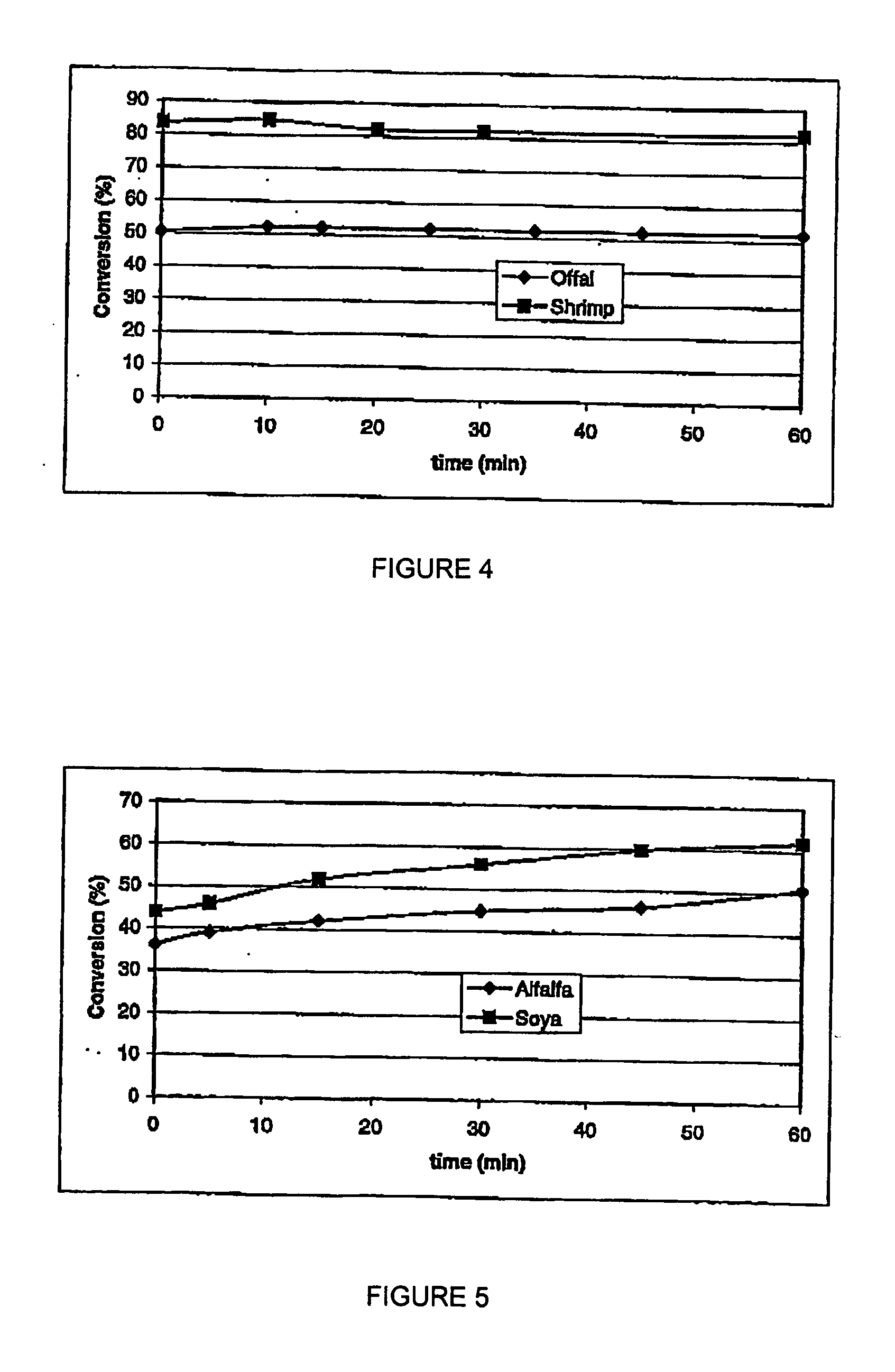
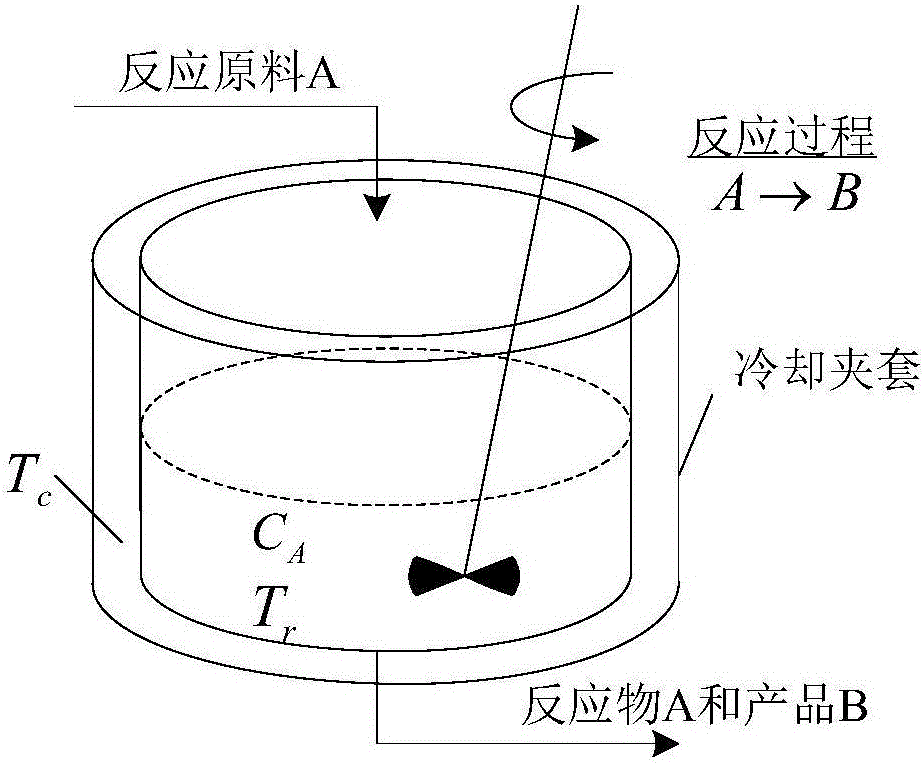
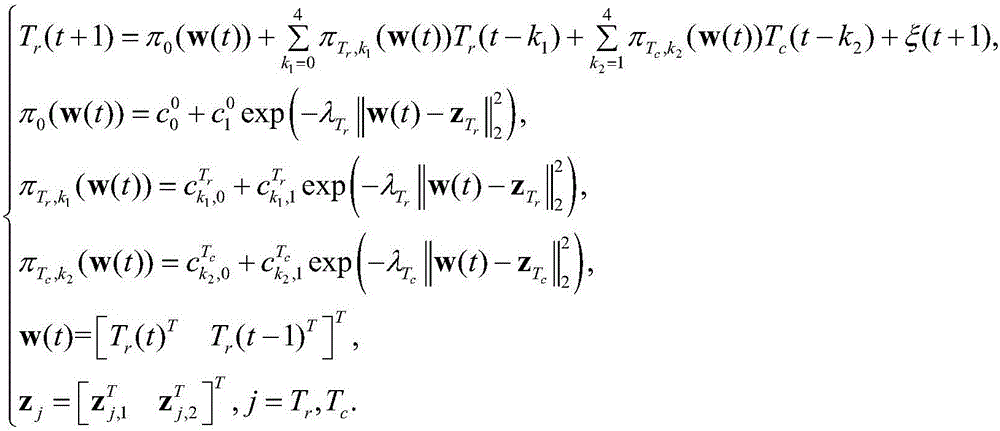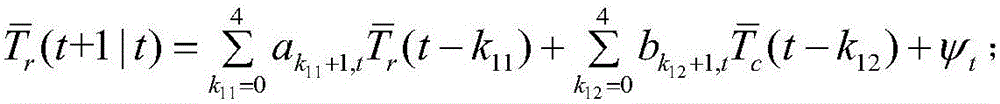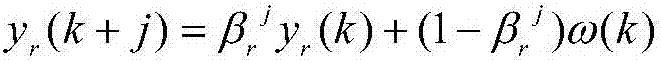Patents
Literature
161 results about "Continuous stirred-tank reactor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
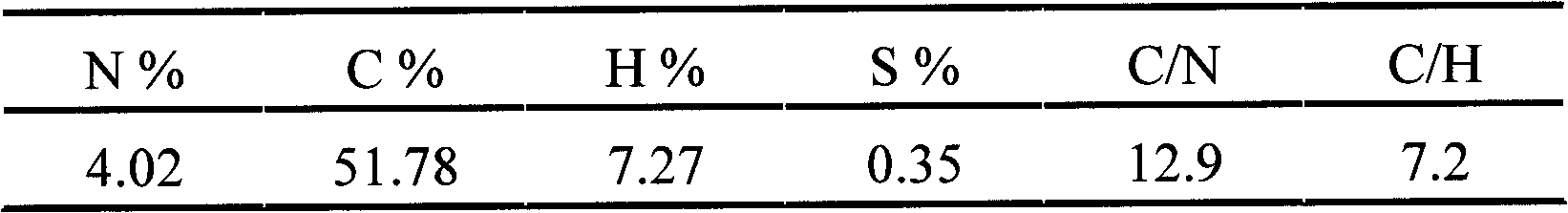
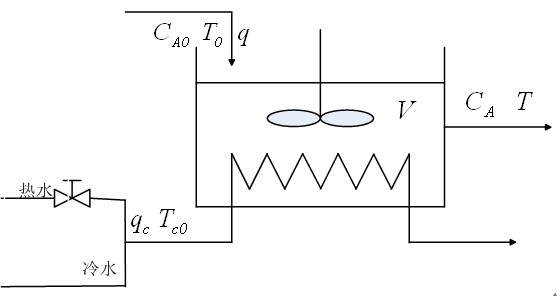
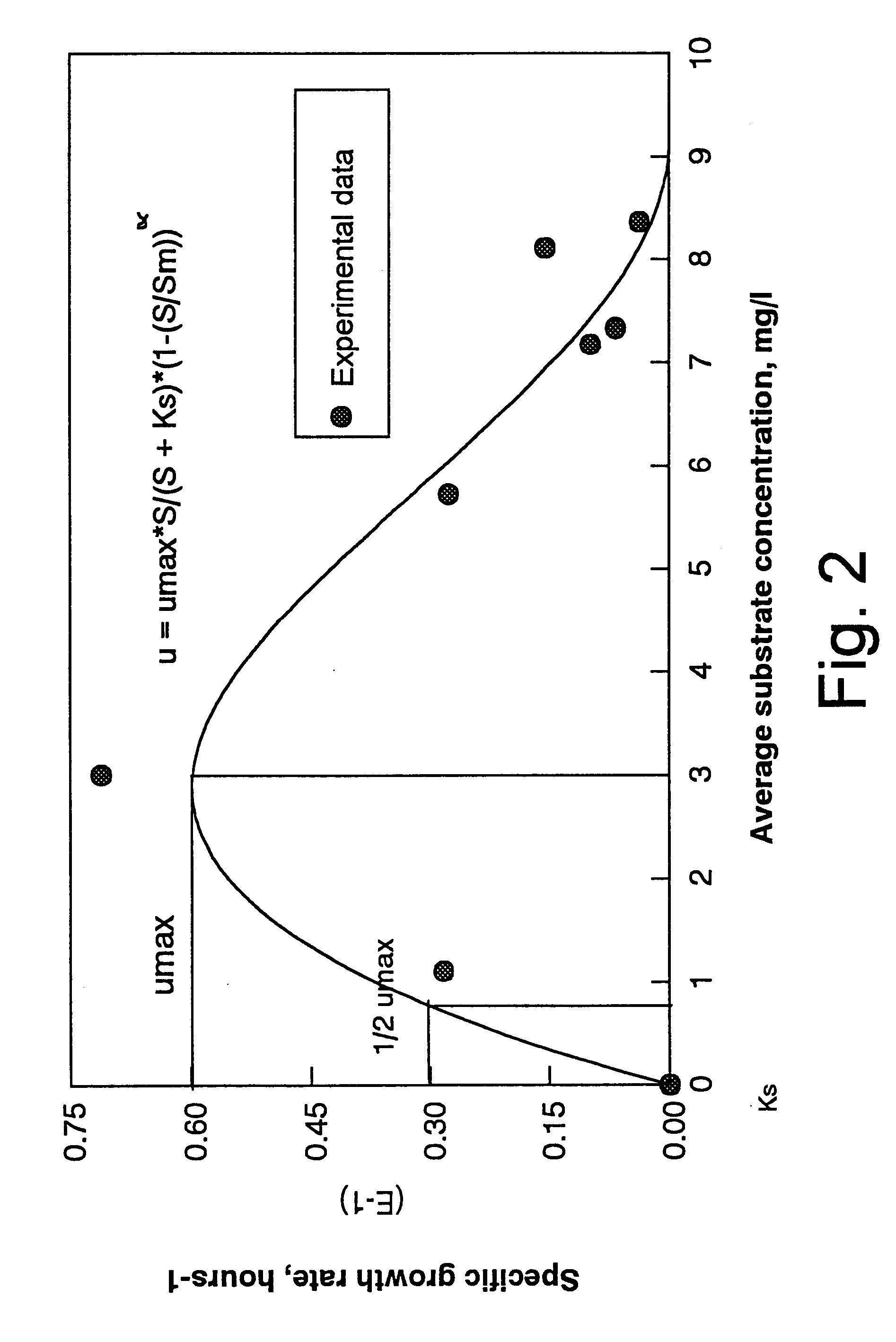
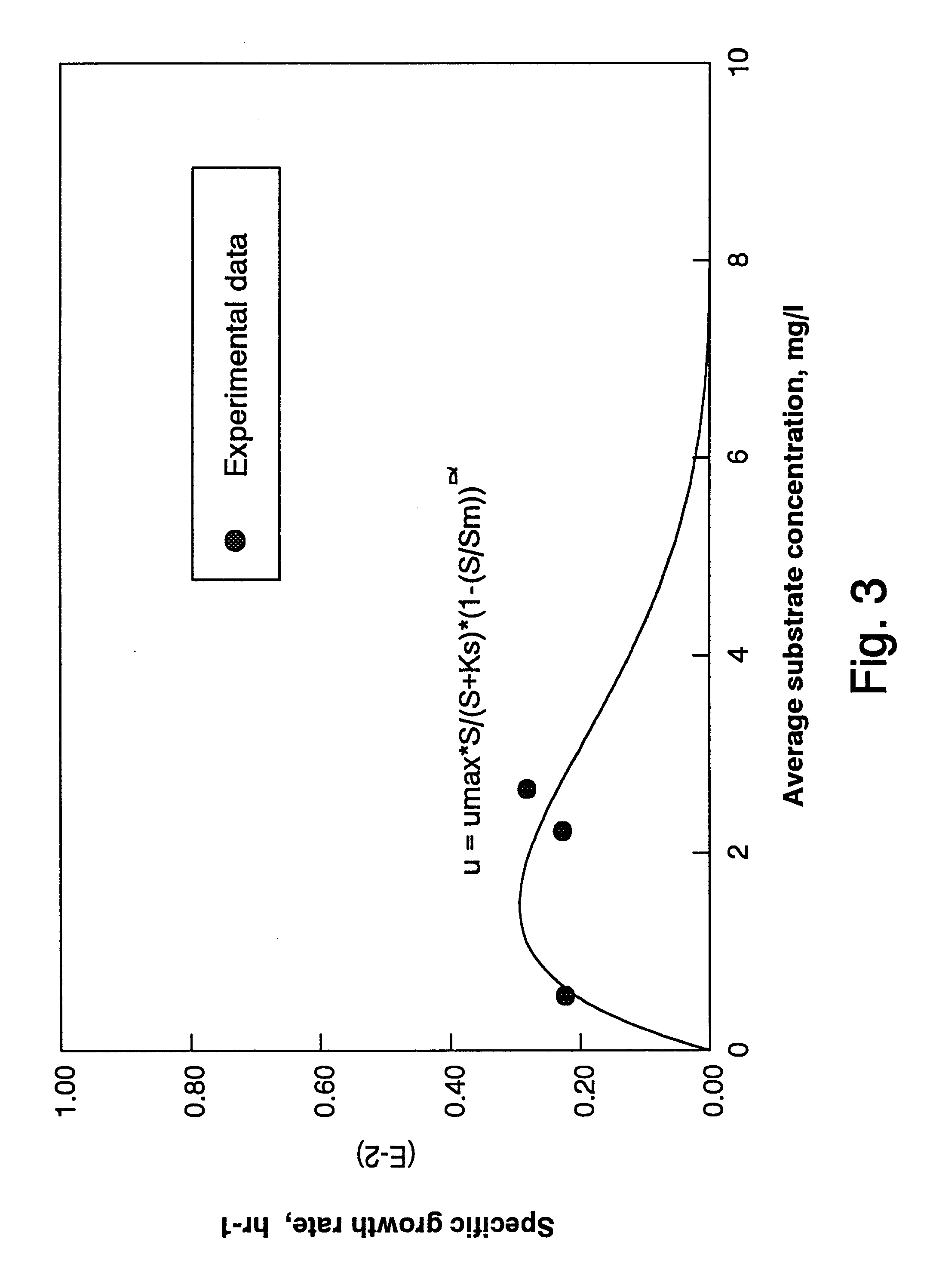
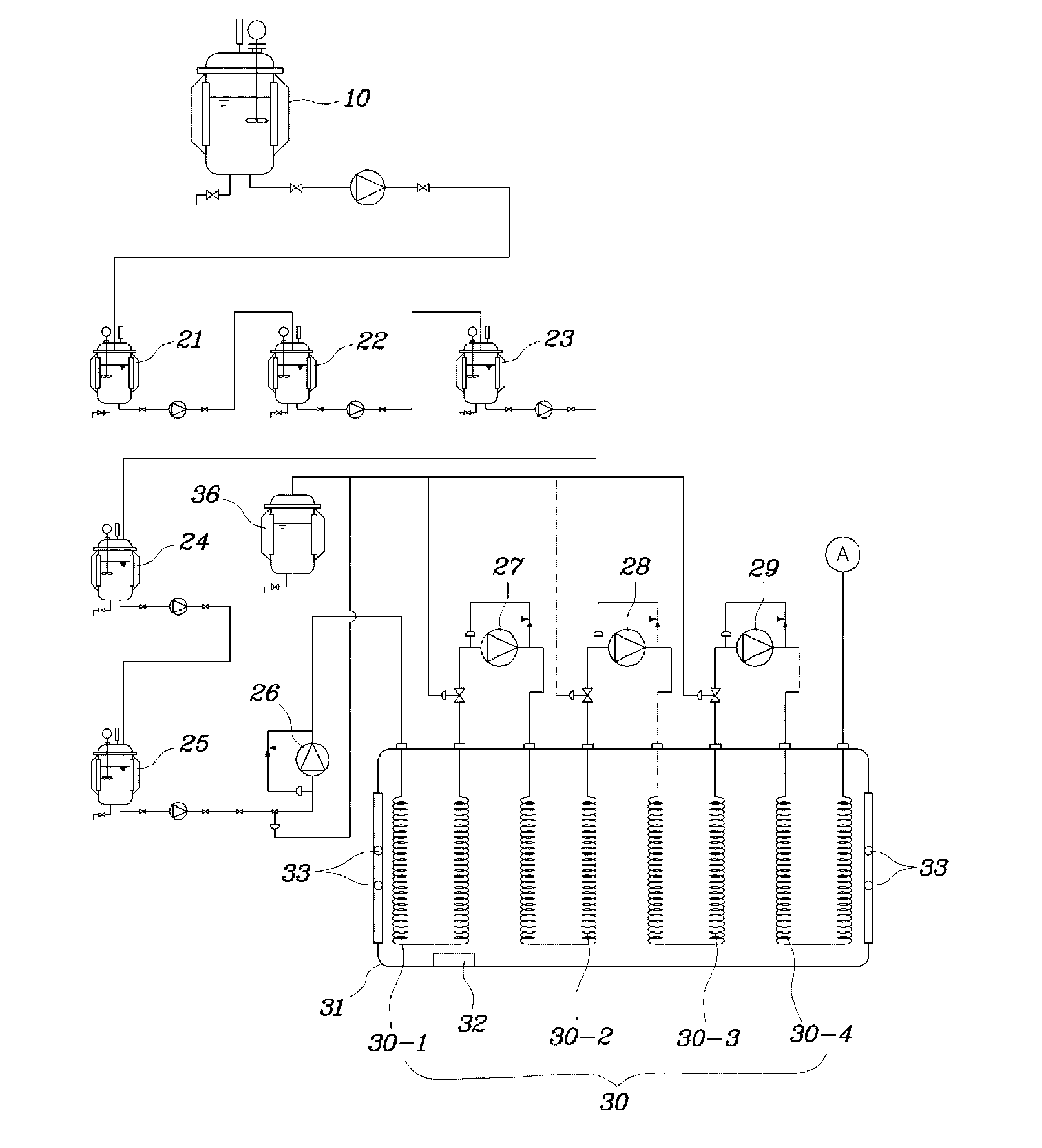
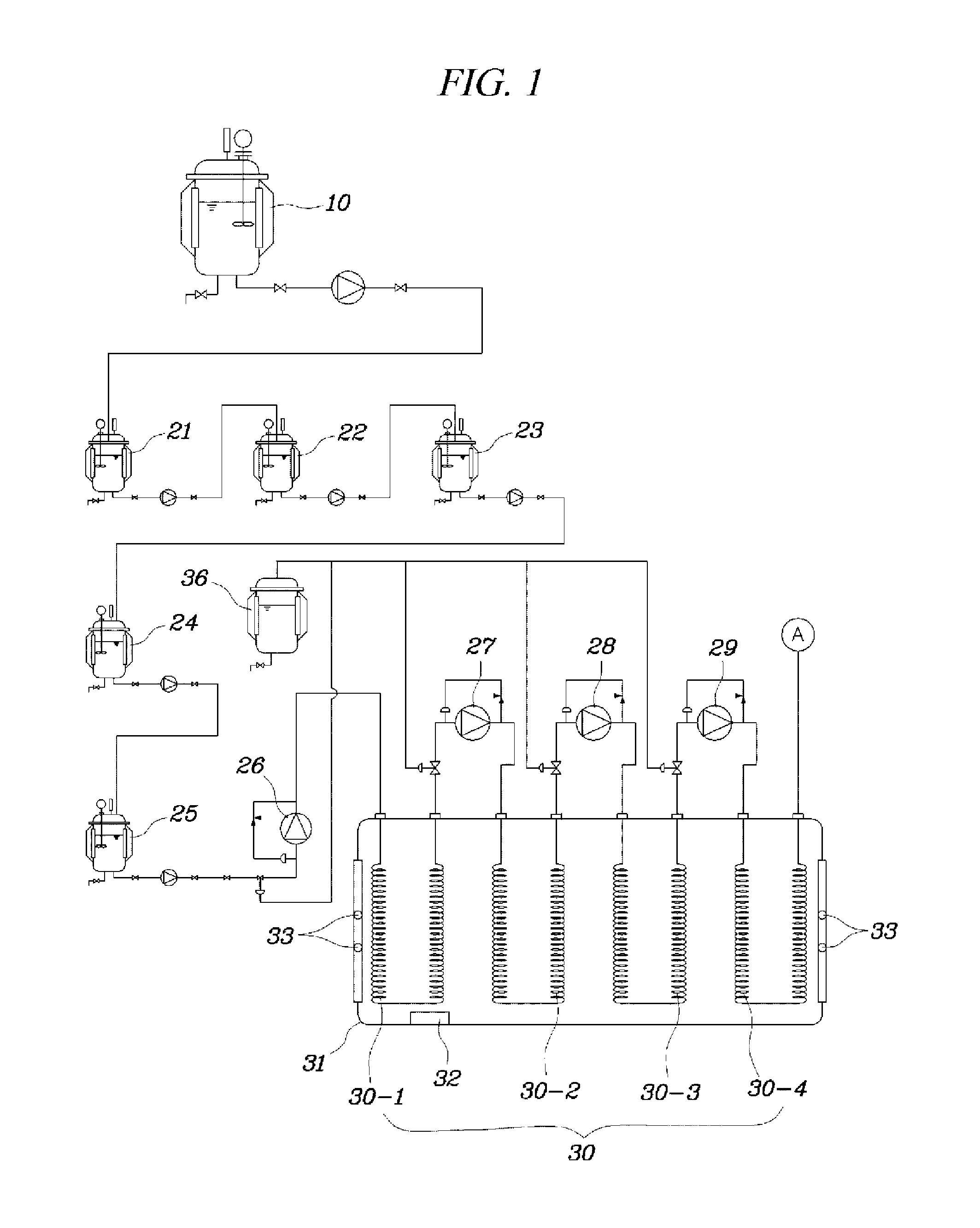
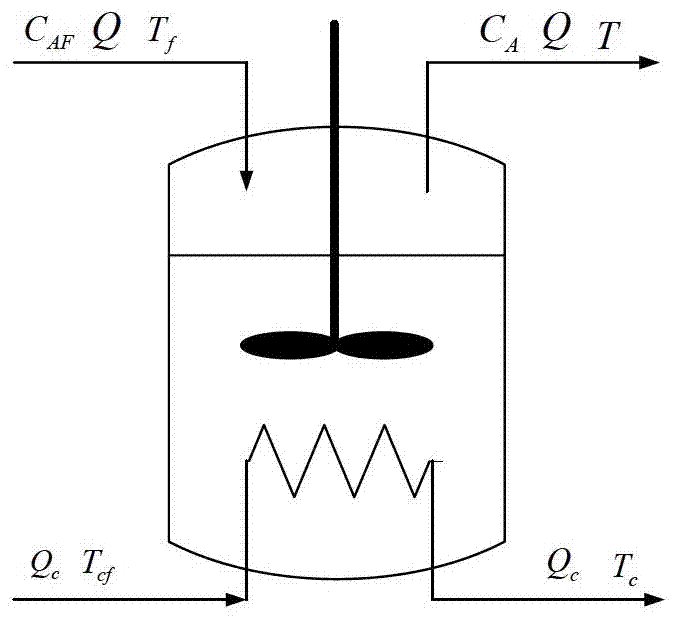
The continuous stirred-tank reactor (CSTR), also known as vat- or backmix reactor, or a continuous-flow stirred-tank reactor (CFSTR), is a common model for a chemical reactor in chemical engineering. A CSTR often refers to a model used to estimate the key unit operation variables when using a continuous agitated-tank reactor to reach a specified output. The mathematical model works for all fluids: liquids, gases, and slurries.
