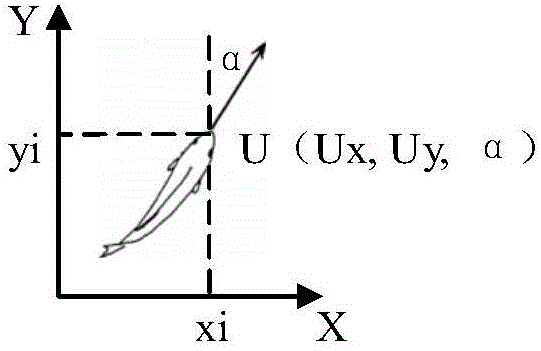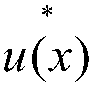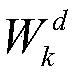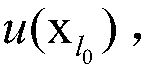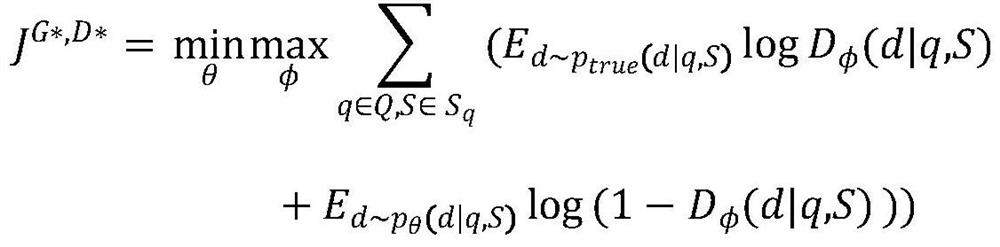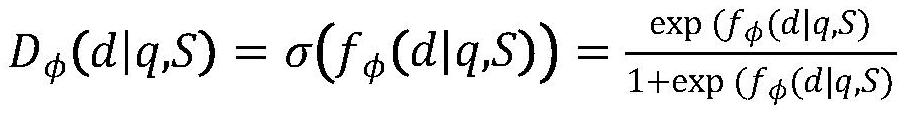Patents
Literature
43 results about "Explicit model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
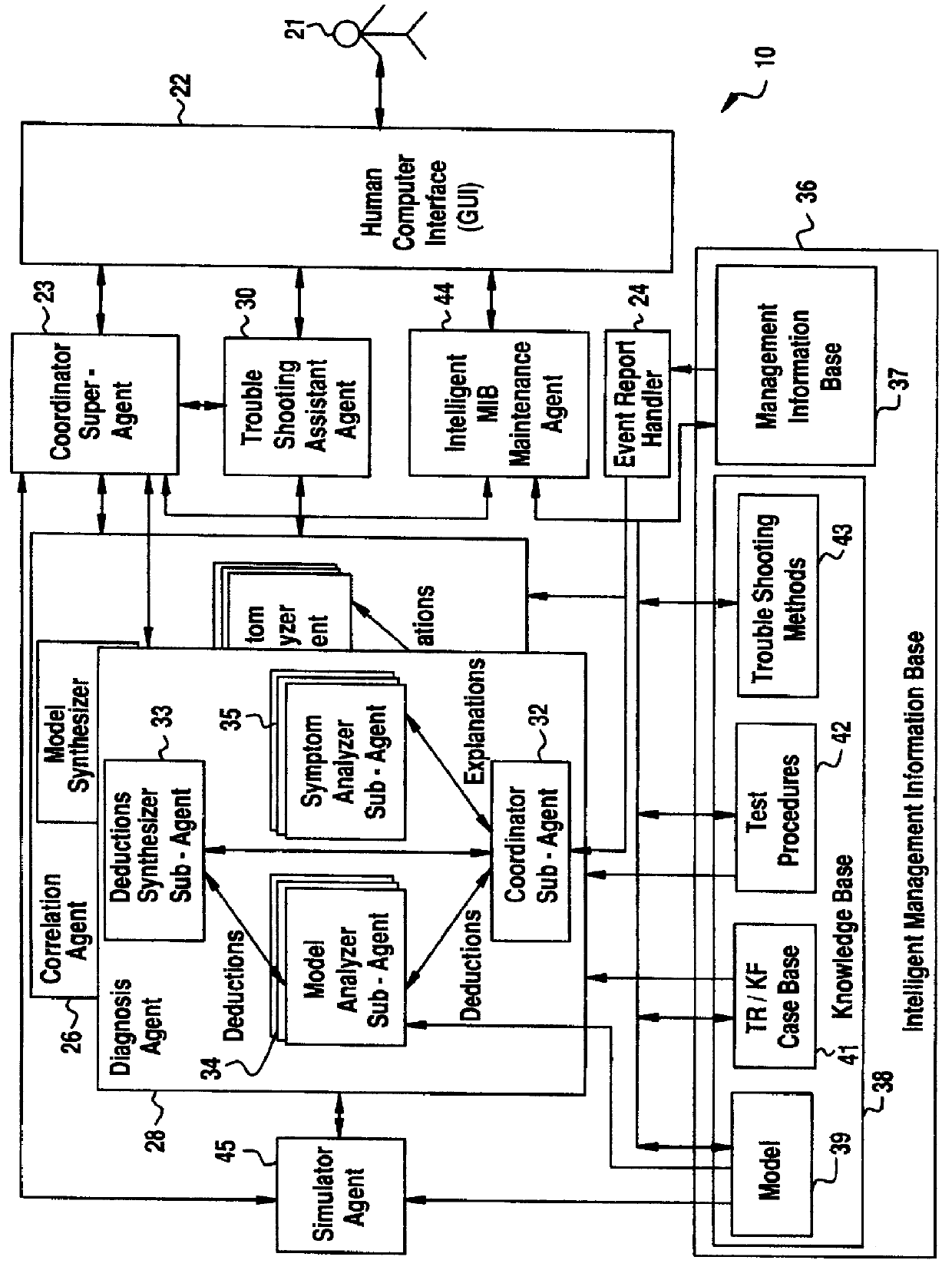
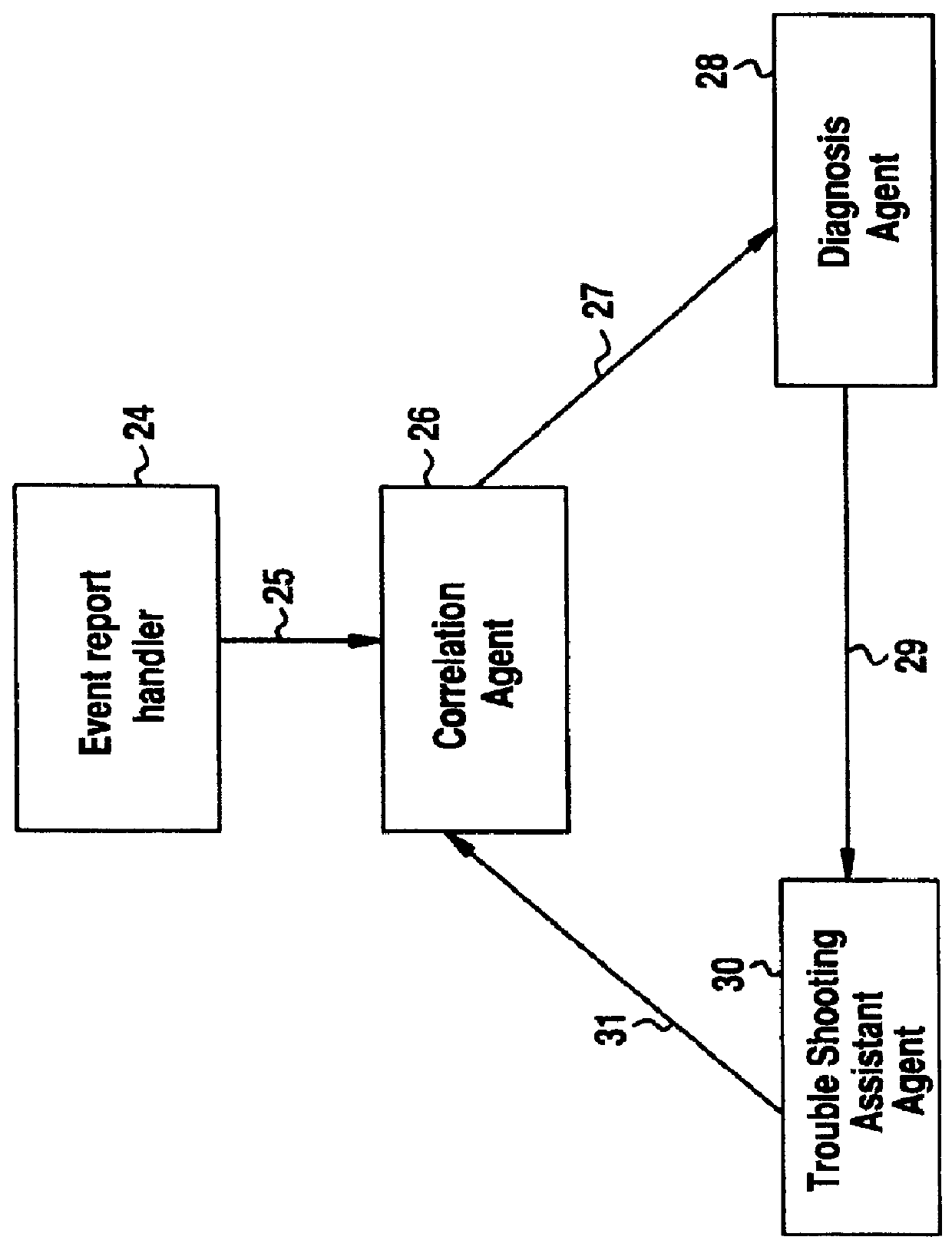
Software fault management system
InactiveUS6012152ASupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsInformation repositoryManagement information systems
A Software Fault Management (SFM) system for managing software faults in a managed mobile telecommunications network. The SFM system includes an Intelligent Management Information Base (I-MIB) comprising a Management Information Base (MIB) and a Knowledge Base (KB) having a functional model of the managed network and a trouble report / known faults (TR / KF) case base. The SFM system also includes an intelligent multi-agent portion having a plurality of agents which process the software faults utilizing the functional model from the I-MIB, case-based information, and other management information. The I-MIB and the intelligent multi-agent portion are compliant with Telecomunications Management Network (TMN) principles and framework. Fault management is both proactive and reactive. The SFM system is made independent of technology-specific implementations by representing the underlying switch design knowledge in a modular and changeable form which is then interpreted by the intelligent multi-agent portion. A clear separation is maintained between the generic procedural inference mechanisms and agents, and the specific and explicit models of the different network elements of a mobile telecommunications network.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
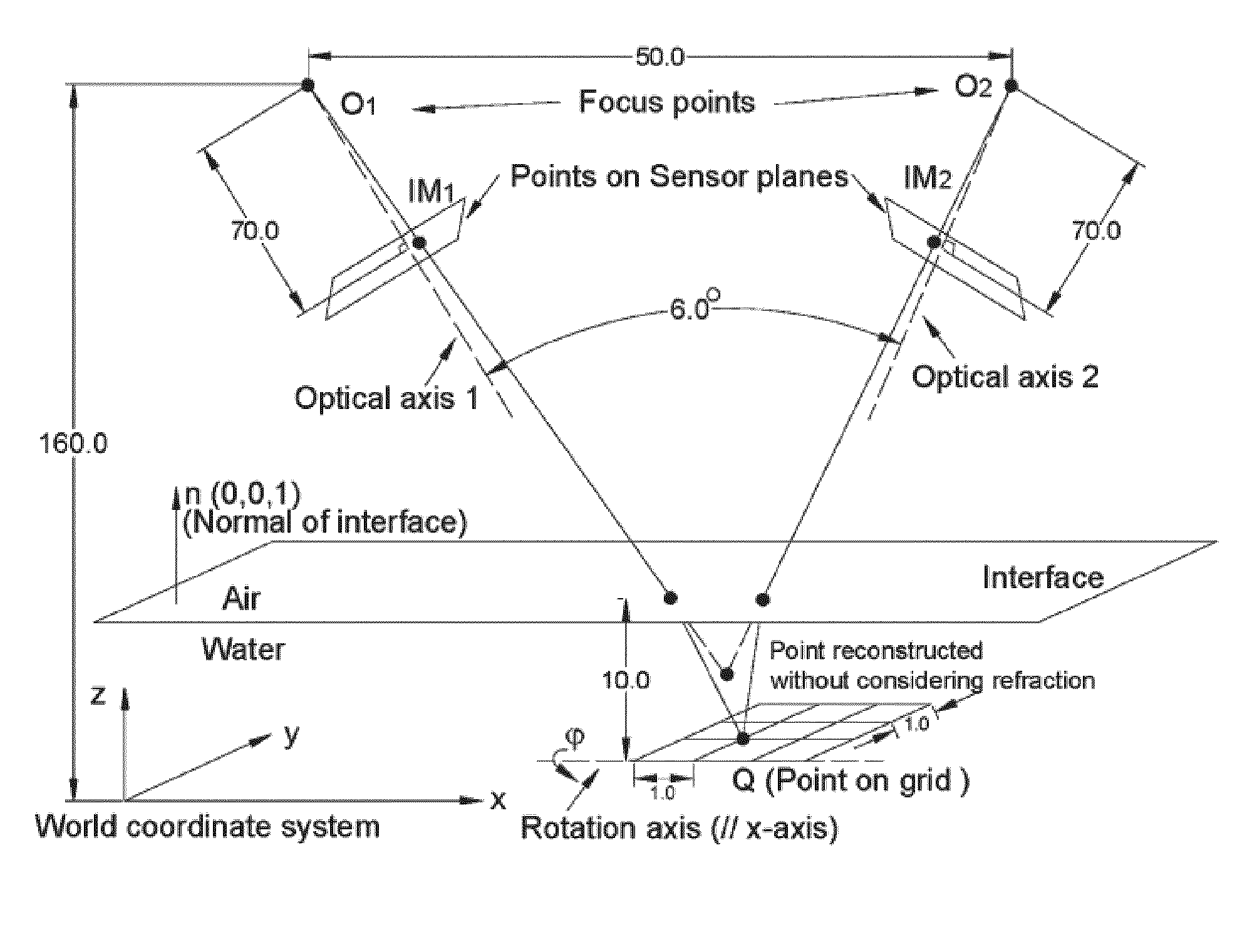
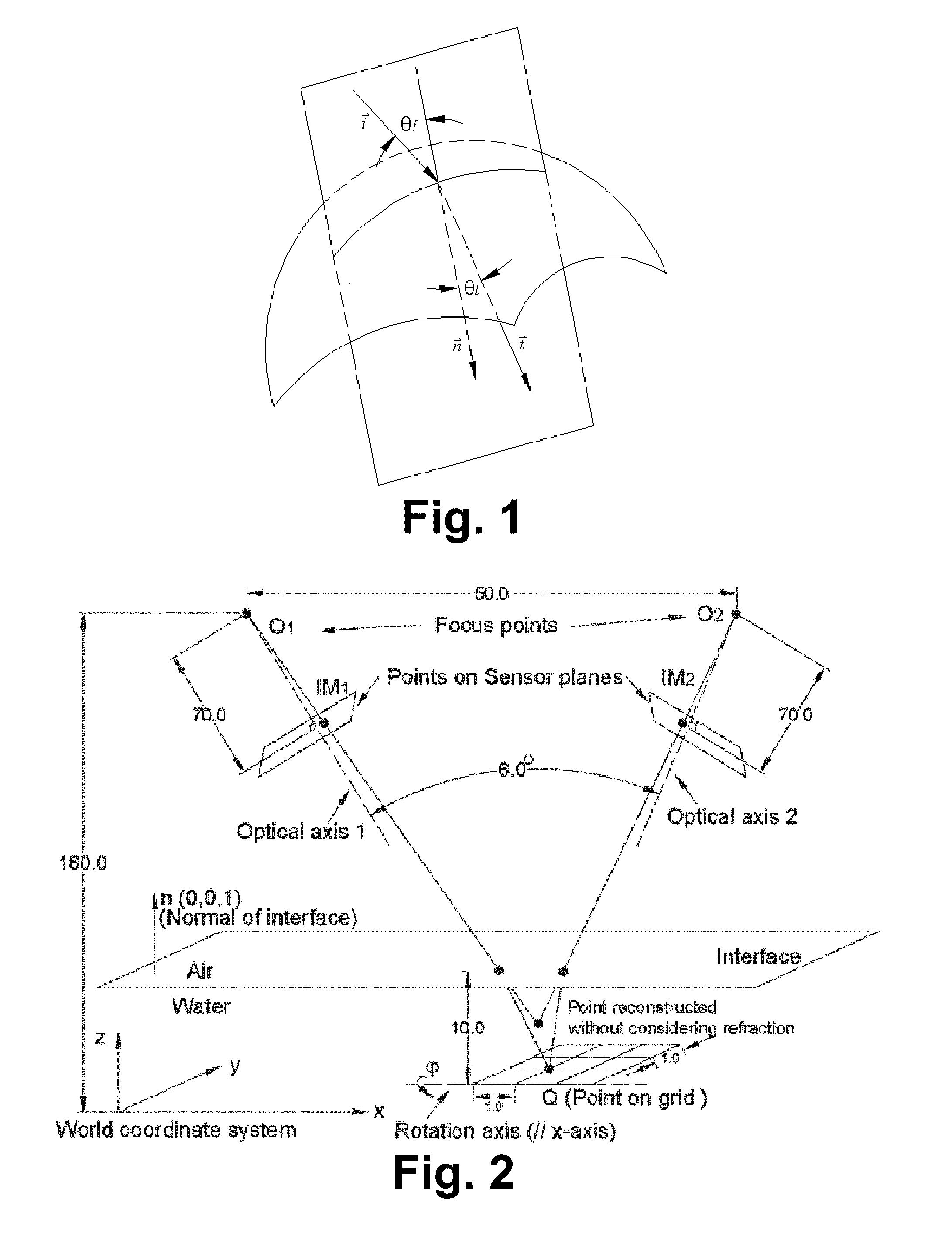
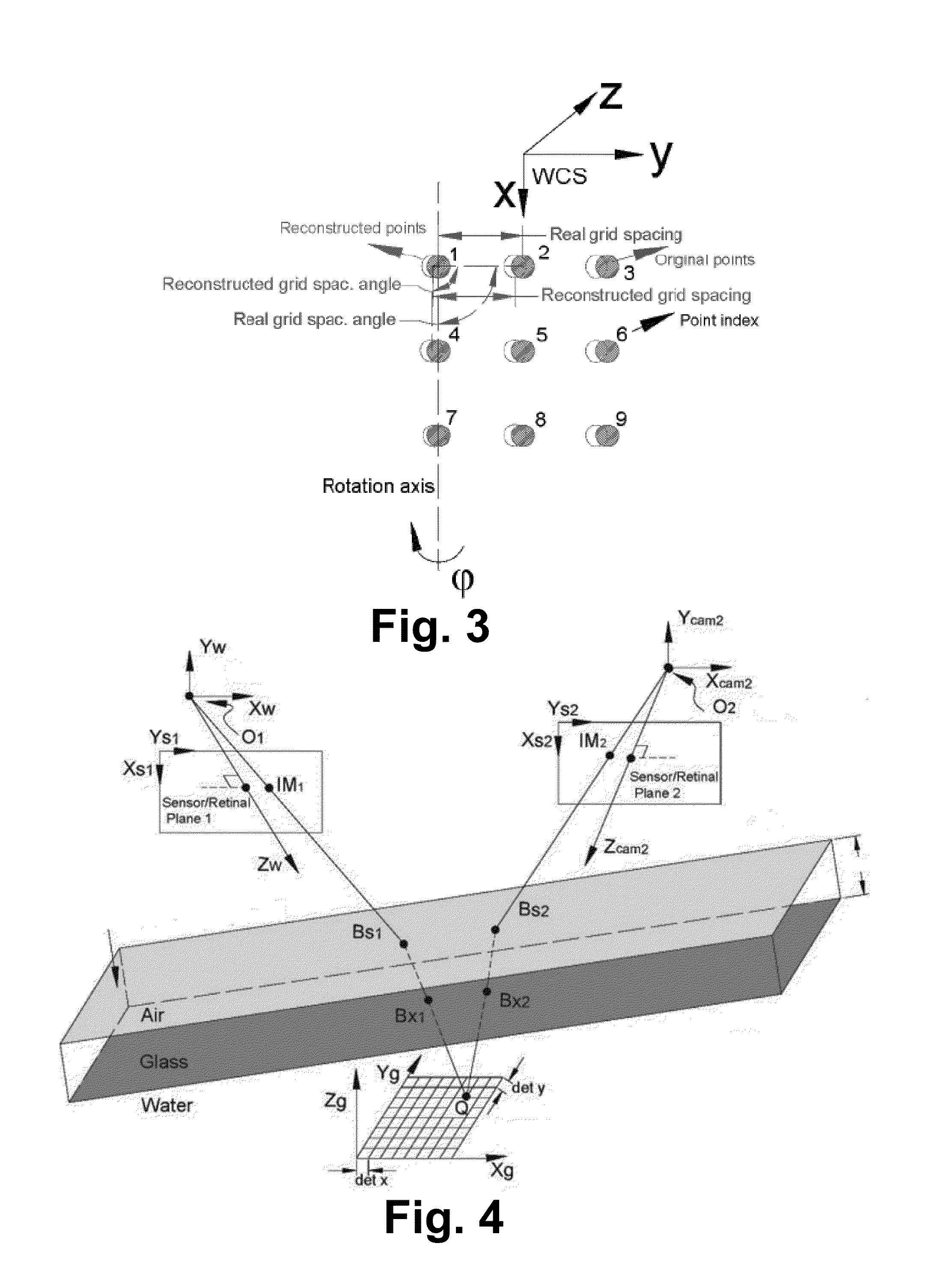
