Lower limb mechanism of biped robot
A bipedal robot and robot technology, applied in the field of robotics, can solve problems such as affecting walking stability, and achieve the effects of solving the limited range of joint motion, fast and stable bipedal walking, and reducing difficulty
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
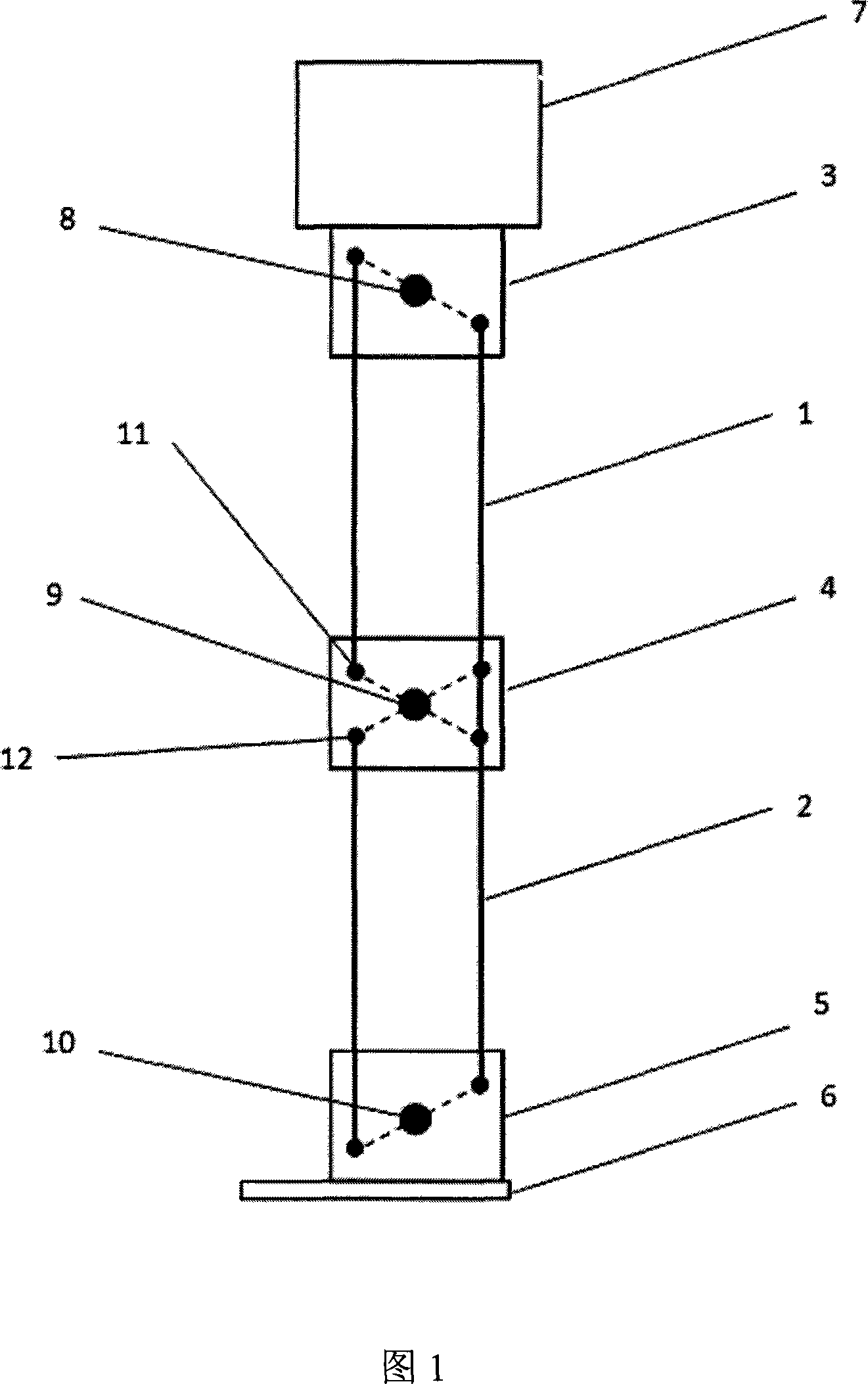
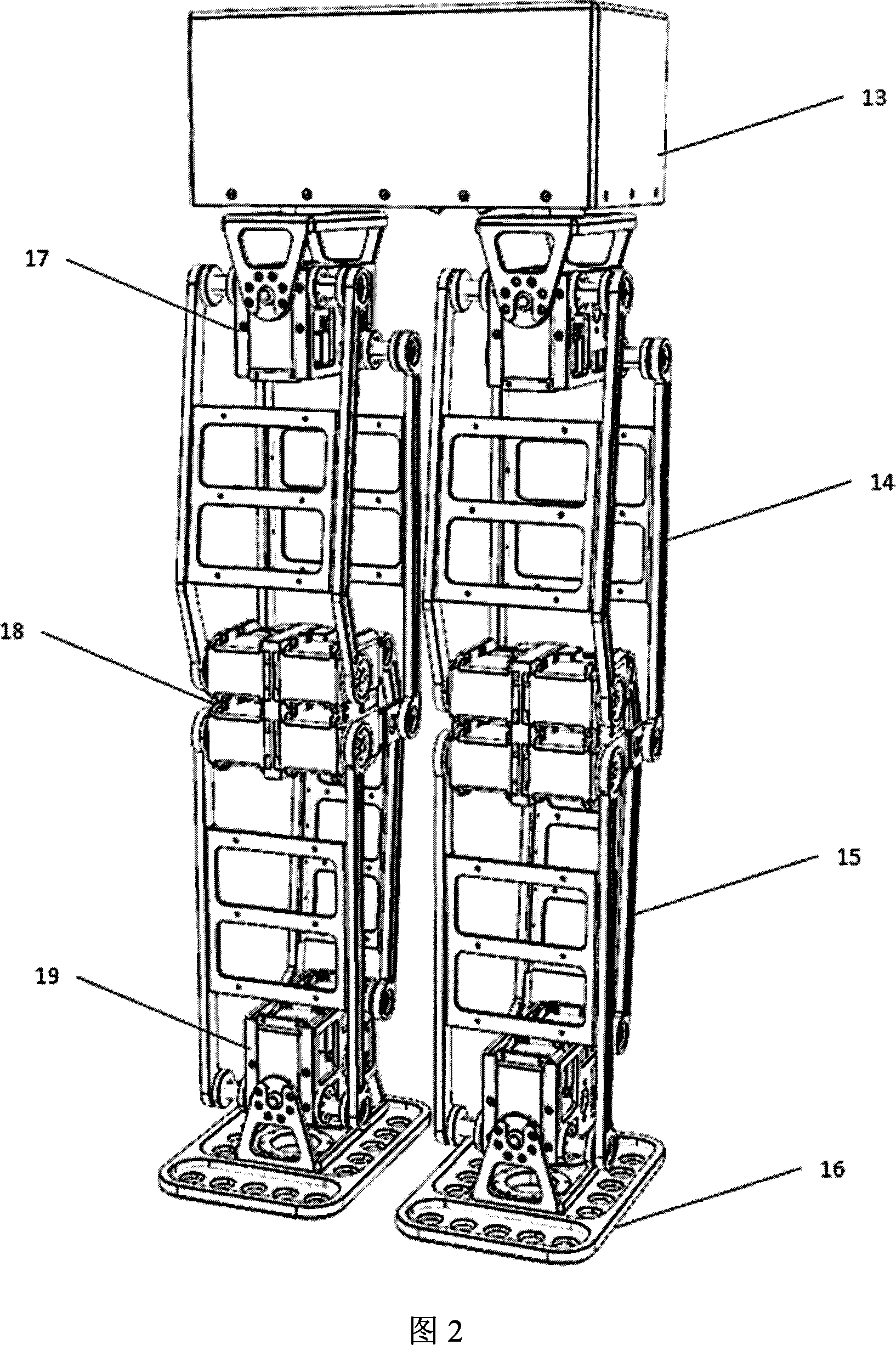
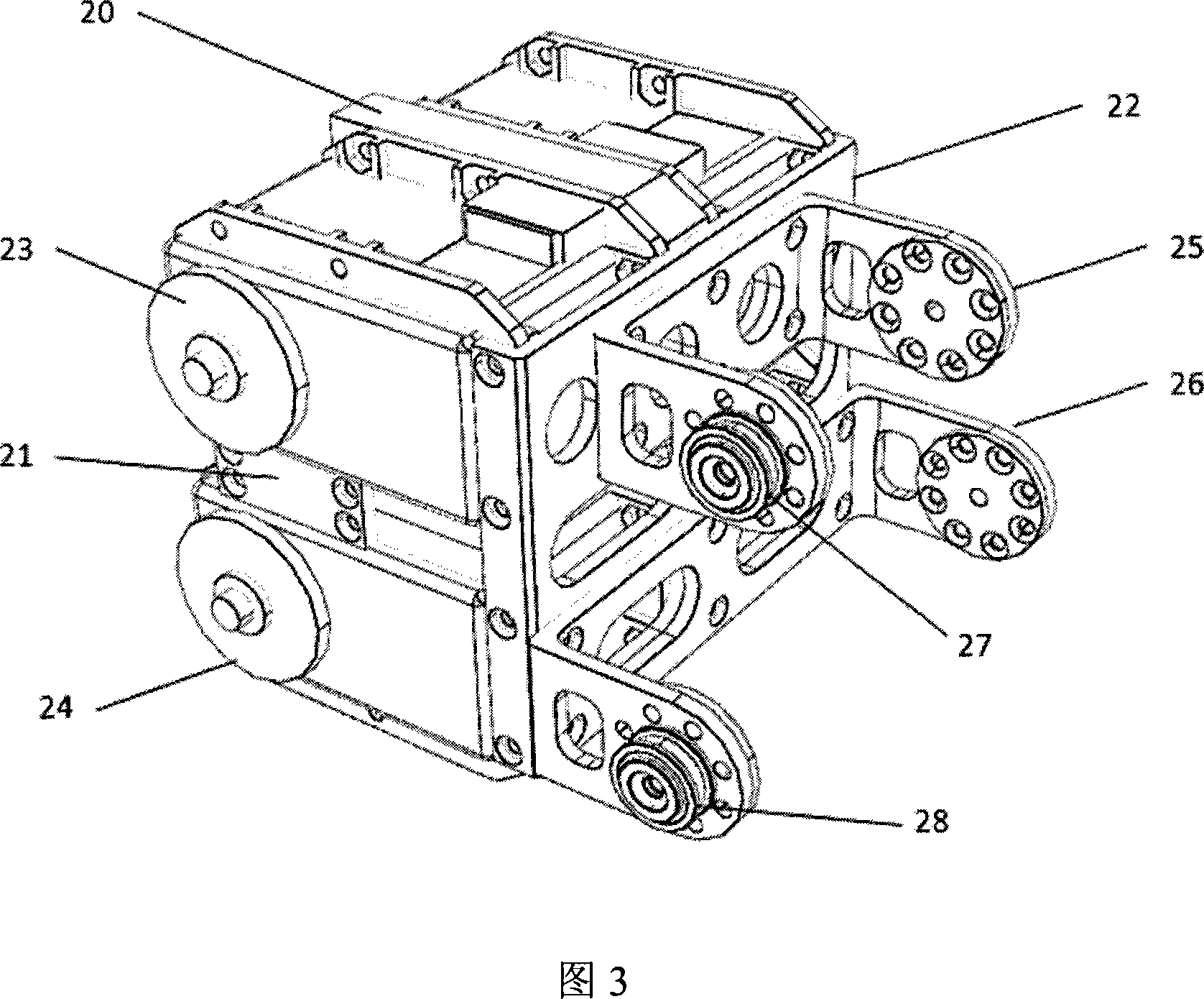
[0019] Fig. 2 is a schematic diagram of the overall mechanism of the biped walking robot of the present invention. The robot can generally be divided into the following parts: torso 13 , thigh 14 , lower leg 15 , foot 16 , hip joint 17 , knee joint 18 , and ankle joint 19 . Wherein the thigh 14 and the lower leg 15 of the robot are respectively formed by a group of parallel four-bar linkages, and the two ends of the four-bar linkage are respectively connected to the hip joint 17, the knee joint 18 and the ankle joint 19 of the robot. The motors driving two groups of parallel four-bar linkages are all located at the knee joint 18, and the rotation points of the linkages located at the hip joint 17 and the ankle joint 19 are all realized by bearings. The overall robot has a total of 10 degrees of freedom, symmetrically distributed on the two legs, each leg has 1 torsion degree of freedom, the drive motor is located inside the trunk 13, 2 forward swing degrees of freedom, the dri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com