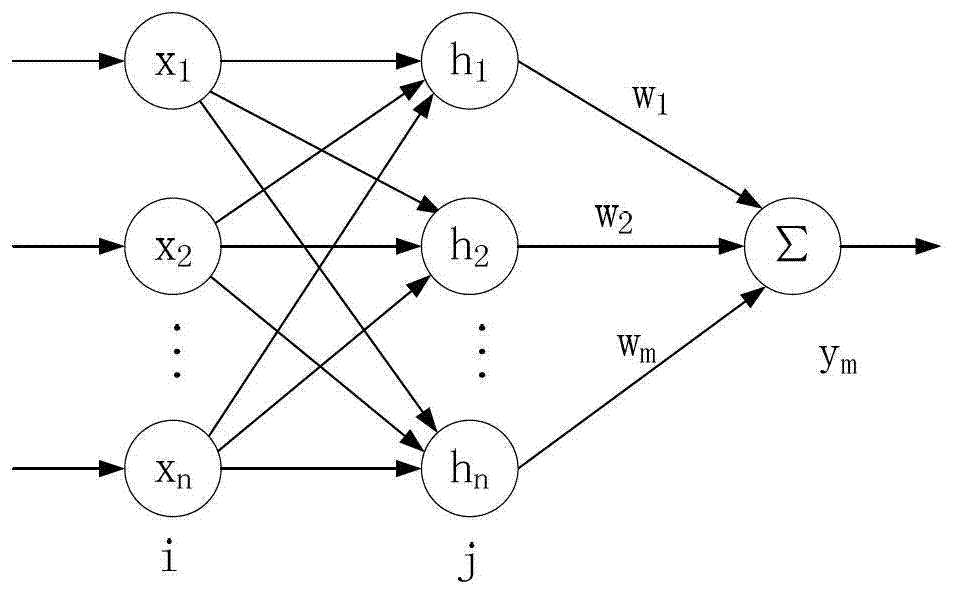
Performance of artificial neural network models in the presence of instrumental noise and measurement errors
ActiveUS20030191728A1Improve accuracy performanceImprove generalization performanceGenetic modelsDigital computer detailsObservational errorData set
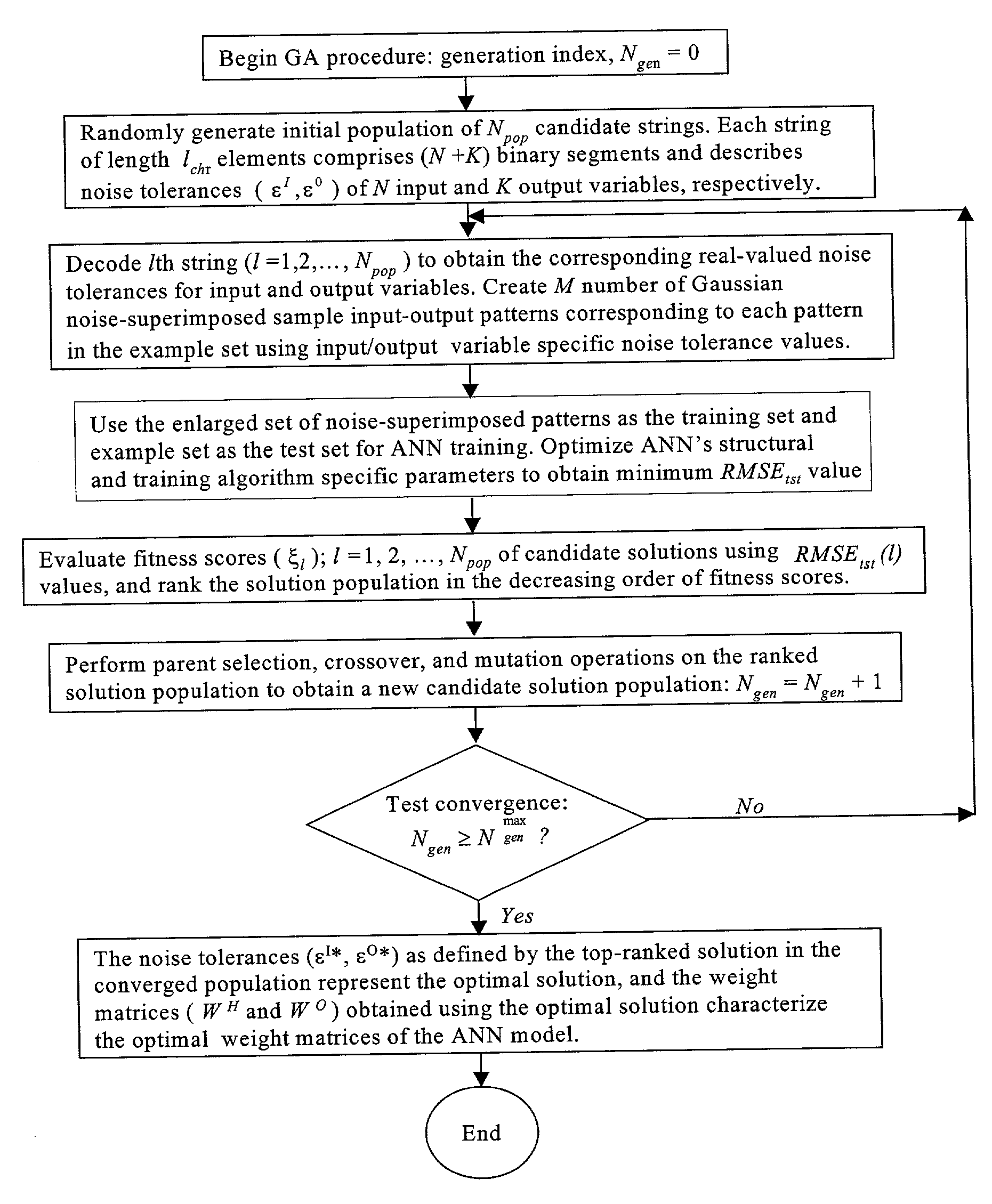
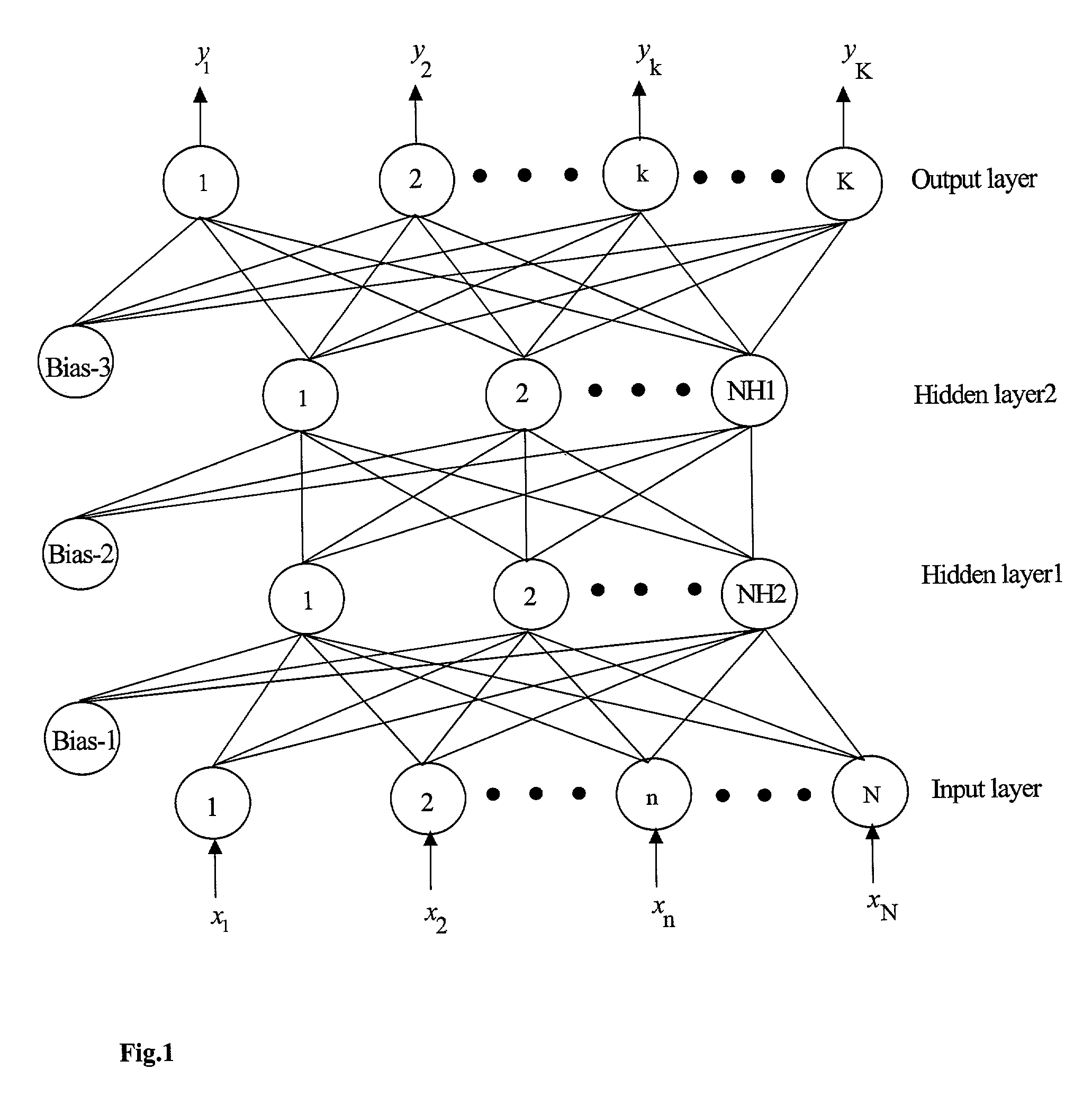
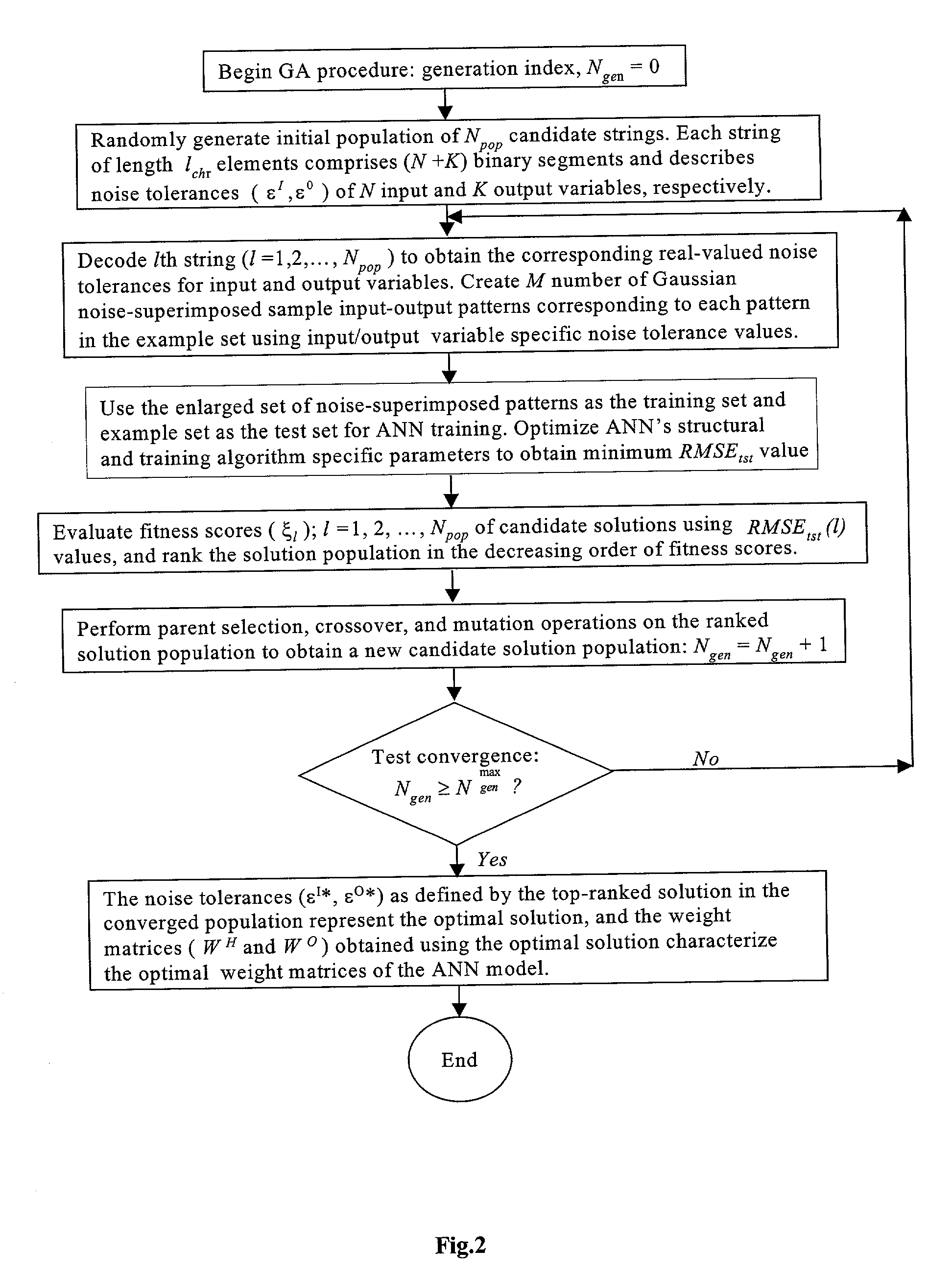
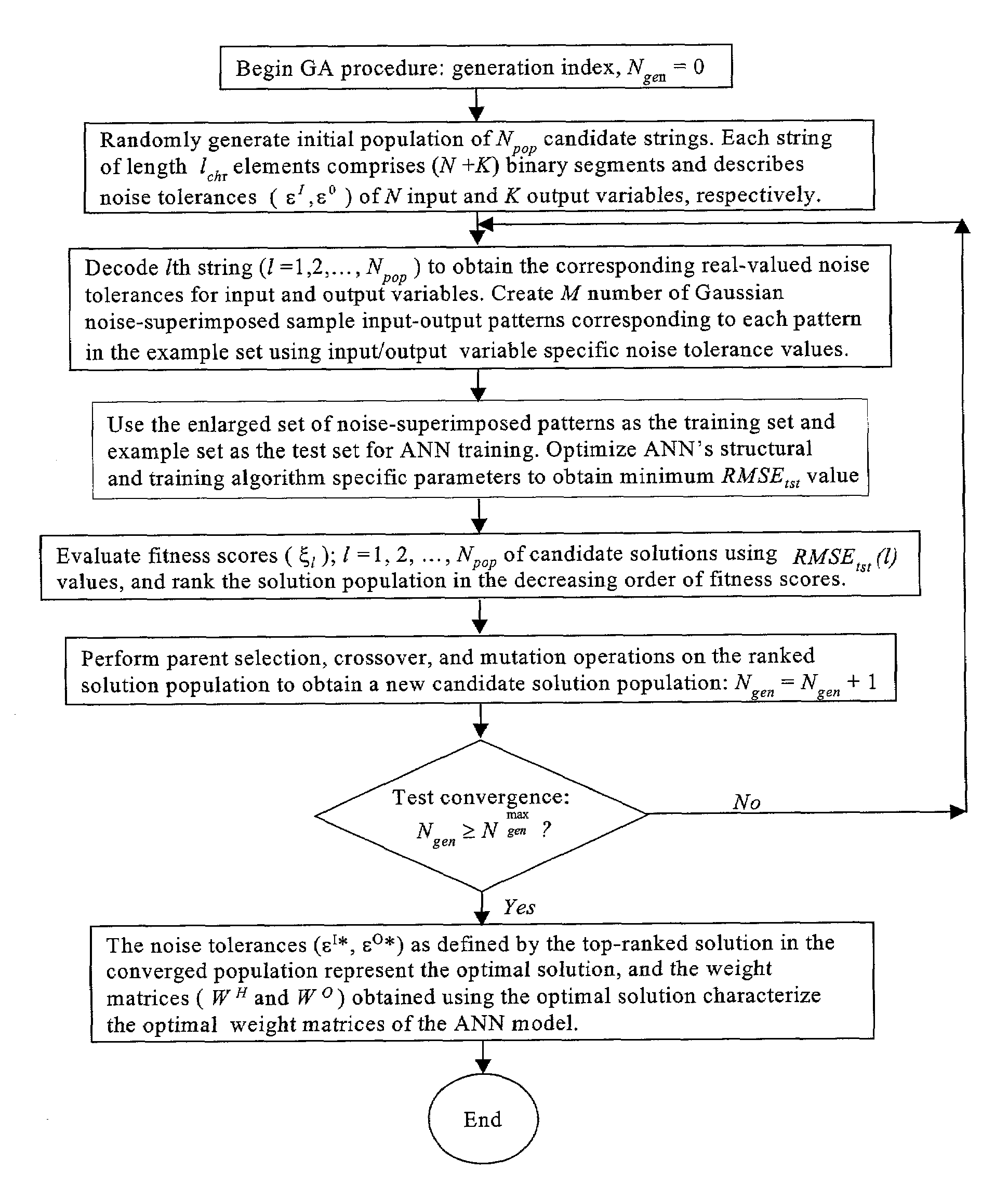
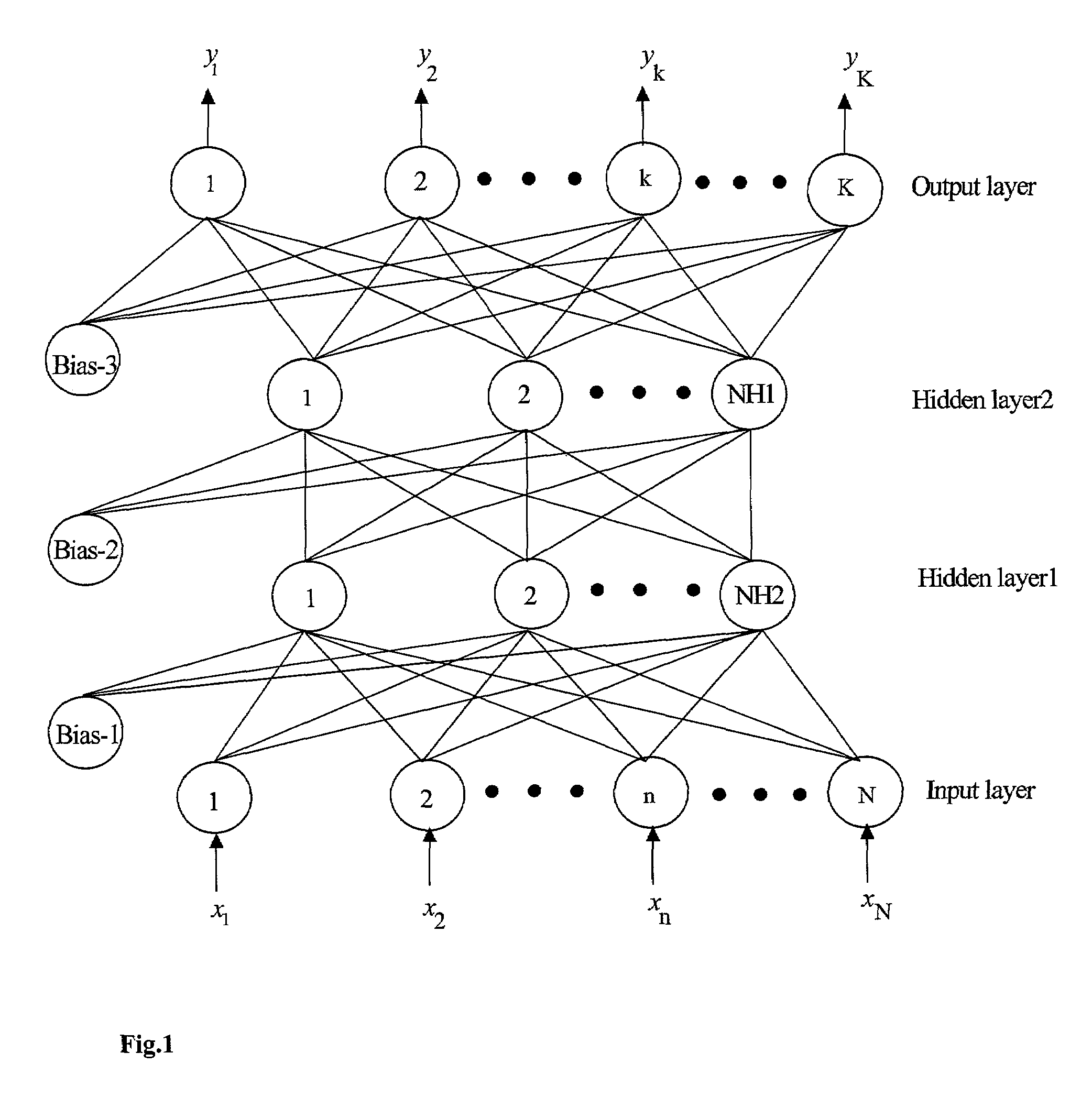
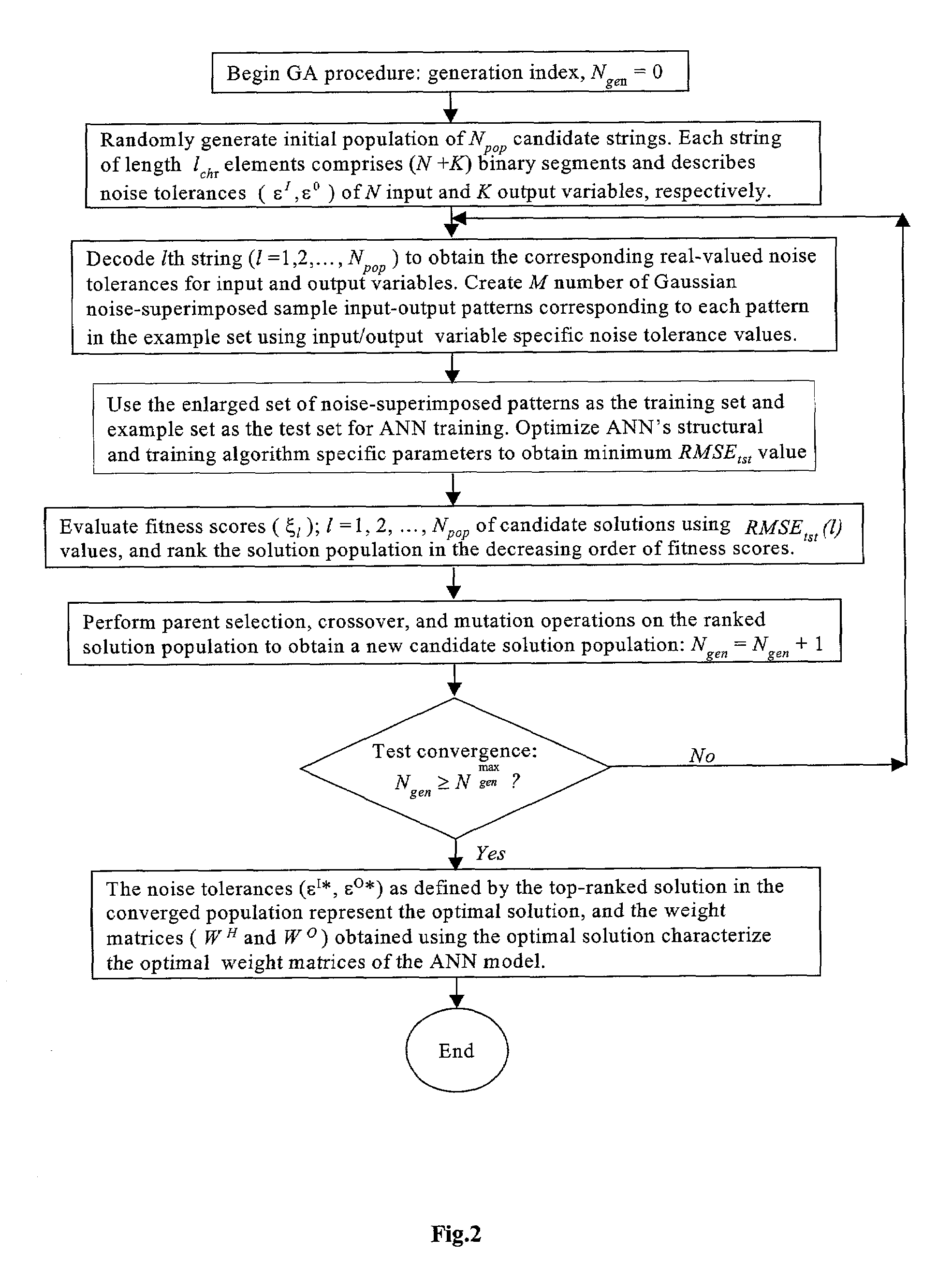
A method is described for improving the prediction accuracy and generalization performance of artificial neural network models in presence of input-output example data containing instrumental noise and / or measurement errors, the presence of noise and / or errors in the input-output example data used for training the network models create difficulties in learning accurately the nonlinear relationships existing between the inputs and the outputs, to effectively learn the noisy relationships, the methodology envisages creation of a large-sized noise-superimposed sample input-output dataset using computer simulations, here, a specific amount of Gaussian noise is added to each input / output variable in the example set and the enlarged sample data set created thereby is used as the training set for constructing the artificial neural network model, the amount of noise to be added is specific to an input / output variable and its optimal value is determined using a stochastic search and optimization technique, namely, genetic algorithms, the network trained on the noise-superimposed enlarged training set shows significant improvements in its prediction accuracy and generalization performance, the invented methodology is illustrated by its successful application to the example data comprising instrumental errors and / or measurement noise from an industrial polymerization reactor and a continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR).
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Performance of artificial neural network models in the presence of instrumental noise and measurement errors
InactiveUS7313550B2Improve accuracyImprove performanceGenetic modelsDigital computer detailsObservational errorData set
A method is described for improving the prediction accuracy and generalization performance of artificial neural network models in presence of input-output example data containing instrumental noise and / or measurement errors, the presence of noise and / or errors in the input-output example data used for training the network models create difficulties in learning accurately the nonlinear relationships existing between the inputs and the outputs, to effectively learn the noisy relationships, the methodology envisages creation of a large-sized noise-superimposed sample input-output dataset using computer simulations, here, a specific amount of Gaussian noise is added to each input / output variable in the example set and the enlarged sample data set created thereby is used as the training set for constructing the artificial neural network model, the amount of noise to be added is specific to an input / output variable and its optimal value is determined using a stochastic search and optimization technique, namely, genetic algorithms, the network trained on the noise-superimposed enlarged training set shows significant improvements in its prediction accuracy and generalization performance, the invented methodology is illustrated by its successful application to the example data comprising instrumental errors and / or measurement noise from an industrial polymerization reactor and a continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR).
