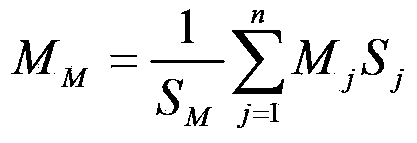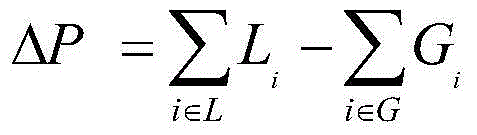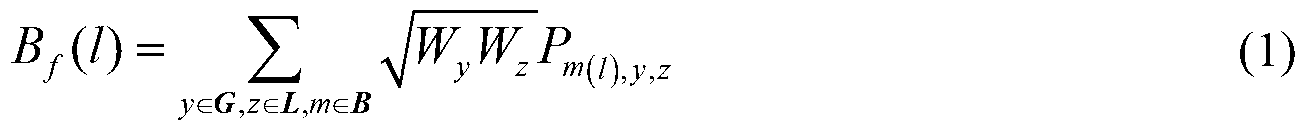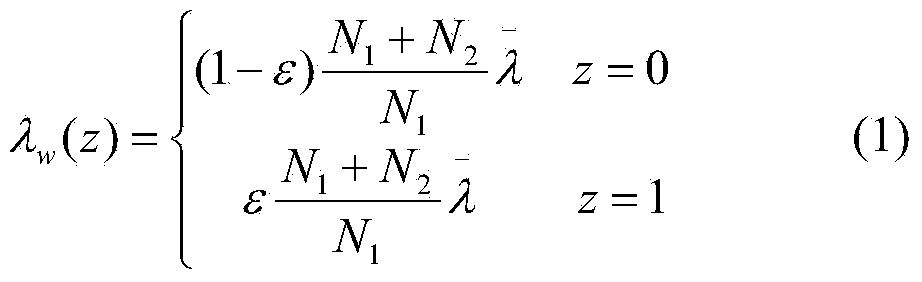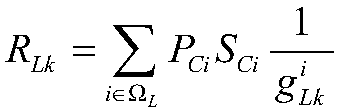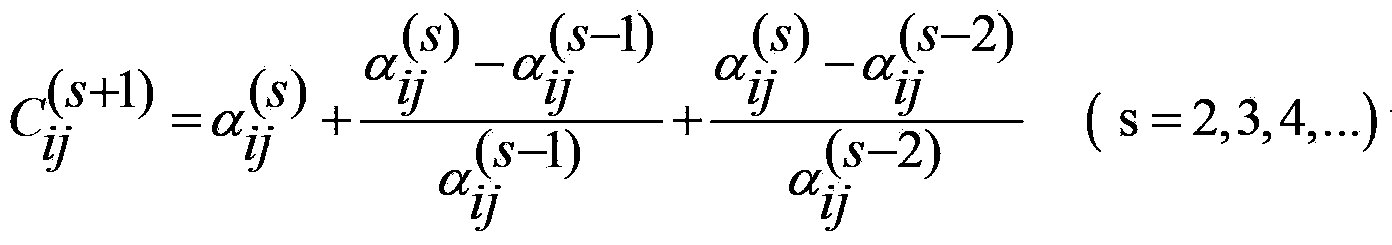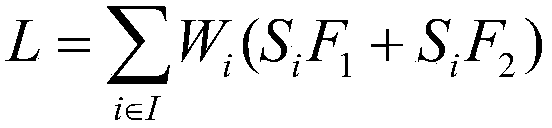Patents
Literature
357 results about "Cascading failure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A cascading failure is a process in a system of interconnected parts in which the failure of one or few parts can trigger the failure of other parts and so on. Such a failure may happen in many types of systems, including power transmission, computer networking, finance, transportation systems, organisms, human body, and ecosystems.
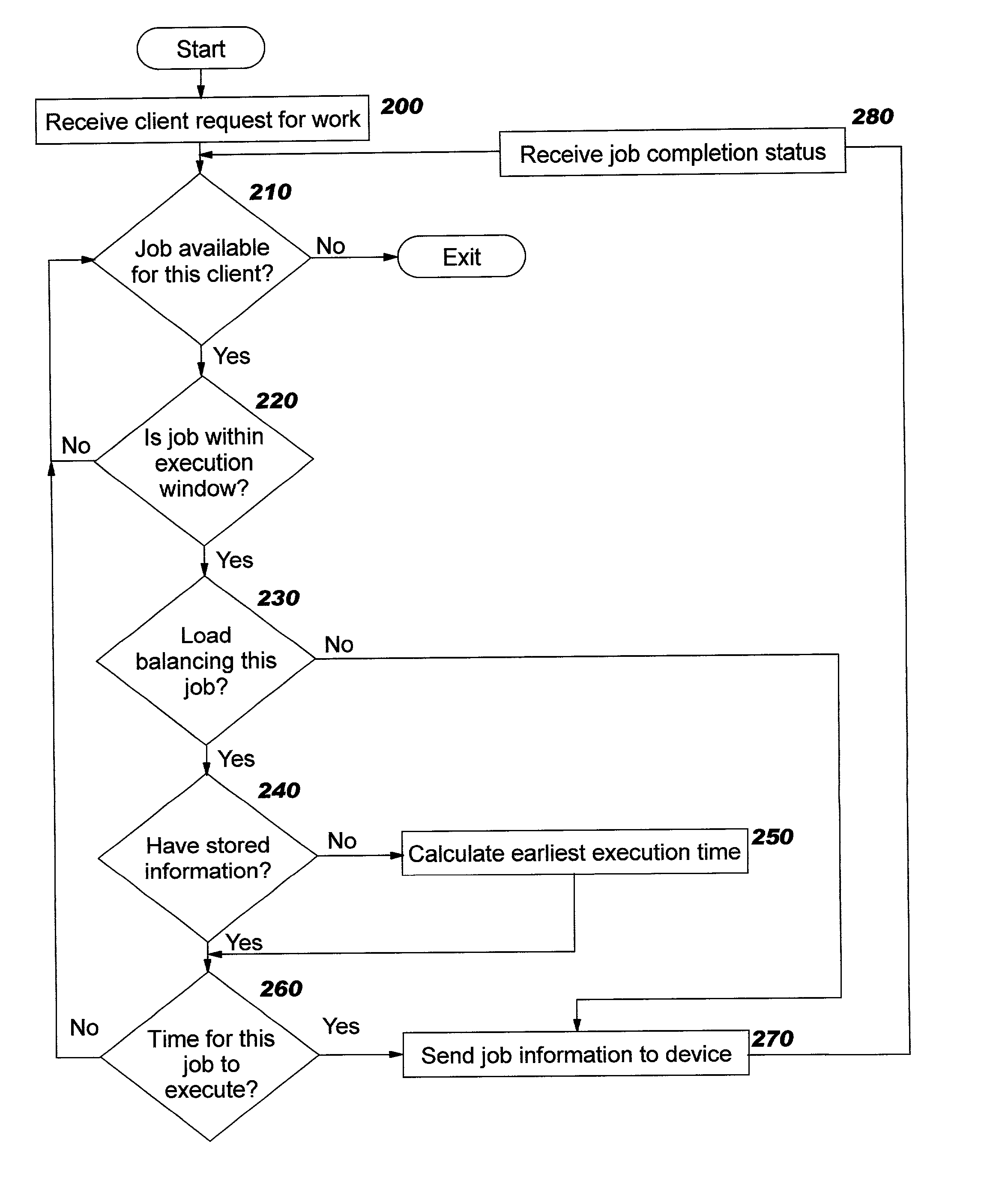
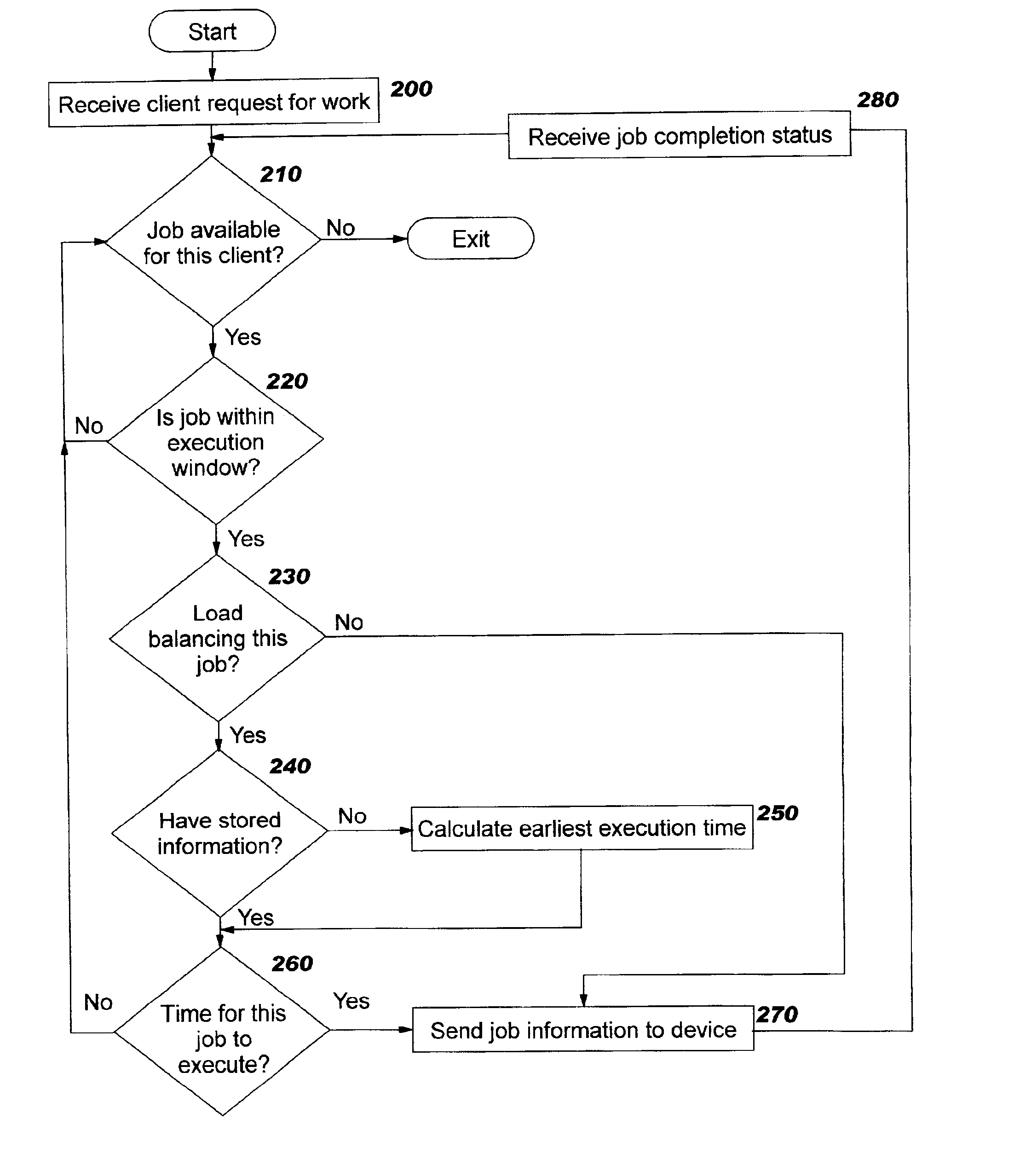
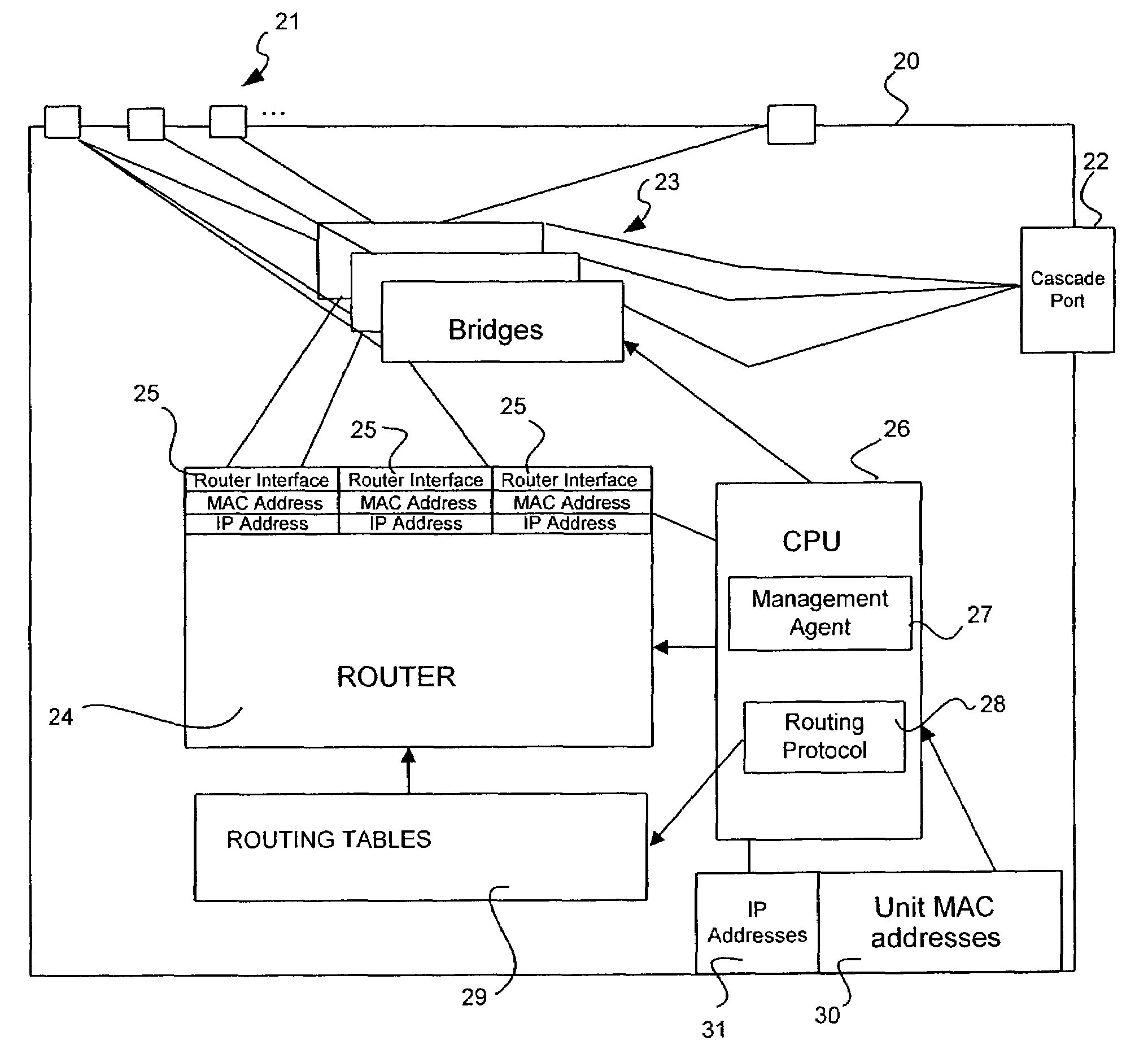
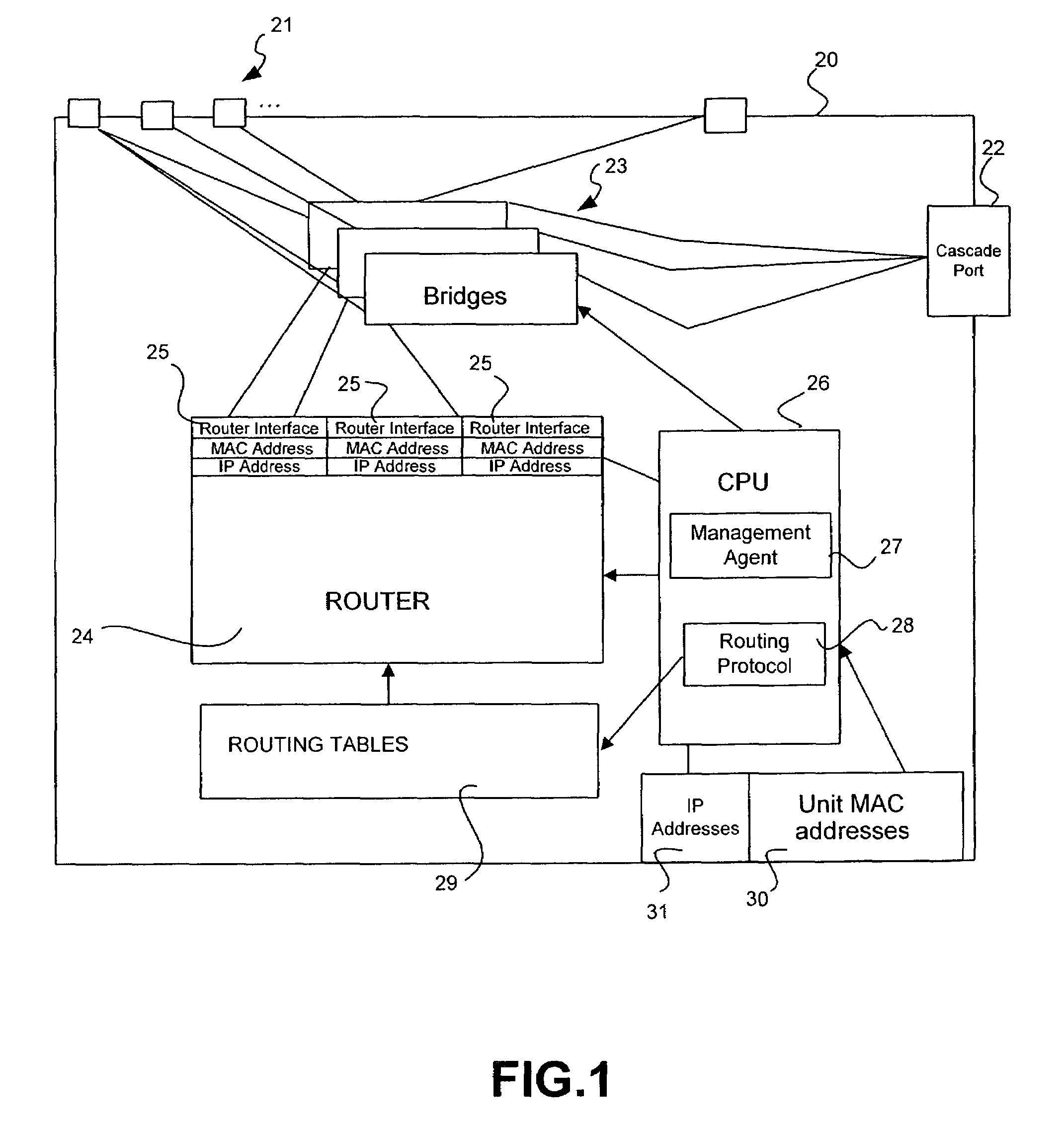
Technique for scheduling execution of jobs for or by network-connected devices
ActiveUS20020198923A1Limitations of prior art device management systems are avoidedAvoid restrictionsResource allocationMemory systemsCascading failureStart time
Methods, systems, computer program products, and methods of doing business by improving the scheduling of execution of jobs for or by network-connected devices, thereby enabling the job execution process to scale more easily, efficiently, and effectively to support large numbers of devices and / or users. Examples of jobs include, but are not limited to, distribution of resources (including software, configuration information, images, and other types of content) to a device, fetching a device's inventory information, backing up a device's contents, and so forth. Jobs are programmatically scheduled based upon a specified time internal, according to a class of the requester. Only if an earliest start time after which the job may be executed for this requester has been reached will the job be executed; otherwise, the job execution is delayed. The disclosed techniques lessen the need for additional servers to handle spikes in processing load, reduce the likelihood of reaching system overload, and reduce the likelihood of cascading failures that may occur when systems are overloaded.
