Patents
Literature
142 results about "Root complex" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
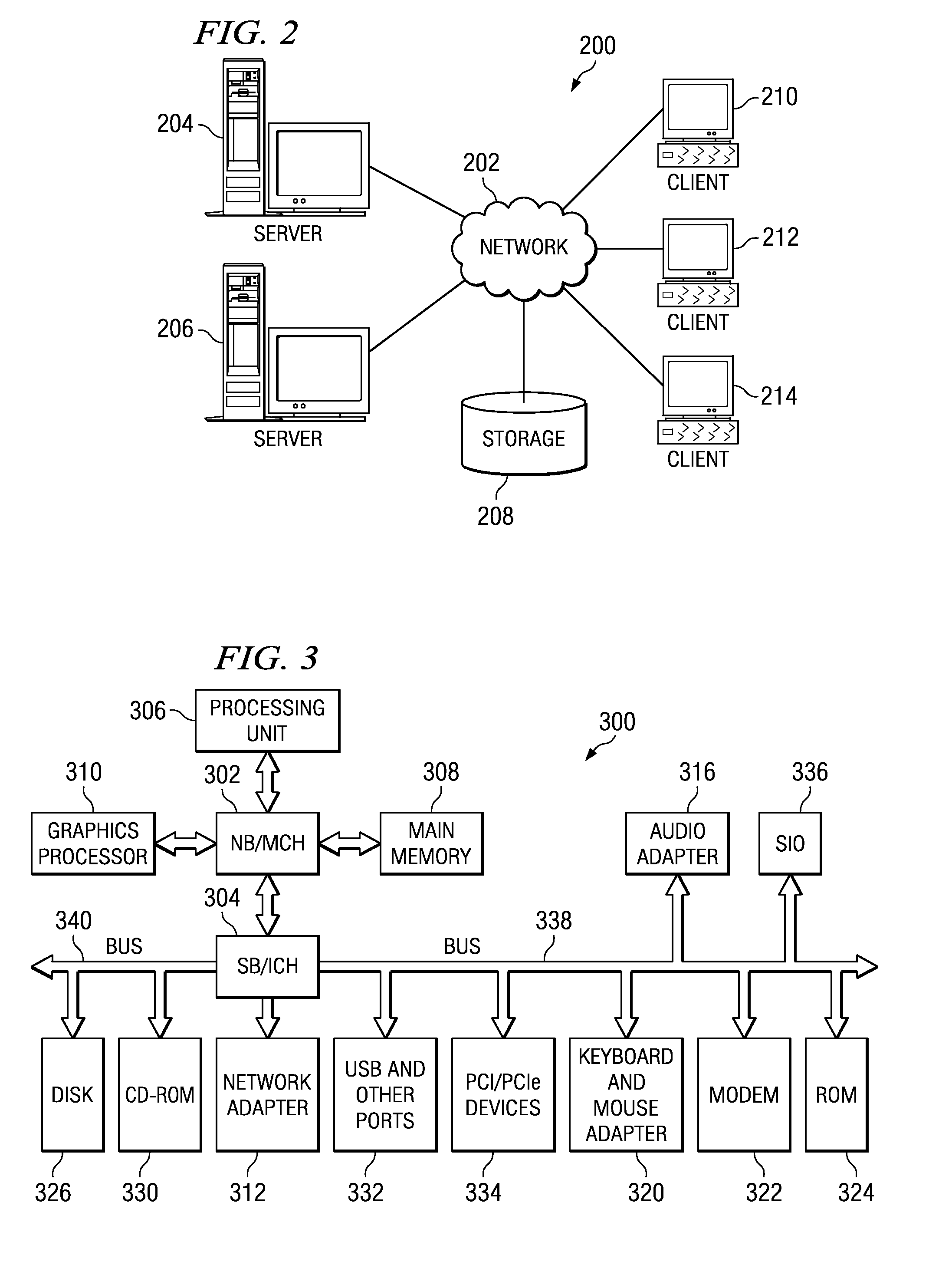
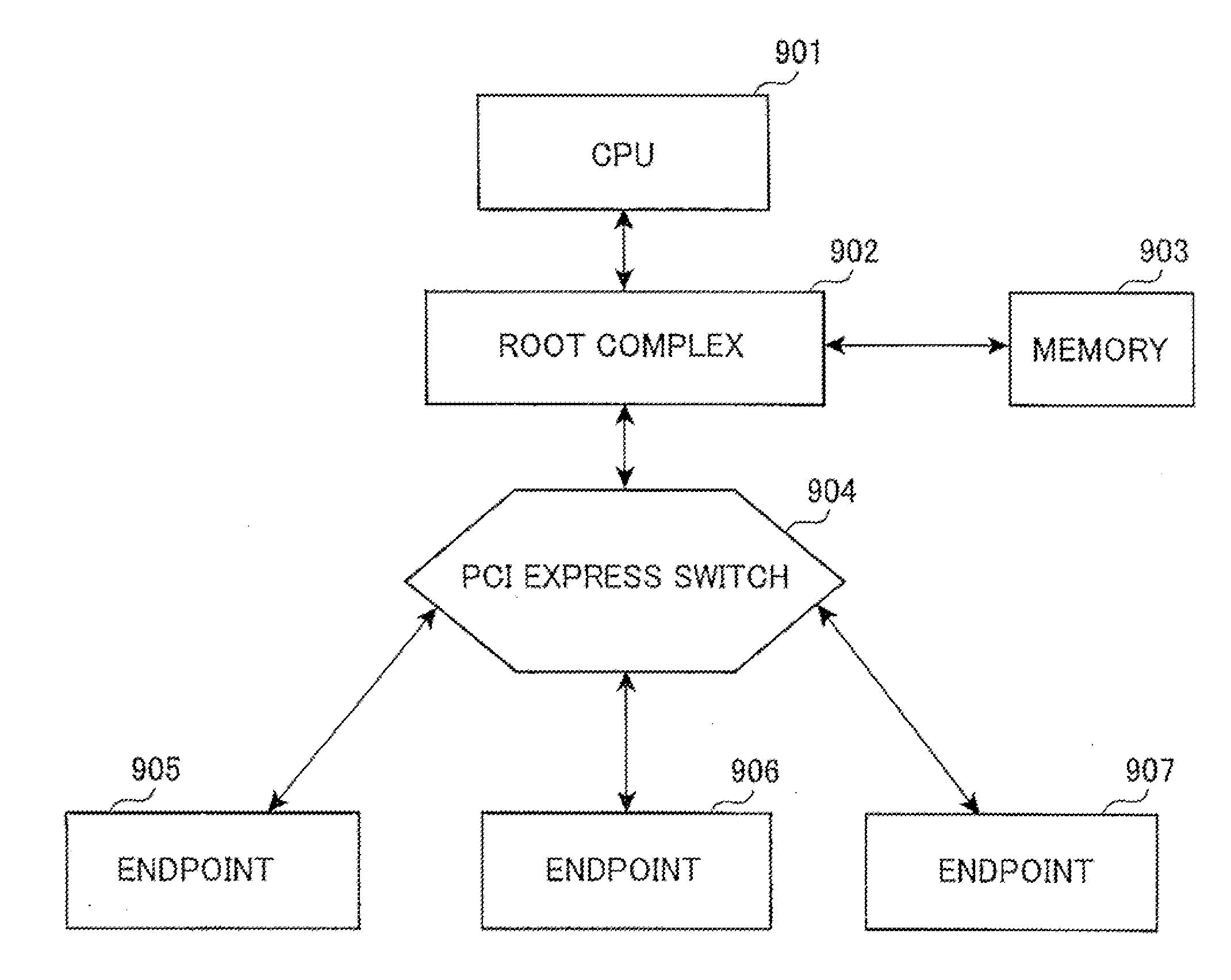
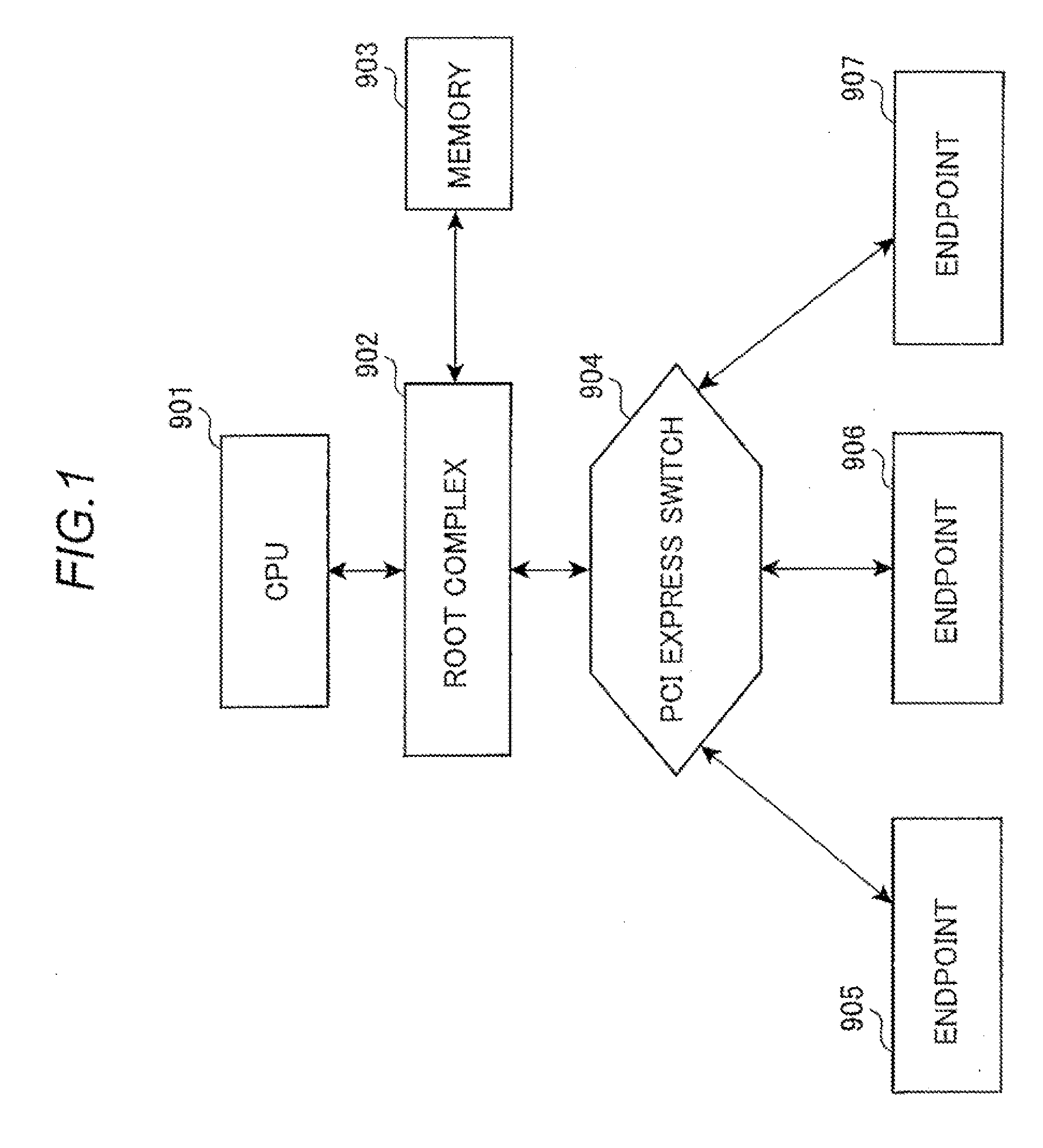
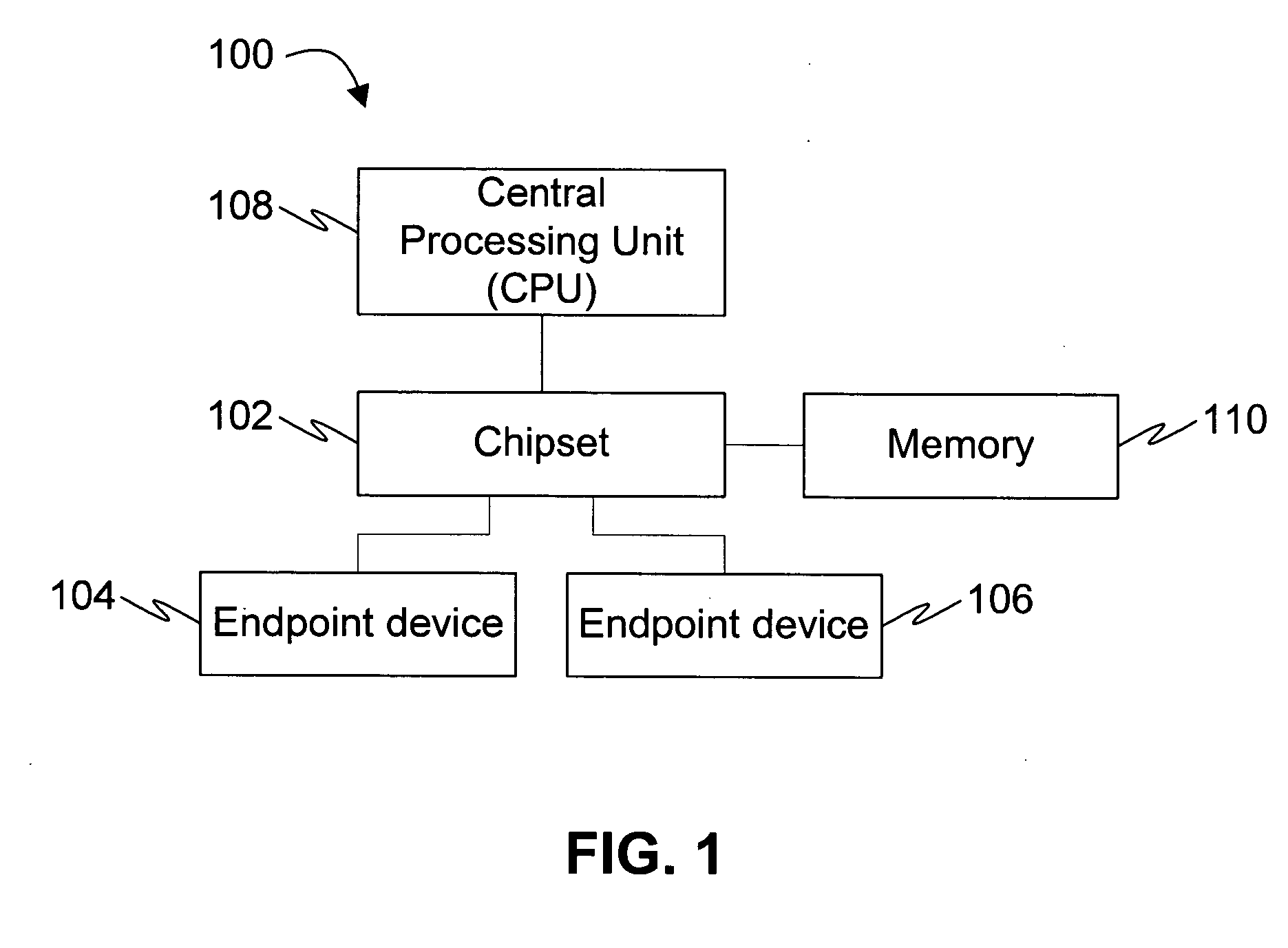
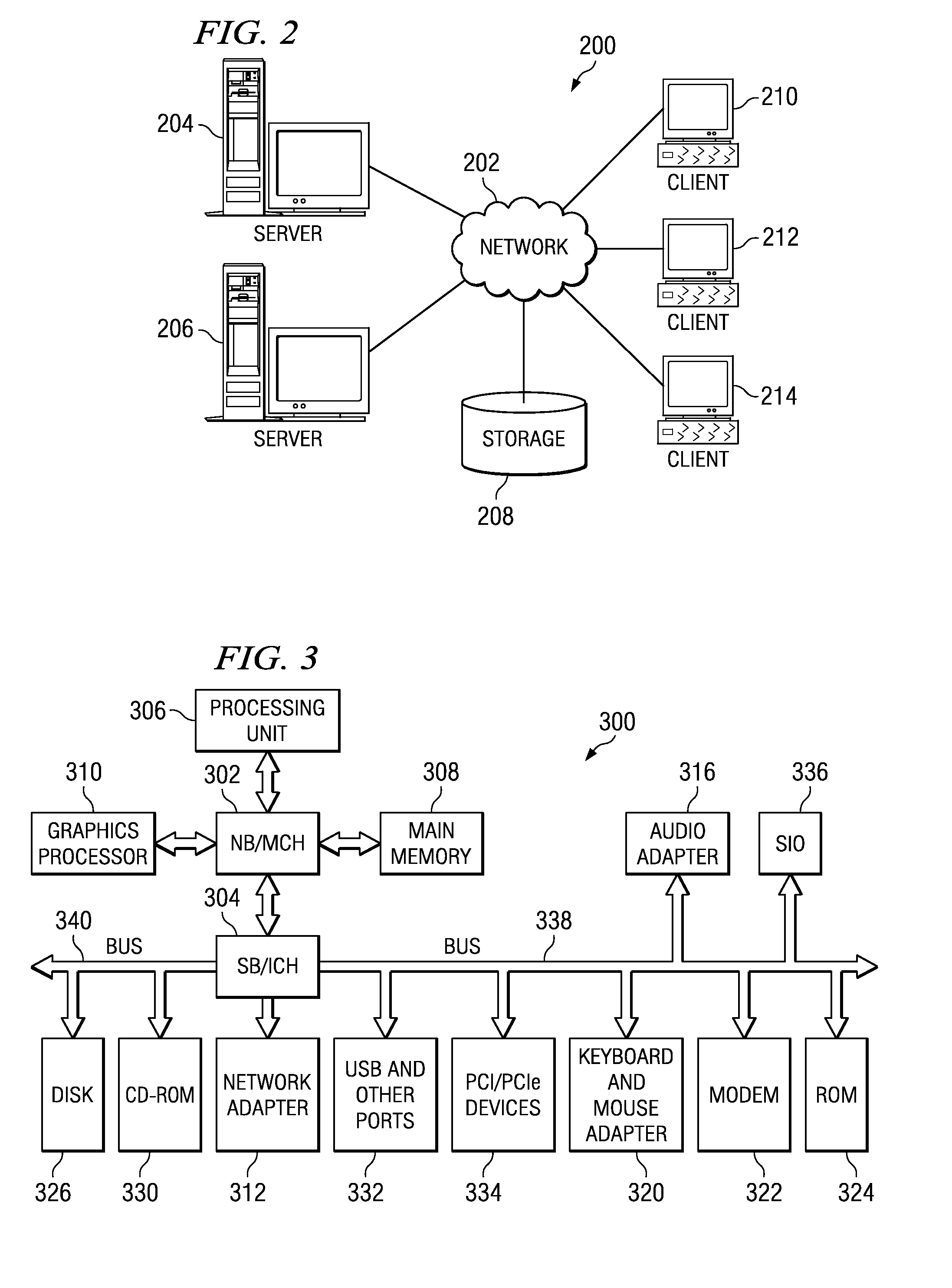
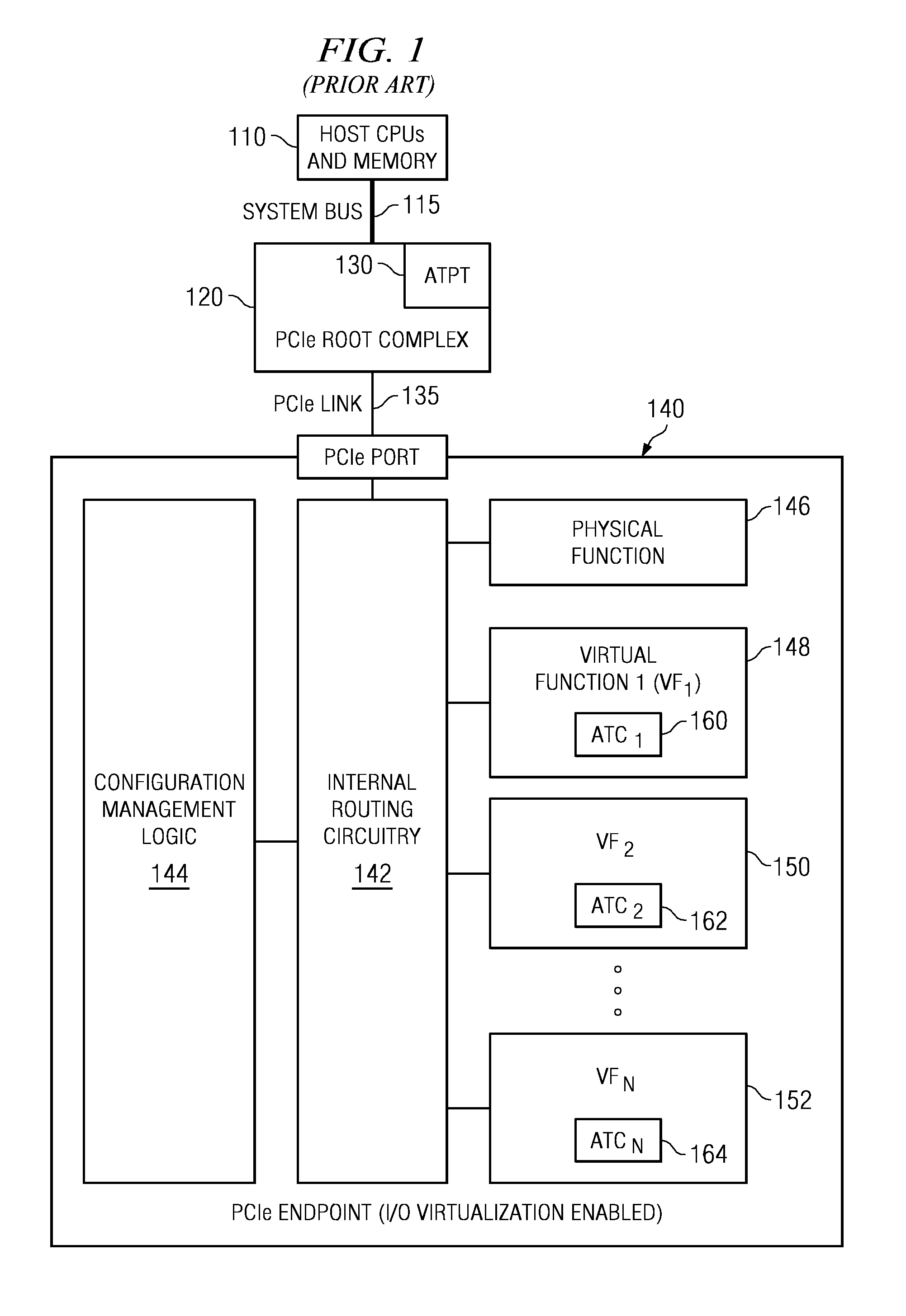
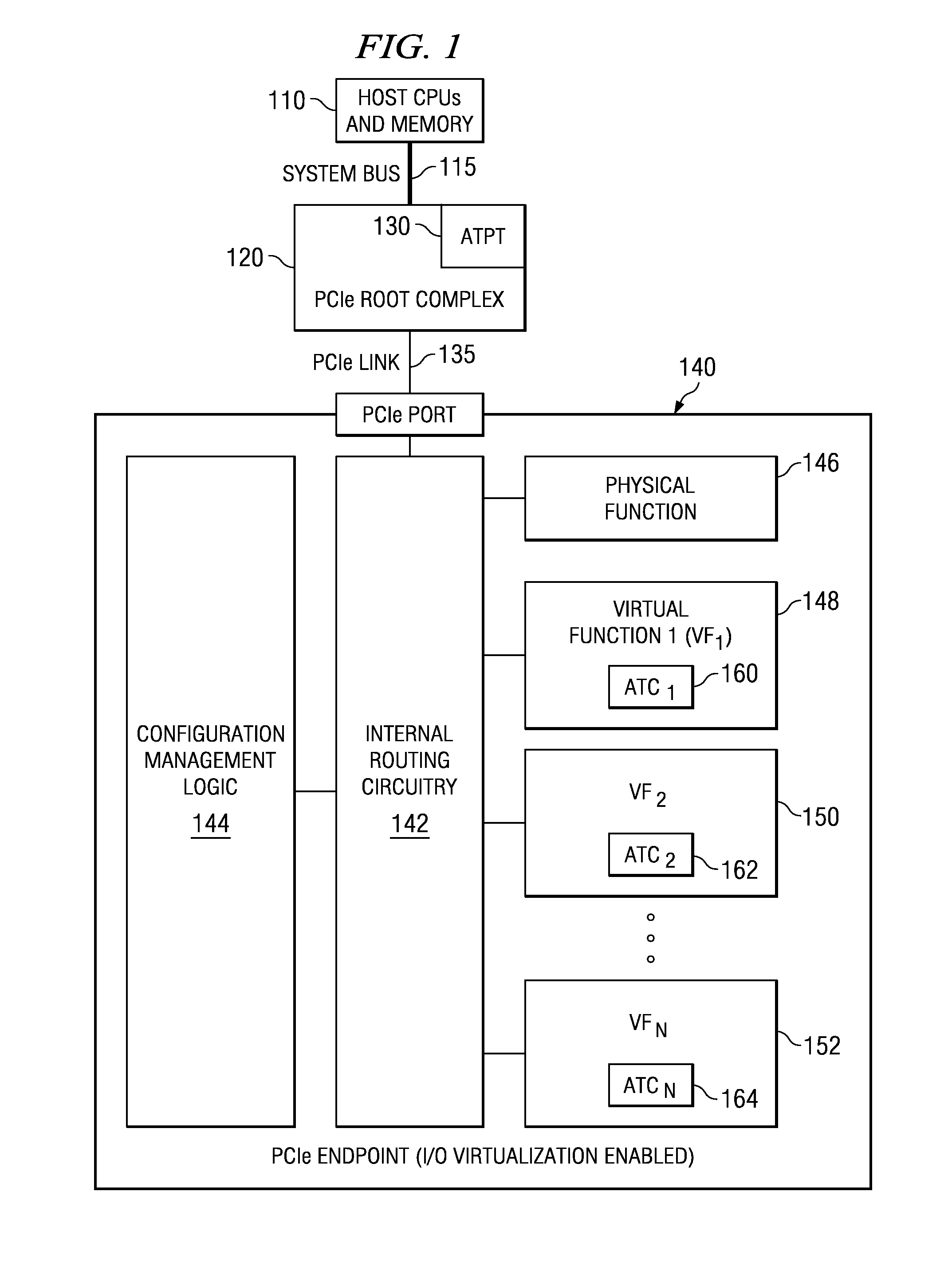
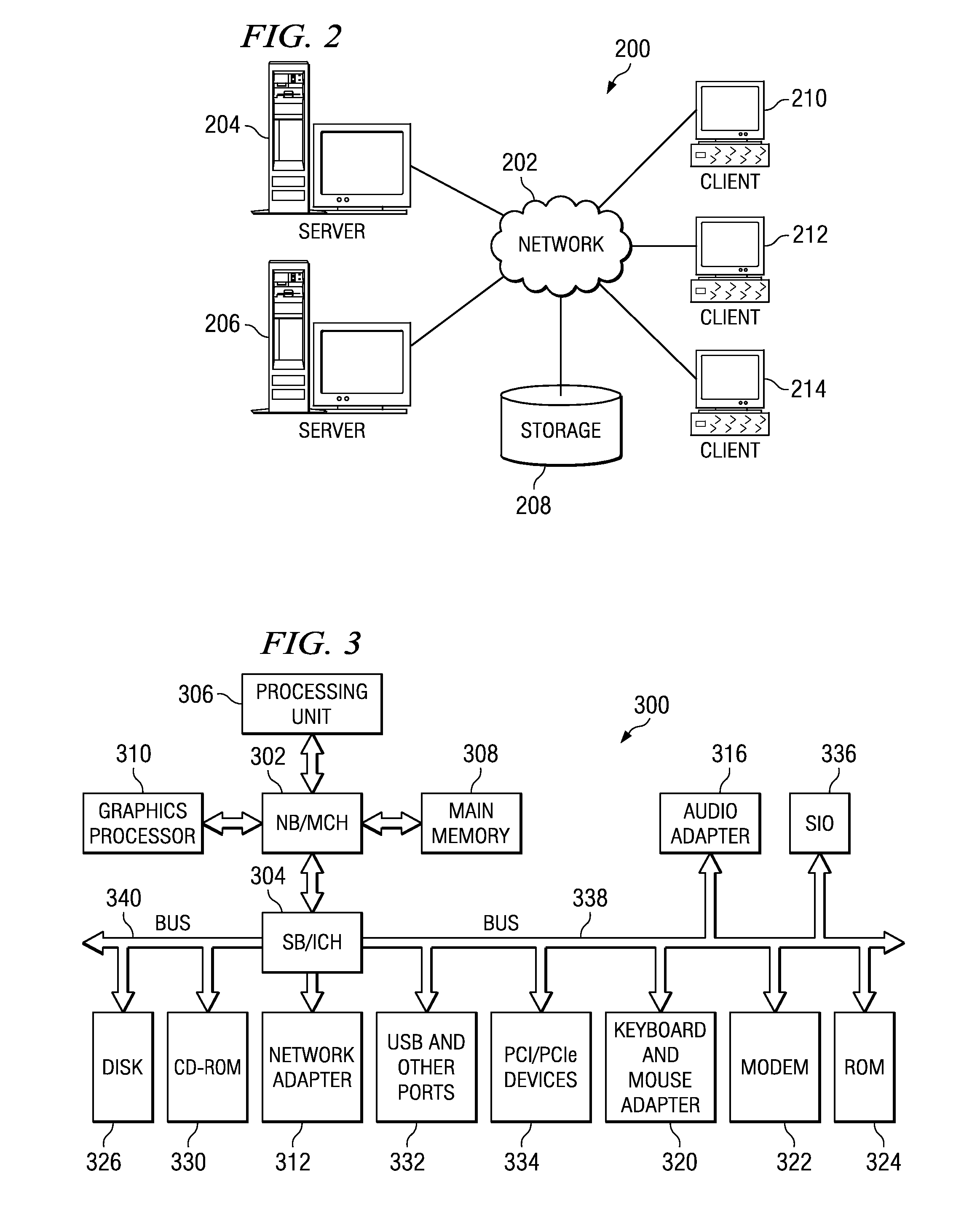
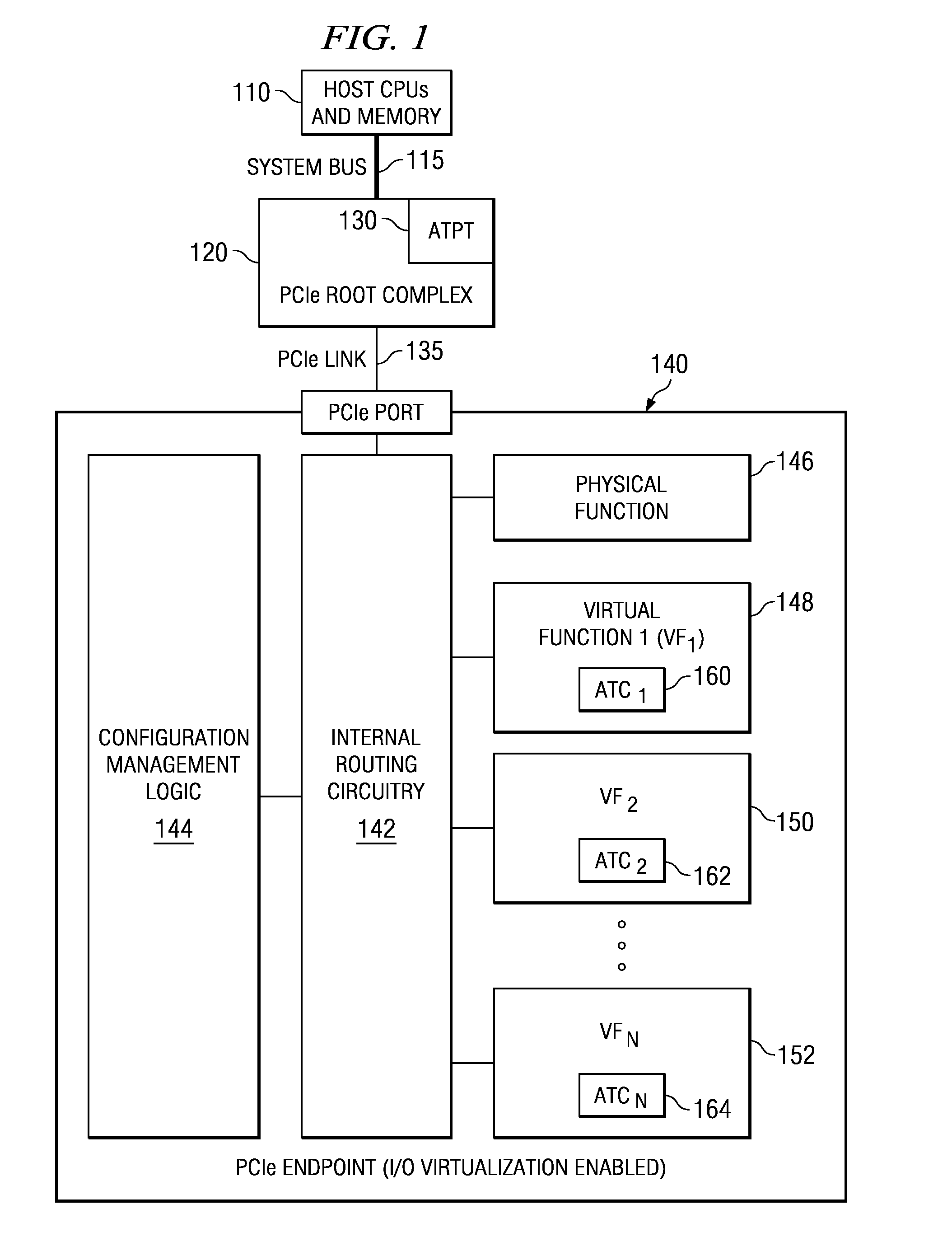
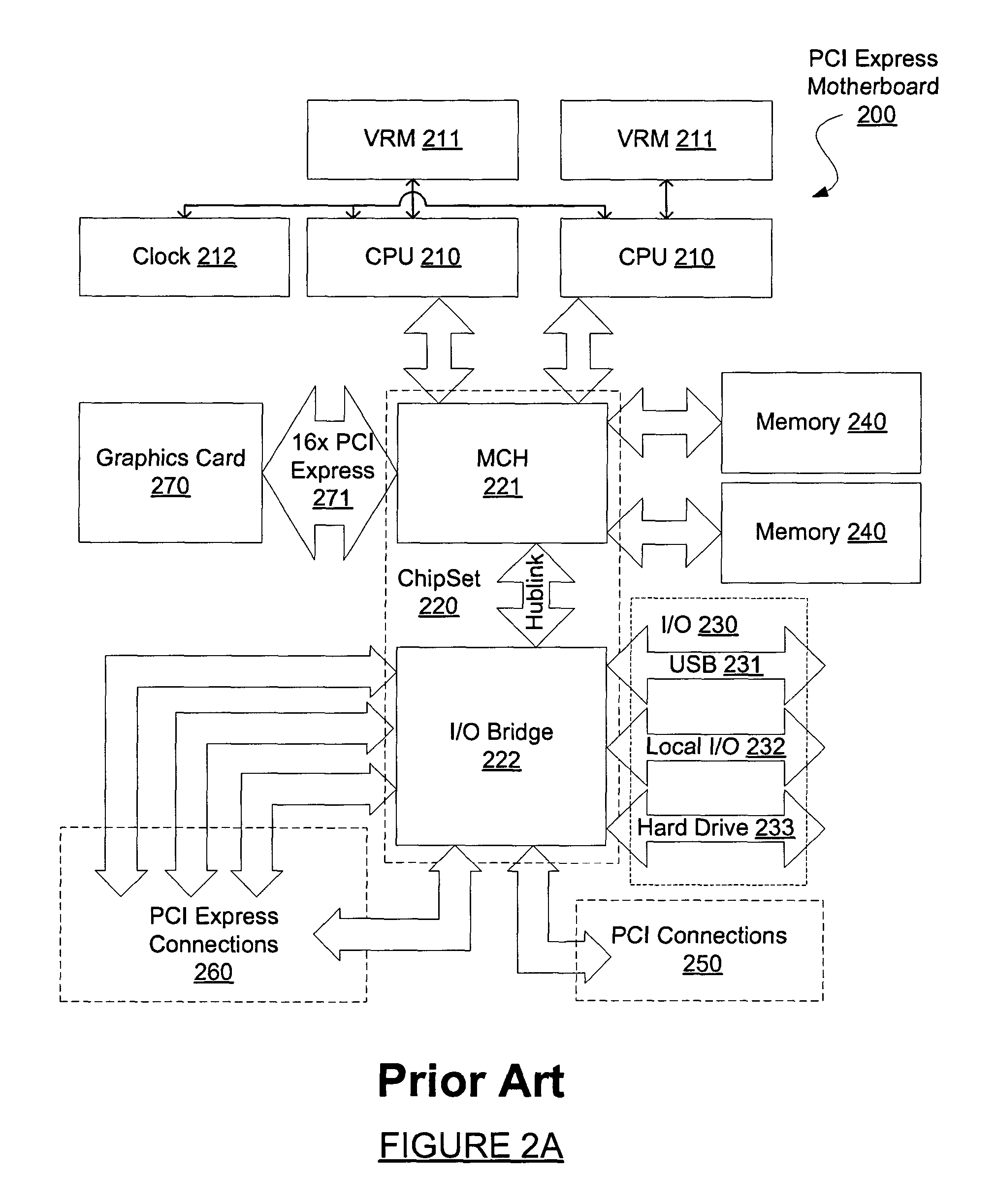
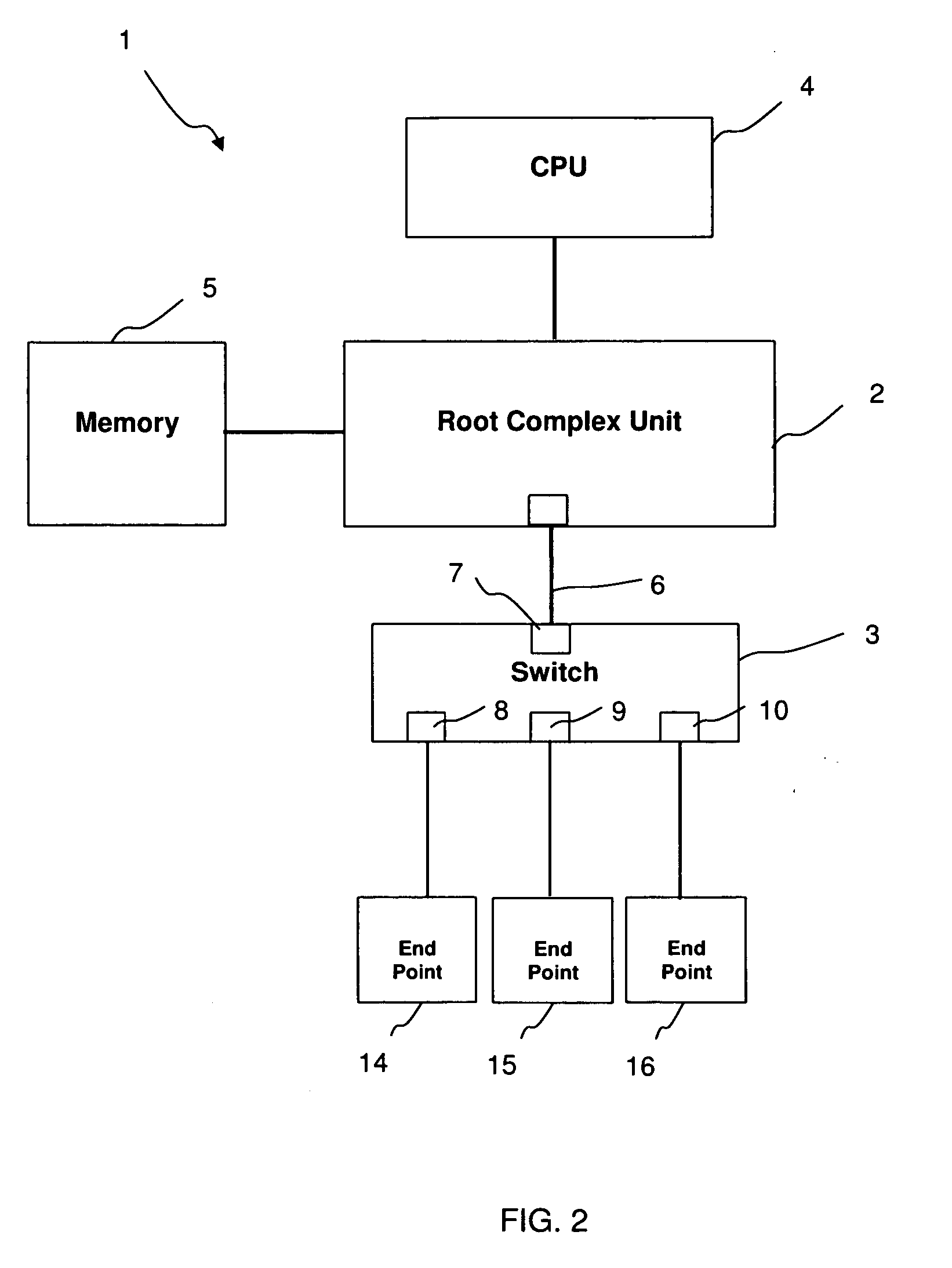
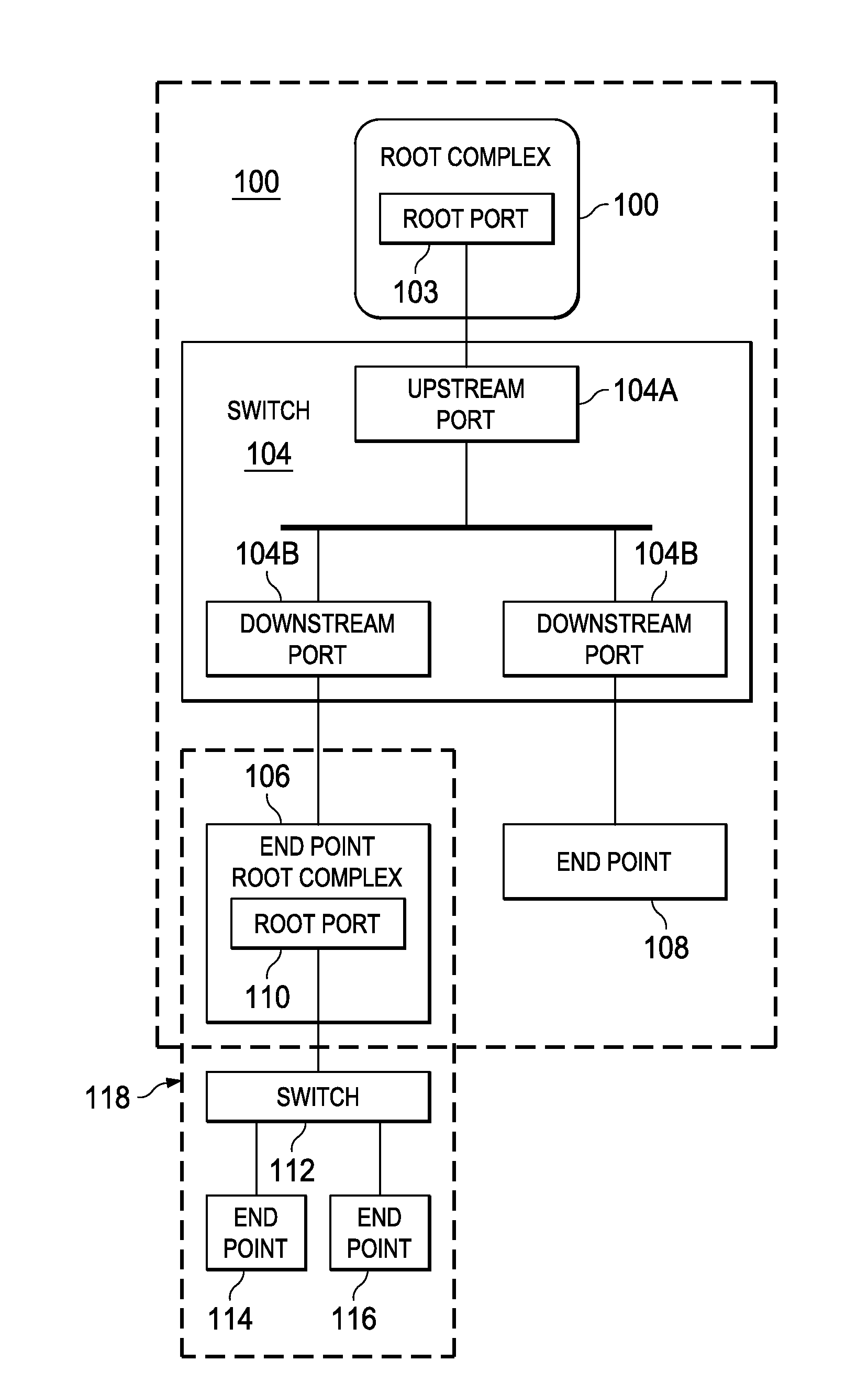
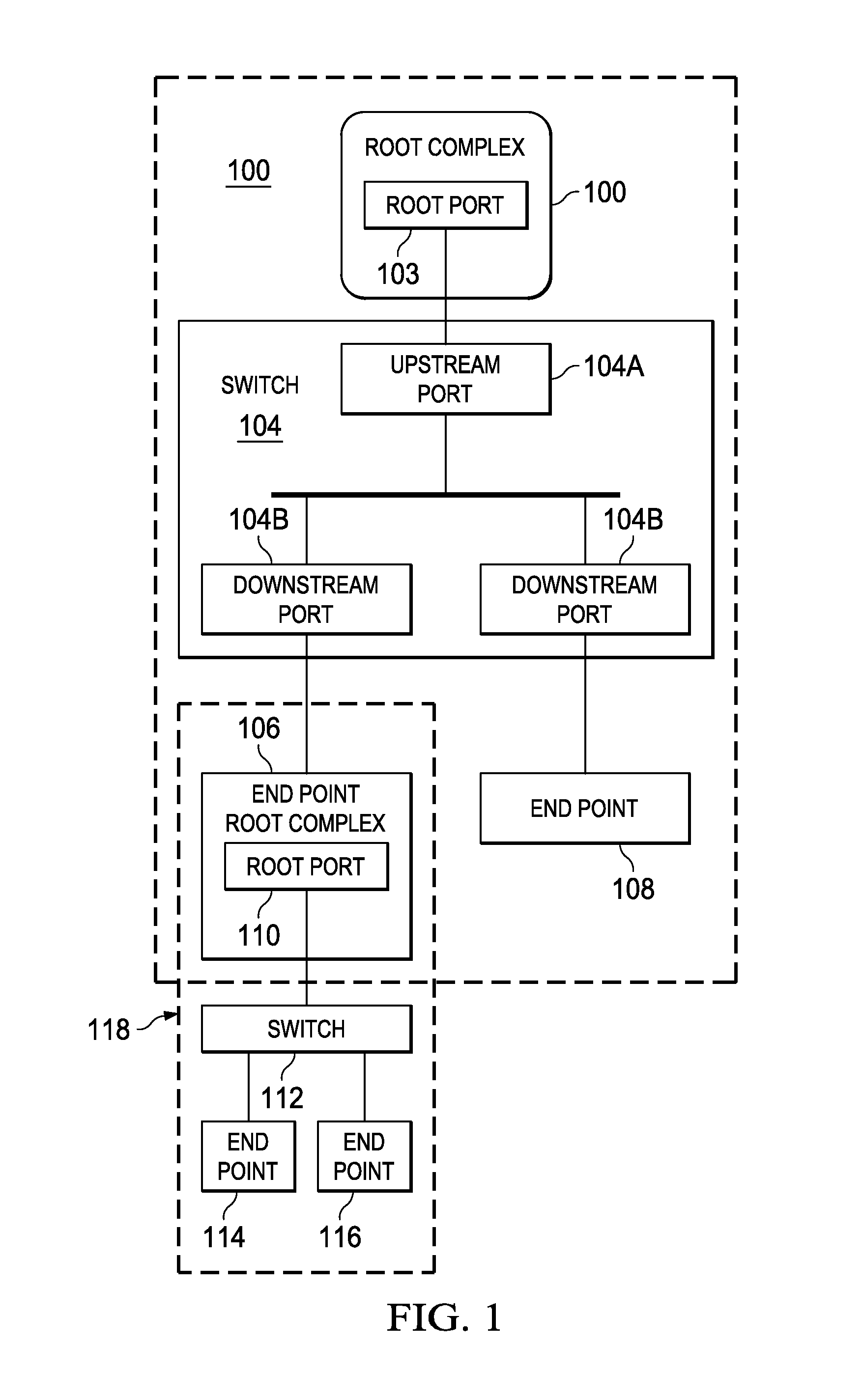
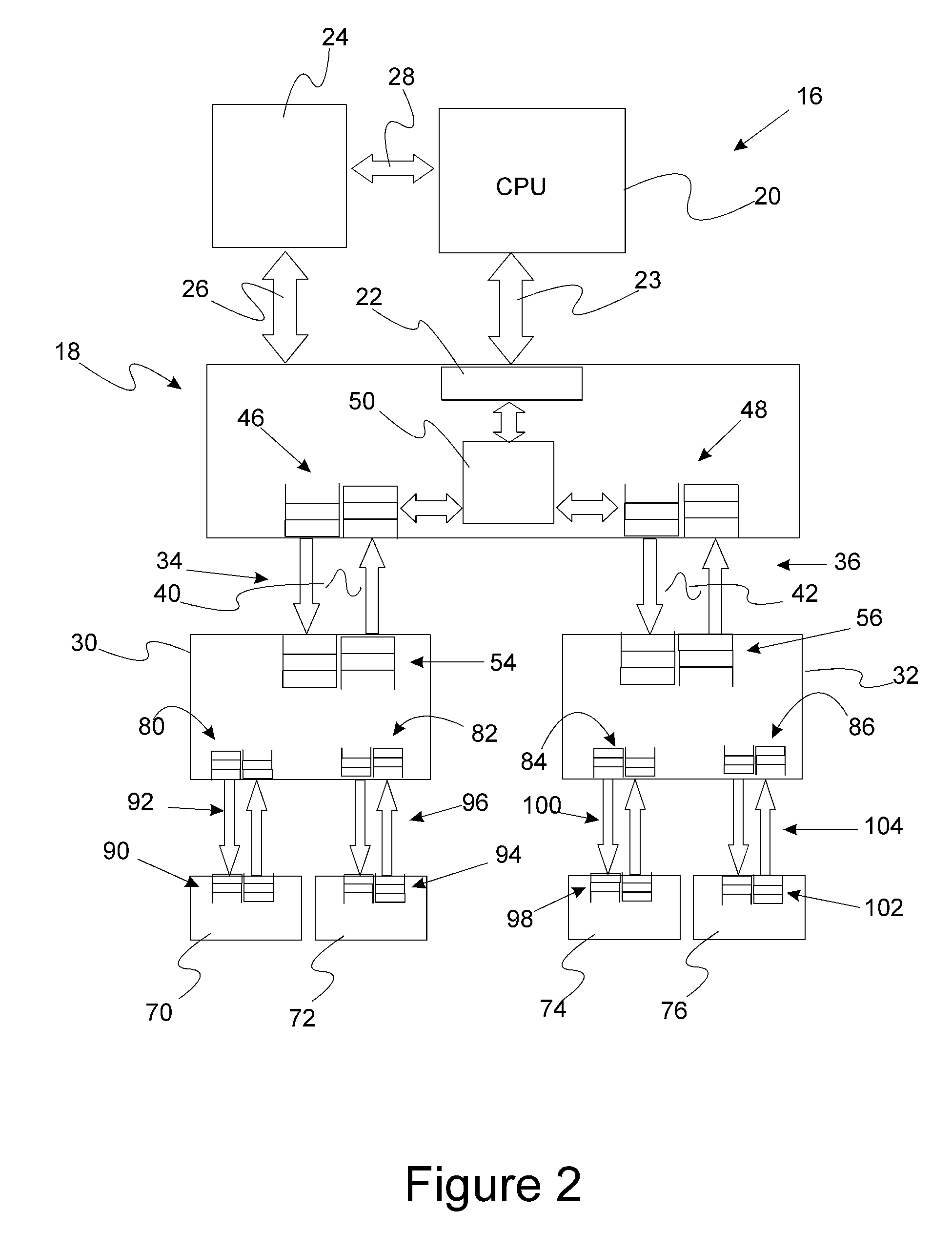
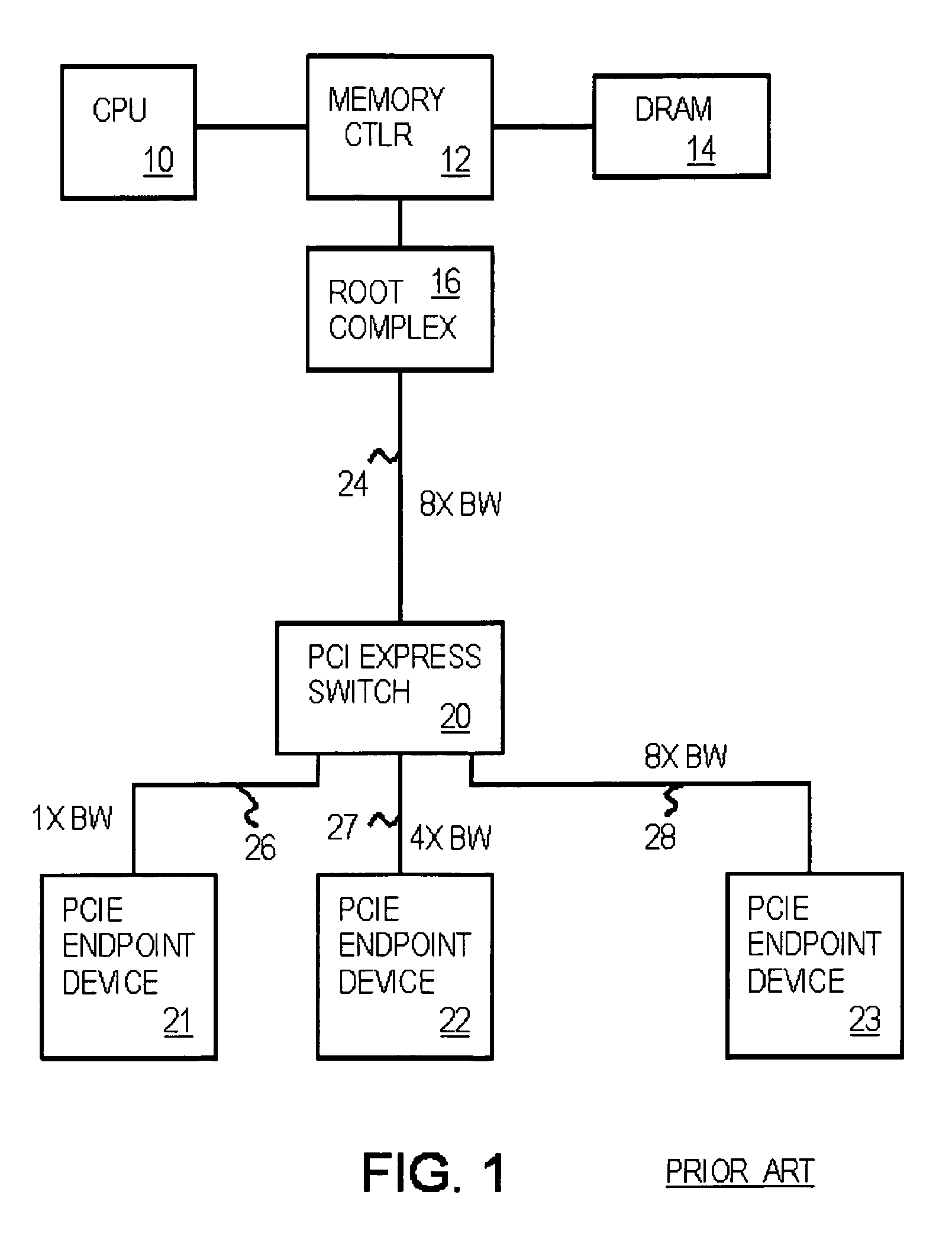
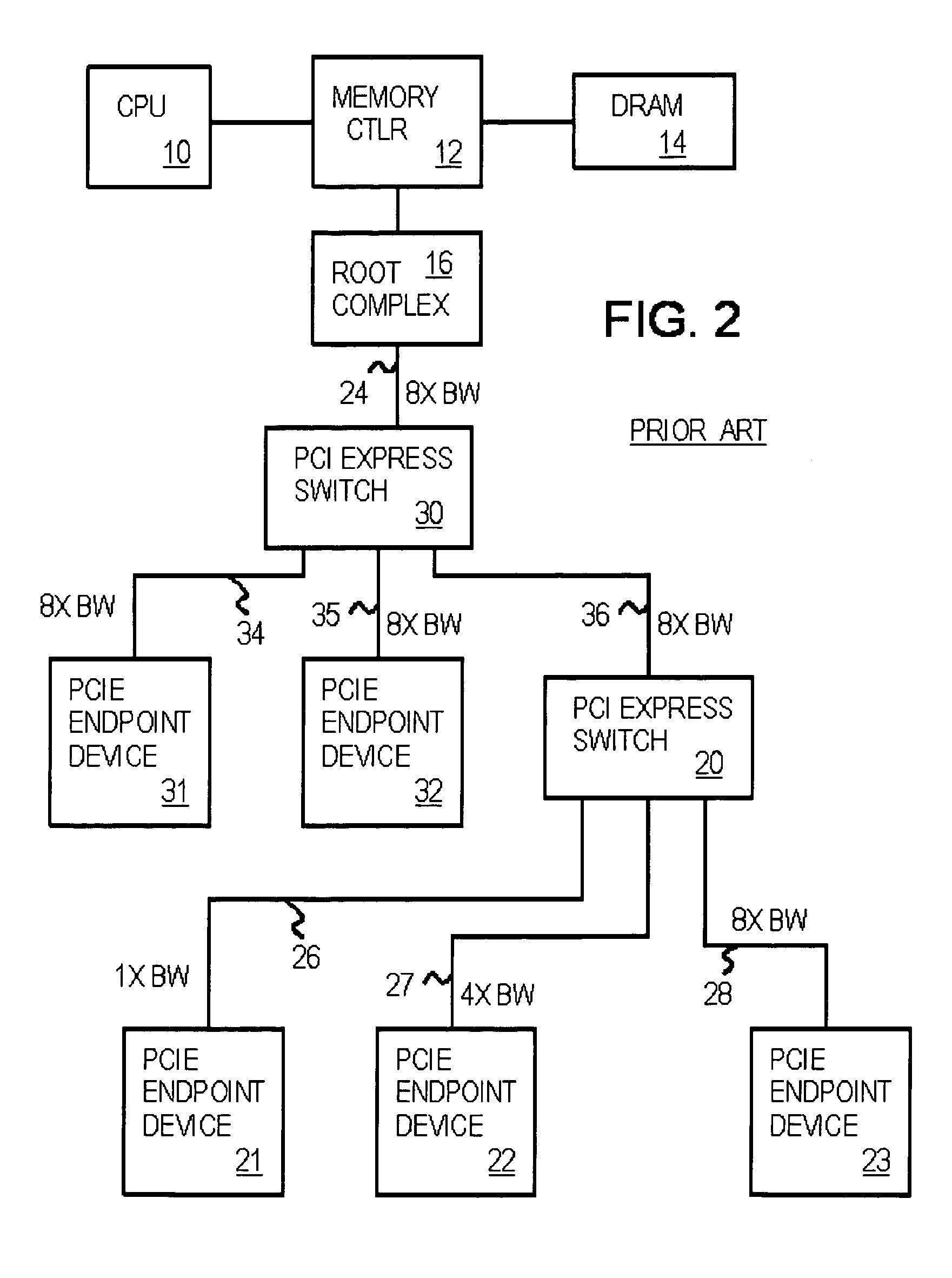
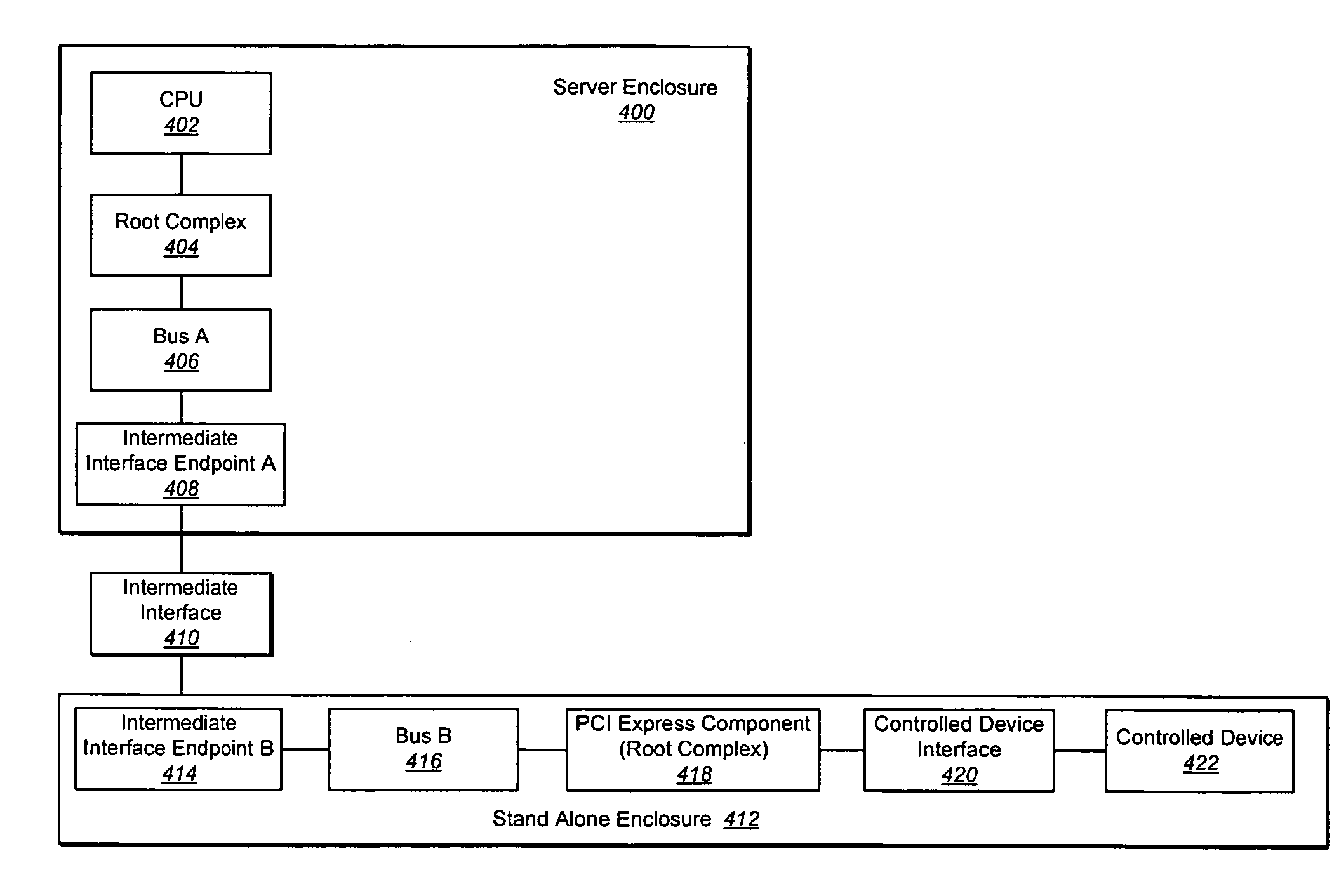
