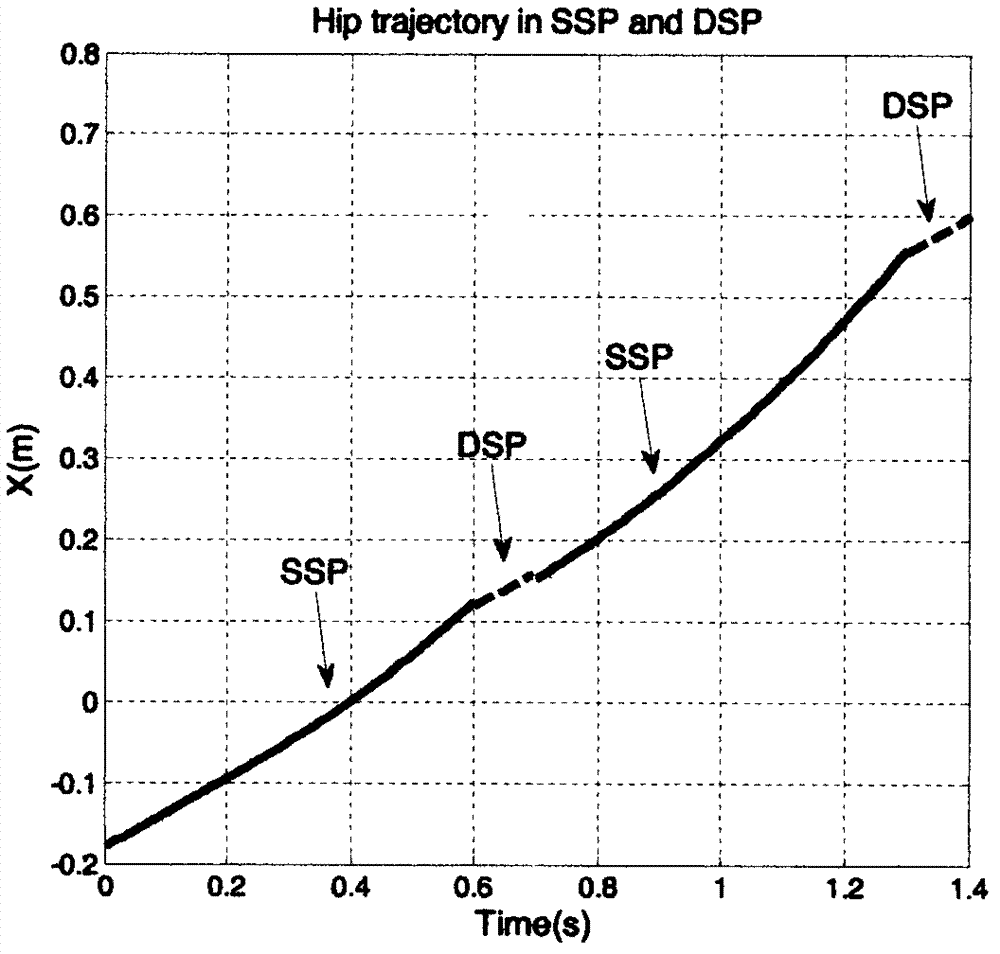
The invention discloses a humanoid robot gait planning and synthesizing method, and belongs to the technical field of humanoid robot motion planning. The humanoid robot gait planning and synthesizing method comprises the following steps that a polynomial function is adopted to represent tracks of hip joints and the tail ends of swing legs of a robot, a one-foot support period gait and a double-feet support period gait are respectively planned when the robot walks according to constraint conditions including geometric constraints, maximum stride height of the tail end of each swing leg, gait periodicity, impact effect, hip joint motions and the like when the humanoid robot walks, then the planned gaits are synthesized, and whether obtained gait tracks are stable is judged according to a zero moment point criterion. According to the humanoid robot gait planning and synthesizing method, the one-foot support period gait and the double-feet support period gait of the robot are planned and synthesized into a complete gait, the problem that collisions between legs of the robot and ground affect walking stability when the robot walks is solved, walking stability of the robot is improved, and an important effect, of the double-feet support period gait of the robot, on a complete gait period is explained at the same time.
Owner:PLA SECOND ARTILLERY ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY
Humanoid biped robot walking posture control method based on genetic algorithm
InactiveCN105965506AAchieve stable anthropomorphic walkingAvoid complexityProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobotic systemsTime response
The invention discloses a walking posture control method of a humanoid biped robot based on a genetic algorithm. A mathematical model of a biped robot is established based on the ZMP control theory and a pose matrix, and the basic gait of a human is simulated. V, height H, arm swing R, body center up and down swing C, body center left and right swing A These six parameters plan the robot's gait, and select optimized T, V, H, R through genetic algorithm The six parameters of , C, and A are brought into the inverse operation of the pose matrix to obtain the values of other joint coordinates of the robot, and solve the method of generating data that stably controls the gait of the robot. It overcomes the problem of large amount of calculation and low efficiency in inverse operation of pose matrix, improves the real-time response ability of the system, and uses the data generated by this method in the humanoid biped robot system to achieve a good control effect.
Owner:北京格分维科技有限公司
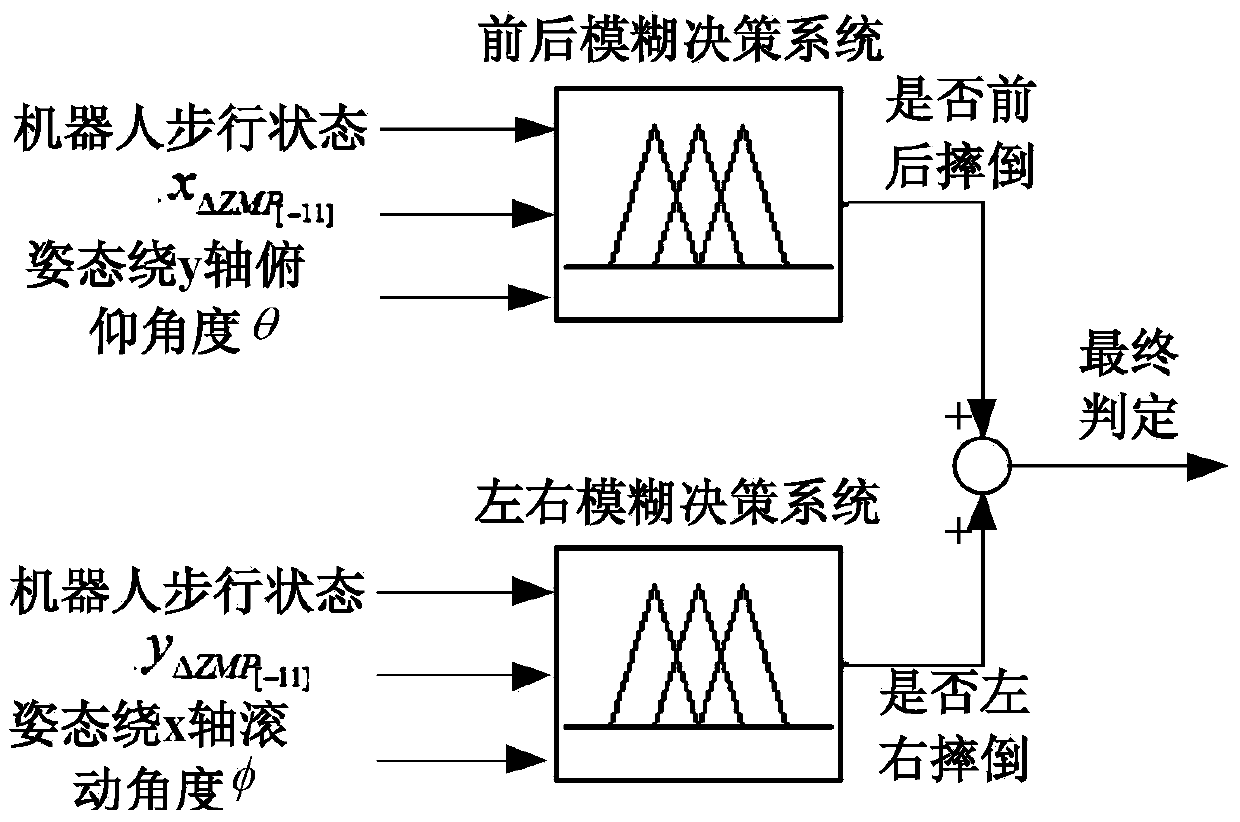
Method for detecting tumbling state of humanoid robot based on multi-sensor information
ActiveCN104217107AAchieving Stability JudgmentReflect stable situationNavigation instrumentsSpecial data processing applicationsFuzzy decisionSimulation
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Humanoid robot and walking control method thereof
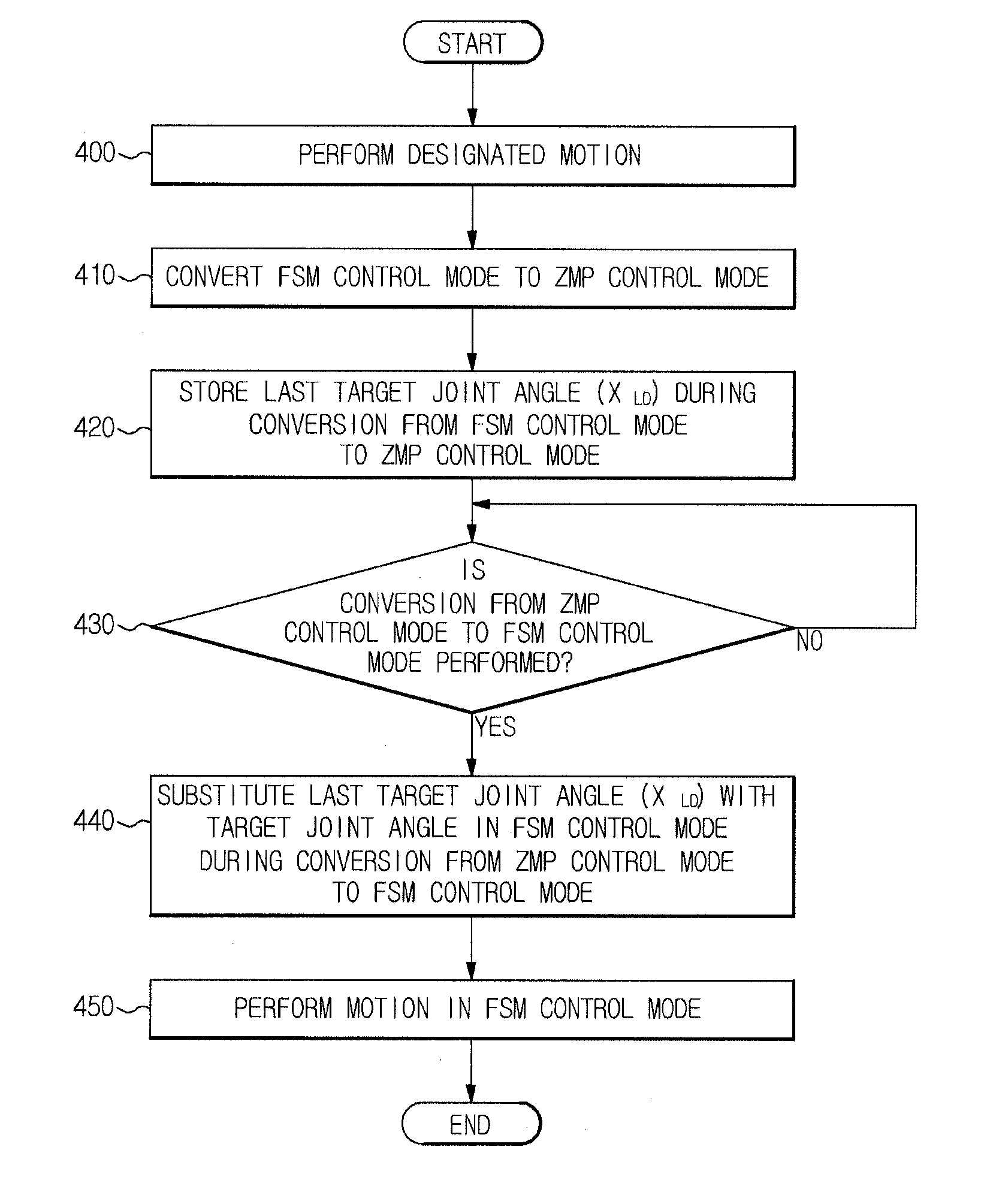
ActiveUS20110178636A1Pointing errorDistrict heating systemLighting and heating apparatusHumanoid robot naoVirtual finite-state machine
Disclosed herein are a humanoid robot that compensates for a zero moment point (ZMP) error during finite state machine (FSM)-based walking to achieve stable walking and a walking control method thereof. The humanoid robot compensates for a joint position trajectory command or a joint torque command using compensation values calculated based on situations divided according to the position of a calculated ZMP and the position of a measured ZMP in a stable region of the robot.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System for Stabilization Control of Mobile Robotics
A system comprises a platform being configured for locomotion in a plurality of directions over a surface. A robotic unit is configured for dexterous manipulation comprising at least lifting of objects. The robotic unit is joined to the platform. At least one extender unit is joined to the platform and is configured for controlled extension beyond the platform to contact the surface to stabilize the system at least during the manipulation by the robotic unit. At least one controlling unit is configured to be operable for at least determining a center of gravity and a zero moment point for the system and for at least controlling an extension of the extender unit.