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Method and system for solubilizing protein
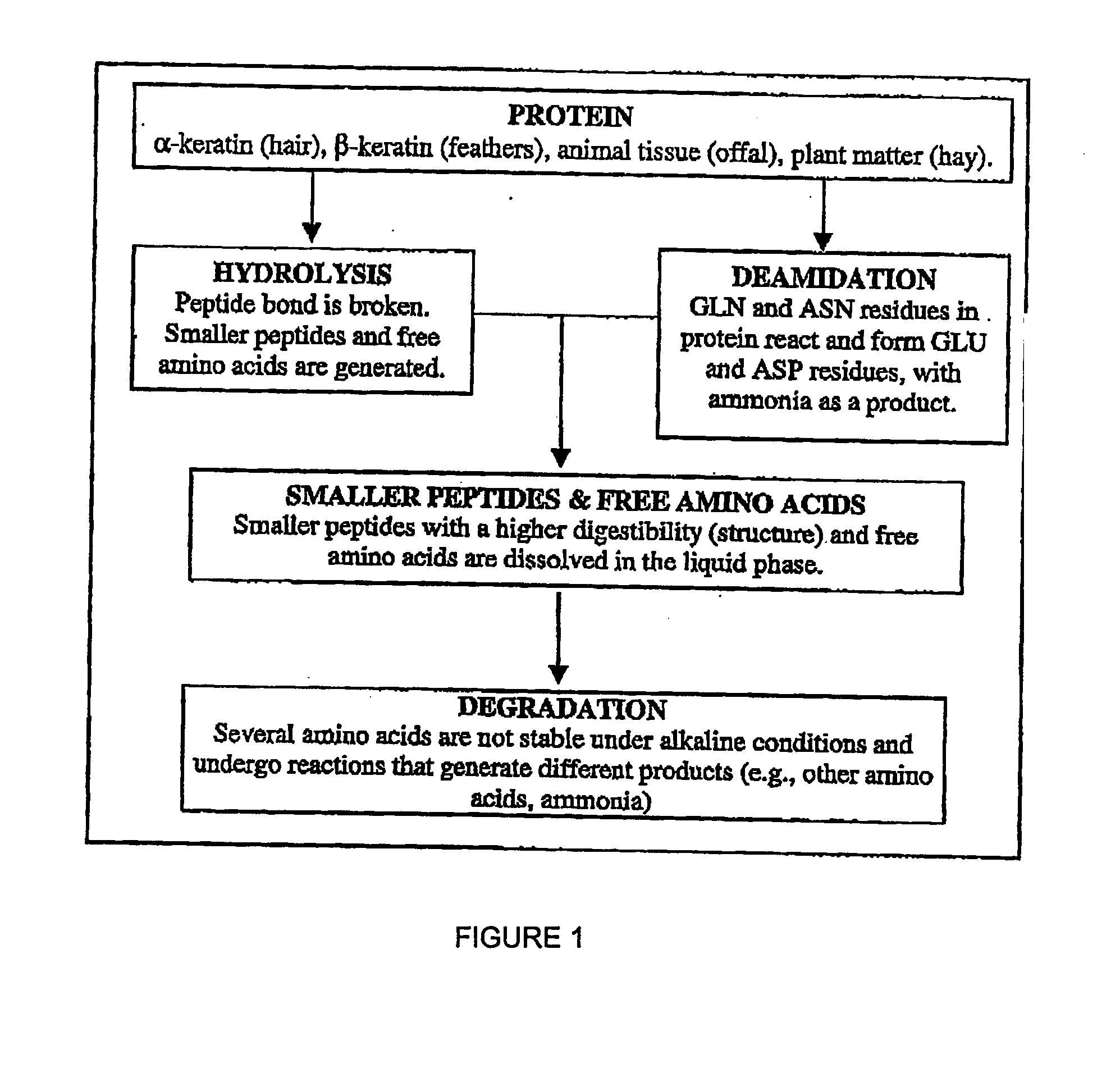
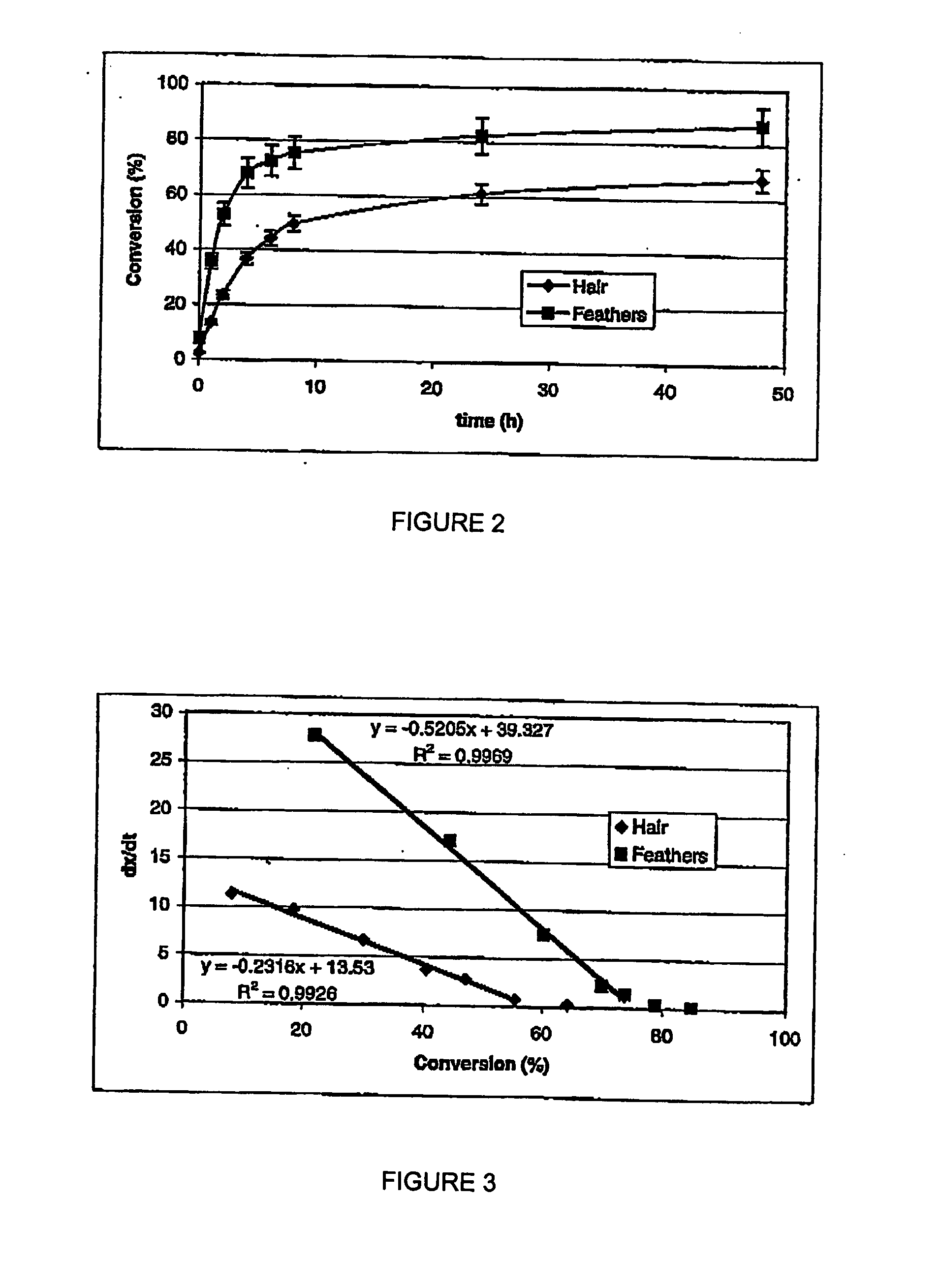
InactiveUS20060069244A1Improve digestibilityRecovery of some componentPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesSingle stagePolymer science
A process for solubilization of protein including application of an alkali, such as lime, and heating. The process may also involve lime recovery and may be accomplished in a single stage or two stages to separate protein solubilized from labile and recalcitrant sources. Systems and devices for use in such process, including a continuous stirred tank reactor and a plug flow reactor are also involved.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Robust predictive control method for first-order continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR)
InactiveCN105893654AReliable controlComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsState dependentMathematical model
The invention discloses a robust predictive control method for a first-order continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR). The method comprises the following steps: building a dynamic mathematical model of a non-linear CSTR system off line through a modeling method of a nonlinear state-dependent ARX model; secondly, constructing a non-linear dynamic variable linear polyhedral model capable of packing the CSTR system by using the structural features of the non-linear ARX model and change information of future non-linear dynamic features of the system contained in the model; and lastly, designing a CSTR system robust predictive control algorithm which is based on the non-linear ARX model, considers the robust stability of a CSTR system restraint, has good control performance and can realize optimal output tracking by resolving a convex optimization problem according to a min-max optimization principle based on an invariant set design method under the situation that steady-state balance point information of the CSTR system is unknown.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
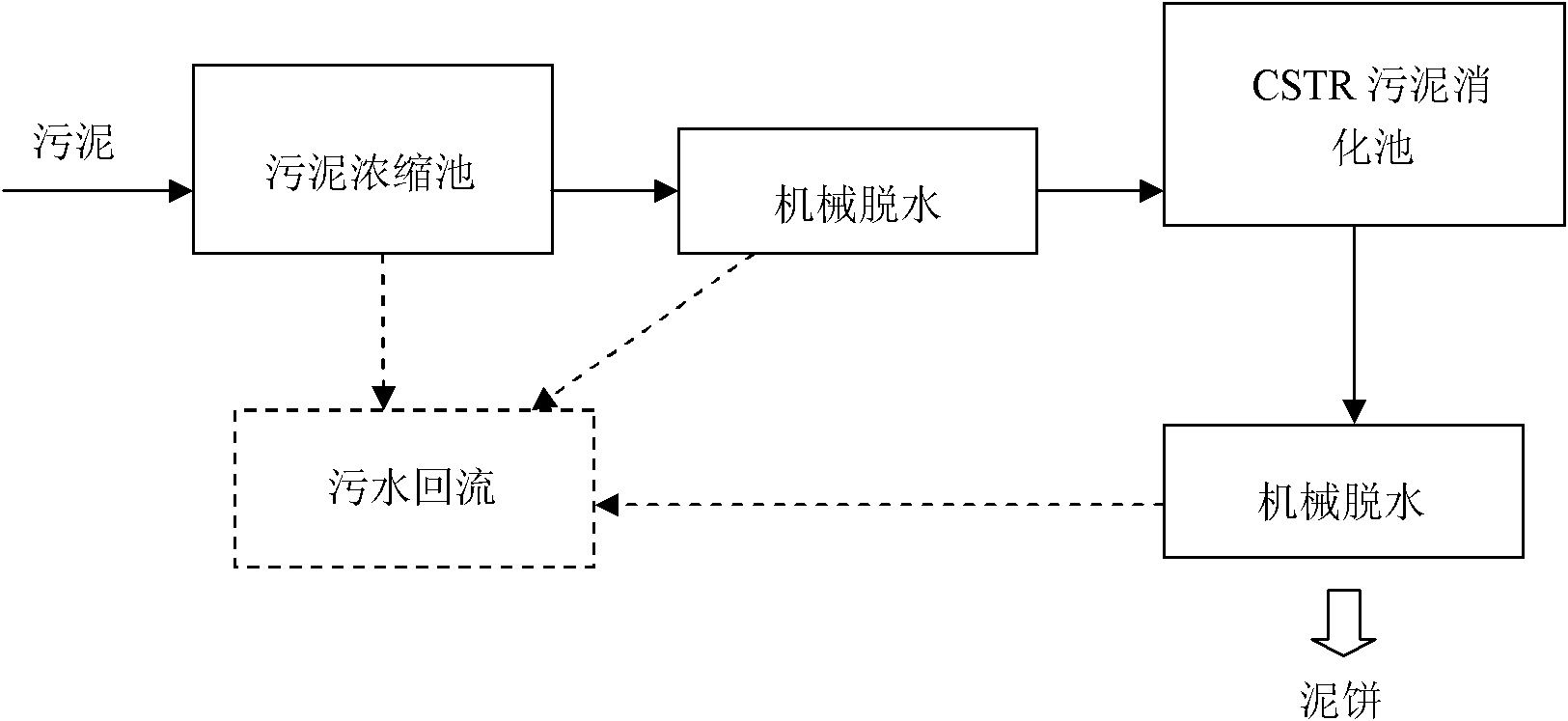
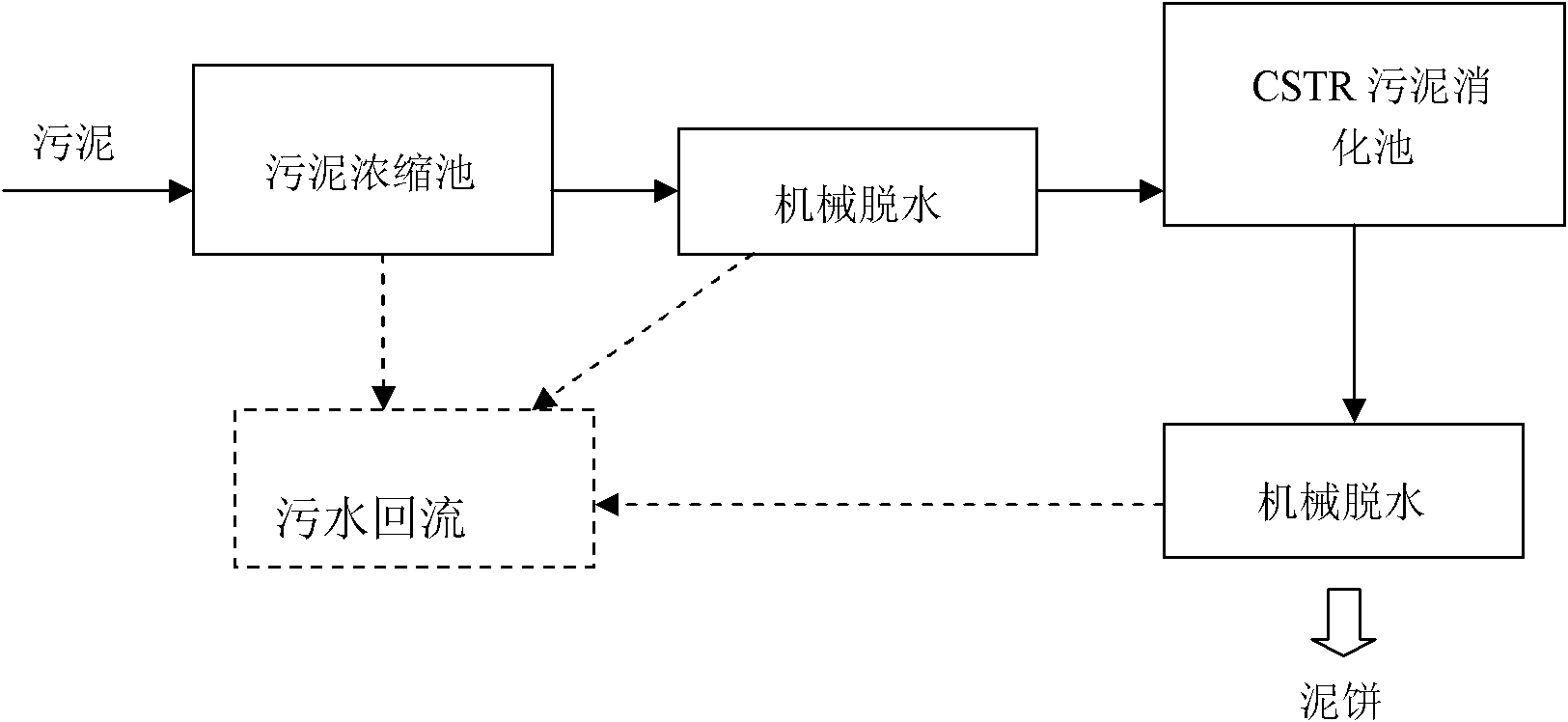
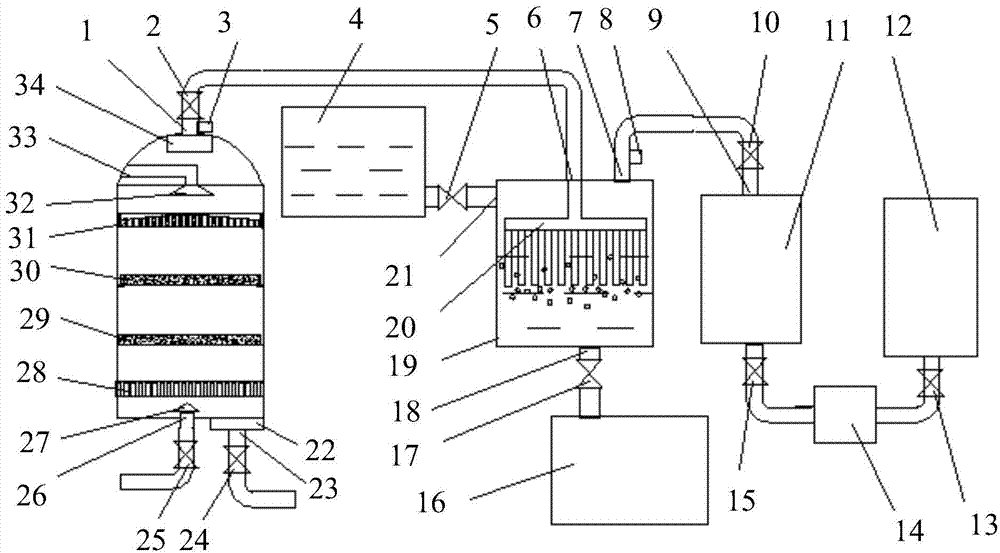
High-concentration anaerobic sludge digestion treatment process for carrying out mechanical dewatering on sludge
ActiveCN101948231AReduce moisture contentReduce volumeSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningBiological sludge treatmentHigh concentrationSludge cake
The invention relates to a high-concentration anaerobic sludge digestion treatment process for carrying out mechanical dewatering on sludge, comprising the following steps of: conveying sludge with high water content into a concentration tank, wherein the water content of the concentrated sludge is reduced to 97 percent, and a supernate reflexes to a sludge treatment system; carrying out mechanical pre-dewatering on the concentrated sludge, wherein the water content is about 88-90 percent after the mechanical pre-dewatering; then carrying out anaerobic digestion on the pre-dewatered sludge under the high concentration condition by adopting a CSTR (Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactor); and further dewatering the sludge after anaerobic digestion, wherein the water content of a treated sludge cake is about 75 percent. The invention has following advantages and positive effects: by adopting the technical scheme, the dewatering effect of the sludge is favorable, the volume of an anaerobic sludge digestion tank is greatly shortened, and the capital construction investment and the operation cost of a sewage treatment plant are reduced; the load of organic matters in the sludge can be effectively improved by carrying out pre-dewatering on the sludge; and the CSTR anaerobic sludge digestion which is suitable for the high-concentration solid materials is used for treatment, which is beneficial to sludge resource utilization.
