Calculation method of traffic network node importance considering cascading failure
A technology of node importance and transportation network, which is applied in the field of calculation of the importance of transportation network nodes considering cascading failures. and its dynamic behavior
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] (1) A traffic network load-capacity cascading failure model based on a two-layer network.
[0042] The load-capacity model assigns a certain load and capacity to each node (edge) in the transportation network. If a node's load exceeds its capacity, a fault will occur. The load of the faulty node follows a certain strategy [such as optimal allocation of users, optimal allocation of random users, etc. 】Distributed to other nodes in the network, the total load of these nodes may exceed their capacity due to the additional load received by these nodes, resulting in a new round of load redistribution. This process is repeated, and the affected nodes gradually spread, resulting in cascading failures.
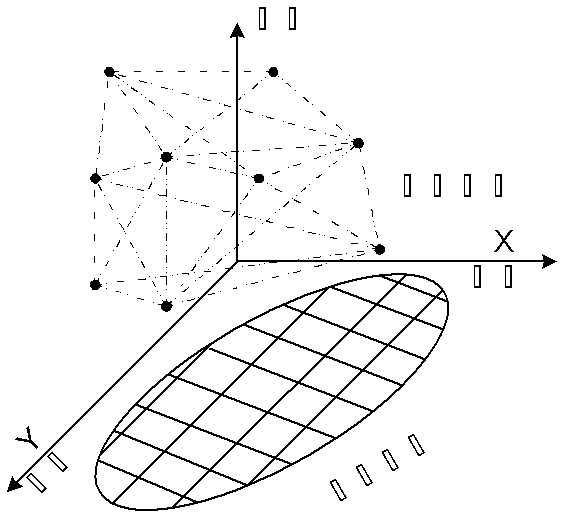
[0043] The load-capacity cascading failure model is attached figure 1 shown.
[0044] combined with figure 1 The cascading failure model of the present invention is further described in detail.
[0045] 1) The lower network of the double-layer network is the road network, t...
Embodiment example
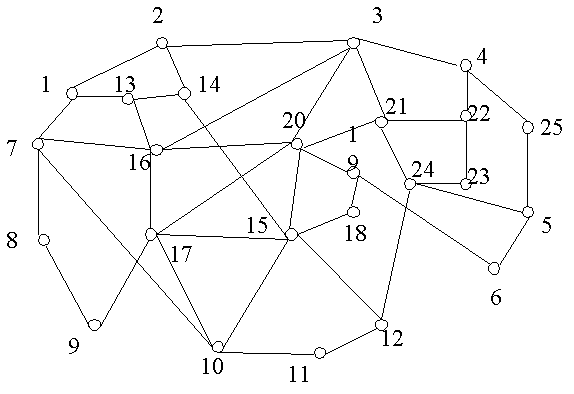
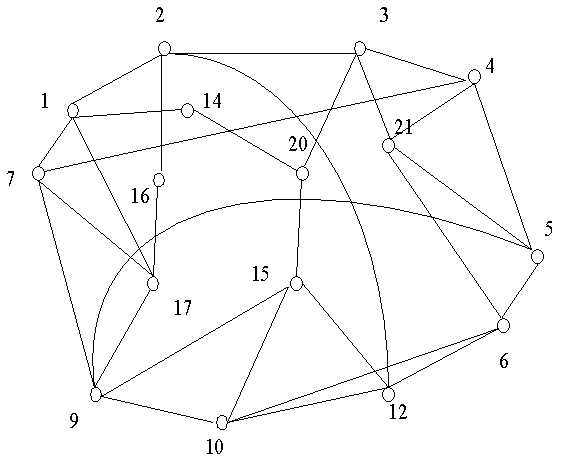
[0068] use as figure 2 The road network shown in the figure has 25 nodes and 40 edges, and the parameters of the road network are shown in Table 1. According to the WS (Watts Strogatz) Small-World Network (Small-World Network, SWN) and BA (Barabasi Albert) scale-free network construction algorithms, two travel networks with 25 nodes were respectively constructed, as shown in Figure 3 (a), (b ) shown. In the WS algorithm, firstly, each node is connected to the left and right adjacent 4 / 2[4 / 2 means that it is connected to two of the adjacent four nodes. ] nodes are connected to build a regular network [that is, a network with regular connections between nodes. ], and then reconnect the edges with a probability of 0.5; the average degree of the constructed scale-free network is 2.
[0069] Assuming that the total demand is 100000pcu / h [pcu / h is vehicle / hour], and the demands of each OD [O represents the starting point of travel, and D represents the end point of travel] are t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com