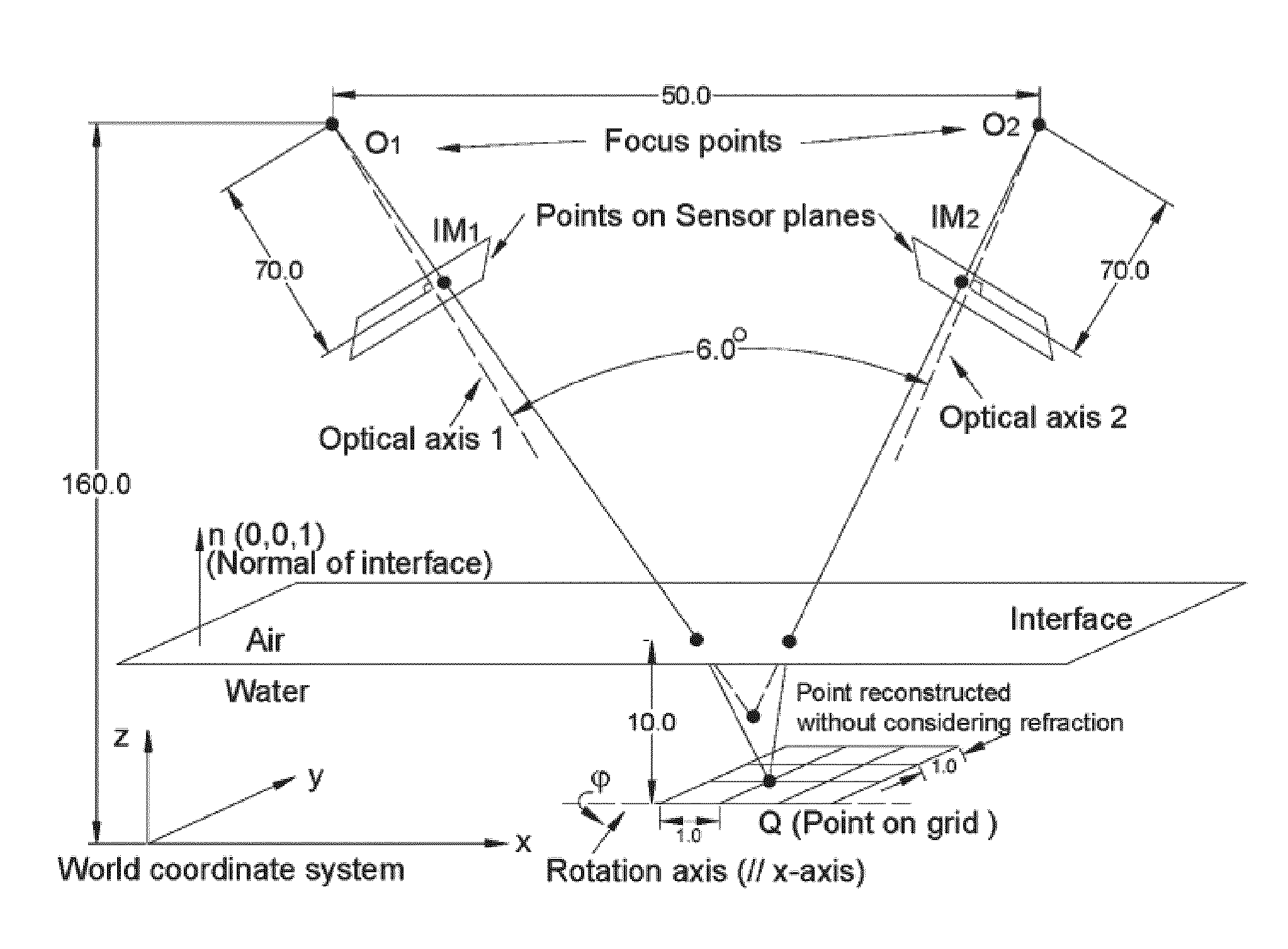
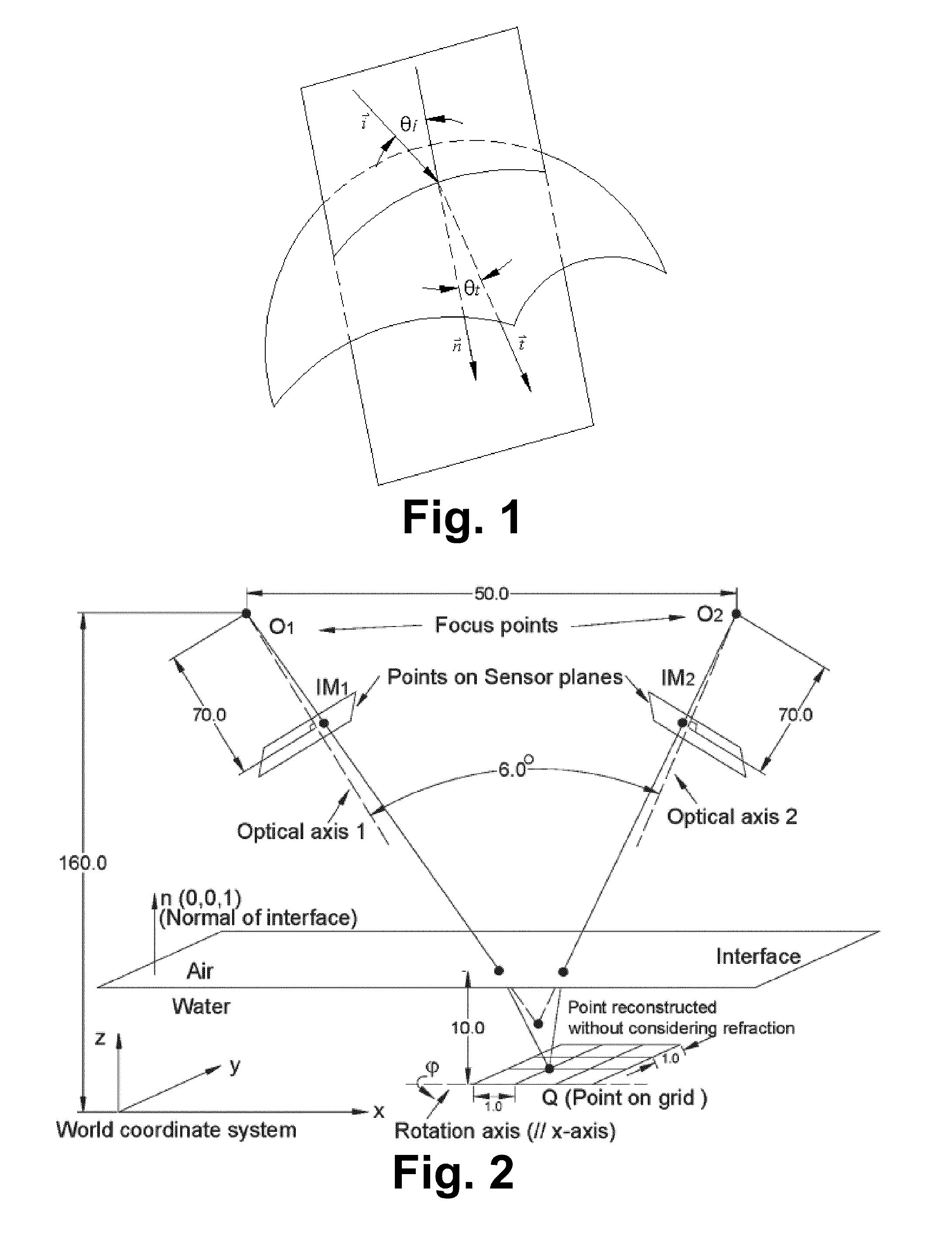
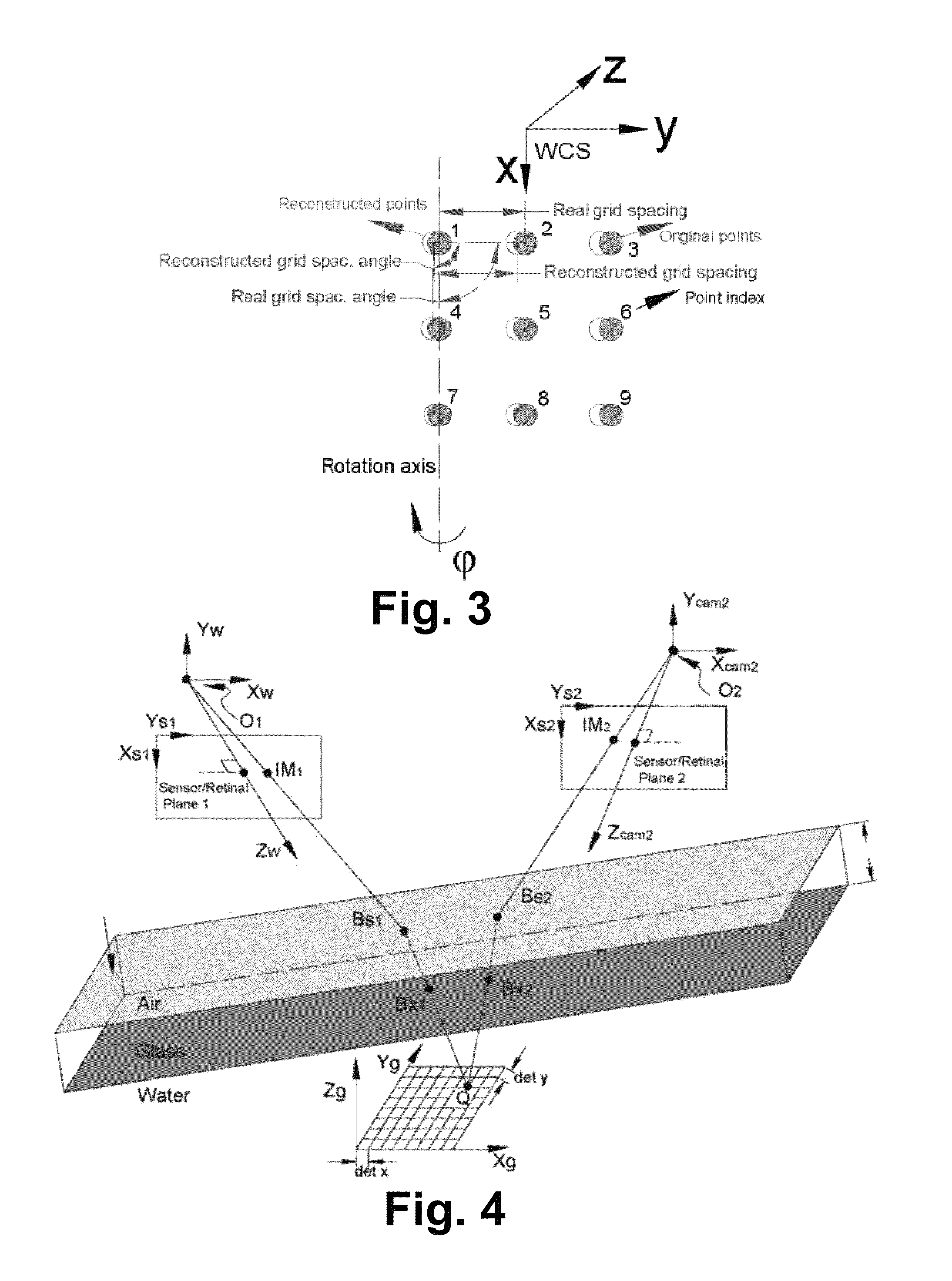
Robust Stereo Calibration System and Method for Accurate Digital Image Correlation Measurements
ActiveUS20100079598A1Maintain accuracyConvenient and accurateUsing optical meansTelevision systemsExplicit modelObject point
A stereo calibration method is proposed to calibrate an interface's shape and position when the measurement system is in one media and measures deformation and strain of an object that is submerged in a different media. After the interface's shape and position are modeled by parameters, an explicit model of object points as measurement is established taking account of refraction happening at the interface. Efficiency and convergence are assured by using measurement of object points to acquire initial estimates for refraction angles at the interface. Then, an optimization method is performed to get the optimized value of interface parameters. Last, based on the resulting interface parameters, 3-dimensional positions of object points in all the subsequent measurement could be reconstructed accurately. Therefore, the distortion induced by refraction in the measurement is corrected. Numerical simulations of the proposed calibration process confirm that it is both robust and accurate for a range of experimental conditions, even in the presence of Gaussian noise in the measurement.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA
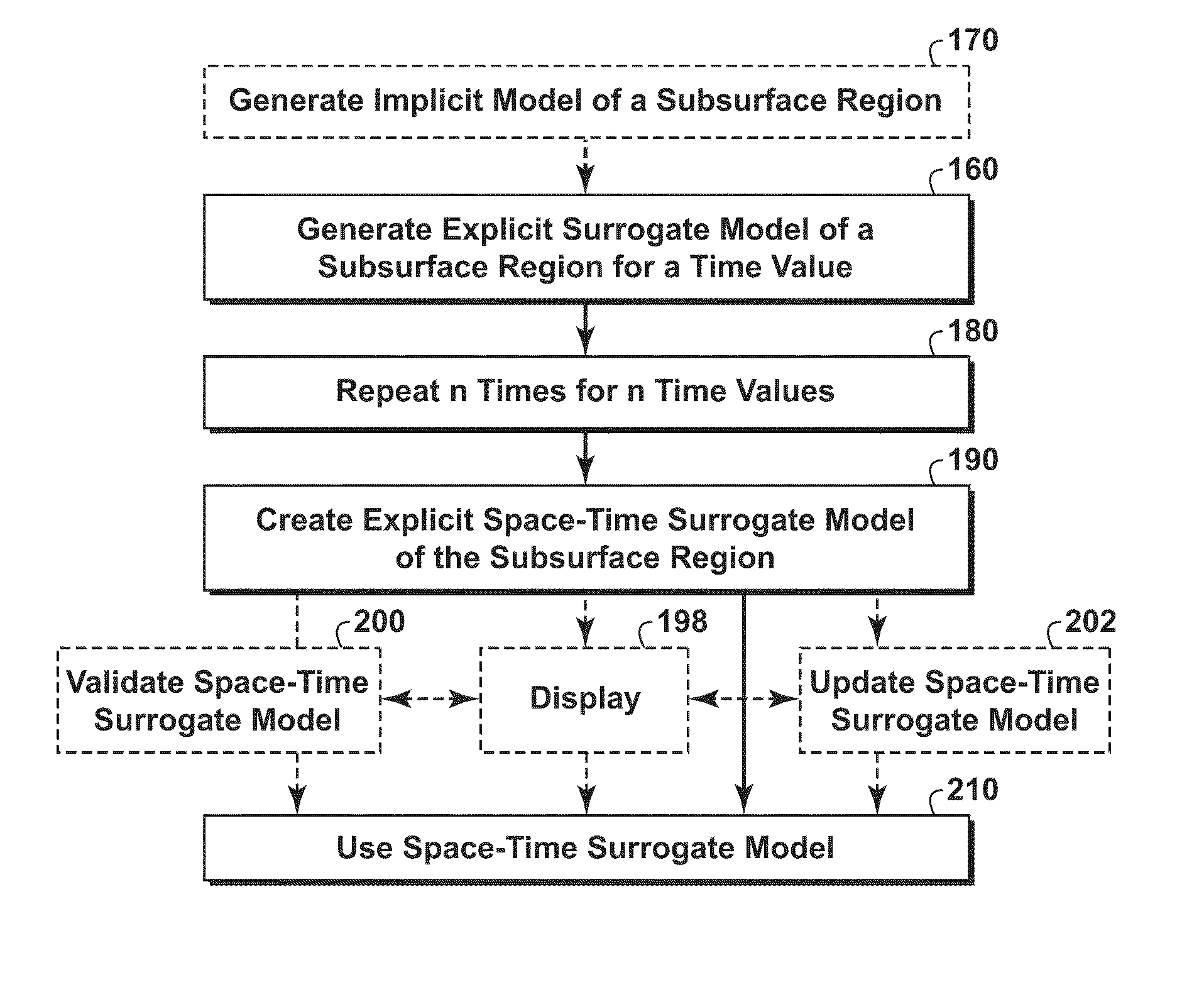
Space-Time Surrogate Models of Subterranean Regions
Methods for creating and using space-time surrogate models of subsurface regions, such as subsurface regions containing at least one hydrocarbon formation. The created surrogate models are explicit models that may be created from implicit models, such as computationally intensive full-physics models. The space-time surrogate models are parametric with respect to preselected