Patents
Literature
760 results about "Blade server" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
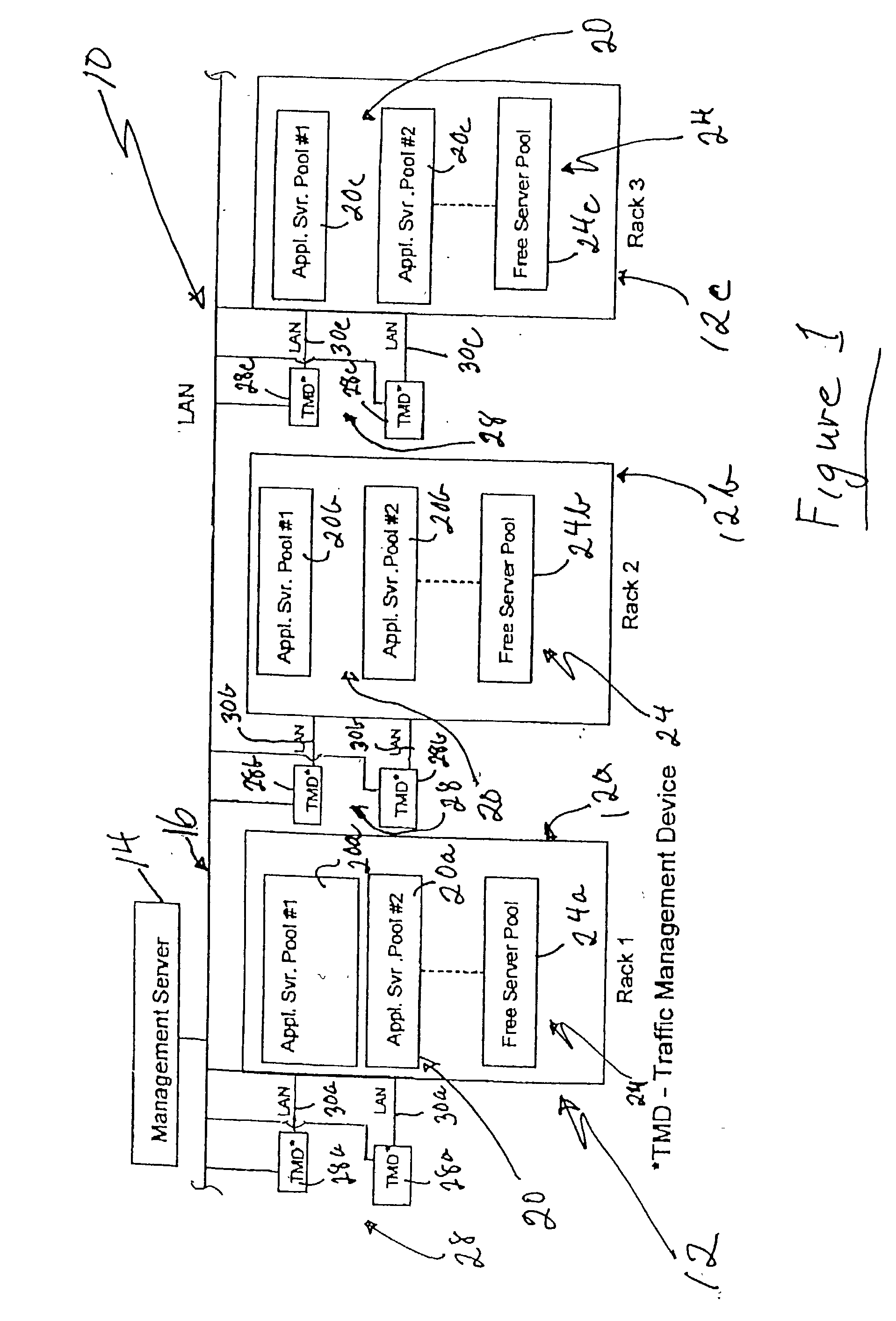
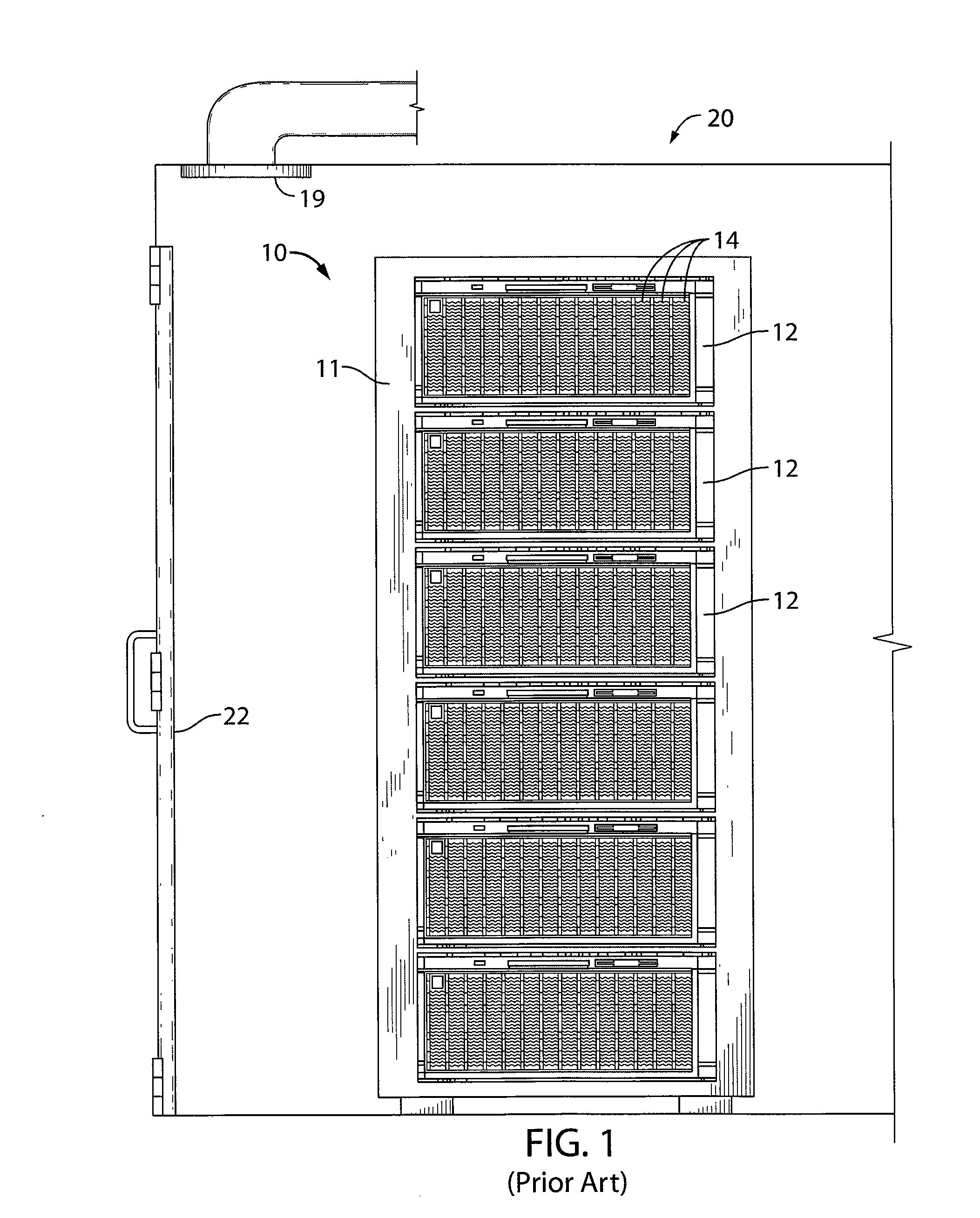
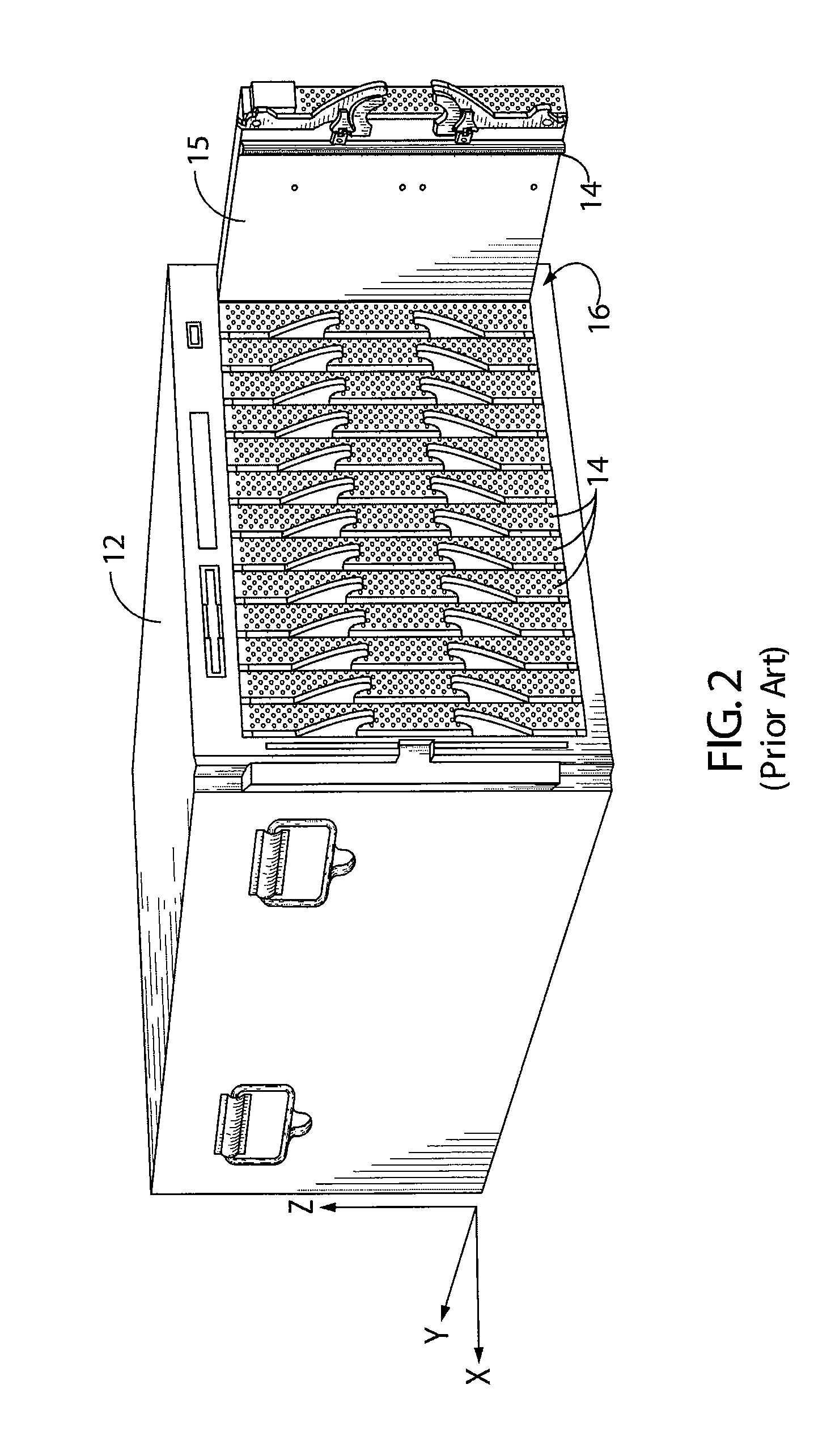
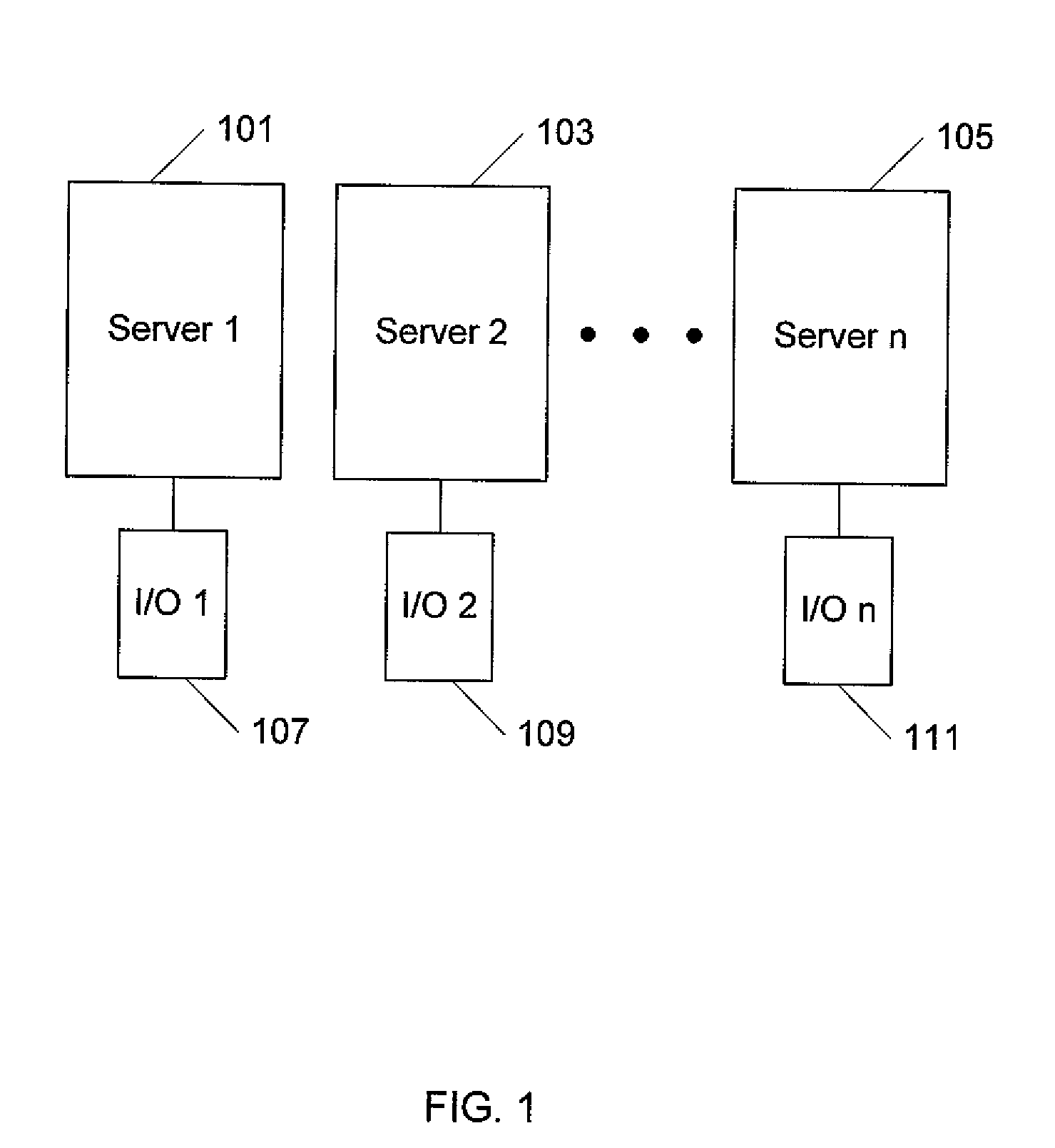
A blade server is a stripped-down server computer with a modular design optimized to minimize the use of physical space and energy. Blade servers have many components removed to save space, minimize power consumption and other considerations, while still having all the functional components to be considered a computer. Unlike a rack-mount server, a blade server fits inside a blade enclosure, which can hold multiple blade servers, providing services such as power, cooling, networking, various interconnects and management. Together, blades and the blade enclosure form a blade system, which may itself be rack-mounted. Different blade providers have differing principles regarding what to include in the blade itself, and in the blade system as a whole.
Dynamic adaptive server provisioning for blade architectures
ActiveUS20040054780A1Resource allocationDigital computer detailsApplication serverApplication software
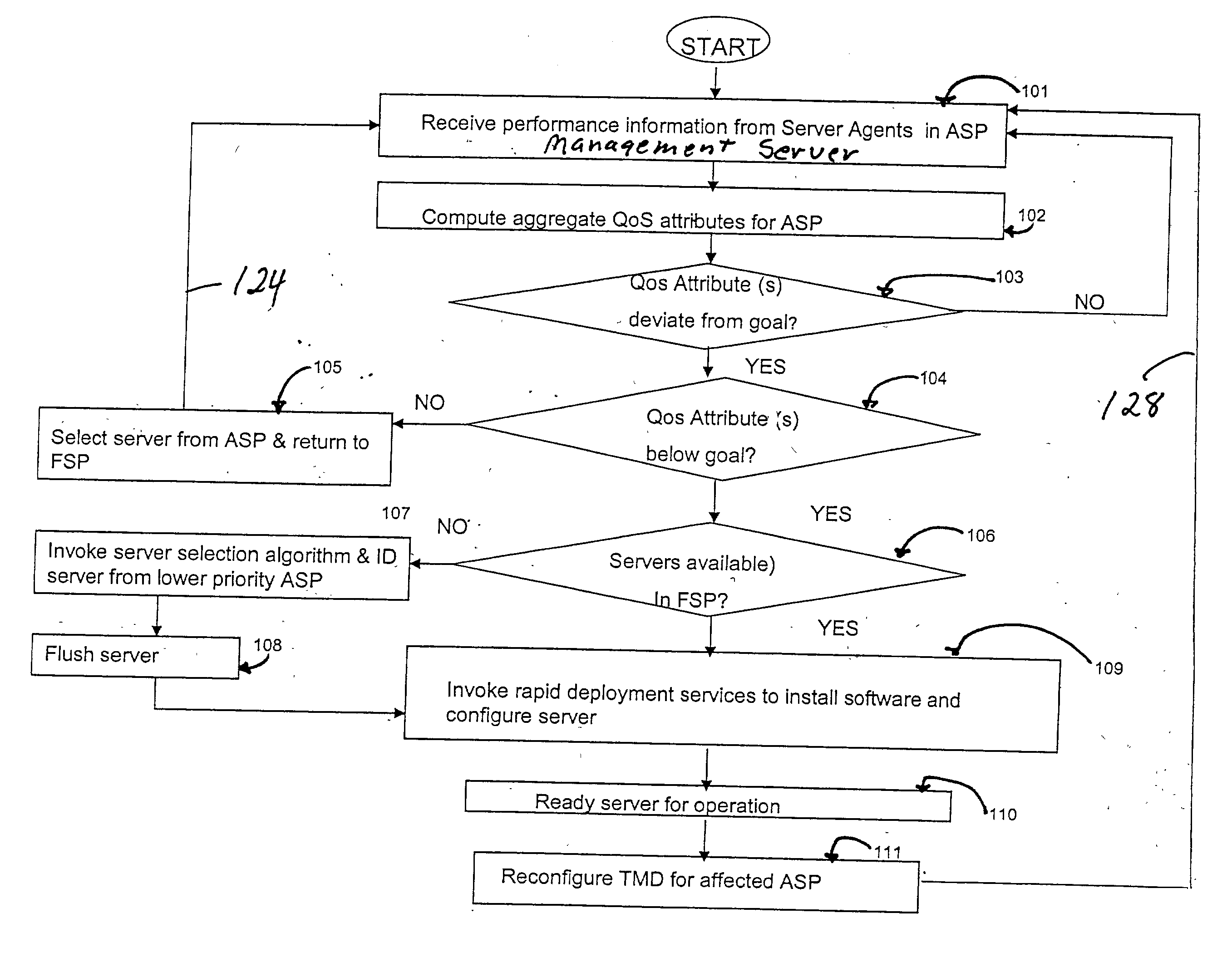
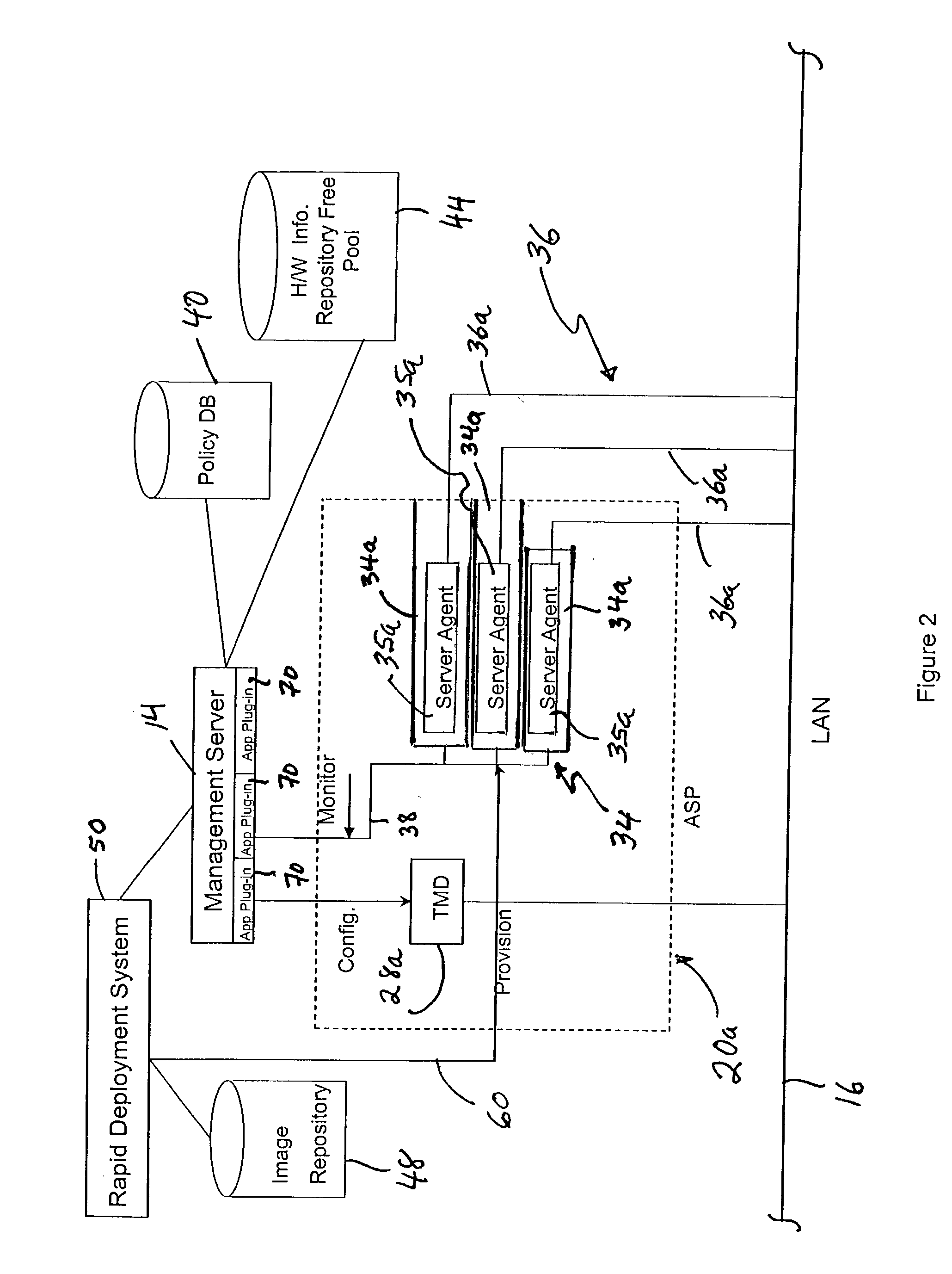
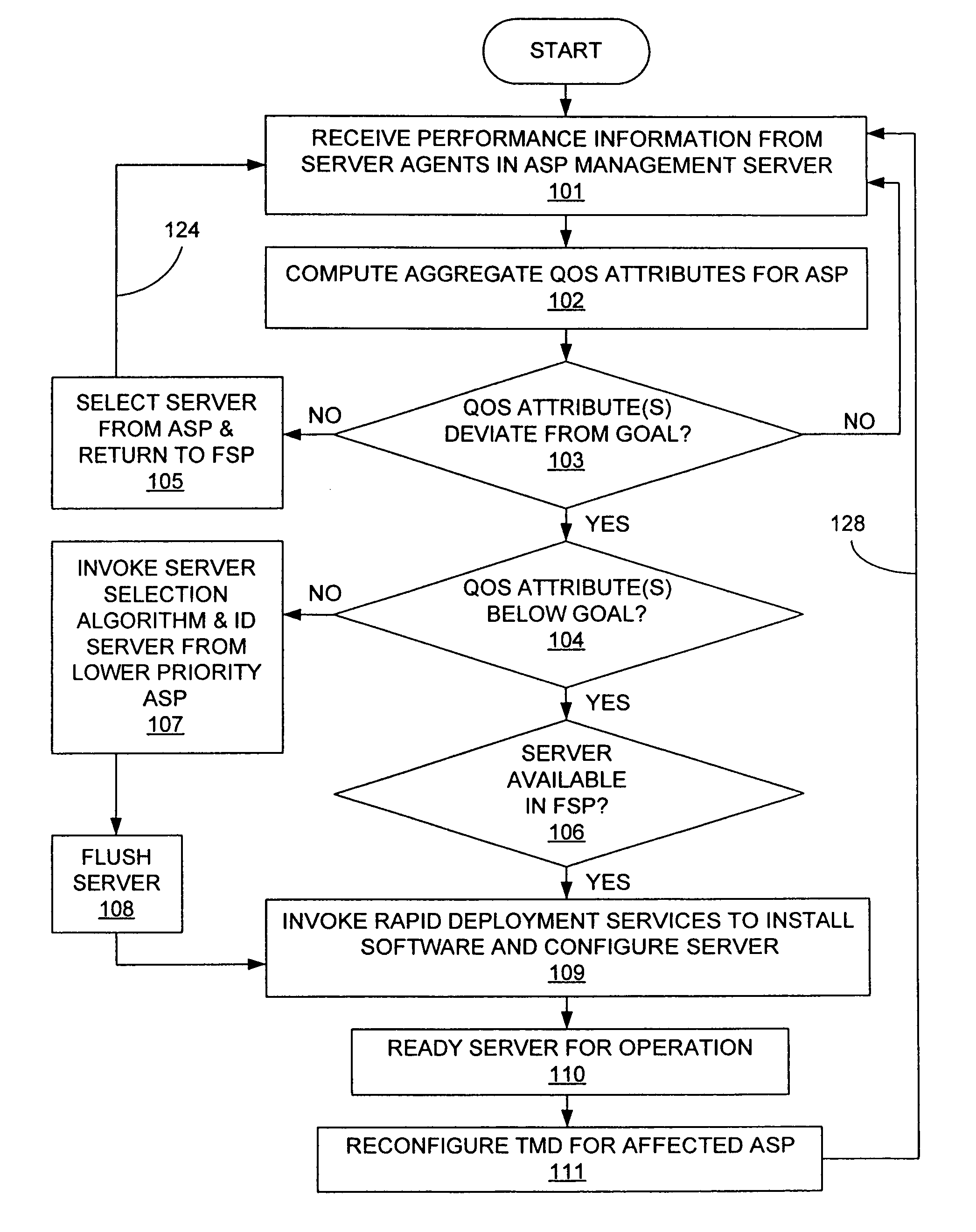
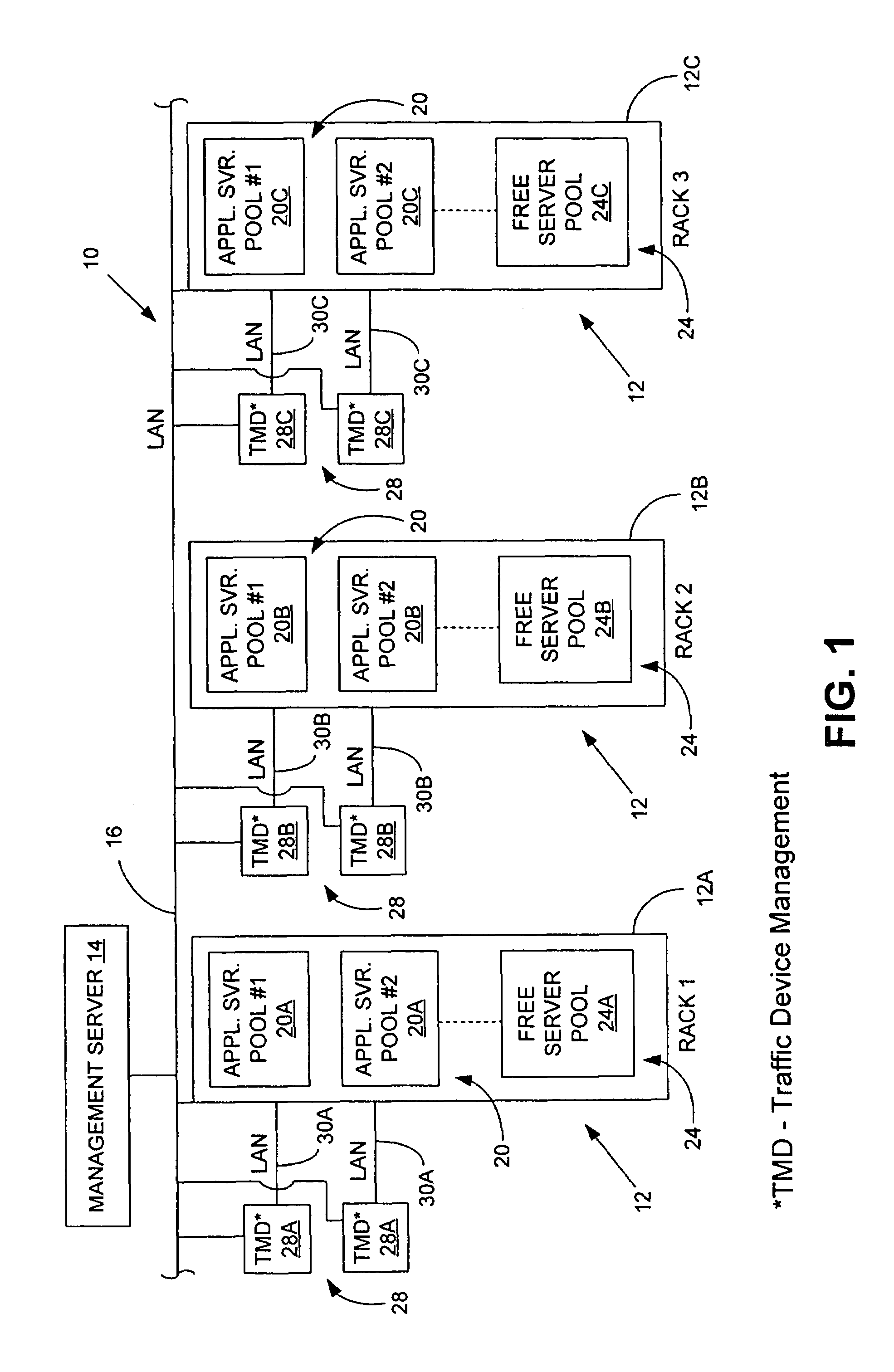
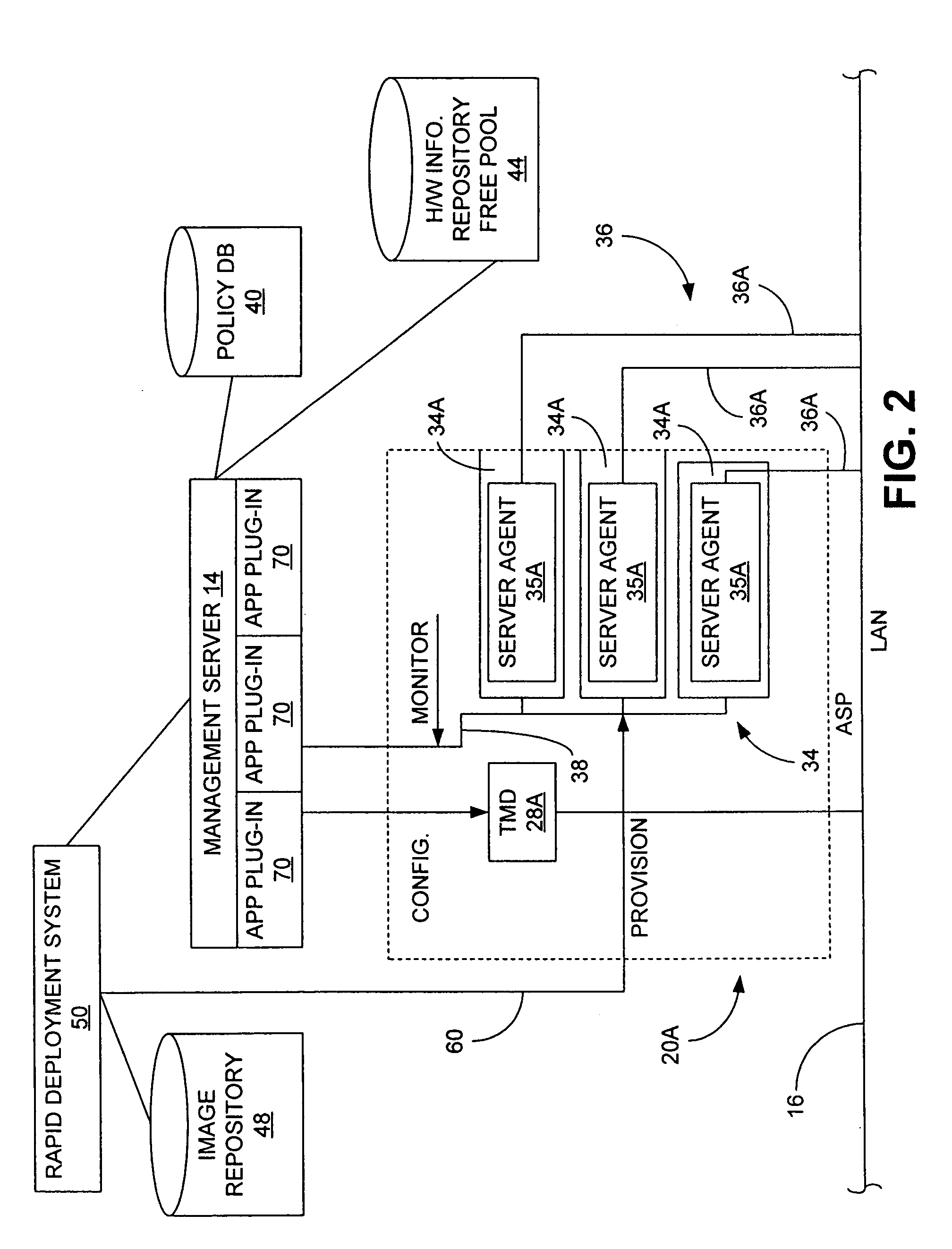
A system and method for automatically allocating computing resources of a rack-and-blade computer assembly. The method includes receiving server performance information from an application server pool disposed in a rack of a rack-and-blade computer assembly, and determining at least one QoS attribute for the application server pool. If the QoS attribute is below a standard, a blade server is allocated from a free server pool for use by the application server pool. If the QoS attribute is above a standard, at least one server is removed from the application server pool. An article of manufacture including a machine-readable medium having stored thereon instructions for automatically allocating computing resources of a rack-and-blade computer assembly.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
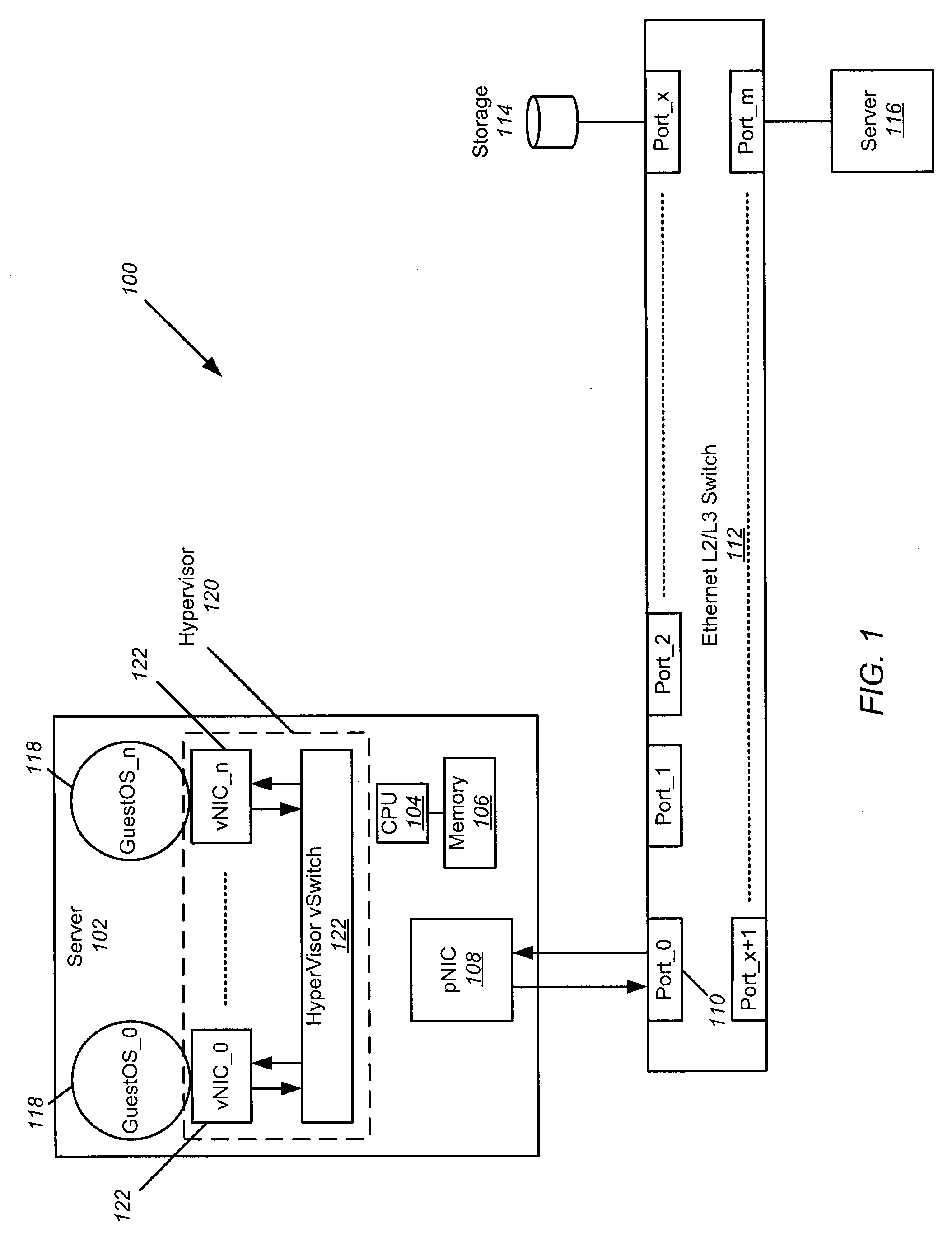
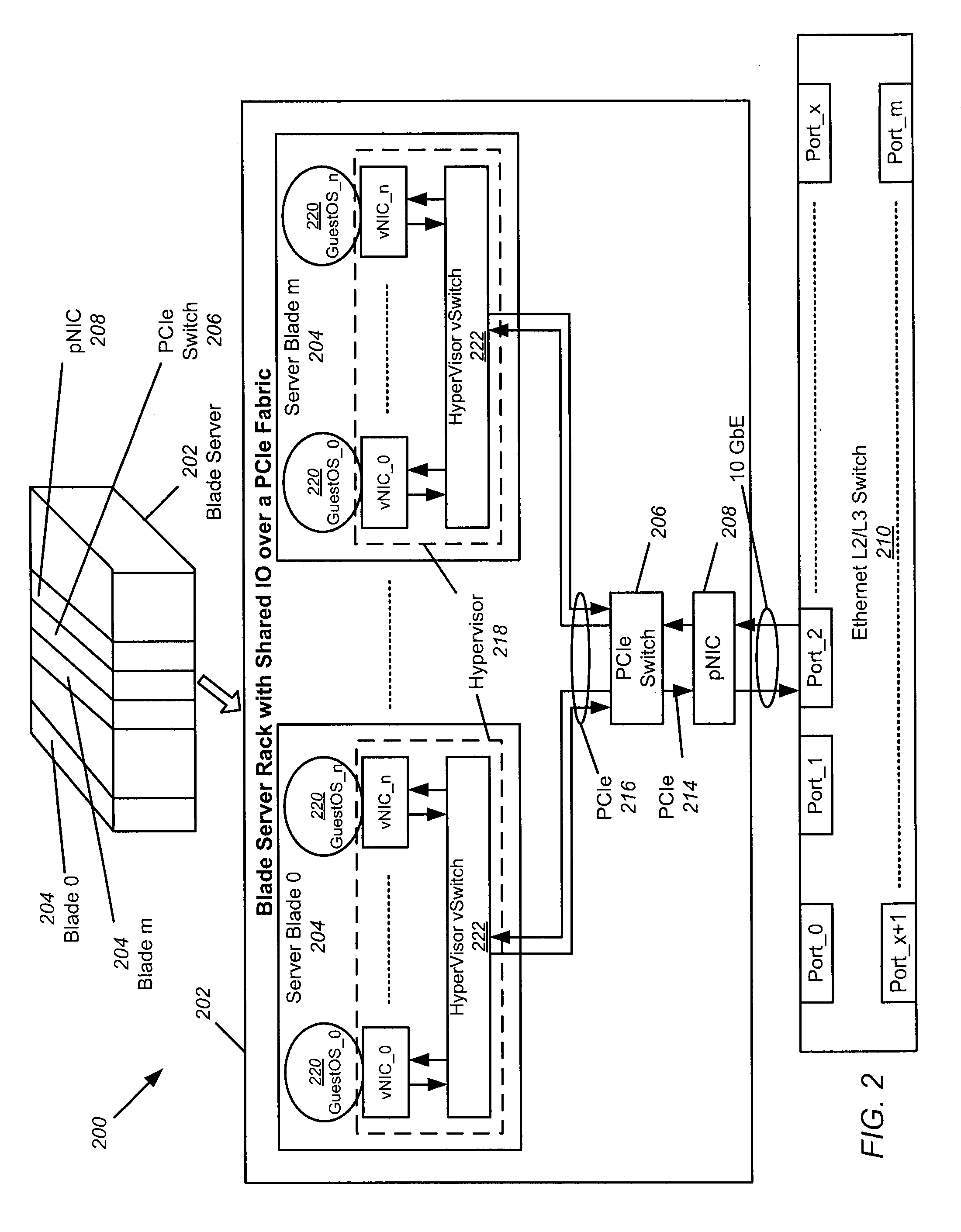
Hardware Switch for Hypervisors and Blade Servers
ActiveUS20100014526A1Quick switchData switching by path configurationMemory systemsFiber10 Gigabit Ethernet