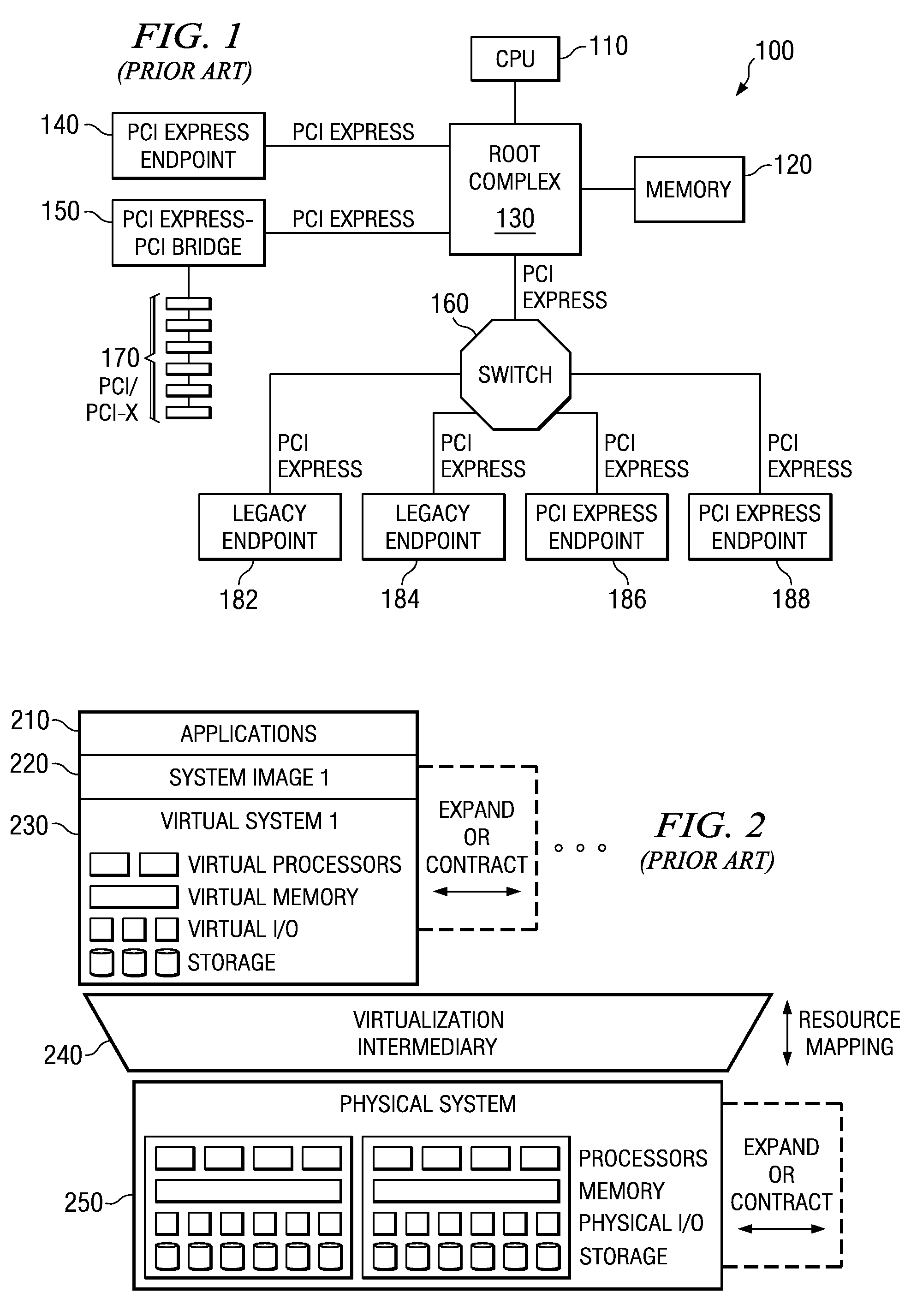
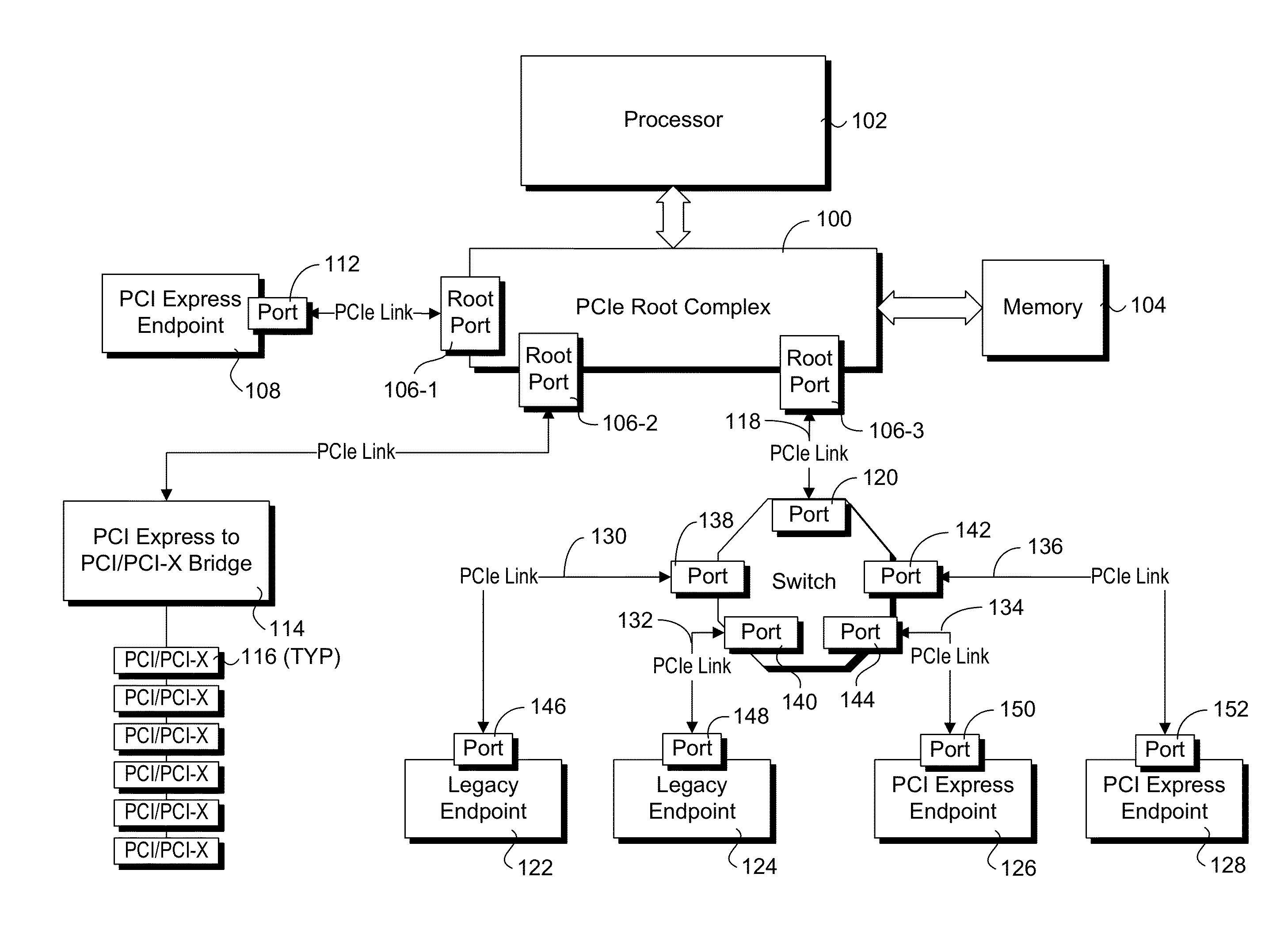
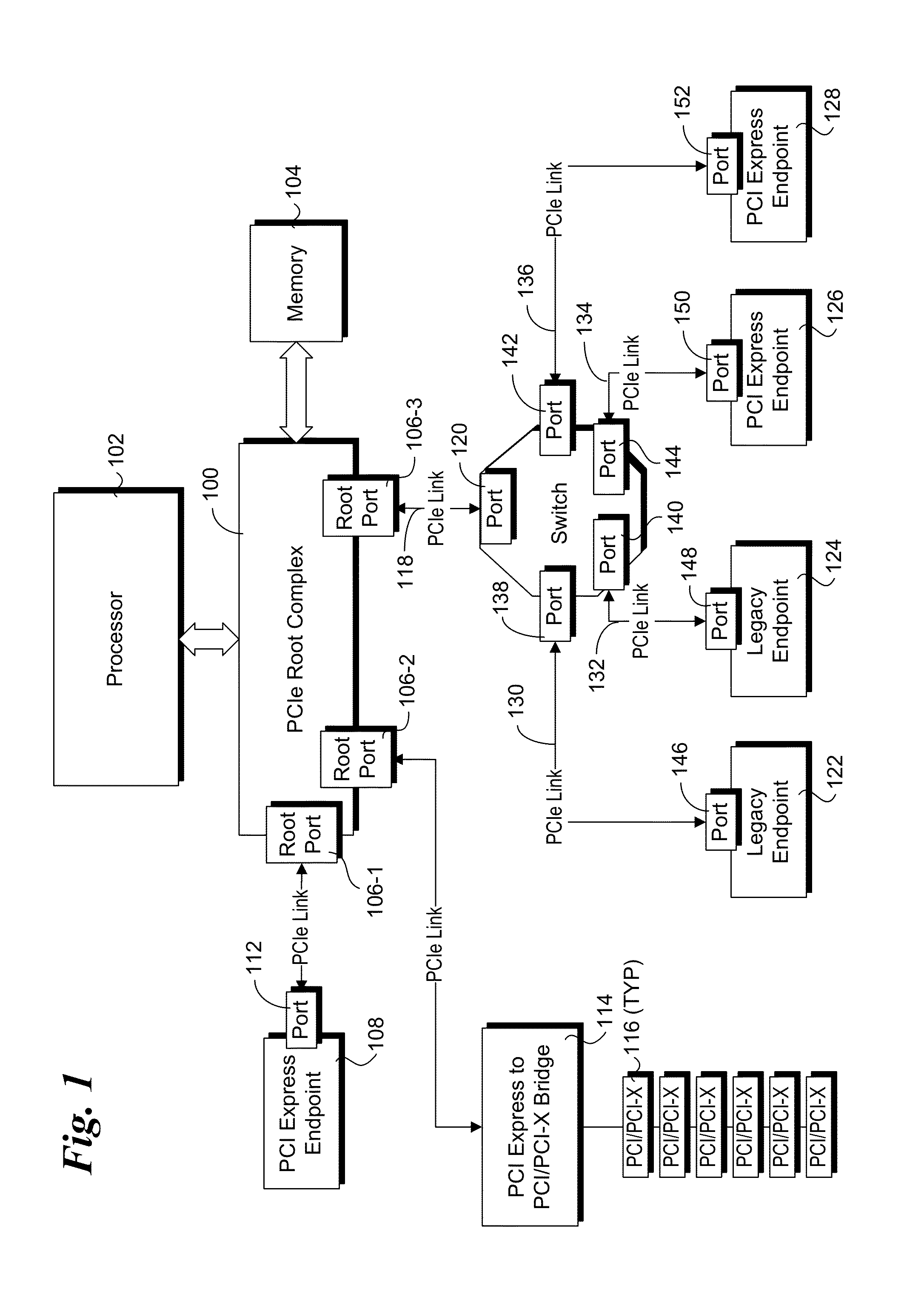
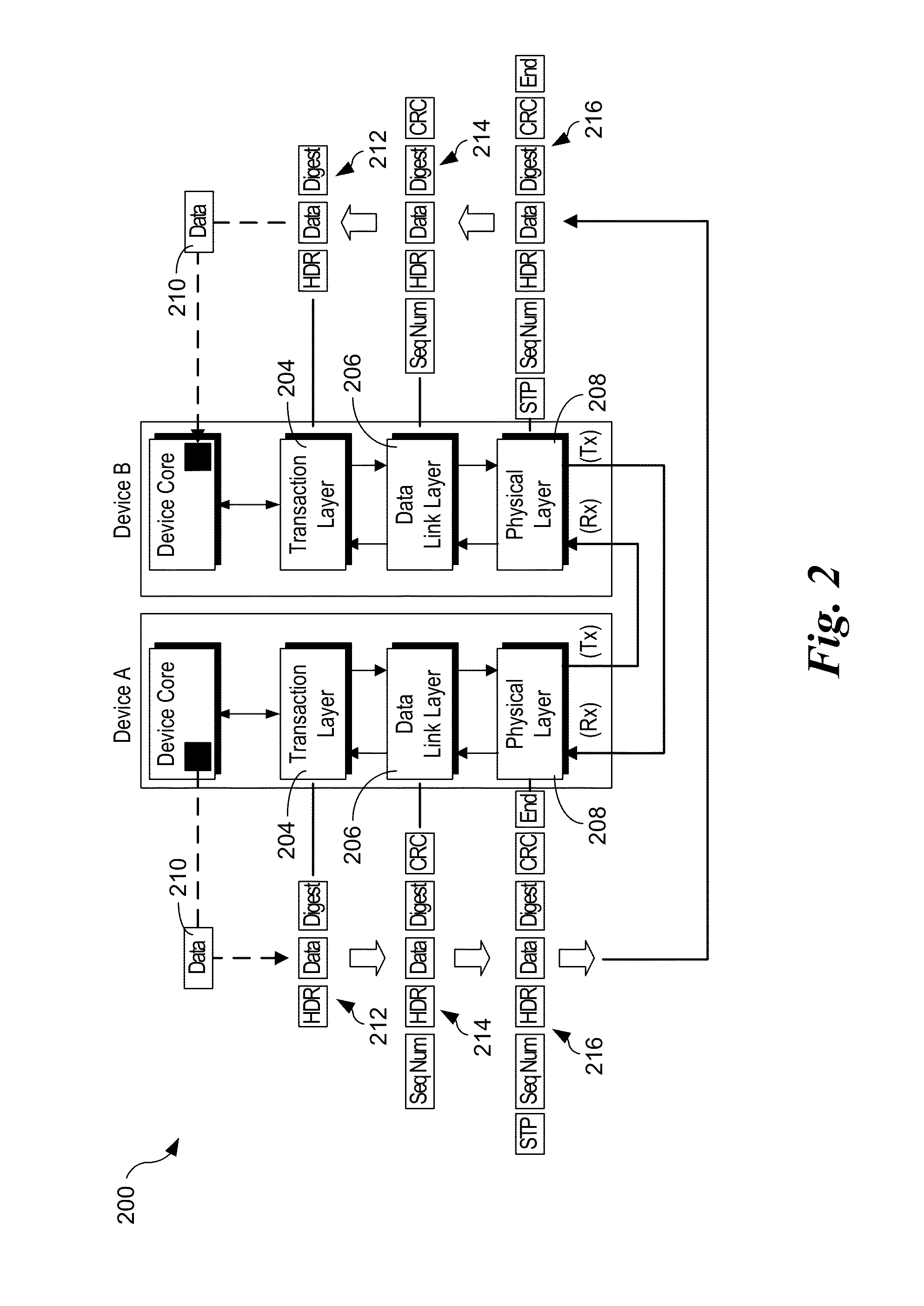
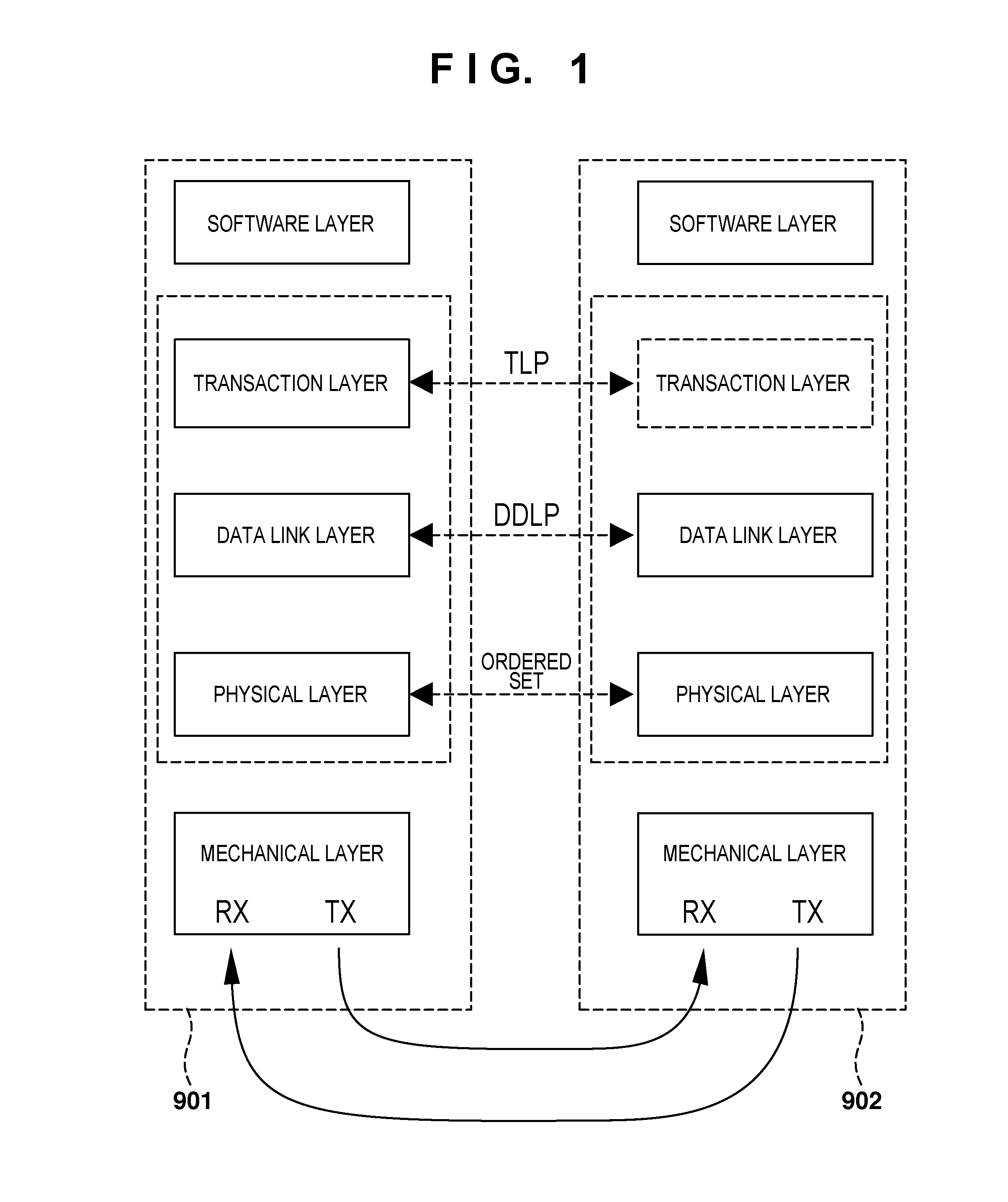
In a PCI Express (PCIe) system, a root complex device connects the processor and memory subsystem to the PCI Express switch fabric composed of one or more switch devices. Similar to a host bridge in a PCI system, the root complex generates transaction requests on behalf of the processor, which is interconnected through a local bus. Root complex functionality may be implemented as a discrete device, or may be integrated with the processor. A root complex may contain more than one PCI Express port and multiple switch devices can be connected to ports on the root complex or cascaded.
