Method and system for controlling apery robot stabilized walking based on effective stable domain
A technology of humanoid robot and stable area, which is applied in the control field of stable walking of humanoid robot based on effective stable area, can solve the problem of not considering robot stability margin, difficult to achieve real-time compensation and correction, and not suitable for robot dynamic walking control, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of simple calculation and stable walking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
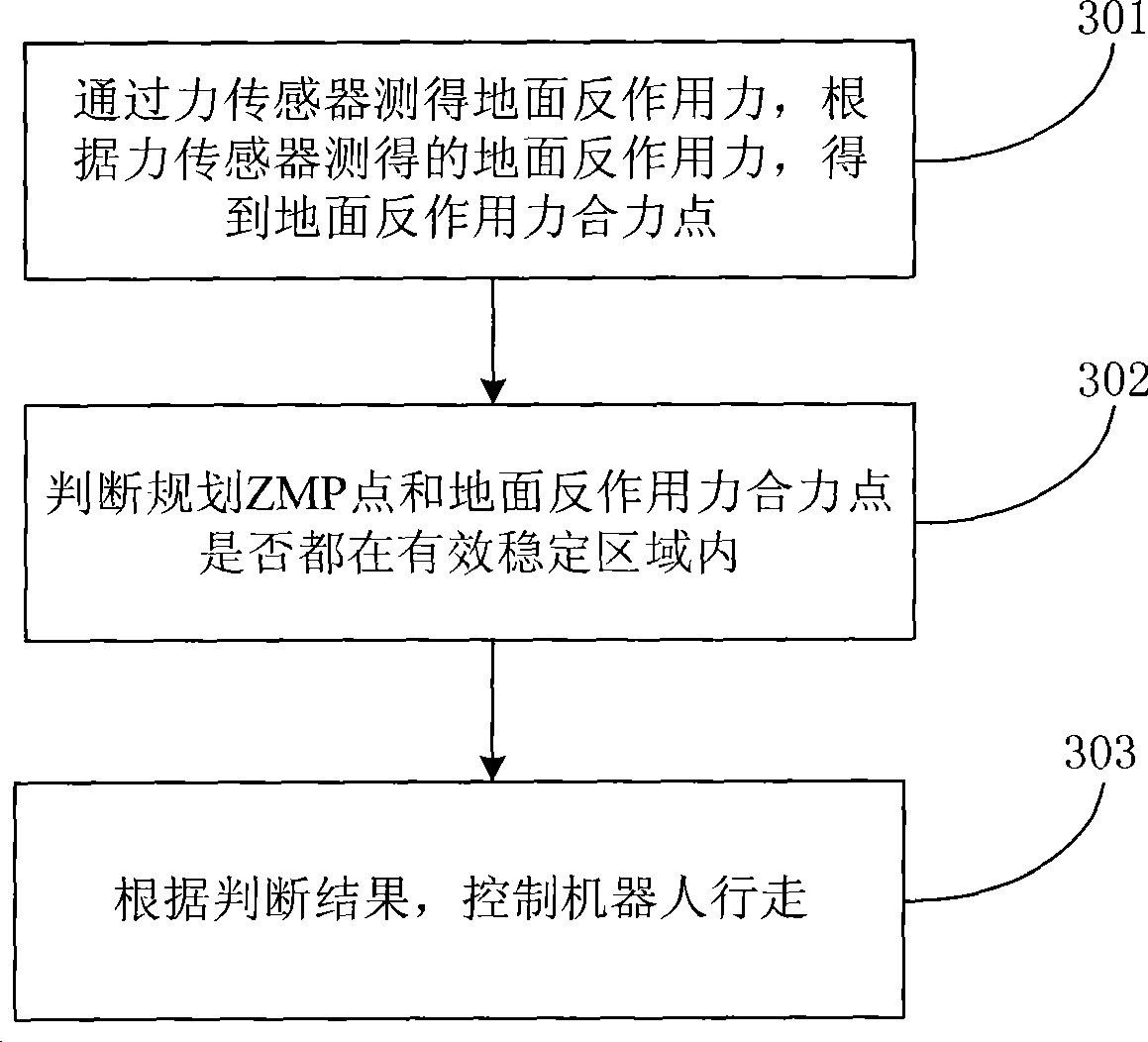
[0038] See image 3 , Is a flow chart of a method for controlling stable walking of a humanoid robot based on an effective stable area provided by an embodiment of the present invention, which is used for real-time correction of the ankle joint angle to ensure stable walking of the robot, which specifically includes:
[0039] 301: The ground reaction force is measured by the force sensor, and the resultant point of the ground reaction force is obtained according to the ground reaction force measured by the force sensor.