Owner:HU JOHN +1
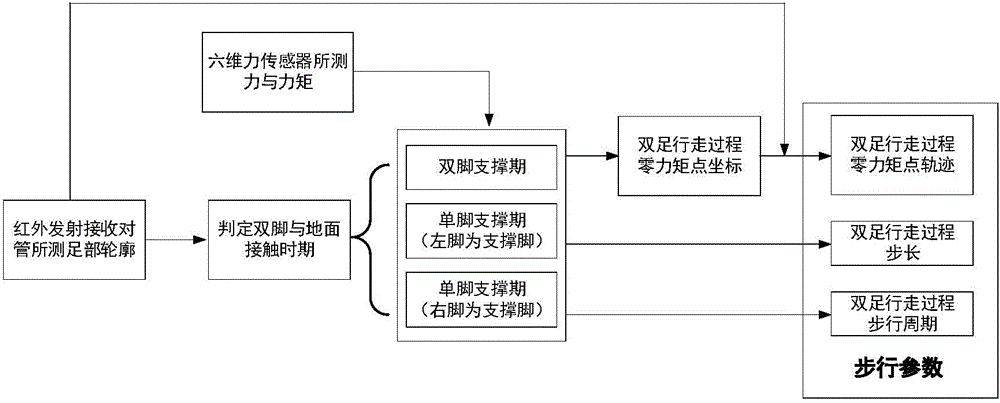
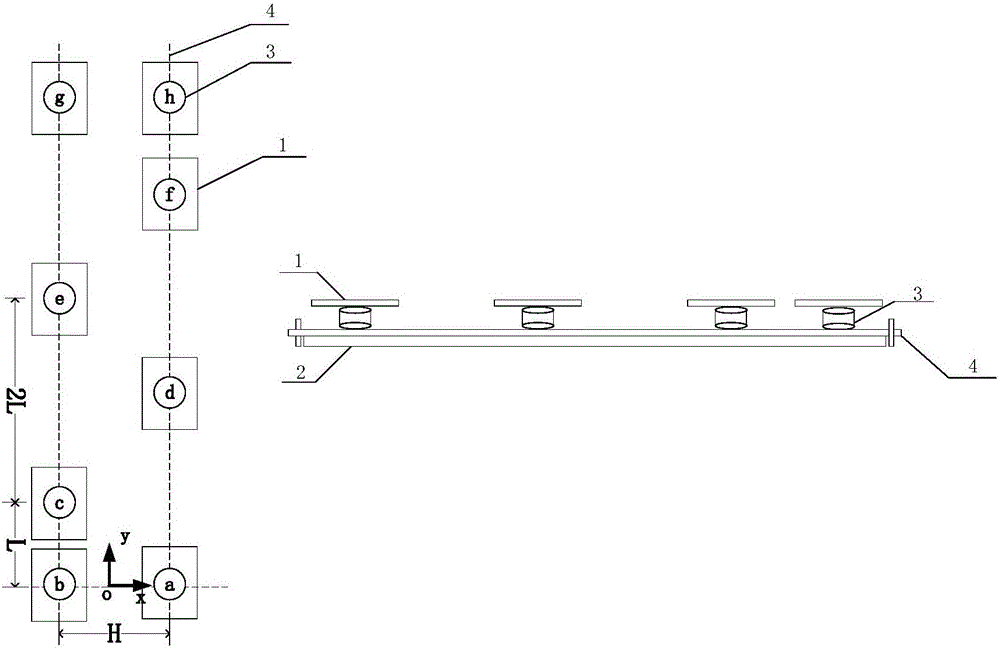
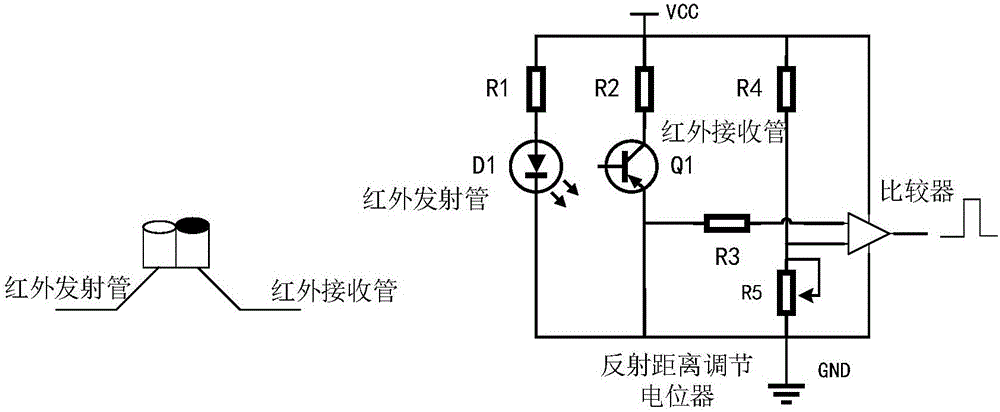
Biped walking parameter measuring method and apparatus
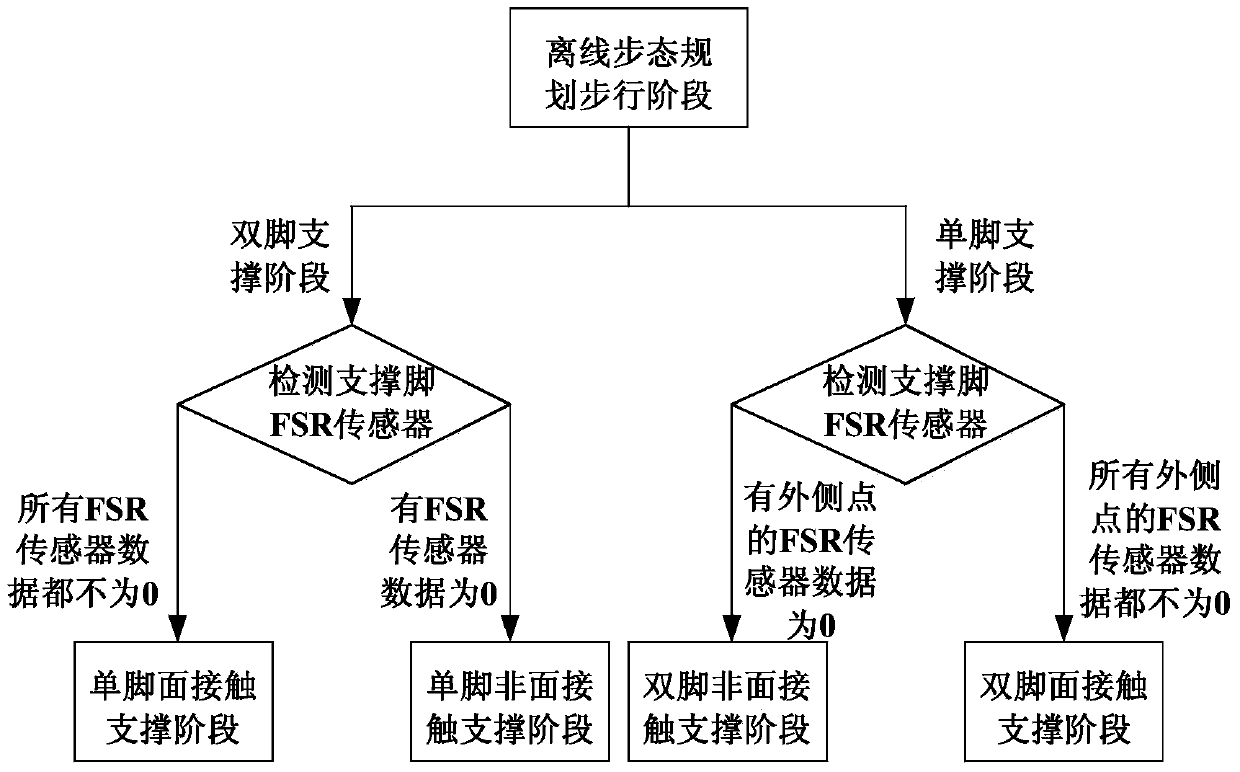
ActiveCN105973143AWalking smoothlyDiagnostic recording/measuringUsing optical meansMeasurement deviceState parameter
The invention provides biped walking parameter measurement and belongs to the technical field of robots. A biped walking parameter measuring apparatus is provided and comprises a zero moment point measuring system, a foot contour measuring system and a walking parameter calculating system. A biped walking parameter measuring method provided can accurately and effectively measure biped walking parameters including stand state parameter before walking, step, step period, zero moment point track, and the contours of feet contacting the ground. The method for measuring biped walking parameters of a human being is of great importance to analysis of walking gaits of the human being, thereby providing important basis for planning track of a biped robot. The method is used for measuring the walking parameters of a biped robot, and feedback parameters of biped robot walking gaits, walking track on-line adjusting, and enclosed control of a host computer and each joint of leg portions are provided. The method is of great significance to stable walking of a biped robot.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method and device for controlling to support foot of humanoid robot in single leg supporting period
InactiveCN103042526ARotate for increased stride lengthGo fastProgramme-controlled manipulatorFoot supportsEngineering
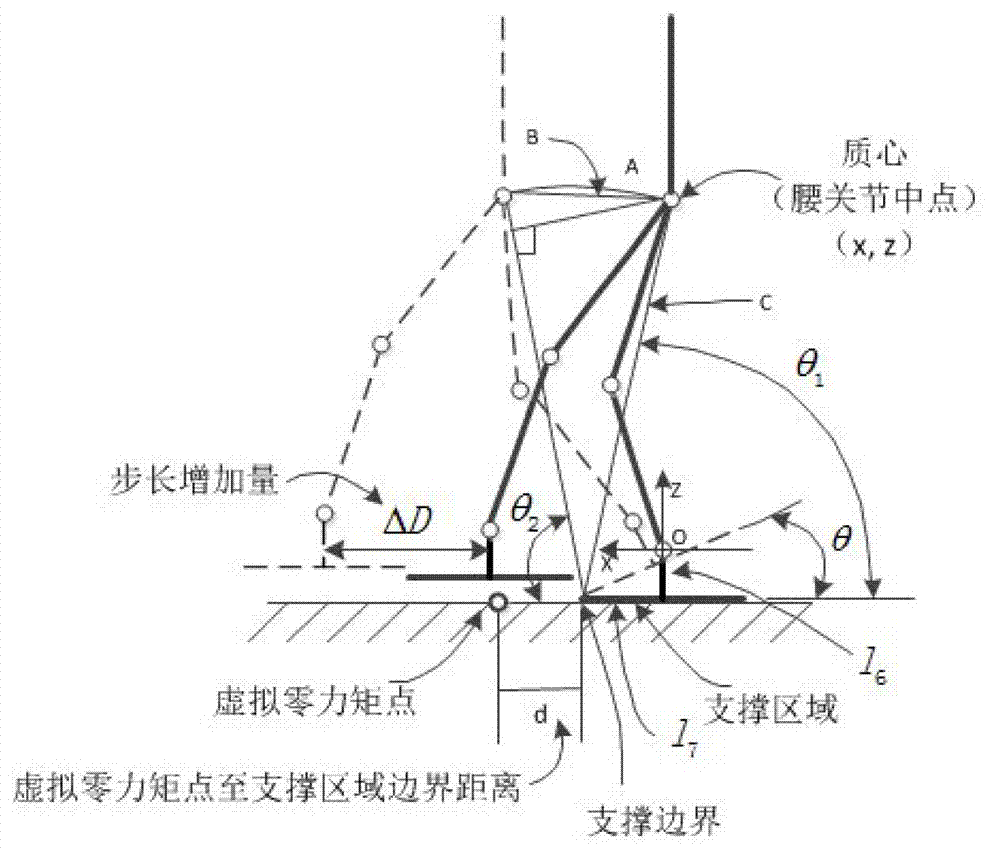
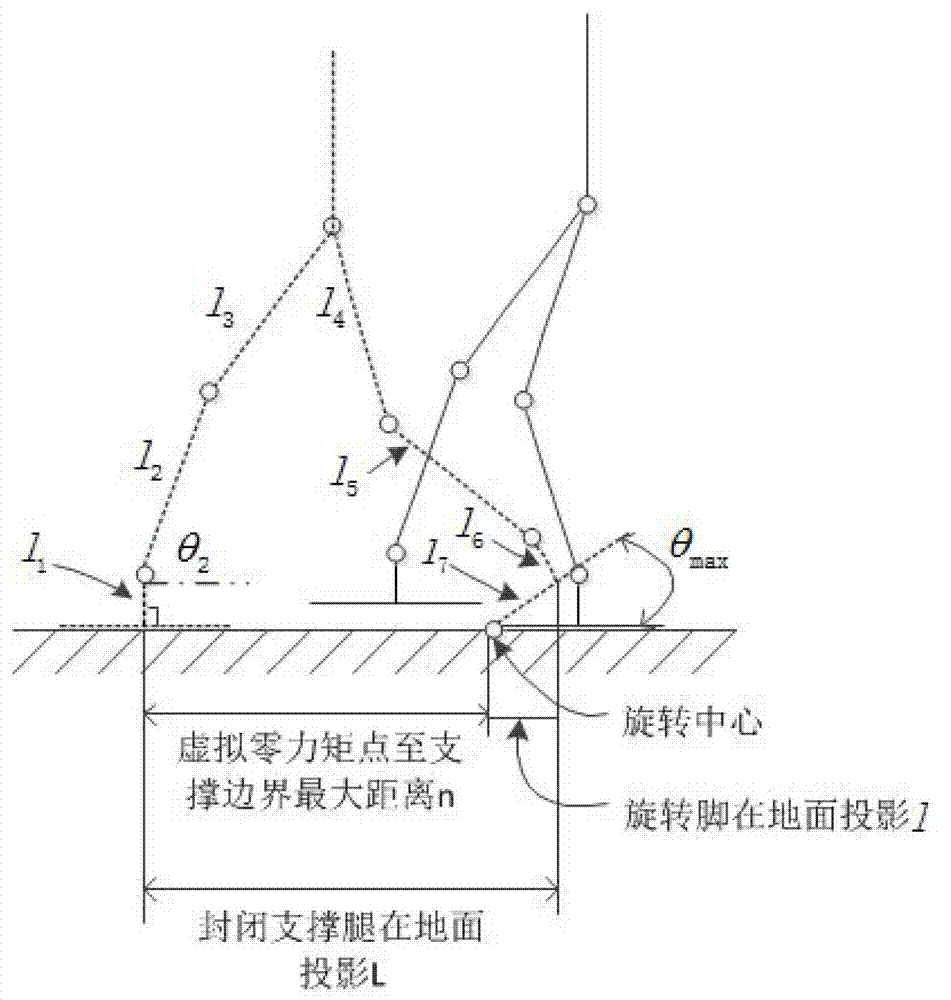
The invention discloses a method and a device for controlling to support a foot of a humanoid robot in a single leg supporting period and belongs to the field of robots. An expected virtual zero moment point is arranged outside the foot supporting region, and a step increasing quantity generated through the rotation of the robot can be acquired. The method comprises steps of calculating the virtual zero moment point and detecting the rotation angle of the supporting foot; determining the rotation angle of the supporting