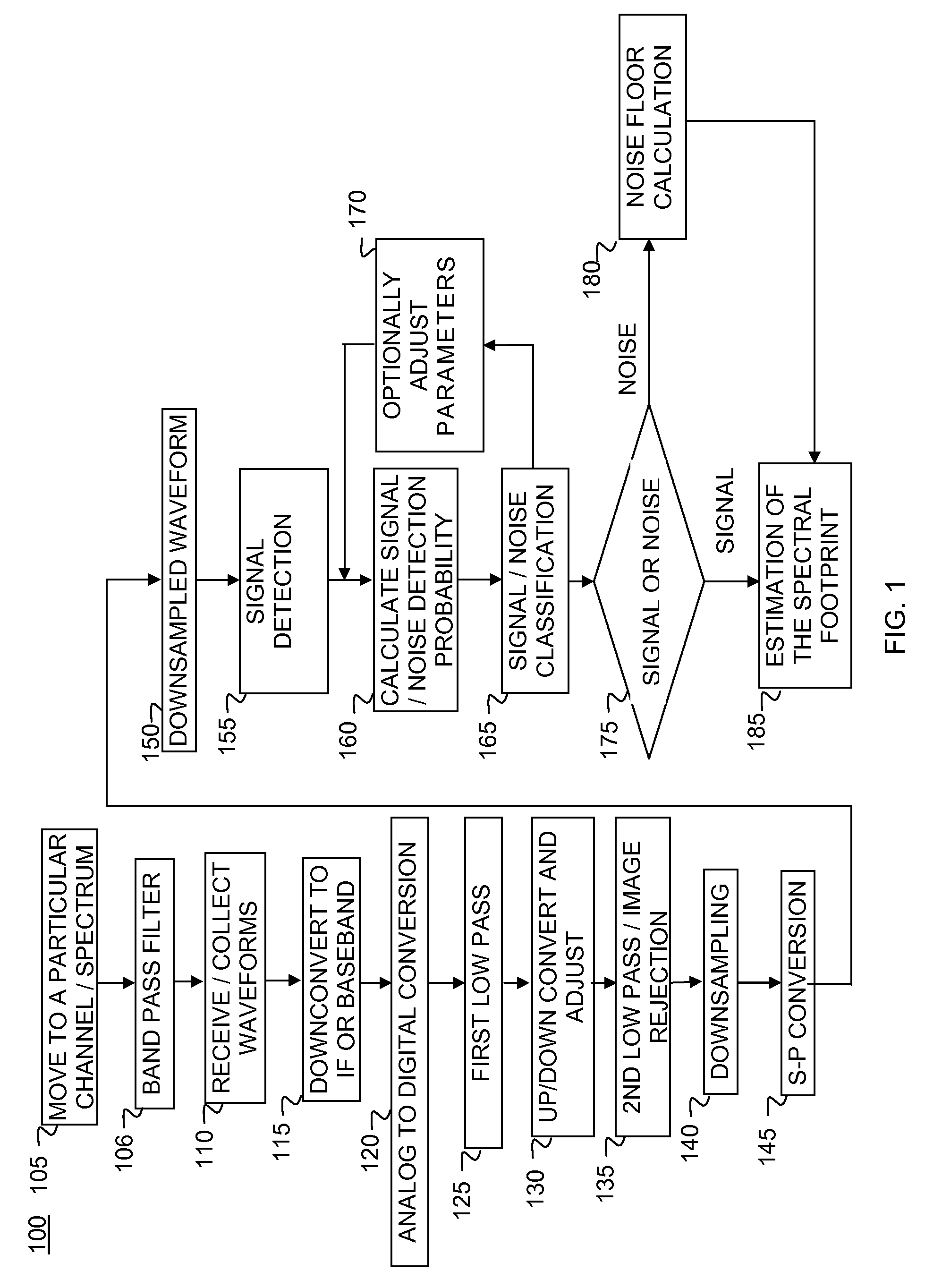
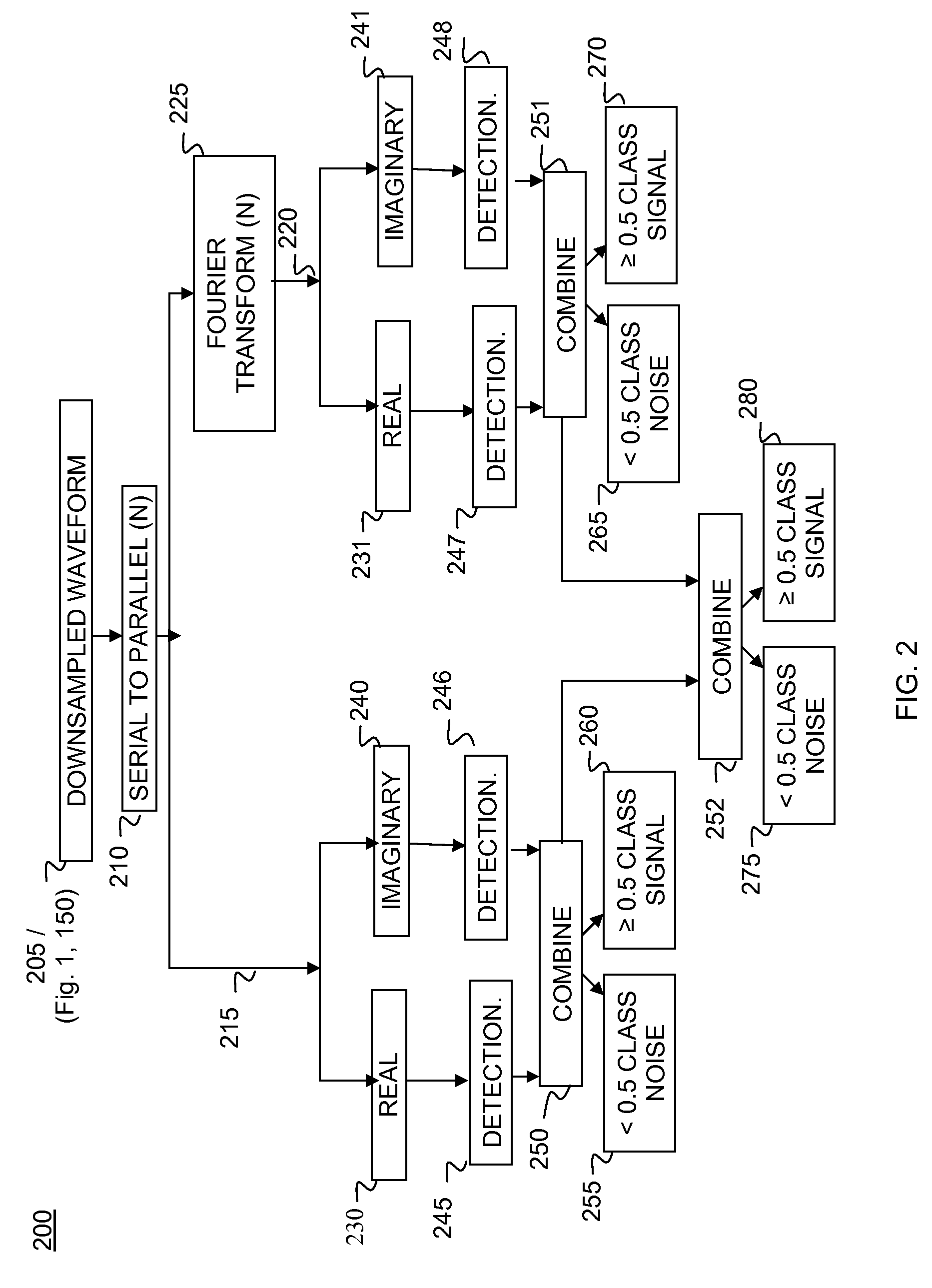
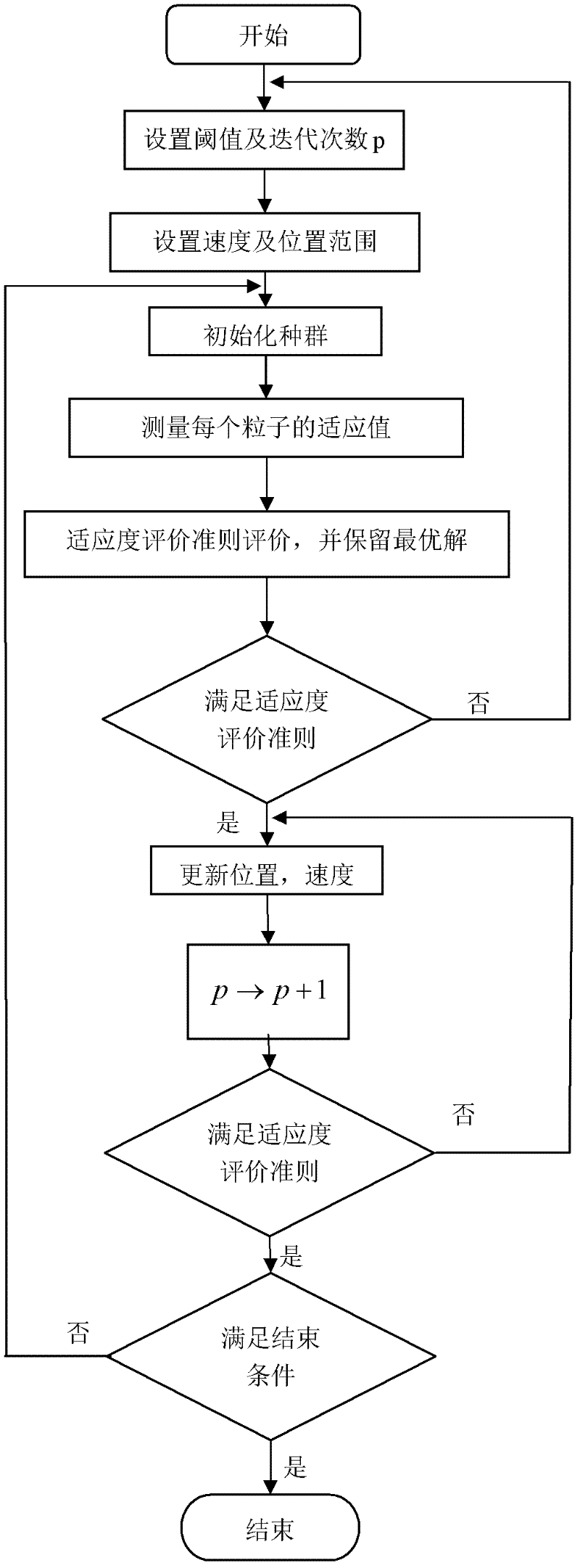
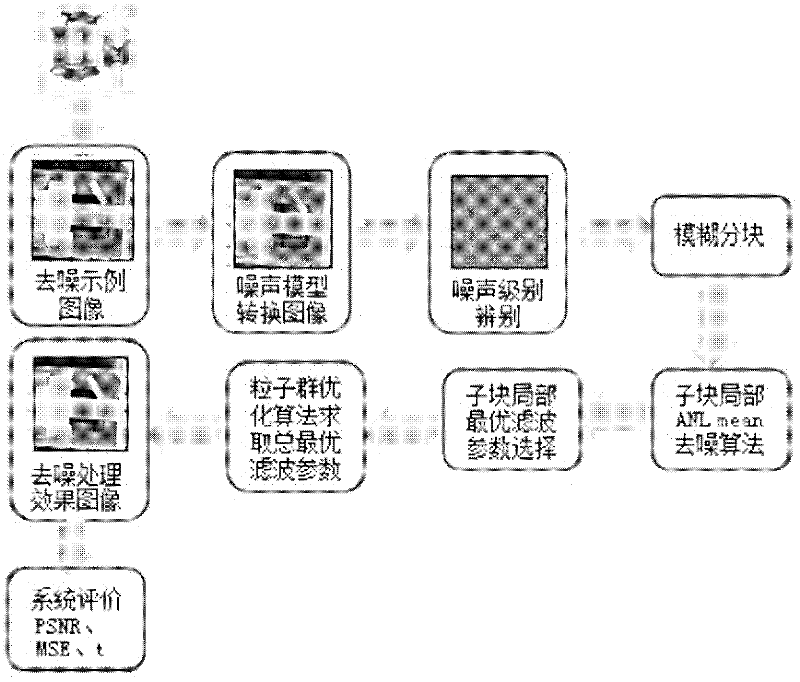
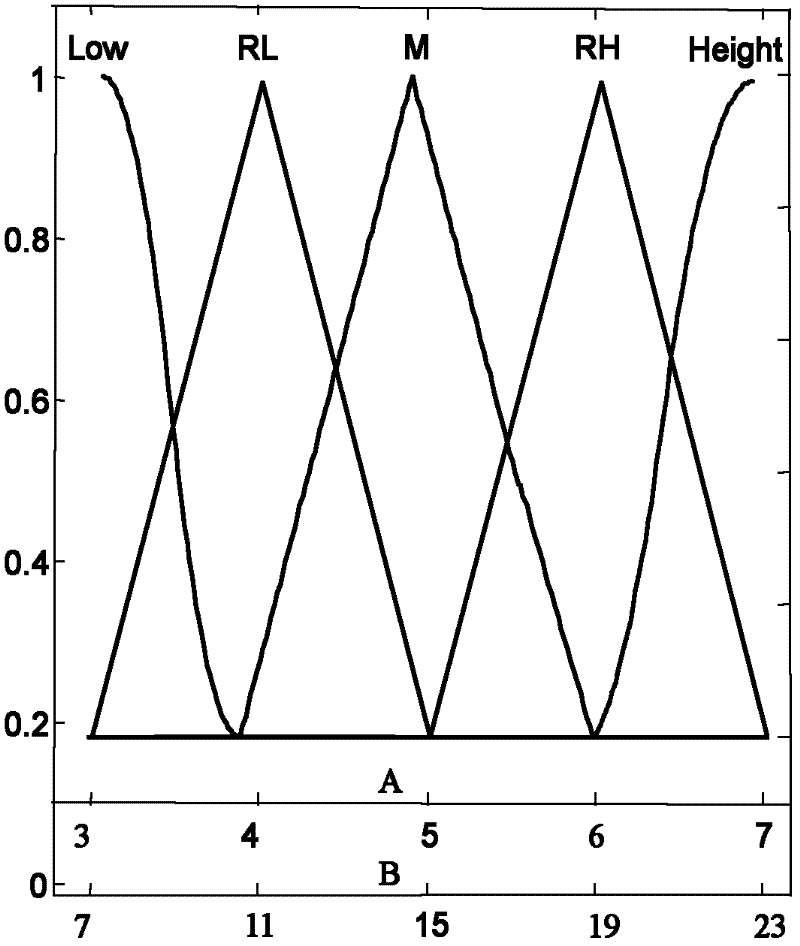
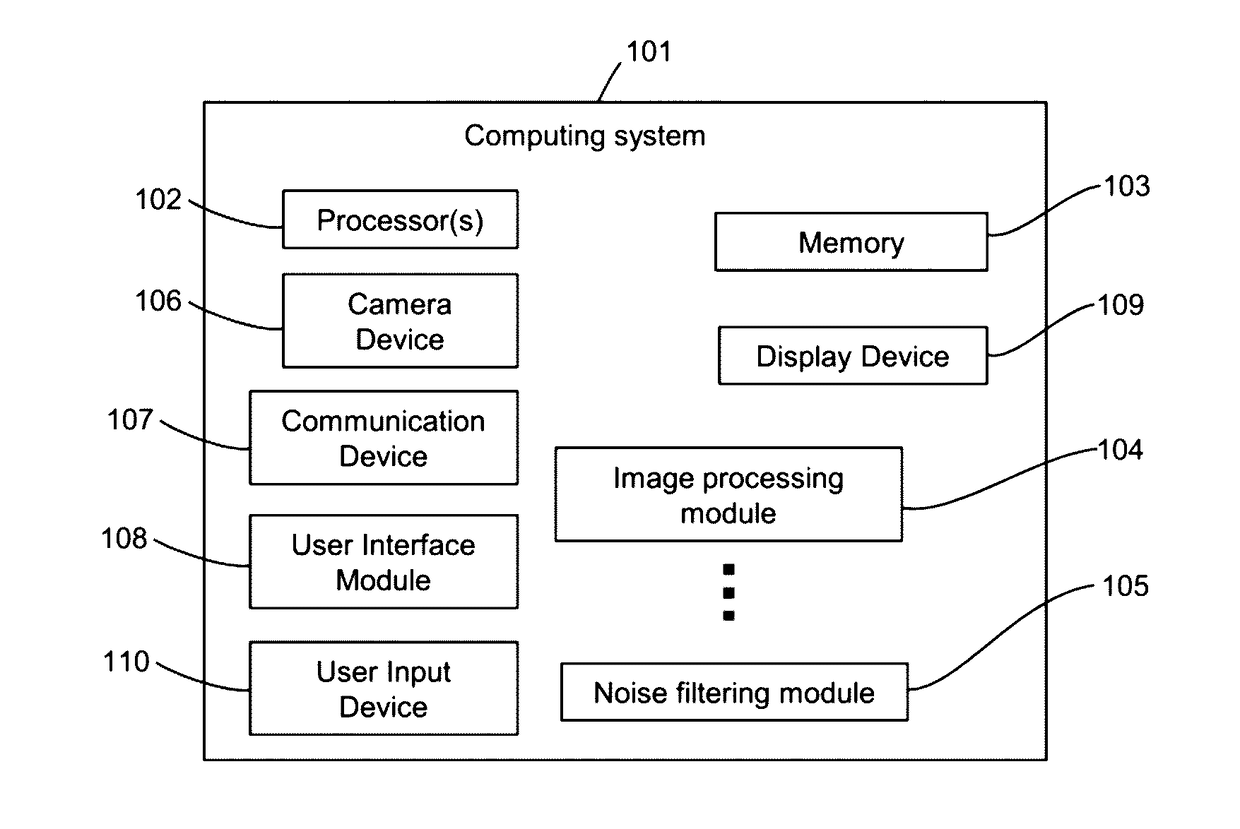
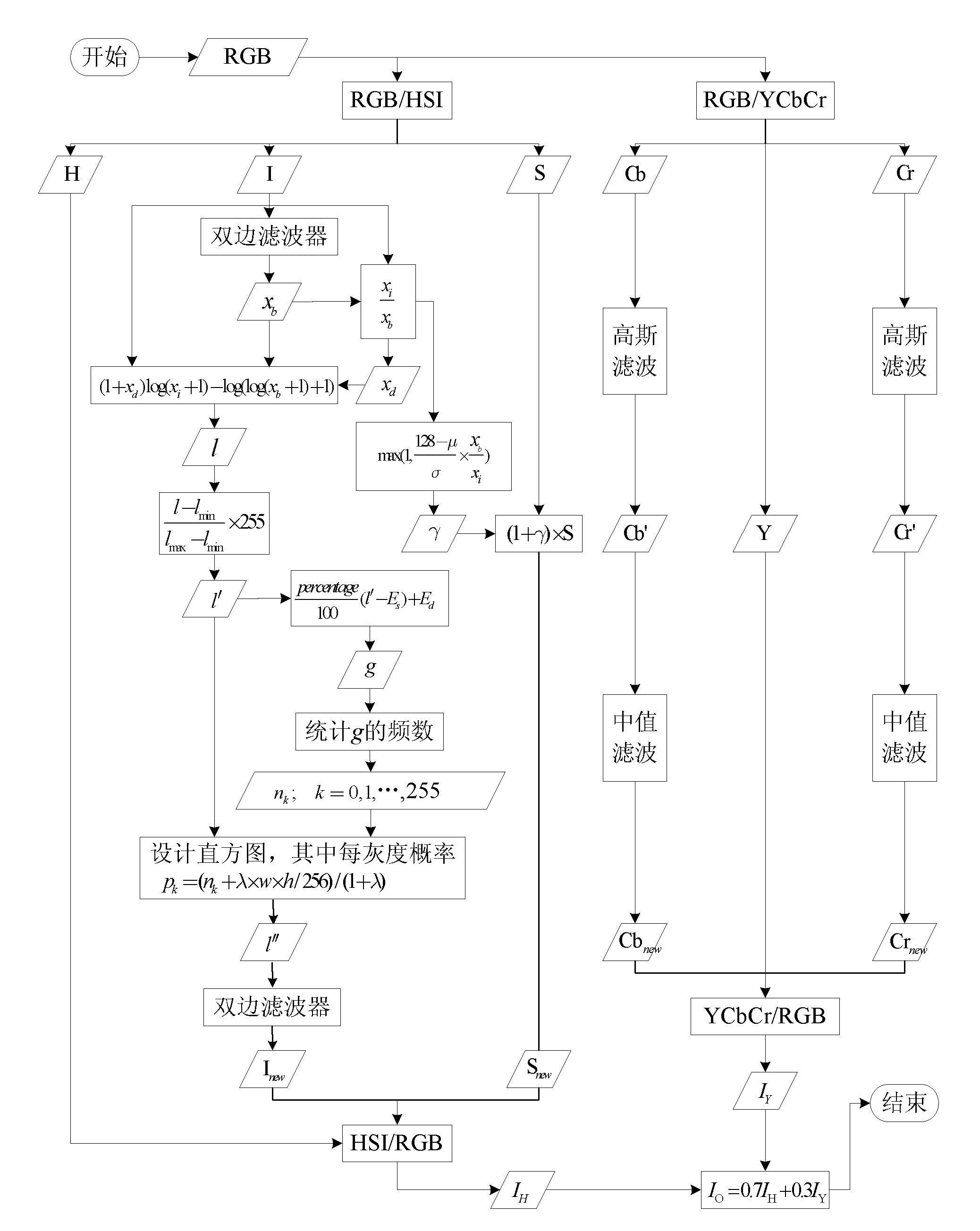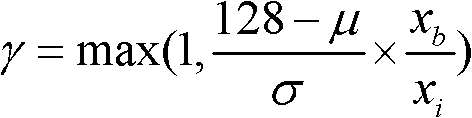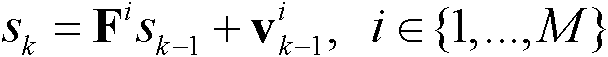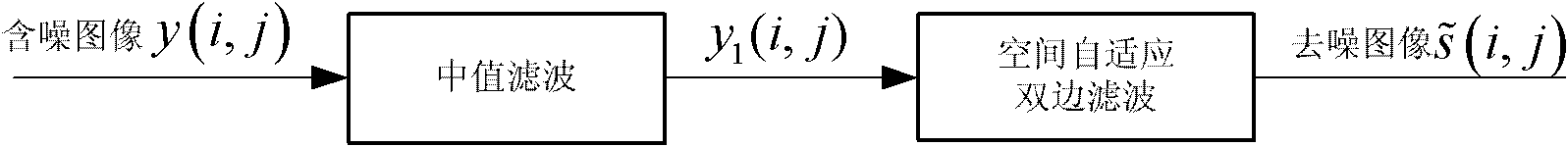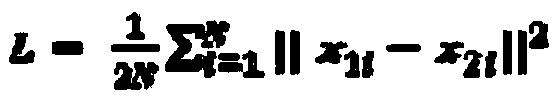Patents
Literature
1066 results about "Gaussian noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
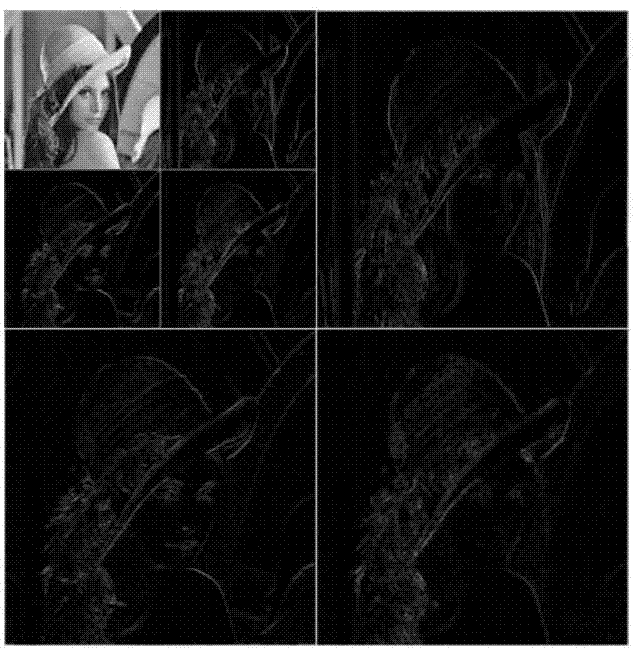
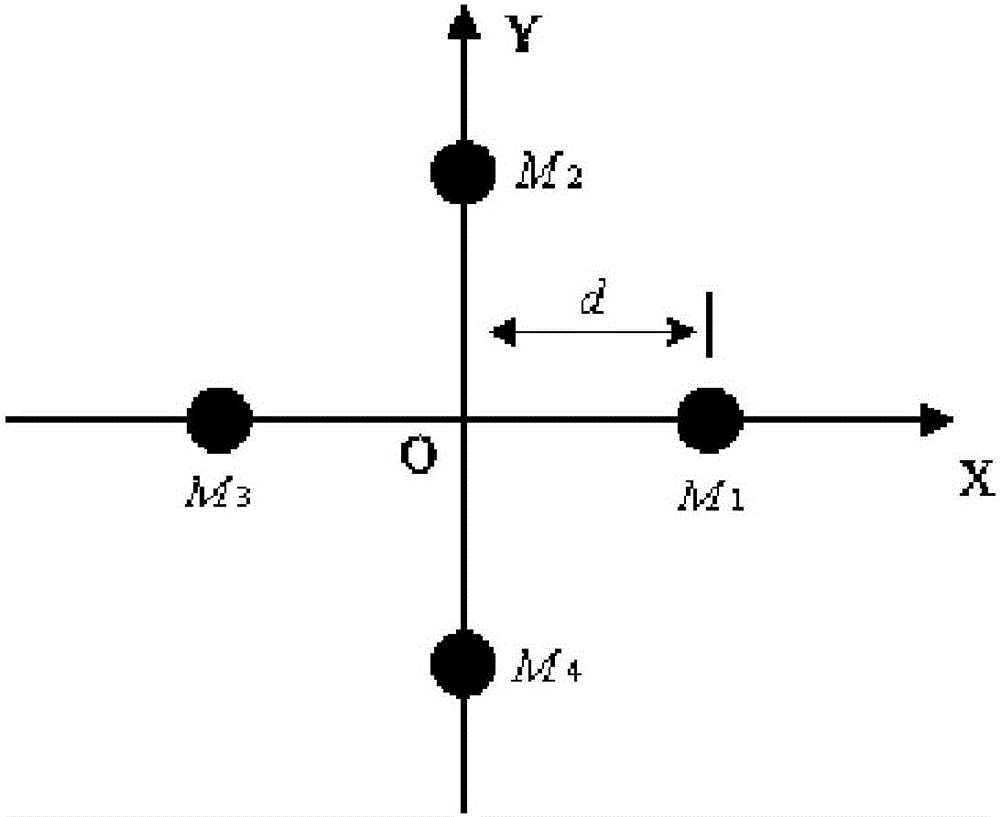
Gaussian noise, named after Carl Friedrich Gauss, is statistical noise having a probability density function (PDF) equal to that of the normal distribution, which is also known as the Gaussian distribution. In other words, the values that the noise can take on are Gaussian-distributed. The probability density function p of a Gaussian random variable z is given by: pG(z)=1/σ√(2π)e⁻⁽⁽ᶻ⁻μ⁾²⁾/²σ² where z represents the grey level, μ the mean value and σ the standard deviation.