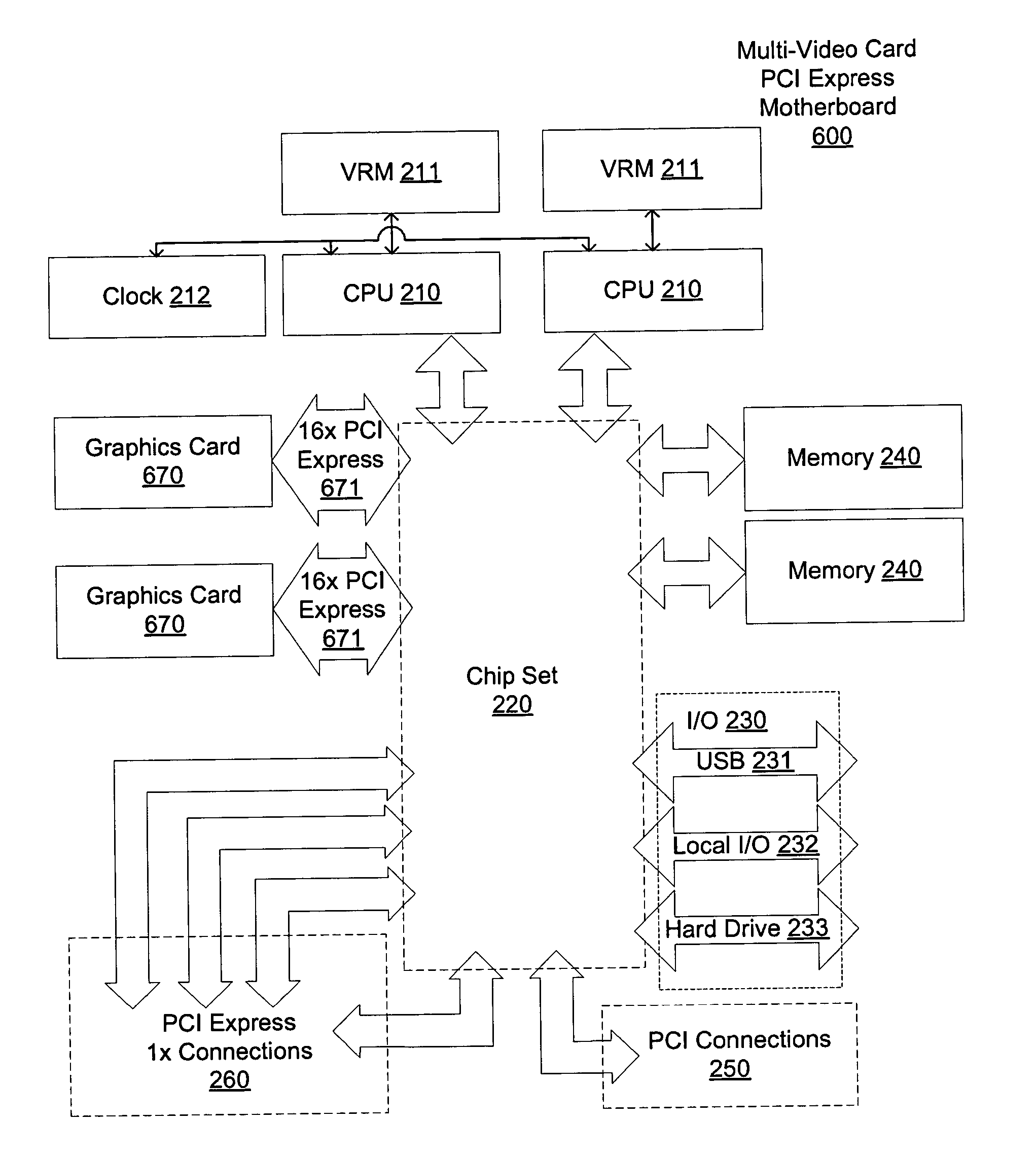
Motherboard for supporting multiple graphics cards
ActiveUS20050088445A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsGraphicsScalable system
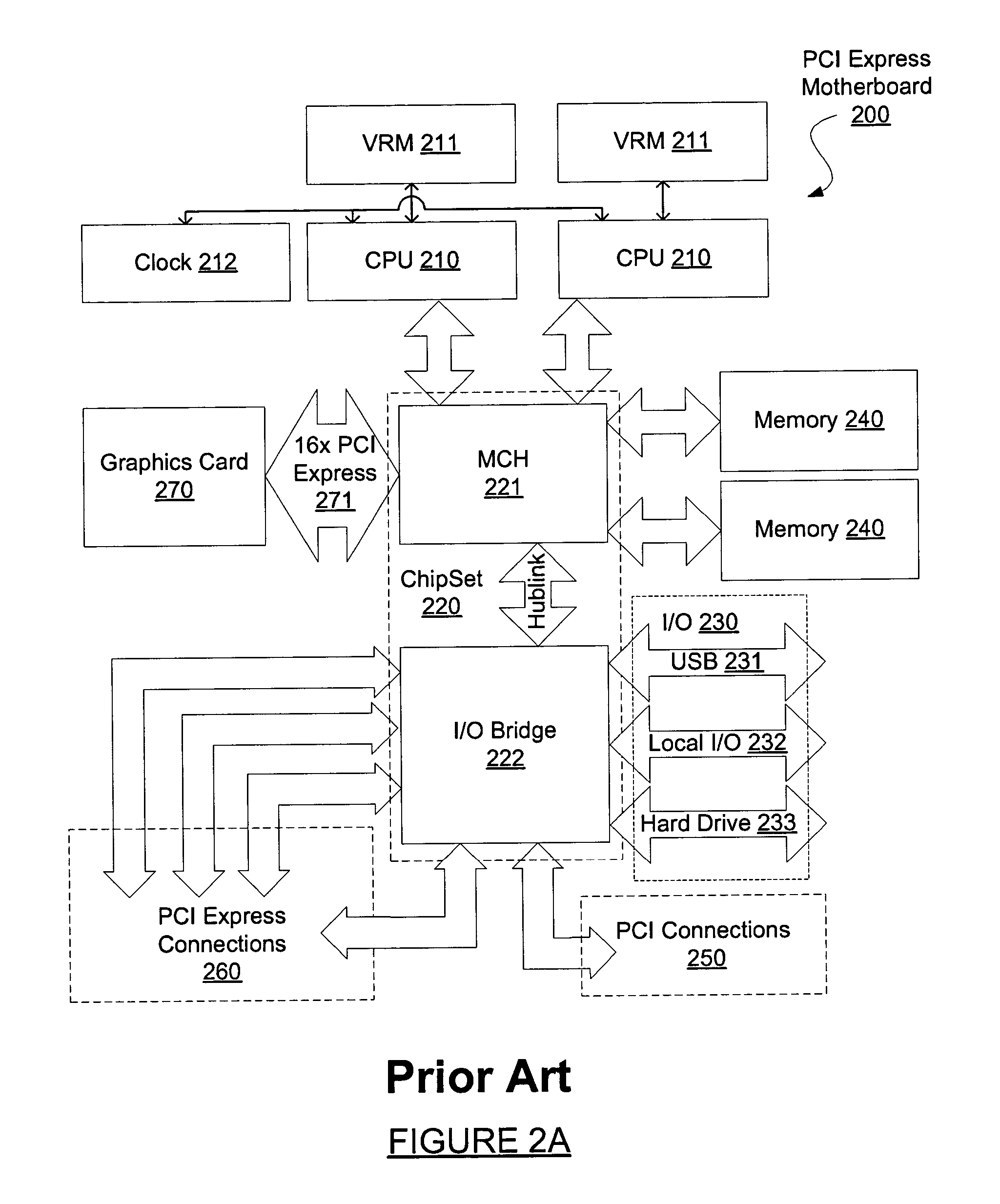
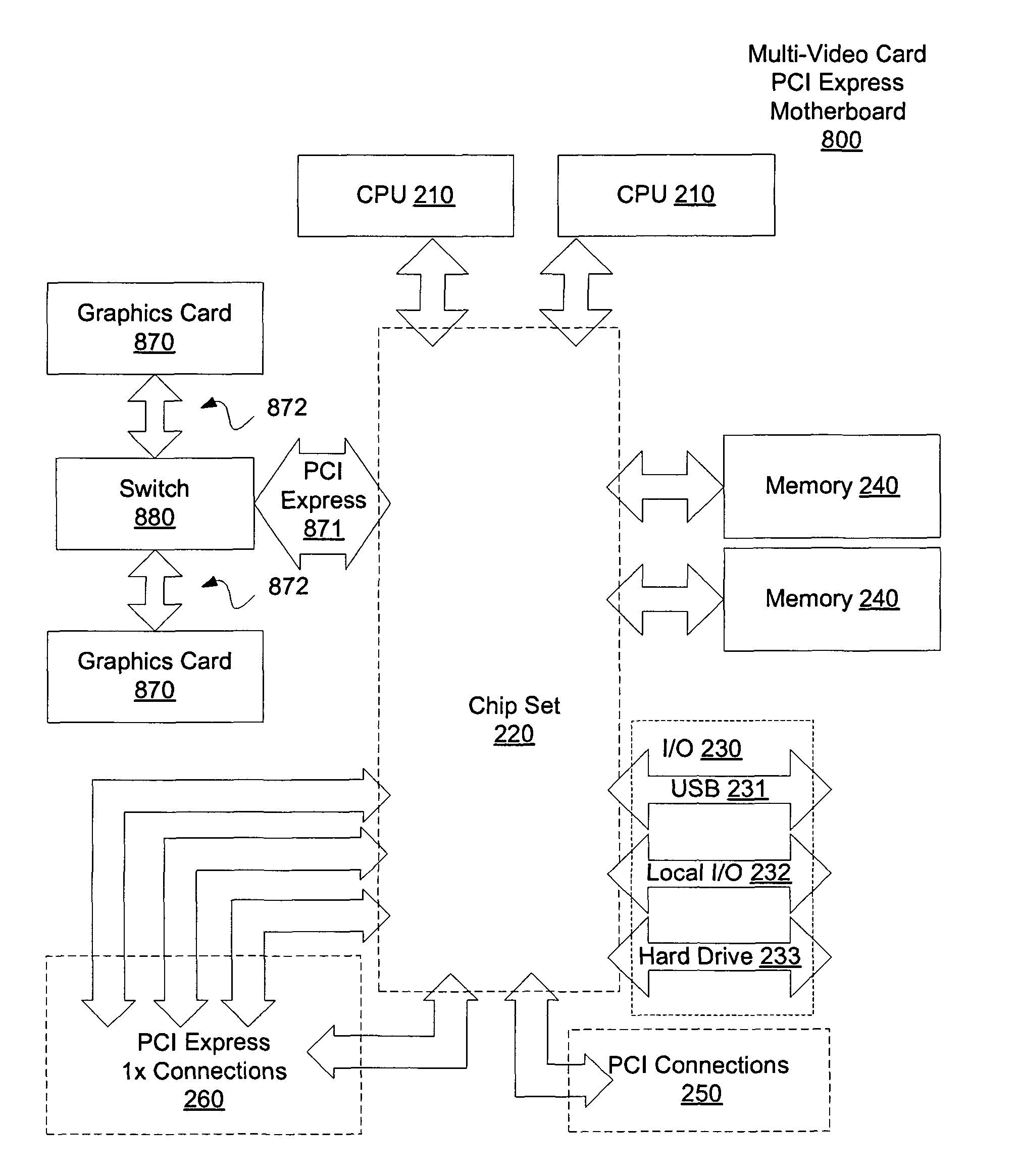
The present invention provides a motherboard that uses a high-speed, scalable system bus such as PCI Express® to support two or more high bandwidth graphics slots, each capable of supporting an off-the-shelf video controller. The lanes from the motherboard chipset may be directly routed to two or more graphics slots. For instance, the chipset may route (1) thirty-two lanes into two ×16 graphics slots; (2) twenty-four lanes into one ×16 graphics slot and one ×8 graphics slot (the ×8 slot using the same physical connector as a ×16 graphics slot but with only eight active lanes); or (3) sixteen lanes into two ×8 graphics slots (again, physically similar to a ×16 graphics slot but with only eight active lanes). Alternatively, a switch can convert sixteen lanes coming from the chipset root complex into two ×16 links that connect to two ×16 graphics slots. Each and every embodiment of the present invention is agnostic to a specific chipset.
Owner:DELL MARKETING
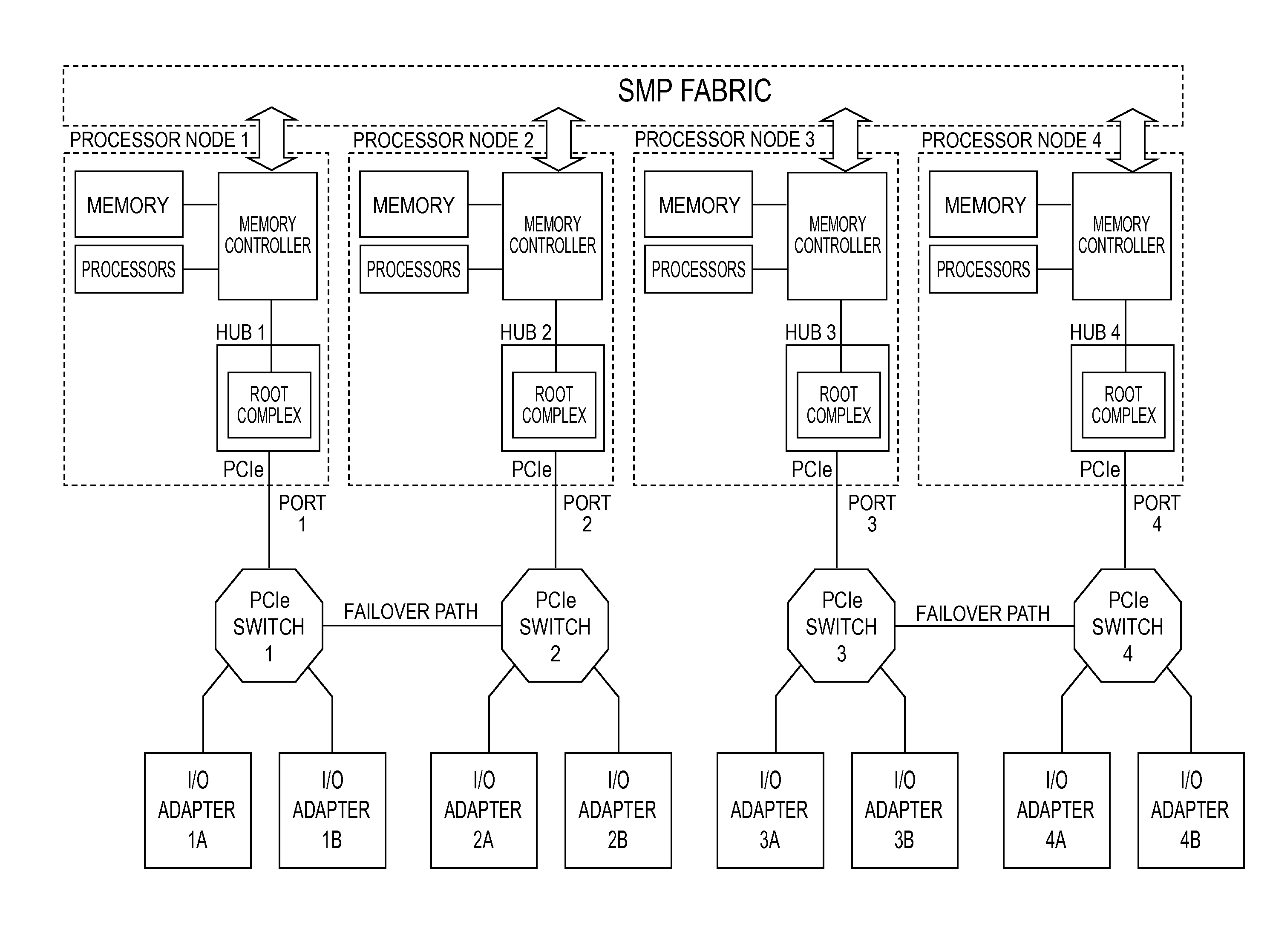
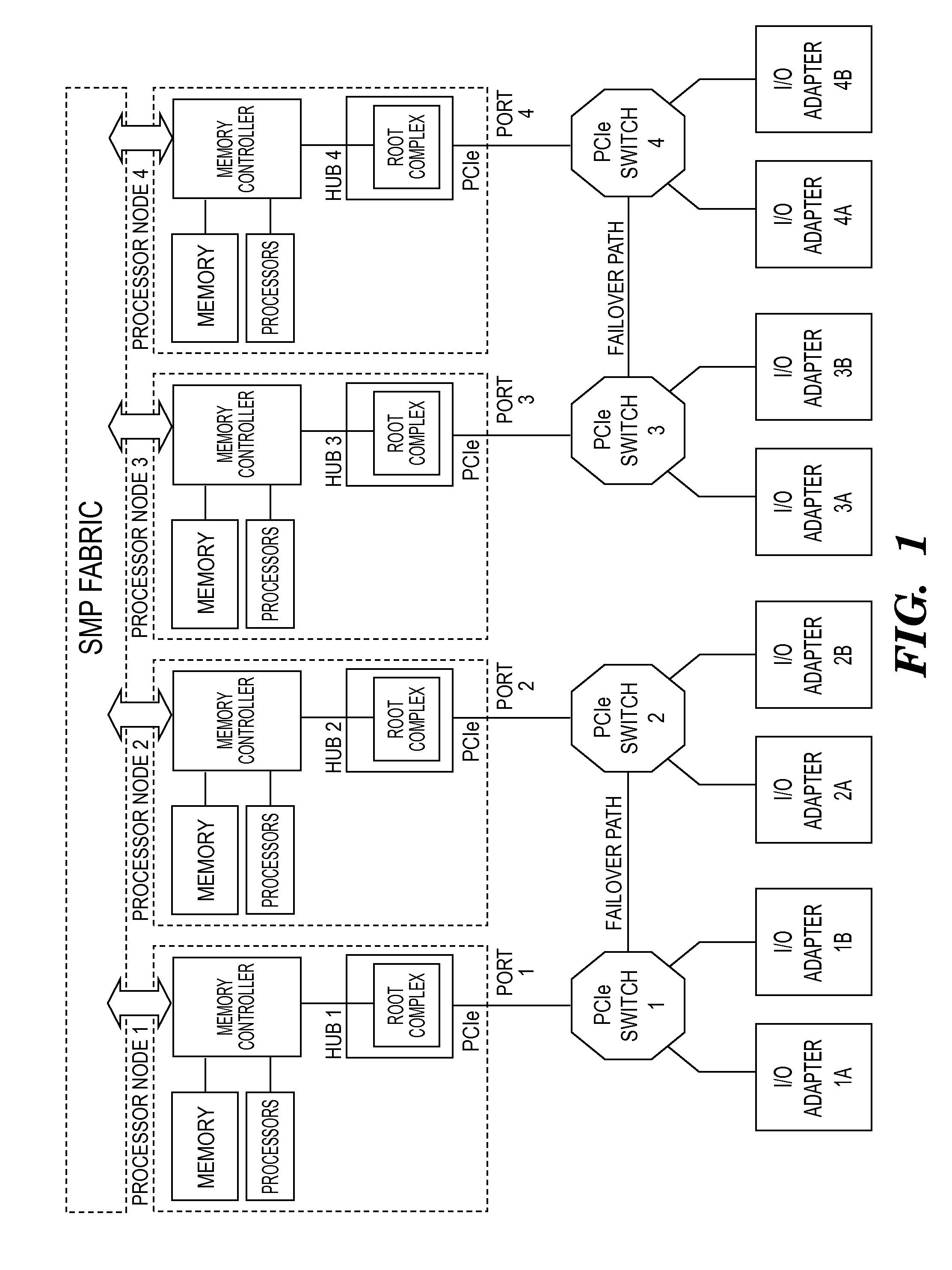
Switch failover control in a multiprocessor computer system
A system and a method for failover control comprising: maintaining a primary device table entry (DTE) in a first table activated for a first adapter in communication with a first processor node having a first root complex via a first switch assembly and maintaining a secondary DTE in standby for a second adapter in communication with a second processor node having a second root complex via a second switch assembly; maintaining a primary DTE in a second table activated for the second adapter and maintaining a secondary DTE in standby for the first adapter; and upon a failover, updating the secondary DTE in the first table as an active entry for the second adapter and forming a path to enable traffic to route from the second adapter through the second switch assembly over to the first switch assembly and up to the first root complex of the first processor node.
Owner:IBM CORP
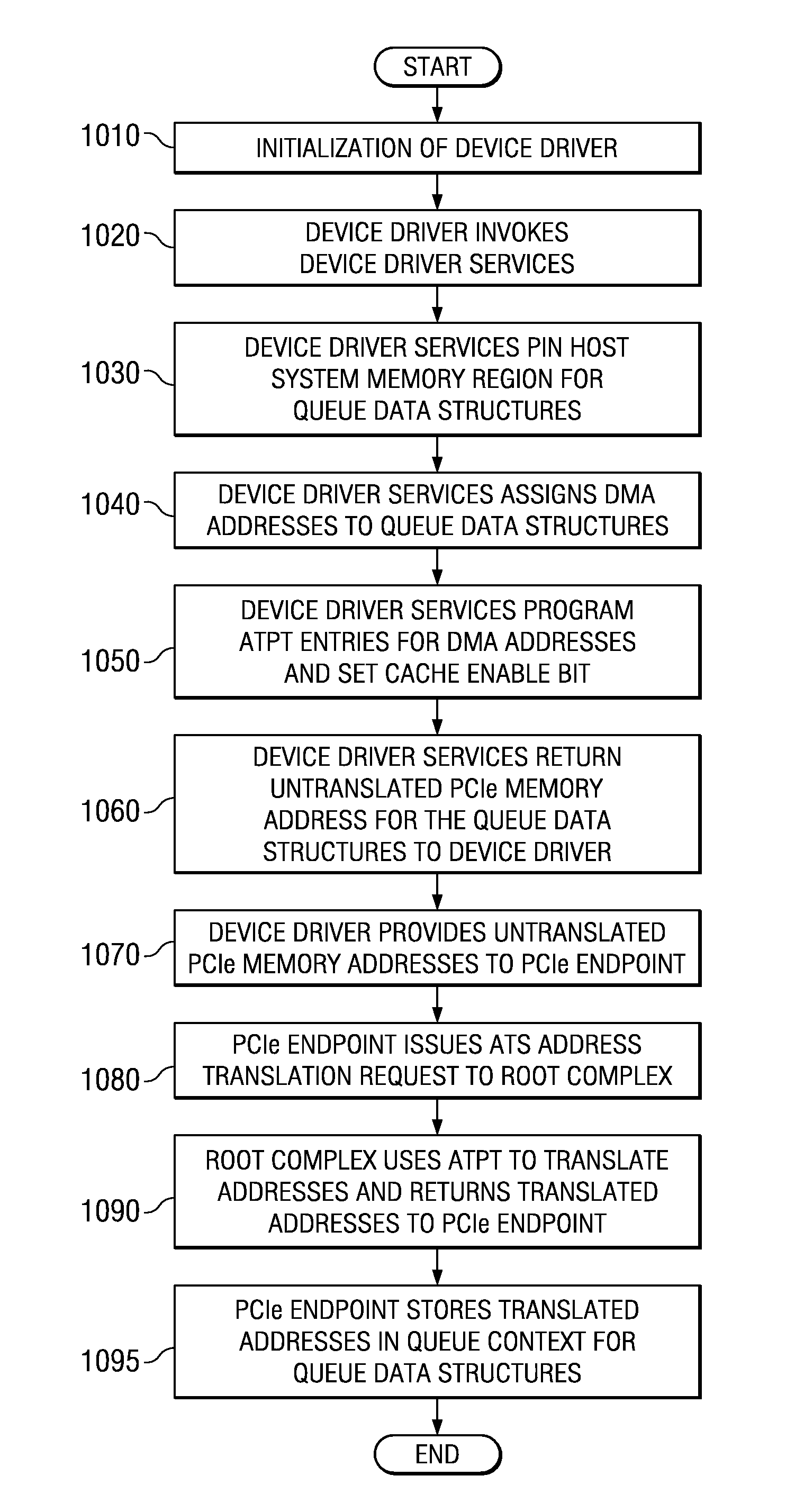
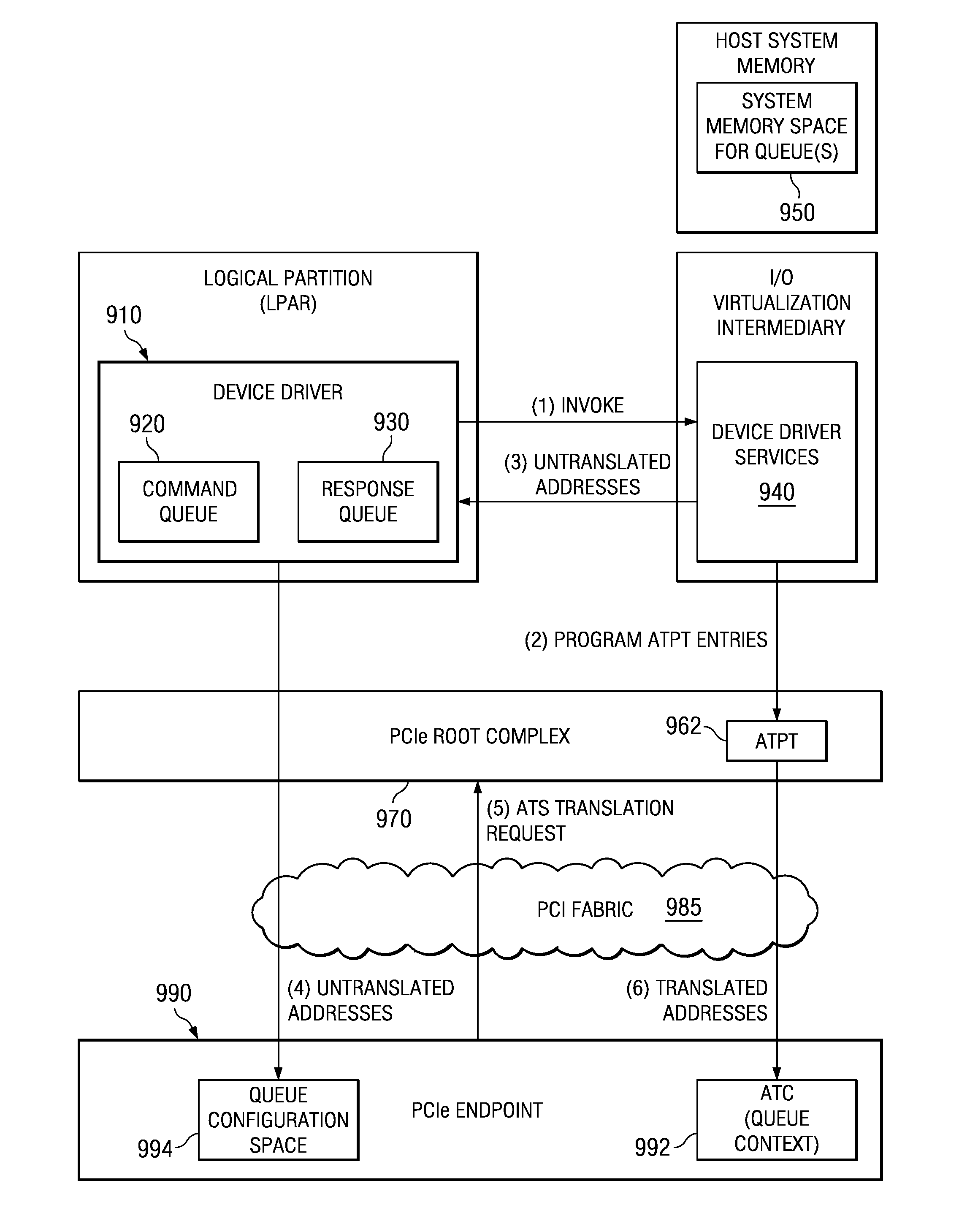
Apparatus and Method for Communicating with a Memory Registration Enabled Adapter Using Cached Address Translations
InactiveUS20080091915A1Lower latencyReduce DMA read latencyComputer security arrangementsMemory systemsRoot complexImage registration
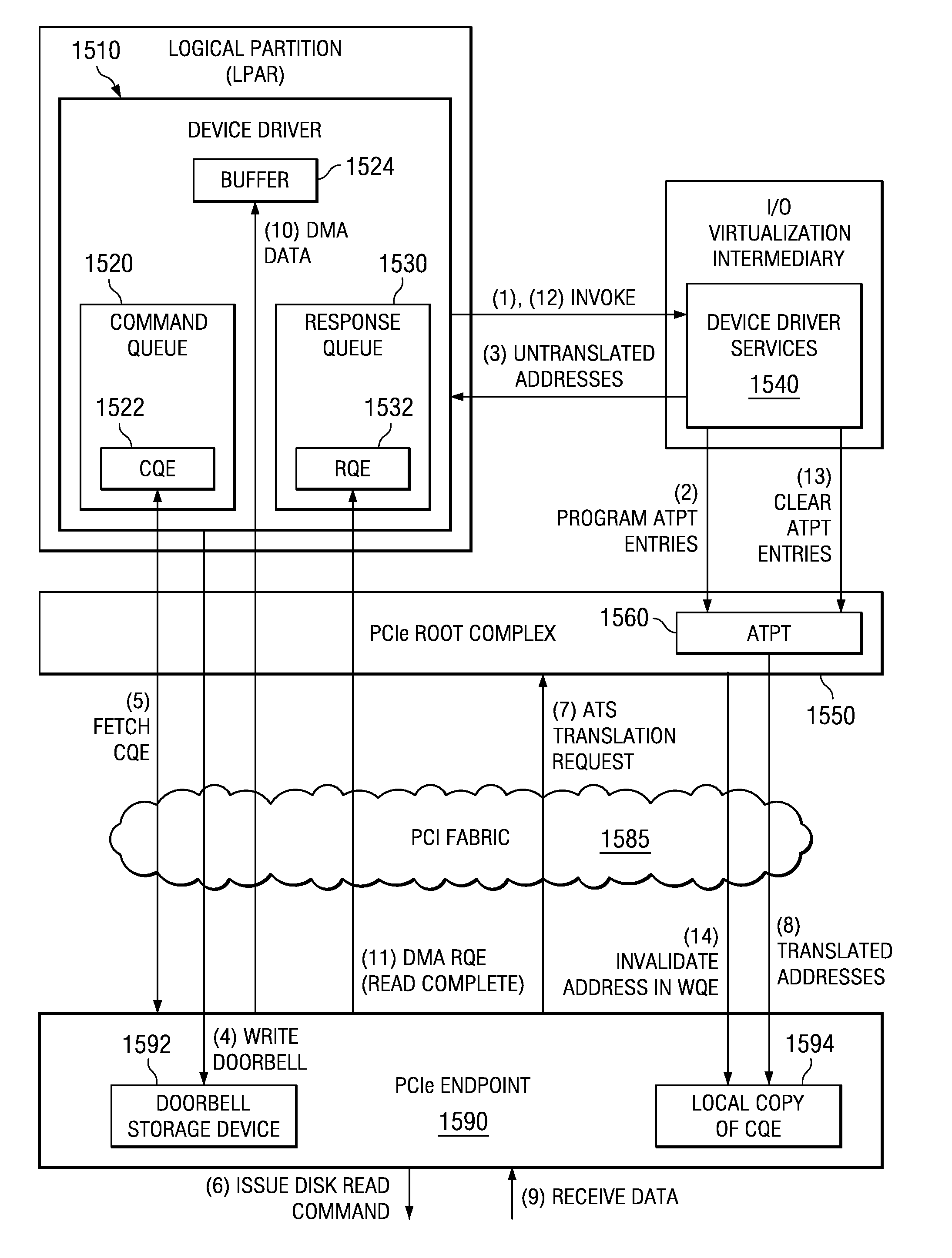
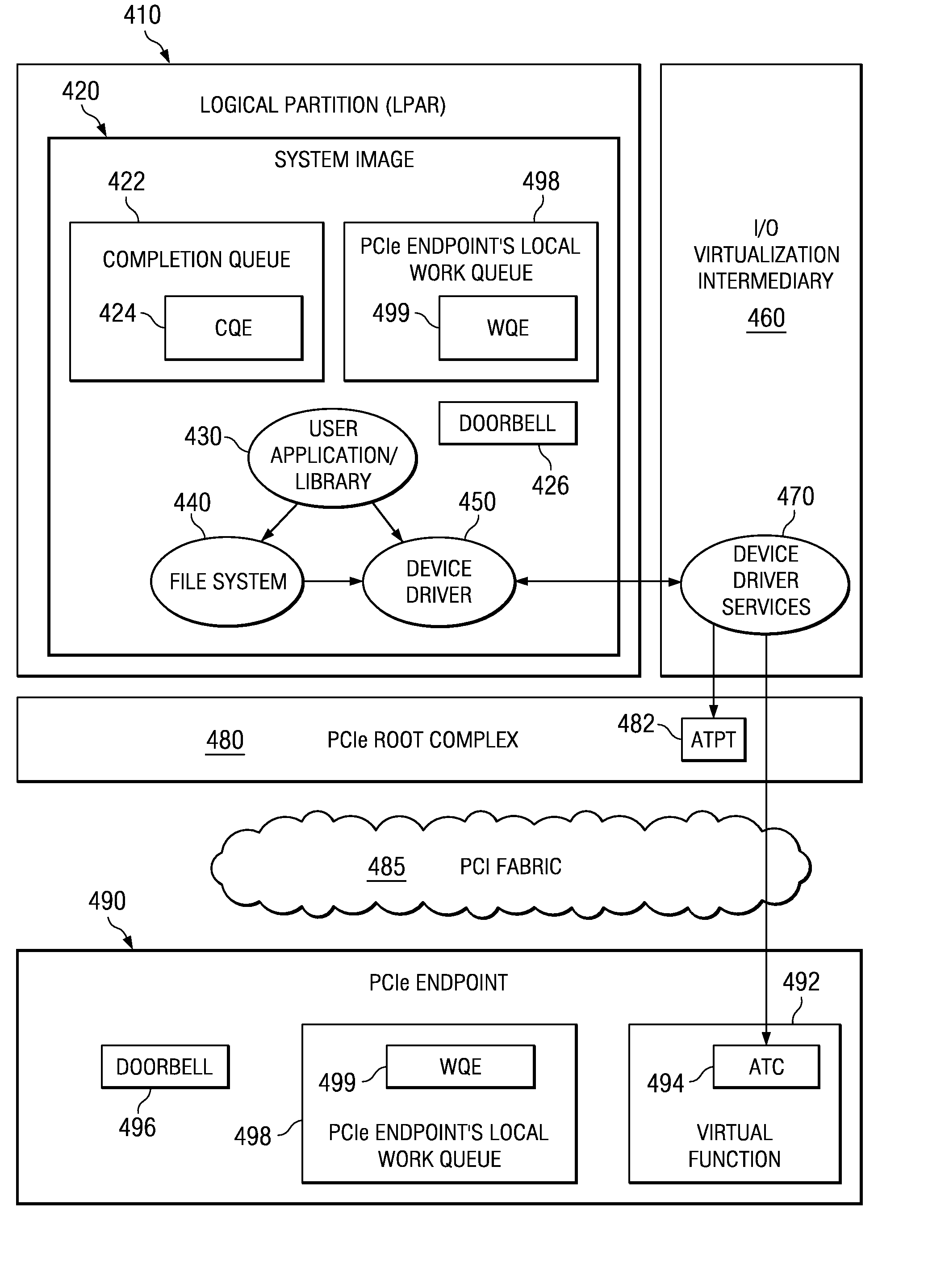
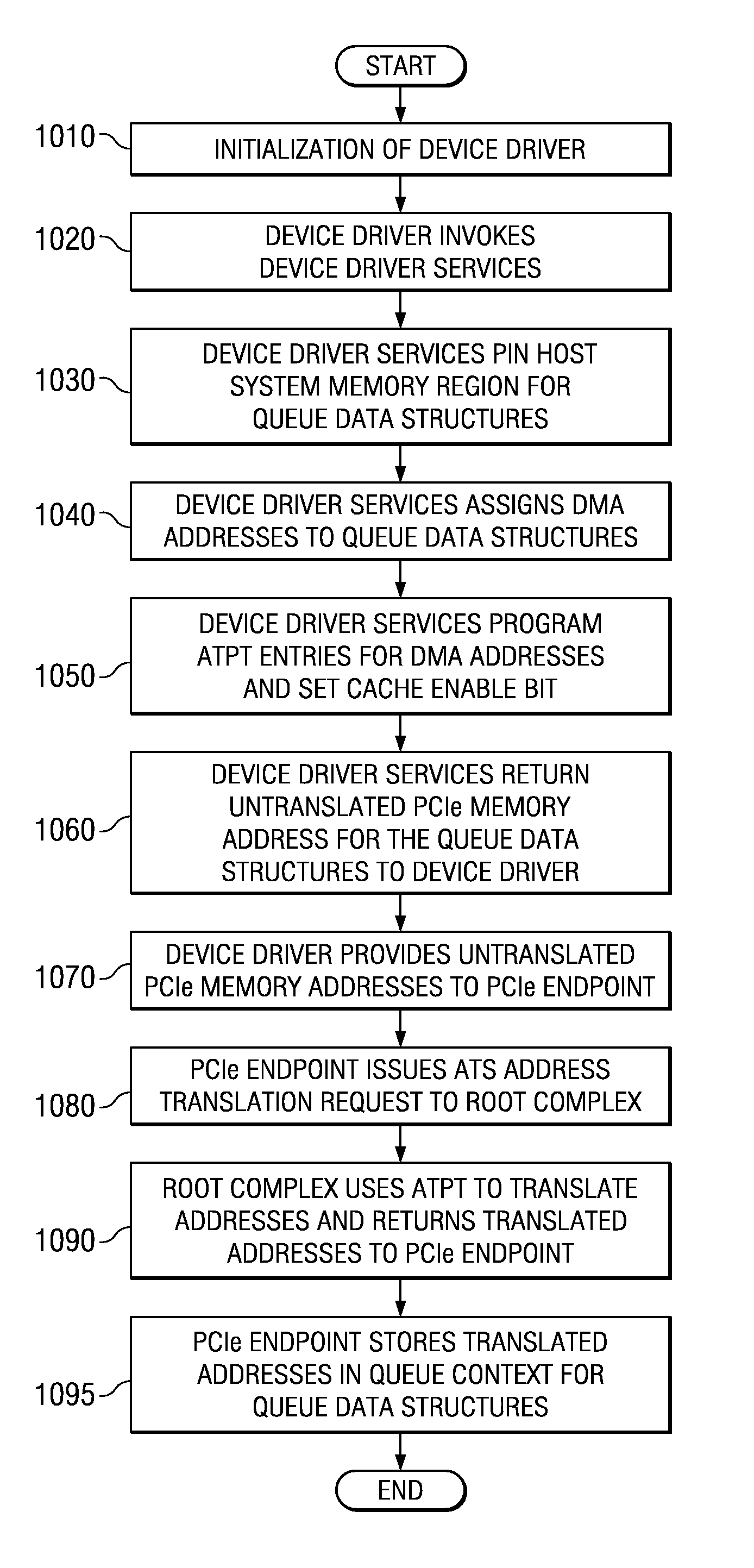
An apparatus and method for communicating with a memory registration enabled adapter, such as an InfiniBand™ host channel adapter, are provided. With the apparatus and method, device driver services may be invoked by a device driver for initializing address translation entries in an address translation data structure of a root complex. An address of a device driver data buffer data structure and registration modifiers may be passed by the device driver to the device driver services. The device driver services may create address translation data structure entries in the address translation data structure associated with the root complex and memory registration (MR) address translation entries in a MR address translation data structure of the adapter. The MR address translation data structure may then be used with I / O operations to bypass the address translation data structure associated with the root complex.