variables, such as space, state, and / or design variables, while also indicating responsiveness of the preselected variables with respect to time. In some embodiments, the space-time surrogate model may be parametric with respect to preselected variables as well as to time. Methods for updating and evolving models of subsurface regions are also disclosed.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Intelligent control with hierarchical stacked neural networks
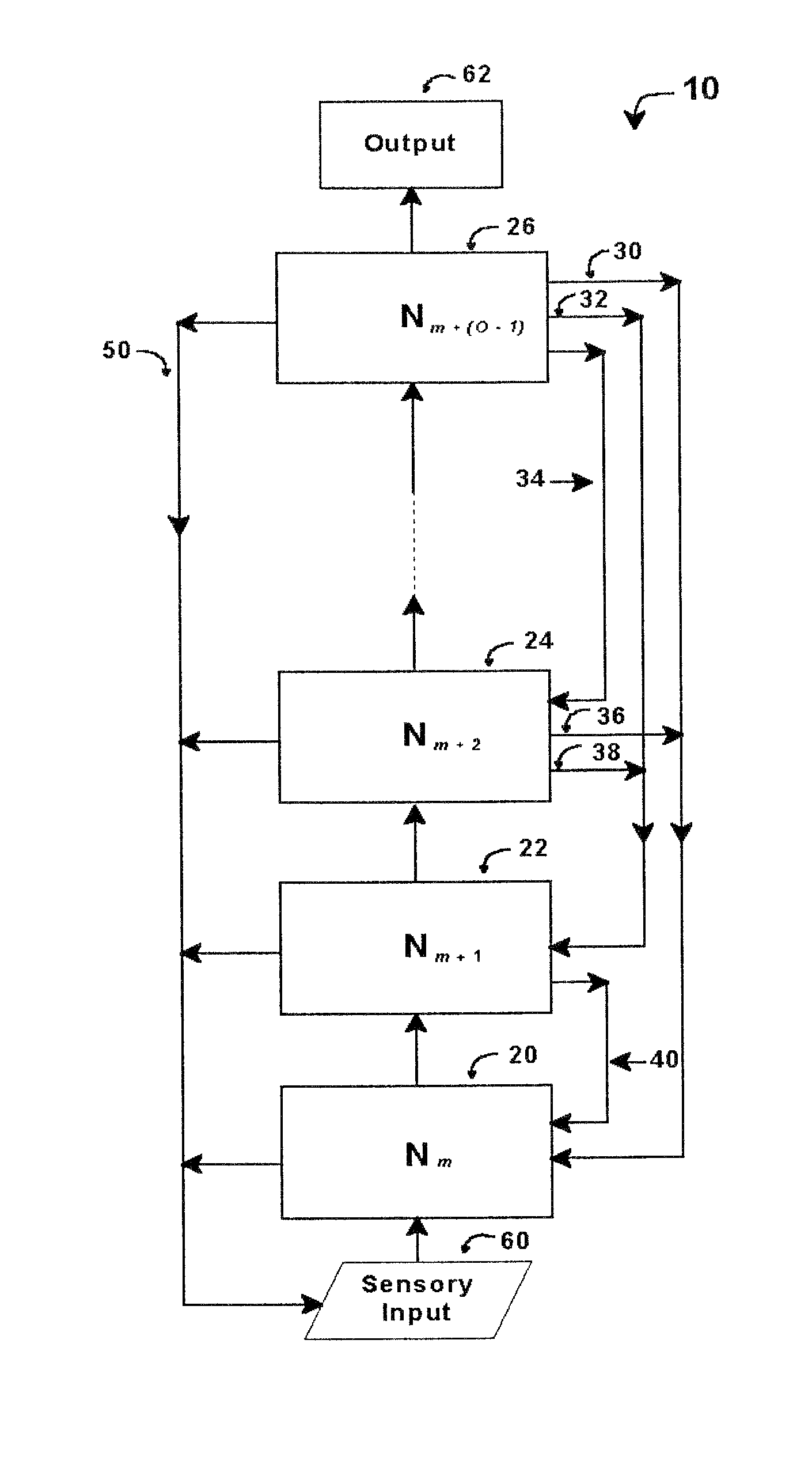
ActiveUS7152051B1Increased complexityDigital computer detailsDigital dataNerve networkExplicit model
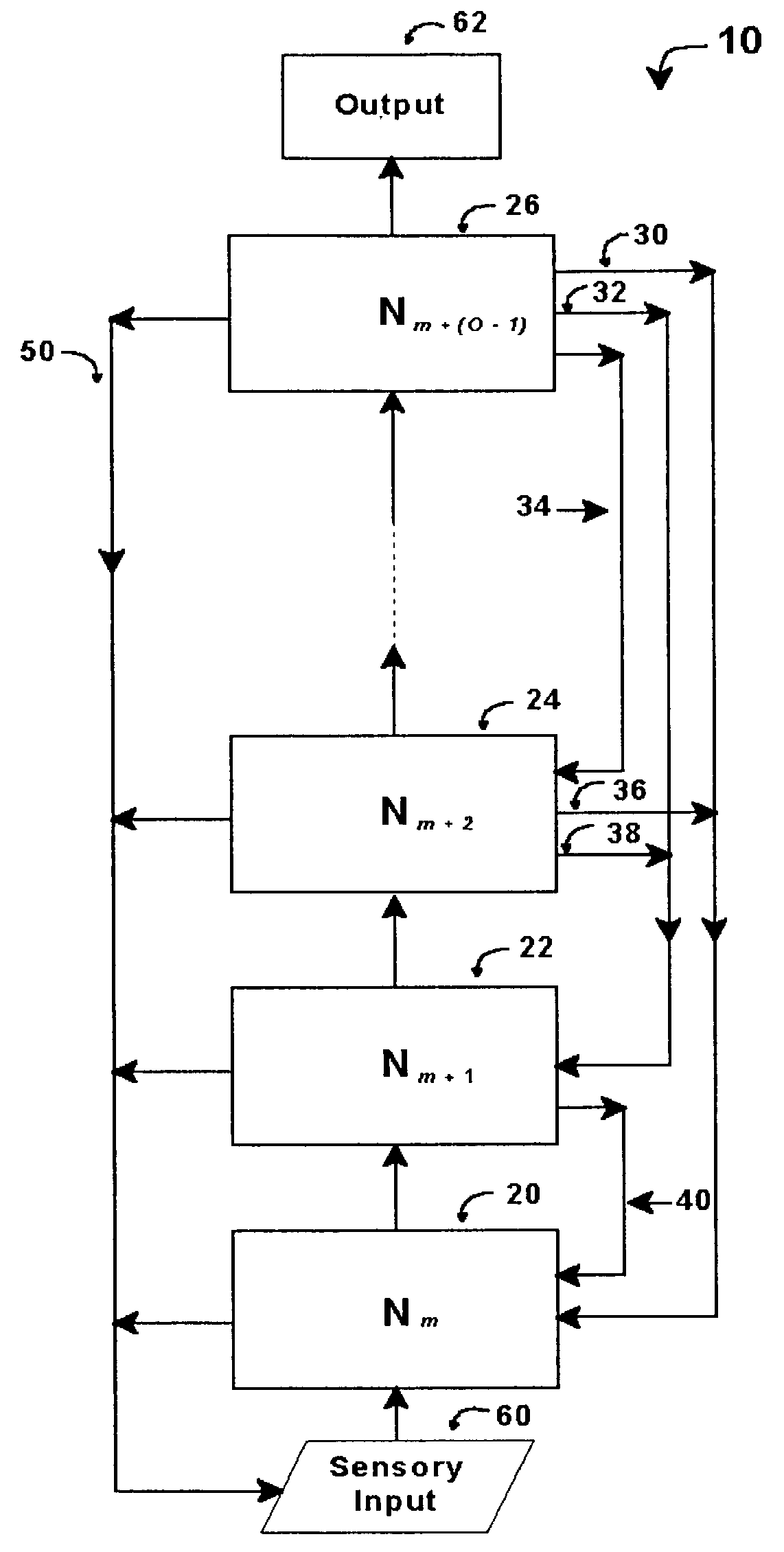
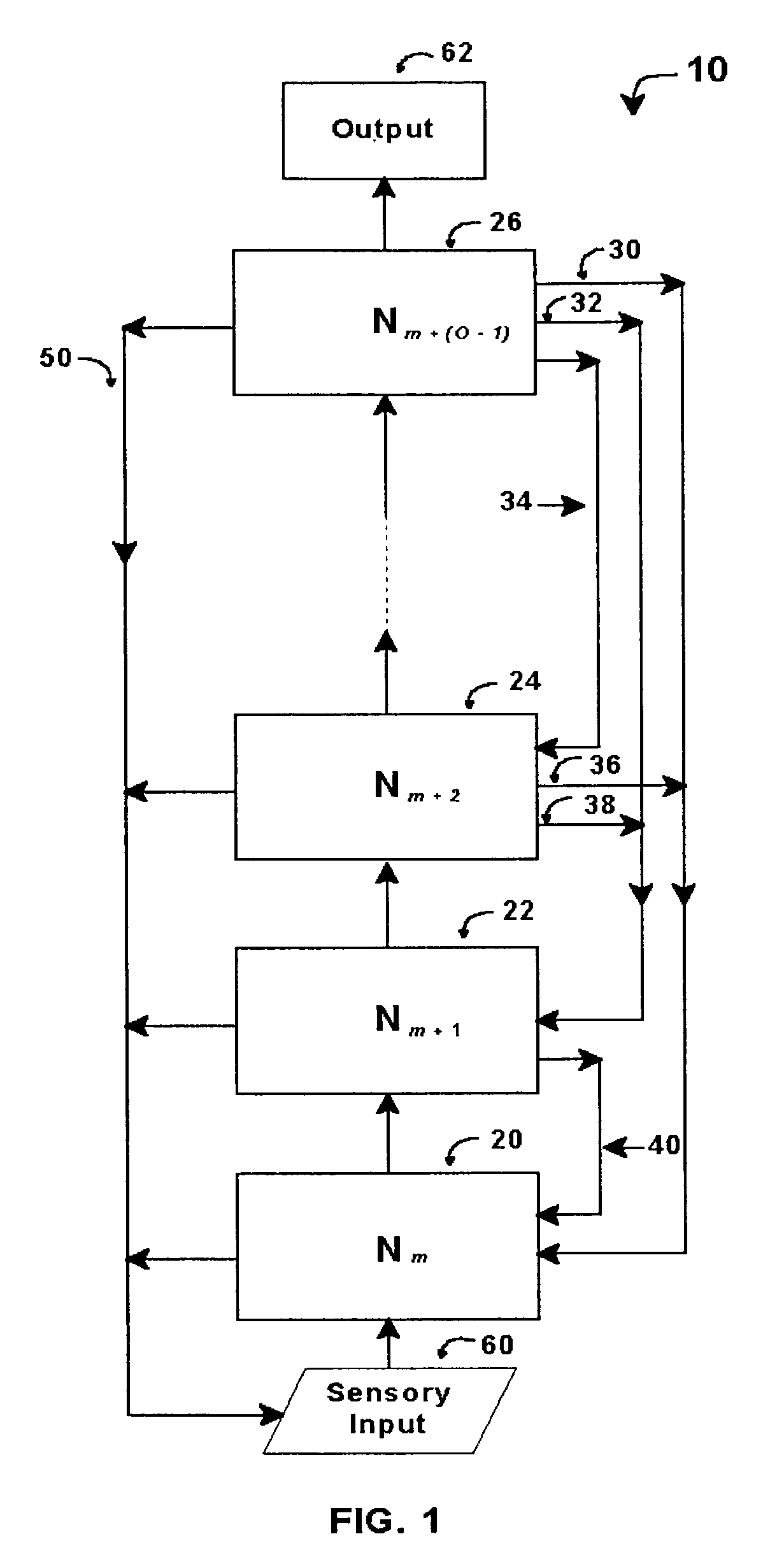
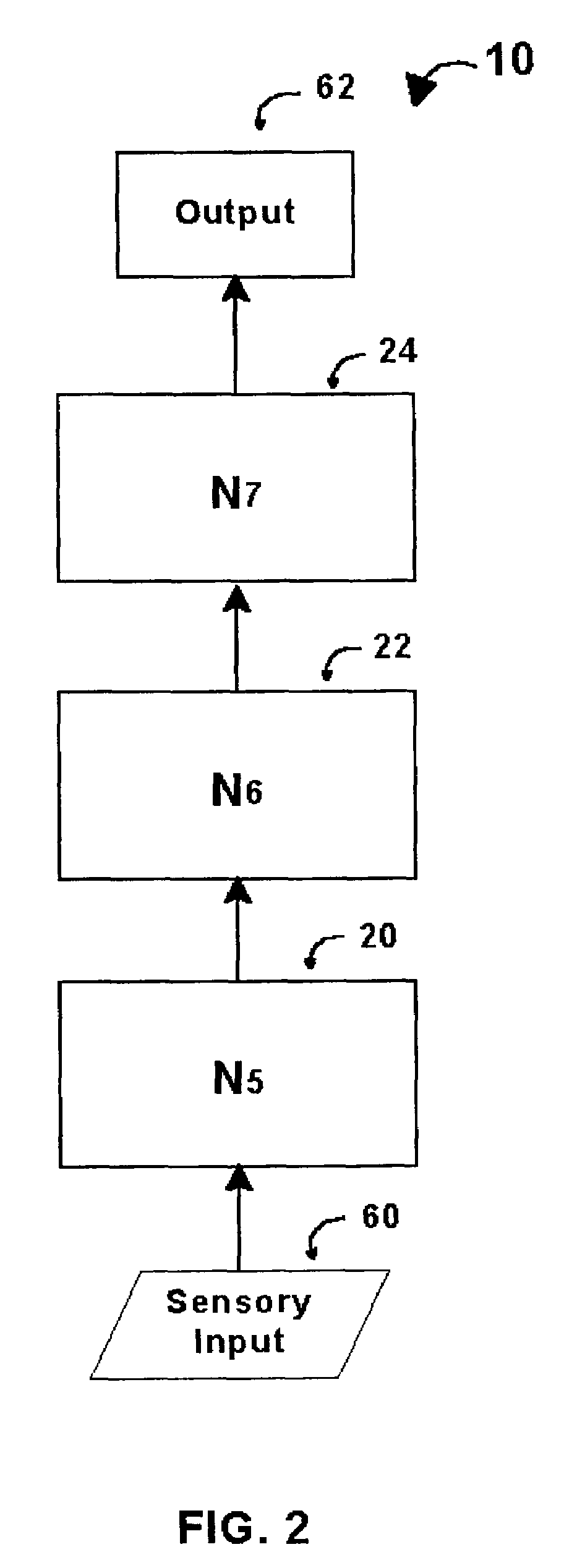
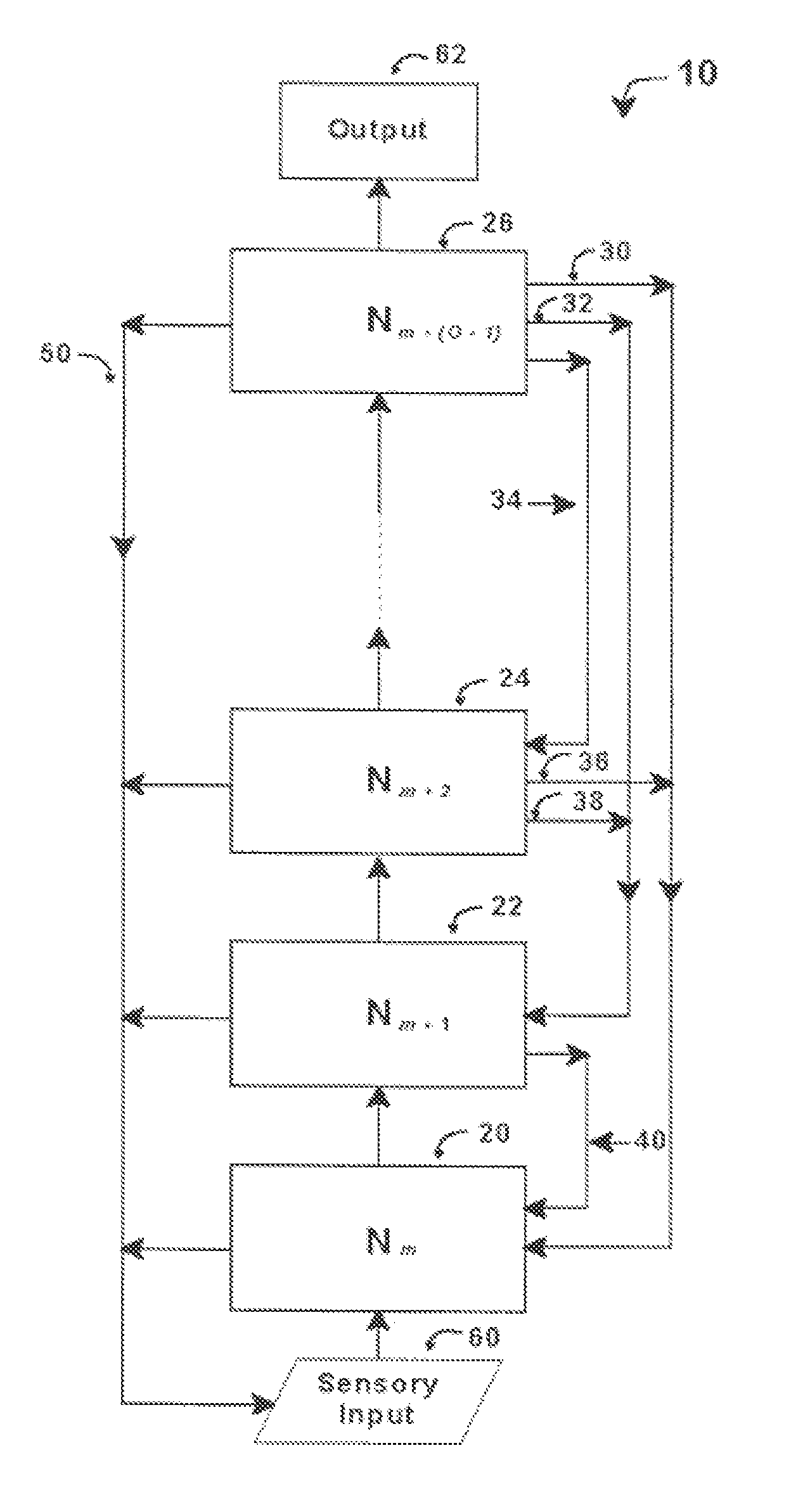
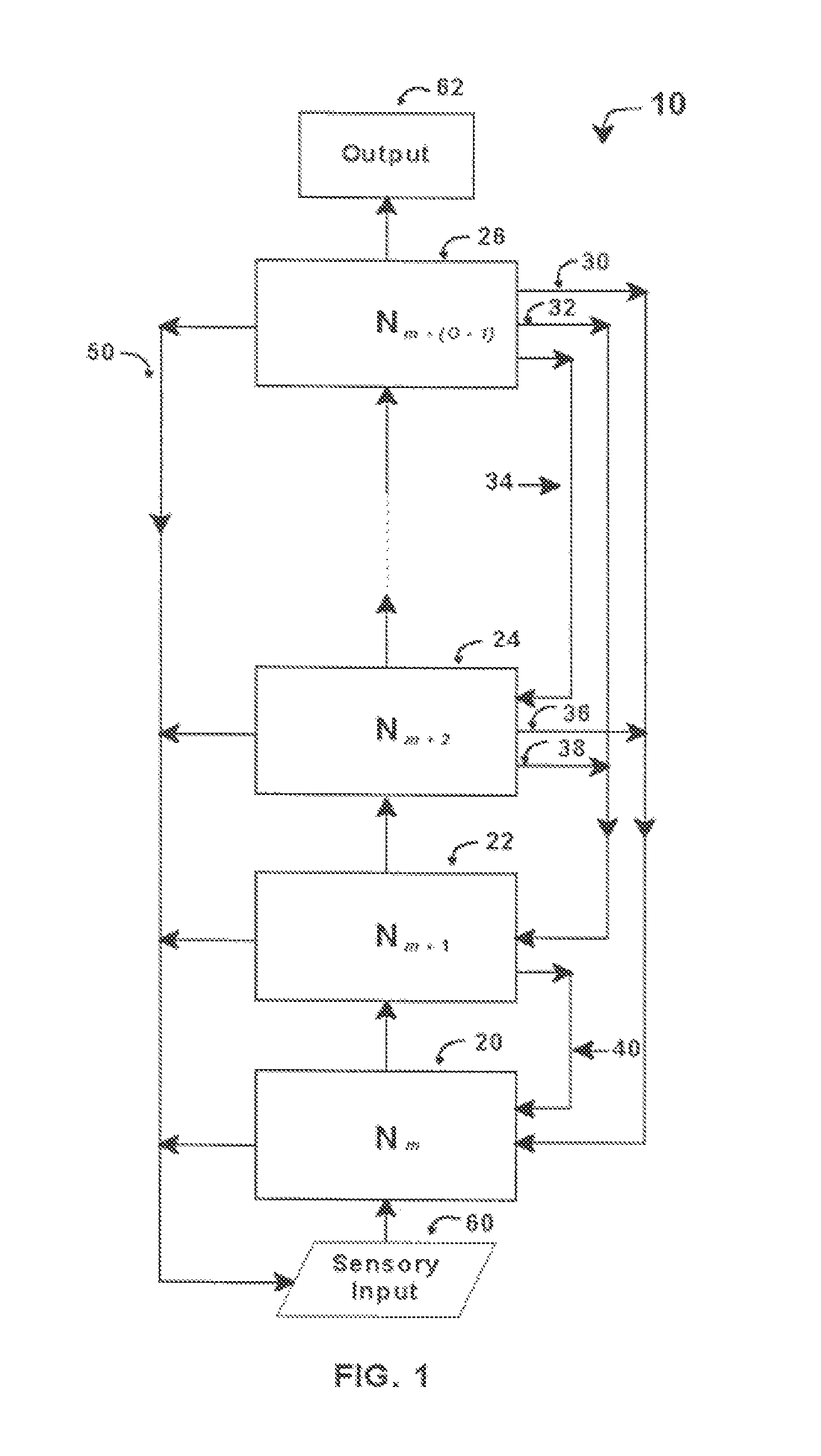
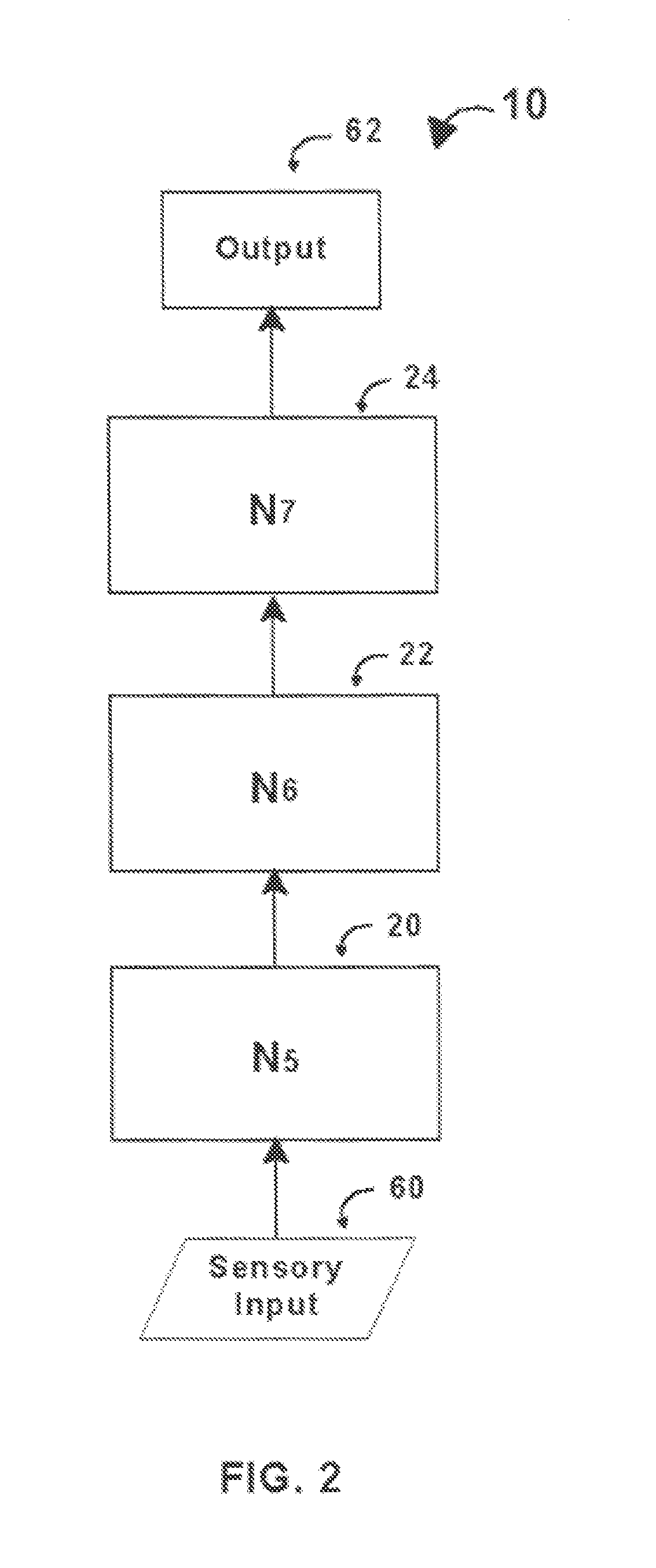
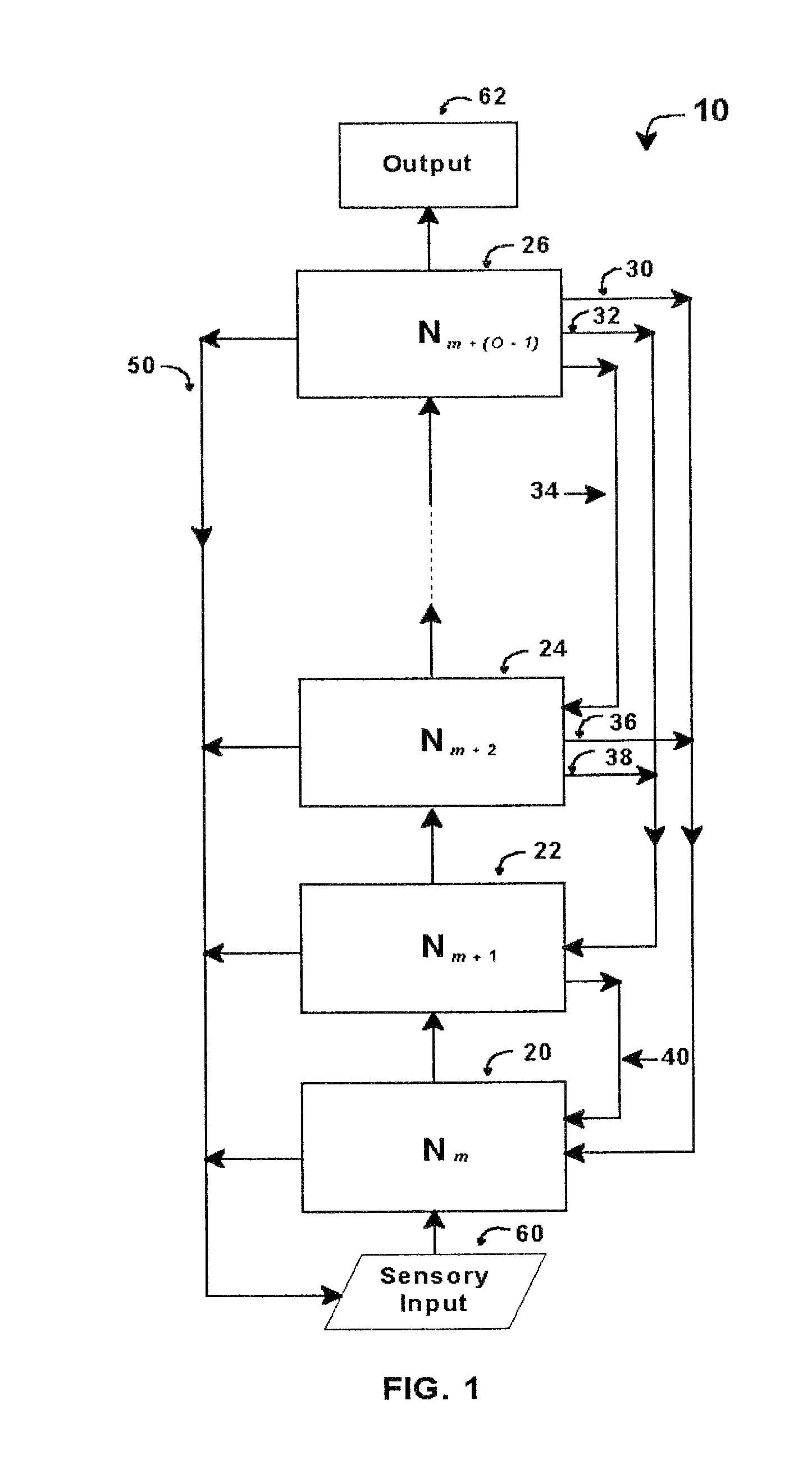
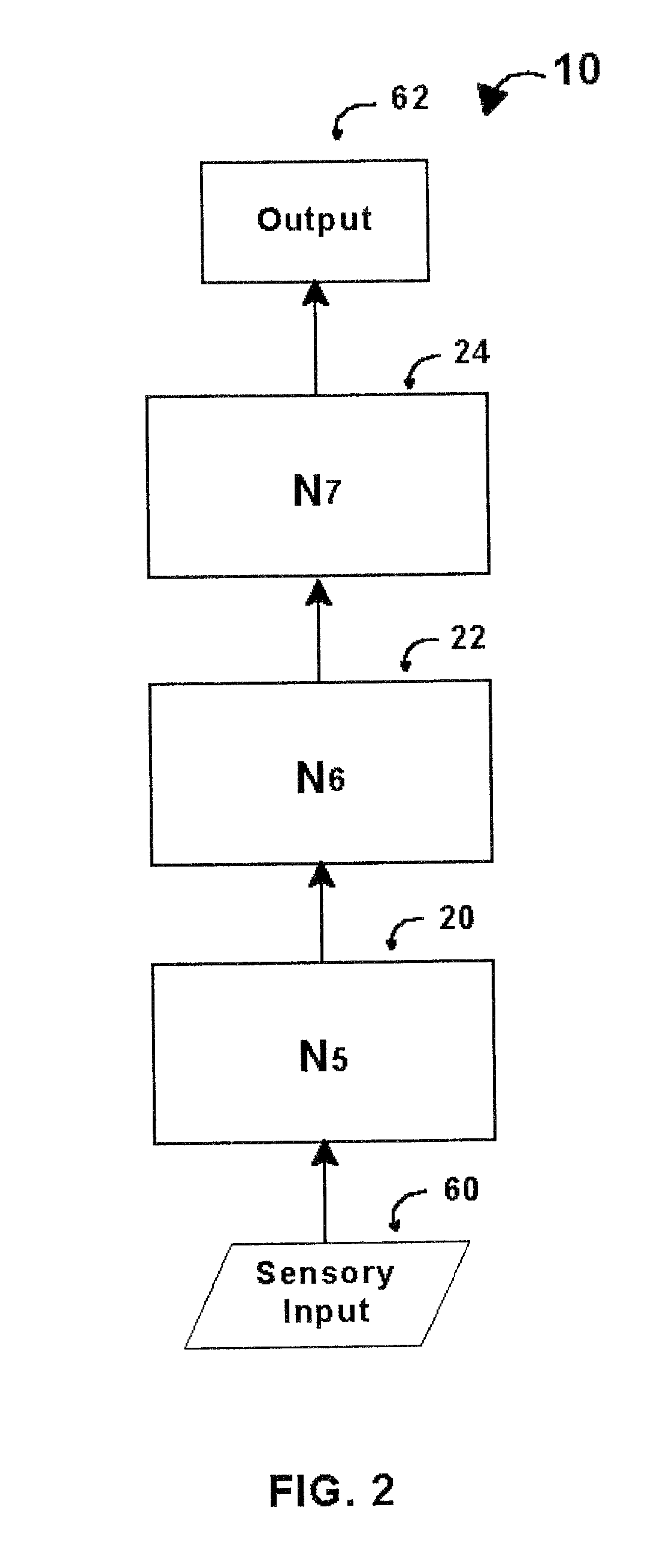
An intelligent control system based on an explicit model of cognitive development (Table 1) performs high-level functions. It comprises up to O hierarchically stacked neural networks, Nm, . . . , Nm+(O−1), where m denotes the stage / order tasks performed in the first neural network, Nm, and O denotes the highest stage / order tasks performed in the highest-level neural network. The type of processing actions performed in a network, Nm, corresponds to the complexity for stage / order m. Thus N1 performs tasks at the level corresponding to stage / order 1. N5 processes information at the level corresponding to stage / order 5. Stacked neural networks begin and end at any stage / order, but information must be processed by each stage in ascending order sequence. Stages / orders cannot be skipped. Each neural network in a stack may use different architectures, interconnections, algorithms, and training methods, depending on the stage / order of the neural network and the type of intelligent control system implemented.