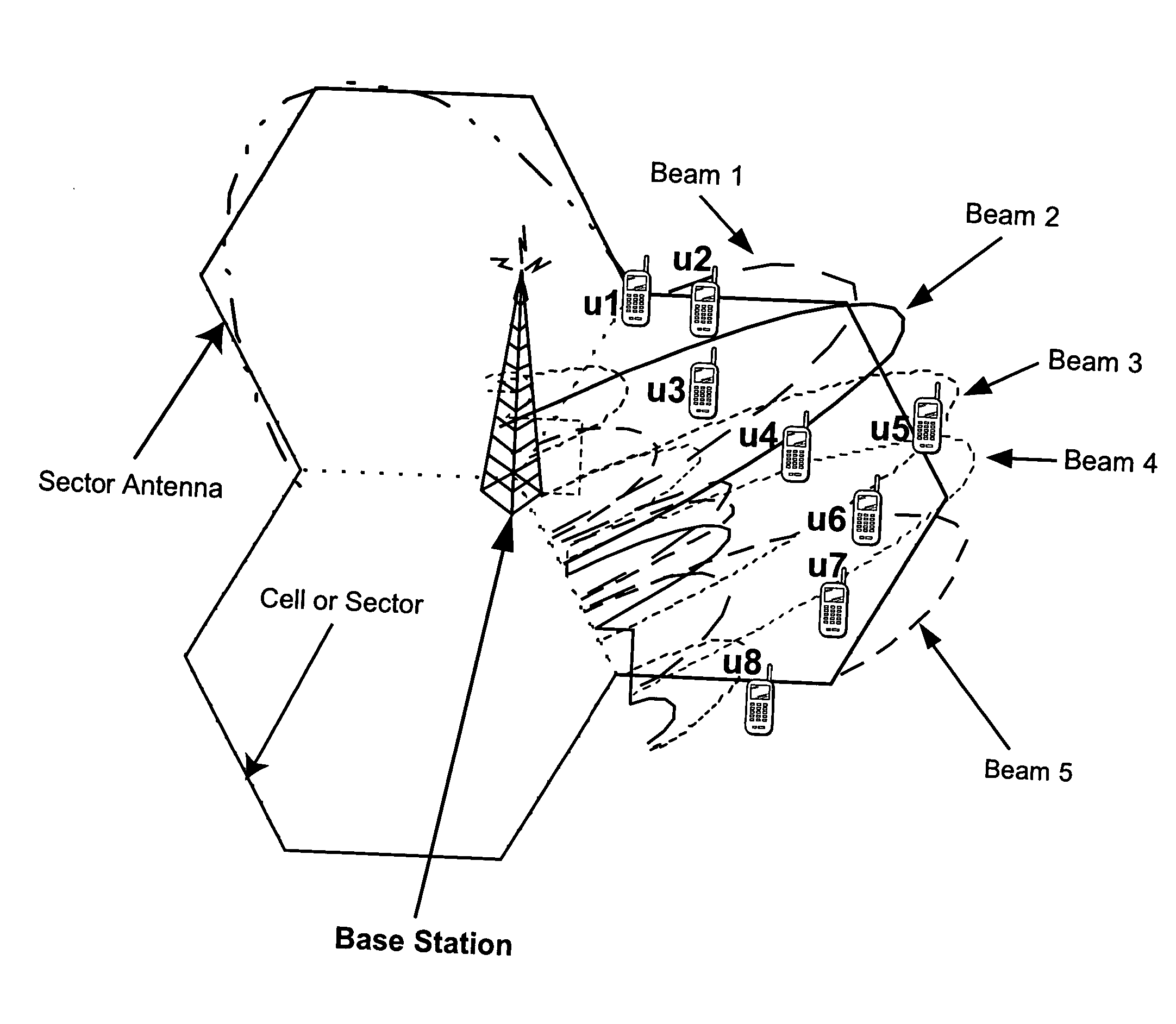
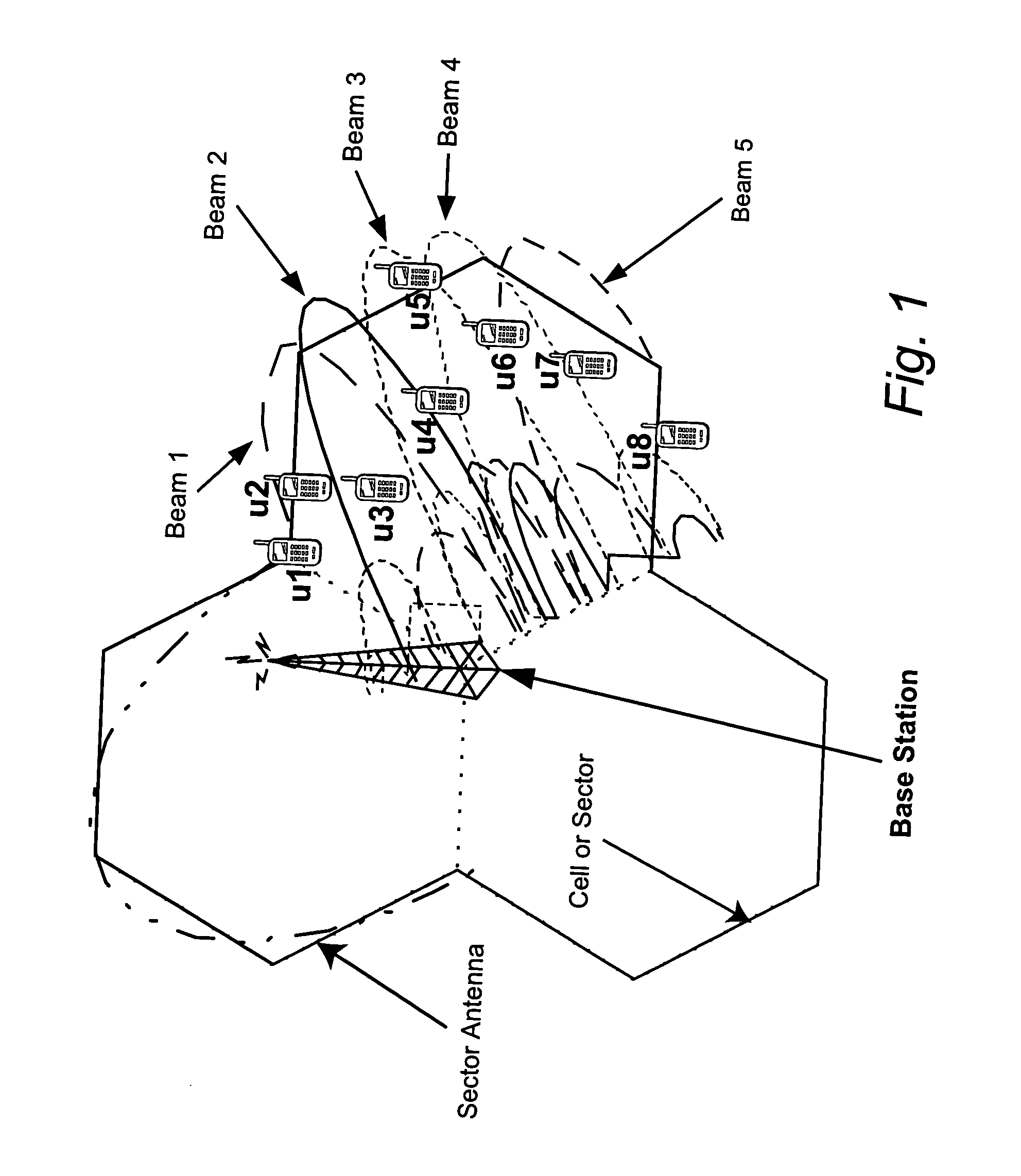
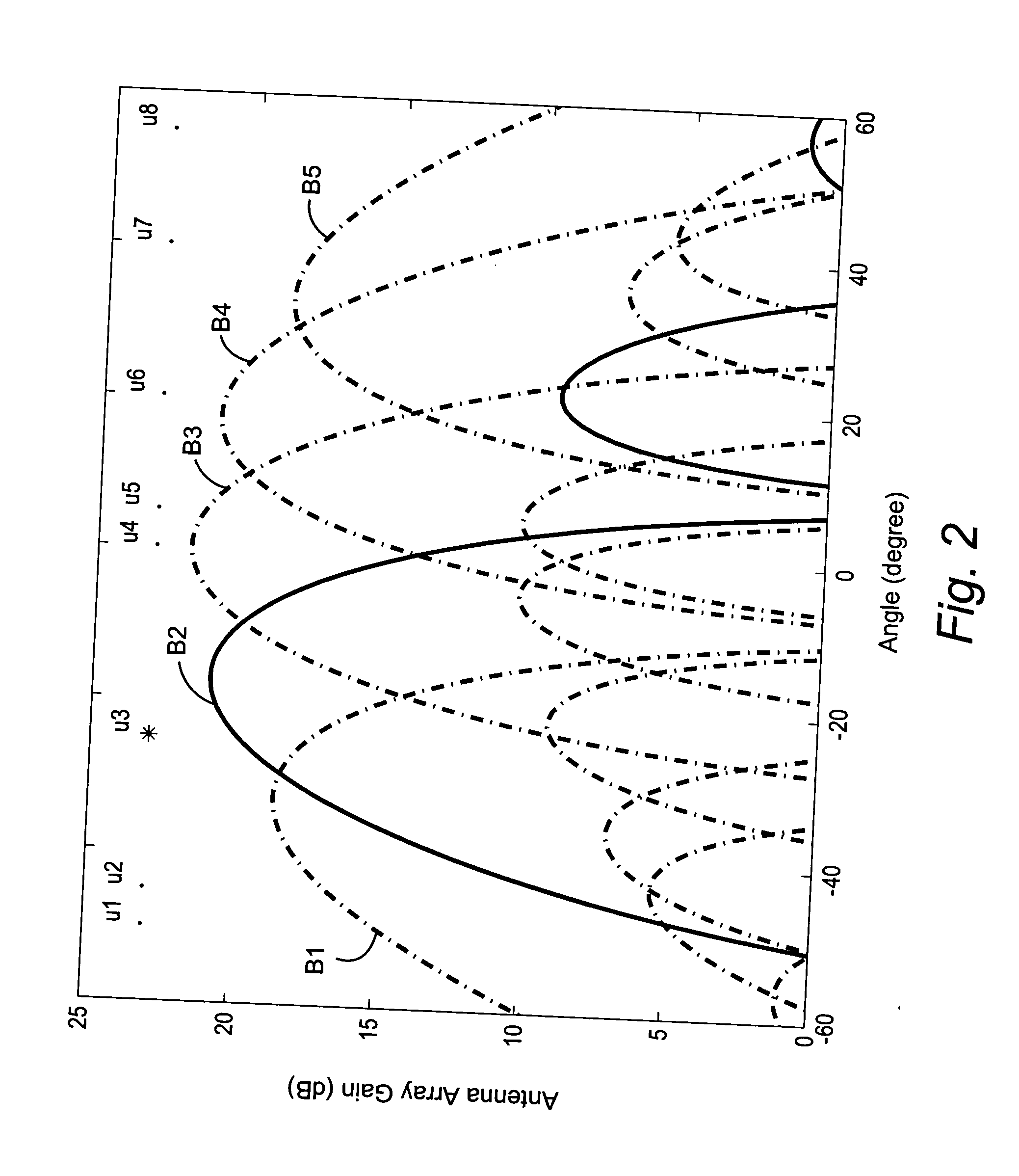
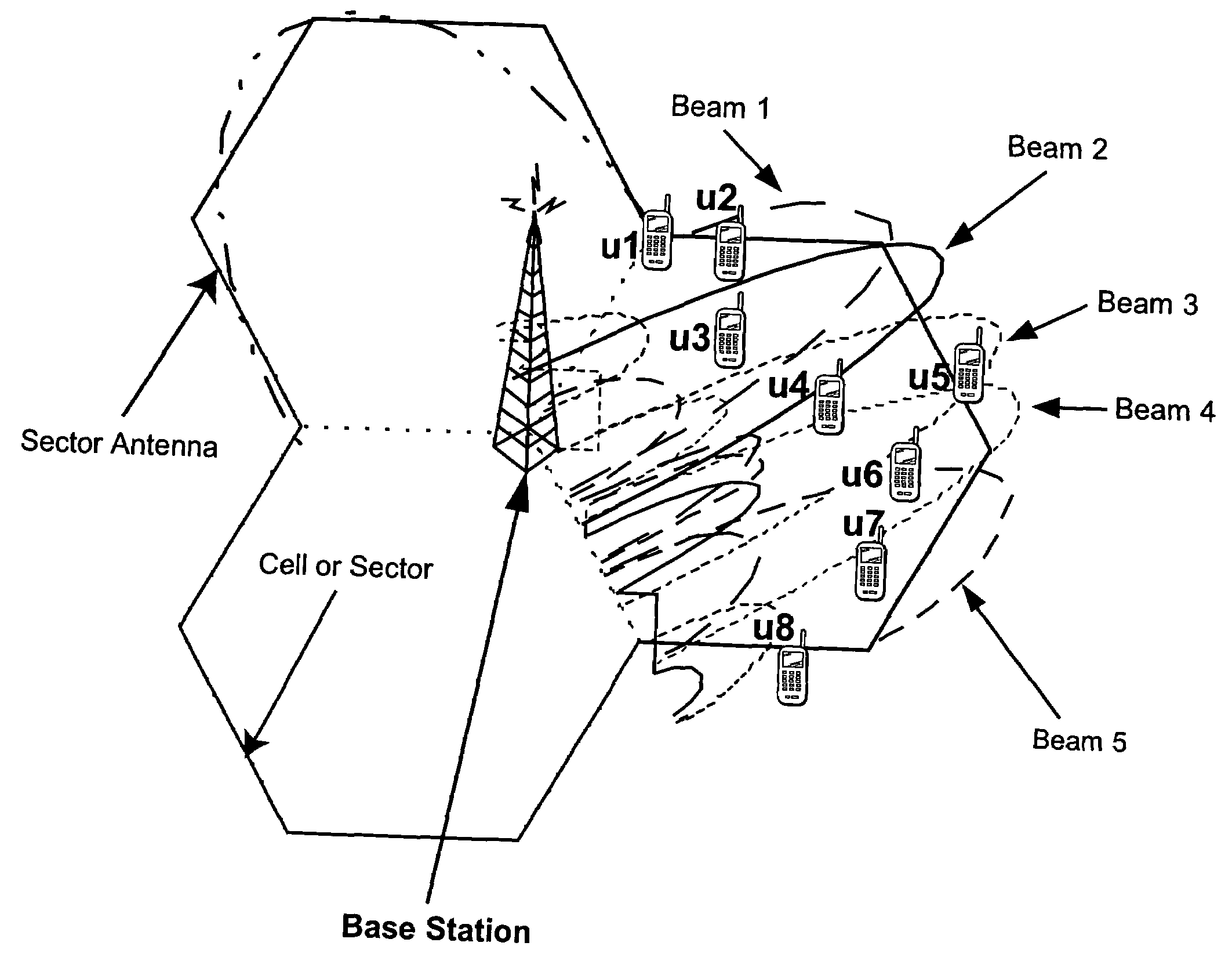
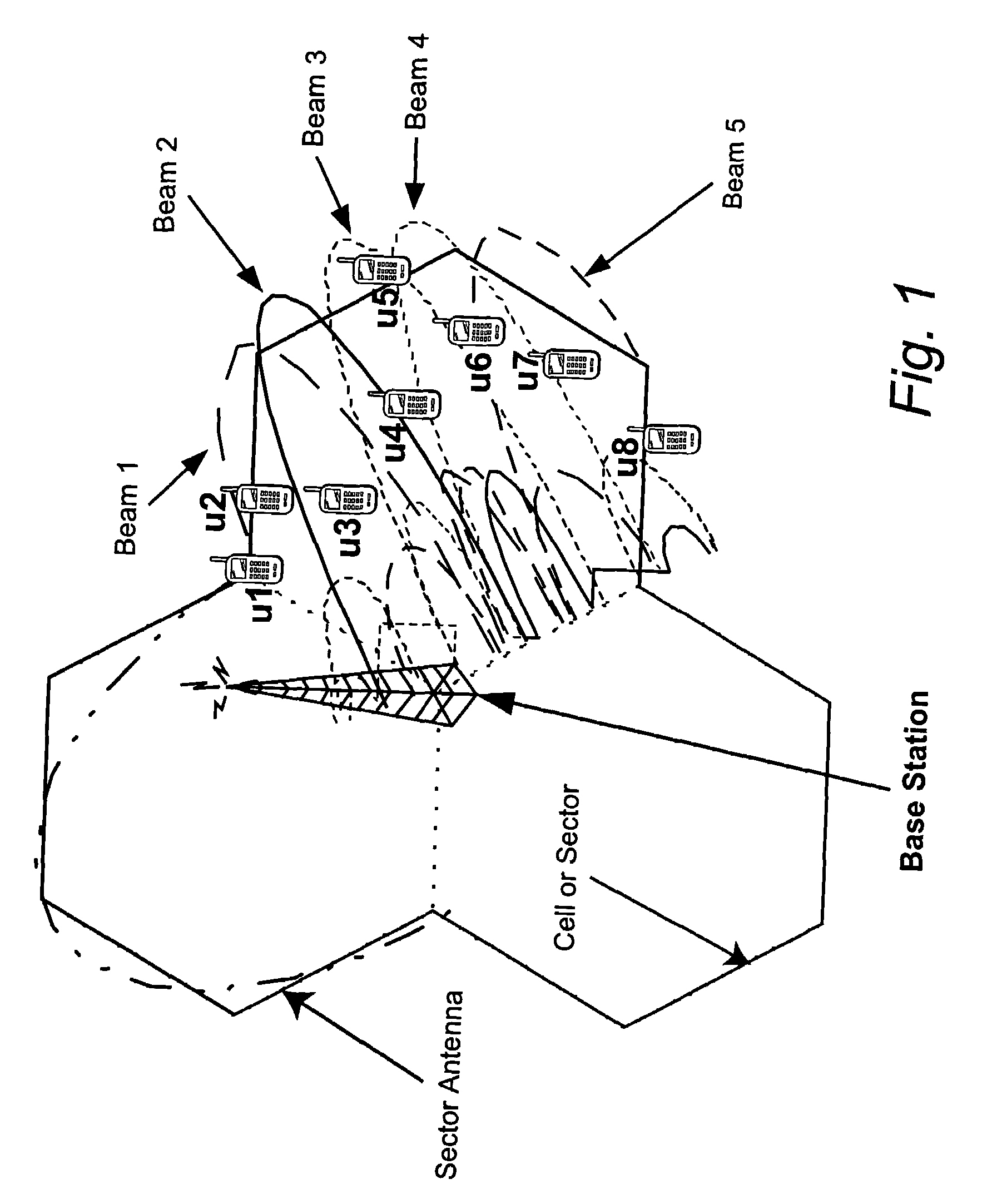
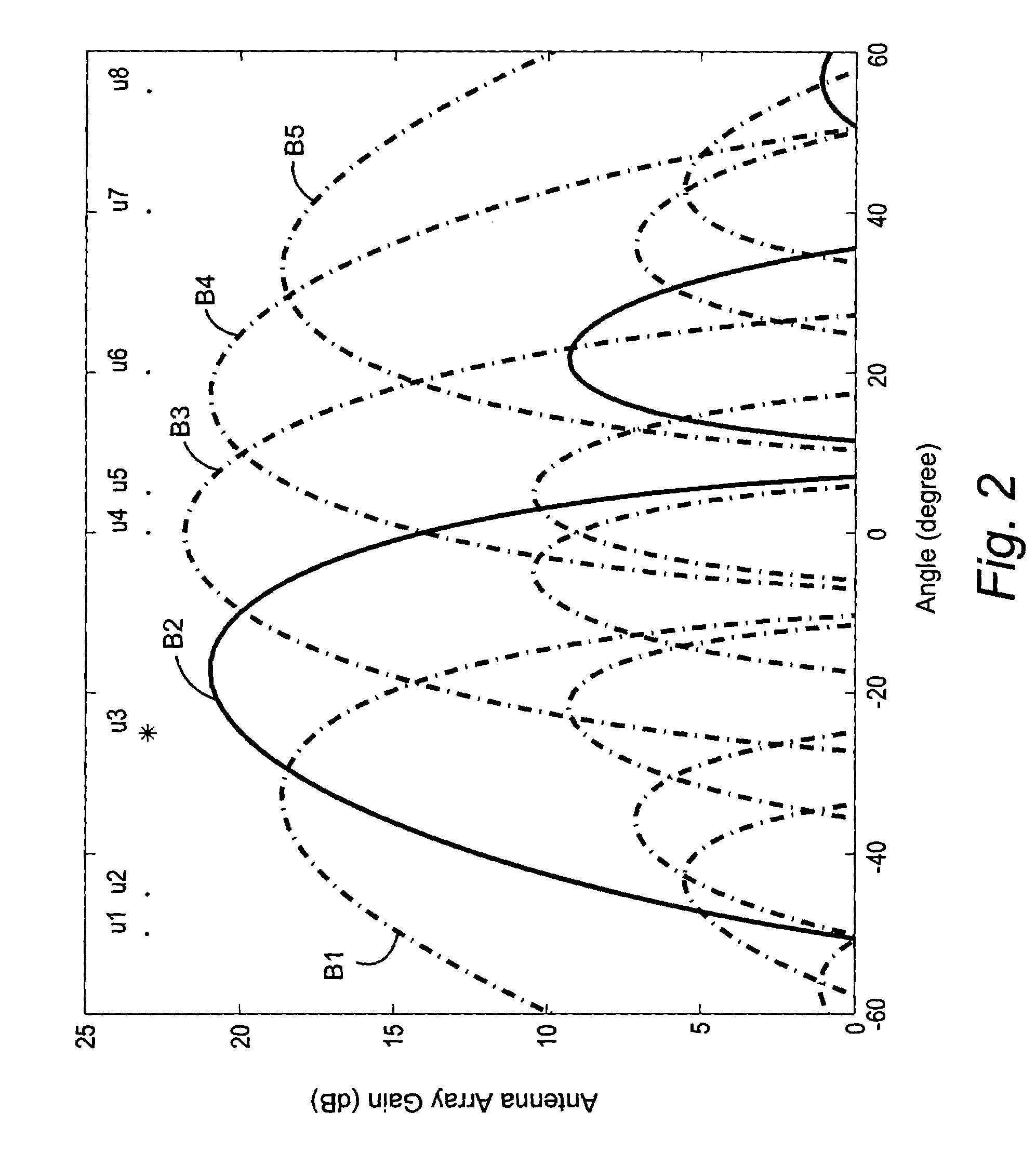
Reducing shared downlink radio channel interference by transmitting to multiple mobiles using multiple antenna beams
ActiveUS20050064872A1Inhibition effectImprove data transfer rateSpatial transmit diversityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio channelMobile radio
A radio base station includes multiple antennas associated with a cell. Multiple mobile radios are selected to receive transmissions over a shared radio channel during a predetermined time interval. Information is transmitted over the shared radio channel to multiple mobile radios in the cell during the predetermined time interval using multiple antenna beams. As a result, interference from the transmission appears as white additive Gaussian noise in time and in space in the cell. A “flashlight effect” caused by a single beam transmission over the shared channel during a predetermined time interval that would normally detrimentally impact mobile channel quality detection is avoided. Other methods for avoiding the flashlight effect are described.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
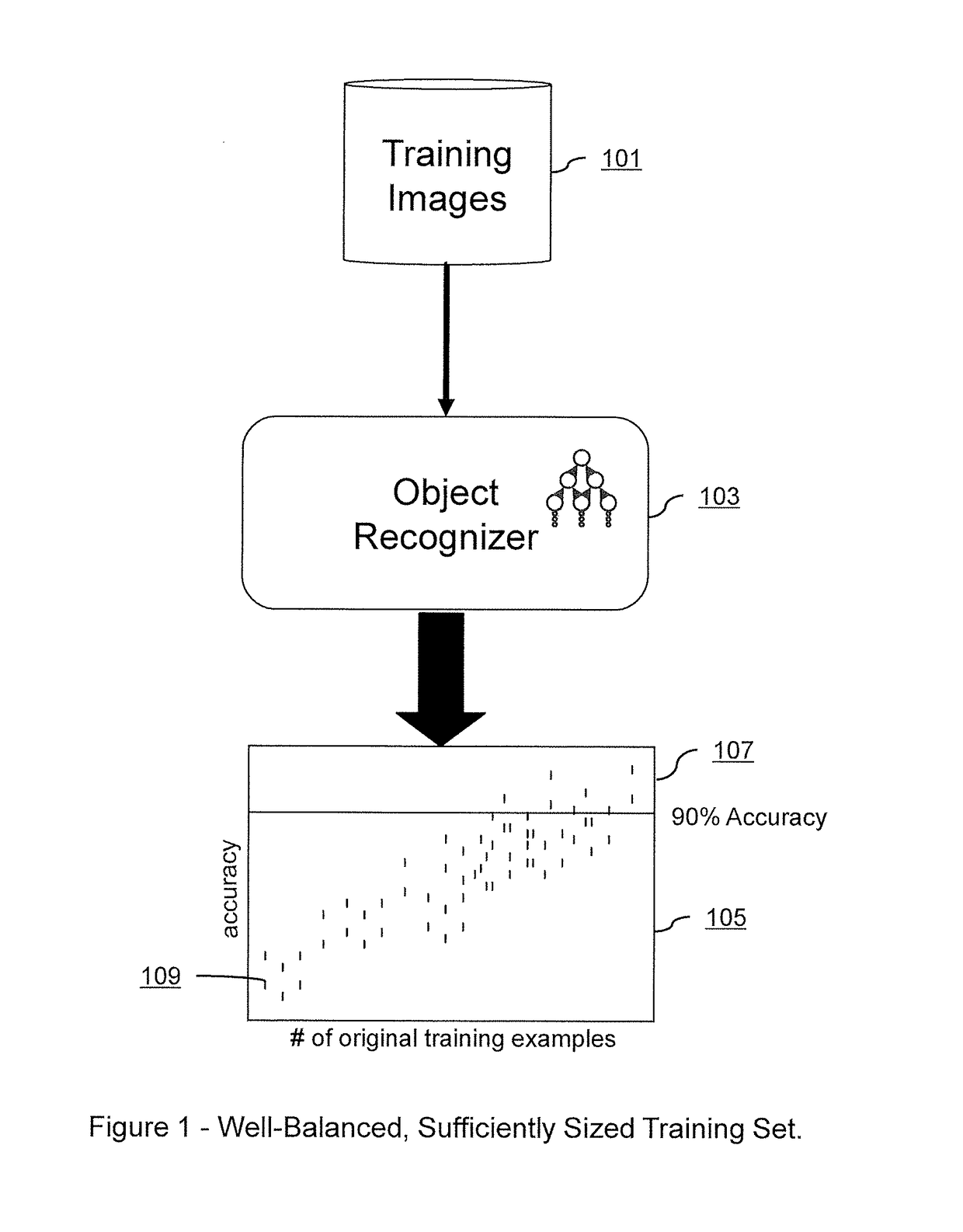
Systems and Methods for Deep Model Translation Generation
ActiveUS20190080205A1Low costAccelerated trainingCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesPattern recognitionGenerative adversarial network
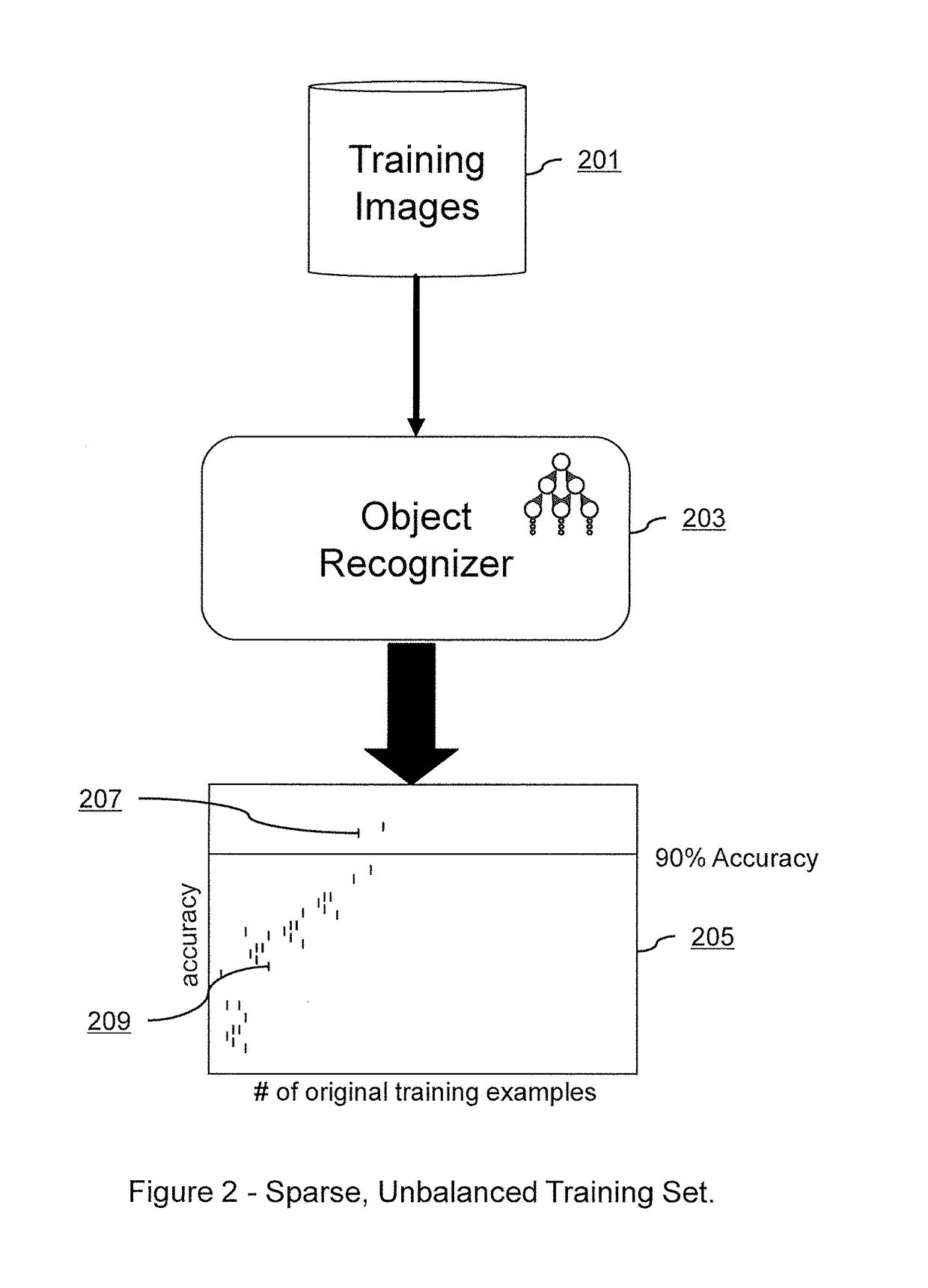
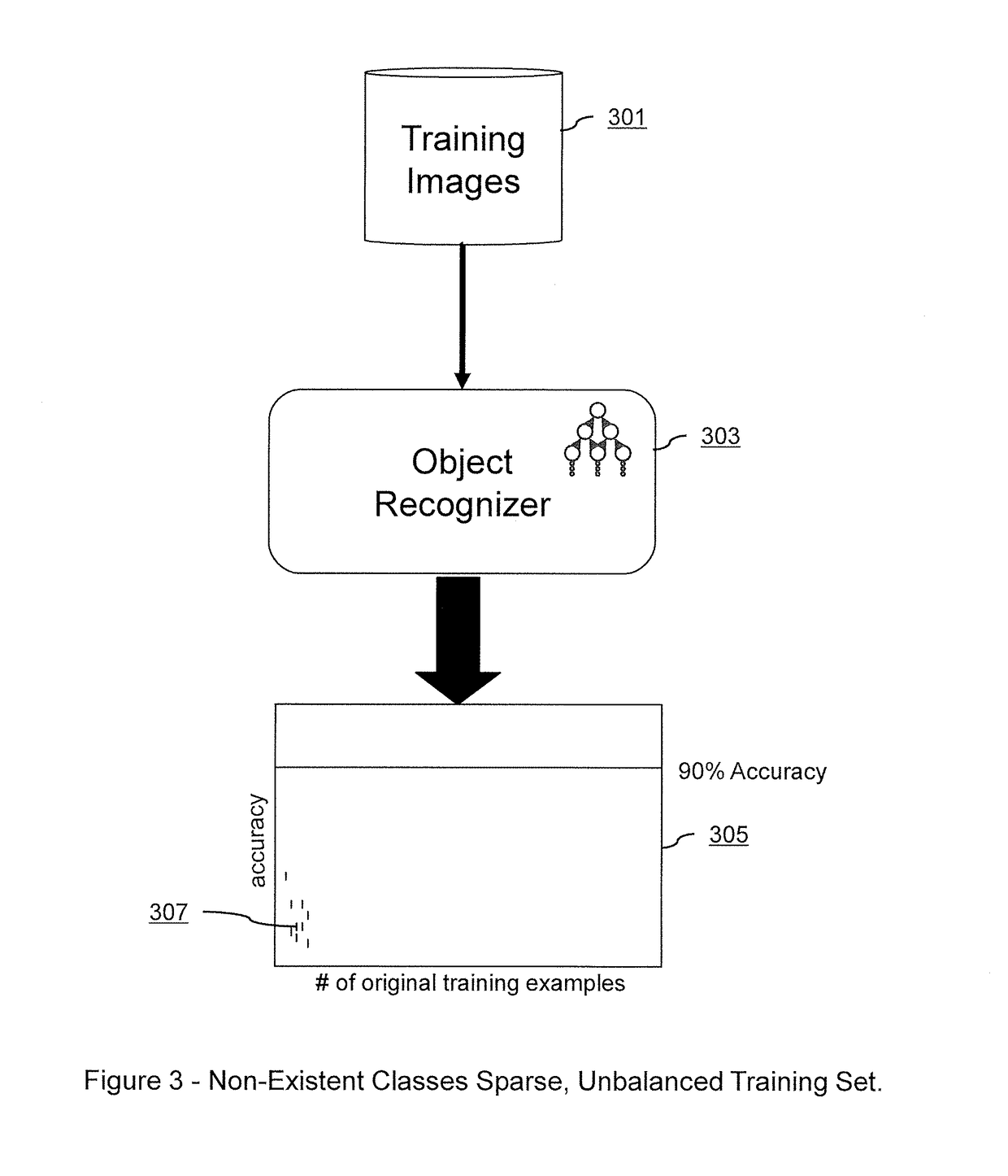
Embodiments of the present invention relate to systems and methods for improving the training of machine learning systems to recognize certain objects within a given image by supplementing an existing sparse set of real-world training images with a comparatively dense set of realistic training images. Embodiments may create such a dense set of realistic training images by training a machine learning translator with a convolutional autoencoder to translate a dense set of synthetic images of an object into more realistic training images. Embodiments may also create a dense set of realistic training images by training a generative adversarial network (“GAN”) to create realistic training images from a combination of the existing sparse set of real-world training images and either Gaussian noise, translated images, or synthetic images. The created dense set of realistic training images may then be used to more effectively train a machine learning object recognizer to recognize a target object in a newly presented digital image.