foot; determining the position of the virtual zero moment point; and limiting the position of the virtual zero moment point. The device comprises a calculating and detecting module, a rotary angle control module, a virtual zero moment point position control module and a virtual zero moment point position limiting module. By the aid of the method and the device, the humanoid robot can support the foot to rotate in the single leg supporting period, the walking step is increased, and the control is simple and reliable.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Linear inverted pendulum model-based robot gait planning method
InactiveCN110286679AImprove stabilityConform to gait processPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesGait planningPlanning approach
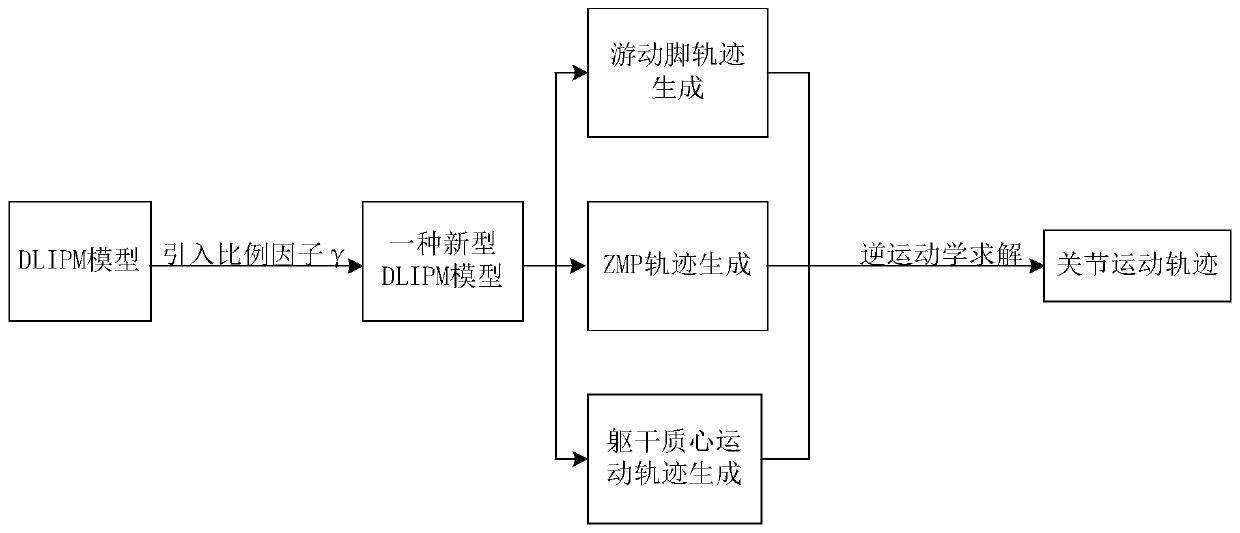
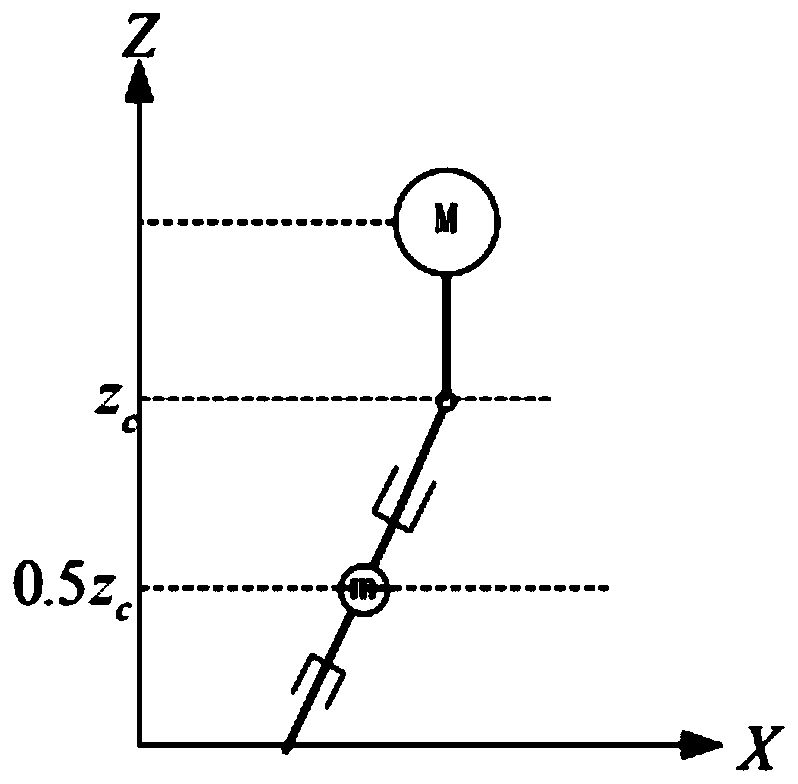
The invention discloses a linear inverted pendulum model-based robot gait planning method. The linear inverted pendulum model-based robot gait planning method comprises the following steps of building a linear inverted pendulum model, in which a proportion factor Gamma is introduced on the basis of a dual-connection rod inverted pendulum model (DLIPM) to build a new linear inverted pendulum model; and performing robot gait planning, in which zero-torque point track, trunk mass center motion track and free foot planning track are generated on the basis of the linear inverted pendulum model, and each joint gait motion curve is solved by inverse kinematics. The linear inverted pendulum model built by the method more conforms to actual mass distribution condition of a humanoid robot, the zero-torque point track, the trunk mass center motion track and the feet foot planning track which are generated on the basis of the model and the each solved joint gait motion curve linear are more reasonable and more conform to the gait process of a natural person dual-foot robot, and the gait planning accuracy is high.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Foot force and moment following control method of bipedal robot
ActiveCN110244791AShock absorbingHave suppleProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical power/torque controlDistribution methodEngineering