Owner:IBM CORP
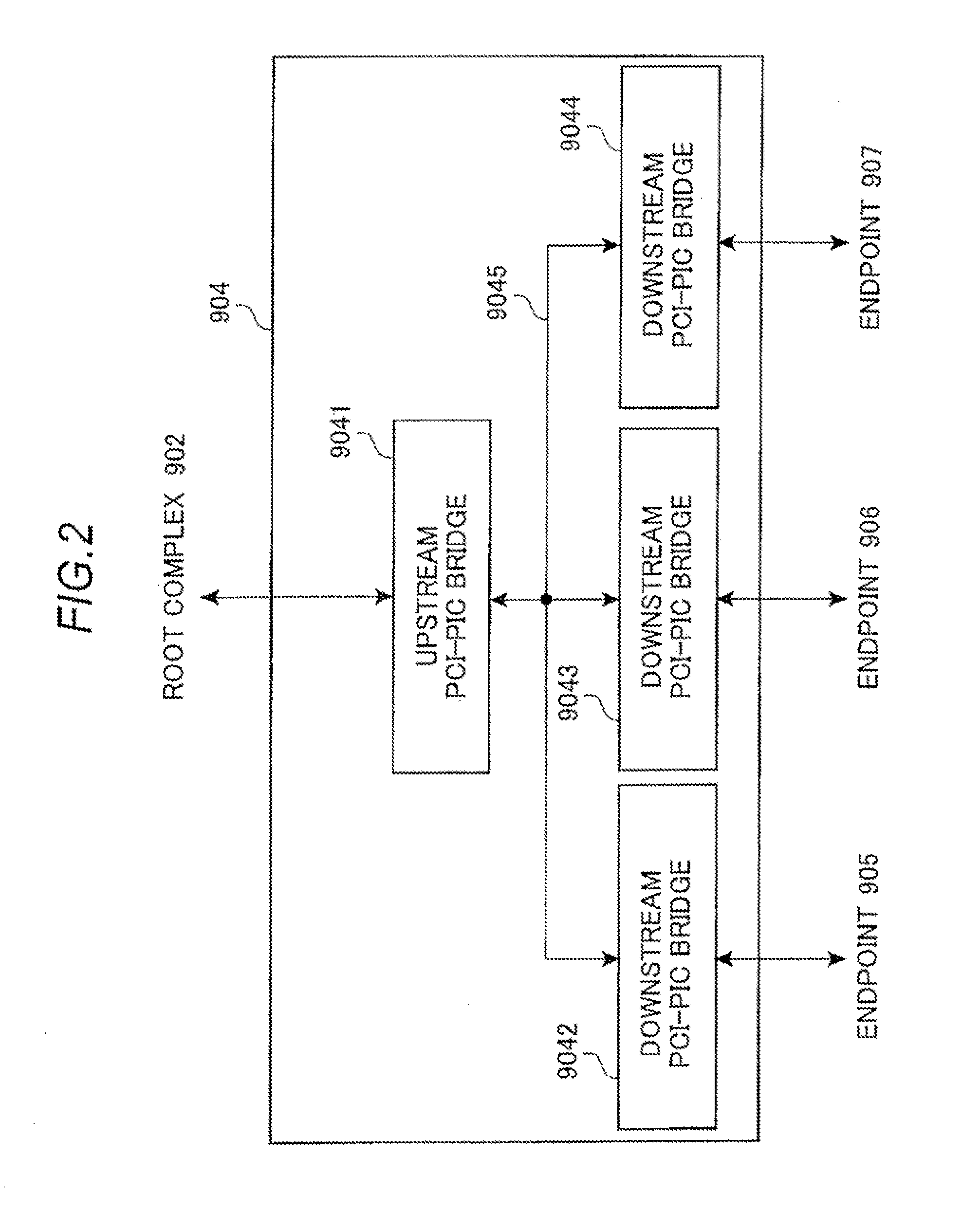
PCI express switch, PCI express system, and network control method
ActiveUS20110064089A1Reduce the overall heightData switching by path configurationElectric digital data processingRoot complexNetwork control
Provided are a first PCI-PCI bridge that handles Multi Root to connect to a plurality of root complexes; a second PCI-PCI bridge that connects to an endpoint; a virtual PCI Express switch that performs a switching process between the first and second PCI-PCI bridges; and a network control device that transfers data that is to be processed in the virtual PCI Express switch to an external switch through a network without passing through a PCI-PCI bridge.
Owner:NEC CORP
Apparatus and Method for Communicating with an I/O Adapter Using Cached Address Translations
InactiveUS20080091855A1Lower latencyReduce DMA read latencyMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsRoot complexInput/output
An apparatus and method for communicating with an input / output (I / O) adapter configured to communicate with a locally attached I / O device are provided using cached address translations. With the apparatus and method, in response to receiving a storage transaction request, a queue element is created in a command queue specifying an untranslated buffer address. The queue element may be retrieved by the I / O adapter and a determination may be made as to whether the queue element contains a read operation command. If so, a translation request may be sent from the I / O adapter to a root complex at substantially a same time as the read operation command is sent to a locally attached external I / O device. The translated address corresponding to the untranslated address of the queue element may be returned and stored in the I / O adapter prior to receiving the data read from the external I / O device.
Owner:IBM CORP
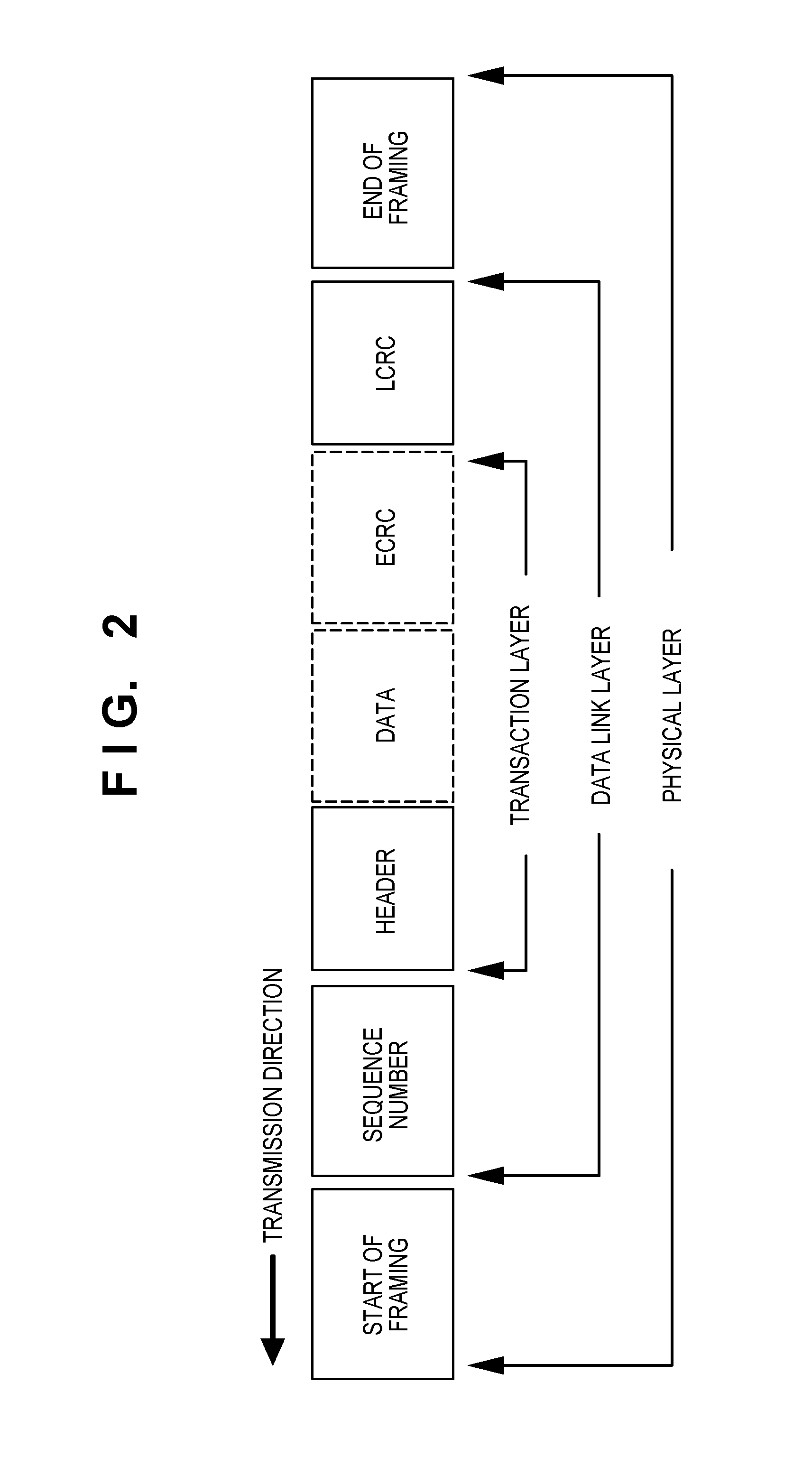
System and method for encoding packet header to enable higher bandwidth efficiency across PCIe links
ActiveUS20070130397A1Improving bus throughput efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTEnergy efficient computingComputer hardwareGraphics
A computer system that employs Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) links includes devices that generate a PCIe packet having a header portion that is smaller than the header portion for a conventional PCI packet. The devices may be an endpoint device, such as a graphics processor, and a chipset, such as a root-complex. The reduced size header improves the bus throughput efficiency of the computer system and reduces power requirements for the computer system.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Communicating with a memory registration enabled adapter using cached address translations
InactiveUS7587575B2Memory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer security arrangementsRoot complexData buffer
Mechanisms for communicating with a memory registration enabled adapter, such as an InfiniBand™ host channel adapter, are provided. With the mechanisms, device driver services may be invoked by a device driver for initializing address translation entries in an address translation data structure of a root complex. An address of a device driver data buffer data structure and registration modifiers may be passed by the device driver to the device driver services. The device driver services may create address translation data structure entries in the address translation data structure associated with the root complex and memory registration (MR) address translation entries in a MR address translation data structure of the adapter. The MR address translation data structure may then be used with I / O operations to bypass the address translation data structure associated with the root complex.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for communicating with an I/O adapter using cached address translations
InactiveUS7506084B2Lower latencyReduce latencyMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsRoot complexInput/output
A method for communicating with an input / output (I / O) adapter configured to communicate with a locally attached I / O device are provided using cached address translations. With the method, in response to receiving a storage transaction request, a queue element is created in a command queue specifying an untranslated buffer address. The queue element may be retrieved by the I / O adapter and a determination may be made as to whether the queue element contains a read operation command. If so, a translation request may be sent from the I / O adapter to a root complex at substantially a same time as the read operation command is sent to a locally attached external I / O device. The translated address corresponding to the untranslated address of the queue element may be returned and stored in the I / O adapter prior to receiving the data read from the external I / O device.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