Owner:NANJING YANJIANG ACAD OF RESCOURCES & ECOLOGY SCI CO LTD
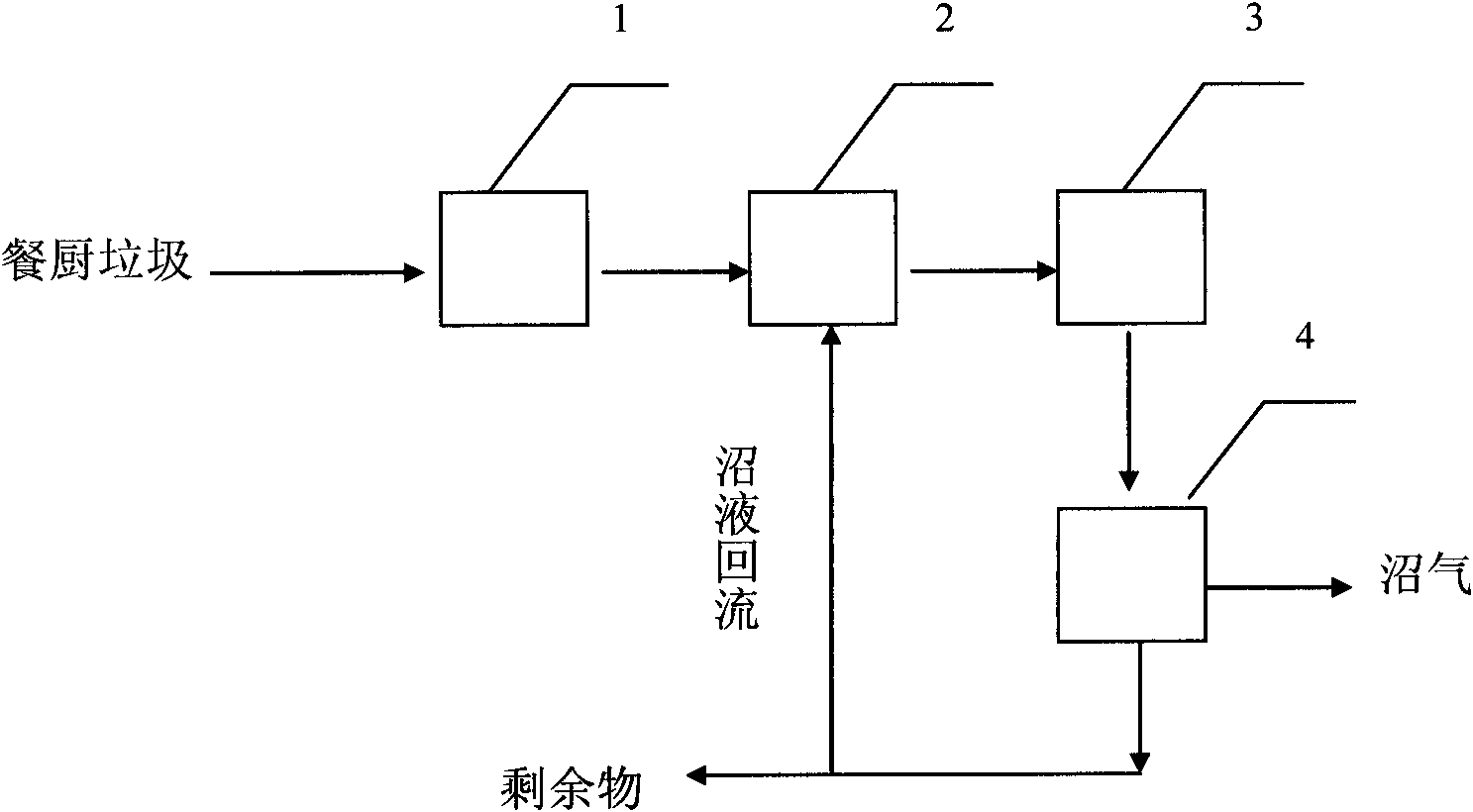
Method for producing methane from kitchen waste by two continuous anaerobic fermentation steps
InactiveCN102757889APromote degradationImprove efficiencyBiological substance pretreatmentsGas production bioreactorsPulp and paper industryContinuous stirred-tank reactor
The invention discloses a method for producing methane from kitchen waste by two continuous anaerobic fermentation steps. The method comprises the following steps: 1) crushing and beating the kitchen waste; 2) adding water into the beaten kitchen waste, and transferring the kitchen waste added with the water to a first continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR) anaerobic fermentation tank for acidification hydrolization; and 3) transferring the fermented materials subjected to the acidification hydrolization to a second CSTR anaerobic fermentation tank for anaerobic fermentation to produce methane, wherein an anaerobic inoculum is adopted. According to the method, the kitchen waste is subjected to the acidification hydrolization at first and then is subjected to the high-temperature anaerobic fermentation to generate the methane by adopting a continuous operation way in the two anaerobic digestion processes; and the fermented materials subjected to the acidification hydrolization does not need to be subjected to solid-liquid separation, so that the problems that the kitchen waste is fast to degrade and the production of the methane is not stable in the anaerobic fermentation process are solved, and the industrial anaerobic digestion treatment of the kitchen waste can be implemented.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Optimal method for controlling mixed model of first-order reaction continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR)
InactiveCN102023574ARun fastRun accuratelyChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsAdaptive controlOperating pointFirst-order reaction
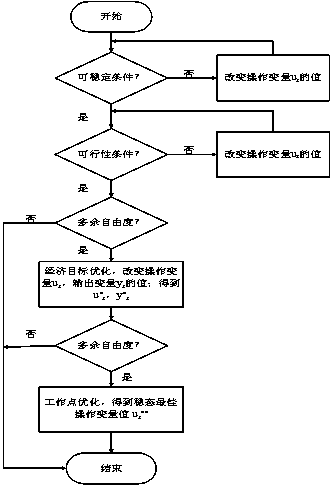
The invention discloses an optimal method for controlling a mixed model of a first-order reaction continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR). The method can ensure that the first-order reaction CSTR can rapidly, accurately, stably operate under the following two conditions: a transient process that a system is started and then operates into a certain stable operating point, and a transient process that the system converts into the other stable working point from a certain stable operating point. Compared with the existing first-order reaction CSTR control method, the method provided by the invention has obvious advantages.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Production of hydrogen from oxygenated hydrocarbons
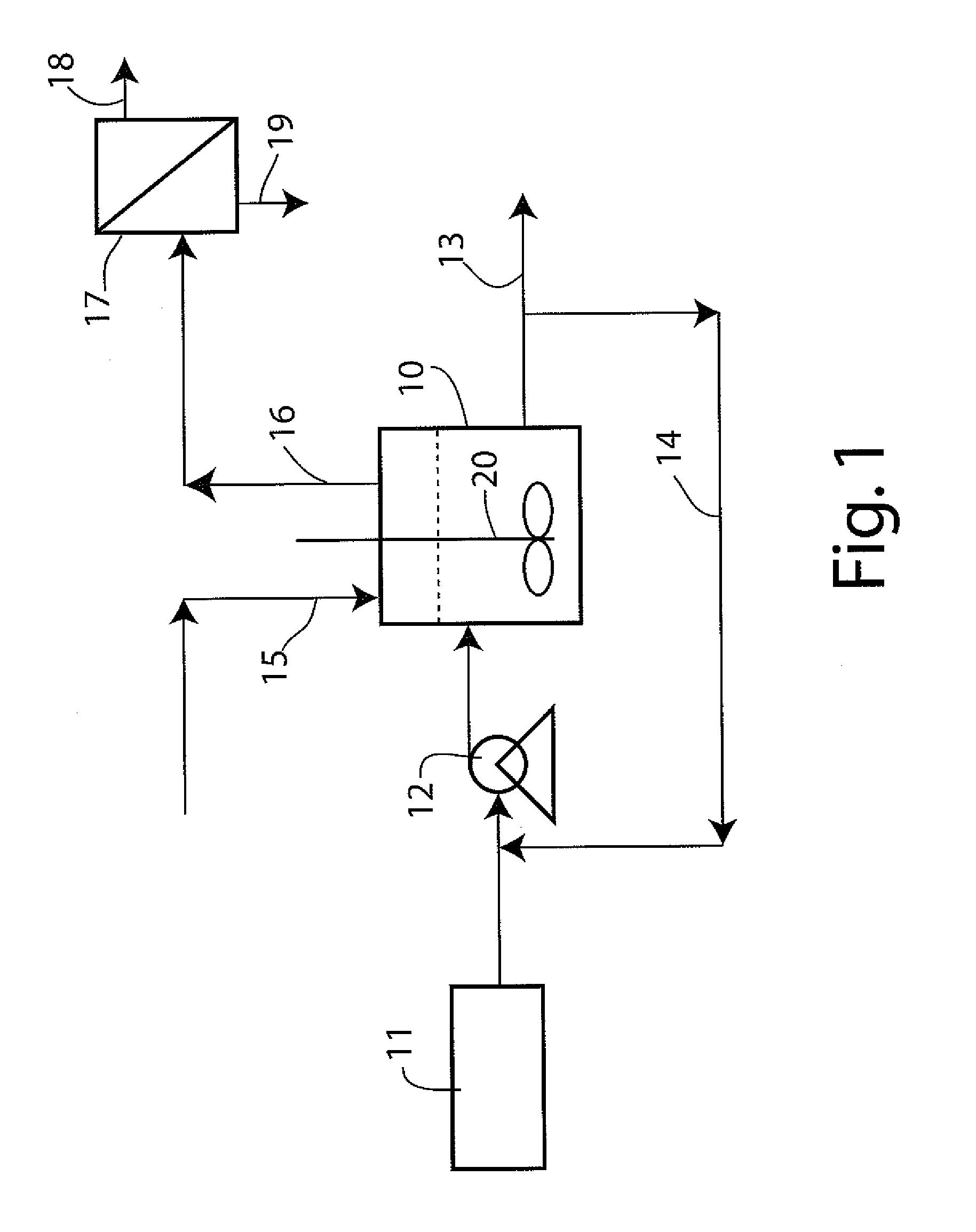
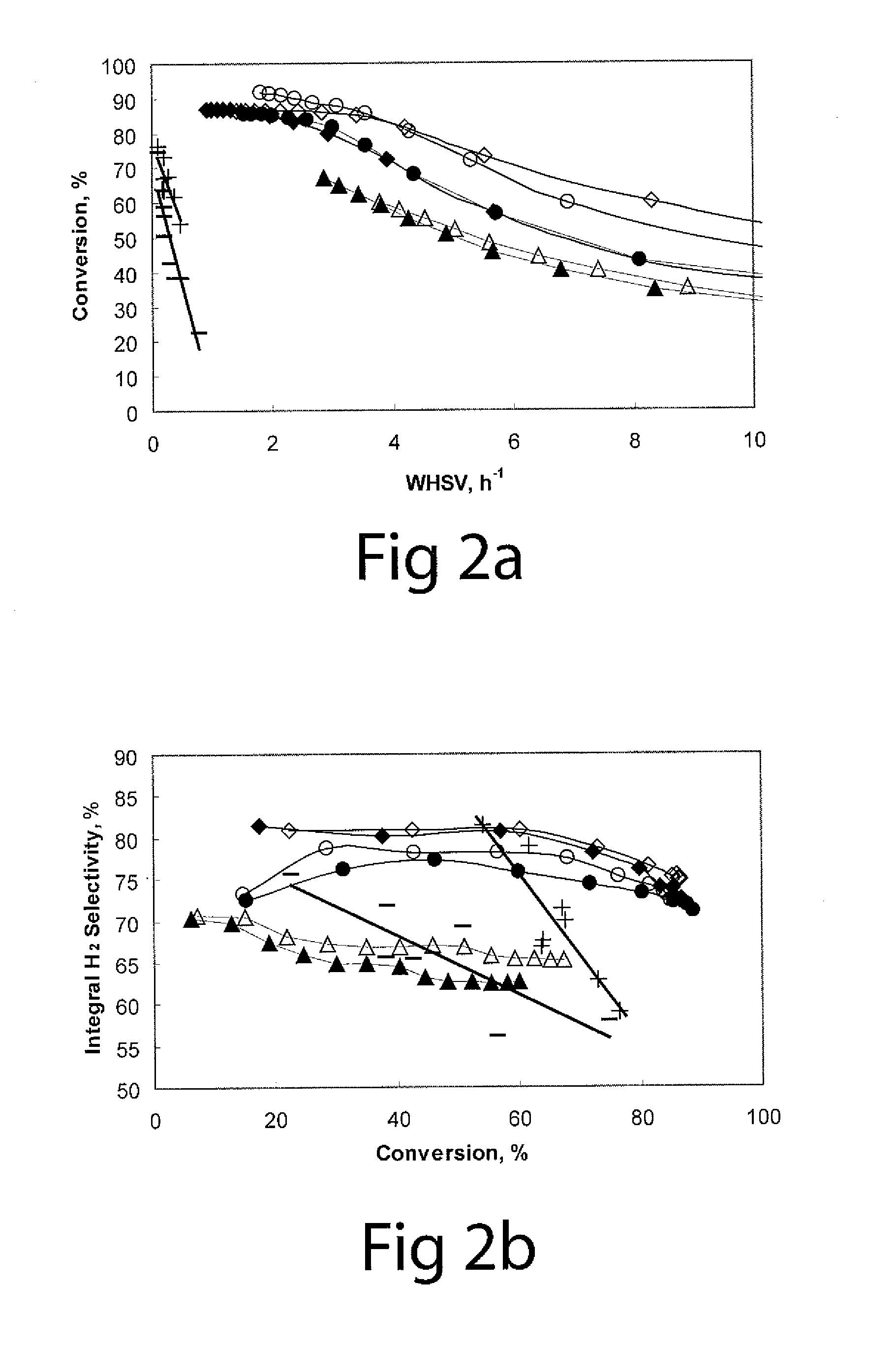
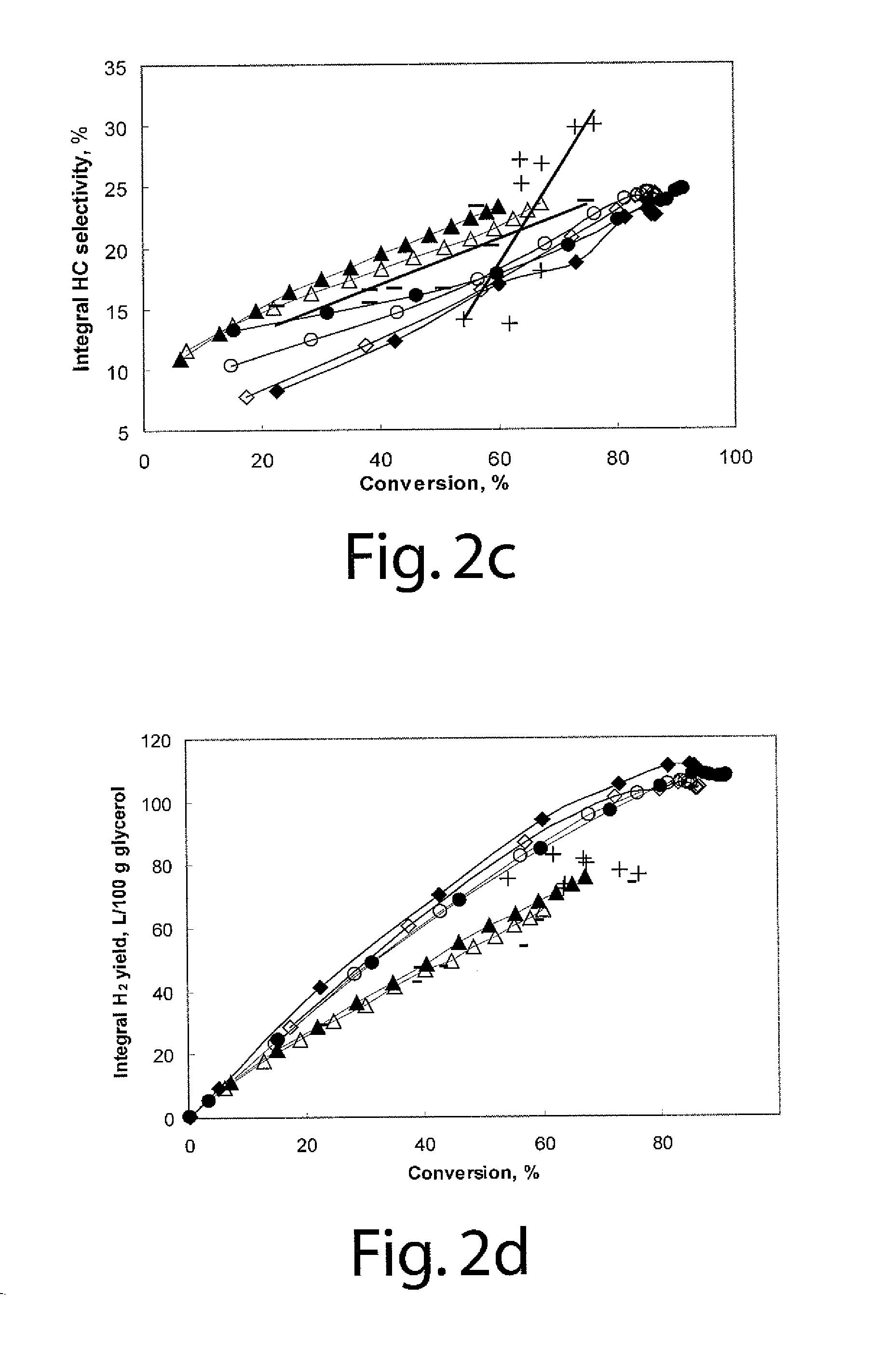
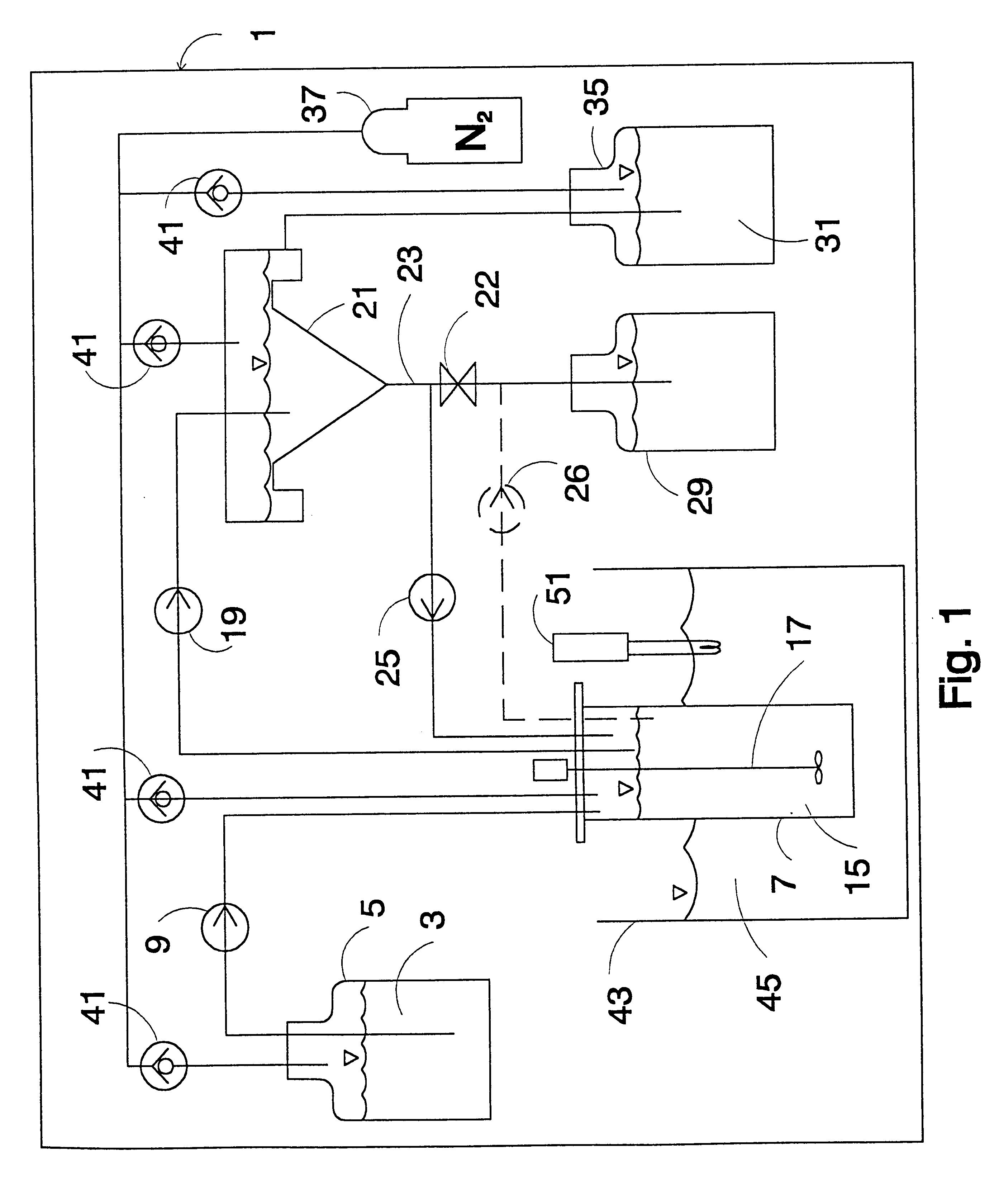
ActiveUS20110027169A1Large specific surface areaIncrease heating capacityHydrogen productionHydrogen/synthetic gas productionParticulatesHydrogen
The invention provides a process of producing hydrogen that involves aqueous phase reforming of an oxygenated hydrocarbon, preferably one obtained from a renewable source such as biomass. The reaction is carried out in the absence of electrolytes and in the presence of a dispersed particulate heterogeneous catalyst. The reaction is carried out under pressure and relatively low temperature in a stirred tank reactor, preferably a continuous stirred tank reactor.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF NATURAL RESOURCES
Anaerobic biodegradation of unsaturated, saturated, aromatic and halogenated hydrocarbons
An apparatus and method for anaerobic biodegradation, bioremediation or bioprocessing of hydrocarbons dissolved in an aqueous matrix, such as wastewater, groundwater, or slurry. Dissolved alkanes (saturated hydrocarbons), alkenes (unsaturated hydrocarbons), aromatic hydrocarbons and / or halogenated hydrocarbons are metabolized or cometabolized. In one form, the invention involves introducing an aqueous stream comprising at least one dissolved aromatic hydrocarbon (such as benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, o-xylene, m-xylene, p-xylene, phenol, o-cresol, m-cresol, or p-cresol) and a dissolved oxide of nitrogen [such as nitrate (NO3-), nitrite (NO2-), nitric oxide (NO) and nitrous oxide (N2O)] to a reactor, and operating said reactor under conditions that support denitrification of the aromatic hydrocarbon. Alternatively, the aqueous stream may comprise at least one alkane (such as ethane) and / or at least one alkene (such as ethene or ethylene) and biodegradation of these compounds is accomplished. In a preferred form, the aqueous stream also comprises at least one dissolved halogenated hydrocarbon (such as tetrachloroethylene, trichloroethylene, or 1,1,1-trichloroethane) and dehalogenation of the halogenated hydrocarbon is accomplished. The reactor may be a continuous stirred tank reactor, a batch (or sequencing batch) reactor, a plug-flow reactor, a fixed-film reactor, or a pore space in an underground aquifer in situ. The reactor is operated in such a way that molecular oxygen is excluded from the space or zone in which the biodegradation is occurring and the other requirements of denitrifying bacteria are met. In some implementations, kinetic control (control of mean cell residence time) is used to enrich a denitrifying culture in the reactor.
Owner:YESTECH
Method and apparatus for manufacturing graphite oxide
ActiveUS20150108400A1Inhibitory responseImprove efficiencyOther chemical processesGraphiteUltrasound - actionProcess engineering
There is provided a method and an apparatus for preparing graphite oxide, in accordance with the present disclosure, when an oxidizer is added by stages into a sequencing batch oxidizer mixer connected in multiple stages at a constantly low temperature, the oxidizer is mixed therein while suppressing an oxidation reaction. During an oxidation reaction of graphite, in a risky range of overheating and explosion, a tube type reactor equipped within a heat exchanger is used to accurately control a local temperature and the oxidizer can permeate between layers of the graphite with increased efficiency under ultrasonication. In an additional reaction range out of the risky range, a continuous stirred tank reactor is used to mature the oxidation reaction, so that a risk of explosion during manufacturing of graphite oxide can be reduced and a great amount of graphite oxide can be mass-produced economically.
Owner:STANDARDGRAPHENE
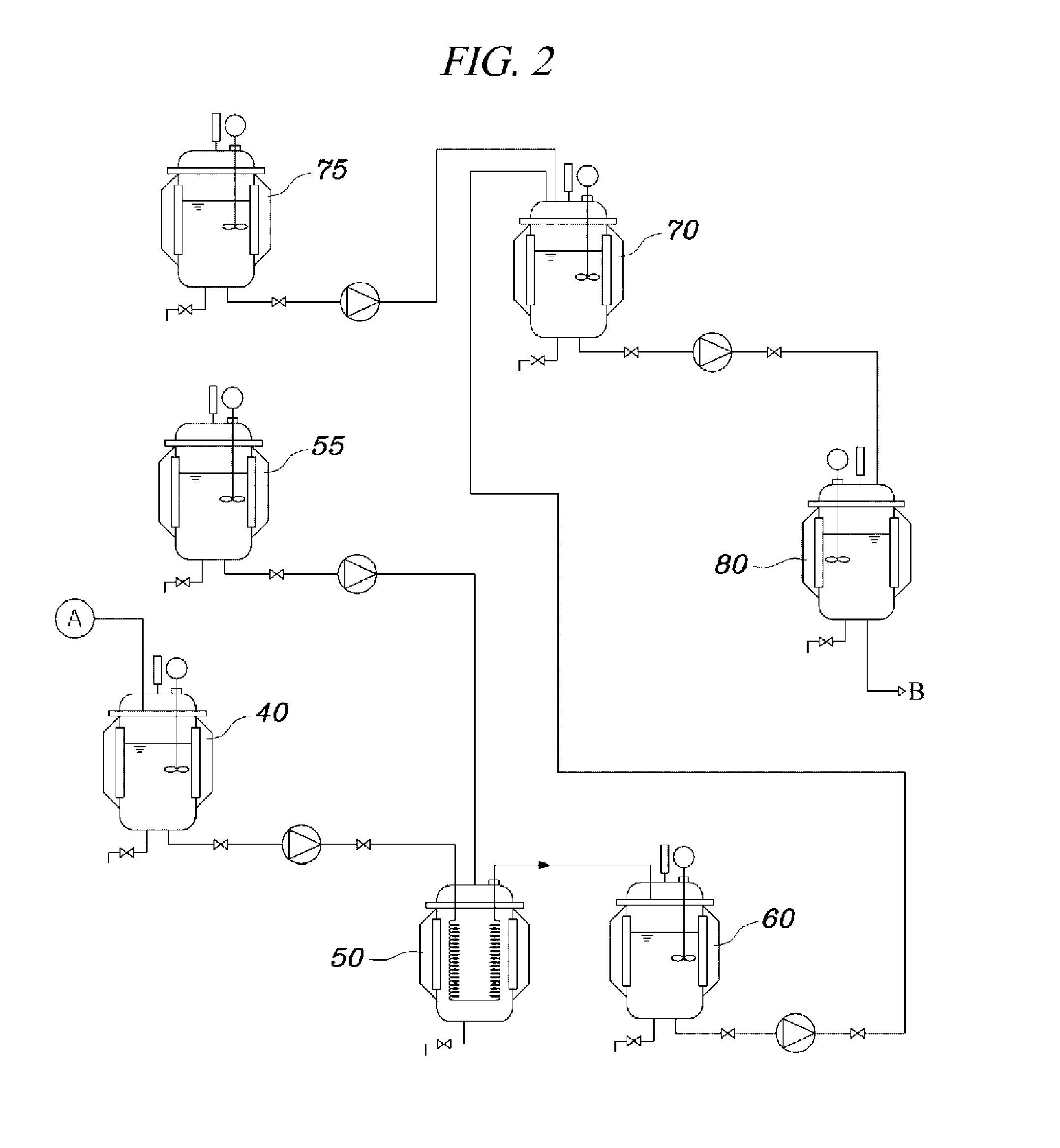
Methods and systems for pretreatment of an oil stream
In one embodiment, a method for pre-treating an oil comprises: introducing a oil, an alcohol, and an acid catalyst to a first continuous stirred tank reactor vessel, wherein the oil comprises free fatty acids; selectively reacting the oil and the alcohol to convert the free fatty acids to alkyl esters, wherein the reaction does not produce glycerol; removing a pre-treated oil stream from a lower portion of the first continuous stirred tank reactor, wherein the pre-treated oil stream comprises the alkyl esters; and recycling the alcohol and acid catalyst from an upper portion of the first continuous stirred tank reactor.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
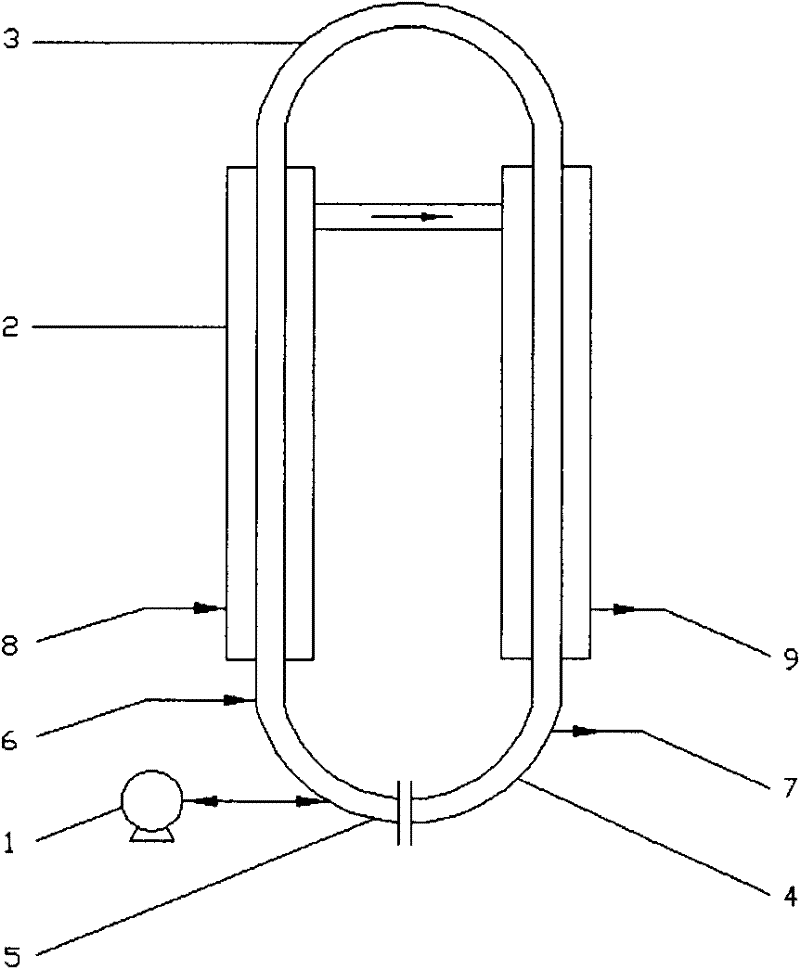
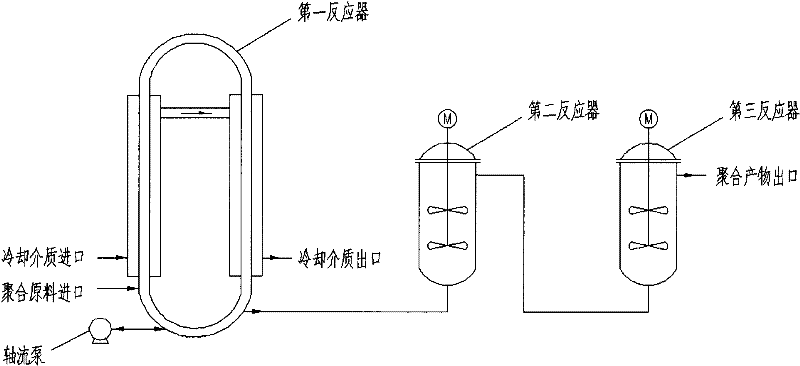
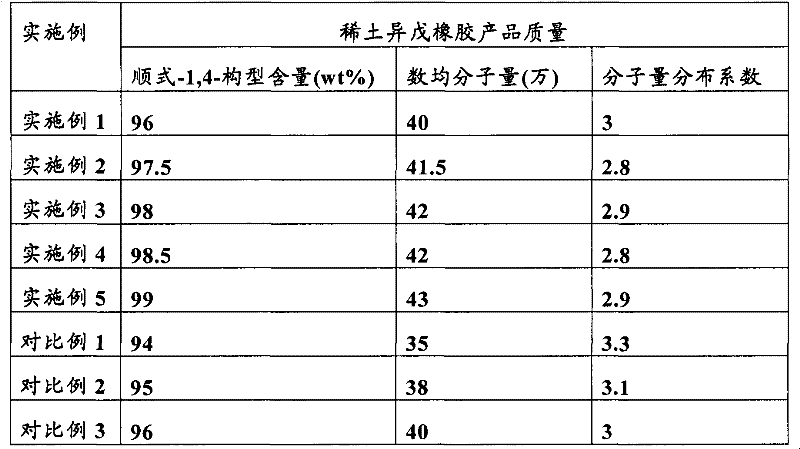
Polymerization method for preparing rare earth isoprene rubber
ActiveCN102532379AIncrease the heat exchange areaAvoid "hanging on the wall" phenomenonRare earthContinuous stirred-tank reactor
The invention relates to a polymerization method for preparing rare earth isoprene rubber, which adopts at least three reactors which are in series connection to conduct a solution polymerization reaction of an isoprene monomer, wherein a first reactor is an annular tube reactor which adopts isothermal operation, a following reactor is a continuous stirrer tank reactor which adopts heat insulation operation. By means of the method, the cis-form-1,4-configuration content of obtained gathering rare earth isoprene rubber can be high as 98wt%, the number-average molar mass can reach over 0.4 million, and molecular weight distribution coefficient is smaller than 3.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Agricultural organic waste anaerobic fermentation recovery biogas reaction apparatus and recovery method thereof
InactiveCN104130942ARelieve blockageRelieve blocked technical bottlenecksBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRecovery methodGeneration rate
The invention relates to an agricultural organic waste anaerobic fermentation recovery biogas reaction apparatus and a recovery method thereof. The apparatus comprises an acidogenic fermentation phase reactor and a methanogenic phase reactor, a filtering device exists between the acidogenic fermentation phase reactor and the methanogenic phase reactor, wherein the acidogenic fermentation phase reactor adopts a continuous stirred tank reactor, the methanogenic phase reactor adopts an anaerobic expanded granular sludge bed reactor with the ratio of height to diameter of 9:1-10:1, a filtering material made of a nylon filter screen or a polyethylene filter screen is arranged in the filtering device, the aperture size of the filter screen is 0.5-3mm, and a total volume ratio of the acidogenic fermentation phase reactor to the filtering device to the methanogenic phase reactor is 2.5-3.5:1:1. The apparatus and the method can improve the degradation efficiency of agricultural organic wastes in an anaerobic fermentation system, alleviate the bottlenecks of the obstruction technology of equipment and pipelines, reduce the fluctuation interference of northern low temperature environment to the whole anaerobic fermentation system, and improve the running stability and the biogas generation rate of the system.
