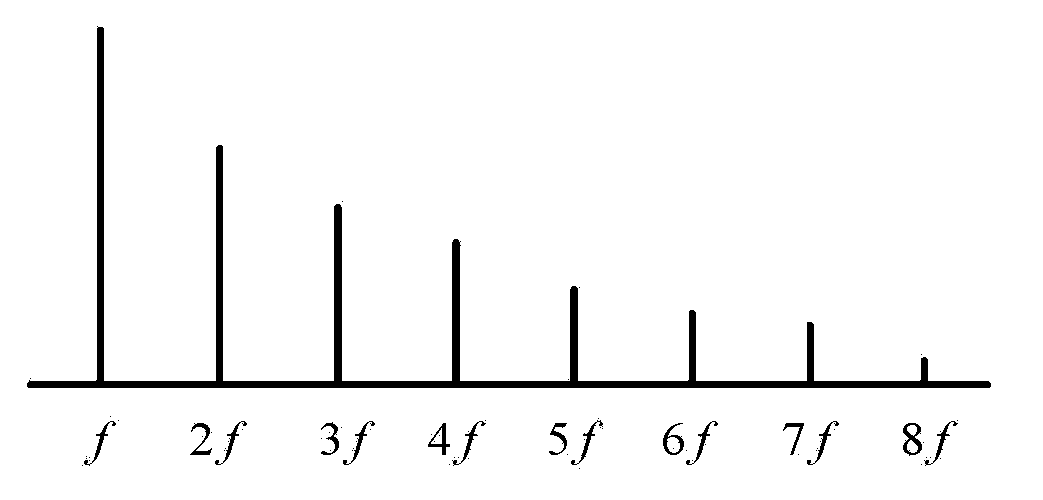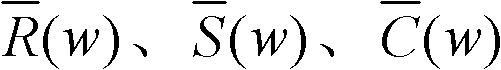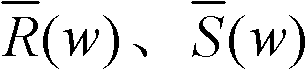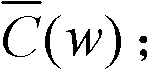Patents
Literature
331 results about "Single tone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
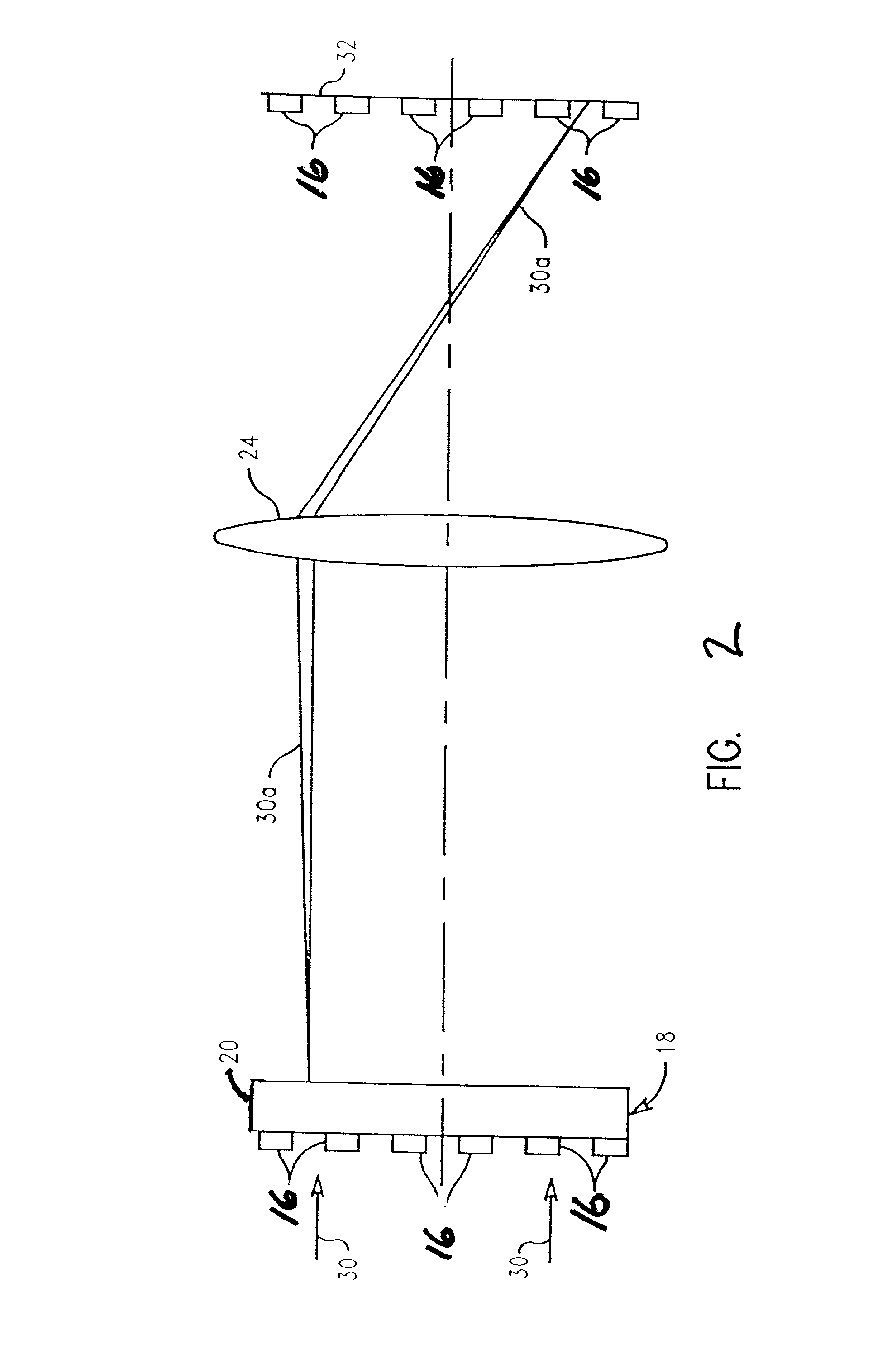
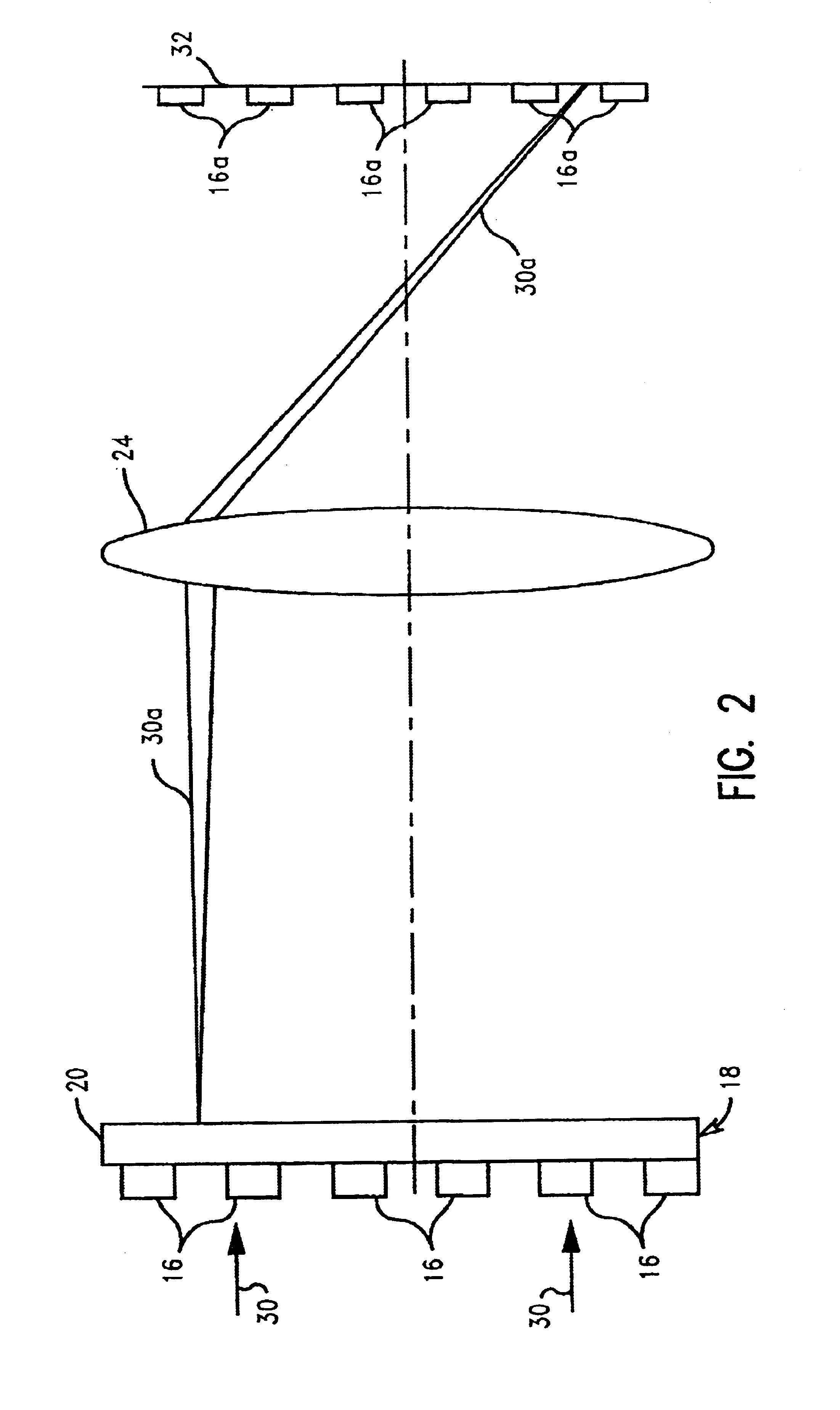
Communications system, methods and apparatus
ActiveUS20060285481A1Benefit in transmitted powerIncrease transmit powerEnergy efficient ICTError prevention/detection by using return channelCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
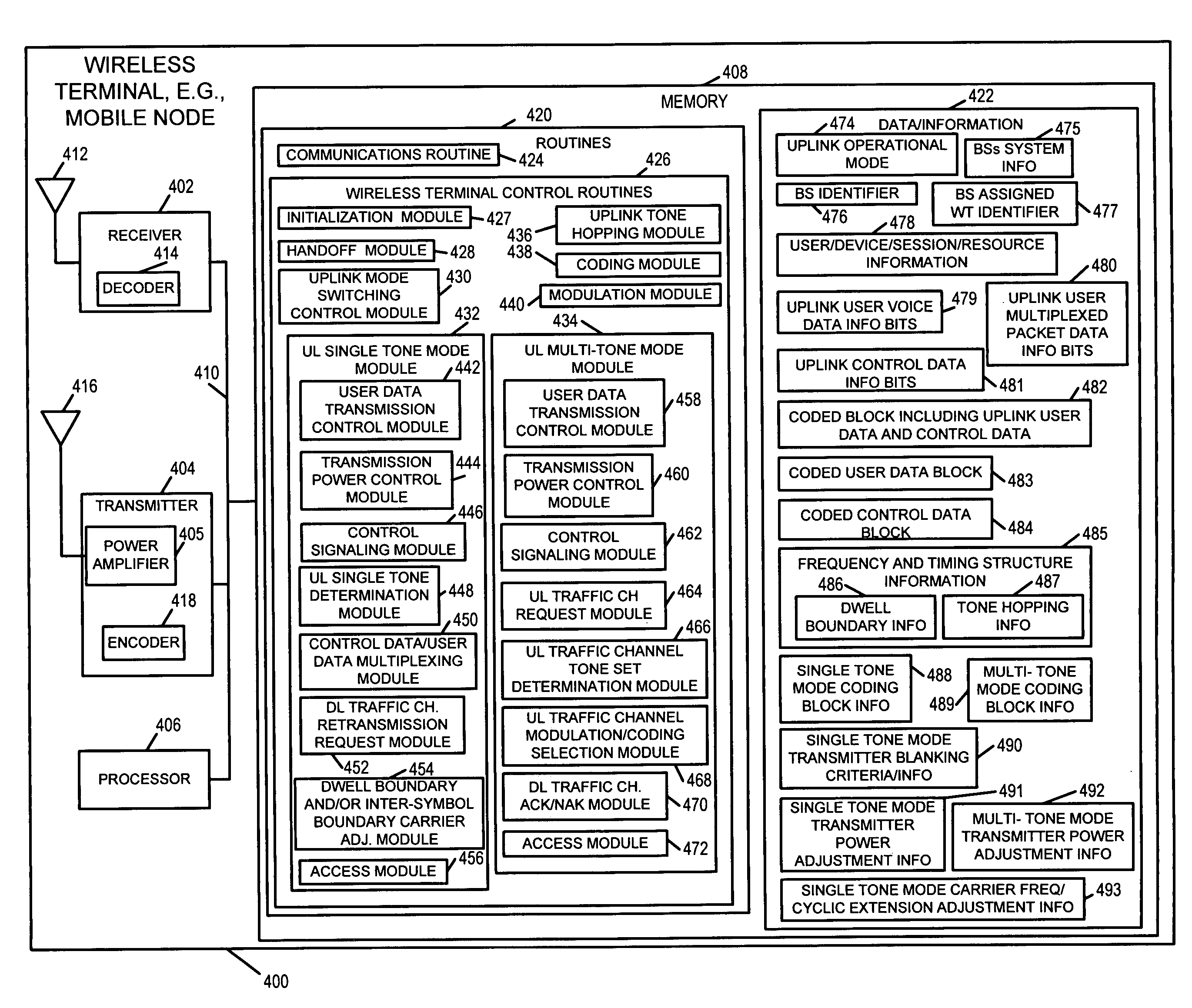
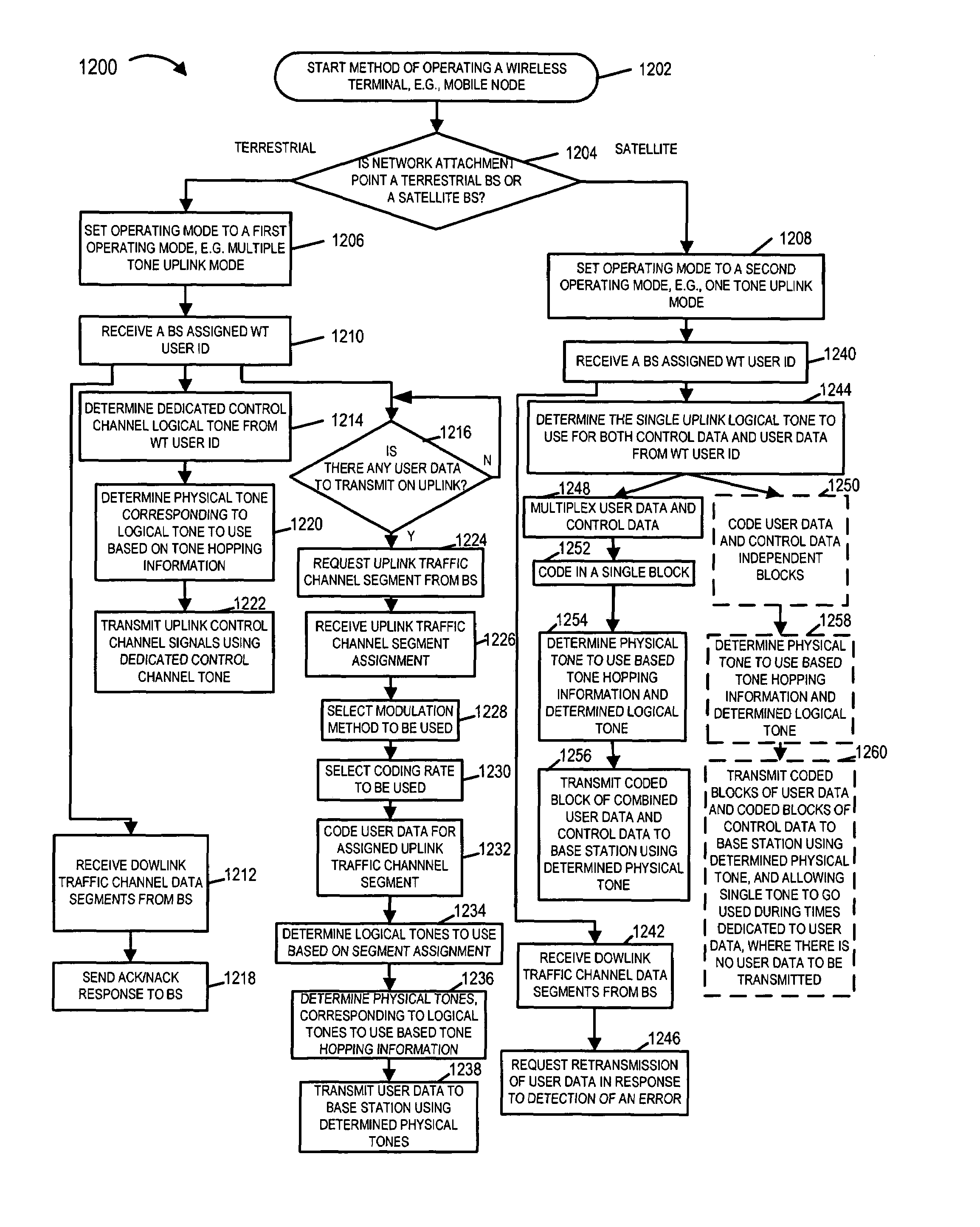
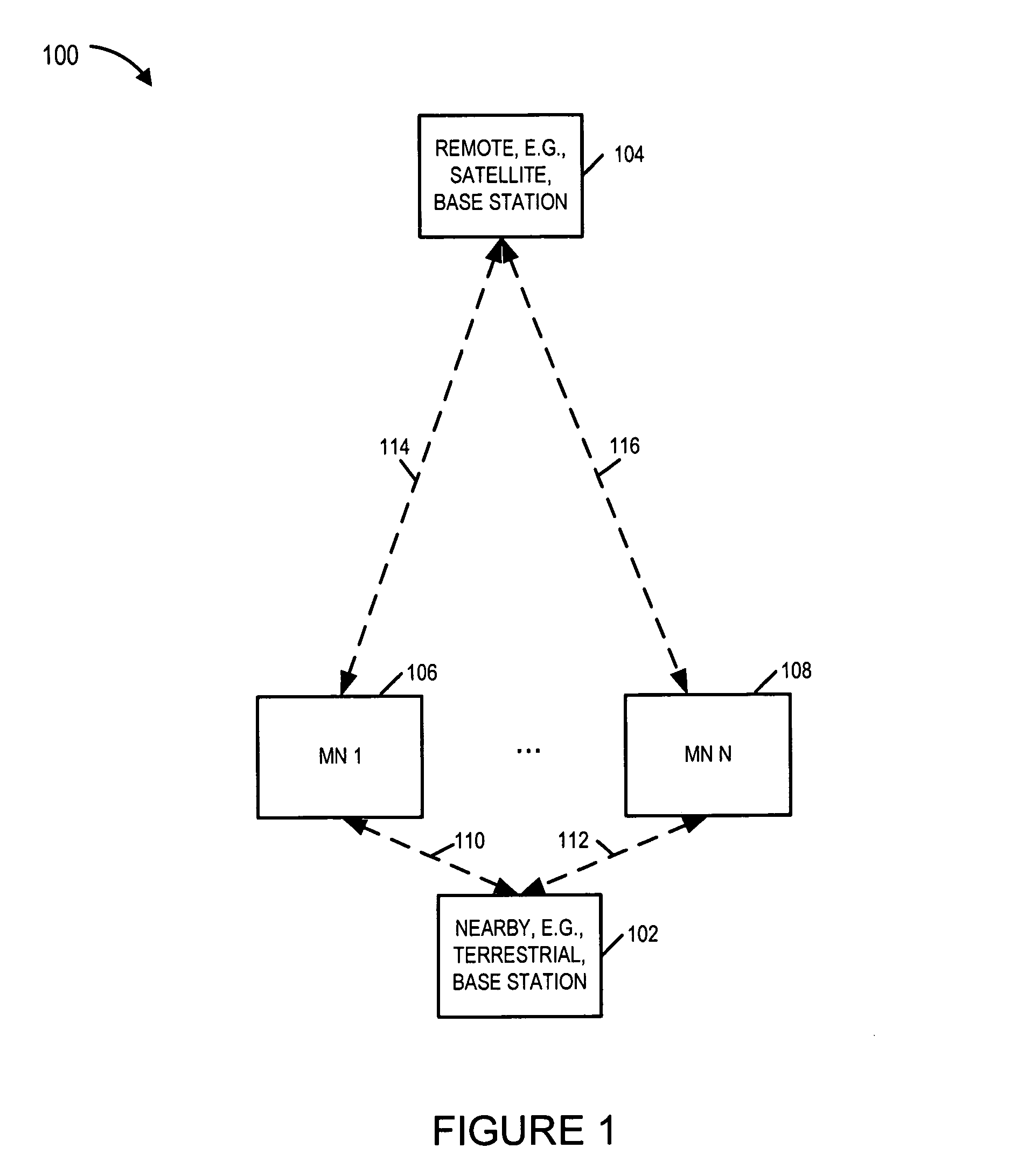
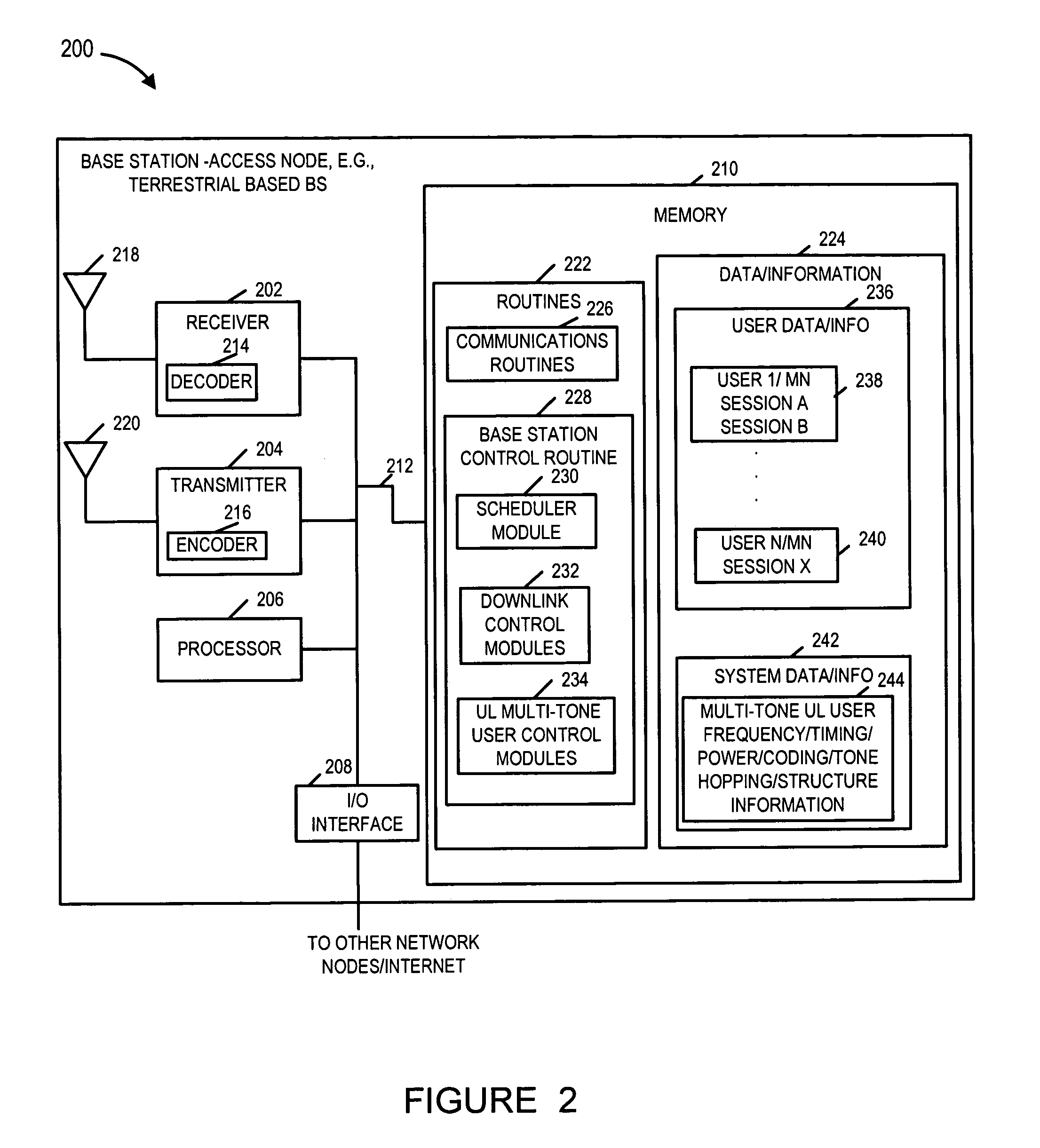
An OFDM wireless communications system includes terrestrial and satellite based base stations. Mobile nodes support two uplink modes of operation, multi-tone mode for terrestrial station interaction and single tone mode for satellite base station interaction. In single tone mode the peak to average power ratio is lower than in the multi-tone mode allowing the same power amplifier to transmit higher average power signals and thus extend range and reach a satellite in geostationary orbit. In multi-tone mode, the mobile node: is temporarily assigned a multi-tone uplink traffic channel segment for user data, is assigned a dedicated control channel for uplink control signals, and supports slaved Ack / Nak for traffic channels. In single tone mode, the mobile node: is assigned a single logical uplink dedicated tone to use for transmitting both user data and control data, and does not use a slaved Ack / Nak mechanism for traffic channels.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Tonal precoding
ActiveUS20060274825A1Mitigate and remove interference signalReduce removalDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationQ-matrixPrecoding
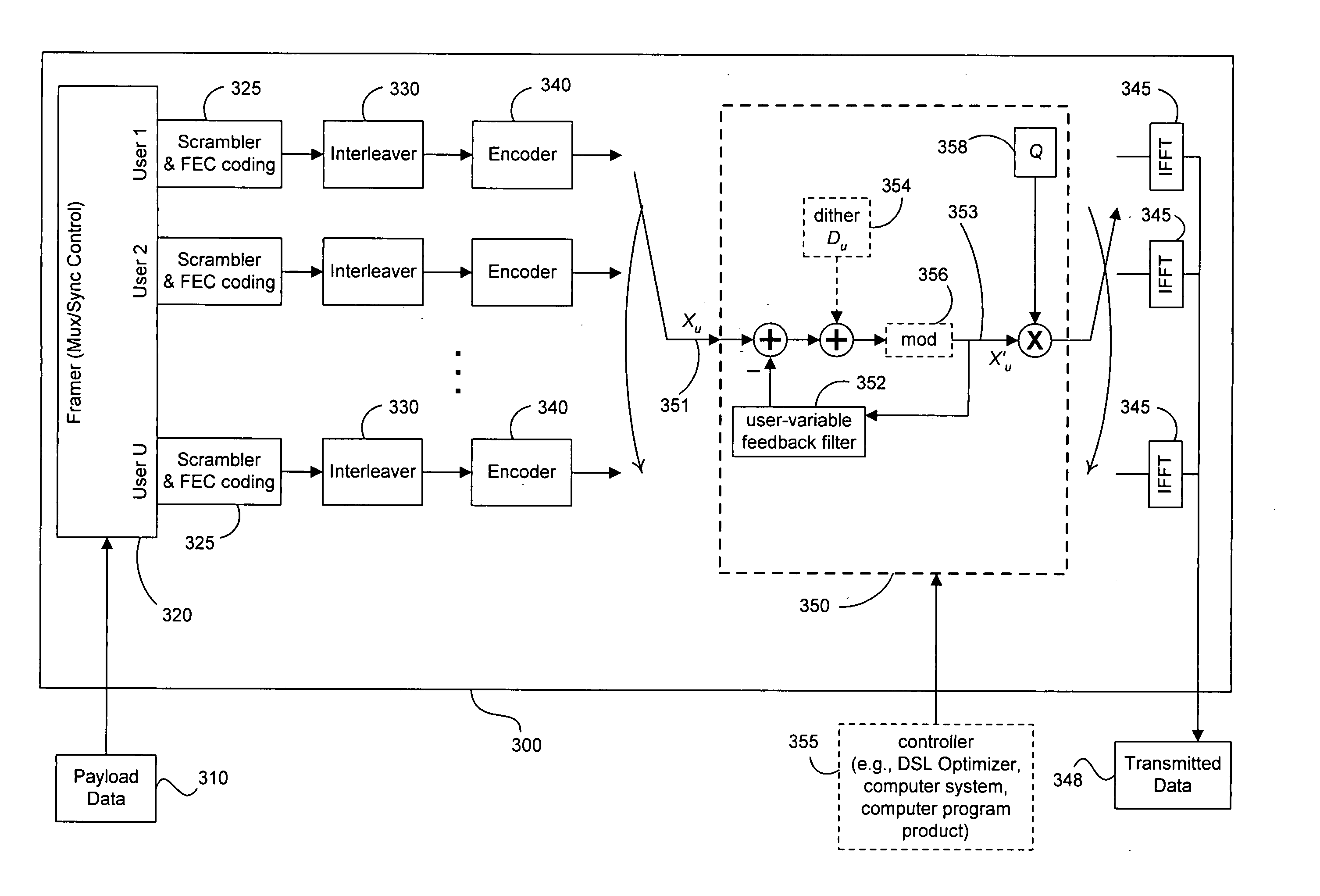
Precoding mitigates or removes interference signals (especially crosstalk) among multiple users with interconnected transmitters in vectored DSL systems and the like. Efficient implementation is provided of the R matrix in RQ factorization that characterizes multi-user downstream vector channels (such as DMT VDSL one-sided or two-sided transmission channels). A set of precoder coefficients can vary with each tone used by each user and depend upon the encoding order of users selected for each tone. In adaptive operation, the coefficients of the R and Q matrices can be updated when changes occur to the transmission environment. Variable modulo arithmetic mitigates the power-enhancement problem, and the base of modular arithmetic also can vary with each user within a single precoder for a single tone. The user order of preceding need not be the same on each tone, and the modular arithmetic progression may thus also be different on each tone because multi-user situations create an unusual situation for precoding in that the modulo arithmetic used for each user can be different (thus imposing a larger power increase) and because digital duplexed or synchronized DMT systems can separately implement a precoder for each tone. Further, the precoding process terminates each DMT symbol, after processing up to the total number of users. An optional dither signal, known to both transmitter and receiver, can be added at the transmit side and removed at the receiver side to smooth the precoding process and ensure that aberrations in the transmitted constellation size and characteristics are consistent despite any unusual variations in the feedback signal that exits the feedback filter matrix G before being subtracted from the user signal of interest. Some embodiments use a “subtraction only” mode while other embodiments use a dither signal and / or modulo arithmetic, though embodiments of the present invention do not require use of identical constellations by both transmitter and receiver.