[0040] When the robot is stationary or walking, the force sensor can measure the magnitude of the ground reaction force.
[0041]During the robot walking, it can be divided into one-foot support period and two-foot support period. In the one-foot support period, the ground reaction force of one foot is measured by the force sensor of one foot; when it is in the two-foot support period, The ground reaction force of both feet is measured by the force sensors of bot...
Embodiment 2
[0072] See Figure 4 , The embodiment of the present invention provides a control device for stable walking of a humanoid robot based on an effective stable area, and the device specifically includes:
[0073] The force sensor 401 is used to measure the ground reaction force of the robot;
[0074] The processing module 402 is used to obtain the ground reaction force resultant point of the robot according to the ground reaction force measured by the force sensor 401;
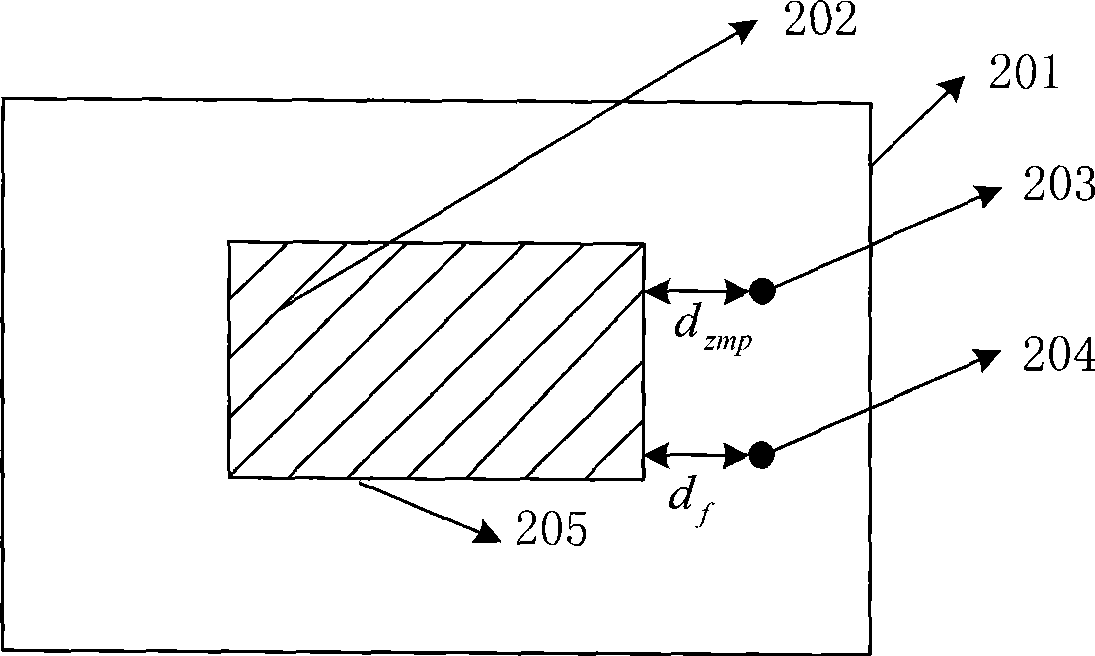
[0075] The judging module 403 is used to judge whether the planned zero moment point and the resultant point of the ground reaction force obtained by the processing module 402 are both within the effective stable area;
[0076] The control module 404 is used to control the robot to walk according to the judgment result of the judgment module 403.