Owner:GENERAL DYNAMICS MISSION SYST INC
Locating and tracking method and apparatus based on sound source array
InactiveCN104991573AImprove accuracyPosition fixationControl using feedbackSound sourcesArrival time
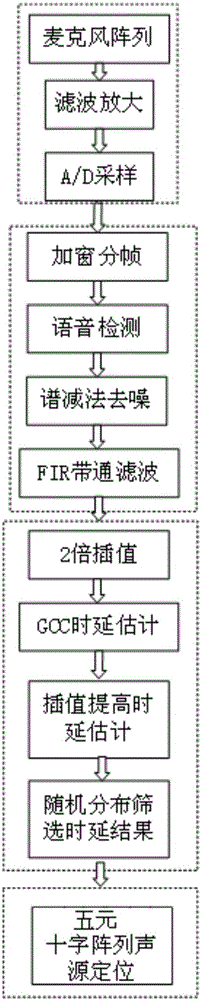
The present invention discloses a locating and tracking method based on a sound source array, comprising the following steps: S1, acquiring on-site sound through a quintuple microphone array, and pre-processing a sound signal acquired by each microphone in the quintuple microphone array to obtain an audio signal; S2, performing sound source locating for the audio signals according to arrival time delay of the audio signals between the microphones and positional information of the microphone array, so as to calculate a pitch angle, an azimuth angle and an object distance; and S3, moving and turning a locating and tracking apparatus to arrive to a sound source position. The locating and tracking method of the present invention performs related processing for influences of non-gauss noises, coherent noises and indoor reverberation of the sound source on accurate locating, thereby improving accuracy of locating of the sound source.
Owner:北京品创智能科技有限公司
De-noising digital radiological images
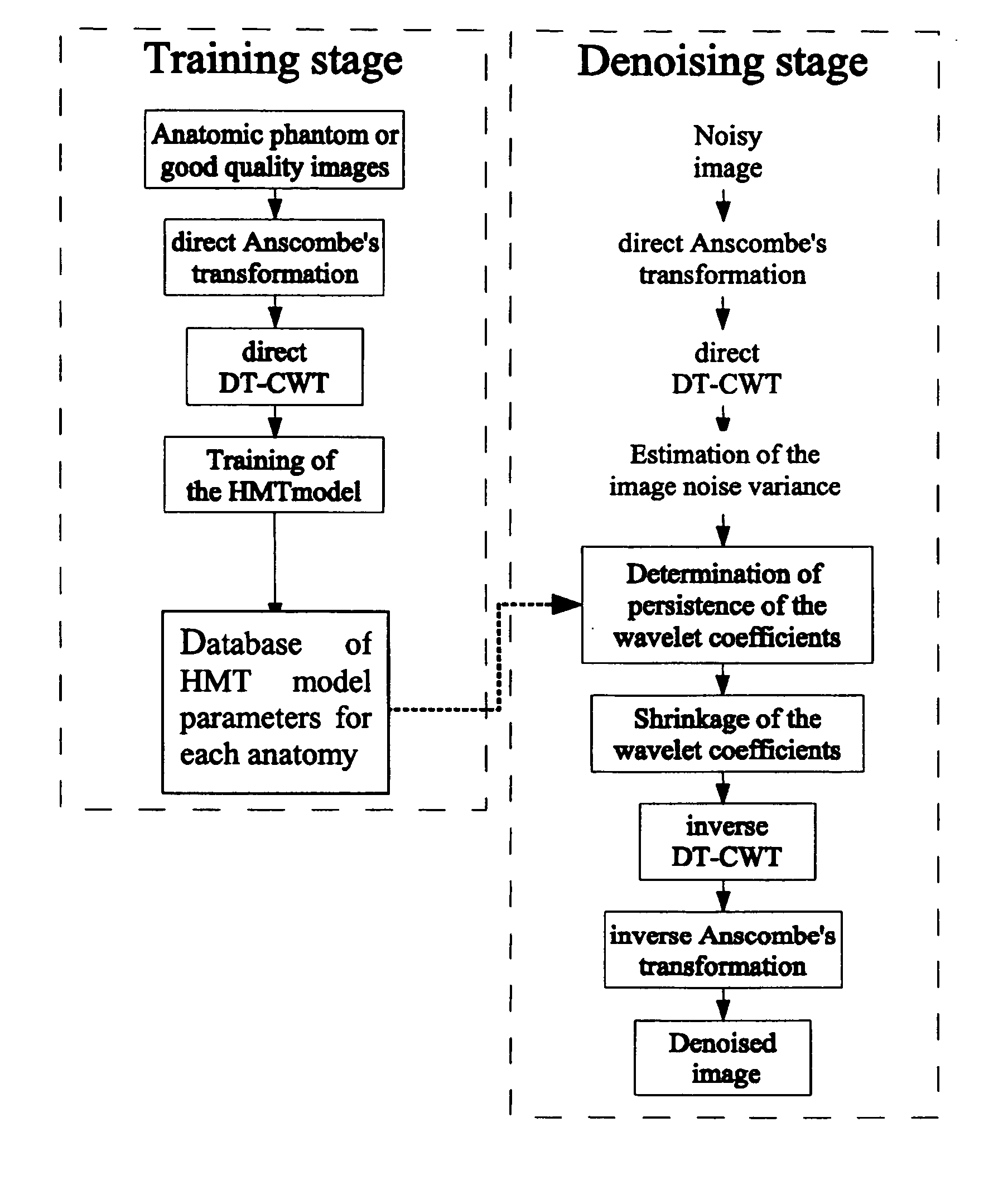
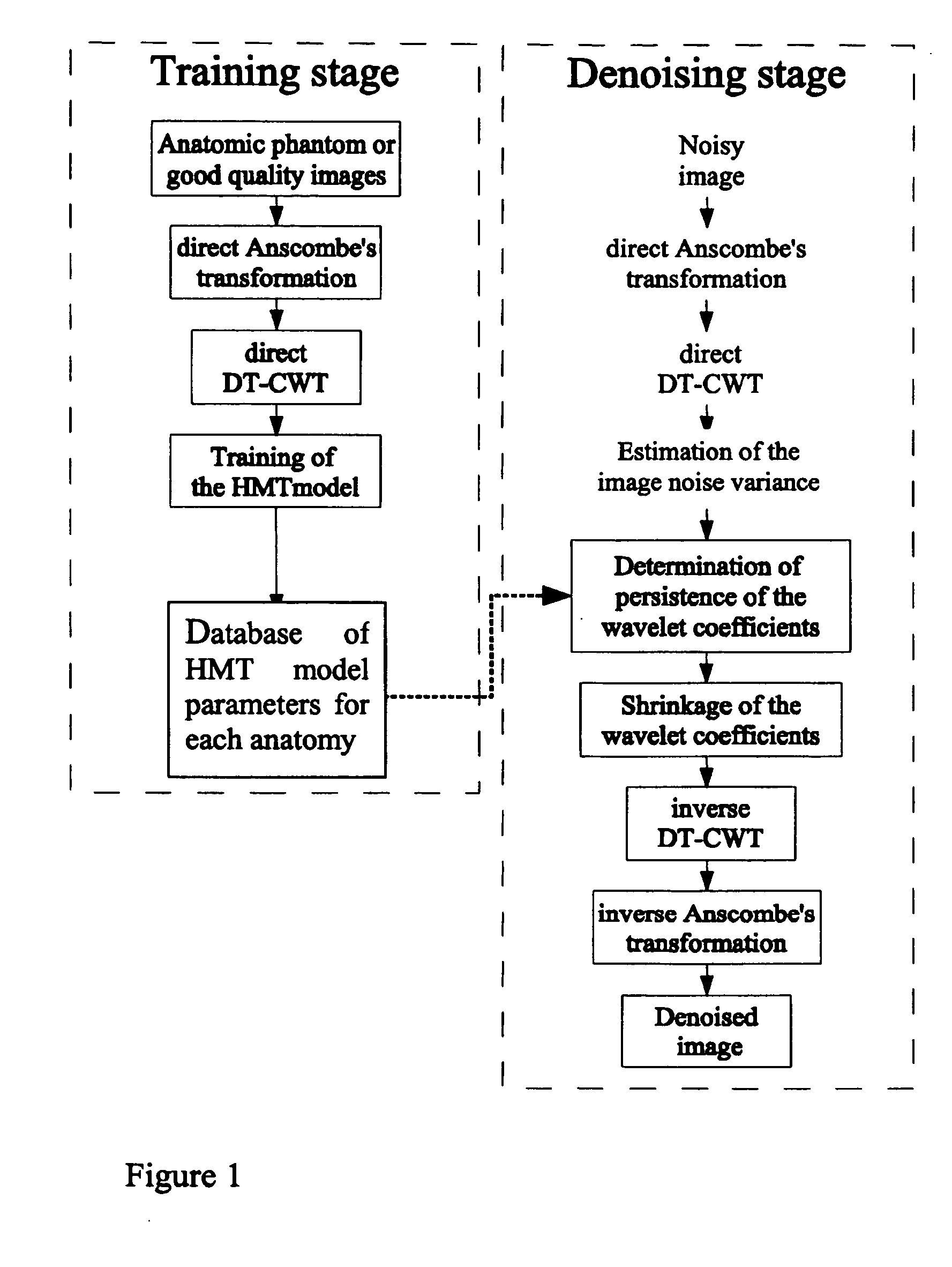
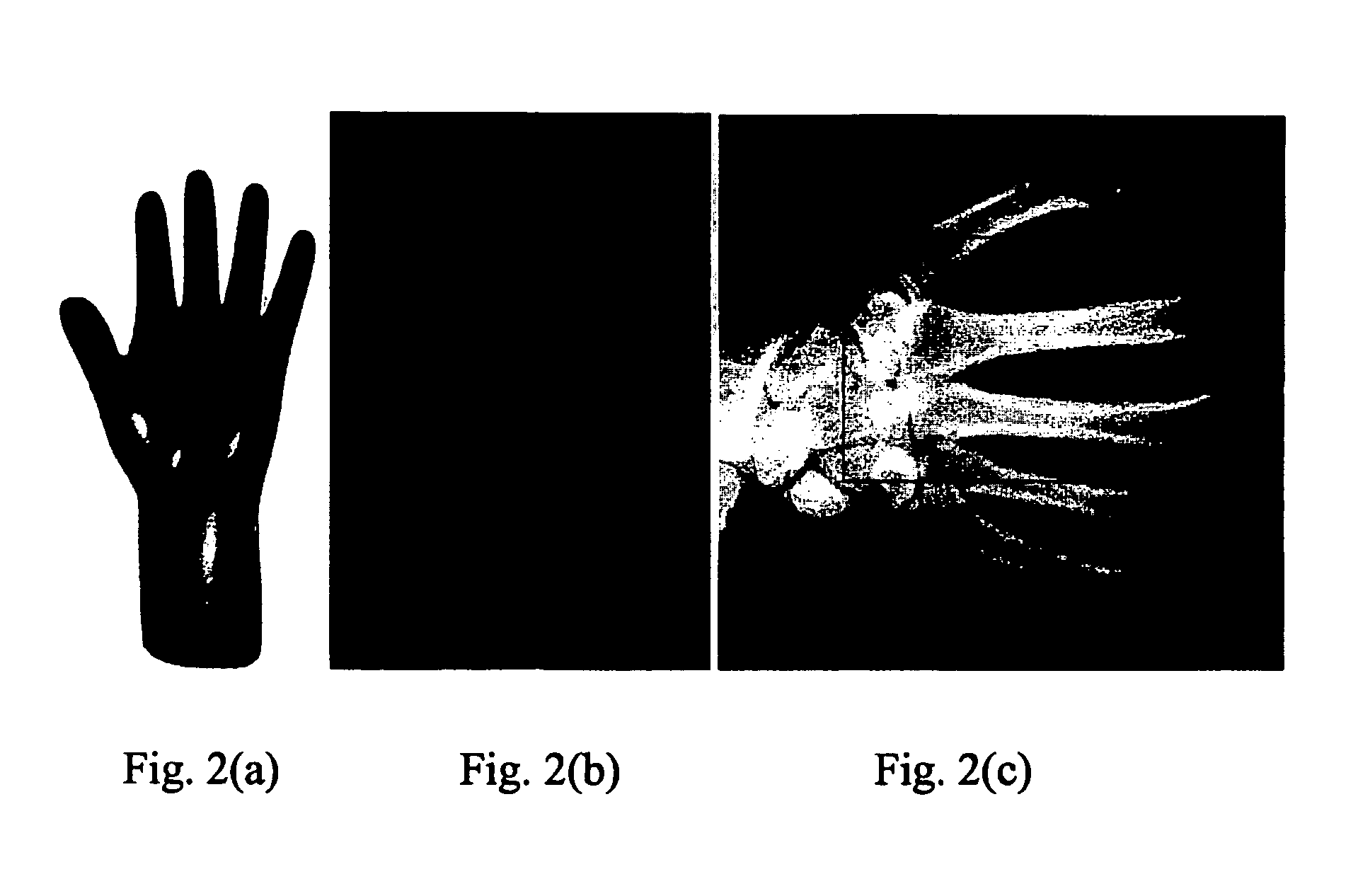
This invention relates to a method for de-noising digital radiographic images based upon a wavelet-domain Hidden Markov Tree (HMT) model. The method uses the Anscombe's transformation to adjust the original image to a Gaussian noise model. The image is then decomposed in different sub-bands of frequency and orientation responses using a dual-tree complex wavelet transform, and the HMT is used to model the marginal distribution of the wavelet coefficients. Two different methods were used to denoise the wavelet coefficients. Finally, the modified wavelet coefficients are transformed back into the original domain to get the de-noised image.
Owner:1370509 ALBERTA
Color digital image enhancing and denoising method under random illumination
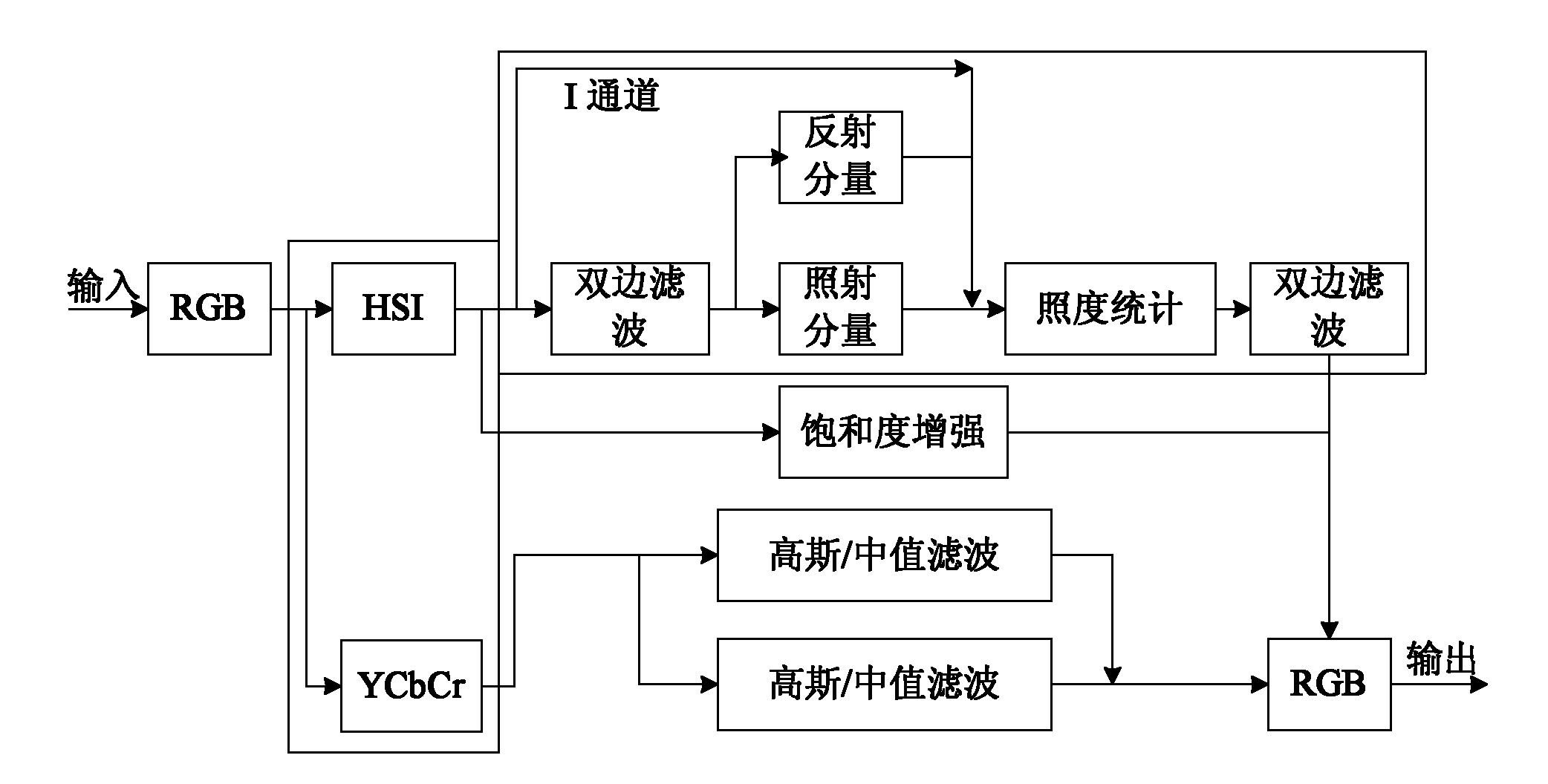
The invention discloses a color digital image enhancing and denoising method under random illumination. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1, image denoising processing, namely converting an original image from an RGB space to a YCbCr space, removing a Gaussian noise by using a Gaussian filter and removing a salt and pepper noise by performing median filter; 2, image brightness / contract stretch processing, converting the image from the RGB space to an HSI space, decomposing the image by using a two-sided filter, processing by an improved Retinex model algorithm, and obtaining a new image saturation by performing saturation compensation; and 3, performing fusion display on the image acquired after denoising the YCbCr space and the image acquired by HSI space processing. By the method, the color constancy of the image can be kept, the dynamic range of the image can be improved well, and simultaneously noises of the image can be inhibited and removed with less texture and detail information loss.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Spectrum sensing function for cognitive radio applications
ActiveUS20090102981A1Television system detailsModulated-carrier systemsWireless microphoneTelevision system
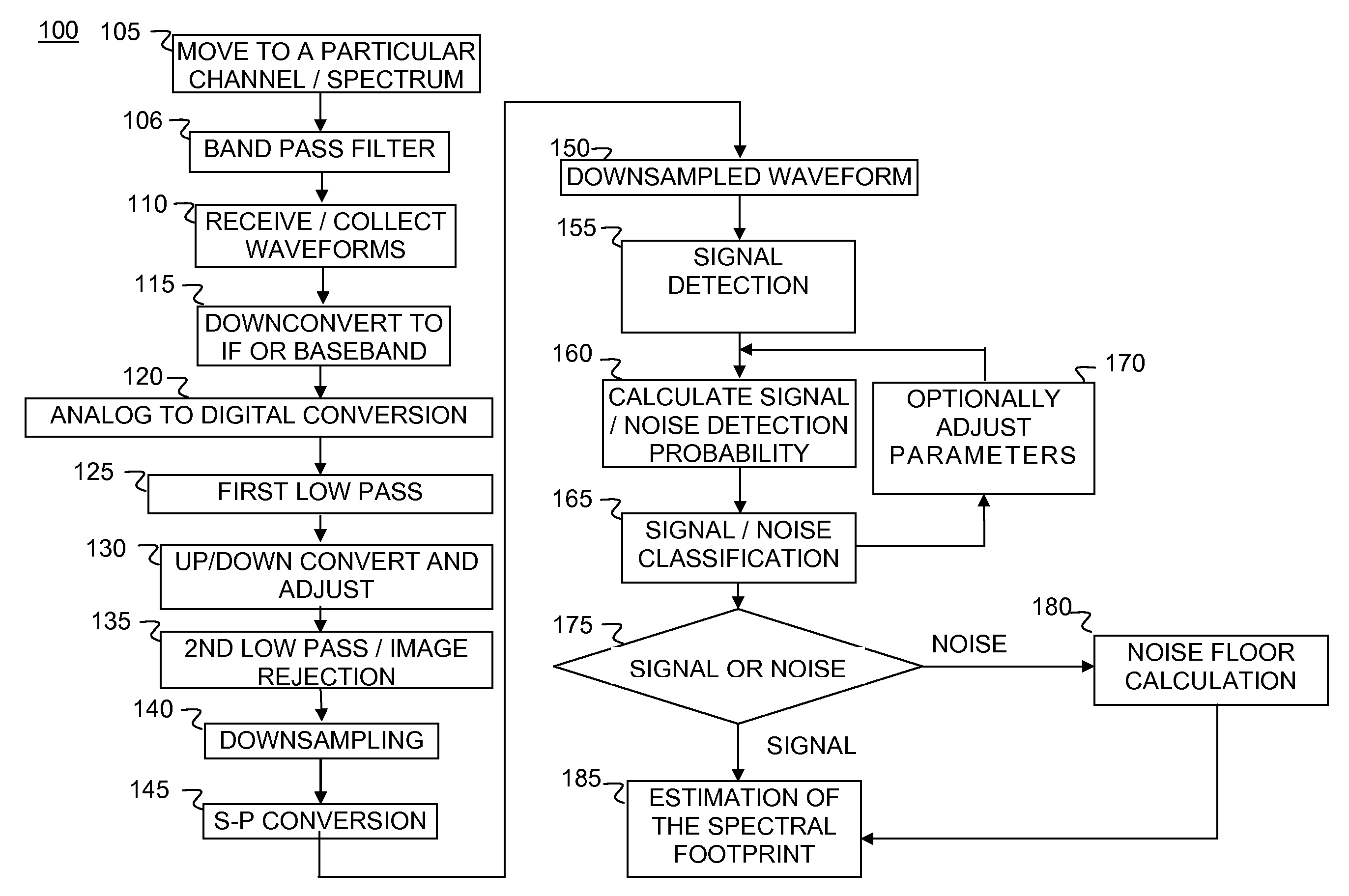
A method and system are disclosed to detect a broad class of signals including Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC) digital television (DTV) and wireless microphone signals. This signal detection method performs in Gaussian noise, employing Higher Order Statistics (HOS). Signals are processed in time and frequency domains as well as by real and imaginary components. The spectrum sensing employed also supports Denial of Service (DoS) signal classification. The method can include parameters that may be tailored to adjust the probability of detection and false alarm.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