A hardware switch for use with hypervisors and blade servers is disclosed. The hardware switch enables switching to occur between different guest OSs running in the same server, or between different servers in a multi-root IOV system, or between different guest OSs running in the same server in single-root IOV systems. Whether embedded in a host bus adapter (HBA), converged network adapter (CNA), network interface card (NIC) or other similar device, the hardware switch can provide fast switching with access to and sharing of at least one external network port such as a Fibre Channel (FC) port, 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10 GbE) port, FC over Ethernet (FCOE) port, or other similar port. The hardware switch can be utilized when no hypervisor is present or when one or more servers have hypervisors, because it allows for switching (e.g. Ethernet switching) between the OSs on a single hypervisor.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
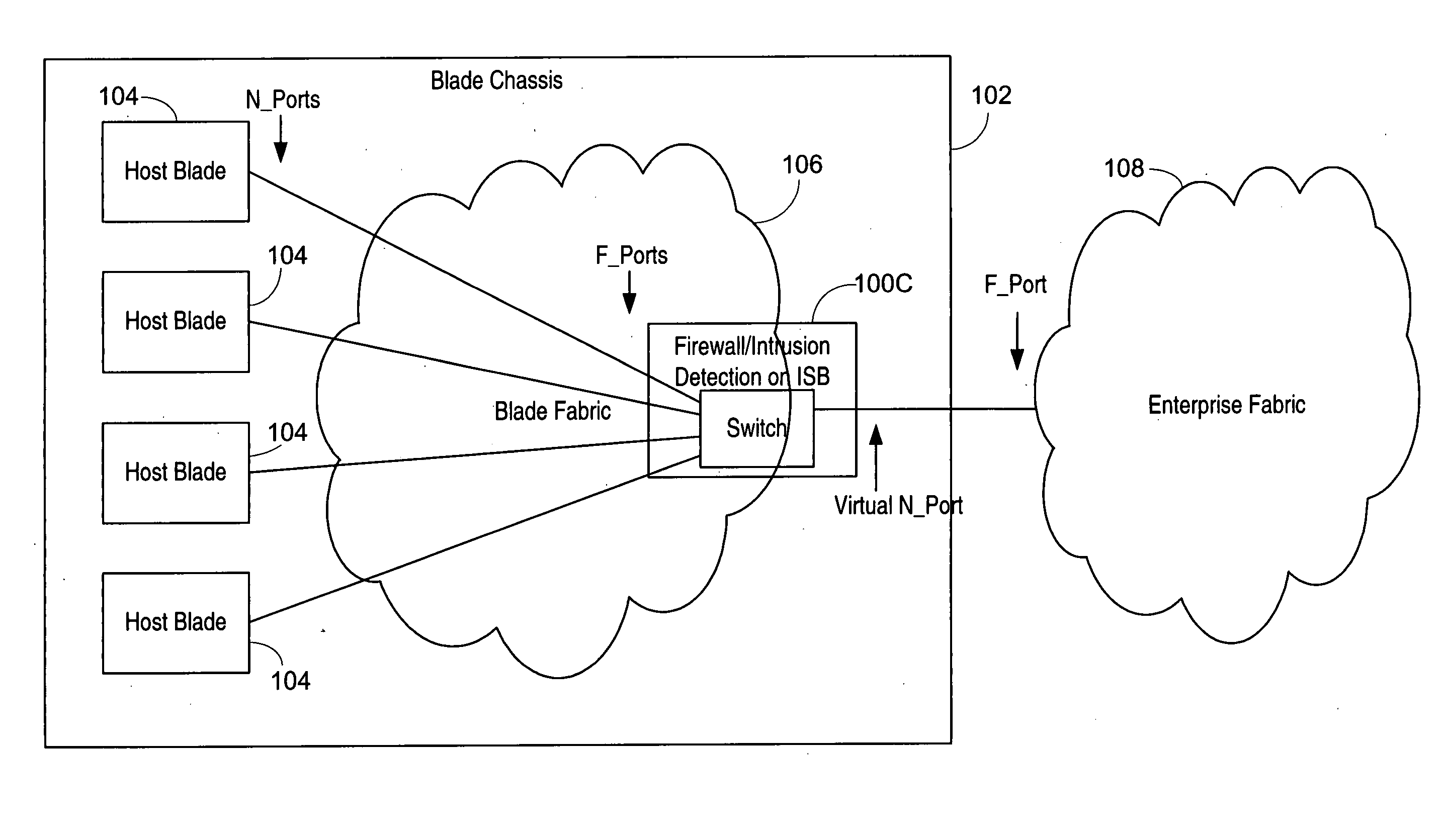
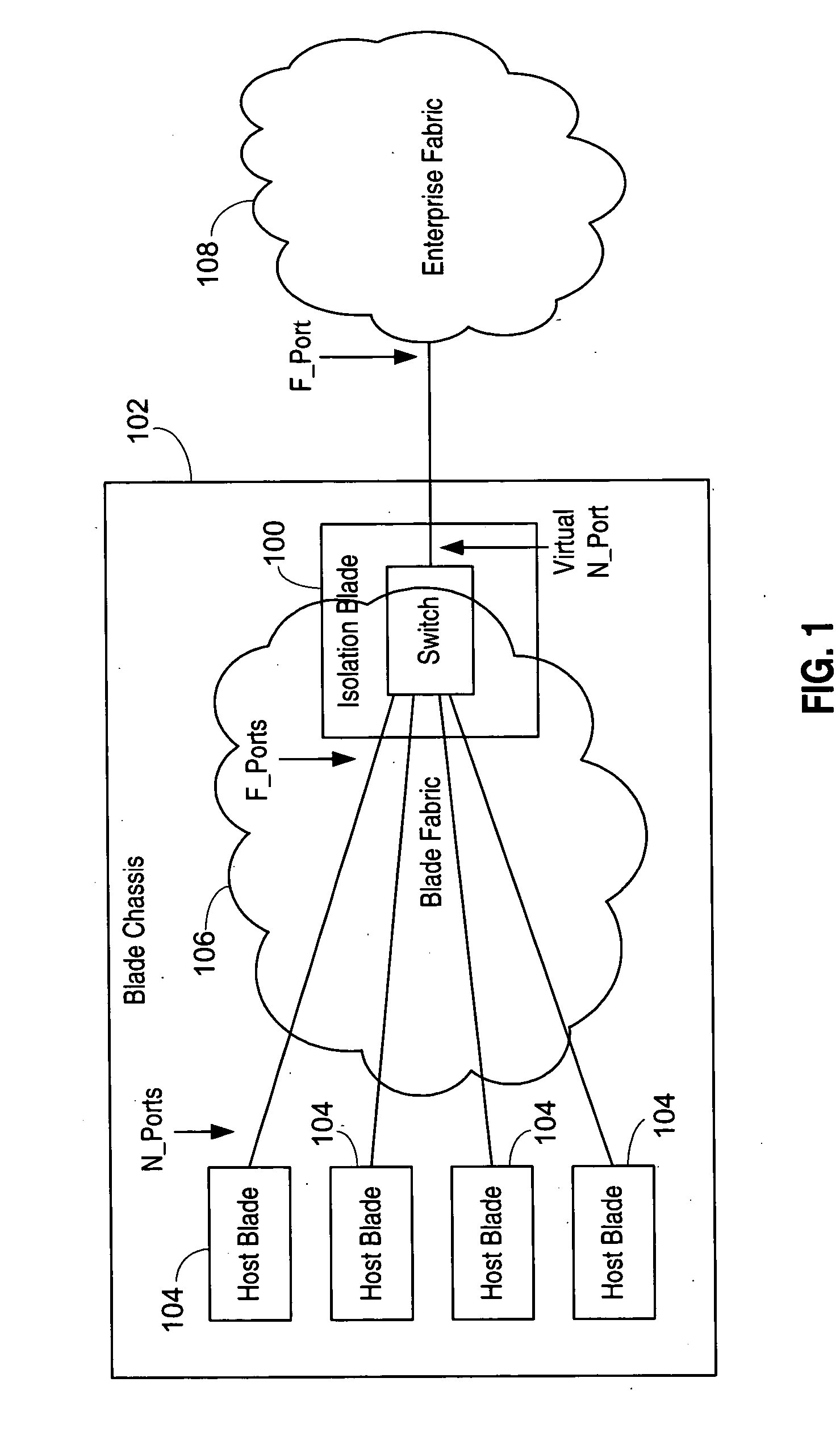
Isolation switch for fibre channel fabrics in storage area networks
ActiveUS20050198523A1Improve scalabilityImprove interoperabilityMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionVirtualizationStorage area network
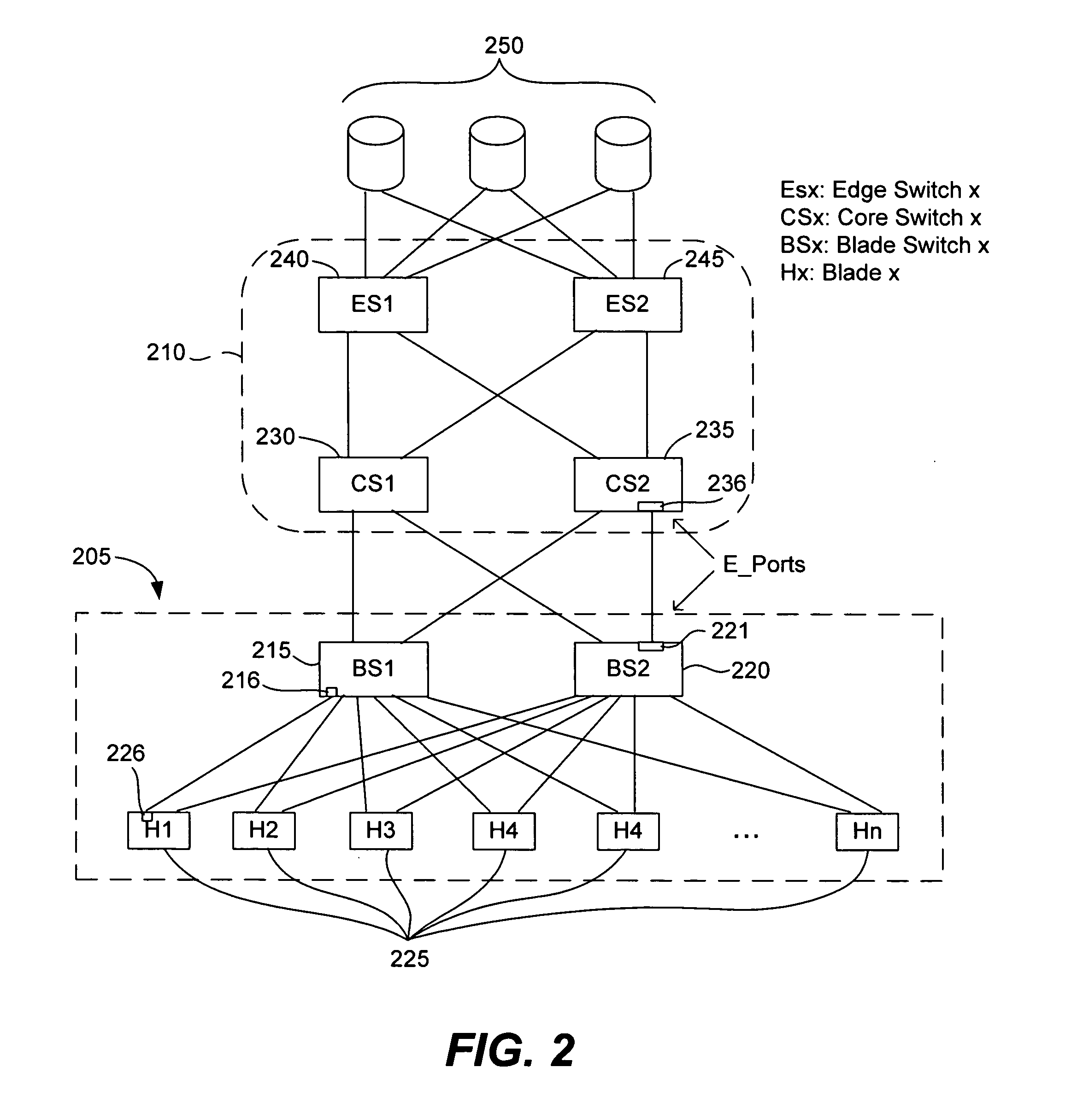
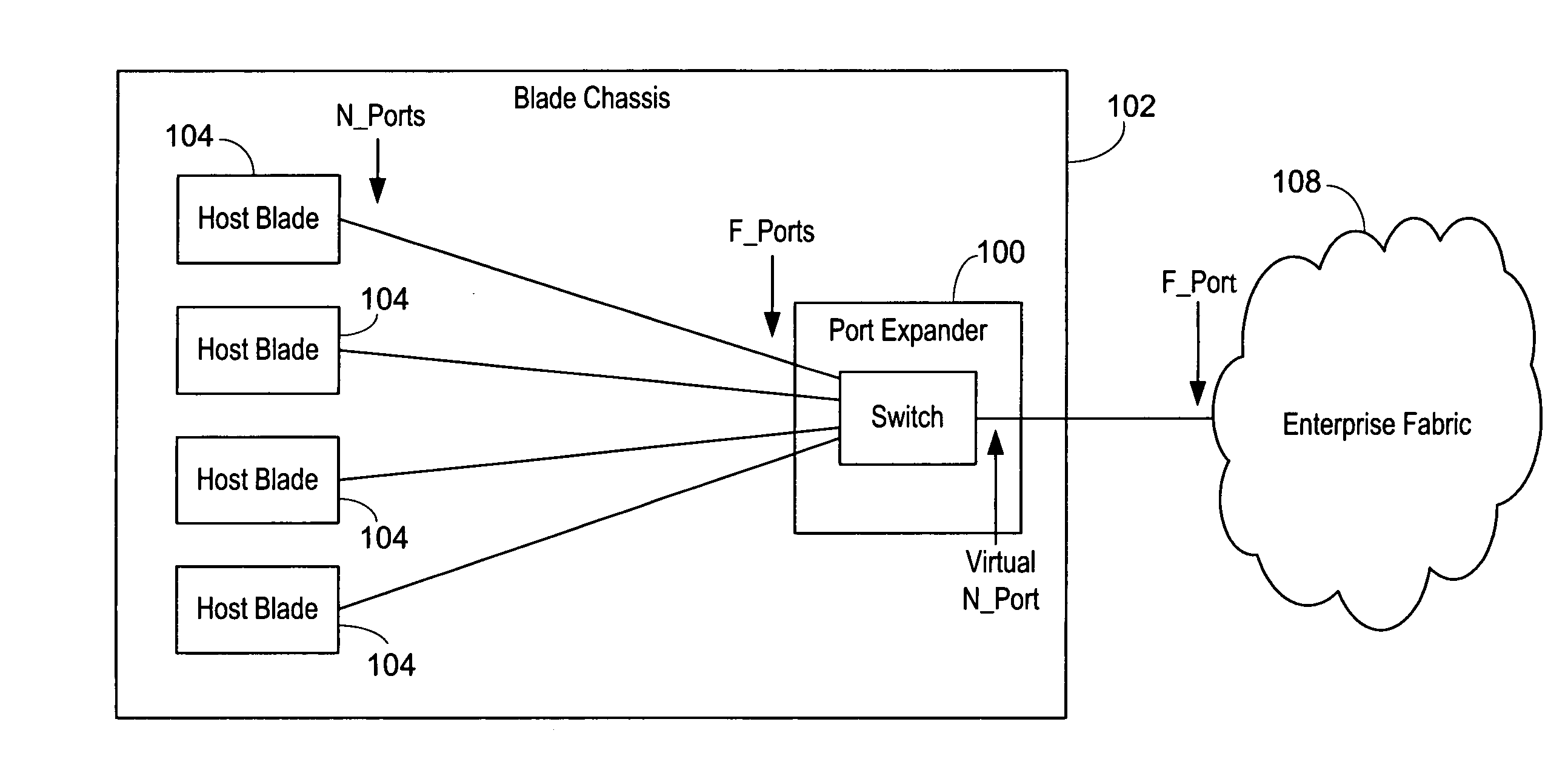
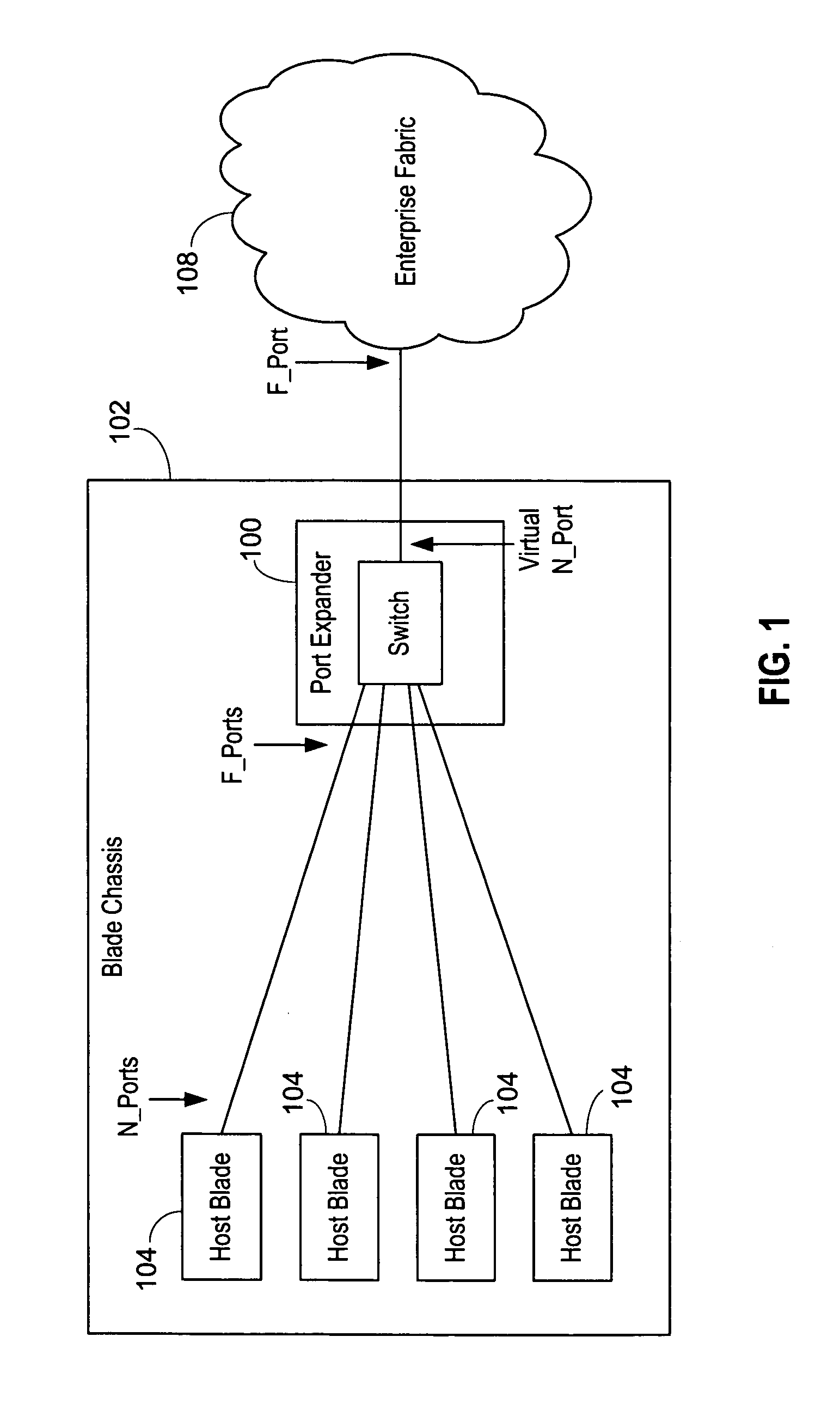
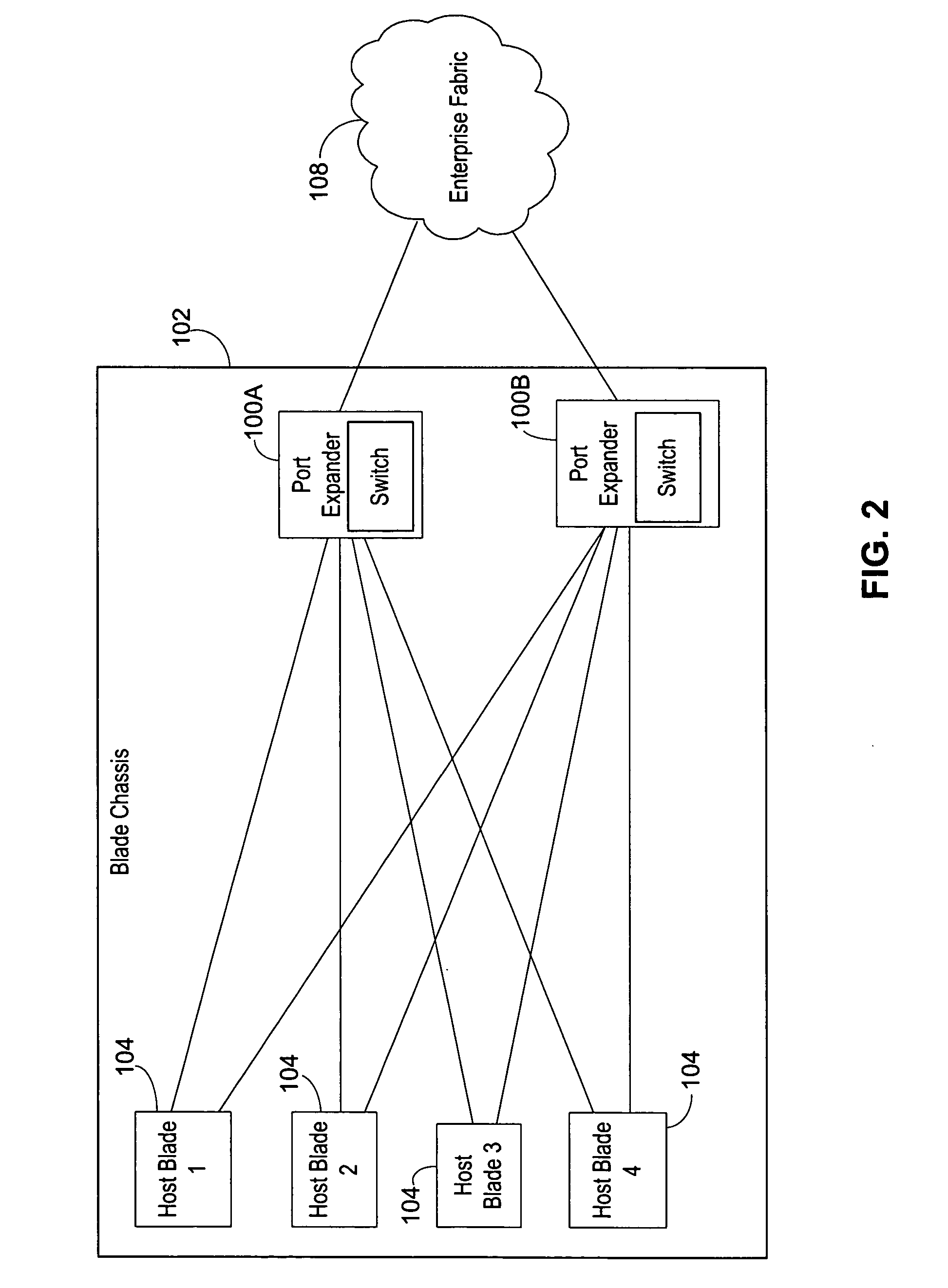
An isolation switch blade Fibre Channel switch presents F_ports to form a first Fibre Channel fabric and N_ports to a second Fibre Channel fabric to appear as node devices. The isolation switch blade may be used to connect a plurality of blade servers to a Fibre Channel fabric. Fabric events engendered by the insertion or removal of hot-pluggable devices are handled by the isolation switch blade and “event storms” on the Fibre Channel fabric are avoided. The isolation switch blade presents the blade servers to the FC fabric as a virtualized N_port.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Fibre channel over ethernet
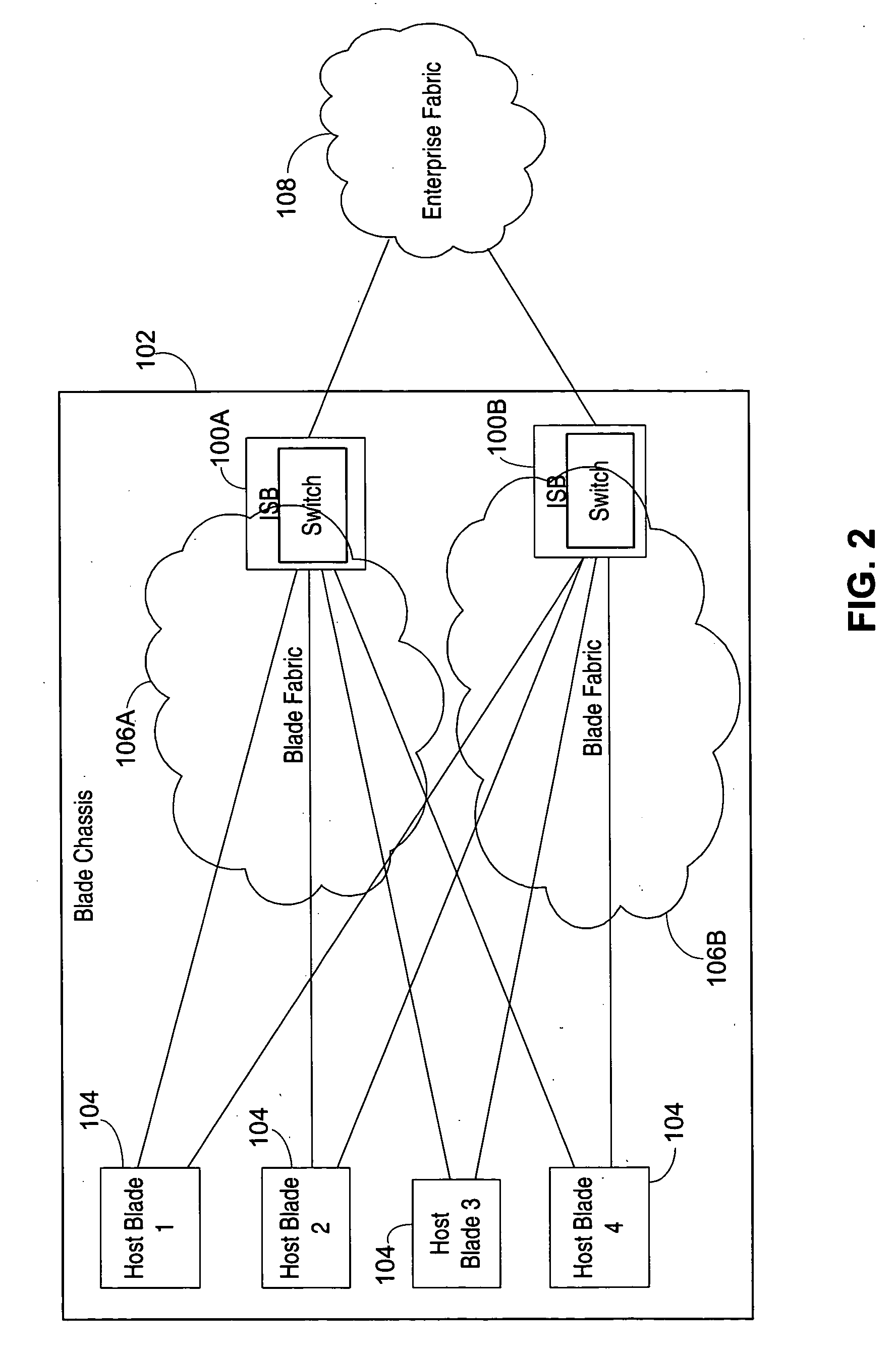
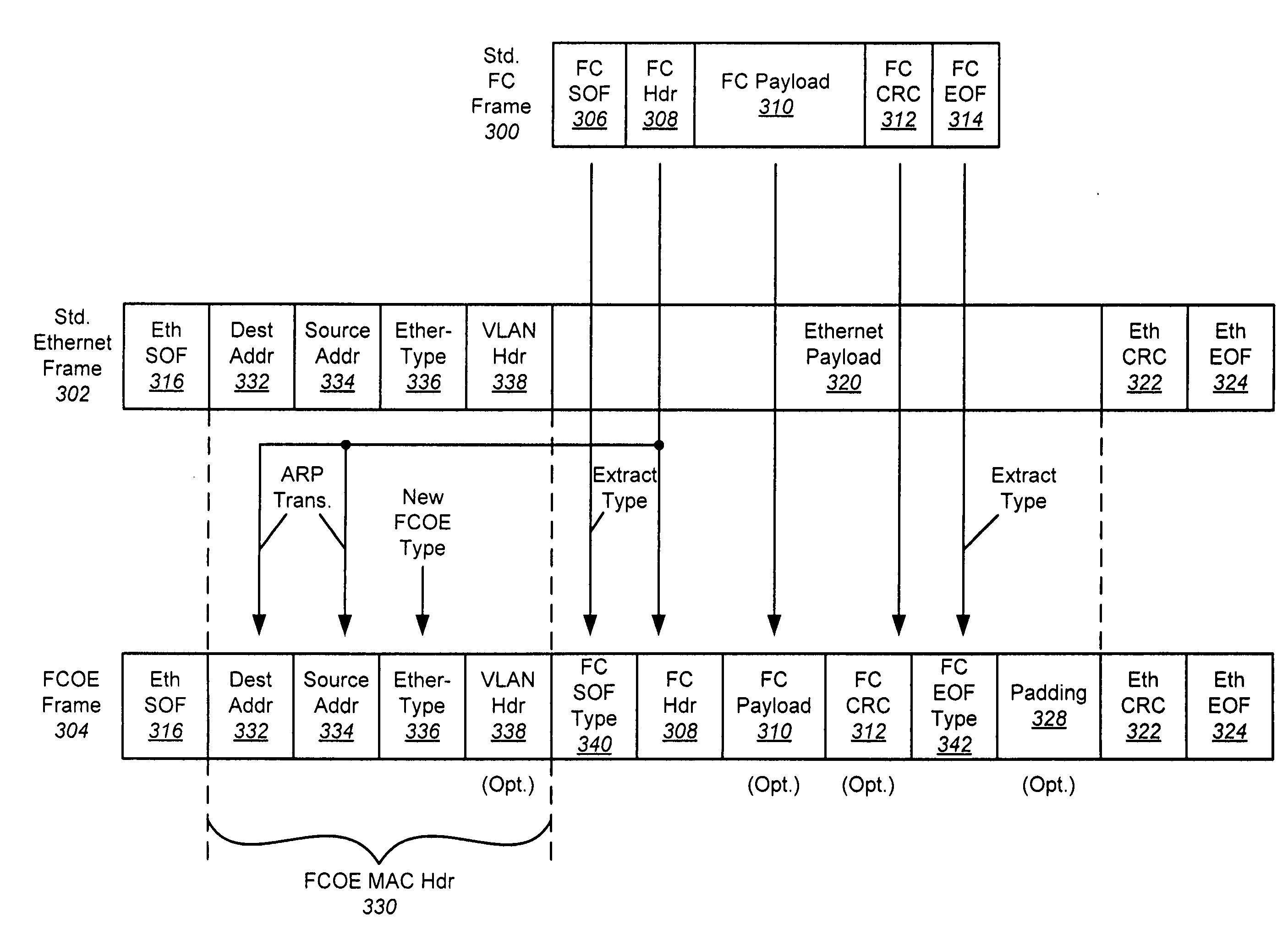
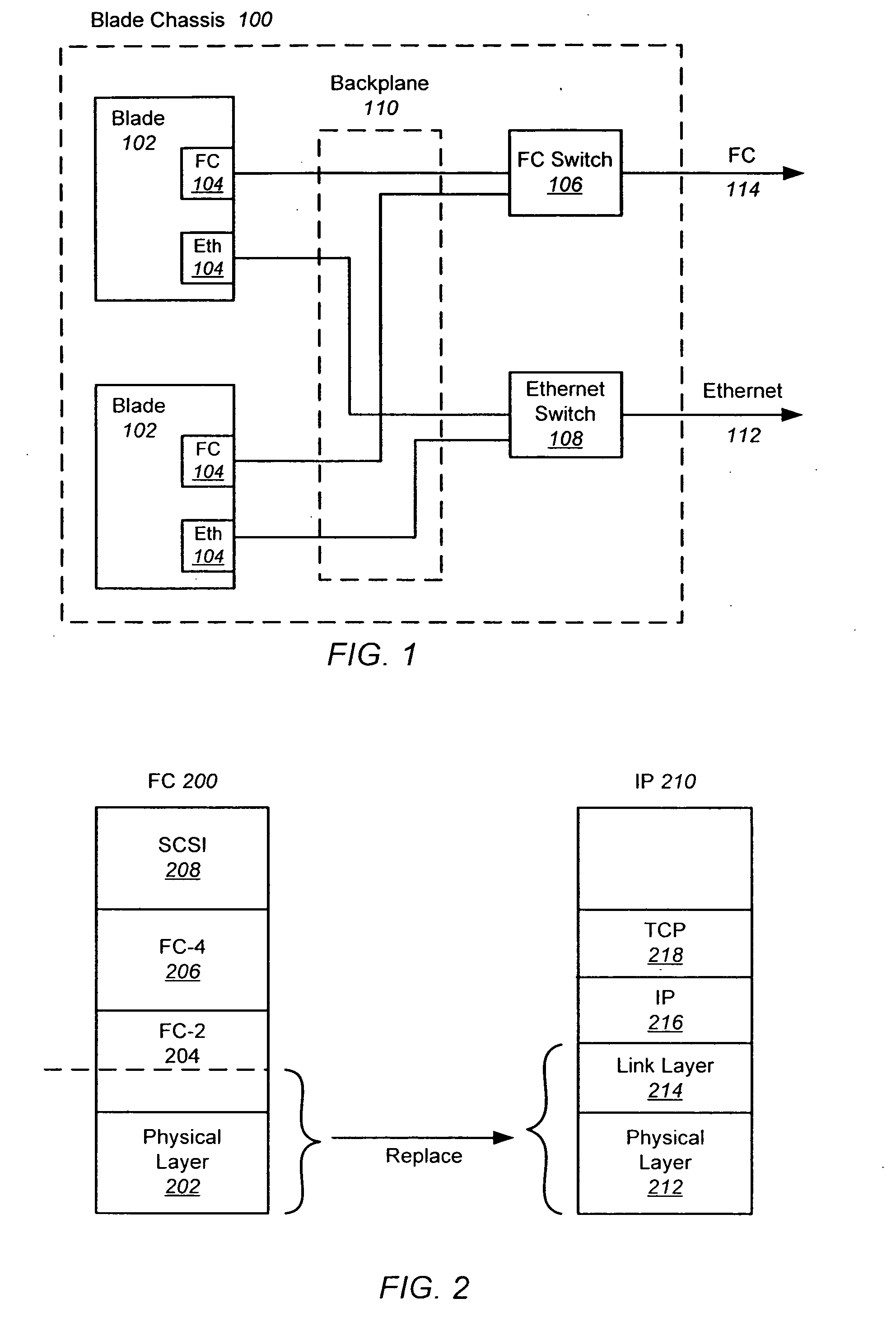
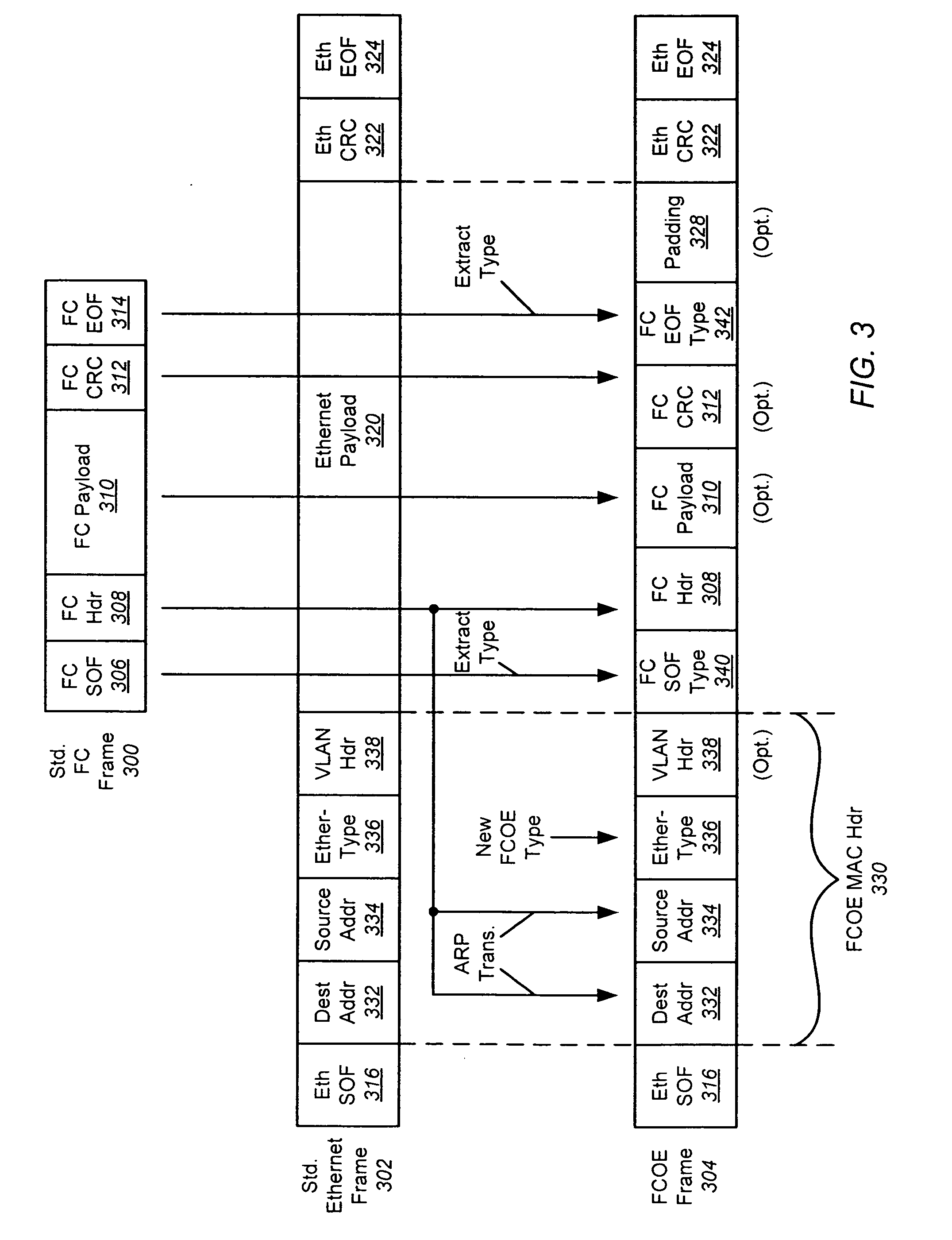
The use of Ethernet as an underlying transport for Fibre Channel (FC) frames is disclosed in the Fibre Channel Over Ethernet (FCOE) protocol. In FCOE, the FC physical layer and part of the FC-2 link layer are replaced with the Ethernet physical and link layers. Each FC frame is encapsulated within an Ethernet Frame. The payload of the FCOE frame contains type information from the FC Start Of Frame (SOF) indicator, the FC header, an optional FC payload, and type information from the FC End Of Frame (EOF) indicator. In one embodiment, an Ethernet network carrying FCOE replaces a standard FC network. In another embodiment, devices implementing FCOE may be implemented in a blade server. The entire backplane is Ethernet, over which both storage and networking traffic can be run. The Ethernet links are connected to an Ethernet switch, a FCOE / FC converter, and a FC switch.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System and method for maximizing server utilization in a resource constrained environment