Owner:COMMONS MICHAEL LAMPORT +1
Intelligent control with hierarchal stacked neural networks
InactiveUS7613663B1Increased complexityDigital computer detailsDiagnostic recording/measuringNerve networkExplicit model
An intelligent control system based on an explicit model of cognitive development (Table 1) performs high-level functions. It comprises up to O hierarchically stacked neural networks, Nm, . . . , Nm+(O−1), where m denotes the stage / order tasks performed in the first neural network, Nm, and O denotes the highest stage / order tasks performed in the highest-level neural network. The type of processing actions performed in a network, Nm, corresponds to the complexity for stage / order m. Thus N1 performs tasks at the level corresponding to stage / order 1. N5 processes information at the level corresponding to stage / order 5. Stacked neural networks begin and end at any stage / order, but information must be processed by each stage in ascending order sequence. Stages / orders cannot be skipped. Each neural network in a stack may use different architectures, interconnections, algorithms, and training methods, depending on the stage / order of the neural network and the type of intelligent control system implemented.
Owner:COMMONS MICHAEL LAMPORT +1
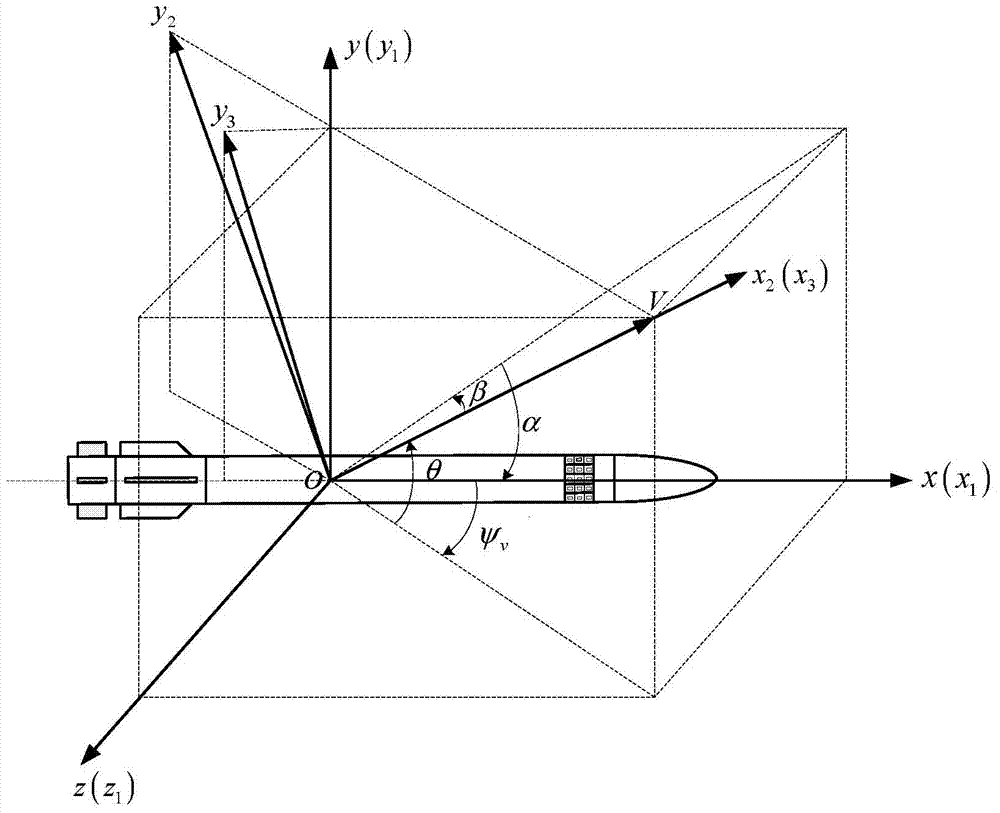
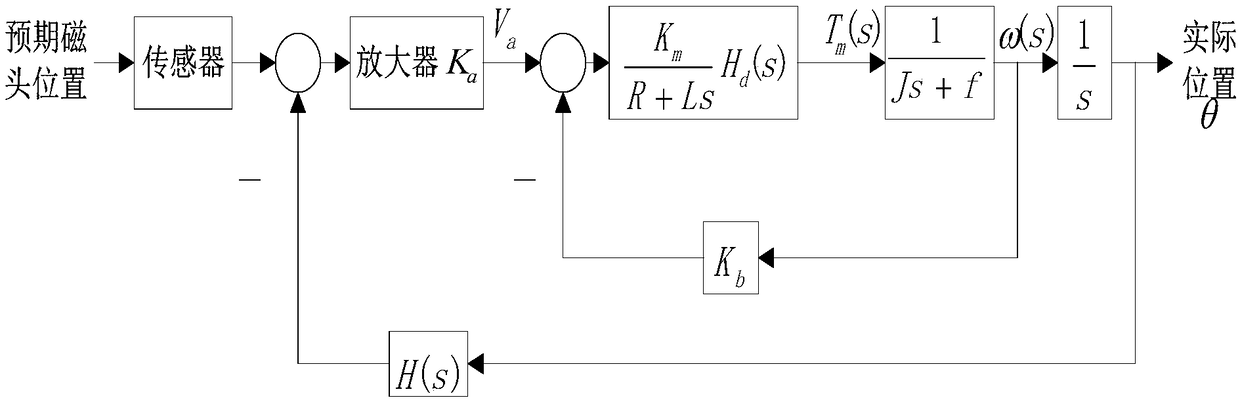
Attitude control type direct lateral force and aerodynamic force composite missile attitude control method based on mixed forecasting control
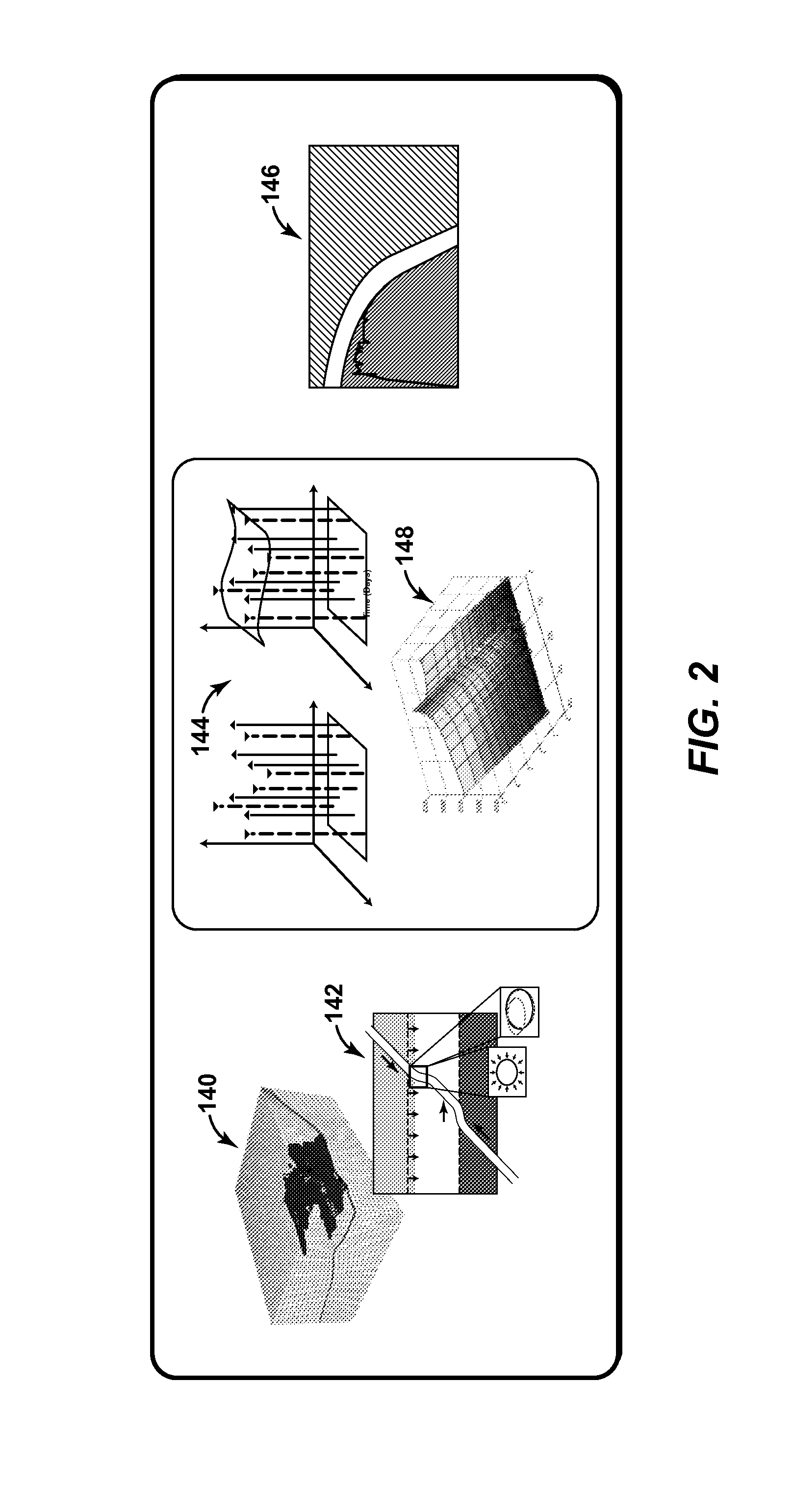
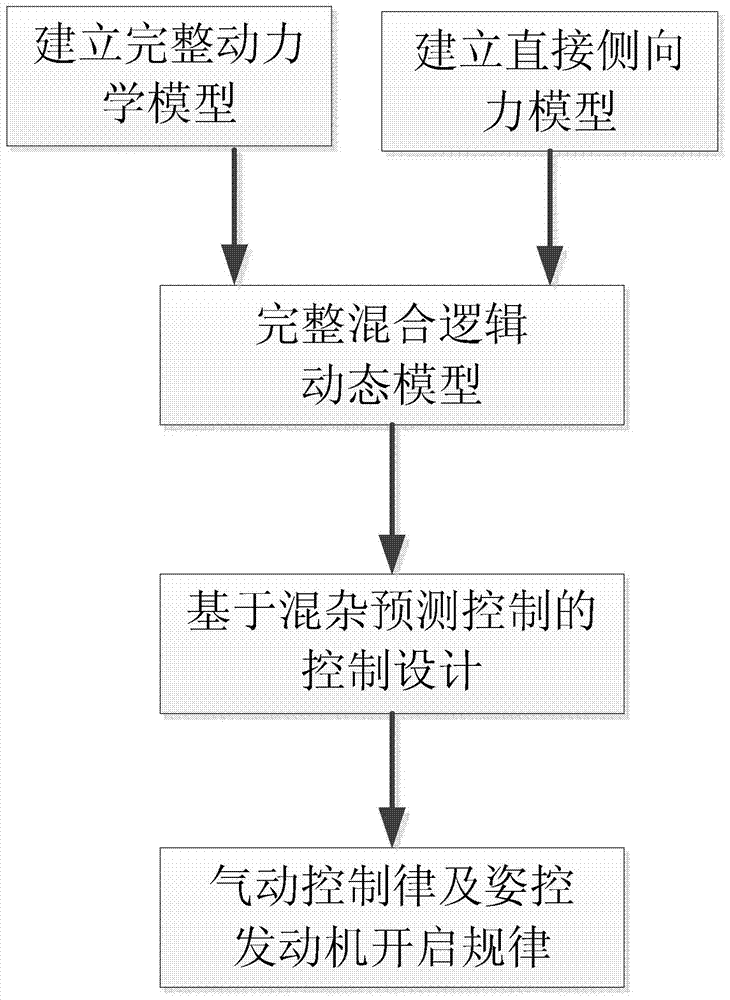
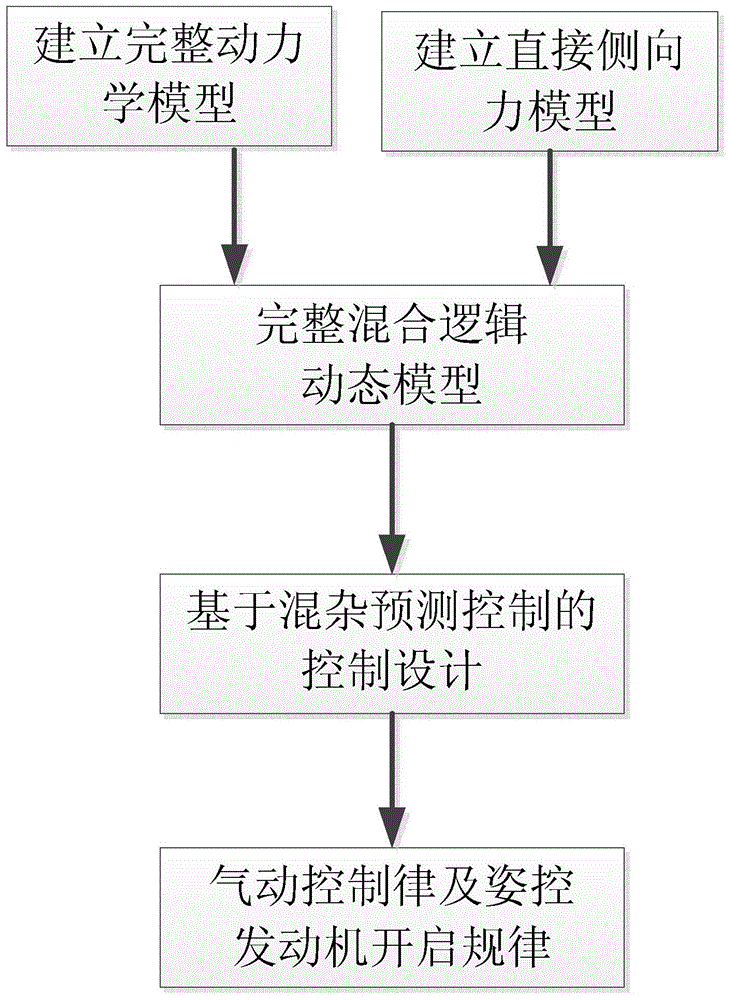
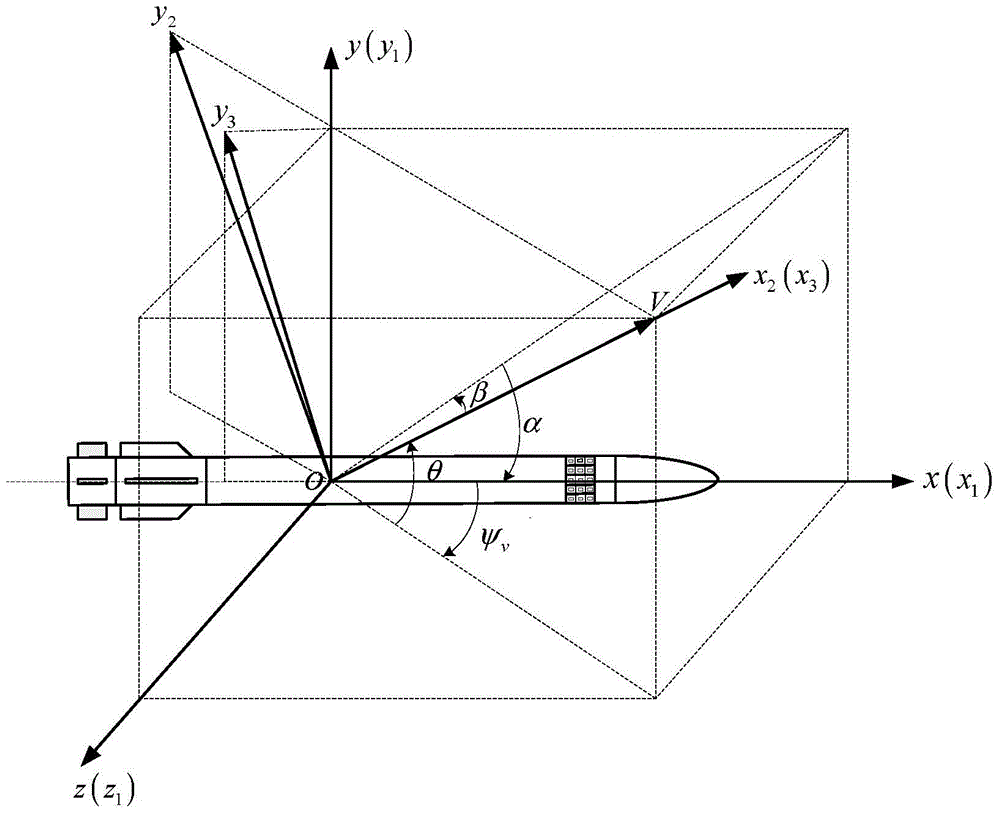
The invention discloses an attitude control type direct lateral force and aerodynamic force composite missile attitude control method based on mixed forecasting control, belongs to the field of aircraft control, and solves the problem that a nonlinear characteristic and a control input mixing characteristic of a model cannot be simultaneously solved by an existing attitude control method. The attitude control type direct lateral force and aerodynamic force composite missile attitude control method is characterized by comprising the following steps: constructing a complete direct lateral force and aerodynamic force composite missile attitude control model and a direct lateral force model, and converting a nonlinear kinetic model into a piecewise affine model by analyzing an aerodynamic characteristic; constructing a composite control missile mixing logic dynamic model by considering the mixing characteristic of a control input according to the equivalence property of the piecewise affine model and the mixing logic dynamic model; designing an explicit model forecasting control rule based on the mixing logic dynamic model so as to determine an aerodynamic steering engine control rule and an attitude control engine starting rule. The method disclosed by the invention is suitable for being used in the field of aircraft missile control.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Robust stereo calibration system and method for accurate digital image correlation measurements
ActiveUS8248476B2Maintain accuracyConvenient and accurateUsing optical meansTelevision systemsExplicit modelObject point
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA
Space-time surrogate models of subterranean regions
Methods for creating and using space-time surrogate models of subsurface regions, such as subsurface regions containing at least one hydrocarbon formation. The created surrogate models are explicit models that may be created from implicit models, such as computationally intensive full-physics models. The space-time surrogate models are parametric with respect to preselected variables, such as space, state, and / or design variables, while also indicating responsiveness of the preselected variables with respect to time. In some embodiments, the space-time surrogate model may be parametric with respect to preselected variables as well as to time. Methods for updating and evolving models of subsurface regions are also disclosed.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
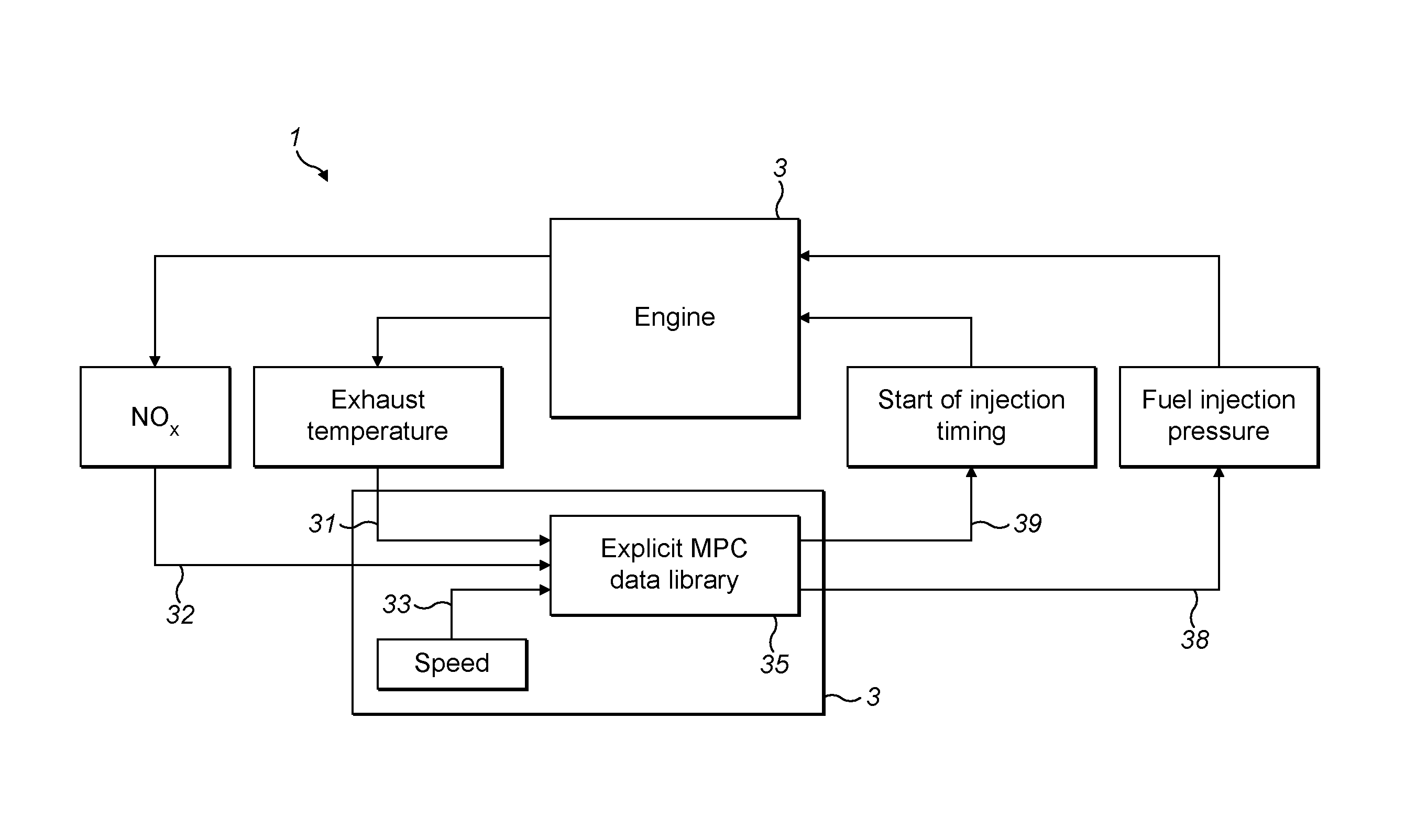
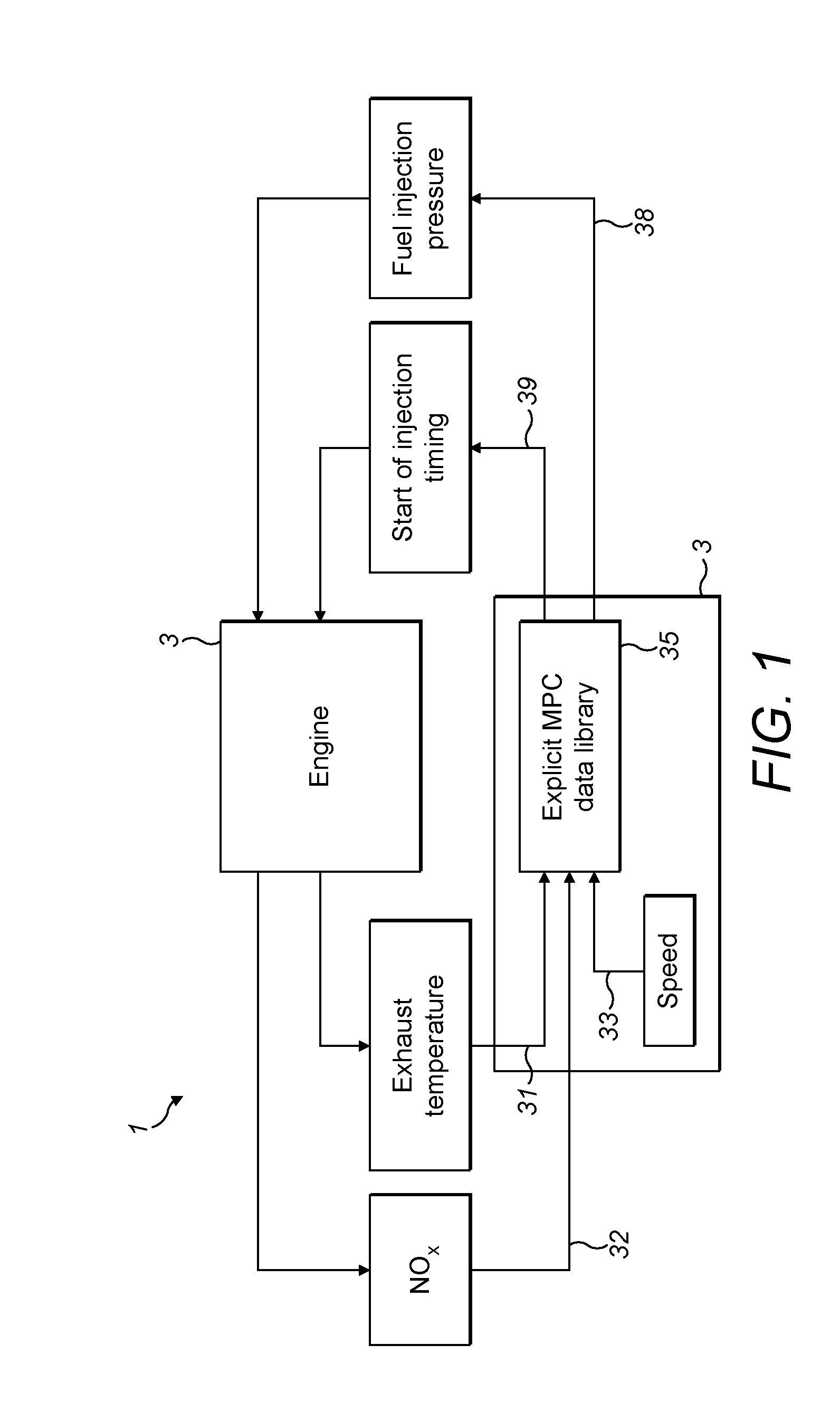
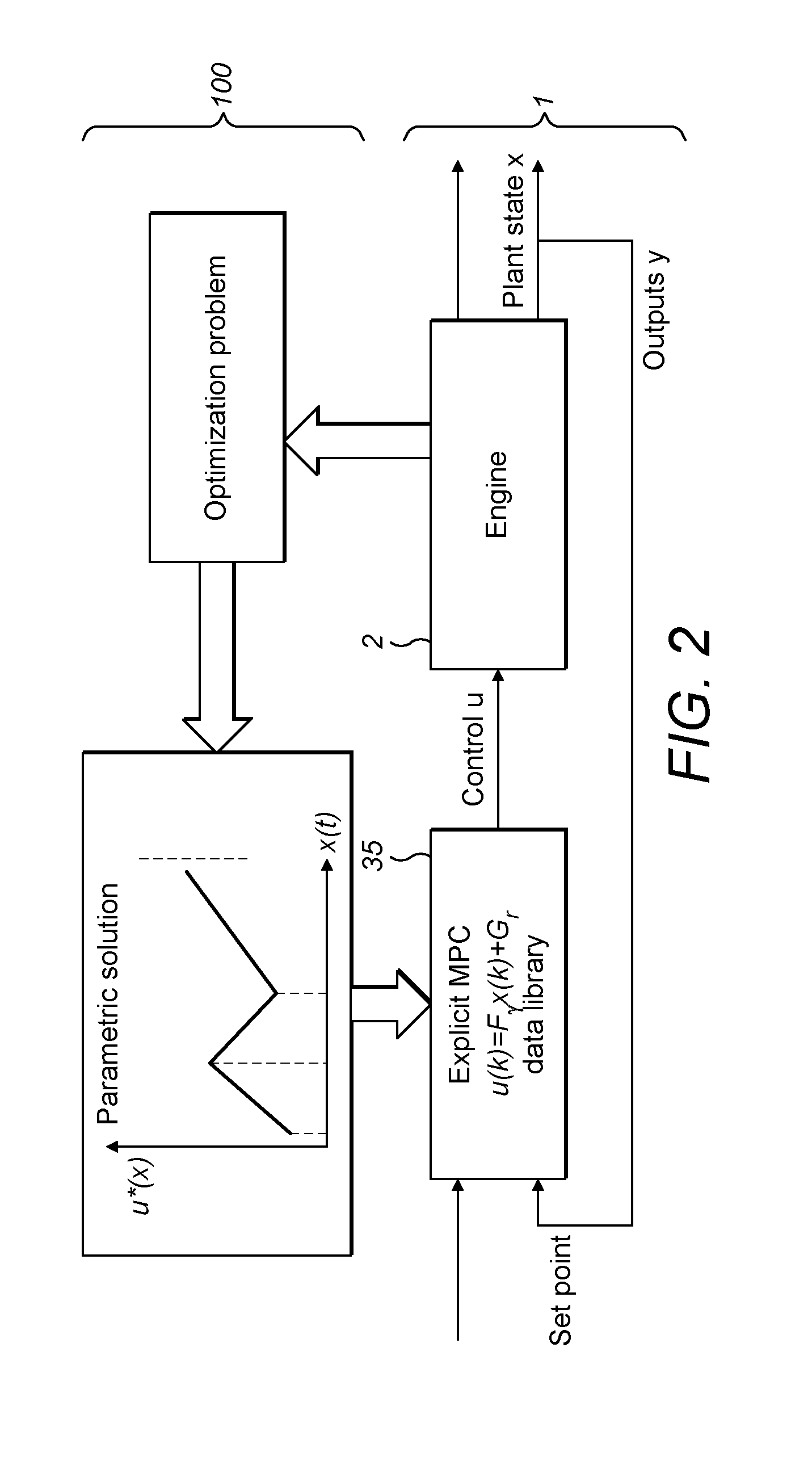
Optimised Real-Time Control of a Highly Dynamic Engine System
InactiveUS20150066337A1Analogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlExplicit modelControl system
Large numbers of engine parameters result in a need for significant processing power to calculate the engine control values using algorithms in real-time. The disclosure provides an engine control system having a data library comprising an explicit model predictive control derived set of output data values. The data library comprises a subset of output data values in respect of each combination of input data values. The subset of output data values may be configured to control one or more aspects of engine performance.