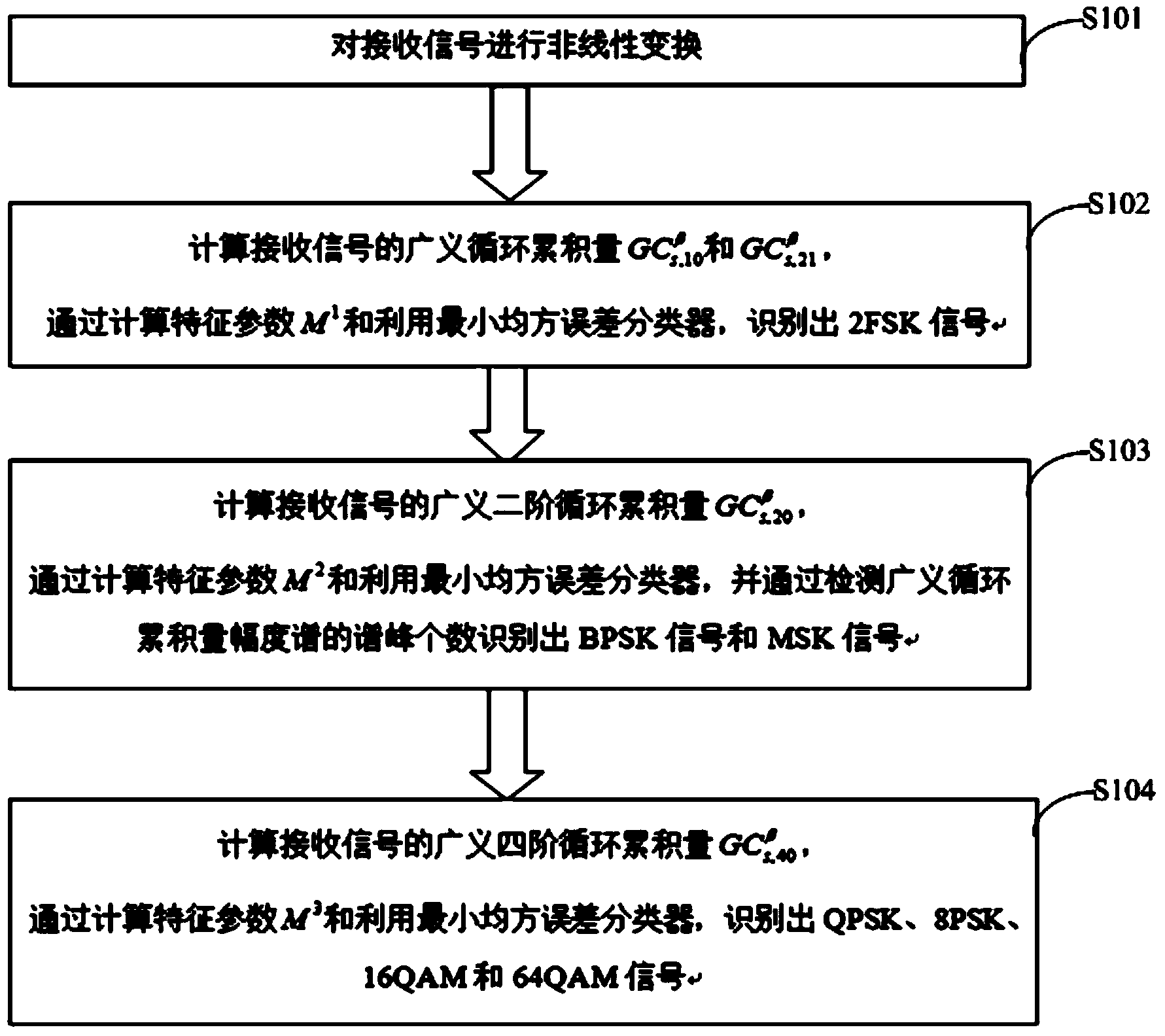
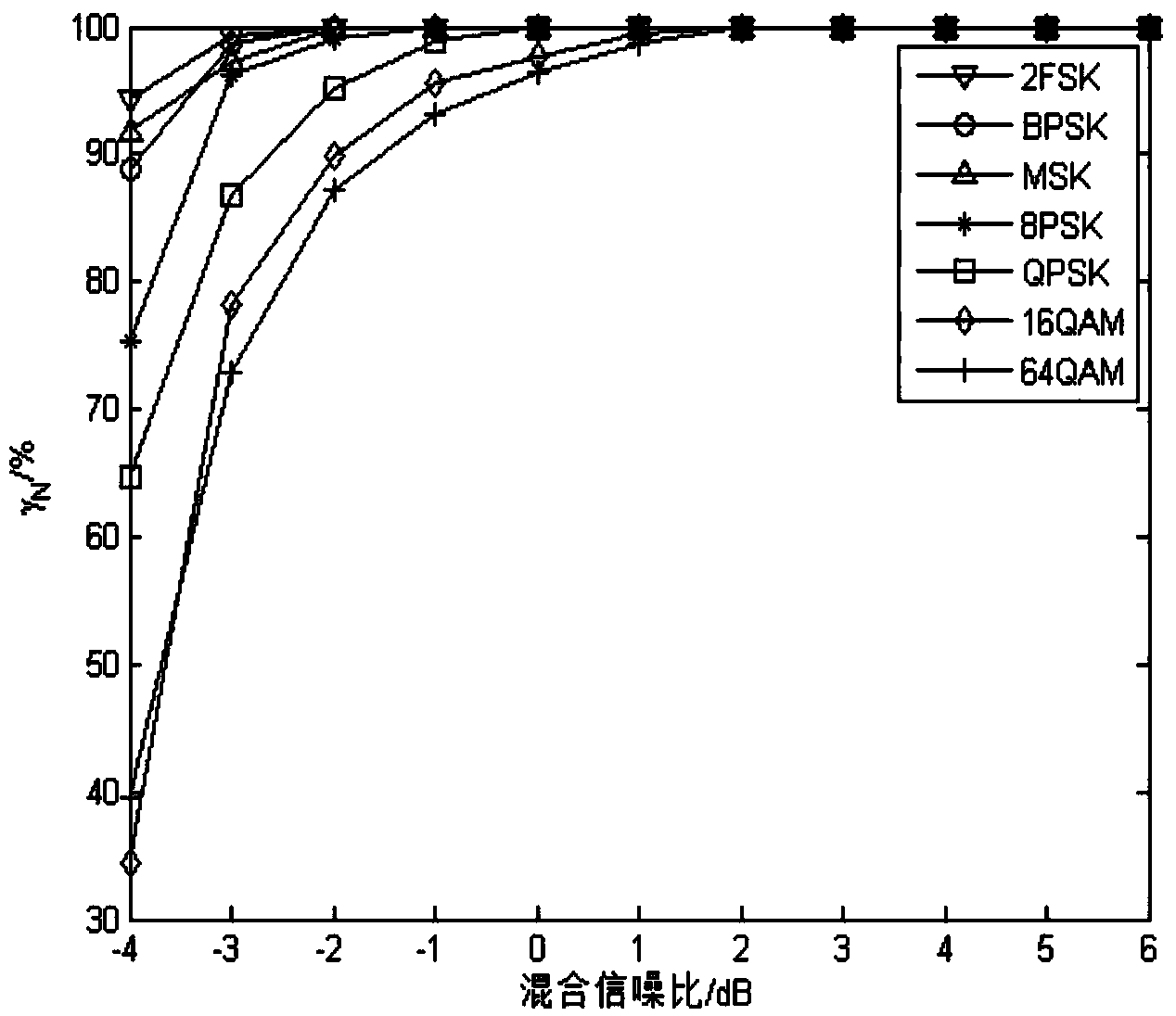
Method for effectively recognizing digital modulating signals in non-Gaussian noise
InactiveCN103457890AImprove performancePracticalModulated-carrier systemsHigher-order statisticsMinimum mean square error
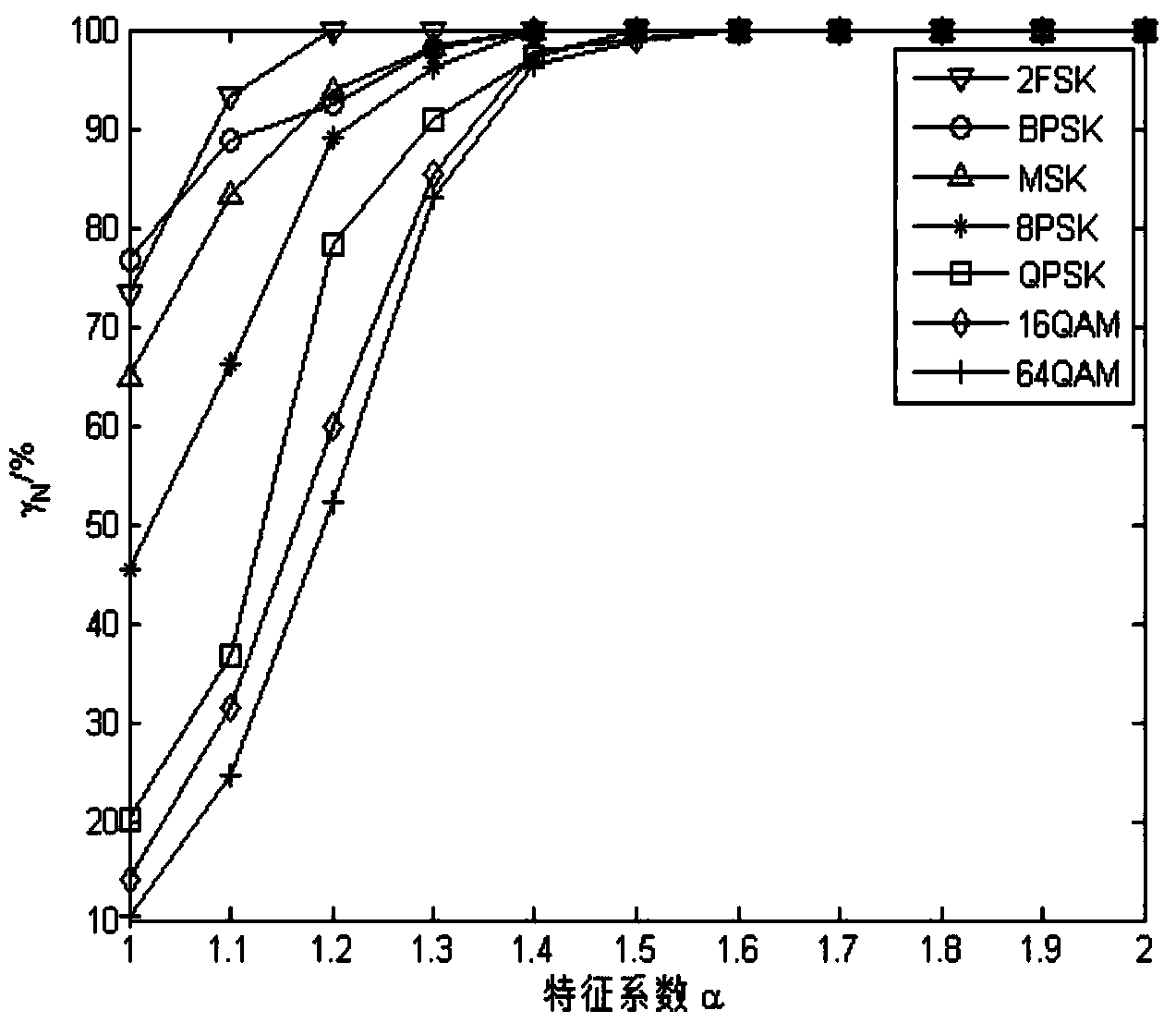
The invention discloses a method for effectively recognizing digital modulating signals in non-Gaussian noise. Non-linear transformation is performed on a received signal s(t); the generalized first-order cyclic cumulant and the generalized second-order cyclic cumulant of the received signal s(t) are calculated, and a 2FSK signal is recognized by calculating the characteristic parameters of the received signal s(t) and utilizing a minimum mean square error classifier; the generalized second-order cyclic cumulant of the received signal s(t) is calculated, and by calculating the characteristic parameters of the received signal s(t) and utilizing the minimum mean square error classifier, the number of spectral peaks of a generalized cyclic cumulant magnitude spectrum is detected so that a BPSK signal and an MSK signal can be recognized; the generalized fourth-order cyclic cumulant of the received signal s(t) is calculated, and a QPSK signal, an 8PSK signal and other signals are recognized through the calculated characteristic parameters and the minimum mean square error classifier. The method for effectively recognizing digital modulating signals in non-Gaussian noise solves the problem that signals in Alpha stable distribution noise do not have second or higher order statistics, effectively recognizes the digital modulating signals and can be used for recognizing the modulation mode of the digital modulating signals in the Alpha stable distribution noise.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Performance of artificial neural network models in the presence of instrumental noise and measurement errors
ActiveUS20030191728A1Improve accuracy performanceImprove generalization performanceGenetic modelsDigital computer detailsObservational errorData set
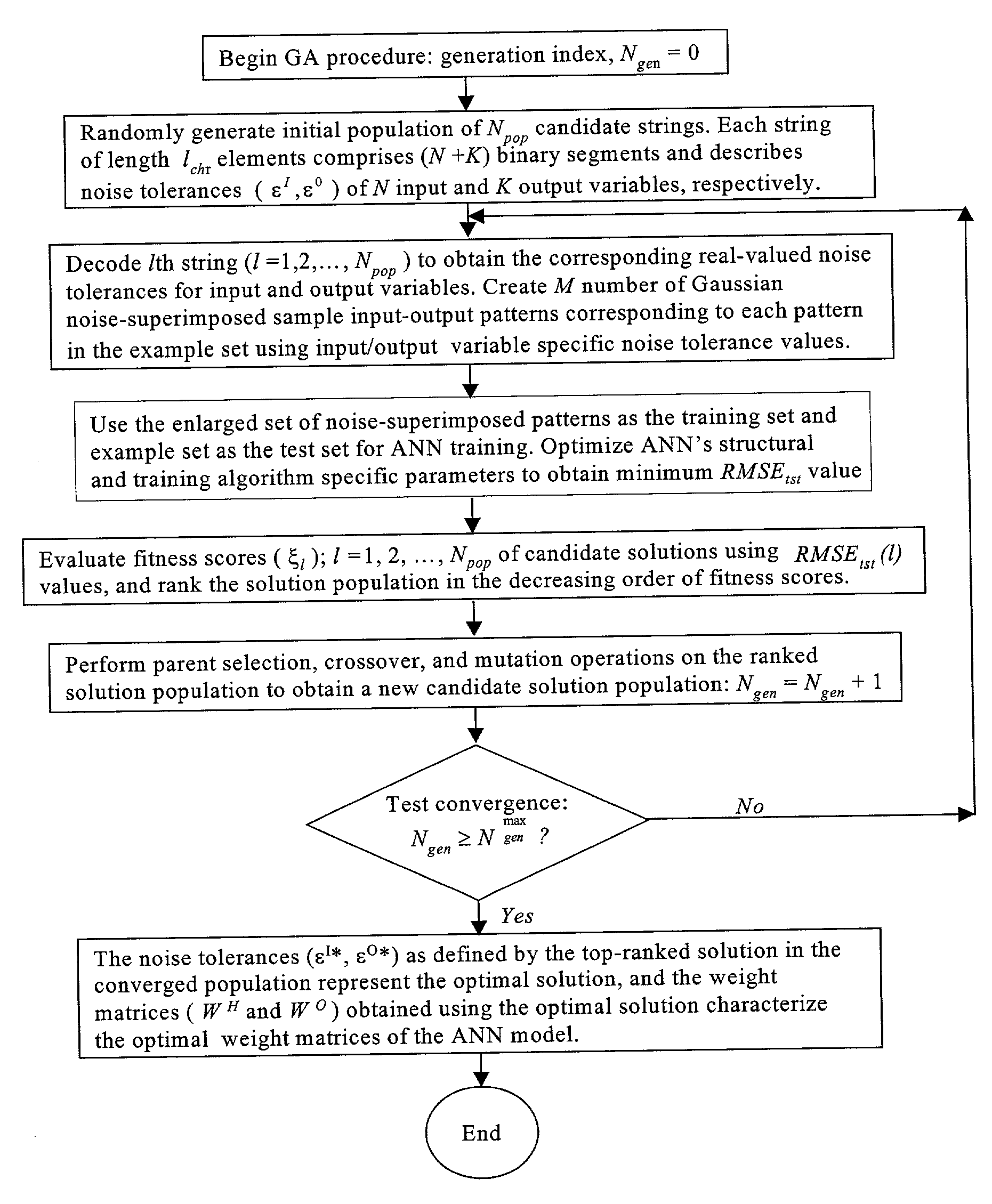
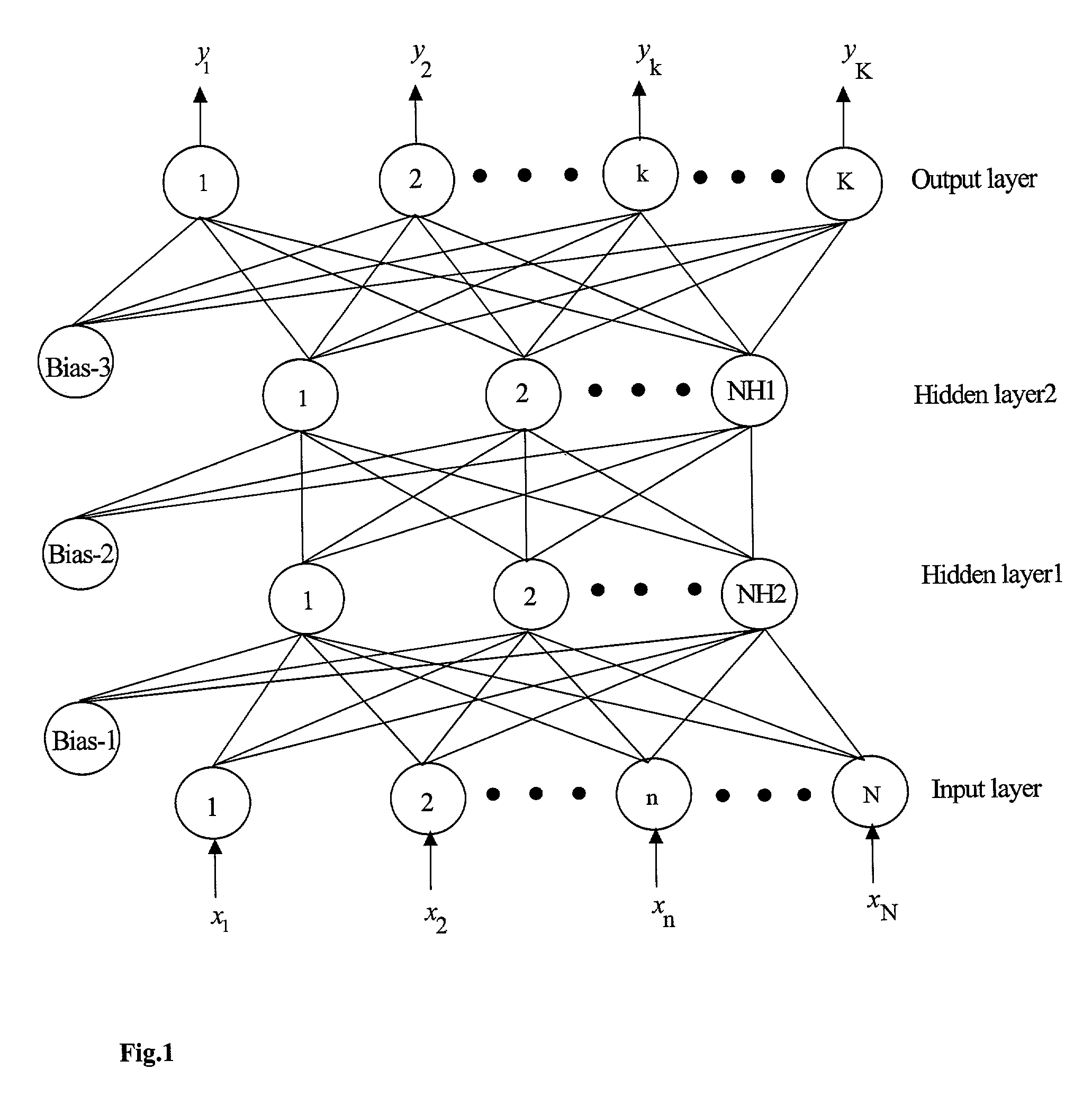
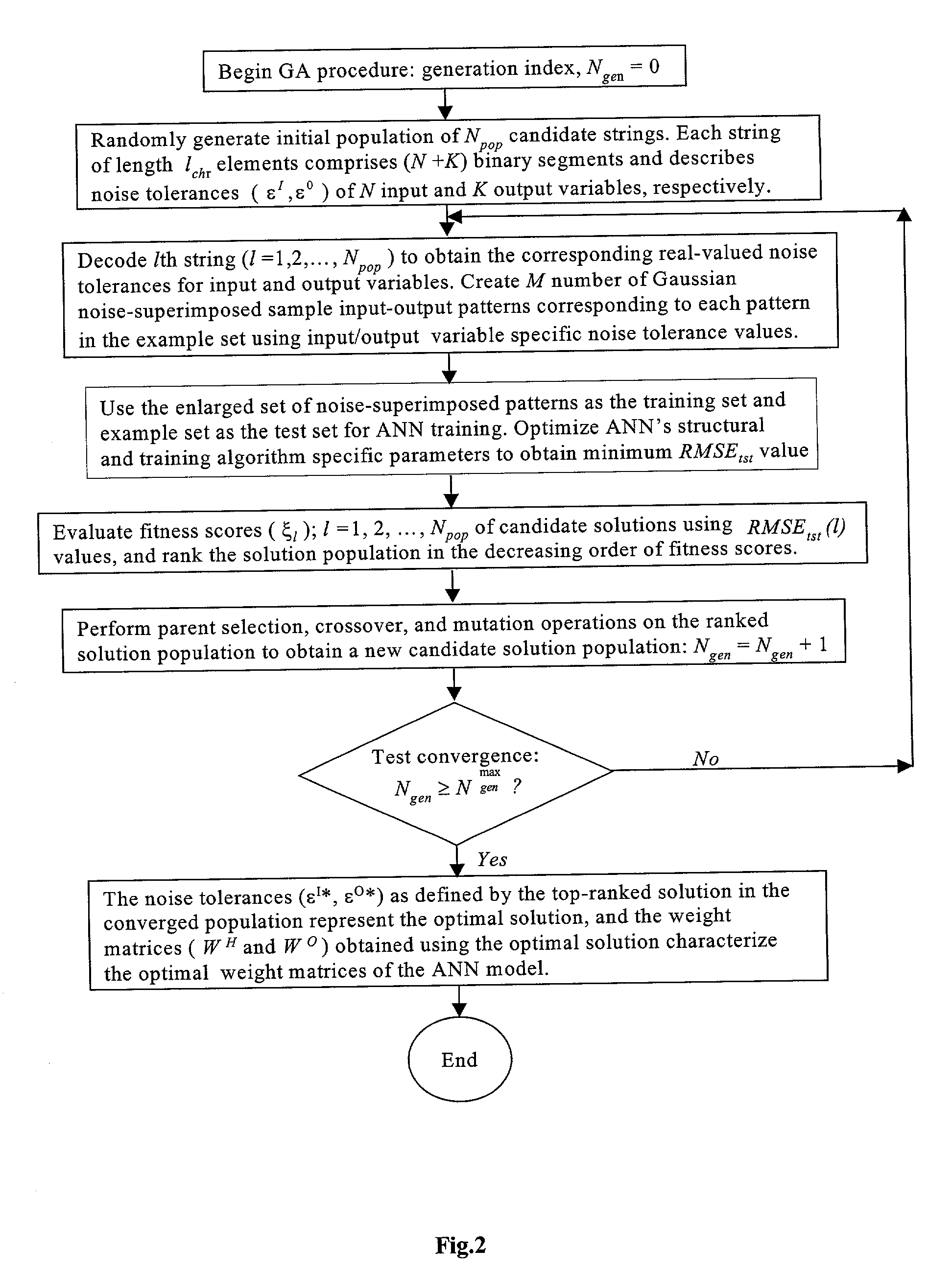
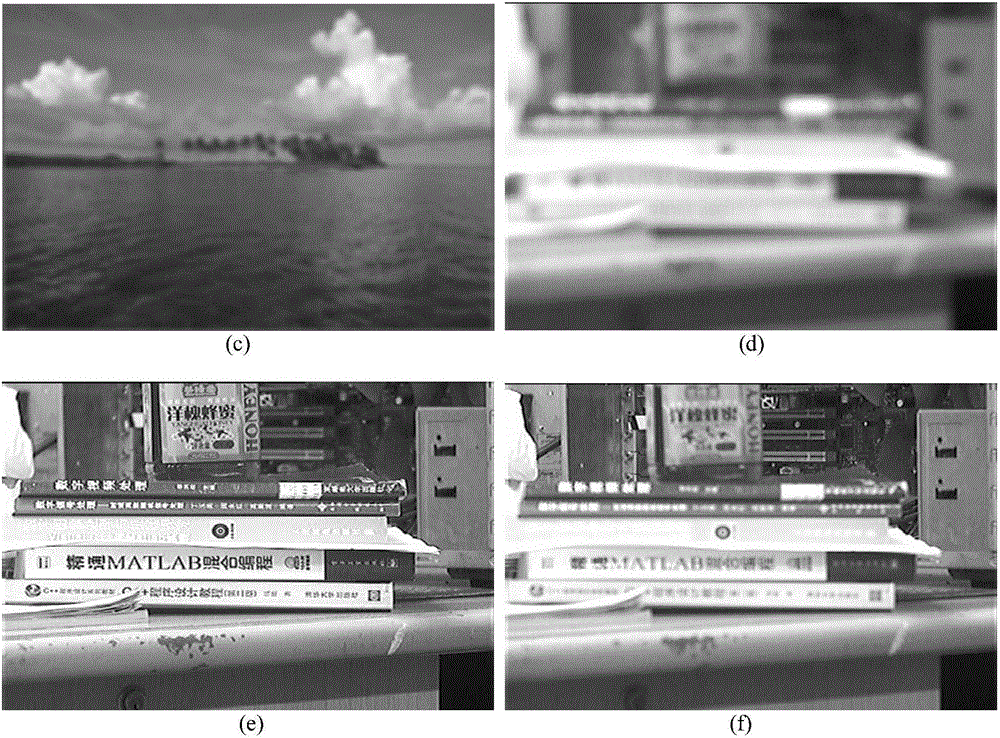
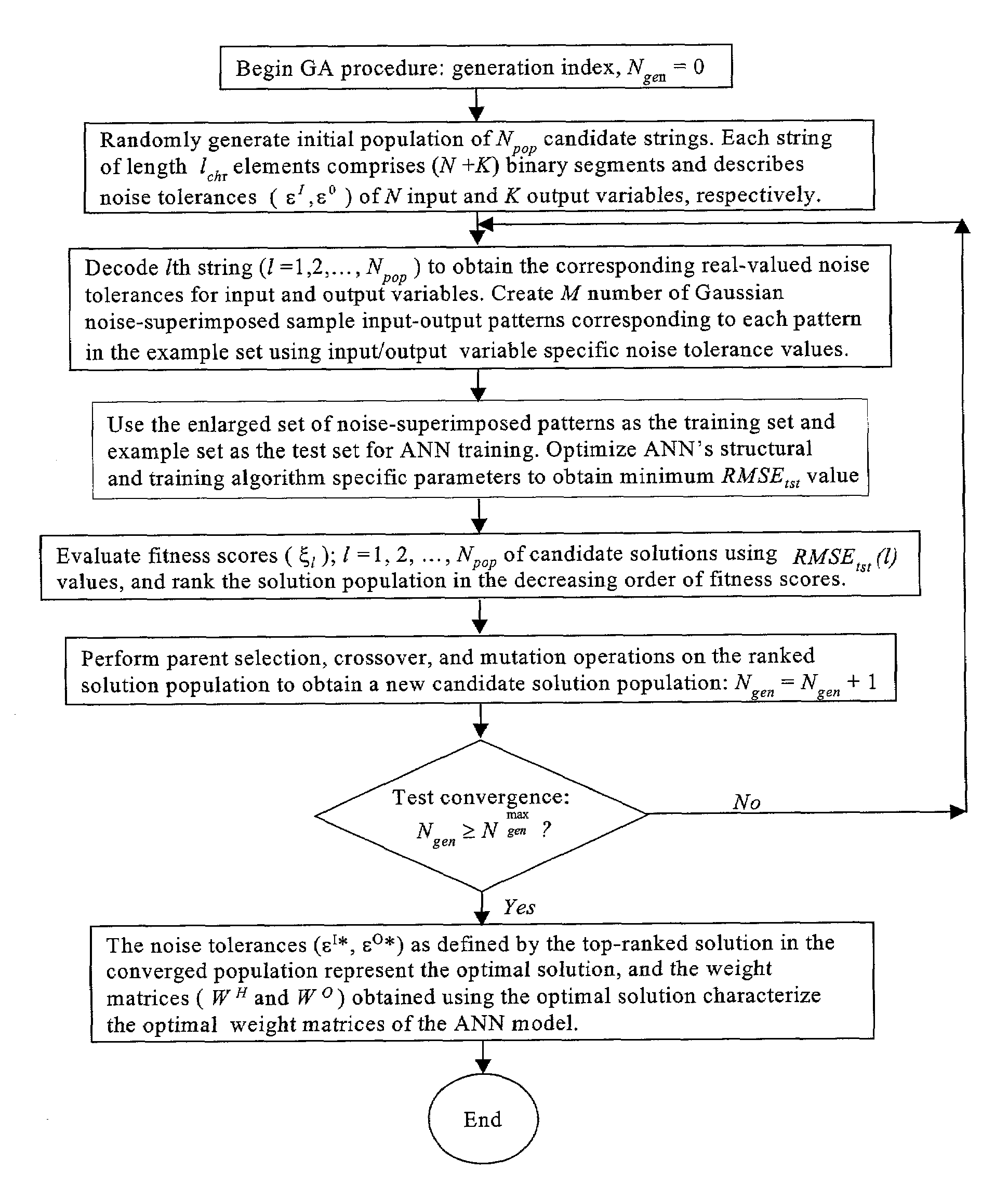
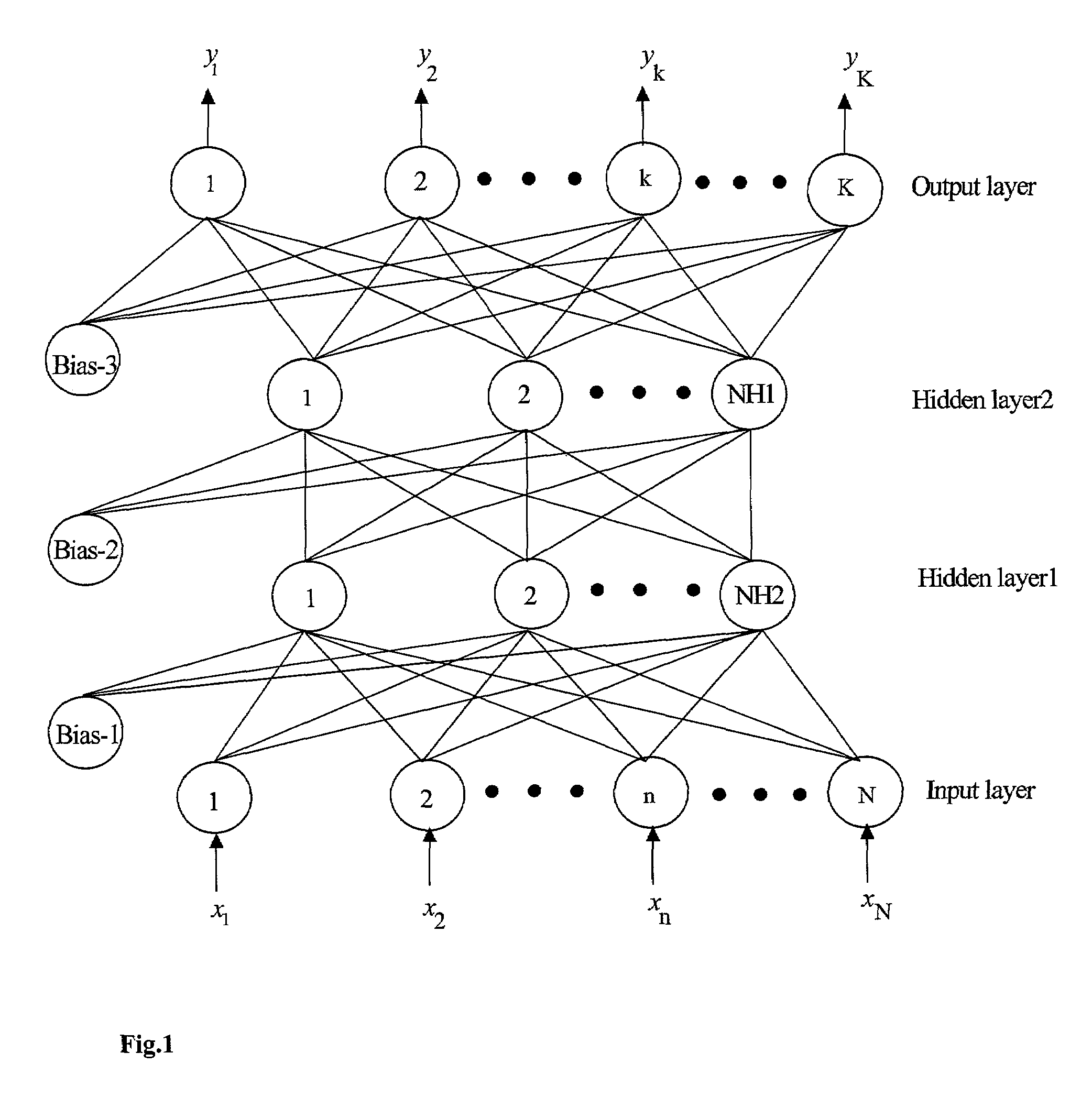
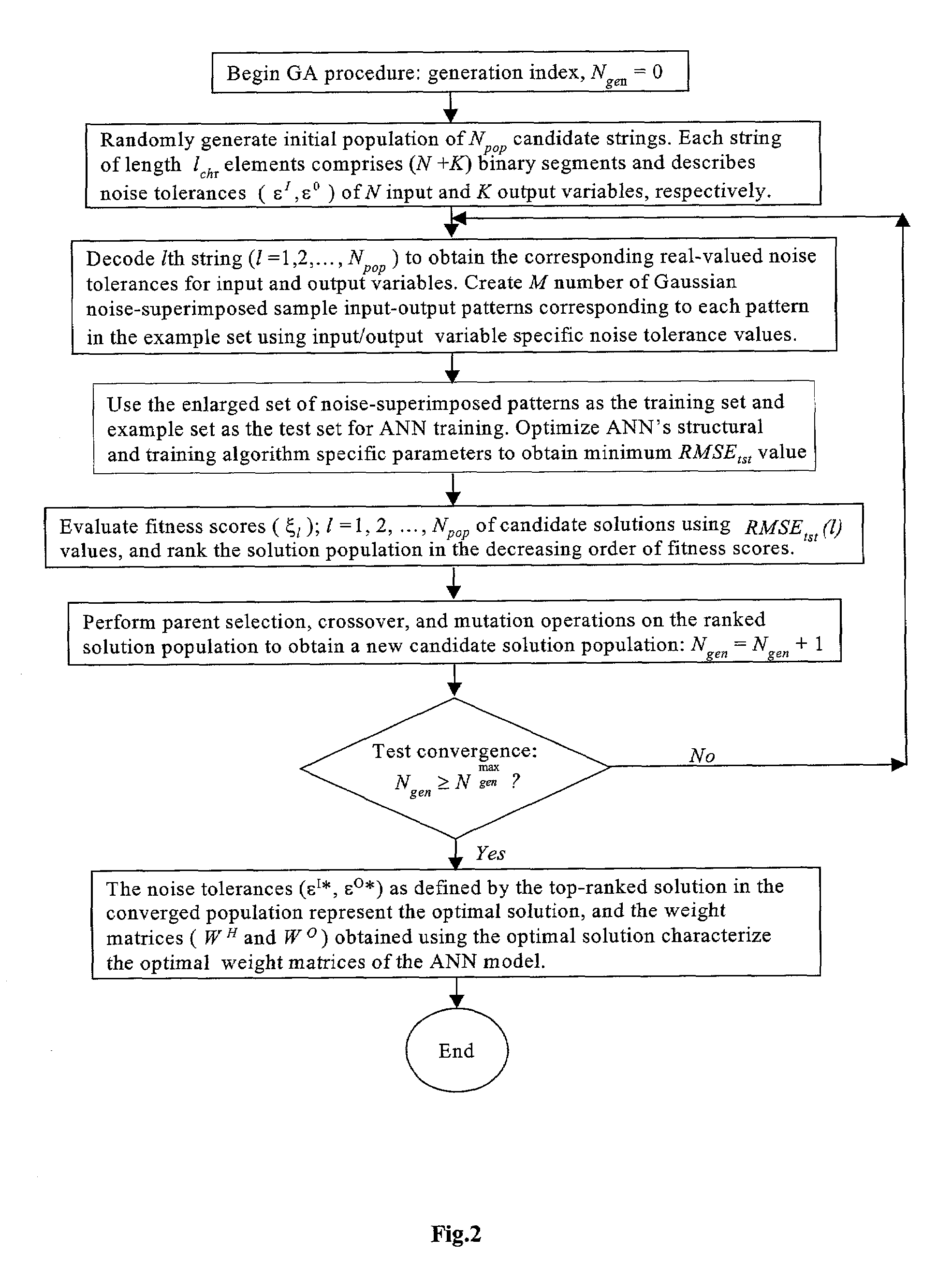
A method is described for improving the prediction accuracy and generalization performance of artificial neural network models in presence of input-output example data containing instrumental noise and / or measurement errors, the presence of noise and / or errors in the input-output example data used for training the network models create difficulties in learning accurately the nonlinear relationships existing between the inputs and the outputs, to effectively learn the noisy relationships, the methodology envisages creation of a large-sized noise-superimposed sample input-output dataset using computer simulations, here, a specific amount of Gaussian noise is added to each input / output variable in the example set and the enlarged sample data set created thereby is used as the training set for constructing the artificial neural network model, the amount of noise to be added is specific to an input / output variable and its optimal value is determined using a stochastic search and optimization technique, namely, genetic algorithms, the network trained on the noise-superimposed enlarged training set shows significant improvements in its prediction accuracy and generalization performance, the invented methodology is illustrated by its successful application to the example data comprising instrumental errors and / or measurement noise from an industrial polymerization reactor and a continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR).