InactiveUS20070050644A1Control power consumptionReduce computing power requirementsEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementOperational systemBase frequency
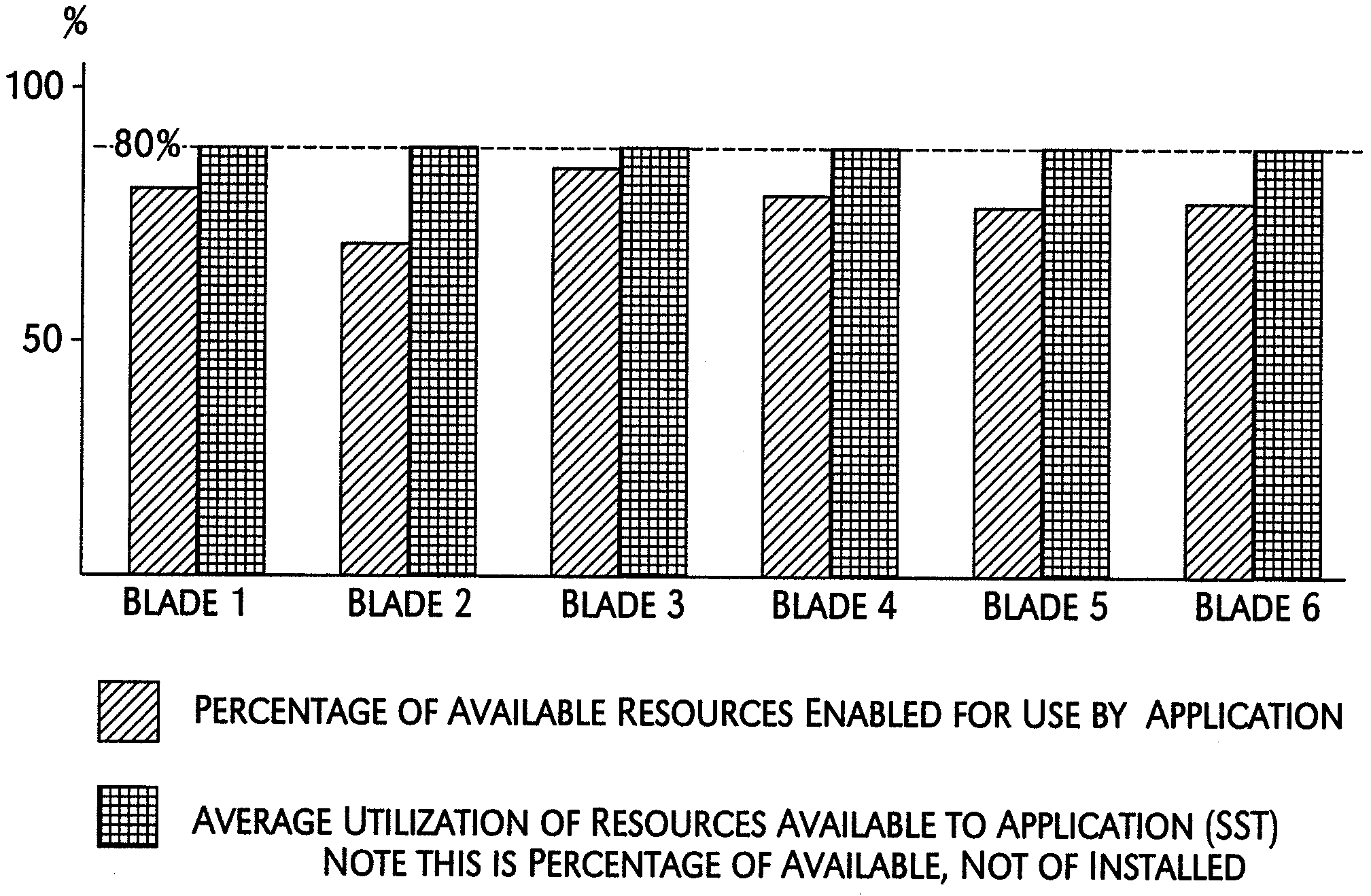
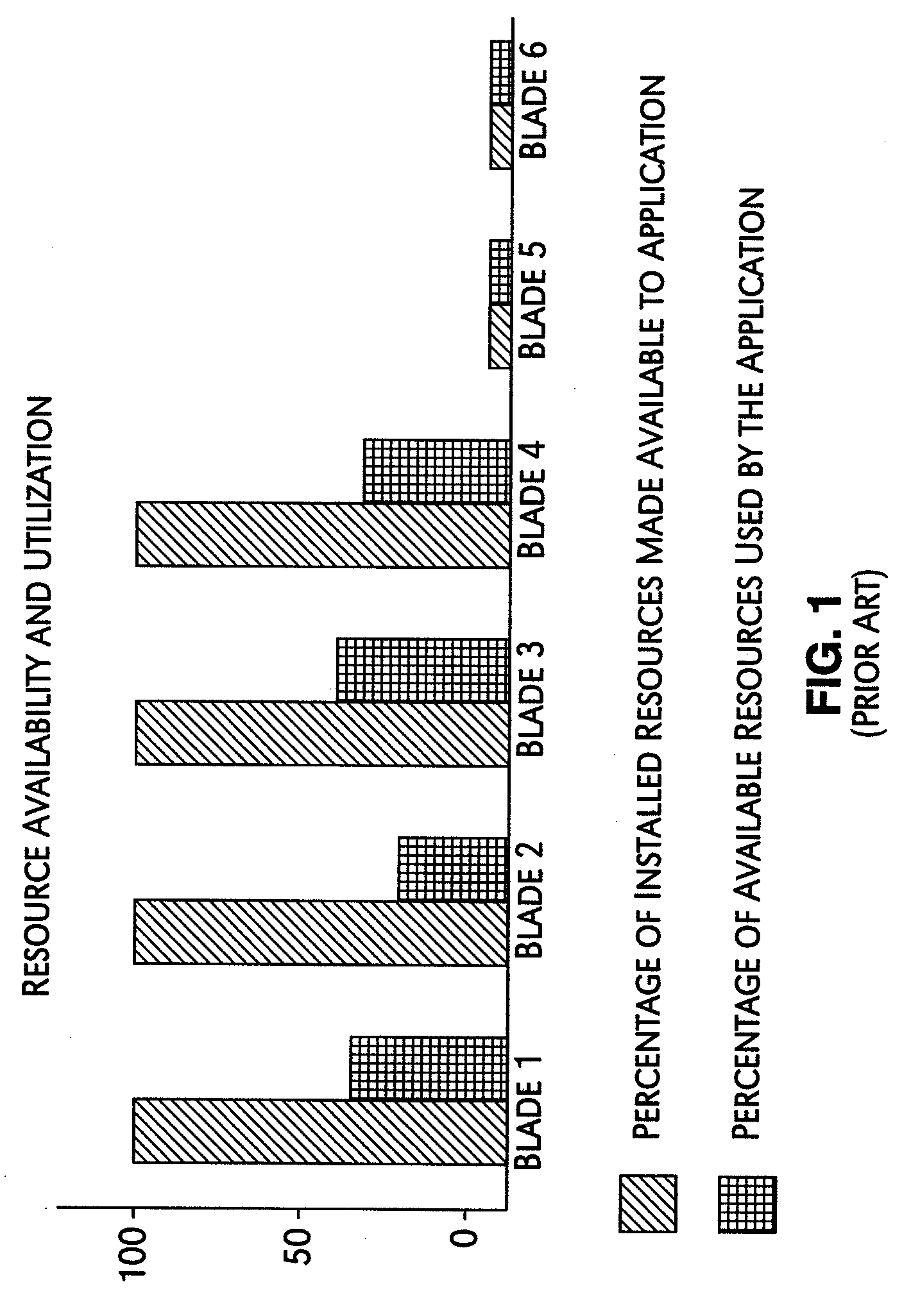
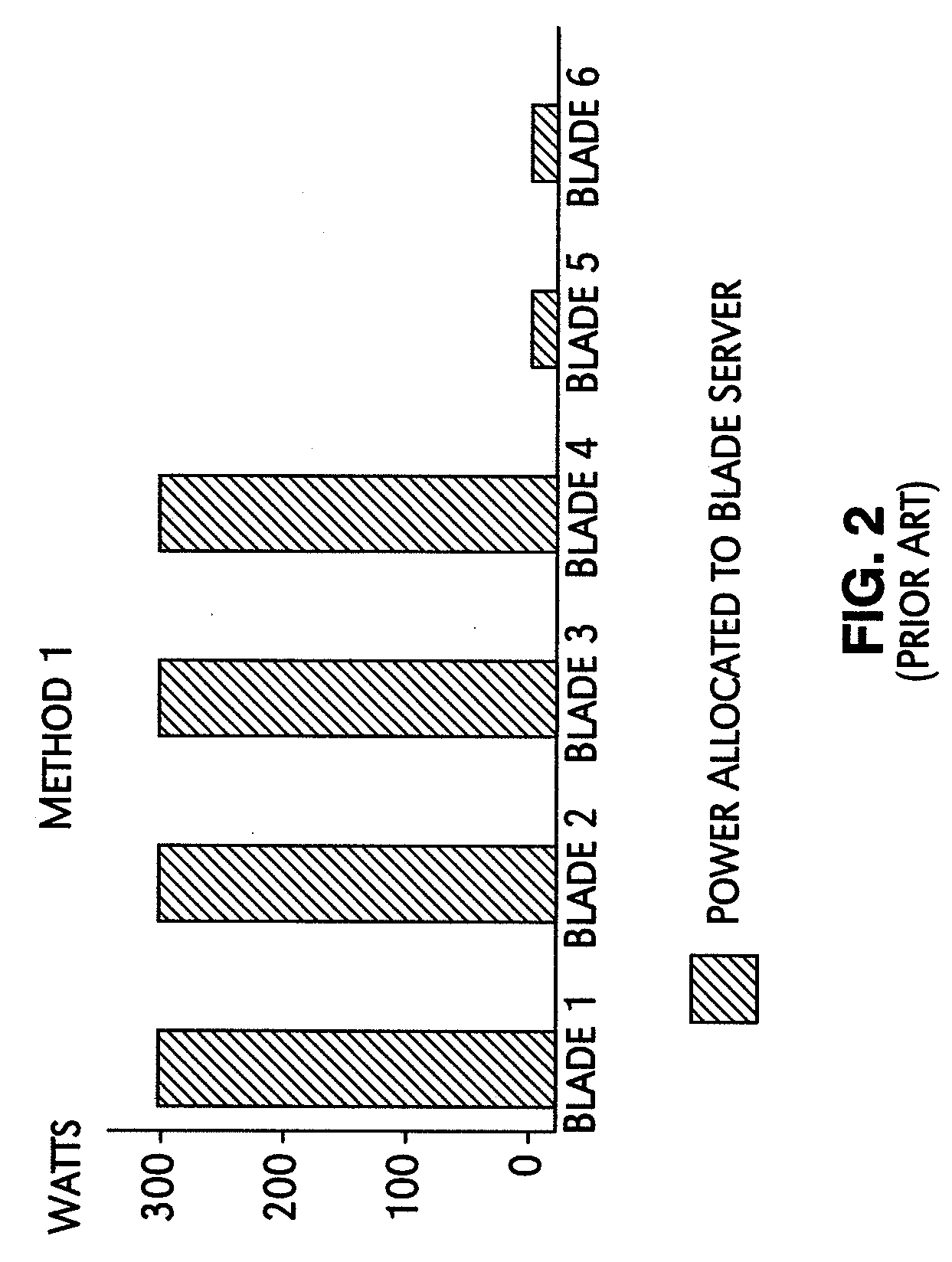
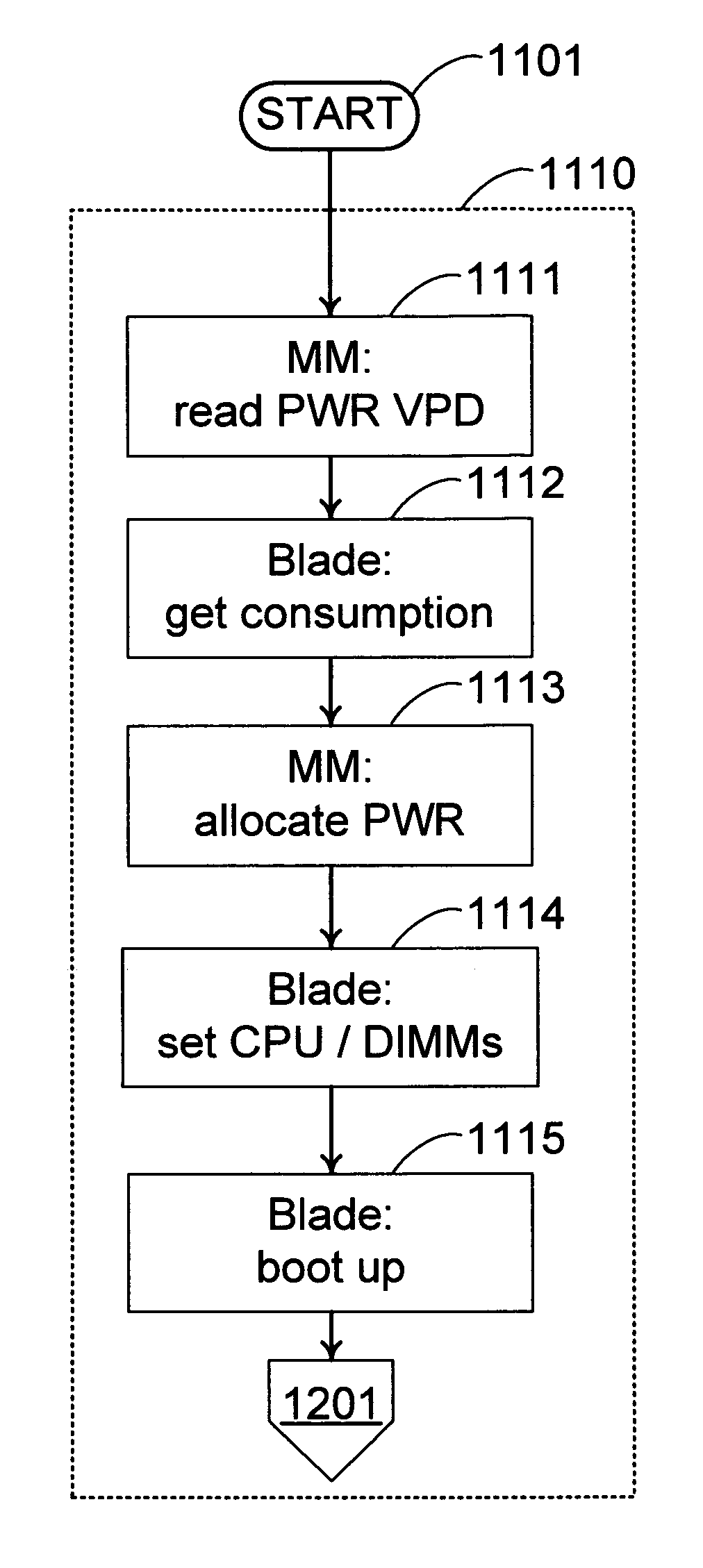
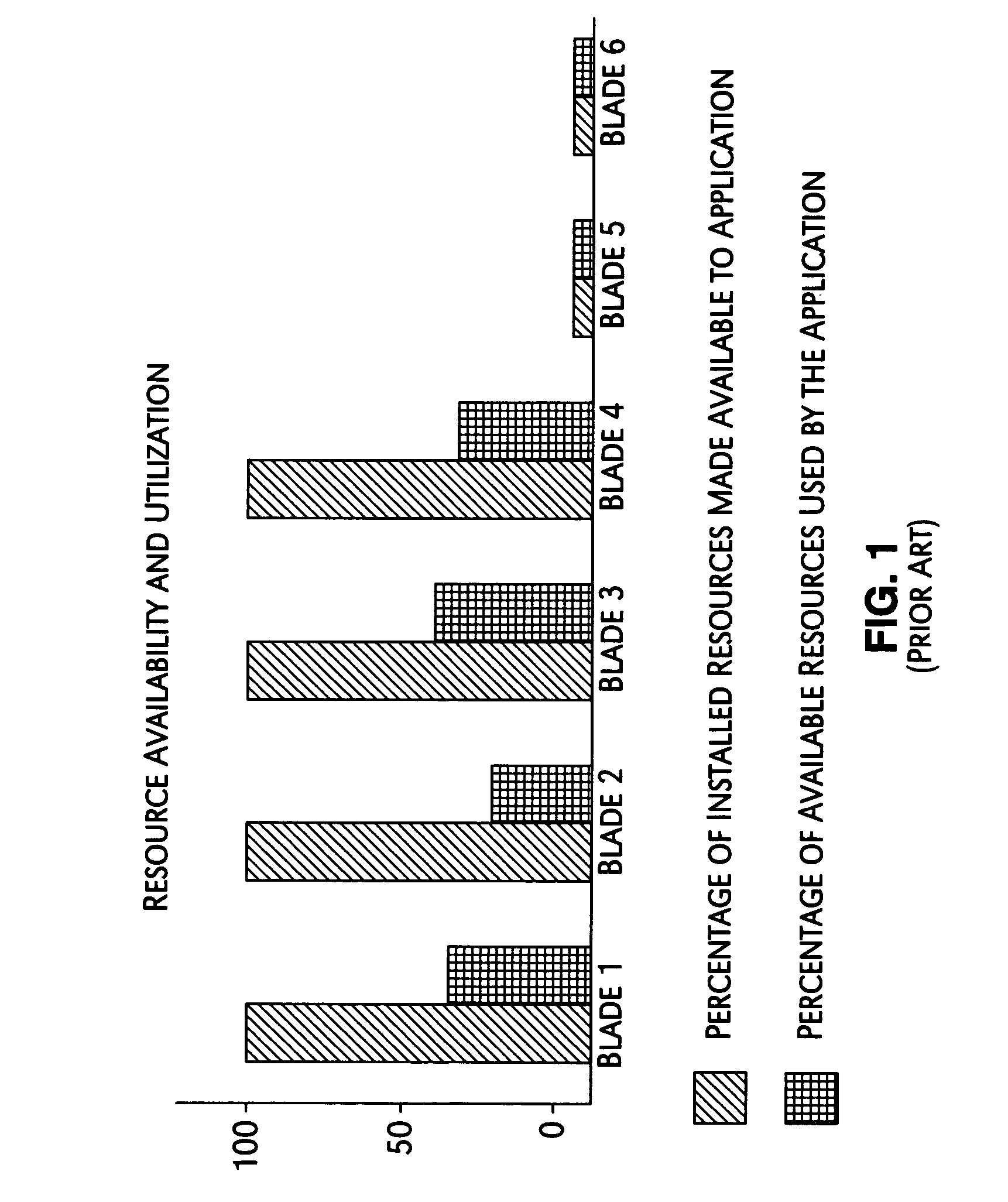
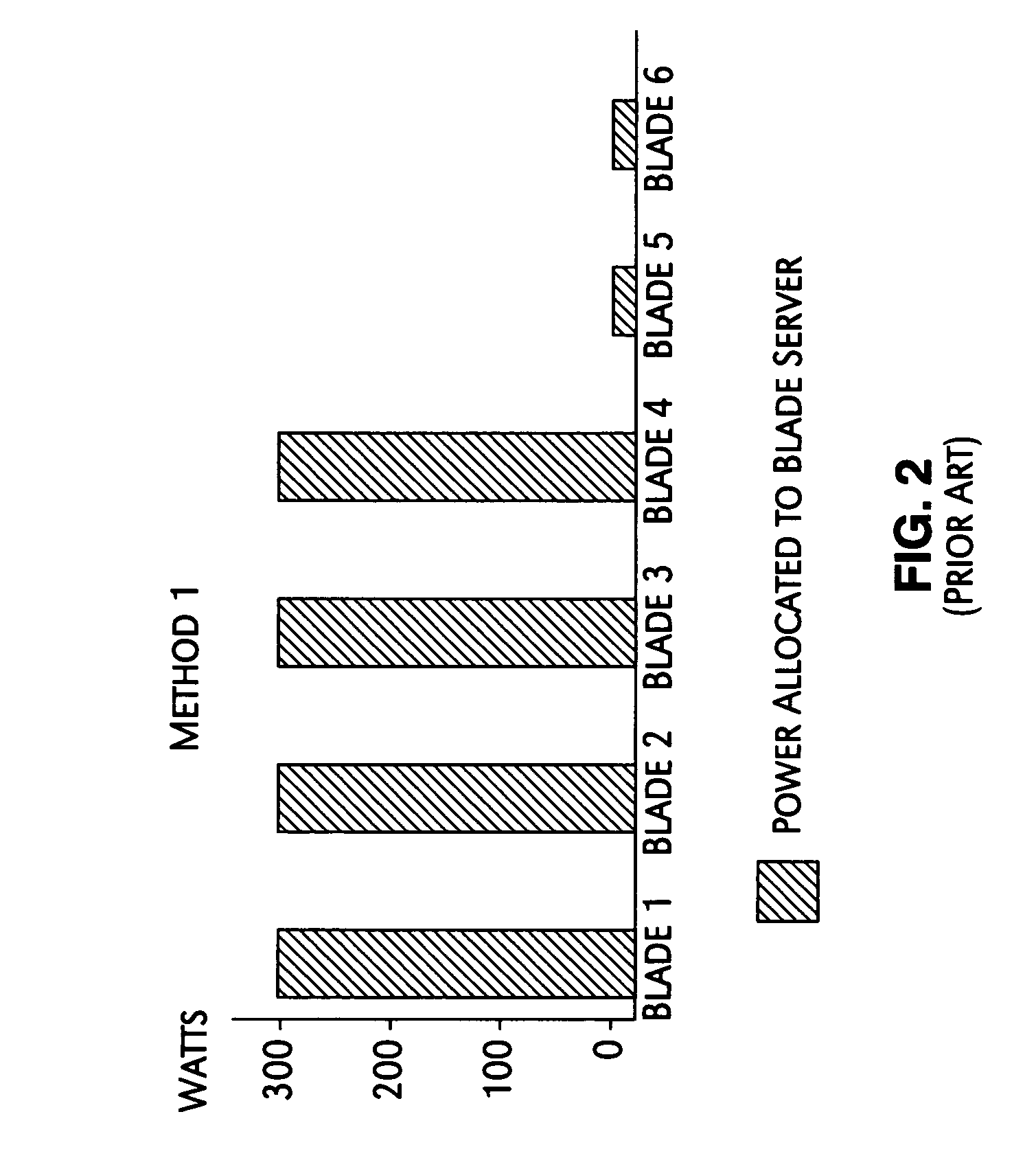
A mechanism for controlling the hardware resources on a blade server, and thereby limiting the power consumption of the blade server is disclosed. The enforceable hardware resources that are controlled include the base frequency of the central processing unit (CPU) as well as power to individual banks of physical memory, for example dual-inline memory modules (DIMMs). The hardware resources are tuned in dependence on actual server utilization such that applications running on the blade only have the allocated hardware resources available to them. Deactivated hardware resources are powered off and are so ‘hidden’ from the operating system when they are not required. In this manner, power consumption in the entire chassis can be managed such that all server blades can be powered on and operate at higher steady-state utilization. The utilization of the powered on resources in a blade center is also improved.
Owner:IBM CORP
Maintenance unit architecture for a scalable internet engine
InactiveUS20050080891A1Error detection/correctionDigital computer detailsManagement unitOperational system
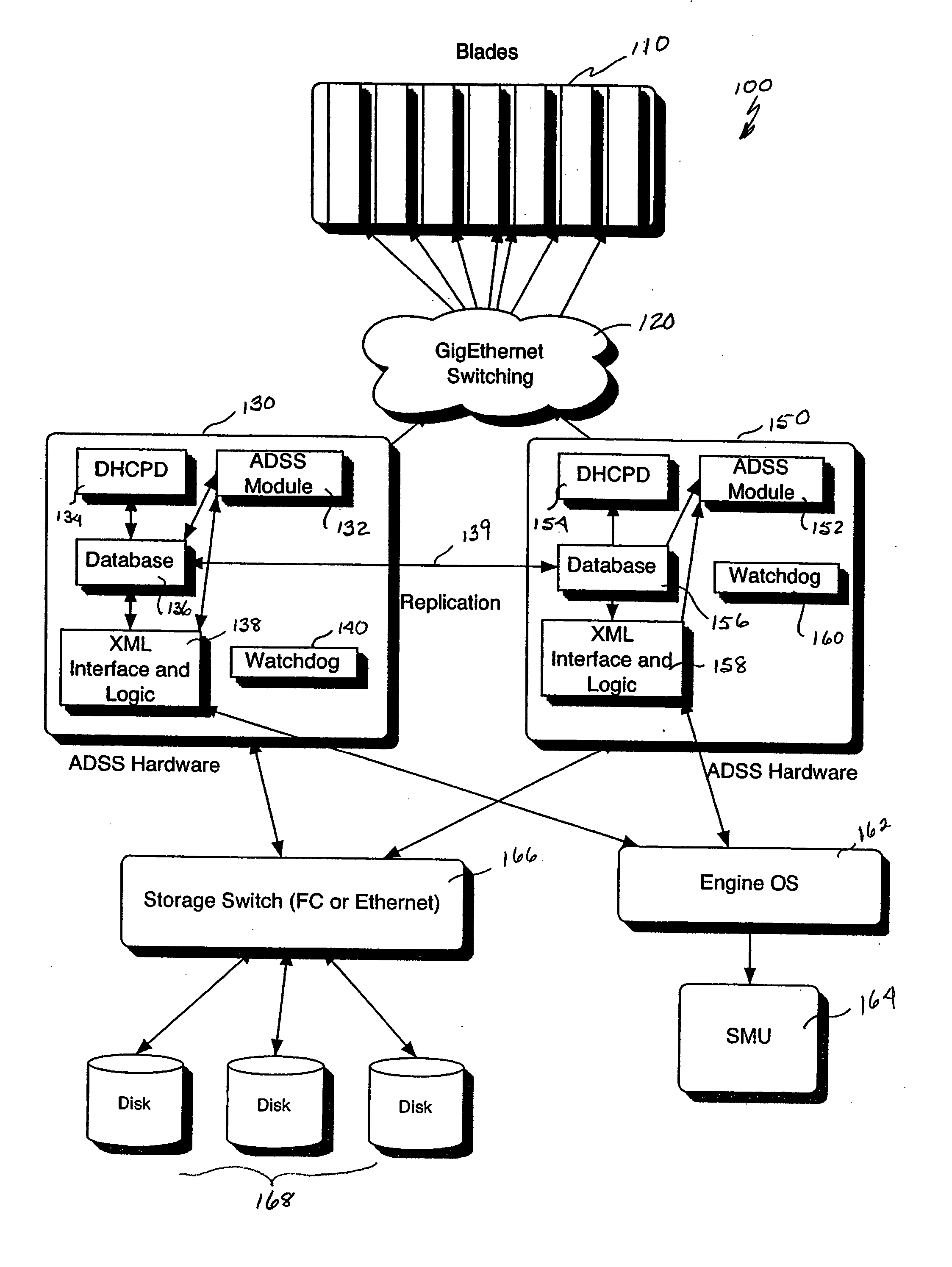
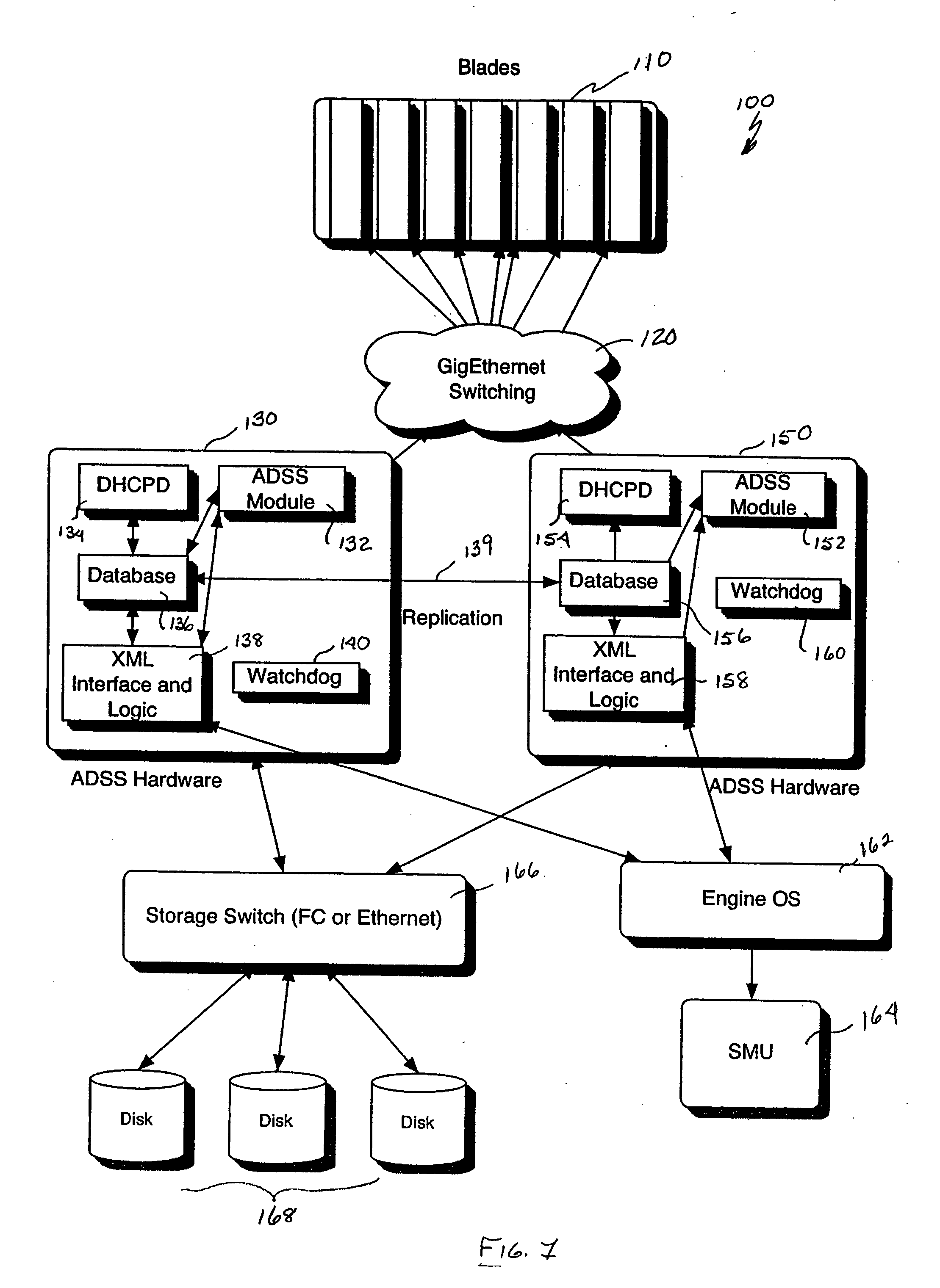
A scalable Internet engine that dynamically reassigns server operations in the event of a failure of an ADSS (Adaptive Data Storage System) server. A first and a second ADSS server mirror each other and include corresponding databases with redundant data, domain host control protocol servers, XML interfaces and watchdog timers. The ADSS servers are communicatively coupled to at least one engine operating system and a storage switch; the storage switch being coupled to at least one storage element. The second ADSS server detects, via a heartbeat monitoring algorithm, the failure of the first ADSS server and automatically initiates a fail over action to switch over functions to the second ADSS server. The architecture also includes a supervisory data management arrangement that includes a plurality of reconfigurable blade servers coupled to a star configured array of data management units.