Owner:ADAPTIVE SPECTRUM & SIGNAL
Method for transmitting dmrs in wireless communication system supporting nb-iot and apparatus therefor
ActiveUS20190036746A1MinimizeReduce Inter-Cell InterferenceError preventionMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsCommunications systemDemodulation
The present specification relates to a method for transmitting, by a terminal, a demodulation reference signal (DMRS) in a wireless communication system supporting narrow-band (NB)-Internet of things (IOT), the method comprising: generating, for single tone transmission, a reference signal sequence to be used for demodulation; mapping the reference signal sequence to a plurality of symbols; and transmitting, in the plurality of symbols, the demodulation reference signal to a base station by using a single tone, wherein phase rotation is applied to each of the plurality of symbols.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method and apparatus for waveform generation
InactiveUS7650080B2Less filteringWide bandwidthCode division multiplexOptical multiplexPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
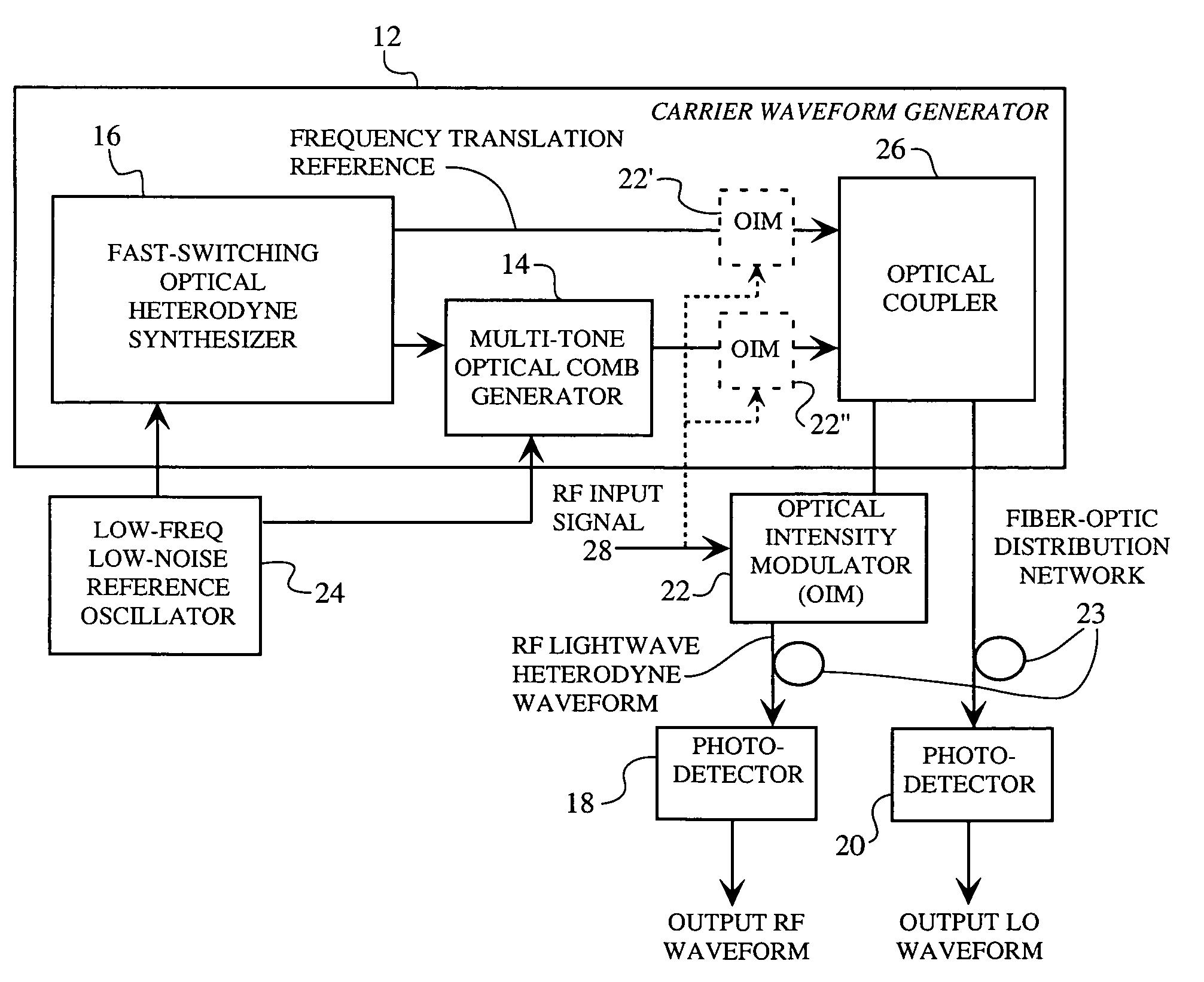
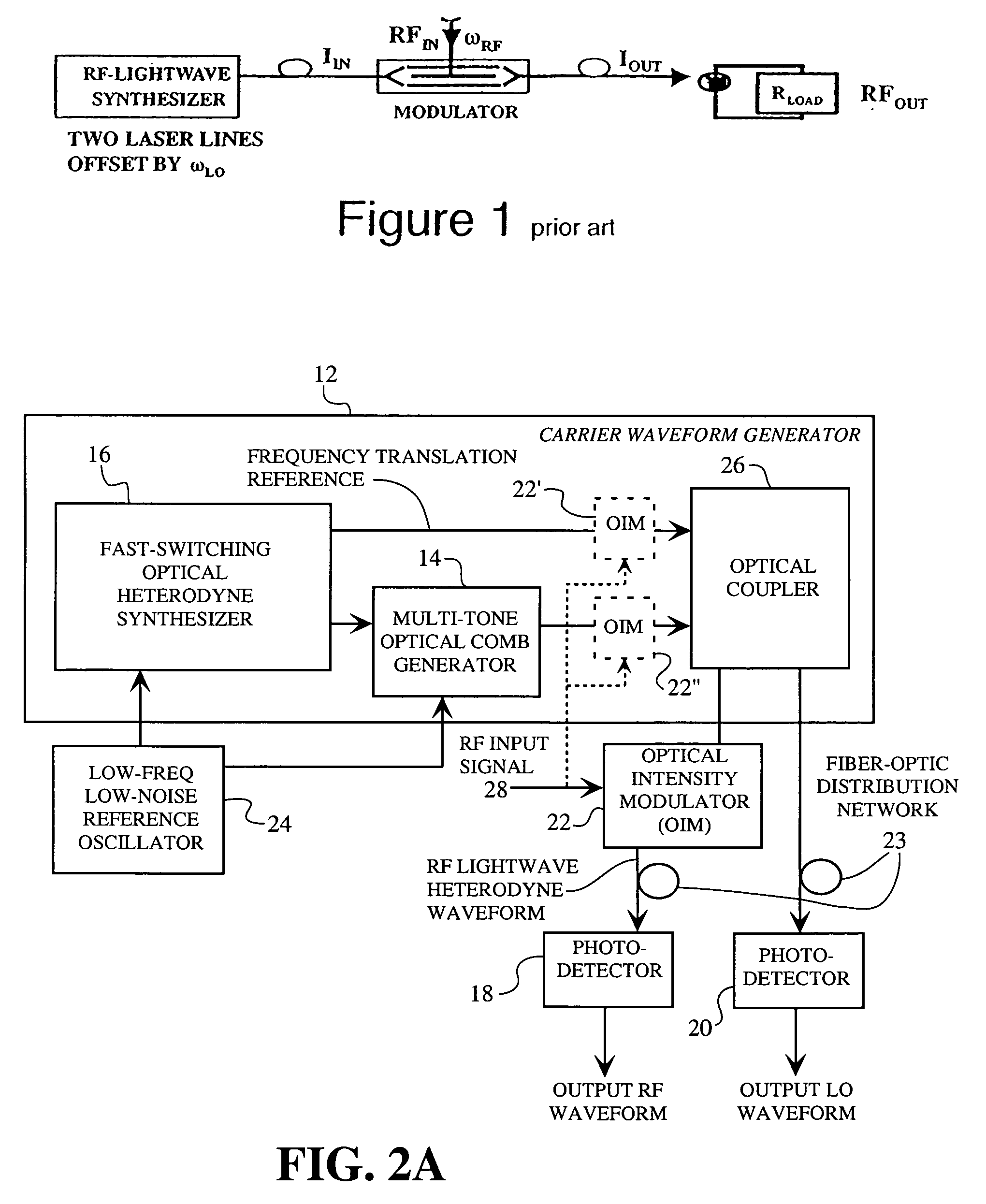
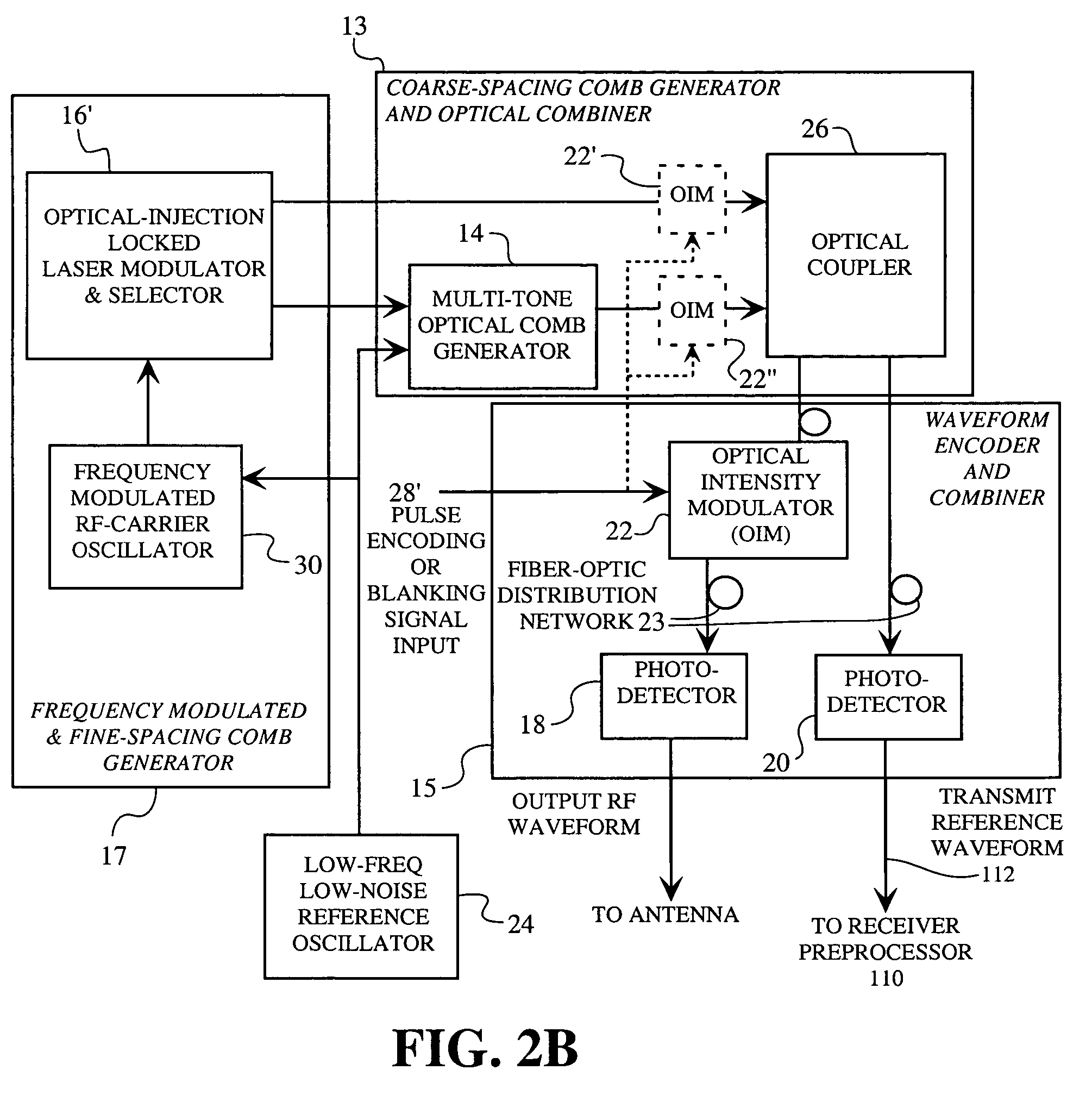
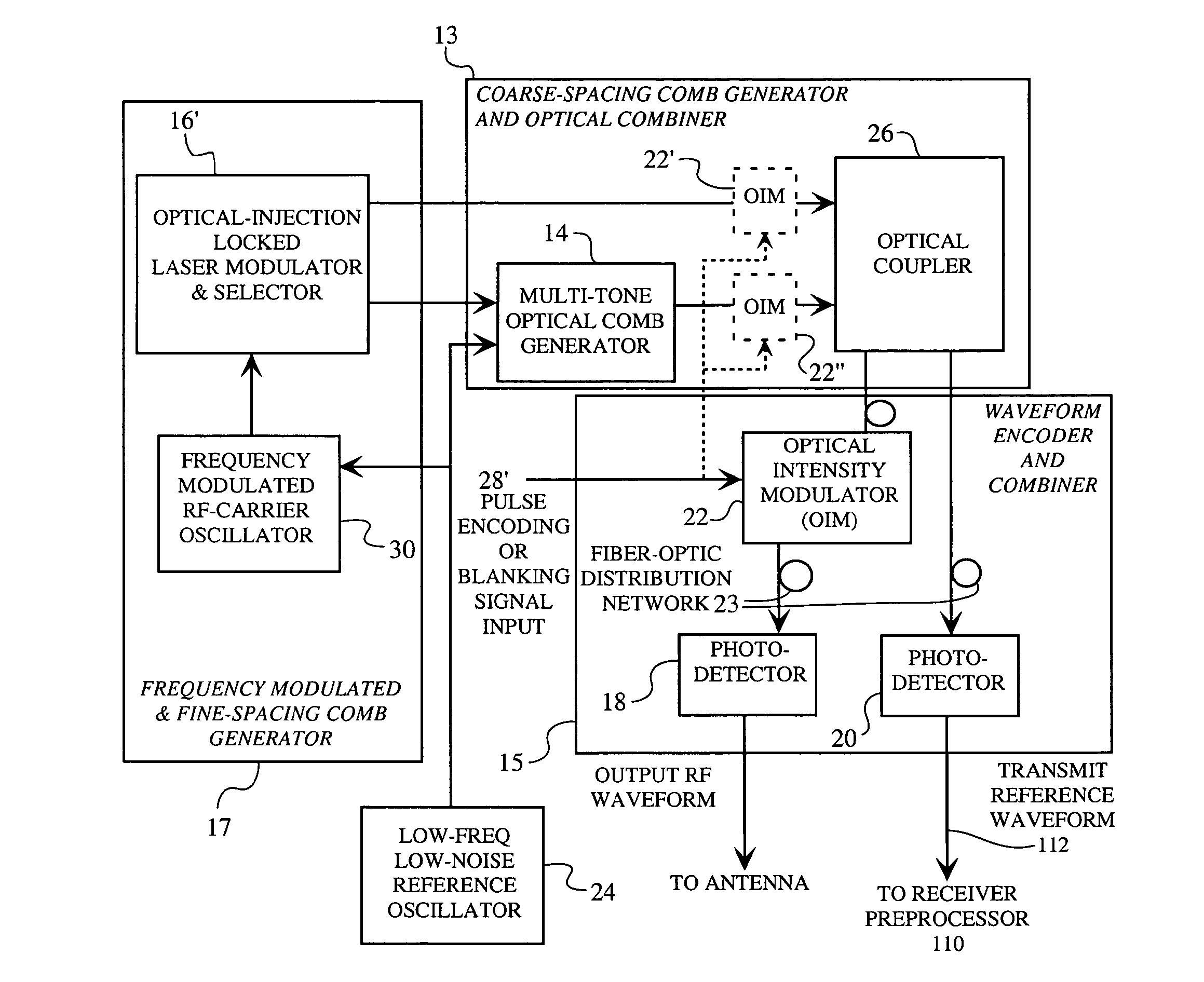
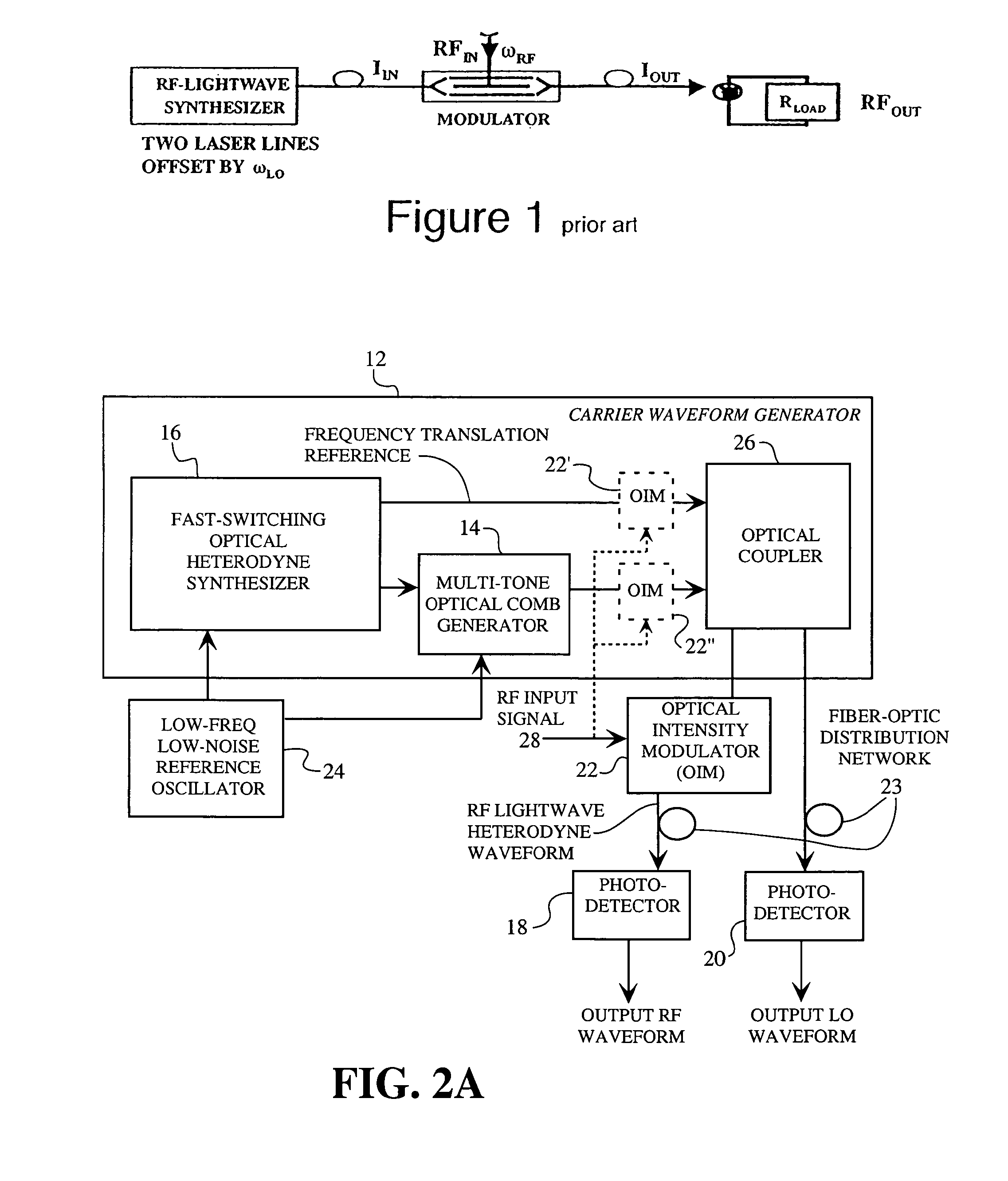
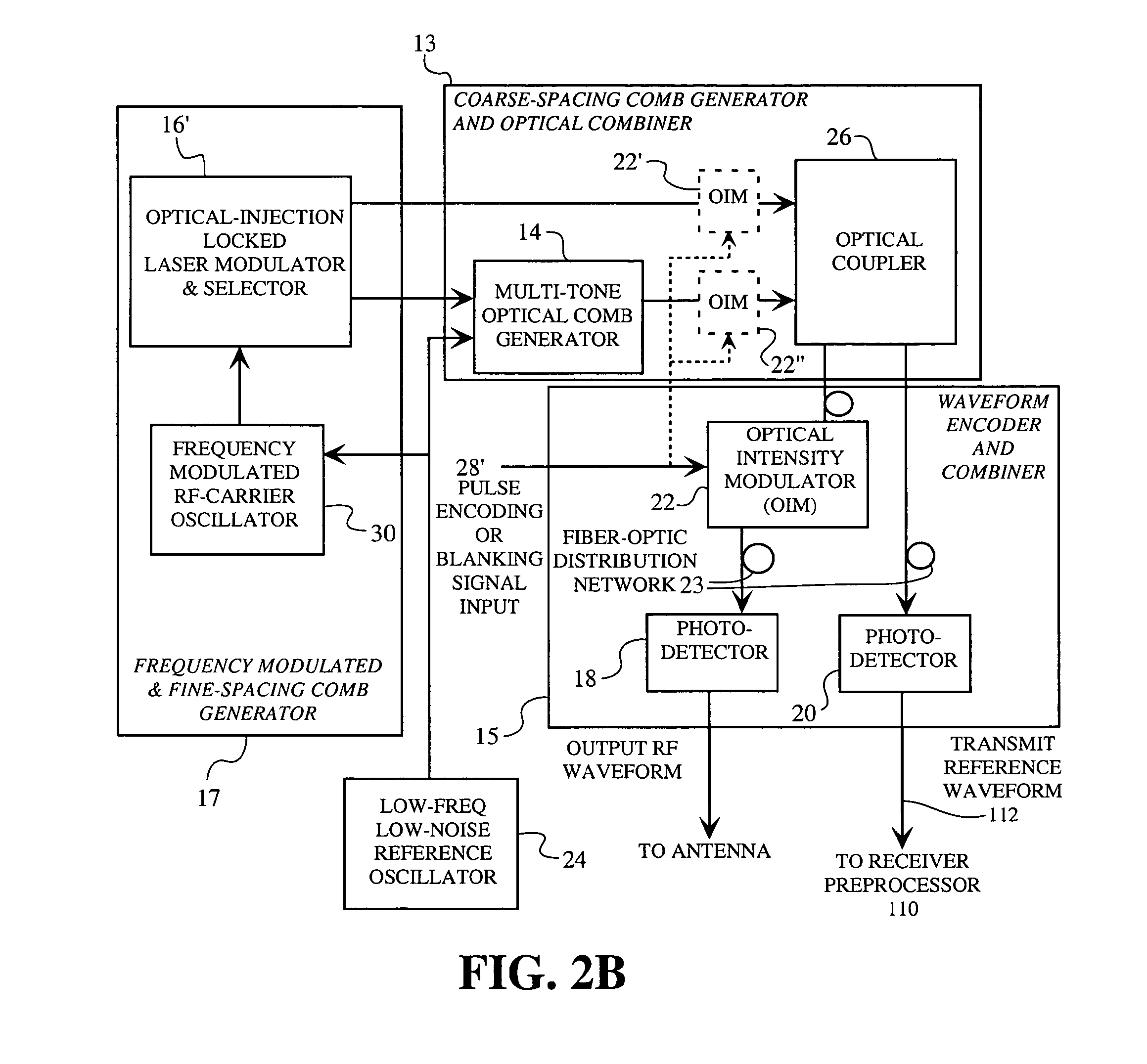
A spread spectrum waveform generator has a photonic oscillator and an optical heterodyne synthesizer. The photonic oscillator is a multi-tone optical comb generator for generating a series of RF comb lines on an optical carrier. The optical heterodyne synthesizer includes first and second phase-locked lasers, where the first laser feeds the multi-tone optical comb generator and the second laser is a single tone laser whose output light provides a frequency translation reference. At least one photodetector is provided for heterodyning the frequency translation reference with the optical output of the photonic oscillator to generate a spread spectrum waveform. A receiver pre-processor may be provided to operate on the spread spectrum waveform.