Owner:TWITTER INC
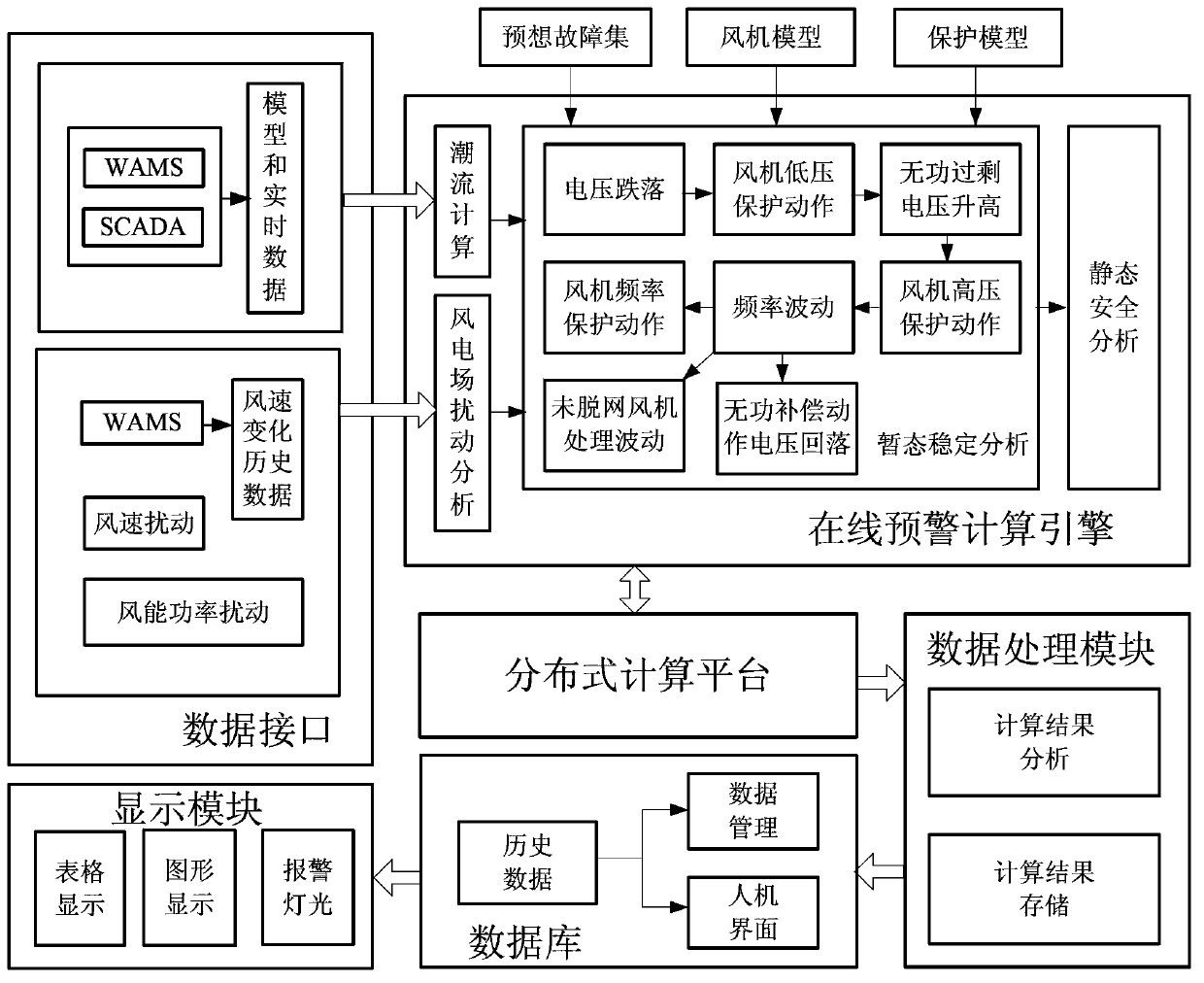
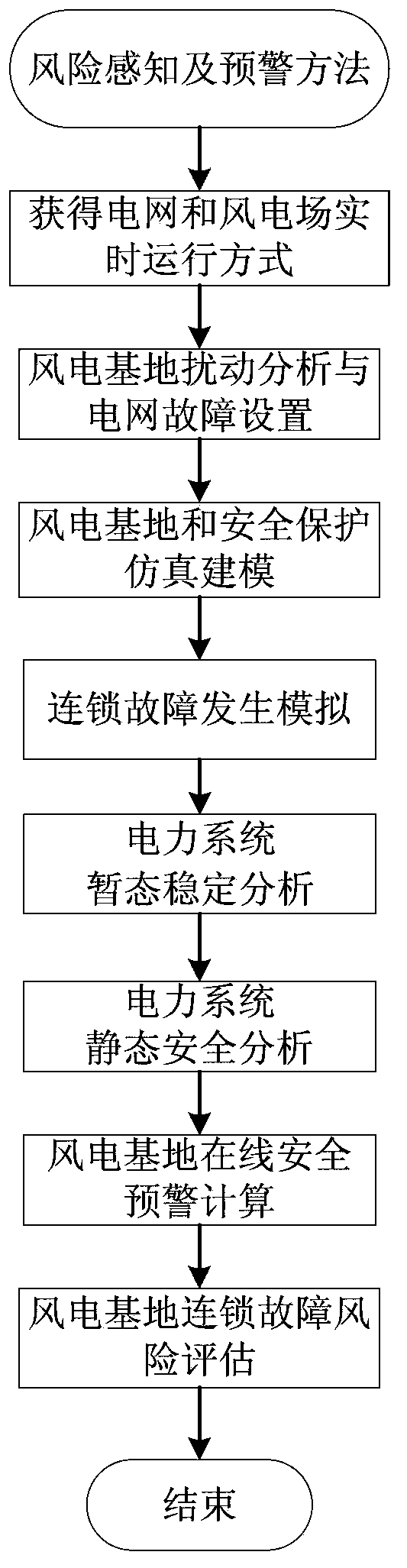
Risk perception and early warning method and system for cascading failures of wind power base
ActiveCN103400302ARealize online security early warningIn line with the real situationData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsWide areaCascading failure
The invention relates to a risk perception and early warning method and a system for cascading failures of a wind power base. The method provided by the invention comprises the steps of acquiring real-time operation mode data of a power grid and a wind power plant through SCADA (supervisory control and data acquisition) and a WAMS (wide area measurement system), acquiring possible wind power disturbance of the current power grid by combining with historical data of the wind power plant so as to establish a reasonable failure set, establishing a wind power generating unit dynamic model and a fan safety protection model, simulating dynamic operating conditions of the wind power plant after the power grid breaks down, carrying out power grid transient stabilization analysis after the wind power base breaks down and carrying out static safety analysis after a failure is removed, carrying out calculation and evaluation on the safety stabilization condition of the current power grid after occurrence of the wind power disturbance through a series of indexes which are applicable to early warning for the cascading failures of large wind power bases, analyzing the risk of the occurrence of cascading failures of the large wind power base, and realizing online safety early warning for an electric power system after the wind disturbance. The method and the system provided by the invention are easy to implement, and can visually reflect safe and stable operation conditions of the electric power system including the large wind power base.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
Circuit cluster-based method for analyzing grid cascading failure based on
InactiveCN102214920AFault controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsAc network circuit arrangementsProbit modelCascading failure
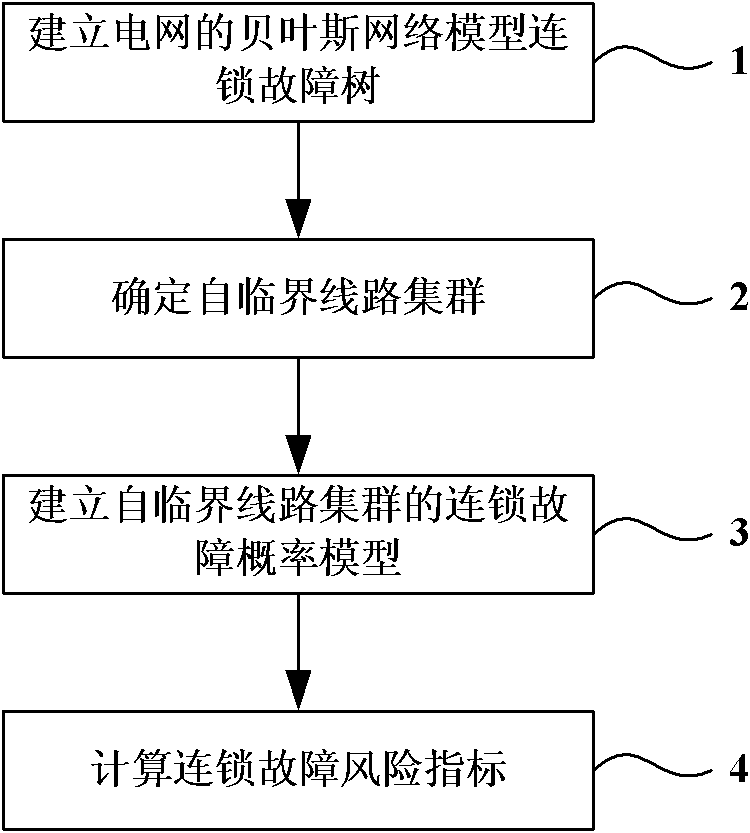
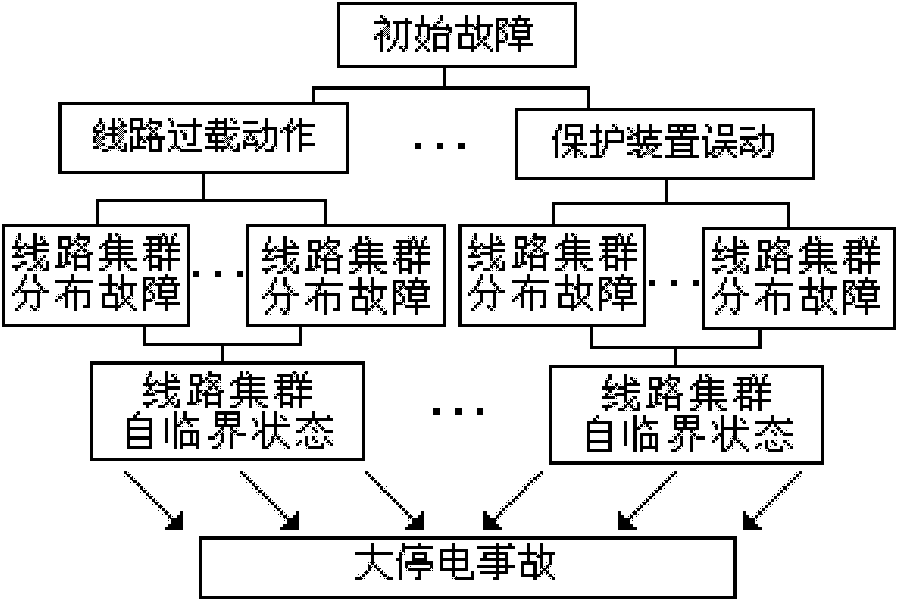
The invention discloses a circuit cluster-based method for analyzing a grid cascading failure, belonging to the technical field of safety protection of a power system. The method comprises the following steps of: applying a Bayes network failure tree theory to cascading failure analysis based on a distribution failure probability model of a self-critical circuit cluster and establishing a probability analysis model for a grid cascading failure based on cascading failure probability analysis of the self-critical circuit cluster in combination with the probability characteristic of a cascading failure developing stage; and through simulating a cascading failure process, performing risk assessment on the cascading failure by using a system load loss index and analyzing weak links of a system. By adopting the method, foundations are provided for a prevention strategy for further research on the reduction of cascading failure risk.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING) +1
Technique for scheduling execution of jobs for or by network-connected devices
InactiveUS6993763B2Avoid limitationsImprove schedulingResource allocationMemory systemsCascading failureStart time
Methods, systems, computer program products, and methods of doing business by improving the scheduling of execution of jobs for or by network-connected devices, thereby enabling the job execution process to scale more easily, efficiently, and effectively to support large numbers of devices and / or users. Examples of jobs include, but are not limited to, distribution of resources (including software, configuration information, images, and other types of content) to a device, fetching a device's inventory information, backing up a device's contents, and so forth. Jobs are programmatically scheduled based upon a specified time internal, according to a class of the requester. Only if an earliest start time after which the job may be executed for this requester has been reached will the job be executed, otherwise, the job execution is delayed. The disclosed techniques lessen the need for additional servers to handle spikes in processing load, reduce the likelihood of reaching system overload, and reduce the likelihood of cascading failures that may occur when systems are overloaded.
Owner:TWITTER INC
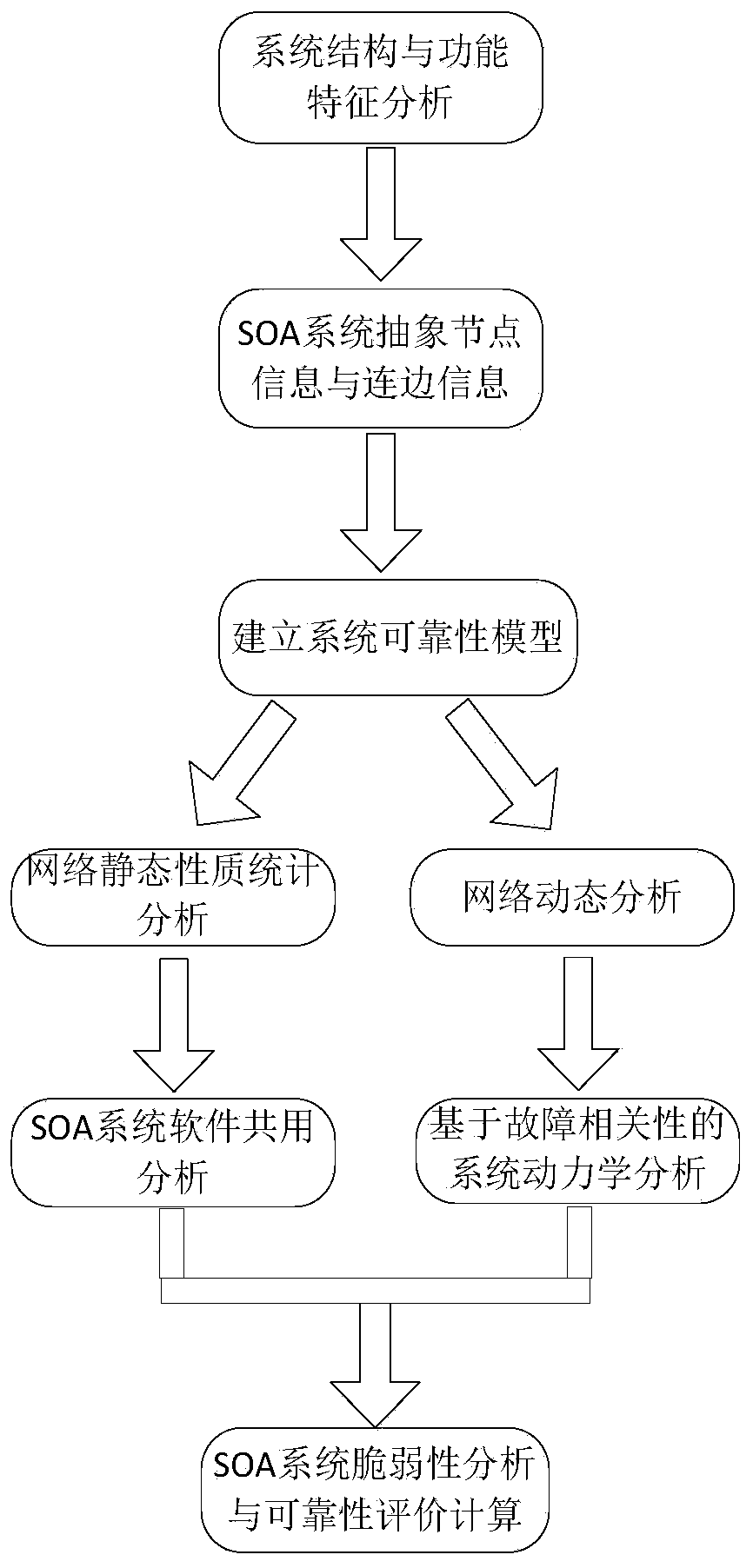
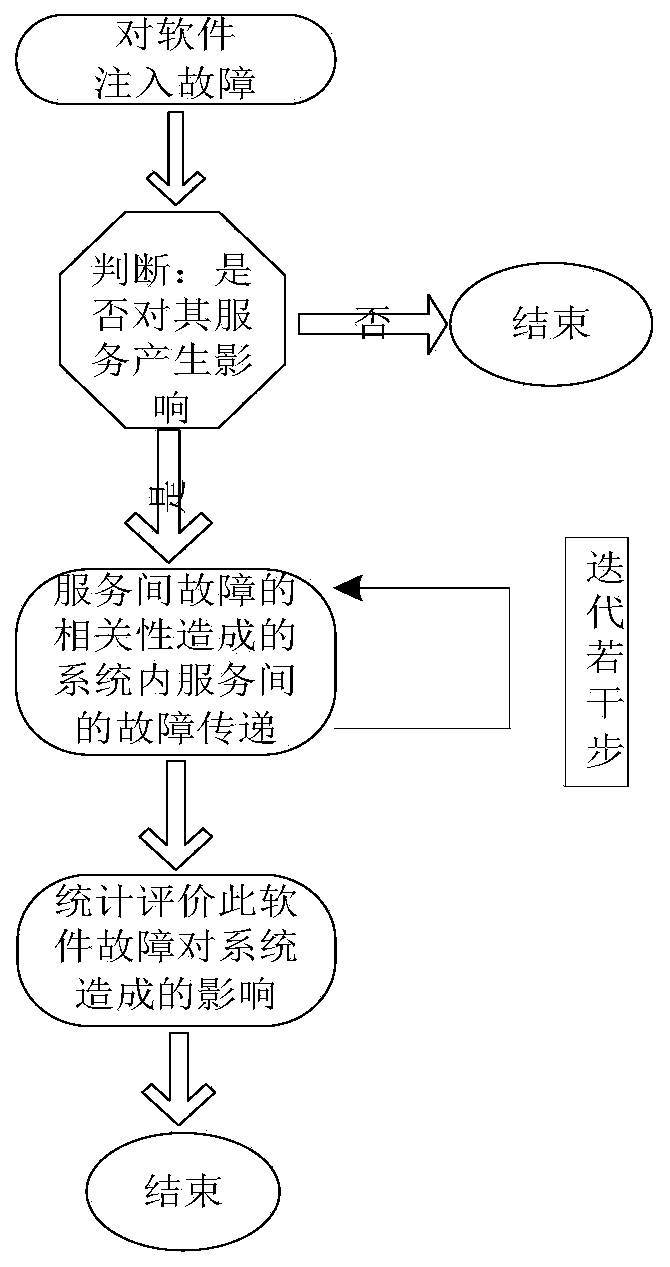
SOA system reliability evaluation method based on complex network theory
ActiveCN104298593AEmphasis on topological featuresEasy to operateSoftware testing/debuggingCascading failureStructure and function
An SOA system reliability evaluation method based on a complex network theory comprises four steps, belongs to the technical field of complex system reliability and aims at solving the problem that an SOA system is complex in structure and function and a traditional reliability analysis method is difficult to implement and even cannot be implemented and putting forward a methodology for effectively analyzing the reliability of the complex SOA system. The SOA system reliability evaluation method is characterized in that the method is innovatively integrated with the complex network theory, objects in the SOA system and the mutual effect of the objects are abstracted to be nodes and connecting lines in a complex network so as to establish a complex network failure model, a cascading failure model for the SOA system is put forward, and reliability analysis work is completed by utilizing a Monte Carlo simulation experiment on the basis so as to find key software and a weak structure influencing the system reliability. The SOA system reliability evaluation method is not limited by system scale, and increase of the system scale does not enable the calculation complex degree of the method to be remarkably improved. The SOA system reliability evaluation method is clear in physical significance and easily operated and implemented by engineers.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
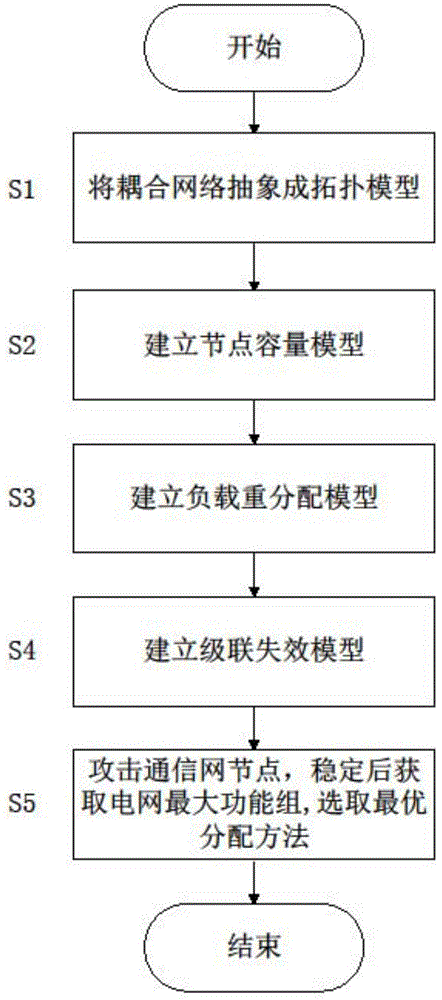
Load redistribution method for electric power coupling network to resist cascade failure
InactiveCN103957032AStrong invulnerabilityPower distribution line transmissionData switching networksCascading failureSocial benefits
The invention discloses a load redistribution method for an electric power coupling network to resist cascade failure. The load redistribution method for the electric power coupling network to resist the cascade failure comprises the steps of abstracting and simplifying equipment in a communication network and a power network as a coupling network topology model; establishing a node capacity model according to the characteristics of the coupling network; establishing a load redistribution model according to a distribution method of loads after node failure; establishing a cascade failure model according to the characteristics of node failure of the coupling network; attacking communications network nodes, obtaining the maximum function set of power grid nodes after the coupling network is stabilized, and selecting the optimal load redistribution method. The method improves the capacity of the electric power coupling network for resisting the cascade failure, is beneficial to reducing maintenance cost, and improves the economic benefits and the social benefits of an electrical power system.