Owner:RPX CORP
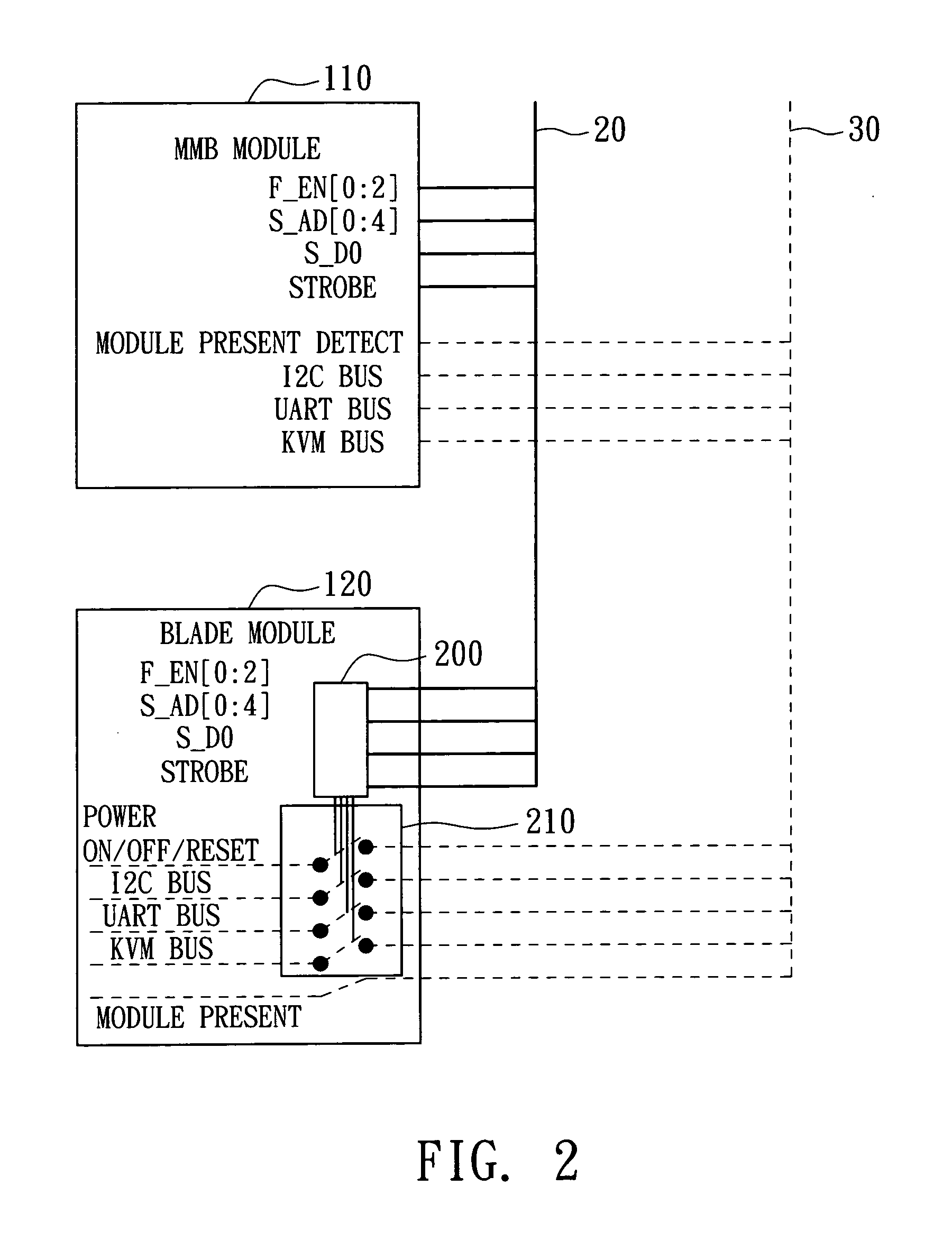
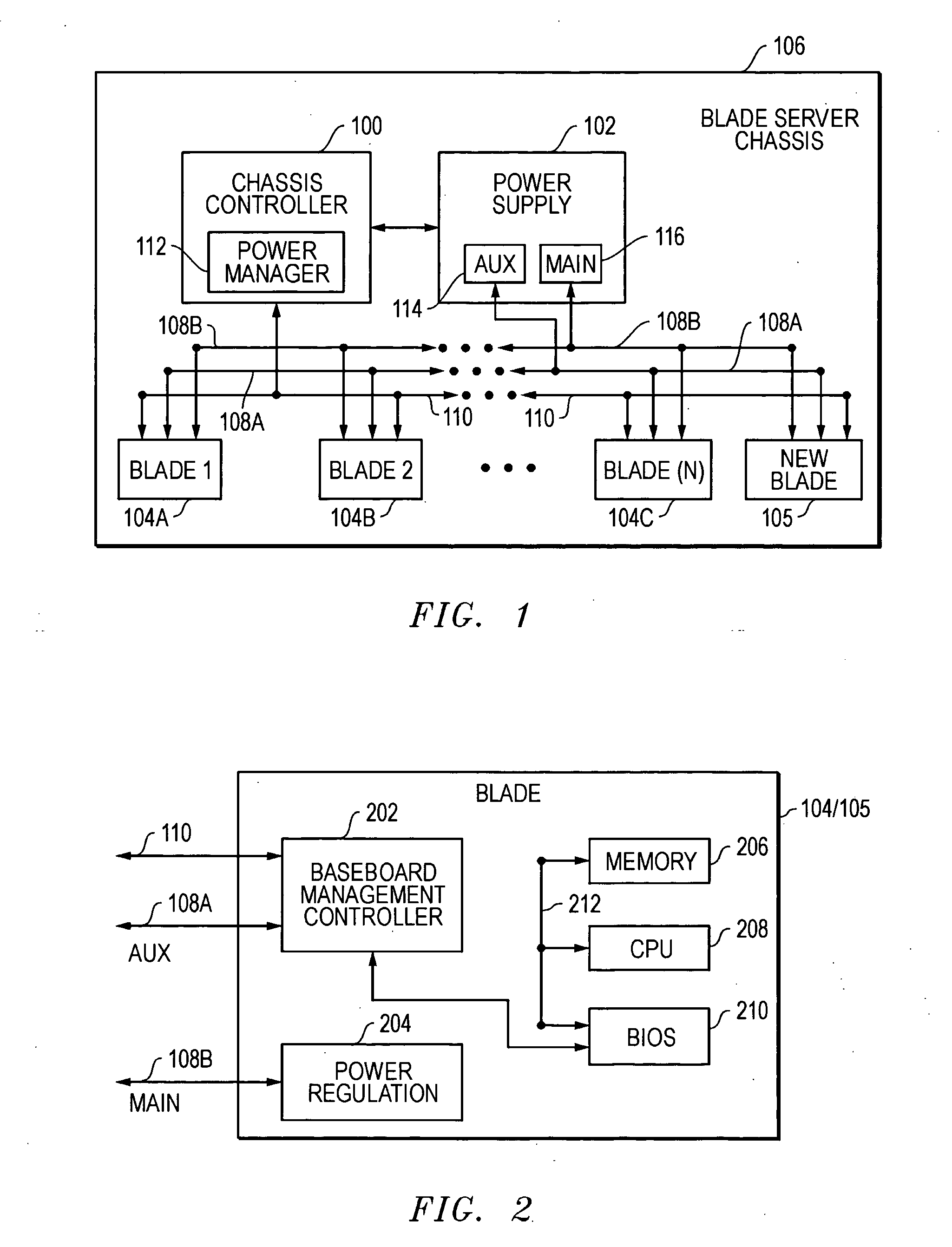
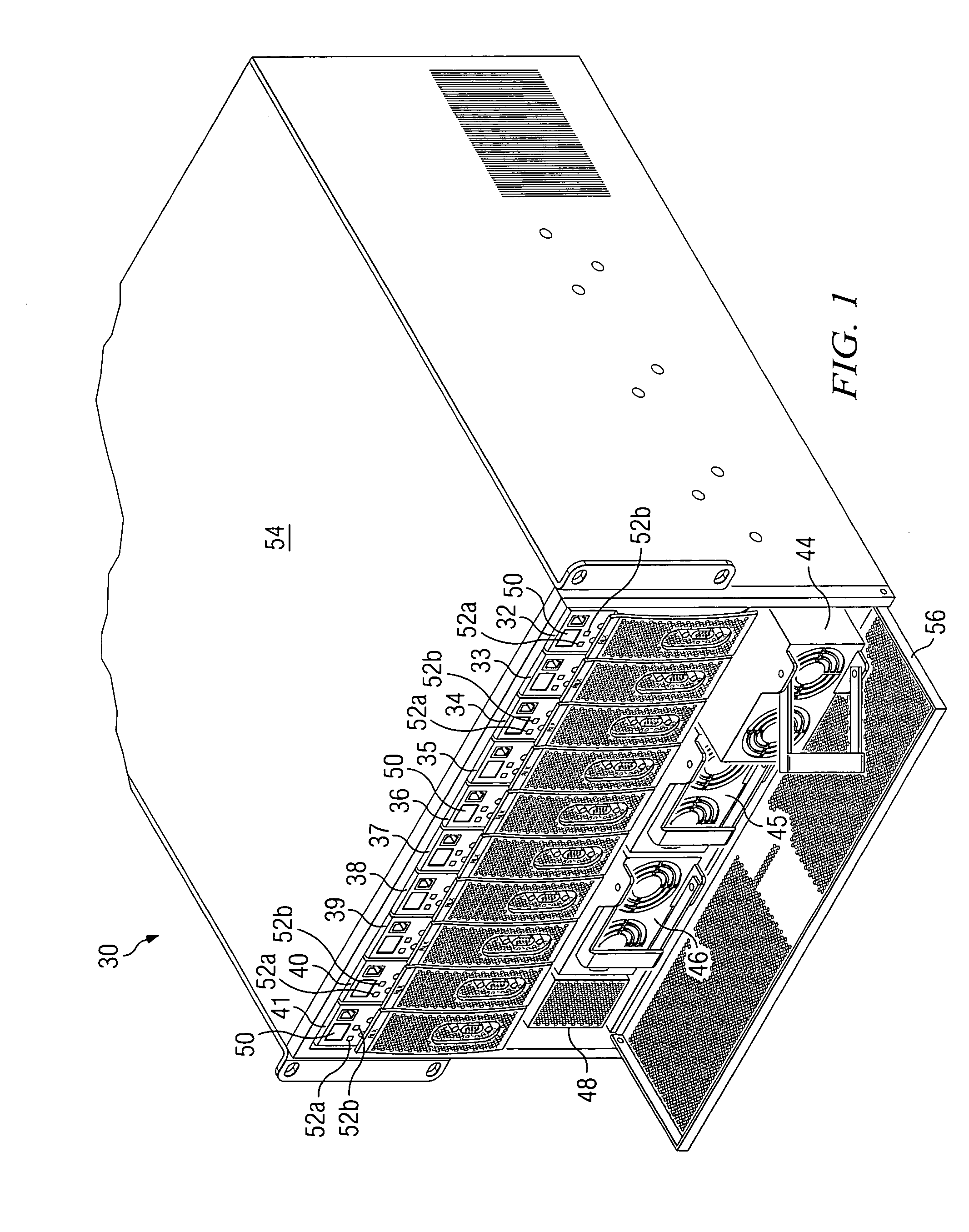
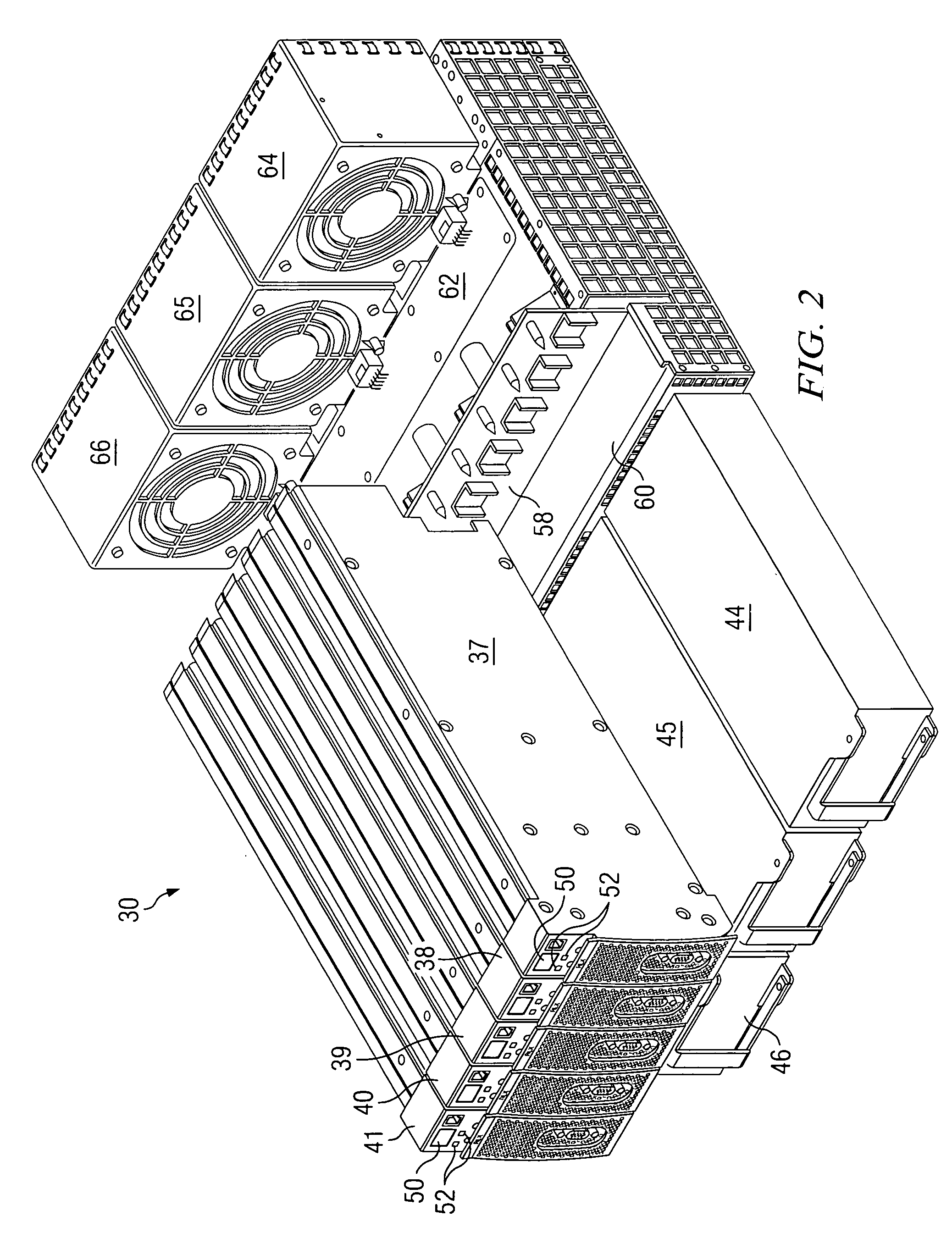
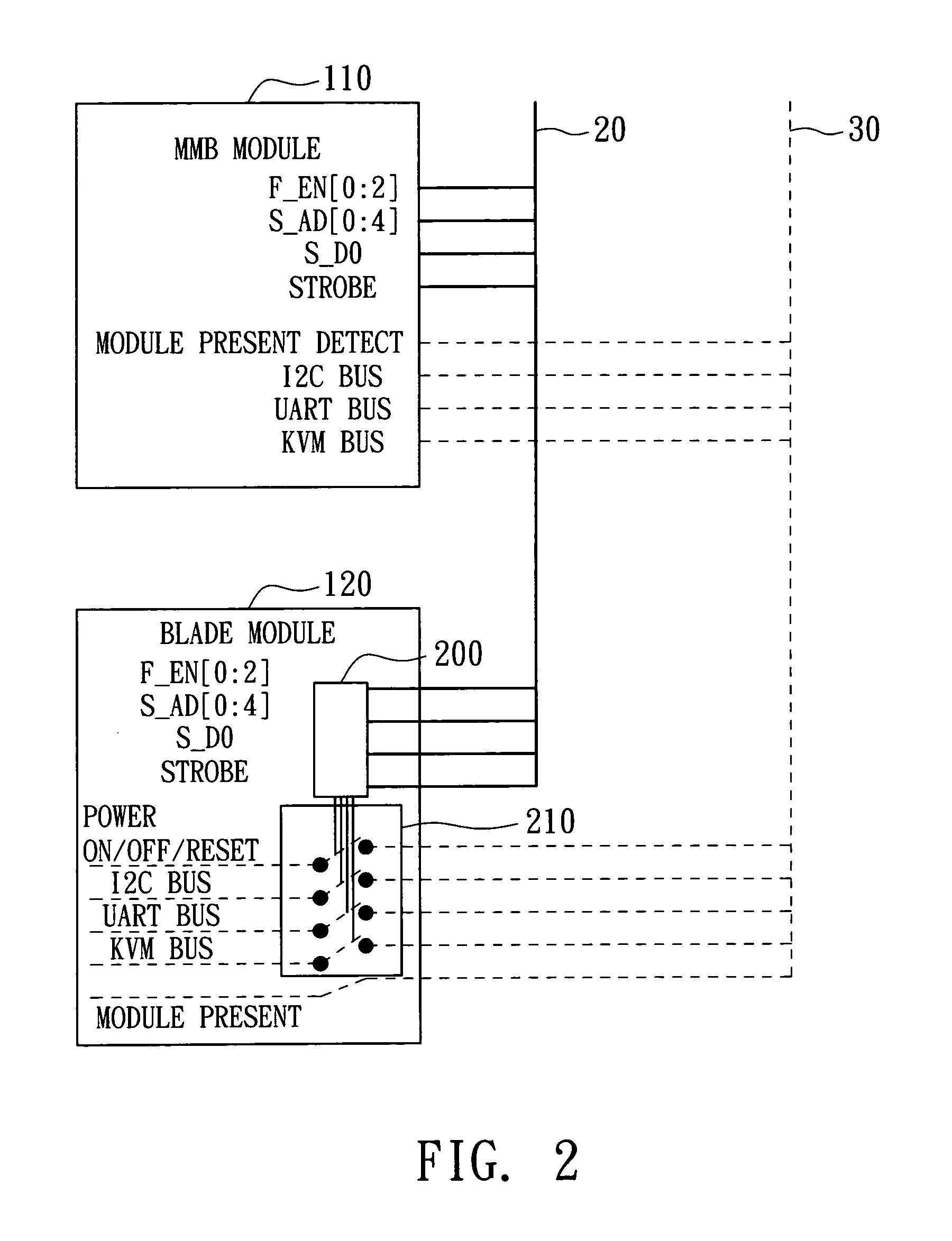
Blade server system with a management bus and method for managing the same
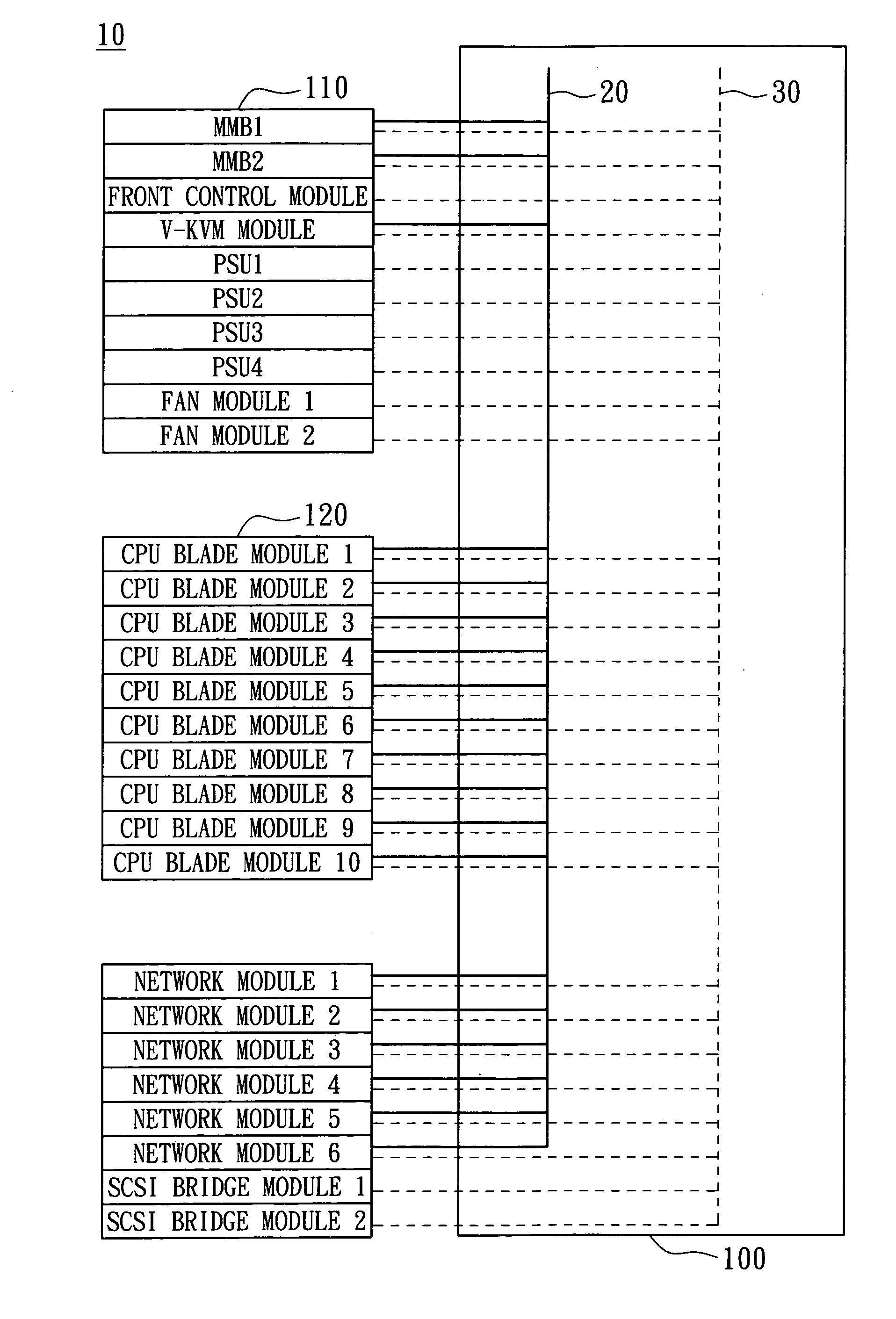
ActiveUS20060140211A1Prevent overloadMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexModularitySystem configuration
A blade server system with a management bus and method for managing the same. The blade server system includes a connection board and a management module. The connection board is used for modular interconnection, including communication paths for conducting signals including a management bus signal group and a first bus signal group. The management module is used for management of the blade server system using signals including the management bus signal group and the first bus signal group. If a module is detected, the management module selects the detected module through the management bus and acquires module configuration information of the detected module through the first bus signal group. Distribution of power from a power source to the blade server system is determined according to system configuration information including the module configuration information of the module so that the power source is prevented from being overloaded.
Owner:QUANTA COMPUTER INC
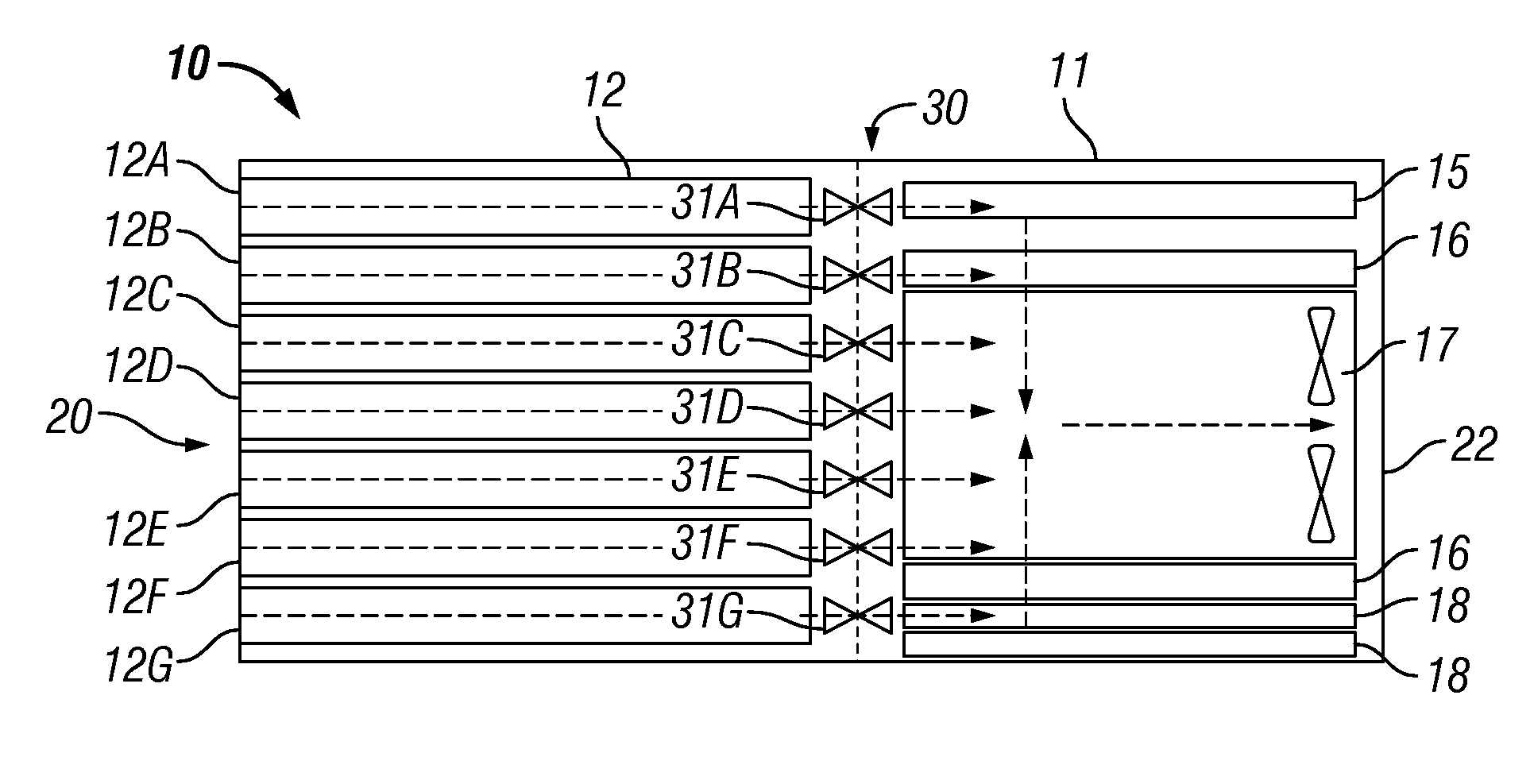
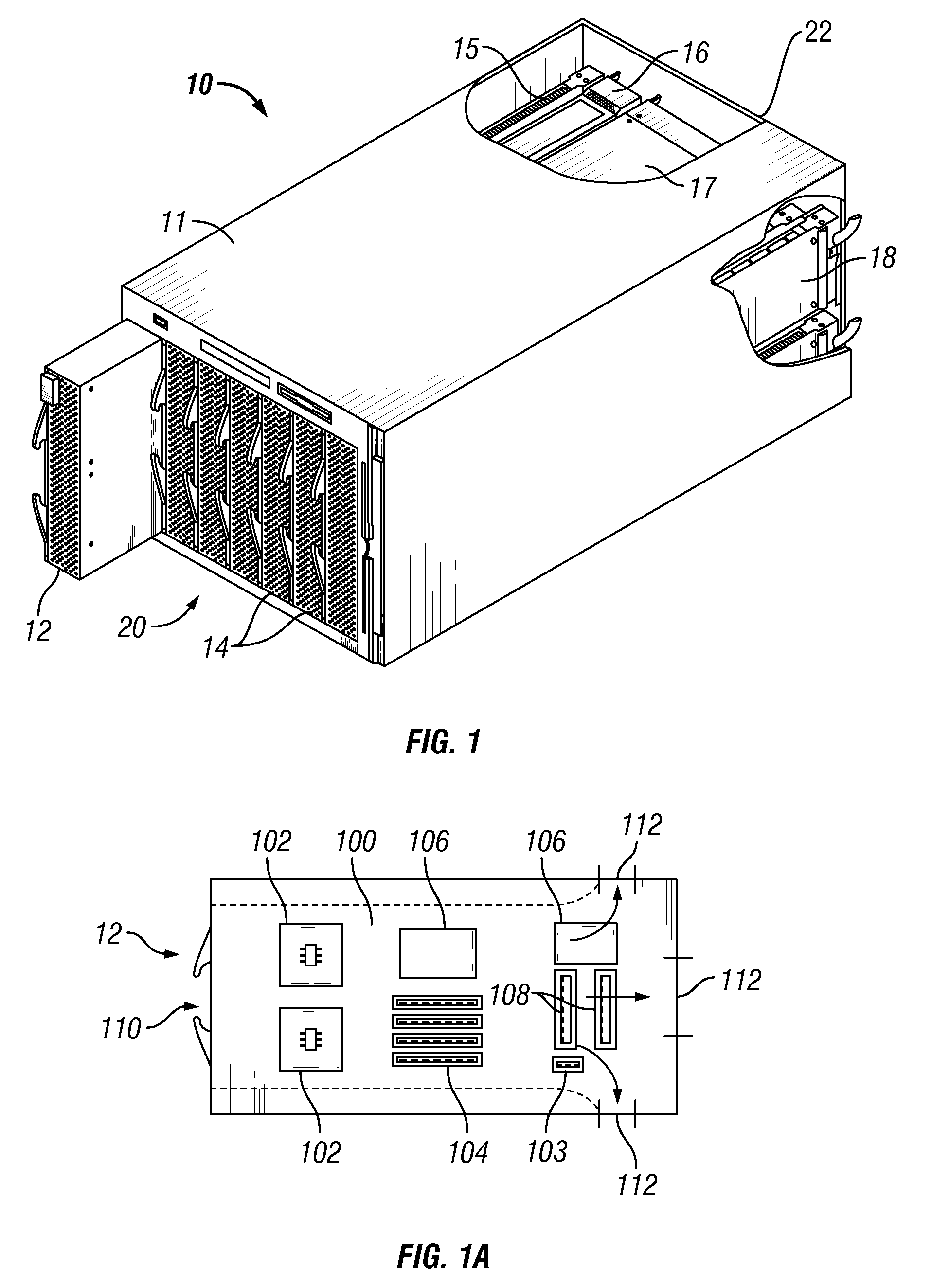
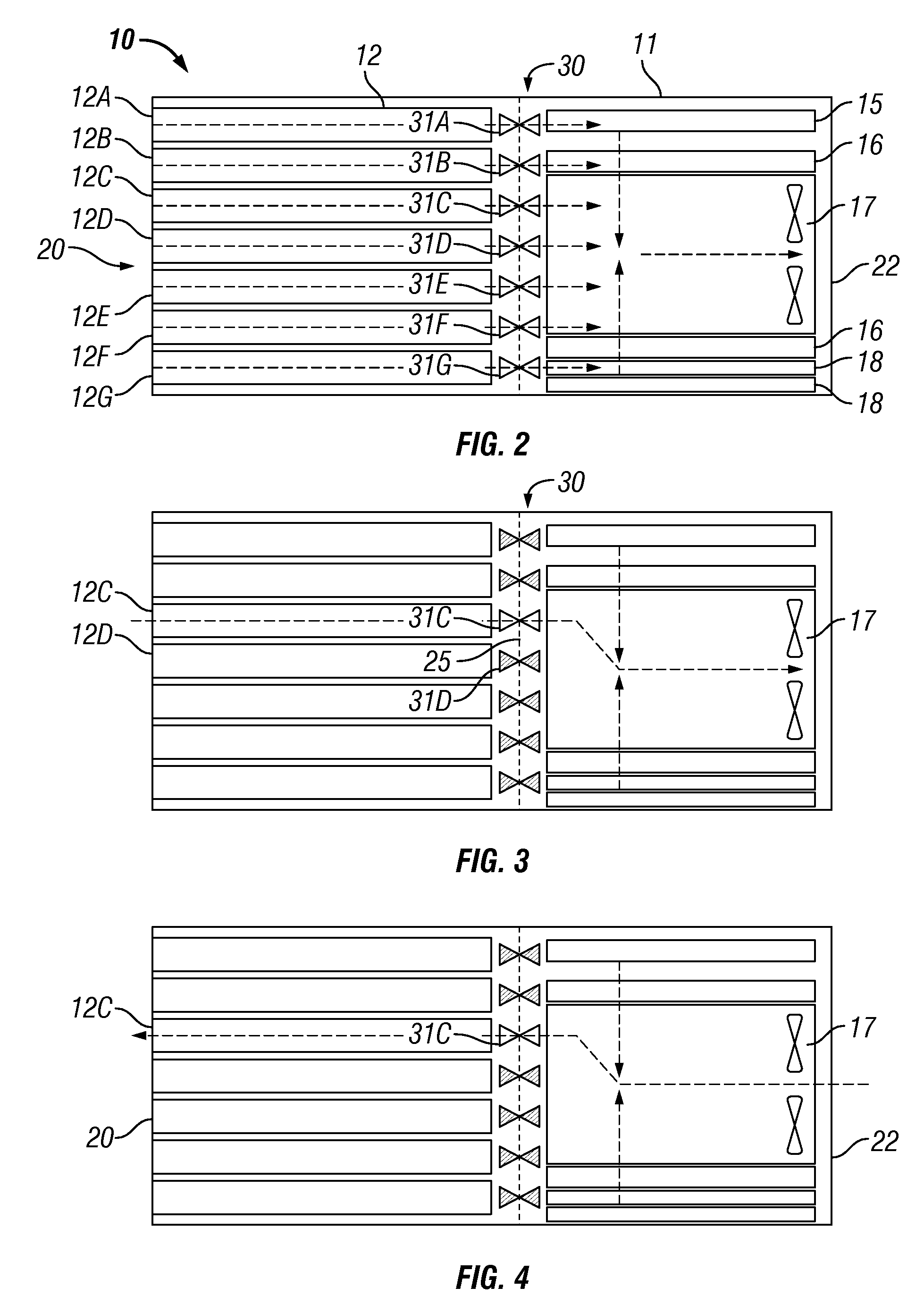
Airflow control and dust removal for electronic systems
InactiveUS20090016019A1Digital data processing detailsHeat exchange apparatusElectronic systemsBlade server
Airflow control and dust removal systems and methods are disclosed. In one embodiment, a plurality of blade servers is mounted in a chassis. A blower generates airflow through the chassis. Air enters the chassis uniformly across the blade servers and flows in parallel through the servers. An airflow directing mechanism is provided for allowing airflow through a selected one of the blade servers while reducing or closing airflow to the other blade servers, to individually clean and remove dust from the selected blade server. The airflow directing mechanism may include a movable vane actuated by a rotary or linear solenoid to selectively block airflow ports of the servers. The vane may be held in a closed position, assisted by an electromagnet. The airflow directing mechanism may alternatively comprise a rolled shade having a pattern of openings. The position of the rolled shade may be controlled to align openings in the shade with airflow ports in the servers, to control which servers airflow may pass through.