Owner:HRL LAB
Communications system, methods and apparatus
ActiveUS7403470B2Increase data rateLow powerEnergy efficient ICTError prevention/detection by using return channelCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
An OFDM wireless communications system includes terrestrial and satellite based base stations. Mobile nodes support two uplink modes of operation, multi-tone mode for terrestrial station interaction and single tone mode for satellite base station interaction. In single tone mode the peak to average power ratio is lower than in the multi-tone mode allowing the same power amplifier to transmit higher average power signals and thus extend range and reach a satellite in geostationary orbit. In multi-tone mode, the mobile node: is temporarily assigned a multi-tone uplink traffic channel segment for user data, is assigned a dedicated control channel for uplink control signals, and supports slaved Ack / Nak for traffic channels. In single tone mode, the mobile node: is assigned a single logical uplink dedicated tone to use for transmitting both user data and control data, and does not use a slaved Ack / Nak mechanism for traffic channels.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method for transmitting uplink signal in a wireleess communication system and apparatus for the same
ActiveUS20170171865A1Avoiding inter-cell interferenceAvoid interferenceTransmission path multiple useWireless communicationMultiplexingCommunications system
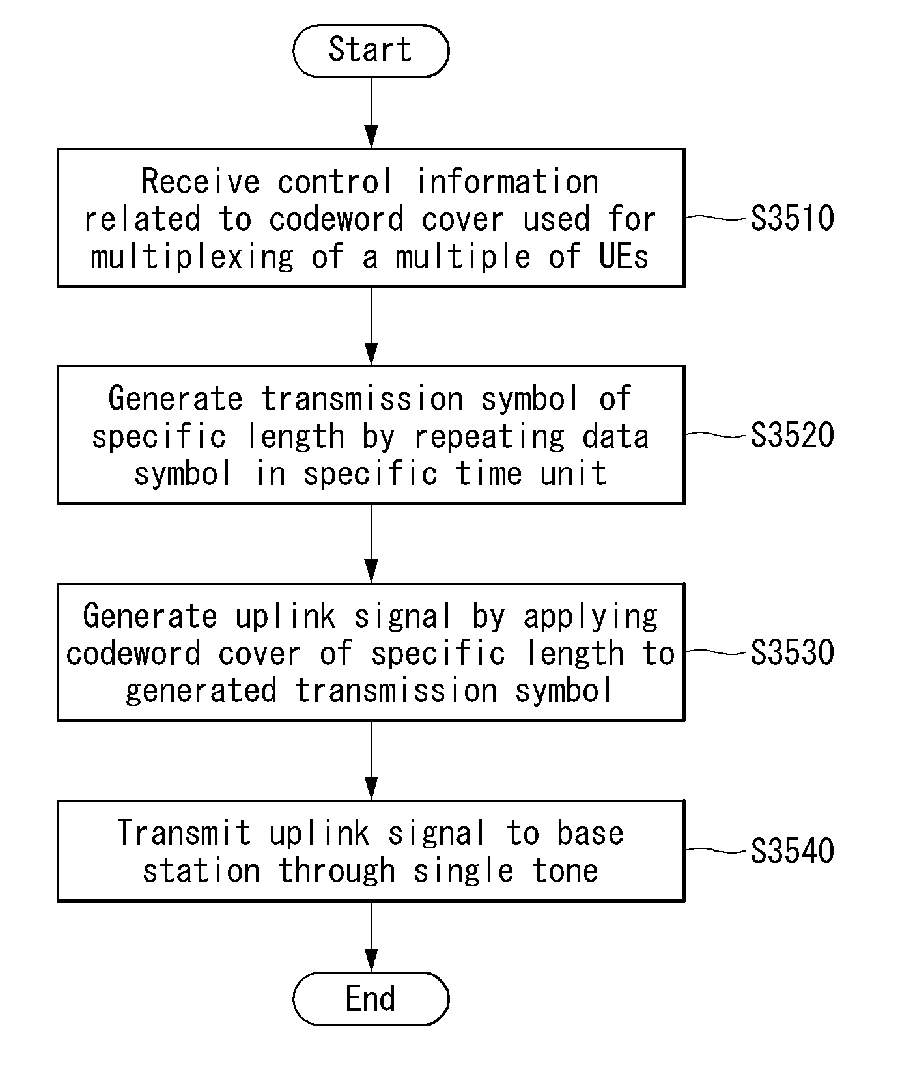
Provided are a method of transmitting, by a user equipment, a uplink signal in a wireless communication system. The method includes receiving control information related to a codeword cover used for a multiplexing of a multiple of user equipments from a base station, generating a transmission symbol of a specific length by repeating a data symbol in a specific time unit, generating the uplink signal by applying the codeword cover of the specific length to the generated transmission symbol, and transmitting the generated uplink signal to the base station through a single tone.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method and apparatus for I/Q mismatch calibration in a receiver
InactiveUS20050047536A1Reduce central frequencyError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionEngineeringCenter frequency
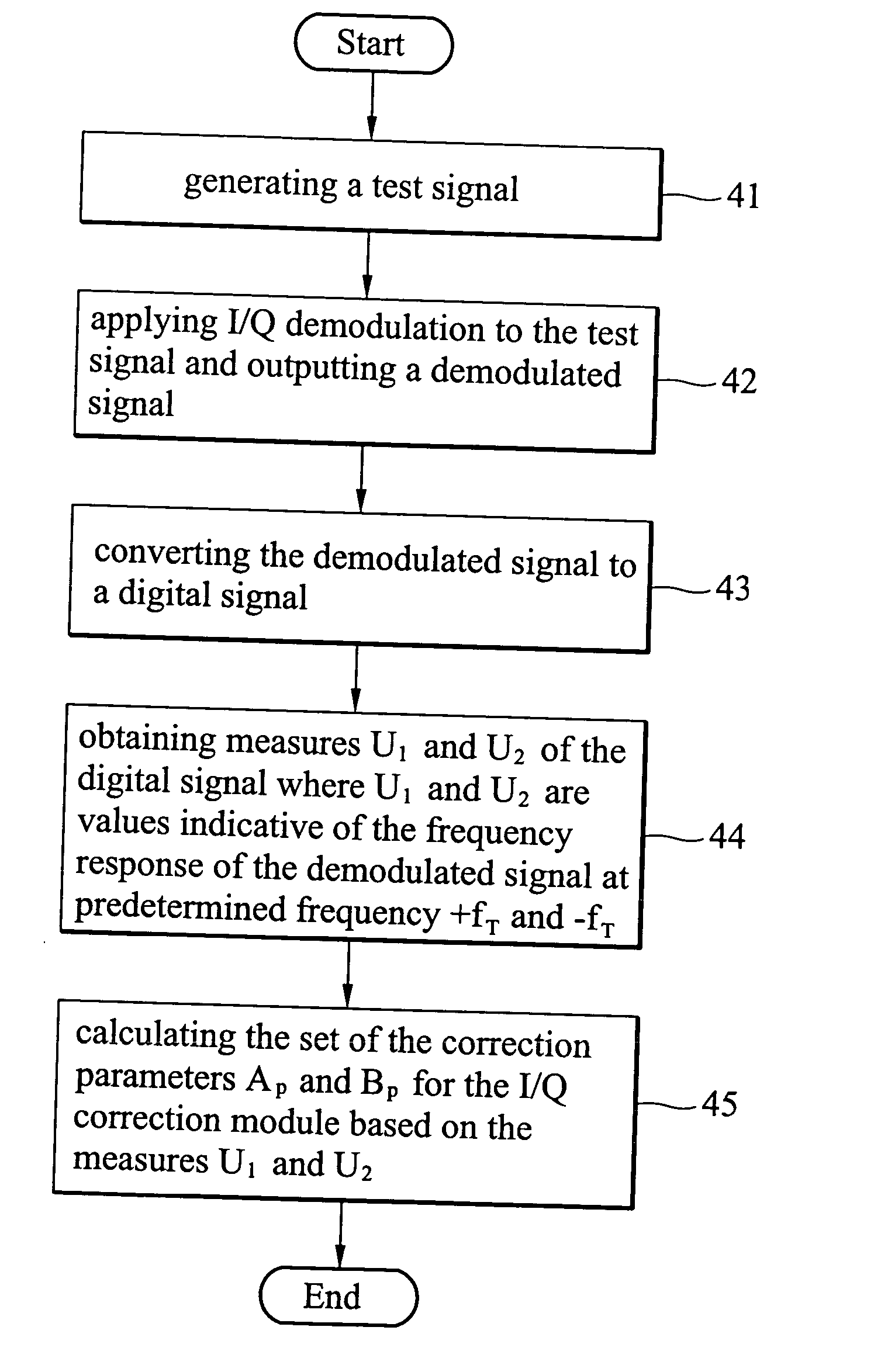
A method for I / Q mismatch calibration of a receiver having an I / Q correction module with correction parameters, comprising the steps of generating a test signal containing a single tone waveform with frequency of a carrier frequency plus a predetermined frequency, applying I / Q demodulation to reduce the central frequency of the test signal and outputting a demodulated signal, converting the demodulated signal to a digital signal, obtaining measures of the digital signal respectively indicative of the frequency response of the digital signal at the plus and minus predetermined frequencies, and calculating the set of the correction parameters for the I / Q correction module based on the measures.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Sound source separation system, sound source separation method, and computer program for sound source separation
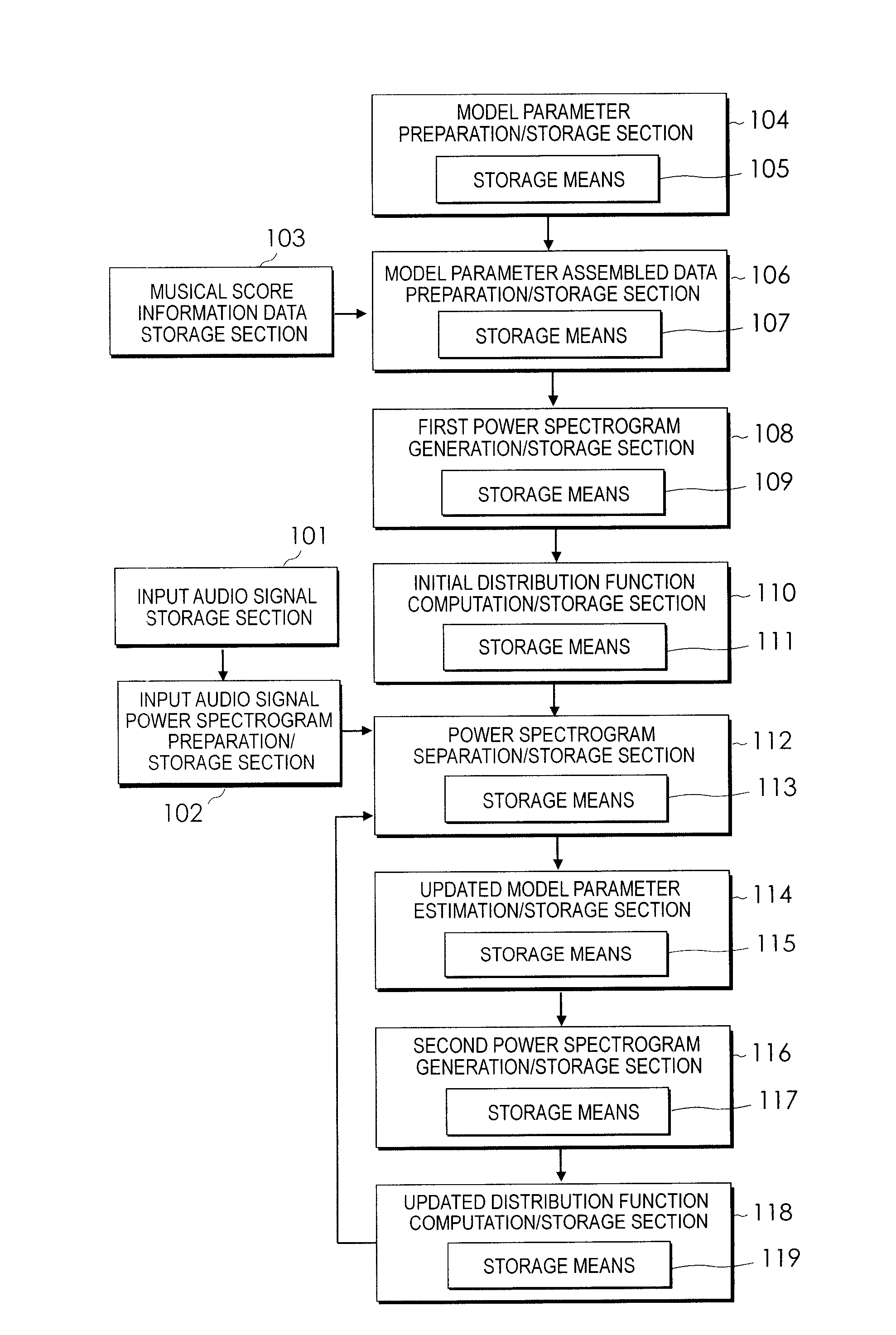
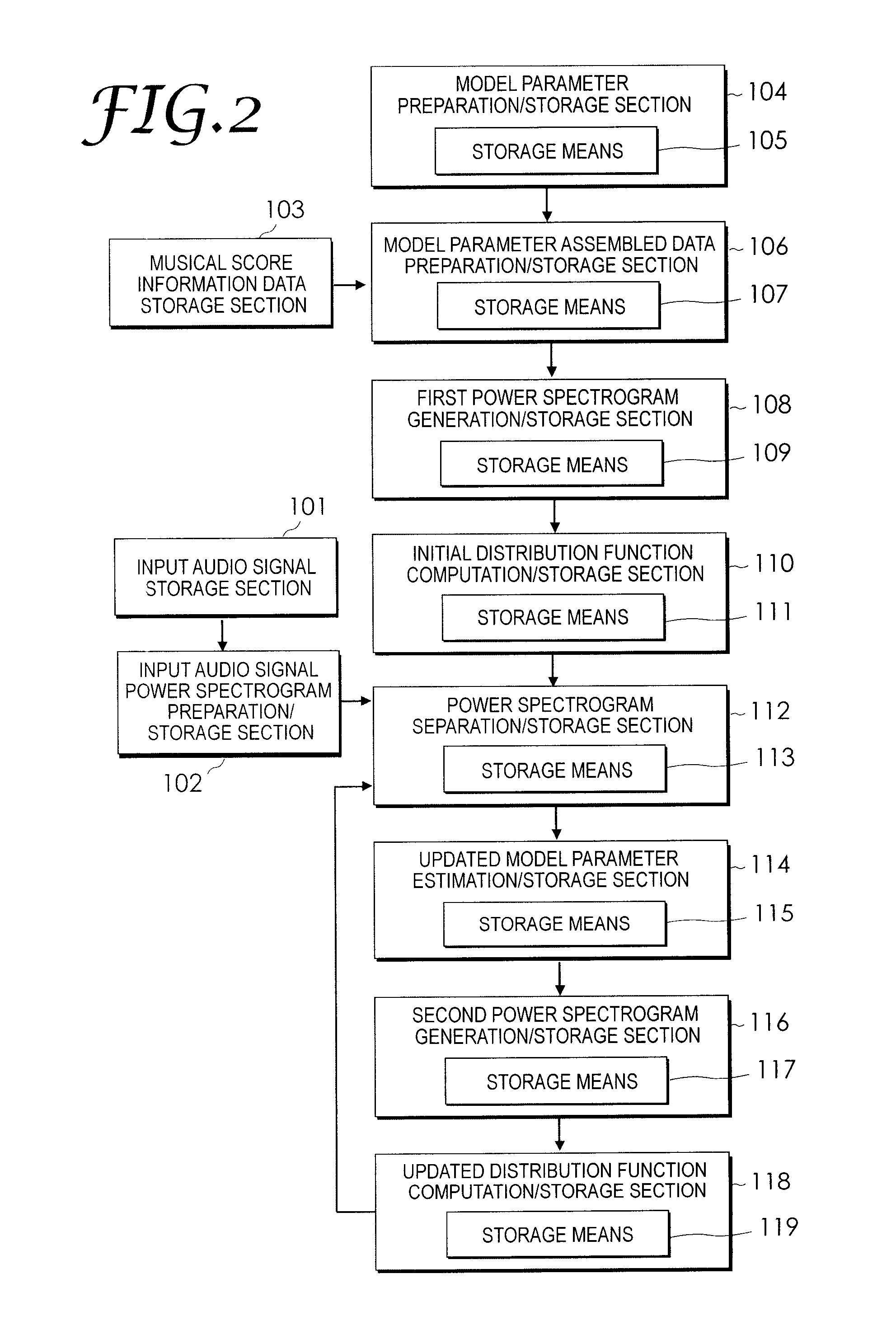
InactiveUS20100131086A1Minimize cost functionHigh precisionElectrophonic musical instrumentsAnalogue computers for electric apparatusSound source separationModel parameters
An audio signal produced by playing a plurality of musical instruments is separated into sound sources according to respective instrument sounds. Each time a separation process is performed, the updated model parameter estimation / storage section 114 estimates parameters respectively contained in updated model parameters such that updated power spectrograms gradually change from a state close to initial power spectrograms to a state close to a plurality of power spectrograms most recently stored in a power spectrogram separation / storage section. Respective sections including the power spectrogram separation / storage section 112 and an updated distribution function computation / storage section 118 repeatedly perform process operations until the updated power spectrograms change from the state close to the initial power spectrograms to the state close to the plurality of power spectrograms most recently stored in the power spectrogram separation / storage section 112. The final updated power spectrograms are close to the power spectrograms of single tones of one musical instrument contained in the input audio signal formed to contain harmonic and inharmonic models.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
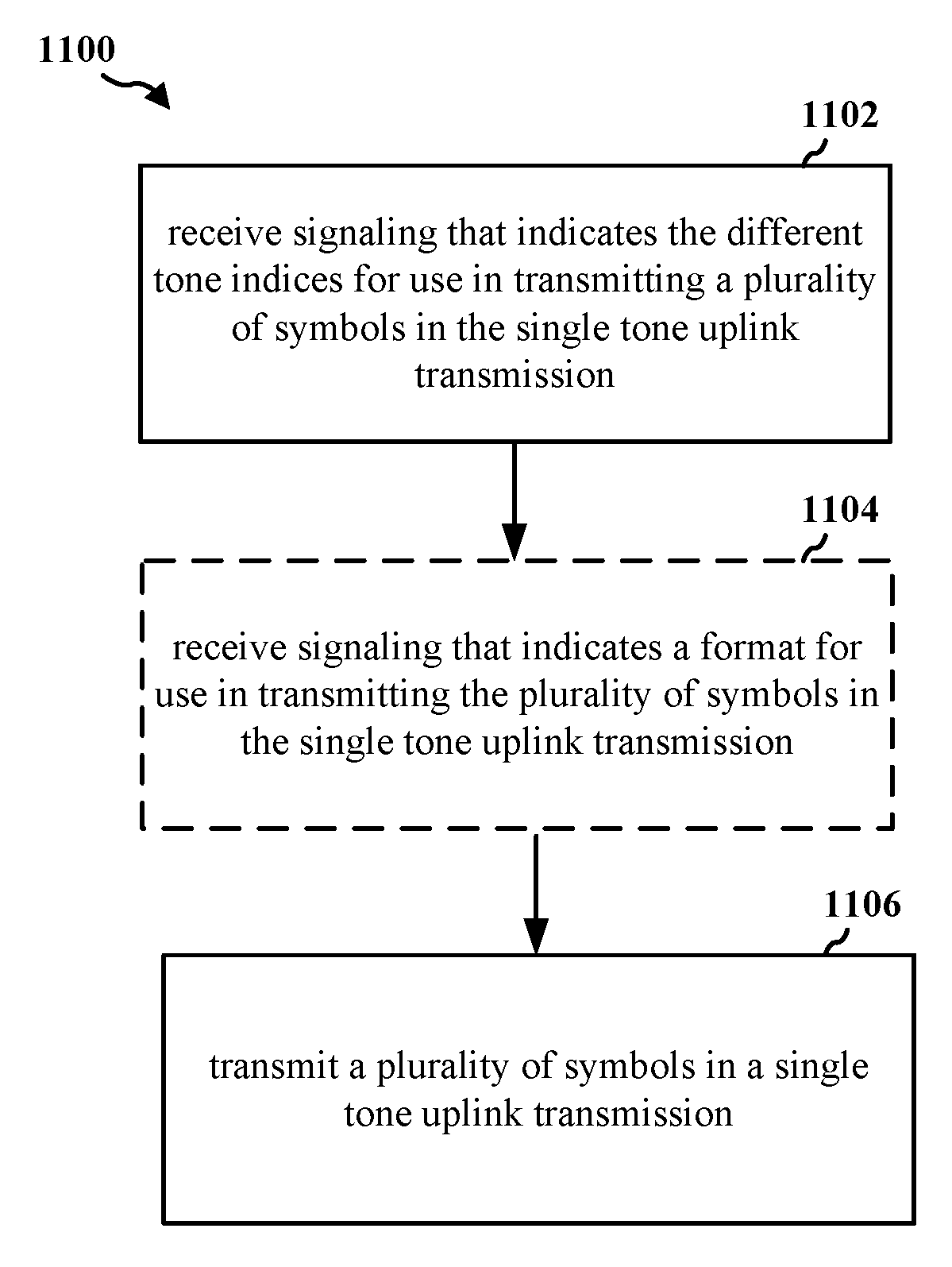
System and method for narrowband uplink single tone transmissions
ActiveUS20170134199A1Well formedTransmission path divisionSignal allocationUplink transmissionUser equipment
An apparatus may receive signaling from a base station that indicates different tone indices. The apparatus may further transmit a plurality of symbols in a single tone uplink transmission. In an aspect, groups of symbols in the plurality of symbols are transmitted using the different tone indices of the single tone uplink transmission indicated by the received signaling. A second apparatus may signal to at least one user equipment (UE) information associated with different tone indices for use in transmitting a plurality of symbols in a single tone uplink transmission. The second apparatus may further receive the plurality of symbols in the single tone uplink transmission. In an aspect, pairs of symbols in the plurality of symbols are received in different tone indices of the single tone uplink transmission.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
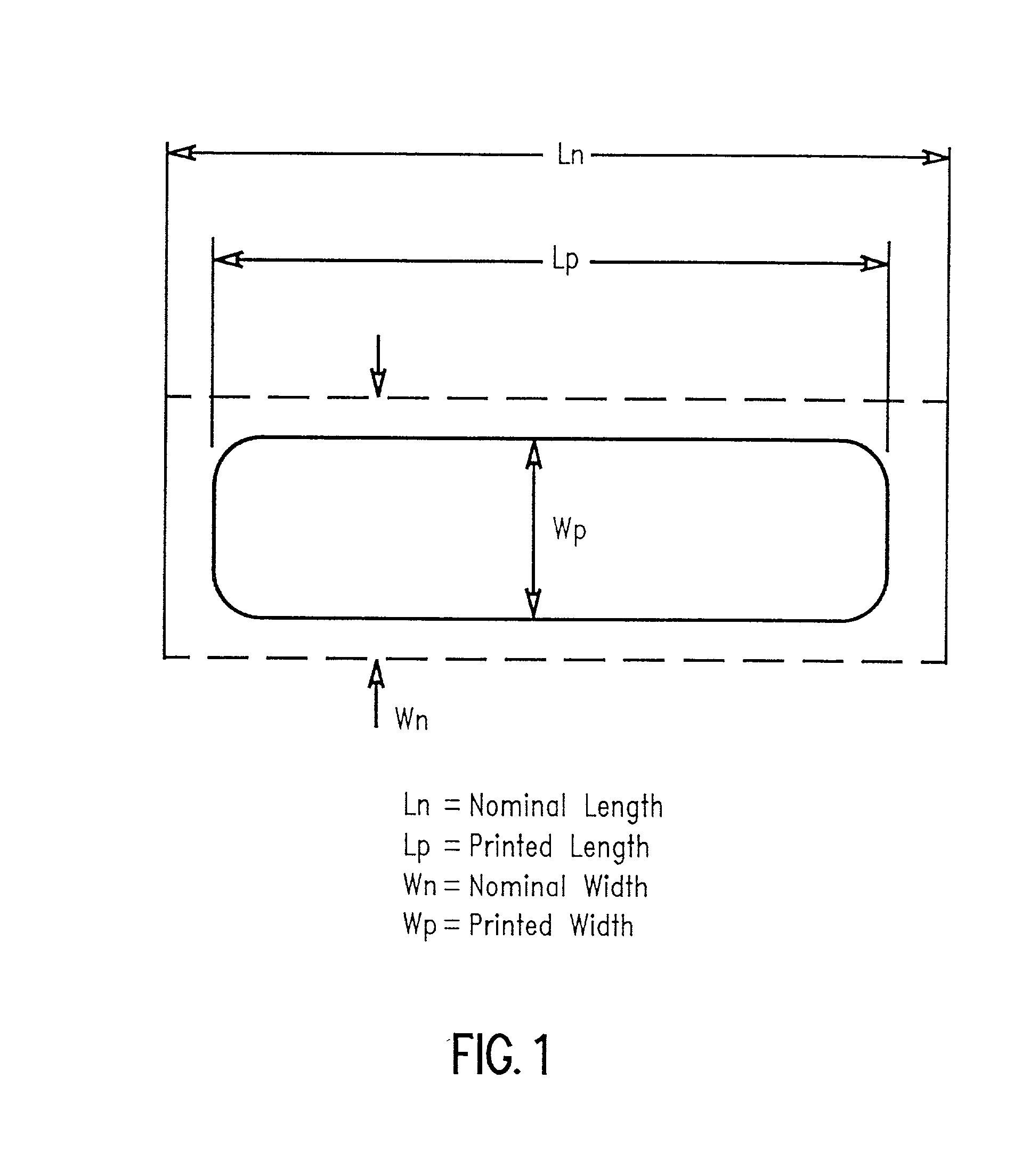
Single tone process window metrology target and method for lithographic processing
InactiveUS20020097399A1Using optical meansPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMetrologyCentral element
A metrology target mask for determining proper lithographic exposure dose and / or focus in a pattern formed in a layer on a semiconductor substrate by lithographic processing. The target mask comprises a mask substrate and a first, dose and focus sensitive mask portion on the mask substrate having a first array of elements comprising a plurality of spaced, substantially parallel elements having essentially the same length and width. Ends of the individual elements are aligned to form first and second opposing array edges, with the lengths of and spaces between the elements being sensitive to both dose and focus of an energy beam when lithographically printed in a layer on a semiconductor substrate. The target mask also includes a second, dose sensitive mask portion on the mask substrate having a second array of elements comprising a central element having a length and a width, and a plurality of spaced, substantially parallel outer elements having a length and a width. The width of the outer elements is less than the width of the central element, with edges of outer elements on each side of and farthest from the central element forming opposing array edges. The pitch of the outer elements is selected such that the outer elements are not resolvable after lithographic printing in a layer on a semiconductor substrate. The resulting printed second target portion width is sensitive to dose but not focus of the energy beam. Dose and / or focus of the energy beam during lithographic processing of the layer may be determined after projecting an energy beam through the mask and lithographically printing the mask portions in a layer on a semiconductor substrate and determining the widths of the first and second target portions in the layer by measuring distance between opposing array edges in each of the first and second portions.