Owner:PERKINS ENGINES
Intelligent control with hierarchical stacked neural networks
InactiveUS8788441B1Increased complexityMajority/minority circuitsGeneral purpose stored program computerExplicit modelInterconnection
An intelligent control system based on an explicit model of cognitive development (Table 1) performs high-level functions. It comprises up to O hierarchically stacked neural networks, Nm, . . . , Nm+(O−1), where m denotes the stage / order tasks performed in the first neural network, Nm, and O denotes the highest stage / order tasks performed in the highest-level neural network. The type of processing actions performed in a network, Nm, corresponds to the complexity for stage / order m. Thus N1 performs tasks at the level corresponding to stage / order 1. N5 processes information at the level corresponding to stage / order 5. Stacked neural networks begin and end at any stage / order, but information must be processed by each stage in ascending order sequence. Stages / orders cannot be skipped. Each neural network in a stack may use different architectures, interconnections, algorithms, and training methods, depending on the stage / order of the neural network and the type of intelligent control system implemented.
Owner:COMMONS MICHAEL LAMPORT +1
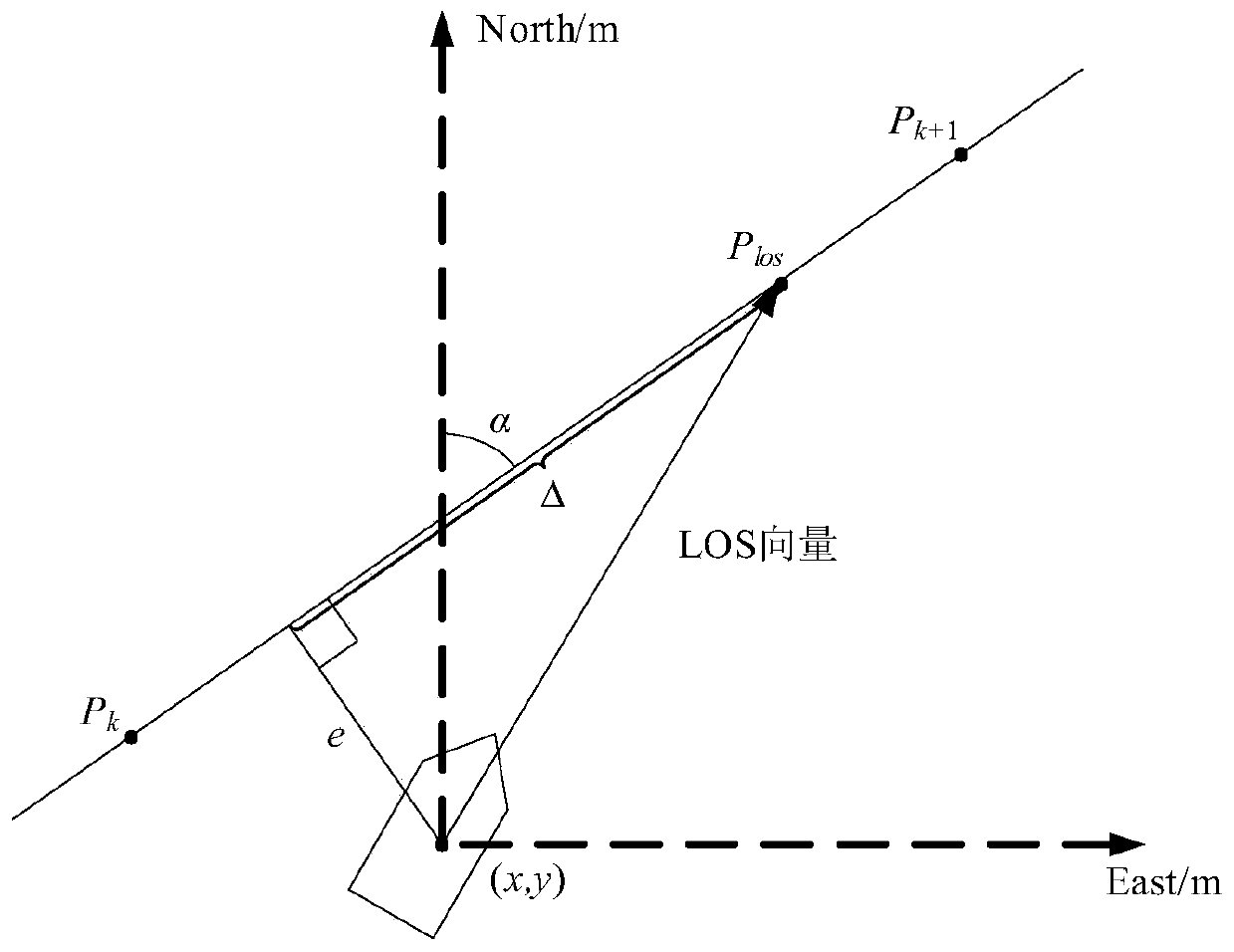
Explicit model forecast control-based flight path control method of unmanned surface vehicle
ActiveCN110618686ARealize no static difference controlSave resourcesAutonomous decision making processSustainable transportationExplicit modelControl system
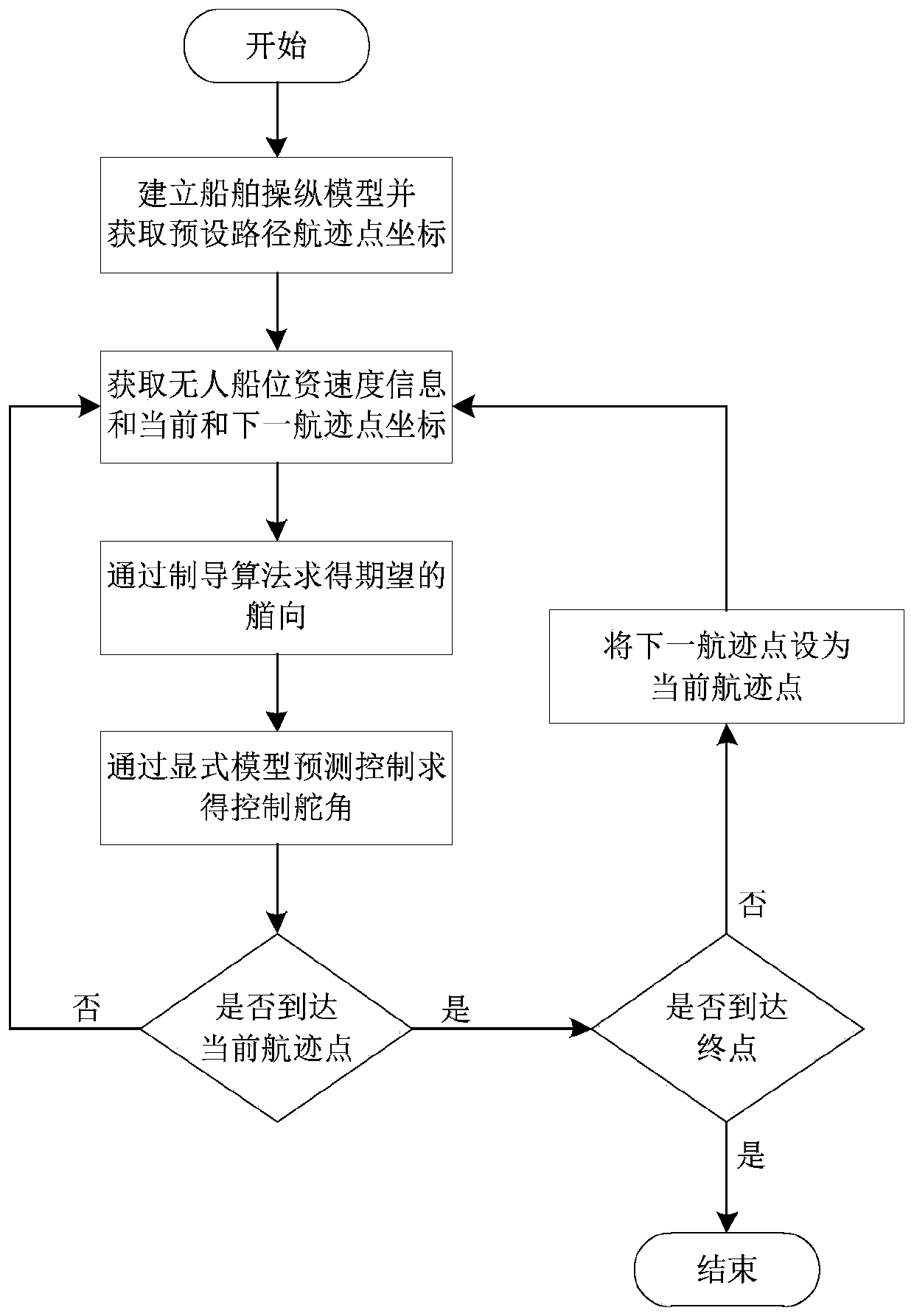
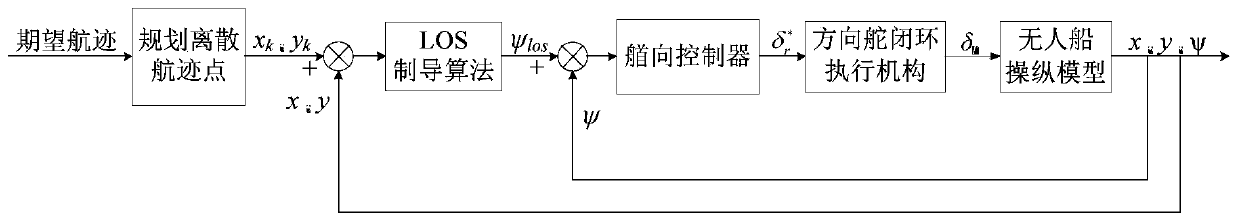
The invention discloses an explicit model forecast control-based flight path control method of an unmanned surface vehicle. The explicit model forecast control-based flight path control method comprises the steps of firstly, building a control model of the unmanned surface vehicle, and acquiring position gesture and reference flight path point information of the unmanned surface vehicle; secondly,calculating expected flight speed and heading direction in real time according to a path planning algorithm, and simplifying ship flight path control to heading direction control; and finally, obtaining a rotational speed and a rudder angle of a propeller by a display model forecast control algorithm for the unmanned surface vehicle to achieve ship flight path control. The explicit model forecastcontrol algorithm is applied to the field of flight path control of the unmanned surface vehicle, the complicated on-line optimization process is converted to simple table lookup process by introducing a multi-parameter secondary planning theory, the on-line calculation complexity is reduced, and the real-time performance of a flight path control system is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
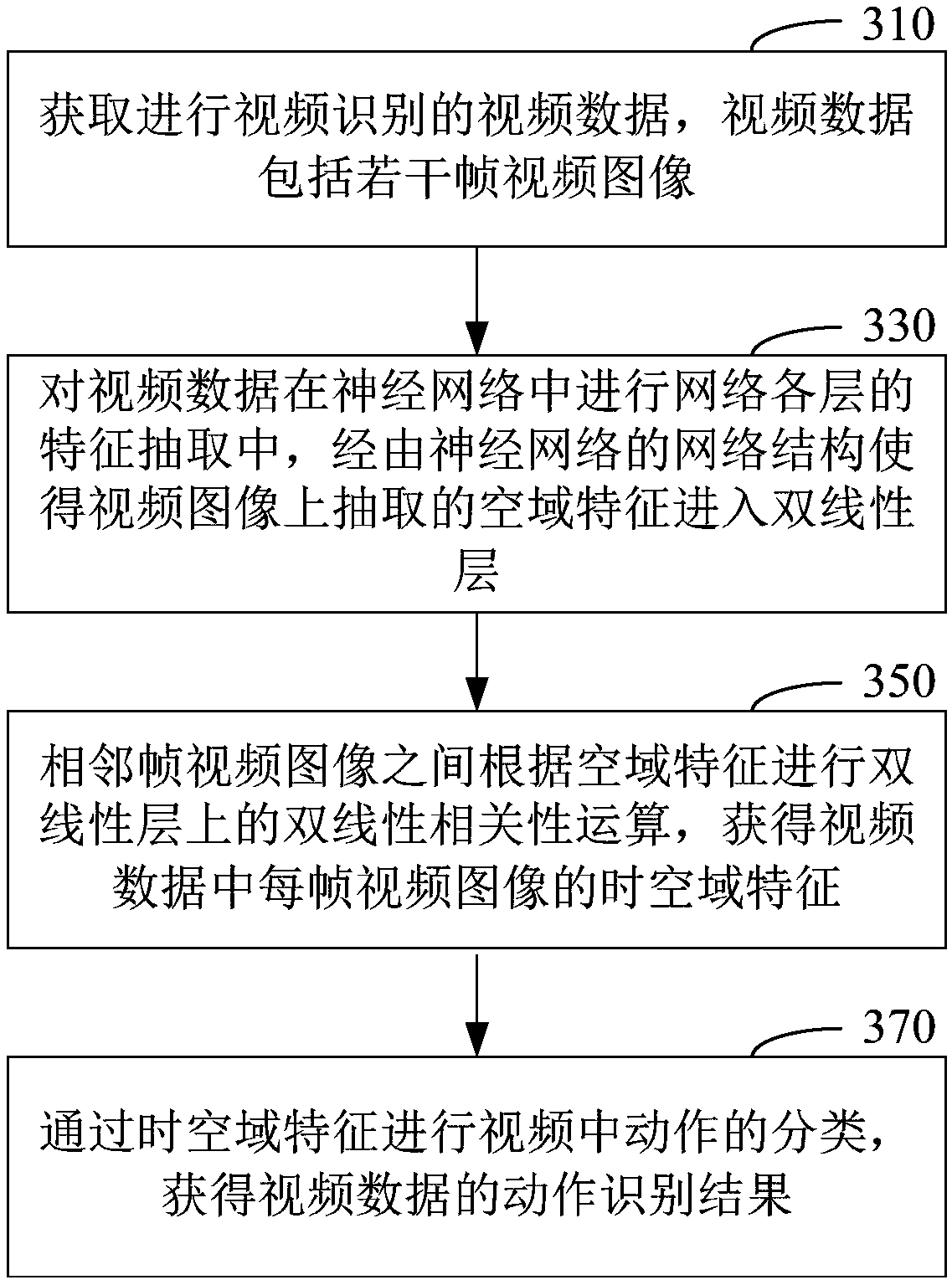
Video action recognition method and device and machine equipment
ActiveCN110163052AImprove performanceImplement explicit modelingCharacter and pattern recognitionTime domainLinear correlation
The invention discloses a video action recognition method and device and machine equipment. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring video data for action recognition; when the video data is subjected to feature extraction of each layer of the network in the neural network, enabling the extracted spatial domain features on the video image to enter a bilinear layer through the network structure of the neural network; performing bilinear correlation operation on the adjacent frames of video images according to the spatial domain characteristics to obtain the time-spatial domain characteristics of each frame of video image in the video data; classifying actions in the video through the time-space domain features to obtain an action recognition result of the video data. For featureextraction of each layer of the network in the neural network, parameters and calculation complexity in bilinear correlation operation on a bilinear layer are controlled, and then time-space domain features are extracted under the condition of control complexity, so that explicit modeling on a time domain relationship is realized, and the performance of action recognition is effectively improved.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
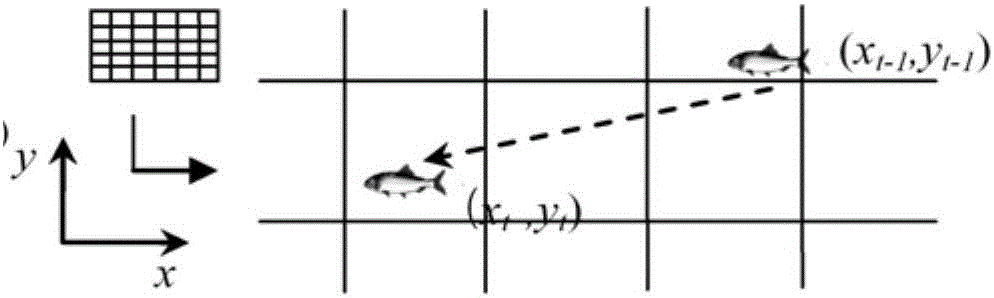
Fish movement and spatial distribution simulation method and system based on individual mode
ActiveCN106611079ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsExplicit modelModel parameters
The invention discloses a fish movement and spatial distribution simulation method and a fish movement and spatial distribution simulation system based on an individual mode. The method comprises the steps of building a fish movement spatial explicit model based on ecological behaviors of fish, and simulating a movement process of each fish individual by coupling with a water environment model; and acquiring space-time dynamic distribution of the fish. According to the method and the system provided by the invention, during a process of building a simulation model, easy acquisition of model parameters and actual ecological significance of the parameters are considered, and the defect of a messy situation based on the fragmented individual fish models is remedied, so that the method and the system are universal.