Owner:HIT YIXING ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION +1
Integrated multi-model method for controlling CSTRs (continuous stirred tank reactors)
The invention discloses an integrated multi-model method for controlling CSTRs (continuous stirred tank reactors), applies to the control of nonlinear systems, especially first-order reaction CSTRs, and can ensure that the industrial process can quickly, accurately and stably transit from a stable operating point to another stable operating point. Since effect of control feedback on the dynamic characteristics of the system is considered, compared with the existing multi-model method for controlling the first-order reaction CSTRs, the method has particularly notable advantages.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
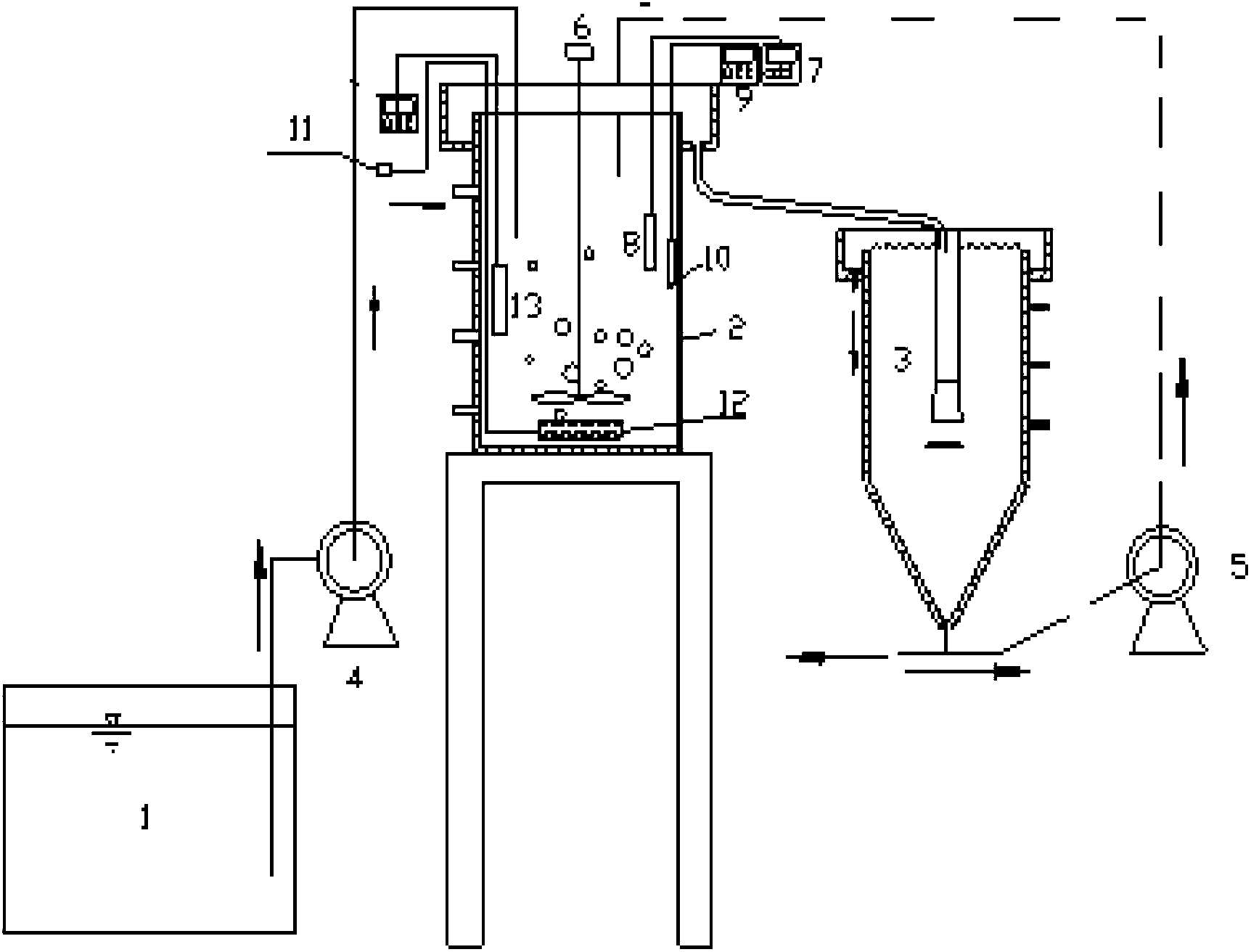
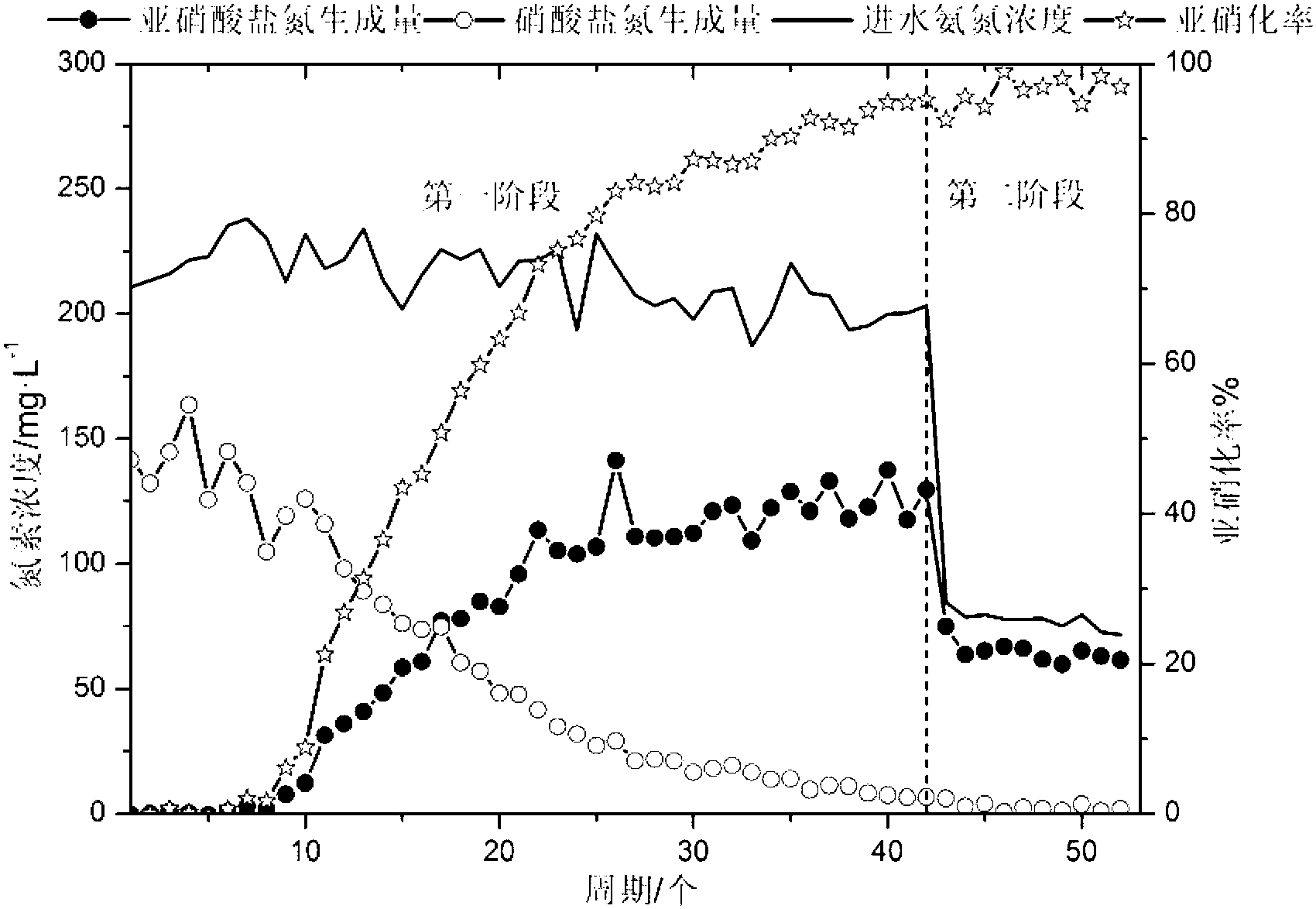
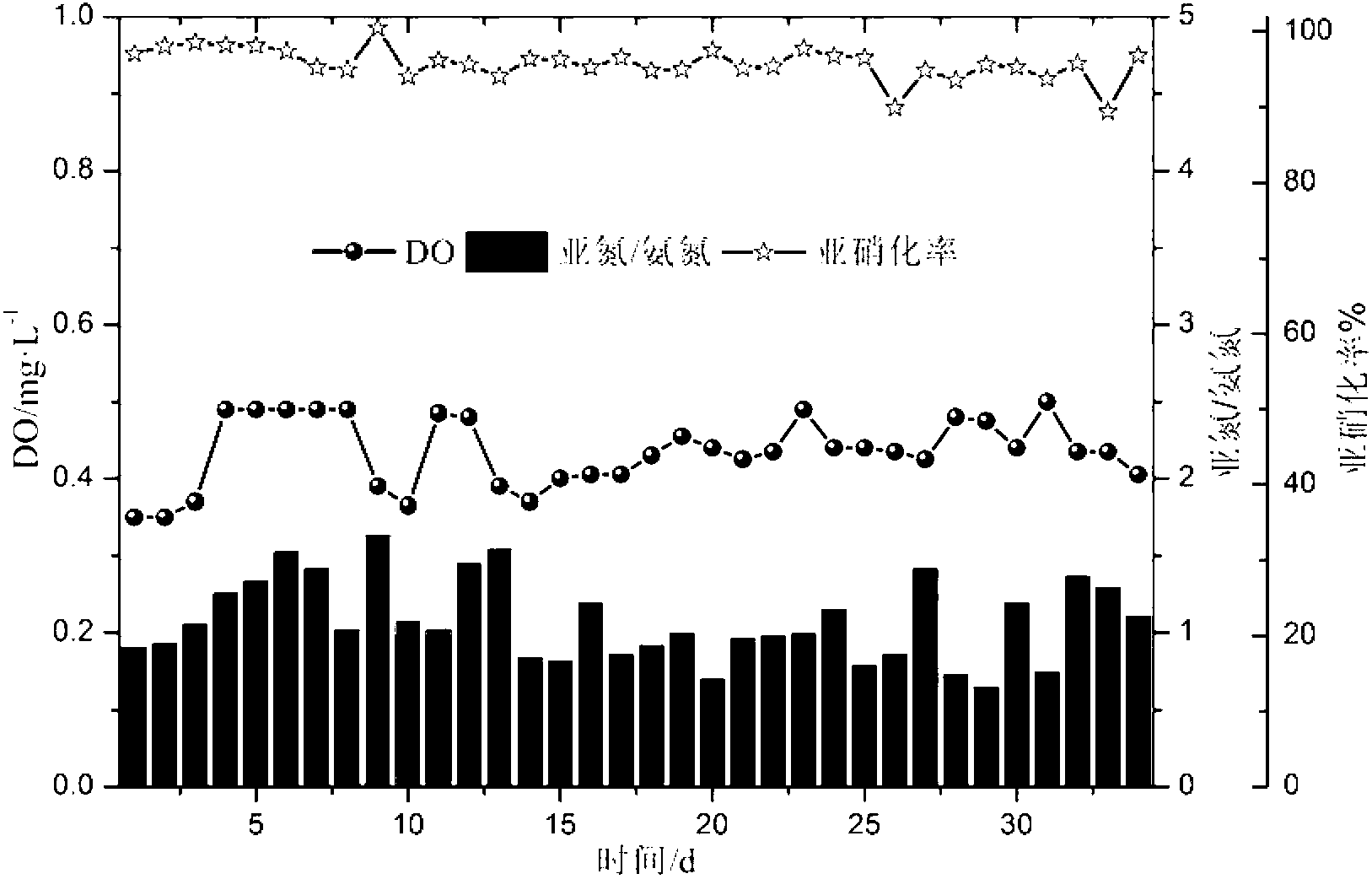
Method for regulating and controlling nitrogen proportion of partial nitrosation effluent of low-ammonia-nitrogen continuous stirred-tank reactor (CSTR) at normal temperature
ActiveCN102701441ALow costReduce volumeWater contaminantsTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesActivated sludgeSequencing batch reactor
The invention provides a method for regulating and controlling nitrogen proportion of partial nitrosation effluent of low-ammonia-nitrogen continuous stirred-tank reactor (CSTR) at normal temperature and belongs to the field of municipal wastewater treatment and recycling. The starting is performed in a four-stage mode, and 80%-100% of ammoxidation load in the low-ammonia-nitrogen operation period of sequencing batch reactor activated sludge process (SBR) serves as initial ammoxidation load of the CSTR to confirm hydraulic retention time (HRT) of the CSTR. DO / ALR serves as an iconic parameter for maintaining a nitrosation system, and a value of the iconic parameter is recommended to be not greater than 1.0 mgO2 / gNd and is regarded as the regulating and controlling standard of the DO and the HRT. First, the HRT is constant, the DO is controlled singly, if the proportion is not reached or the ammoxidation load is not enough, the DO and the HRT can be regulated and controlled synchronously. The NO2--N / NH4+-N and ammonia-nitrogen oxidation rate (a) / nitrite nitrogen generating rate (b) and nitrite nitrogen generating rate (b) / nitrate nitrogen generating rate (c) of the effluent are compared. If an average value of the proportions of the effluent under the different working conditions is in a range of 1-1.32:1, when b / a is greater than 0.9 and more approximates to 1.0, b / c is greater, and the working condition is more suitable for long-term operation of the system. The NO2--N / NH4+-N of the effluent of the CSTR is guaranteed to be in a range of 1-1.32:1 so as to meet the water feeding requirement of an anaerobic oxidation technology.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
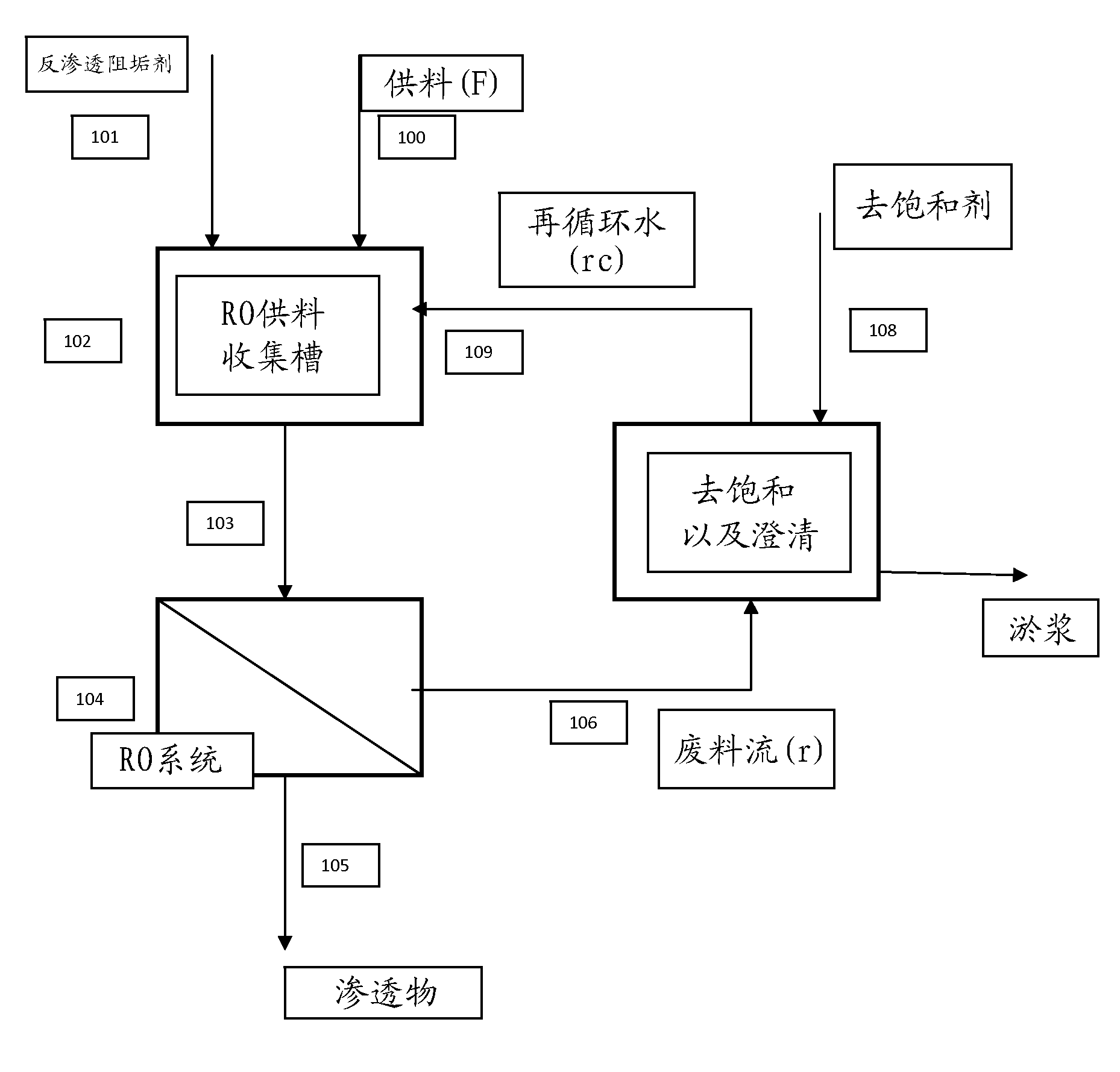
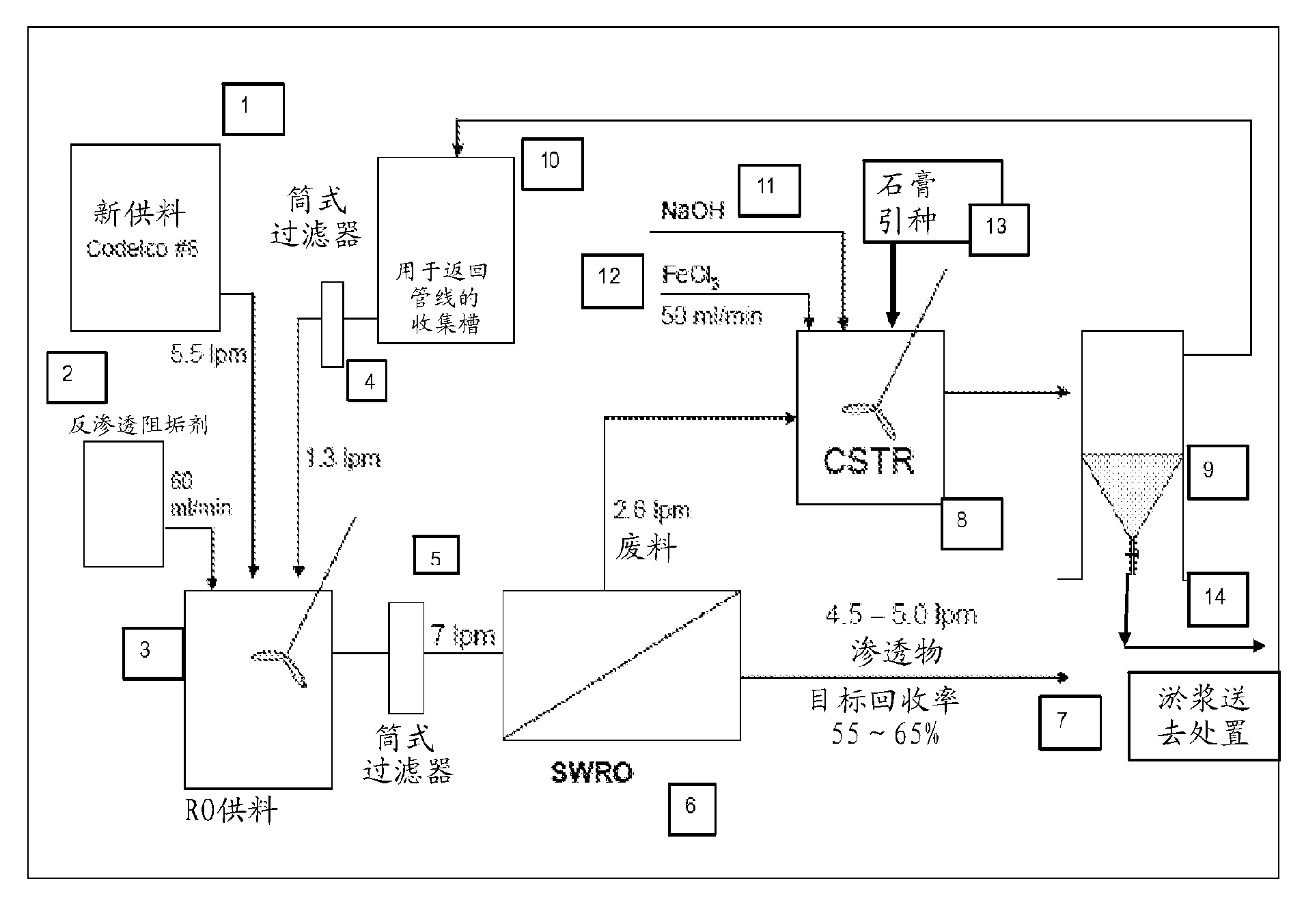
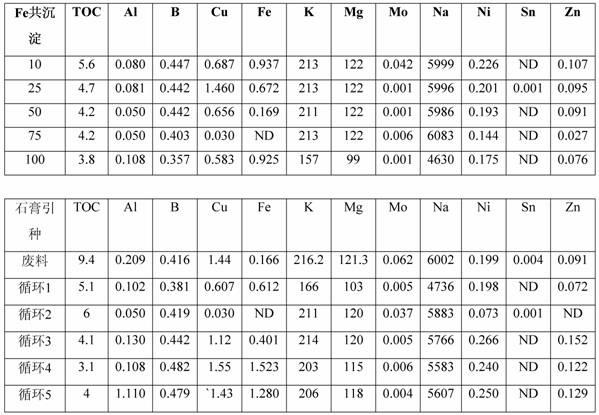
High recovery sulfate removal process
InactiveCN102216224AWaste water treatment from quariesWater treatment parameter controlSludgeWaste stream
A high recovery sulfate removal process comprises treating a feed water stream conditioned with antiscalant from a source with a reverse osmosis membrane system to produce a purified water permeate stream and a reject stream containing the retained or rejected ions and organic matter. The reject stream is further treated to remove dissolved and suspended species. The reject stream flows to a desaturation / clarification process. A preferred process includes a constant stirred tank reactor (CSTR) where co - precipitation agent is added followed by a clarifier. Water recycled from the clarifier overflow is blended with feed water stream. The removed solids are collected as sludge or a slurry and disposed of in a manner consistent with applicable regulations.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH PTE LTD
Variable-search-space ribonucleic acid (RNA) genetic algorithm modeling method for continuous stirred tank reactor
ActiveCN103177291ASimple structureImprove generalization abilityGenetic modelsBiological neural network modelsNerve networkNetwork model
The invention discloses a variable-search-space ribonucleic acid (RNA) genetic algorithm modeling method for a continuous stirred tank reactor. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) respectively performing dimension removal normalization processing on each group of input data and corresponding output data which are acquired by the continuous stirred tank reactor, wherein the input data comprise cyclic coolant temperature and material inlet flow in an inner clamping sleeve of the continuous stirred tank reactor, and the output data comprise reactant concentration conversion rate to be monitored; (2) constructing a radial basis function (RBF) nerve network model of the continuous stirred tank reactor according to the input data and the output data which are subjected to dimension removal normalization processing, wherein a basis function in the RBF nerve network model is a thin plate spline function; and (3) based on the input data and the output data which are subjected to dimension removal normalization processing, optimizing values of hidden layer node numbers and basis function central points in the RBF nerve network model by a variable-search-space RNA genetic algorithm, so that the output error of the RBF nerve network model is minimum, wherein a weight value of an output layer of the RBF nerve network model is obtained by a recursive least-squares method during optimization.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methane recycling treatment system having high-efficiency purification function
PendingCN104745258ARealize resource utilizationFully contactedDispersed particle separationGaseous fuelsElectric controlDistributor
The invention discloses a methane recycling treatment system having a high-efficiency purification function; the methane recycling treatment system comprises a straw storage warehouse, a rapid degrading tank, a hydrolysis tank, an independent heat exchanger, a CSTR (Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor) integrated reactor, a methane purification device, a leaf fertilizer warehouse, a biogas slurry temporary storage tank, a solid-liquid separator and an organic fertilizer warehouse; the methane purification device comprises a desulfuration device, a decarbonisation device, a dehydration device, a compressor, a gas storage tank, a pipeline and a valve; the desulfuration device is used for removing H2S in methane by adopting an alkaline solution spraying method; methane and an alkaline solution are respectively dispersed through a gas uniform distributor and a liquid uniform distributor; H2S gas in the methane is sufficiently reacted with the alkaline solution through two-stage reaction plates; by means of the decarbonisation device, CO2 gas can be sufficiently contacted with the alkaline solution effectively; furthermore, a new alkaline solution is provided in real time by utilizing a sensor and an electric control valve, and the concentration of the alkaline solution is ensured, so that higher decarbonisation efficiency is ensured.