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Robust Stereo Calibration System and Method for Accurate Digital Image Correlation Measurements
ActiveUS20100079598A1Maintain accuracyConvenient and accurateUsing optical meansTelevision systemsExplicit modelObject point
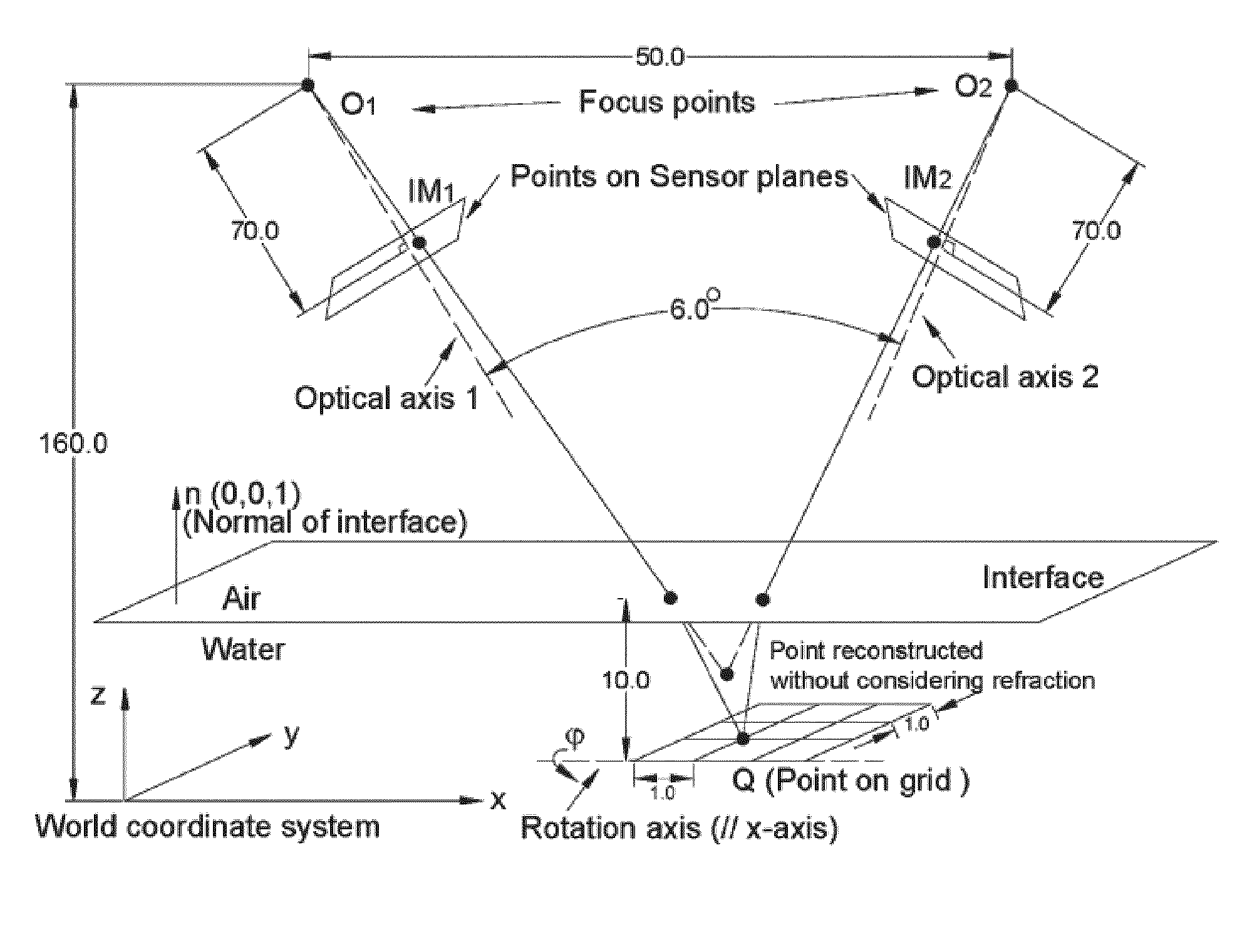
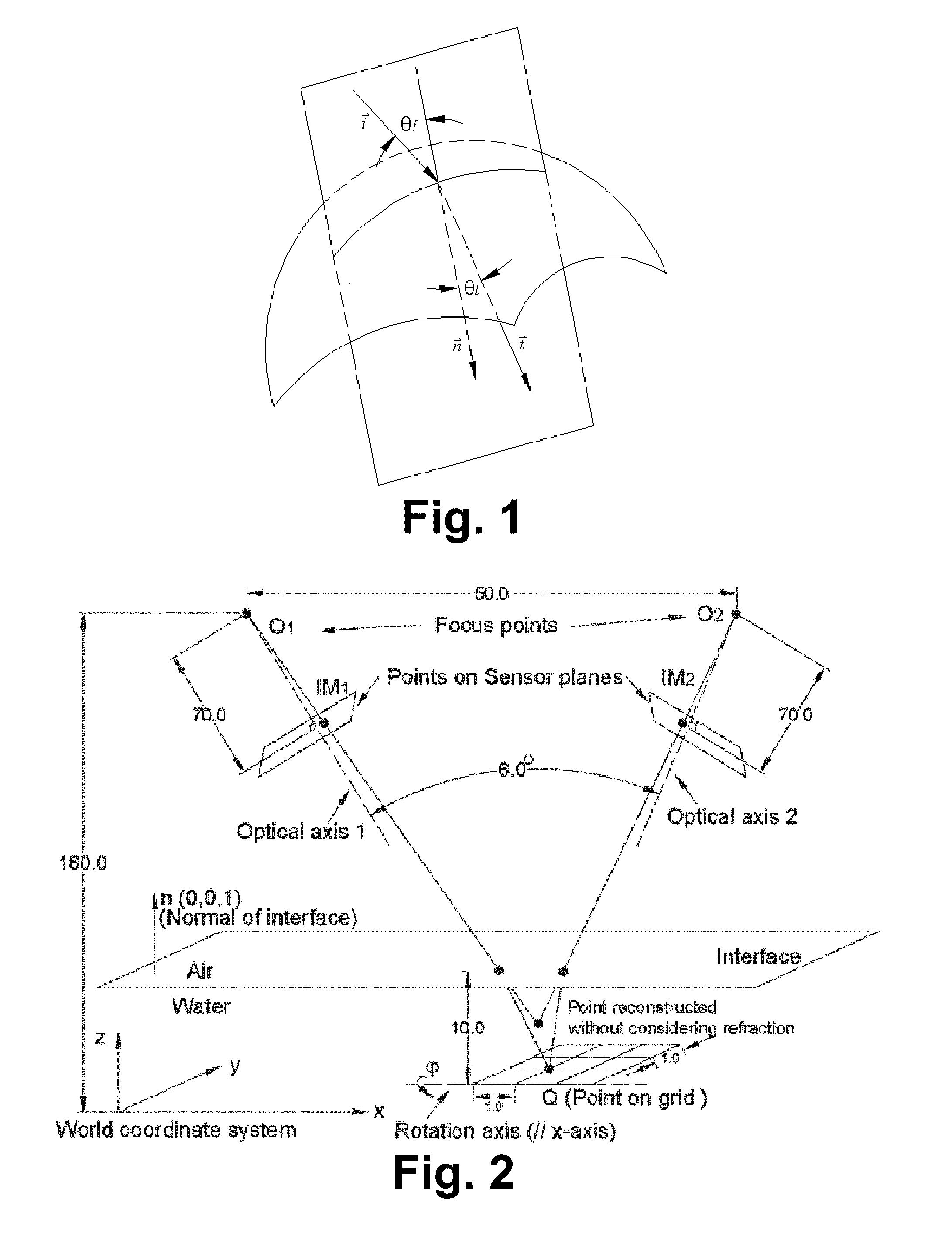
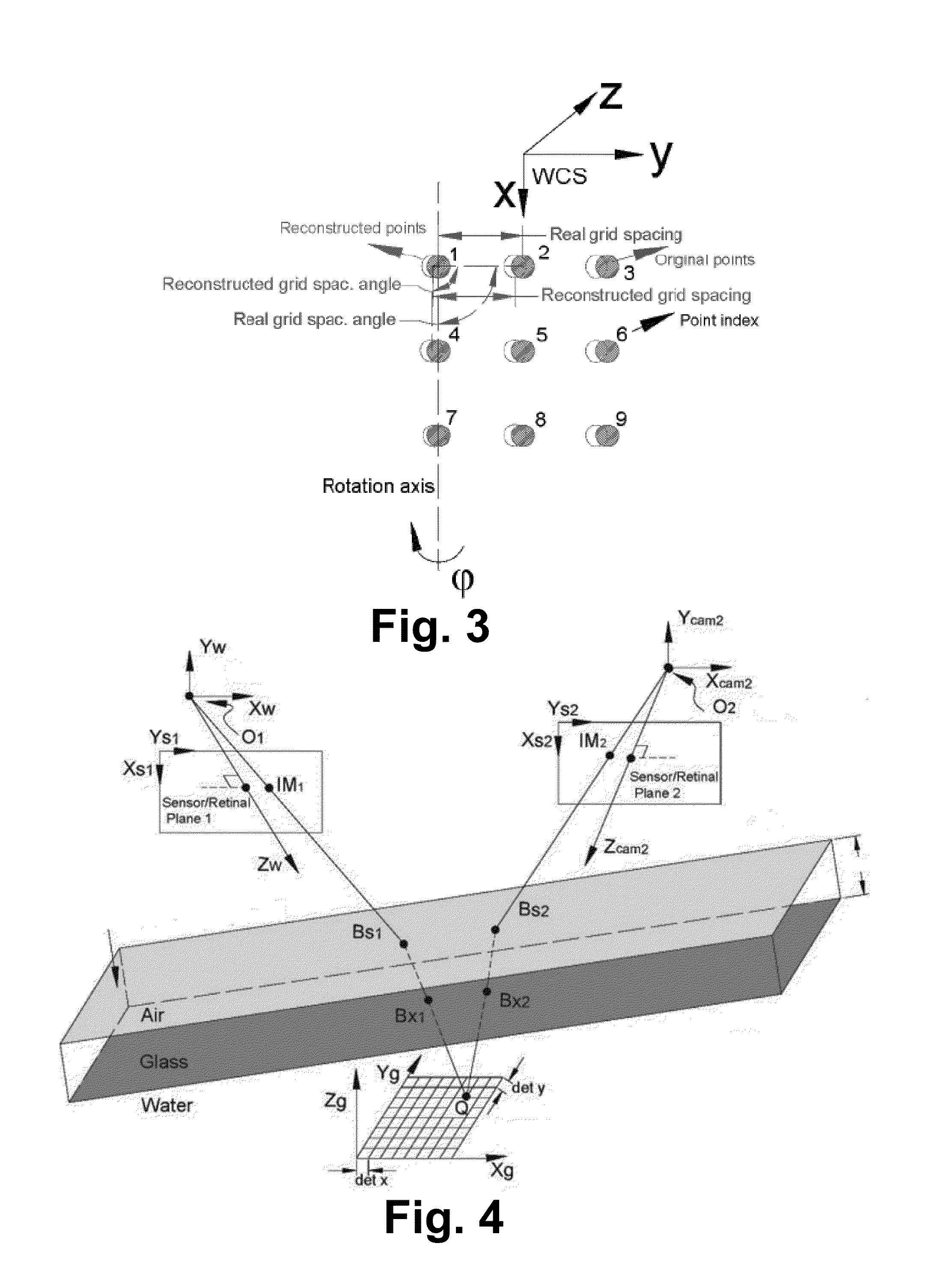
A stereo calibration method is proposed to calibrate an interface's shape and position when the measurement system is in one media and measures deformation and strain of an object that is submerged in a different media. After the interface's shape and position are modeled by parameters, an explicit model of object points as measurement is established taking account of refraction happening at the interface. Efficiency and convergence are assured by using measurement of object points to acquire initial estimates for refraction angles at the interface. Then, an optimization method is performed to get the optimized value of interface parameters. Last, based on the resulting interface parameters, 3-dimensional positions of object points in all the subsequent measurement could be reconstructed accurately. Therefore, the distortion induced by refraction in the measurement is corrected. Numerical simulations of the proposed calibration process confirm that it is both robust and accurate for a range of experimental conditions, even in the presence of Gaussian noise in the measurement.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA
Multidimensional constellation mapping based coding and modulating method, demodulating and decoding method and system
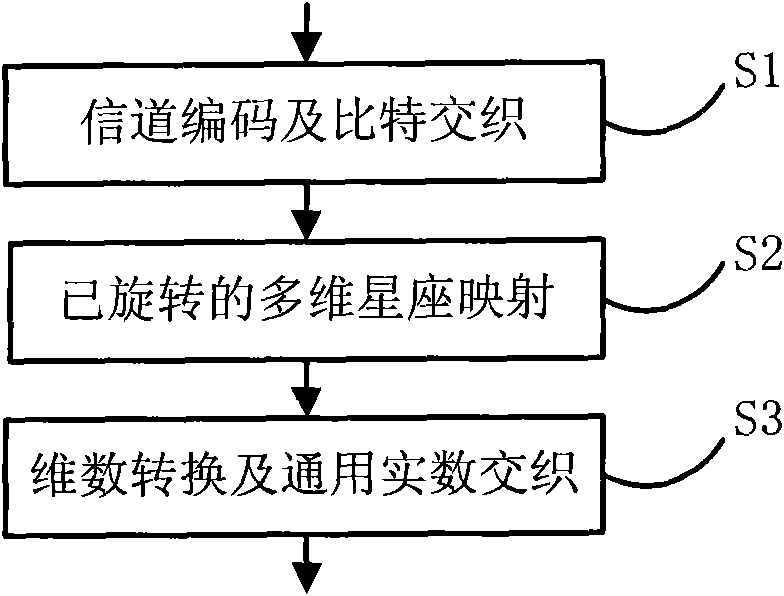
ActiveCN102075487AIncrease the order of diversityError preventionMultiple carrier systemsBase codeFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to a multidimensional constellation mapping based coding and modulating method, demodulating and decoding method and system. The coding and modulating method comprises the following steps of: carrying out channel coding and bit interleaving on input information bits to obtain coded interleaved bits; carrying out K-dimensional pulse amplitude modulated constellation mapping on the coded and interleaved bits to obtain a constellation mapping symbol of a K-dimensional real-number vector, wherein K is a positive integer; carrying out constellation rotation on the constellation mapping symbol to obtain a multidimensional rotated constellation mapping symbol of the K-dimensional real-number vector; and carrying out dimension conversion and general real-number interleaving on the multidimensional rotated constellation mapping symbol to obtain a coded and modulated symbol, and outputting the coded and modulated symbol. The method and system in the invention can ensure that the performances of a coding and modulating system and a corresponding demodulating and decoding system approach the channel capacity at medium and low frequency spectrum efficiency under the AWGN (Added White Gaussian Noise) and fading channel conditions and meanwhile, the throughput of the system is taken into consideration.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Filtering of noisy images
ActiveUS20050276510A1Easy to implementImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionOne pass
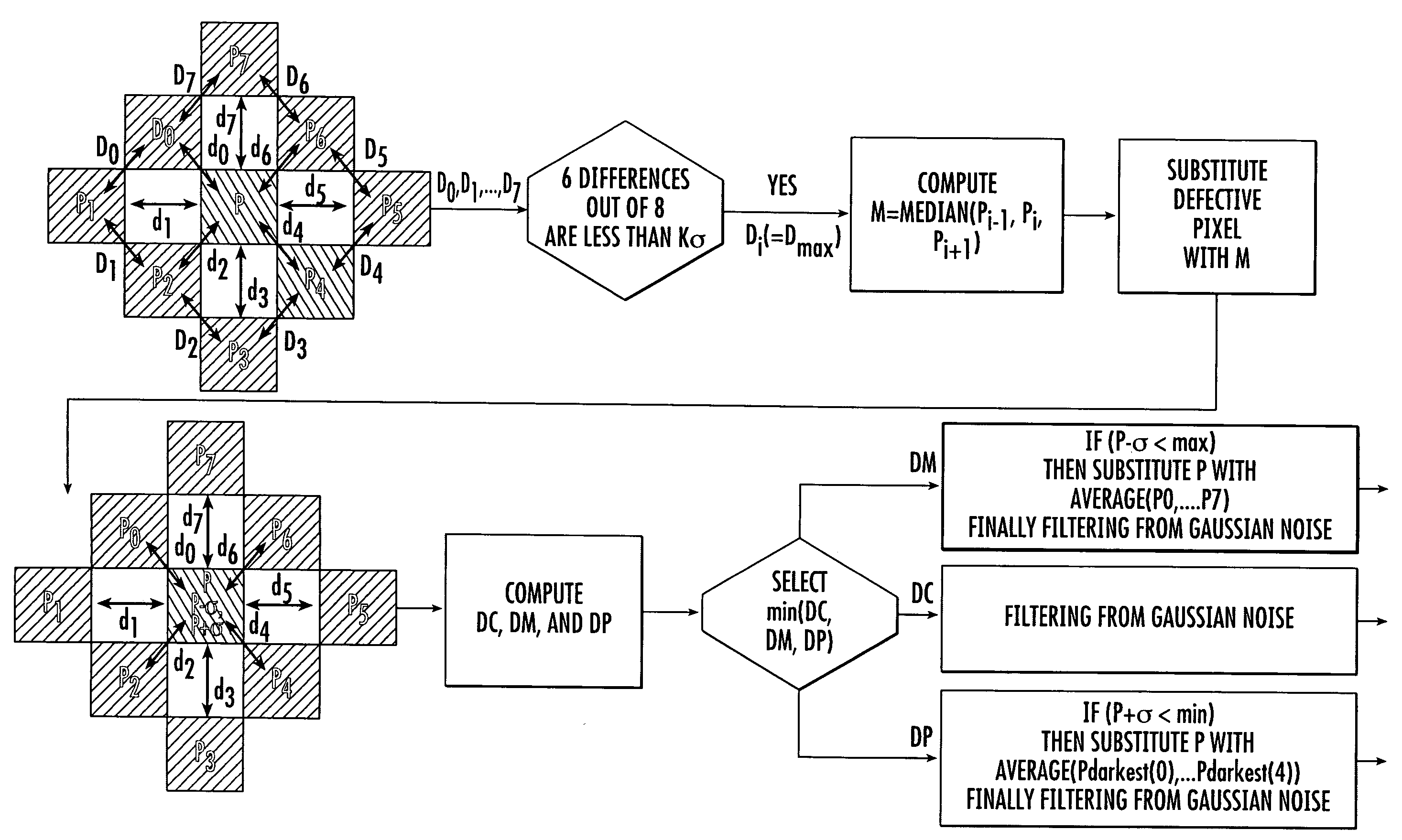
A method for correcting an image from defects and filtering from Gaussian noise corrects each pixel of the image when it is considered defective and filters it from Gaussian noise in one-pass. The one-pass improves the speed for performing the correcting and filtering. The drawbacks associated with choosing incompatible defect correction and filtering operations are overcome.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
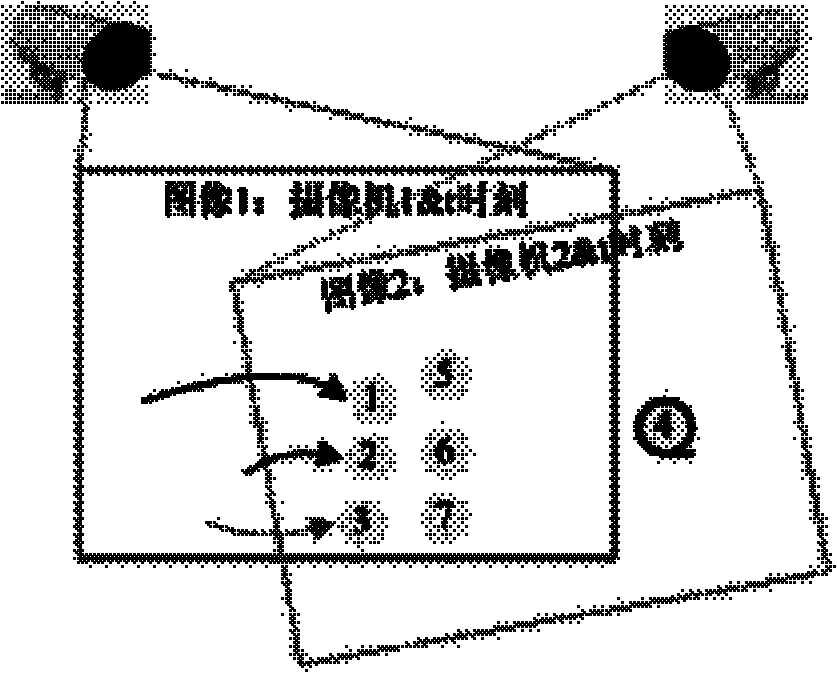
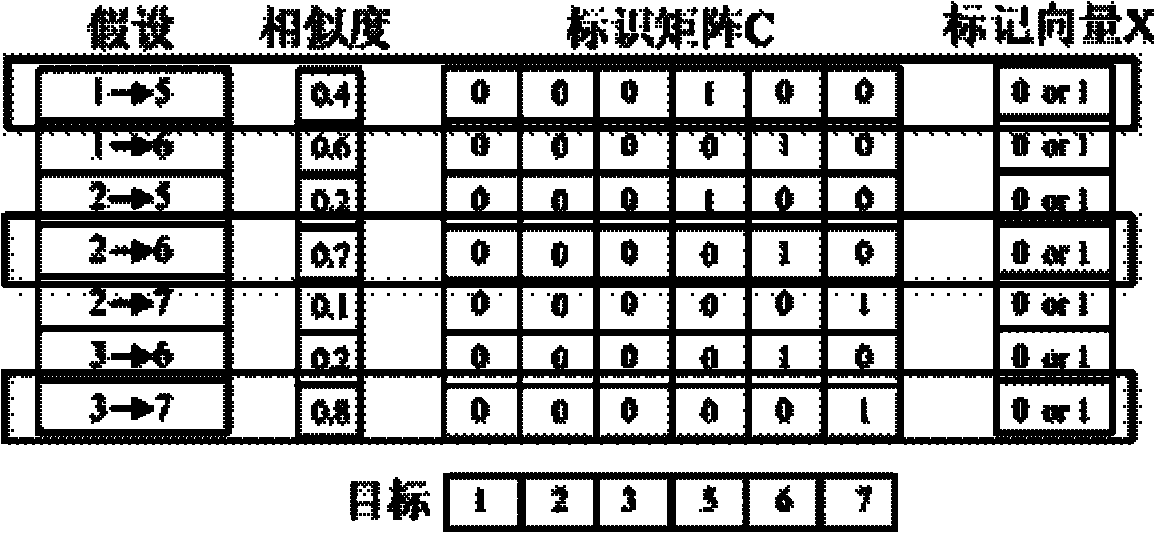
Cross-camera tracking method for multiple moving targets
ActiveCN102156863AComplete descriptionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman bodyFilter model
The invention relates to image process, motion analysis and the like. In order to implement cross-camera tracking of moving targets, the invention uses the technical scheme that the cross-camera tracking method for the multiple moving targets comprises the following steps of: 1, motion filtering for a single camera, specifically, decomposing complex motions of human body into a finite number of combinations of relatively simple motion filtering models, wherein each single motion filtering model is represented by a combination of a linear motion state transition model and a gaussian noise, and the motion filtering method comprises the two following core parts: a motion model: an observation model; zk = Hsk + wk2, cross-camera oriented motion association: (1) creation of a panorama; (2) target similarity measurement; (3) motion trail association; and transforming the problem of cross-camera association of multiple motion trails into the problem of matching of bipartite graphs, and solving the problem through the integer programming under the following constraint conditions. The cross-camera tracking method for the multiple moving targets is mainly used in the image processing, the motion analysis and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG E VISION ELECTRONICS TECH
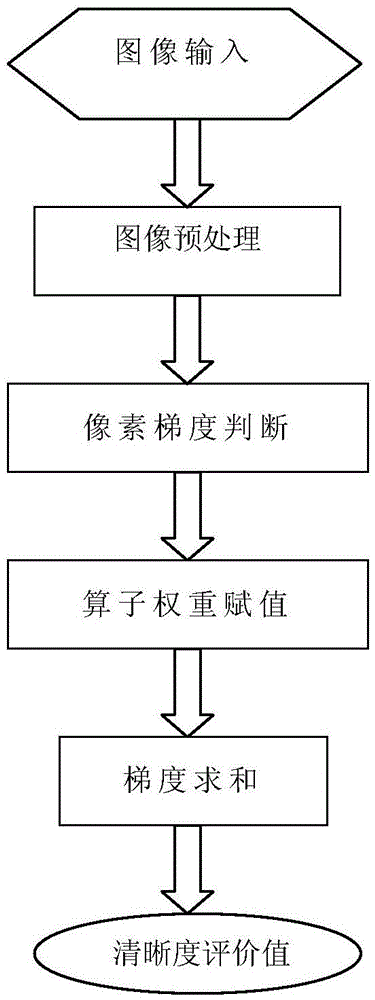
Defocus blurred image definition detecting method based on edge strength weight
ActiveCN104637064AImprove balanceAmplified equalizationImage enhancementImage analysisConstant powerEdge strength
The invention provides a defocus blurred image definition detecting method based on edge strength weight. The defocus blurred image definition detecting method comprises the following steps: firstly, pre-processing an input image, correcting brightness and a contrast ratio through a histogram equalization method, performing Wiener filtering processing on constant power addition noises in a digital camera system, and respectively processing impulse noises and Gaussian noises through a median filter and a Gaussian filter; then, adopting four direction edge gradient operators to detect gradient of each pixel point, eliminating interferences of local bright dark points and isolated noise points according to the detected gradient size, and further processing the residual pixels; comparing direction gradient of the residual pixels with a set threshold value, distinguishing strong edge pixels with relatively large edge gradient values and weak edge pixels with relatively small boundary vicinity gradient values, and respectively endowing different weights; finally, adding up maximum gradient square of all pixels to obtain a definition detected value of the whole image.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Performance of artificial neural network models in the presence of instrumental noise and measurement errors
InactiveUS7313550B2Improve accuracyImprove performanceGenetic modelsDigital computer detailsObservational errorData set
A method is described for improving the prediction accuracy and generalization performance of artificial neural network models in presence of input-output example data containing instrumental noise and / or measurement errors, the presence of noise and / or errors in the input-output example data used for training the network models create difficulties in learning accurately the nonlinear relationships existing between the inputs and the outputs, to effectively learn the noisy relationships, the methodology envisages creation of a large-sized noise-superimposed sample input-output dataset using computer simulations, here, a specific amount of Gaussian noise is added to each input / output variable in the example set and the enlarged sample data set created thereby is used as the training set for constructing the artificial neural network model, the amount of noise to be added is specific to an input / output variable and its optimal value is determined using a stochastic search and optimization technique, namely, genetic algorithms, the network trained on the noise-superimposed enlarged training set shows significant improvements in its prediction accuracy and generalization performance, the invented methodology is illustrated by its successful application to the example data comprising instrumental errors and / or measurement noise from an industrial polymerization reactor and a continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR).
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Self-adapting method for filtering image with edge being retained
InactiveCN101094312AGood removal effectEfficient removalTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSelf adaptiveSalt-and-pepper noise
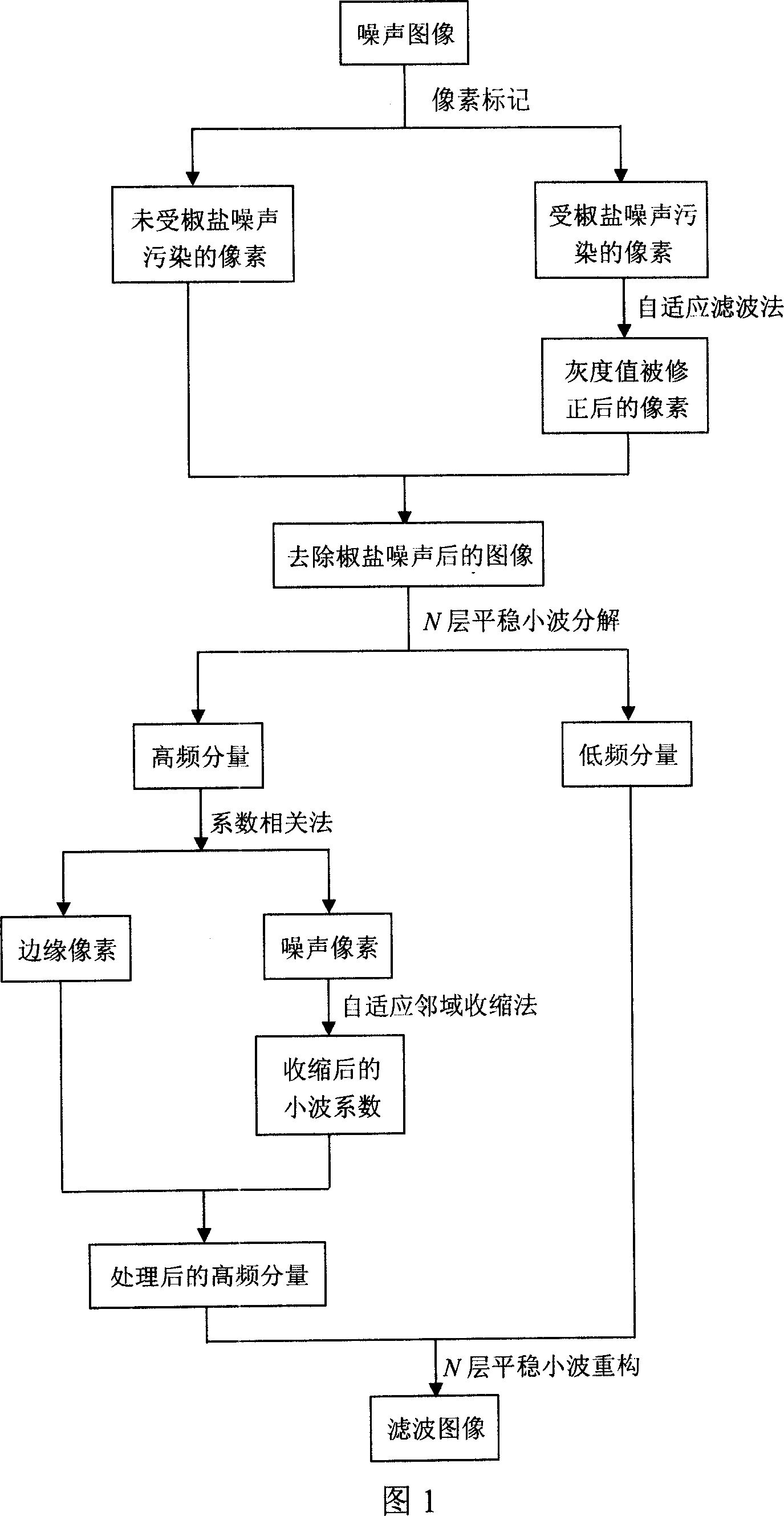
The method comprises: using an extreme-value method to detect the image pixels polluted by the salt-and-pepper noise; using a self-adaptive filter method to correct the grey value of noise pixels to get an image removing the salt-and-pepper noise; making stationary wavelet de-composition to get relevant low-frequency component and high-frequency component; keeping an unchanged state for the low-frequency component, and using the coefficient correlation method for the high-frequency component to mark its pixels as noise or edge; if a pixels is marked as edge, then its value is unchanged; otherwise, using self-adaptive adjacent domain method to contract the wavelet coefficient; making stationary wavelet inverse transformation for the processed wavelet coefficient to get a noise-removed image.