Owner:北京华泽云通网络科技有限公司
Method for configuring PMU taking regard of high risk cascading failure path
InactiveCN101013812AImprove robustnessGuaranteed ObservabilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsSystems intergating technologiesCascading failureStatistical analysis
The invention discloses one power system broad measurement system PMU device optimization method, wherein, the current method concentrated on small PMU for total observation and this invention considers the minimum generation tree method to improve PMU system robust property on N-1 false without impact on multiple linkage.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
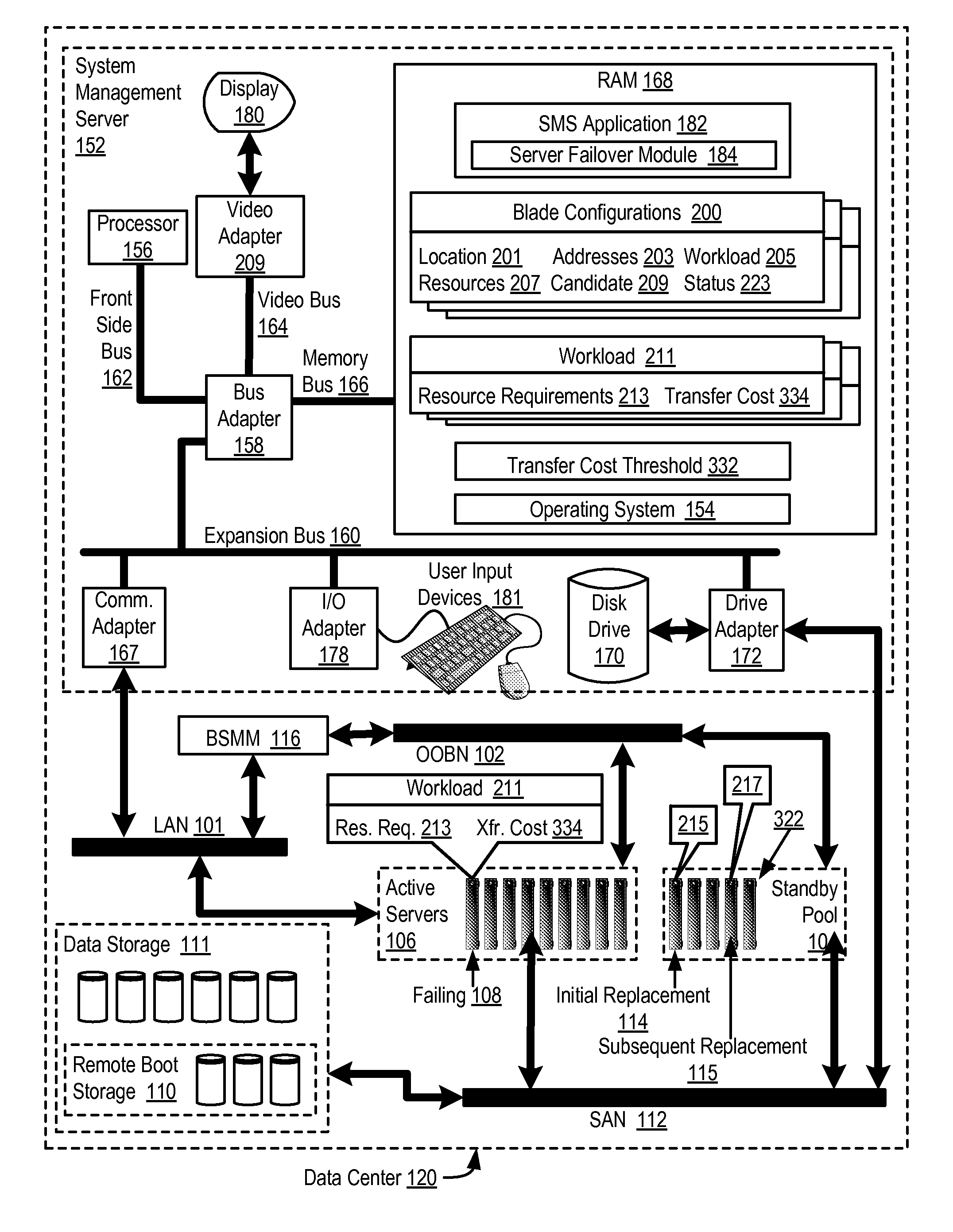
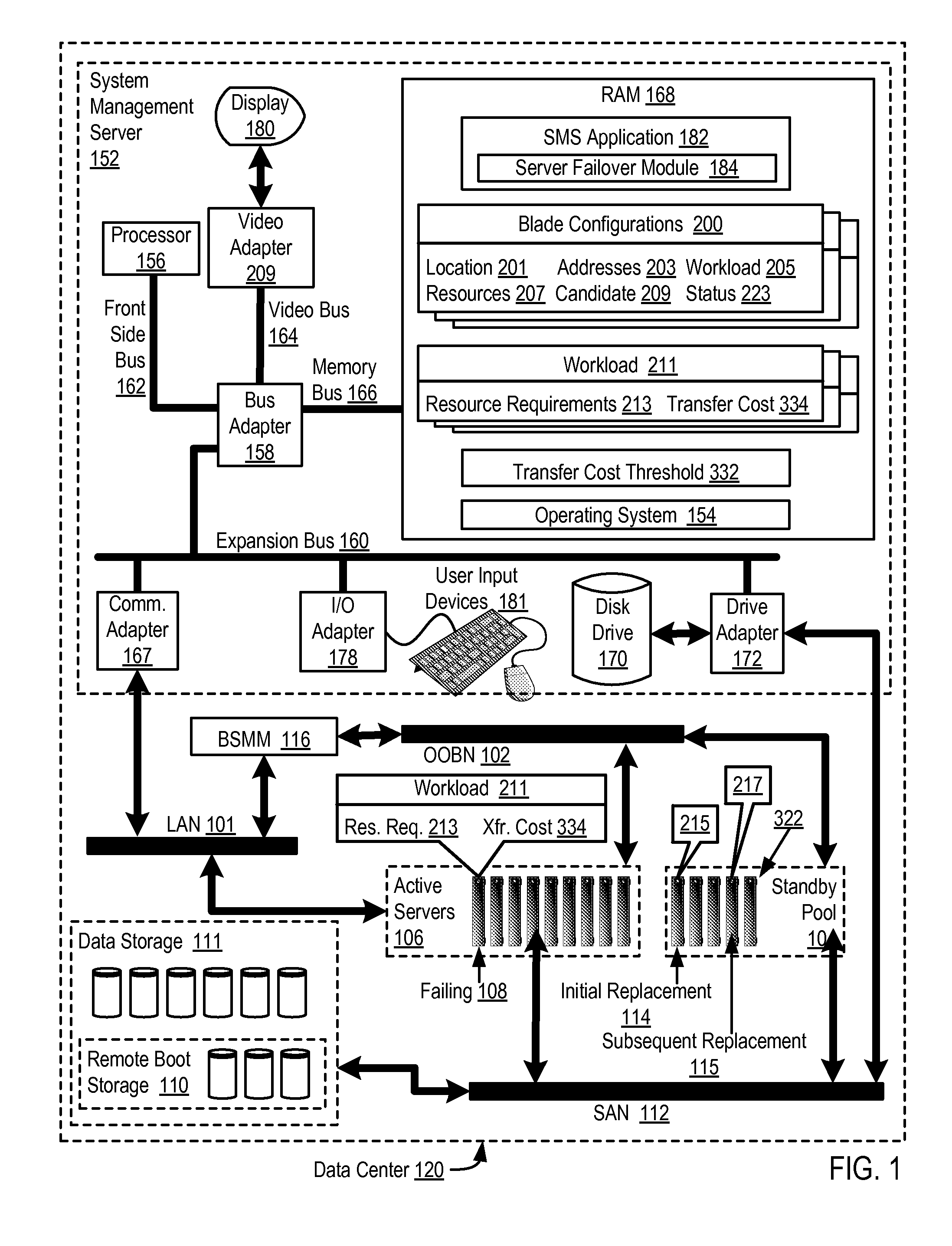
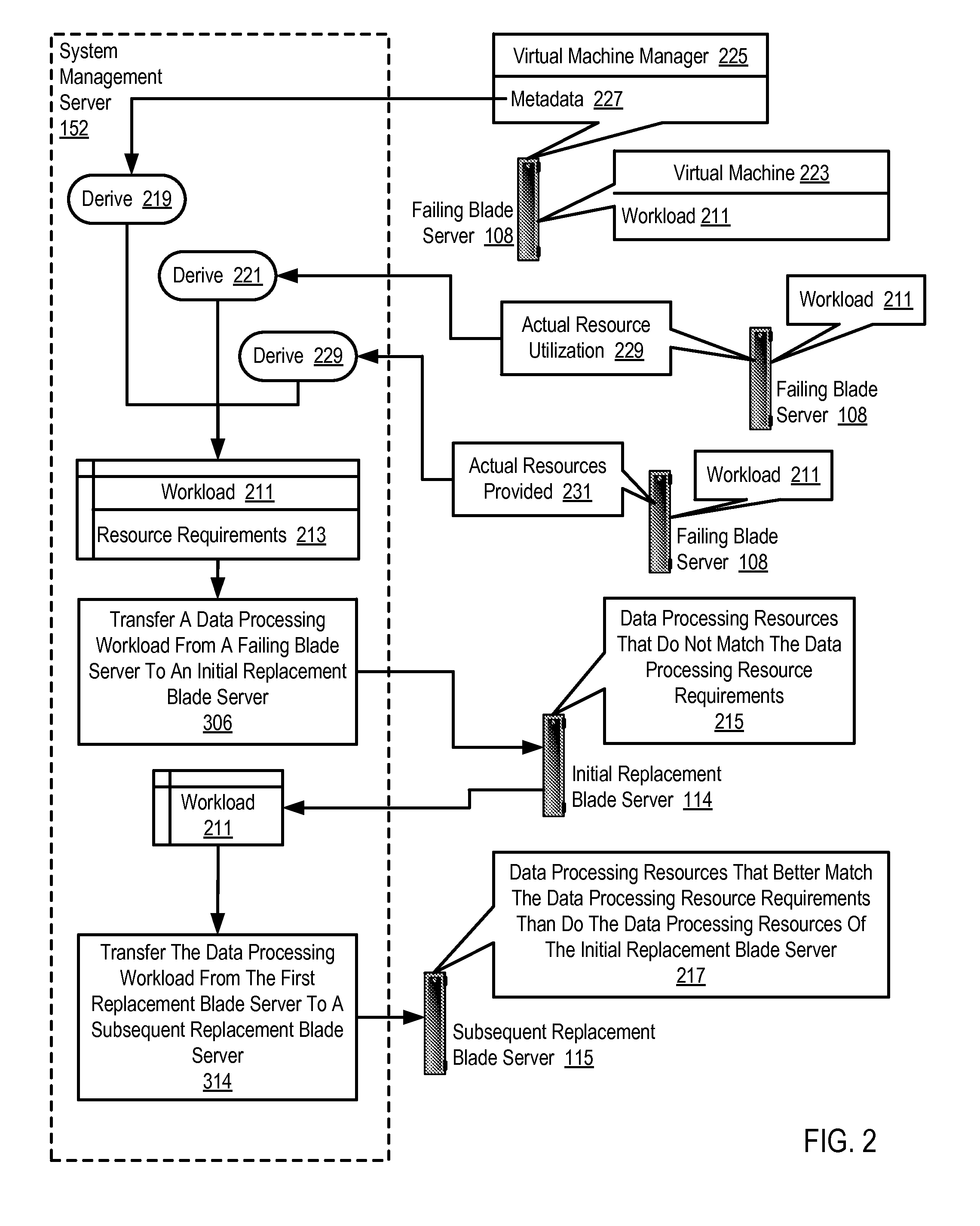
Cascading failover of blade servers in a data center
ActiveUS20140173336A1Improve matchRedundant hardware error correctionCascading failureSystems management
Cascading failover of blade servers in a data center that includes transferring by a system management server a data processing workload from a failing blade server to an initial replacement blade server, with the data processing workload characterized by data processing resource requirements and the initial replacement blade server having data processing resources that do not match the data processing resource requirements; and transferring the data processing workload from the initial replacement blade server to a subsequent replacement blade server, where the subsequent replacement blade server has data processing resources that better match the data processing resource requirements than do the data processing resources of the initial replacement blade server, including transferring the workload to the subsequent replacement blade server only if the data processing cost of the transfer of the workload to the subsequent replacement blade is less than the value of a transfer cost threshold.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
Calculation method of traffic network node importance considering cascading failure
InactiveCN102270388AThe calculation method is not complicatedEasy to masterRoad vehicles traffic controlCascading failureNODAL
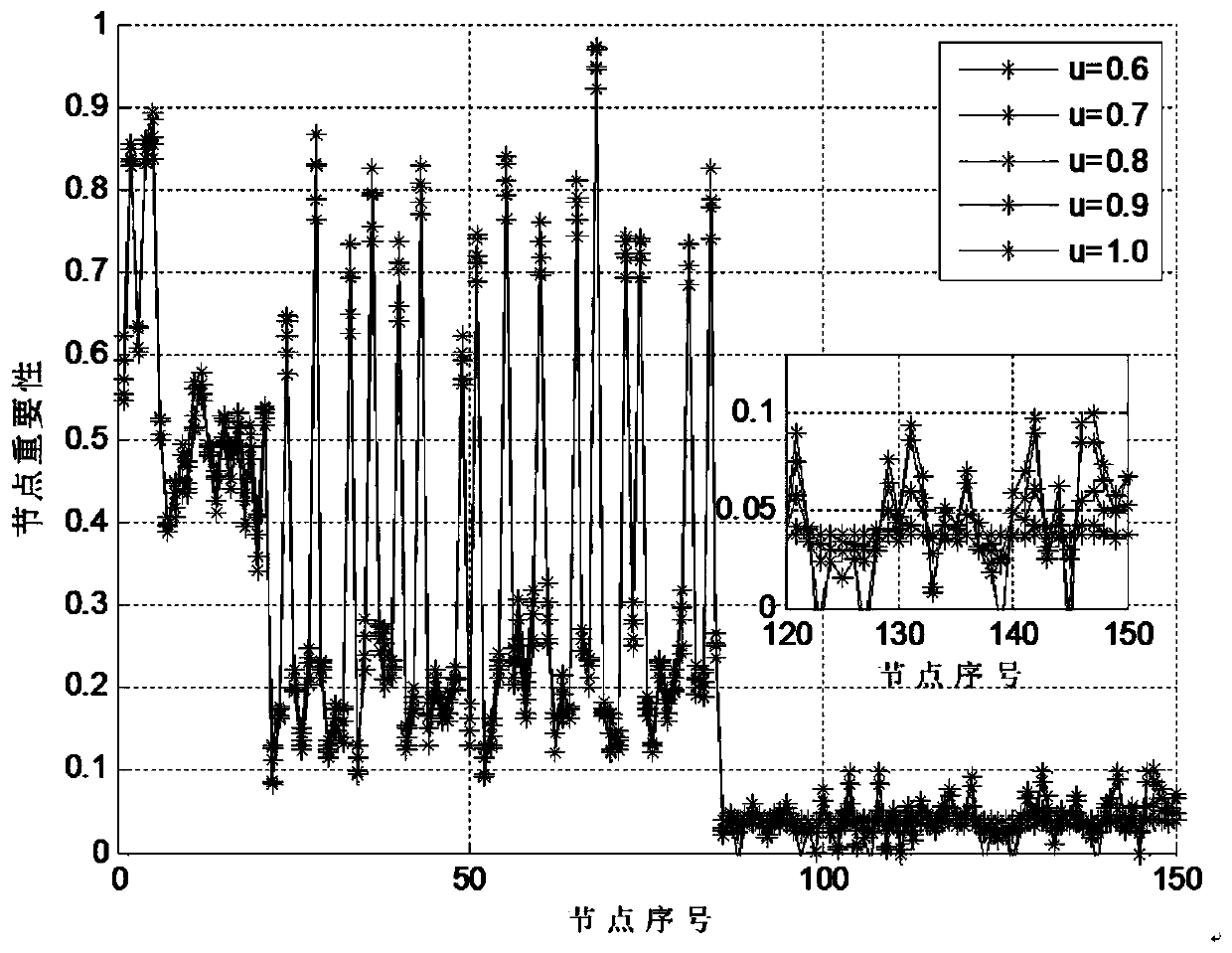
The invention discloses a method for measuring and calculating the importance of traffic network nodes with a consideration of cascading failure, wherein a double-layer network is used as the basis of the measurement and calculation on the importance of traffic network nodes; the lower network of the double-layer network is a road network, and the upper network thereof is a travel network; the method comprises the following specific steps of: step 1, determining the initial capacity of each side of the road network according to the road network and the travel network; describing the state andthe capacity change law of the side by a travel time; and step 2, measuring and calculating the importance of all nodes of a road, wherein the larger the jam degree index J of the network after a cascading failure is, the more important the node is. The method for measuring and calculating the importance of traffic network nodes with a consideration of cascading failure can exactly calculate the importance of all nodes and find the key node by ordering the nodes according to the importance.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Cascading failure search and weak link analysis method based on operation reliability model
ActiveCN106327034ASimplify the difficulty of research questionsDifficulty of SimplificationResourcesCascading failurePower flow
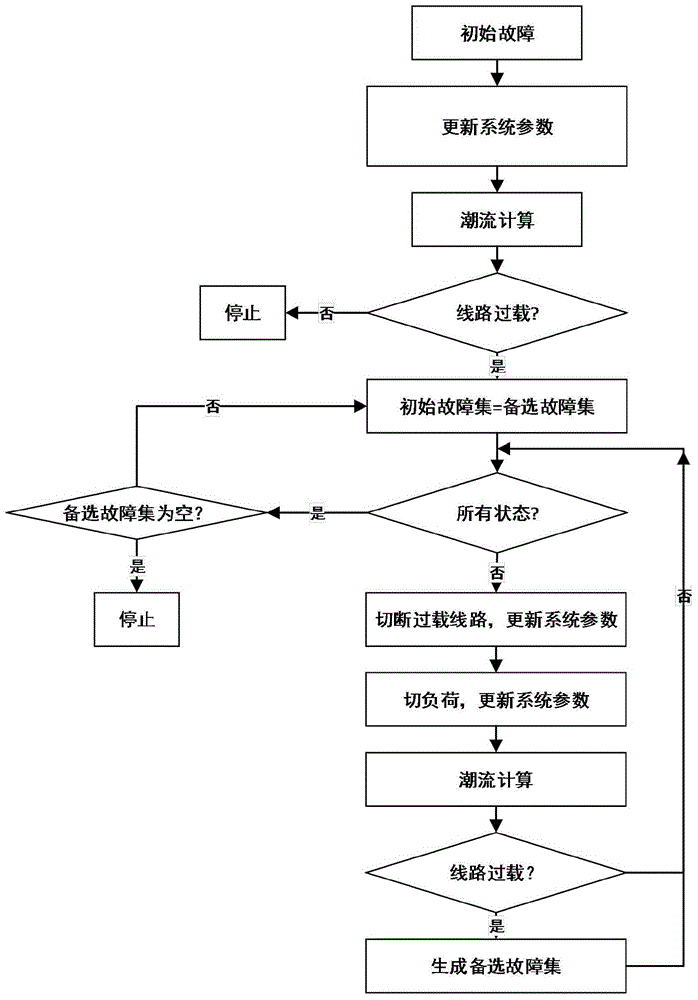
The invention relates to a cascading failure search and weak link analysis method based on an operation reliability model. The method comprises steps: initial failure is generated randomly; a DC power flow is calculated, whether a load threshold-crossing line exists in a power system is judged, if yes, a next step is carried out, or otherwise, the operation is stopped; an initial failure set is generated, and through the operation reliability model, the threshold-crossing line outage probability is calculated; the power system state probability is calculated; if the power state probability is larger than a set threshold and the failure scale is smaller than a set threshold, the power state is added to an alternative failure set, and if no state meeting the condition exists, search is stopped; the initial failure set is taken as an alternative failure set, the current alternative failure set is emptied, and the above steps are repeated. Through searching a cascading failure event in different initial failure and analyzing a system weak link, a corresponding system reform scheme is provided, happening of the cascading failure is prevented, a subsequent event is found during an event development process, and further evolution of the cascading event can be prevented.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +3
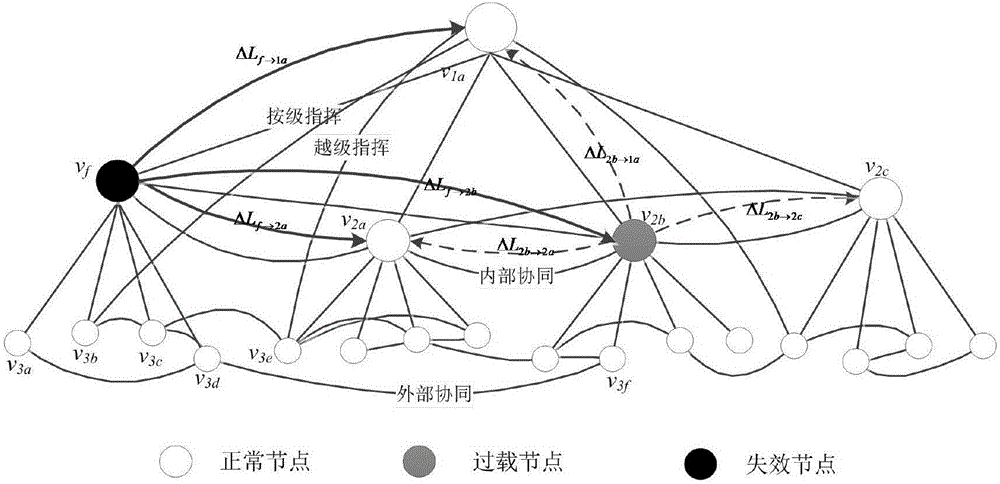
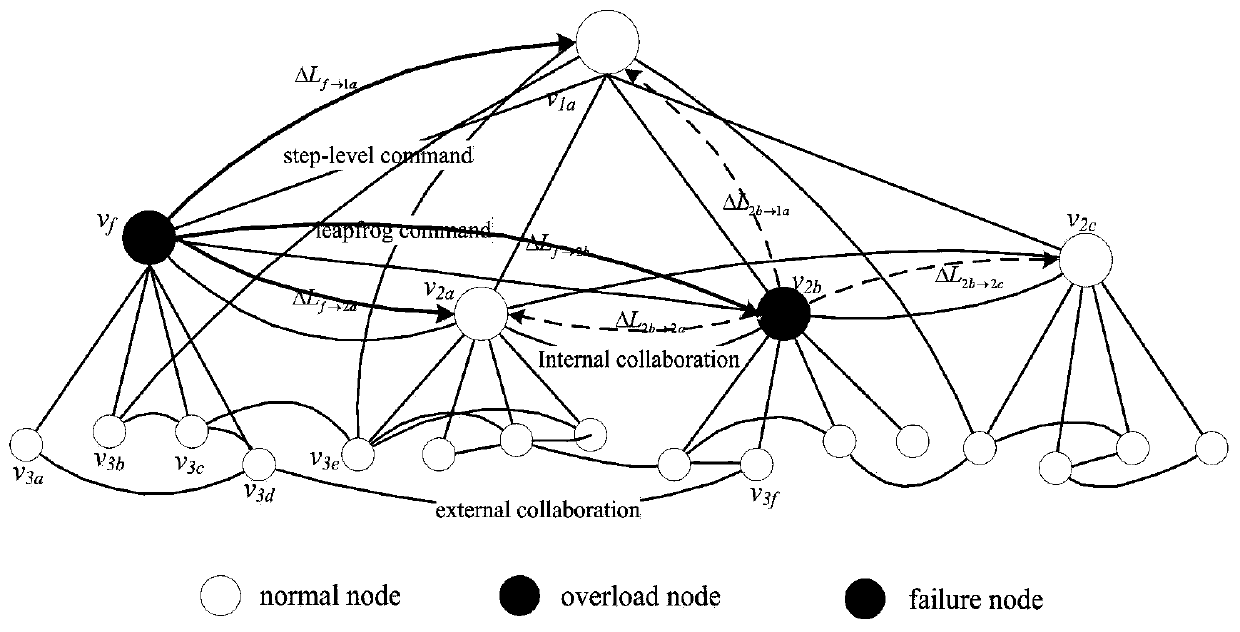
Establishment method of command network cascading failure model having hierarchical structure
ActiveCN106789376AEffectively analyze the problem of invulnerabilityImprove survivabilityData switching networksCascading failureLoad redistribution
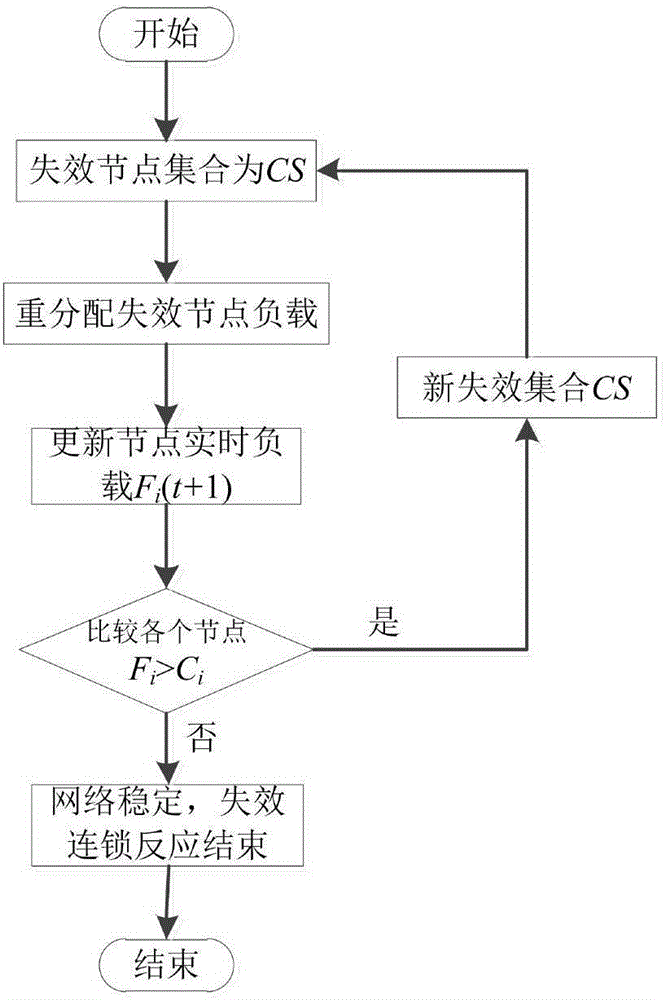