Owner:NANJING HYDRAULIC RES INST
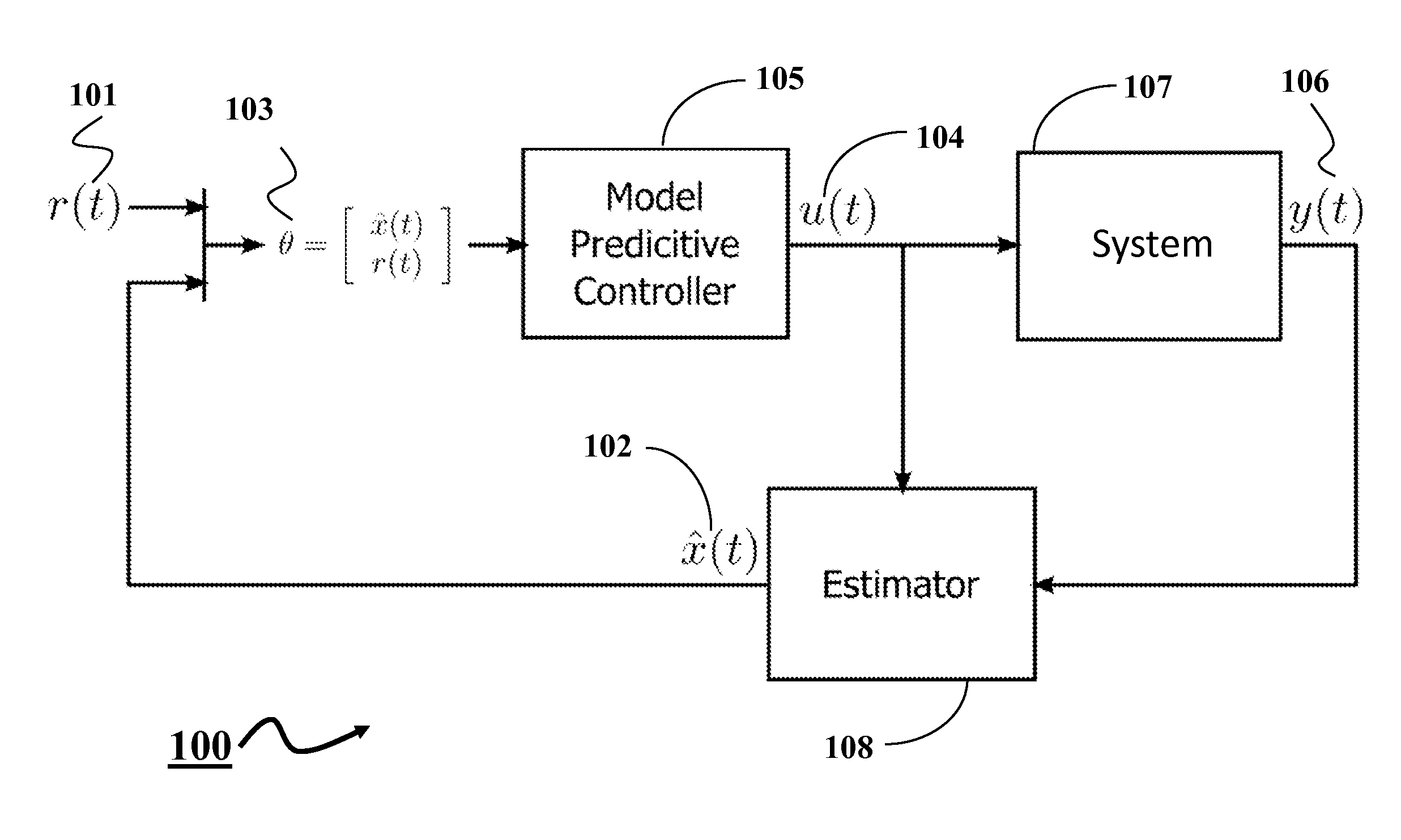
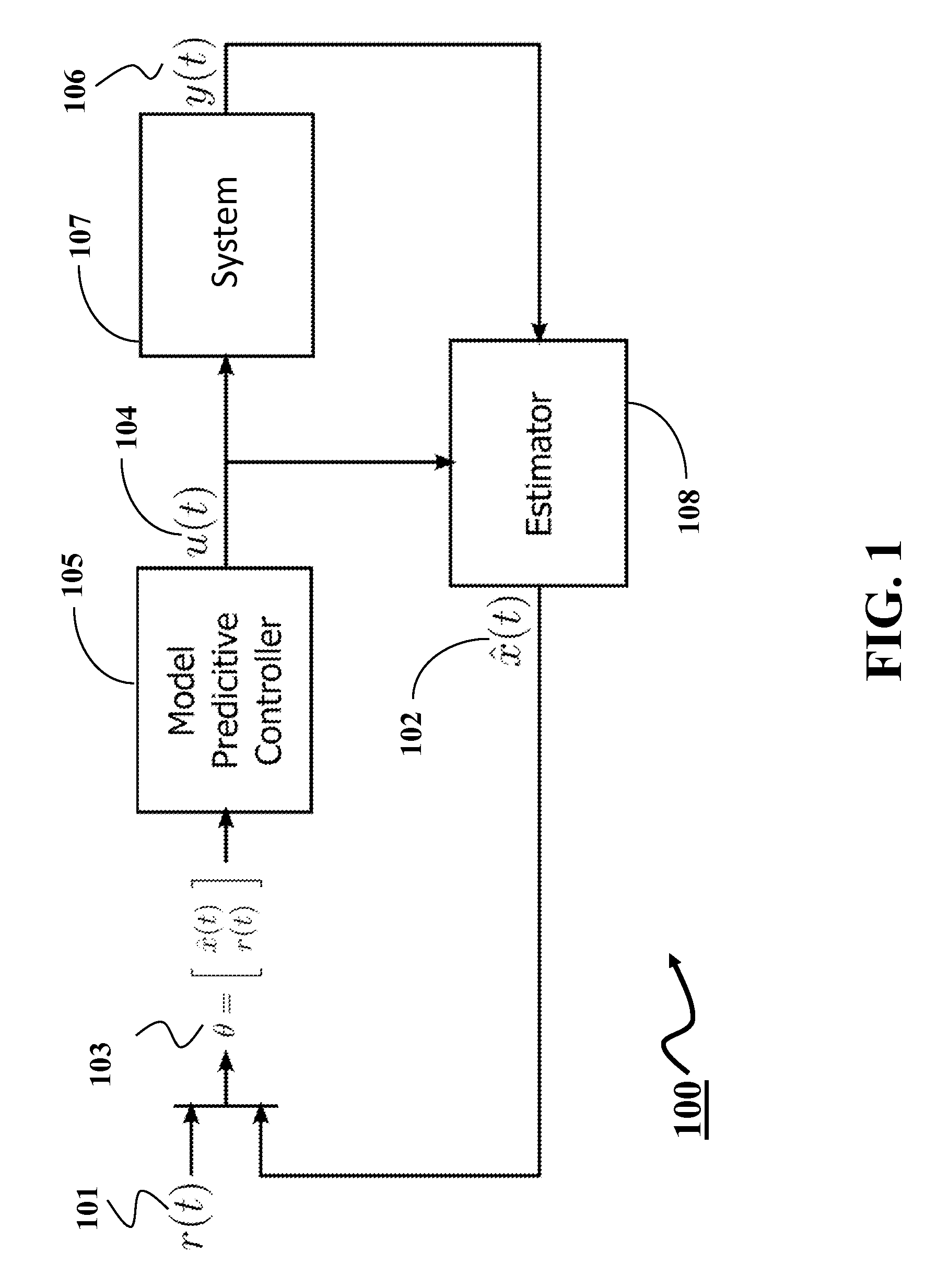
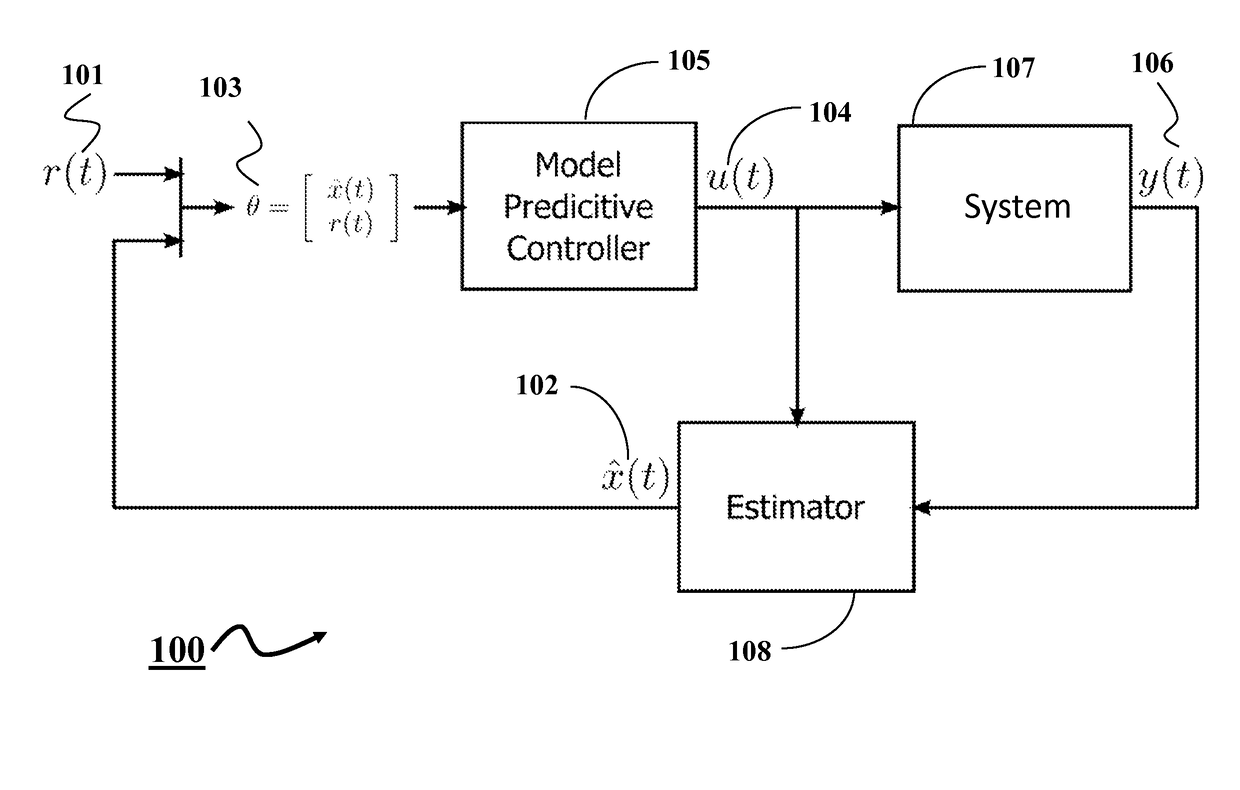
System and Method for Explicit Model Predictive Control
A method for controlling a system using an explicit model predictive control (EMPC) evaluates, with respect to a state of the system, each inequality in a set of inequalities defining a set of regions of a state space of the system to produce a set of Boolean results. At least some of the inequalities are evaluated concurrently, and a size of the set of Boolean results equals a size of the set of inequalities. The method determines a region including the state by applying a Boolean function to elements of the set of Boolean results corresponding to inequalities forming boundaries of the region and determines a control for the system based on the state and a gain associated with the region. At least some Boolean functions are applied to corresponding elements concurrently after all elements in the set of Boolean results are evaluated.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Automatic in-situ registration and calibration of robotic arm/sensor/workspace system
Various technologies described herein pertain to automatic in-situ calibration and registration of a depth sensor and a robotic arm, where the depth sensor and the robotic arm operate in a workspace. The robotic arm can include an end effector. A non-parametric technique for registration between the depth sensor and the robotic arm can be implemented. The registration technique can utilize a sparse sampling of the workspace (e.g., collected during calibration or recalibration). A point cloud can be formed over calibration points and interpolation can be performed within the point cloud to map coordinates in a sensor coordinate frame to coordinates in an arm coordinate frame. Such technique can automatically incorporate intrinsic sensor parameters into transformations between the depth sensor and the robotic arm. Accordingly, an explicit model of intrinsics or biases of the depth sensor need not be utilized.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
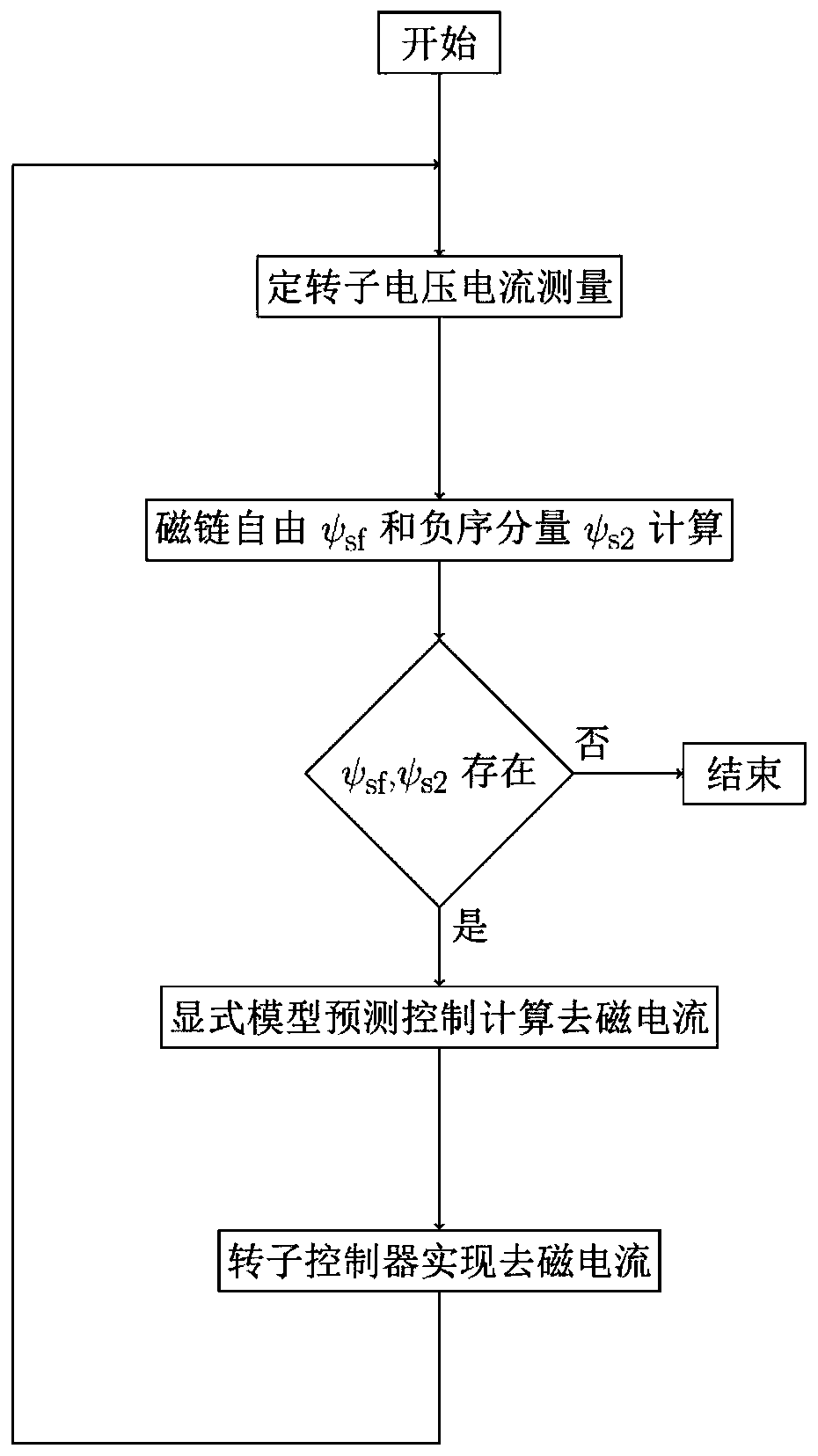
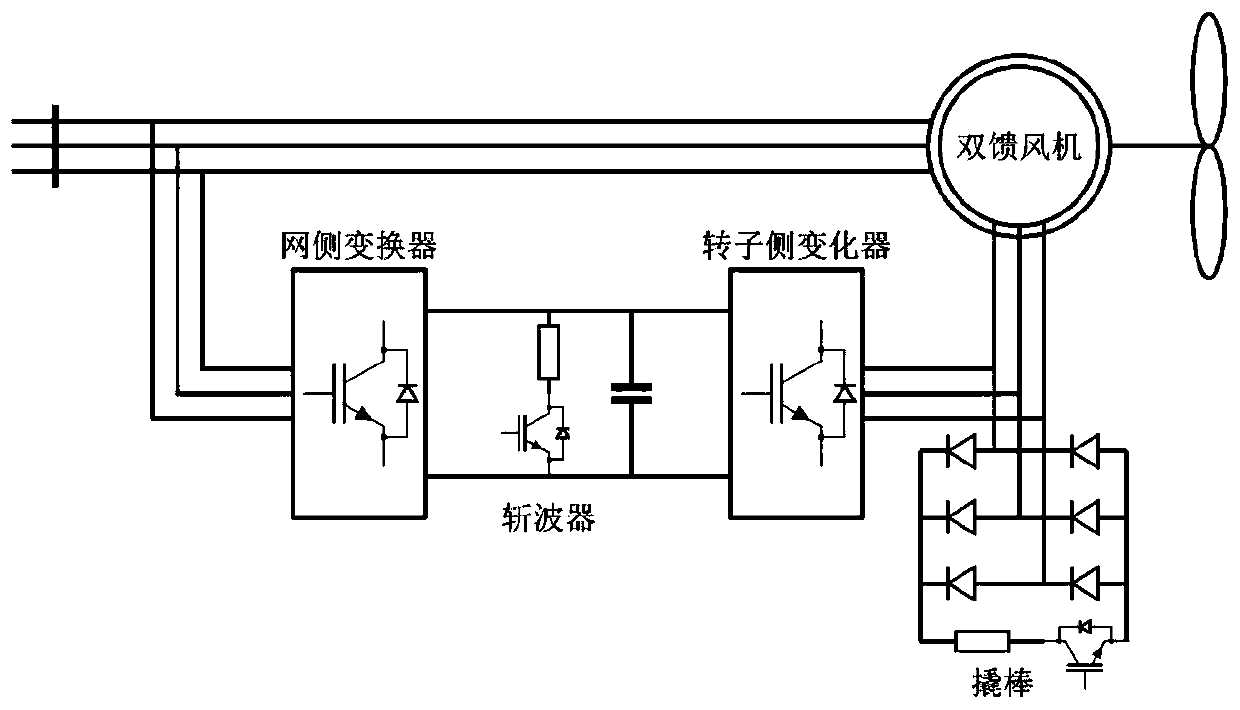
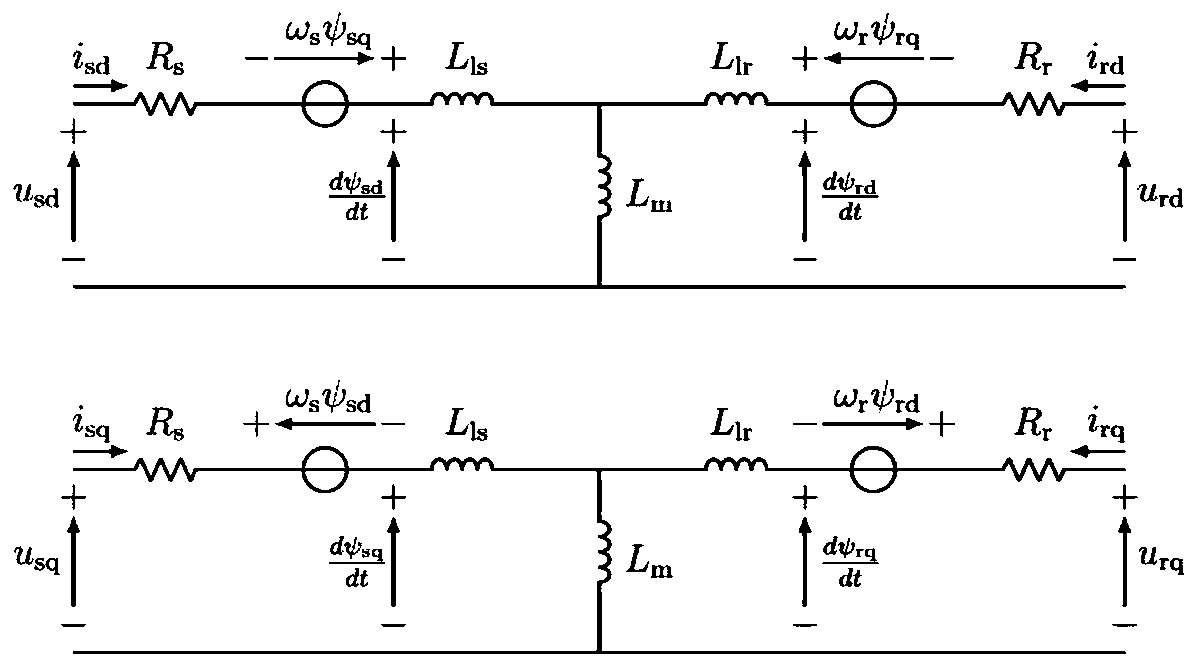
Doubly-fed fan fault ride-through method and system based on explicit model predictive control
ActiveCN110635513AFlexible adjustmentFull use of capacityGenerator control circuitsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsTransient stateExplicit model
The invention provides a doubly-fed fan fault ride-through method and system based on explicit model predictive control. The defect of fixed coefficients of traditional demagnetization control is overcome; demagnetization current can be flexibly adjusted according to a fault condition to give full play to the capacity of a rotor side converter; on the basis of the traditional demagnetization control, redundant measurement links are not needed, and the method and the system can be suitable for various fault types and fault depths, suitable for online optimization control, and can meet the transient response requirements of the doubly-fed fan in the power grid fault period.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
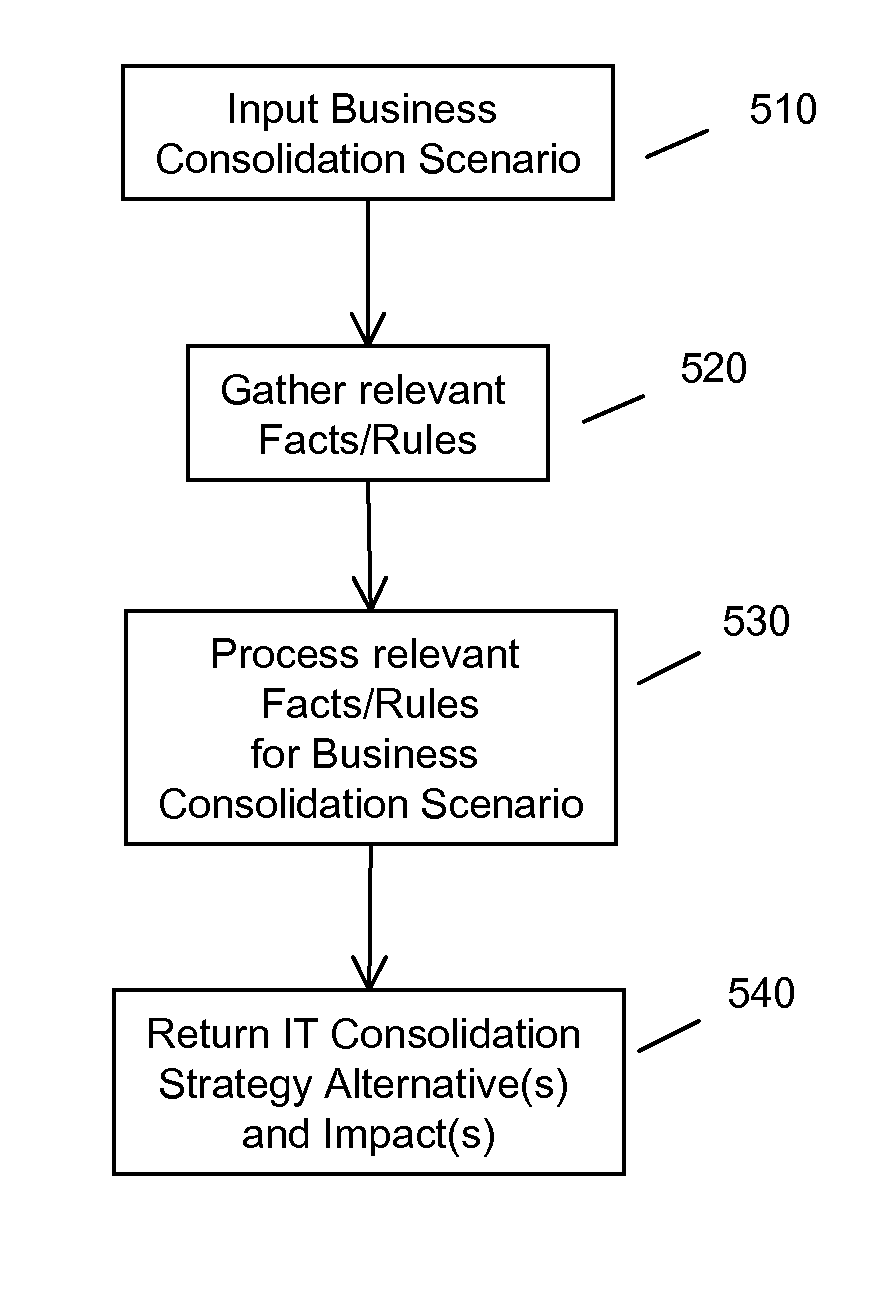
Business driven combination of service oriented architecture implementations
Systems, methods, apparatuses and program products configured to provide information technology (IT) system combination strategies are described. An explicit model of business to IT dependency is described and utilized by the systems and methods described to expose trade-offs in different combination alternatives, thus assisting in making proactive choices regarding business combination of disparate IT systems and resources.