Owner:IBM CORP
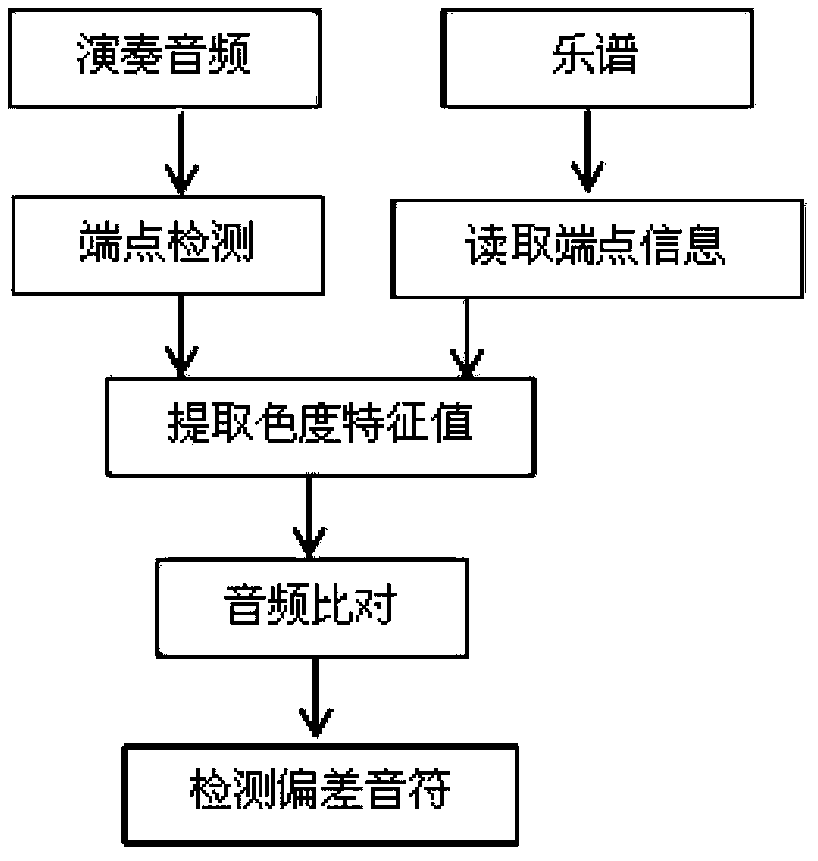
Audio music-score comparison method with error detection function
ActiveCN103354092AHigh precisionImprove execution efficiencyElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech analysisTemporal informationStart time
The invention discloses an audio music-score comparison method with an error detection function. The audio music-score comparison method comprises extracting starting time information of every note in a MIDI file, converting the MIDI file to an audio WAV file, carrying out endpoint detection to performance audio frequency P in order to determine starting time of every single-tone or chord, extracting eigenvalues of music score audio frequency S and the performance audio frequency P to obtain a 12-dimension chrominance vector of every single-tone or chord, calculating Euclidean distance matrices of the characteristic vectors of the performance audio frequency P and the music score audio frequency S, comparing the two matrices of the eigenvalues, utilizing a DTW algorithm and finally realizing an aligning function of the performance audio frequency and the music score audio frequency, so that the comparison method can detect whether conditions of redundant playing, missing playing and wrong playing appear in the performance audio frequency. According to the audio music-score comparison method provided by the invention, on-site music performance can be listened to by a computer, positions of performance notes in music score are finally tracked and determined, aligning time is relatively accurate without affecting by beat change and the audio music-score comparison method with the error detection function can detect whether error notes appear in the performance audio frequency.
Owner:天津画国人动漫创意有限公司
Automatic duplicating method and device for single track polyphonic music signals
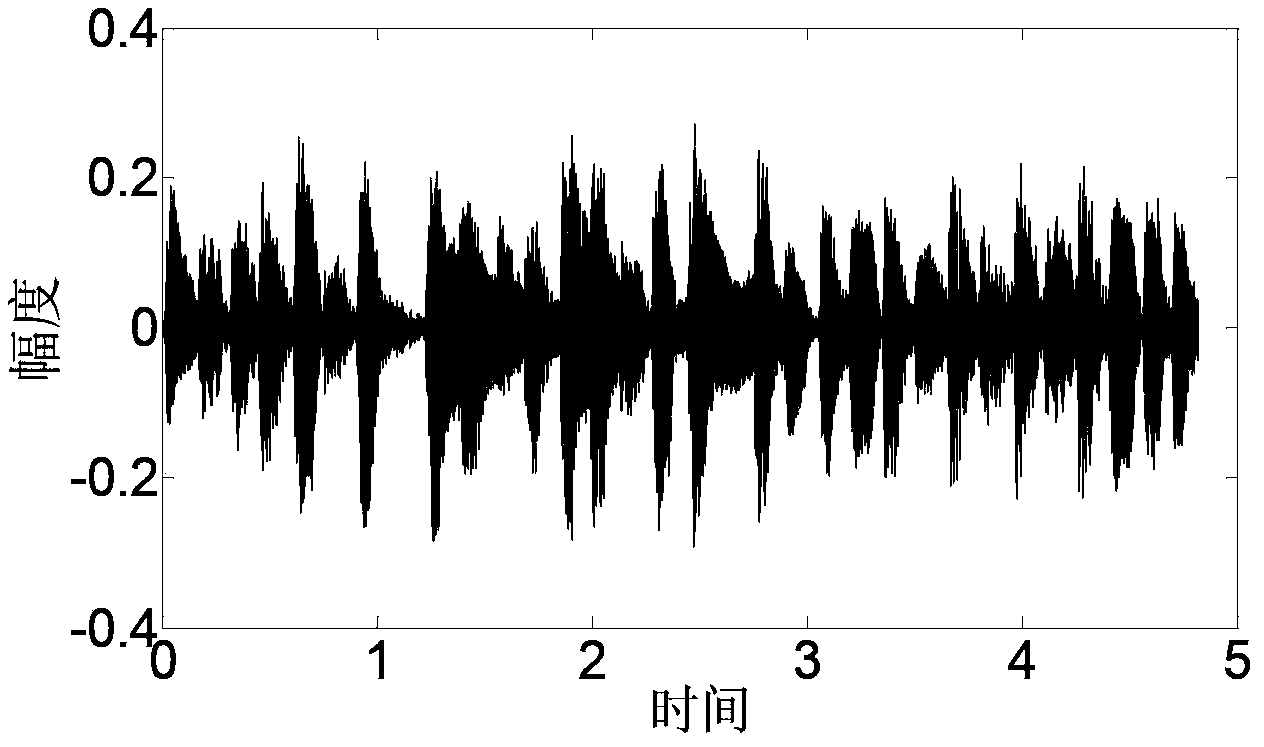
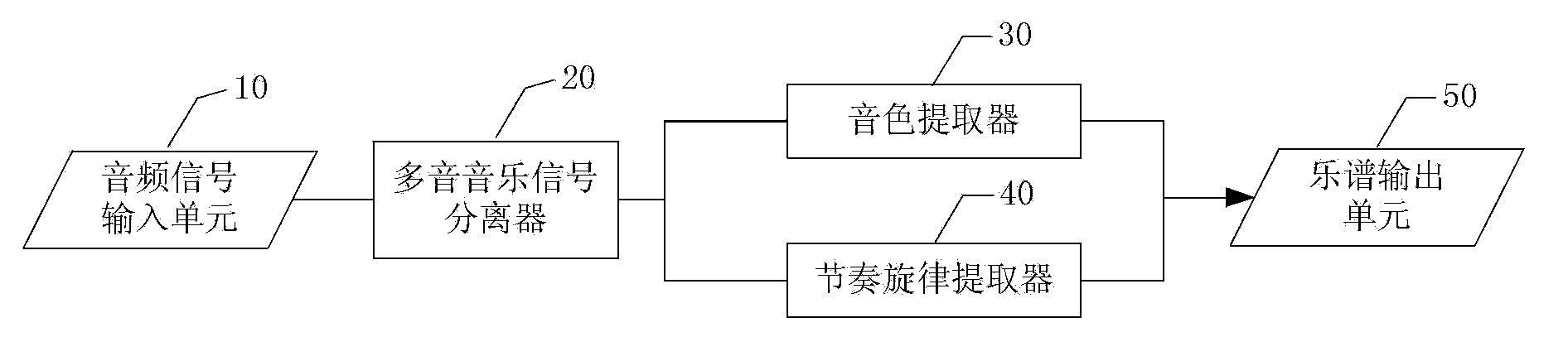
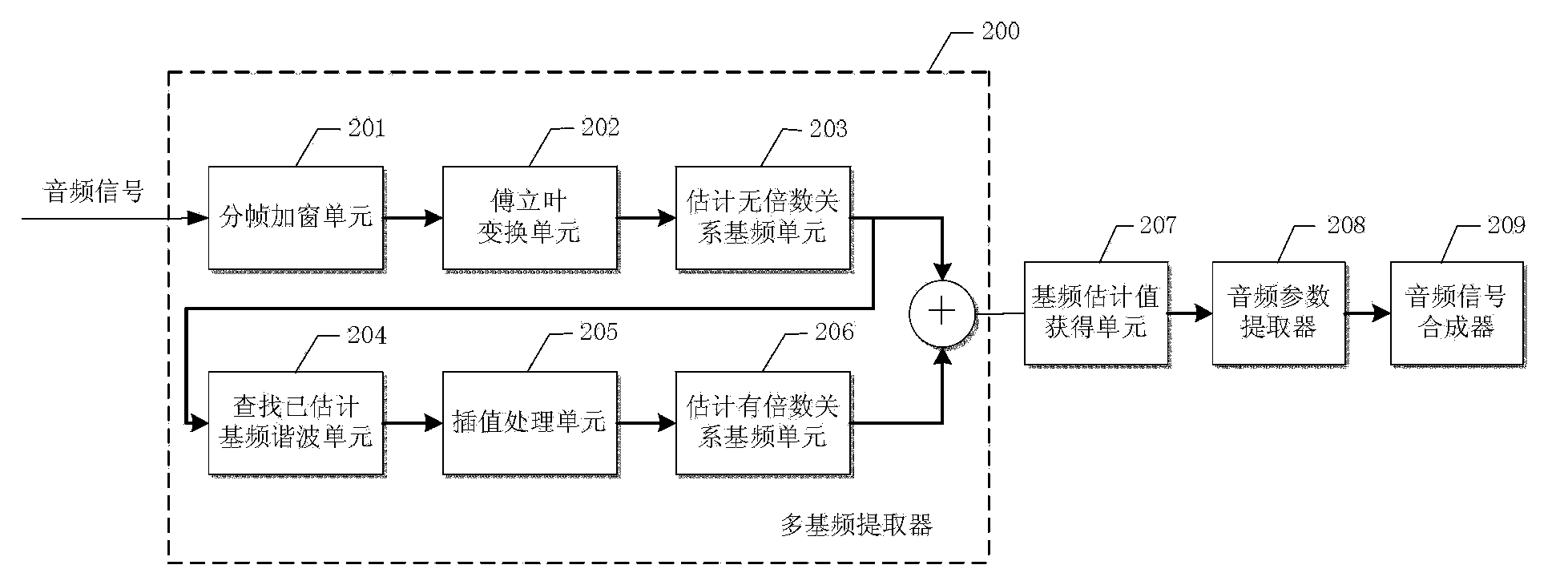
The invention provides an automatic duplicating method and device for single track polyphonic music signals. The automatic duplicating method comprises the steps of receiving the single track polyphonic music signals, separating the single track polyphonic music signals to obtain multipath single-tone music signals, carrying out tone extraction on each single-tone music signal to determine musical instrument playing information, carrying out melody extraction, rhythm extraction and beat extraction on each single-tone music signal to obtain audio information, and obtaining polyphonic music score according to the musical instrument playing information and the audio information. According to the automatic duplicating method and device for the single track polyphonic music signals, the single track polyphonic music signals are separated into the multipath single-tone music signals, the melody extraction, the rhythm extraction and the beat extraction are carried out on each separated single-tone music signal to obtain the musical instrument playing information and the audio information, and therefore the polyphonic music score with a high accuracy rate is obtained according to the musical instrument playing information and the audio information.
Owner:COMMUNICATION UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
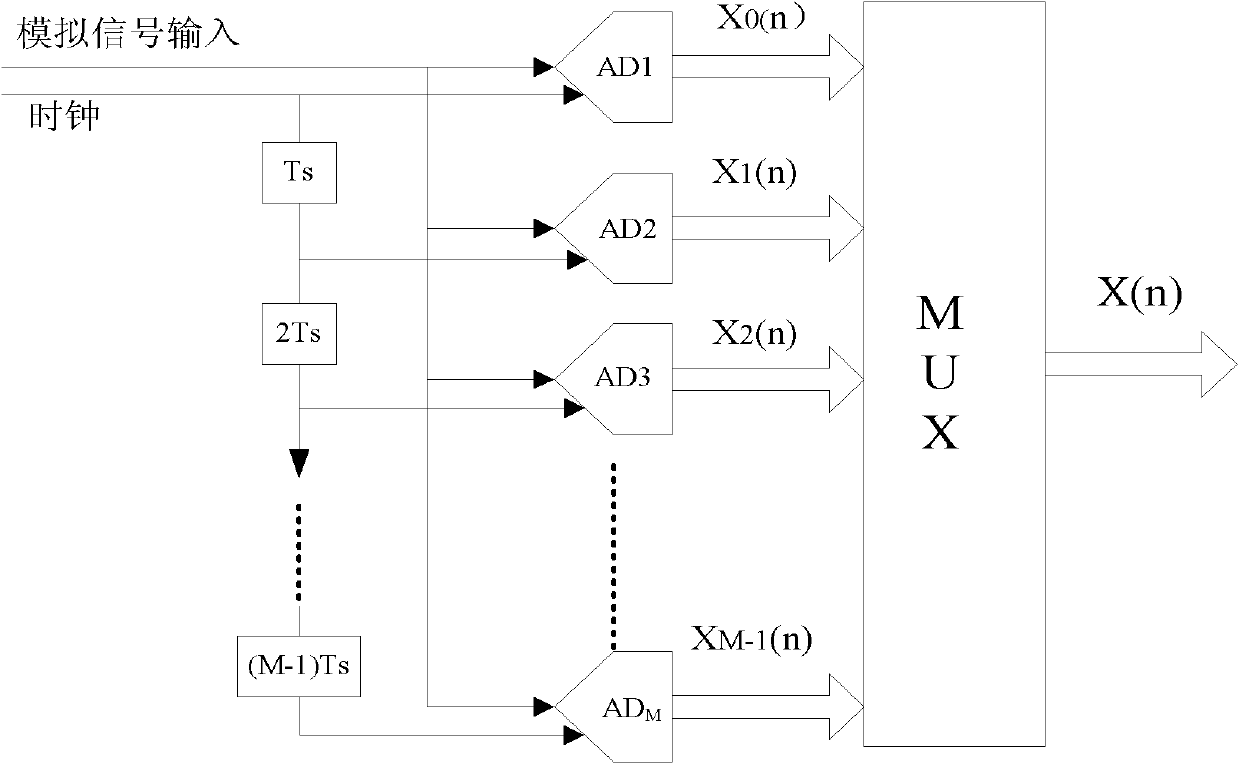
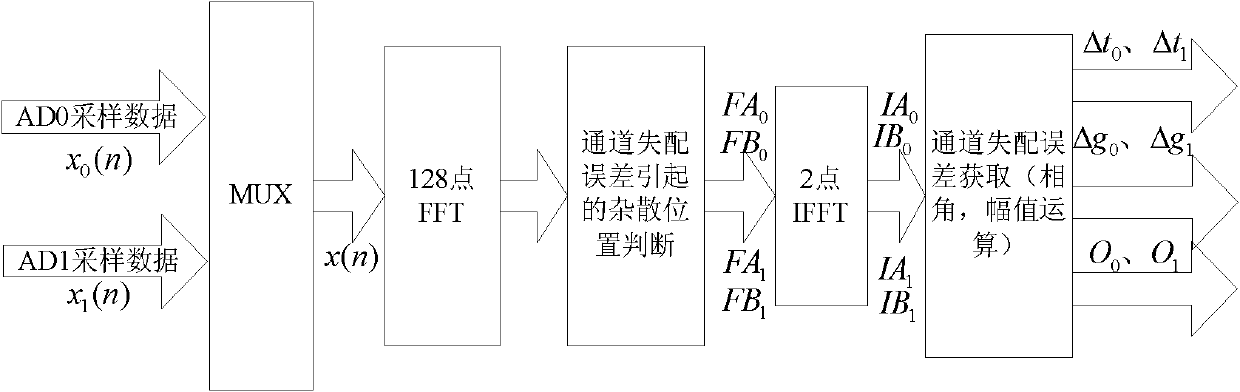
Joint estimation and real-time correction method for channel error of TIADC system
InactiveCN102075464AReduce overheadAvoid introducingTransmitter/receiver shaping networksFast Fourier transformTime error
The invention discloses a joint estimation and real-time correction method for channel error of a time-interleaved ADC (TIADC) system. The method for implementing joint estimation comprises the steps of: sampling a single-tone signal with input frequency of f0 to obtain a sampling sequence xk(n) of various channels of the system, wherein k=0, 1, L M-1; performing fast Fourier transform (FFT) on sampling data x(n) which is reduced into a single-tone signal after the split joint; and in an FFT result, selecting a value FAk at the position where the frequency is 1fs / M+ / -f0,1=0, 1L M-1 and selecting a value FBk at the position where the frequency is 1fs / M,1=0, 1L M-1 to perform inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) to obtain M complex numbers, namely IAk and IBk, and finally, obtaining the joint estimation on time error delta tk, gain error gk, and offset error ok, k=0, 1, L M-1 through phase angle extraction and a modulus operation algorithm module. The method for implementing real-time correction comprises the step of: utilizing a comprehensive correction mechanism formed by a subtractor, a divider and a fractional delay filter to correct the offset error, the gain error and the time error existing in the sampling data of the channels respectively. By the method, joint estimation is performed on the three errors, SFDR of the sampling sequence is improved through the real-time correction, and a filter coefficient is not required to be updated or a correction module is not required to be redesigned even if channel errors are changed, so the aim of the real-time correction is fulfilled.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Single tone process window metrology target and method for lithographic processing
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
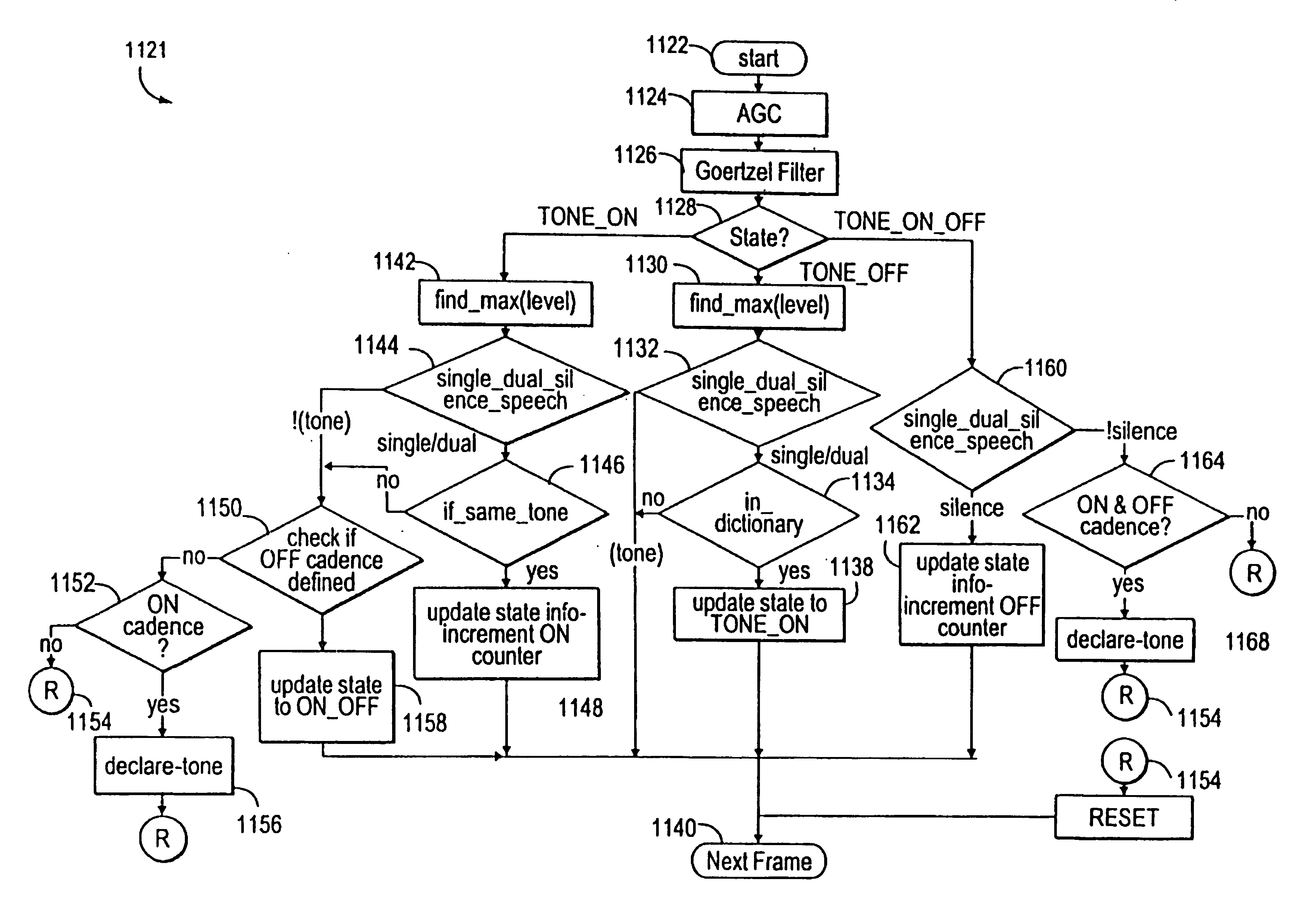
Tone detection for integrated telecommunications processing
InactiveUS7003093B2Facilitate communicationInterconnection arrangementsManual exchangesSpeech soundAutomatic gain control
Disclosed is an integrated tone detection processor for discriminating between tone and voice signals and determining the tones. The tone detection processor performs Automatic Gain Control (AGC) to normalize the power of the tone or voice signal. Further, the energy of the tone or voice signals are determined at specific frequencies utilizing a Goertzel Filter process. The tone detection processor determines whether or not a tone is present, and if a tone exists, determines the type of tone. Based upon determining the two maximum energy levels of the Goertzel filtered tone, whether the tone is a single tone, dual tone, silence, or other (e.g. speech) can be discriminated. The tone can then be identified by a user-defined dictionary of tones. Based upon various ON and OFF cadence checks in combination with the use of TONE ON and TONE OFF counters, tones can be declared.