Owner:HAOYUN TECH CO LTD
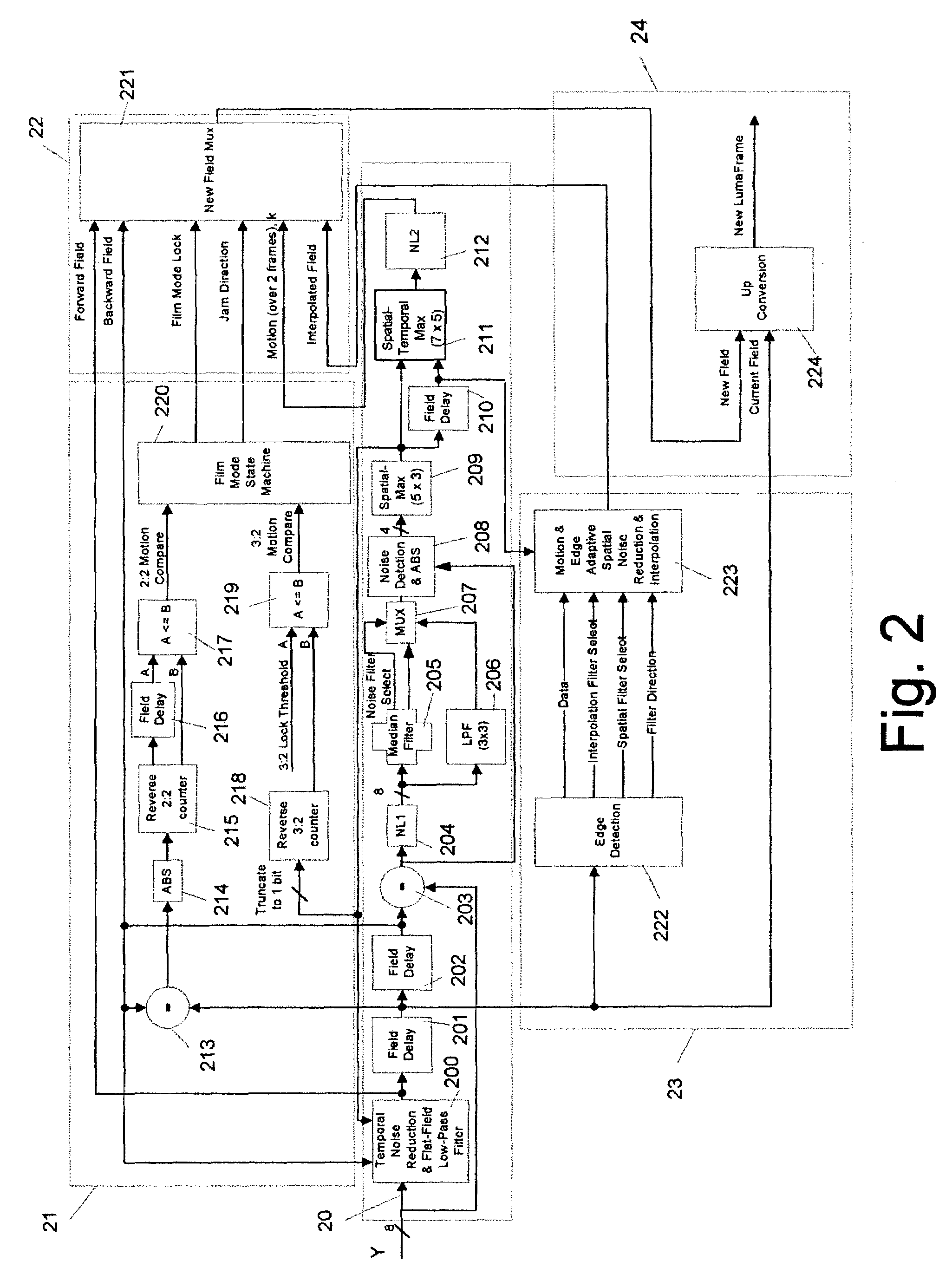
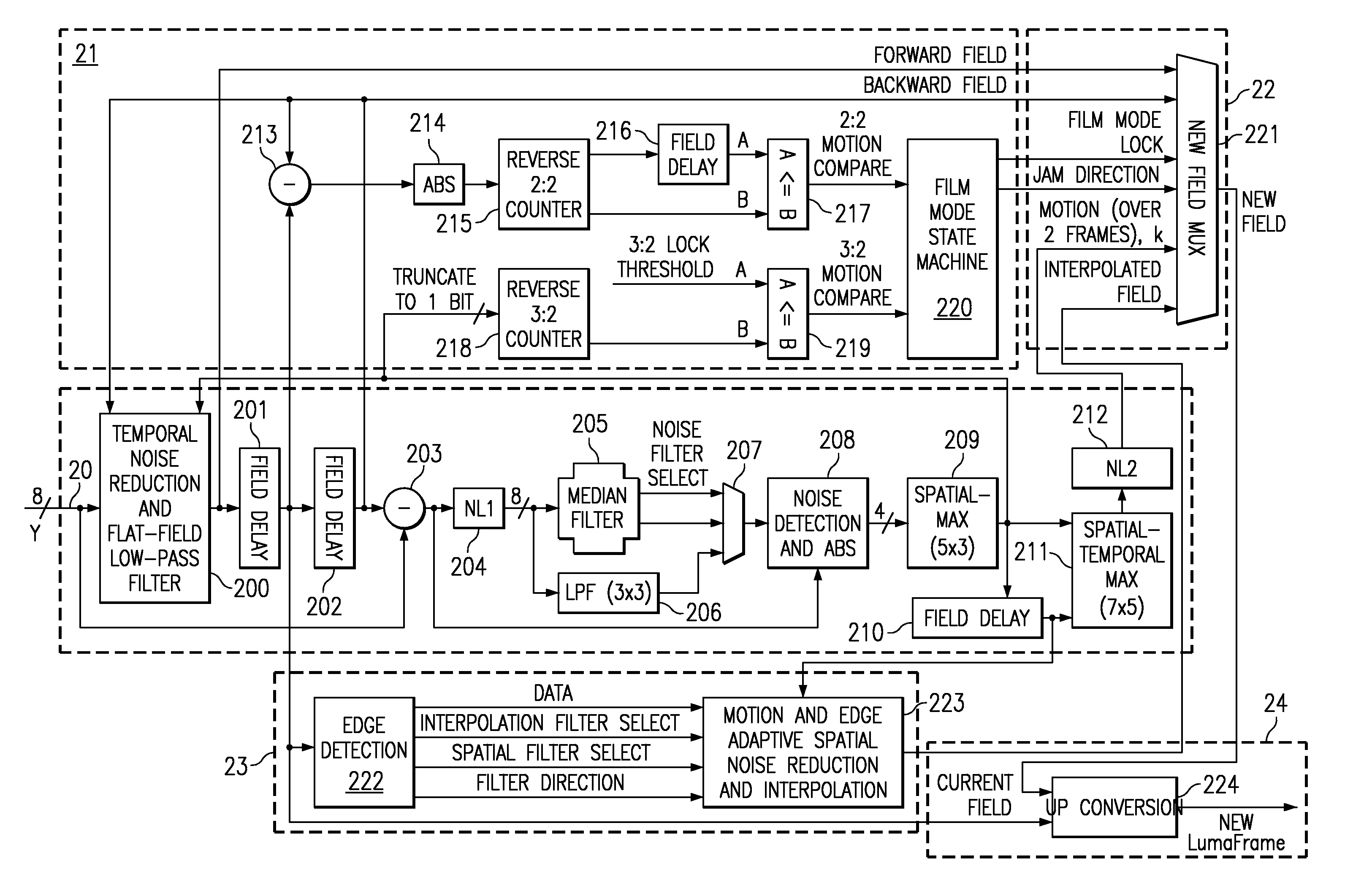
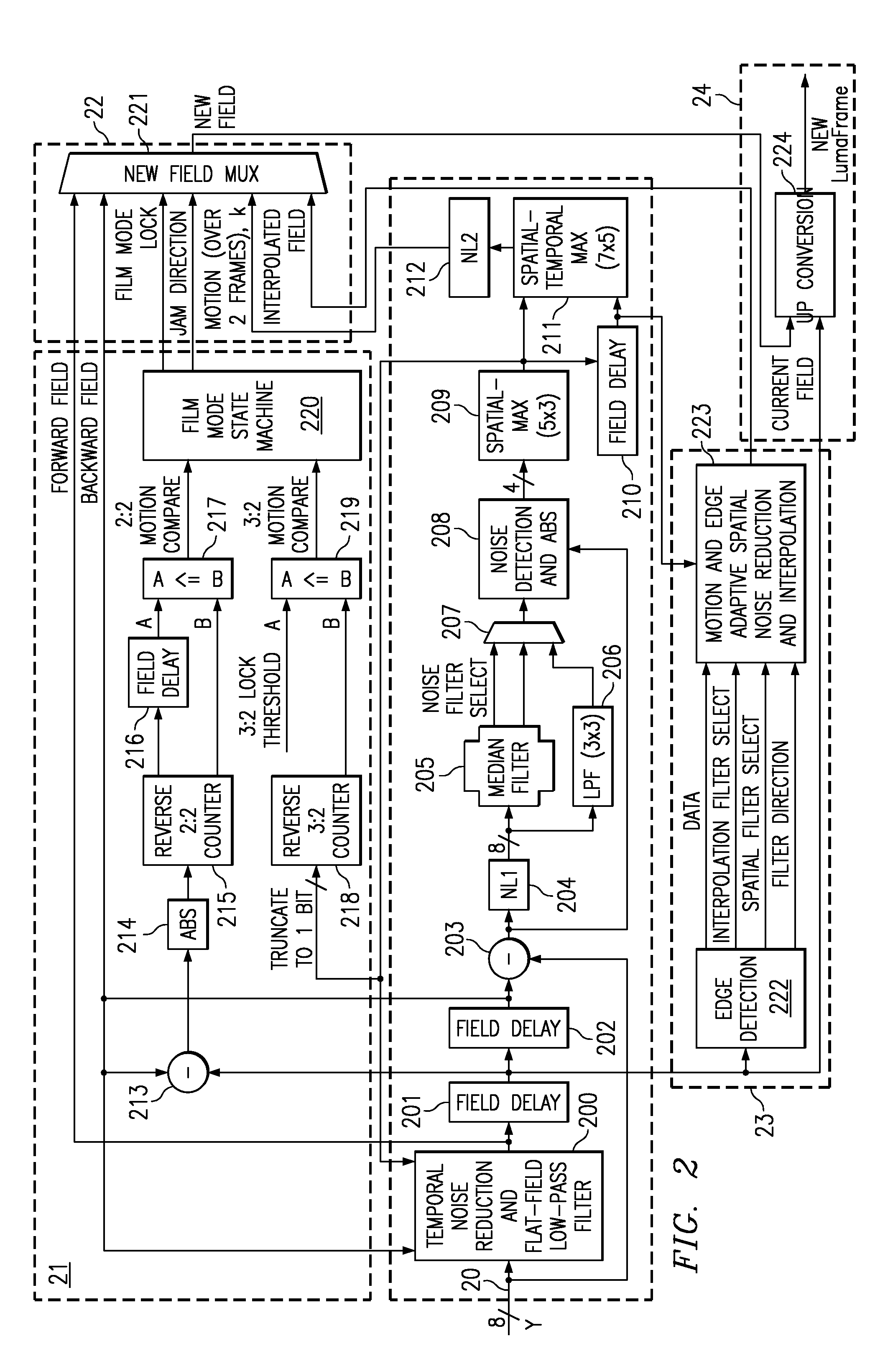
Content-dependent scan rate converter with adaptive noise reduction
ActiveUS7375760B2Quantity minimizationReduce noiseTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionLow-pass filter
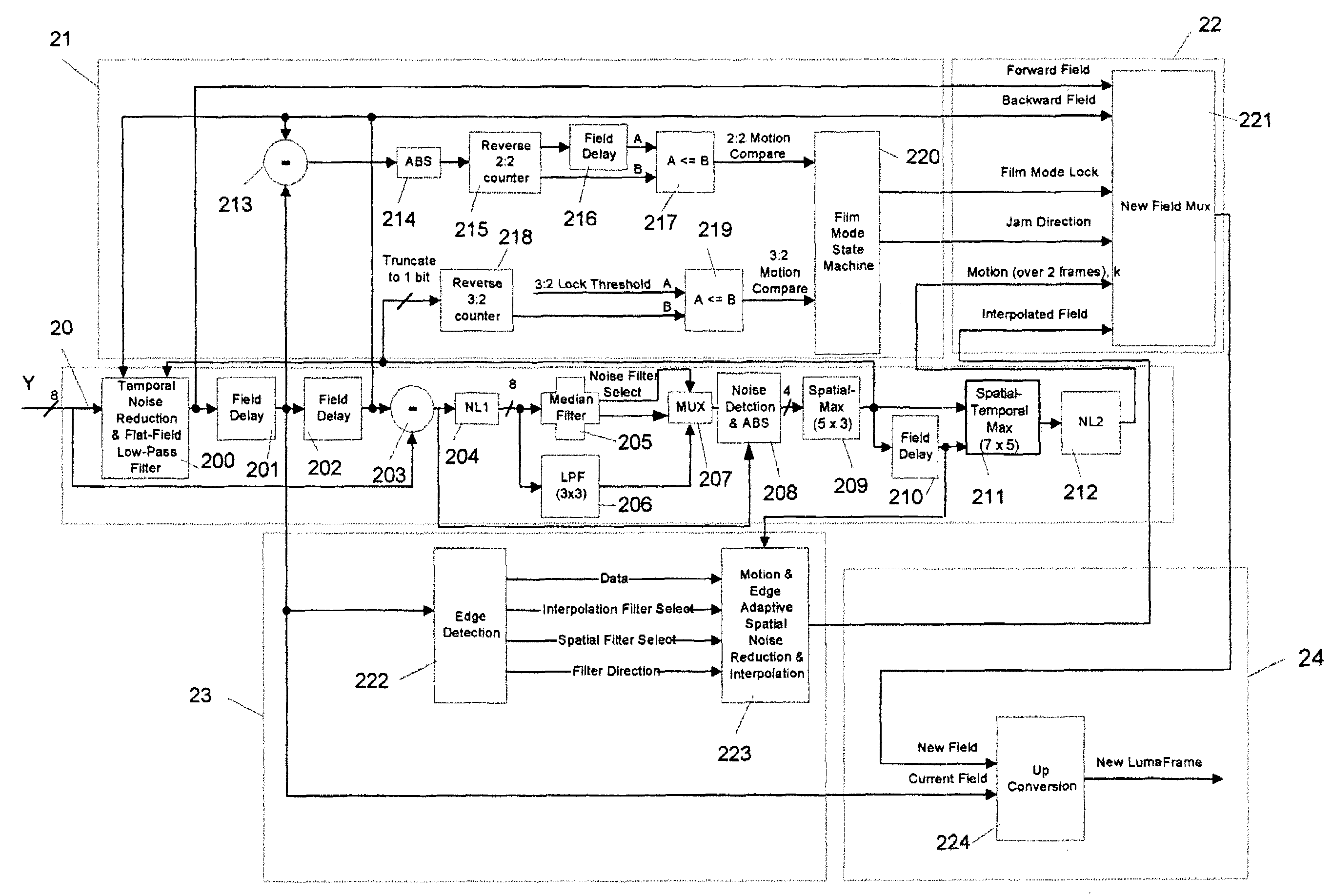
A content-dependent scan rate converter with adaptive noise reduction that provides a highly integrated, implementation efficient de-interlacer. By identifying and using redundant information from the image (motion values and edge directions), this scan rate converter is able to perform the tasks of film-mode detection, motion-adaptive scan rate conversion, and content-dependent video noise reduction. Adaptive video noise reduction is incorporated in the process where temporal noise reduction is performed on the still parts of the image, thus preserving high detail spatial information, and data-adaptive spatial noise reduction is performed on the moving parts of the image. A low-pass filter is used in flat fields to smooth out Gaussian noise and a direction-dependent median filter is used in the presence of impulsive noise or an edge. Therefore, the selected spatial filter is optimized for the particular pixel that is being processed to maintain crisp edges.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
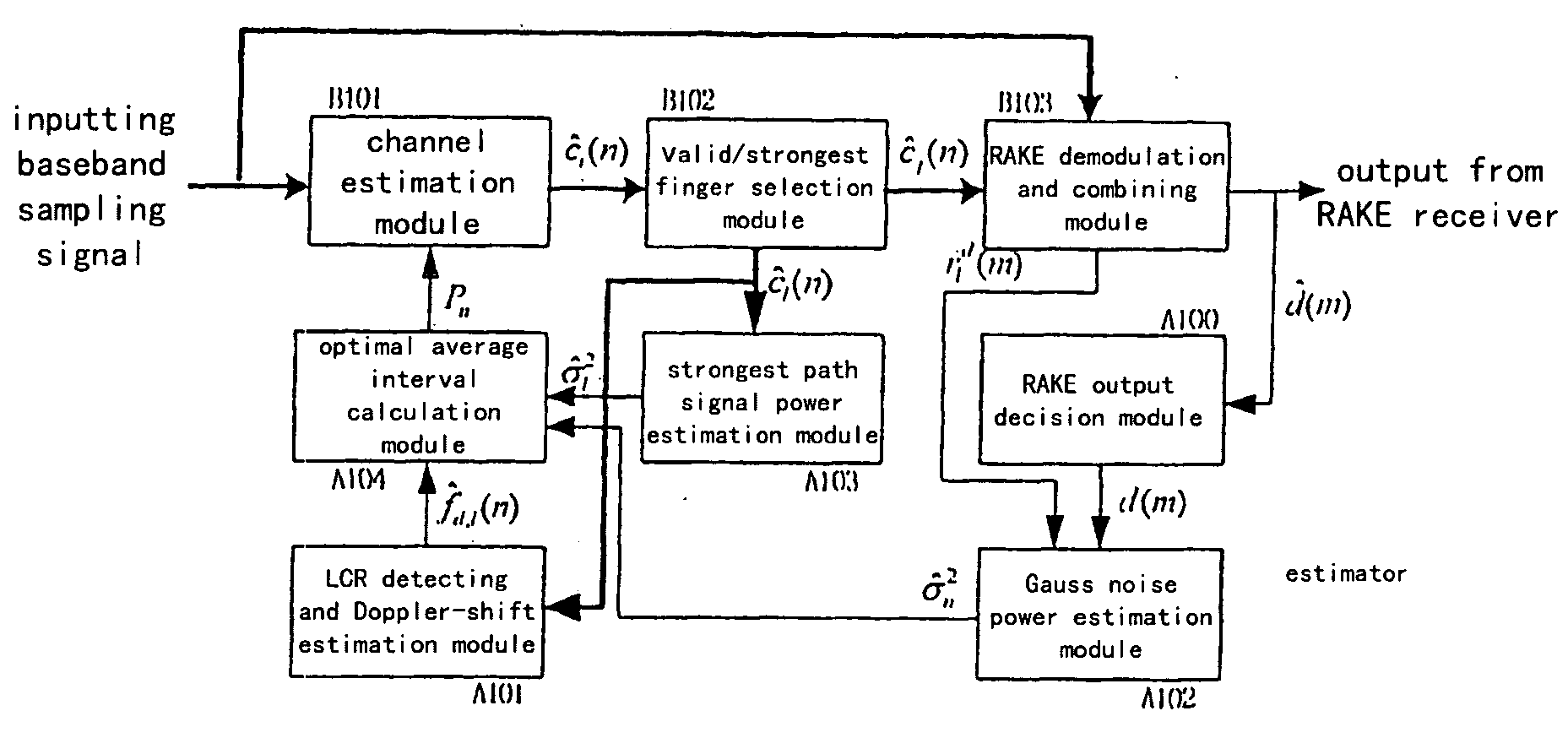
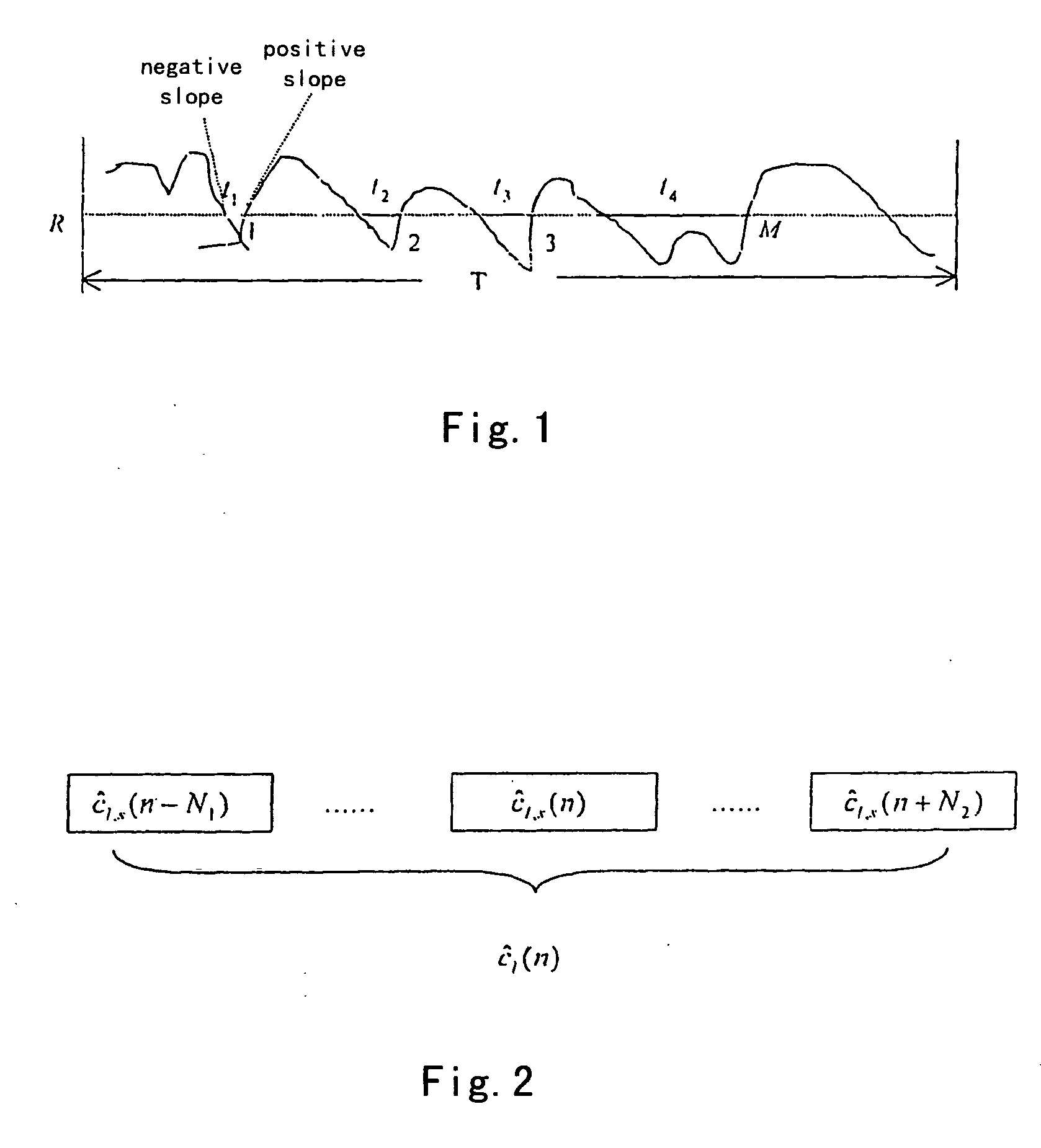
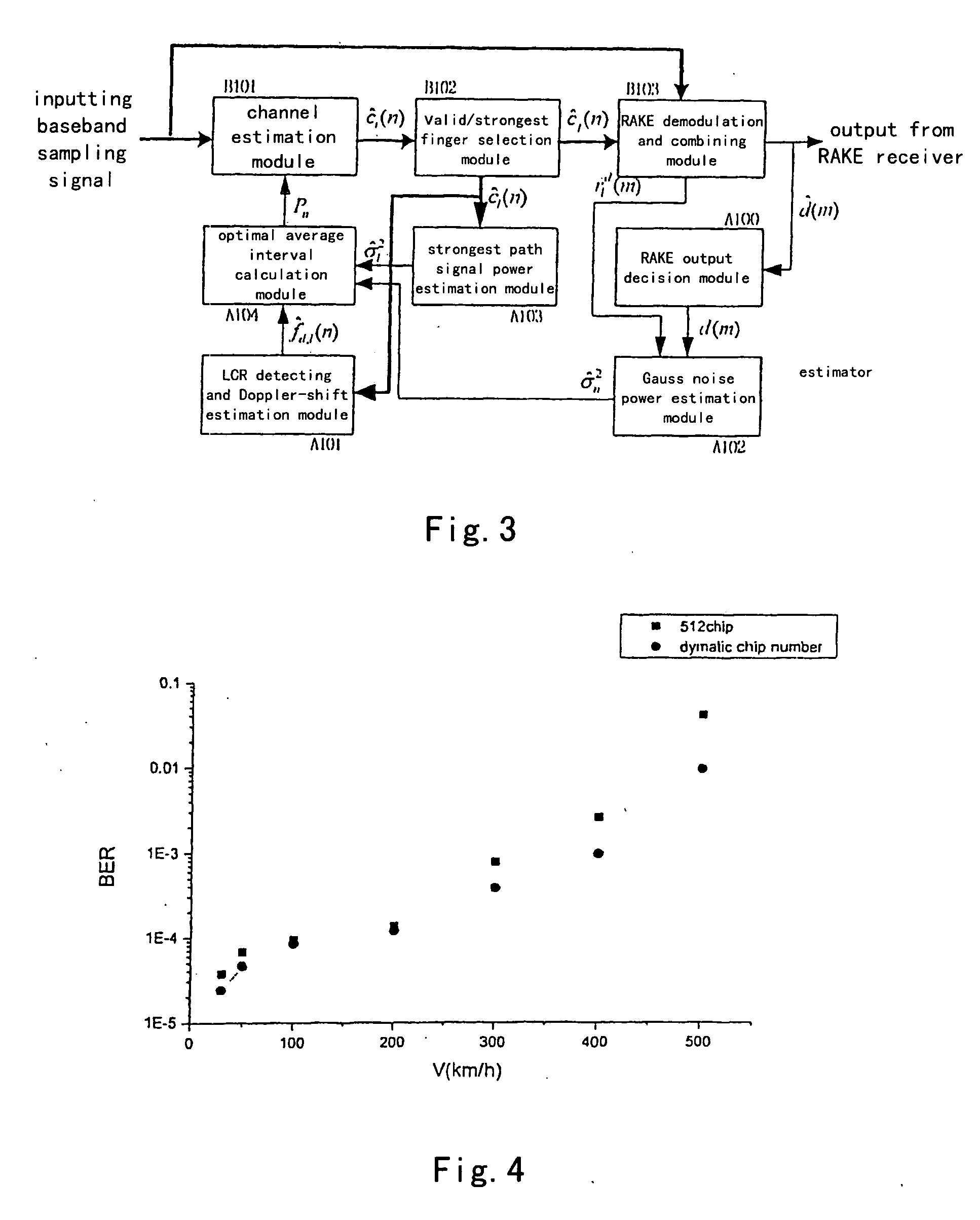
Method and equipment for regulating dynamically an average area of a channel estimation
ActiveUS20050018641A1Overcome disadvantagesImprove estimation performanceError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionComputer scienceDemodulation
The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus for adjusting an average interval of channel estimation dynamically based on Doppler-shift. The method comprises the steps of estimating Doppler-shift by using level cross rate (LCR) according to differently moving speeds of mobile terminals, determining the optimal average interval of channel estimation based on the relationship between the existing Doppler-shift and the optimal average interval of channel estimation, dynamically adjusting the average interval of channel estimation according to the determined the optimal average interval of channel estimation to make the coherent receiver obtain the optimal estimation performance at different moving speeds. The apparatus of the present invention comprises a channel estimation module, a valid / strongest finger selection module, a RAKE demodulation and combining module, a RAKE output decision module, an LCR detection and Doppler-shift estimation module, a Gaussian noise power estimation module, a strongest path signal power estimation module, and an optimal average interval calculation module.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
Bivariate nonlocal average filtering de-noising method for X-ray image
The invention provides a bivariate nonlocal average filtering de-noising method for an X-ray image. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1) a selecting method of a fuzzy de-noising window; and 2) a bivariate fuzzy adaptive nonlocal average filtering algorithm. The method has the beneficial effects that in order to preferably remove the influence caused by the unknown quantum noise existing in an industrial X-ray scan image, the invention provides the bivariate nonlocal fuzzy adaptive non-linear average filtering de-noising method for the X-ray image, in the method, a quantum noise model which is hard to process is converted into a common white gaussian noise model, the size of a window of a filter is selected by virtue of fuzzy computation, and a relevant weight matrix enabling an error function to be minimum is searched. A particle swarm optimization filtering parameter is introduced in the method, so that the weight matrix can be locally rebuilt, the influence of the local relevancy on the sample data can be reduced, the algorithm convergence rate can be improved, and the de-noising speed and precision for the industrial X-ray scan image can be improved, so that the method is suitable for processing the X-ray scan image with an uncertain noise model.