Owner:IBM CORP
Fan tray for electronics enclosure
A fan tray for mounting in a housing to move between a retracted position within the housing and an extended position at which the fan tray extends from the front of the housing. The fan tray may comprise a flow passage having fan receptacles adapted to support removable fans such that the fans are operable to provide continuous airflow through the flow passage. In one embodiment, the housing may be provided by a blade server through which the fans direct air for cooling purposes.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Input/output router for storage networks
ActiveUS20070047536A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexVirtualizationComputer compatibility
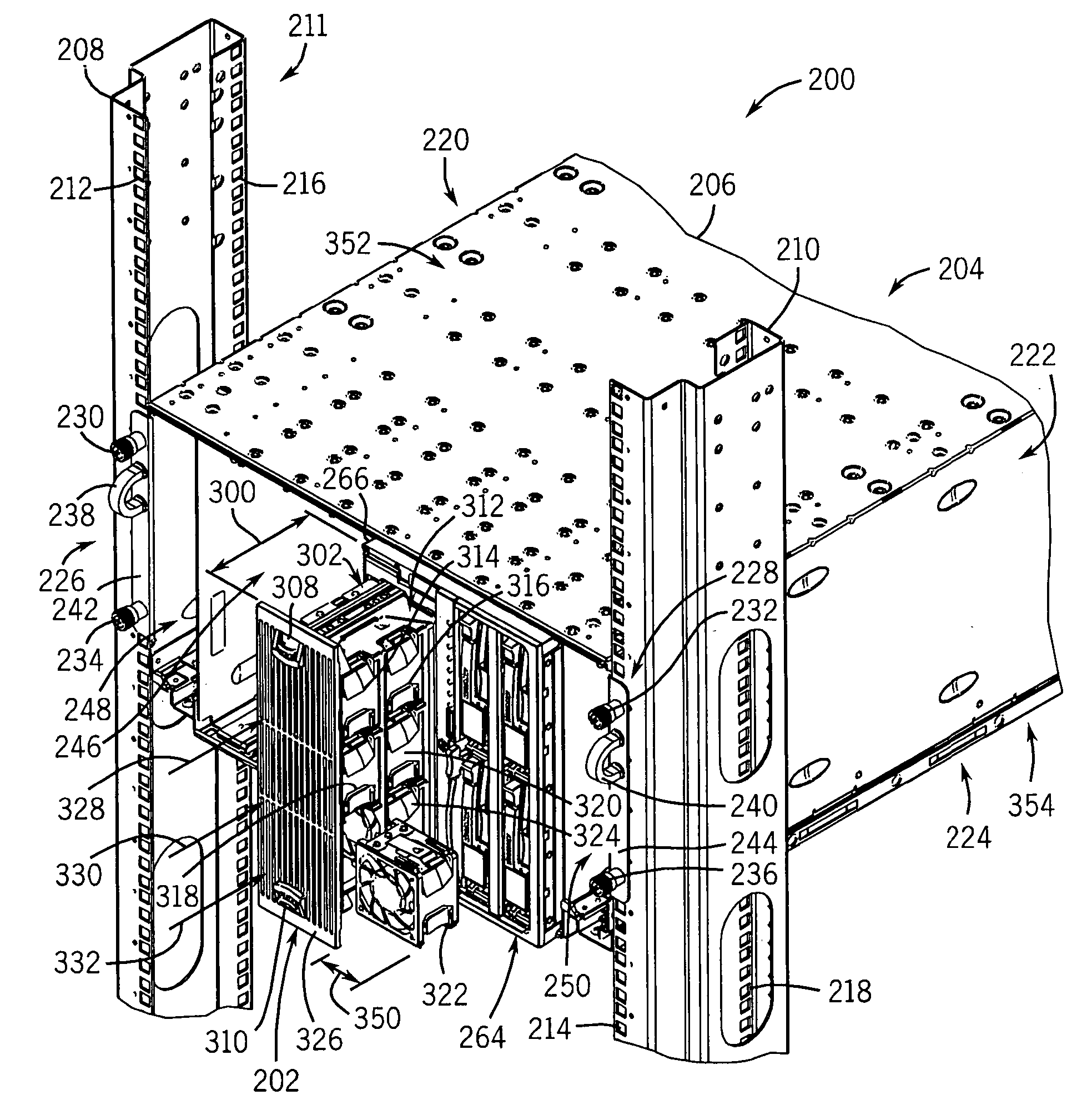
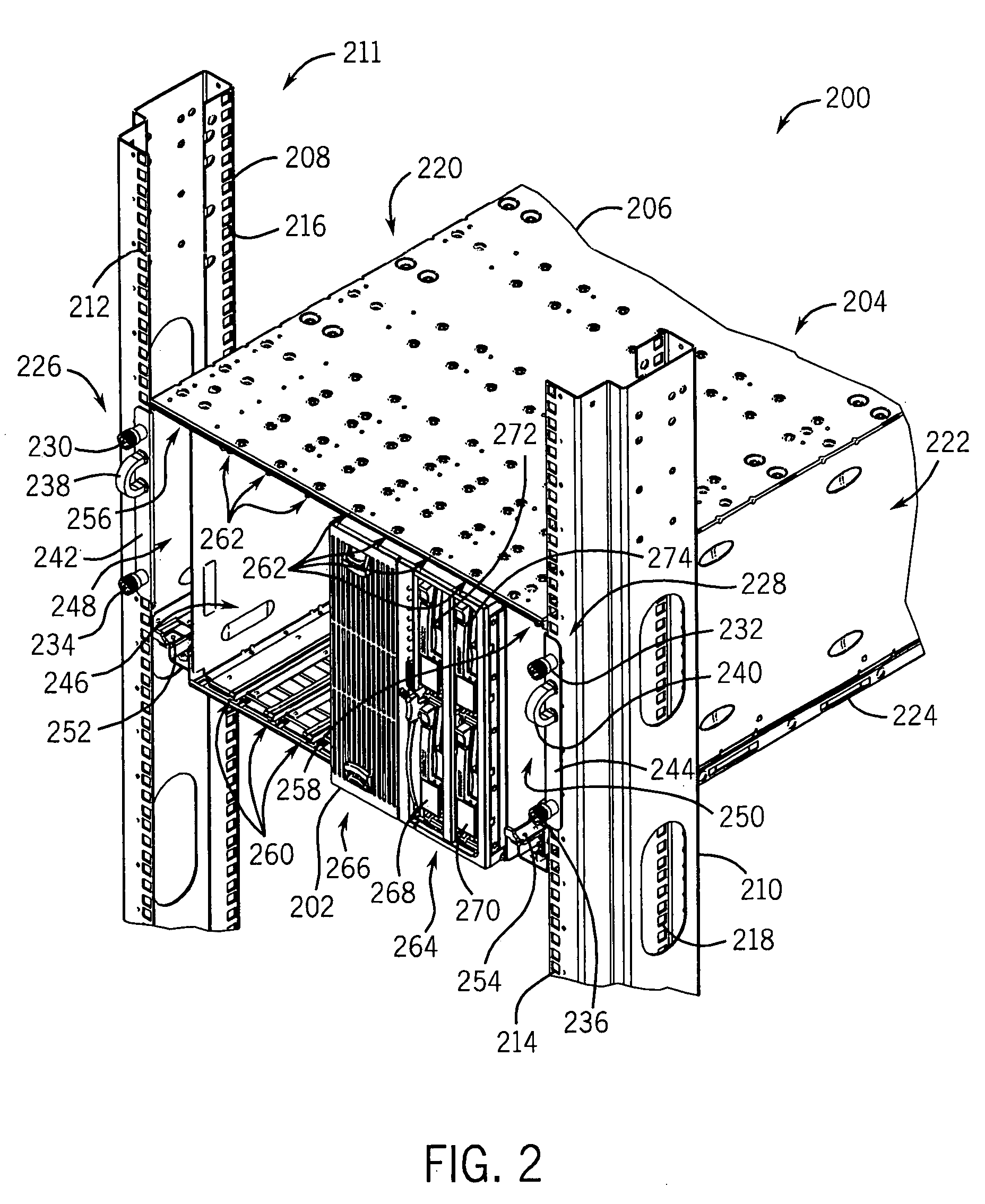
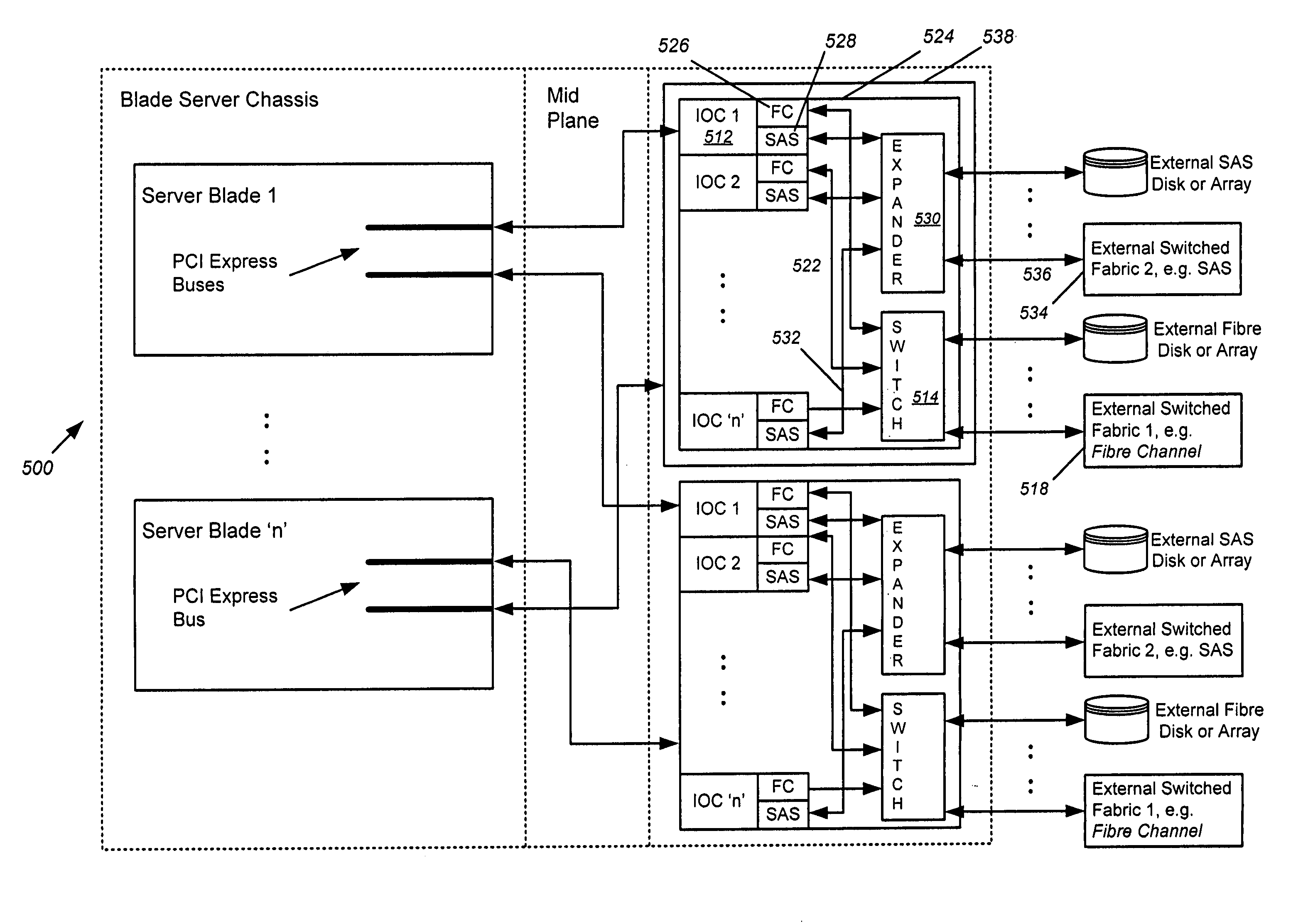
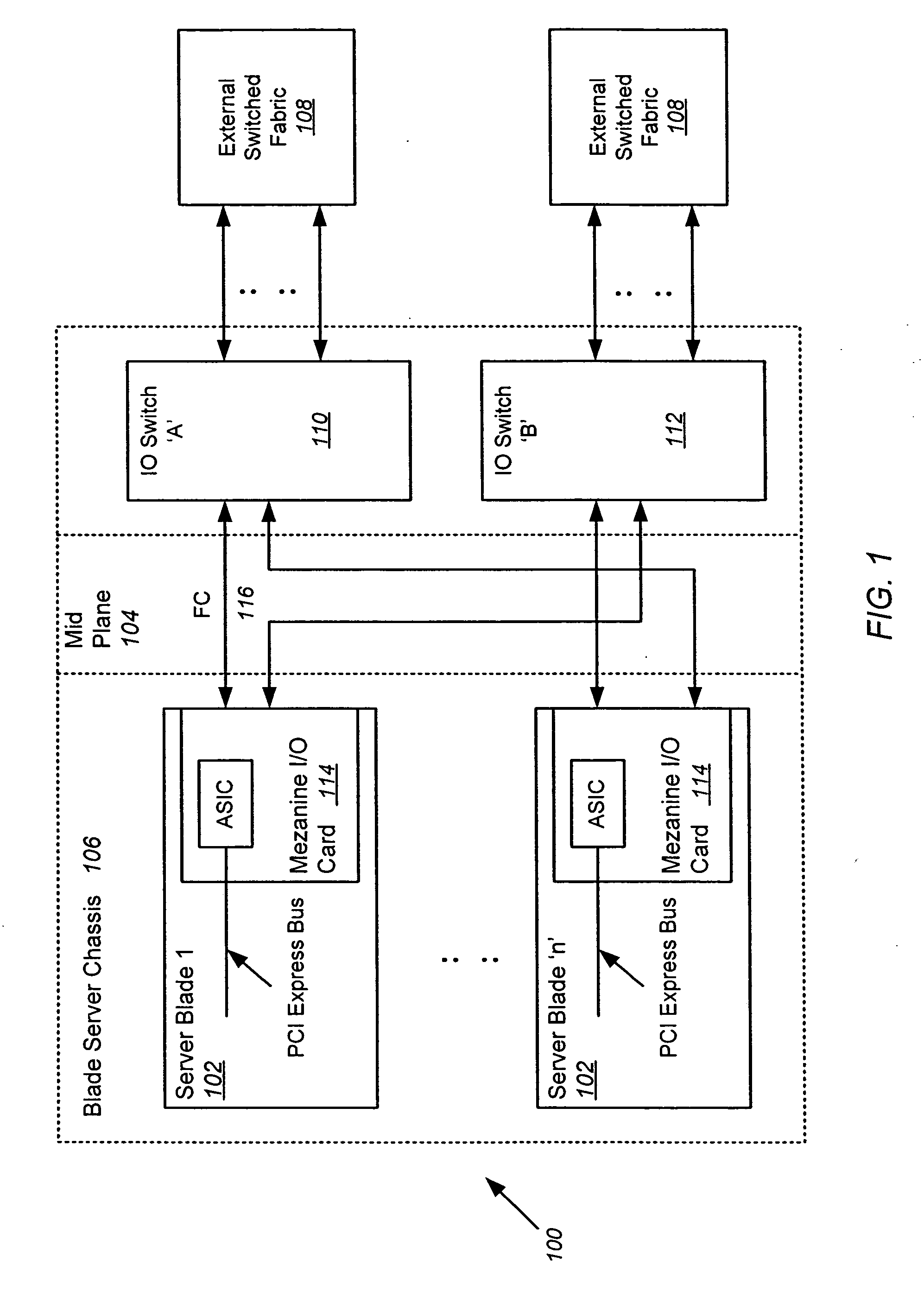
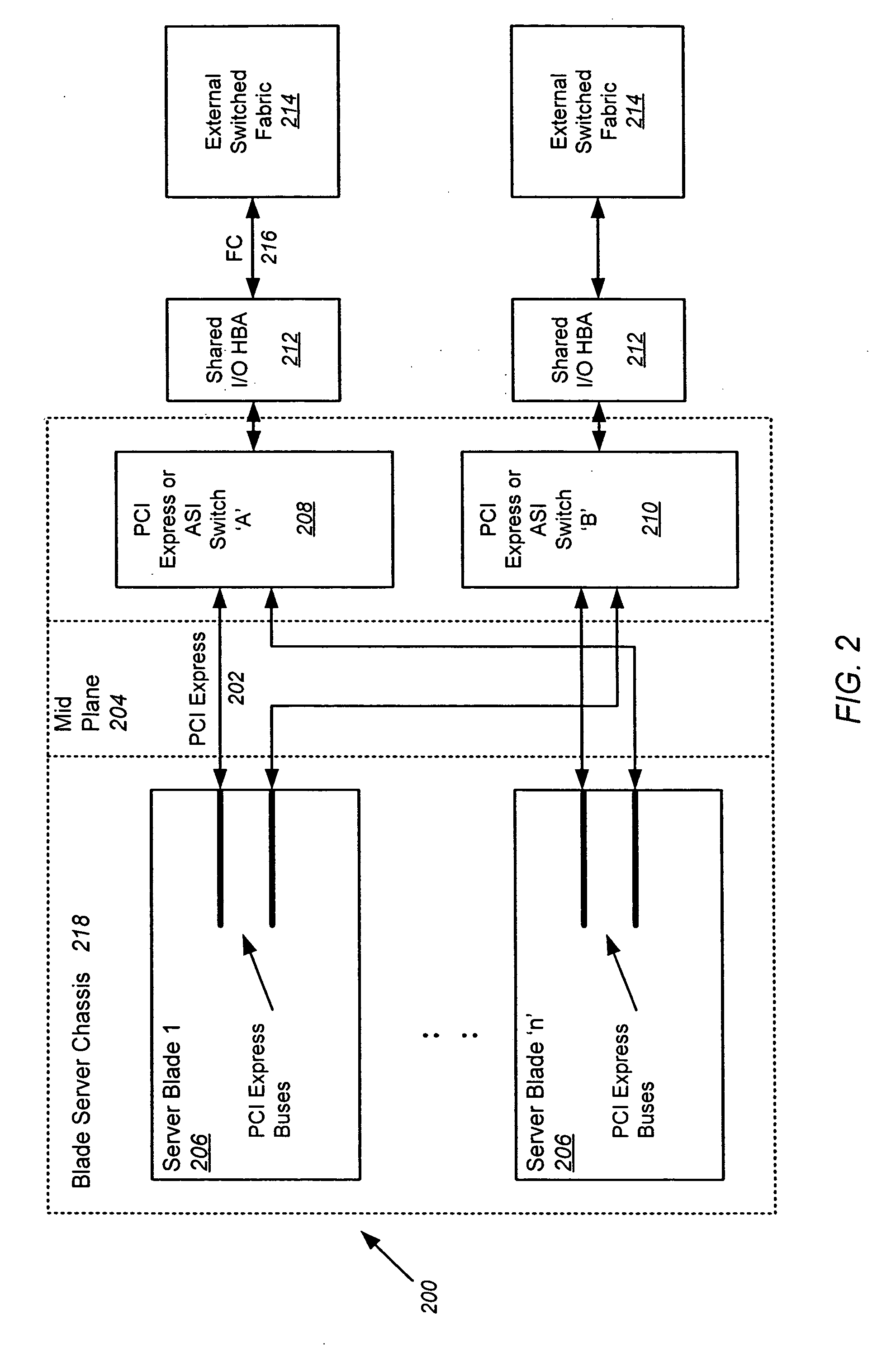
A blade server is disclosed, comprised of multiple server blades that plug into a midplane from the front, and an I / O router including multiple IOCs (one for each server blade) and an embedded switch that plugs into the midplane from the back. The midplane carries PCI Express lanes for connecting the server blades to the I / O router. Each of the IOCs is physically couplable to a server blade over a separate PCI Express connection in the midplane, preserving existing driver compatibility, and is coupled to the embedded switch via an internal FC link within the I / O router. Each embedded switch may contain full fabric services ports. Alternatively, the full fabric services may be left out, and N_PORT virtualization or FC_AL stealth mode may be employed to allow the embedded switch to interoperate transparently with the external fabric switch and eliminate the third hop in the blade server chassis.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System and method for information handling system PCI express advanced switching
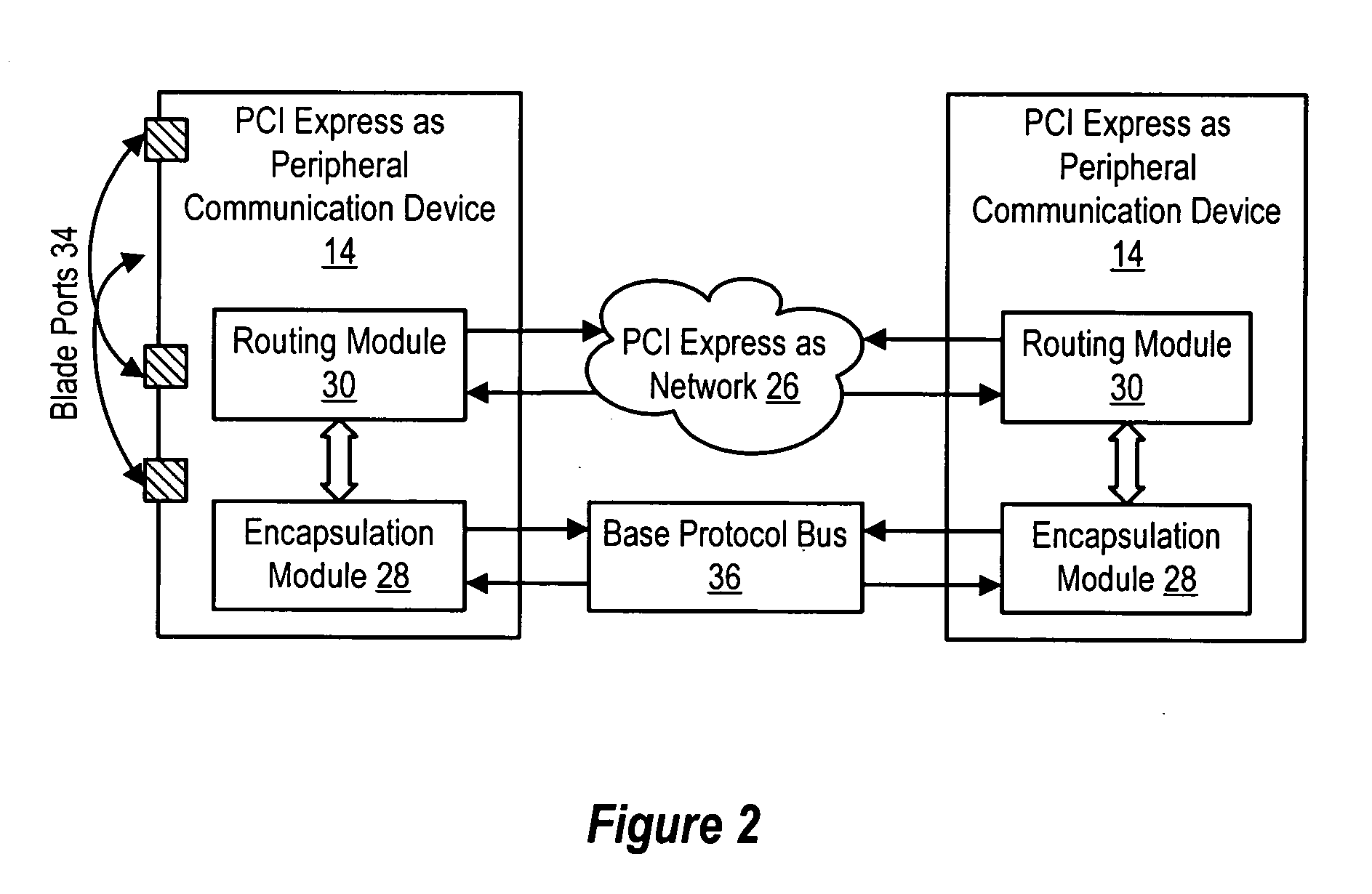
InactiveUS20050262269A1Simple processReduce disadvantagesConcurrent instruction executionMultiple digital computer combinationsInformation processingData pack
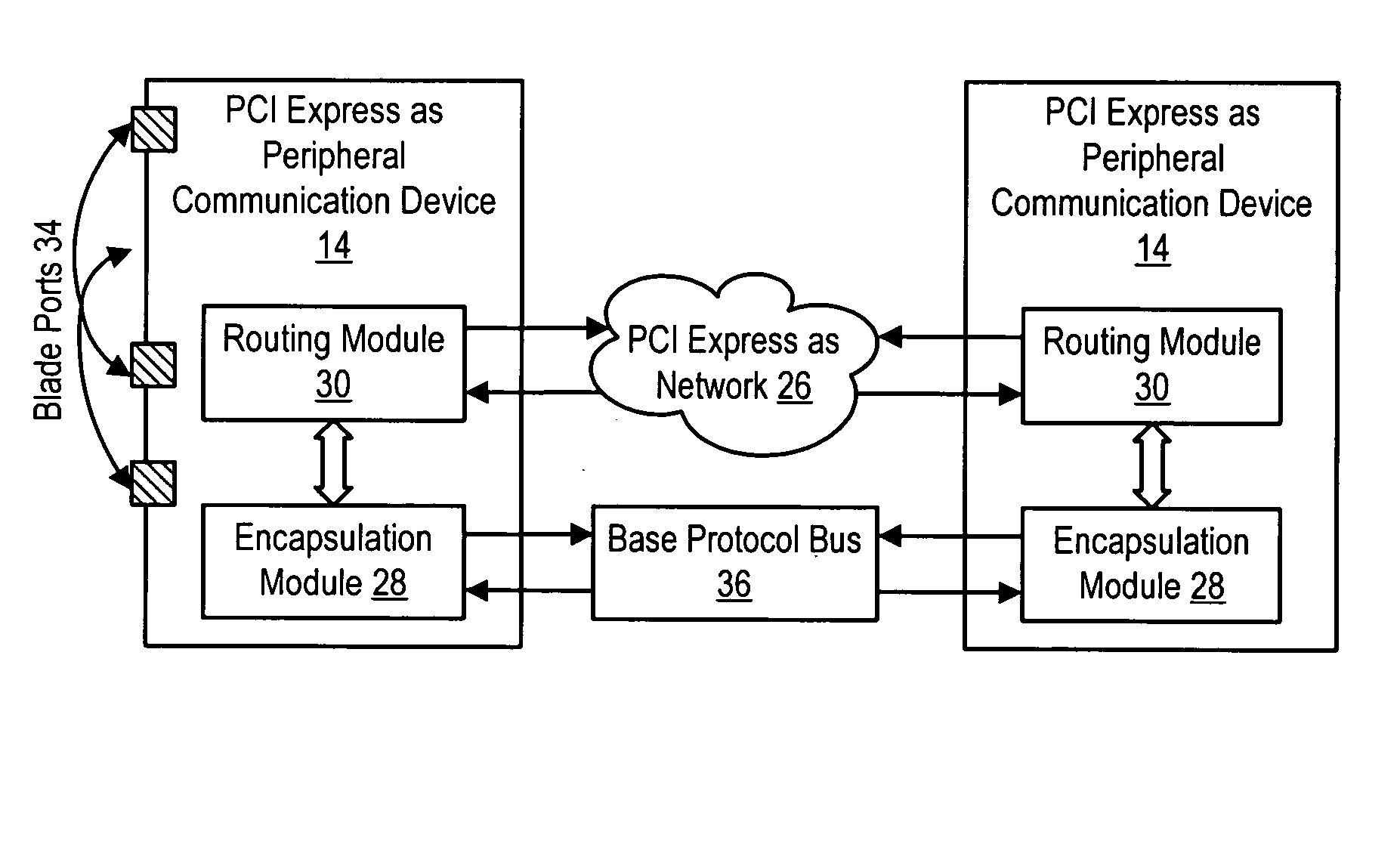
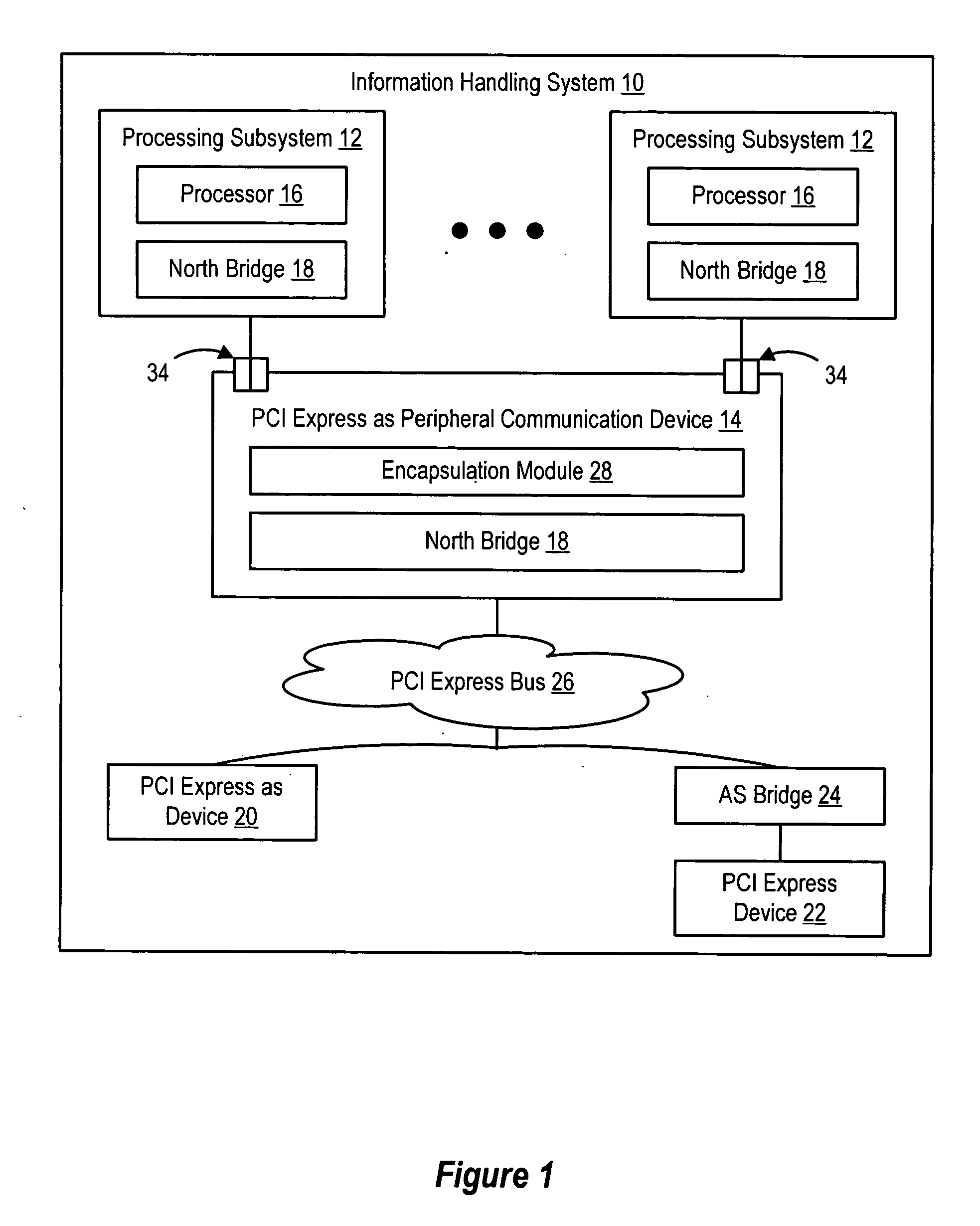
Plural processing subsystems of an information handling system, such as plural blades of a blade server, communicate through a base protocol, such as PCI Express, to a peripheral communication device with each processing subsystem interfaced through a port of the peripheral communication device. An encapsulation module of the peripheral communication device encapsulates the base protocol in an advanced switching packet, such as a packet formed with the PCI Express Advanced Switching protocol. A routing module of the peripheral communication device routes the packets through a bus, such as a blade server backplane bus, for use of the information by a selected peripheral. Peripherals communicate with selected processing subsystems by sending advanced switching packets to the routing module for the encapsulation module to extract the peripheral information from the packets and send the peripheral information to the port associated with the selected processing subsystem.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
System for maximizing server utilization in a resource constrained environment
InactiveUS20090044036A1Control power consumptionReduce computing power requirementsEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementOperational systemBase frequency
A mechanism for controlling the hardware resources on a blade server, and thereby limiting the power consumption of the blade server is disclosed. The enforceable hardware resources that are controlled include the base frequency of the central processing unit (CPU) as well as power to individual banks of physical memory, for example dual-inline memory modules (DIMMs). The hardware resources are tuned in dependence on actual server utilization such that applications running on the blade only have the allocated hardware resources available to them. Deactivated hardware resources are powered off and are so ‘hidden’ from the operating system when they are not required. In this manner, power consumption in the entire chassis can be managed such that all server blades can be powered on and operate at higher steady-state utilization. The utilization of the powered on resources in a blade center is also improved.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method for maximizing server utilization in a resource constrained environment
InactiveUS7461274B2Control power consumptionReduce computing power requirementsEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementOperational systemService utilization
A mechanism for controlling the hardware resources on a blade server, and thereby limiting the power consumption of the blade server is disclosed. The enforceable hardware resources that are controlled include the base frequency of the central processing unit (CPU) as well as power to individual banks of physical memory, for example dual-inline memory modules (DIMMs). The hardware resources are tuned in dependence on actual server utilization such that applications running on the blade only have the allocated hardware resources available to them. Deactivated hardware resources are powered off and are so ‘hidden’ from the operating system when they are not required. In this manner, power consumption in the entire chassis can be managed such that all server blades can be powered on and operate at higher steady-state utilization. The utilization of the powered on resources in a blade center is also improved.
Owner:IBM CORP
Electronic system modules and method of fabrication
InactiveUS6927471B2Good dimensional stabilityLow costPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureDielectricEngineering
This specification describes techniques for manufacturing an electronic system module. The module includes flexible multi-layer interconnection circuits with trace widths of 5 microns or less. A glass panel manufacturing facility, similar to those employed for making liquid crystal display, LCD, panels is used to fabricate the interconnection circuits. A polymer base layer is formed on a glass carrier with an intermediate release layer. Alternate layers of metal and dielectric are formed on the base layer, and patterned to create an array of multi-layer interconnection circuits on the glass panel. A thick layer of polymer is deposited on the interconnection circuit, and openings formed at input / output (I / O) pad locations. Solder paste is deposited in the openings to form wells filled with solder. After dicing the glass carrier to form separated interconnection circuits, IC chips are stud bumped and assembled using flip chip bonding, wherein the stud bumps on the components are inserted into corresponding wells on the interconnection circuits. The IC chips are tested and reworked to form tested circuit assemblies. Methods for connecting to testers and to other modules and electronic systems are described. Module packaging layers are provided for hermetic sealing and for electromagnetic shielding. A blade server embodiment is also described.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
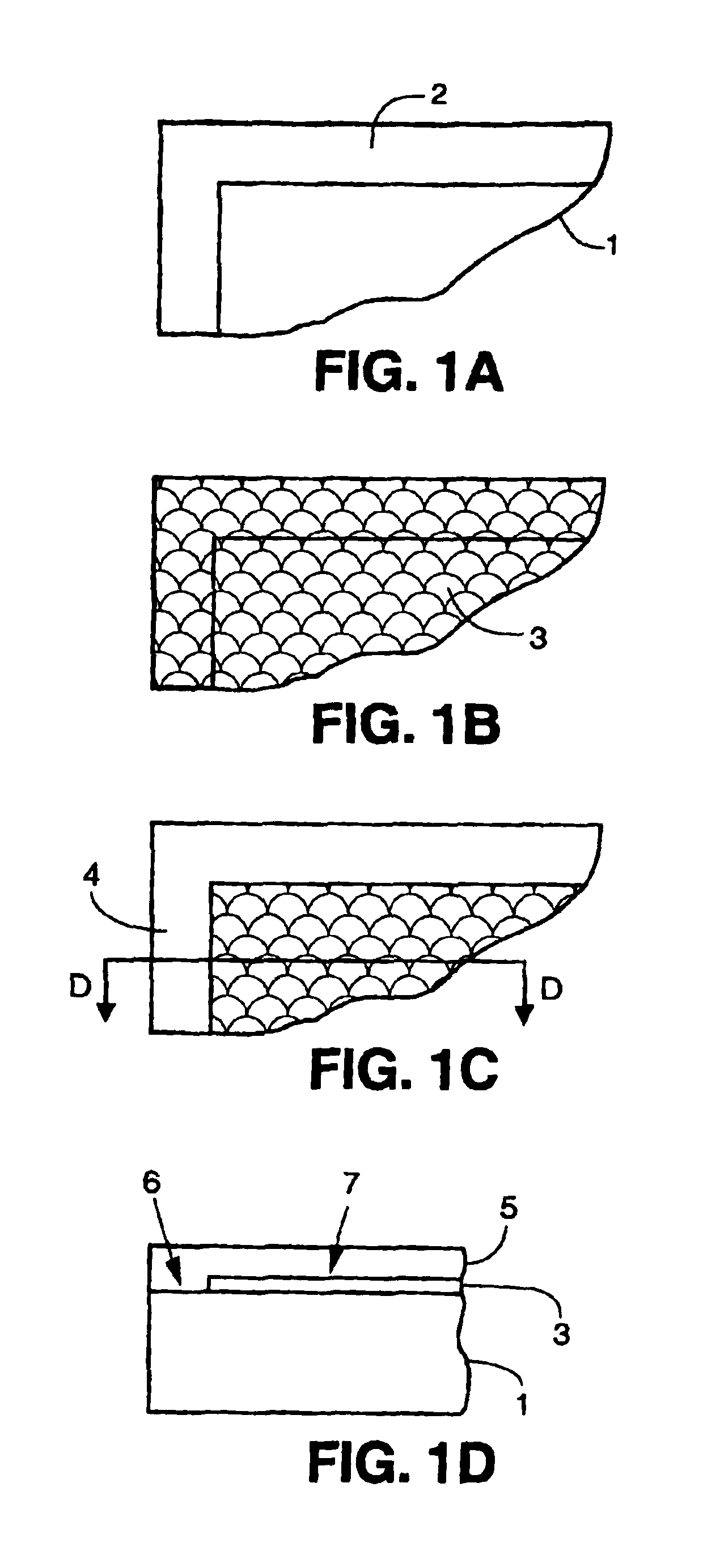
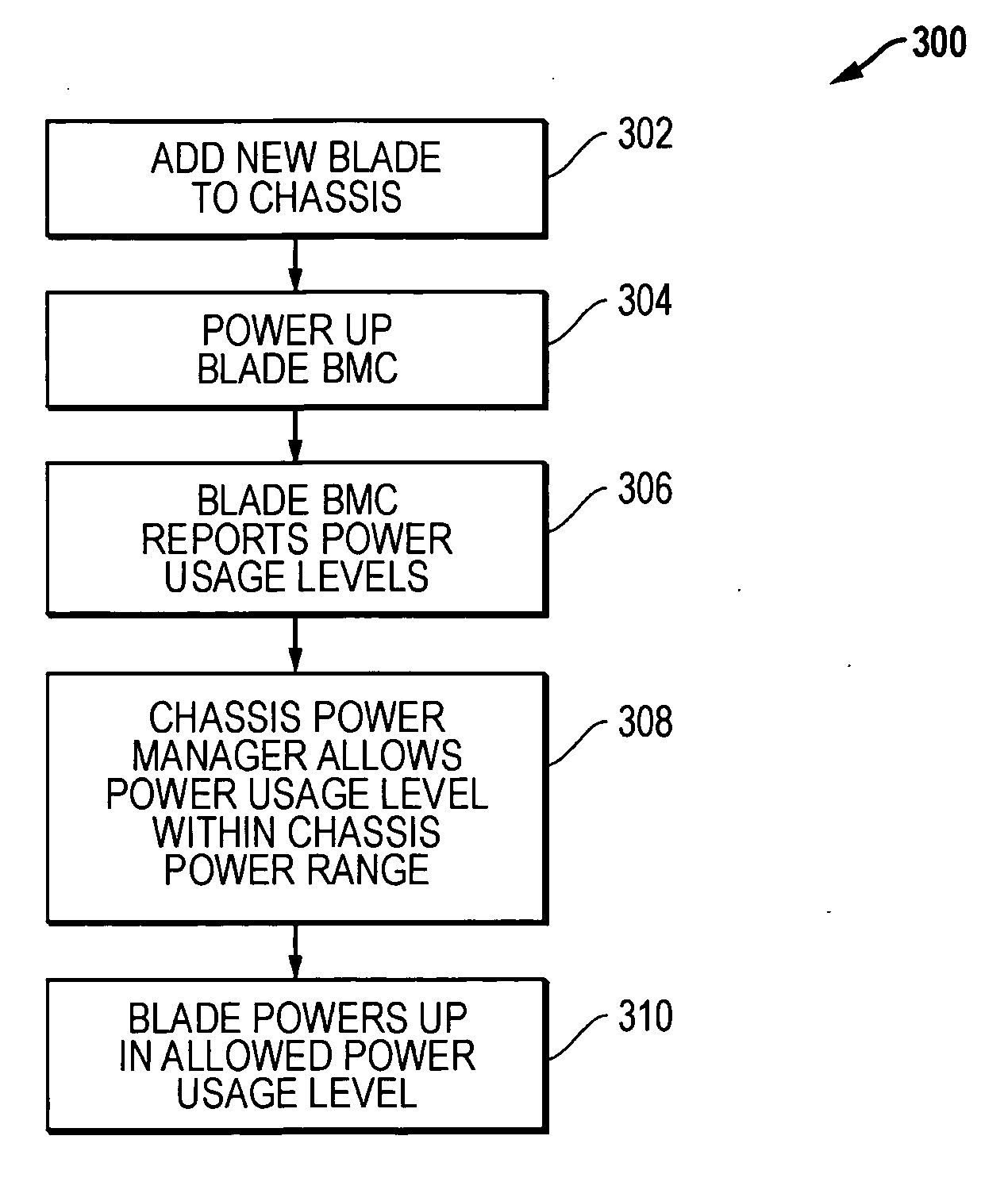
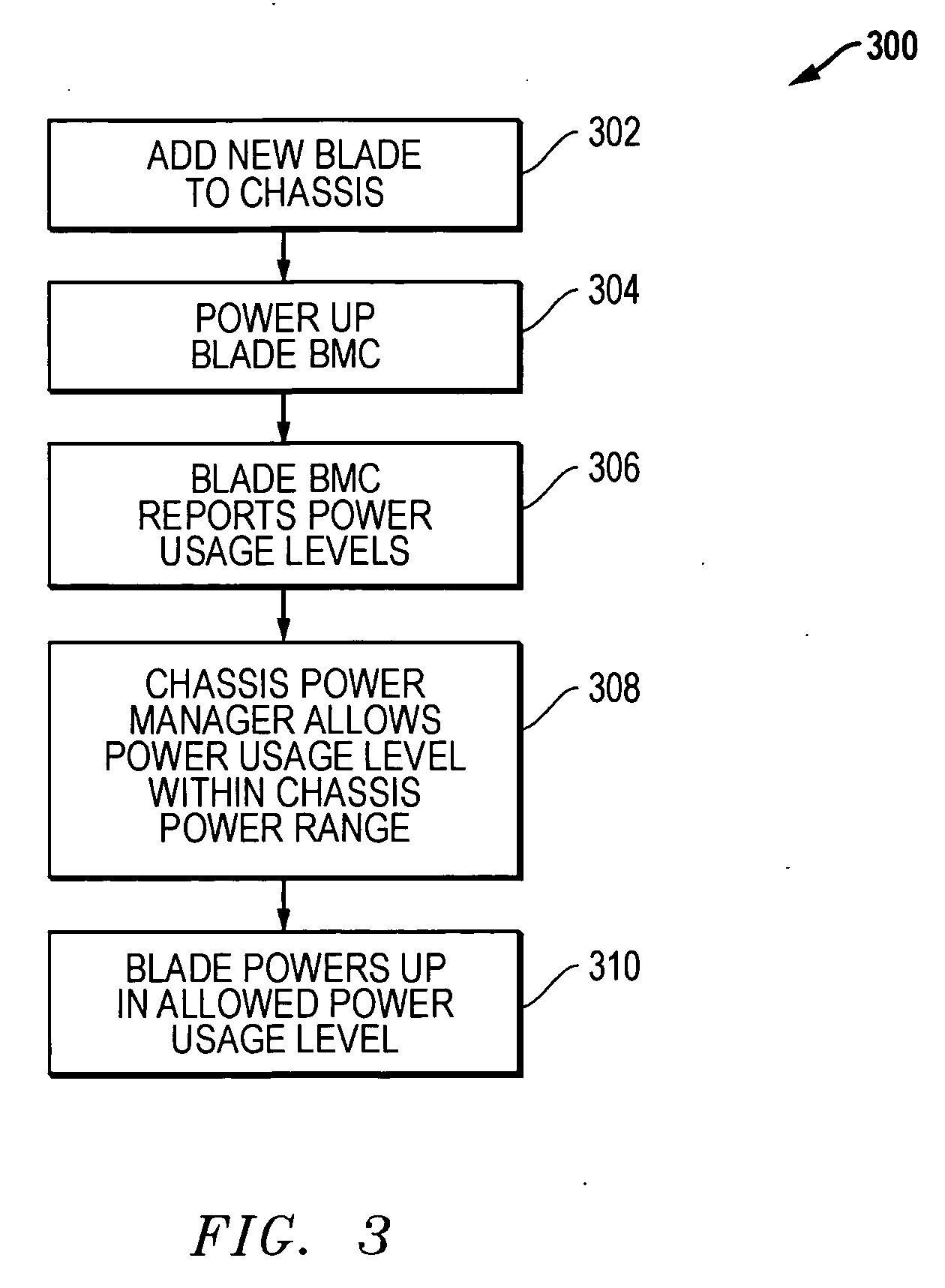
System and method for power usage level management of blades installed within blade servers
ActiveUS20060230299A1Volume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingPower usageEmbedded system
Methods and systems are disclosed for power usage level management of blades installed in blade servers. When a new blade added is to a blade server, possible power usage levels for the new blade are assessed to determine possible effects on the total power usage level of the chassis. By assessing the different power usage levels, the chassis controller can then make intelligent decisions as to the power usage levels at which new blades will be allowed to operate while still keeping within chassis power supply capabilities. Blade power usage levels can be based upon a variety of considerations, including processor performance modes and blade configuration options.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
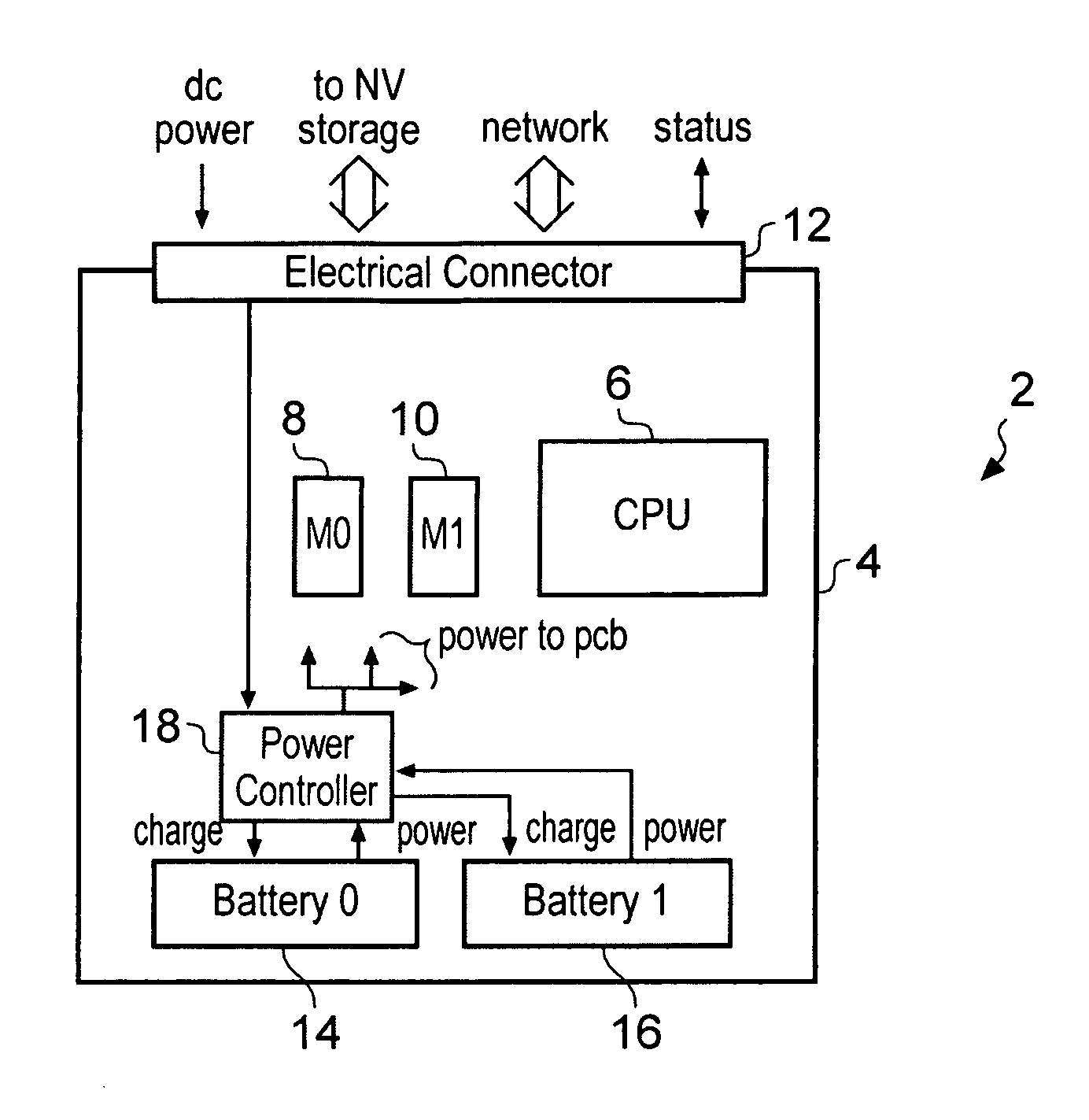
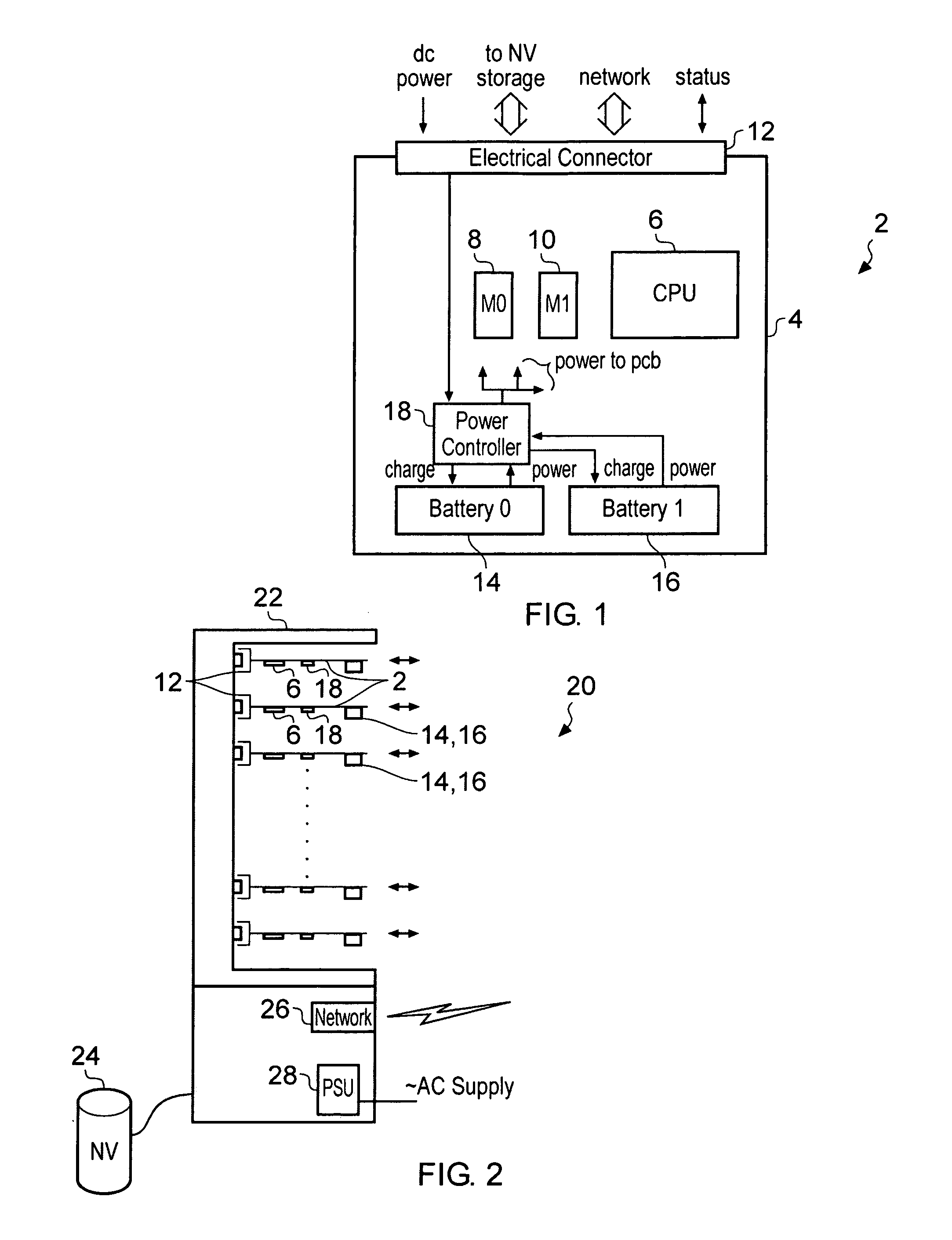
Blade server
InactiveUS20100299548A1Solve insufficient capacityMore power efficientHardware monitoringPower supply for data processingElectricityPower controller
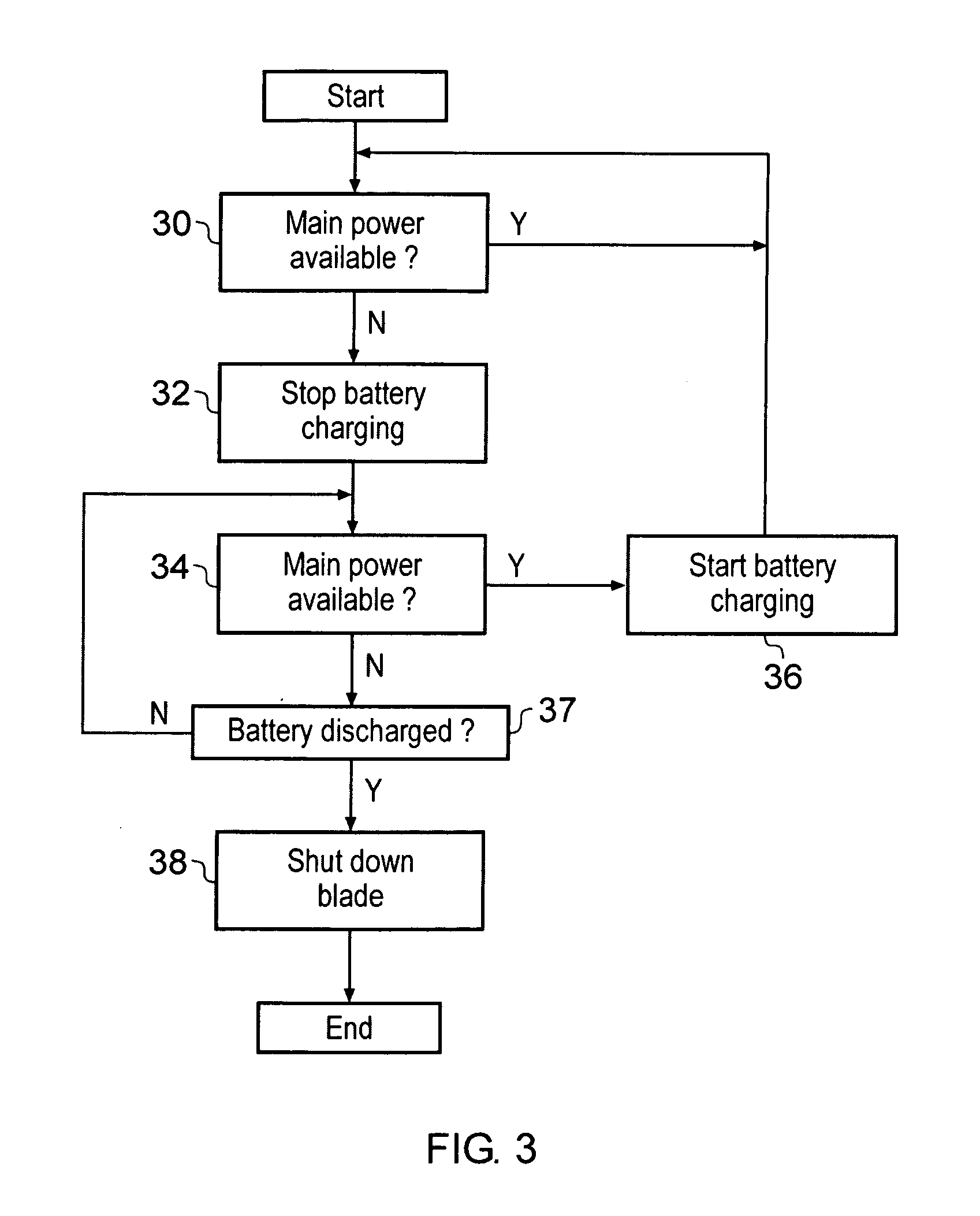
A blade server 2 is provided with a processor 6 for executing program instructions and an electrical connector 12 for connecting to a blade enclosure 22. The blade server 2 also includes a power controller 18 connected to a plurality of power supply batteries 14, 16 which are provided on the blade server 2 itself. If the power controller 18 detects that the main power supply supplied via the electrical connector 12 has been interrupted, then a backup power supply to the processor is provided from the on-board power supply batteries 14, 16. The batteries 14, 16 on each blade are periodically discharged and recharged in turn to check their proper function.