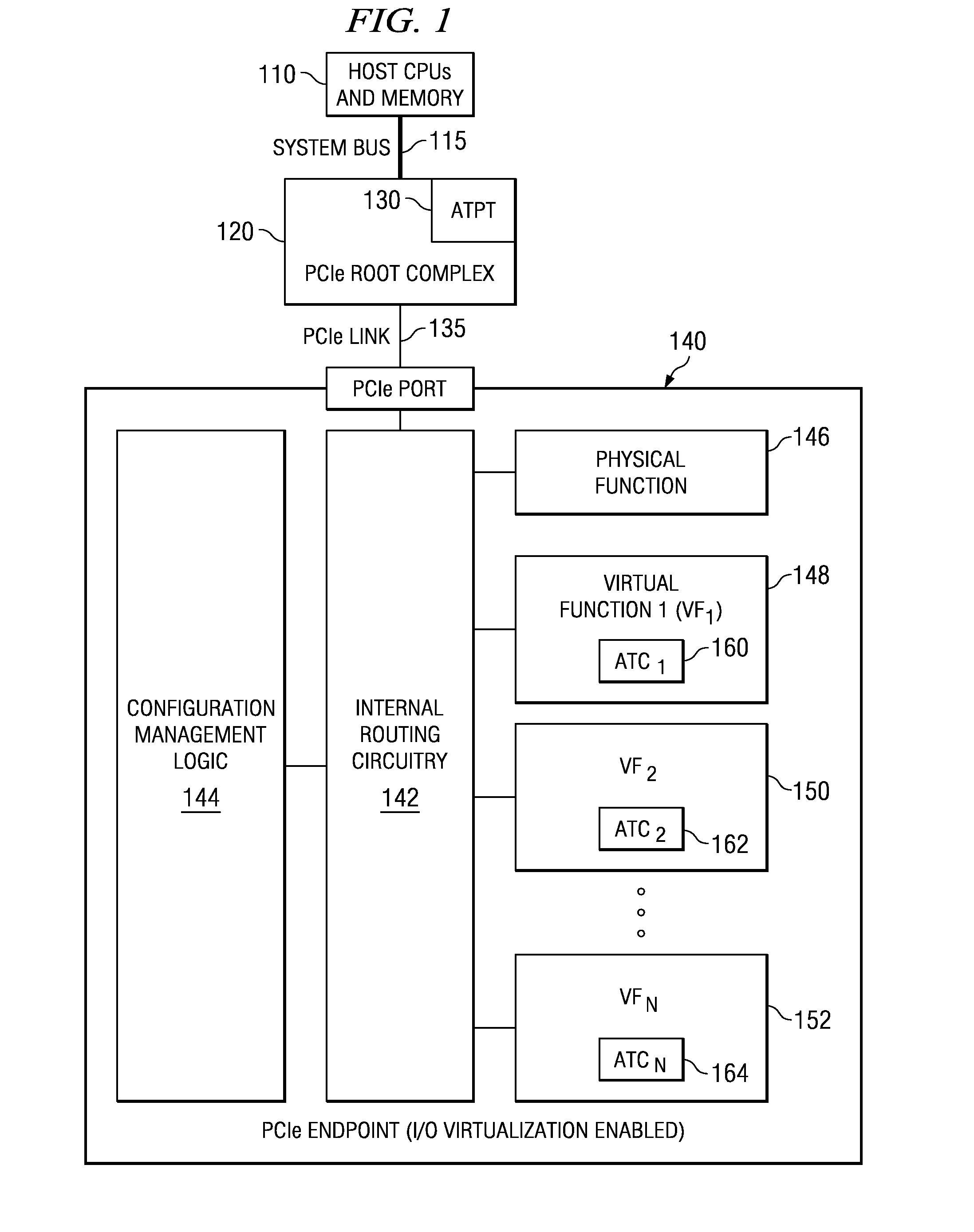
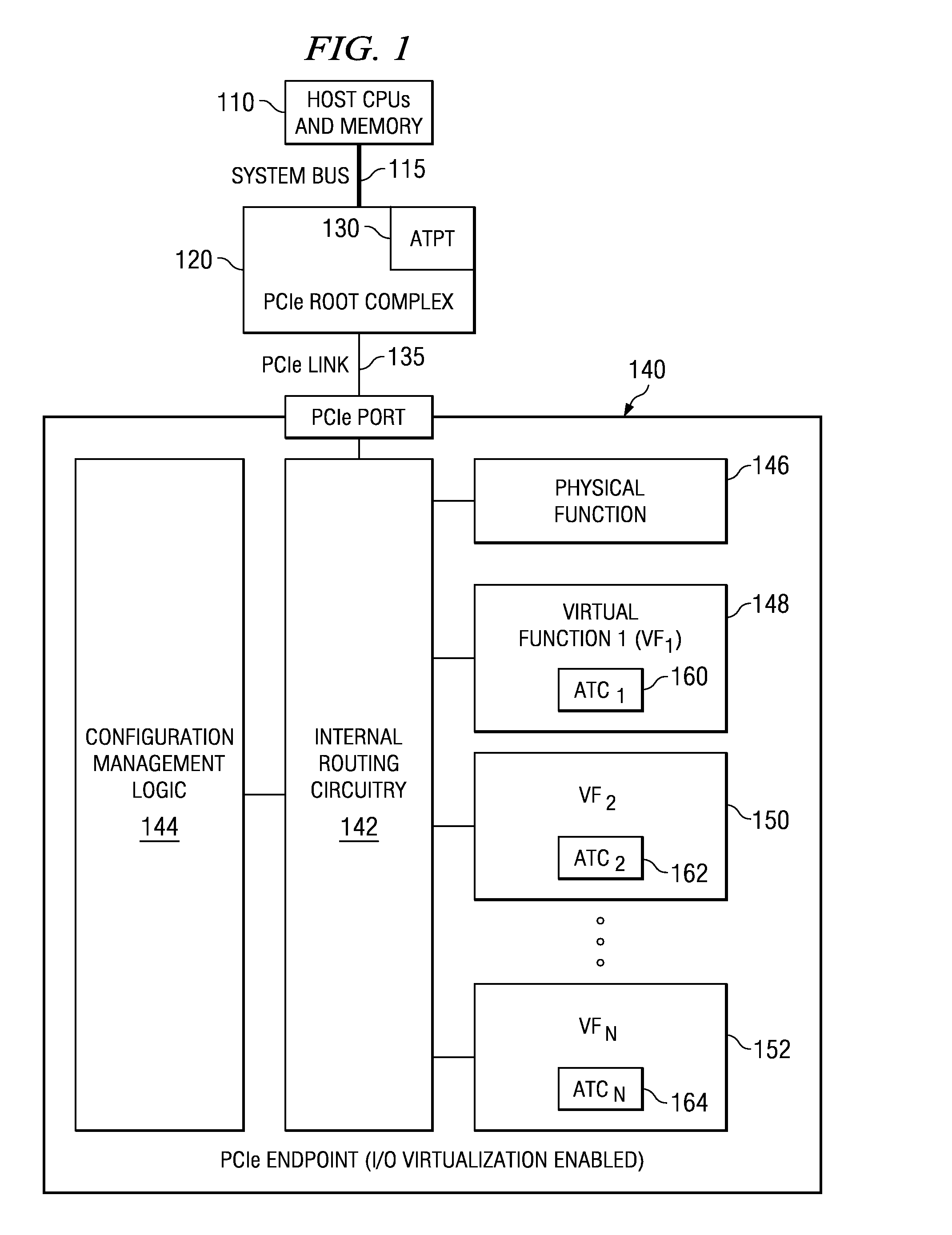
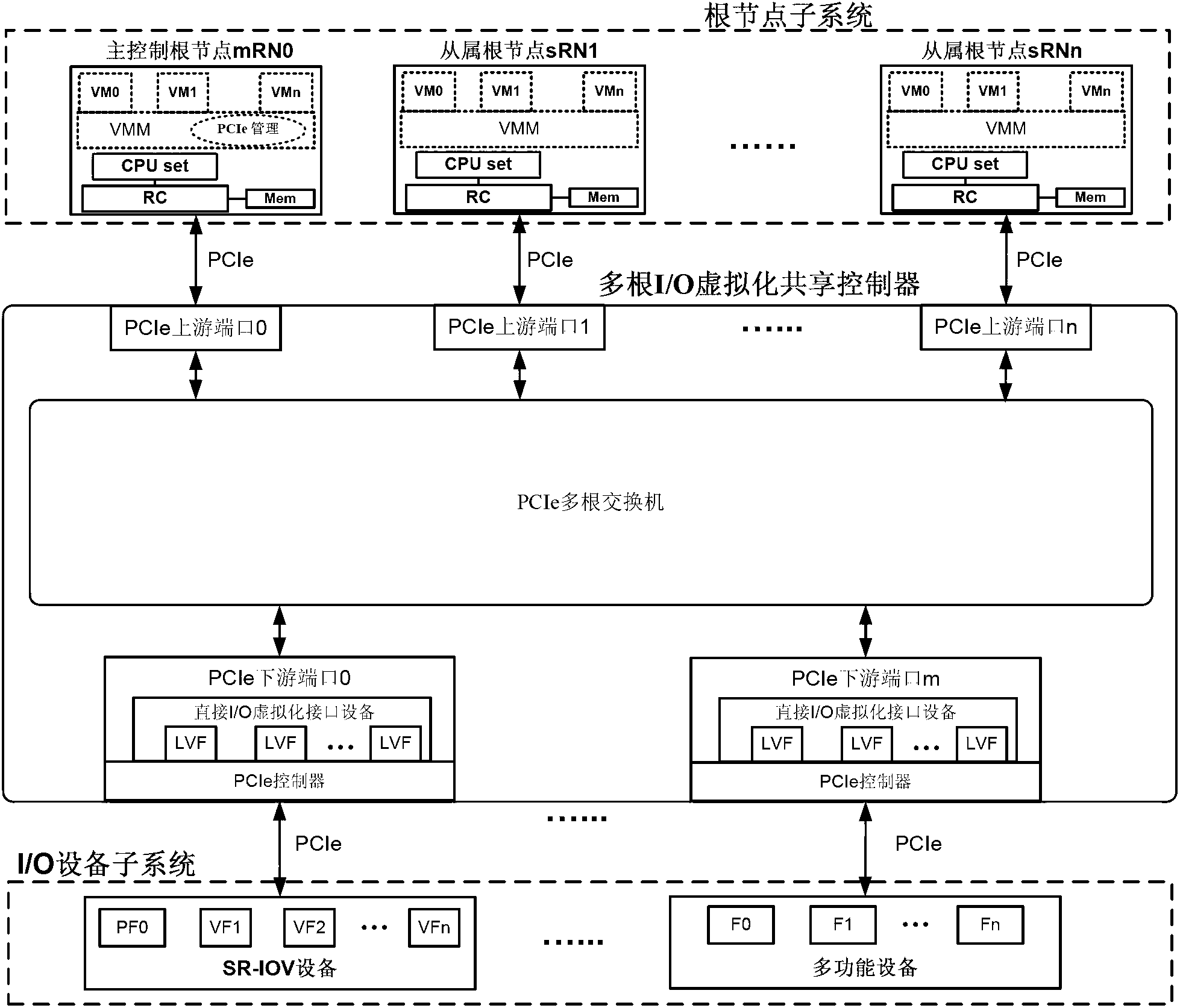
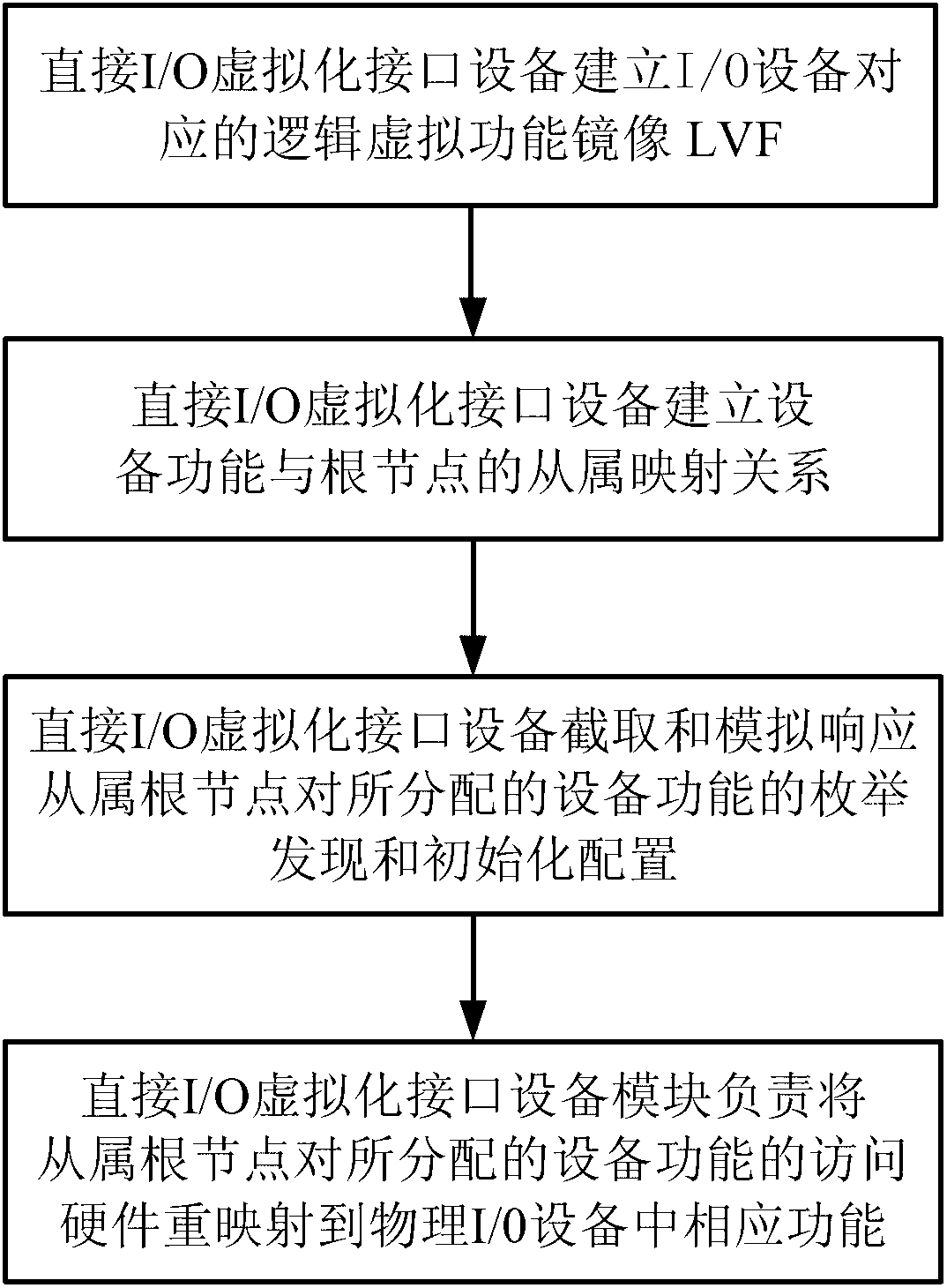
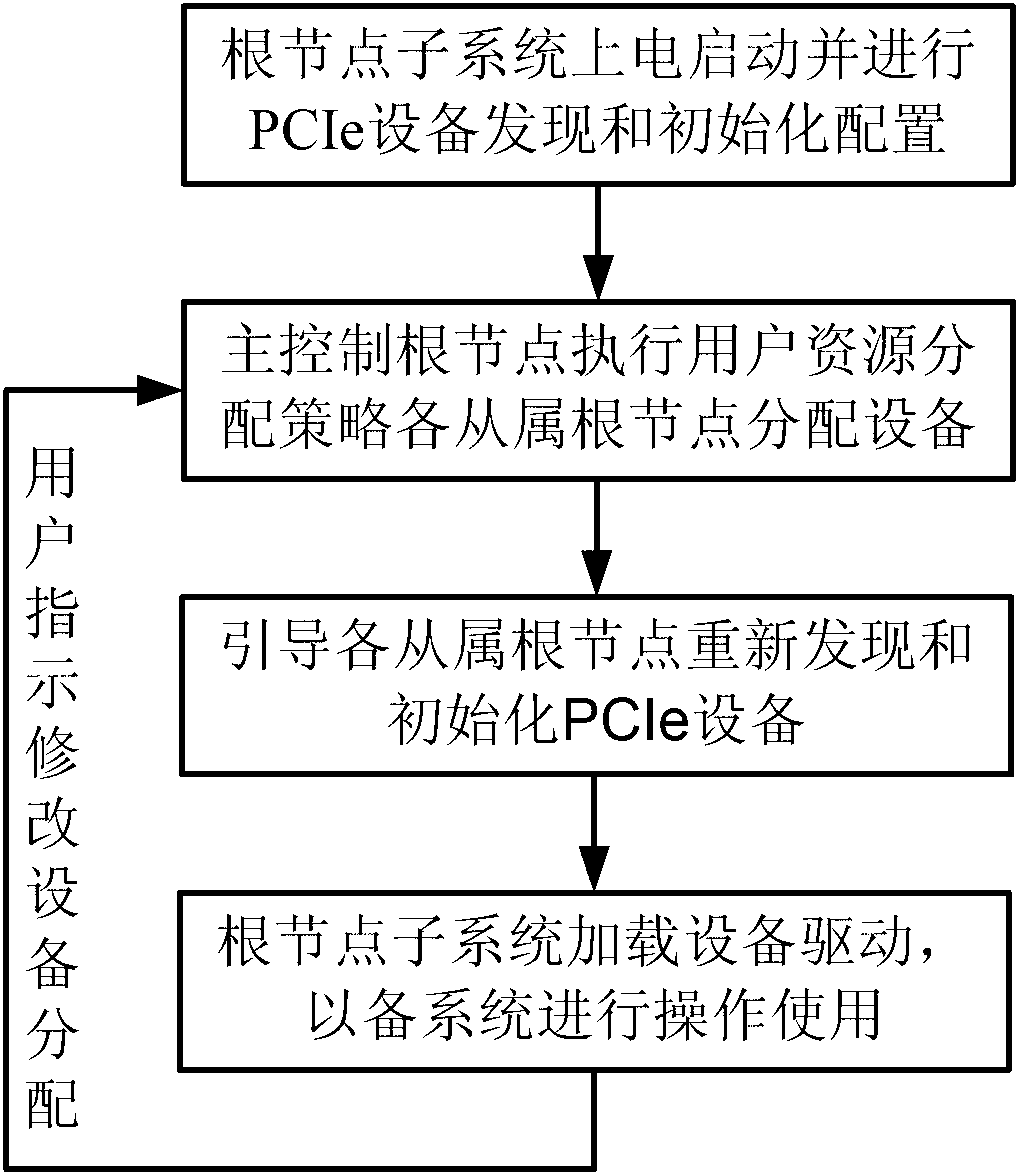
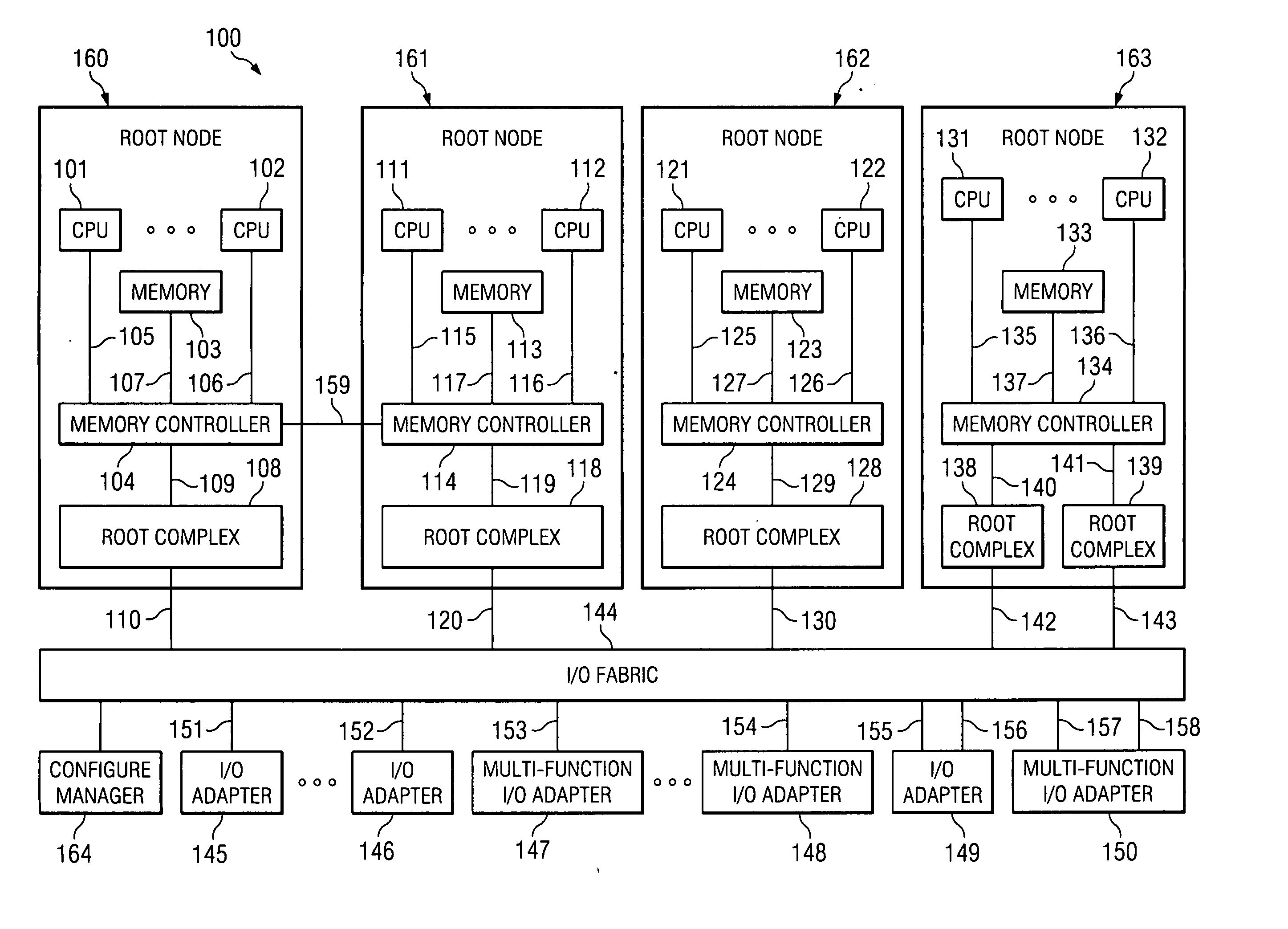
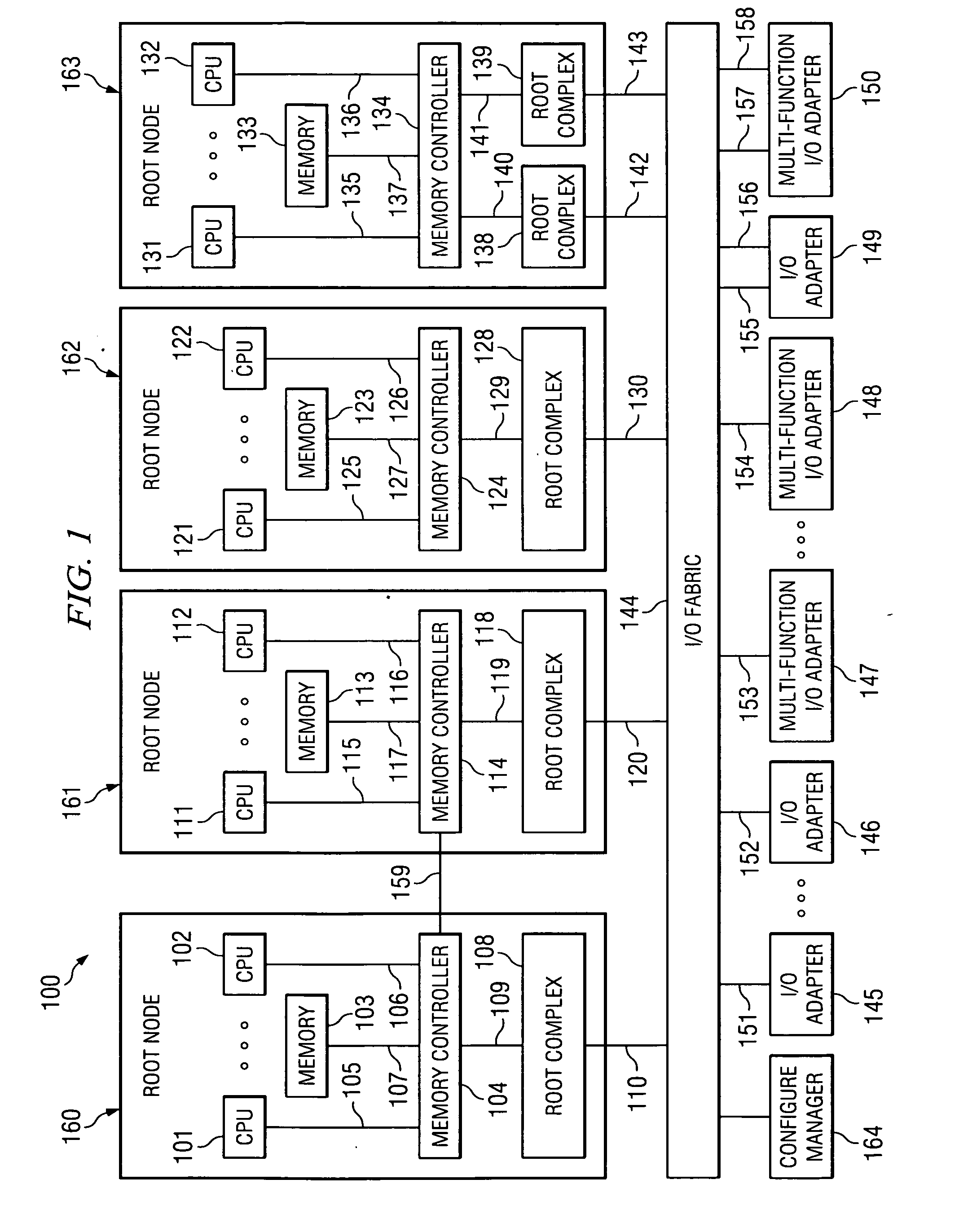
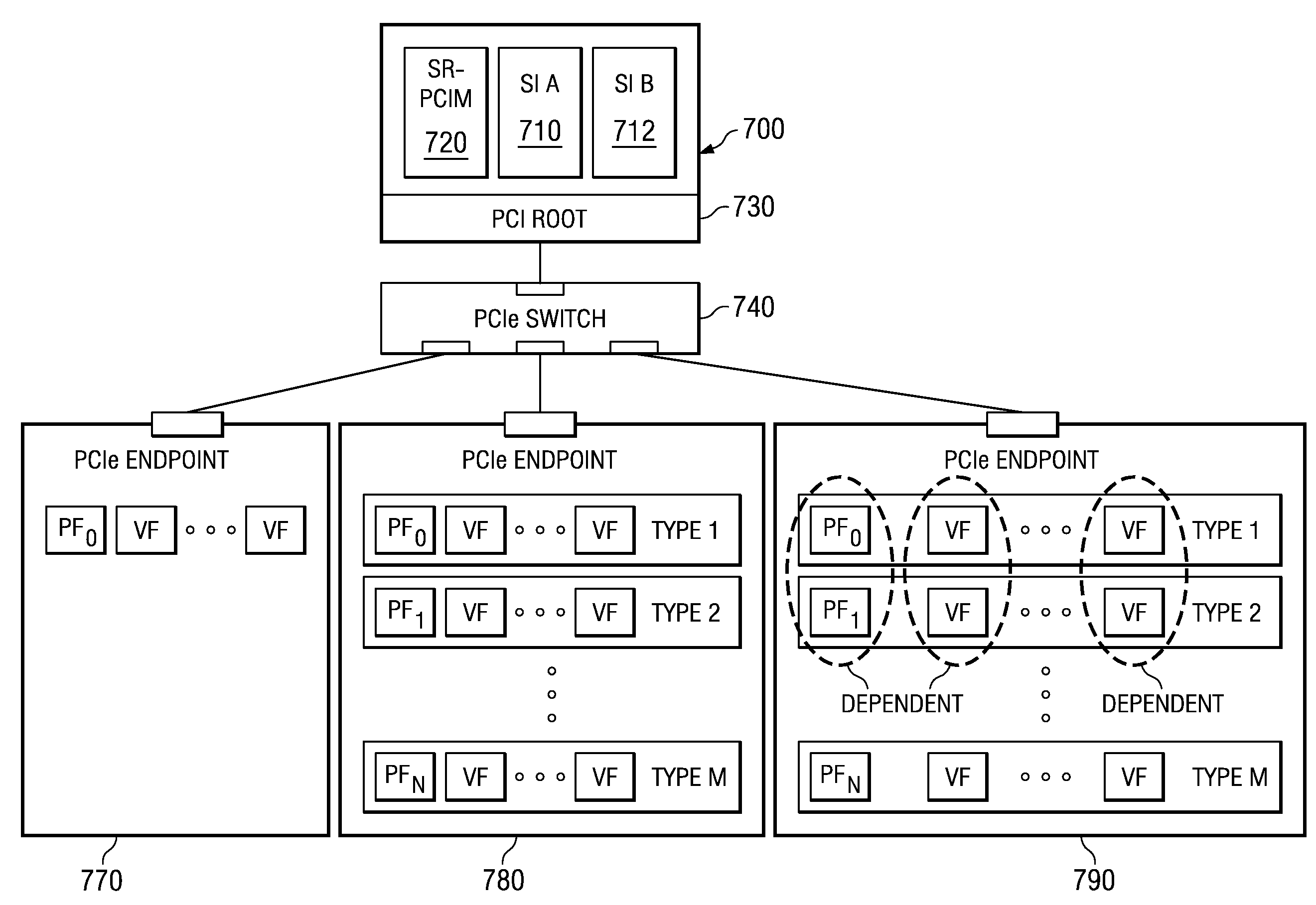
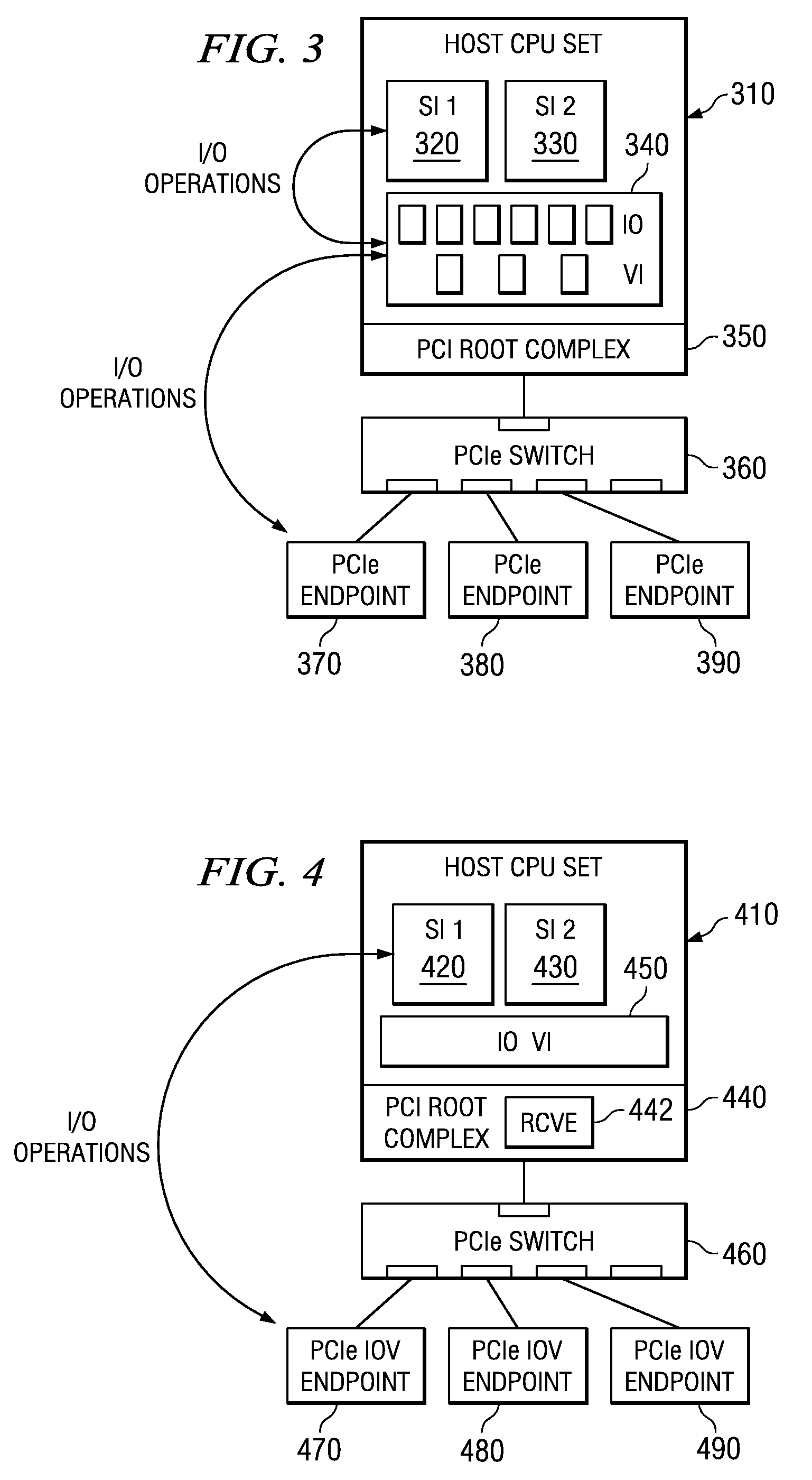
Multi-root I/O (Input/Output) virtualization sharing method and system
ActiveCN102707991AImprove utilization efficiencyImprove good performanceTransmissionSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationVirtualizationInternal memory
The invention provides a multi-root I / O (Input / Output) virtualization sharing method and system. The multi-root I / O virtualization sharing system comprises a root node subsystem, an I / O equipment subsystem and a multi-root I / O virtualization sharing controller, wherein the root node subsystem comprises N root nodes; each root node consists of a root complex, a CPU (Central Processing Unit) and an internal memory; the CPU and the internal memory are connected with the root complex; the I / O equipment subsystem comprises M I / O equipment; each I / O equipment can provide services for a plurality of virtual machines simultaneously; the multi-root I / O virtualization sharing controller consists of PCIe (Peripheral Component Interface Express) upstream ports, a PCIe multi-root switchover and PCIe downstream ports; and the multi-root I / O virtualization sharing controller is used for coupling the root node subsystem with the I / O equipment subsystem through a PCIe port protocol, so that I / O equipment resources are directly shared by a plurality of root nodes.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
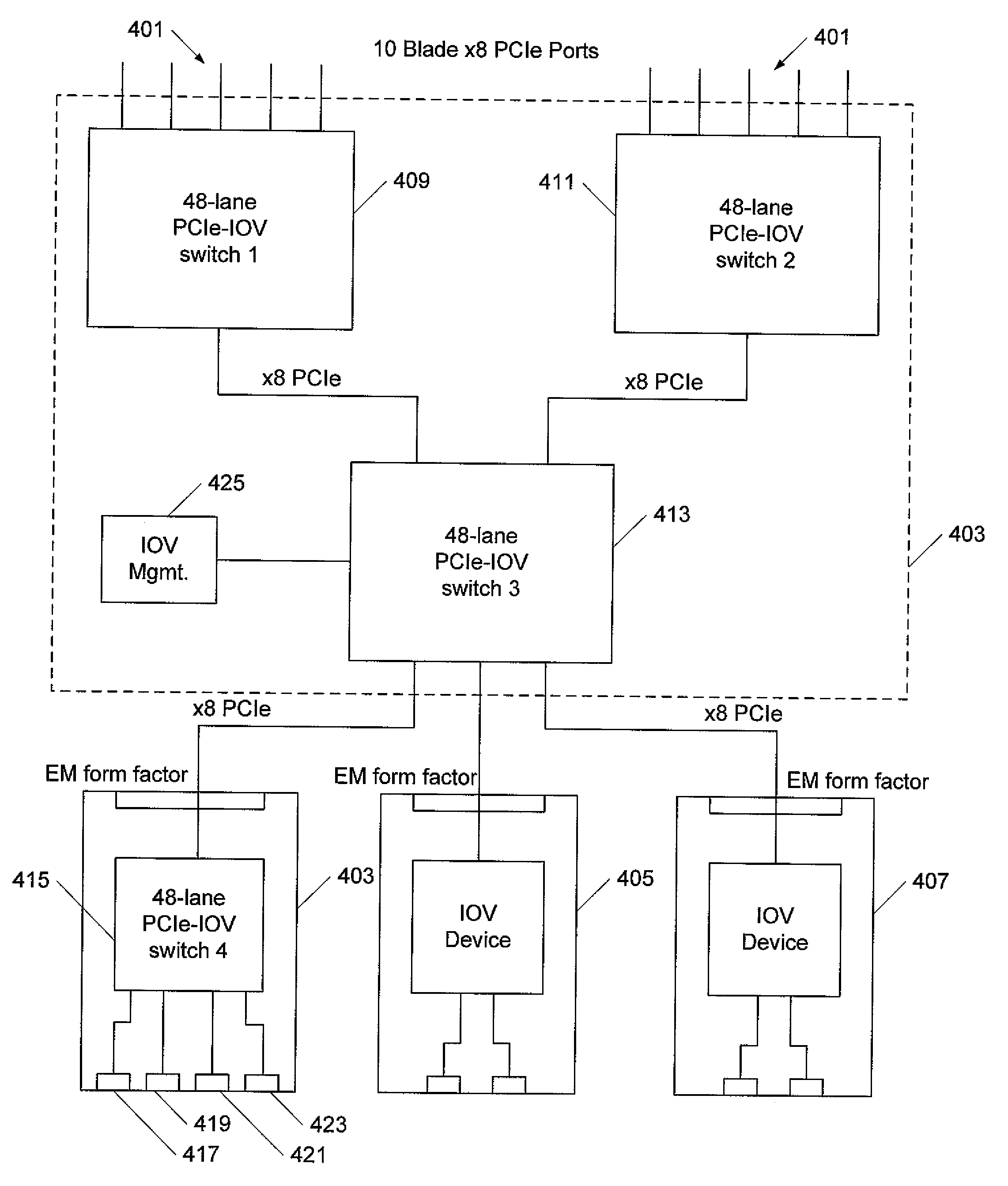
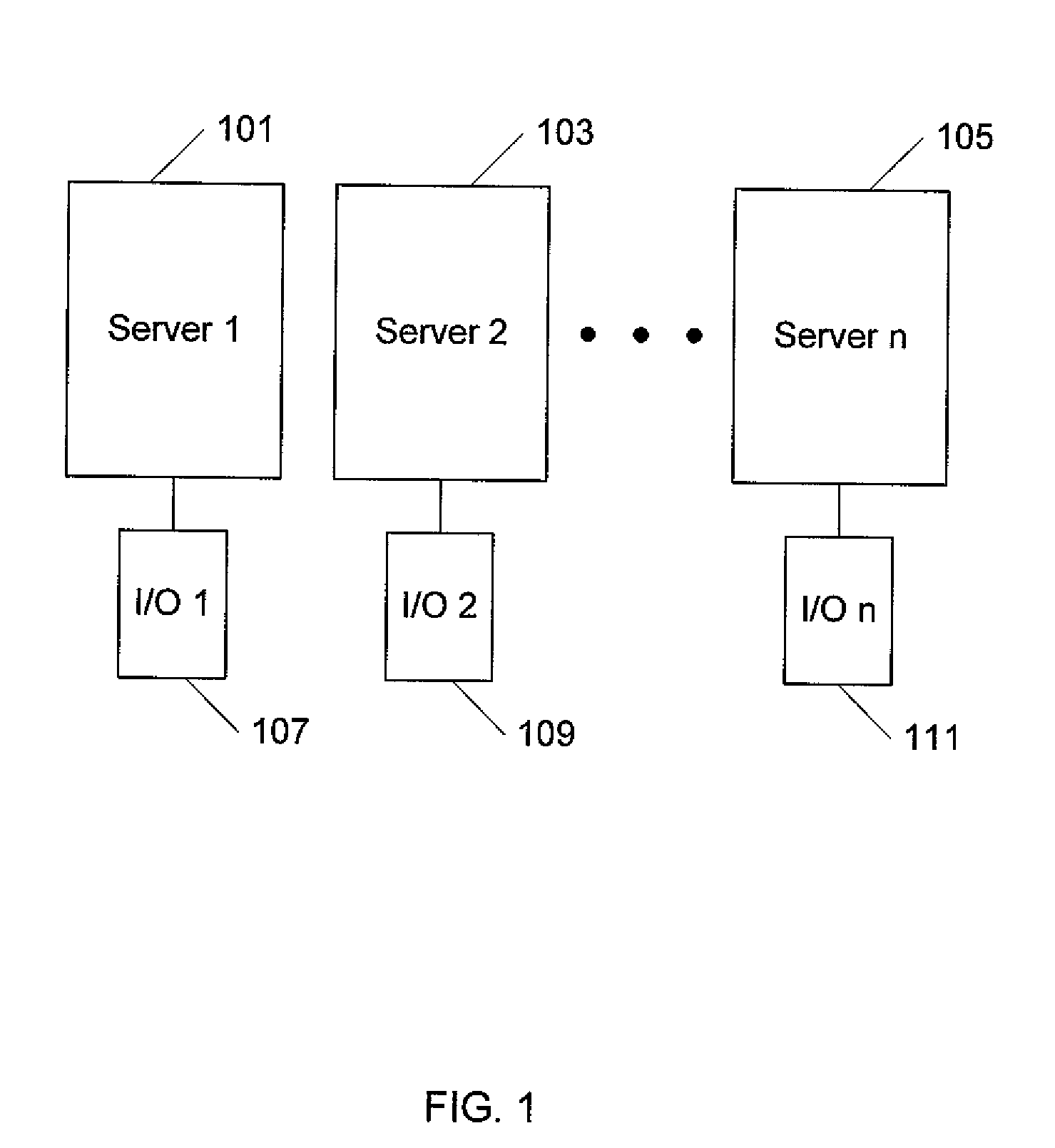
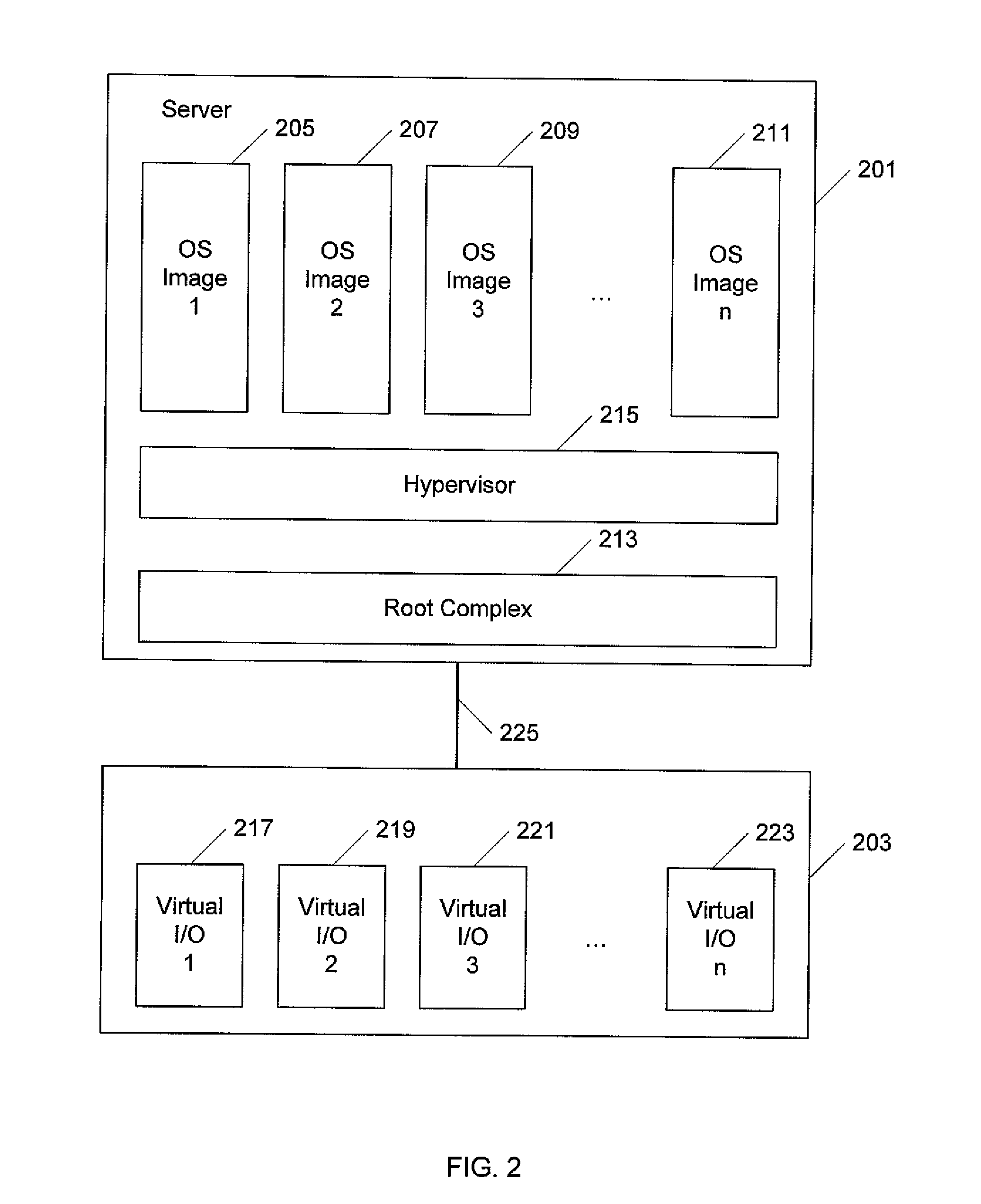
Modular I/O virtualization for blade servers
An apparatus includes a server comprising n operating system images and an IOV aware root complex; a plurality of physical I / O devices comprising n virtual I / O functions; and a PCI Express bus operatively connected to the server and the plurality physical I / O devices via the root complex, wherein the root complex is operable to provide communication between the n operating system images and the n virtual I / O function, and wherein the server and the plurality of physical I / O devices are modules in a chassis.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Communicating with an I/O device using a queue data structure and pre-translated addresses
InactiveUS7590817B2Memory adressing/allocation/relocationMicro-instruction address formationRoot complexData structure
Mechanisms for communicating with an I / O device or endpoint using a queue data structure and pre-translated addresses associated with the queue data structure are provided. With the mechanisms, a device driver invokes device driver services for initializing address translation and protection table (ATPT) entries in a root complex for the queue data structure. The device driver services return untranslated addresses to the device driver which are in turn provided to the I / O device or endpoint. The I / O device or endpoint may then request a translation of these untranslated addresses and store them in the I / O device or endpoint prior to receiving an I / O operation targeting the queue data structure. The cached translation may be used to directly access the queue data structure from the I / O device or endpoint by bypassing the root complex's address translation facilities.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
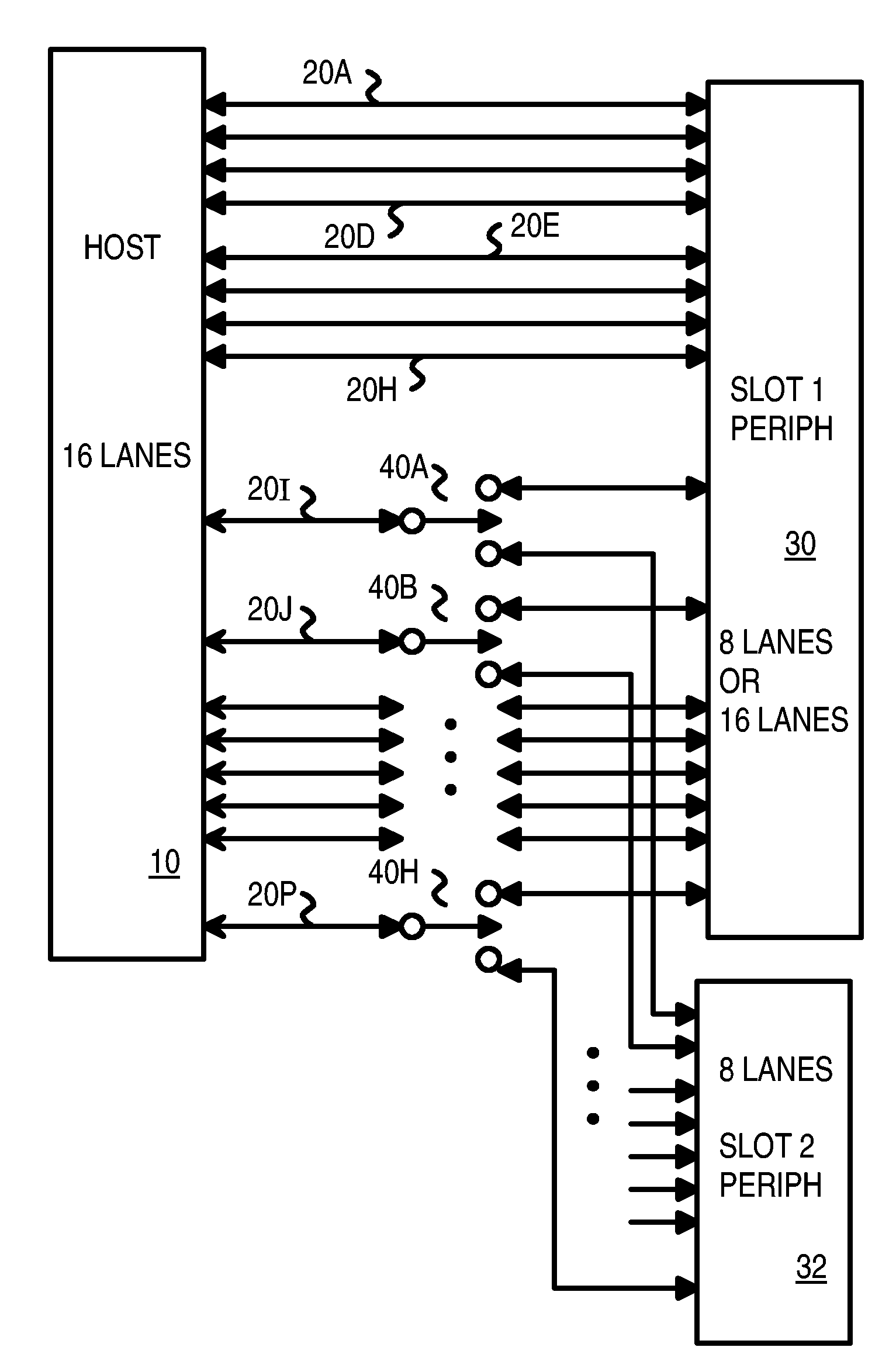
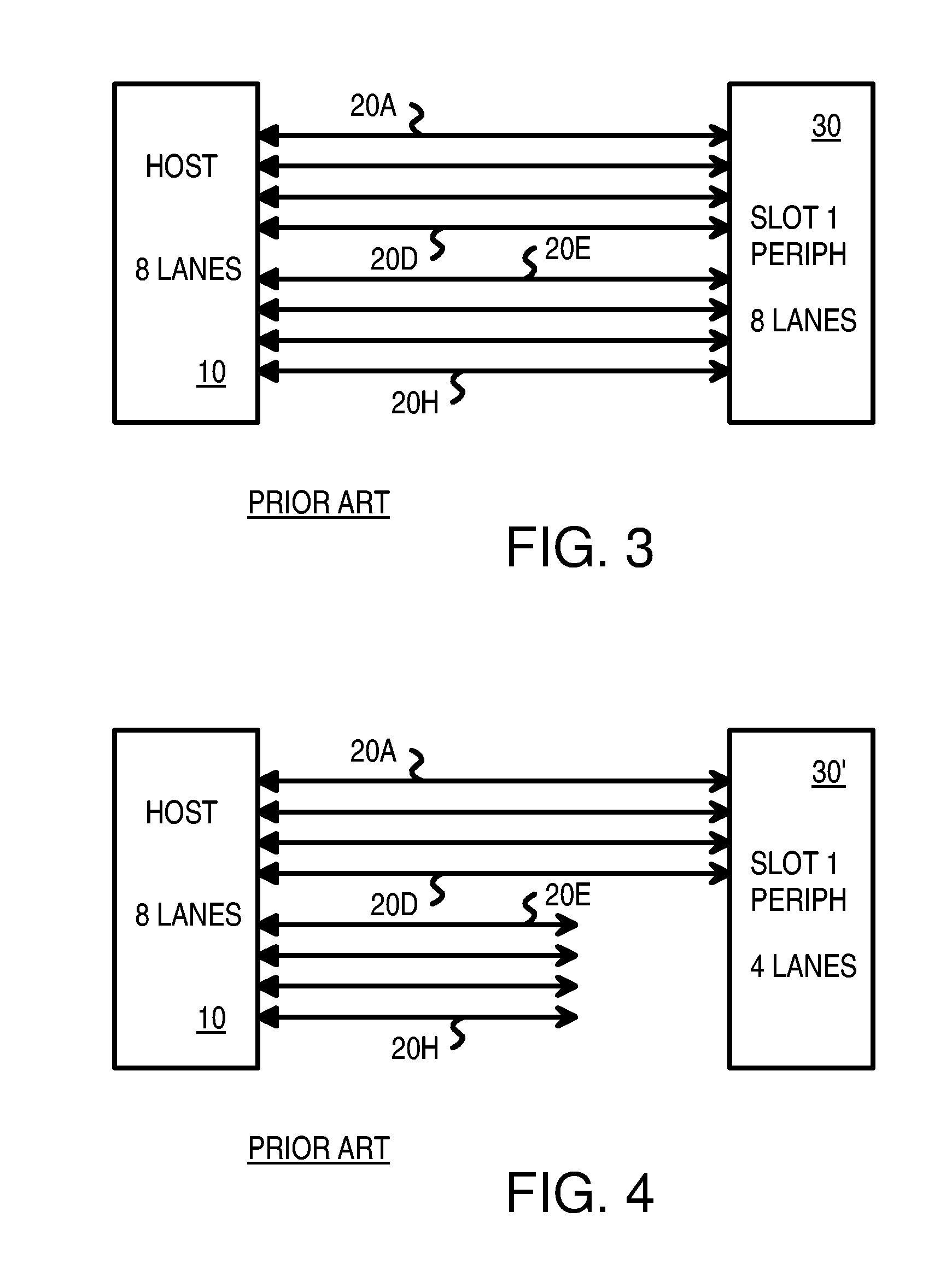
Optimized topographies for dynamic allocation of PCI express lanes using differential muxes to additional lanes to a host
Many Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIE) lanes are available between a root complex host and peripherals inserted into slots. Each PCIE lane is a bi-directional serial bus, with a transmit differential pair and a receive differential pair of data lines. Some lanes are directly connected from the root complex host to each slot. Each slot is driven by a different port and a different direct physical layer on the host. Other lanes are configurable and can be driven by any port and use a configurable physical layer on the host. These configurable lanes pass through an external switch or crossbar that connects the lanes from the host to one or more of the slots. The direct-connect lanes can be the first lanes to a slot while the configurable lanes are the higher-numbered lanes.