The invention discloses a foot force and moment following control method of a bipedal robot. According to the method, a double-spring damping model is designed, a force following controller is designed by using an LQR optimization method, and the following of the foot force and moment of the bipedal robot is realized; and the foot expected force and the foot expected moment are calculated by a planned ZMP (Zero Moment Point) distribution method, and finally, the ZMP following of the bipedal robot is better, and can adapt to a certain uneven ground. According to the foot force and moment following control method of the bipedal robot provided by the invention, the traditional ZMP following is abandoned, so that a control mode adaptive to the stable walking and the uneven ground of the bipedal robot can be realized, the foot expected force and the force moment that enable the robot to stably work are directly calculated, and the following of the foot force and the force moment is realized by directly controlling the foot expected force and the force moment, so that stable control is carried out in a more intrinsic and easier implementation manner, the control response is faster, the capability of adapting to the uneven ground is stronger, and the ZMP following effect is very ideal.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Walking robot and control method thereof
A walking robot and a control method in which conversion between walking servo control methods is stably carried out. The walking robot includes a sensor unit to measure angles and torques of joints, and a control unit to calculate voltages applied in a Finite State Machine (FSM) control mode and a Zero Moment Point (ZMP) control mode according to the angles and torques of the joints to drive respective joint motors, to store last target joint angles in the FSM control mode during conversion from the FSM control mode to the ZMP control mode, and to perform a motion based on the FSM control mode by substituting the last target joint angles in the FSM control mode for target joint angles in the FSM control mode during conversion from the ZMP control mode to the FSM control mode, thereby performing stable conversion between walking servo control modes without joint sagging.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and device for controlling gait of biped robot