The invention relates to an establishment method of a command network cascading failure model having a hierarchical structure. The method concretely comprises the following steps: S1, defining the initial load and capacity of nodes in a command network; S2, using a command network failure node load redistribution method to update the loads of all the intact nodes in the network for once; S3, evaluating the cascading anti-destruction performance of the command network; S4, establishing the command network cascading failure model; S5, adjusting parameters in the model according to the established cascading failure model, using the provided cascading anti-destruction performance evaluation to estimate the anti-destruction performance of the command network, and enabling the cascading anti-destruction performance of the command network to be optimal. The method combines the hierarchical structure of the command network and takes the strict affiliation in the command network into account, thus being capable of better reflecting the internal mechanism and extrinsic behavior of command network cascading failure effectively and accurately.
Owner:DALIAN UNIVERSITY
Multi-mode hidden-fault risk analysis method of relaying protection system
ActiveCN103488873AImprove calculation accuracyImprove reliabilitySpecial data processing applicationsCascading failureEngineering
The invention belongs to the field of relaying protection and risk analysis of power systems, and discloses a multi-mode hidden-failure risk analysis method of a relaying protection system. The method comprises the steps of building a multi-mode hidden-failure model of the relaying protection system; according to the multi-mode hidden-failure model, performing risk analysis on power grid N-k failures caused by relaying protection hidden failures, and obtaining risk index values of hidden failures of the relaying protection system. According to the method, simplified modeling analysis is performed on the hidden failures of the protection system; the multi-mode hidden-failure model is built by analyzing the characteristics of protection hidden failures with various typical modes; a power N-k grid failure analysis method is provided by aiming at the risk analysis problem of the hidden failures. An N-k failure probability solving method based on an improved functional group decomposition method and an event tree analysis method is adopted during the analysis, and corresponding cascading failure risk indexes are set up; the calculation accuracy of the power grid N-k failure probability is improved, and risk assessment and analysis can be performed on the hidden failures of the relaying protection system.
Owner:POWER DISPATCHING CONTROL CENT OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD
Power system cascading failure simulation method based on unified power flow controller
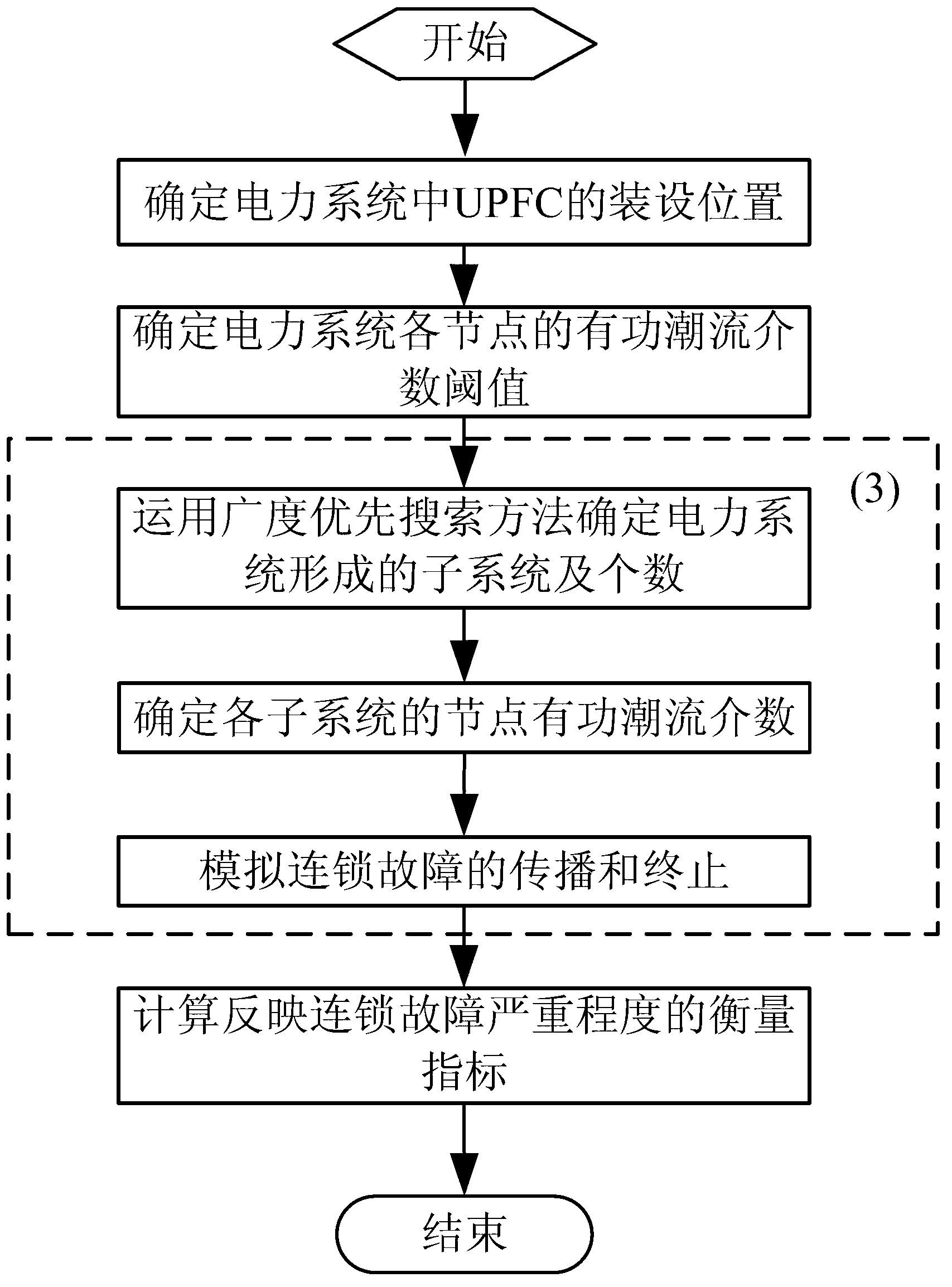
ActiveCN103311926AIn line with actual operating conditionsPracticalSpecial data processing applicationsAc network circuit arrangementsCascading failureSimulation
The invention provides a power system cascading failure simulation method based on a unified power flow controller and belongs to the technical field of power system security and reliability protection. A computer is used for determining the installation position of the unified power flow controller in a power system firstly, determining an active power flow betweenness threshold value of each node of the power system, performing power system cascading failure simulation based on the unified power flow controller and finally calculating measurement index for reflecting severity of cascading failure through procedures. The power system cascading failure simulation method gives consideration to power flow directivity and the operation mode of the system, optimizes the installation position for installing the unified power flow controller, effectively performs line parameter regulation while meeting safe operation constraints of the power system, and can reflect the propagation process of the cascading failure of the power system actually. The power system cascading failure simulation method based on the unified power flow controller can be widely applied to the cascading failure simulation of the power system, is particularly suitable for the cascading failure simulation of a large-scale complicated power system, and provides a scientific basis for preventing occurrence of the cascading failure of the power system.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
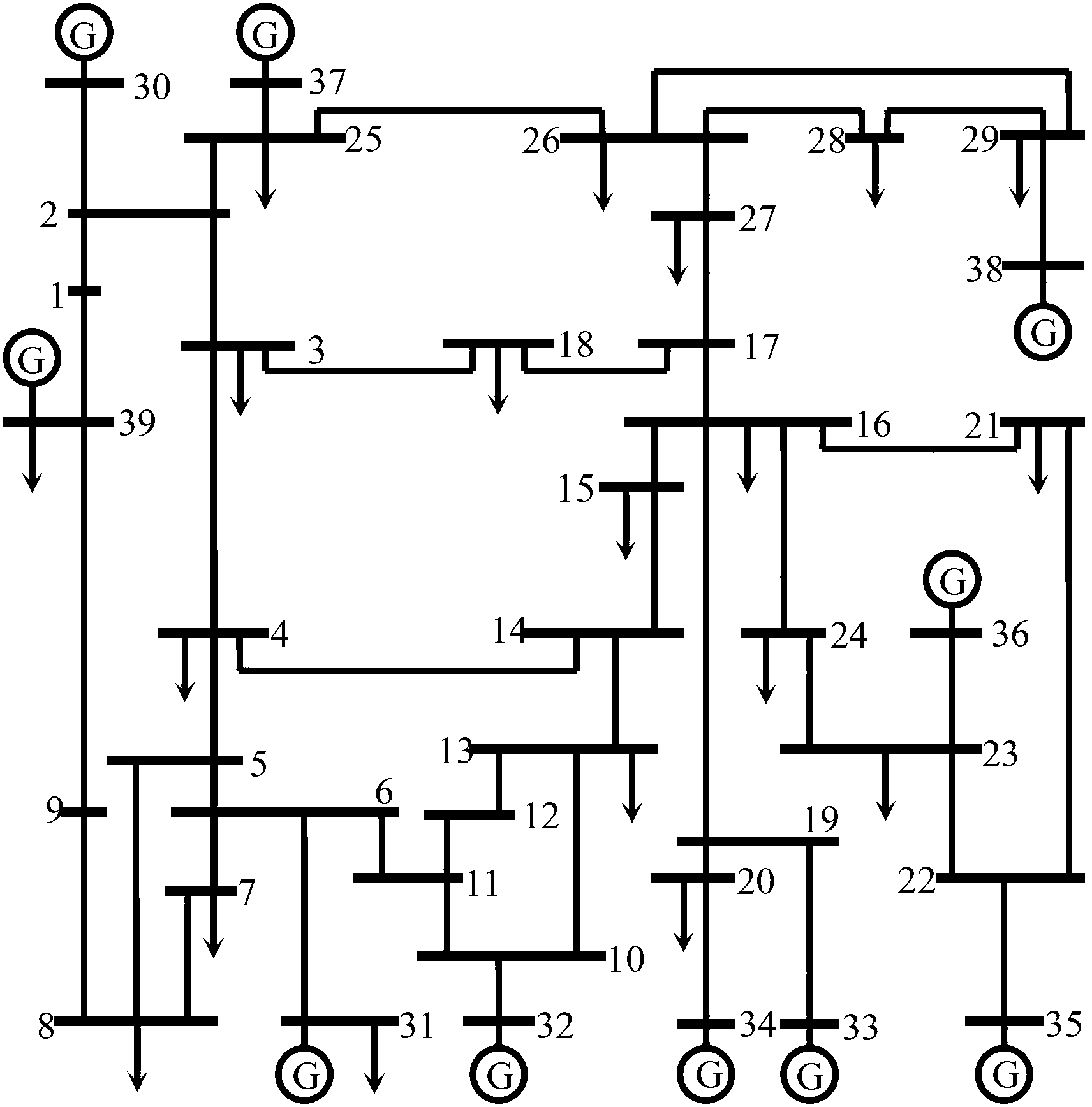
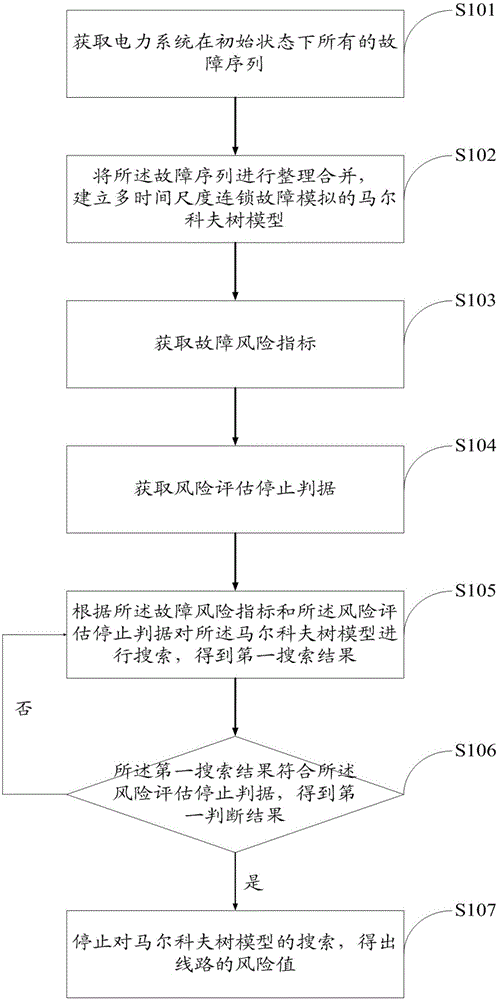
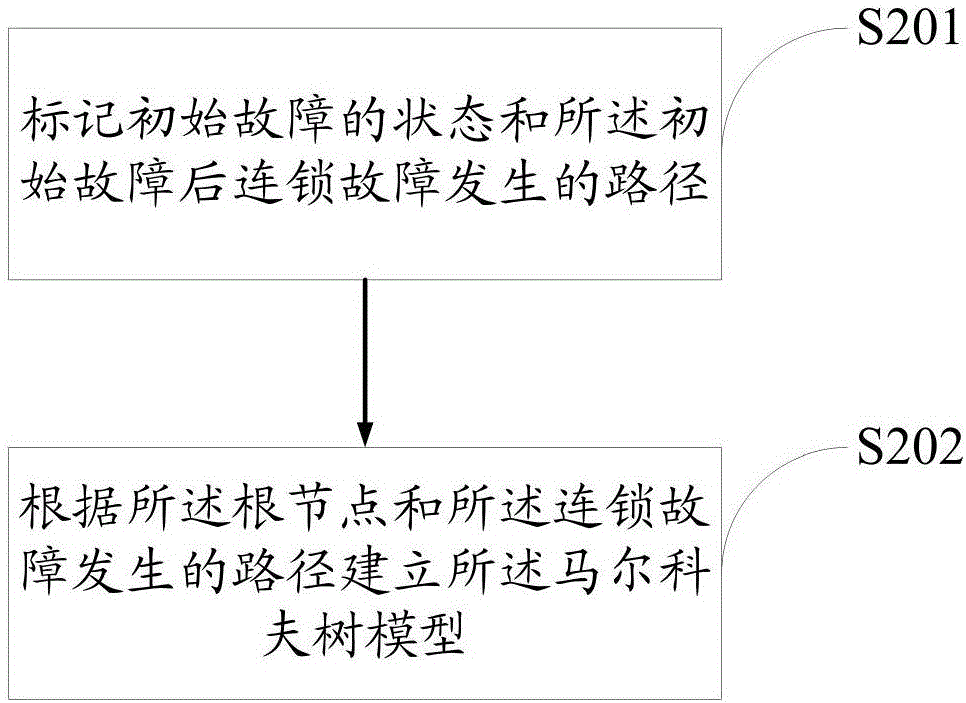
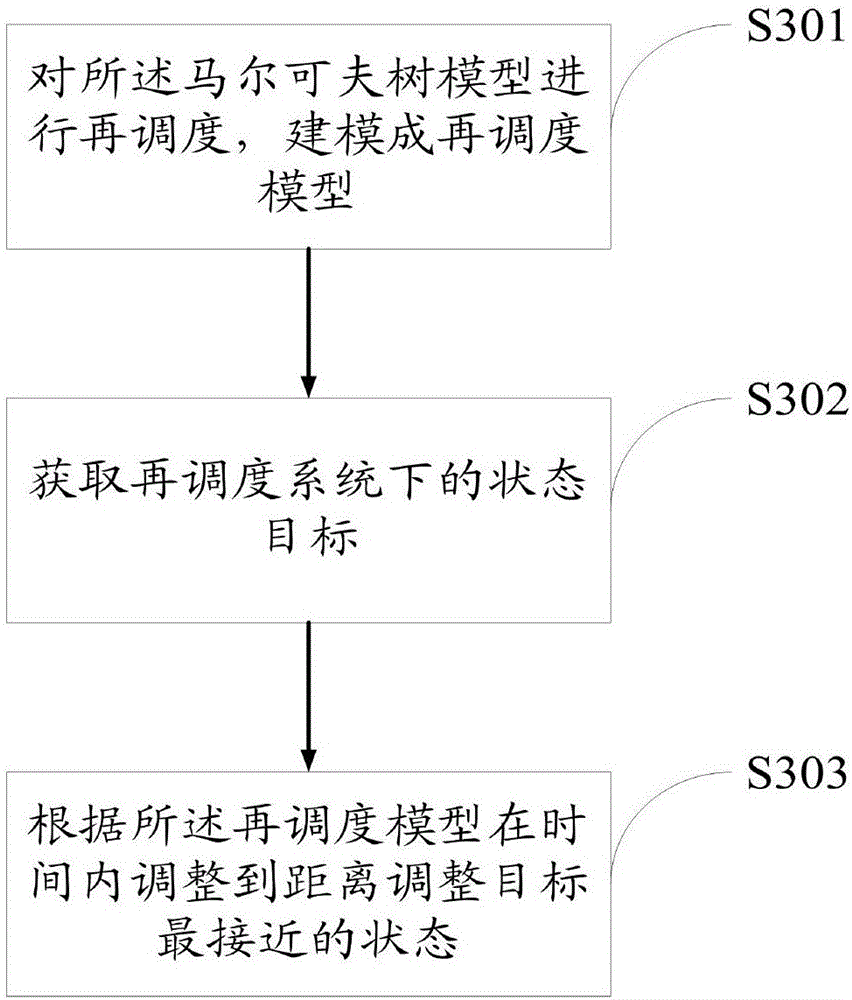
Power system cascading failure risk assessment method and power system cascading failure risk assessment system
The invention discloses a power system cascading failure risk assessment method and a power system cascading failure risk assessment system. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring all failure sequences of a power system in an initial state; sorting and combining all the failure sequences, and building a Markov tree model of multi-time-scale cascading failure simulation; acquiring failure risk indicators; acquiring a risk assessment stop criterion; searching for the Markov tree model according to the failure risk indicators and the risk assessment stop criterion to get a first search result; judging whether the first search result is in accordance with the risk assessment stop criterion to get a first judgment result; and when the first judgment result indicates that the first search result is in accordance with the risk assessment stop criterion, stopping searching for the Markov tree model, and getting the risk value of a line. By using the risk assessment method and the risk assessment system, maximum coverage of the possible development path space of cascading failure can be realized under the condition of limited computing resources, and therefore, the computation efficiency is improved significantly.