Owner:DIODES INC
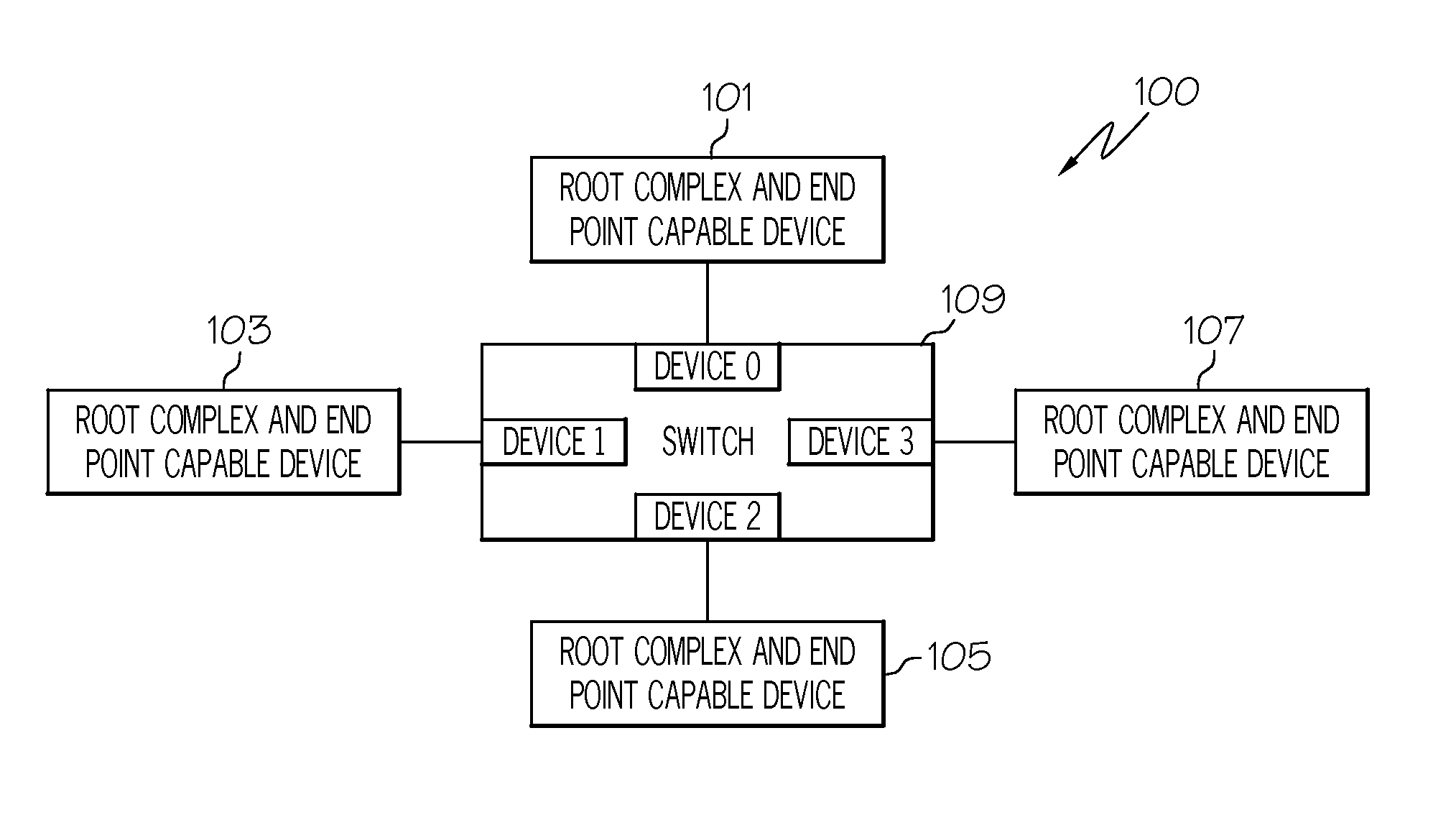
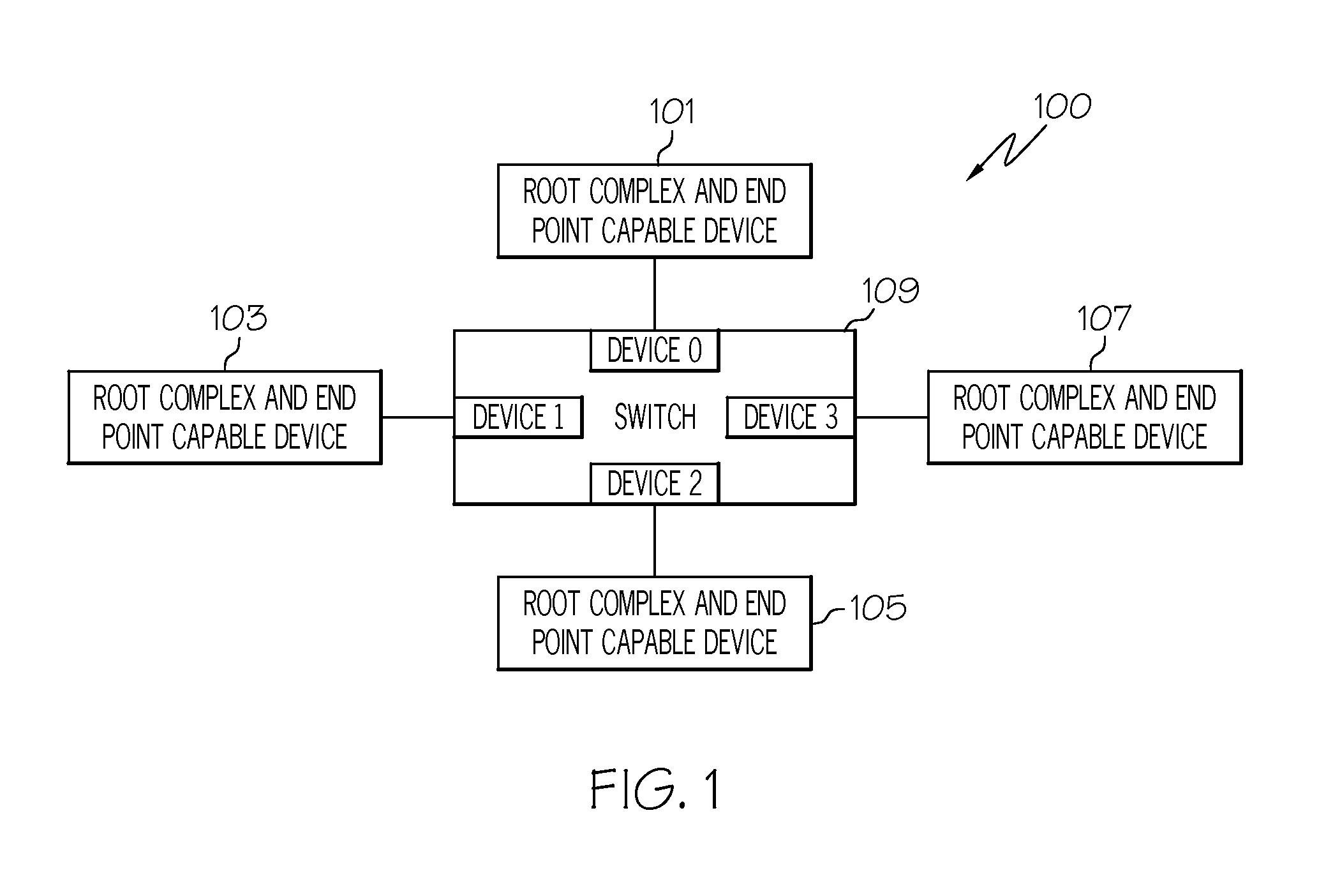
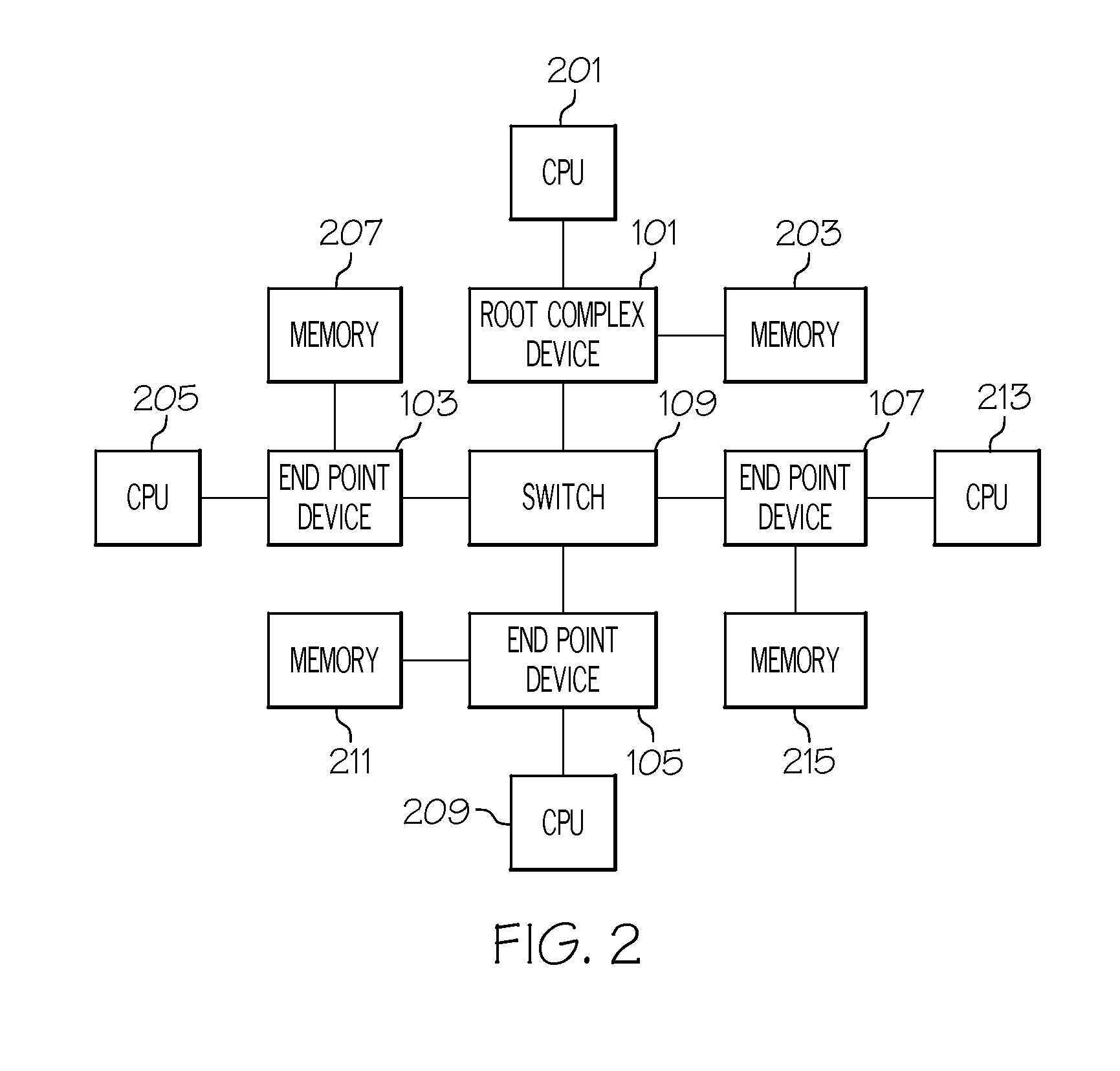
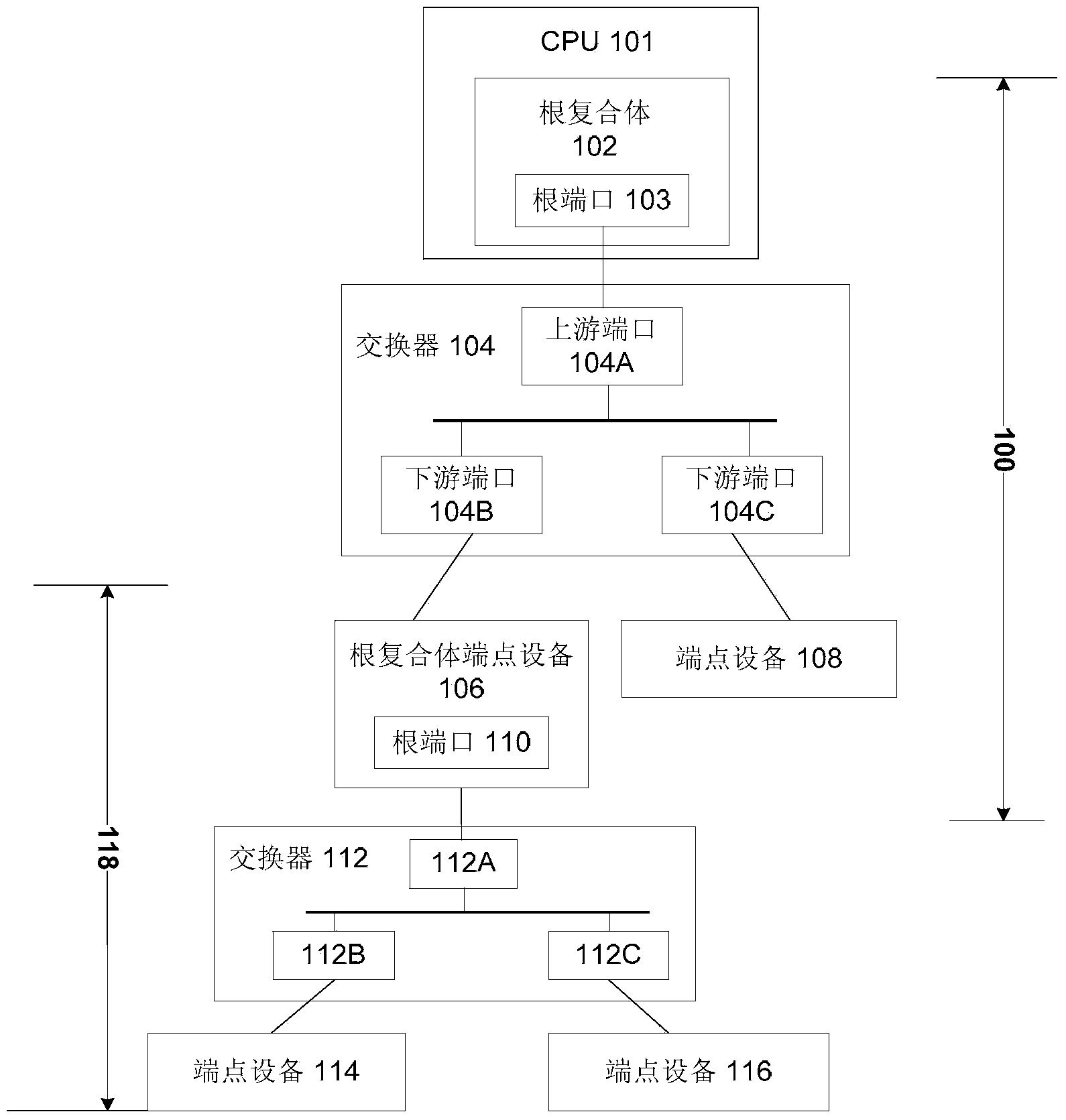
Root complex connection system
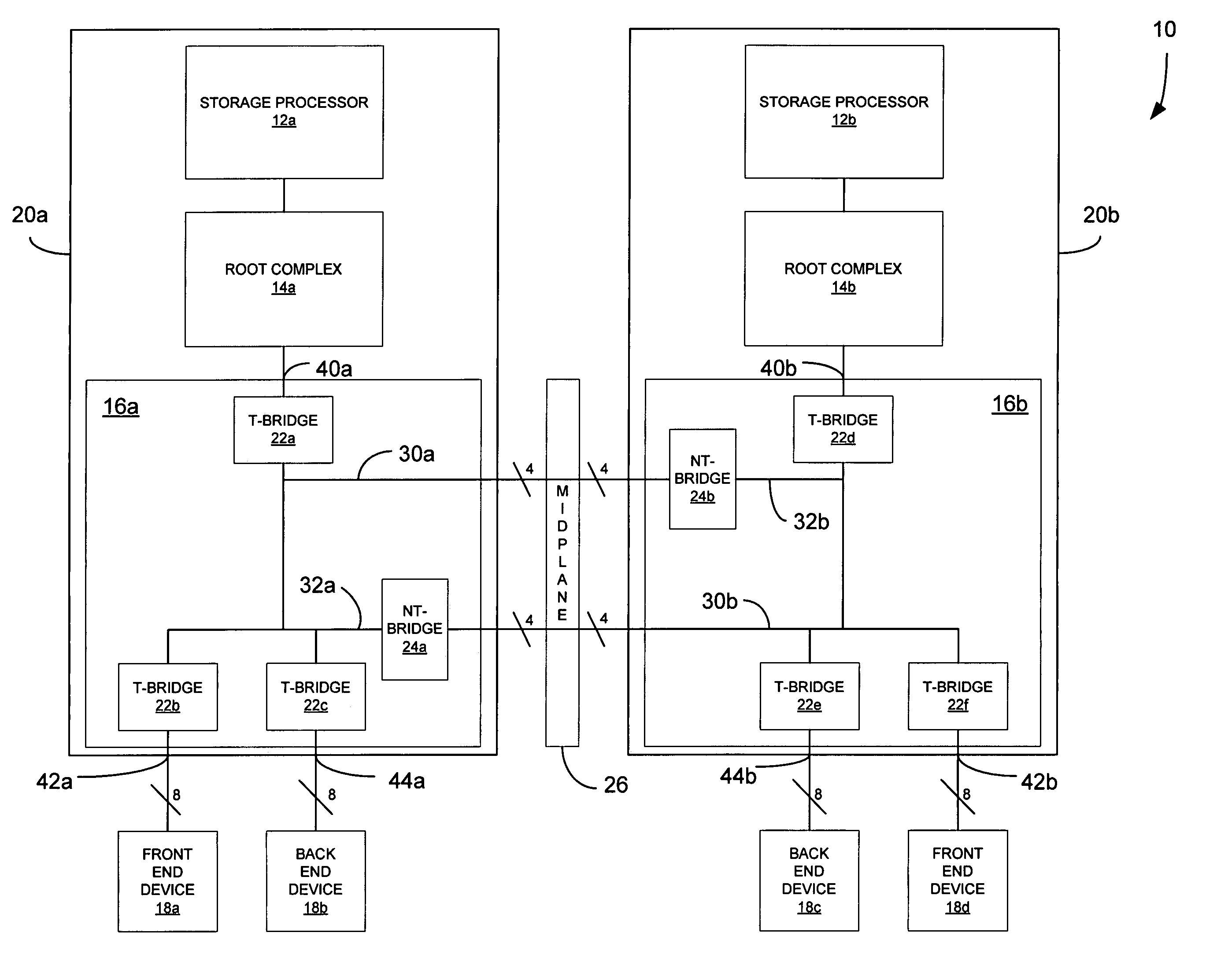
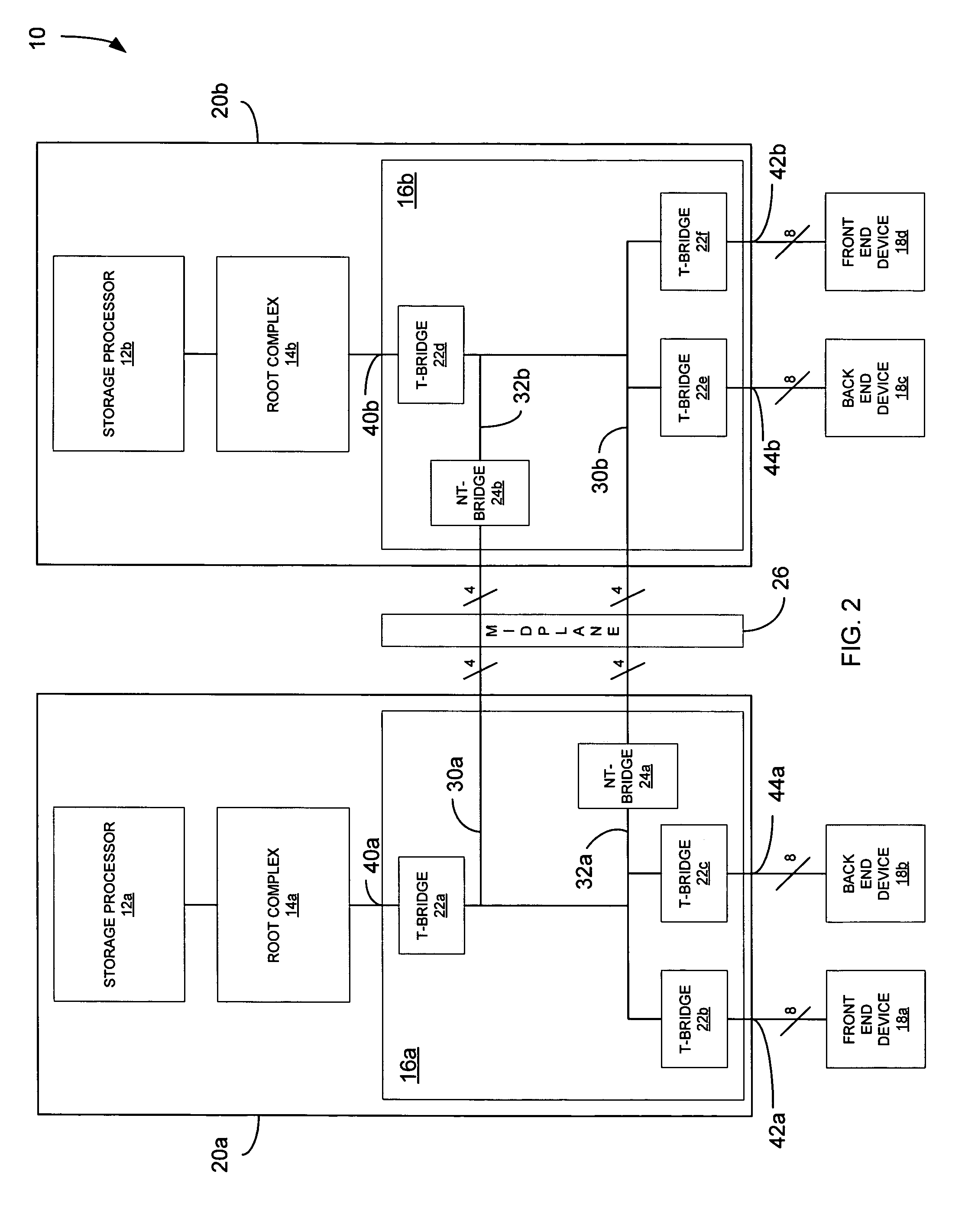
ActiveUS7062594B1Low costReduce complexityElectric digital data processingData processing systemRoot complex
A data processing system includes first and second data processing devices coupled to each other through a midplane. Each data processing device includes a data storage processor; a root complex coupled to the data storage processor; and a switch device coupled between the root complex and at least one end point device. The switch device includes a first transparent bridge coupled to the root complex and a second transparent bridge coupled between the first transparent bridge and the at least one end point device, a first data path connected between the first transparent bridge and the midplane and a second data path connected between the first transparent bridge and the midplane through a non-transparent bridge. The first data path of the first data processing device is connected to the second data path of the second data processing device through the midplane and the second data path of the first data processing device is connected to the first data path of the second data processing device through the midplane, such that data transmitted between the root complexes of each of the first and second data processing devices is transmitted through only one non-transparent bridge.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
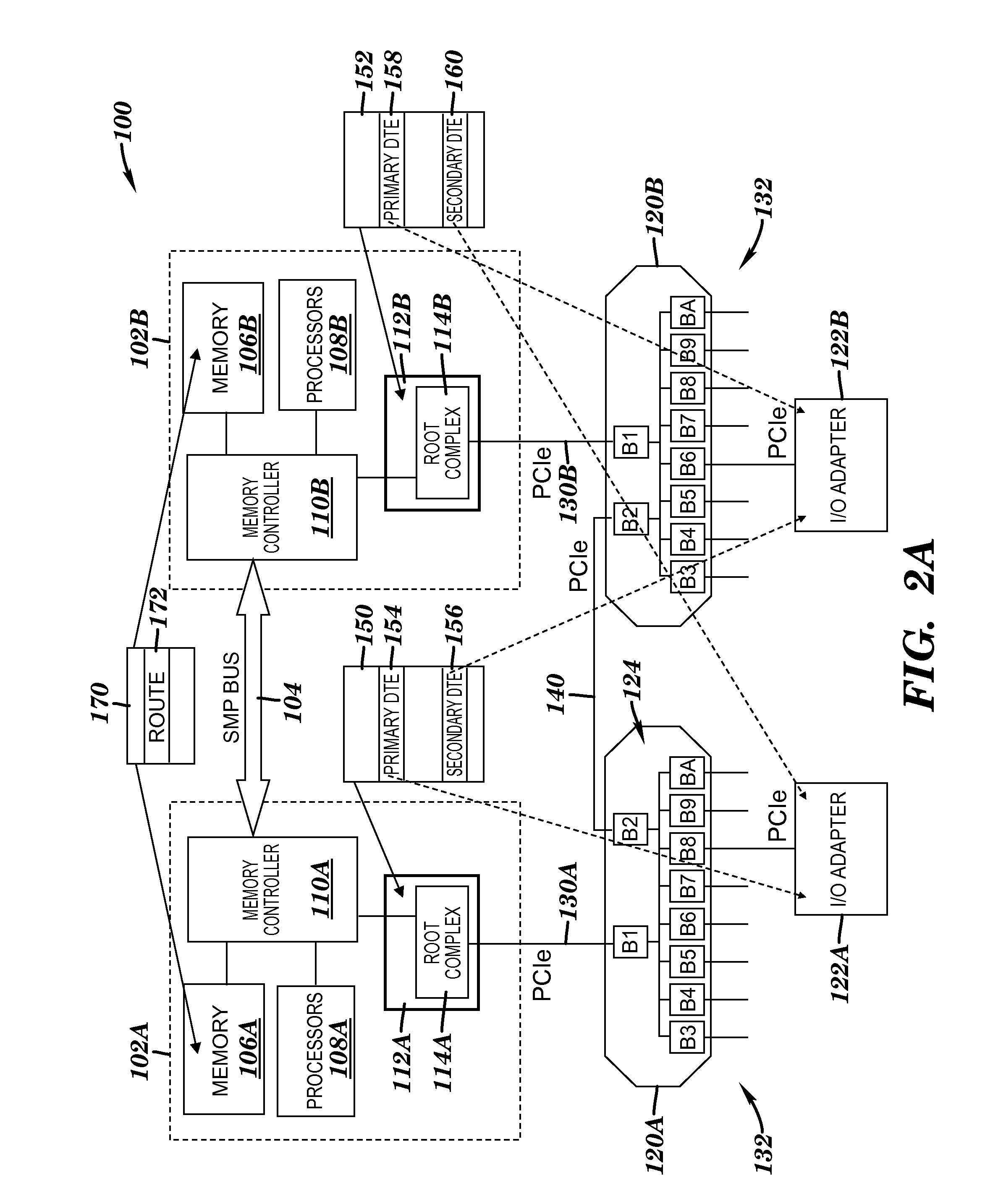
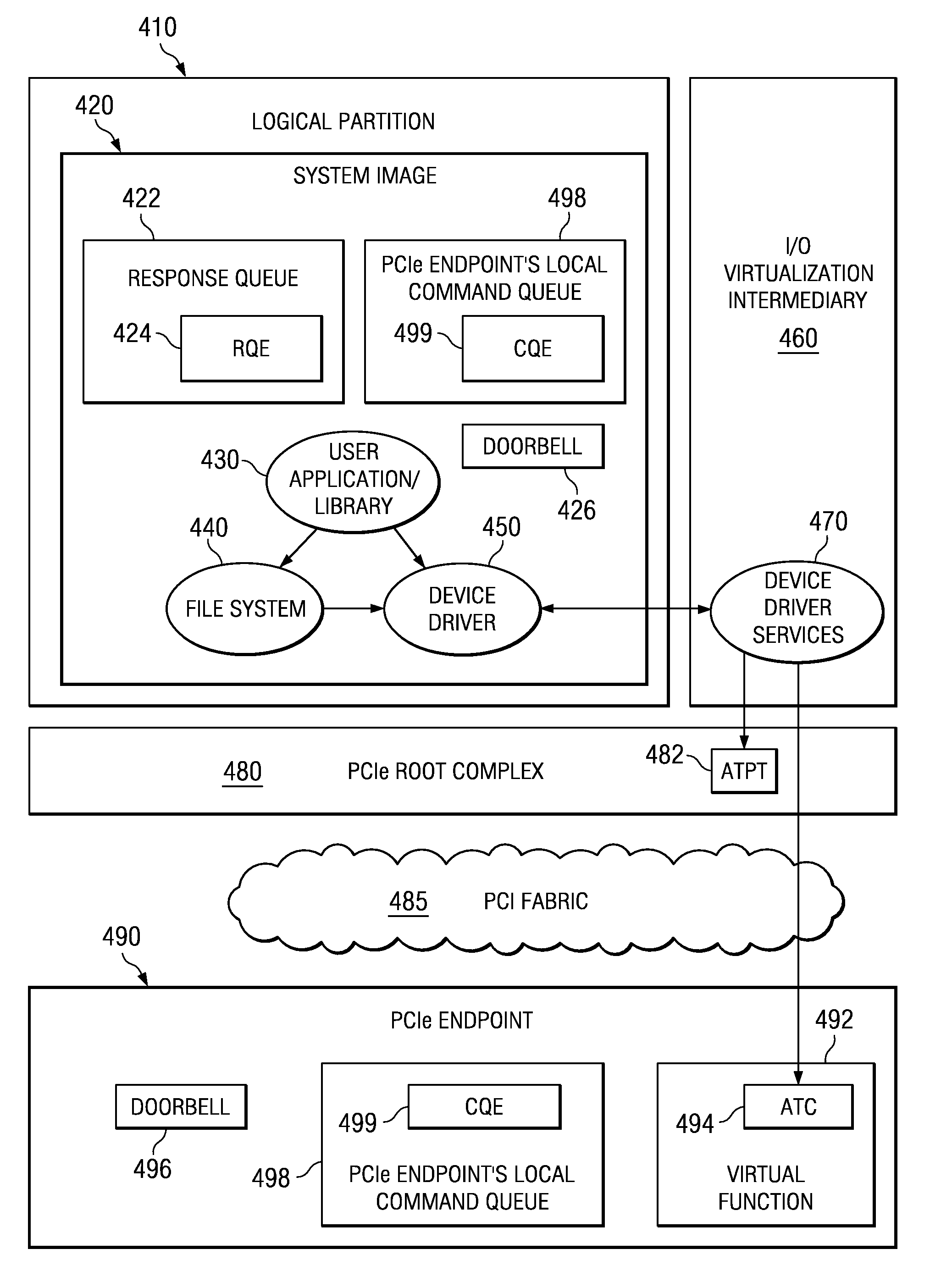
Splitting endpoint address translation cache management responsibilities between a device driver and device driver services
InactiveUS7617377B2Memory adressing/allocation/relocationMicro-instruction address formationRoot complexVia device
Owner:IBM CORP
Motherboard for supporting multiple graphics cards
InactiveUS7782325B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsScalable systemGraphics
The invention provides a motherboard that uses a high-speed, scalable system bus such as PCI Express® to support two or more high bandwidth graphics slots. The lanes from the motherboard chipset may be directly routed to two or more graphics slots. For instance, the chipset may route (1) thirty-two lanes into two ×16 graphics slots; (2) twenty-four lanes into one ×16 graphics slot and one ×8 graphics slot (the ×8 slot using the same physical connector as a ×16 graphics slot but with only eight active lanes); or (3) sixteen lanes into two ×8 graphics slots (again, physically similar to a ×16 graphics slot but with only eight active lanes). Alternatively, a switch can convert sixteen lanes coming from the chipset root complex into two ×16 links that connect to two ×16 graphics slots. The system according to the invention is agnostic to a specific chipset.