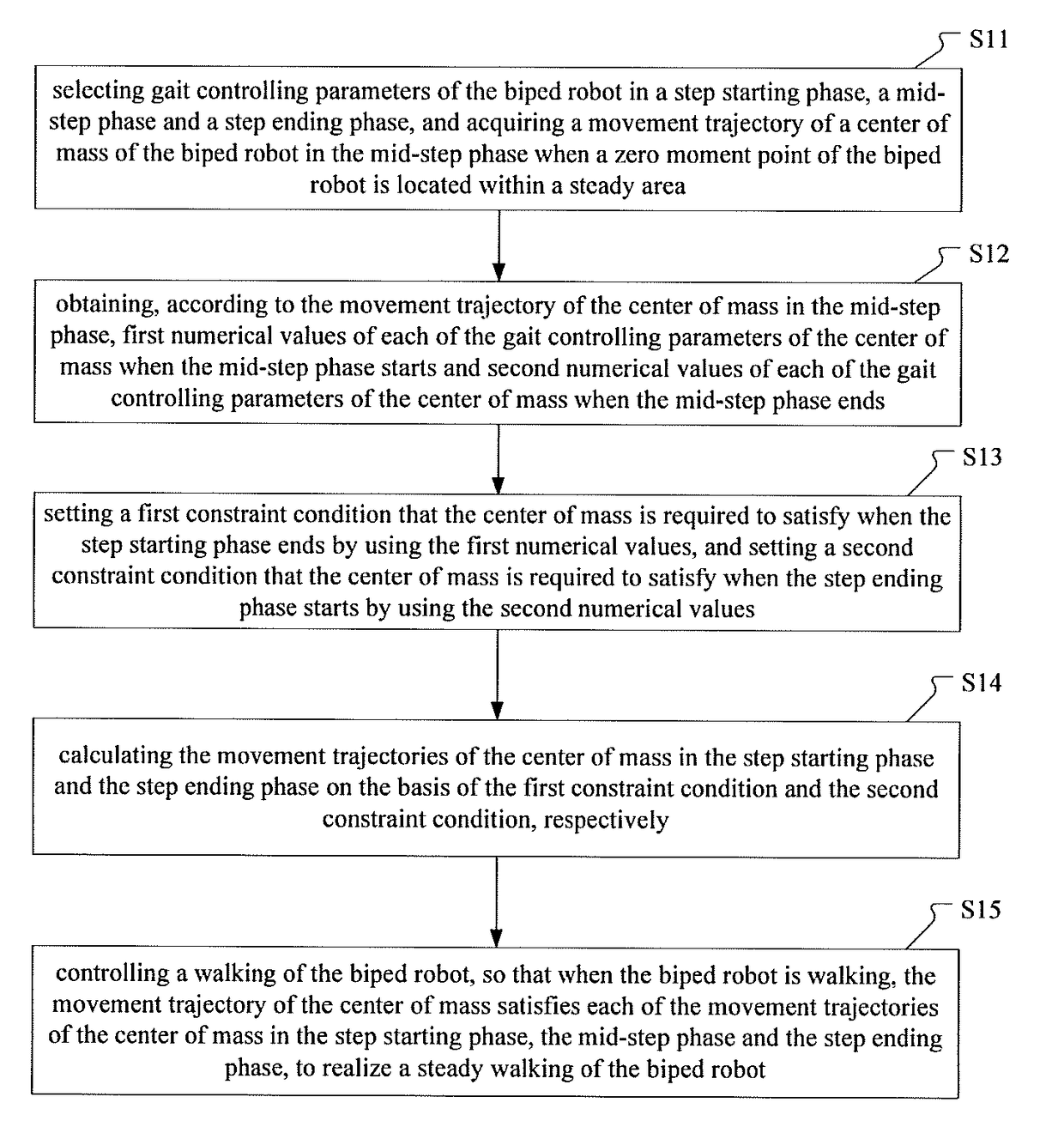
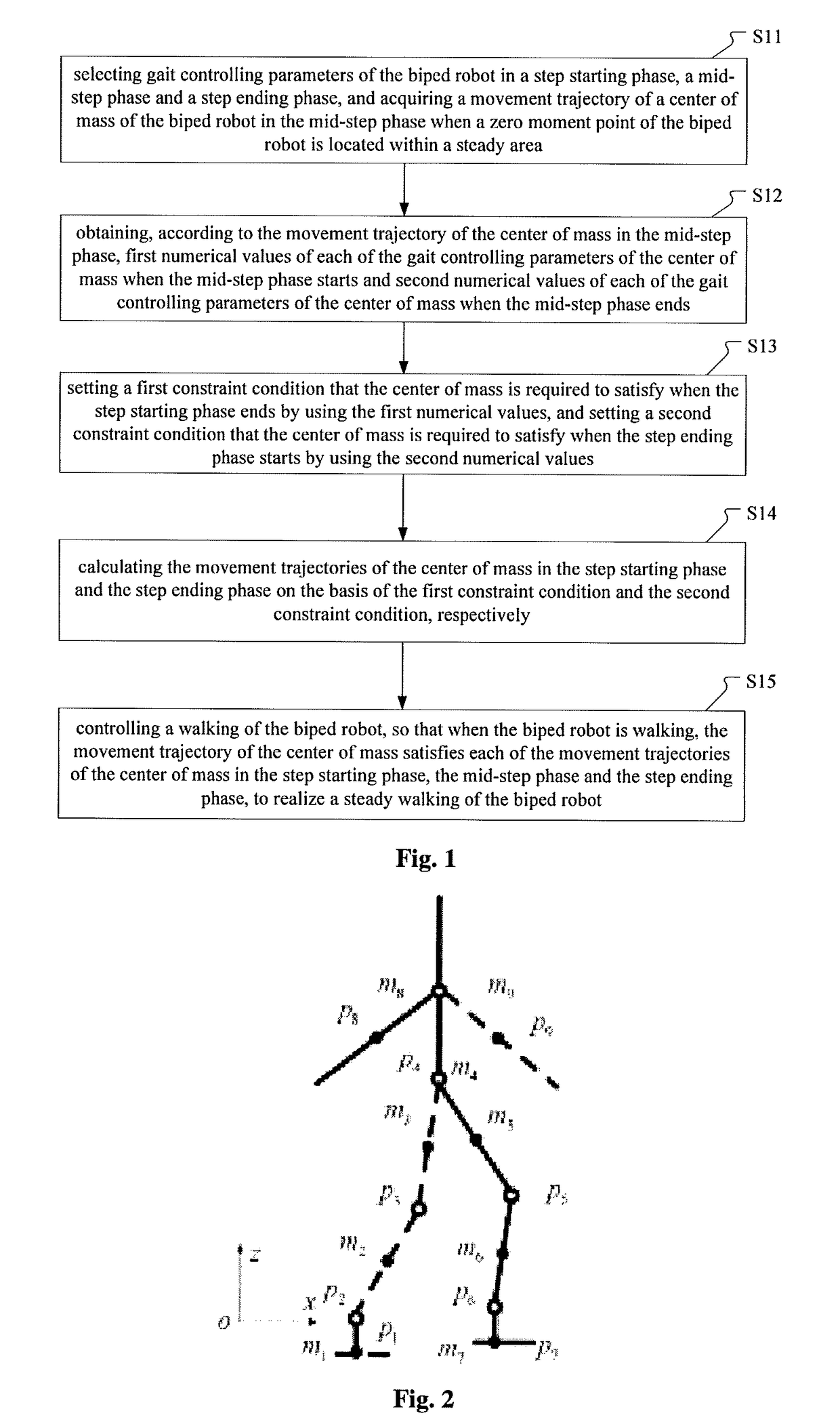
ActiveUS20180004208A1Improve stabilityImprove efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorNumerical controlEngineeringZero moment point
A method and a device for controlling a gait of a biped robot. The method includes: selecting gait controlling parameters, and acquiring a movement trajectory of a center of mass when a zero moment point of the biped robot is located within a steady area; obtaining first numerical values of each of the gait controlling parameters of the center of mass and second numerical values of the center of mass; setting a first constraint condition when the step starting phase ends by using the first numerical values, and setting a second constraint condition when the step ending phase starts by using the second numerical values; calculating the movement trajectories of the center of mass in the step starting phase and the step ending phase on the basis of the first constraint condition and the second constraint condition, respectively; and controlling a walking of the biped robot.
Owner:GOERTEK INC
Wheel-foot switching robot system and control method thereof
ActiveCN111497965AReduce the problem of low accuracyLower requirementProgramme-controlled manipulatorVehiclesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a wheel-foot switching robot system and a control method thereof, a robot comprises a robot trunk, a mechanical leg mechanism mounted at the bottom of the robot trunk and a wheel type mechanism mounted at the upper part of the robot, and the wheel type mechanism and the mechanical leg mechanism are independent of each other; the mechanical leg mechanisms achieve switching of the motion postures of the robot through contraction or extension. The control method of the robot system comprises the following steps of switching real-time postures of a robot before switching; planning a gravity center motion track of the robot trunk part; judging whether each zero moment point in the planned gravity center motion trail of the robot trunk part meets a balance condition within a stability threshold of the robot or not; and if the balance condition is met, contracting or stretching the mechanical leg mechanisms according to the rotating angles of all joints of the robot toachieve stable switching, the problem that the robot loses balance due to the fact that the gravity center of the robot changes during trade wheel-foot switching is avoided, and stable wheel-foot switching can be conducted on complex terrains.