Owner:IBM CORP
A method for predicting the temperature rise of transformer hot spots by comparing optical fiber temperature measurement
InactiveCN109344559AImprove robustnessStrong global optimizationArtificial lifeDesign optimisation/simulationExplicit modelElectric power system
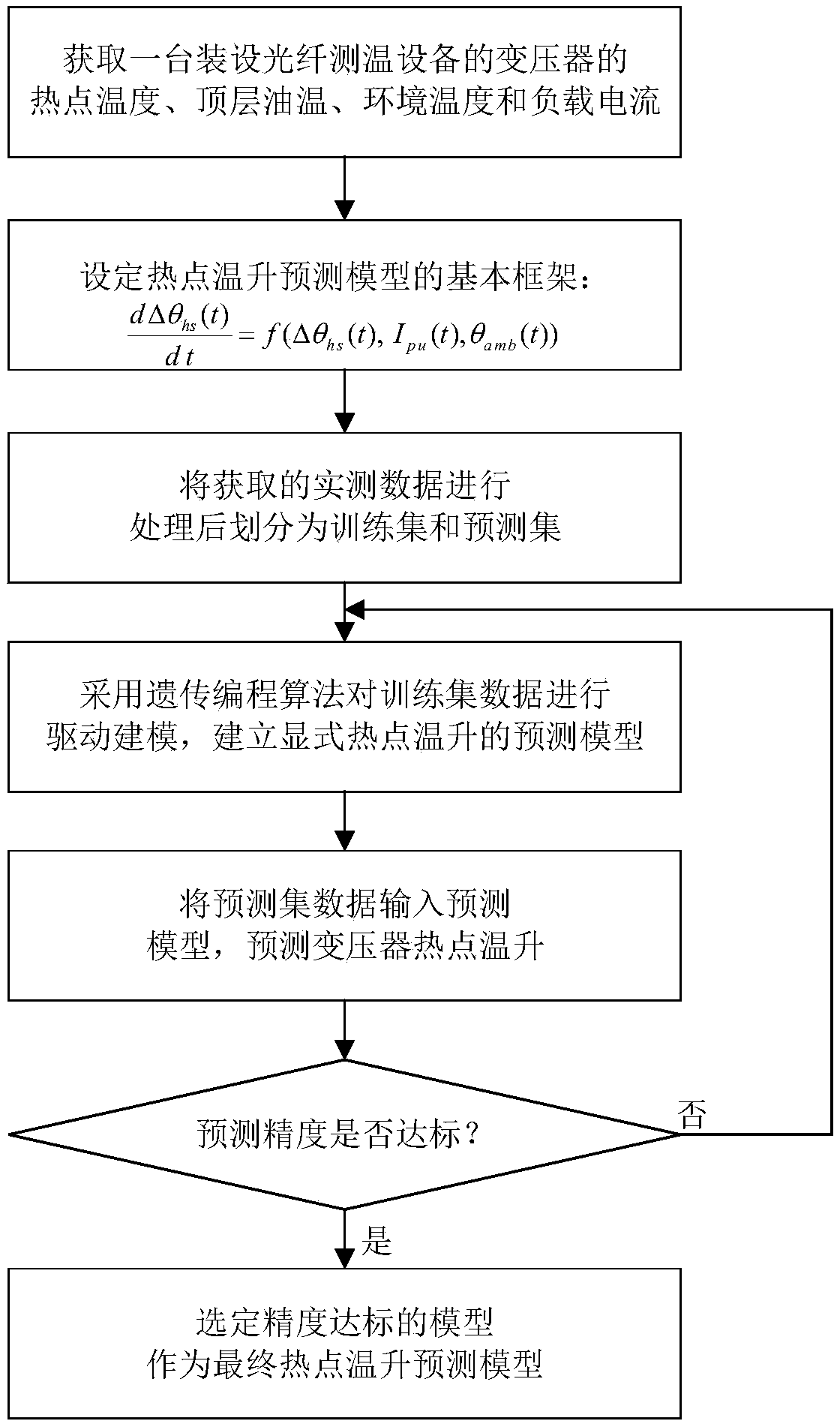
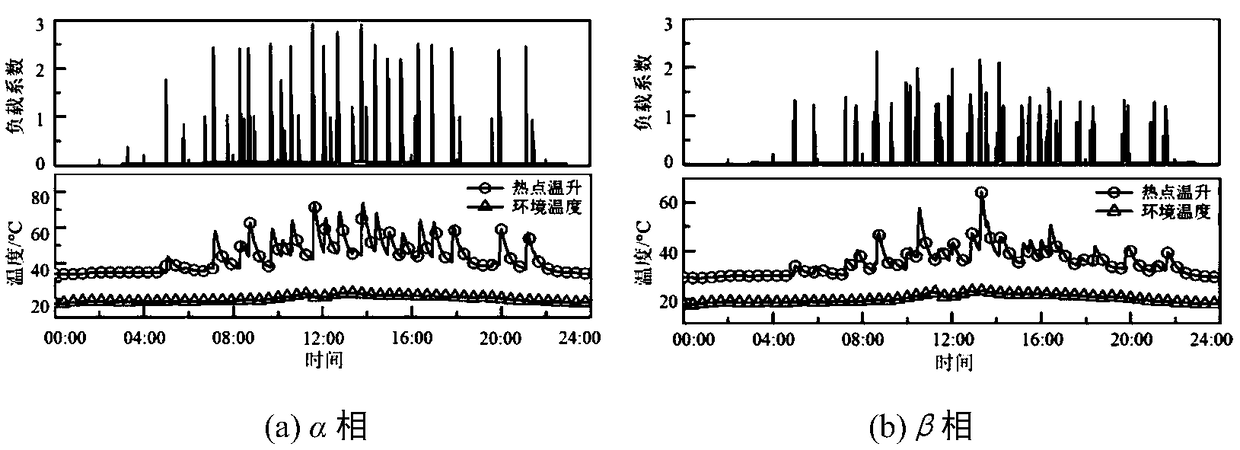
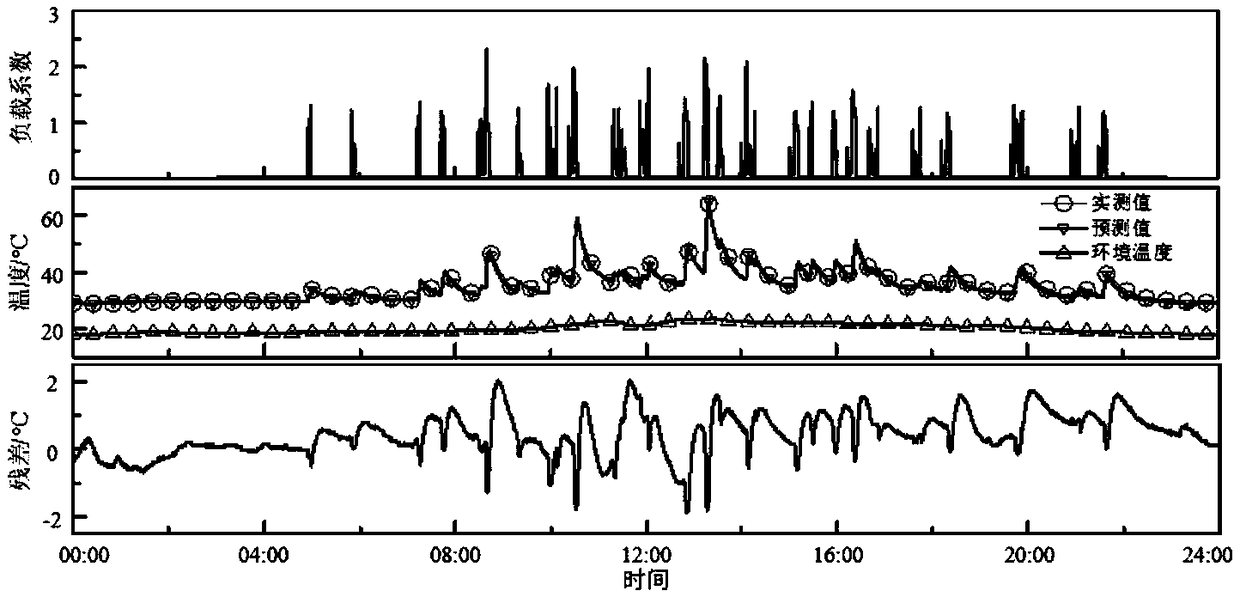
The invention discloses a transformer hot spot temperature rise prediction method for comparing optical fiber temperature measurement, which comprises the following steps: obtaining the measured hot spot temperature, top layer oil temperature, ambient temperature and load current data of an oil-immersed transformer equipped with optical fiber temperature measurement equipment; obtaining the measured hot spot temperature, ambient temperature and load current data of an oil-immersed transformer installed with optical fiber temperature measurement equipment; Setting up the basic frame of the hotspot temperature rise prediction model; dividing The measured data into training set and prediction set after being processed. Adopting Genetic Programming (GA) to model the data of training set, andsetting up an explicit model for predicting the temperature rise of hot spots. Inputting the data of prediction set into the prediction model to predict the temperature rise of transformer hot spots.The invention has the beneficial effects that an explicit hot spot temperature rise prediction model is finally established, and the mechanism of the hot spot temperature rise dynamic change with theload can be intuitively disclosed; With strong generalization performance, it can realize batch prediction and on-line monitoring of hot spot temperature rise of oil-immersed transformers with the same capacity in power system.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
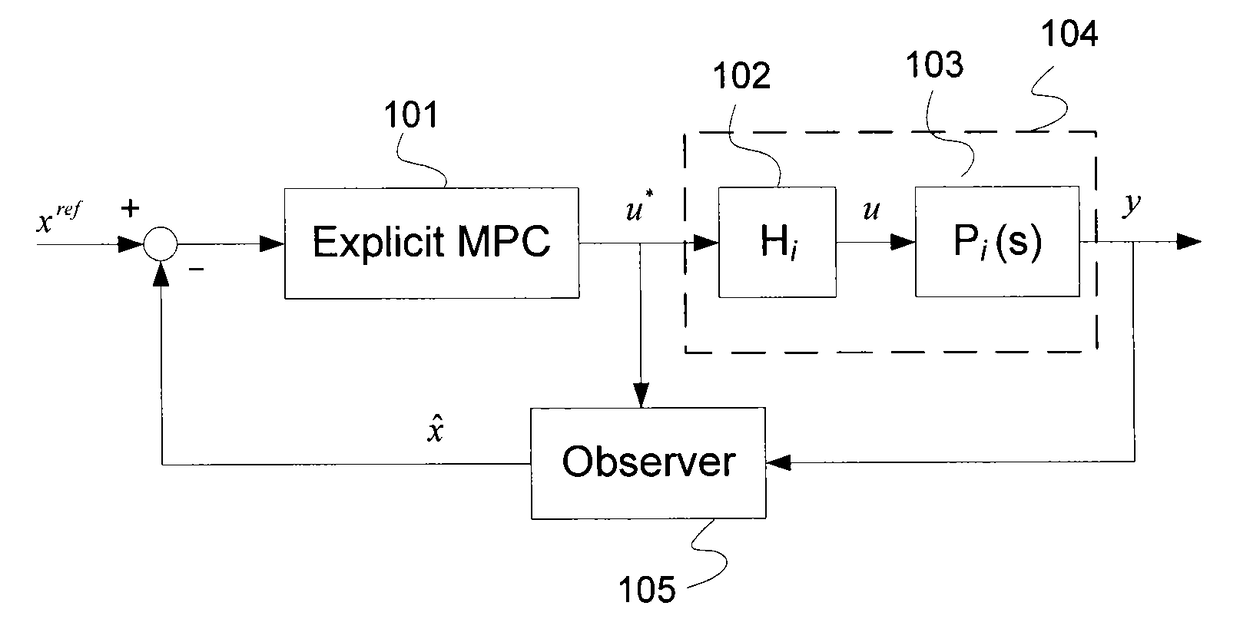
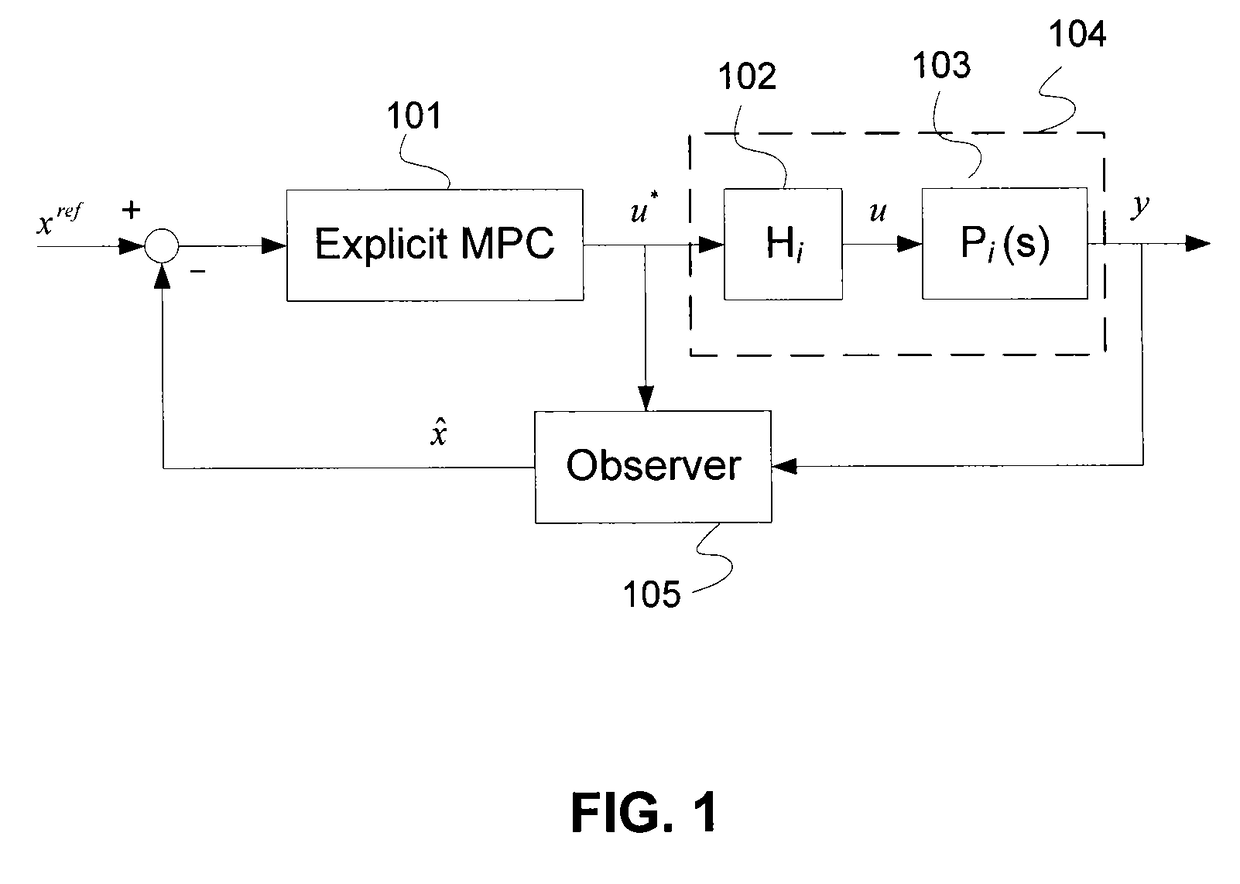
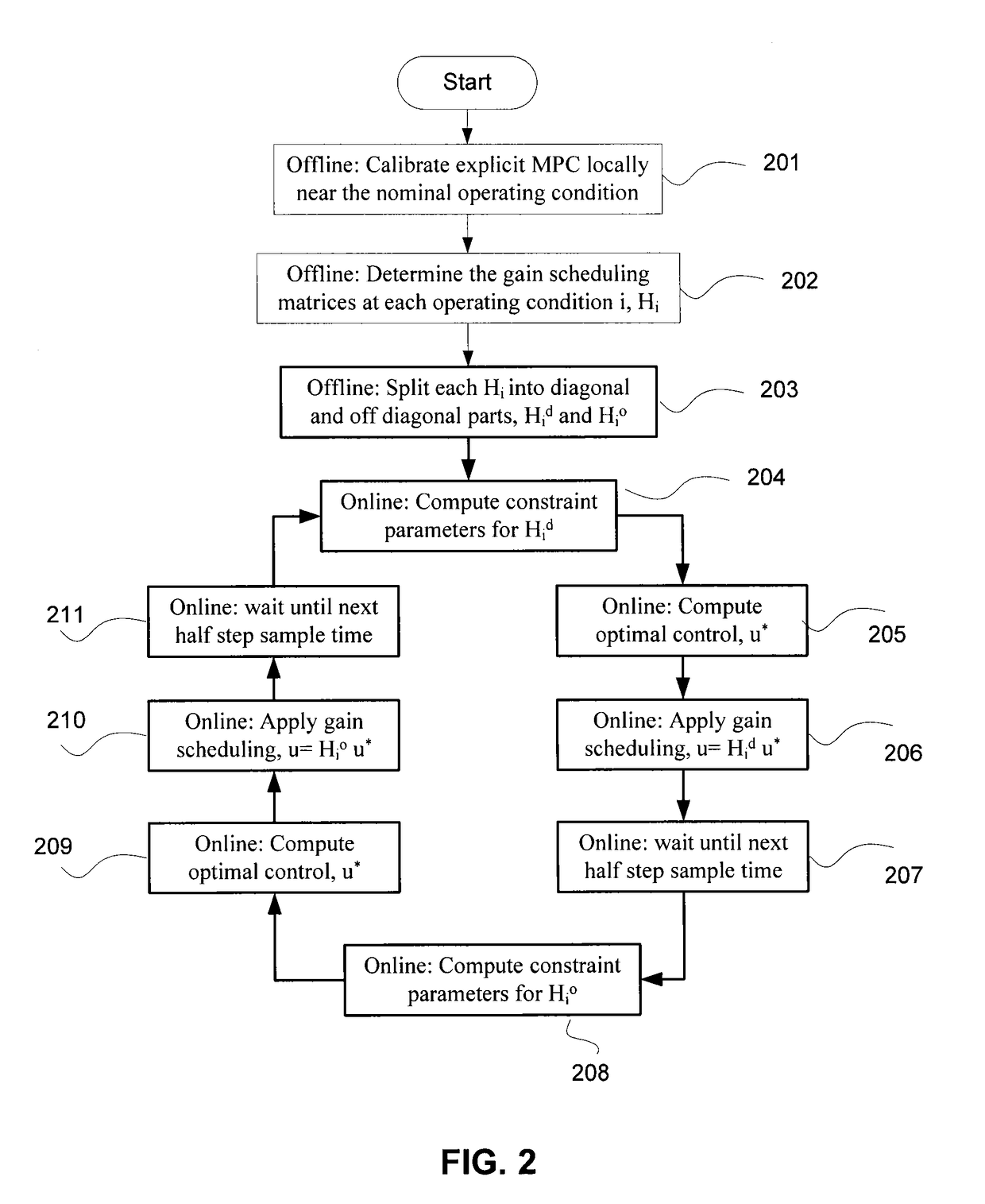
Switch gain scheduled explicit model predictive control of diesel engines
ActiveUS9765621B2Shorten the timeElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExplicit modelVariable geometry turbine
A method for controlling an internal combustion engine using a controller that controls an air flow path by adjusting at least one of a variable geometry turbine (VGT) and an exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) flow rate during engine operation. The method determines inputs, such as engine speed and fuel rate from the sensor data, and employs a switch based gain-scheduled explicit model predictive controller (MPC) responsive to the inputs to determine the air flow path.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
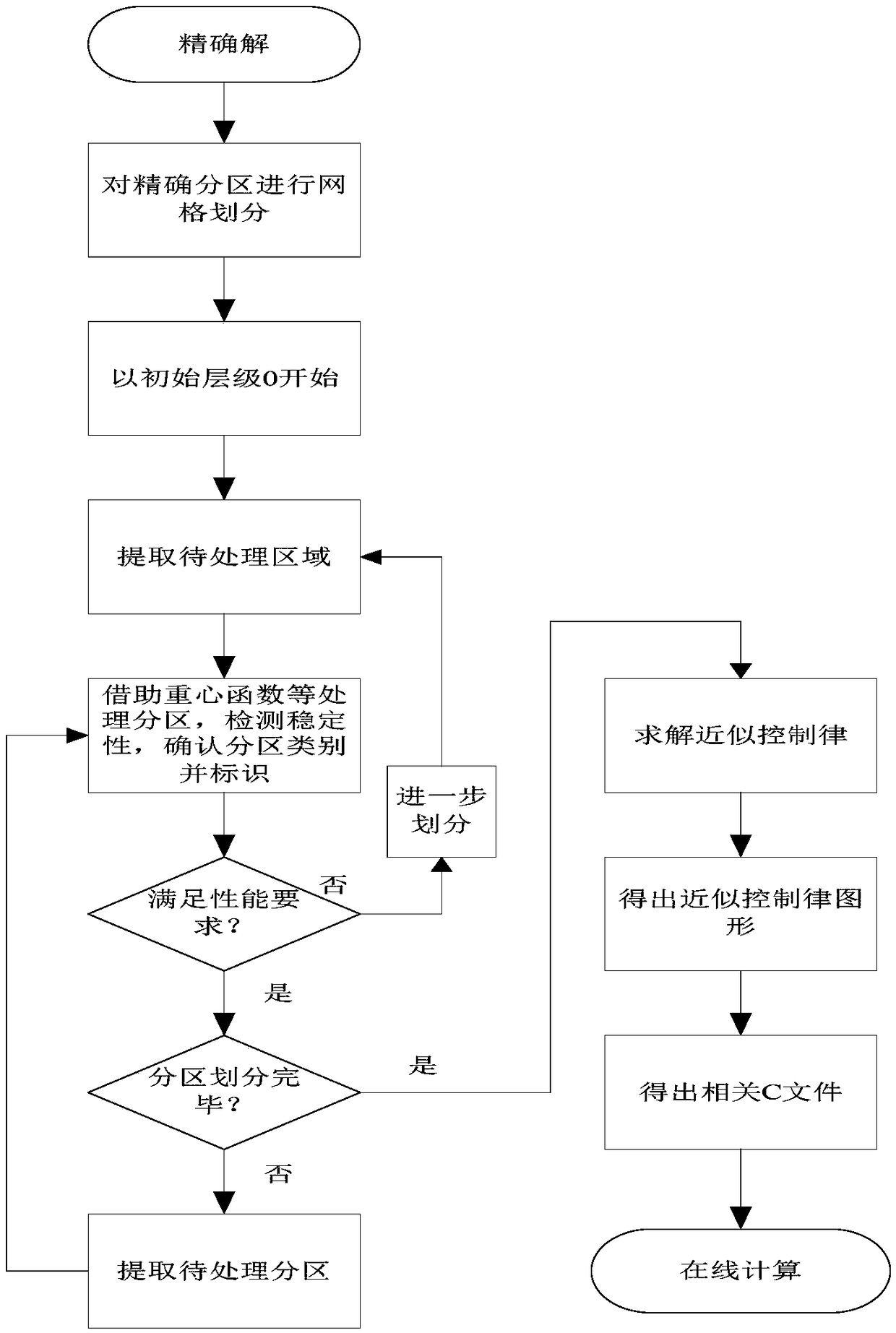
Multi-scale approximate explicit model predictive control method for mechanical vibration of high-speed elevator
ActiveCN109541939AOvercome the defects of predictive controlEasy to find onlineAdaptive controlExplicit modelPerformance index
The invention provides a multi-scale approximate explicit model predictive control method for the mechanical vibration of a high-speed elevator. The method comprises the steps that 1) an elevator mechanical vibration system is modeled to acquire the performance index function of the elevator mechanical vibration system, and the function is an object to be approximated; 2) a piecewise linear interpolation method is used to initially acquire an approximate control law; 3) adaptive hierarchical function approximation is carried out to transform the form of the approximate control law; 4) a centroid function is introduced to acquire the approximate control law based on the centroid function by using centroid interpolation; and 5) multi-scale approximate explicit model predictive control of thehigh-speed elevator mechanical vibration system is carried out.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
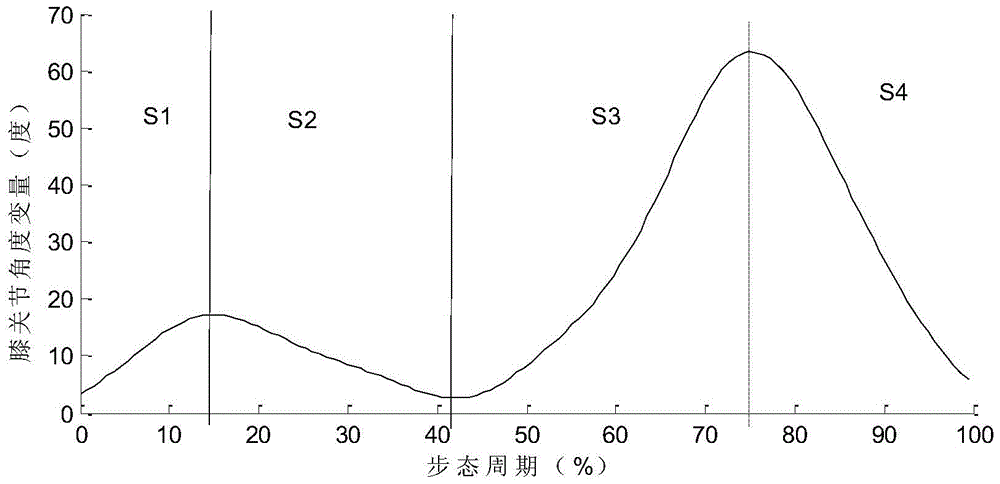
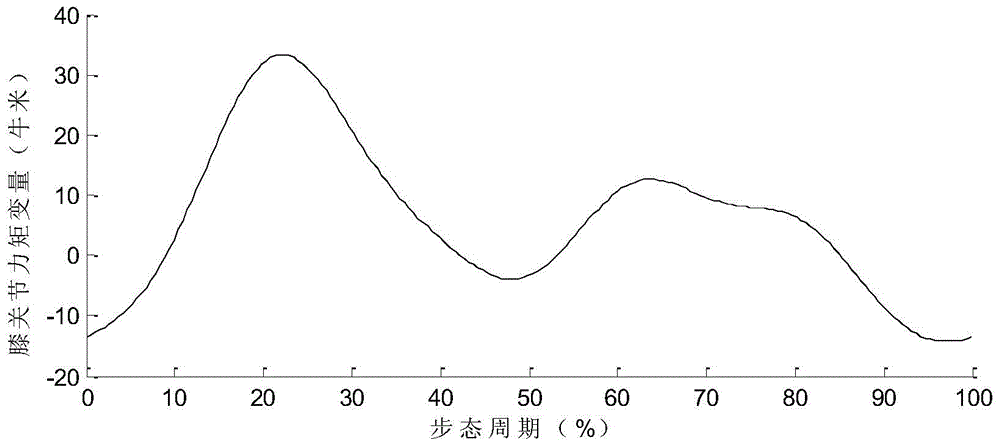
Predictive control method of knee joint of active upper-knee prosthesis
InactiveCN104921851BSimple online control processModel form is simpleProsthesisHuman bodyClosed loop
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
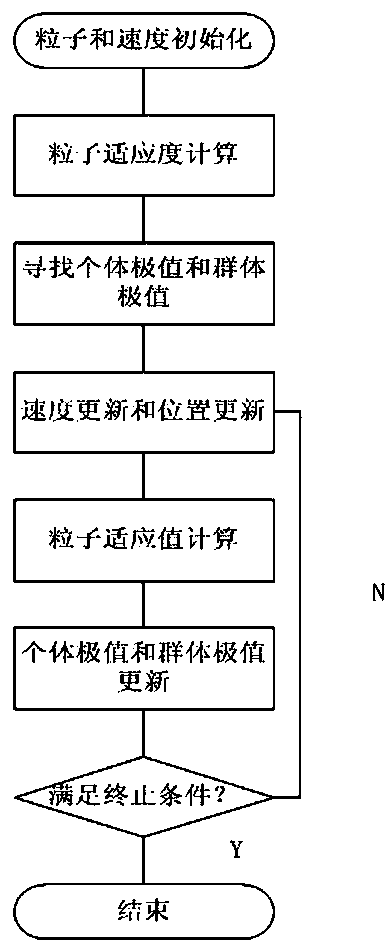
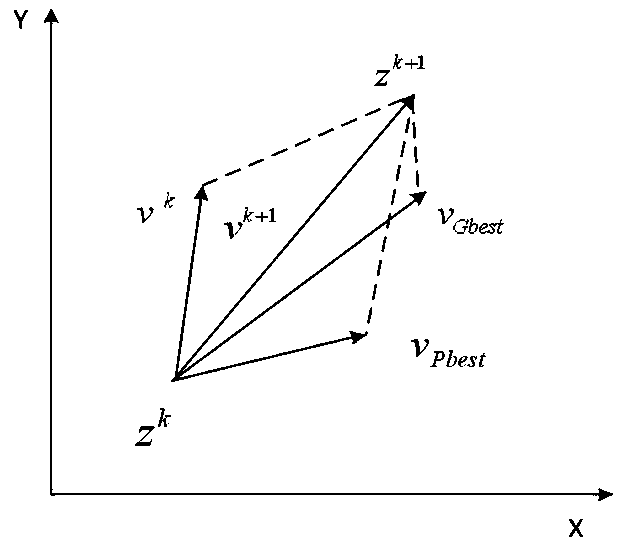
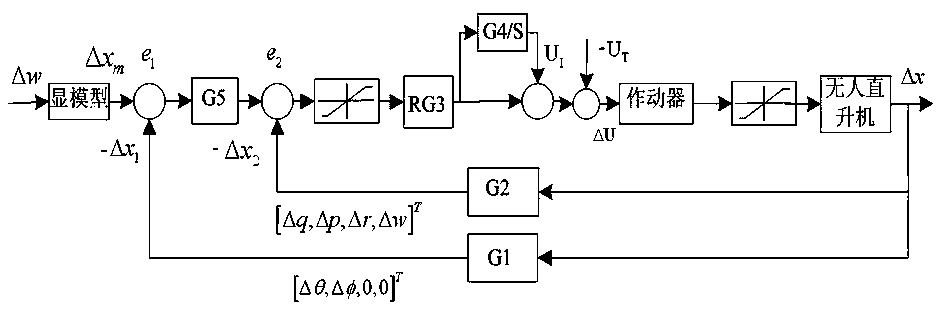
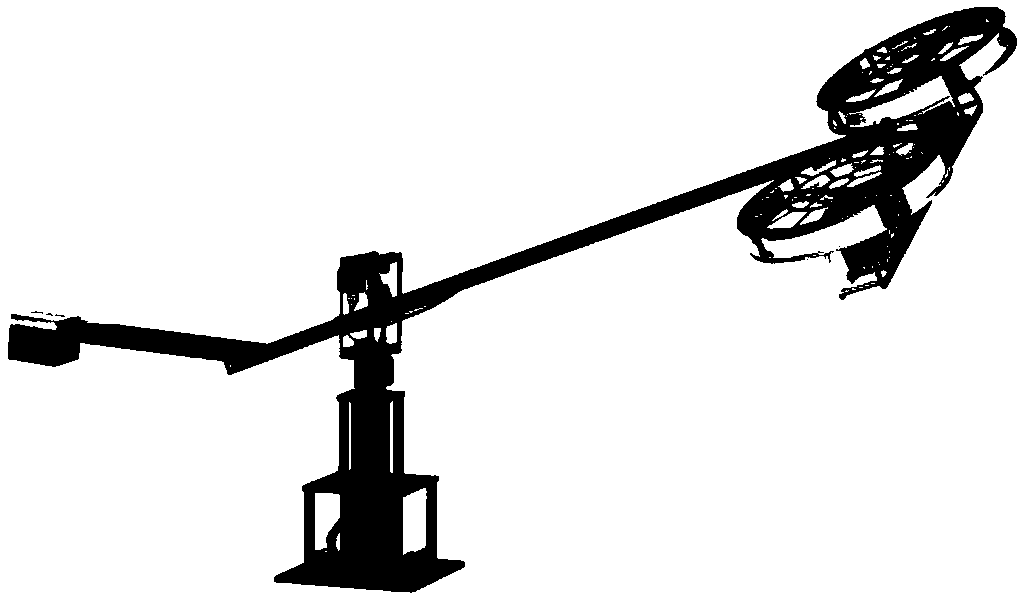
Unmanned helicopter control optimization method based on particle swarm algorithm
ActiveCN110502860AImprove handling qualityImprove robustnessArtificial lifeSpecial data processing applicationsExplicit modelControl system
The invention relates to an unmanned helicopter control optimization method based on a particle swarm algorithm, and belongs to the field of unmanned helicopter explicit model tracking control. The method comprises the following steps: determining an unmanned helicopter explicit model control system to obtain an integral constant matrix G4 and a gain diagonal matrix R; g4 and R being used as parameters in the particle swarm to be optimized through a particle swarm algorithm, and outputting a controller. According to the method, the particle swarm optimization algorithm is introduced into the explicit model control method, parameters in the unmanned helicopter controller are optimized, the control quality of the unmanned helicopter is improved, and the robustness of a controlled object is improved. The obtained controller can enable the performance of the controlled object to be optimal in a constraint range, the design is simpler, and the use is more flexible. The method also solves the disadvantage that the selection of the integral constant matrix G4 and the gain diagonal matrix R in the traditional explicit model tracking control method depends on expert experience through a trial and error method, so that the G4 and the R can be constructed more conveniently and the optimal controller can be obtained.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