Owner:STATE GRID SICHUAN ELECTRIC POWER CORP ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
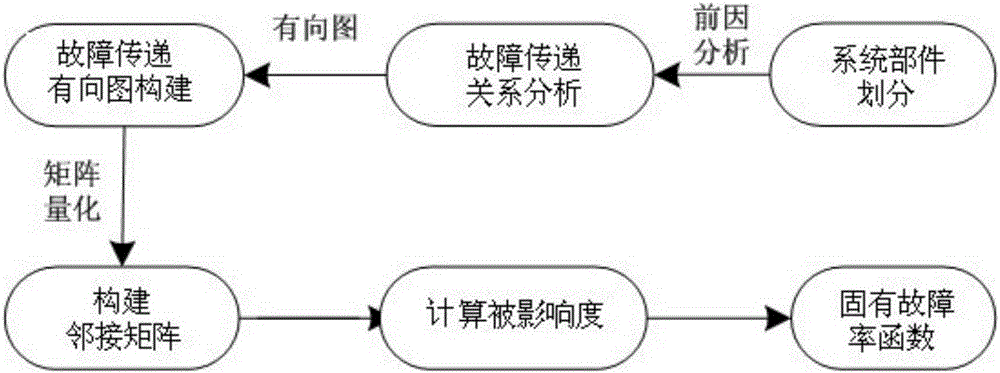
Numerical control machine tool system component reliability evaluation method based on cascading fault analysis
The invention relates to a numerical control machine tool system component reliability evaluation method based on cascading fault analysis. The method comprises the following steps that the entire numerical control machine tool system components are divided into multiple subsystems, and a fault transfer directed graph model is established according to the fault transfer relation between all the subsystems; the fault transfer directed graph model is described by using an adjacency matrix; a fault-correlation-based influence degree CK value of each subsystem is calculated; an inherent fault probability function of each subsystem is obtained according to the fault-correlation-based influence degree CK value of each subsystem and a comprehensive fault probability function through calculation; and reliability evaluation is performed on the numerical control machine tool system components by utilizing the inherent fault probability function. The cumulative fault process of the elements of the subsystems is considered by a reliability model, and fault correlation influence degree factors of other subsystem are also integrated so that the reliability model meets the reality further in comparison with the reliability model based on mutually independent assumption between systems.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Key transmission section identification-based cascading failure analysis method for alternating current/direct current power network
The invention provides a key transmission section identification-based cascading failure analysis method for an alternating current / direct current power network. The method comprises the following steps: (A) searching all transmission sections between a direct current transmitting end and a direct current receiving end by a graph theory-based transmission section traversal algorithm, forming a node set S0={vS} from a node vS of the direct current transmitting end, searching all cut sets of branches between S0 and the adjacent point thereof, and finishing traversal searching in a manner of expanding the node set S0 outwards step by step; (B) further identifying key transmission sections which can cause a relatively large cascading failure risk by indexes of a power flow transfer coefficient and section maximum overload rate; and (C) giving cascading failure sets with relatively large risks and key branches which should be mainly monitored in the key transmission sections through transient stability calculation. By the method provided by the invention, the key transmission sections and the key braches, which are prone to cascading failures after a direct current monopole is locked can be effectively determined.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD +1
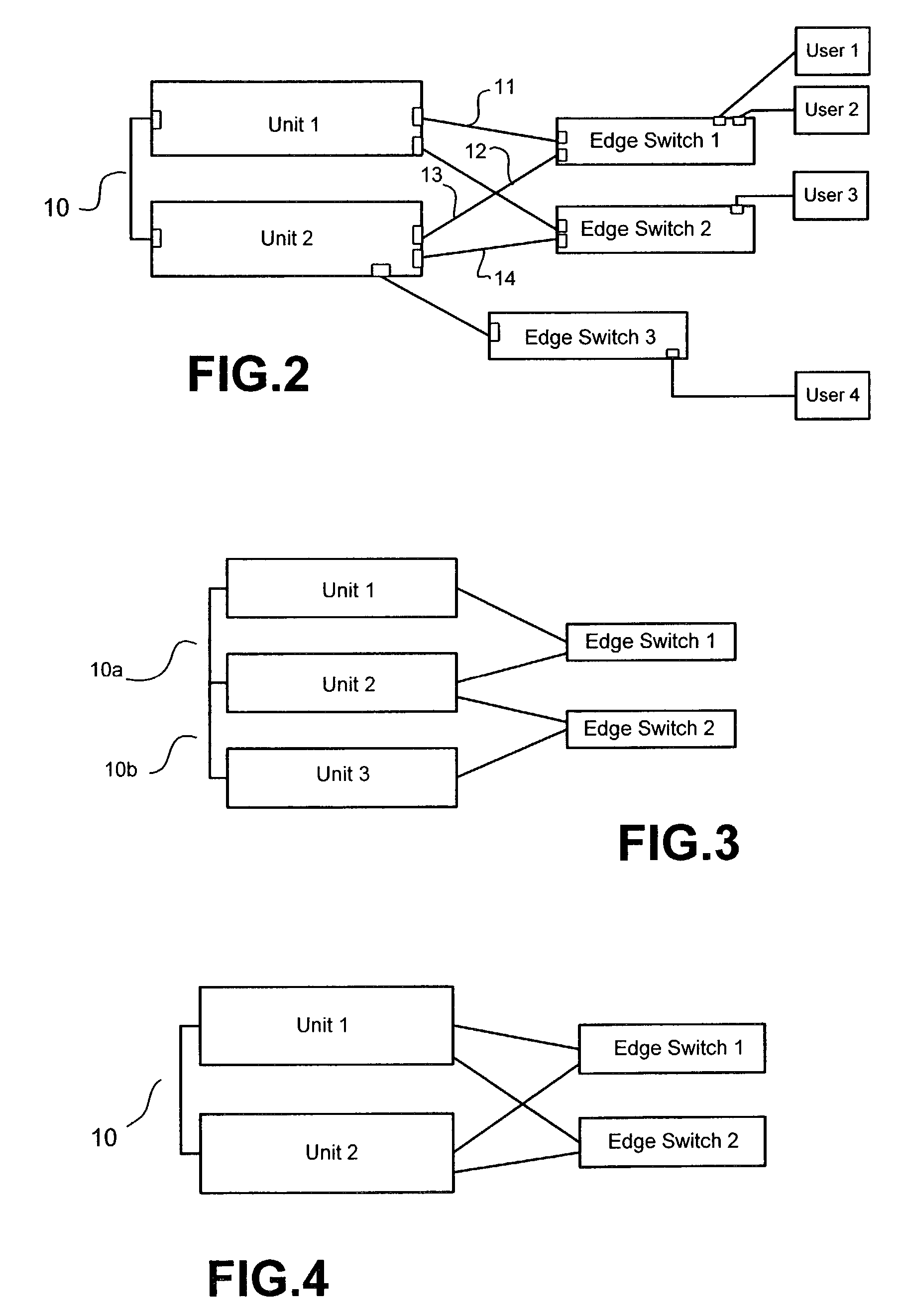
Stackable network units with resiliency facility
A network unit comprises a multiplicity of ports for transmitting and receiving data packets, a bridging facility and a routing facility. The network unit has a multiplicity of mutually exclusive states which includes an initial state from which said network unit can transition to either a slave state; or a waiting state from which in the absence of receipt from elsewhere of a broadcast advertisement including an advertised address corresponding to an address of the unit, the unit transitions to a master routing state in which the routing facility is enabled and the unit broadcasts a corresponding advertisement including an address of the unit. The unit transitions from the waiting state, when it receives from elsewhere (i.e., another unit) such a broadcast advertisement, to a master bridging state in which the routing facility is disabled and the unit provides commands for disabling a routing facility of other similar units to which the network is connected. The states include a slave routing state, in which the routing facility is enabled, and a slave bridging state, in which the routing facility is disabled. In the slave states the advertisements are not broadcast and the unit responds to routing enabling and disabling commands from a unit in a master state. The scheme provides in conjunction with external connectivity resilience in the event of a cascade failure.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Complex network node importance assessment method and system thereof
ActiveCN107453919ATrue importance assessmentMateriality assessment scienceData switching networksCascading failureLoad capacity
The invention discloses a complex network node importance assessment method and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps of S1, initializing an actual load of each node in a complex network and calculating an initial total load of the complex network; S2, successively carrying out failure investigation on each node of the complex network and carrying out cascade failure simulation; during a cascade failure simulation process, after a failure node is deleted, adjusting and updating an actual load of a neighbor node, updating a load capacity of each complex network node, according to the updated load and the updated load capacity, carrying out a new round of failure determination on the complex network till that the complex network is stable, and calculating a residual total load of the complex network; and S3, according to the initial total load and the residual total load, assessing importance of each node. The method and the system possess a dynamic deepening characteristic of fully considering the complex network cascade failure, an inherent property of an important node can be prompted, and node importance in the complex network can be really and accurately assessed.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