Owner:YUN NAN ELECTRIC TEST & RES INST GRP CO LTD ELECTRIC INST +1
Reducing shared downlink radio channel interference by transmitting to multiple mobiles using multiple antenna beams
ActiveUS7437166B2Improve data transfer rateReduce round-trip delaySpatial transmit diversityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio channelMobile radio
A radio base station includes multiple antennas associated with a cell. Multiple mobile radios are selected to receive transmissions over a shared radio channel during a predetermined time interval. Information is transmitted over the shared radio channel to multiple mobile radios in the cell during the predetermined time interval using multiple antenna beams. As a result, interference from the transmission appears as white additive Gaussian noise in time and in space in the cell. A “flashlight effect” caused by a single beam transmission over the shared channel during a predetermined time interval that would normally detrimentally impact mobile channel quality detection is avoided. Other methods for avoiding the flashlight effect are described.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Image denoising method based on self-adaptive wavelet threshold and two-sided filter
InactiveCN103700072AEfficient removalKeep detailsImage enhancementDenoising algorithmAdaptive wavelet
The invention provides an image denoising method based on a self-adaptive wavelet threshold and a two-sided filter and aims to improve the effect of a wavelet threshold denoising algorithm and better protect the edge and the detailed information of an image. The algorithm comprises the following steps of decomposing the image by adopting a discrete wavelet to obtain a plurality of sub-bands and the wavelet coefficients of the sub-bands; selecting a threshold which is self-adaptively changed along with the changes of wavelet-decomposing scales and the sub-bands, and carrying out quantitative threshold processing by adopting a soft threshold function; carrying out inverse wavelet transformation to obtain a reconstructed image; filtering the reconstructed image by adopting the two-sided filter so as to obtain the clear image. According to the image denoising method, wavelet threshold denoising is carried out by utilizing the threshold which is self-adapted to the wavelet-decomposing scales and the sub-bands, and filtering is carried out by combining the two-sided filter, so that through the designed denoising algorithm, not only can white gaussian noise be effectively removed, but also the edge and the detailed information of the image can be well reserved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
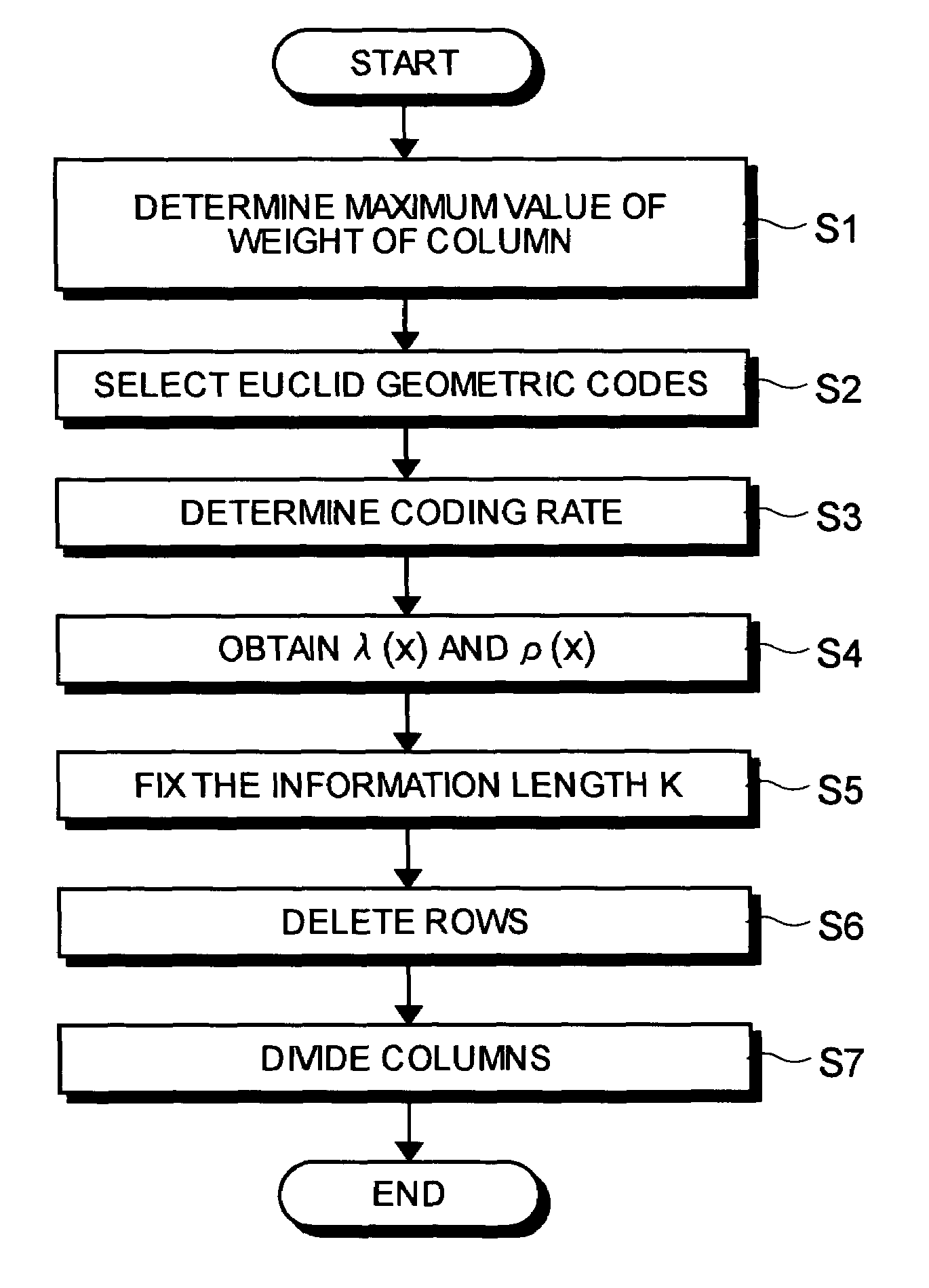
LDPC code inspection matrix generation method and inspection matrix generation device
InactiveUS7089479B2Maximize noiseNon-binary linear block codesError detection/correctionLow-density parity-check codeLow density
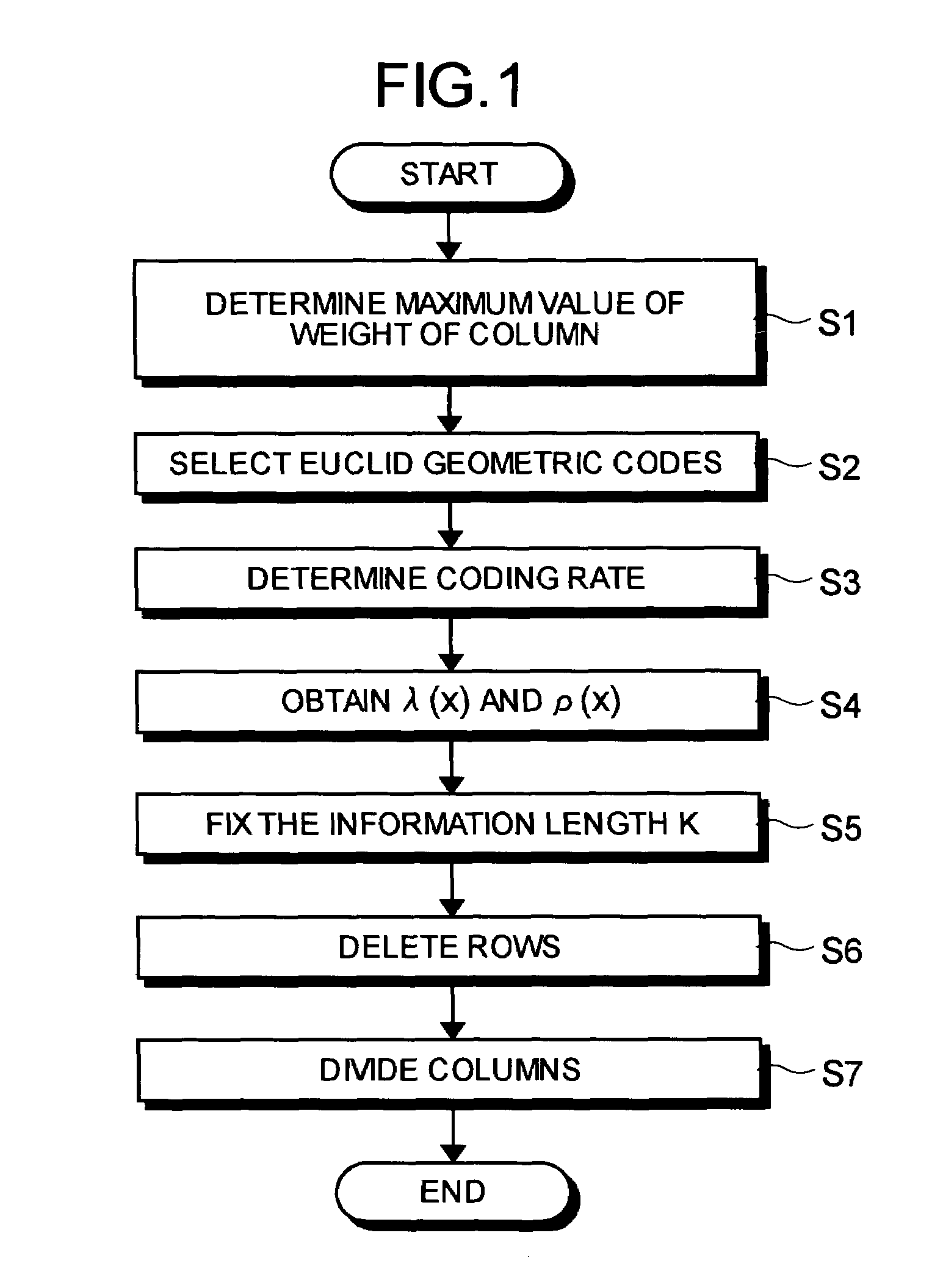
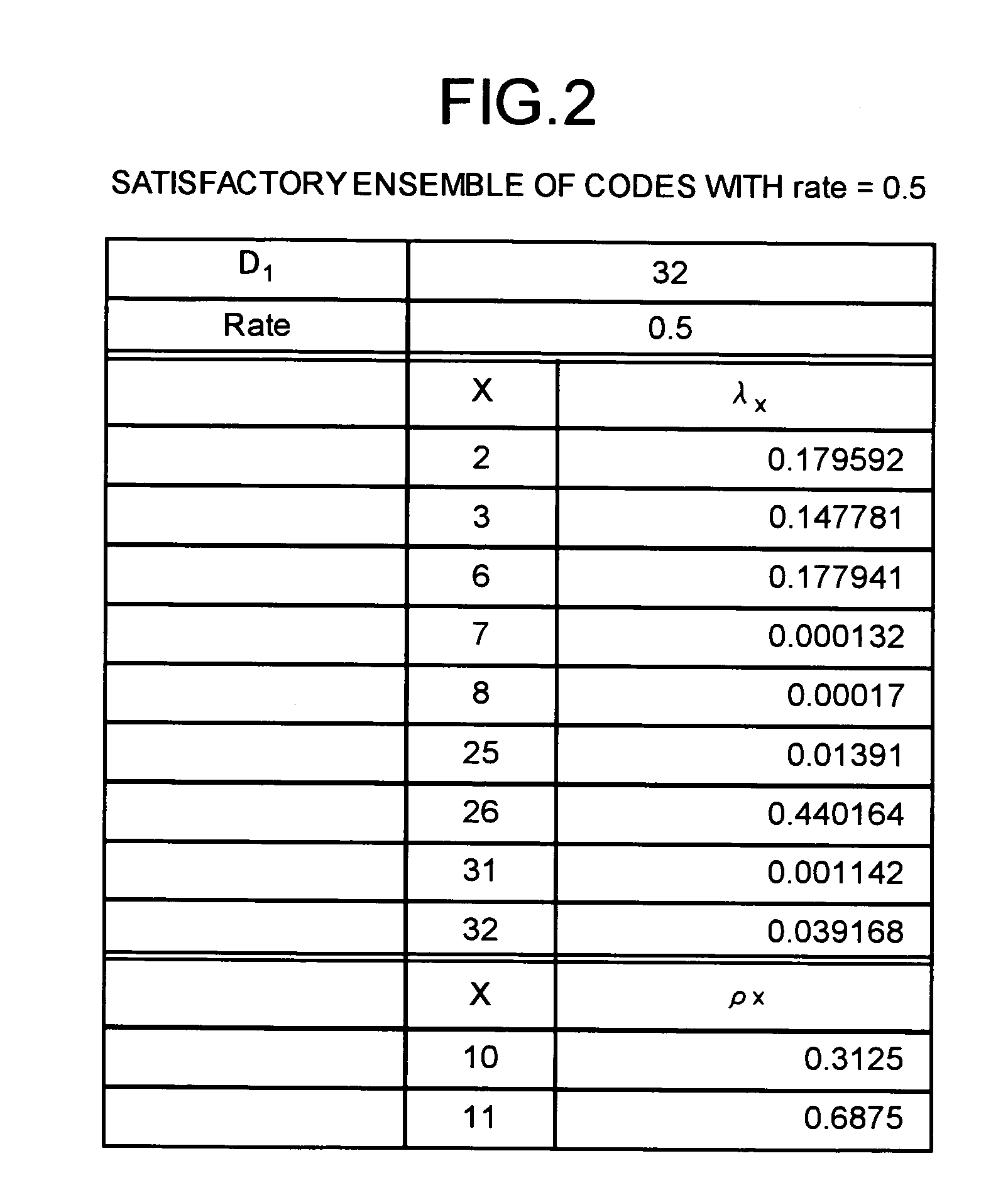
A method of generating check matrixes for Low-Density Parity-Check codes includes determination steps of determining a maximum value of a column weight, basic Euclid geometric codes, and a coding rate respectively; a weight searching step of searching an optimum ensemble of a row weight and a column weight at one time according to a linear programming method in a state of a fixed coding rate, and so as to maximize a Gaussian noise; an information calculation step of calculating an information length based on a predetermined block length and the coding rate; a row deletion step of deleting a predetermined row based on the information length using the Euclid geometric codes; and a division step of dividing at random a row or a column of the matrixes after the row deletion in a predetermined order.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Gear fault diagnosis method based on SVD decomposition and noise reduction and correlation EEMD entropy features
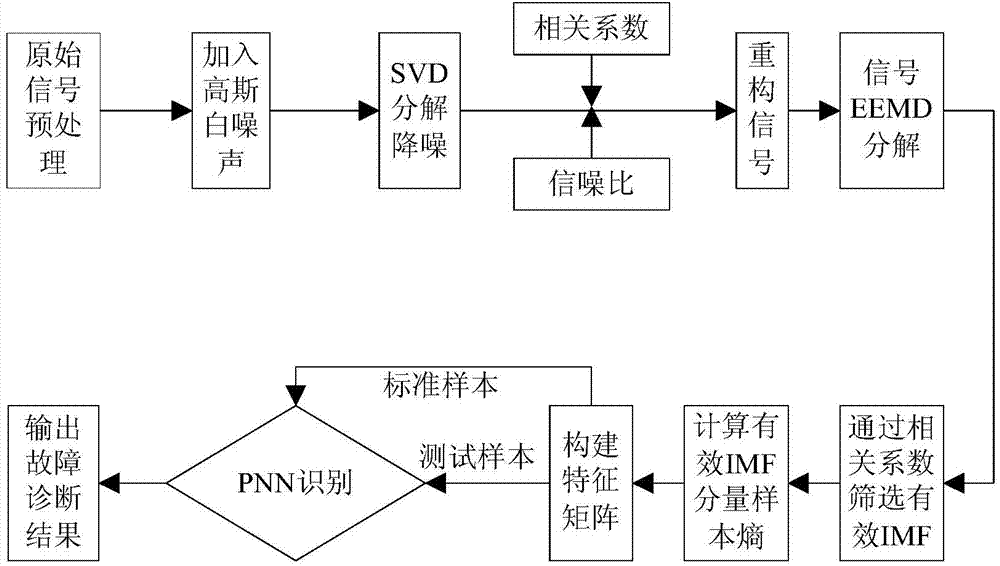
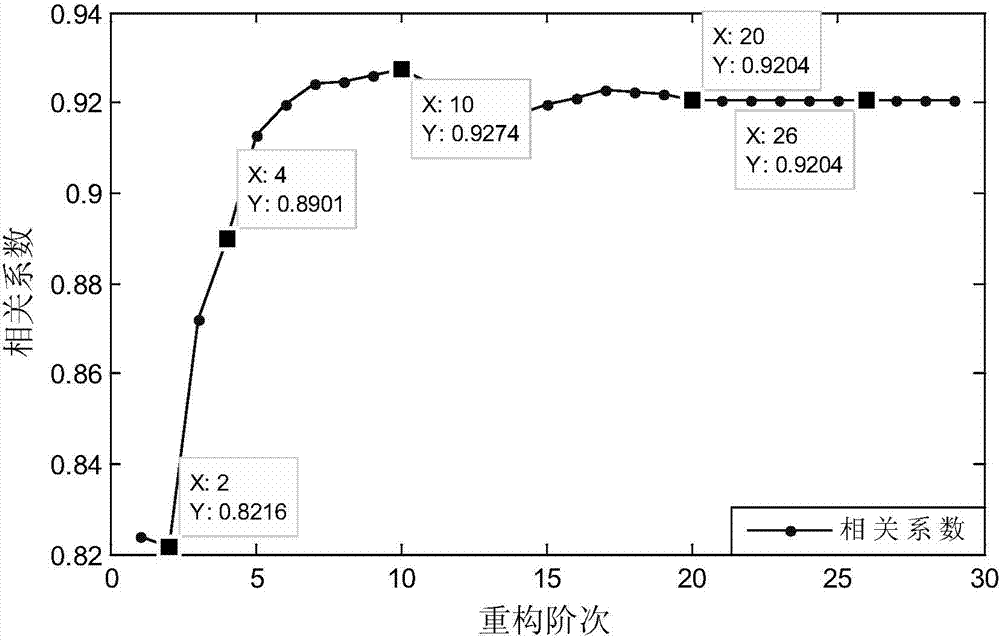
InactiveCN104748961AImprove signal-to-noise ratioAccurate extractionMachine gearing/transmission testingBiological neural network modelsDecompositionEngineering
The invention discloses a gear fault diagnosis method based on the SVD decomposition and noise reduction and correlation EEMD entropy features. The method includes utilizing an acceleration vibration sensor to acquire experimental platform gear vibration signals including four types of faults, namely gear normality, gear tooth breaking, gear tooth missing and gear wearing; performing noise reduction on the signals, of four gear states, containing simulated strong noise background of Gaussian white noise by the SVD decomposition method with correlation analysis and noise ratio optimization; decomposing the four types of noises by the EEMD method after noise reduction, and selecting valid IMF components according to correlative coefficients; performing sample entropy calculation on the valid IMF components, and establishing feature vectors composed of the IMF samples; identifying the four different types of gear faults through a PNN neural network. The method is effective and is capable of recognizing the gear fault types on the strong-noise background effectively.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Method of quickly eliminating composite noise in images
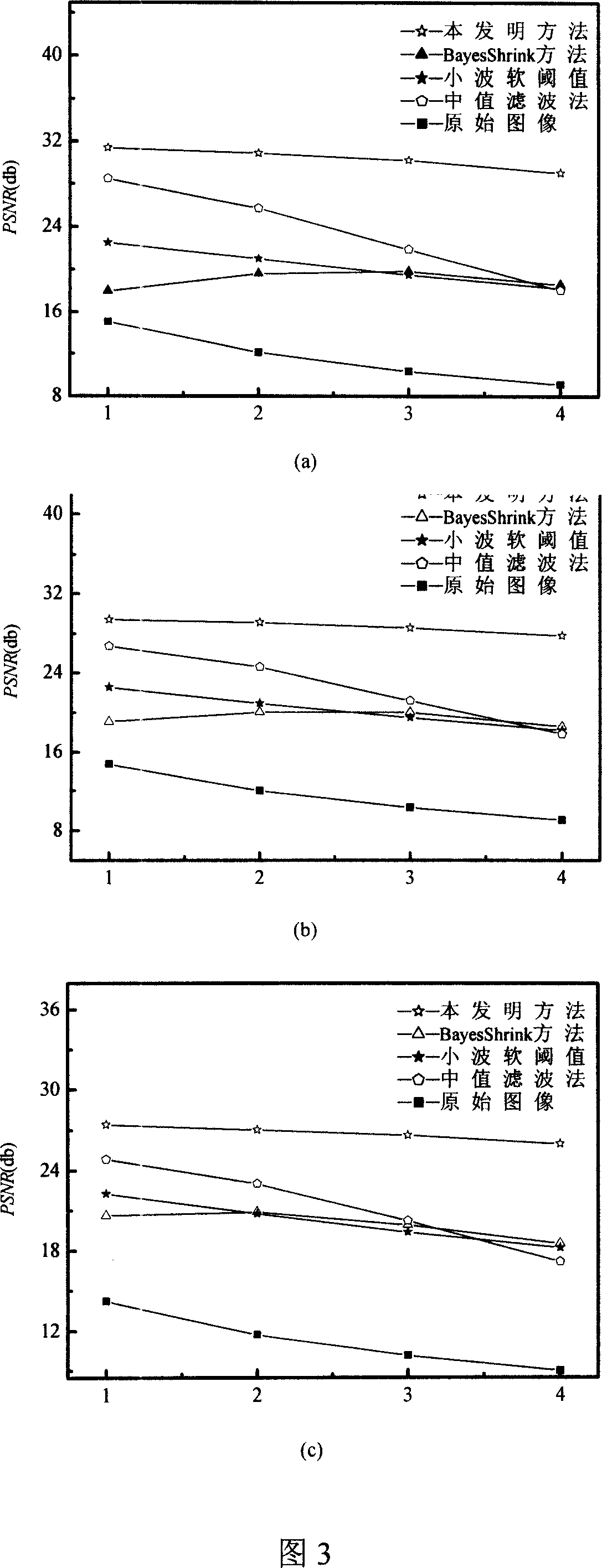
ActiveCN101860667AImprove peak signal-to-noise ratioEasy to handleImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
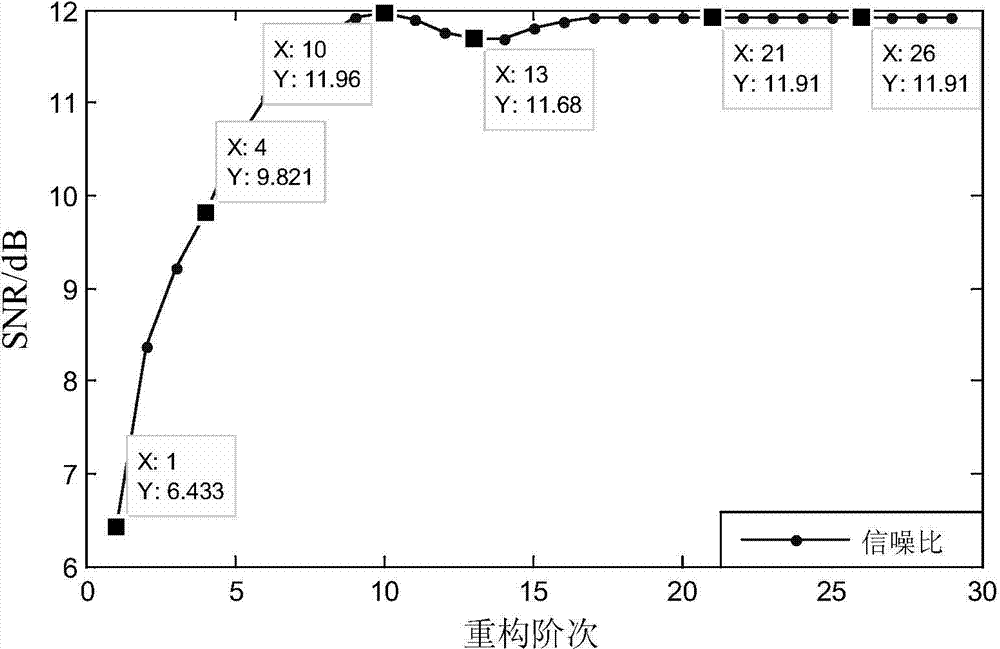
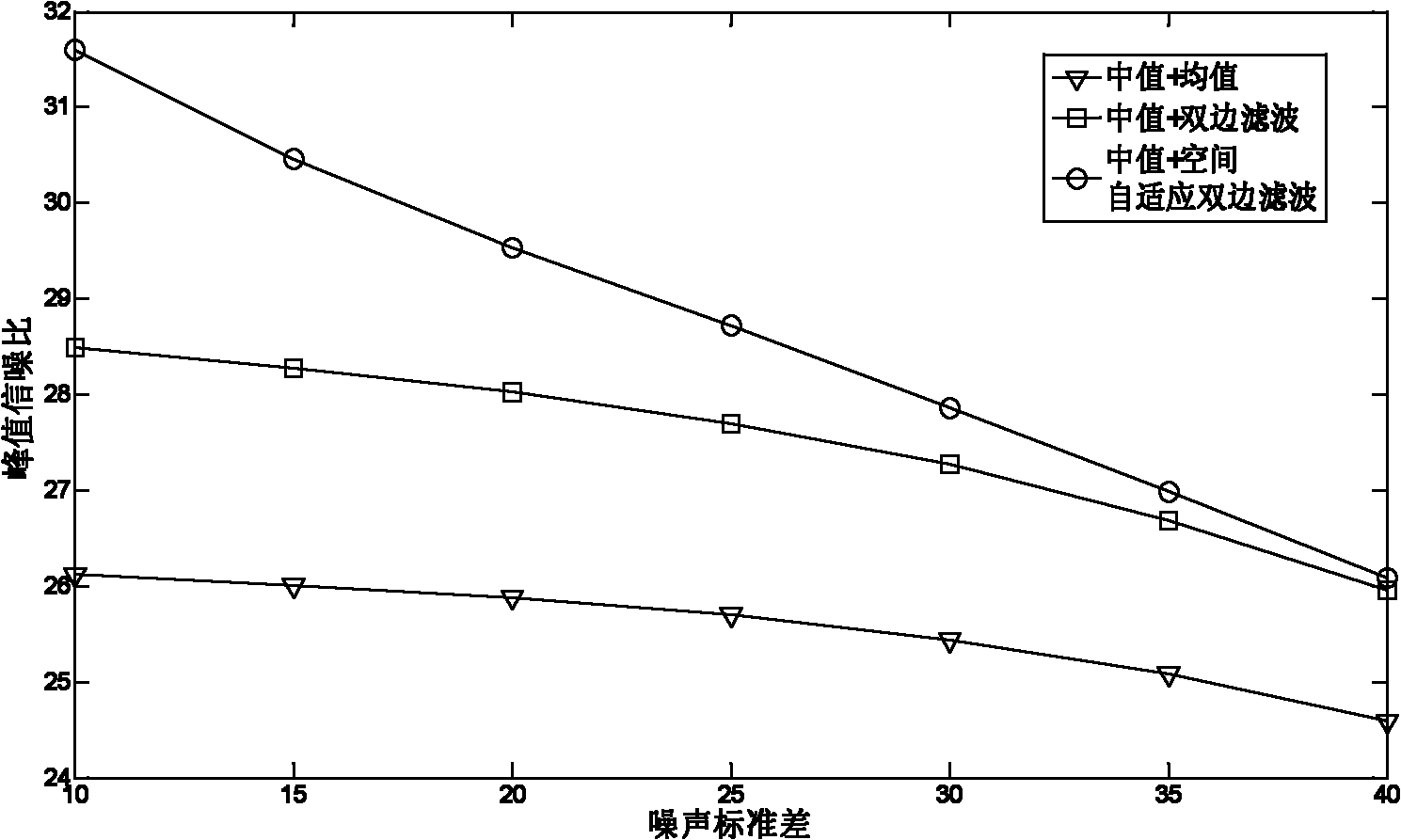
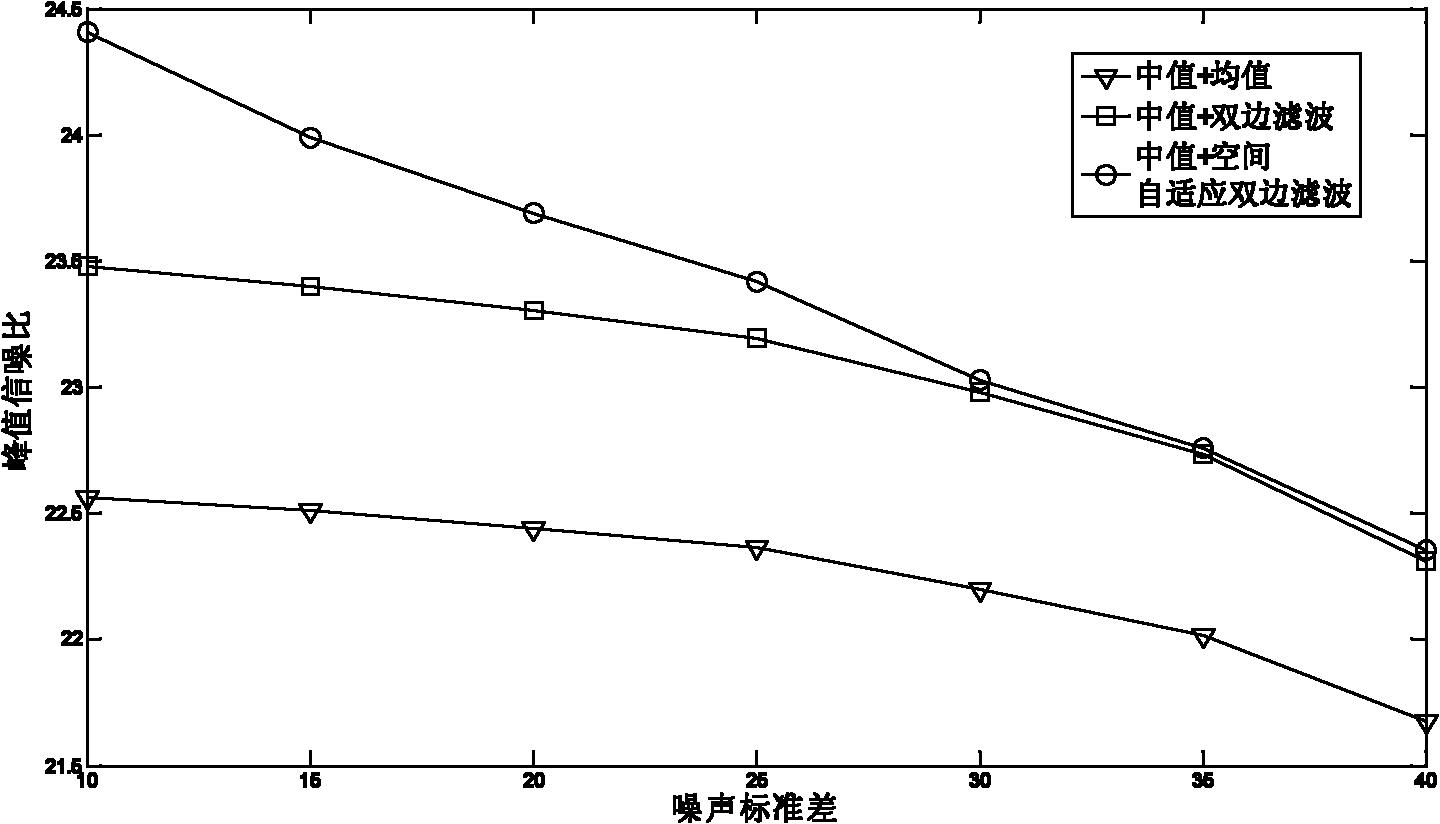
The invention discloses a method of quickly eliminating composite noise in images, which can eliminate salt and pepper noise and Gaussian noise at the same time, improve the peak signal to noise ratio(PSNR) of the images and obtain more clear images. The main technical idea comprises the following steps: the median of the images containing noise is filtered to obtain the images the salt and pepper noise of which is eliminated and space self-adaption two-sided filter is carried out on the images the salt and pepper noise of which is eliminated to obtain the images the Gaussian noise of which is eliminated, i.e. the final noise-free images. The calculation, data processing of the algorithm of the invention is definitely adapted to the real-time image quick process. The technical flow can be adjusted according to concrete application and requirement.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Time-space methods and systems for the reduction of video noise
A time-space domain video denoising method is provided which reduces video noise of different types. Noise is assumed to be real-world camera noise such as white Gaussian noise (signal-independent), mixed Poissonian-Gaussian (signal-dependent) noise, or processed (non-white) signal-dependent noise. This method comprises the following processing steps: 1) time-domain filtering on current frame using motion-compensated previous and subsequent frames; 2) restoration of possibly blurred contents due to faulty motion compensation and noise estimation; 3) spatial filtering to remove residual noise left from temporal filtering. To reduce the blocking effect, a method is applied to detect and remove blocking in the motion compensated frames. To perform time-domain filtering weighted motion-compensated frame averaging is used. To decrease the chance of blurring, two levels of reliability are used to accurately estimate the weights.