Owner:INTEL CORP
A frequency mixer and frequency mixing method
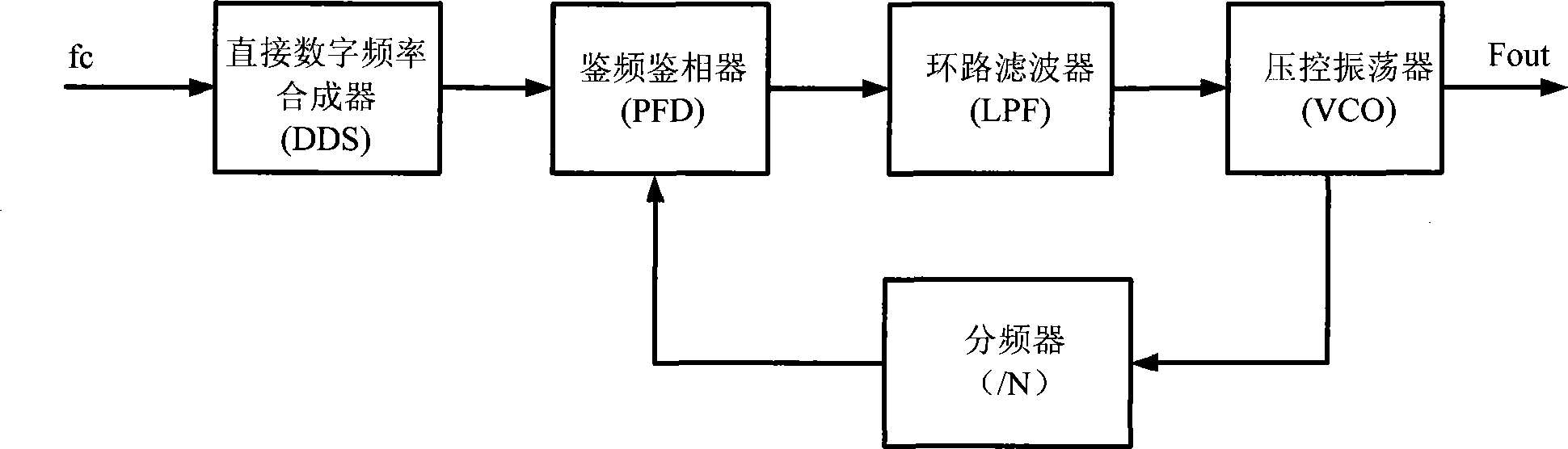
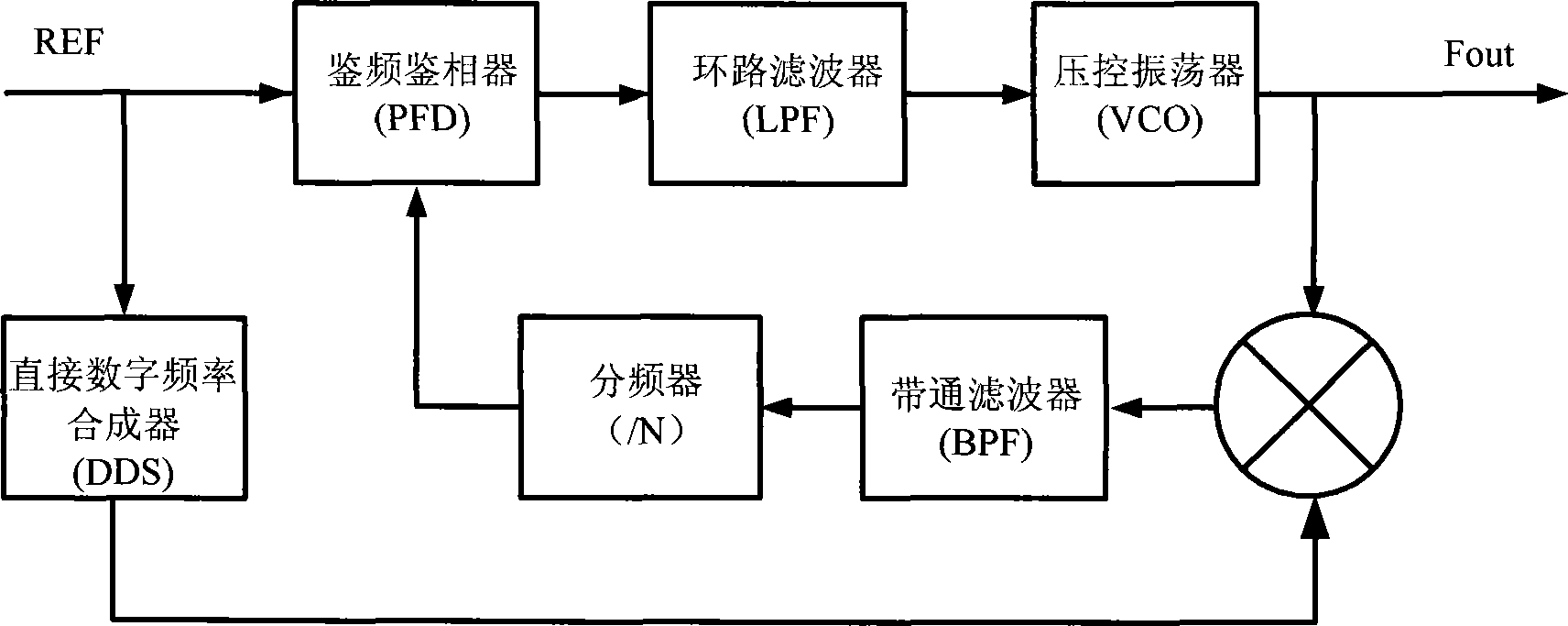
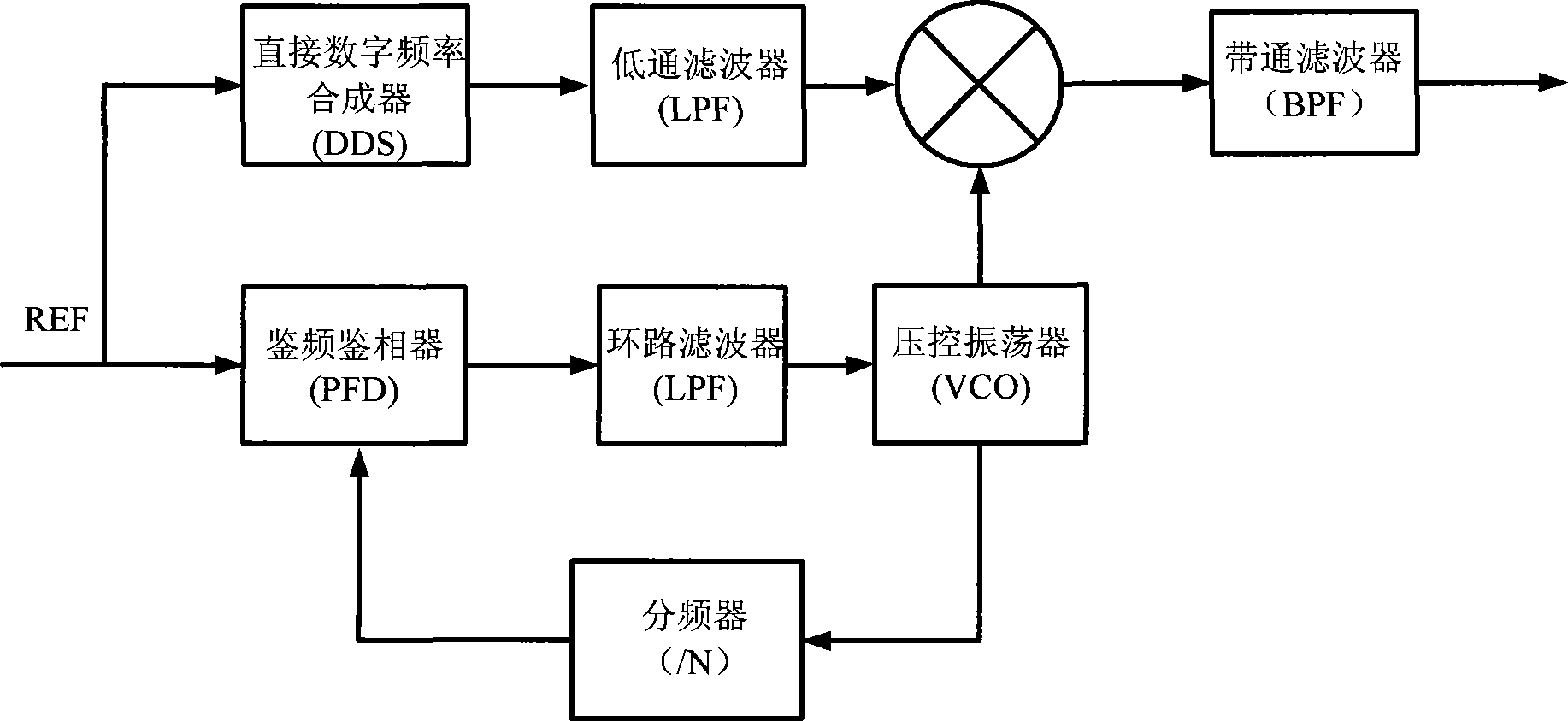
InactiveCN101242181ALarge spurLow spurs generated by large-step phase-locked loopPulse automatic controlTransmissionLow noiseFrequency mixer
The invention discloses a frequency synthesizer and a frequency synthesis method. The frequency synthesizer comprises: a large-stepping phase lock loop and a direct digital frequency synthesizer, an orthogonal mixer and a tracking phase lock loop. The orthogonal mixer is connected with the large-stepping phase lock loop and the digital frequency synthesizer respectively for mixing the frequency generated by the large-stepping phase lock loop and the low frequency generated by the direct digital frequency synthesizer to generate a single-sideband single tone; the tracking phase lock loop is connected with the orthogonal mixer for receiving the single-sideband single tone output by the orthogonal mixer and filtering the sideband leakage and oscillation leakage of the signal. The invention provides a frequency synthesizer with wide band width, small stepping, low stray and low noise and a frequency synthesis method. The invention has simple hardware structure and is easy to accomplish.
Owner:INNOFIDEI TECHNOLOGIES INC
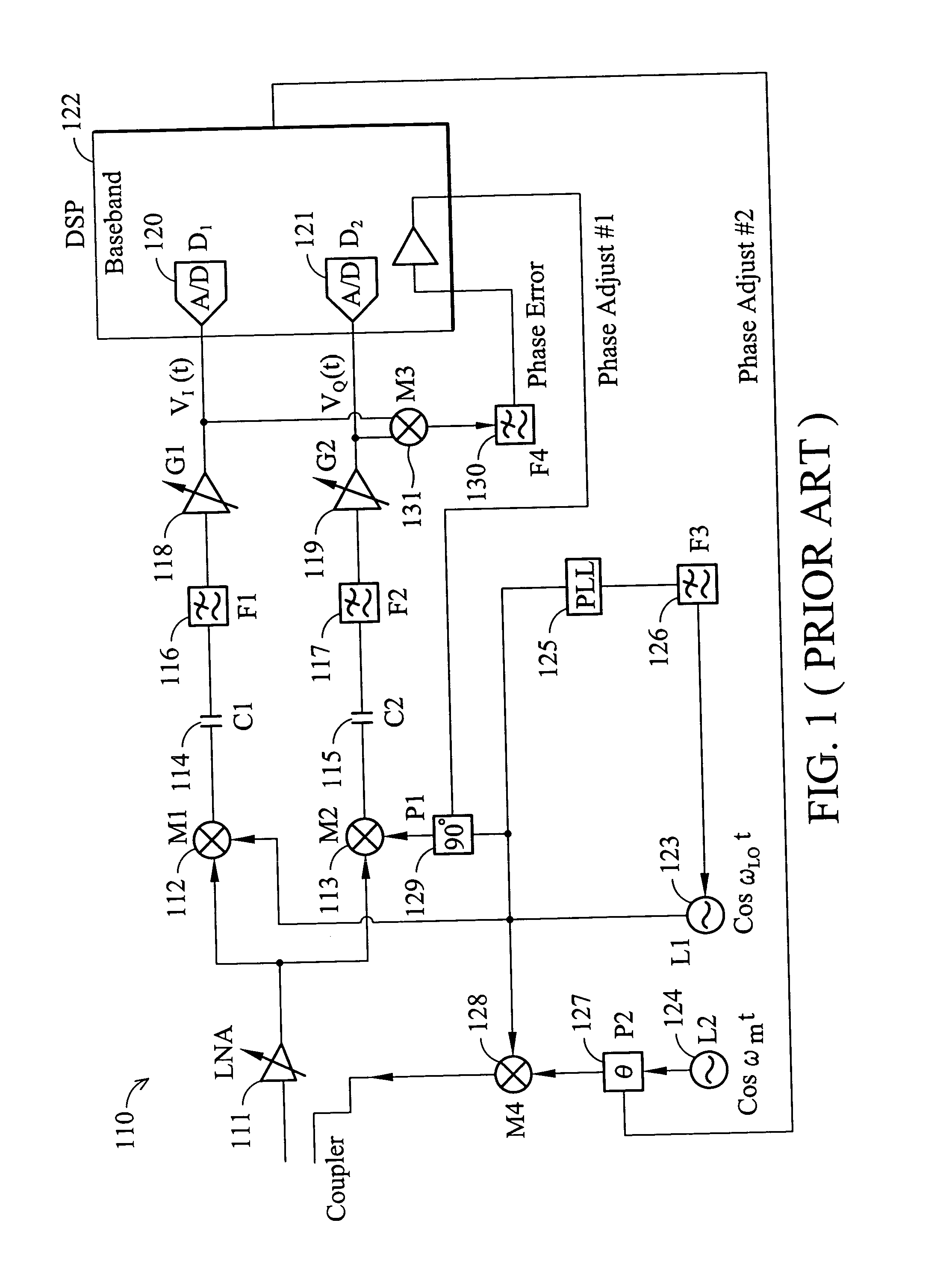
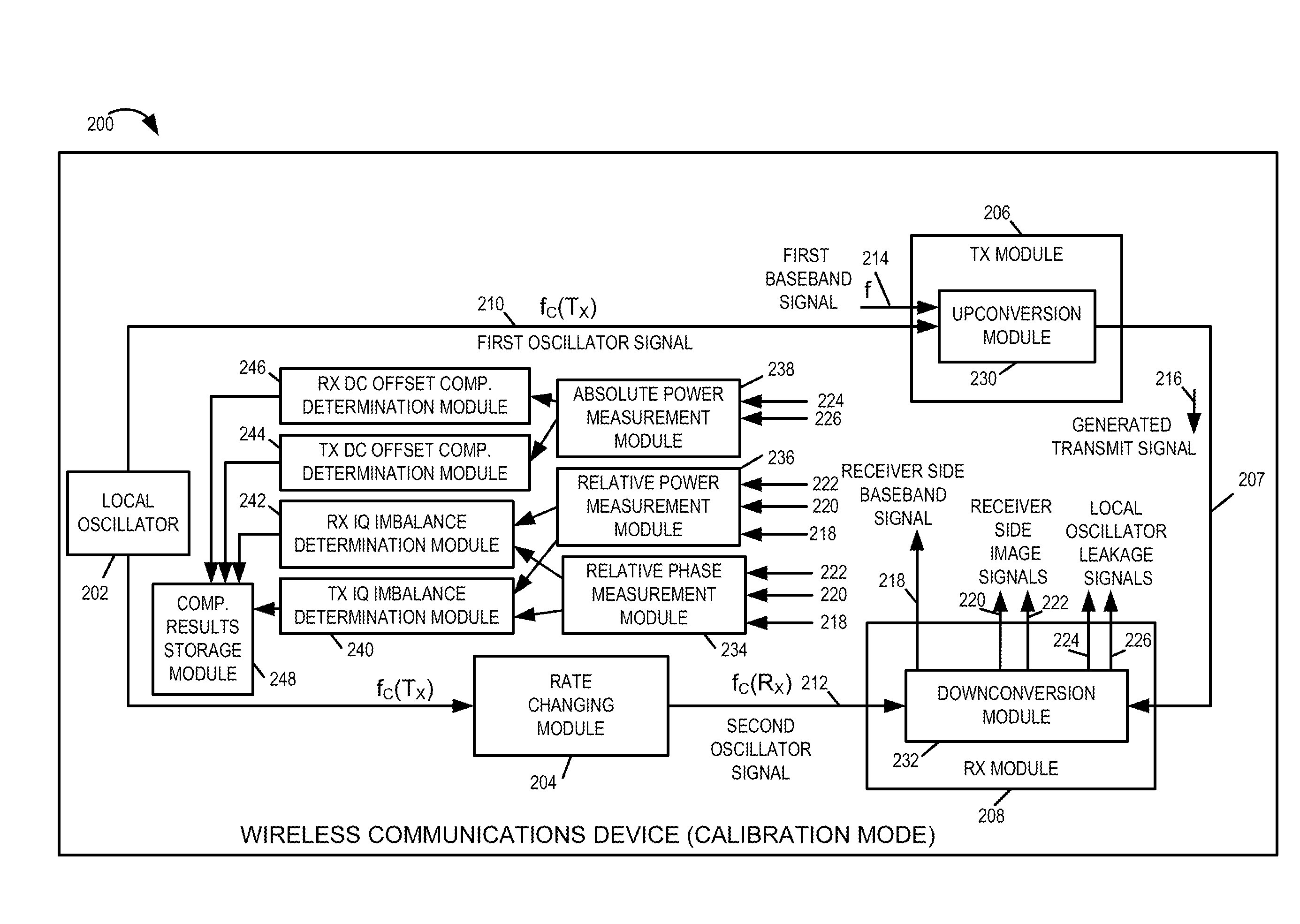
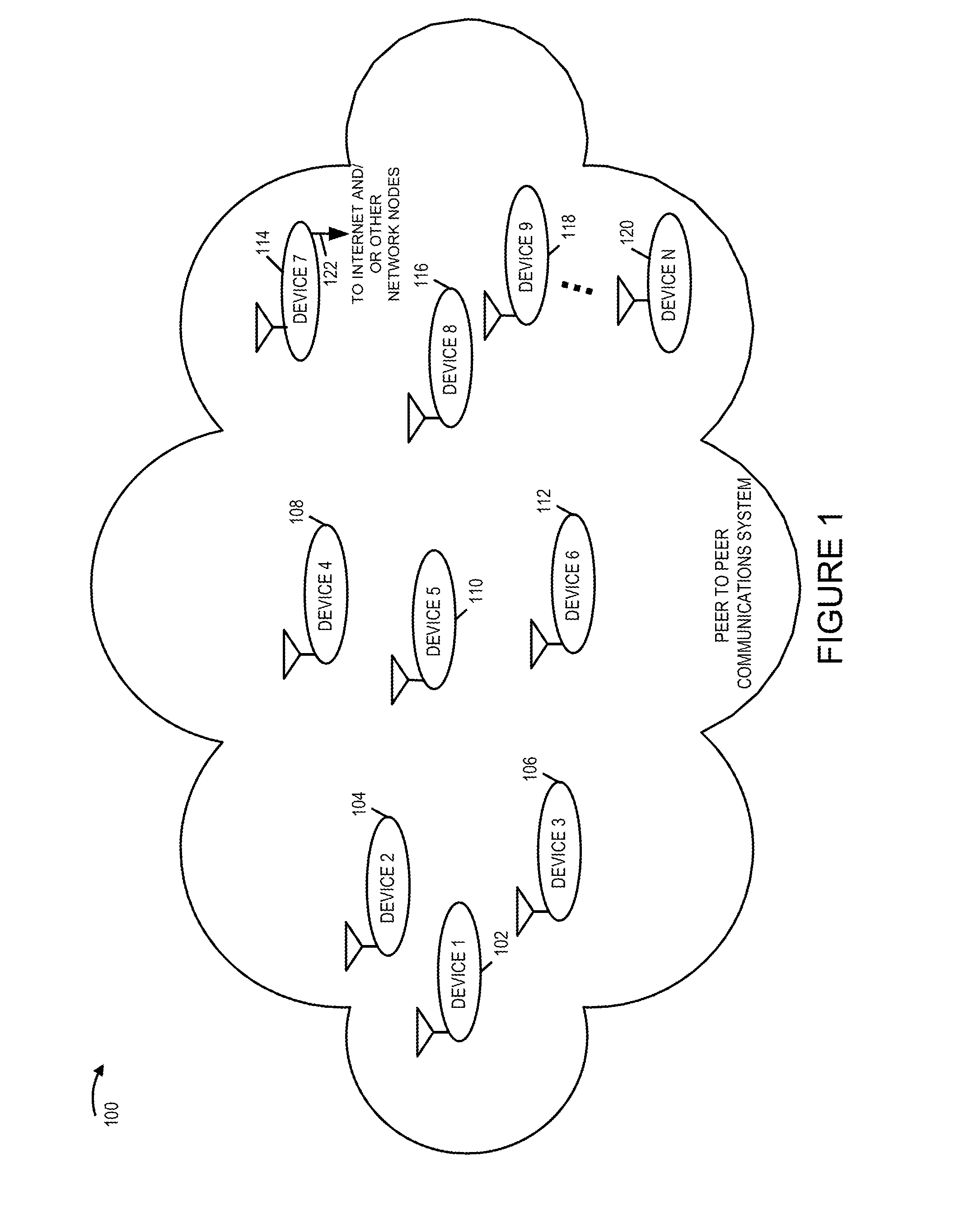
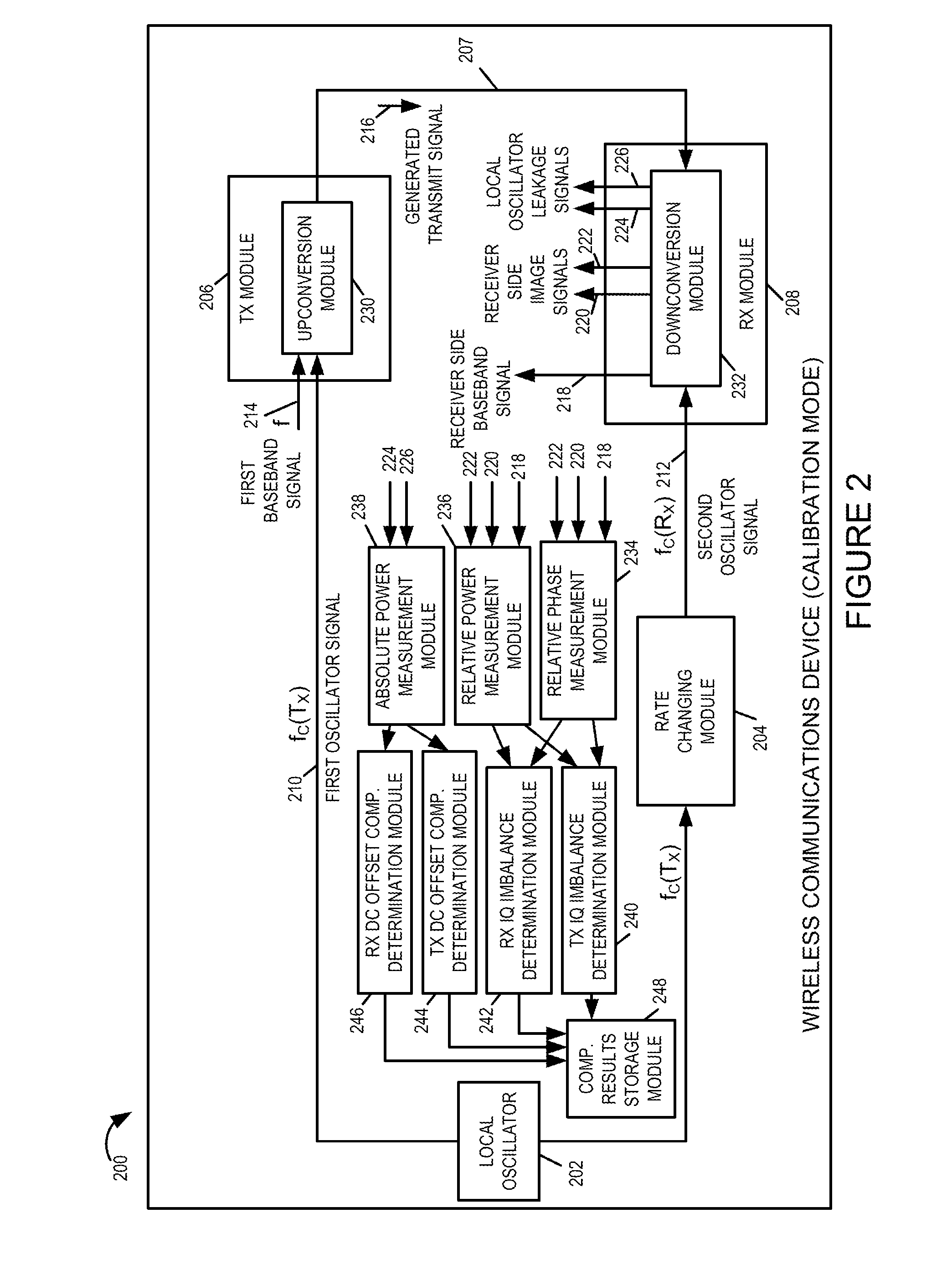
Methods and apparatus for measuring and/or using transmitter and/or receiver iq imbalance information and/or DC offset information
A wireless communications device, e.g., a mobile node supporting direct peer to peer communications, performs a self-calibration of one or more of: receiver IQ imbalance, transmitter IQ imbalance, receiver DC offset, and transmitter DC offset. The wireless communications device, operating in calibration mode, intentionally sets the oscillator frequency used for downconversion in its receiver module to a different frequency than the oscillator frequency used for upconversion in its transmitter module. A first baseband signal, e.g., a single tone test signal, is input to the transmitter module and an upconverted transmit signal is generated. The transmit signal is routed via a feedback loop to the receiver, which performs a downconversion operation. Power and / or phase measurements of the signals output from the downcoversion are used to determine IQ imbalance compensation information and DC offset compensation information. The determined compensation information is used subsequently when operating in a communications mode of operation.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
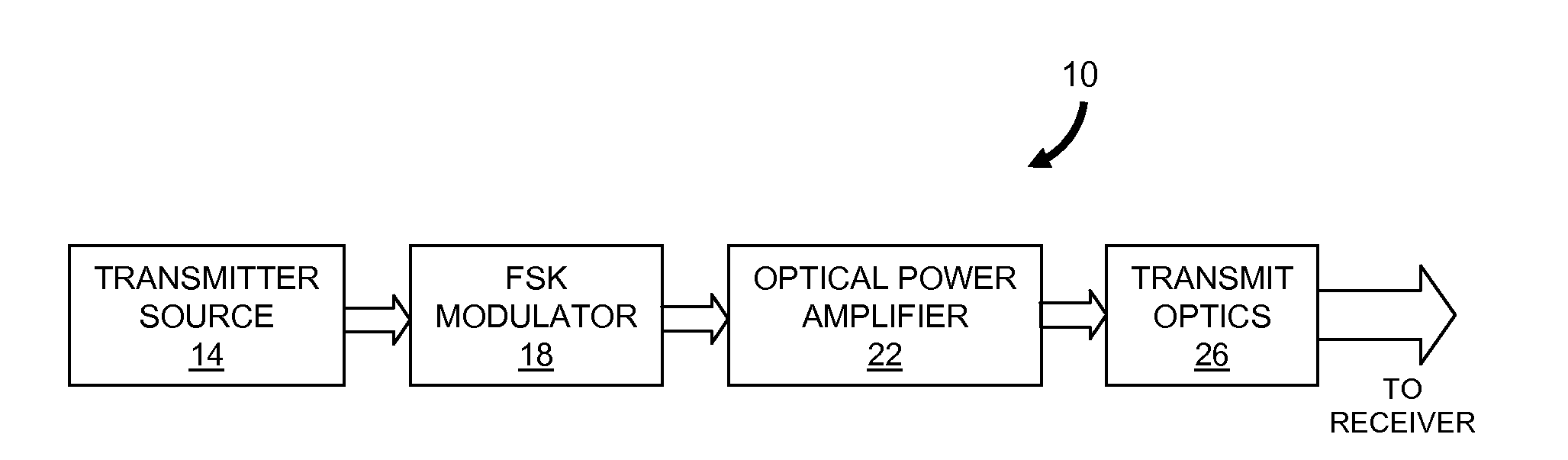
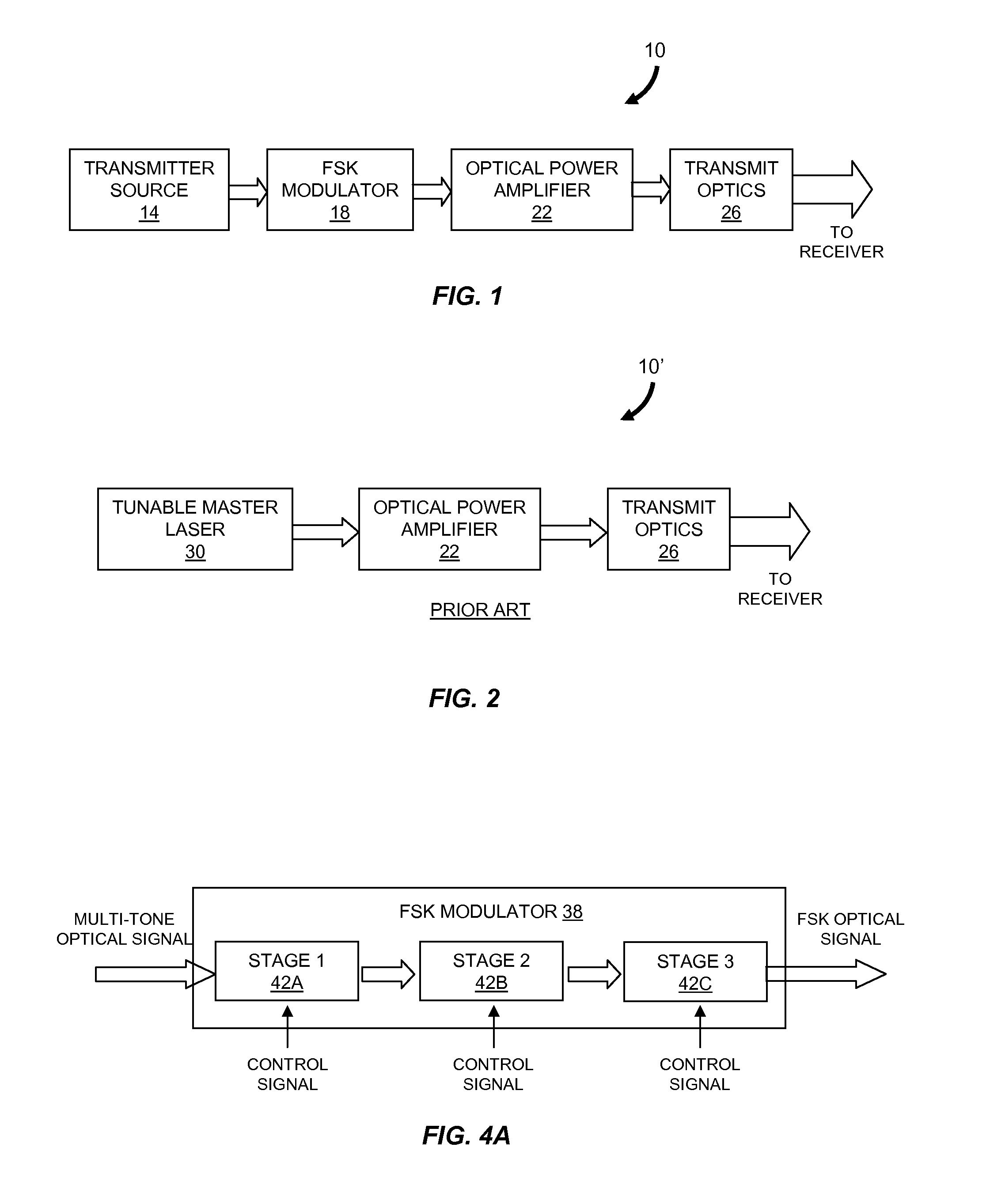
Modulator for frequency-shift keying of optical signals
ActiveUS20100104277A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringResonator filterMach–Zehnder interferometer
Described are an FSK modulator and a method for large-alphabet FSK modulation. The FSK modulator and the method are based on filtering of a multi-tone optical source such as a mode-locked laser which provides a comb distribution of tones. A frequency-selective component selects for transmission a subset of the tones. In various embodiments the frequency-selective component is a Mach-Zehnder interferometer filter or a microring resonator filter. A second frequency-selective component selects a subset of the tones from the comb distribution provided by the first frequency-selective component. Still more frequency-selective components can be used according to the number of tones supplied by the multi-tone optical source to the FSK modulator. The optical signal exiting the last frequency-selective component includes only a single tone which corresponds to the symbol to be transmitted.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