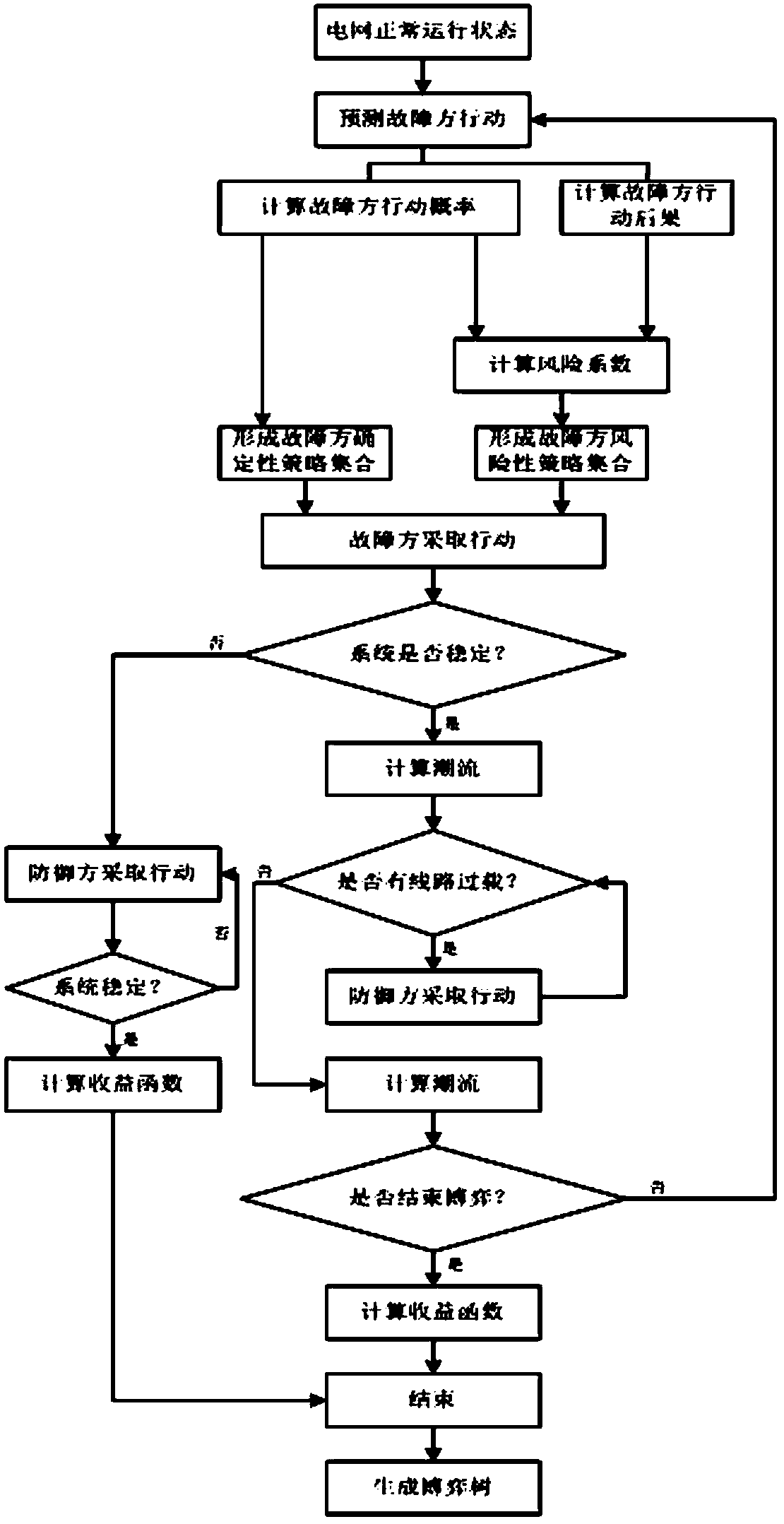
Cascading failure multi-stage dynamic game defense method
InactiveCN104268410ASimplify workloadPrevent blackoutsSpecial data processing applicationsCascading failureInstability
The invention discloses a cascading failure multi-stage dynamic game defense method applied to a power system. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly setting the total stage number of a game process and initial values of stages of a failure party and a defense party; then generating a deterministic strategy set and a risky strategy set by calculating the probability, the consequence and the risk factor of each action adopted at the stage of a bounded rationality failure party in sequence; stipulating a strategy selection sequence of the bounded rationality failure party; judging whether line overload or power angle instability is caused by the action adopted by the bounded rationality failure party, wherein direct current tide sensitivity-based overload control or extended equal area criterion-based stability control can be selectively adopted by a perfect rationality defense party according to a judgment result; judging whether an ending condition of the game process is met; finally calculating revenue functions of the bounded rationality failure party and the perfect rationality defense party; ending the multi-stage dynamic game defense process. According to the method, the blockage of cascading failure is realized, and power blackout accidents are prevented.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH +3
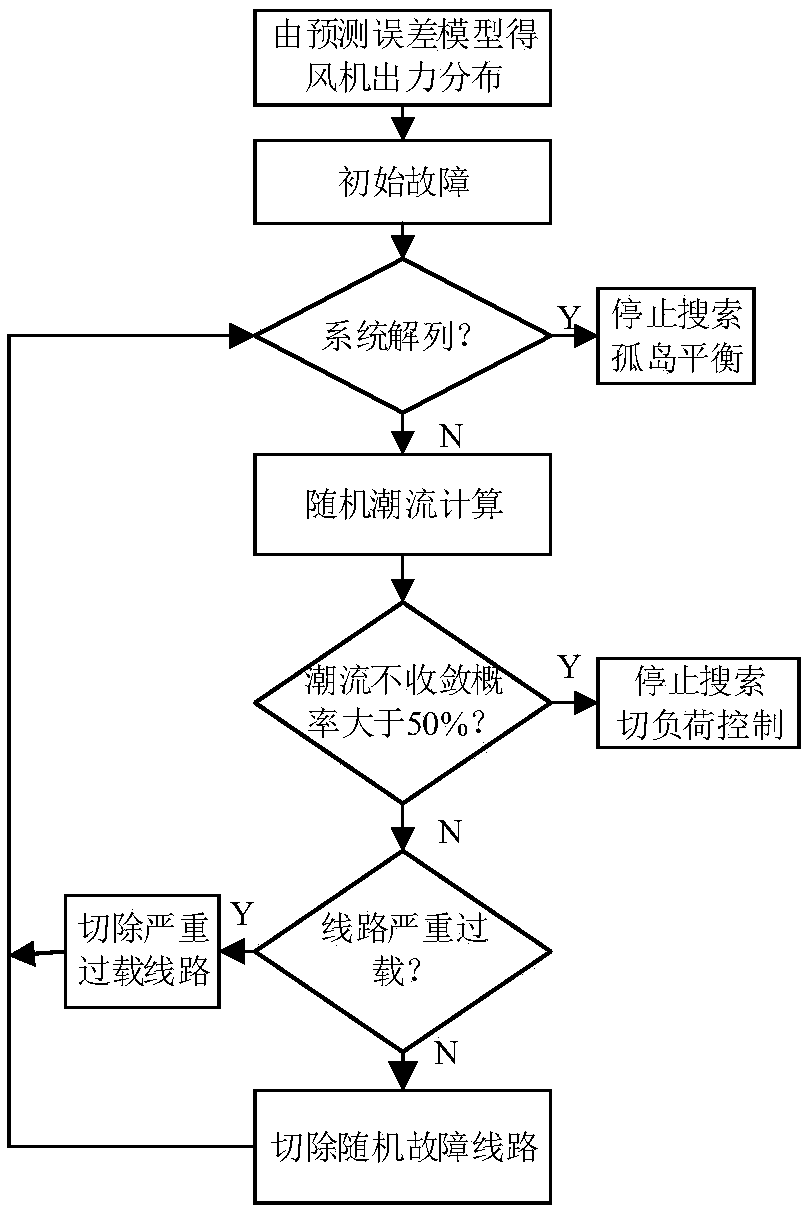
Method and system for cascading failure risk assessment of high proportion wind power grid-connected
ActiveCN109118098AImprove risk assessmentGuaranteed accuracyForecastingResourcesCascading failureLoad Shedding
The invention discloses a cascading fault risk assessment method and a cascading fault risk assessment system for high-proportion wind power grid connection. The cascading fault risk assessment methodand the cascading fault risk assessment system comprise the following steps: establishing a wind power prediction error model according to the wind power prediction error historical data to obtain the wind power output distribution; Select the initial fault set; When a fault occurs in the initial fault set, the fault chain search is started: whether the power system is disconnected or not is judged; if the fault is disconnected, the island balance is carried out and the current fault chain search is stopped; If the power system is not disconnected, the stochastic power flow calculation is carried out. If the non-convergence probability of the power flow calculation result is greater than the set value, the load shedding control is carried out. According to the accident chain set generatedabove, the power system loss risk index and line importance index are calculated. The technical proposal provided by the invention fully considers the influence of wind power uncertainty in the evolution process of the accident chain, has more comprehensive risk assessment to the system, and is suitable for the background of high-proportion wind power grid connection.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +2
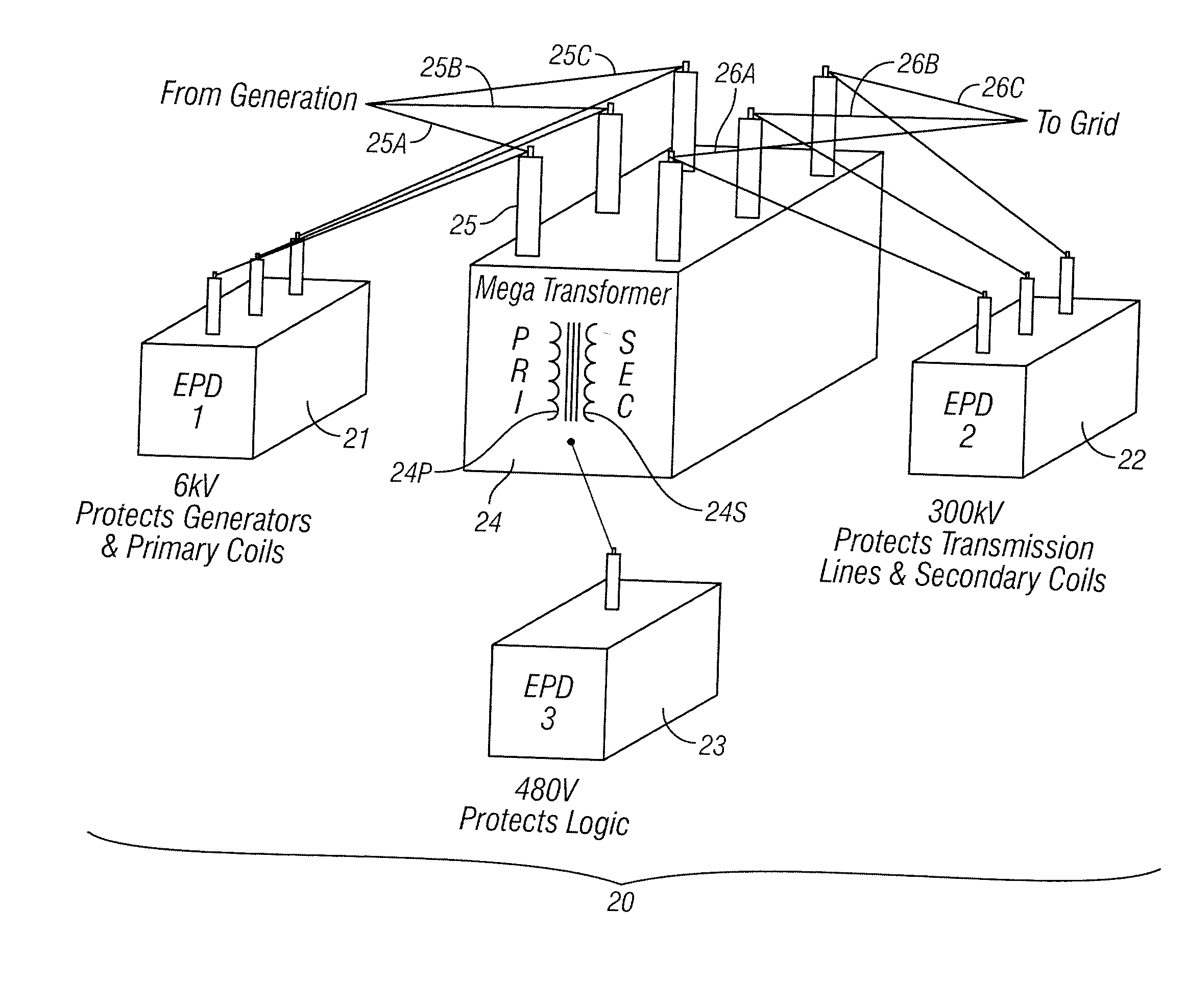
Surge suppression system for medium and high voltage
ActiveUS20160126738A1Guaranteed to workInhibit currentReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionCascading failurePower utility
A system of surge suppressor units is connected at multiple locations on a power transmission and distribution grid to provide grid level protection against various disturbances before such disturbances can reach or affect facility level equipment. The surge suppressor units effectively prevent major voltage and current spikes from impacting the grid. In addition, the surge suppressor units included various integration features which provide diagnostic and remote reporting capabilities required by most utility operations. As such, the surge suppressor units protect grid level components from major events such as natural geomagnetic disturbances (solar flares), extreme electrical events (lightning) and human-generated events (EMPs) and cascading failures on the power grid.
Owner:ASATOR GLOBAL TECH LLC
Identification method and system for cascading failure critical line of power system
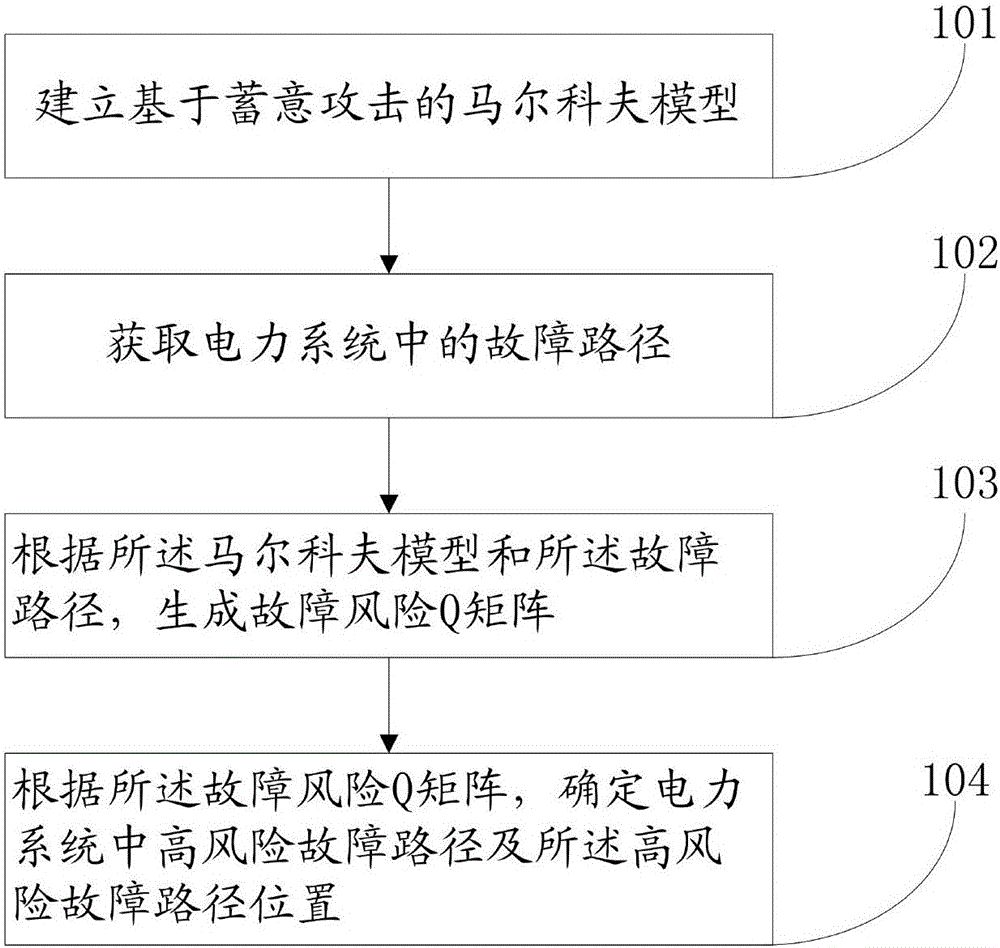
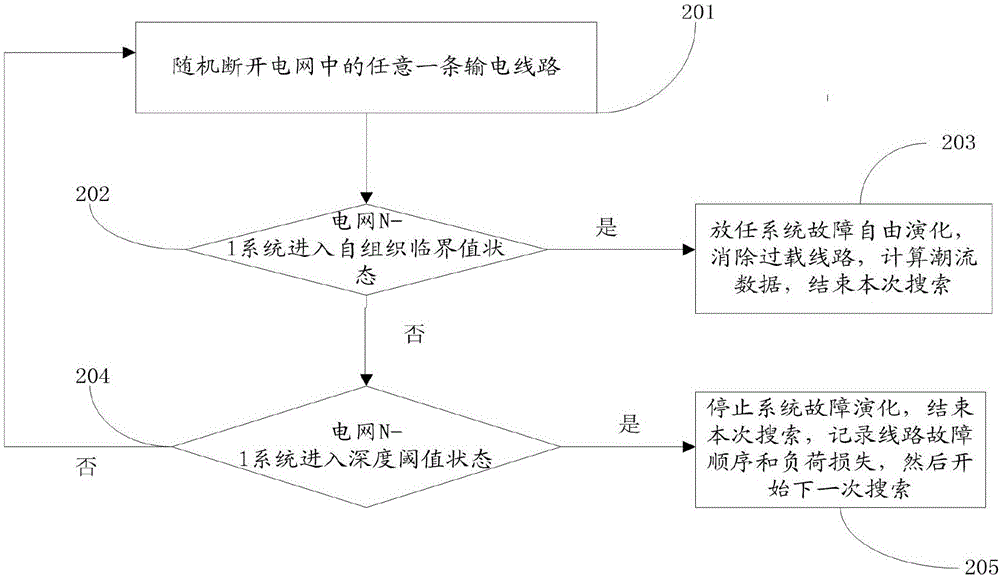
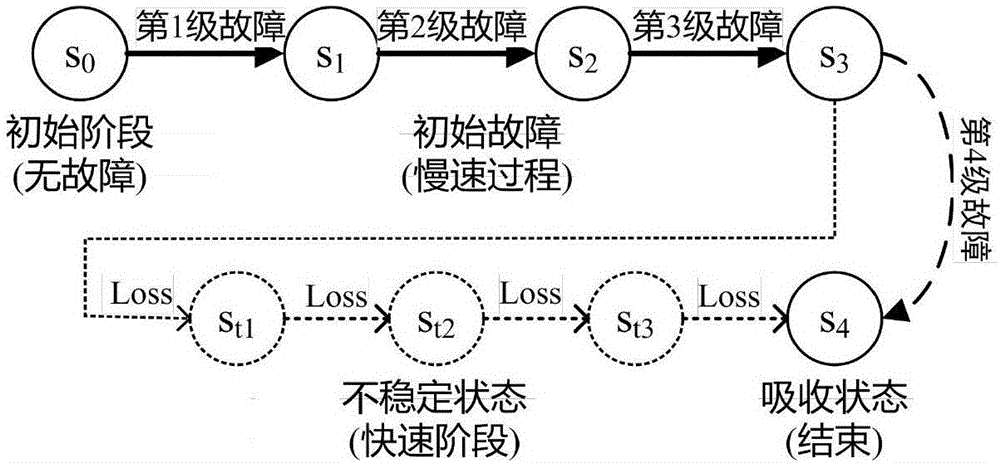
The invention provides an identification method and system for a cascading failure critical line of a power system. The method comprises the steps of establishing a Markov model based on an intentional attack; obtaining a failure path in the power system; generating a failure risk Q matrix according to the Markov model and the failure path; and determining a high risk failure path in the power system and a position of the high risk failure path according to the failure risk Q matrix. According to the method and the system, the line combinations in the power system are taken into full consideration; and the accuracy of identifying the high risk failure path is improved.