Owner:暗物智能科技(广州)有限公司
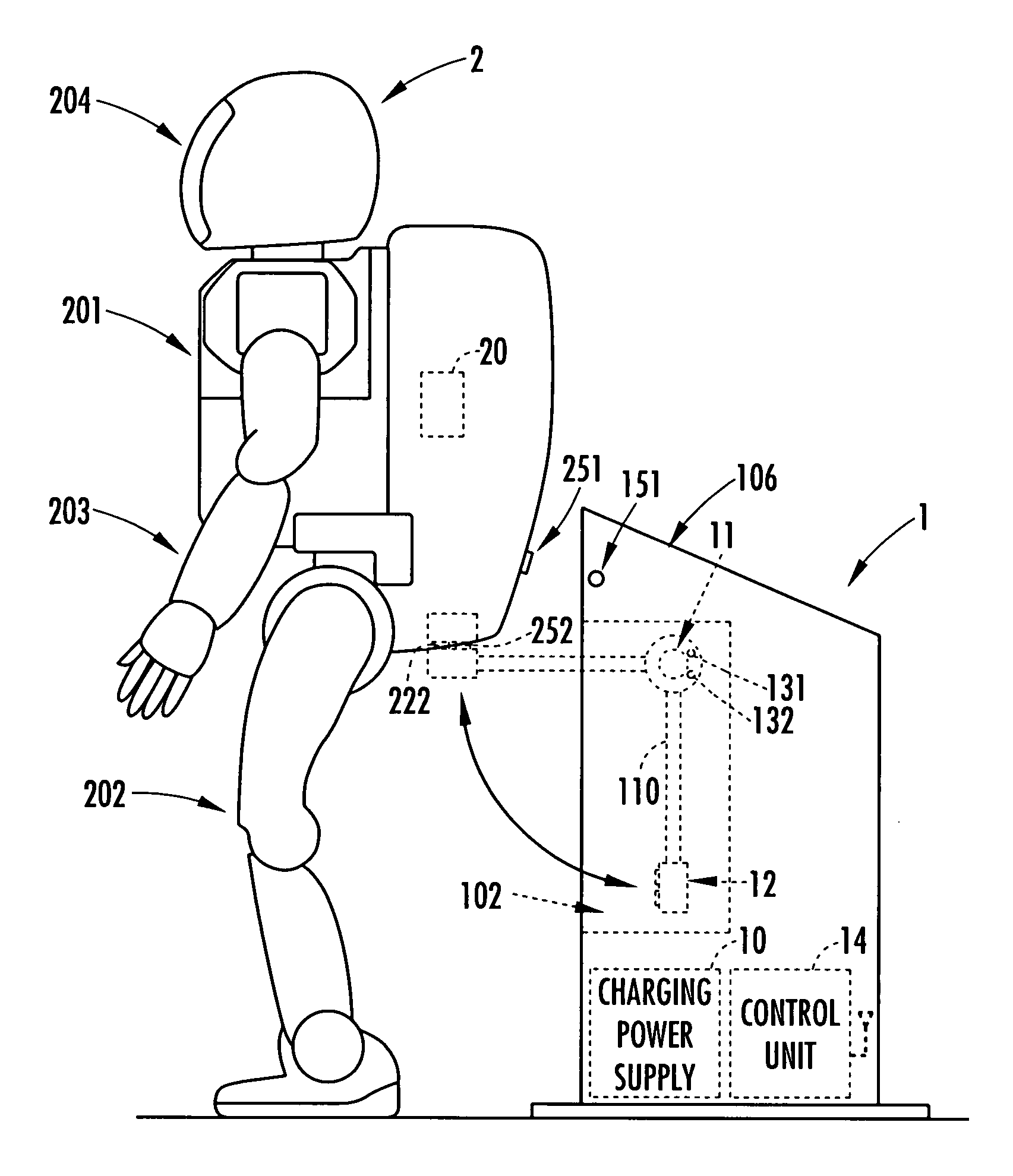
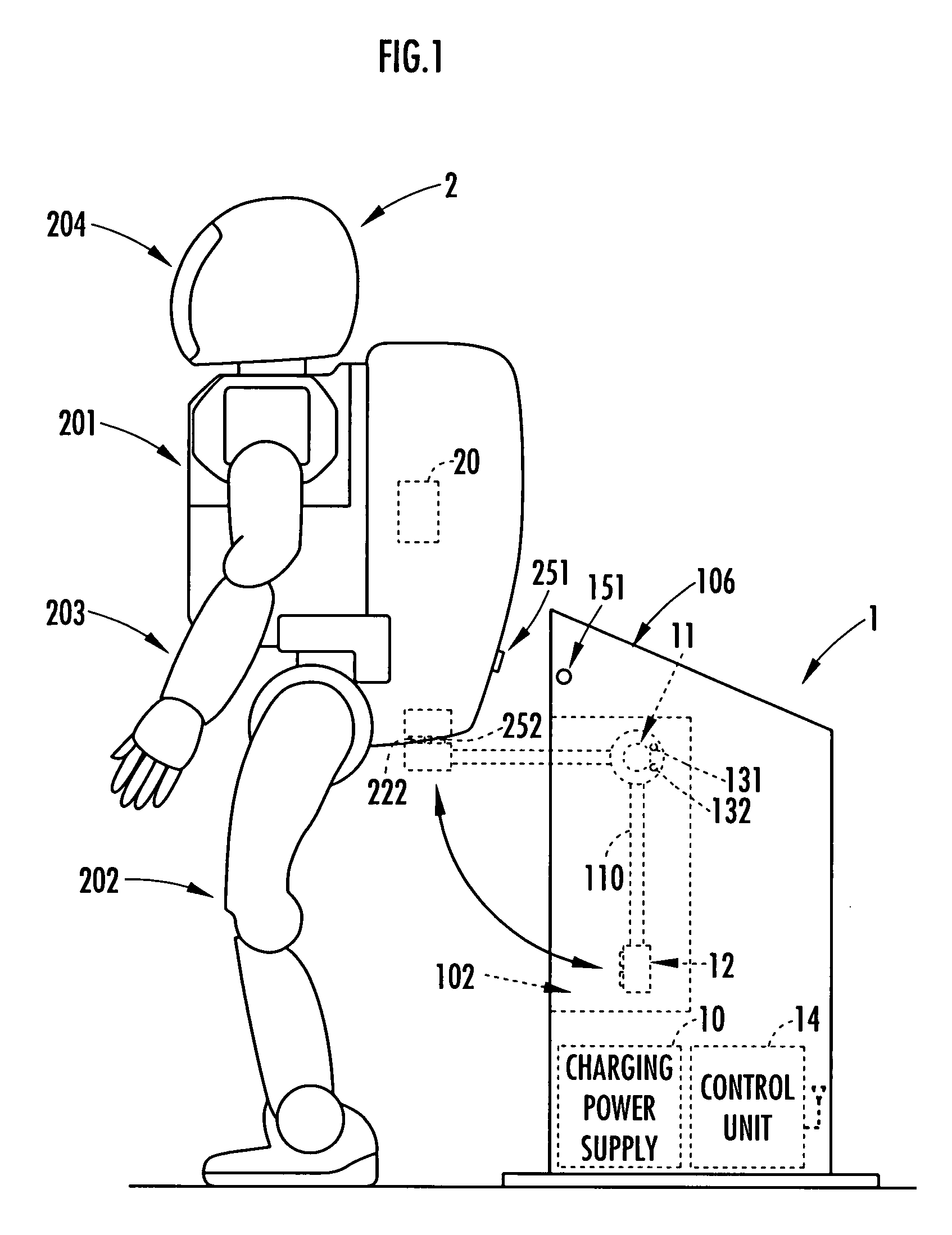
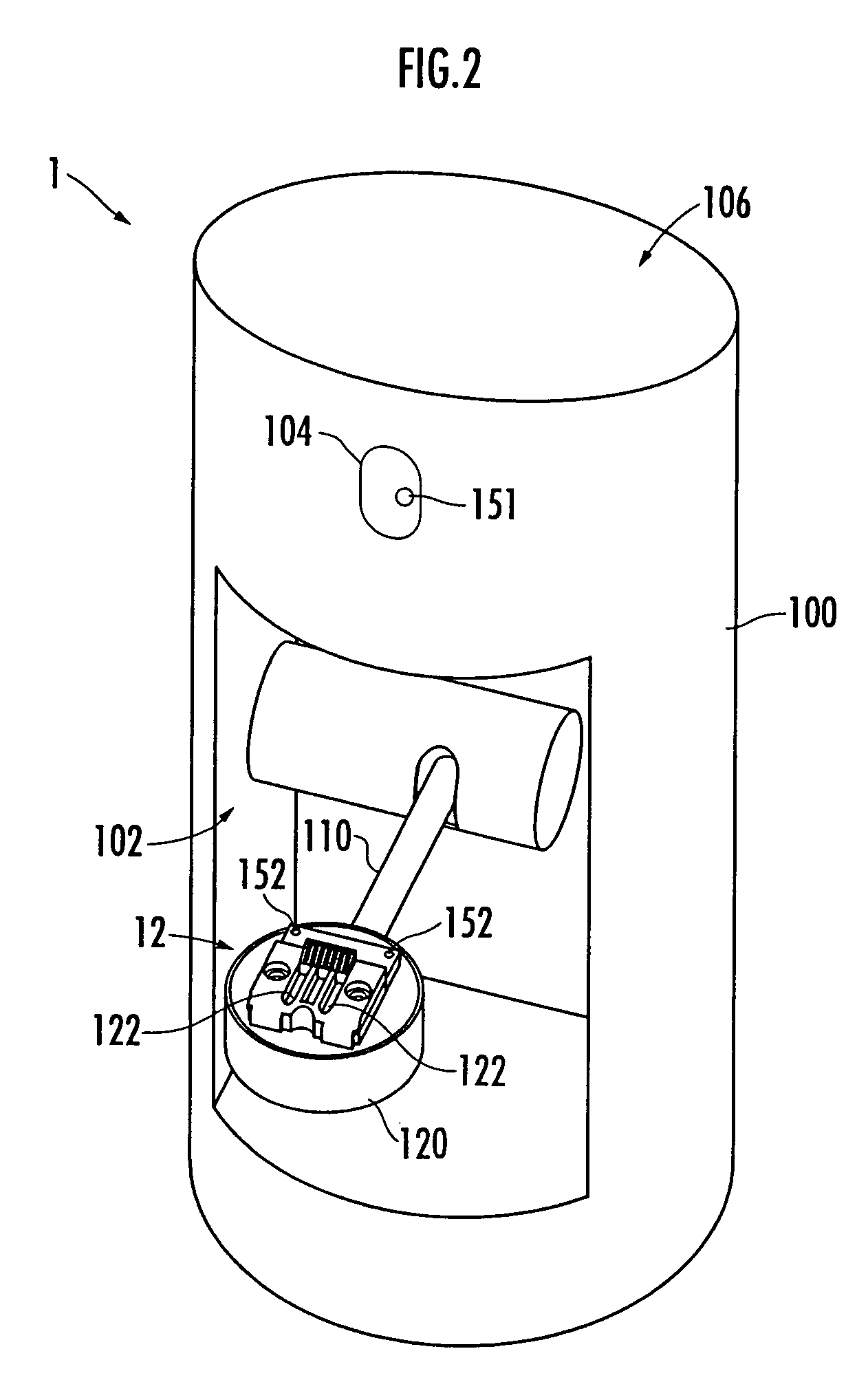
Battery charger
InactiveUS7825633B2Avoiding an unstable posture of the robotUnstable posture of the robot can be avoidedBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerEngineeringElectric power
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Multi-objective particle swarm algorithm-based humanoid robot gait planning method
InactiveCN108009680AWalking smoothlyJoint dexterityProgramme-controlled manipulatorForecastingGait planningGait
The invention provides a multi-objective particle swarm algorithm-based humanoid robot gait planning method. The method comprises the following steps of S1, by applying a cubic spline interpolation function, generating motion tracks of hip joints and ankle joints; S2, according to the generated motion tracks of the hip joints and the ankle joints, calculating out motion situations of joints of both legs, and further calculating out a track of a zero moment point and moments of the hip joints of the both legs; S3, according to an optimized objective function and a task constraint condition, determining fitness functions of the joints of the both legs; S4, according to the fitness functions, obtaining a Pareto optimal solution set corresponding to the optimized objective function by utilizing a multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm; and S5, selecting a solution as an optimal solution from the Pareto optimal solution set, and substituting the optimal solution into plannedgaits, thereby guiding a humanoid robot to walk.
Owner:航天科工智能机器人有限责任公司
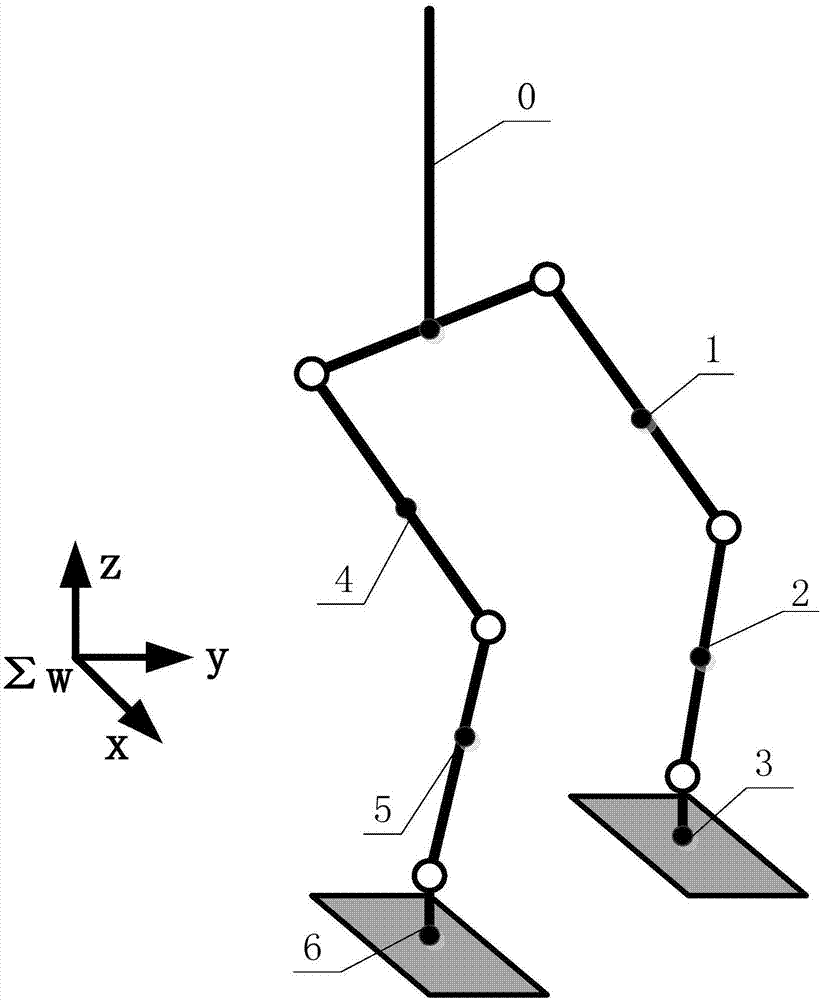
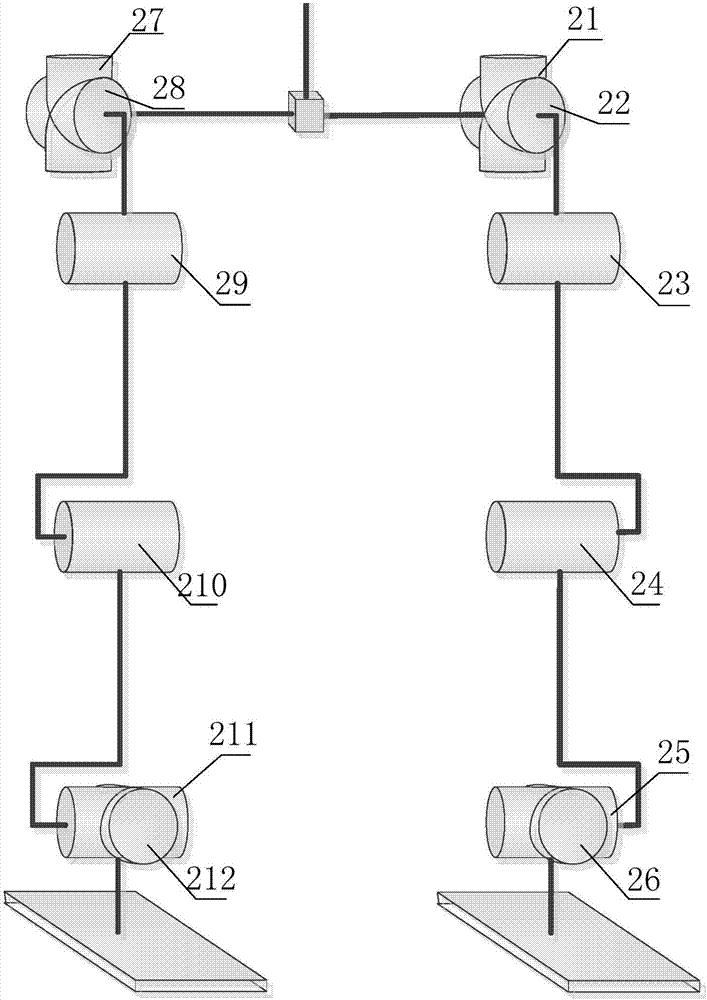
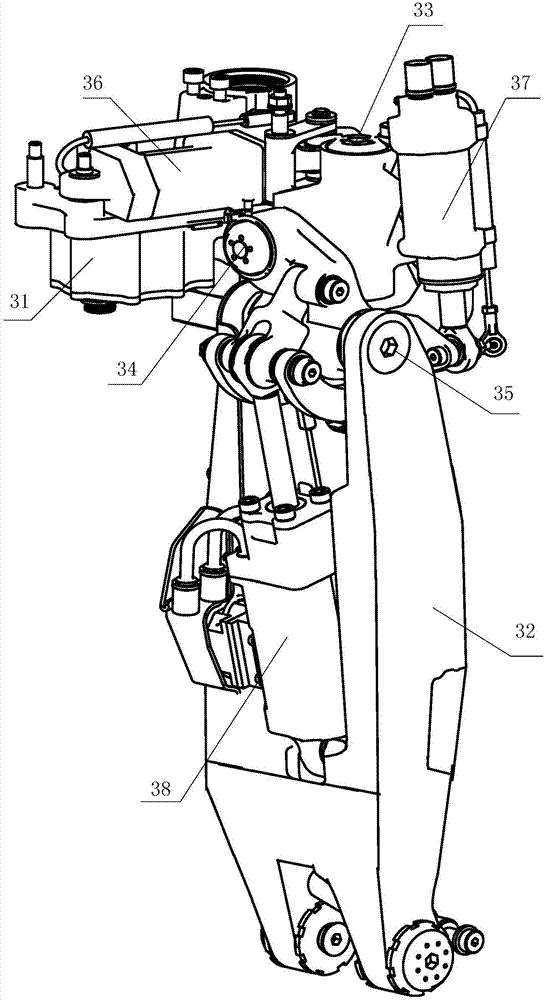
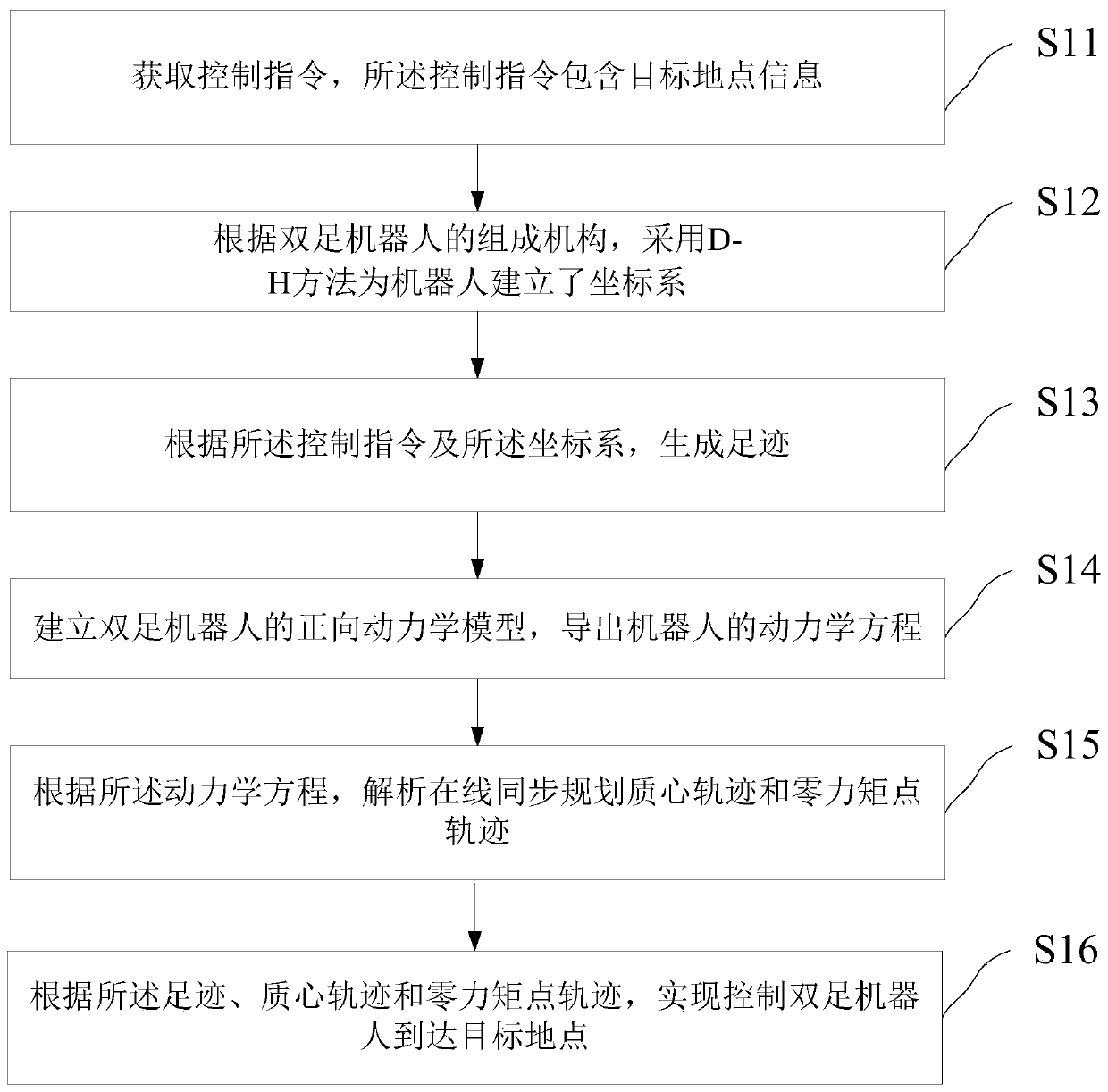
Biped robot walking planning and control method