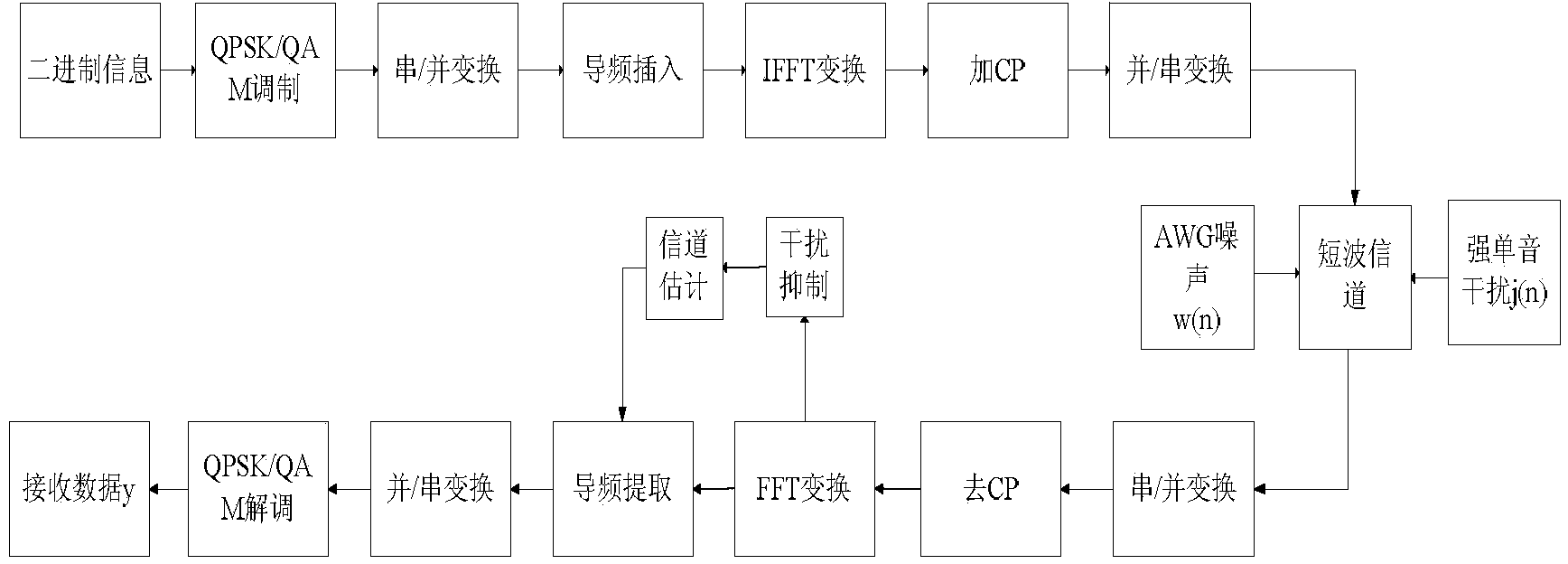
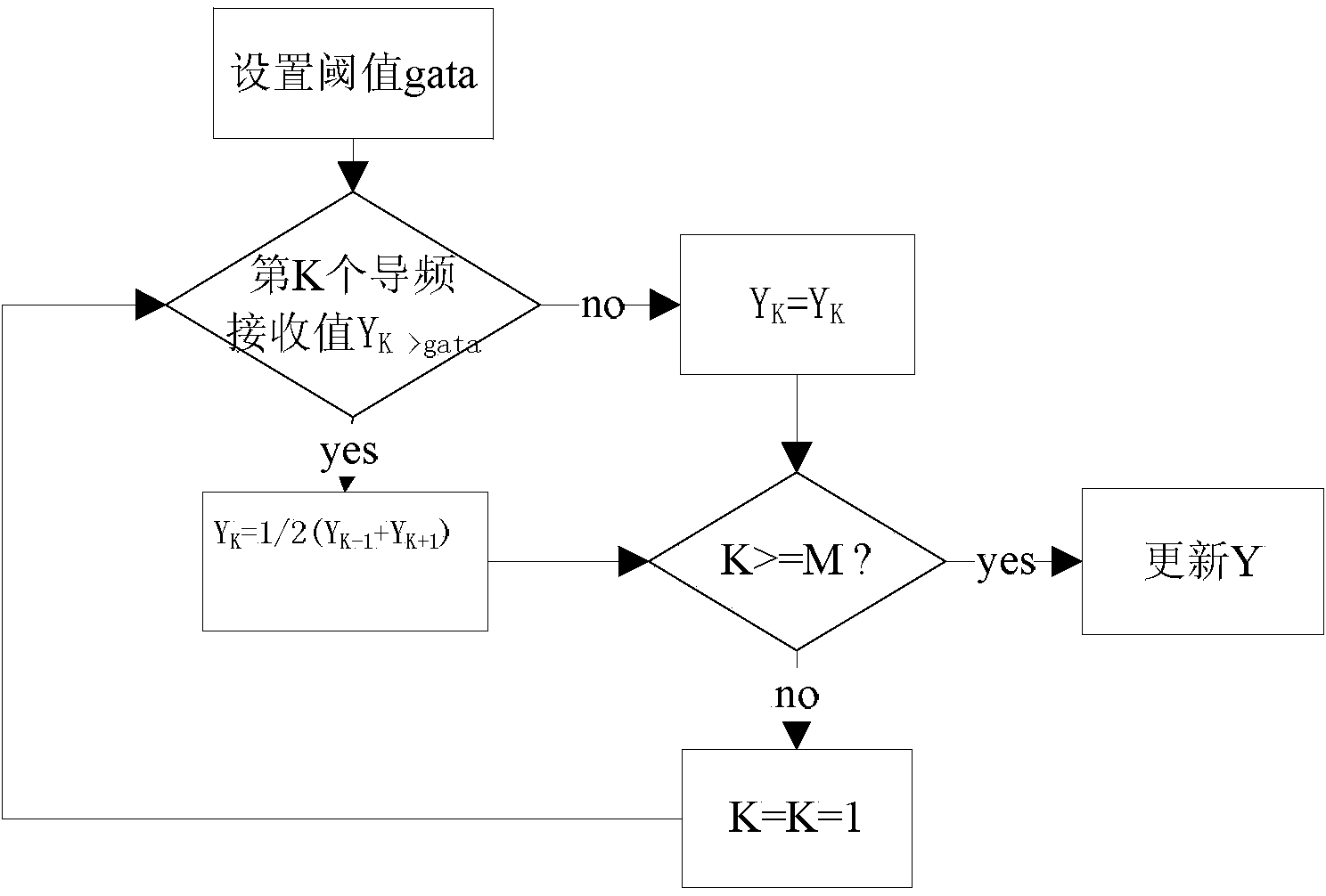
Short-wave OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) interference suppression joint channel estimation method based on compressed sensing
InactiveCN104410590AImprove reconstruction accuracyImprove anti-interference abilityBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumEstimation methods
The invention discloses a short-wave OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) interference suppression joint channel estimation method based on compressed sensing, relating to the field of short-wave communication and the technical field of mobile communication. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, acquiring reception values YM*1 of M pilot signals transmitted from a transmitting end by a receiving end; step 2, performing strong single-tone interference suppression; and step 3, reconstructing a short-wave channel h according to a reconstruction algorithm MCoSaMP, thereby obtaining the short-wave channel frequency domain response H. According to the channel estimation method provided by the invention, fewer pilot symbols can be used compared with those in a traditional channel estimation method, and the frequency spectrum utilization rate is improved. Moreover, channel estimation error can be effectively reduced by suppressing strong single-tone interference in the short-wave channel, and the channel estimation performance is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Signal interference method and device
ActiveCN103795474AReduce manual operationsSimplify the maintenance processTransmission noise suppressionBroadband noiseComputer module
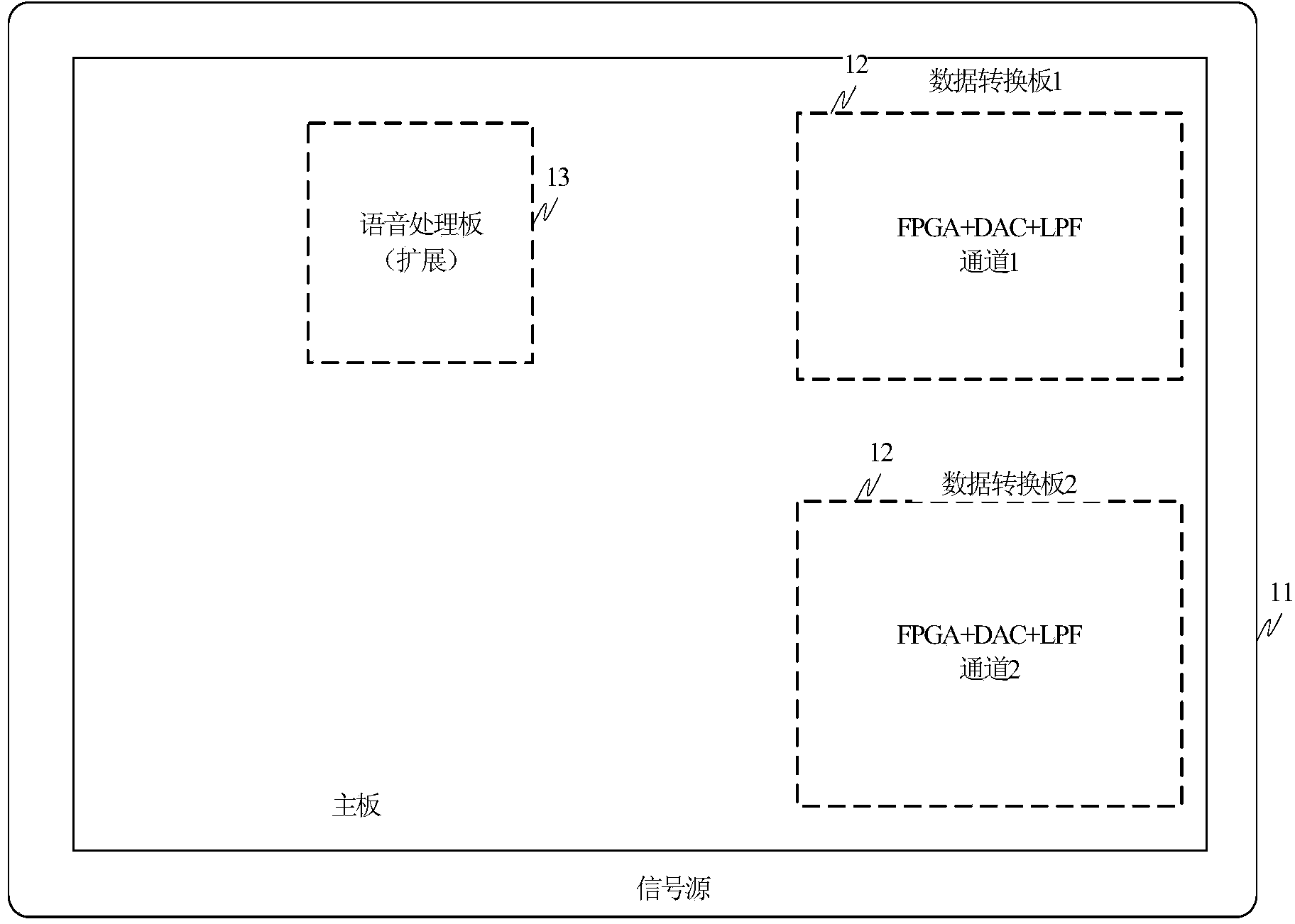
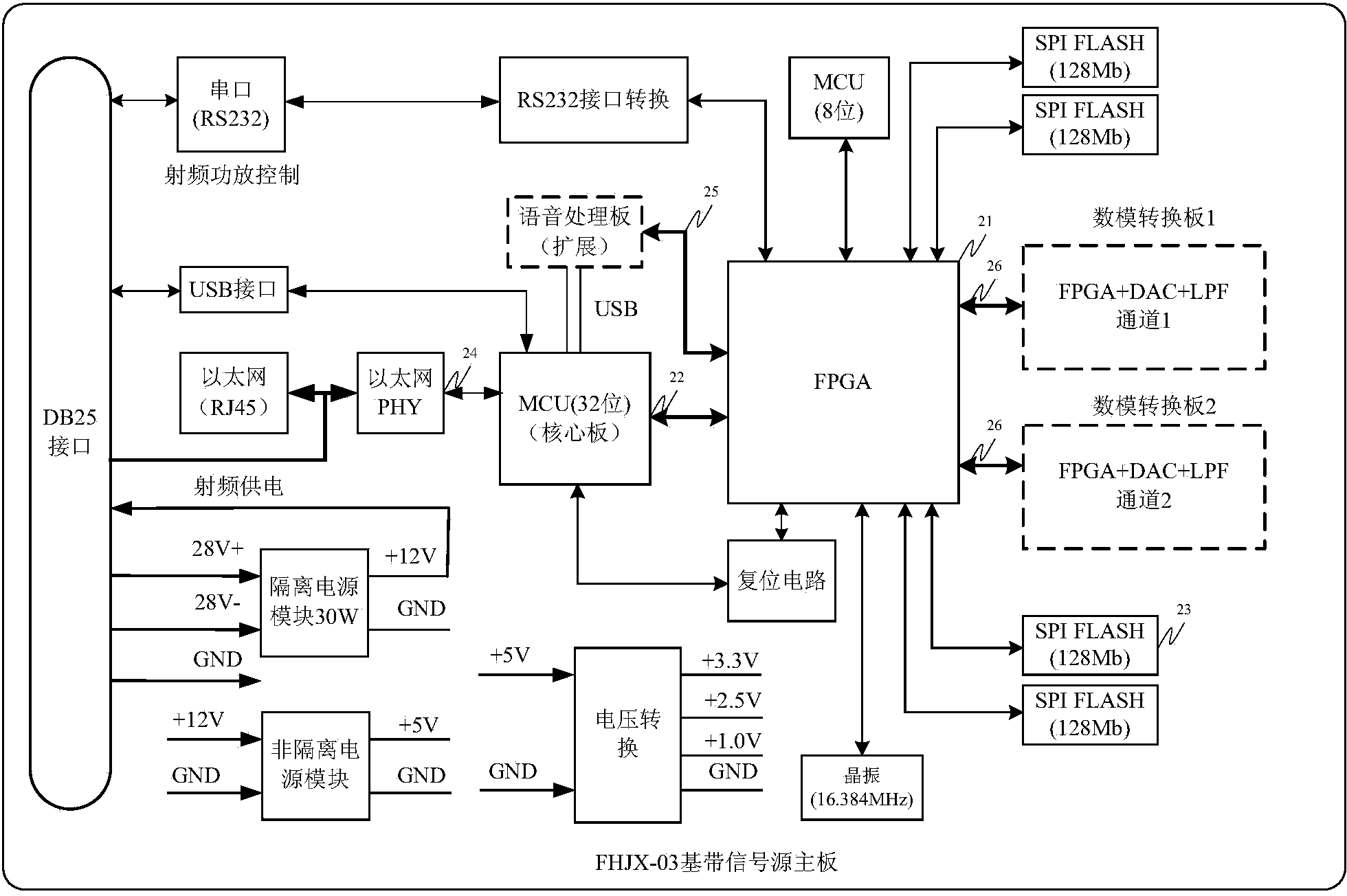
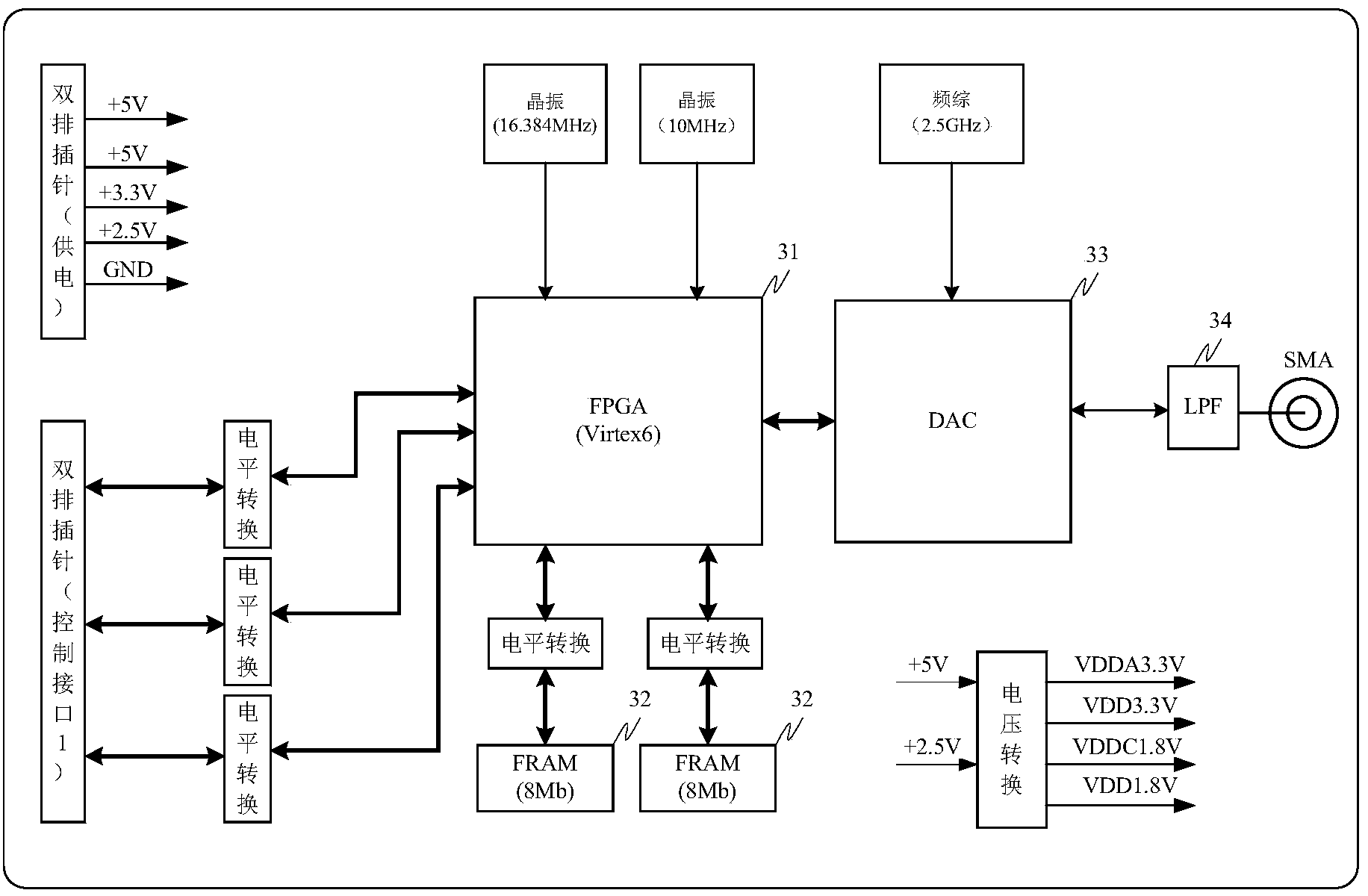
The invention discloses a signal interference device. The signal interference device comprises a signal source mainboard and a data conversion board, wherein the data conversion board is used for converting the stored interference signal digital waveforms into analog waveforms through a DAC chip in a storage transmitting mode, interference signals comprise broadband multi-carrier signals, or multitone signals, or single-tone signals, or broadband noise signals, or swept-frequency signals, in the DDS mode, the multiple interference signal digital waveforms are generated through multiple DDS modules and then are converted into the analog waveforms through the DAC chip, and the signal source mainboard is used for controlling the data conversion board to switch between the storage transmitting mode and the DDS mode. According to the signal interference device, the generated interference signals are stored, corresponding interference signals can be generated when equipment is started, work can be conducted in the mode that real-time calculation and real-time loading of waveforms are achieved according to requirements, the interference modes are diversified, the manual operation processes of workers are simplified, and operation and maintenance of interference equipment are facilitated.