Owner:ARM LTD
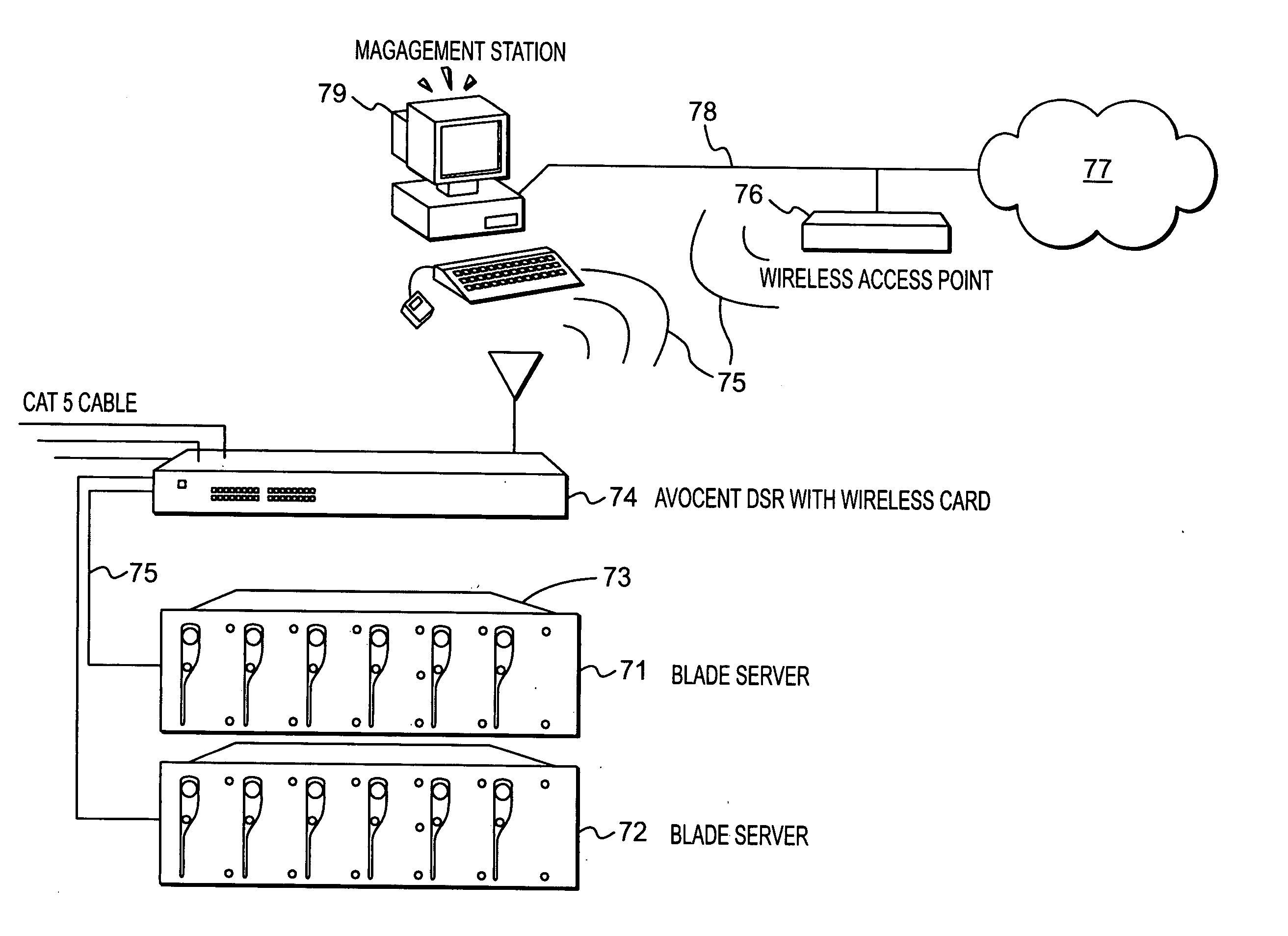
Wireless computer system
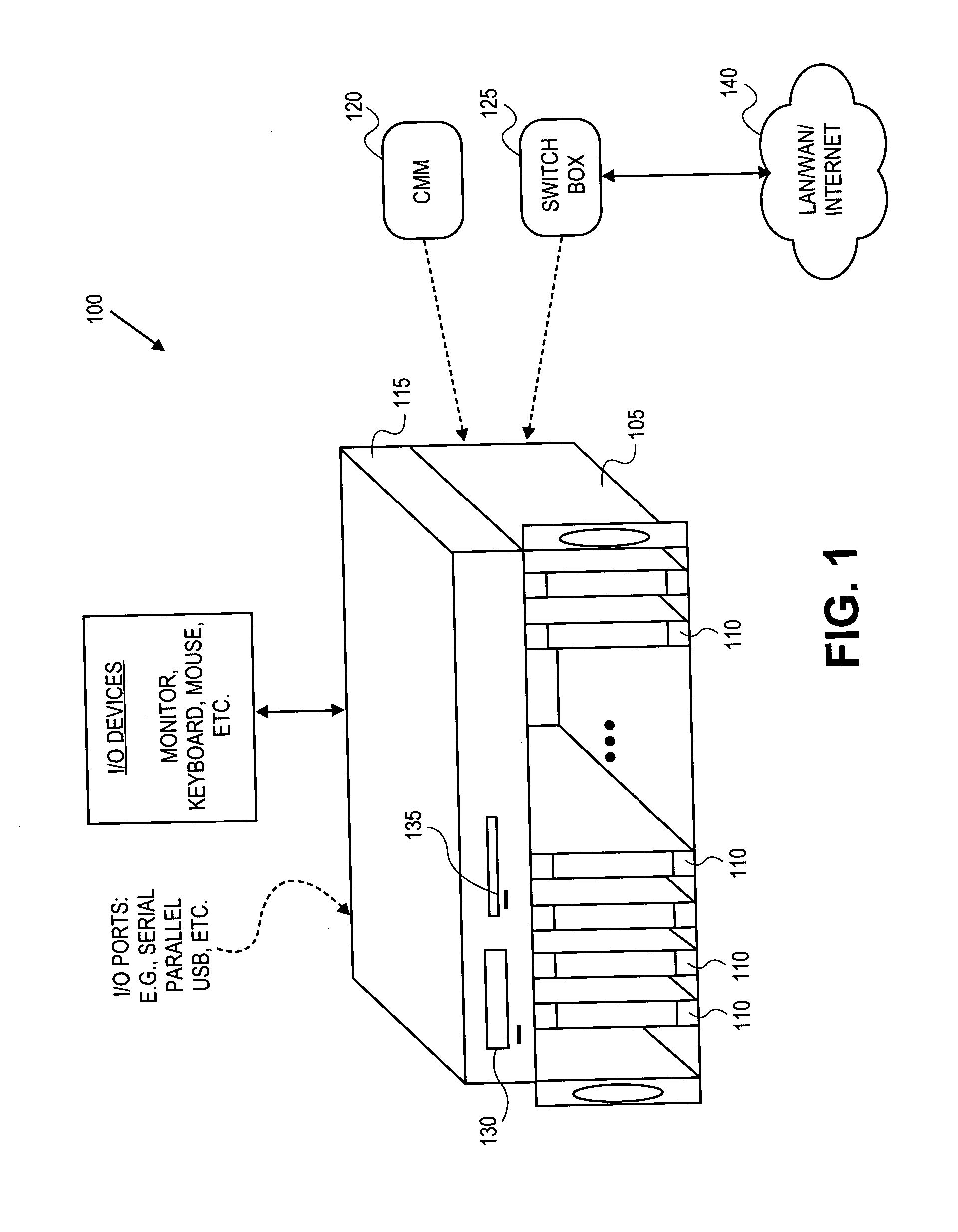
InactiveUS20050027890A1Reduce transmit powerEnhanced signalMultiple digital computer combinationsInput/output processes for data processingTelecommunicationsKVM switch
A system and method of communicating keyboard, video and cursor control (or mouse) data from a plurality of servers to one or more client workstations through one or more keyboard, video, mouse (KVM) switches is disclosed. Wireless communication techniques are used to transmit data between the system components including between the servers and the KVM switches. The servers, which may be blade servers, are typically co-located in single rack environment. Wireless communication techniques may also be used to communicate between the client workstations and the KVM switches.
Owner:VERTIV IT SYST INC
Design structure for an interposer for expanded capability of a blade server chassis system
InactiveUS20080239649A1Digital data processing detailsSupport structures on hinges/pivotsEmbedded systemBlade server
A design structure embodied in a machine readable storage medium for designing, manufacturing, and / or testing a system chassis includes multiple chassis bays configured for receiving either of a single, conventional server blade or an adapter blade is provided. The adapter blade can selectively secure a plurality of compact blades, such as a blade PC. The adapter blade includes an interposer disposed for electronically communicating each compact blade with a server interface as a separate node upon securing a compact blade within any of the adapter bays. Each compact blade may be configured as a server, a “client blade” or “blade PC”, or a companion blade providing application-specific features. Therefore, the use of an adapter blade increases the flexibility of and capability of the processor system.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methods and devices for networking blade servers
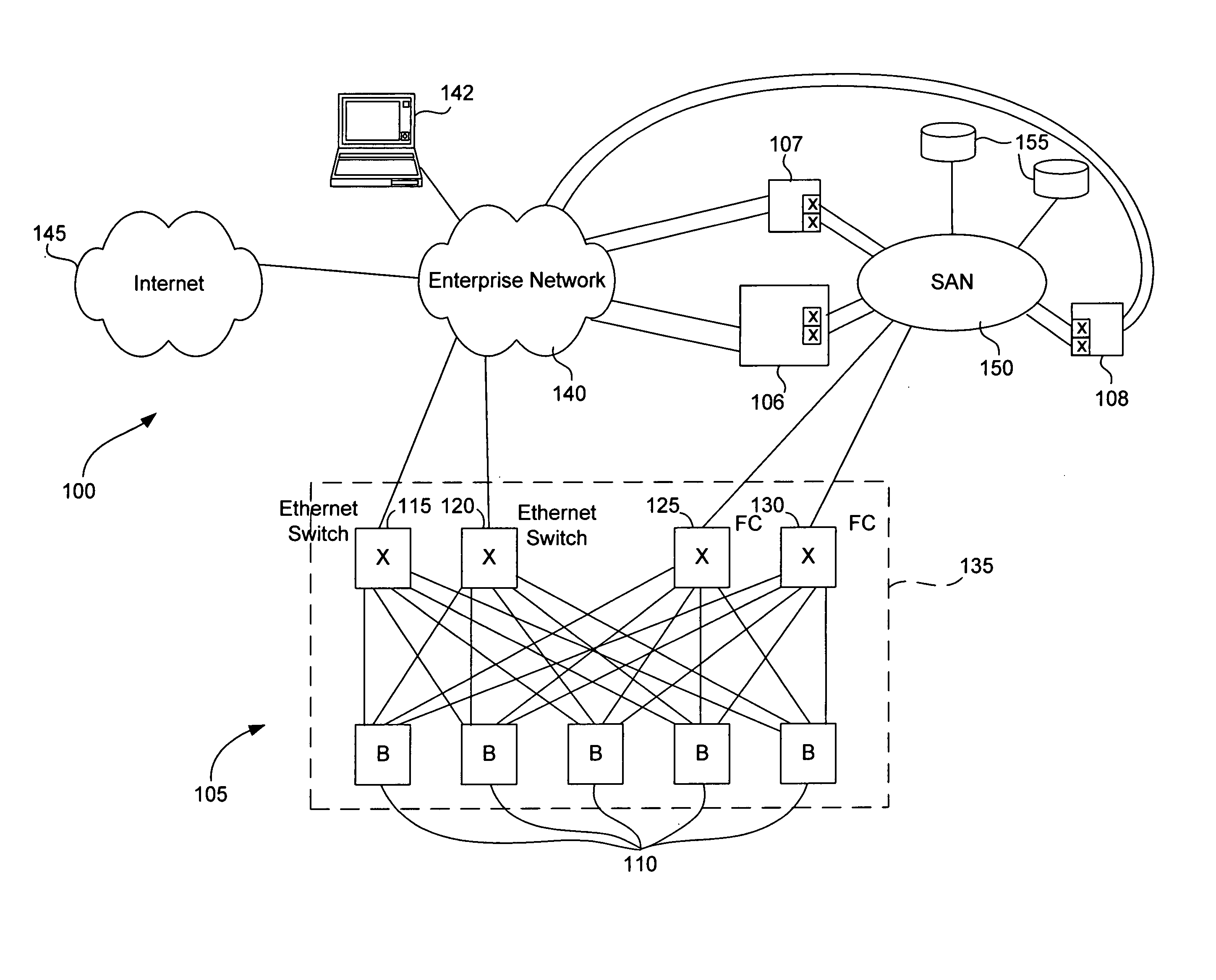
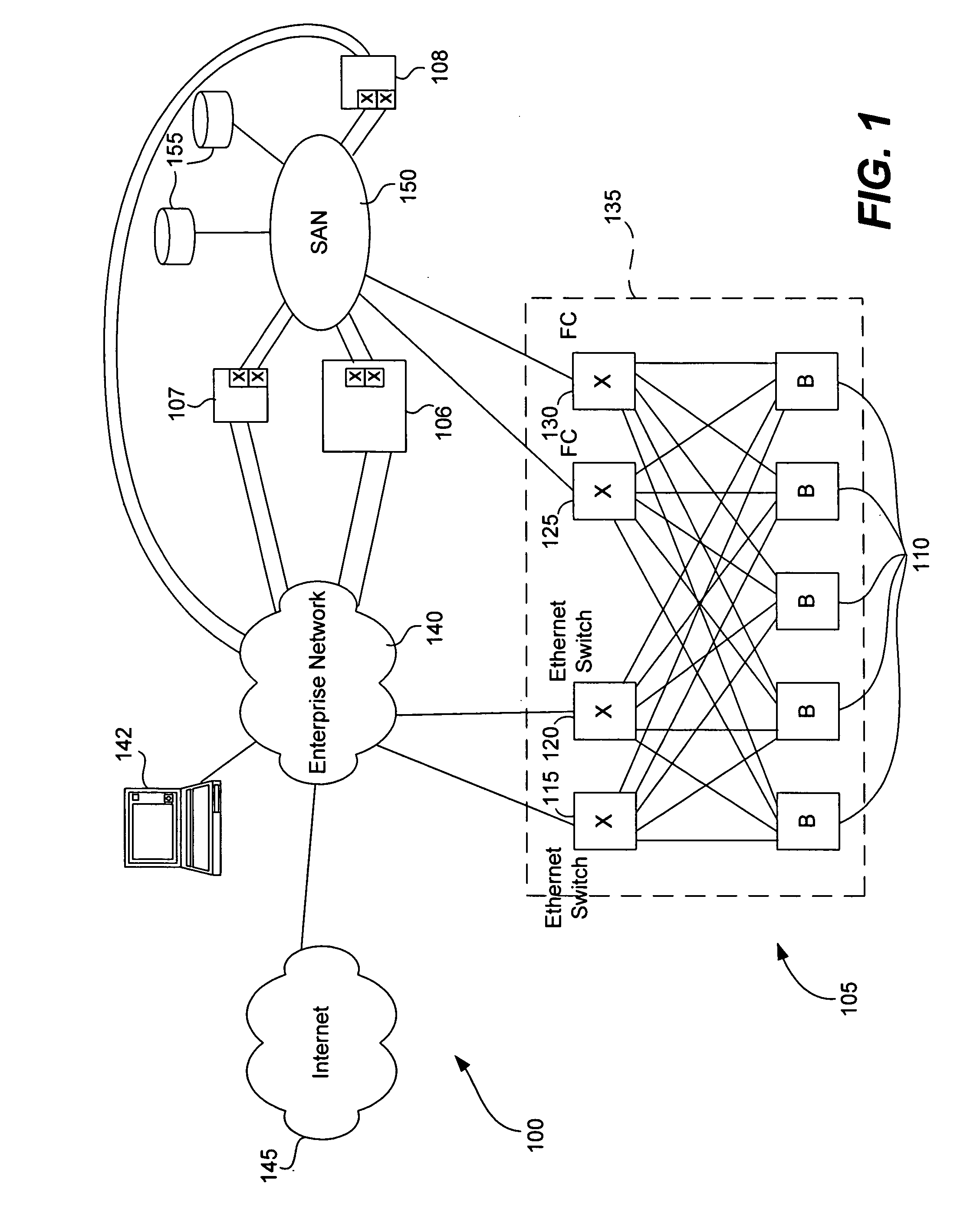
Some embodiments of the present invention provide blade servers having blade switches that function as switches in the data plane, but do not have a Domain_ID. Control plane switching functions are performed by a fabric switch (e.g., a core switch) to which the blade server is attached. A fabric switch to which a blade switch is attached may perform address assignment functions for blades of the blade server. The blade switch preferably converts FLOGI requests to FDISC requests that are forwarded to an attached fabric switch. Some implementations provide for the multiple fabric switches, all of which are configured for communication with at least one blade switch, to establish and maintain the state of a virtual Domain_ID.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
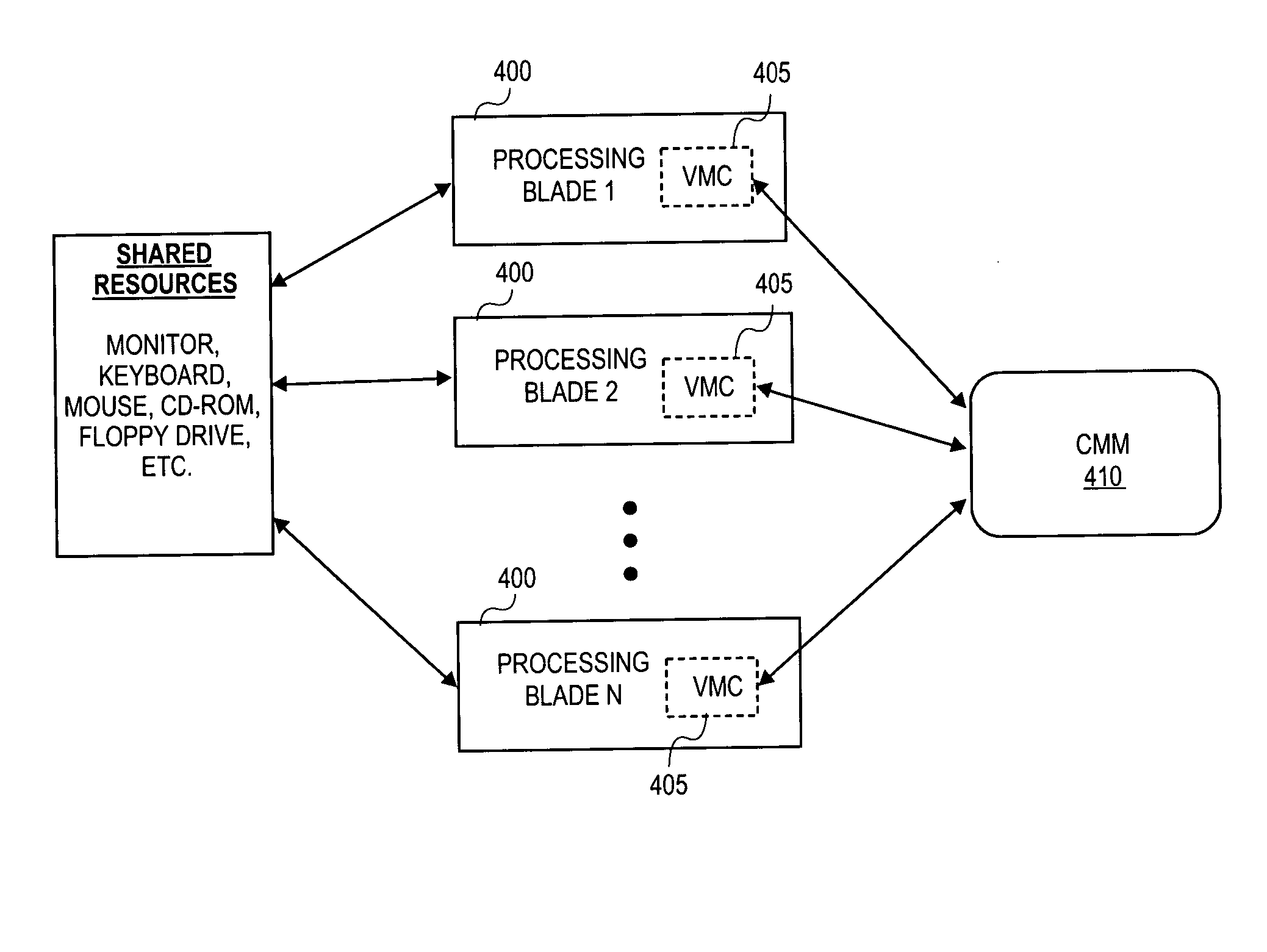
Virtual management controller to coordinate processing blade management in a blade server environment
A method and apparatus to implement a virtual management controller to coordinate processing blade management in a blade server environment. A management mode of operation of a processing blade of a blade server is activated. During the management mode of operation, a chassis management module is interacted with to manage operation of the processing blade. Thereafter, the management mode of operation of the processing blade is deactivated.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Dynamic adaptive server provisioning for blade architectures
A system and method for automatically allocating computing resources of a rack-and-blade computer assembly. The method includes receiving server performance information from an application server pool disposed in a rack of a rack-and-blade computer assembly, and determining at least one QoS attribute for the application server pool. If the QoS attribute is below a standard, a blade server is allocated from a free server pool for use by the application server pool. If the QoS attribute is above a standard, at least one server is removed from the application server pool. An article of manufacture including a machine-readable medium having stored thereon instructions for automatically allocating computing resources of a rack-and-blade computer assembly.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
System and method for displaying chassis component information
ActiveUS20050195075A1Eliminates and reduces of disadvantageEliminates and reduces of and problemServersElectric lighting sourcesEmbedded systemBlade server
A system for displaying chassis component information includes a chassis and a plurality of server blades each coupled to the chassis. Each server blade comprises a respective liquid crystal display (LCD) positioned upon the server blade. The respective LCD is operable to display chassis component information.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
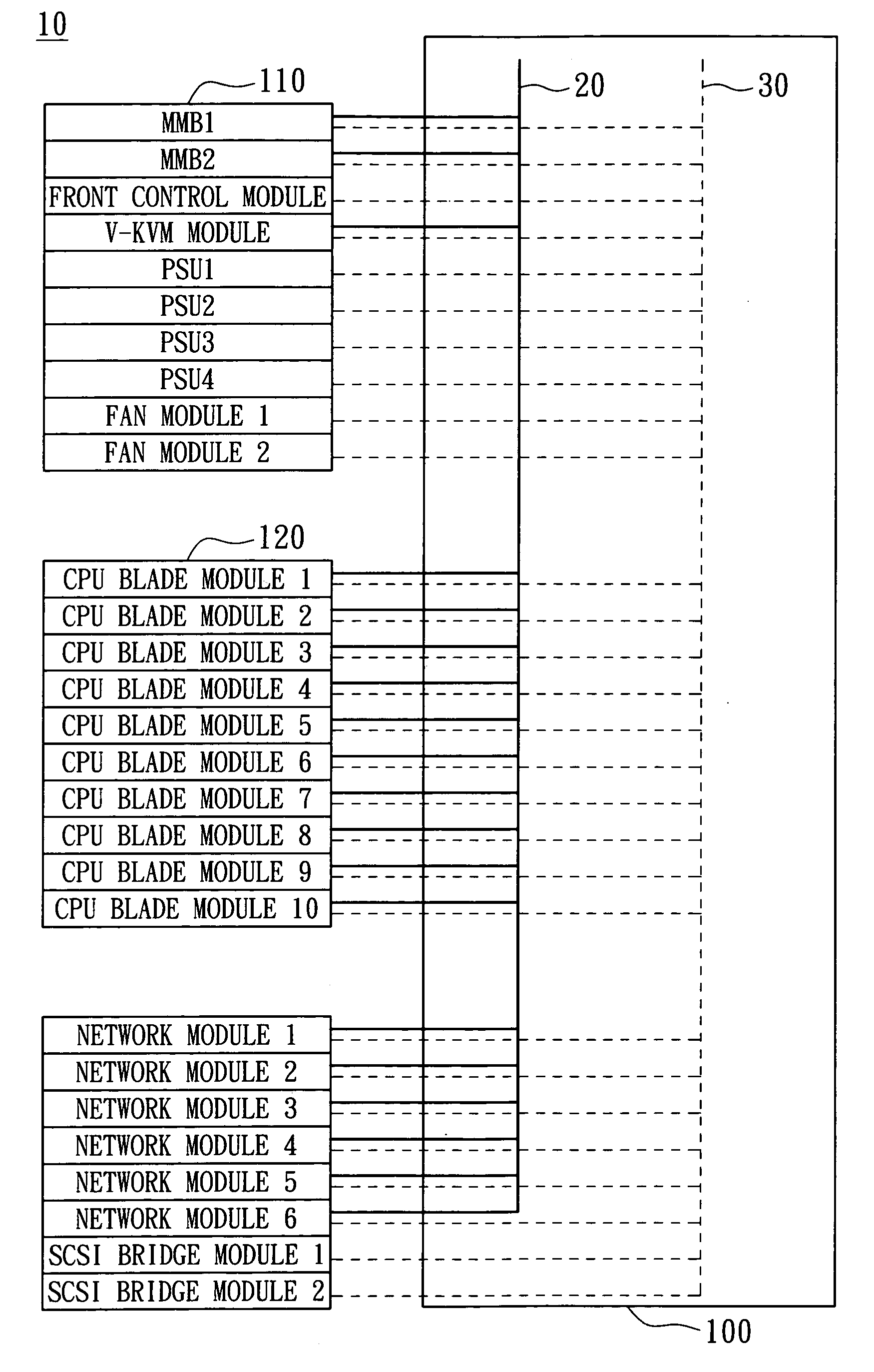
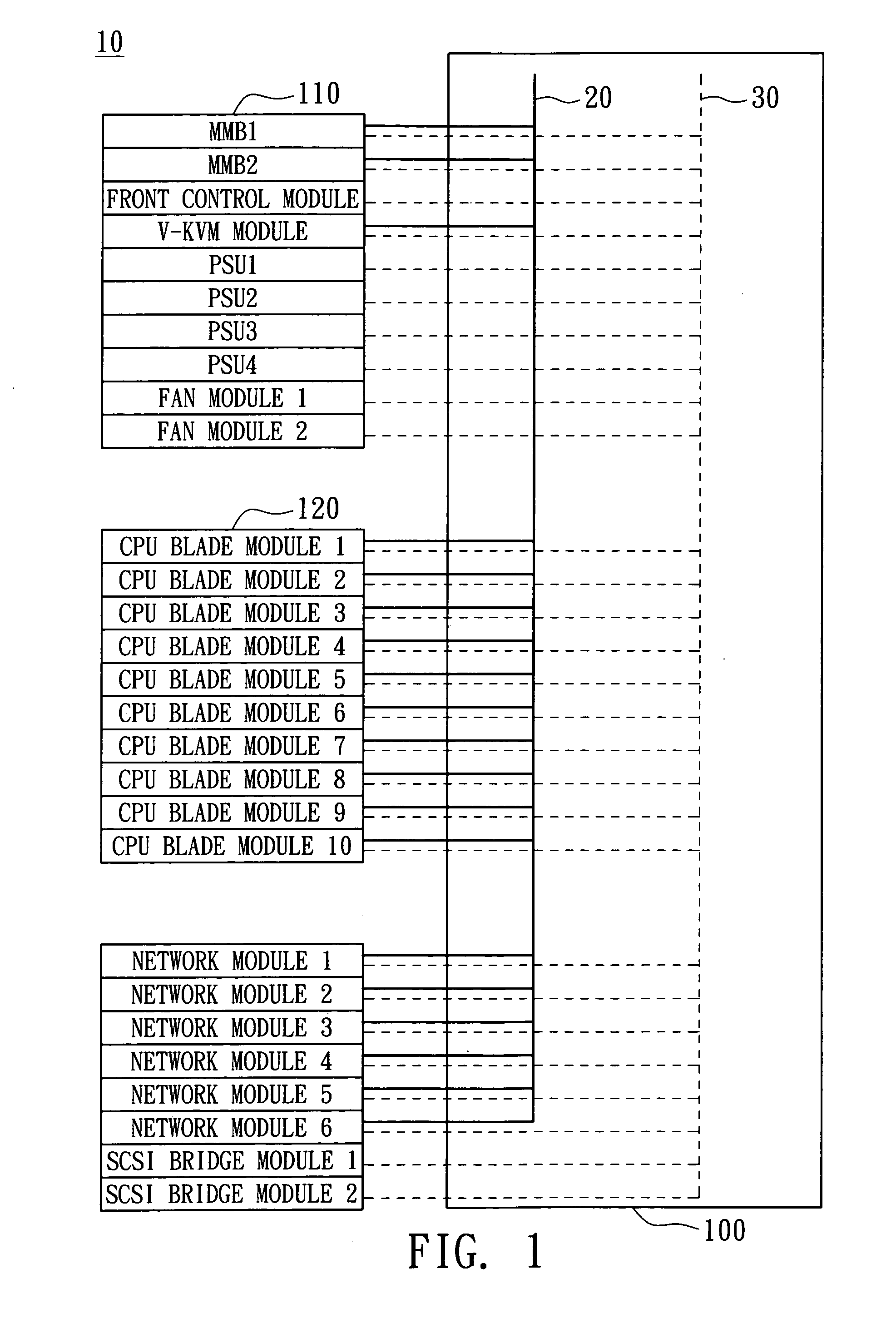
Blade server system with a management bus and method for managing the same
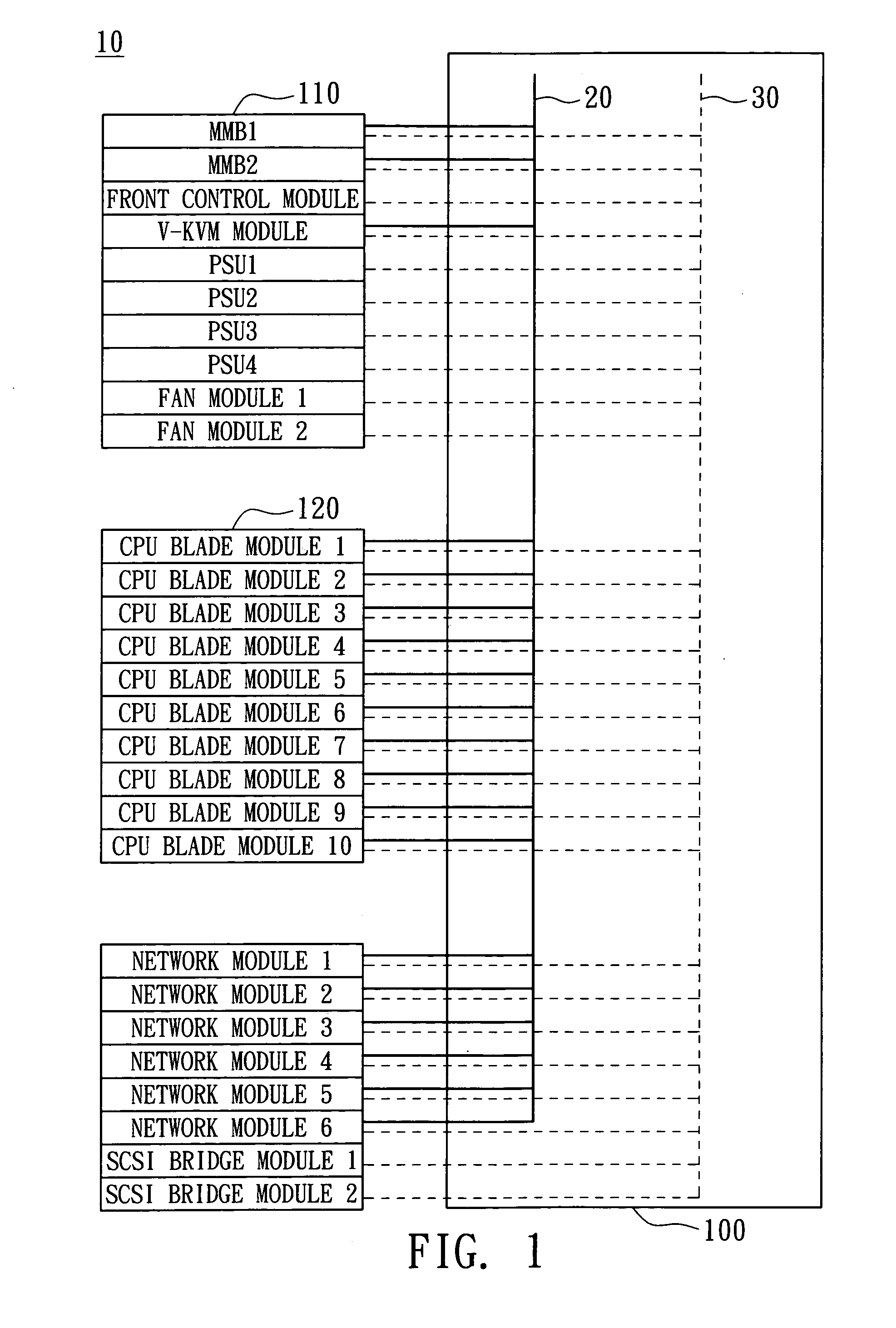
ActiveUS7657677B2Prevent overloadMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexComputer moduleInterconnection
A blade server system with a management bus and method for managing the same. The blade server system includes a connection board and a management module. The connection board is used for modular interconnection, including communication paths for conducting signals including a management bus signal group and a first bus signal group. The management module is used for management of the blade server system using signals including the management bus signal group and the first bus signal group. If a module is detected, the management module selects the detected module through the management bus and acquires module configuration information of the detected module through the first bus signal group. Distribution of power from a power source to the blade server system is determined according to system configuration information including the module configuration information of the module so that the power source is prevented from being overloaded.