[0077] Among them, the control module 404 specifically includes:
[0078] The processing unit is used to make the robot walk according to the planned dynamic gait when the j...
Embodiment 3
[0087] See Figure 5 , The embodiment of the present invention provides a control system for stable walking of a humanoid robot based on an effective stable area, and the system specifically includes:
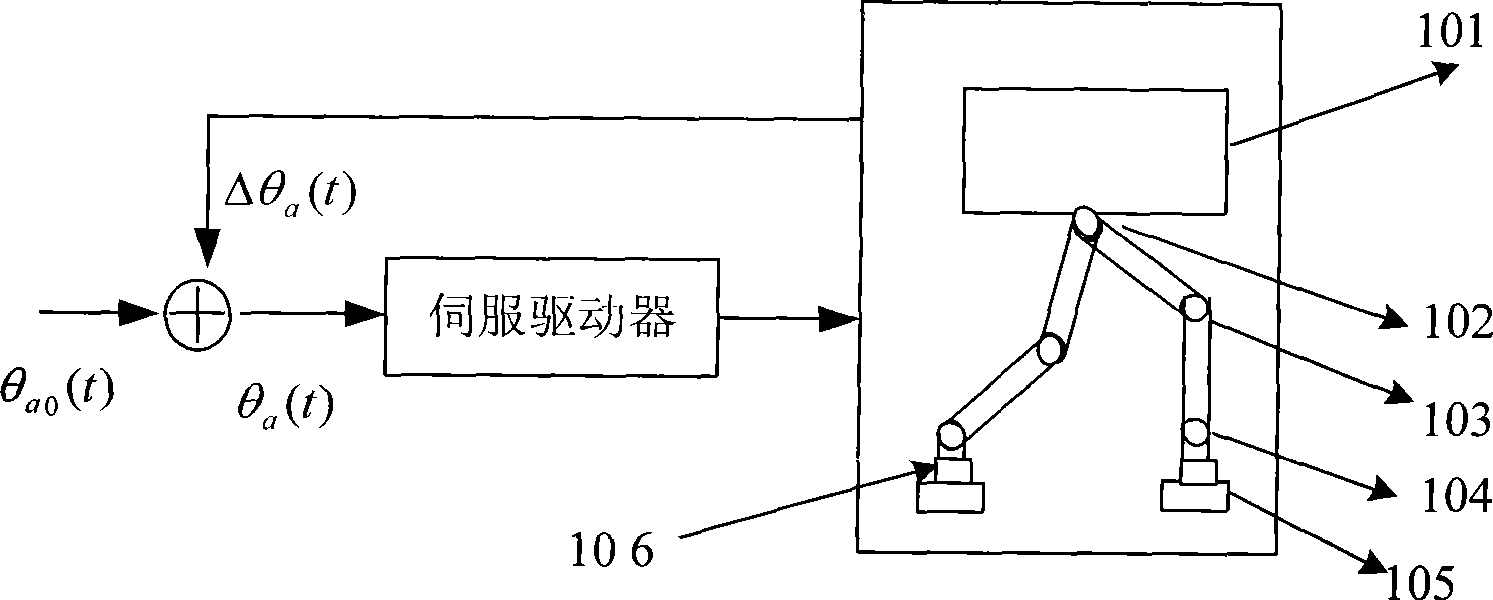
[0088] The feedforward 501 is used to provide the dynamic gait θ of the ankle joint for offline planning of the robot a0 (t);
[0089] The real-time corrector 502 is used to provide a control of the dynamic gait in the feedforward device 501 when the resultant point of the ground reaction force and / or the planned zero-moment point of the robot is not within the effective stable area. a0 (t) Real-time correction amount Δθ of the ankle joint to be corrected a (t);
[0090] When the planned ZMP point is not in the effective stable area, and the resultant point of the ground reaction force is in the effective stable area, the real-time correction amount Δθ a (t) Calculate according to the formula (1) in Example 1;
[0091] When the resultant point of the ground reaction force is not in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com