Owner:北京中科飞鸿科技股份有限公司
Method and system for evaluating non-linear distortion, method and system for adjusting parameters
InactiveCN102866296ASpectral/fourier analysisFrequency response correctionNonlinear distortionHarmonic
The invention describes embodiments for evaluating non-linear distortion and adjusting parameter for improving sound. A test signal comprising at least two of simultaneously audible single-tone signals can be generated. A single tone is a fundamental tone, and the other single tones are the harmonic waves of the fundamental tone. As an example, the ratio of the number of the non-linear distortion products which is not fit with the frequency of the single tone to the number of all the products is greater than 0.80. The spectrum analysis is carried out aiming at the response of a loudspeaker to the test signal. A non-linear distortion value is evaluated by taking the energy which is under the harmonic frequency of the fundamental tone signal rather than the frequency of the single tone signal as the contribution of the non-linear distortion. The subjectivity-related measurement of the non-linear distortion is obtained for adjusting parameters for improving the low-frequency output of one or multiple loudspeaker(s).
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Shaped Reflectors for Enhanced Optical Diffusion in Backlight Assemblies
InactiveUS20120176786A1Increased ability to diffuseConvenient lightingNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceFluorescent lampReflectivity
An assembly for diffusing a plurality of light sources. A diffusing device is placed adjacent to the plurality of light sources and preferably contains a plurality of shaped reflectors placed on the diffusing device where a shaped reflector is positioned adjacent to each light source. The shaped reflectors are placed in a one-to-one relationship with the light sources, which can be LED or fluorescent or any other type of light source. The reflectors may be single-tone, multi-tone, or gradient-tone and generally have a higher amount of reflectivity near the central axis of the light source and a lower reflectivity away from the central axis of the light source. The shaped reflectors may be used in both direct-lit and edge-lit orientations.
Owner:AMERICAN PANEL CORP INC
Reversing alarm
InactiveUS6885295B2Facilitate sound source locationImprove practicalityAcoustic signal devicesOptical signallingSound sourcesZener diode
A reversing alarm for a vehicle emits an audible signal in the form of pulses of broad band sound when the vehicle is put into reverse gear. The broad band sound allows persons in the vicinity to locate the vehicle, as the human brain is able to process broad band sound to pinpoint the location of the sound source in a way which is not possible with single tone sounds. The alarm is implemented via a simple electronic circuit which uses a zener diode as a signal generator 20 to generate the broad band sound.
Owner:YAMAGUCHI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD +1
Audio single tone separation method, audio single tone separation device, computer equipment and storage medium
PendingCN110335622AMonophonic separation implementationSpeech recognitionTime domainFrequency spectrum
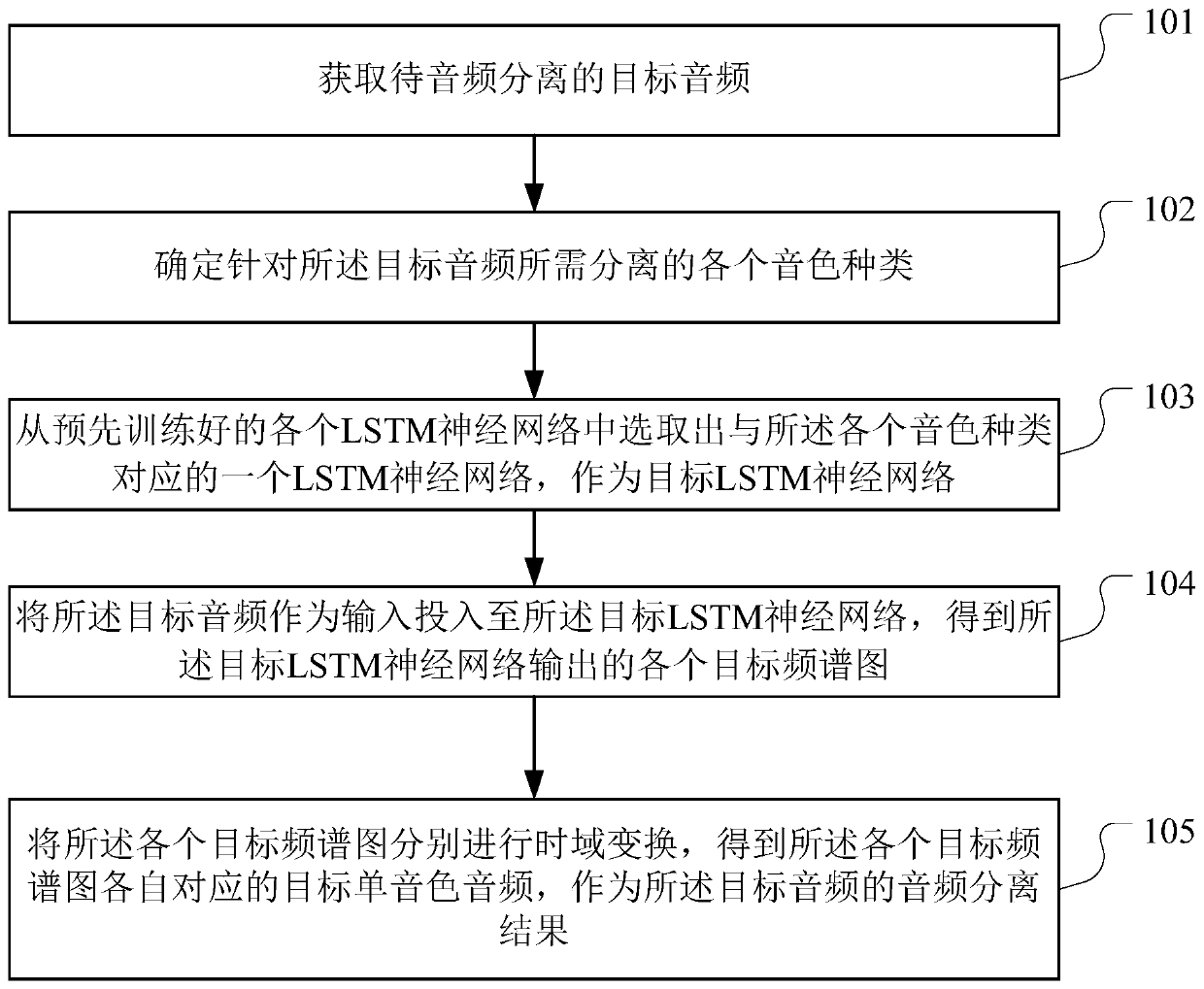
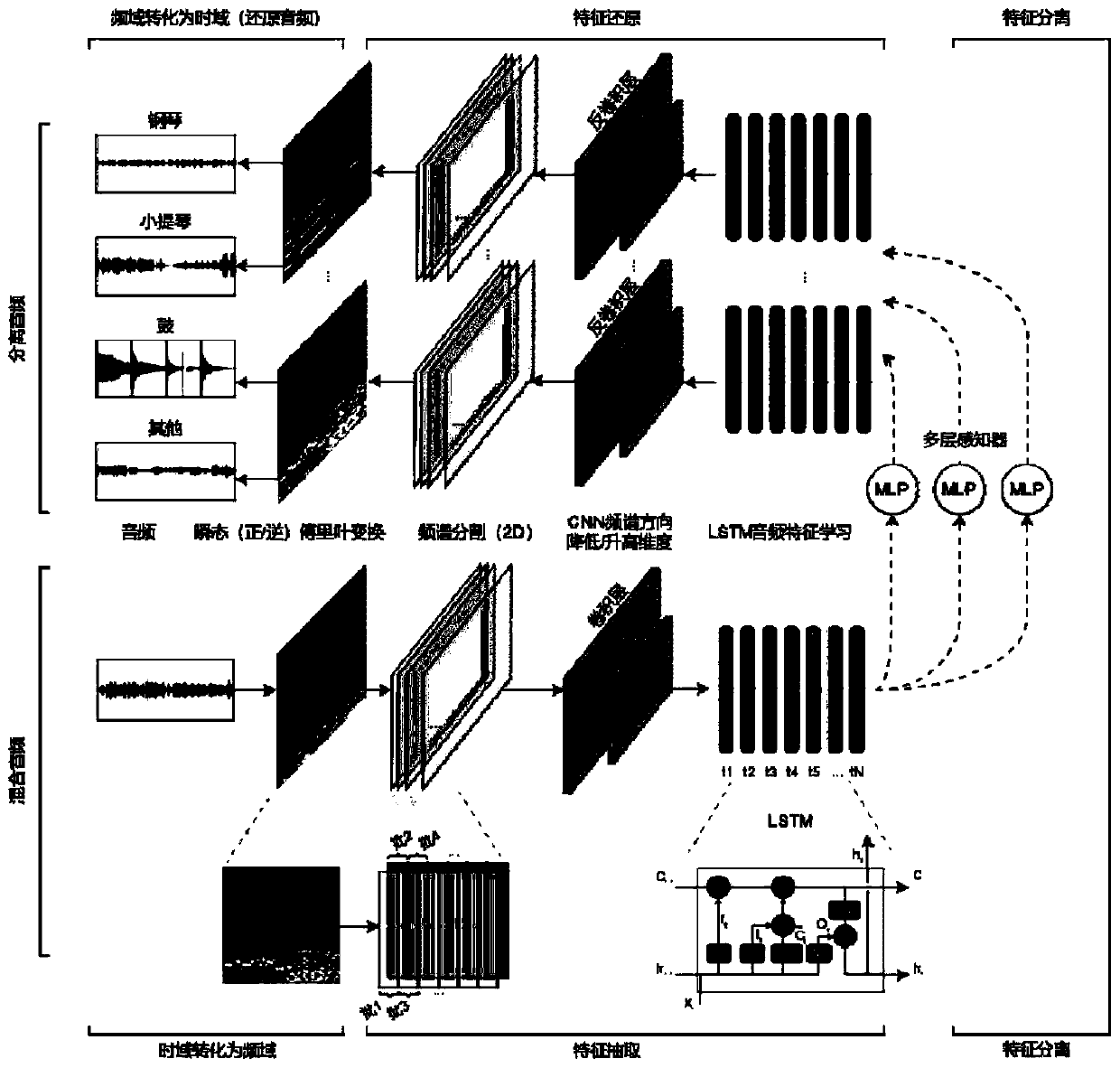
The invention discloses an audio single tone separation method, an audio single tone separation device, computer equipment and a storage medium. The invention is applied to the technical field of audio processing, and is used for solving the problem that single tone separation cannot be realized in the prior art. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: acquiring a target audio to be subjected to audio separation; determining each tone type required to be separated for the target audio; selecting one LSTM neural network corresponding to each tone type from each pre-trained LSTM neural network, wherein the LSTM neural networks serve as target LSTM neural networks, each LSTM neural network is obtained by pre-training audio samples corresponding to different timbretype combinations, and each timbre type combination is composed of more than two timbre types; inputting the target audio as input into a target LSTM neural network to obtain each output target spectrogram; and performing time domain transformation on each target spectrogram to obtain a target single-tone audio corresponding to each target spectrogram, and taking the target single-tone audio as anaudio separation result of the target audio.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Method and apparatus for waveform generation
ActiveUS8554085B1Wide bandwidthCreate efficientlyCode division multiplexOptical multiplexPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A spread spectrum waveform generator has a photonic oscillator and an optical heterodyne synthesizer. The photonic oscillator is a multi-tone optical comb generator for generating a series of RF comb lines on an optical carrier. The optical heterodyne synthesizer includes first and second phase-locked lasers, where the first laser feeds the multi-tone optical comb generator and the second laser is a single tone laser whose output light provides a frequency translation reference. At least one photodetector is provided for heterodyning the frequency translation reference with the optical output of the photonic oscillator to generate a spread spectrum waveform. A receiver pre-processor may be provided to operate on the spread spectrum waveform.
Owner:HRL LAB
Frequency domain arrival detection method of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system
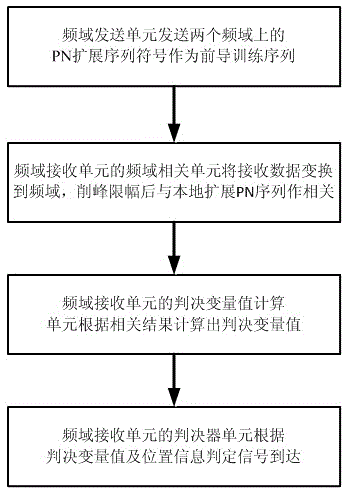
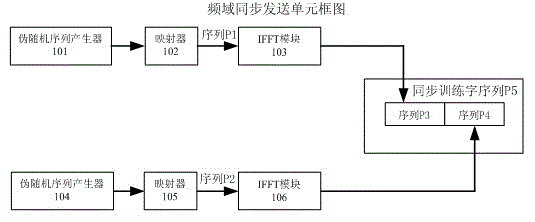
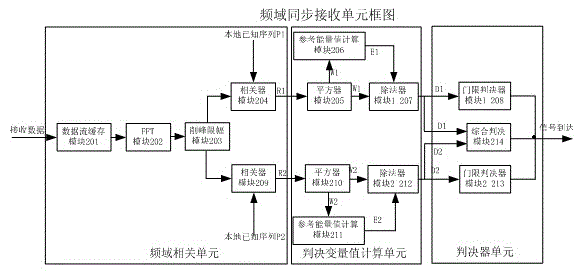
ActiveCN102752257AReliable Arrival DetectionAvoid interferenceMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTime domainFast Fourier transform
The invention discloses a frequency domain arrival detection method of an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system. A frequency domain synchronous transmitting unit adopts two frequency domain pseudorandom sequences with identical length but different phases, a zero is respectively compensated to each pseudorandom sequence to obtain a pseudorandom expanded sequence, then rapid Fourier inverse transformation operation is carried out on the pseudorandom expanded sequences to obtain time domain sequences, and then the two time domain sequences are cascaded to obtain a synchronous pilot training sequence. A frequency domain synchronous receiving unit adopts a time window with a length being identical to that of one pseudorandom expanded sequence, rapid Fourier transformation operation is carried out on data inside the window, then the data is correlated with a known local pseudorandom expanded sequence after being subjected to peak clipping and amplitude limitation processing, and the signal arrival is judged by utilizing excellent autocorrelation property of the pseudorandom sequence and simultaneously considering a threshold and position-based detection method. Due to the adoption of the frequency domain arrival detection method of the orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system, interference of a single tone, narrow band and the like can be effectively resisted, and reliable signal arrival detection can also be realized under a severe channel condition.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A kind of interleaving method used in wlan frequency hopping system
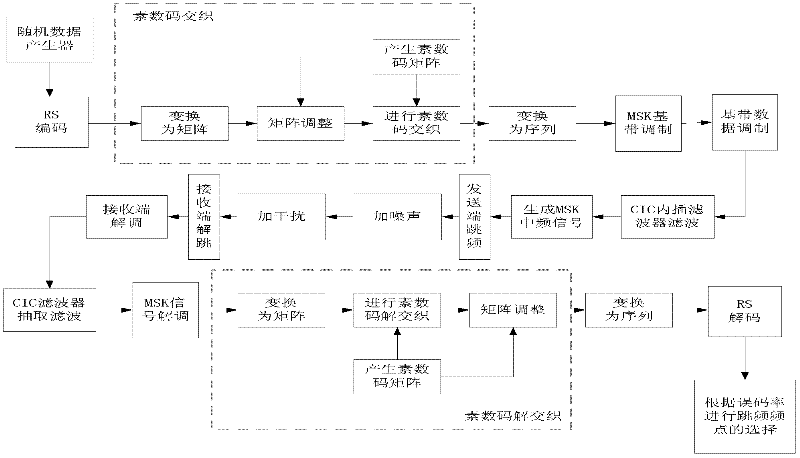
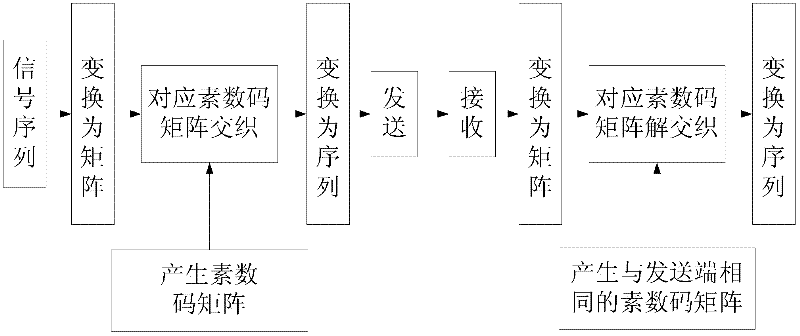
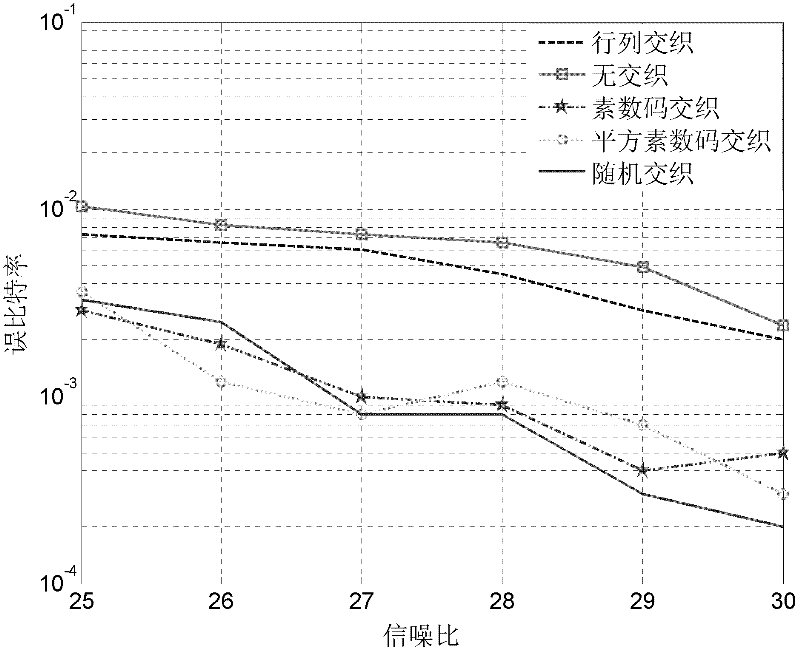
InactiveCN102299727AImprove anti-interference abilityImproved latency is higherError preventionTime delaysMatrix sequence
The invention relates to an interlacing method used for a WLAN frequency hopping system, and belongs to the communication signal processing technology field. An information sequence is converted into an m*n matrix, according to a matrix size of a signal sequence, a prime code matrix of an appropriate dimension is generated, according to a prime code matrix sequence the signal sequence is subjected to interlacing, and after prime code interlacing the signal sequence is converted into a signal sequence and is sent. After receiving the signal sequence, a receiving terminal converts the signal sequence into an m*n matrix with a same dimension of the sending terminal, the signal sequence is subjected to deinterlacing by using a prime code matrix which is synchronous with the sending terminal, and the signal sequence after deinterlacing is converted into a signal sequence used for post processing. The method is flexible in realization, and when a series of errors appear, error code resistance performance which exceeds error correction capability of an error correction code can be improved; the method has a good inhibition effect on single-tone interference; situations of high time-delay and large memory space in the prior art are improved, and anti-interference performance of frequency hopping communication is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Narrow-band short-wave channel equalization algorithm under variable channel coefficient
InactiveCN102325102AImprove performanceImprove signal-to-noise ratioTransmitter/receiver shaping networksSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Algorithm
The invention relates to the technical field of short-wave data communication and specifically discloses a narrow-band short-wave channel equalization algorithm under a variable channel coefficient. The algorithm comprises the following specific steps: step 1) modeling a short-wave channel and performing initial estimation on the short-wave channel; step 2) utilizing a DDEA (data directed equalization algorithm) channel equalization algorithm to estimate the best estimation value of a user data sequence, and solving the user data sequence; step 3) performing short-wave channel tracking and solving the channel coefficient at any sampling time; step 4) utilizing a VCC-DDEA (variable channel coefficient-data directed equalization algorithm) to eliminate inter-symbol interference introduced in a training sequence and solving the best estimation value of the user data sequence under a time-varying channel; and step 5) amending user data which is estimated by the DDEA algorithm, further tracking the channel and amending a short-wave channel tracking value. The DDEA equalization algorithm using the variable channel coefficient to eliminate the inter-symbol interference introduced in the training sequence is adopted in the algorithm provided by the invention, thereby effectively improving the performance of narrow-band short-wave single-tone serial data communication and improving the signal-noise ratio by more than 5dB under the conditions of the same communication data rate and the same error rate.