Owner:TIANZI ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION INVESTMENT HLDG LIMITED
Multistage moving bed biomembrane reactor
InactiveCN101870542ASimple structureAvoid hydraulic congestionMultistage water/sewage treatmentStationary phaseMoving bed biofilm reactor
The invention relates to a multistage moving bed biomembrane reactor belonging to devices for treating urban domestic sewage, medium and low-concentration chemical wastewater and food wastewater. The multistage moving bed biomembrane reactor is mainly used for treating the urban domestic sewage, the medium and low-concentration chemical wastewater and the food wastewater and comprises a plurality of aeration basins partitioned by partition boards, the length-width ratios of the aeration basins vary with the change of the types of sewage to be treated, and a novel suspending carrier, an aeration device, a mud discharging tube, a water inlet tube and an overflow weir are respectively arranged in each aeration basin. The reactor integrates the advantages of a plug flow reactor and a continuous stirred tank reactor, not only prevents the phenomenon of filler accumulation in the plug flow reactor, but also solves the problems that because the sewage concentrations at the water inlet end and the water outlet end in the continuous stirred tank reactor are approximate, microorganisms are always in a logarithmic phase or a stationary phase, and the maturation of the microorganisms are insufficient, which causes a poor treatment effect. The invention has the advantages of simple structure, science and reasonability, high treatment efficiency, stable water discharge, wide application range and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Soft measurement method of reactant concentration in a continuous stirred tank reactor based on positive-strand RNA-GA and meter thereof
InactiveCN101587113AStrong online correction abilityImprove real-time performanceComputer simulationsMaterial analysisAfter treatmentGenetic algorithm
The invention discloses a soft measurement method of reactant concentration in a continuous stirred tank reactor based on positive-strand RNA-GA and meter thereof, which is used for solving the problem of variable on-line estimation that on-line real-time measurement is difficultly carried out by using a sensor or analysis meter in the process of a continuous stirred tank reactor. The on-site collected input / output data in various working conditions is used as sample data of RBF neural network after treatment; the Centroid and the weight of the RBF neural network are optimized by using genetic algorithm based on positive-strand RNA so as to obtain the optimal neural network soft measurement model; and the on-line real-time measurement of reactant concentration in a continuous stirred tank reactor is realized by using the soft measurement model. The invention has high precision and real-time performance, and provides necessary conditions for efficiently optimizing and controlling the continuous stirred tank reactor in advanced manner.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
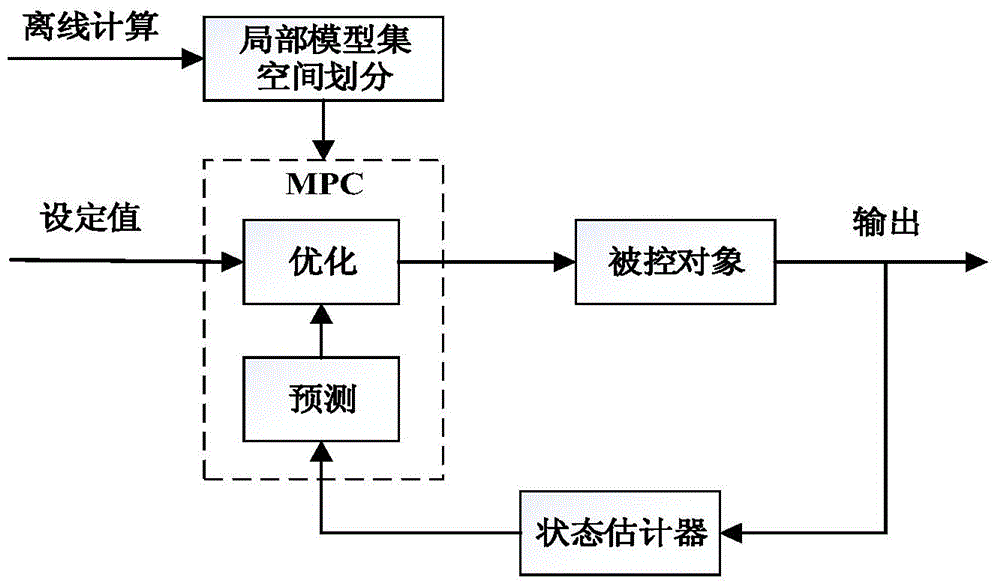
Multi-target hierarchical prediction control method based on continuous stirred tank reactor
ActiveCN104536294AEnhanced inhibitory effectHandling Model AccurateAdaptive controlAlgorithmControl system
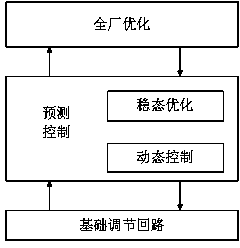
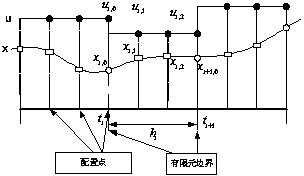
The invention discloses a multi-target hierarchical prediction control method based on a continuous stirred tank reactor. According to the control method, a double-layer prediction control algorithm is introduced and changes the situation that in the control process of the CSTR, only a dynamic control target is controlled, and economic indexes are ignored. In the control process, a two-level hierarchical prediction control structure is adopted, an expansion Kalman observer is introduced in a dynamic control layer to perform unbiased estimation on the state, a multi-target hierarchical optimization is adopted in a steady-state optimization layer, and important optimization targets are met preferentially. Meanwhile, a finite element orthogonal configuration method is adopted in a whole control system so that a nonlinear optimization control proposition can be converted into a nonlinear programming problem, a model equation serves as a constraint condition, values on configuration points serve as prediction values, a prediction model can be obtained without linearization or step response, and therefore linear errors can be avoided, and integral objects need to be independently processed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
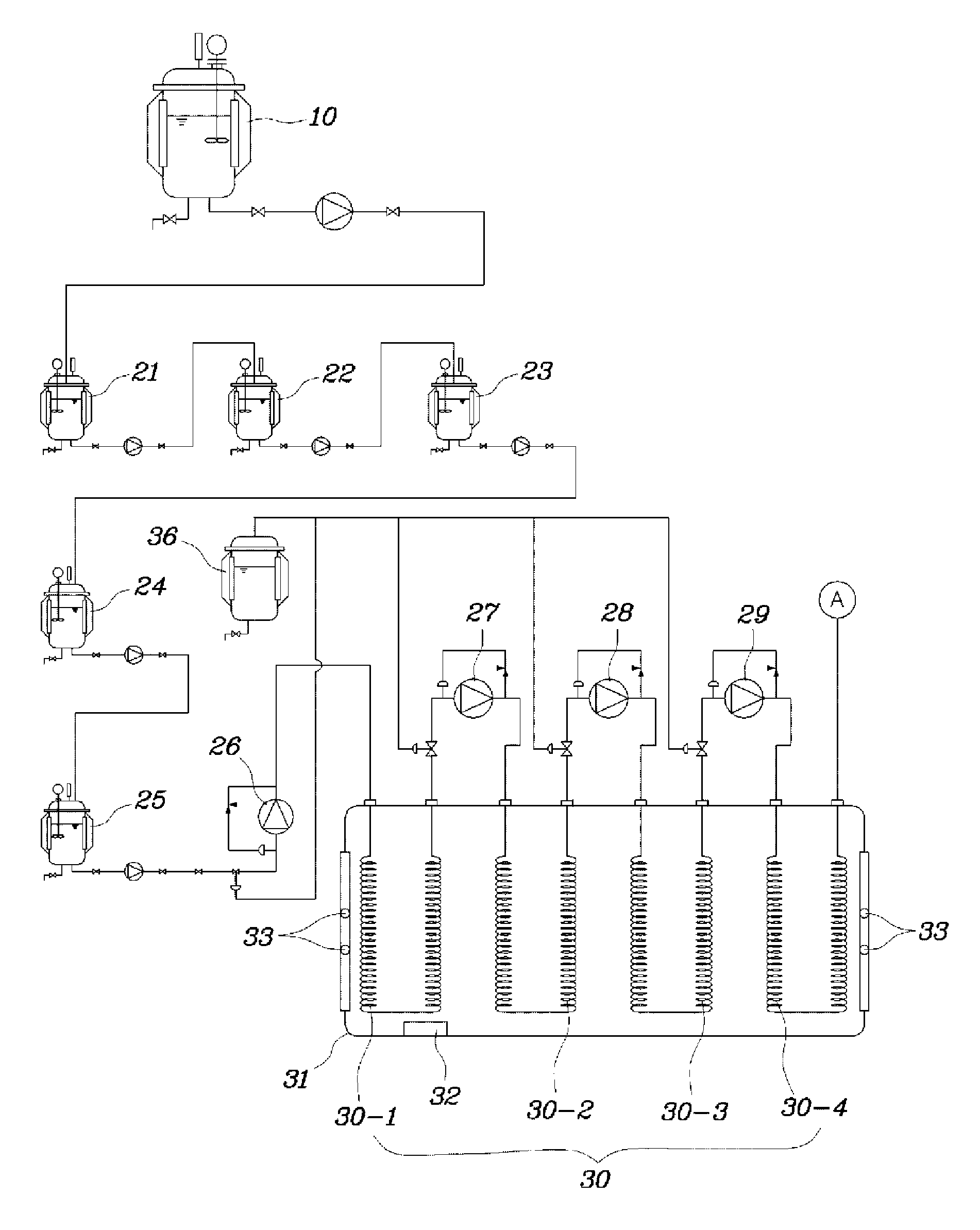
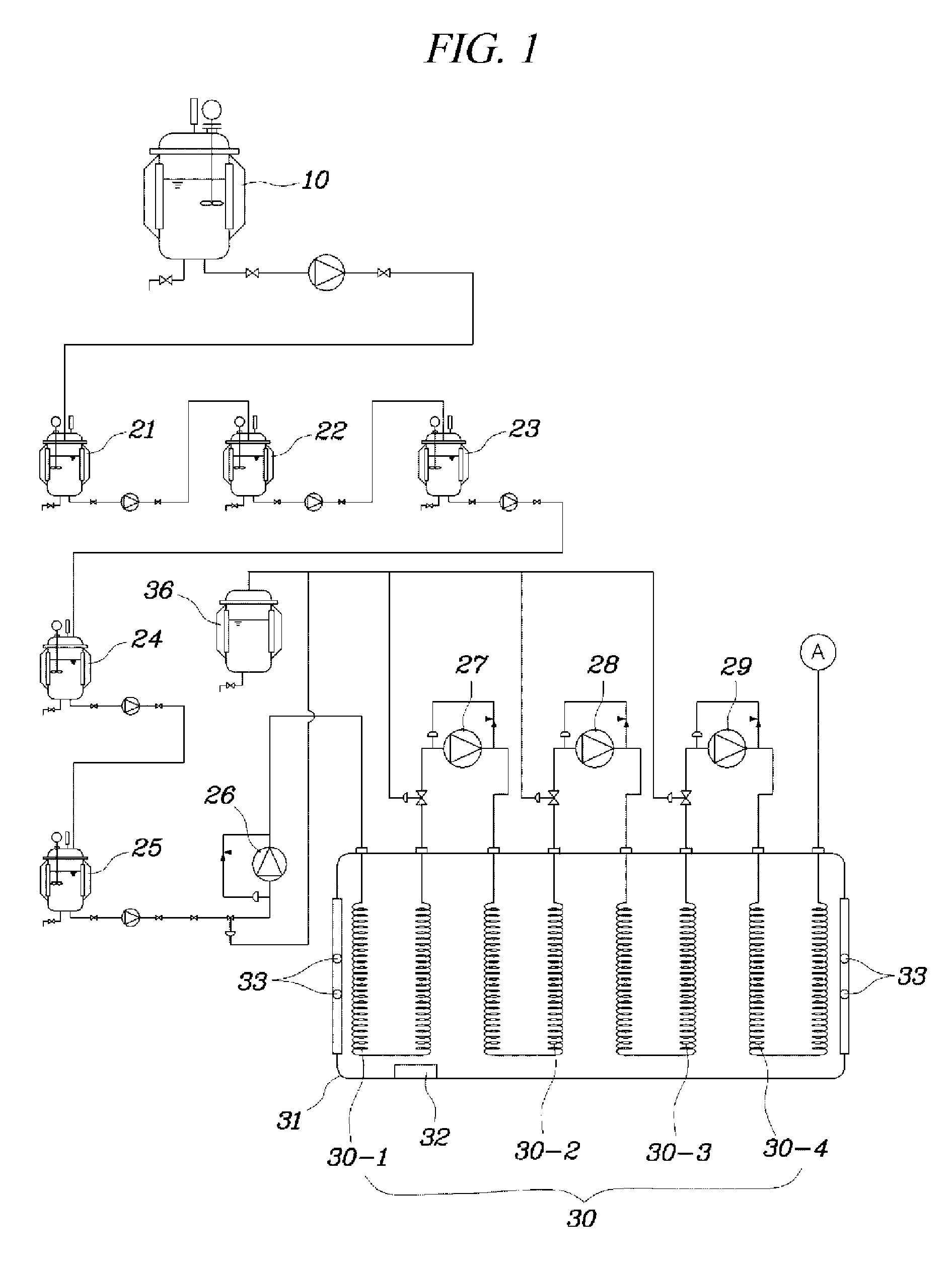
Continuous tank reactor and continuous tank reaction system with n-butyllithium participating in production
InactiveCN107537423AReduce drippingReduce operational riskLithium organic compoundsChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsChemical reactionN-Butyllithium
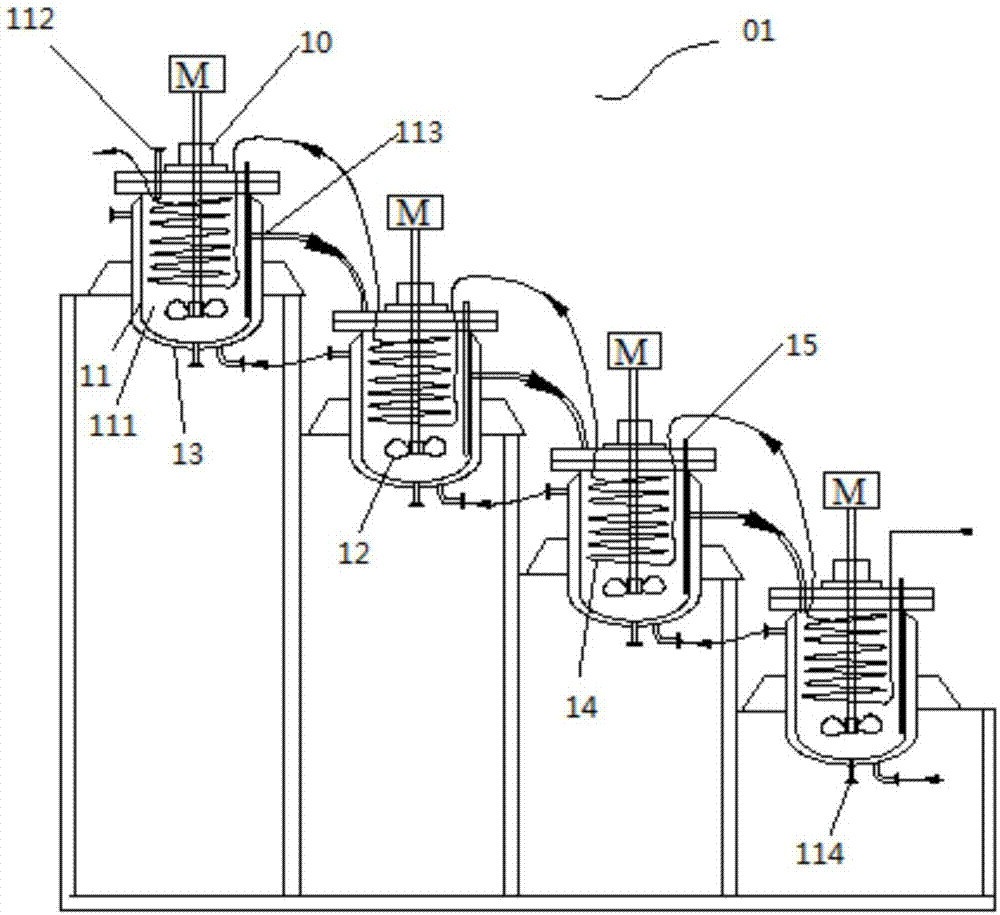
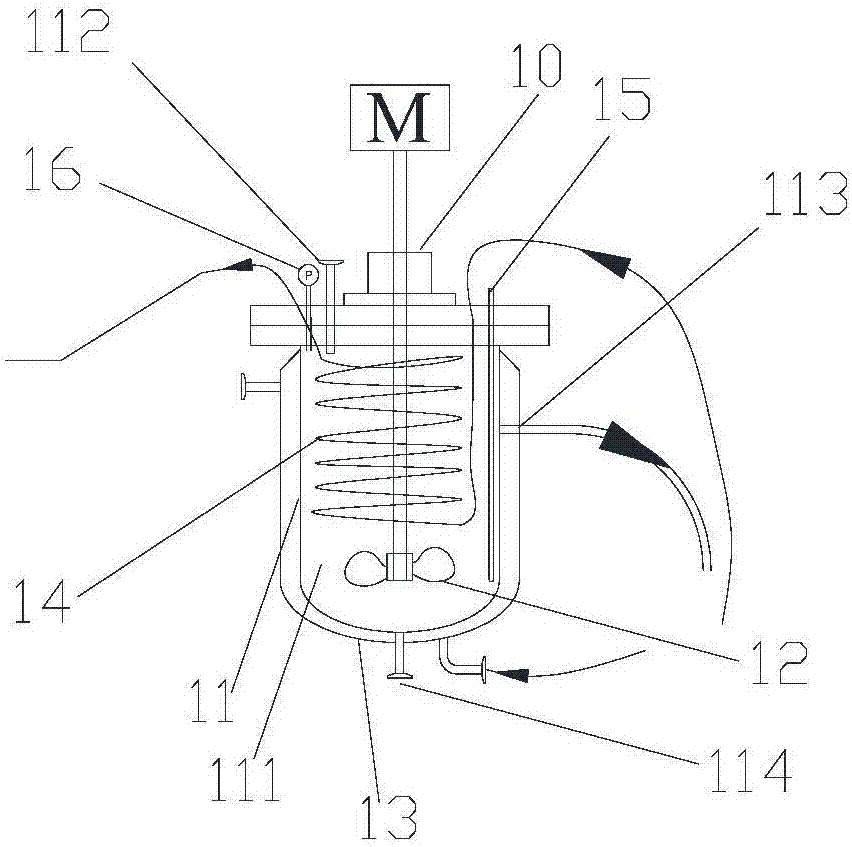
The invention provides a continuous tank reactor and a continuous tank reaction system with n-butyllithium participating in production. The continuous tank reactor comprises N continuous reaction kettles successively connected in series. Each continuous reaction kettle comprises a body, which has a reaction chamber, a feed inlet, an overflow mouth and a discharge port. N is a natural number whichis greater than or equal to 2. The overflow mouth of the N-1 continuous reaction kettle is communicated with the feed inlet of the N continuous reaction kettle. The continuous tank reactor issuitable for chemical reactions with chemical substances having active chemical properties such as n-butyllithium, etc. participating in the reactions. In actual production, an appropriate number of the continuous reaction kettles can be selected according to the need of reacting dose for a continuous reaction. Thus, lots of reaction raw materials transferred at a time or dropwise added for a longtime in single-kettle batch production are reduced, reaction operational risk is reduced, and safety and reaction efficiency are enhanced.
Owner:ASYMCHEM LIFE SCI TIANJIN
Method for producing size selected particles
ActiveUS20140341797A1Improve featuresHigh tap densityCell electrodesLiquid-gas reaction processesSufficient timeProcess engineering
The invention provides a system for preparing specific sized particles, the system comprising a continuous stir tank reactor adapted to receive reactants; a centrifugal dispenser positioned downstream from the reactor and in fluid communication with the reactor; a particle separator positioned downstream of the dispenser; and a solution stream return conduit positioned between the separator and the reactor. Also provided is a method for preparing specific sized particles, the method comprising introducing reagent into a continuous stir reaction tank and allowing the reagents to react to produce product liquor containing particles; contacting the liquor particles with a centrifugal force for a time sufficient to generate particles of a predetermined size and morphology; and returning unused reagents and particles of a non-predetermined size to the tank.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Generalized prediction control algorithm of continuous stirring tank reactor system
InactiveCN107092188AAvoiding Derivative ProblemsReduce computing timeAdaptive controlReactor systemNonlinear model
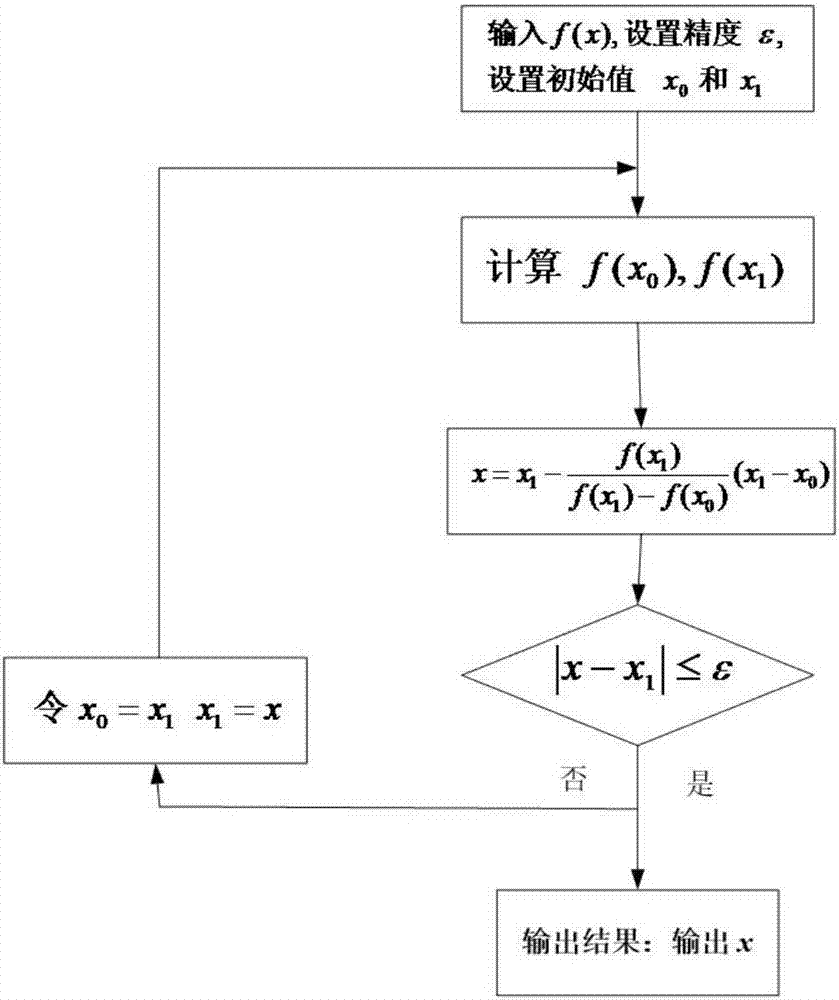
The invention relates to a generalized prediction control algorithm of a continuous stirring tank reactor system. A nonlinear model is established for the continuous stirring tank reactor system and is converted into an output prediction model based on a U model. A reference trajectory is set, the generalized prediction control of the output prediction model is carried out, and a pseudo input of the system is obtained. Then a secant method is used to carry out iterative calculation to obtain an actual input of the system. According to the generalized prediction control algorithm, the combination of the secant method and the U model is used, thus when a nonlinear equation about the actual input is solved, a derivation problem in using a Newton iterative algorithm is avoided, the computation time is reduced, at the same time the convergence rate is fast, and a nonlinear system control design problem is simplified.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
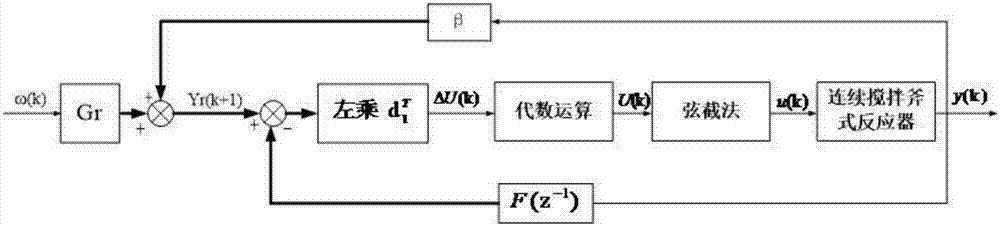
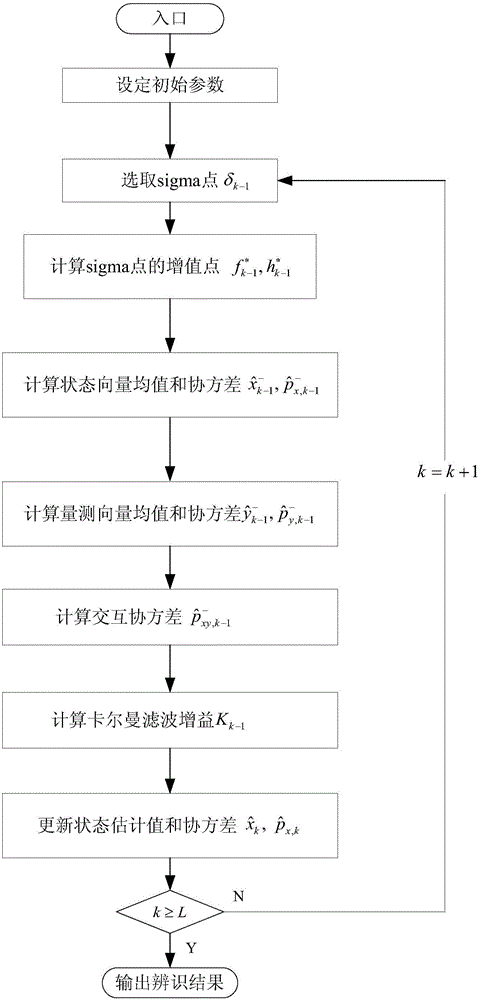
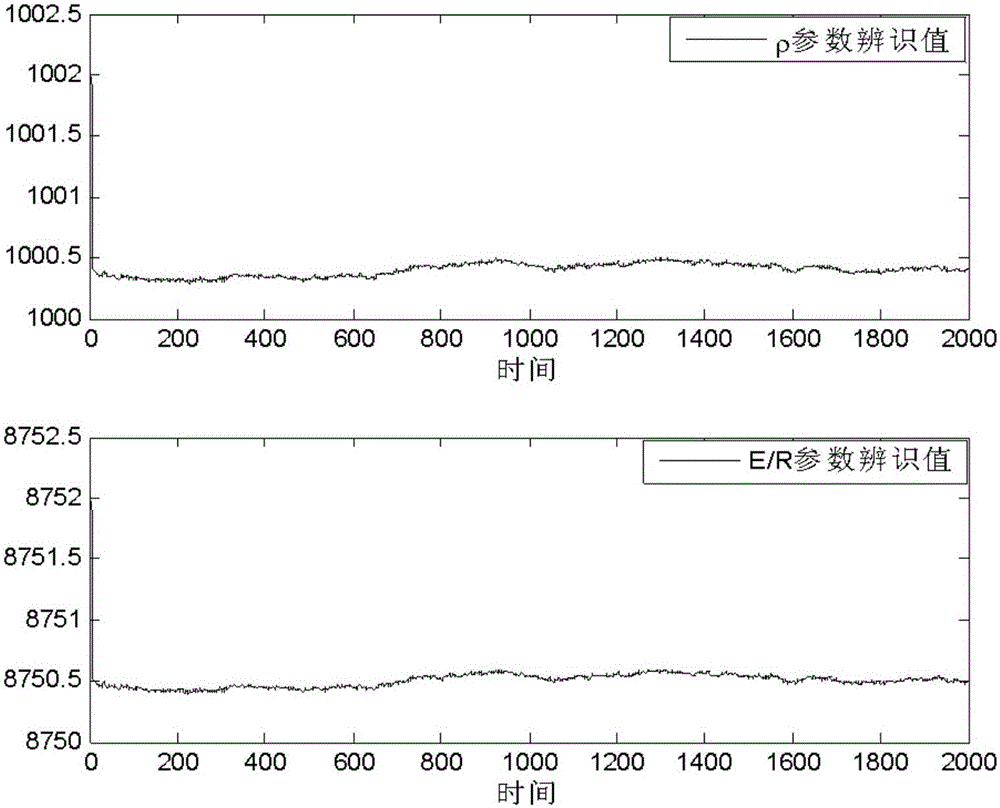
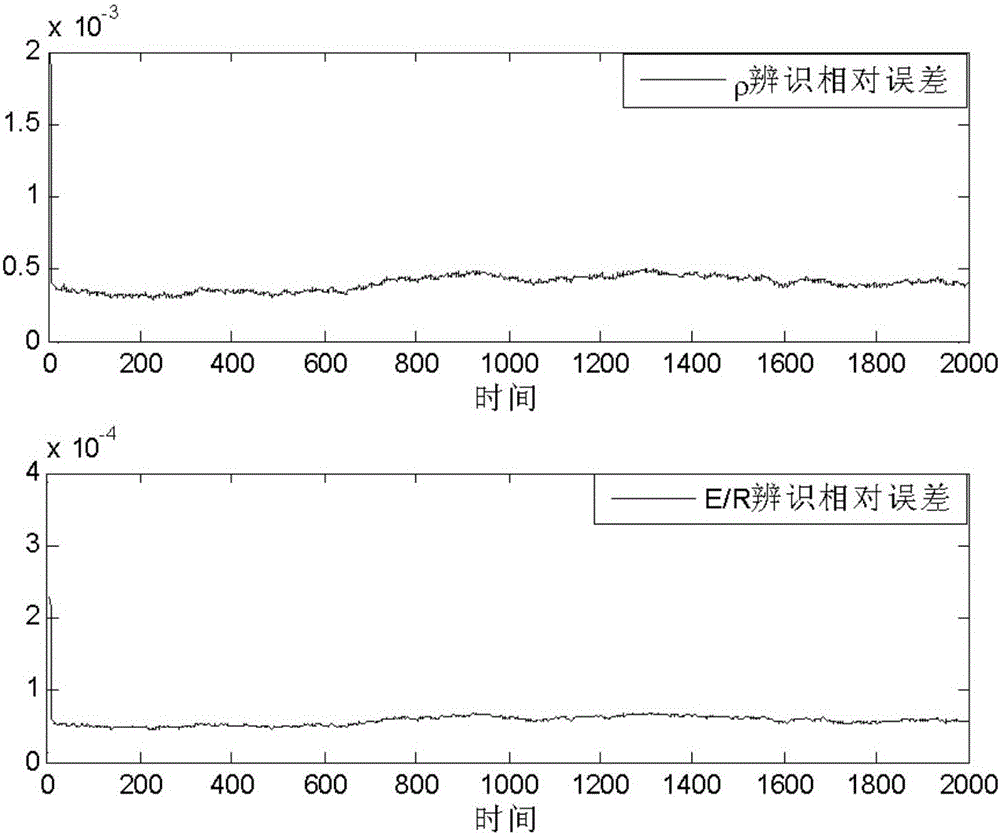
CSTR (Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor) model parameter identification method based on unscented Kalman filtering algorithm
InactiveCN105975747AOvercoming divergenceImprove efficiencyInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmAlgorithm convergence
The invention discloses a CSTR (Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor) model parameter identification method based on an unscented Kalman filtering algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: according to a CSTR continuous system model, obtaining a state spatial expression of which the state component contains a parameter to be identified; then, in virtue of an Euler algorithm, carrying out discretization processing on the obtained non-linear continuous state spatial expression to obtain a corresponding discrete iteration model; and finally, applying the unscented Kalman filtering algorithm to carry out multi-time iteration identification, and obtaining an accurate identification result. The algorithm has good astringency, is easy in combining with traditional software and has a good engineering application prospect.