Owner:QUANTA COMPUTER INC
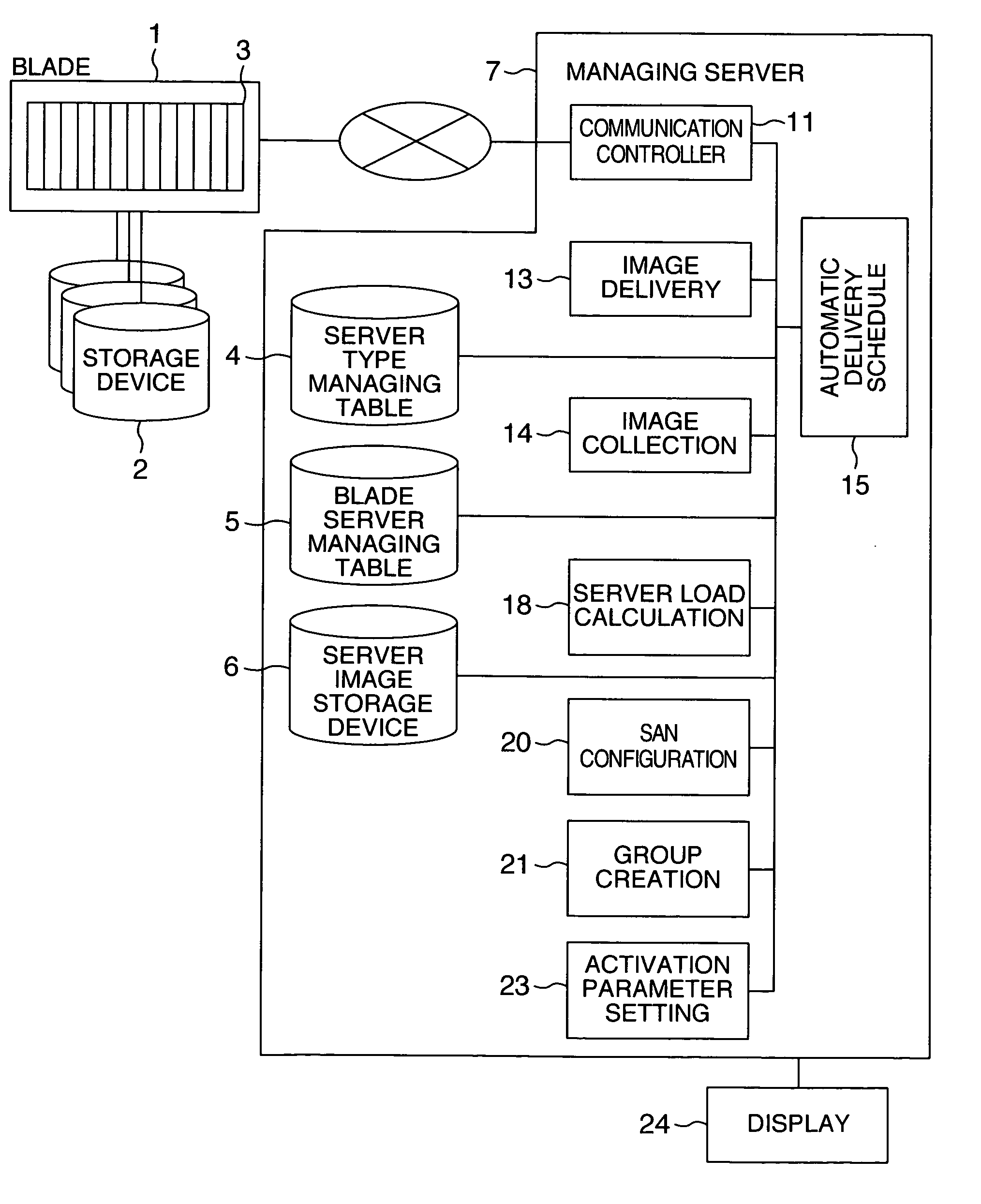
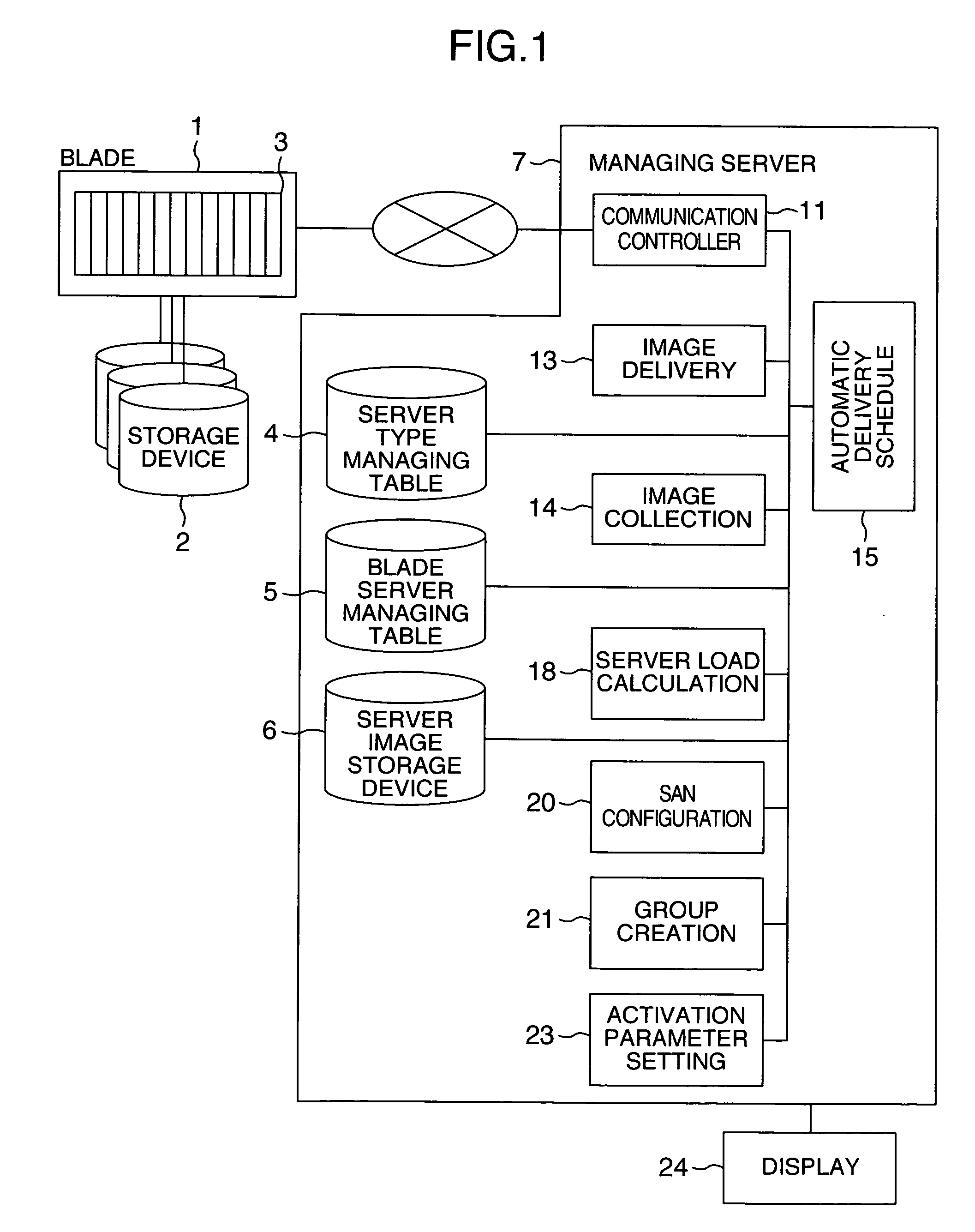
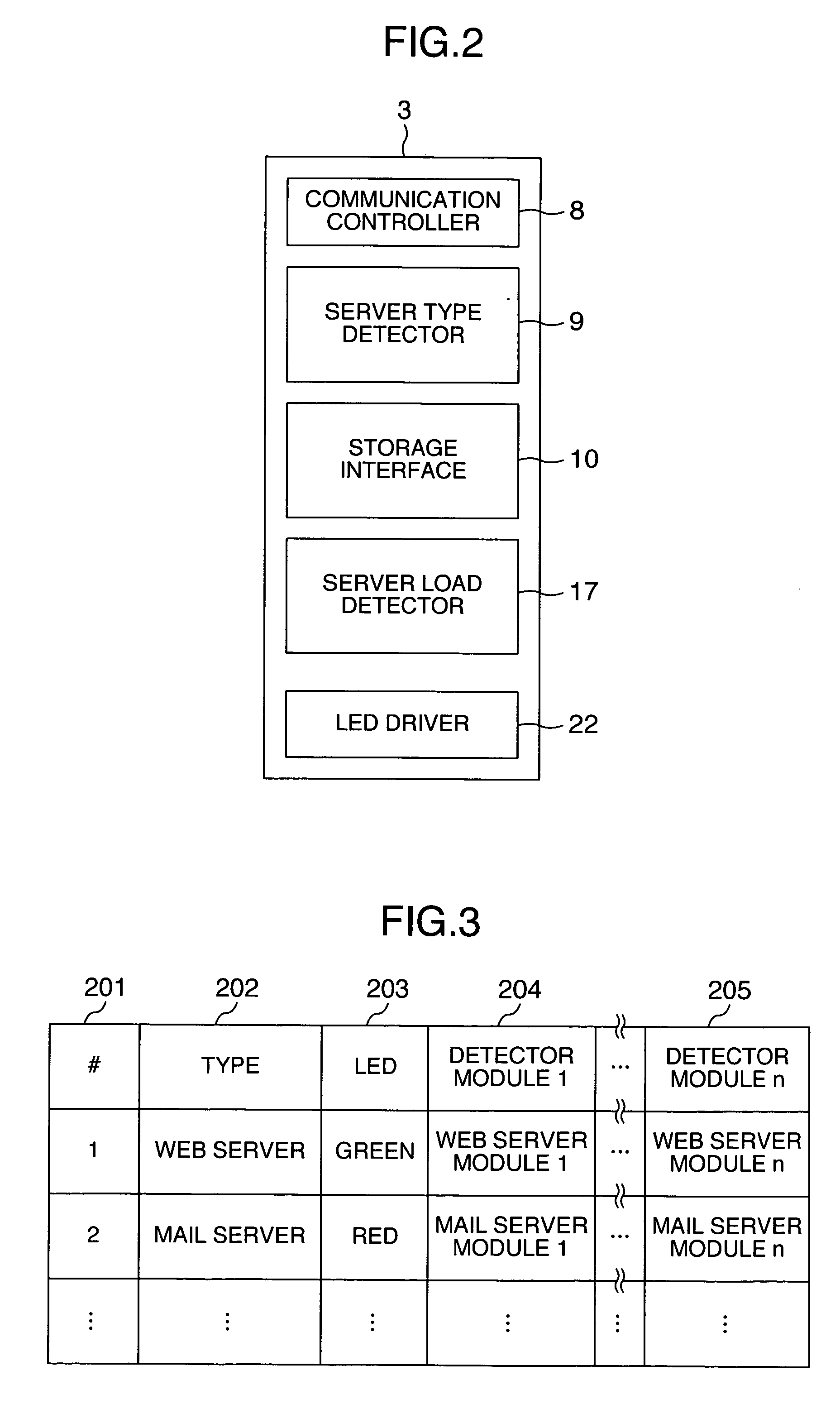
Server system and a server arrangement method
InactiveUS20060004909A1Easy maintenanceAutomatically replace functions of the serversMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionSystem configurationEmbedded system
In a server system, functions of blade servers can be visually recognized at a glance. A change in load due to a failure can be detected to modify the system configuration by changing functions of blade servers. The server system includes a blade system including servers having different function types, the servers being installed in one or more stages in one enclosure, and a managing server for managing the blade system. The managing server includes a first managing section for classifying the servers into groups, a second managing section for managing a state of arrangement of the servers in the enclosure, and an arrangement changing section for changing functions of the servers discretely and for changing arrangement of the servers in the enclosure by replacing functions of the servers. The arrangement changing section arranges the servers in the enclosure on a function basis of the servers.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Port expander for fibre channel fabrics in storage area networks
ActiveUS20070058619A1Improve scalabilityImprove interoperabilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsCircuit switching systemsVirtualizationTelecommunications
An port expander Fibre Channel switch presents F_ports to form a first Fibre Channel fabric and N_ports to a second Fibre Channel fabric to appear as node devices. The port expander may be used to connect a plurality of blade servers to a Fibre Channel fabric. Fabric events engendered by the insertion or removal of hot-pluggable devices are handled by the port expander and “event storms” on the Fibre Channel fabric are avoided. The port expander presents the blade servers to the FC fabric as a virtualized N_port.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
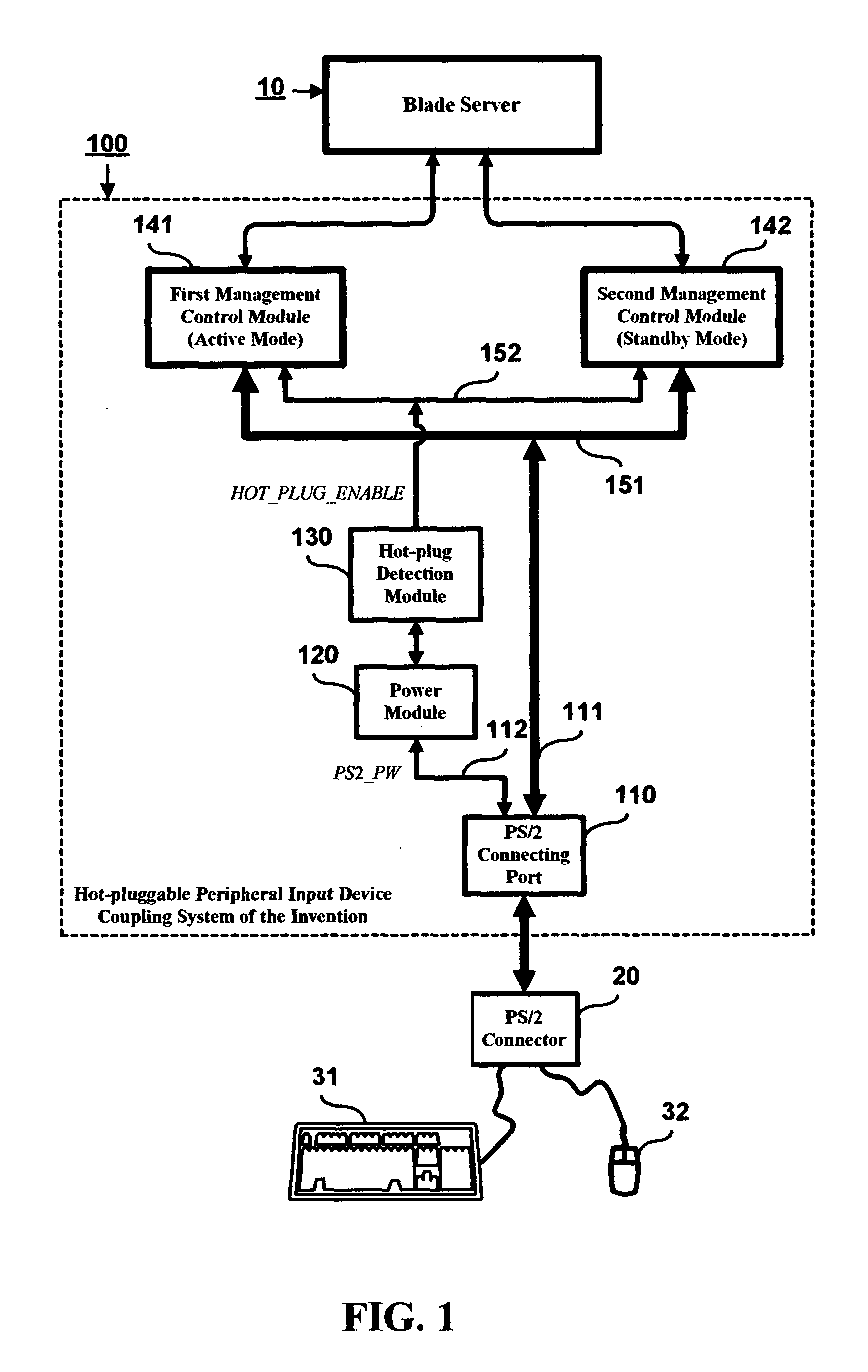
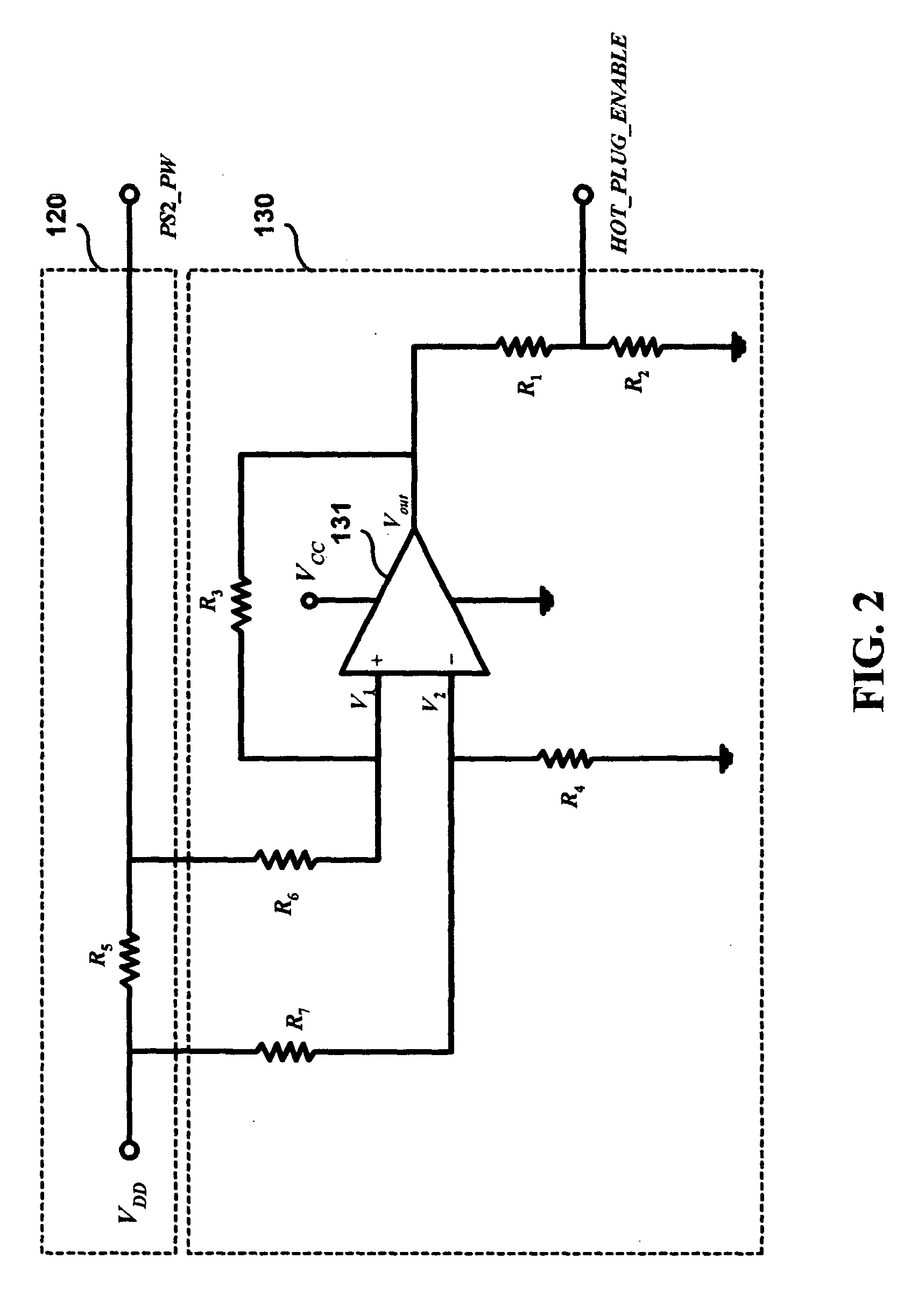
Hot-pluggable peripheral input device coupling system
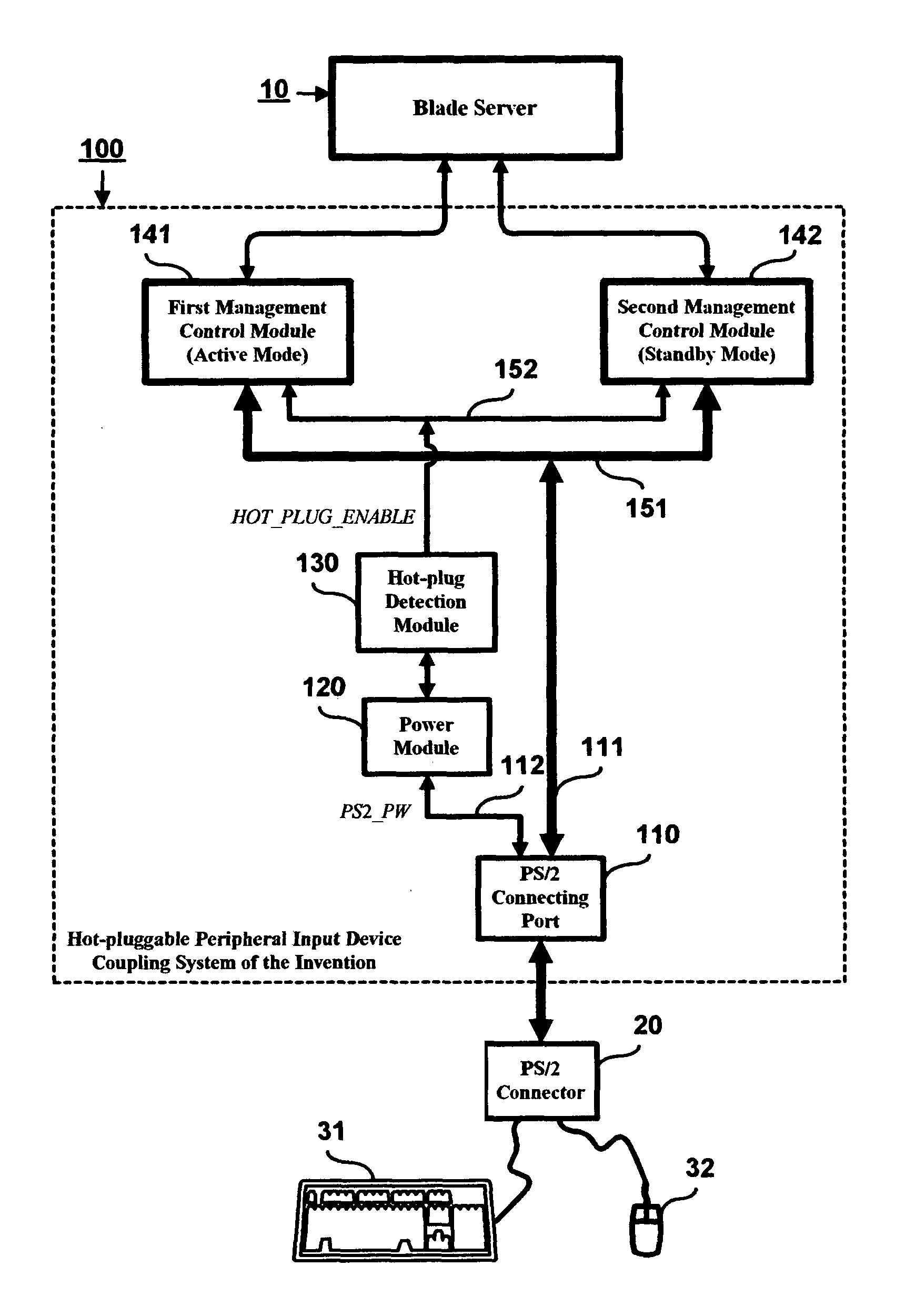
InactiveUS20050033890A1Improve efficiencyComponent plug-in assemblagesElectric digital data processingBlade serverExternal connection
A hot-pluggable peripheral input device coupling system is proposed, which is designed for use to couple one or more peripheral input devices, such as a keyboard and a mouse, to a network server, such as a blade server, for the purpose of allowing the user to input data and commands to the blade server via the keyboard and mouse. The proposed hot-pluggable peripheral input device coupling system is characterized by the provision of at least two management control modules with one serving as a redundant backup module to the other so that in the event of a failure to the active one, the blade server can nevertheless be functionally linked to the externally connected keyboard and mouse via the redundant backup module. The invention can therefore help enhance the efficiency of network system management on blade servers.
Owner:INVENTEC CORP
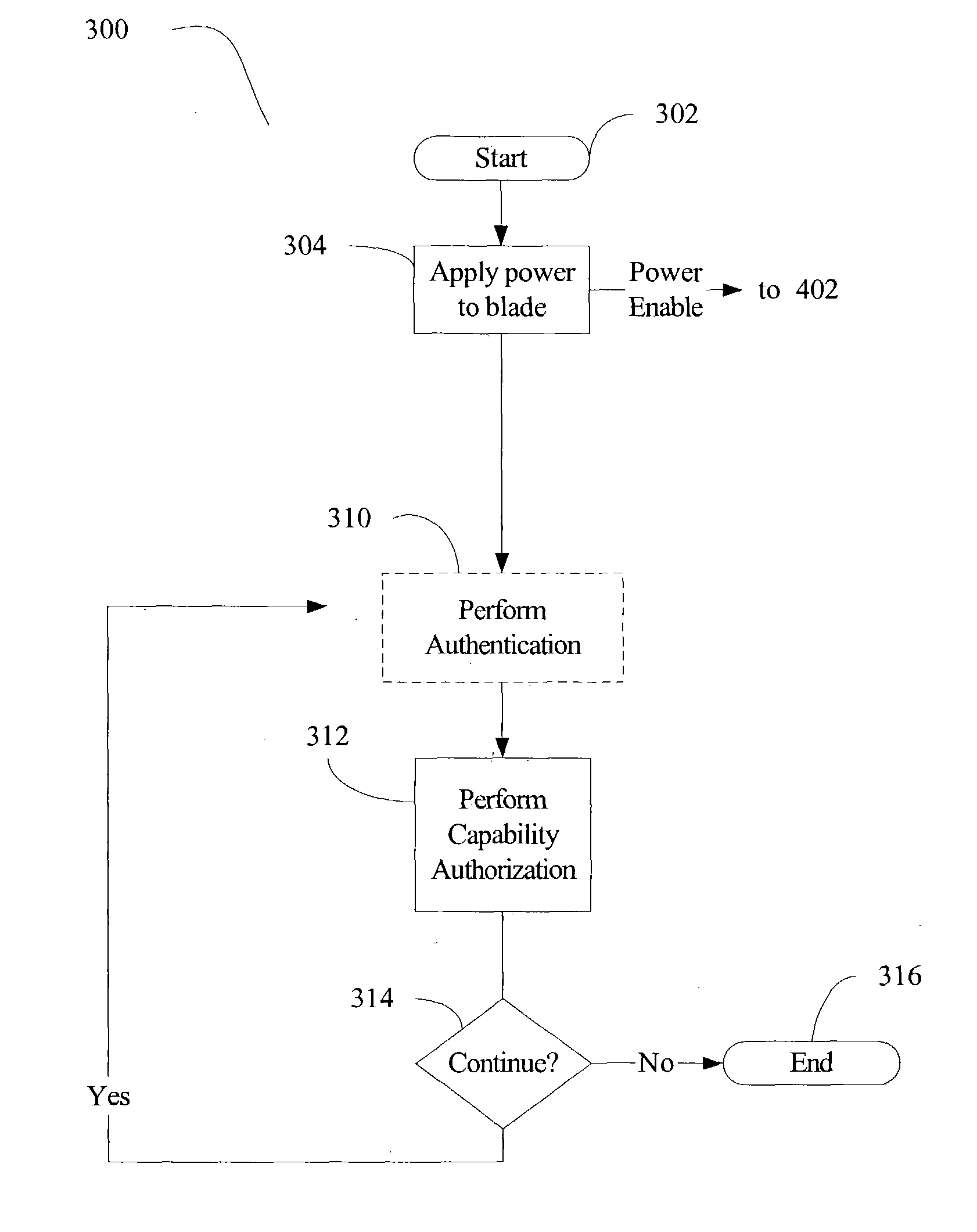
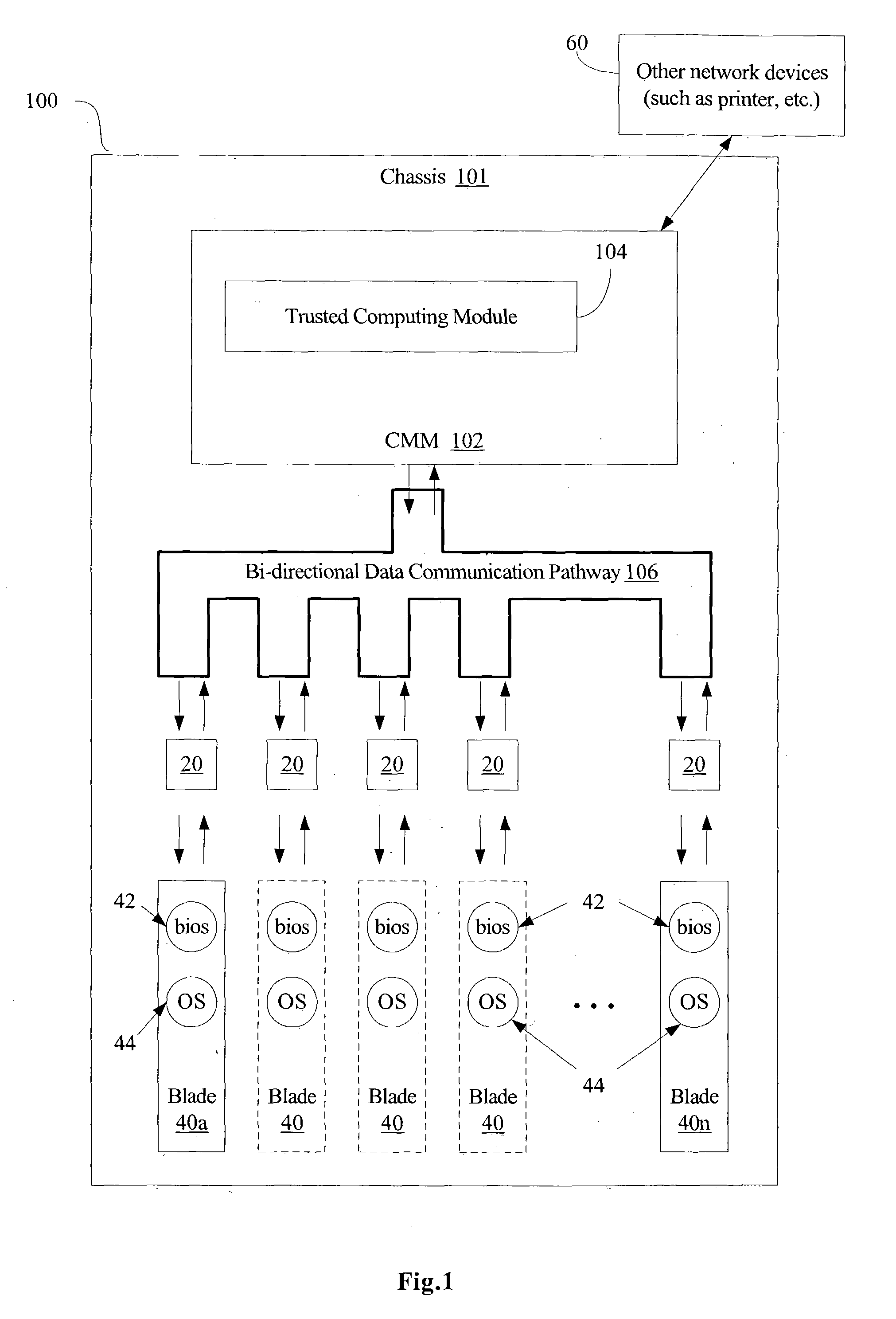
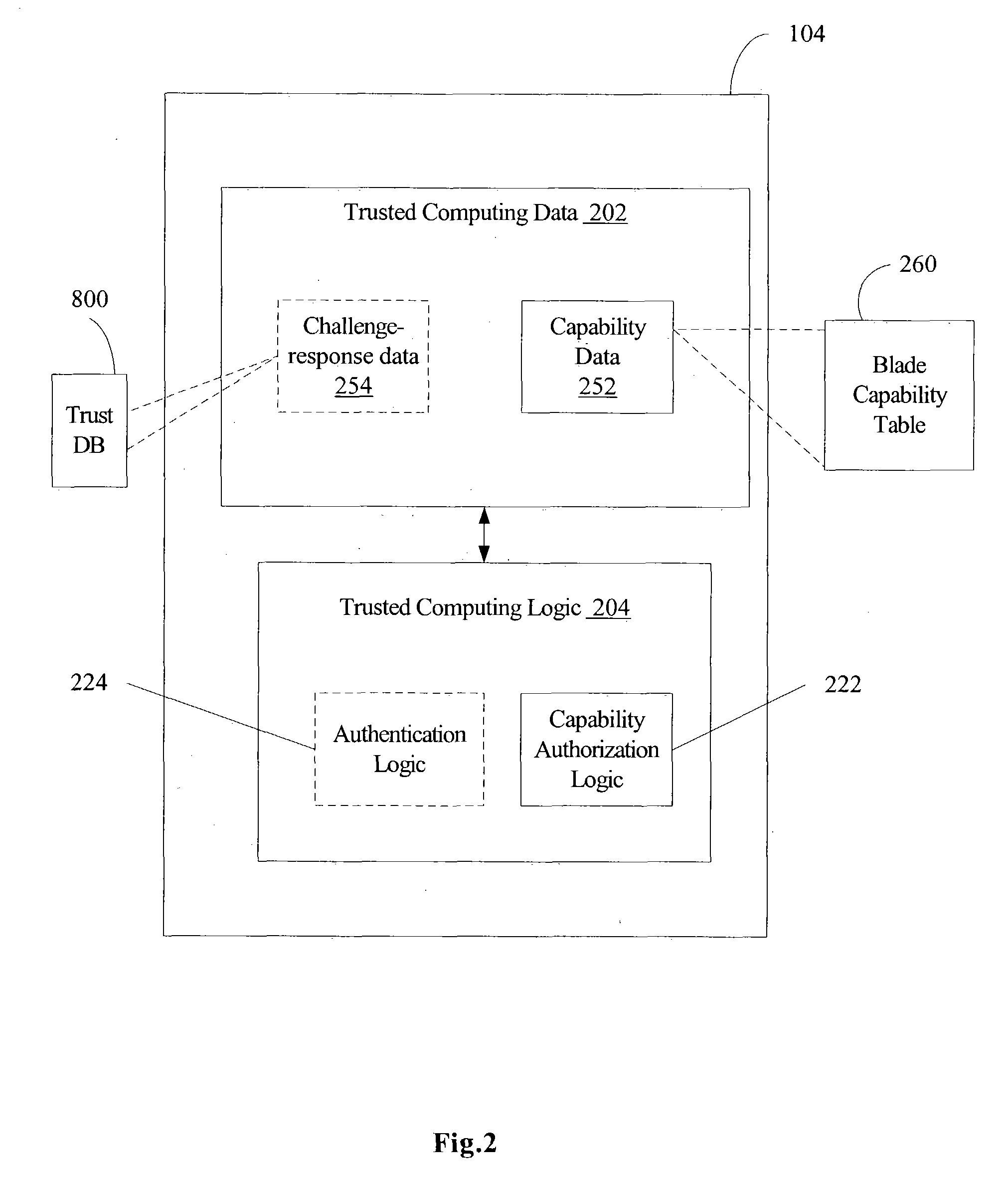
Method and apparatus for trusted blade device computing
ActiveUS20050028000A1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsTrusted ComputingLogic module
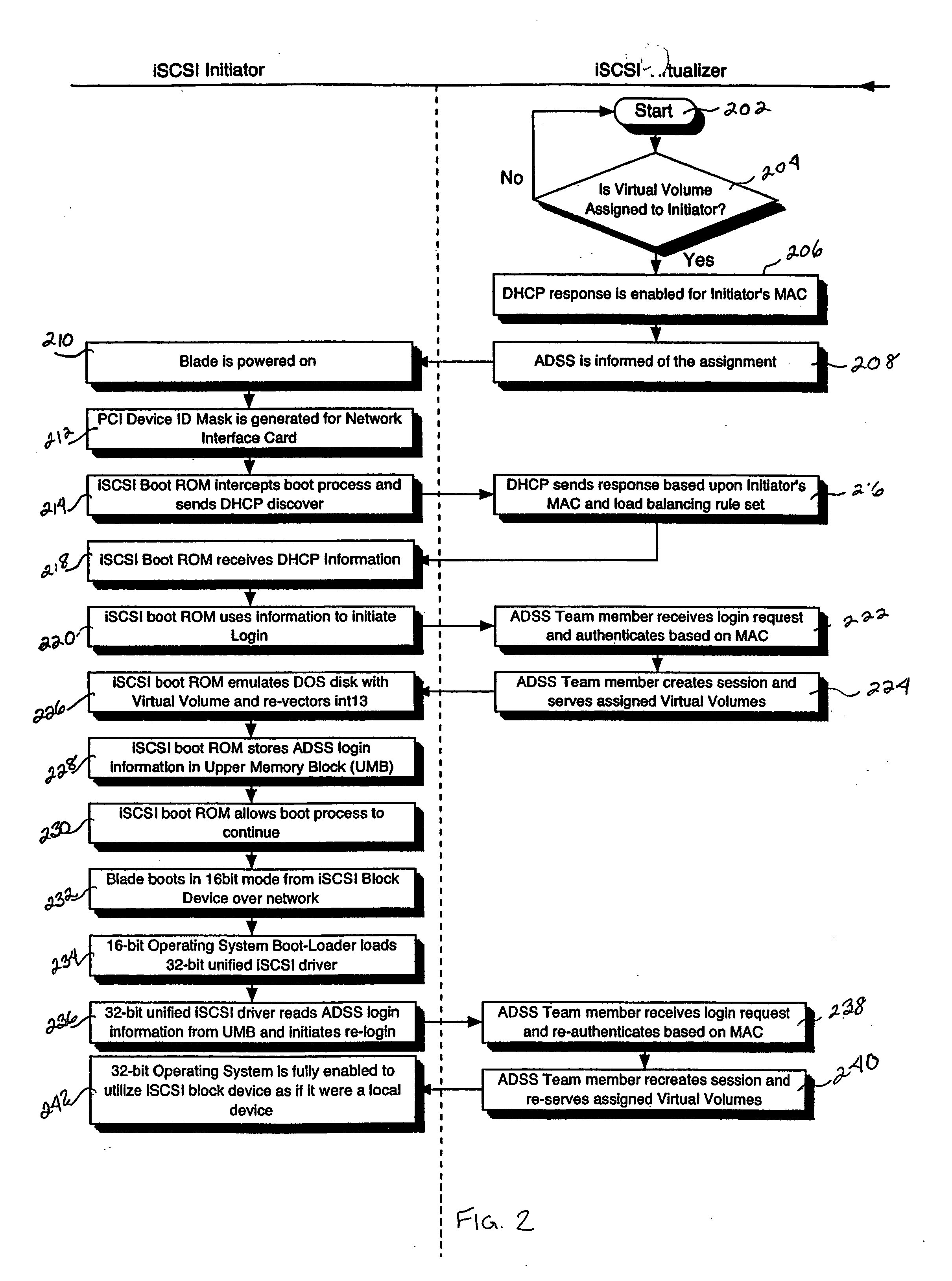
A method and system are disclosed for performing trusted computing for blade devices, such as blade servers or other blade devices. The computing domain for the blade devices is managed by a chassis management logic module. Methods for performing blade capability authorization and optional blade authentication are provided. A method for performing blade device boot processing is also provided.