Owner:NAVAL AERONAUTICAL & ASTRONAUTICAL UNIV PLA
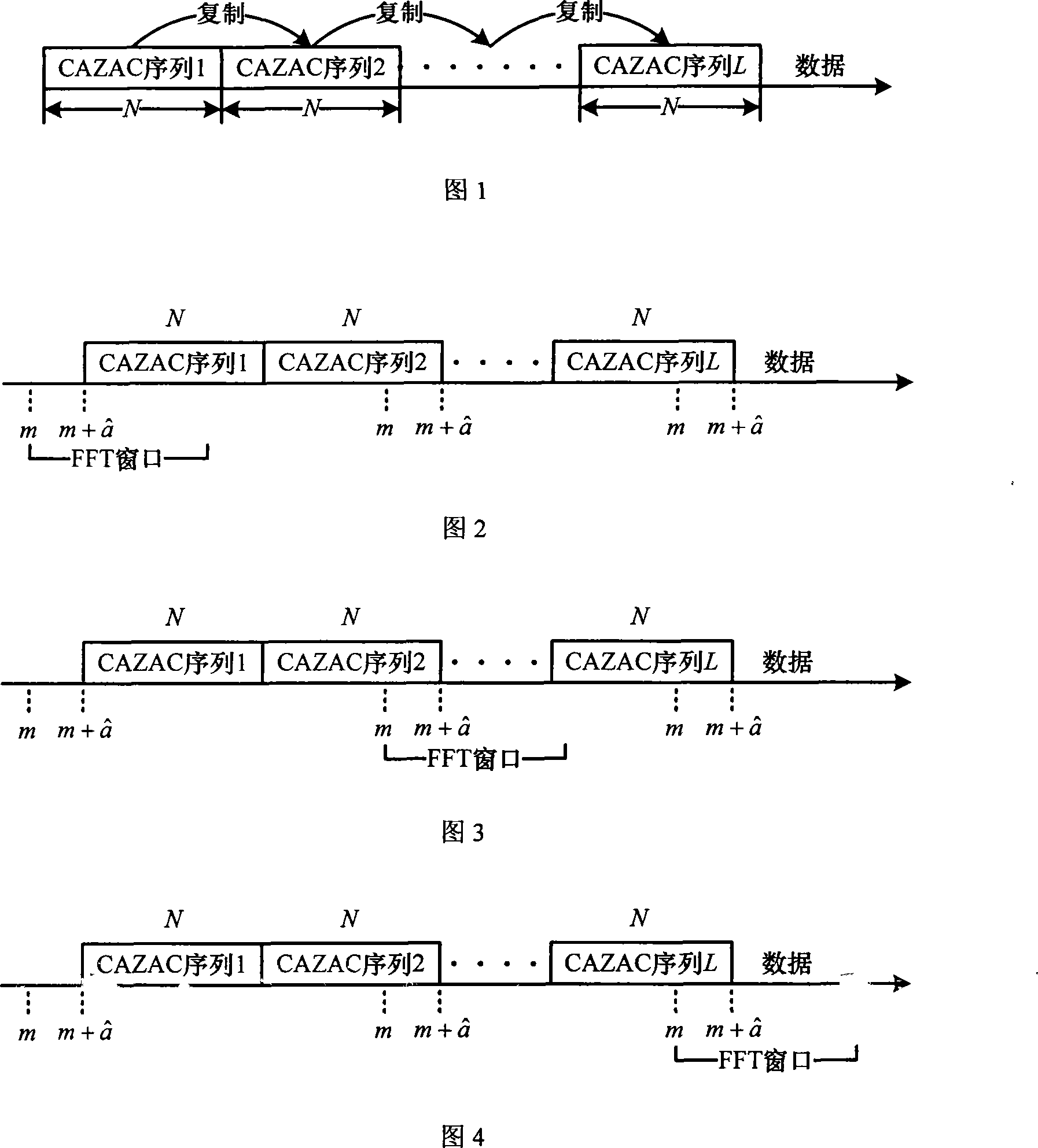
A frame synchronization method
InactiveCN101242389AConvenient interference filteringEasy to filterRadio transmission for post communicationMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemComputer science
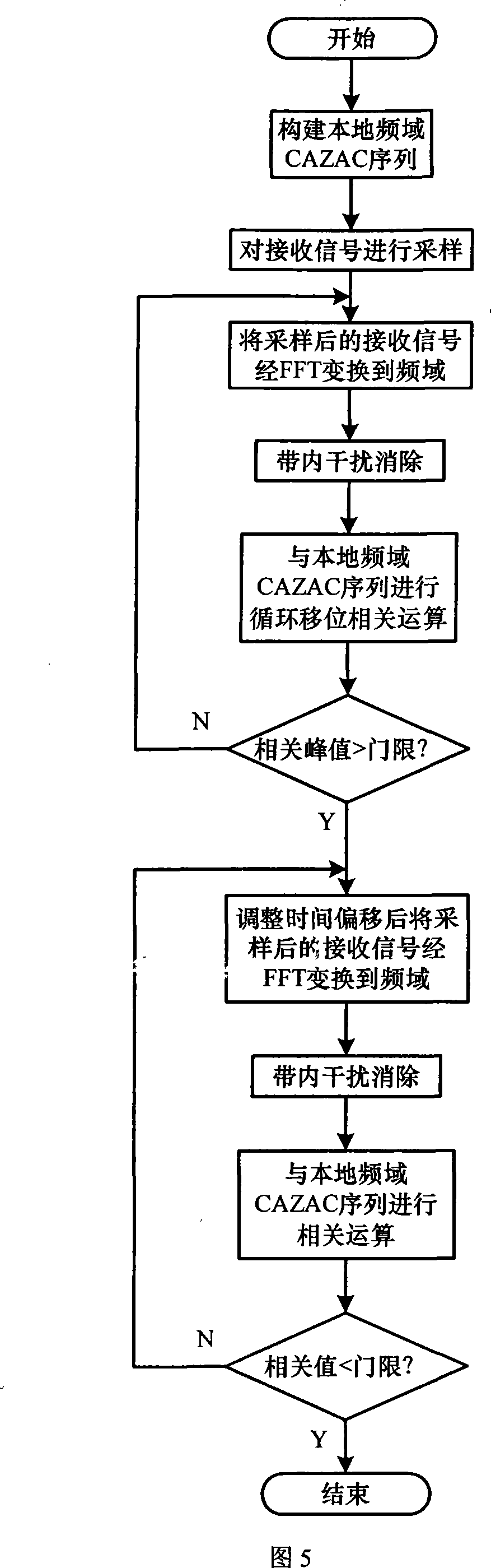
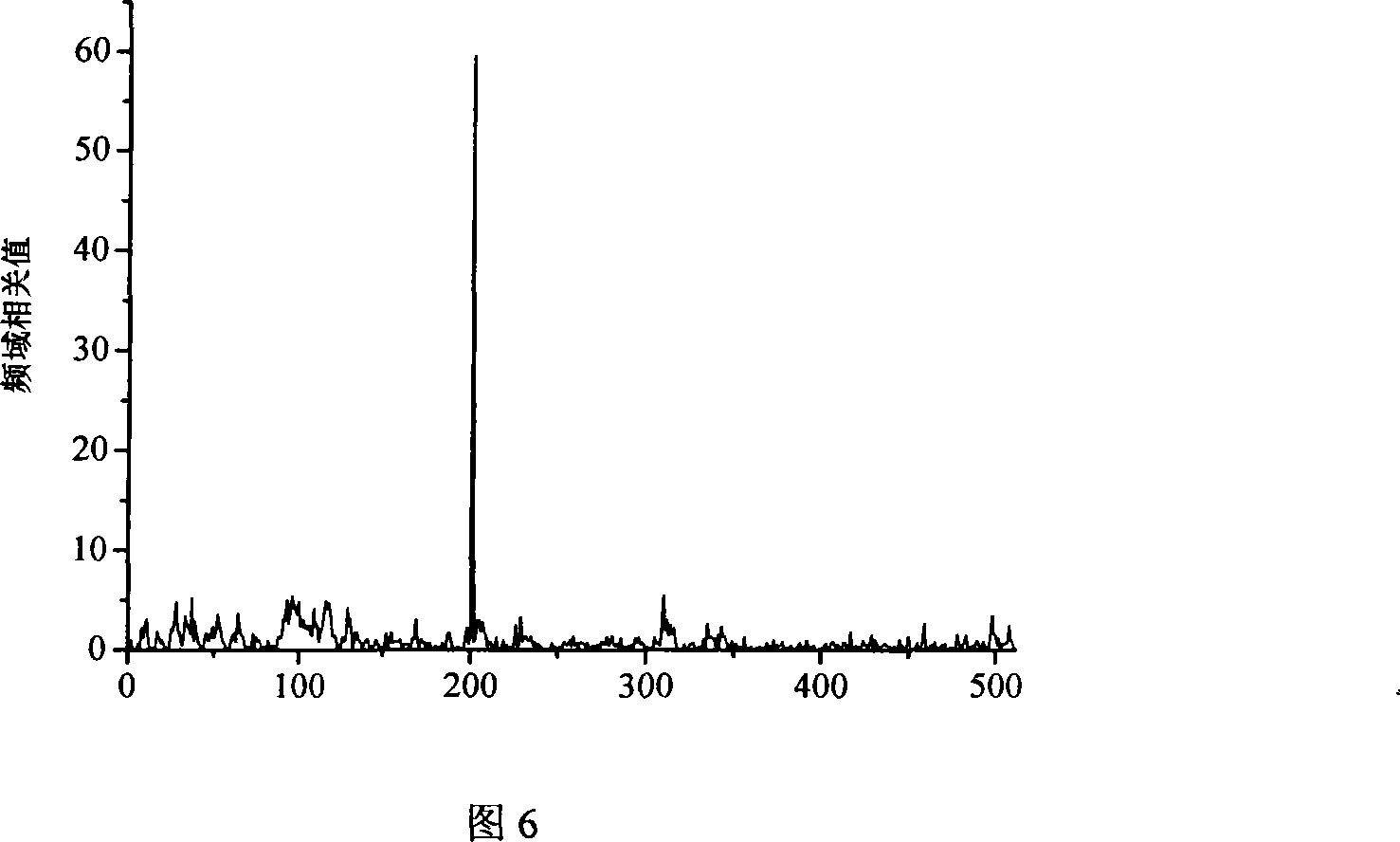
The invention provides a frame alignment method which uses constant amplitude zero auto-correlation (CAZAC) sequence as training sequence and frame synchronization tests in frequency domain, by use of CAZAC sequence characteristic and frequent denise property. The method comprises: generating same CAZAC sequence as training sequence at the receiving and emitting ends of a communication system, carrying out interface processing the received signal in frequency domain at the receiving end firstly, then carrying out correlation processing of the CAZAC sequence produced at the receiving end, and acquiring synchronous information by judging correlation peak. Since single-tone interference, multi-tone interference or narrow-band interference can be filtered conveniently in frequency domain, the invention can also get good performance when in-band interface exists in channel.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
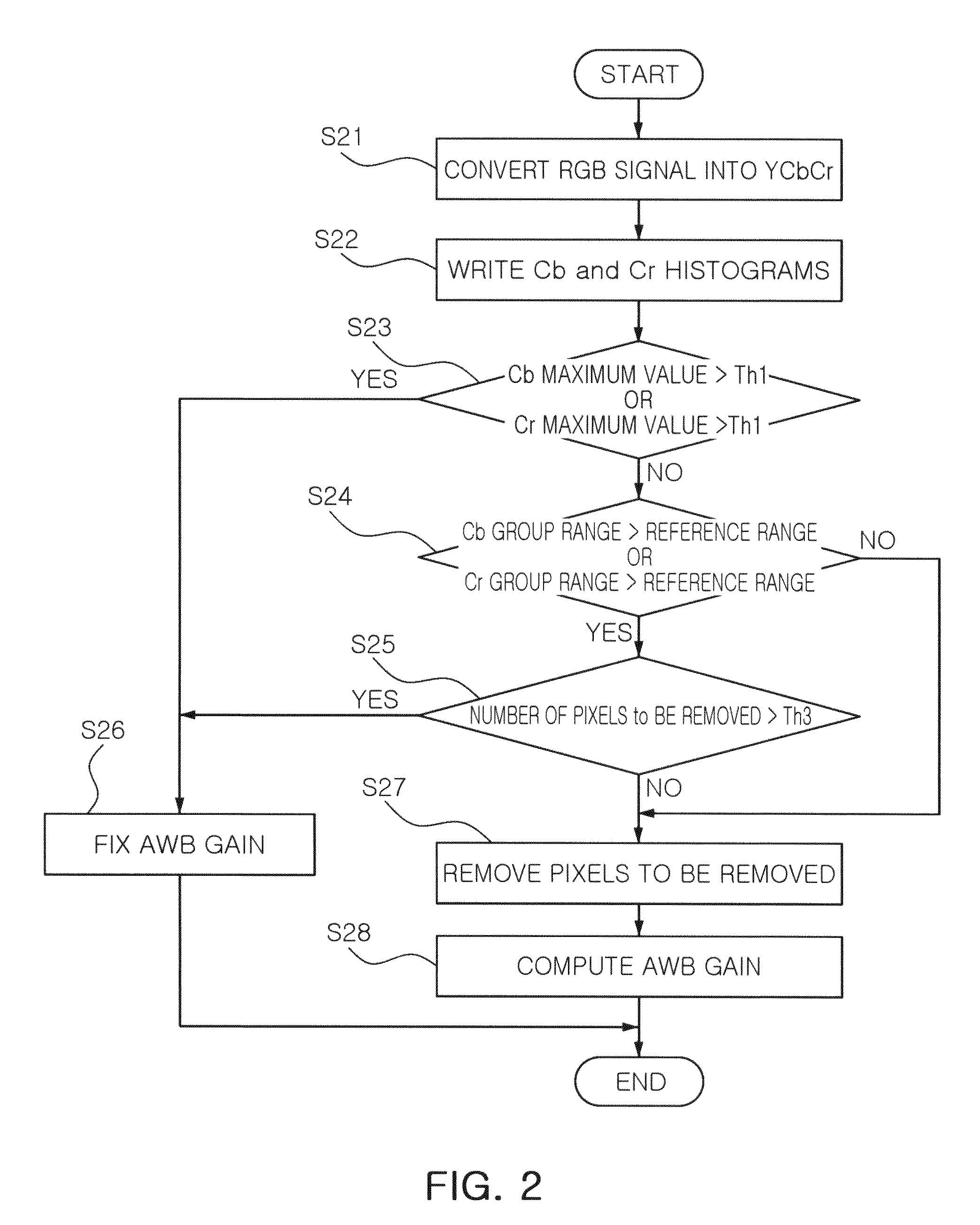
Apparatus and method for auto white balance control considering the effect of single tone image
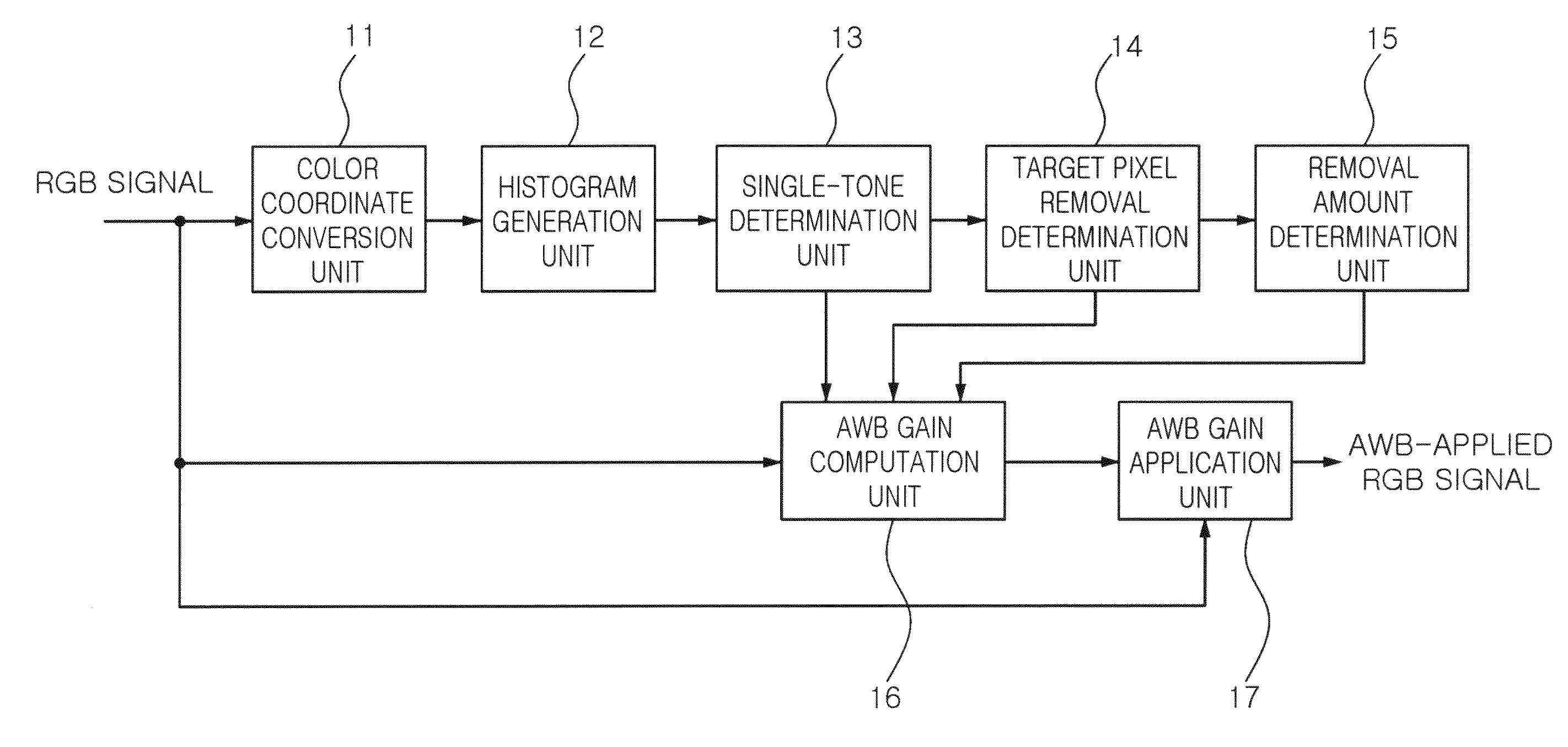
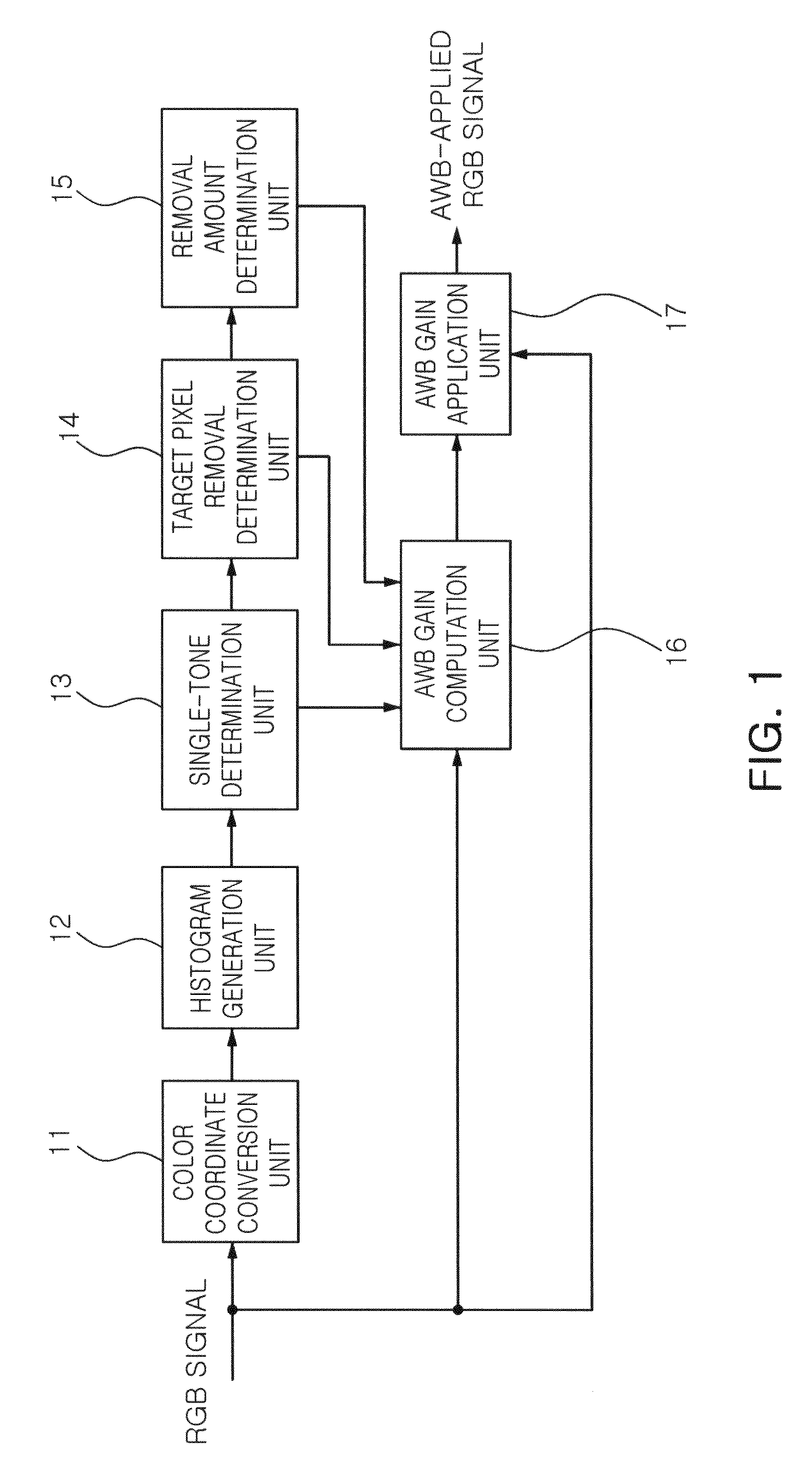
ActiveUS20100194991A1Prevent erroneous white balanceTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsEquilibrium controlHistogram
An apparatus for auto white balance includes a histogram generation unit writing respective histograms of Cb values and Cr values with regard to pixels included in an input image frame, a single-tone determination unit comparing respective maximum values of the histograms of Cb values and Cr values with a first threshold value, and determining the input image frame as a single-tone image if at least one of the maximum values is higher than the first threshold value, and an auto white balance gain computation unit computing and an auto white balance gain by using color information of an input image frame and outputting the computed auto white balance gain, wherein if the input image frame is determined to be a single-tone image, the auto white balance gain computation unit outputs an auto white balance gain computed with respect to a previous input image frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com