Method for predicting surface roughness in single-point diamond turning
A single-point diamond and surface roughness technology, which is applied in metal processing, stone processing equipment, stone processing tools, etc., can solve the problems of large errors in surface roughness prediction methods and achieve the effect of improving prediction accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0023] Specific implementation mode one: as Figure 1-10 As shown, the establishment steps of a single-point diamond turning surface roughness prediction method described in this embodiment are as follows:
[0024] Step 1. Select a typical workpiece material to be tested, design an experimental plan by changing the feed speed, spindle speed and back cutting amount, and conduct a pre-single-point diamond cutting experiment on an ultra-precision machine tool;
[0025] Step 2, using a stylus profiler to predict the surface profile curve of a typical workpiece to be measured;
[0026] Step 3, extracting the amplitude information of the relative vibration between the tool and the workpiece during the machining process from the detection results of the processed surface, the amplitude information of the relative vibration between the tool and the workpiece is obtained by the following method:
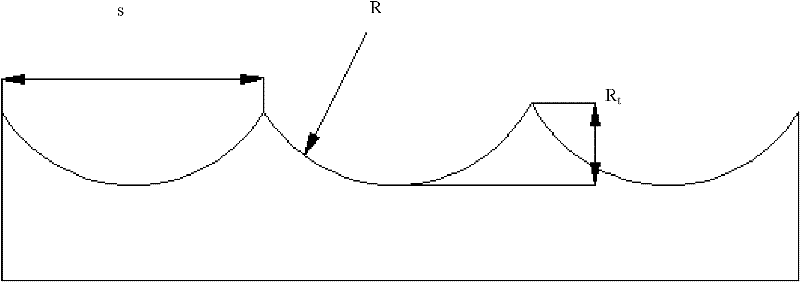
[0027] Step 3 (1), according to the detected surface contour curve and data, establish t...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0036] Under the condition that the rotation speed is 1000r / min, the back cutting amount is 2μm, and the feed speed is 25mm / min, for NiP, the relative vibration amplitude information is extracted 5nm, for Cu, to extract relative vibration amplitude information 15nm, through Calculation of equivalent relative vibration;
[0037] Such as Figure 5-7 As shown, the expansion ratio SP is calculated. Under this processing condition, the expansion ratio SP of NiP is 1.3, and the expansion ratio SP of Cu is 0.65. Calculate the contour curve of the processed surface after the expansion effect occurs;
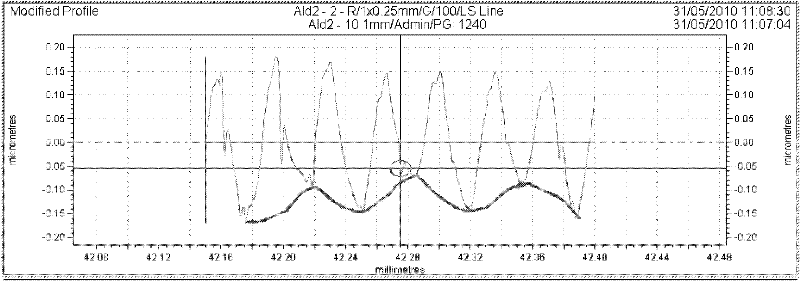
[0038] Using matlab software, the contour curve of the machined surface after the expansion effect occurs and the equivalent relative vibration are superimposed and the data is processed and calculated to obtain the predicted results. The comparison between the predicted results and the actual results is as follows Figure 8 and Figure 9 ;
[0039] Such as Figure 8-9 As shown,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com