Owner:STATE GRID SICHUAN ELECTRIC POWER CORP ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Recognition method for vulnerable lines of power system
ActiveCN105656039ADetermine vulnerabilityAvoid large sample cascading failure simulationsAc network circuit arrangementsCascading failurePower flow
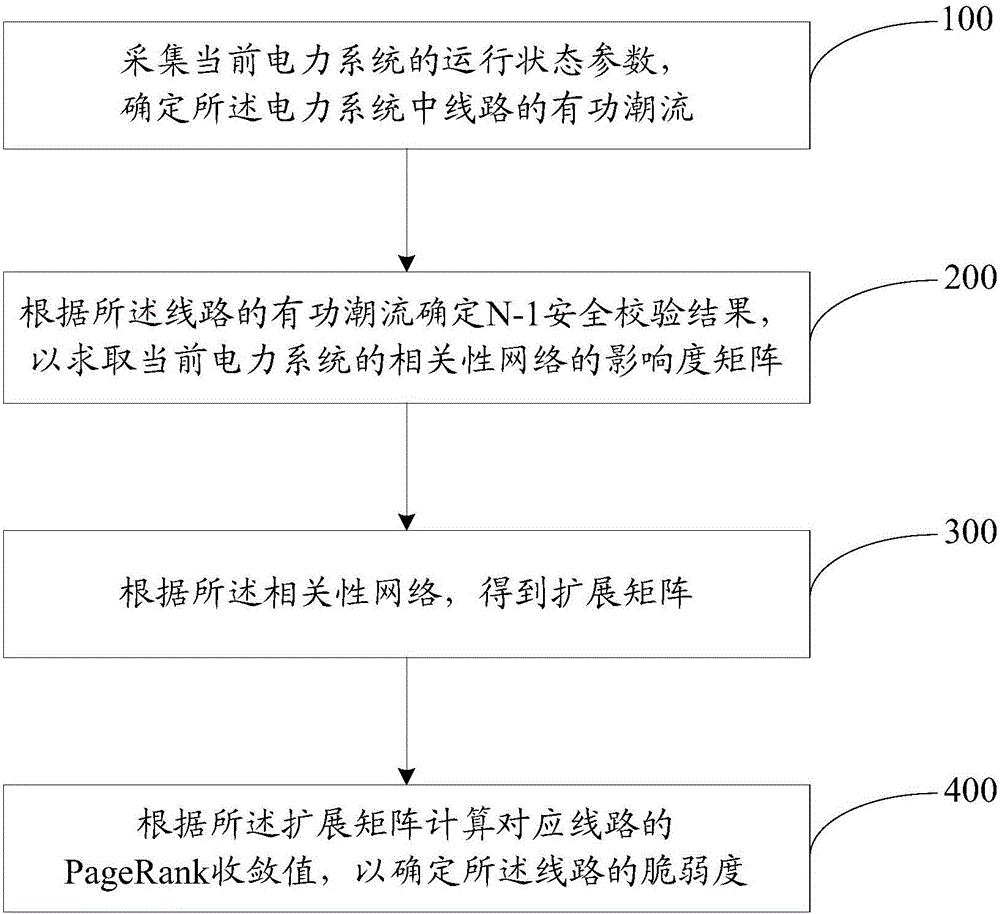
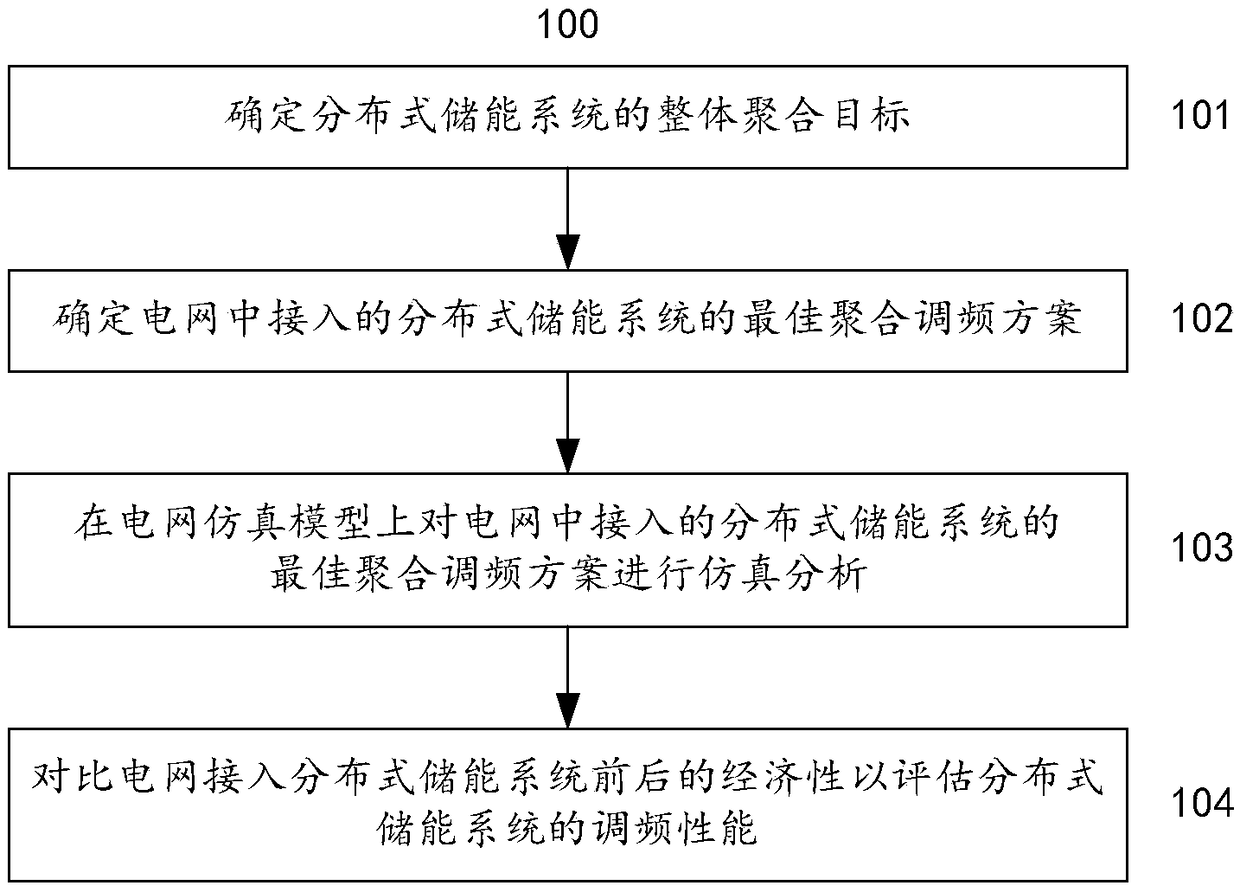
The invention discloses a recognition method for vulnerable lines of a power system. The recognition method comprises the steps that 1, running state parameters of a current power system are collected, and the real power flow P<m> of one line in the power system is determined; 2, an N-1 safety verification result is determined according to the real power flow P<m> of the line, so that an influence degree matrix S of a correlation network of the current power system is solved; 3, an extensive matrix S<extend> is obtained according to the influence degree matrix S; 4, a PageRank convergency value of the corresponding line is calculated according to the extensive matrix S<extend> to determine the vulnerable degree of the line. According to the recognition method for the vulnerable lines of the power system, by collecting the running state parameters of the current power system and constructing the correlation network and the extensive matrix, the PageRank convergency values of all the lines are accurately calculated to determine the vulnerable degrees of all the lines, therefore, large-sample cascading failure simulation is prevented from being performed, and the recognition efficiency is improved on the premise that the recognition accuracy is guaranteed.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF STATE GRID NINGXIA ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY +1
Power system cascading failure mode prediction method
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER SCHEDULING CONTROL CENT OF GUIZHOU POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Network function end node propagation prediction method based on cascading failure
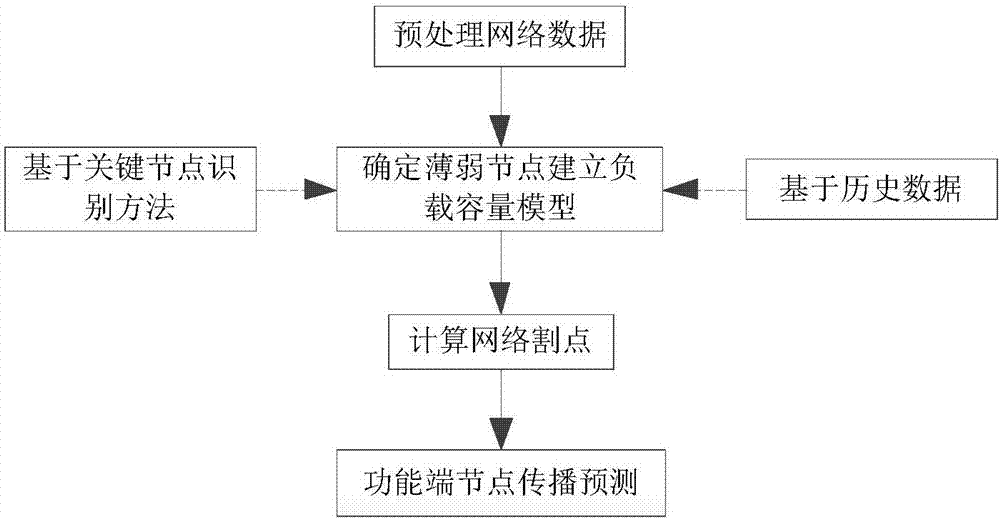
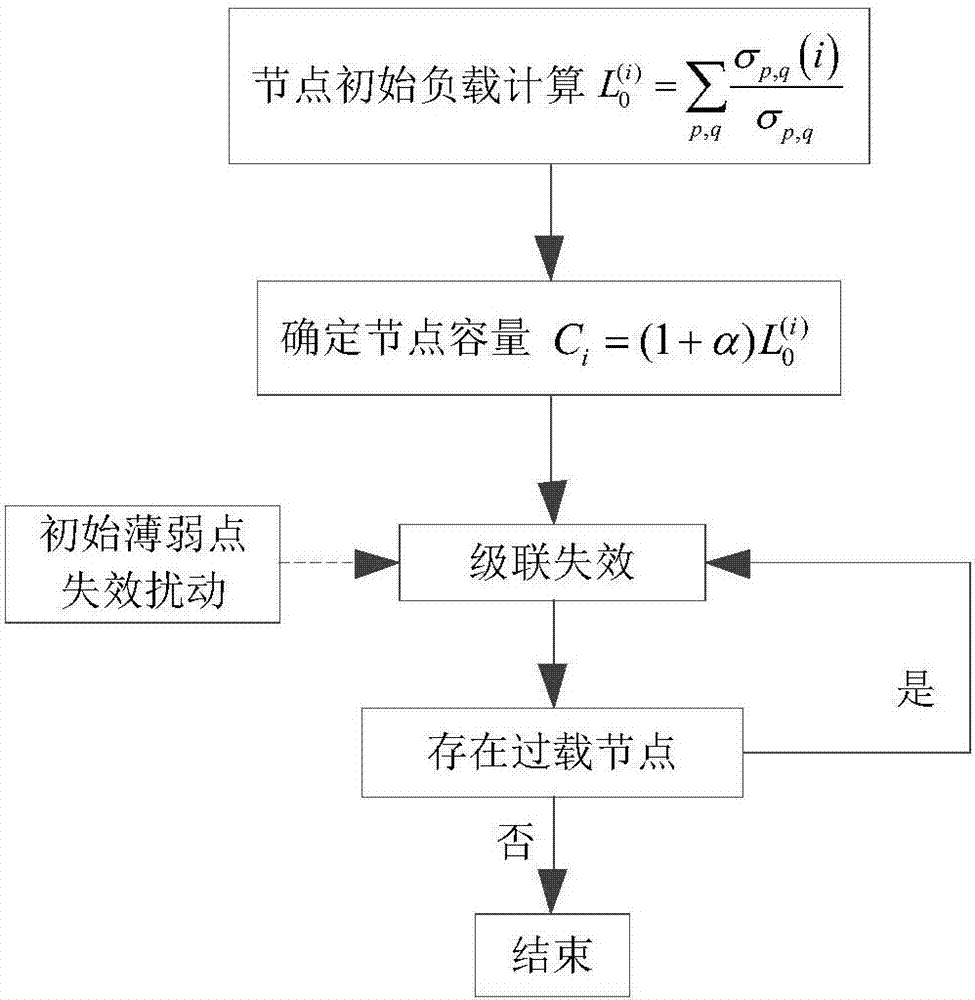
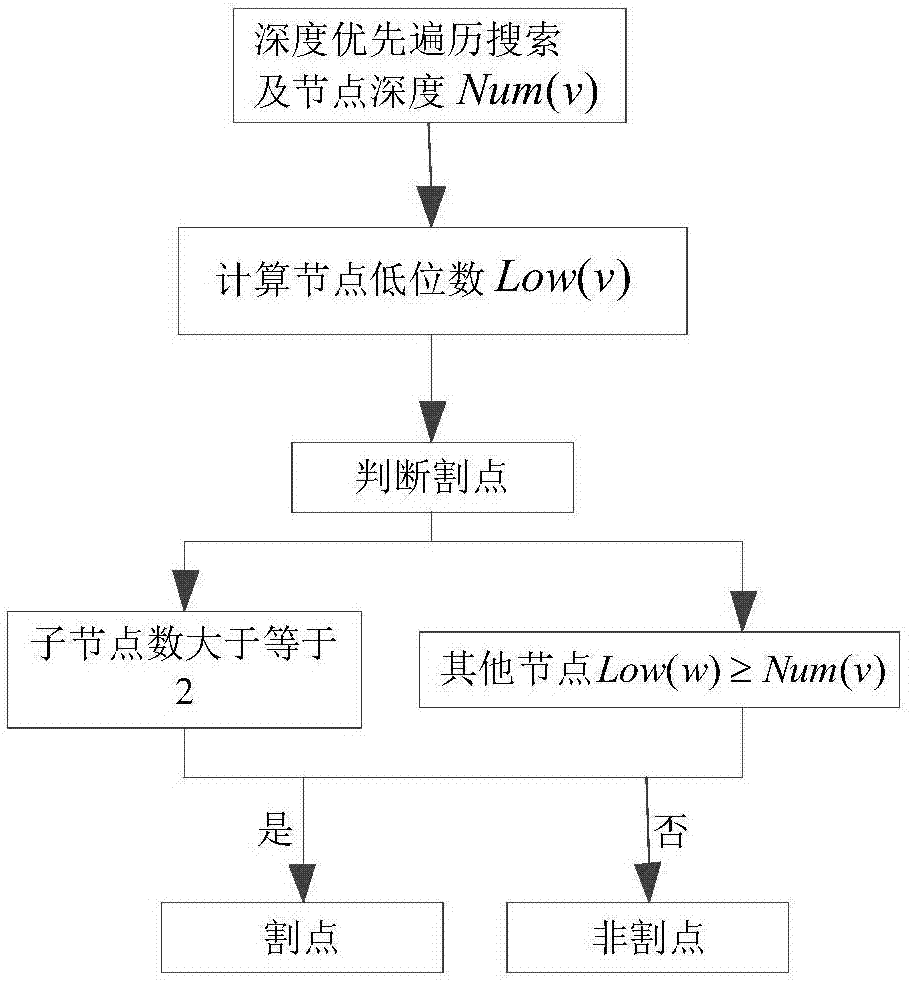
ActiveCN107092984ARealize functional end node computingSolving the function end node propagation prediction problemForecastingCascading failurePredictive function
The invention provides a network function end node prediction method based on cascading failure. The method comprises steps that 1, data pre-processing on the infrastructure network is carried out, and actual network abstraction is carried out to establish a network model; 2, an initial weak node is determined based on a key node identification method or historical data, and a load capacity model is further established; 3, network segmentation points during cascading failure are calculated; and 4, a propagation distance of a function end node is predicted according to an overload cascading failure propagation distance. The method is advantaged in that the function end node in a cascading failure process can be discovered in advance at a protection stage before cascading failure, a key node or a not-easy-to-restore node is designed and distributed at the function end node in advance, through propagation prediction of the function end node, real-time control in the cascading failure process is carried out, and thereby cascading failure control and repair work afterwards are facilitated.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Cloud management using a component health model
ActiveUS8996932B2Prevents cascading failureDetecting faulty hardware by remote testCascading failureComputerized system
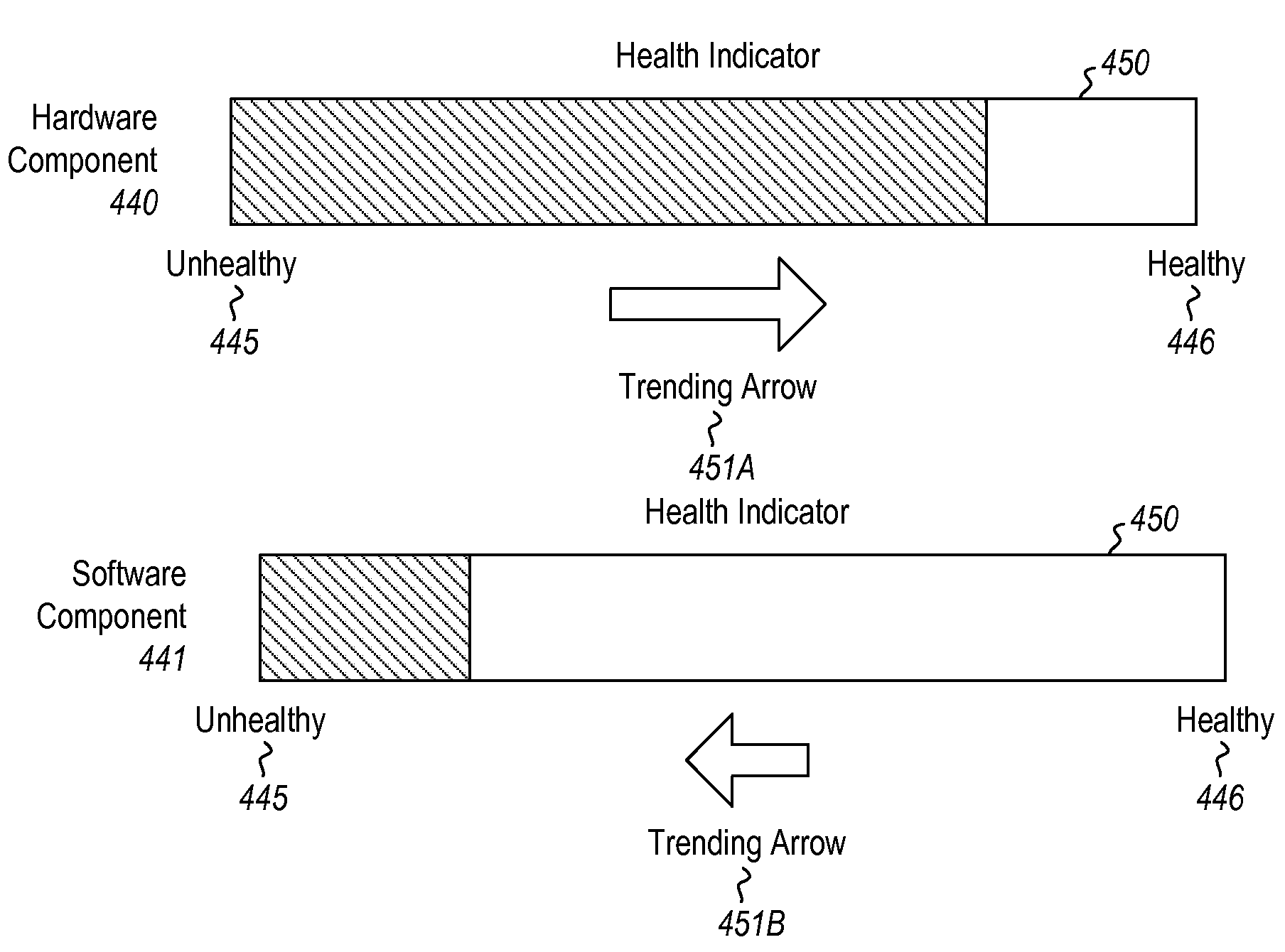
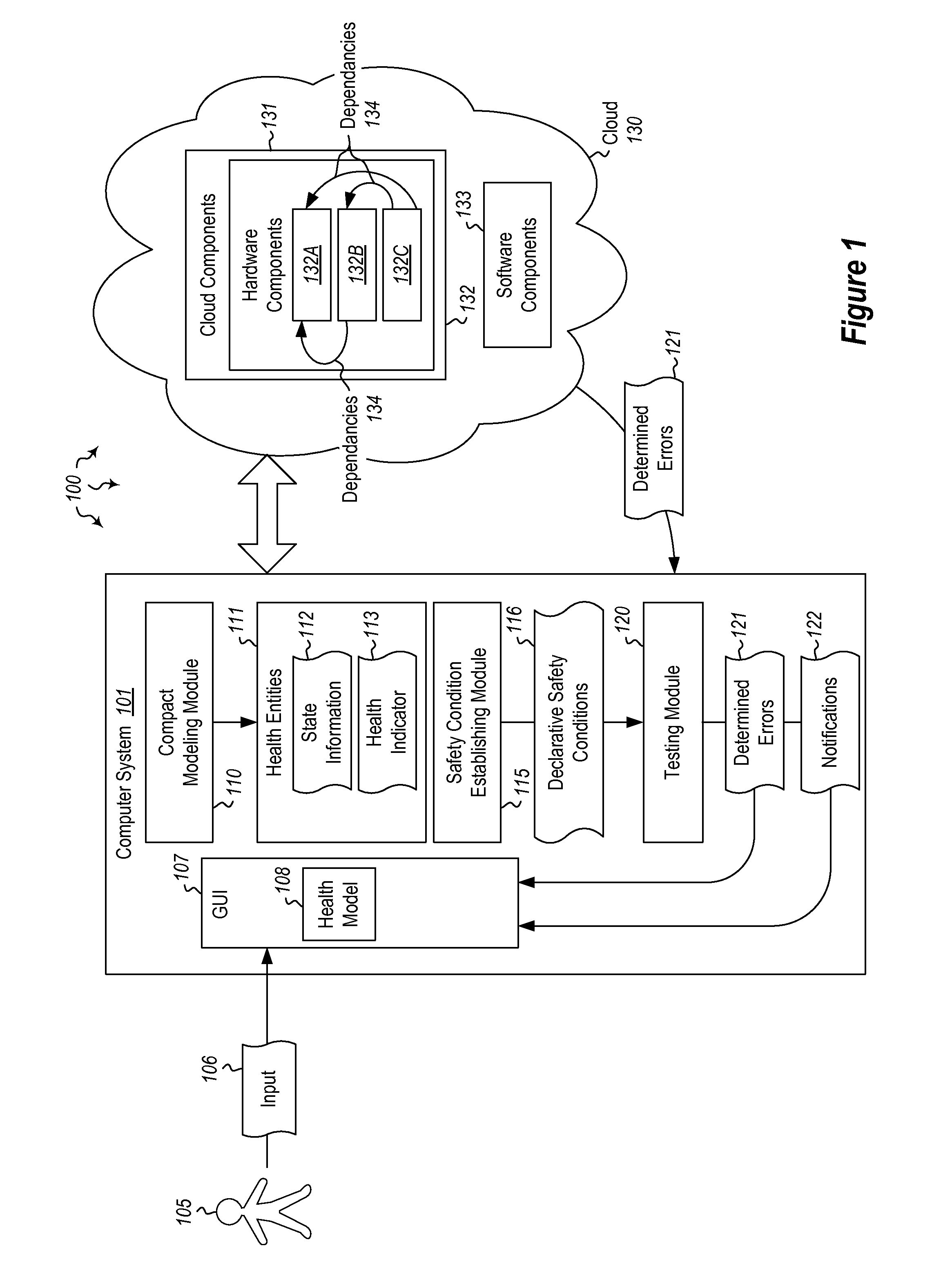
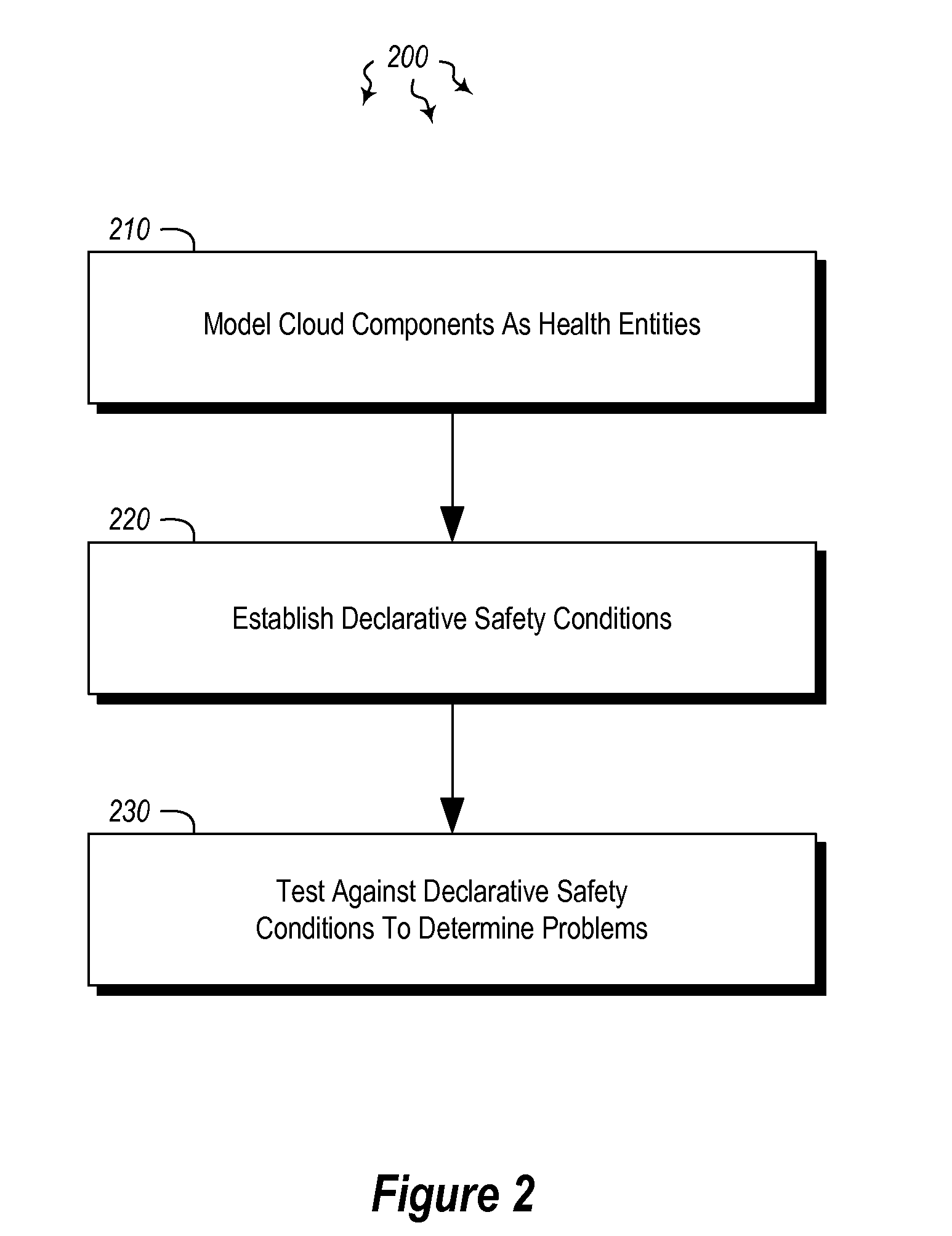
Embodiments are directed to establishing a model for testing cloud components and to preventing cascading failures in cloud components. In one scenario, a computer system models identified cloud components (including cloud hardware components and / or cloud software components) as health entities. Each health entity is configured to provide state information about the cloud component. The computer system establishes declarative safety conditions which declaratively describe cloud computing conditions that are to be maintained at the identified cloud components. The computer system then tests against the declarative safety conditions to determine which cloud components are or are becoming problematic. Upon determining that an error has occurred, the computer system notifies users of the error and the component at which the error occurred. Guarded interfaces are established to ensure that actions taken to fix the error do not cause further failures.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Software key function identification method based on complex network fault propagation
InactiveCN105045574ACompliant with the actual software systemGuaranteed uptimeSpecific program execution arrangementsCascading failureNODAL
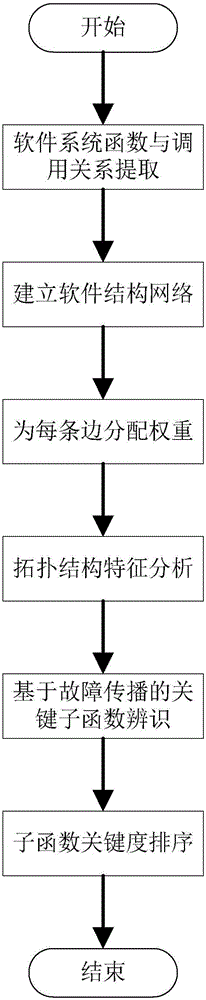