Owner:INTEL CORP
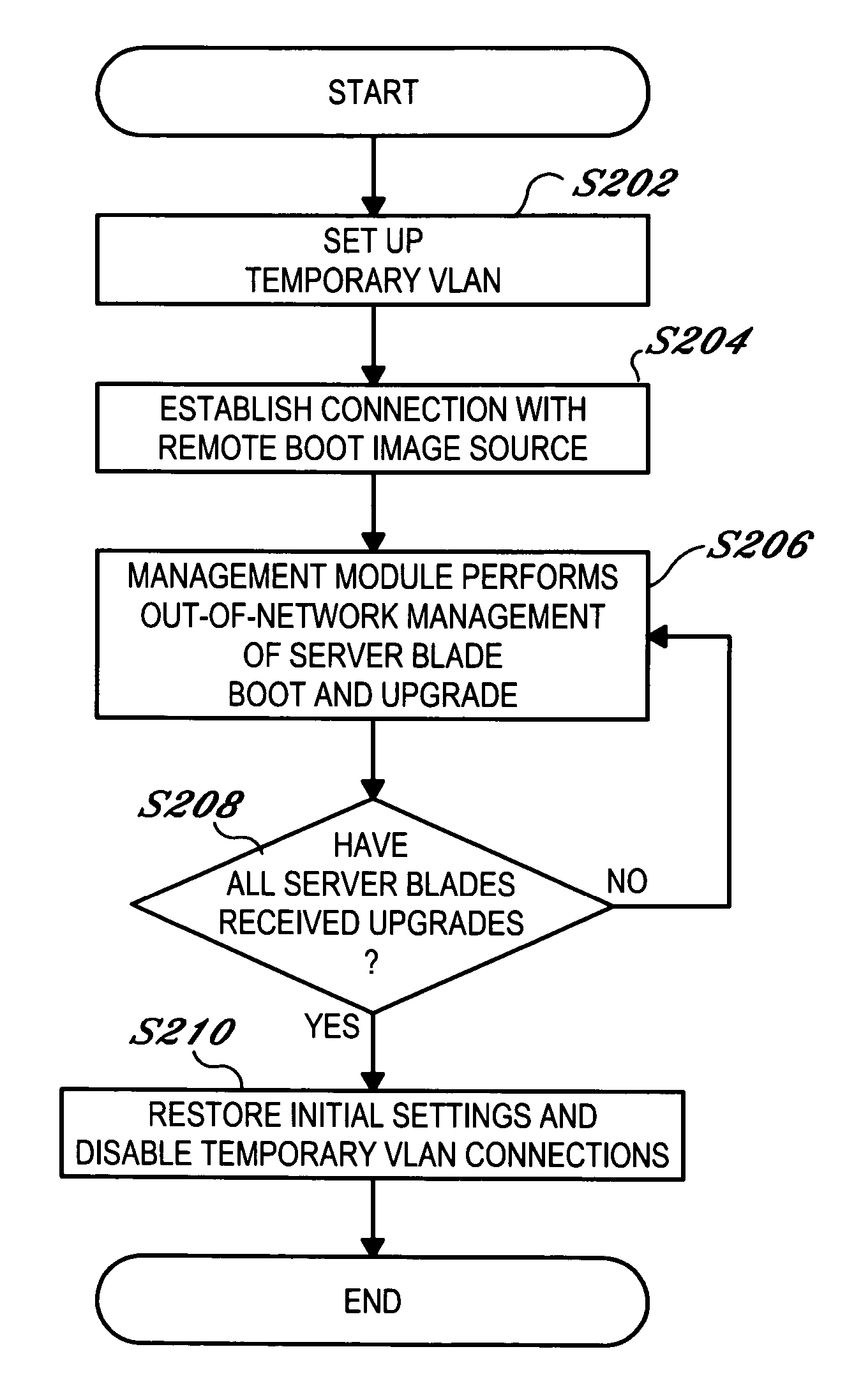
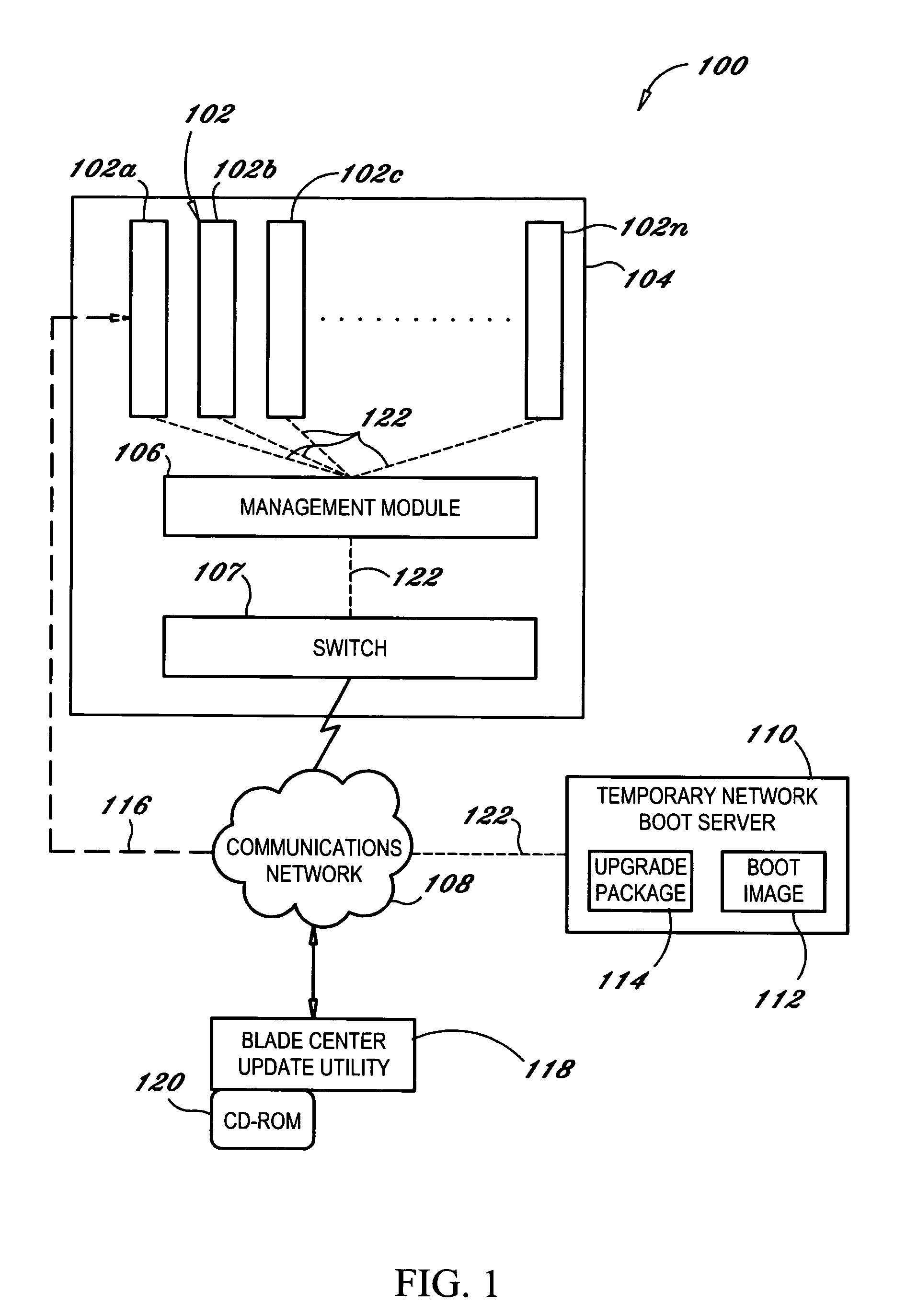
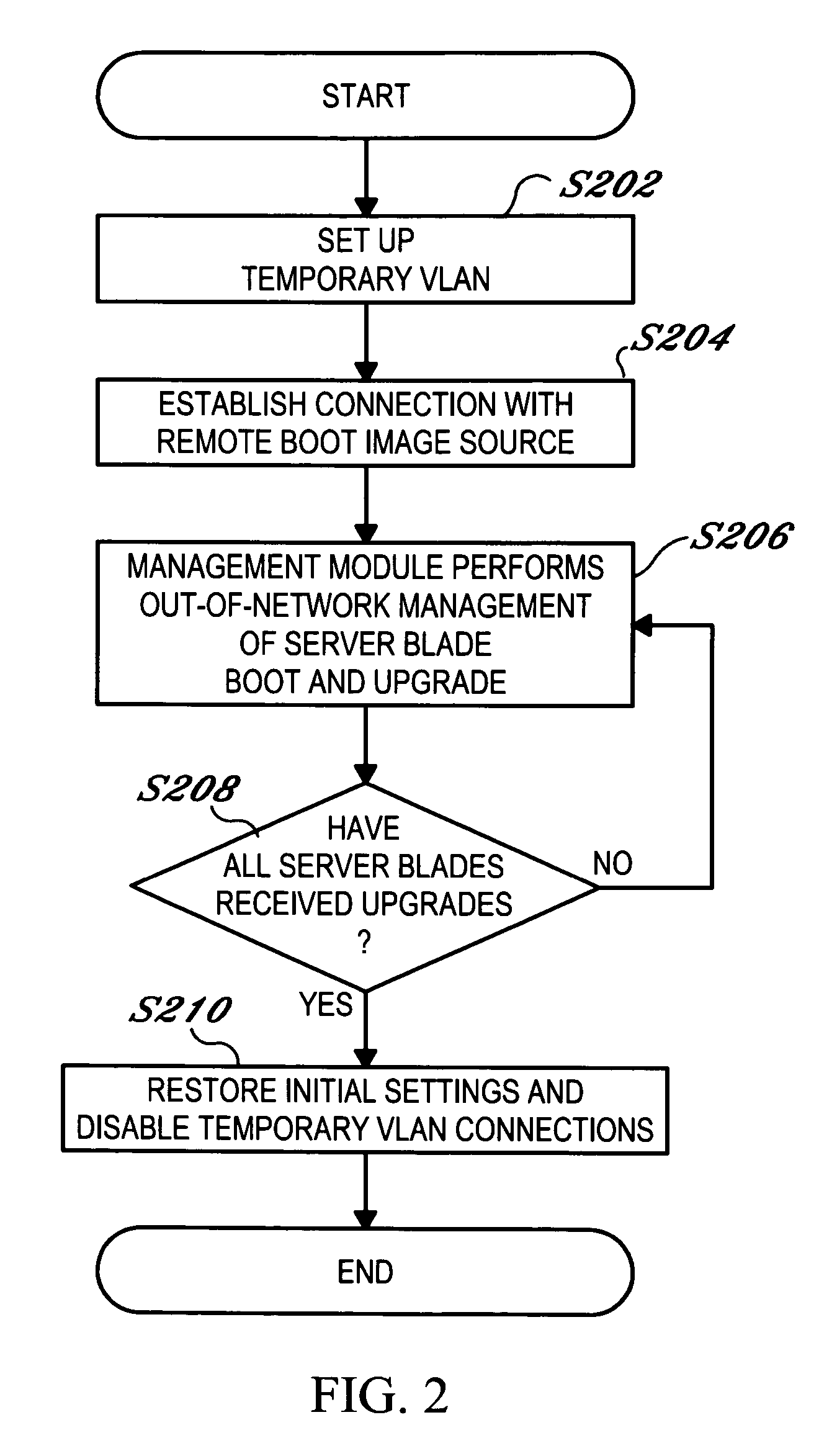
Server blade network boot method that minimizes required network bandwidth
ActiveUS7350068B2Use minimizedMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlNetwork bootingEmbedded system
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
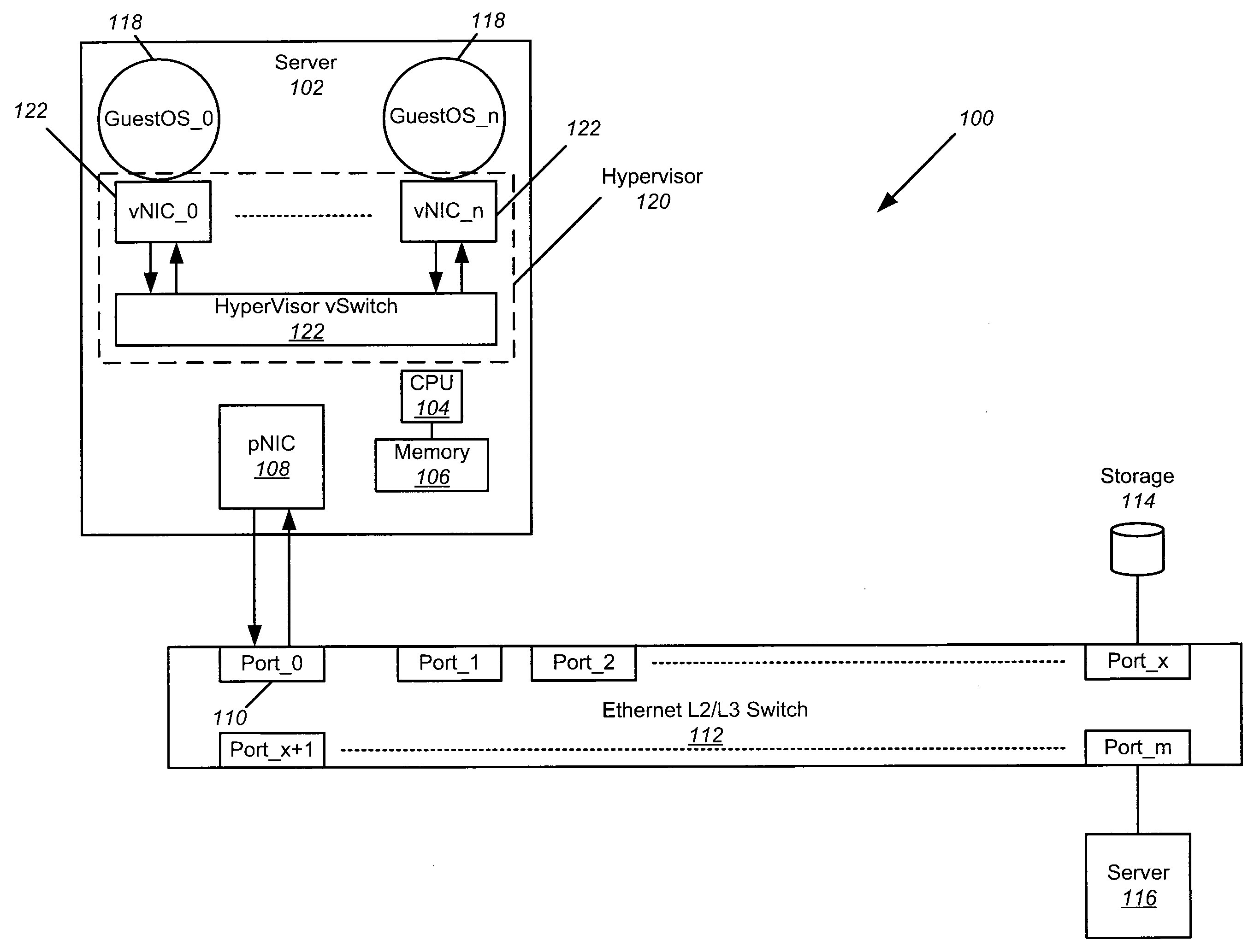
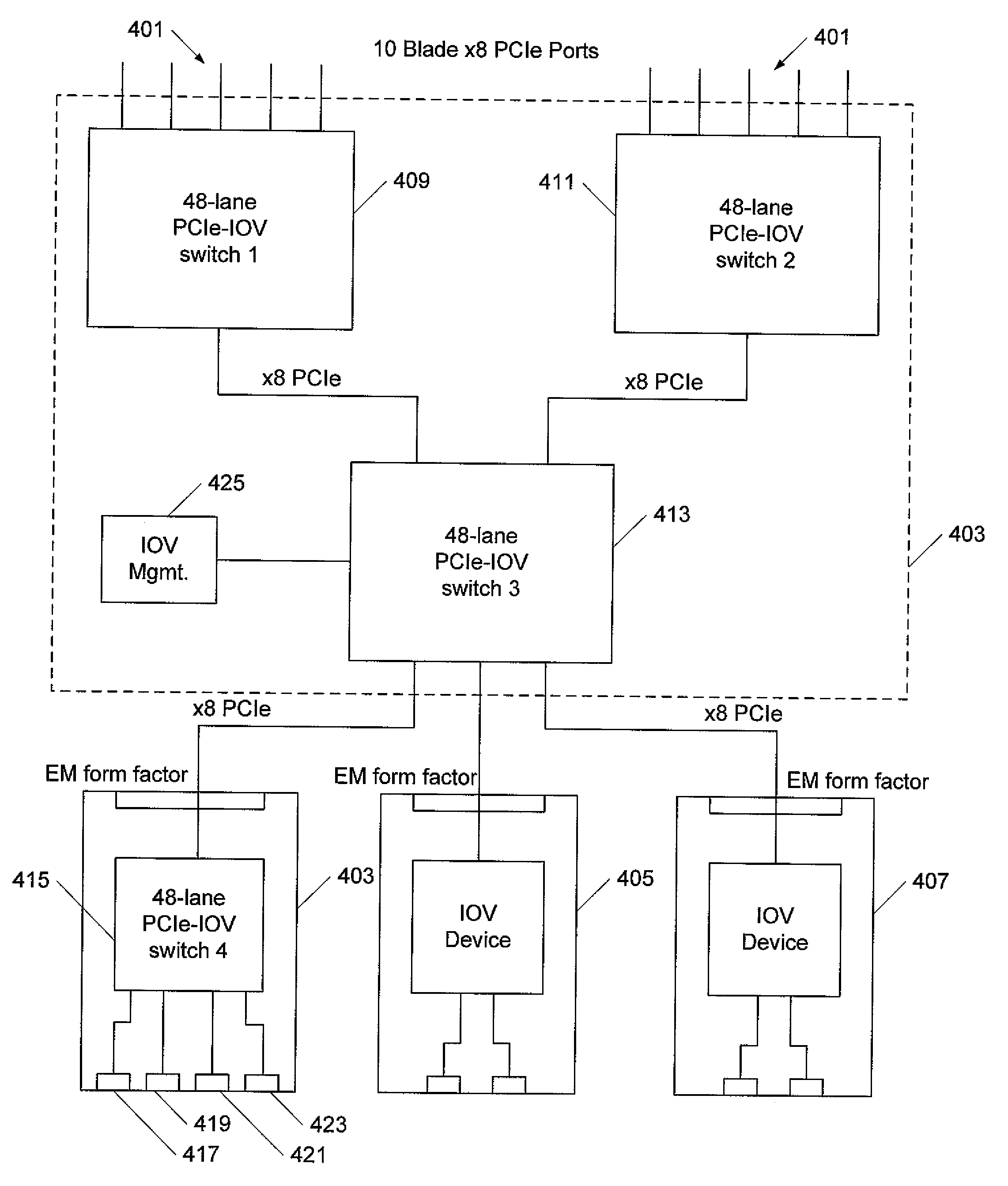
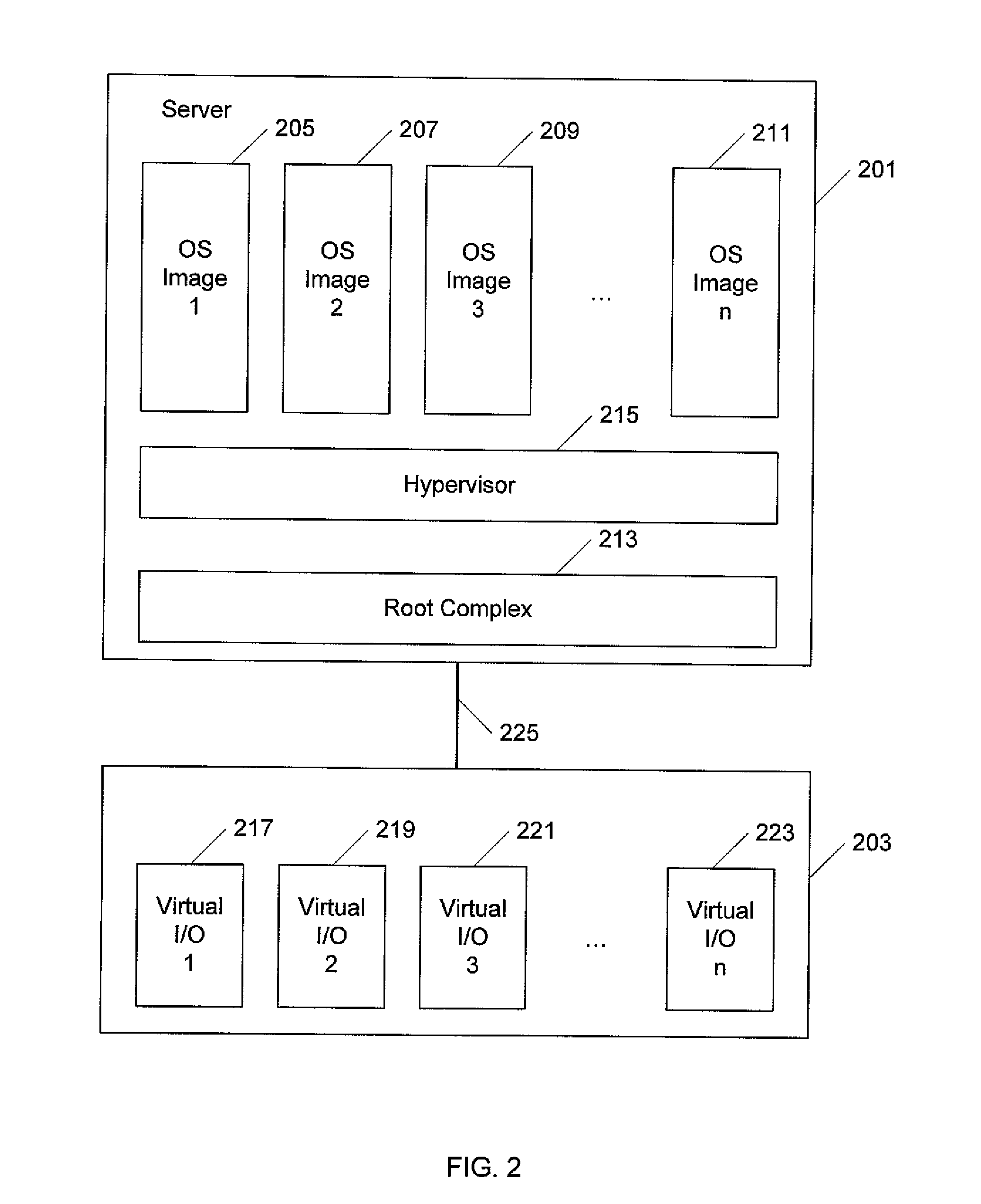
Modular I/O virtualization for blade servers
An apparatus includes a server comprising n operating system images and an IOV aware root complex; a plurality of physical I / O devices comprising n virtual I / O functions; and a PCI Express bus operatively connected to the server and the plurality physical I / O devices via the root complex, wherein the root complex is operable to provide communication between the n operating system images and the n virtual I / O function, and wherein the server and the plurality of physical I / O devices are modules in a chassis.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Method and apparatus for enforcing of power control in a blade center chassis
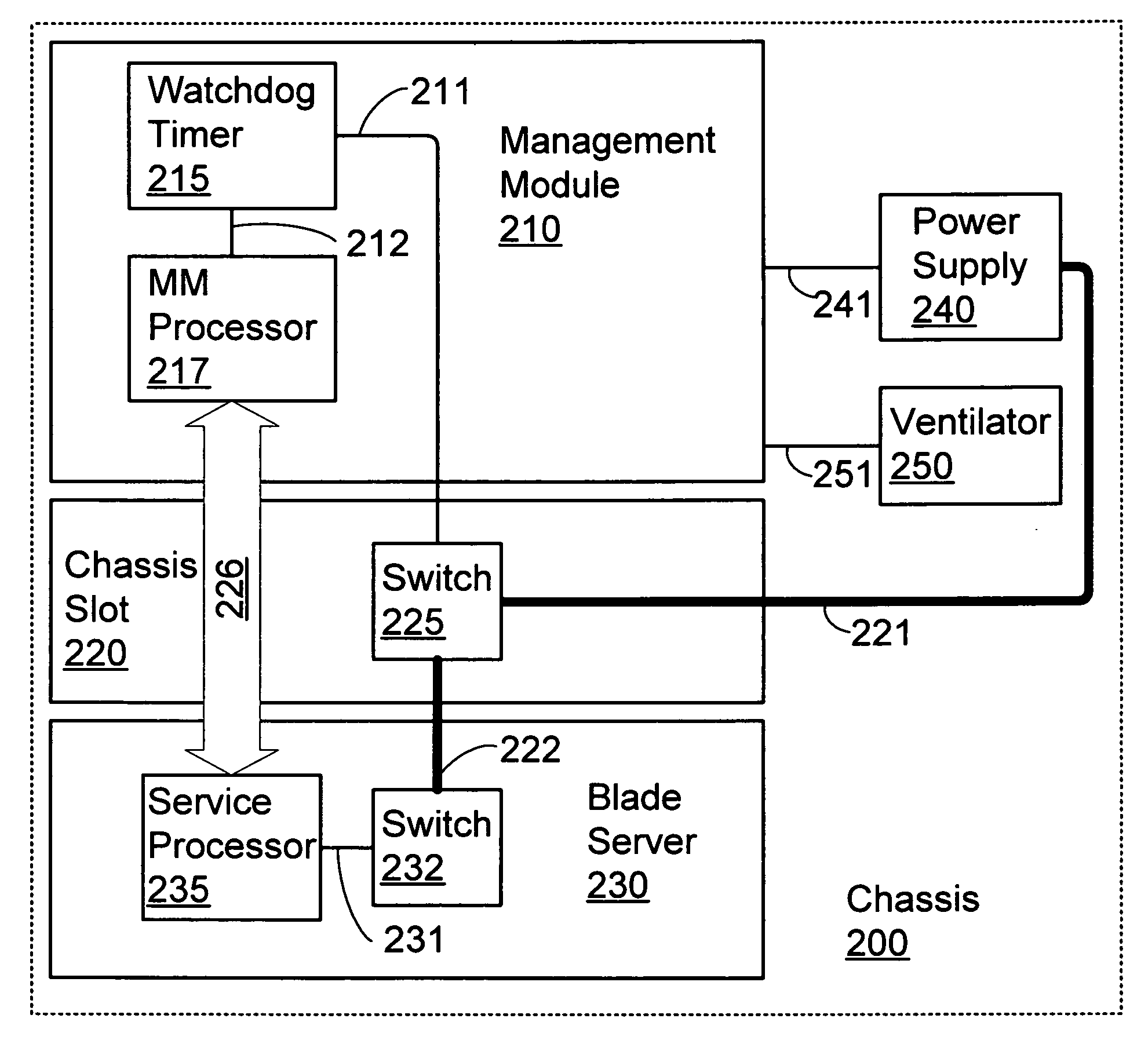
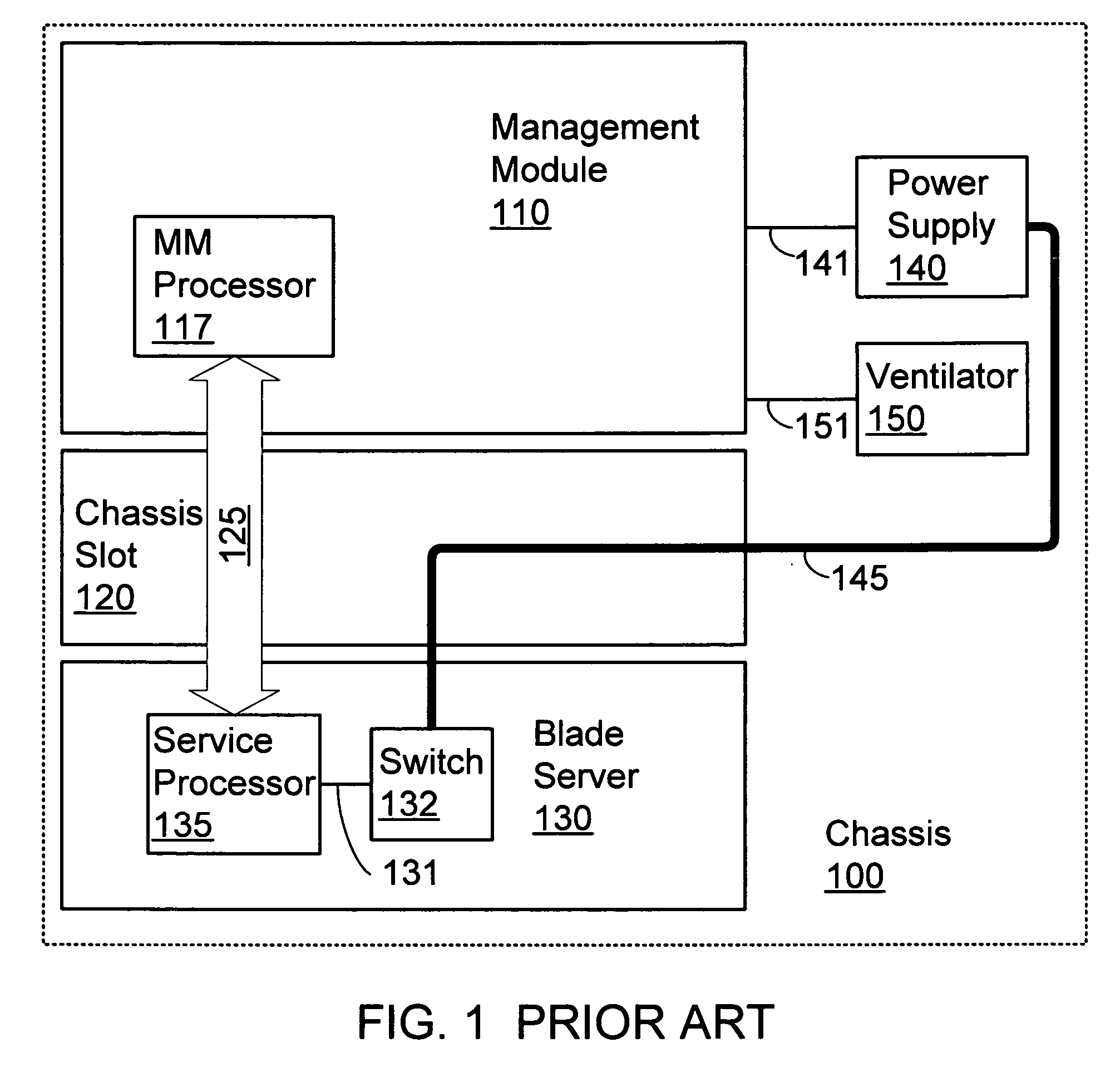
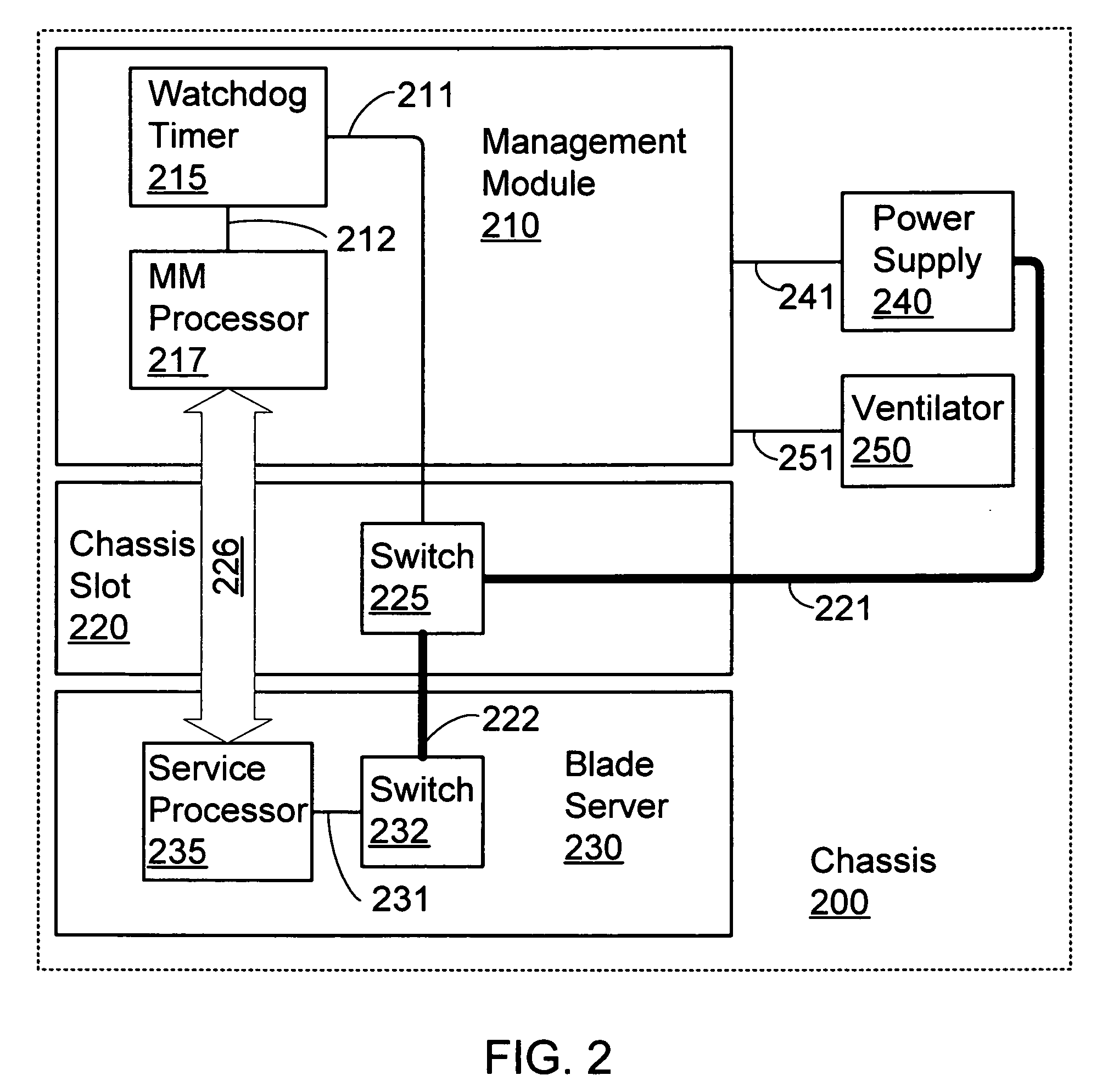
InactiveUS20070047195A1Guaranteed uptimeAvoid failureVolume/mass flow measurementDigital computer detailsEmbedded systemBlade server
A mechanism for changing ownership over the physical power to a blade server in a blade center chassis that prevents a malfunctioning blade from jeopardizing other components in the chassis. When the management module is not present, control over power to the blade is switched to a service processor on the blade. This arbitration of control over power to a blade is accomplished by implementing a watchdog timer mechanism. The management module is responsible for tickling the watchdog timer when the present in the chassis and operating normally. This mechanism provides the management module with control over power. If the management module malfunctions or is removed, control over power is switched to the local service processor on the blade server as soon as the watchdog timer is not tickled.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com