Owner:DELL MARKETING
Creation and management of ATPT in switches of multi-host PCI topologies
InactiveUS20070136458A1Digital computer detailsElectric digital data processingRouting tableRoot complex
A PCI control manager provides address translation protection tables in switches in a PCI fabric. The PCI control manager discovers the fabric and provides a virtual tree for each root complex. A system administrator may then remove endpoints that do not communicate with the root complex to configure the PCI fabric. The PCI control manager then provides updated ATPT tables to the switches. When a host or adapter is added, the master PCM goes through the discovery process and the ATPT tables and adapter routing tables are modified to reflect the change in configuration. The master PCM can query the ATPT tables and adapter routing tables to determine what is in the configuration. The master PCM can also destroy entries in the ATPT tables and adapter routing tables when a device is removed from the configuration and those entries are no longer valid.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for transferring packets between devices connected to a PCI-Express bus
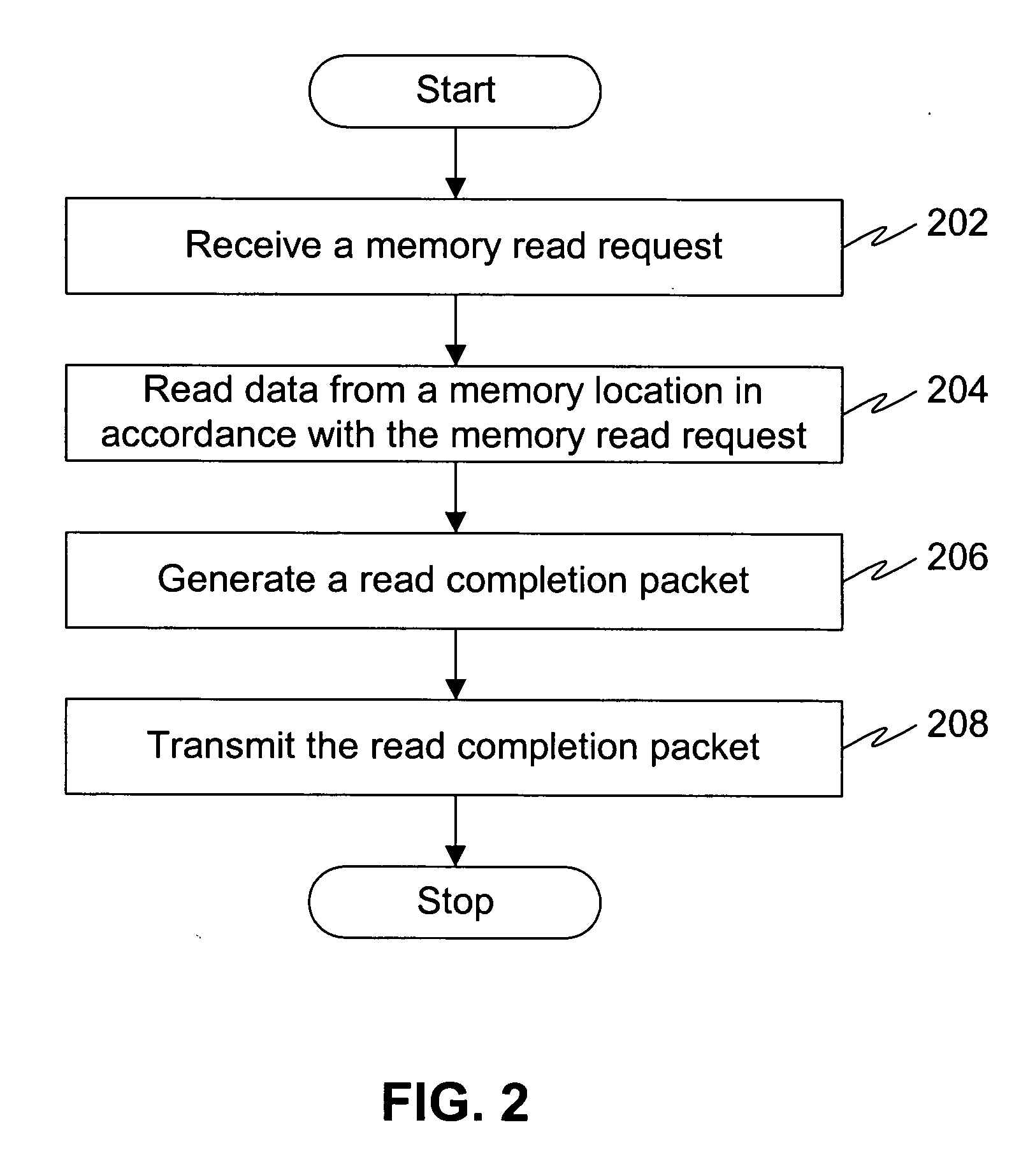
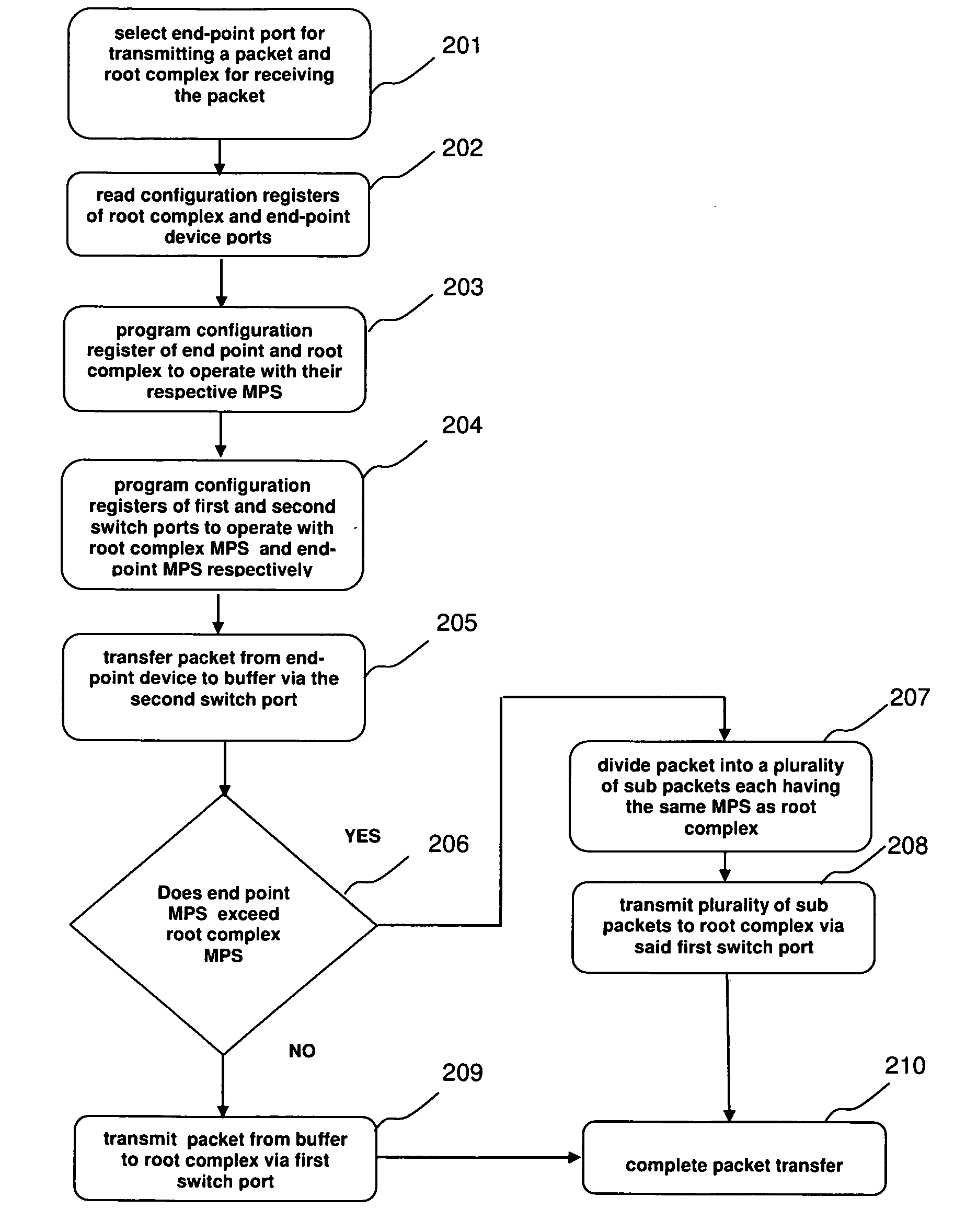
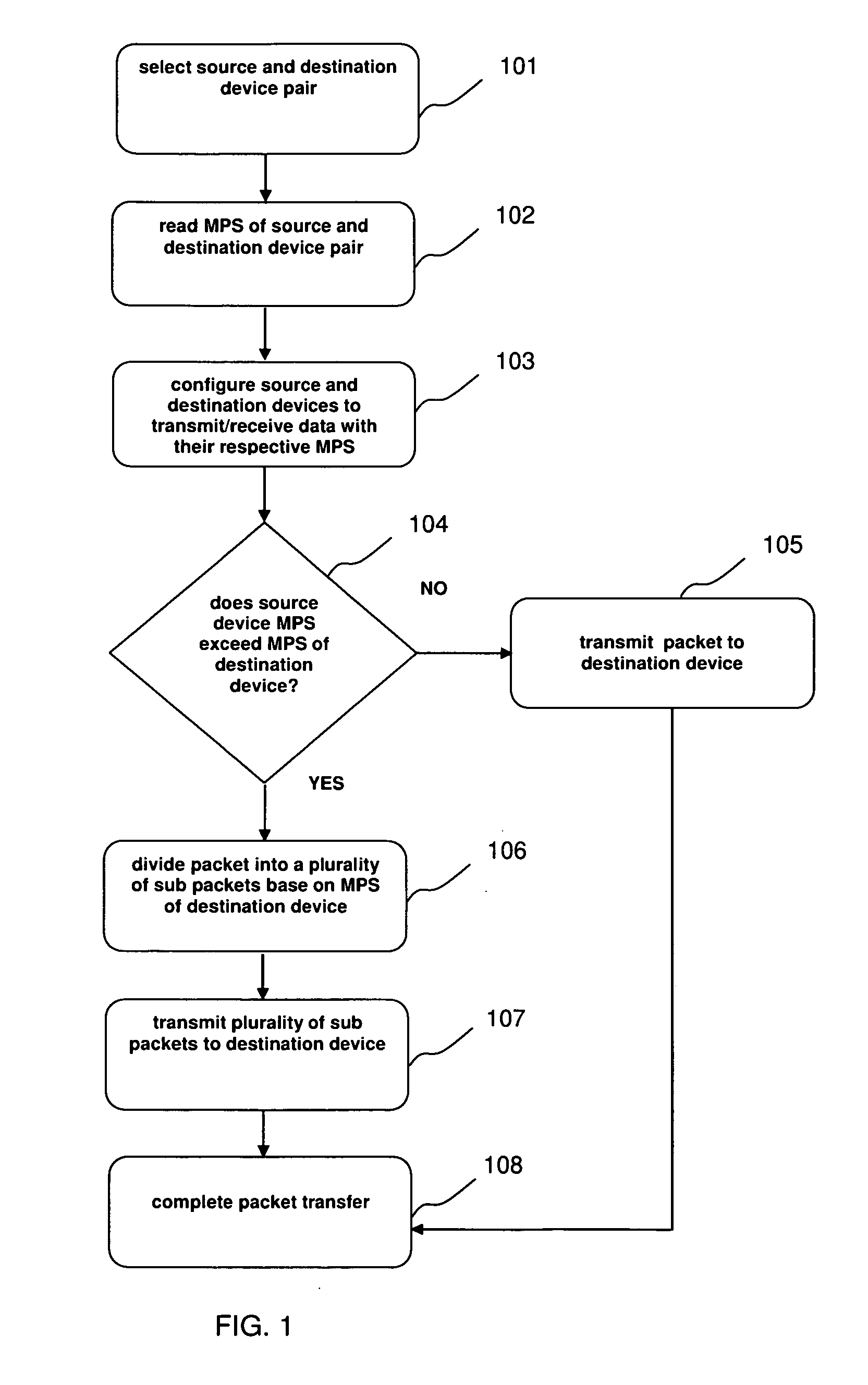
InactiveUS20080034147A1Improve system performanceSolve excessive overheadElectric digital data processingRoot complexPCI Express
A method, system and computer program for transferring packets between devices connected to a PCI-Express bus of a computer. A selected pair of devices, such as for example a root complex device and an endpoint device or a pair of endpoint devices, connected to the PCI-Express bus, are configured to transmit / receive data with their respective maximum payload size (MPS). A packet, such as for example a read completion packet, a write memory packet or a message request packet, can then be transmitted from the source device to the destination device. If the source device MPS exceeds the destination device MPS, the packet can be divided into a plurality of sub-packets. Each of sub packets has a maxmimum payload size based on the MPS of the destination device. The sub-packets can then be transmitted to the destination device so that the packet can be delivered to the destination device.
Owner:LSI CORPORATION
System and Method for Extended Peripheral Component Interconnect Express Fabrics
An exemplary embodiment extended peripheral component interconnect express (PCIe) device includes a host PCIe fabric comprising a host root complex. The host PCIe fabric has a first set of bus numbers and a first memory mapped input / output (MMIO) space on a host CPU. An extended PCIe fabric includes a root complex endpoint (RCEP) as part of an endpoint of the host PCIe fabric. The extended PCIe fabric has a second set of bus numbers and a second MMIO space separate from the first set of bus numbers and the first MMIO space, respectively.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
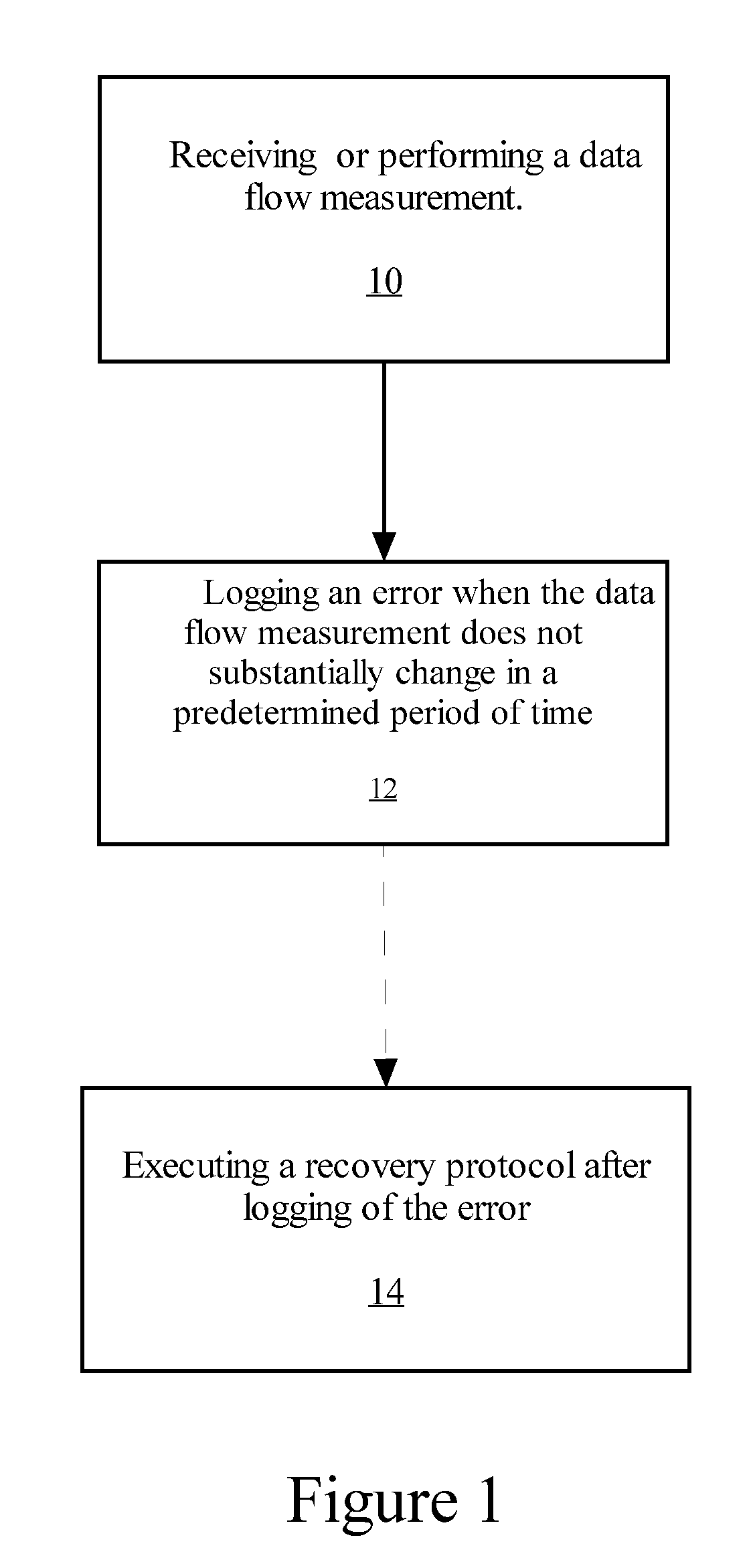
Flow control timeout mechanism to detect pci-express forward progress blockage
A method for detecting lack of forward progress in a PCI Express includes a step in which a data flow measurement is received or performed. This data flow measurement provides the capacity of the connected Switch or Endpoint device to receive data packets from a Root Complex transmit channel. An error is logged when the data flow measurement does not substantially change in a predetermined period of time. A recovery protocol is executed after logging of the error. A system implementing the method of the invention is also provided.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Apparatus and Method for Splitting Endpoint Address Translation Cache Management Responsibilities Between a Device Driver and Device Driver Services
InactiveUS20080092148A1Lower latencyReduce latencyMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsRoot complexVia device
An apparatus and method for splitting responsibilities for communicating with an endpoint between a device driver and device driver services are provided. With the apparatus and method, the device driver is responsible for managing queues for communicating requests between applications in a logical partition and the endpoint. The device driver further invokes memory management via device driver services. The device driver services are responsible for managing memory accessible by the endpoint, including the address translation and protection table (ATPT) or a root complex and the address translation caches (ATCs) of the endpoint. The device driver services may associate untranslated addresses for data structures used to communicate between a system image and the endpoint. The endpoint may request translations of the untranslated addresses and may cache the translations in the ATCs.
Owner:IBM CORP
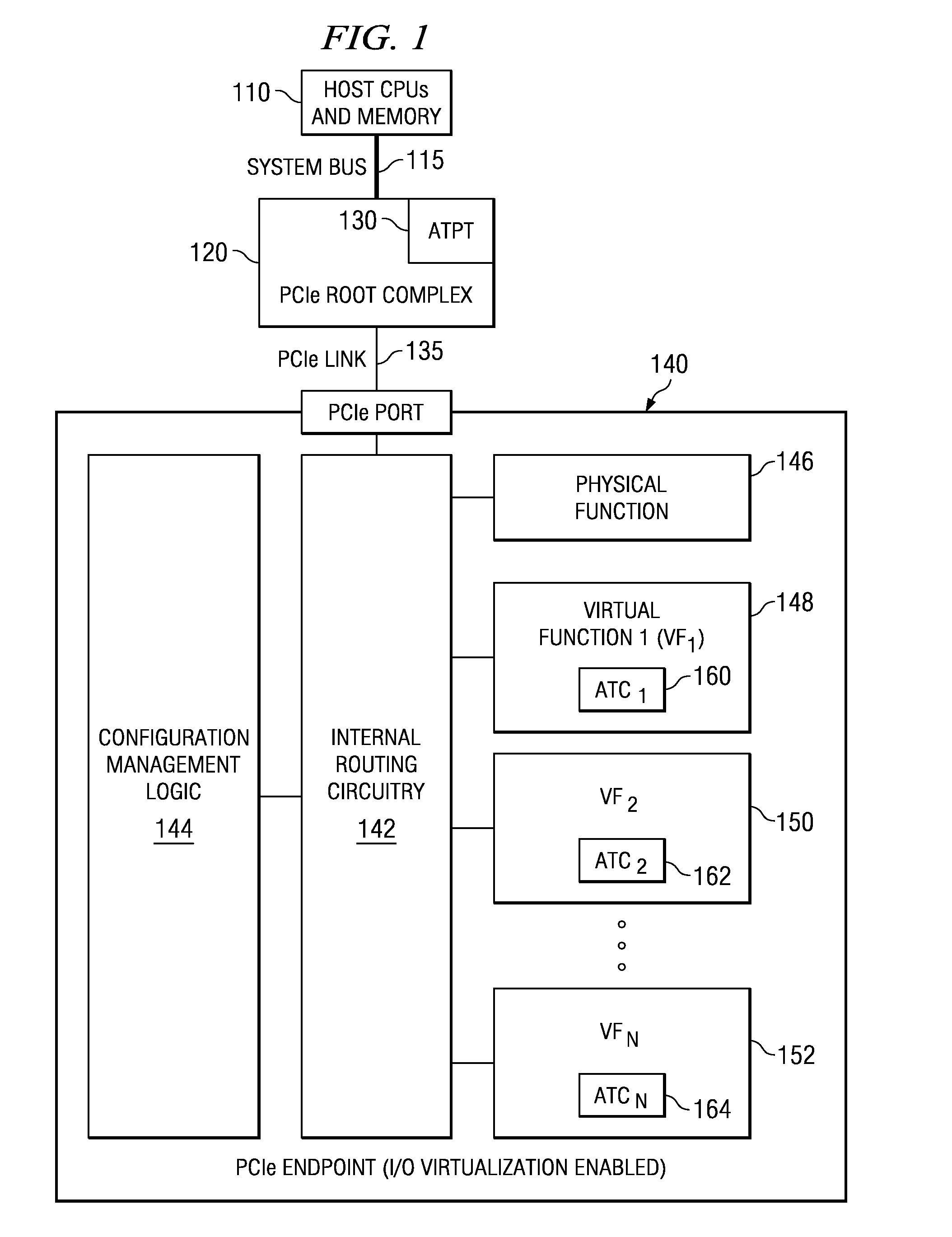
Pcie switch for aggregating a large number of endpoint devices
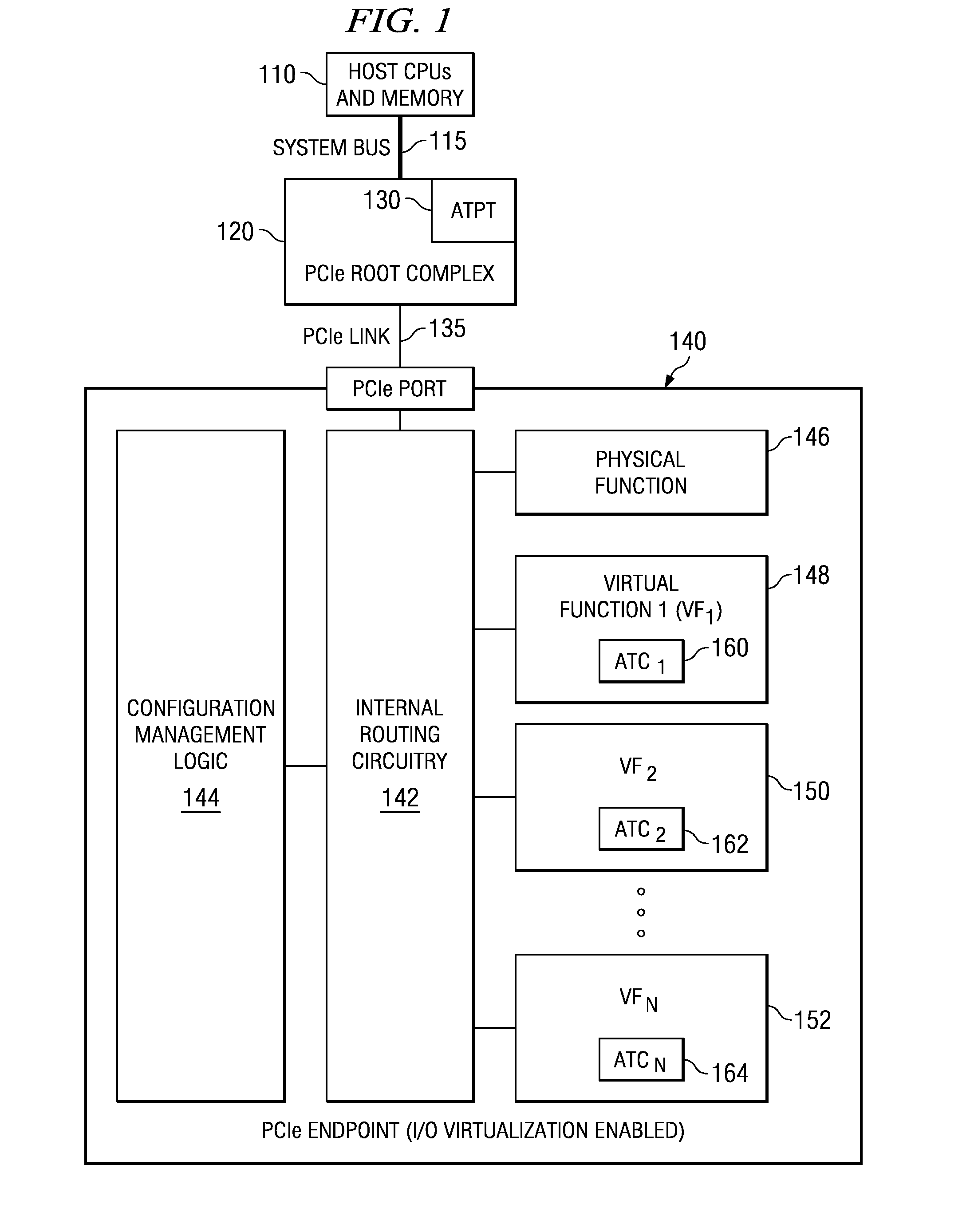
ActiveUS20180101498A1Energy efficient computingElectric digital data processingRoot complexComputer science
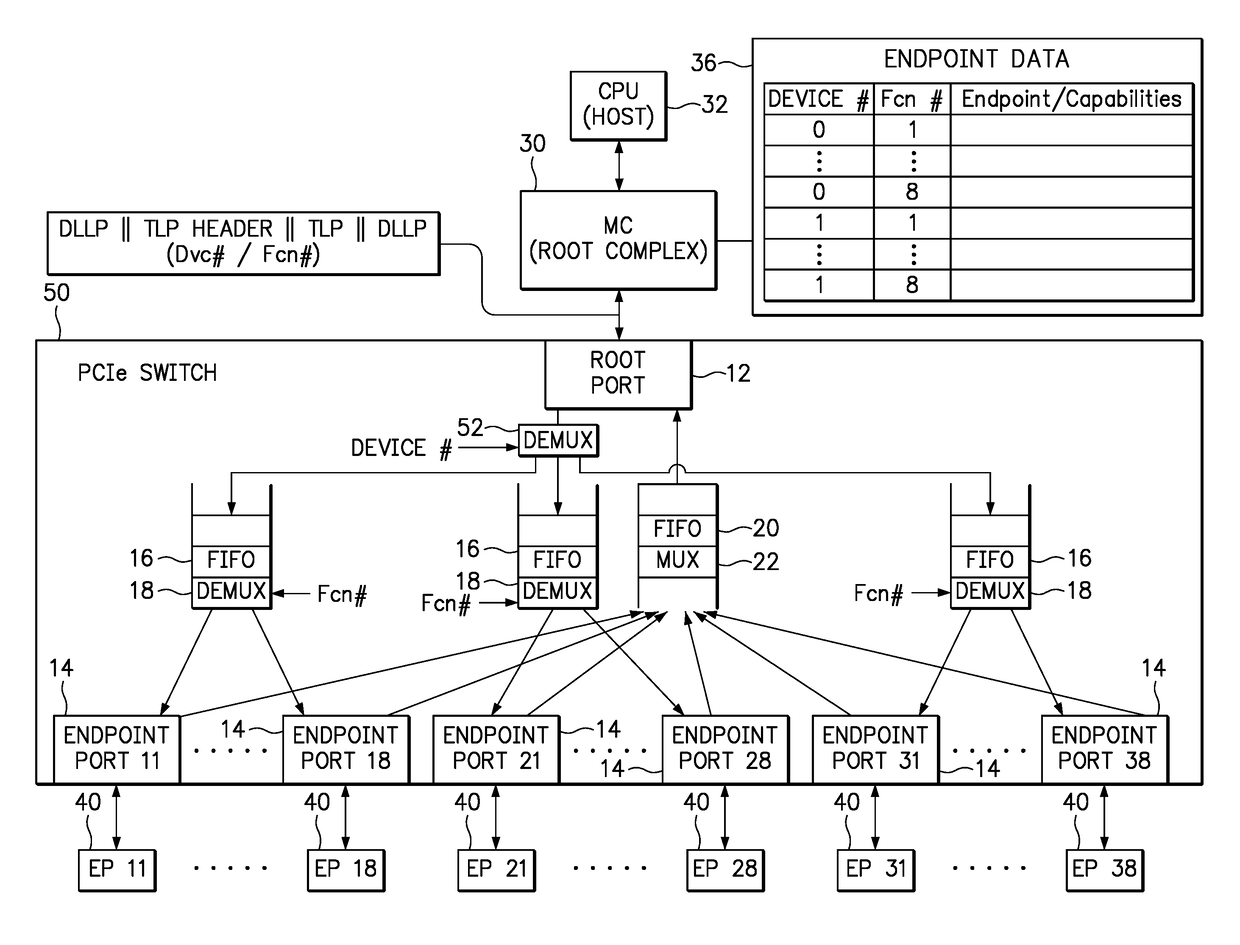
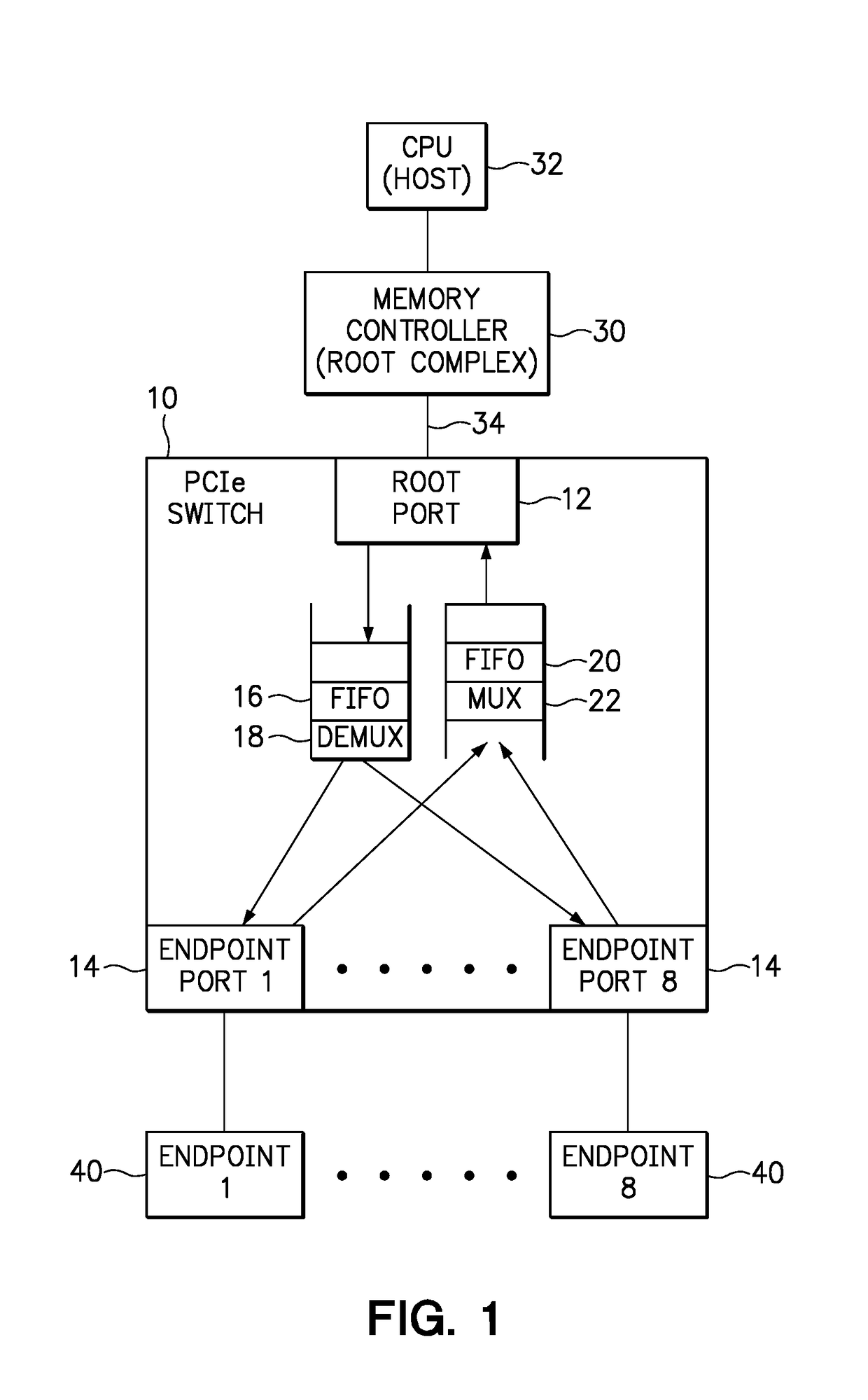
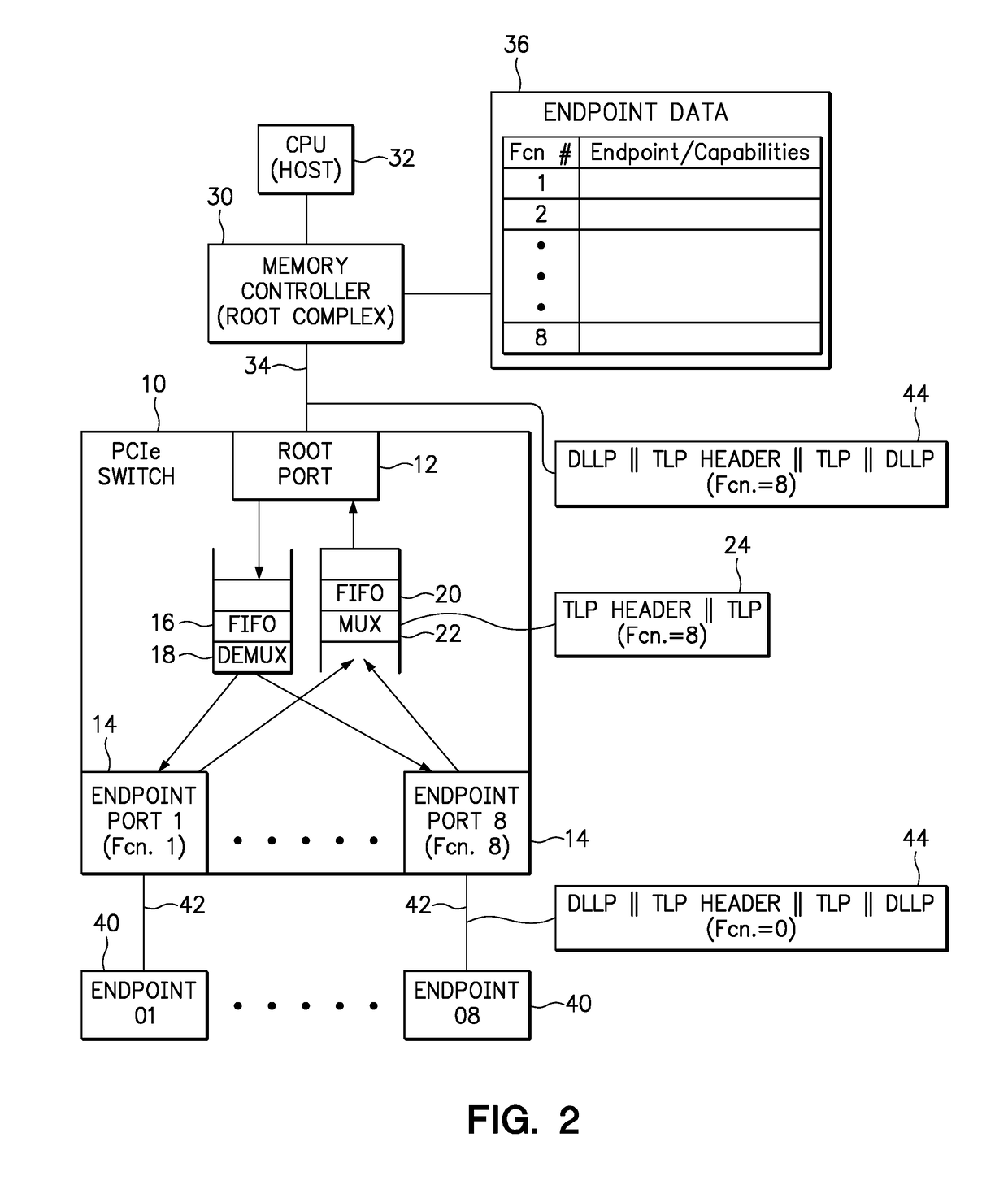
An apparatus includes a root port for coupling to a root complex, and a plurality of endpoint ports for coupling to endpoint devices, wherein each endpoint port is associated with a function number. A downstream buffer queues transaction layer packets (TLPs) received from the root port, wherein each TLP in the downstream buffer is directed to an endpoint port associated with the identified function number. An upstream buffer queues TLPs received from each endpoint port, and directs the queued TLPs to the root port. A method includes associating a function number with each endpoint port of a switch, wherein each endpoint port is adapted for coupling to an endpoint device. The method further includes receiving a first TLP from a root complex, identifying a function number within the first TLP, and directing the first TLP to an endpoint device through the endpoint port associated with the identified function number.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
Flow-splitting and buffering PCI express switch to reduce head-of-line blocking
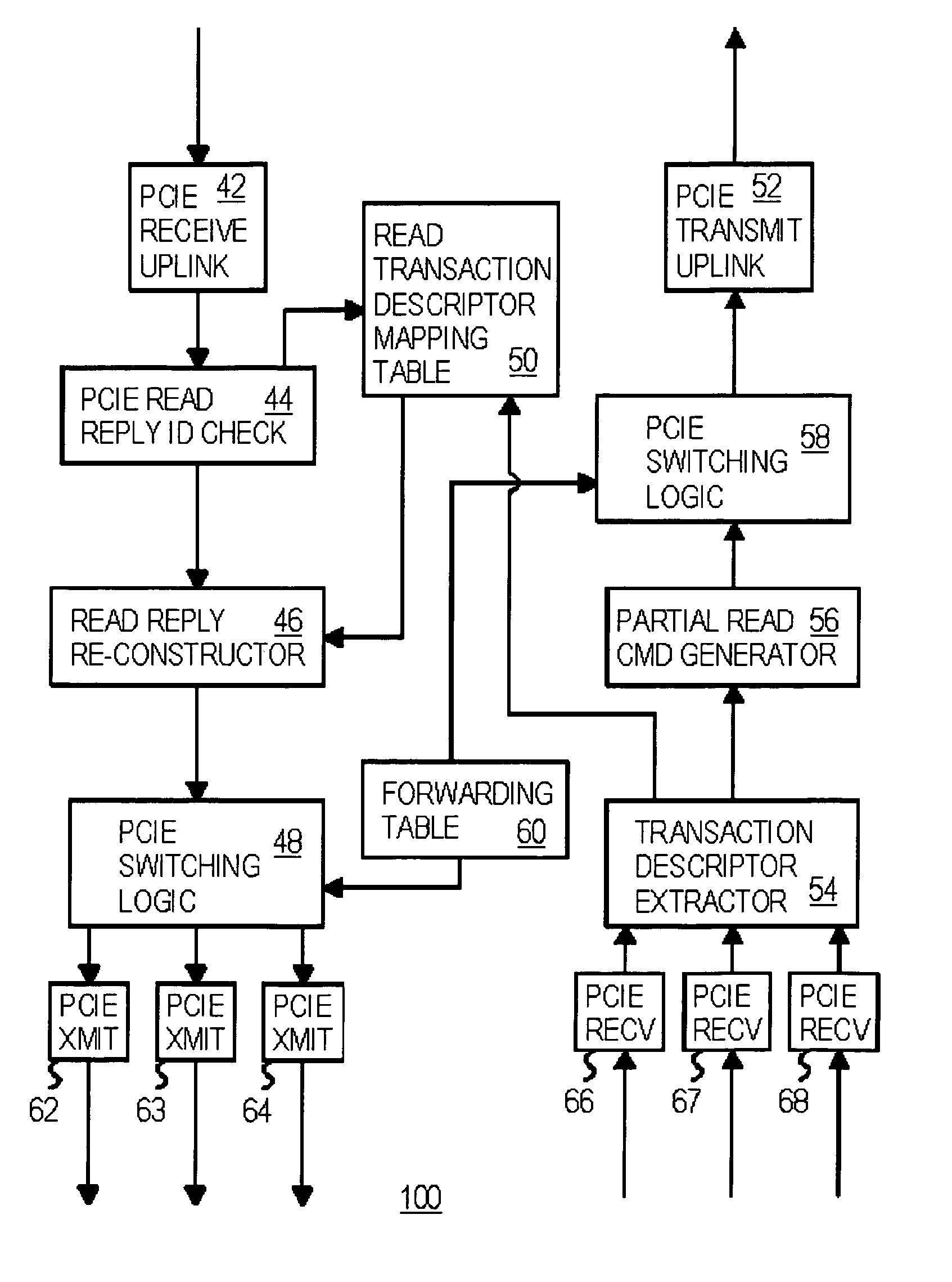
An enhanced Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) switch eliminates or reduces head-of-line blocking for memory reads initiated by peripheral endpoint devices. A memory-read request packet from a first peripheral endpoint device is intercepted by the enhanced PCIe switch, which generates a series of substitute request packets to the root complex and memory. The same requestor ID is used in all packets, but the original tag is replaced with a sequence of substitute tags in the substitute packets. The switch receives a sequence of reply packets with memory-read data, replaces substitute tags with original tags, and sends the reply packets to the peripheral endpoint device. Substitute request packets for different peripheral endpoint devices are alternately sent from the switch to the root complex to prevent head-of-line blocking by one peripheral endpoint device. The amount of data in each substitute request packet is smaller than the original requests to reduce blocking latencies.