Owner:BOHAI UNIV
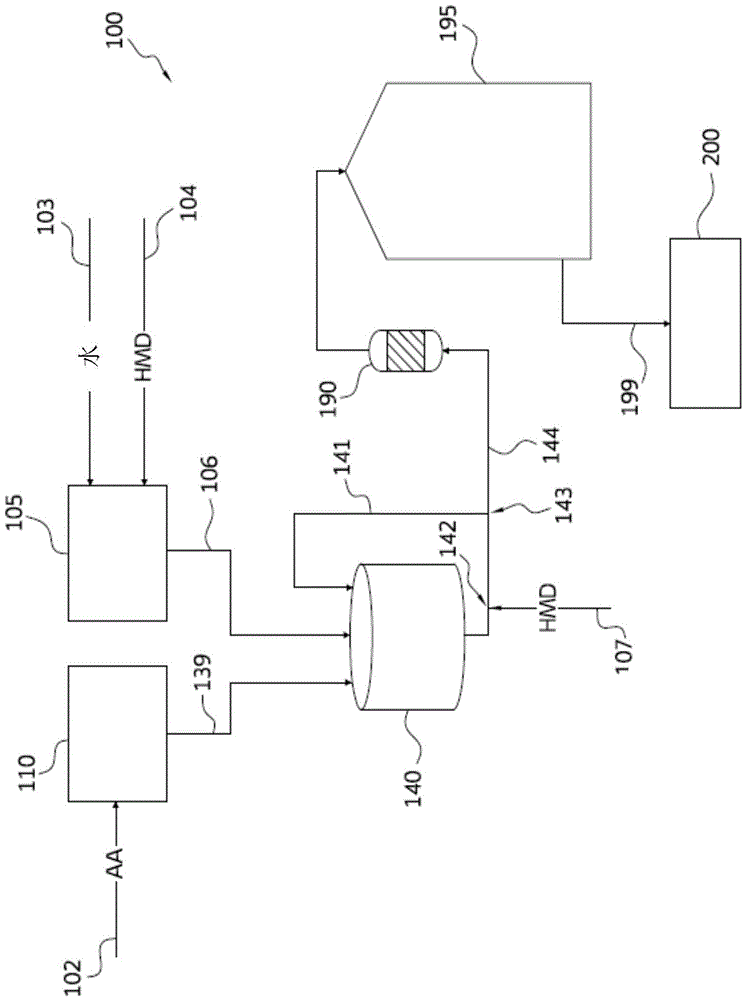
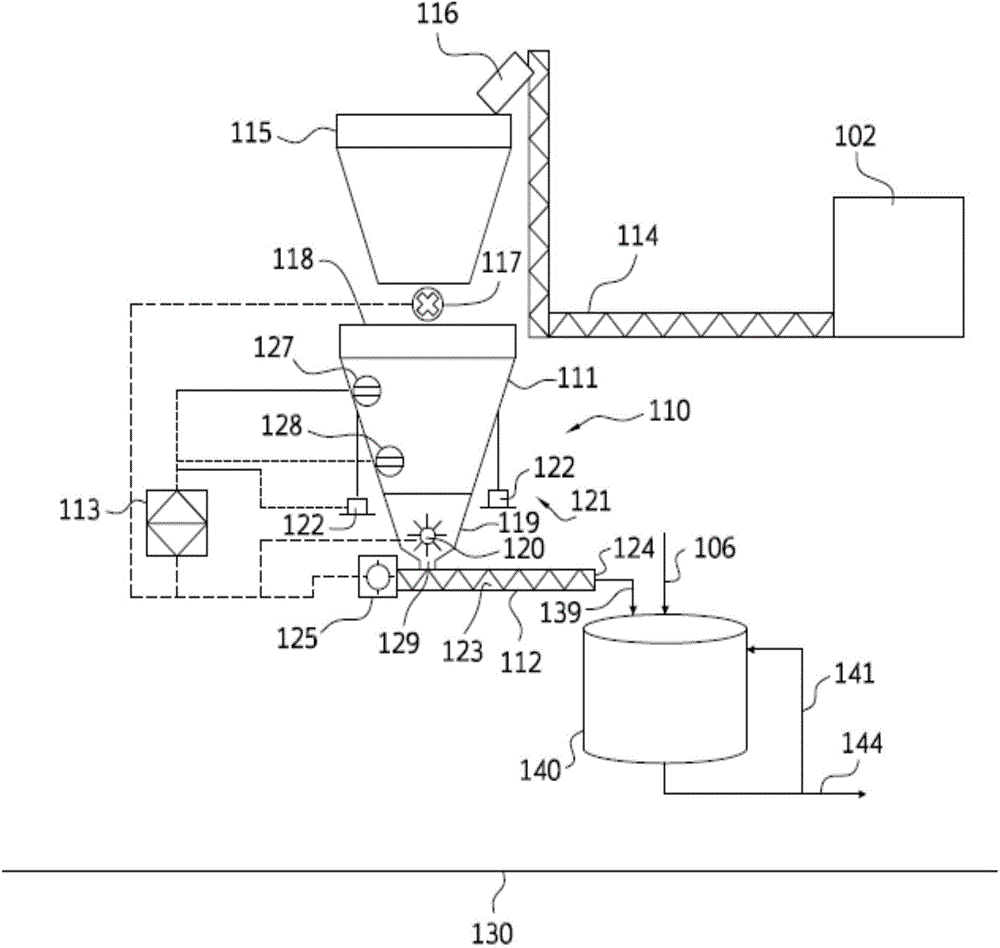
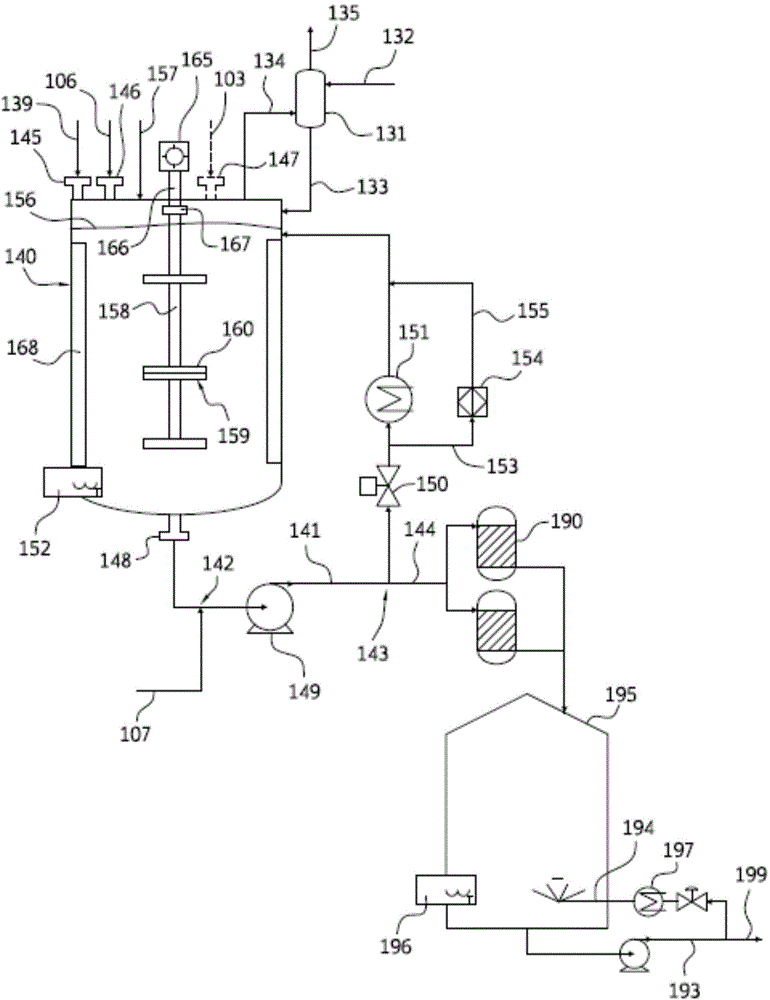
Nylon salt solution preparation processes with trim diamine
ActiveCN104130396AAmino preparation from aminesOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acidDicarboxylic acid
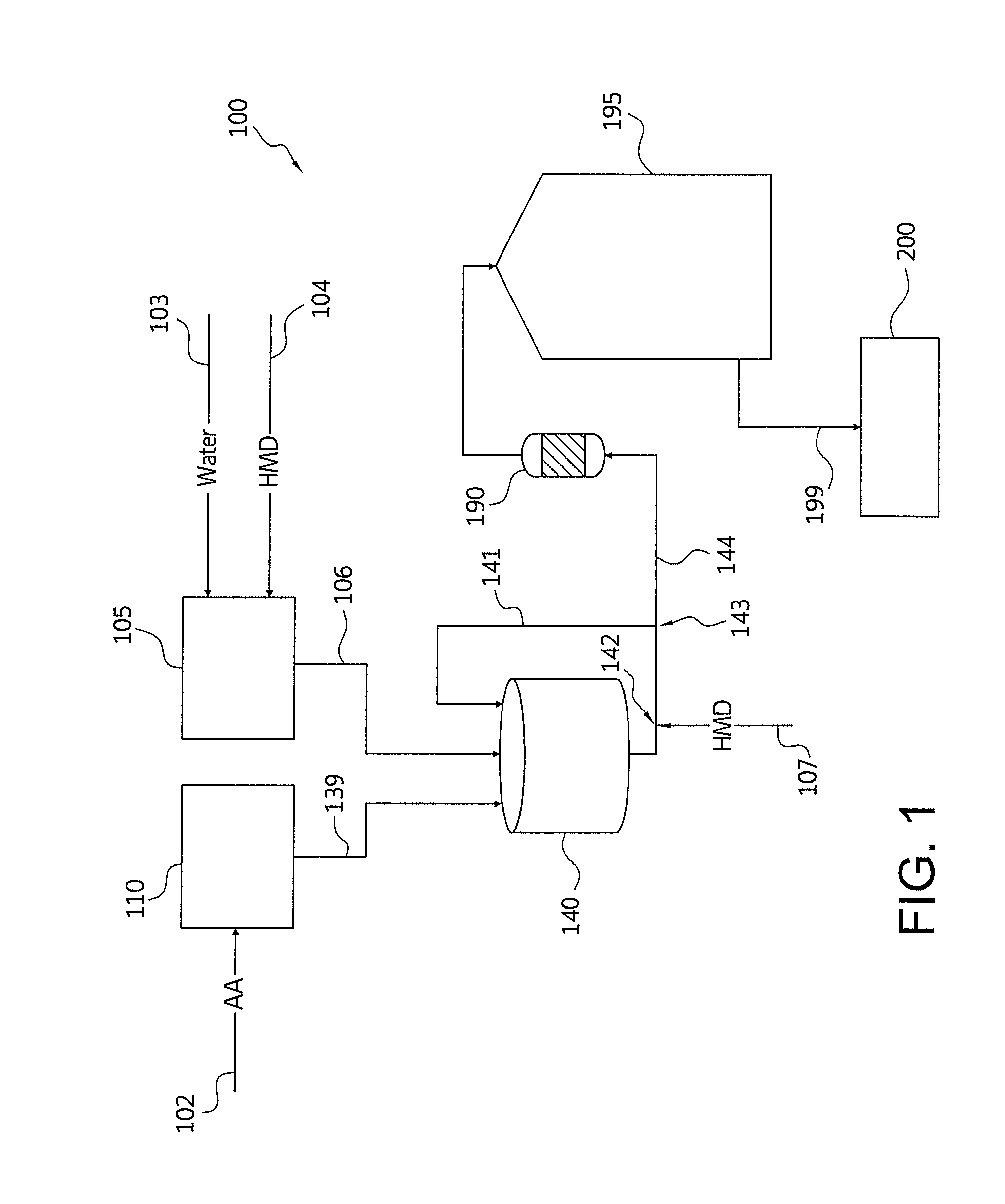
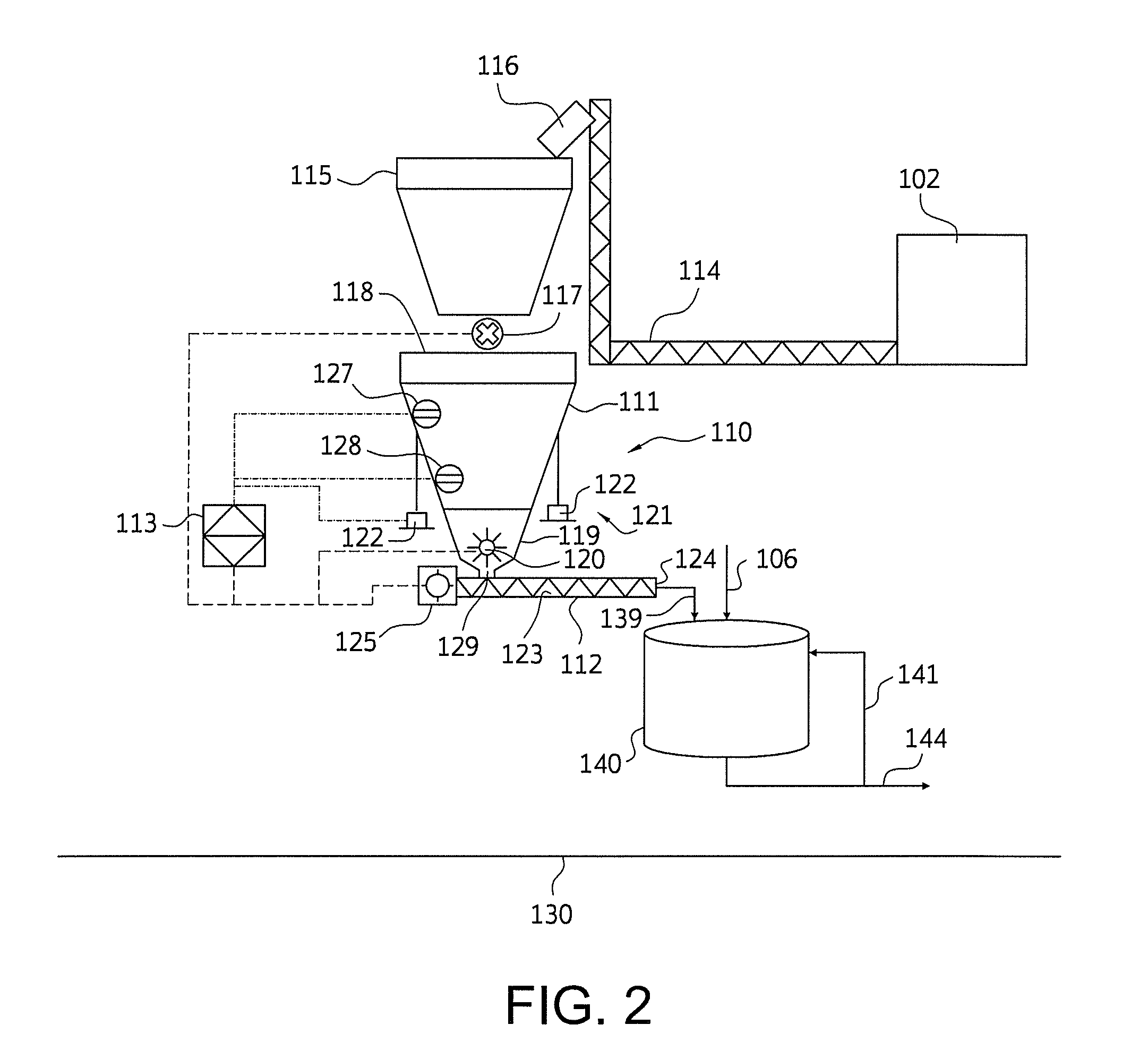
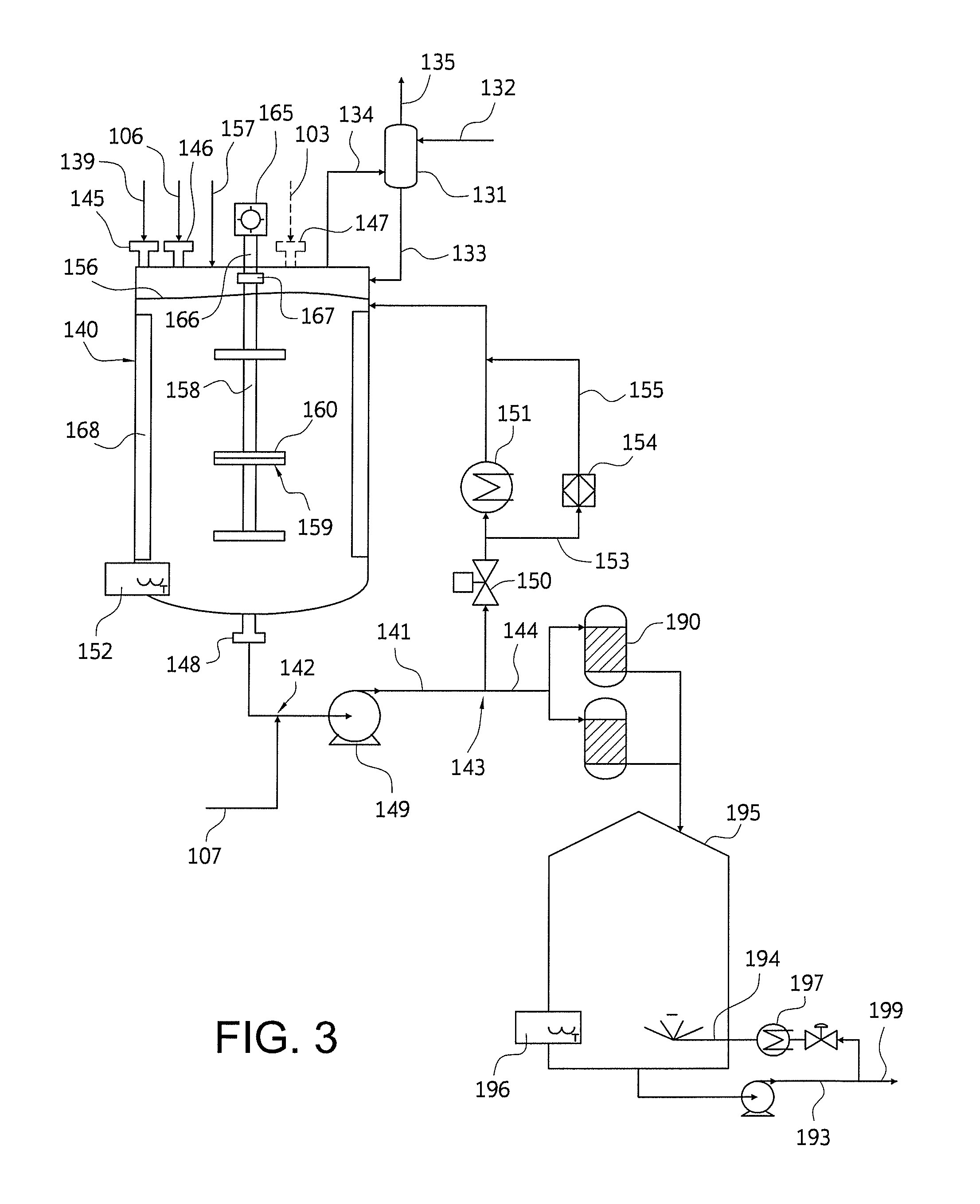
Disclosed are nylon salt solution preparation processes including a trim diamine feed. The nylon salt solution is prepared by feeding a dicarboxylic acid monomer and a diamine monomer to a single continuous stirred tank reactor. The dicarboxylic acid is metered, based on weight, from a loss-in-weight feeder to the reactor. The nylon salt solution is formed continuously and has low variability from a target pH and / or a target salt solution concentration. The nylon salt solution is transferred directly to a storage tank, without further monomer addition, pH adjustment, or salt solution adjustment after exiting the continuous stirred tank reactor.
Owner:INVISTA TEXTILES (U K) LTD
Nylon salt solution preparation processes with trim diamine
InactiveUS20160075827A1Amino preparation from aminesOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acidDicarboxylic acid
Disclosed are nylon salt solution preparation processes including a trim diamine feed. The nylon salt solution is prepared by feeding a dicarboxylic acid monomer and a diamine monomer to a single continuous stirred tank reactor. The dicarboxylic acid is metered, based on weight, from a loss-in-weight feeder to the reactor. The nylon salt solution is formed continuously and has low variability from a target pH and / or a target salt solution concentration. The nylon salt solution is transferred directly to a storage tank, without further monomer addition, pH adjustment, or salt solution adjustment after exiting the continuous stirred tank reactor.