The invention discloses a biped robot walking planning and control method, which comprises the following steps of acquiring a control instruction, wherein the control instruction comprises target place information; establishing a coordinate system for a robot by adopting a D-H method according to a composition mechanism of the biped robot; generating a footprint according to the control instruction and the coordinate system; establishing a forward dynamics model of the biped robot, and deriving a dynamics equation of the robot; analyzing an on-line synchronized planning mass center orbit and azero moment point track according to the dynamics equation; and controlling the biped robot to reach a target place according to the footprint, the mass center orbit and the zero moment point track.According to the method, the technical problem of poor maneuverability of the existing biped robot can be solved, the stability is higher, and any footprint of the biped robot can be stably changed ina walking process.
Owner:沈阳城市学院
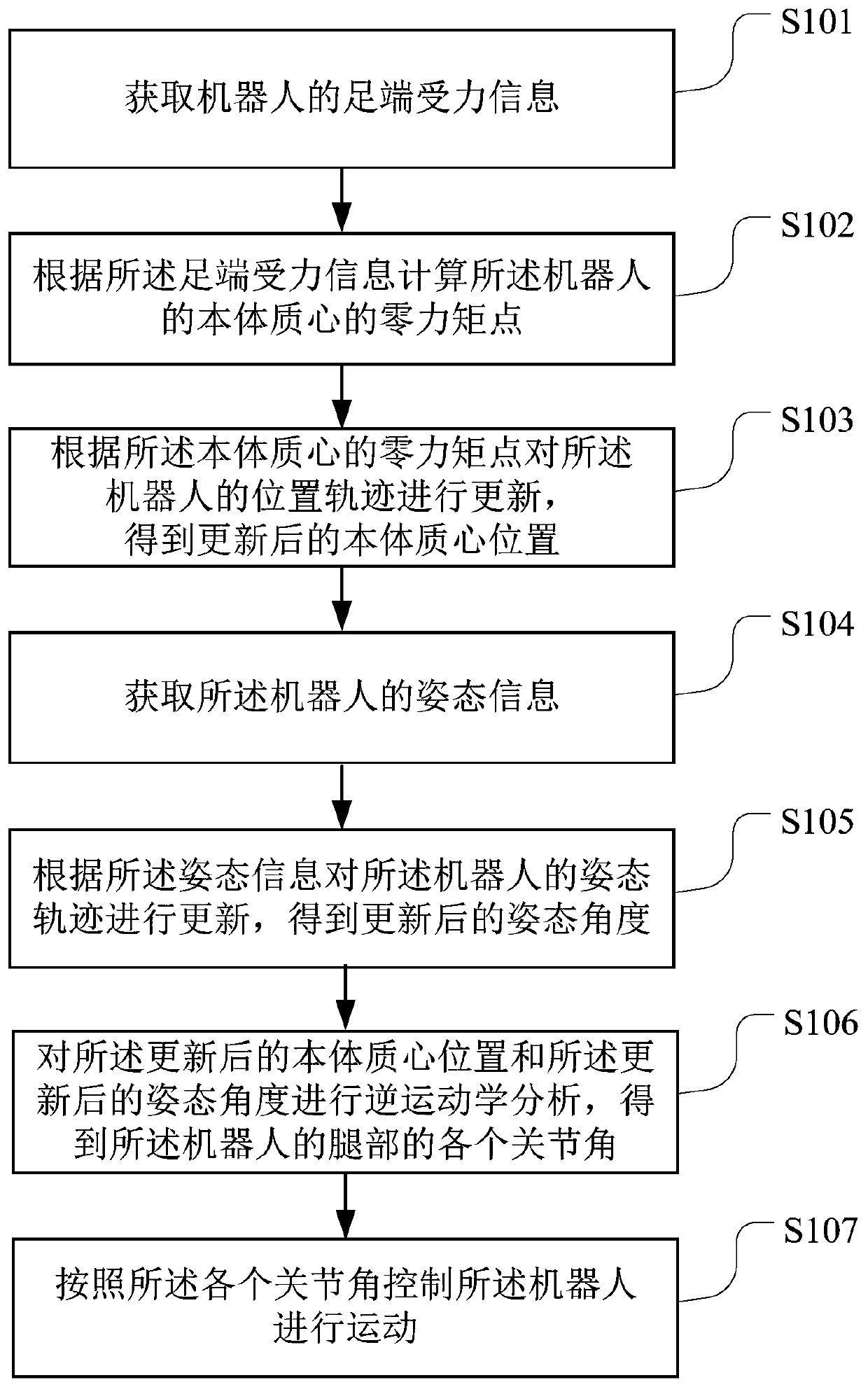
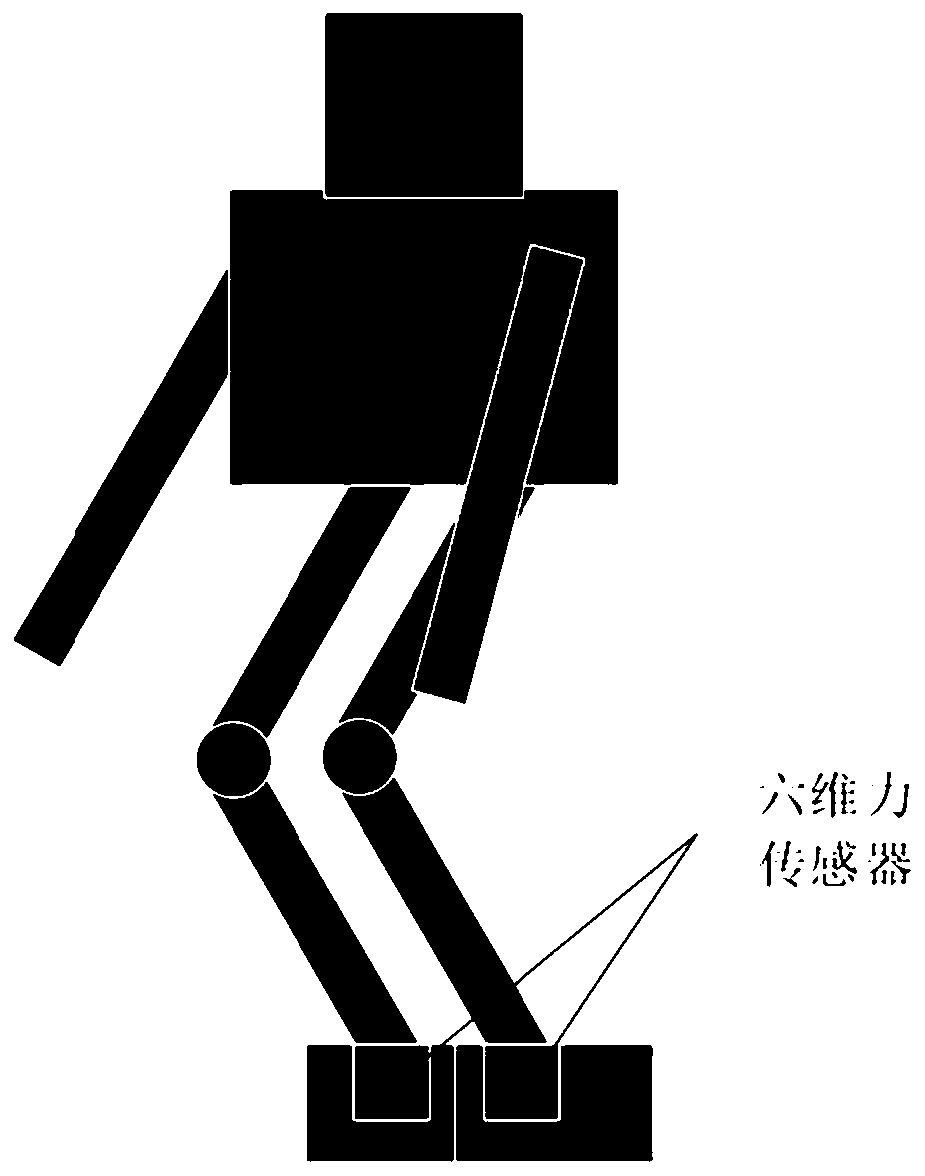
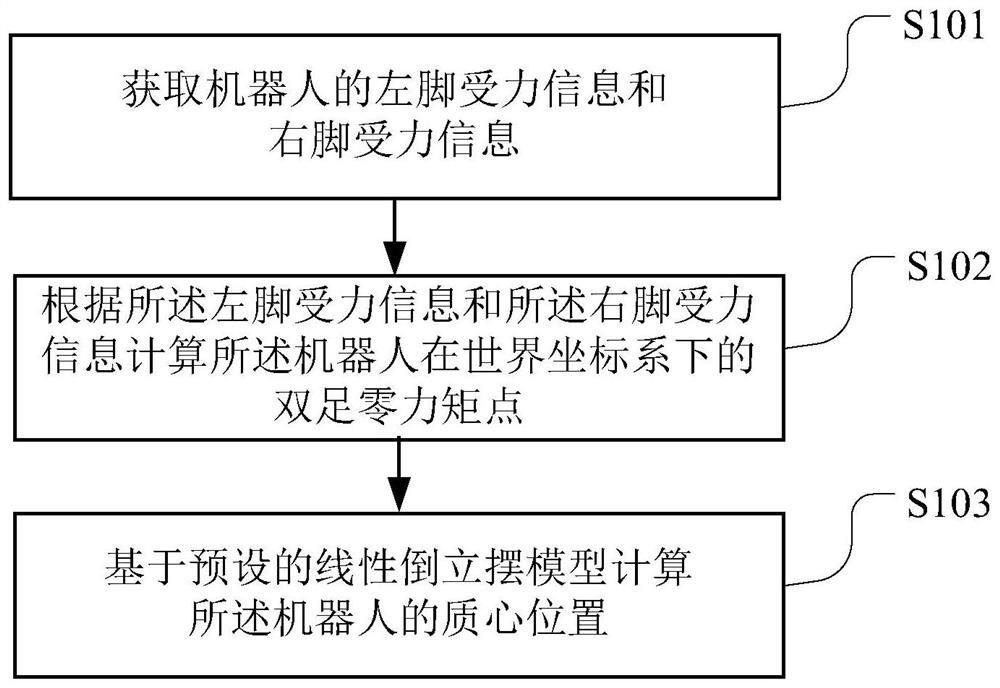
Robot balance control method and device, readable storage medium and robot
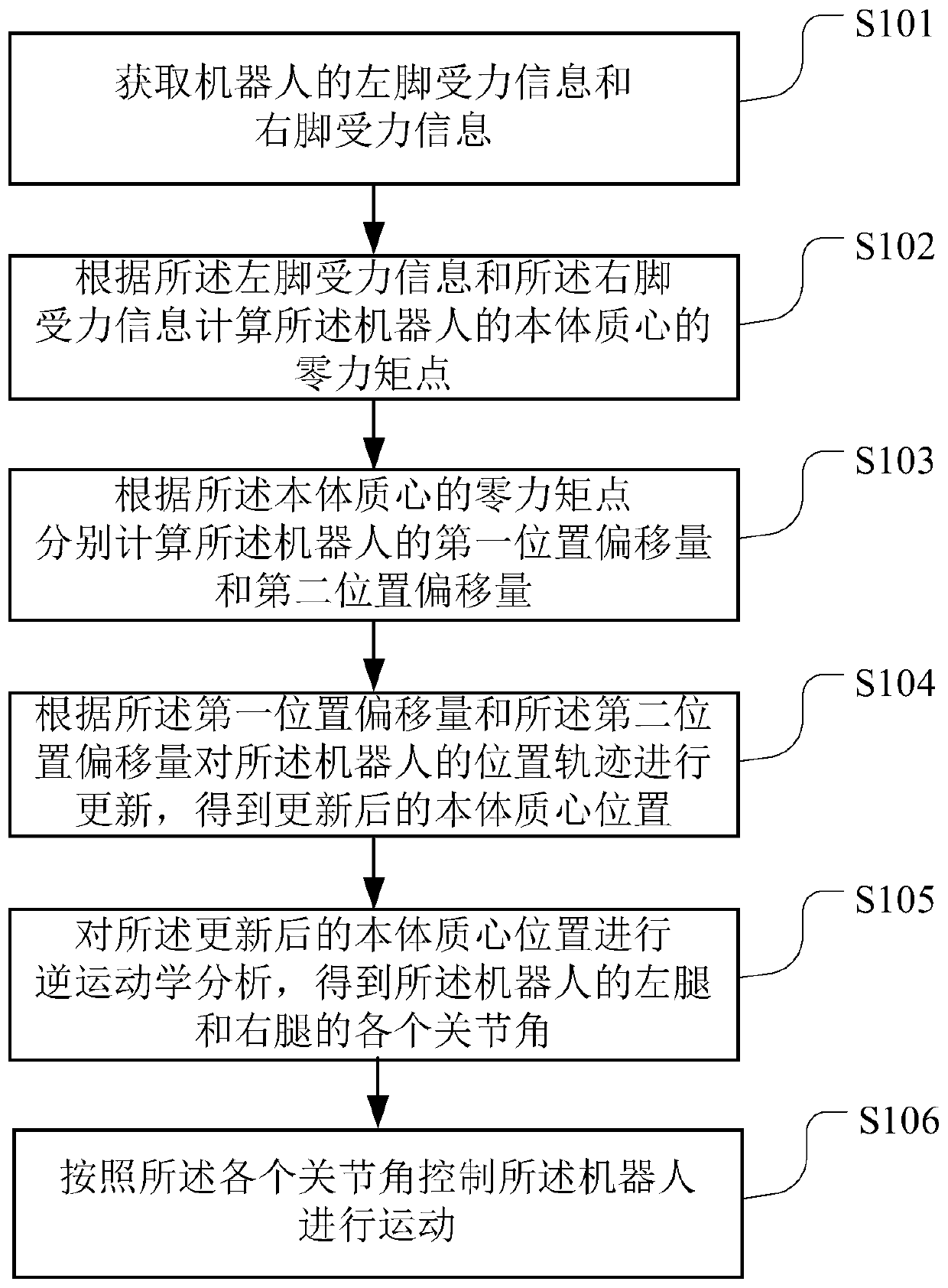
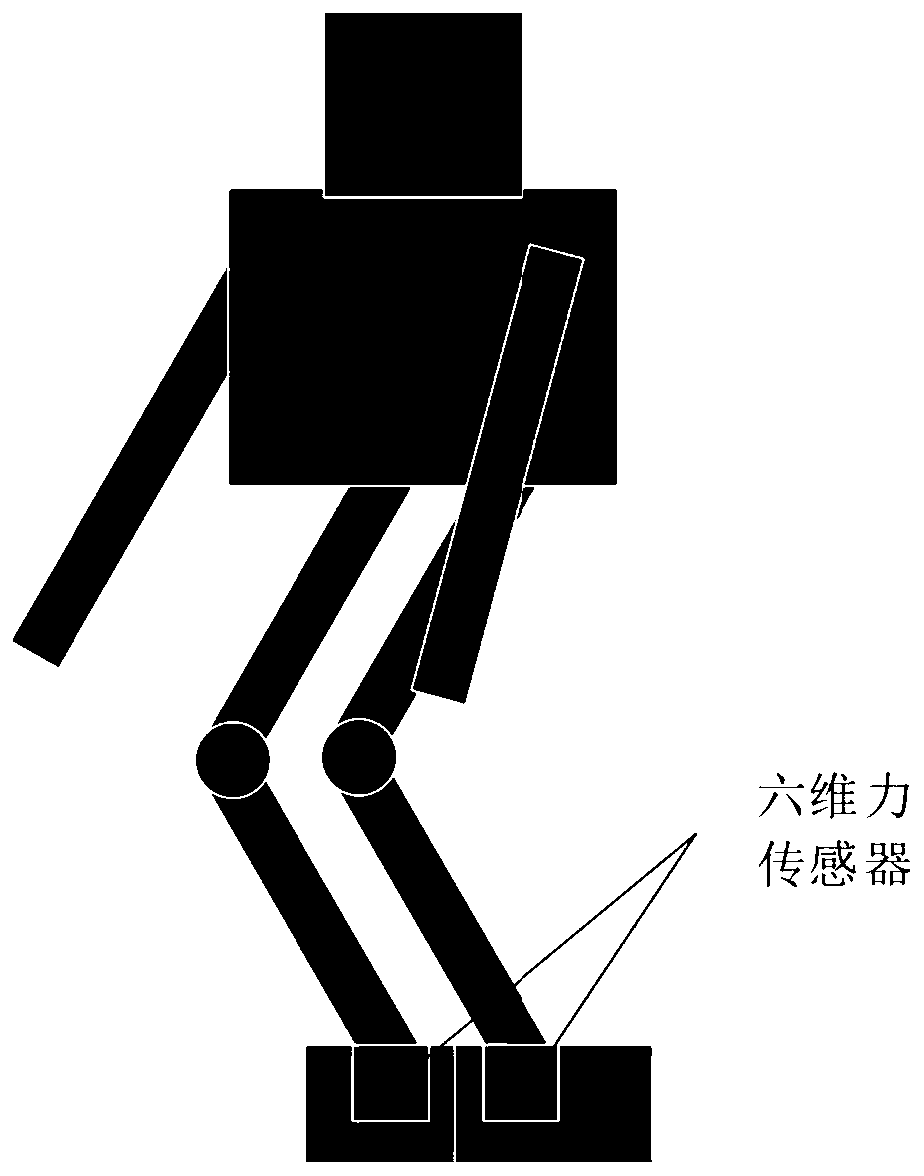
ActiveCN111098300AImprove stabilityPrevent dumpingProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorSimulationControl theory
The application belongs to the technical field of robots, and particularly relates to a robot balance control method and device, a computer readable storage medium and a robot. The method comprises the steps as follows: acquiring left and right foot stress information of the robot; calculating a zero moment point of a body centroid of the robot according to the left and right foot stress information; calculating a first position offset and a second position offset of the robot according to the zero moment point of the body centroid respectively; updating the position track of the robot according to the first position offset and the second position offset to obtain an updated body centroid position; performing inverse kinematics analysis on the updated body centroid position to obtain eachjoint angle of the left leg and the right leg of the robot; and controlling the robot to move according to each joint angle. Stability of the robot in the bending process is improved, and toppling isavoided.