Owner:DIODES INC
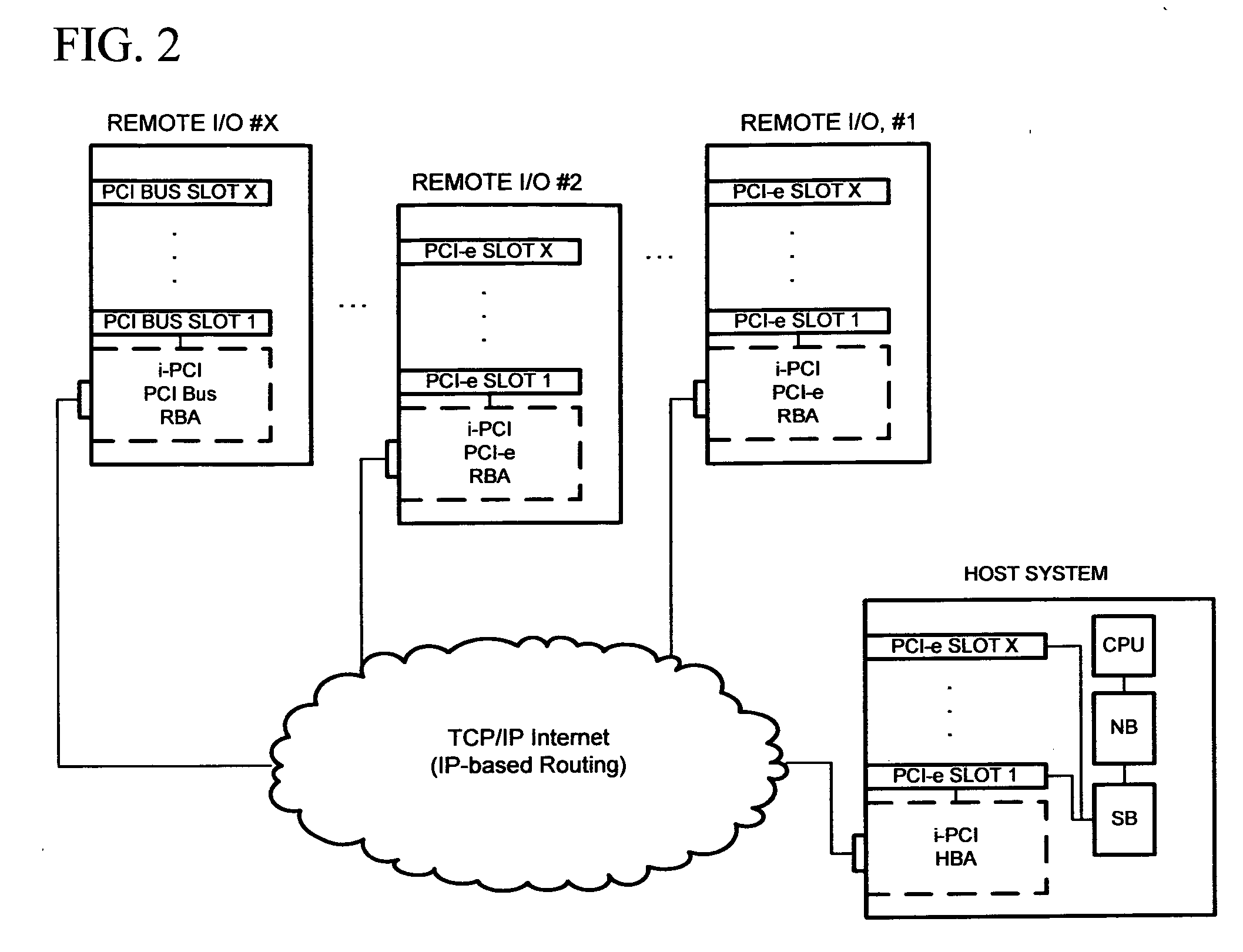
Software-based virtual PCI system
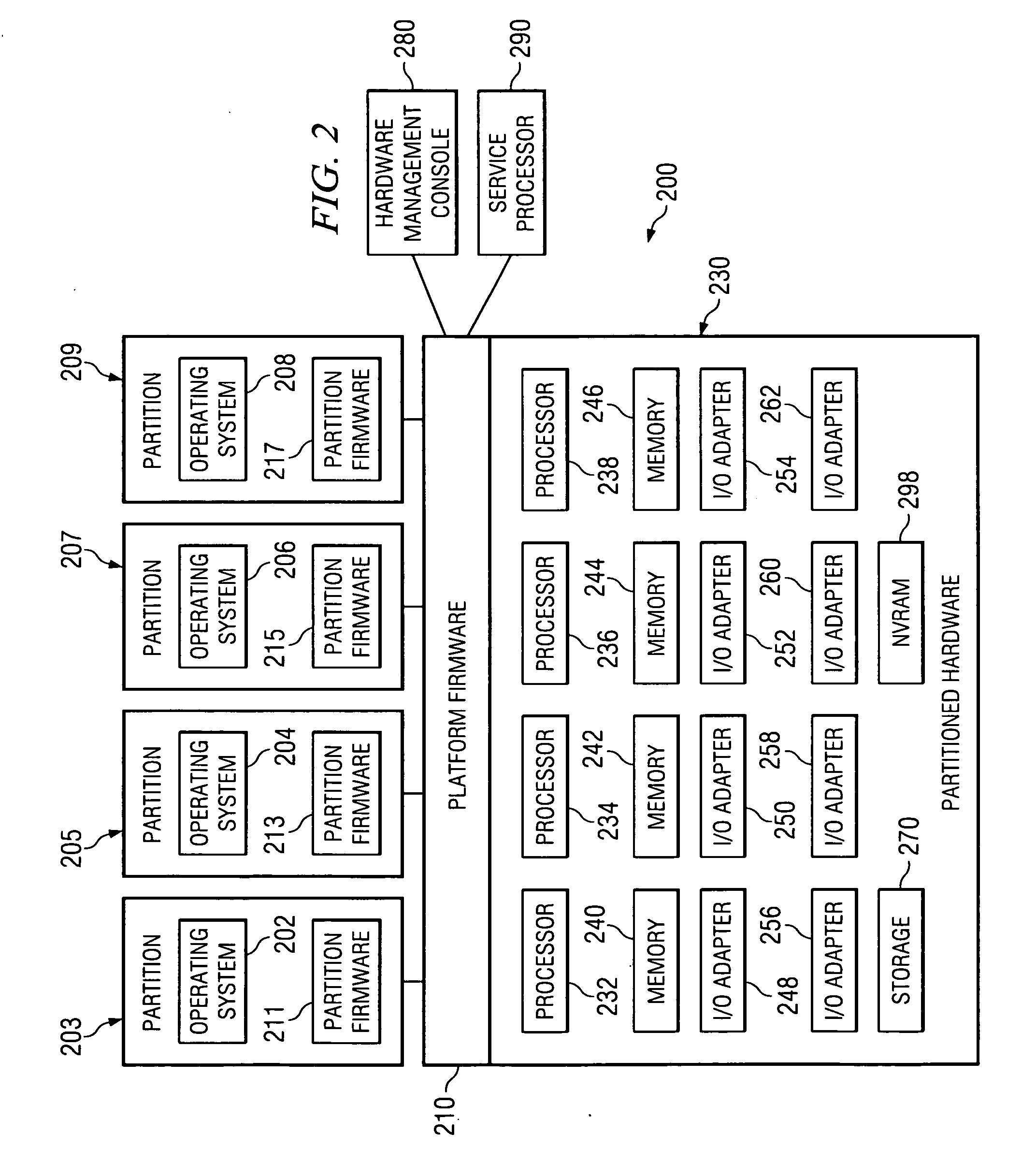
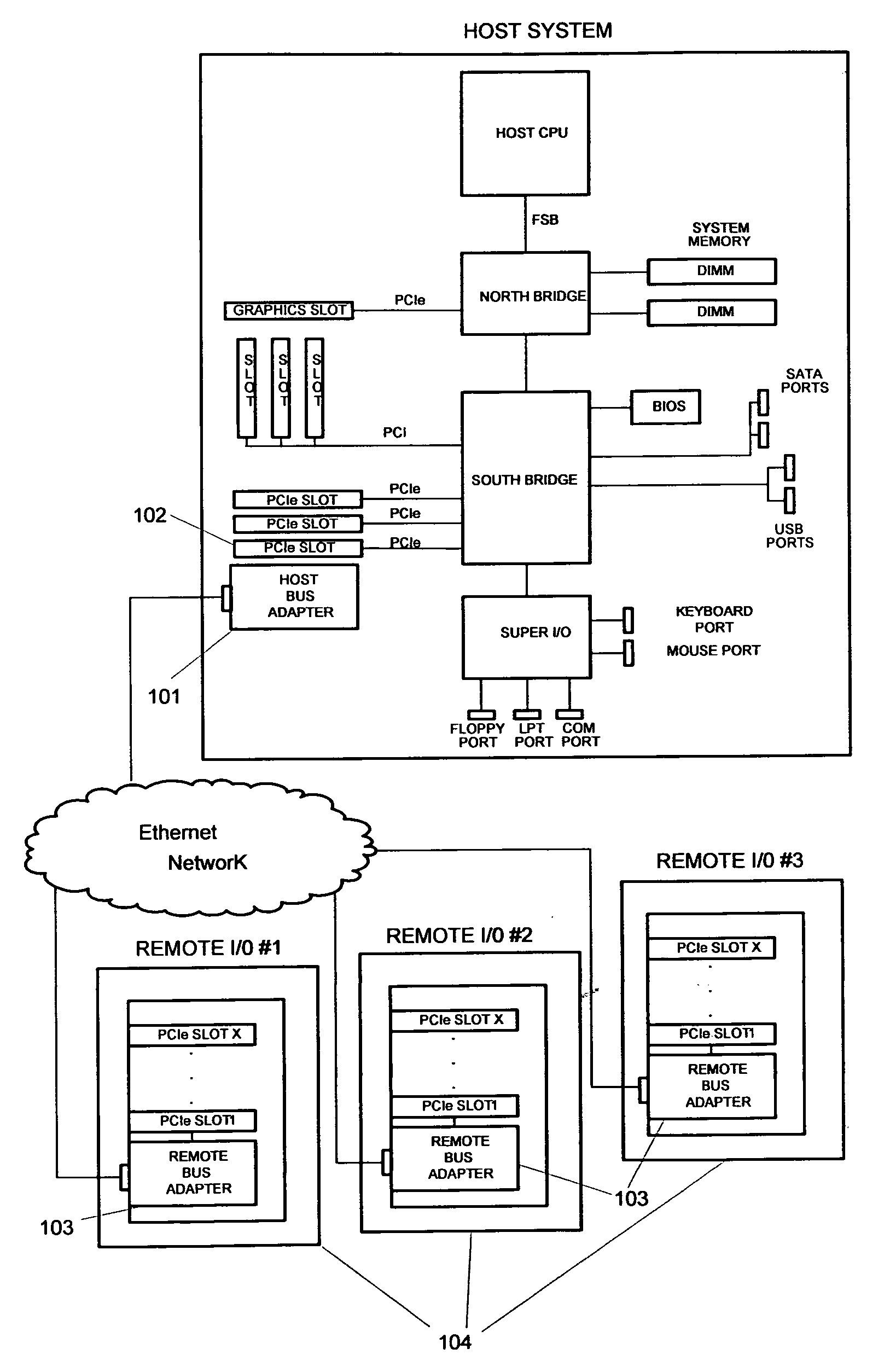
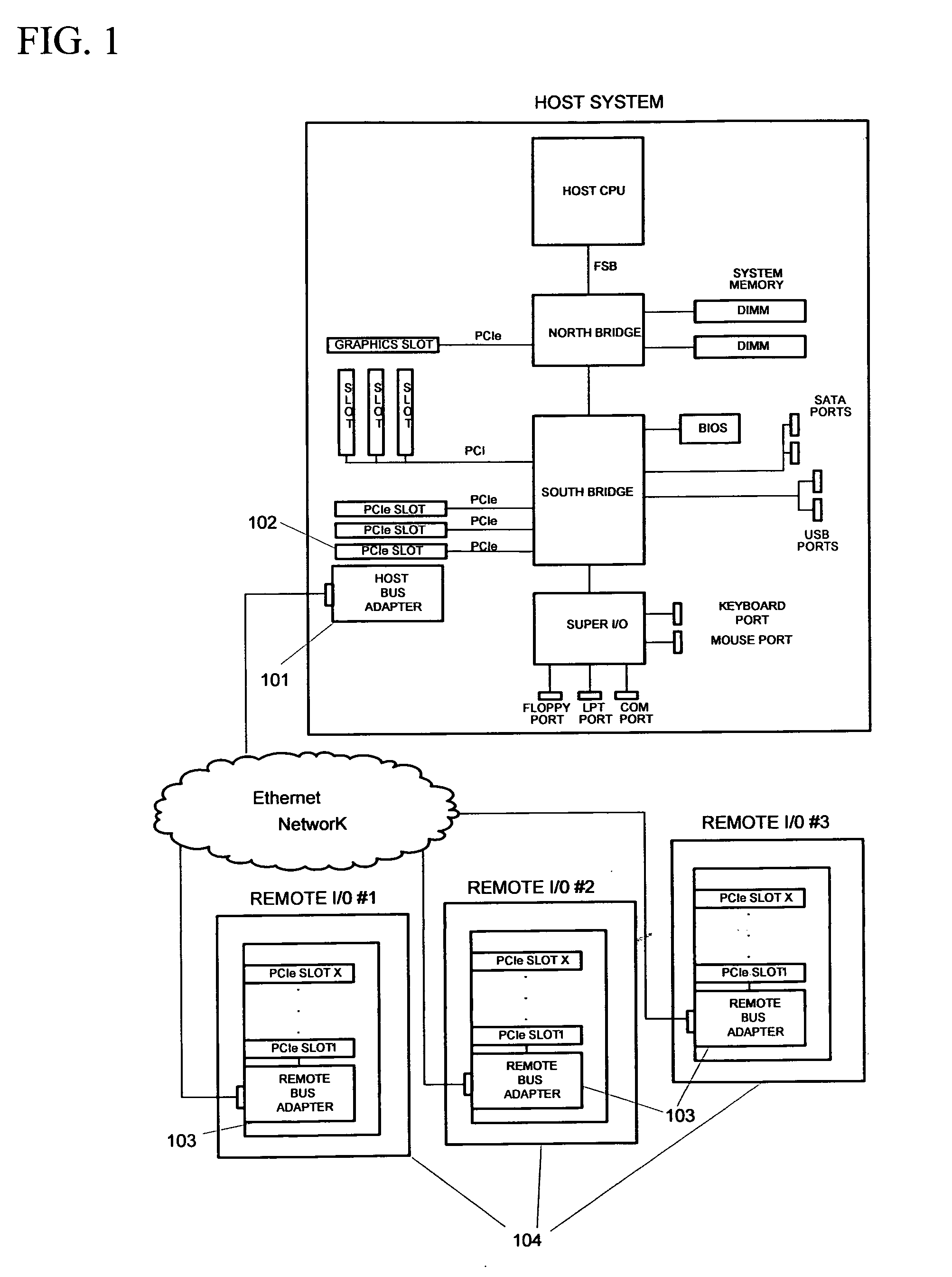
A means for extending a PCI System of a host computer via software-centric virtualization. A Root Complex is virtualized at the host computer, and physically separated with a portion located remotely at an Endpoint, such as at a Remote Bus Adapter. One aspect of the invention avoids the need for a Host Bus Adapter. The invention utilizes 1 Gbps-10 Gbps or greater connectivity via the host's existing standard LAN adapter along with unique software to form the virtualization solution. The invention works within a host's PCI Express topology, extending the topology by adding an entire virtual I / O hierarchy via virtualization. The invention enables I / O virtualization in those implementations where a specialized host bus may not be desirable or feasible. Some examples of this may be a laptop computer, an embedded design, a cost-sensitive design, or a blade host where expansion slots are not available or accessible.
Owner:NUON
Autonomic PCI Express Hardware Detection and Failover Mechanism
A system with an autonomic PCI Express hardware detection and failover mechanism includes a plurality of combination root complex capable and endpoint capable devices. A combination root complex capable and endpoint capable device may be selectively configured to operate in either a root complex mode or an endpoint mode. One of the devices assumes the root complex mode and the remaining devices each assume the endpoint mode. Each of the endpoint mode devices is adapted to detect a failure of the root complex mode device. In response to detection of the failure of the root complex mode device, one of the endpoint mode devices assumes root complex mode. An endpoint device may include a timer with a timeout value. Whenever, an endpoint device receives a communication from the root complex device, the endpoint device restarts its timer. If the timer times out with the endpoint device receiving a communication from the root complex device, the endpoint device issues a read request to the root complex device. If the root complex device does not respond to the read request, the endpoint device assumes root complex mode. Different endpoint devices may be assigned different timeout values. Accordingly, the endpoint device that is assigned the shortest time out value will assume root complex mode upon detection of a root complex device failure.
Owner:IBM CORP
Bus system with multiple modes of operation
An apparatus and a computer-implemented method for processing data in a bus system component. The bus system component is configured to operate in one of an endpoint mode and a root complex mode. Responsive to configuring the bus system component to operate in endpoint mode, the data is processed through the bus system component according to an endpoint process. Responsive to configuring the bus system component to operate in root complex mode, the data is transferred through the bus system component according to a root complex mode. In an illustrative example, the bus system component is a peripheral control interconnect express component.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System and method for communication between host systems using a transaction protocol and shared memories
InactiveUS20080147938A1Digital computer detailsElectric digital data processingPush and pullRoot complex
A system and method for communication between host systems using a transaction protocol and shared memories are provided. Shared memories are initialized based on a discovery process in a communication fabric such that at least one endpoint has address ranges in shared memories of at least two host systems. A transaction oriented protocol may be established for using the shared memories of the host systems to communicate between root complexes and endpoints of the same or different host systems. The transaction oriented protocol specifies a series of transactions to be performed by the various elements, e.g., root complex or endpoint, to push or pull data. Various combinations of push and pull transactions may be utilized.
Owner:IBM CORP
Dual casting pcie inbound writes to memory and peer devices
Methods and apparatus for supporting dual casting of inbound system memory writes from PCIe devices to memory and a peer PCIe device. An inbound system memory write request from a first PCIe device is received at a PCIe root complex and the memory address is inspected to determine whether it falls within an address window defined for dual casting operations. If it does, an IO write request is generated from the inbound system memory write request and sent to a second PCIe device associated with the address window. During a parallel operation, the original inbound system memory write request is forwarded to a system agent configured to receive such write requests.
Owner:INTEL CORP
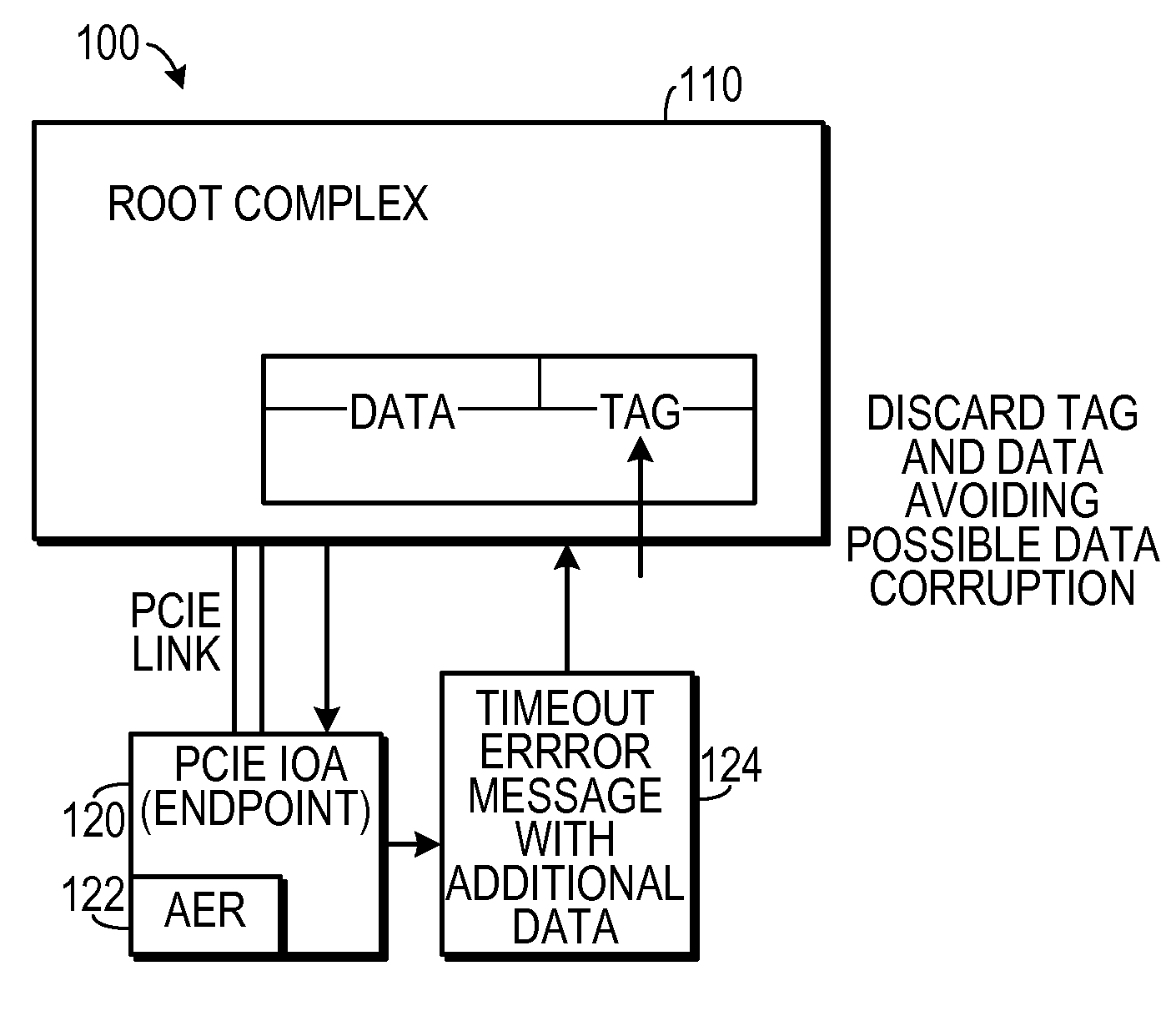
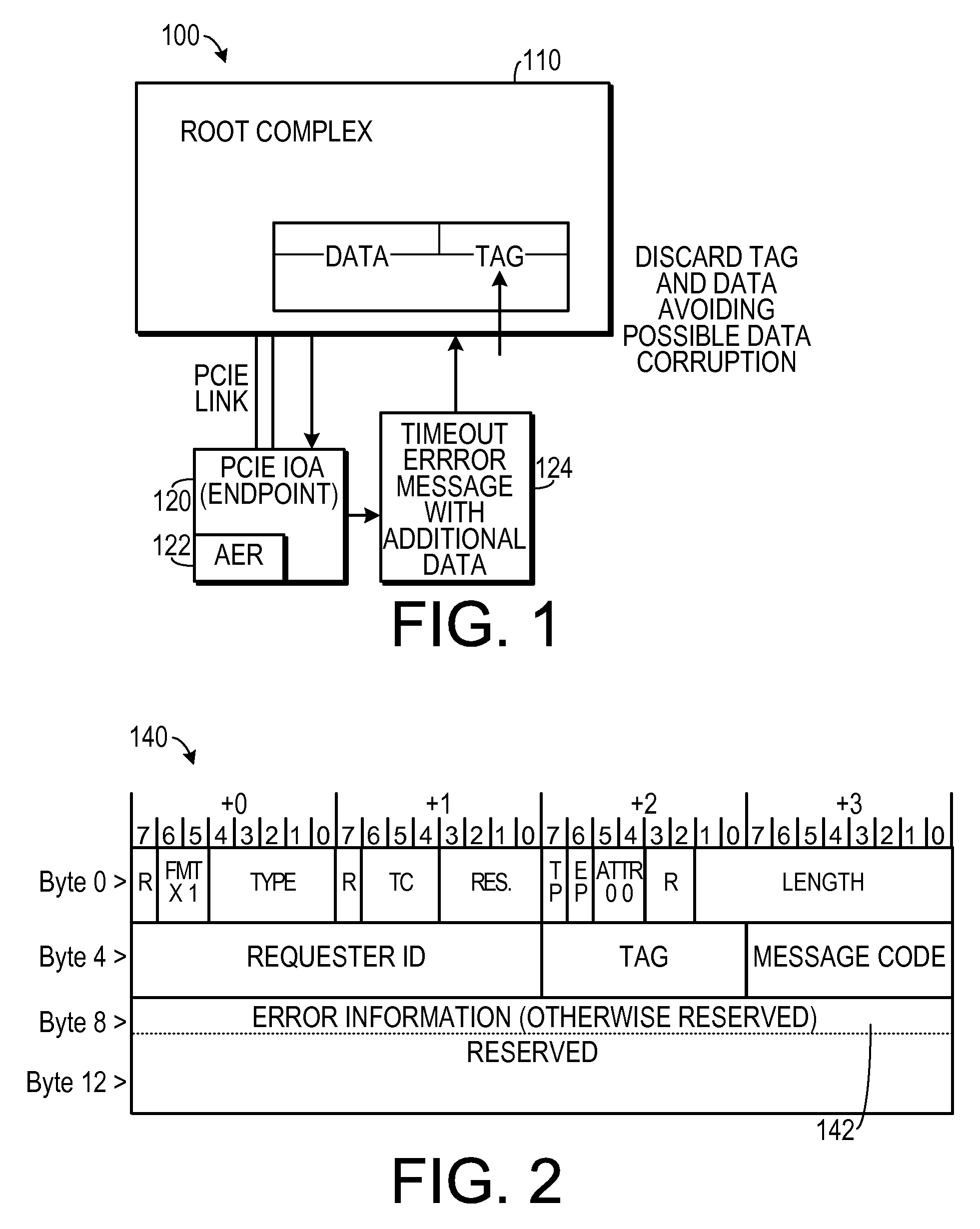
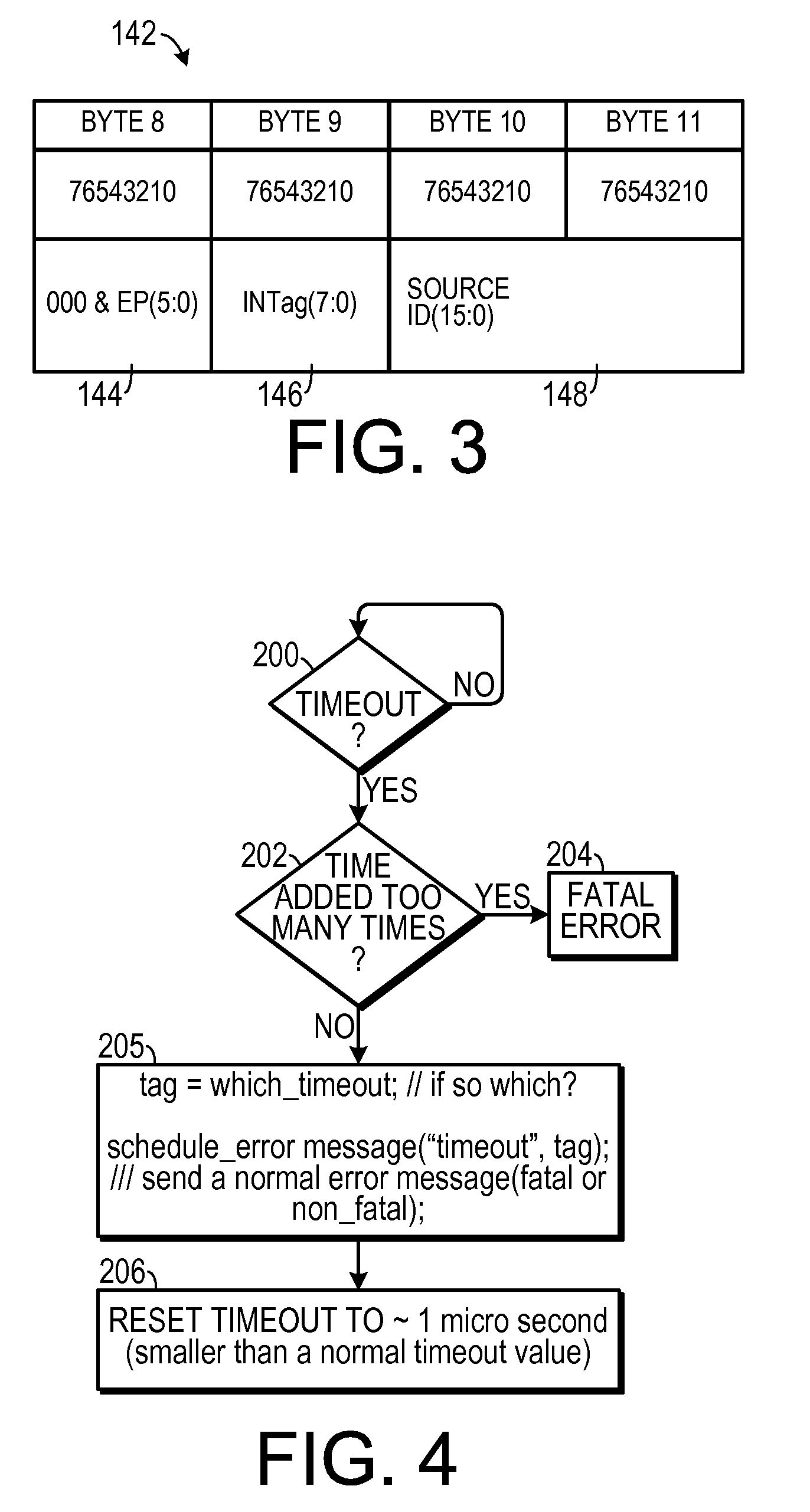
Method for Correlating an Error Message From a PCI Express Endpoint
ActiveUS20090292960A1Electronic circuit testingRedundant data error correctionRoot complexProcessor register
In a method of handling errors in a digital system that includes a root complex in data communication with at least one endpoint, the endpoint including at least one advanced error reporting register, an error is detected by the endpoint. Error data indicative of the error is stored in an advanced error reporting register. An indication of which transaction caused the error is stored in a secondary location. An error message packet that includes the error data and the indication of which transaction caused the error is generated. The error message packet is transmitted to the root complex. The root complex is caused to take a preselected action in response to the error message packet.
Owner:IBM CORP
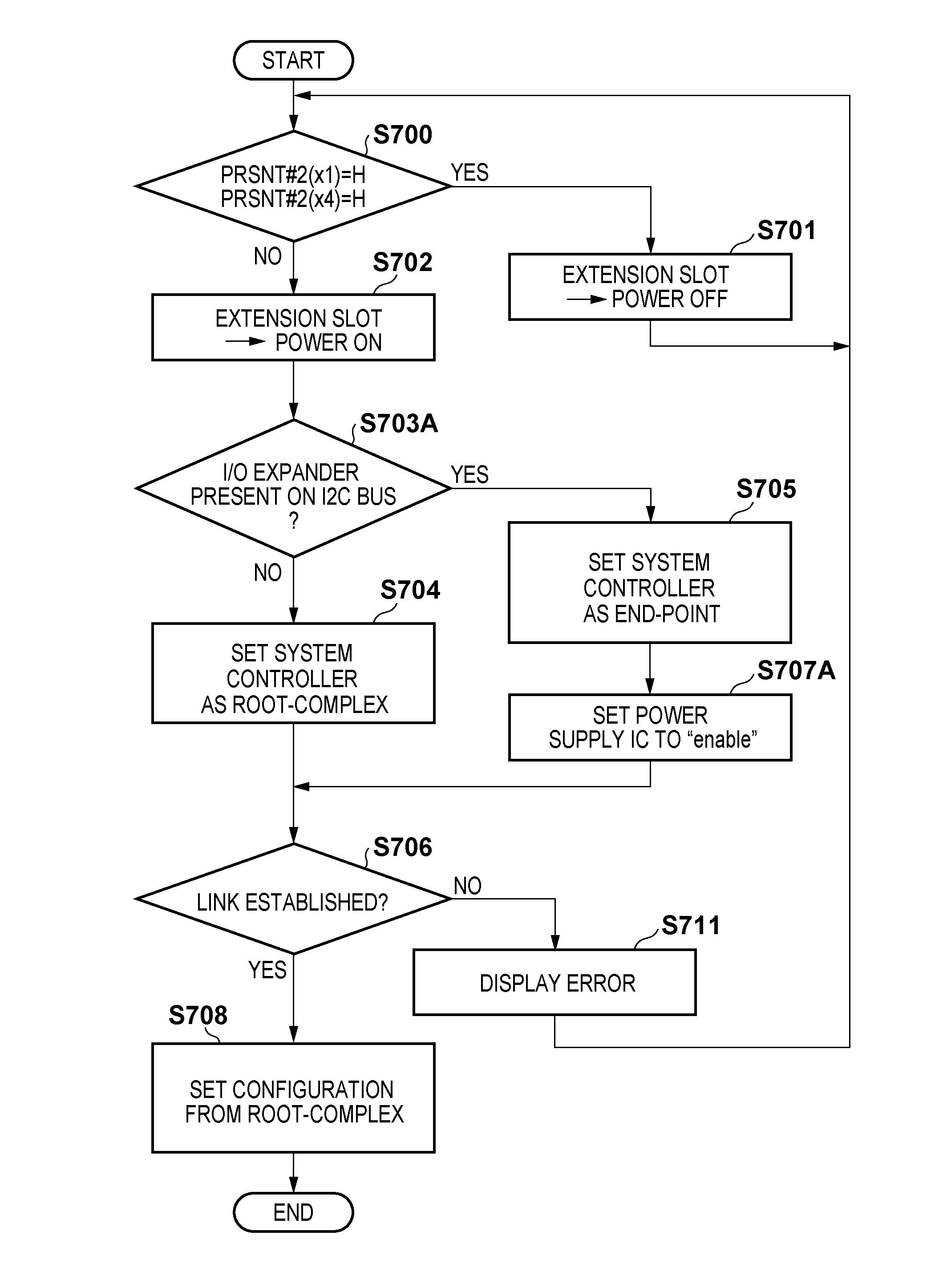
Printing apparatus and operation setting method thereof
InactiveUS8990467B2Easy to operateFunction increaseComponent plug-in assemblagesEnergy efficient computingRoot complexEngineering
This invention is directed to enhancement of flexibility when connecting an add-in card conforming to the PCI-Express specification. More specifically, the operation mode of the system board of a printing apparatus is configured to cope with both a root-complex and end-point. When an add-in card is inserted into an extension slot, the type of add-in card is discriminated by confirming the ON state of a detection pin. When the inserted add-in card operates as a root-complex, the system board is set to operate as an end-point. When the inserted add-in card operates as an end-point, the system board is set to operate as a root-complex.
Owner:CANON KK
Method and device for expanding PCIe bus region
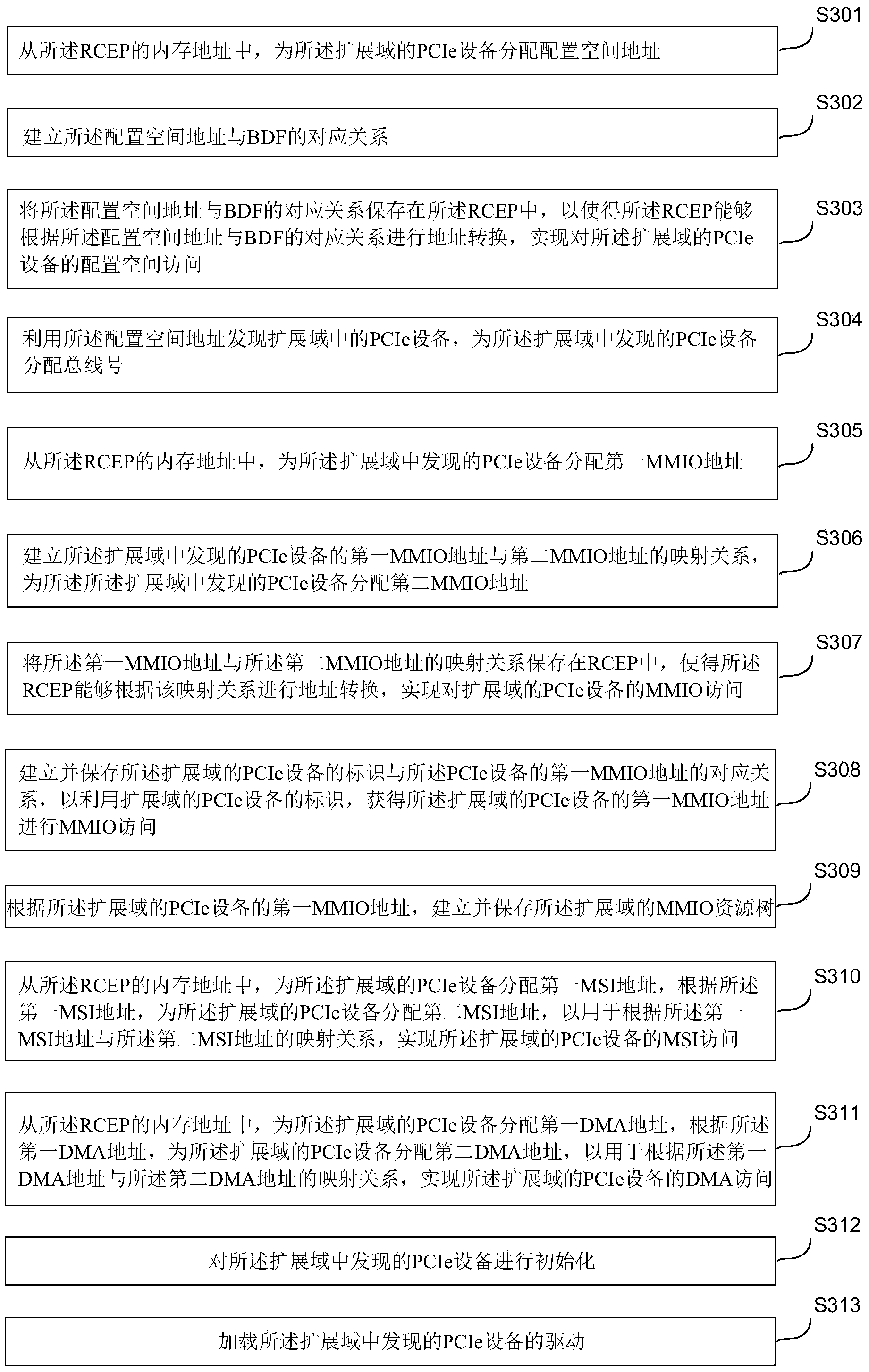
ActiveCN104285218ARealize communicationImplement extensionsElectric digital data processingMemory addressProcessor register
An embodiment of the present invention relates to a method for expanding a PCIe bus region, capable of allocating configuration space address to a PCIe device of an expanded region from memory address of an endpoint device of a root complex, establishing a corresponding relationship between the configuration space address and bus number / device number / function number (BDF), and allocating a bus number to the PCIe device found in the expanded region from a second bus assembly of the expanded region, wherein the bus number is used for determining the BDF of the PCIe device found in the expanded region, so that a configuration space register of the PCIe device found in the expanded region can be accessed through the BDF of the PCIe device found in the expanded region according to the corresponding relationship between the configuration space address and the BDF, in this way, expansion of the PCIe bus region is achieved, and the problem that expansion of the PCIe bus region cannot be performed in the prior art is solved, thus the number of the PCIe devices in a system cannot be limited by 256 buses.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com