Owner:INVISTA NORTH AMERICA R L
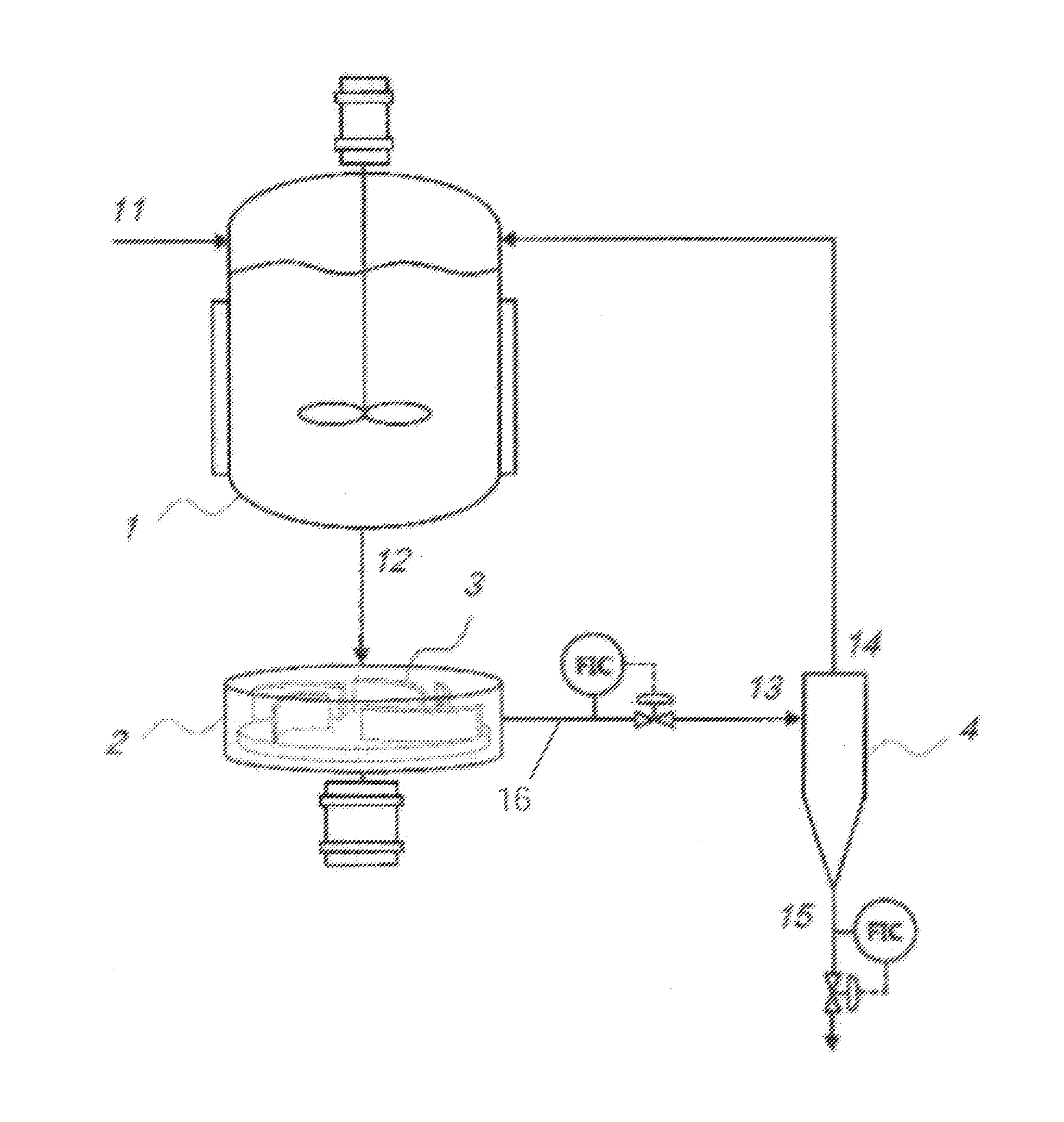
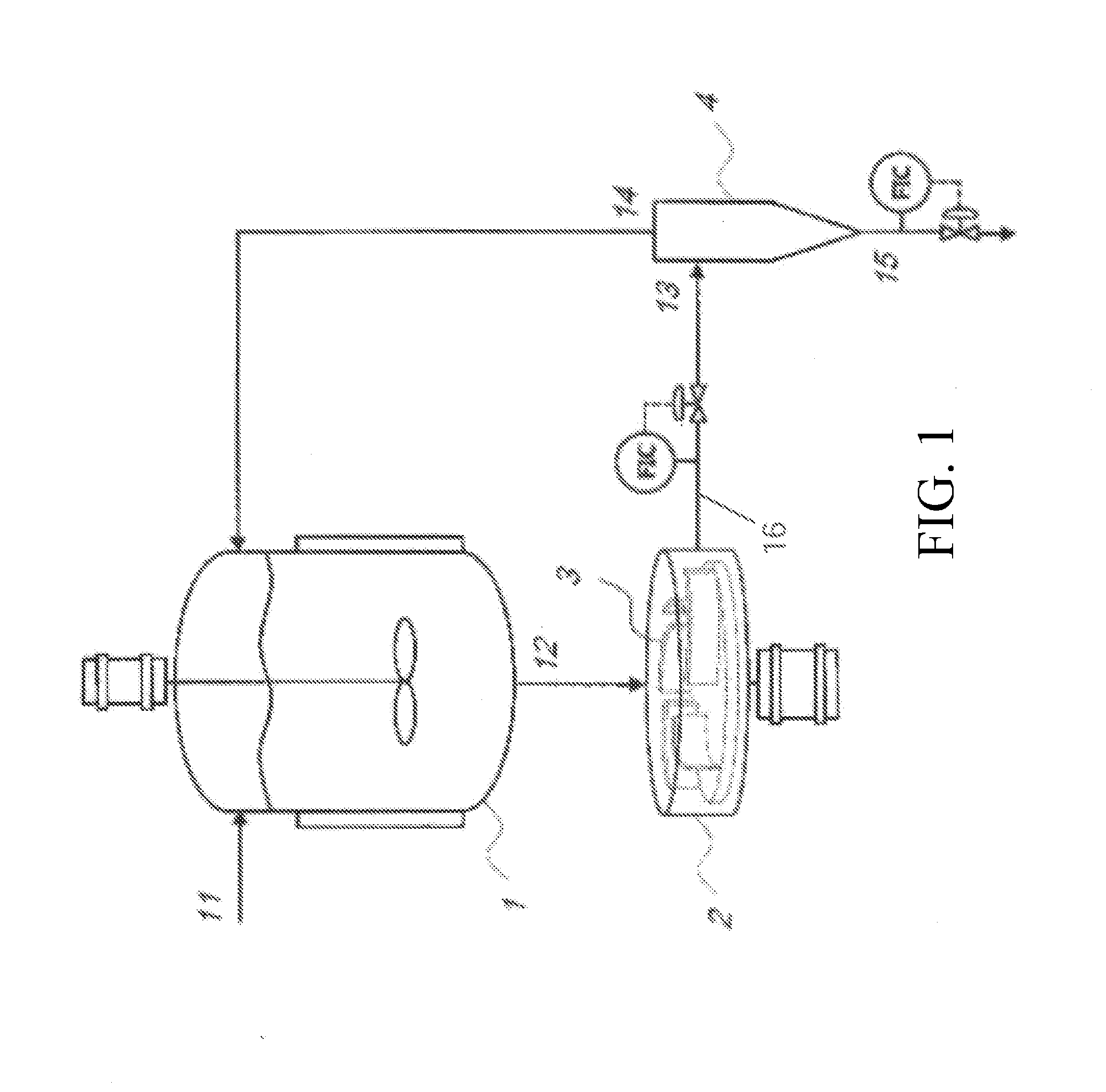
Metallic element carbon hot melting reduction continuous reactor
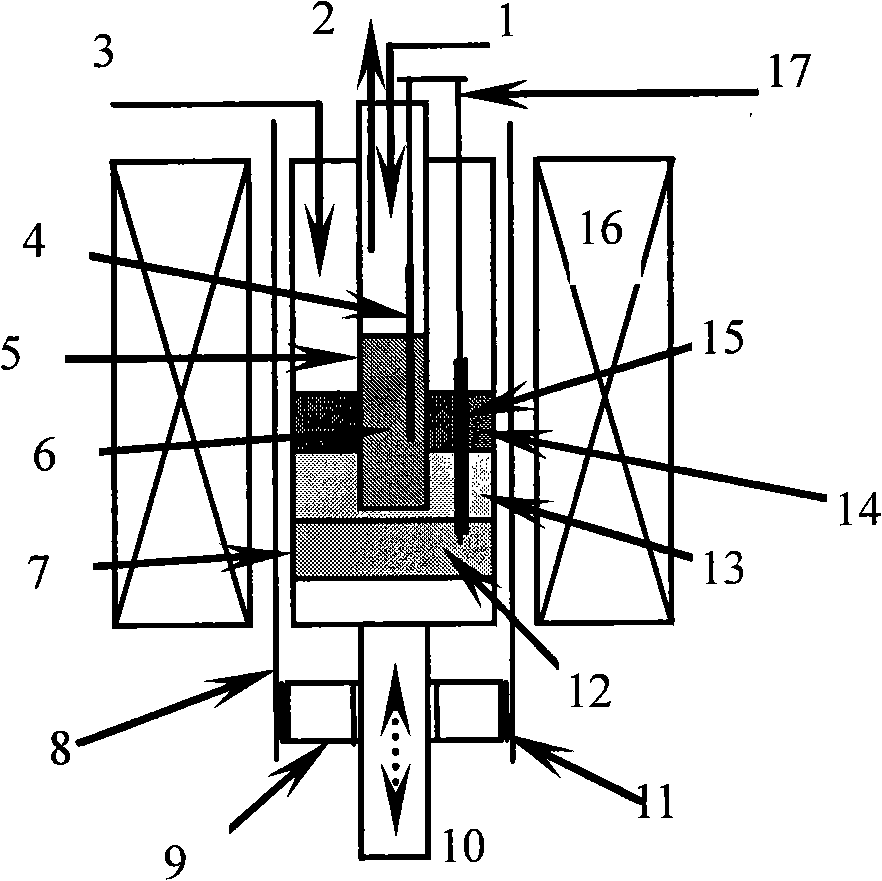
The invention discloses a continuous reduction reactor for the carbothermy smelting of metallic elements, which belongs to the field of metallurgy materials, and is applicable to reduction of pure metals or alloys. The continuous reduction reactor for the carbothermy smelting of metallic elements comprises a carbonaceous reducing agent inlet 1, a carbon monoxide outlet 2, a metallic oxide inlet 3, a graphite rod 4, an oxygen ion conducting pipe 5, a liquid metallic anode 6, a pot 7, an atmosphere protecting pipe 8, a sealing plug 9, a controllable moving branch 10, a sealing ring 11, an initial cathode 12, the pure metals or the alloys 13, slag 14, a protecting pipe 15 of an electrode connecting line, a thermostatic heater 16 and the electrode connecting line 17. The continuous reduction reactor for the carbothermy smelting of metallic elements is a reactor that is designed on the basis of the electrochemical reduction reaction theory of metallic oxides under drive of chemical energy and uses cheap raw carbon as a reducing agent, and compared with traditional carbon reduction, the continuous reduction reactor avoids carbon from entering the metals or the alloys, solves the pollution problem of the reducing agent, and can shorten metallurgy process; compared with traditional electrolysis reduction, the continuous reduction reactor overcomes the problems of large energy consumption, environmental pollution caused by low thermoelectric conversion efficiency and low electrolysis current efficiency.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
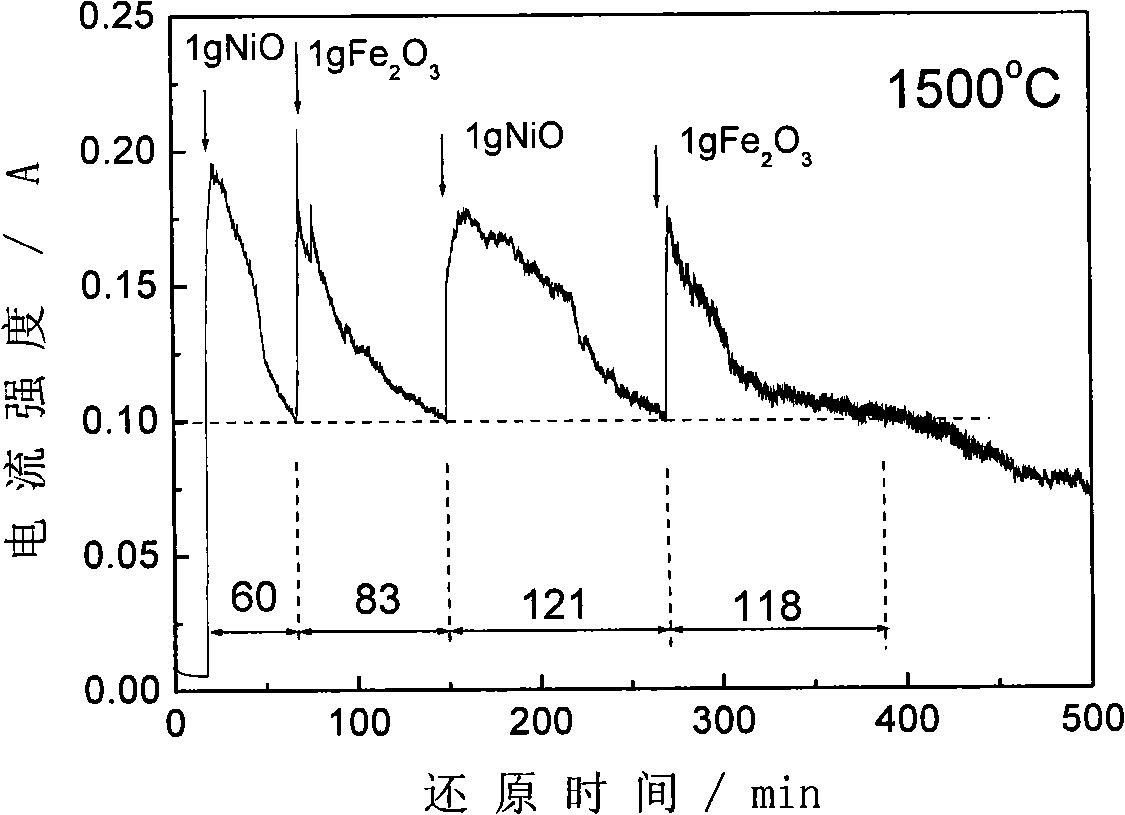
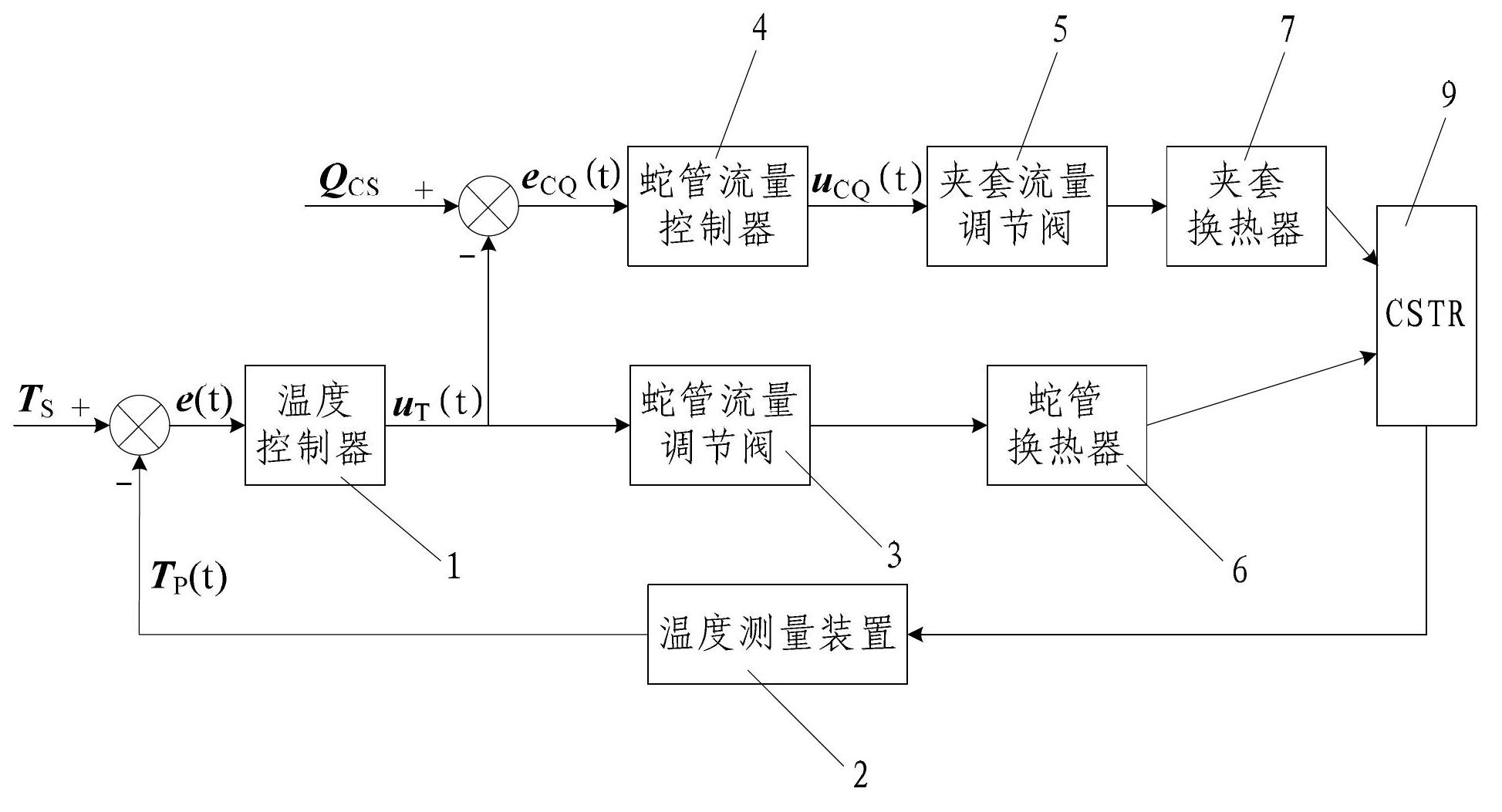
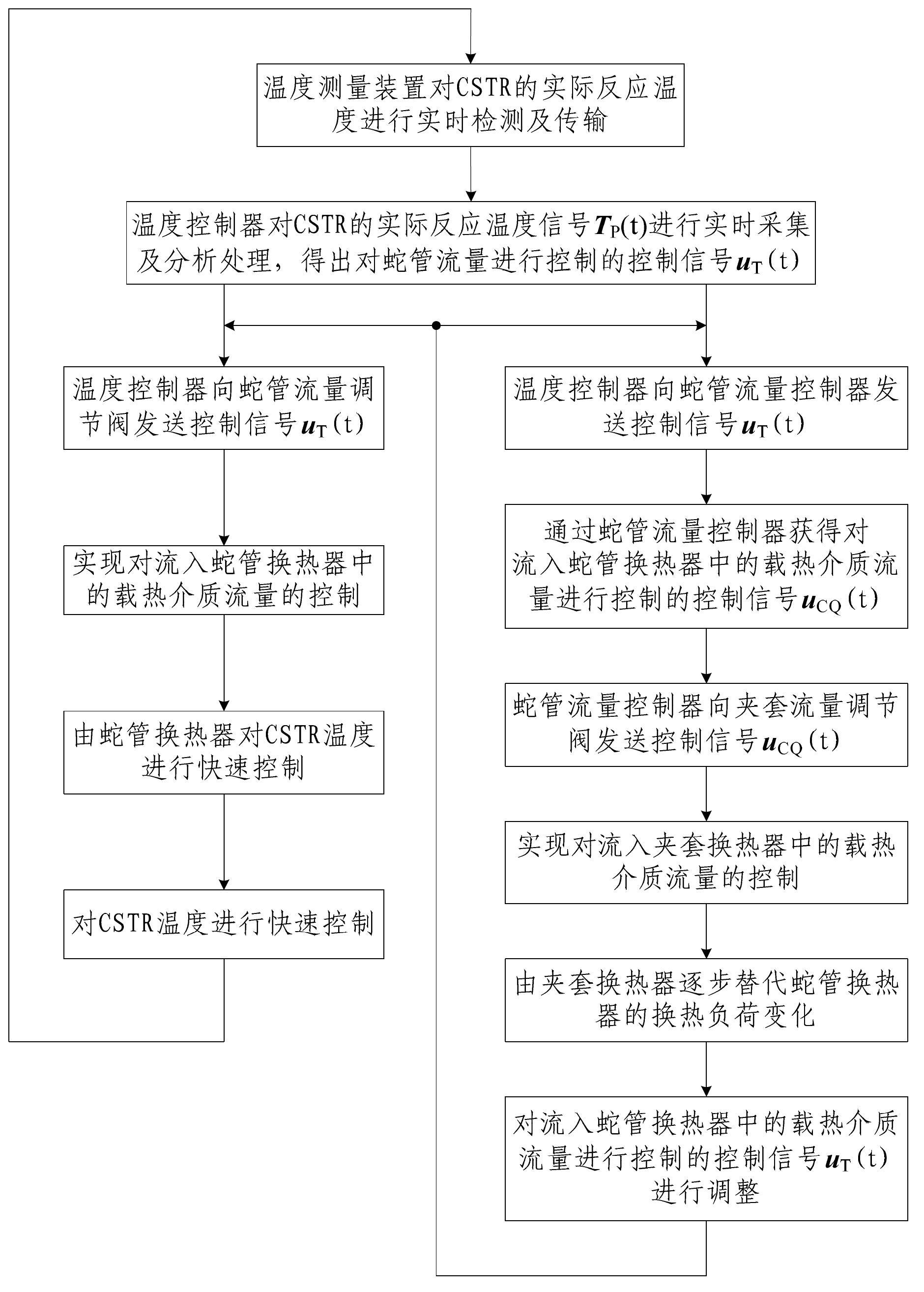
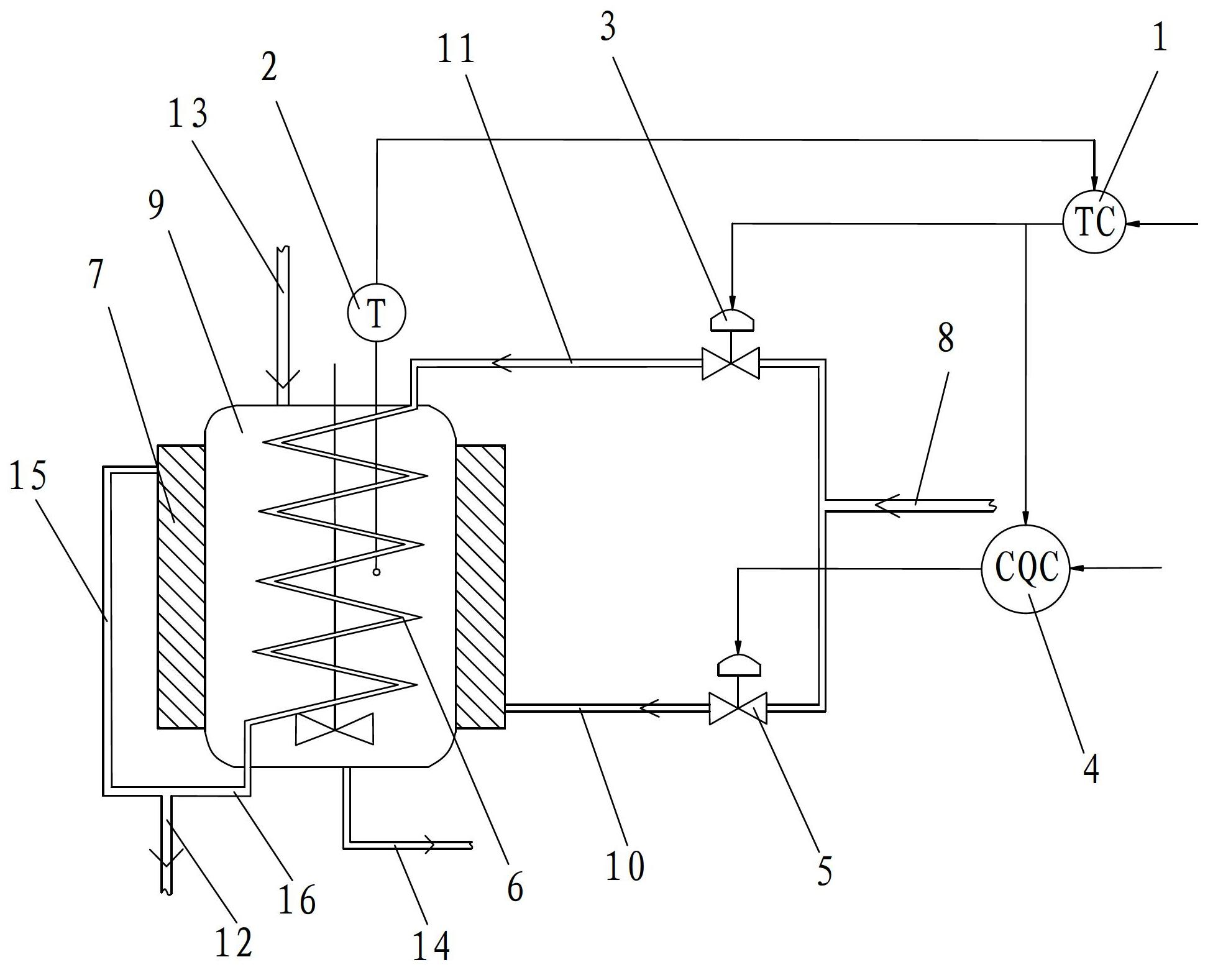
CSTR (continuous stirred-tank reactor) temperature control system and method based on coil heat exchanger and jacketed heat exchanger
InactiveCN102681565ANovel and reasonable designEasy to implementTemperature control using electric meansHeat exchange apparatusTemperature controlControl system
The invention discloses a CSTR (continuous stirred-tank reactor) temperature control system and method based on a coil heat exchanger and a jacketed heat exchanger. The control system comprises a temperature controller. An input end of the temperature controller is connected with a temperature measuring device, an output end of the temperature controller is connected with a coil flow regulating valve and a coil flow controller, and an output end of the coil flow controller is connected with a jacket flow regulating valve. The control method includes detecting a CSTR temperature signal in real time and transmitting the same; collecting the CSTR temperature signal in real time and analyzing and processing the same; controlling heat-carrying agent flow of the coil heat exchanger by the temperature controller and the coil flow regulating valve; and controlling the heat-carrying agent flow of the jacketed heat exchanger by the coil flow controller and the jacket flow regulating valve to correspondingly regulate heat-carrying agent flow of the coil heat exchanger. The CSTR temperature control system and the control method are novel and reasonable in design, quick in control speed, high in control precision, high in heat exchanging efficiency, low in heat-carrying agent consumption, favorable for saving energy and reducing consumption, and convenient to implement.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and apparatus for manufacturing graphite oxide
ActiveUS9266737B2Inhibitory responseImprove efficiencyGraphiteNanotechnologyUltrasound - actionProcess engineering
Owner:STANDARDGRAPHENE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com