Owner:UBTECH ROBOTICS CORP LTD
Method of controlling balance of walking robot
InactiveUS20130173054A1Maintain stabilityEnsure walking stabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorAttitude controlEngineeringZ-Coordinate
Disclosed herein a method of controlling the balance of a walking robot. In the method, a location and an acceleration of a center of gravity of the walking robot are detected in a three-dimensional (3D) x, y, z coordinate system. A location of a Zero Moment Point (ZMP) on an xy plane is detected using the location of the center of gravity and the acceleration of the center of gravity in x- and y-axis directions. Walking of the walking robot is controlled so that the ZMP is located inside a stable area including a bottom of a foot of the walking robot on the xy plane.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Humanoid robot gait generation method
ActiveCN104656440AFlexible adjustment performanceImprove environmental adaptabilityAdaptive controlStretch reflexEngineering
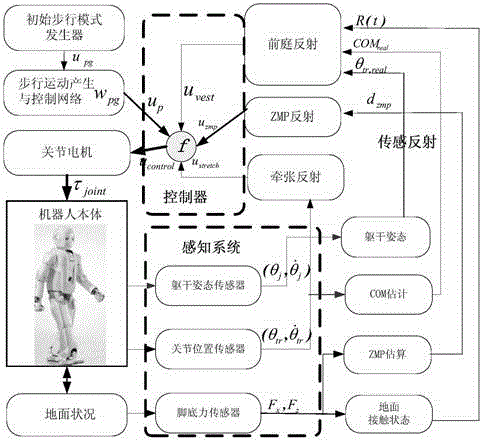
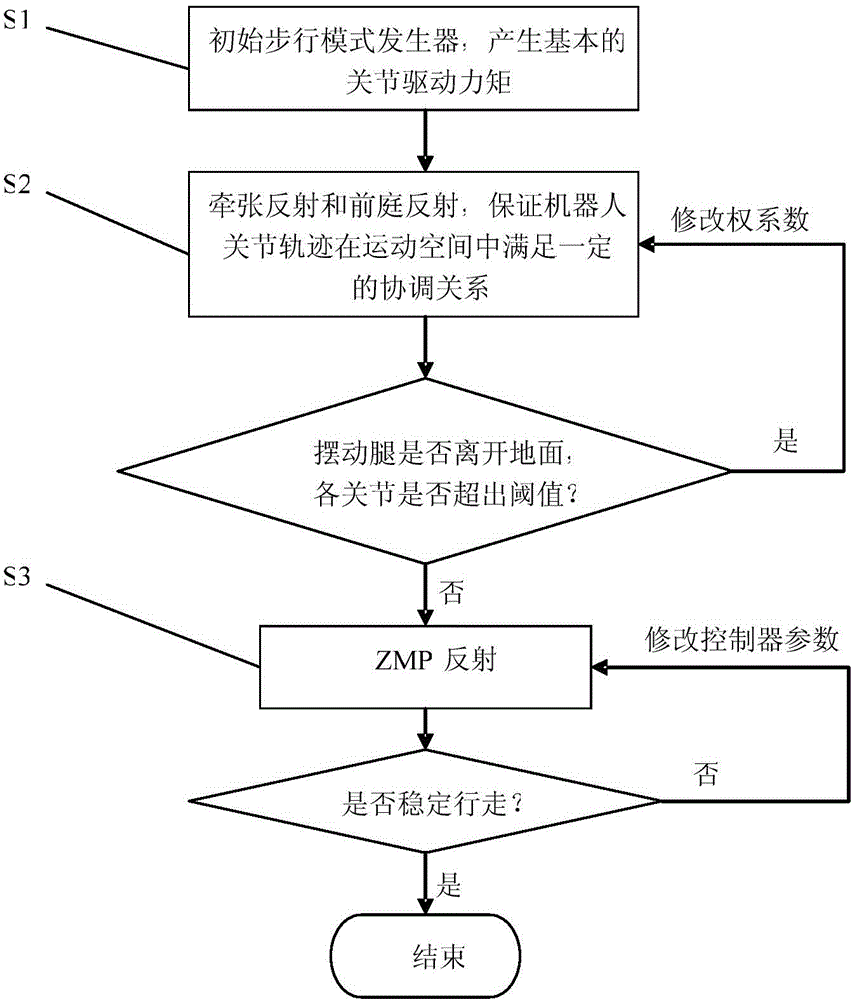
The invention provides a humanoid robot gait generation method. The method comprises the following steps: S1, establishing an initial walking pattern generator by analyzing the driving characteristic of human walking, and generating a joint driving torque up used for realizing basic walking movement; S2, establishing a mathematical model of a stretch reflex and a mathematical model of a vestibular reflex through the partial characteristic of a sensory reflex, overlaying a joint driving torque ustretch generated by the stretch reflex and a joint driving torque uvest generated by the vestibular reflex to the joint driving torque up, and adjusting the joint trajectory of a robot in the movement space by adjusting the joint driving torques ustretch and uvest, so as to ensure that a supporting leg of the robot does not leave the ground and a swinging leg of the robot can reach a right position in the walking process; S3, establishing a ZMP (Zero Moment Point) reflex model, overlaying a joint driving torque uzmp generated by a ZMP reflex to the joint driving torques ustretch, uvest and up, further adjusting the joint trajectory by adjusting the joint driving torque uzmp. Thus, the robot can realize stable walking movement, and the adaptive capacity to environment of movement of the robot is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Humanoid robot walking self-learning control method
ActiveCN108237531ARaise attentionImprove controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorVertical stabilityLinear relationship
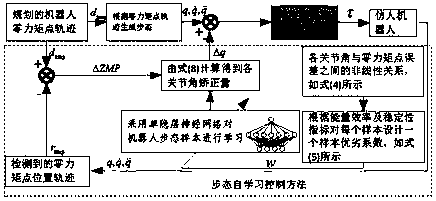
The invention discloses a humanoid robot walking self-learning control method. The method is characterized in that performance evaluation indexes can be made from the energy efficiency, the horizontalstability degree and the vertical stability degree respectively through the self-learning control method; the non-linear relationship between all joint angles and zero moment point errors is obtainedby learning walking samples of a robot; the correction quality of all the joint angles is obtained according to the actual zero moment point error, and stable walking is achieved. In order to improvethe learning effect, a sample excellent-inferior coefficient is distributed to each learning sample according to the energy efficiency margin J<ee>, the horizontal stability margin J<zmp> and the vertical stability margin J<yaw> of walking samples, and the control performance is improved according to the principle that the larger the excellent-inferior coefficient is, and the higher the given attention degree is in the learning process. Through the method, the influence of the robot walking sample quality on the control performance is fully considered. The method has the advantages that the application range is wide, and the energy efficiency is high.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA ZHONGSHAN INST
Robot control method and device, computer readable storage medium and robot
PendingCN112731953AAdapt quicklyImprove stabilityProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorPhysical medicine and rehabilitationSimulation
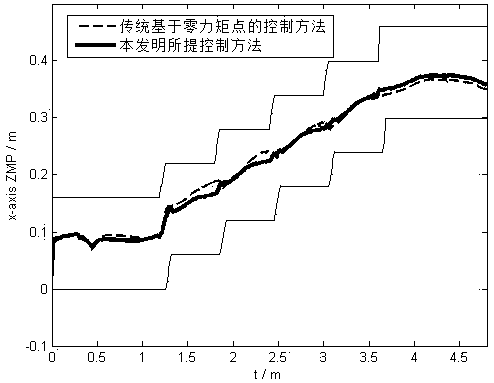
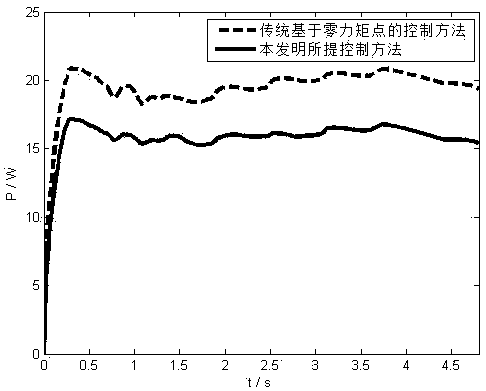
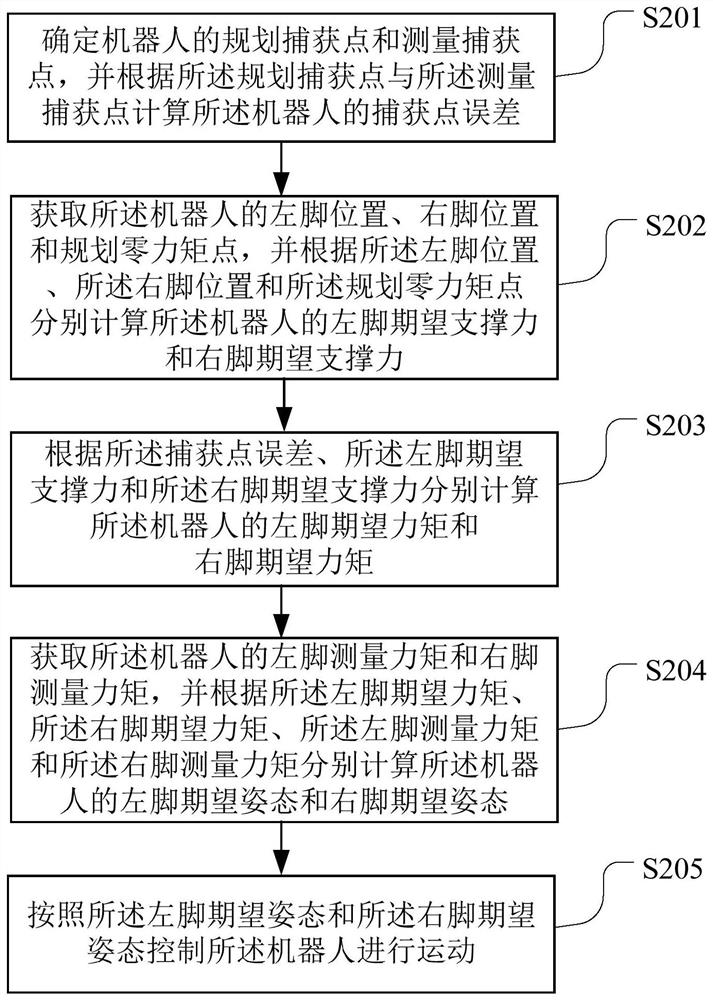
The invention belongs to the technical field of robots, and particularly relates to a robot control method and device, a computer readable storage medium and a robot. The method comprises the following steps of: determining a planned capture point and a measured capture point of a robot, and calculating a capture point error of the robot; acquiring a left foot position, a right foot position and a planned zero moment point of the robot, and respectively calculating an expected left foot supporting force and an expected right foot supporting force of the robot; according to the capture point error, the expected left foot supporting force and the expected right foot supporting force, calculating the expected left foot torque and the expected right foot torque of the robot respectively; acquiring a measured left foot moment and a measured right foot moment of the robot, and respectively calculating an expected left foot posture and an expected right foot posture of the robot; and controlling the robot to move according to the expected left foot posture and the expected right foot posture. According to the invention, the two feet of the robot can quickly adapt to the uneven ground, and good stability can be kept.
Owner:UBTECH ROBOTICS CORP LTD
Robot state estimation method and device, readable storage medium and robot
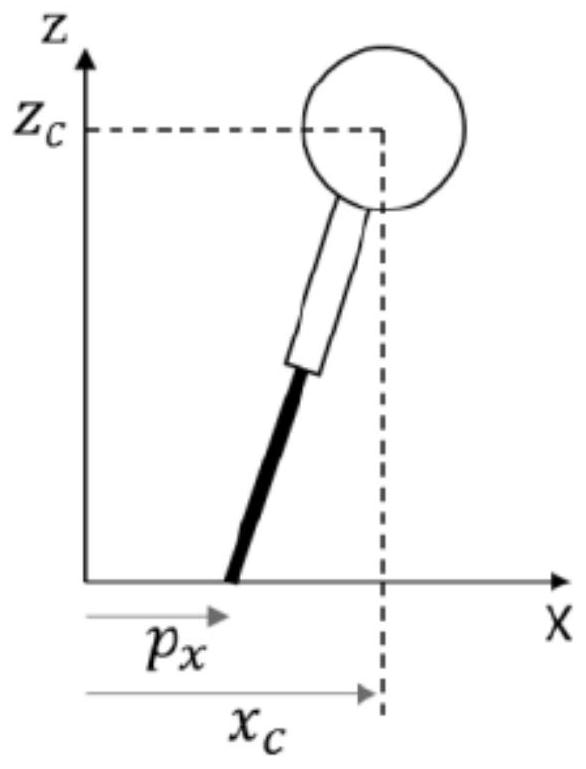
ActiveCN112744313AThe estimate is accurateStatic/dynamic balance measurementVehiclesSimulationControl theory
The invention belongs to the technical field of robots, and particularly relates to a robot state estimation method and device, a computer readable storage medium and a robot. The method comprises the steps: acquiring left foot stress information and right foot stress information of the robot; according to the left foot stress information and the right foot stress information, calculating a double-foot zero moment point of the robot under a world coordinate system; and calculating the mass center position of the robot based on a preset linear inverted pendulum model. According to the method, the brand new linear inverted pendulum model is pre-constructed, the biped zero moment point of the robot is taken as the supporting point of the model, the influence of the position change of the biped zero moment point on the position of the center of mass is fully considered, and a more accurate estimation result can be obtained based on the model.
Owner:UBTECH ROBOTICS CORP LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com