Owner:WRNCH INC
Content-Dependent Scan Rate Converter with Adaptive Noise Reduction
InactiveUS20080218630A1Quantity minimizationReduce noiseTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionLow-pass filter
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
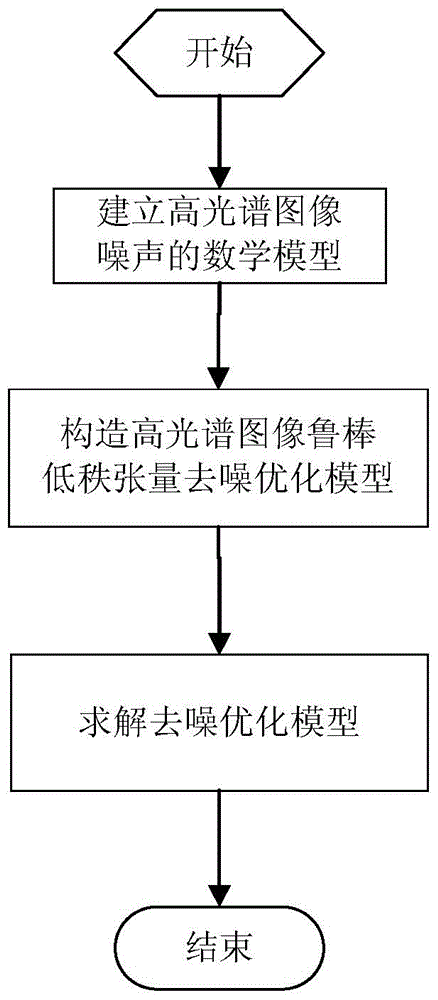
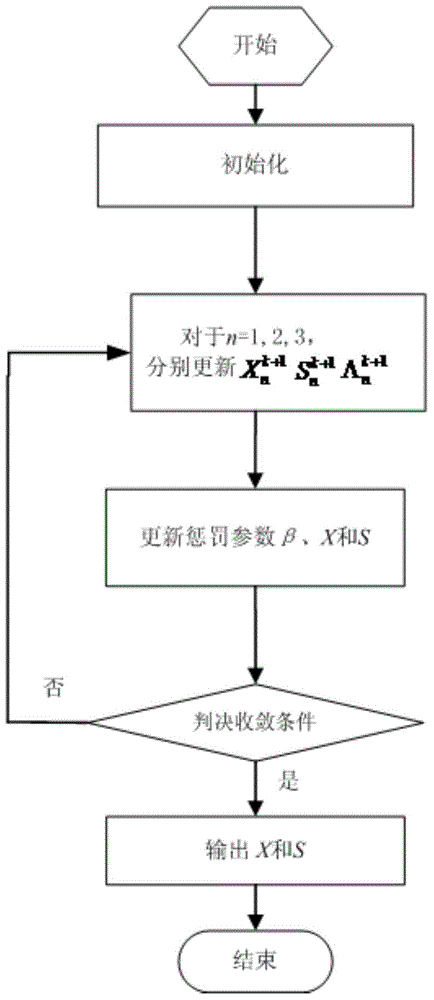
Hyperspectral image denoising method based on robust low-rank tensor
The invention proposes a hyperspectral image denoising method based on robust low-rank tensor, which comprises the steps of establishing a mathematical model of hyperspectral image noise, constructing a hyperspectral image robust low-rank tensor (RLRTR) denoising optimization model, and solving the RLRTR denoising optimization model. The hyperspectral image denoising method fully utilizes the prior knowledge of hyperspectral images (HSI) which are polluted by different kinds of noise such as Gaussian noise, impulse noise, dead pixels and striping noise. The hyperspectral image denoising method utilizes the potential low-rank tensor property of clean hyperspectral image data and the sparsity property of abnormal and non-Gaussian noise, and adopts a nuclear norm and an l2,1 norm for representing the low-rank and sparsity properties. The technical scheme of the hyperspectral image denoising method fully uses the prior information and internal structure characteristics of the hyperspectral image, and can remove Gaussian noise, abnormal and non-Gaussian noise simultaneously.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Depth residual convolution neural network image denoising method based on PReLU
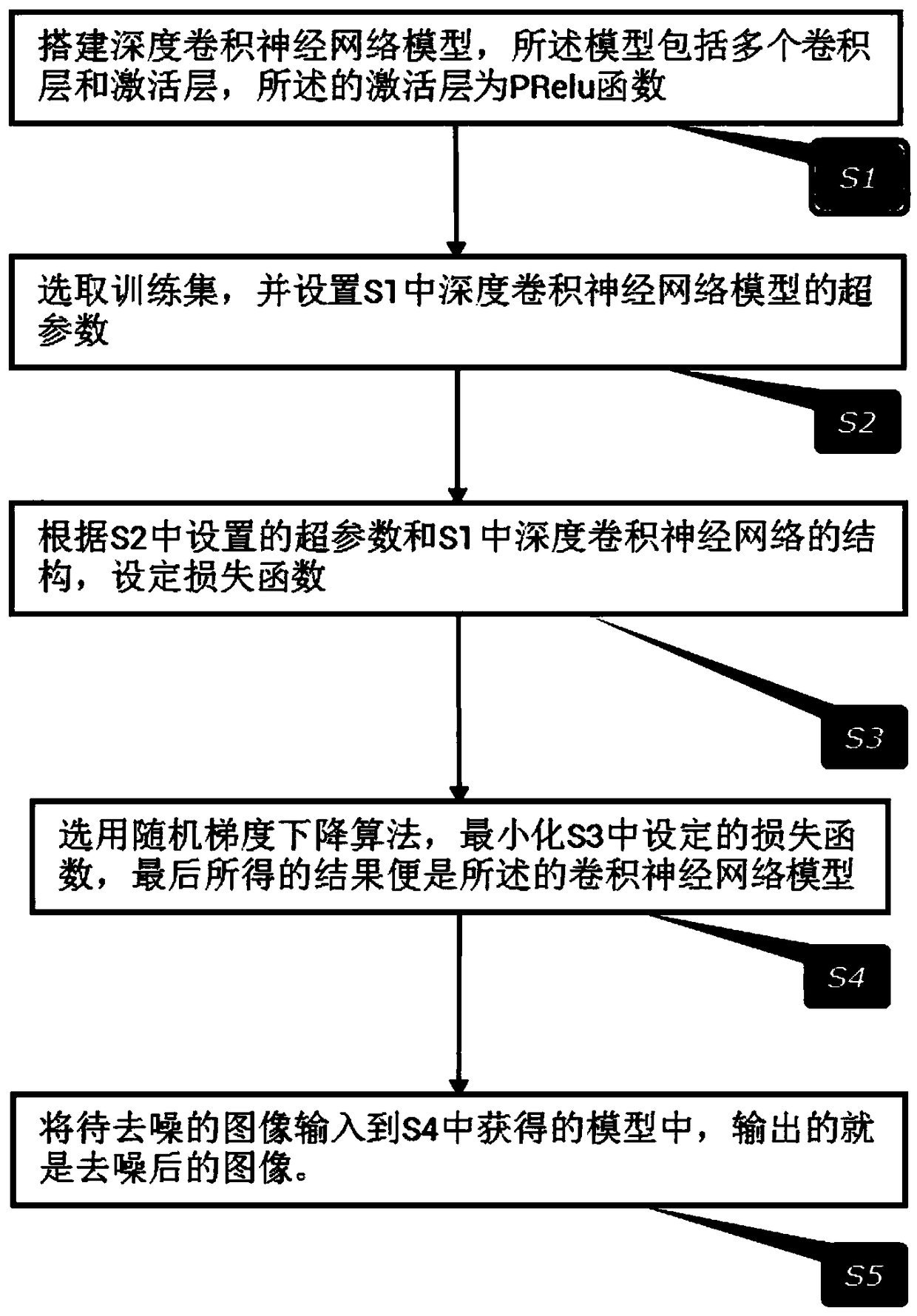
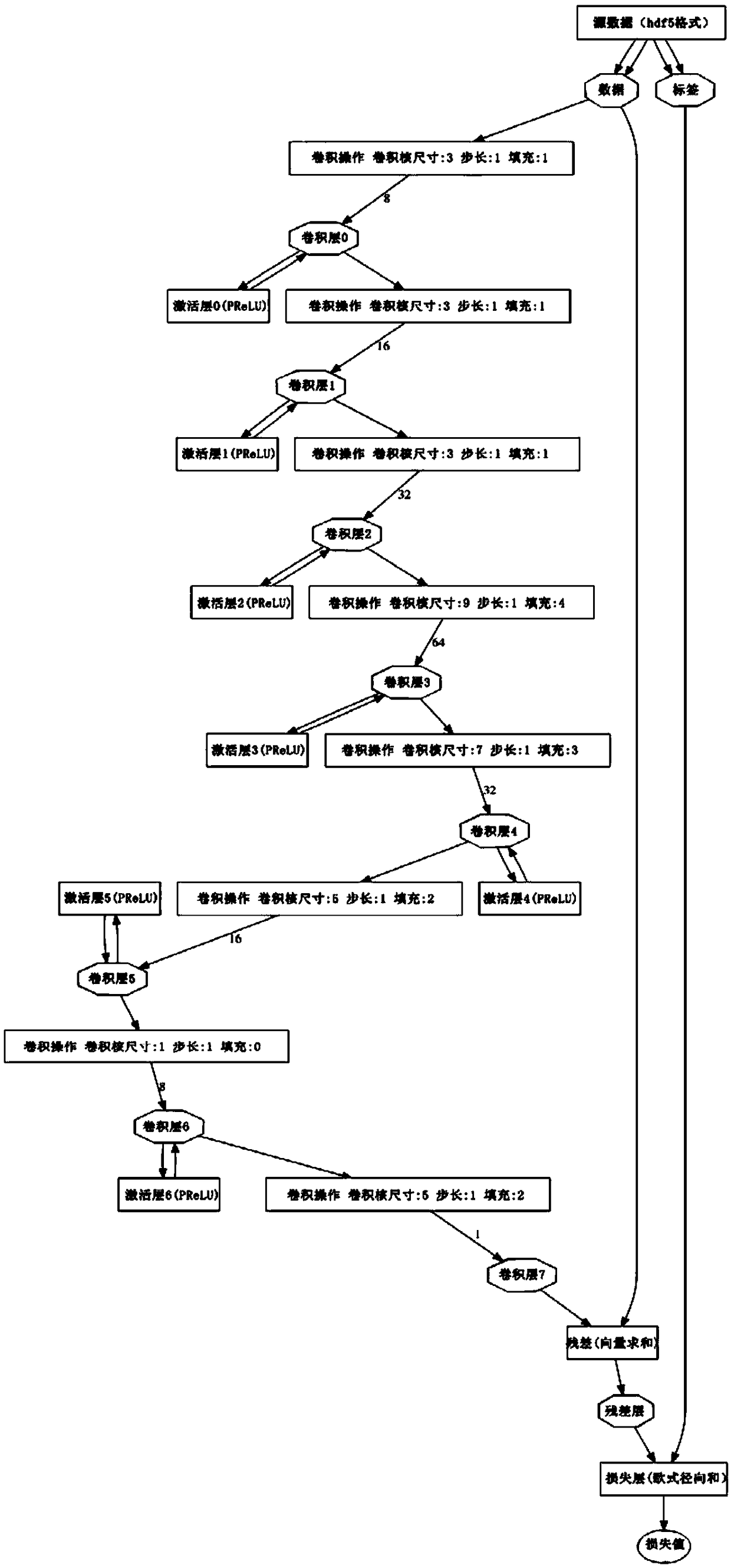
InactiveCN109118435AOptimizationAvoid computational overheadImage enhancementImage analysisDenoising algorithmActivation function
The invention relates to a depth residual convolution neural network image denoising method based on PReLU, based on deep convolution neural network, combined with Gaussian noise simulating unknown real noise image denoising task, in this paper, a deep convolution neural network for image denoising is proposed, which uses PReLU activation function instead of Sigmoid and ReLU function, increases residual learning and reduces mapping complexity, and adopts optimized network training techniques and network parameter settings to improve the denoising ability of the network. Compared with other existing denoising algorithms, the present invention performs very well under various Gaussian noise environments in which the standard variance is mixed, and the detailed information in the image can bewell preserved while the noise is eliminated.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
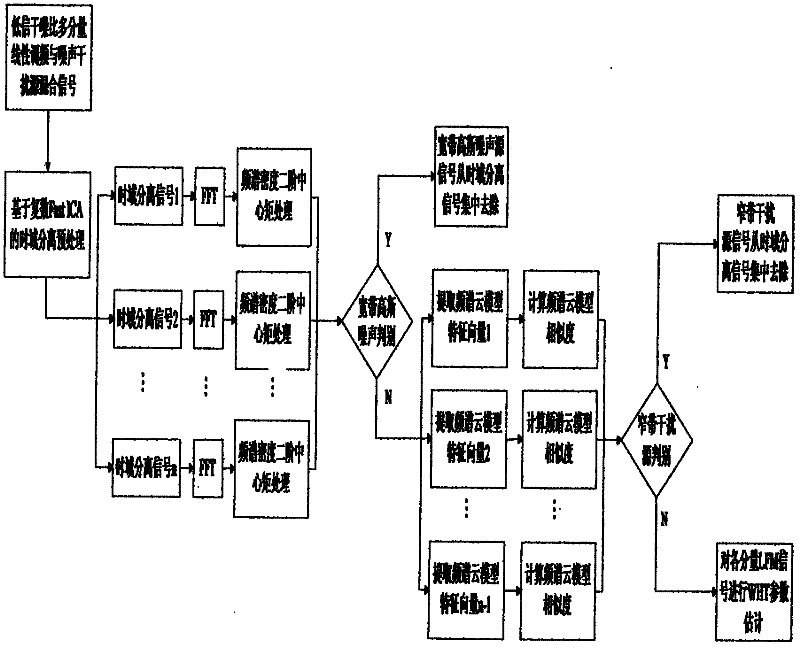
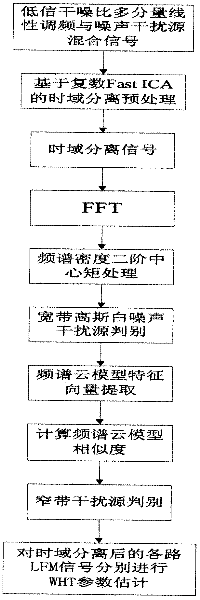
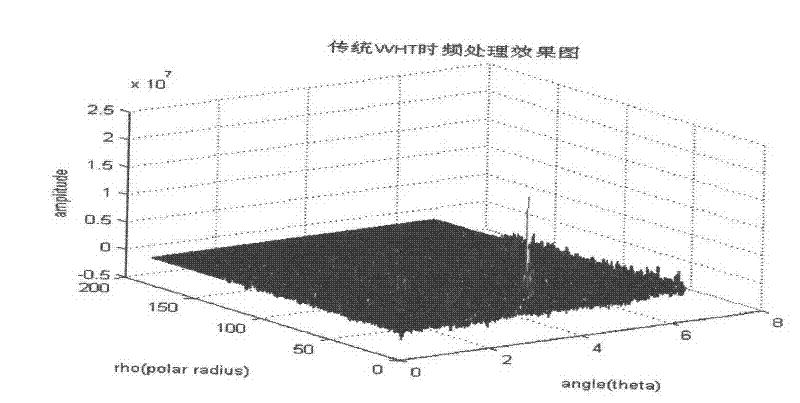
LFM (linear frequency modulation) signal detecting method under strong interference source environment
InactiveCN102510363AInhibition effectEliminate the effects ofError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumSignal on
The invention discloses an LFM (linear frequency modulation) signal detecting method under a strong interference source environment, belonging to the technical field of the signal processing. The LFM signal detecting method comprises the following steps of: firstly, carrying out time domain separation on received multi-component signals and various interference source signals by employing a array receiving time domain complex blind separating technology, decomposing the signals into multiple paths of time domain receiving signals; then respectively judging the signal and the interference of each path of time domain receiving signals respectively; selecting a broadband Gaussian noise interference source signal according to the broadband receiving system of an electronic reconnaissance receiver and the signal spectrum width characteristic represented by a second-order central moment of the spectrum density function; extracting the similarity judgment of the signal spectrum sequence via a cloud model feature vector and selecting a co-frequency narrow-band interference source signal; and at last, carrying out detection and parameter estimation of the multi-component LFM signal on remaining time domain separating signals by Wigner-Hough conversion respectively. The method can be used for effectively extracting single-component linear frequency-modulating signals in the multi-component signals and performing the accurate parameter estimation on the single-component linear frequency-modulating signals.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
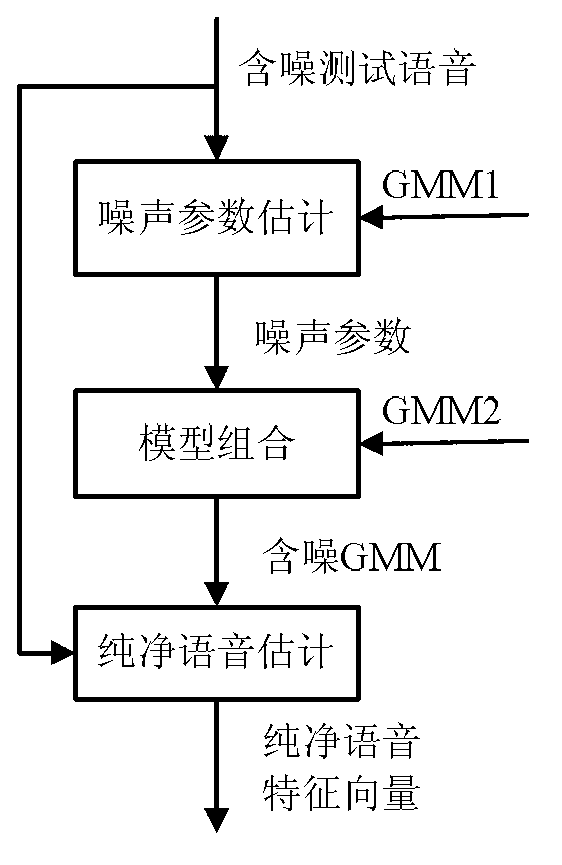
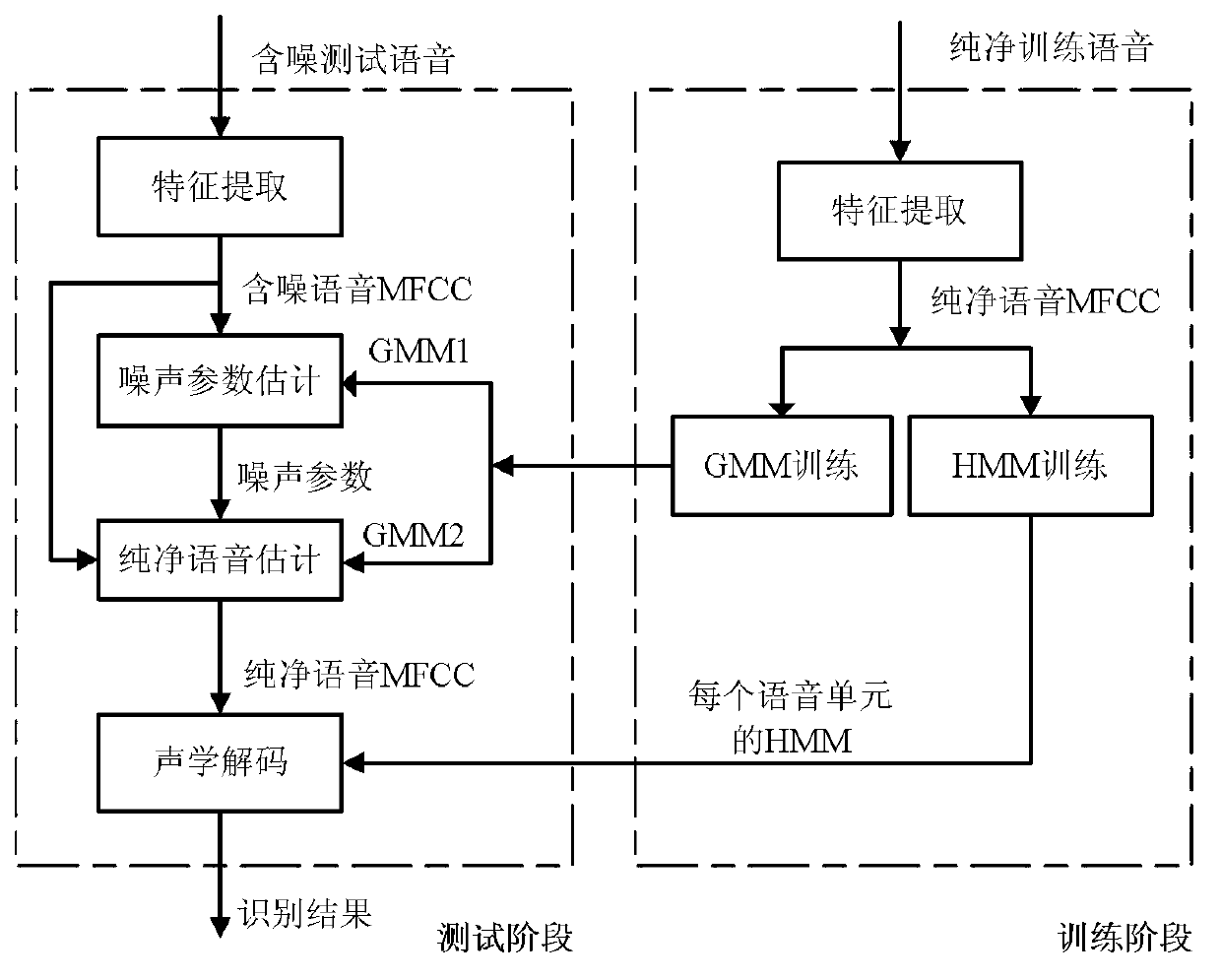
Feature compensation method based on rapid noise estimation in speech recognition system
InactiveCN103000174AGuaranteed accuracySmall amount of calculationSpeech recognitionFeature vectorSpeech identification
The invention discloses a feature compensation method based on rapid noise estimation in a speech recognition system. The method is characterized in that noise parameter estimation in the feature compensation is separated from pure speech estimation, and noise estimation and pure speech estimation are achieved through different Gaussian mixture models (GMMs). A GMM containing less Gaussian units is used for extracting noise parameters from a noisy tested speech; another GMM containing more Gaussian units is used for being combined with an estimated single Gaussian noise model to obtain a noisy GMM matched with the current test environment; and finally the noisy GMM is used for calculating the posterior probability of the noisy tested speech and the pure speech feature vector is estimated from the noisy tested speech through the minimum mean square error method. According to the method, estimation accuracy of the pure speech can be guaranteed while the calculated amount is reduced.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
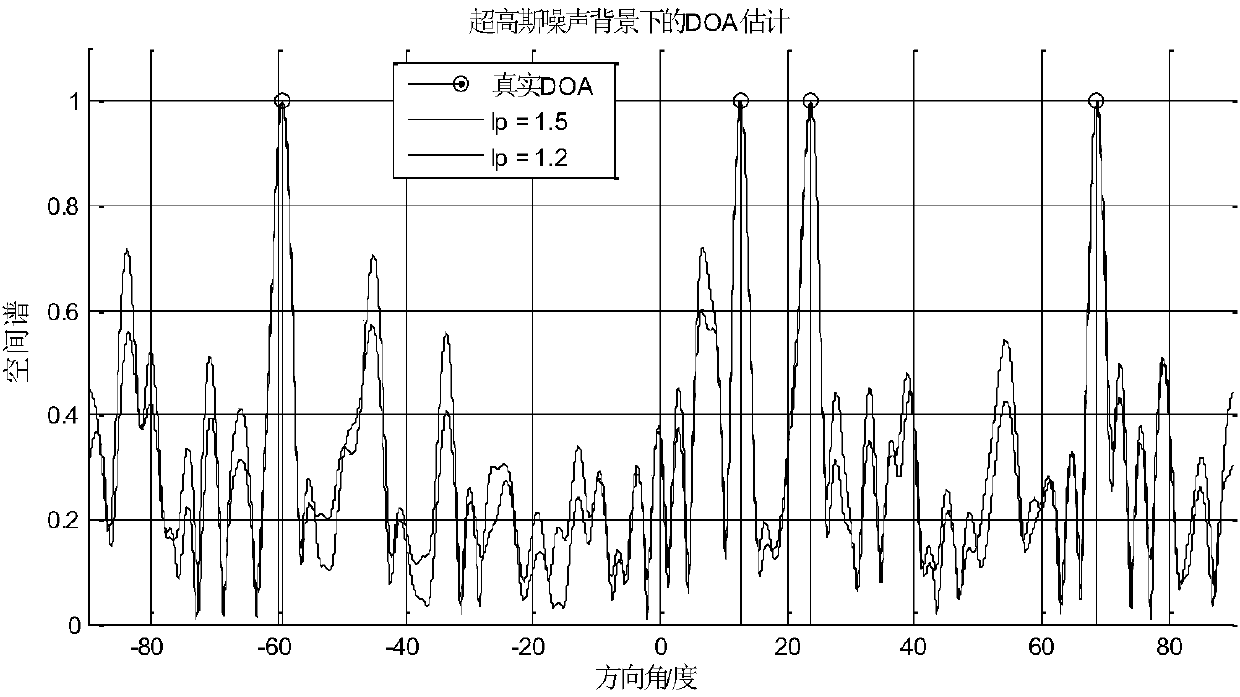
DOA (Direction-of-Arrival) estimation method based on grid-less compressive sensing in background of super-Gaussian noise
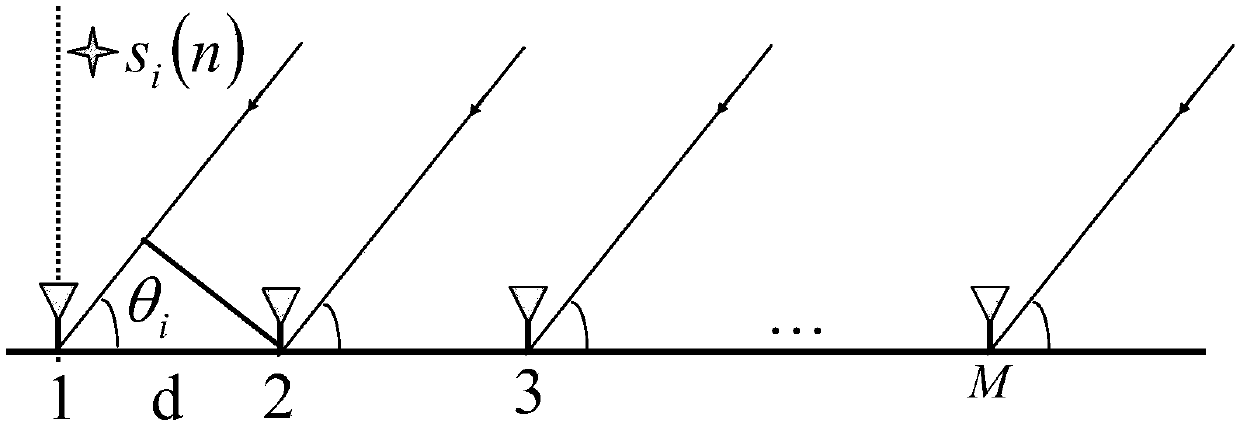
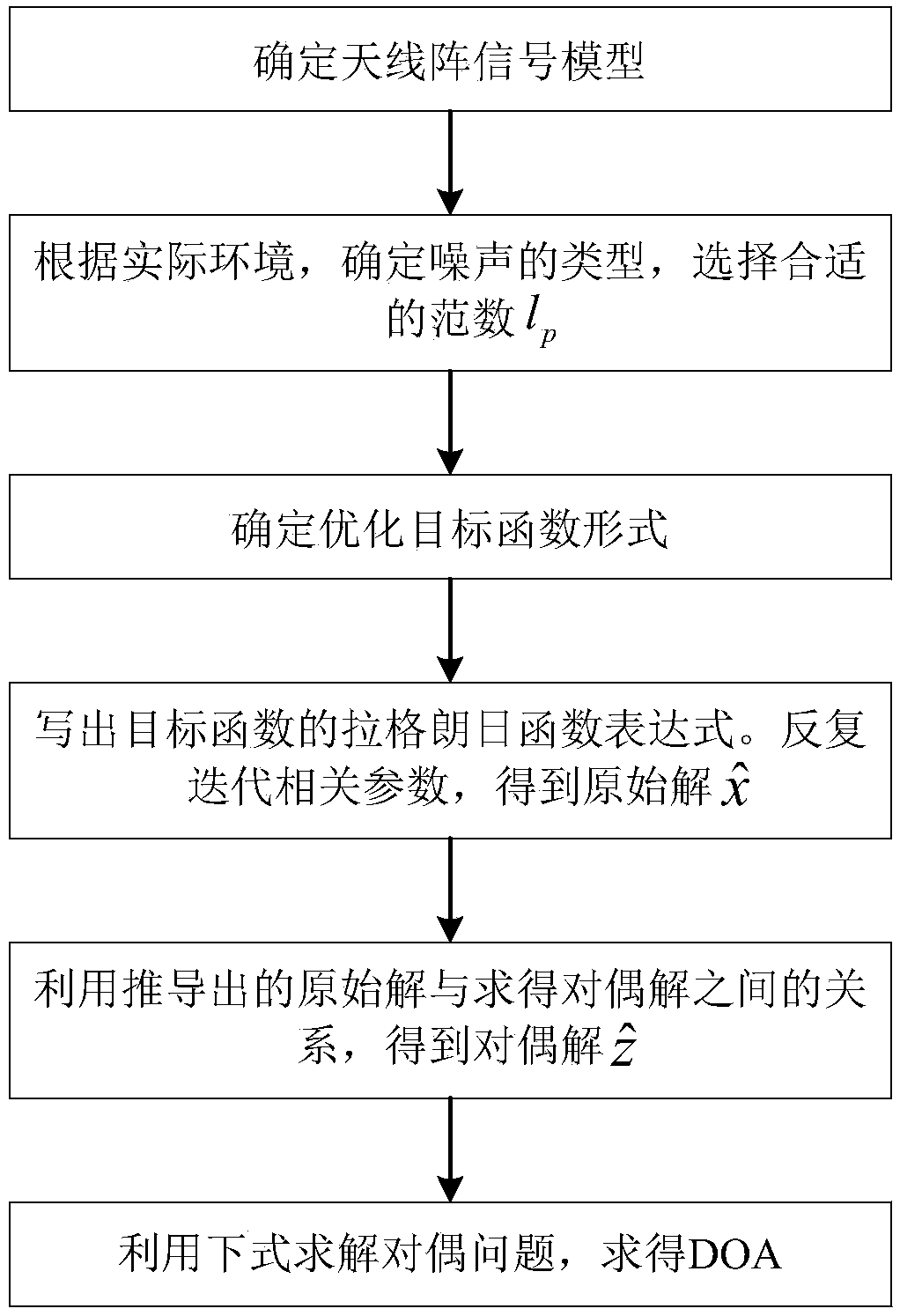
ActiveCN107817465AHigh precisionEasy to implementRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsAtomic normEstimation methods
The invention discloses a DOA (Direction-of-Arrival) estimation method based on grid-less compressive sensing in the background of super-Gaussian noise, which comprises the steps of firstly determining an antenna array signal model, that is, receiving signals through a linear antenna array with the number of array elements being M and the spacing between the array elements being equal, selecting anorm of lp to perform constraint according a noise distribution type measured in the actual environment, then determining a function expression for solving a noiseless signal x, describing a problemof recovering the noiseless signal x into a problem of minimizing an atomic norm, and solving by adopting a theoretical method of semi-definite programming; then solving a primitive solution accordingto an ADMM algorithm, then solving a dual solution z^, finally solving the DOA, enabling the DOA to more approach to an angle support set of the primitive signal so as to complete DOA estimation. According to the invention, a noise item is effectively constrained by adopting an appropriate norm through using statistical characteristics of the noise, and finally the angle support set of the primitive signal is solved by using a relation between the primitive solution and the dual solution so as to achieve effective and accurate DOA estimation.
Owner:ARMY ENG UNIV OF PLA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com