The invention discloses a software key function identification method based on complex network fault propagation. The software key function identification method comprises the following steps: 1) according to a source code, carrying out subfunction and calling relation extraction on a program, and carrying out abstraction to obtain a network chart of a software structure; 2) according to a probability of calling and executing each subfunction, endowing each side with a certain weight w, wherein the weight is a failure probability of inter-function cascading faults; 3) analyzing the topological structure characteristics of software, and calculating an in-degree value and an out-degree value of each node, wherein the in-degree value of the node is a frequency that the function is called by other functions, and the out-degree value of the node is the frequency that the function calls other functions; 4) carrying out a cascading failure simulation experiment on each node of a software network, and calculating the node numbers G, i.e., the criticality, of a maximum connected subgraph of the software network after each node is subjected to stable failure; and 5) sorting the G in an increasing sequence to obtain the criticality of each function. The software key function identification method is simple and reliable. Compared with a traditional method, the software key function identification method can precisely identify a software key function.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
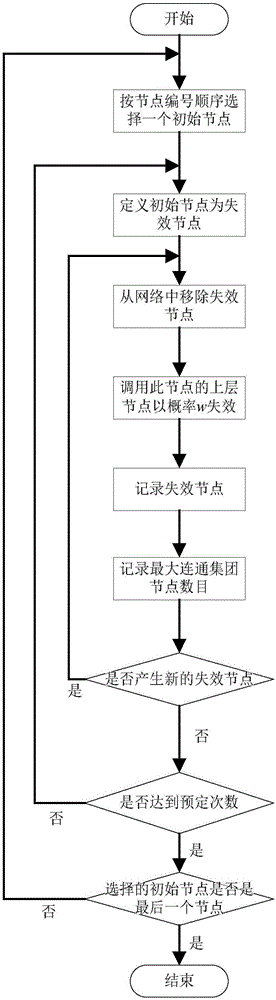
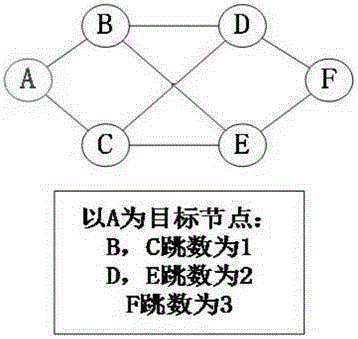
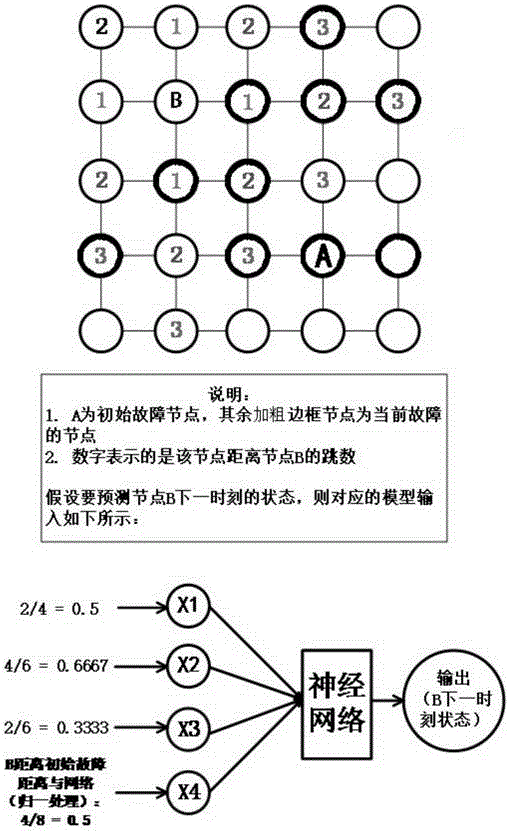
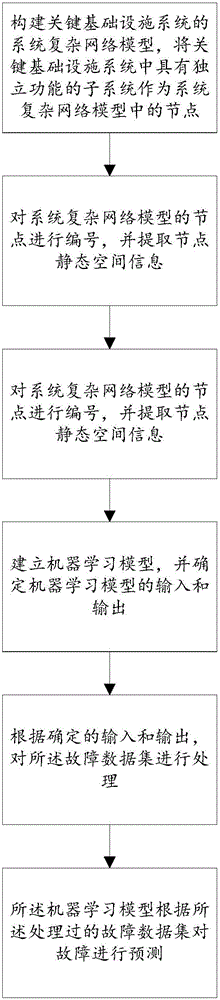
Method for predicting key infrastructure fault propagation
The invention provides a method for predicting key infrastructure fault propagation. The method comprises steps that a system complex network model of a key infrastructure system is constructed; nodes of the system complex network model are numbered; the historical fault data of cascade failure of the key infrastructure system is searched, the historical fault data of the key infrastructure system is cut according to time intervals, and a fault data set of the key infrastructure system is constructed; a machine learning model is established, and input and output of the machine learning model are determined; the fault data set is processed; faults are predicted through the machine learning model. Through the method, when cascade failure of the network occurs, a state of the network at the next moment is predicted through utilizing the state information of a node itself, the state information of a next node adjacent to the node and space attributes of the node, and the useful information is provided for system microscopic dynamic evolution control.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
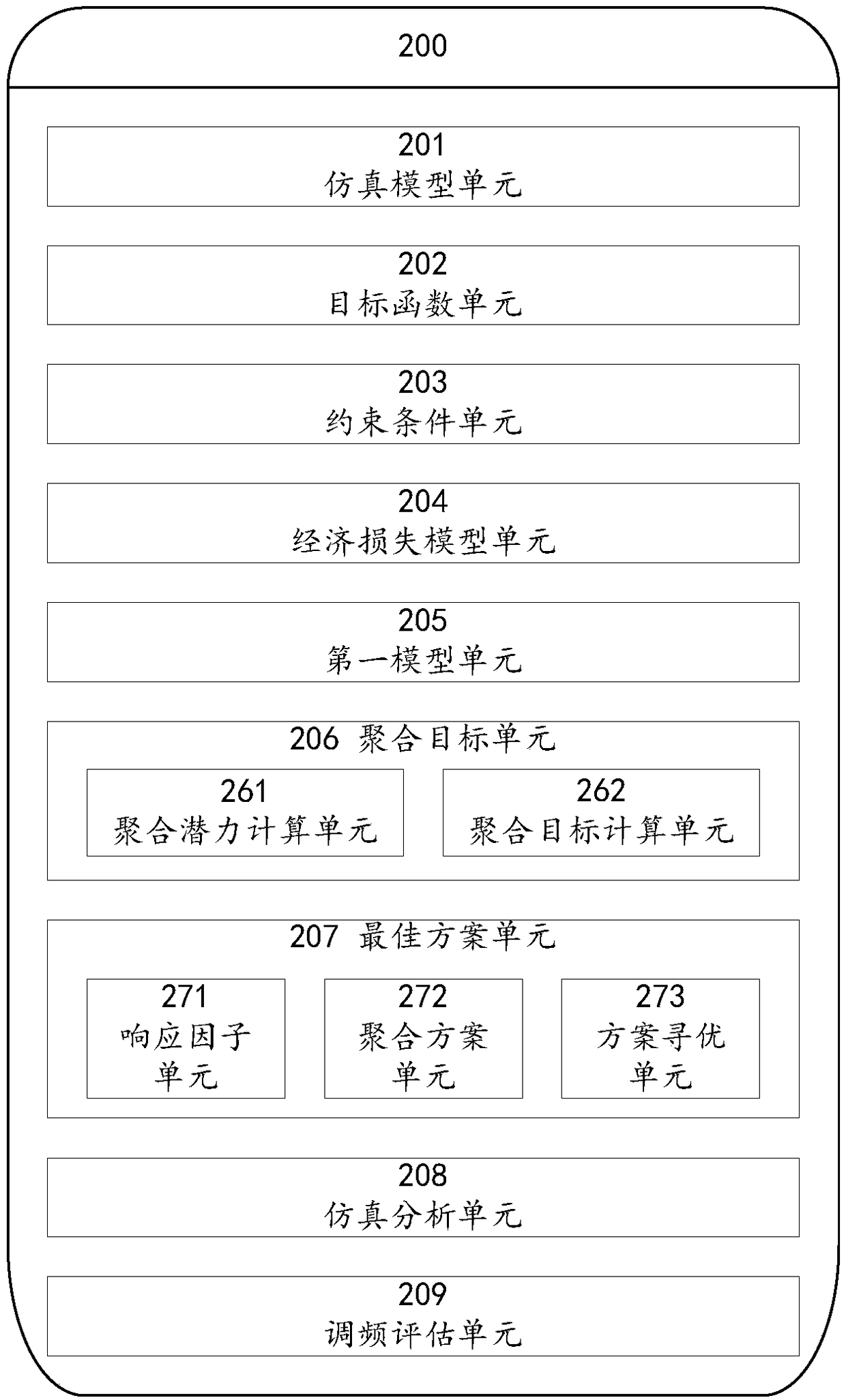
A modeling method and system for evaluating aggregation frequency modulation performance of a distributed energy storage system
ActiveCN109193719AMeet market demandIncrease static safety marginAc network load balancingCascading failureResponse factor
The present invention provides a modeling method and system for evaluating aggregation frequency modulation performance of a distributed energy storage system. A method and system can be implement bydetermining a power grid aggregation target, and calculating the response factor of each distributed energy storage unit of the distributed energy storage system to the power grid aggregation frequency modulation, combining with the preset constraints of distributed energy storage system and power grid, adopting particle swarm optimization (PSO) to optimize the pre-established objective function of power system, determining the optimal aggregation frequency modulation scheme of distributed energy storage system, and then performing simulation analysis on the economy of the grid before and after the access of distributed energy storage system according to the preset model on the simulation model,so as to evaluate the frequency modulation performance of distributed energy storage system after the access of distributed energy storage system to grid. By optimizing the output of the distributed energy storage system, the method and the system realize the timely treatment of the frequency problems existing in the power grid, prevent the occurrence of large-scale cascading failures, and give full play to the application potential of the distributed energy storage system.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
Command and control network cascade failure model construction method based on node importance
InactiveCN110290006AImprove cascade invulnerabilityImprove accuracyData switching networksCascading failureCommand and control
The invention discloses a command and control network cascading failure model construction method based on node importance. The cascading failure resistance of a command and control network can be remarkably improved by reasonably adjusting corresponding parameters in a model, and the cascading destruction resistance of the command and control network is optimal due to the existence of optimal model parameters. According to the OODA combat theory and in combination with the concept of combat link betweenness, a new initial load definition method, a nonlinear load capacity model and a load redistribution strategy are given, and the internal mechanism and the external behavior of command and control network cascade failure can be reflected more effectively and accurately.
Owner:DALIAN JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com