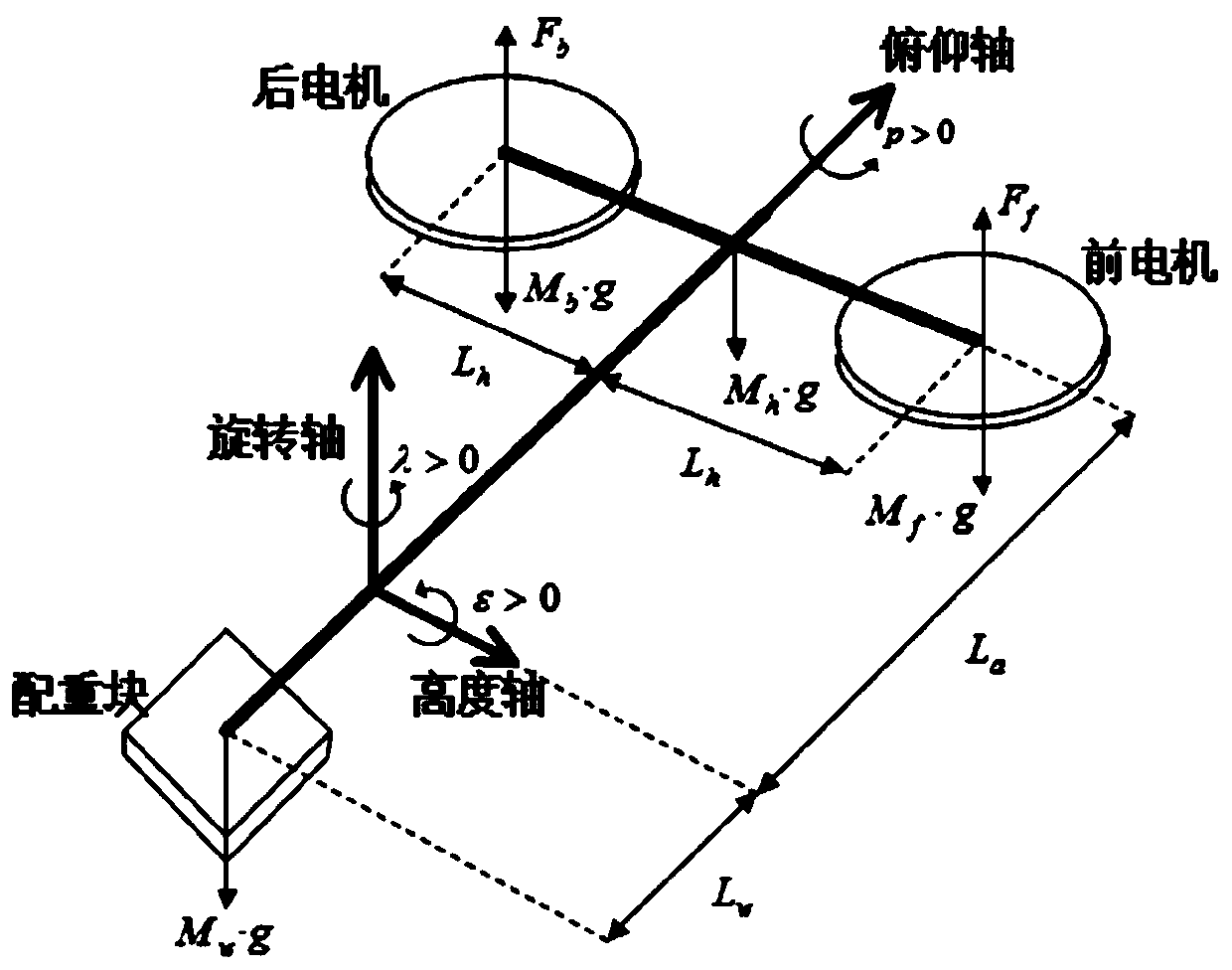
Explicit model predictive control method based on connected graph for three-degree-of-freedom helicopter
InactiveCN110471280AHigh simulationImprove the efficiency of offline computingPosition/course control in three dimensionsAdaptive controlExplicit modelThree degrees of freedom
An explicit model predictive control method based on a connected graph for a three-degree-of-freedom helicopter comprises the following steps: step 1) modeling the three-degree-of-freedom helicopter to a model predictive control problem (MPC), and transforming the model predictive control problem (MPC) into a multi-parameter programming (MP-QP) problem, that is, a problem to be solved in offline calculation; step 2) introducing a critical domain, an effective constraint set and a concept of the connected graph; step 3) initializing a solving algorithm of the connected graph to obtain an initial critical domain and an optimal effective set; 4) judging feasibility of an effective candidate set; step 5) calculating on the feasible effective candidate set to obtain a critical domain and a control law; step 6) using the connected graph to generate a new candidate set and repeating the steps 4) - 6) until all solutions are generated; step 7) conducting the explicit model predictive control based on the connected graph for the three-degree-of-freedom helicopter system. The explicit model predictive control method based on connected graph proposed by the invention improves rate of off-linecalculation while ensuring good control performance of the system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Multi-scale approximate explicit model predictive control method for three-degree-of-freedom helicopter
InactiveCN109062038AOvercome the defects of predictive controlEasy to find onlineAdaptive controlGravity centerOptimization problem
The invention discloses a multi-scale approximate explicit model predictive control method for a three-degree-of-freedom helicopter. The multi-scale approximate explicit model predictive control method comprises the following steps that step (1), modeling is carried out on the three-degree-of-freedom helicopter to obtain a parameter optimization problem, namely an object to be approximated below;step (2), a piecewise linear insertion method is carried out to initially obtain an approximate control law; step (3), self-adaptive separation function approximation is carried out, and the form of the approximate control law is transformed; step (4), a barycenter function is introduced, and barycenter interpolation is utilized to obtain an approximate control law based on the barycenter function; and step (5), multi-scale approximate explicit model predictive control over a three-degree-of-freedom helicopter system is carried out. According to the multi-scale approximate explicit model predictive control method, the real-time performance of the three-degree-of-freedom helicopter control system is improved, the control complexity is reduced, the storage capacity requirement of a controller is reduced, the online calculation time is saved, and a good control effect is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG COLLEGE OF ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECHOLOGY
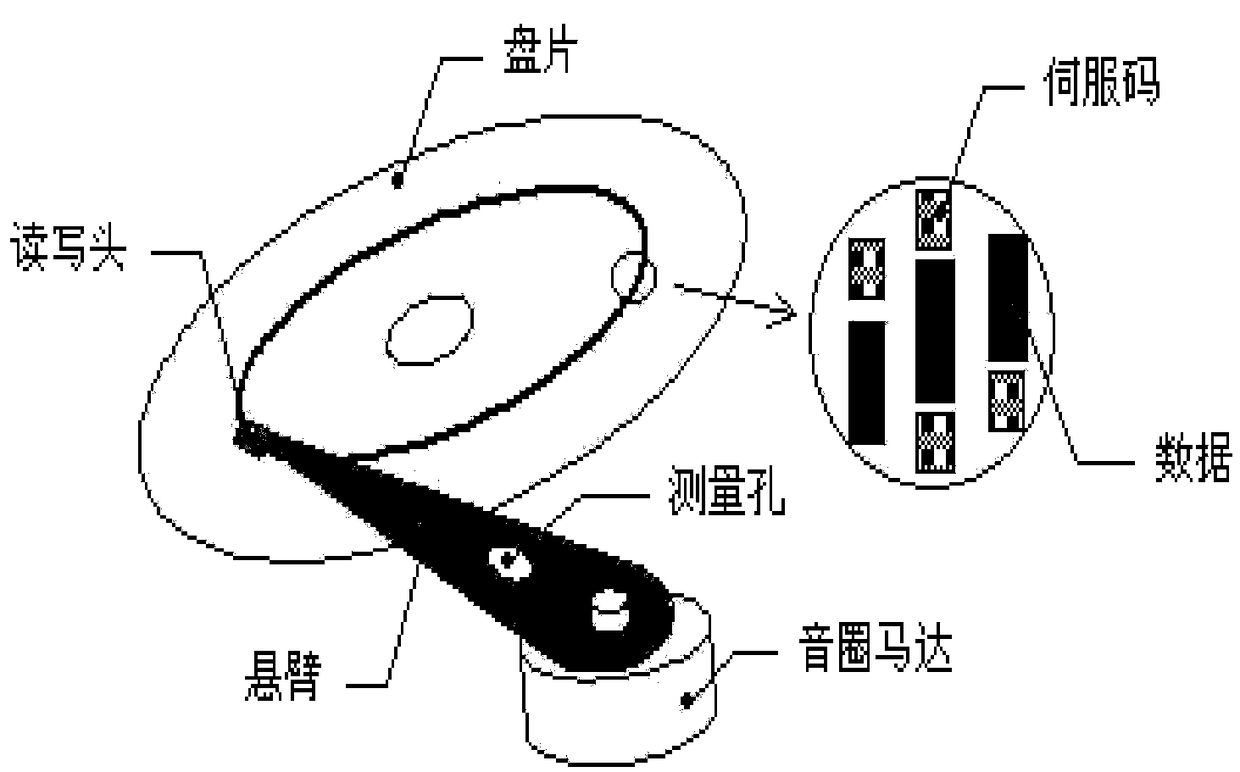
Multi-scale approximate explicit model predictive control method for disk drive systems
InactiveCN109003631AEasy to find onlineReduced storage capacity requirementsRecord information storageFluid-dynamic spacing of headsExplicit modelControl system
A multi-scale approximate explicit model predictive control method for disk drive systems comprises the following steps: 1) modeling the disk drive system to obtain a parameter optimization problem; 2) performing a piecewise linear insertion method to obtain an approximate control law; 3) converting the form of the approximate control law into an adaptive layered function approximation; 4) introducing a center of gravity function to obtain an approximate control law base on the center of gravity function by using the center of gravity interpolation; 5) performing multi-scale approximate explicit model predictive control of the disk drive system. The invention improves the real-time performance of the disk drive control system, reduces the control complexity, reduces the requirement of thestorage capacity of the controller, saves the on-line calculation time, and has good control effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG COLLEGE OF ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECHOLOGY
Multi-scale approximate explicit model predictive control method for brushless dc motor
InactiveCN109039168AEasy to find onlineSolve problems that are too complexSingle motor speed/torque controlGeneral control strategiesExplicit modelControl system
A multi-scale approximate explicit model predictive control method for a brushless DC motor comprises the following steps: (1) modeling a brushless DC motor system to obtain a parameter optimization problem, that is, an object to be approximated below; 2) piecewise linear insertion method to obtain an approximate control law; 3) convert that form of the approximate control law into an adaptive layered function approximation; 4) introducing a barycenter function to obtain an approximate control law based on that barycenter function by use the barycenter interpolation value; and 5) multi-scale approximate explicit model predictive control of the motor control system. The invention improves the real-time property of the motor control, reduces the requirement of the memory capacity of the control, saves the on-line calculation time, and has a good control effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG COLLEGE OF ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECHOLOGY
Implementation method for explicit model predictive control of permanent magnet synchronous motor
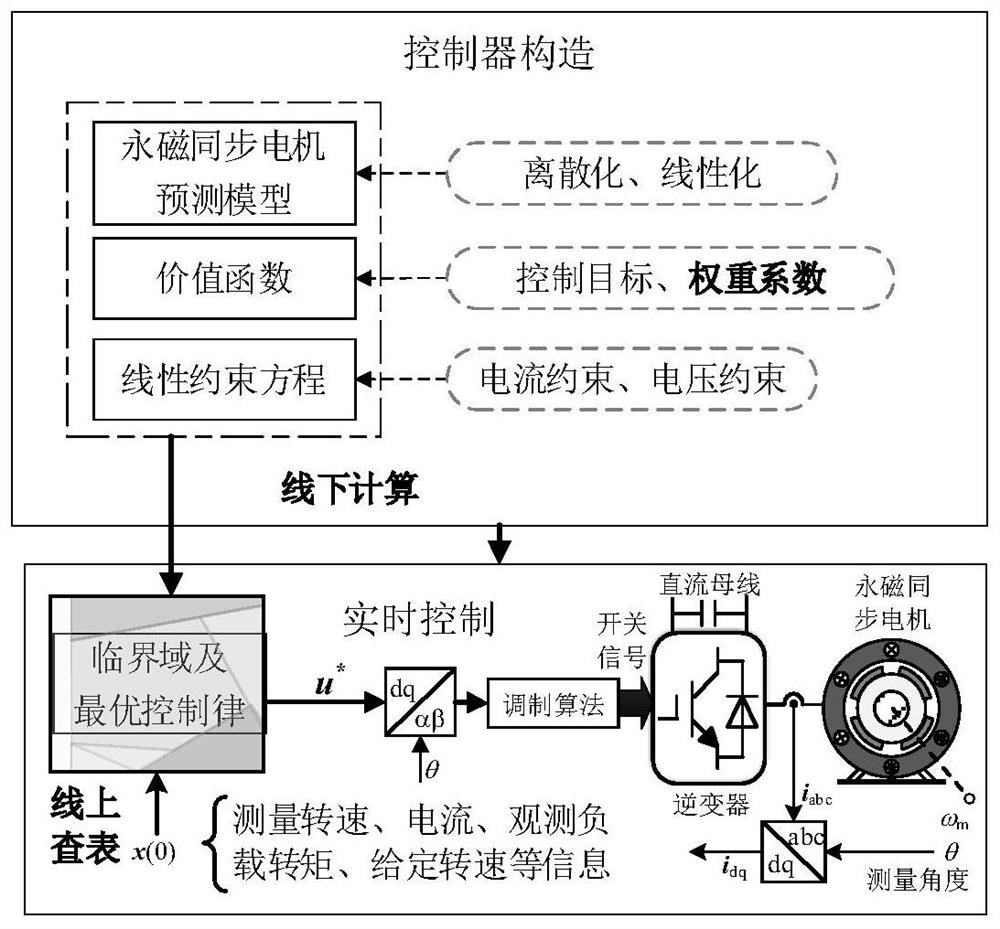
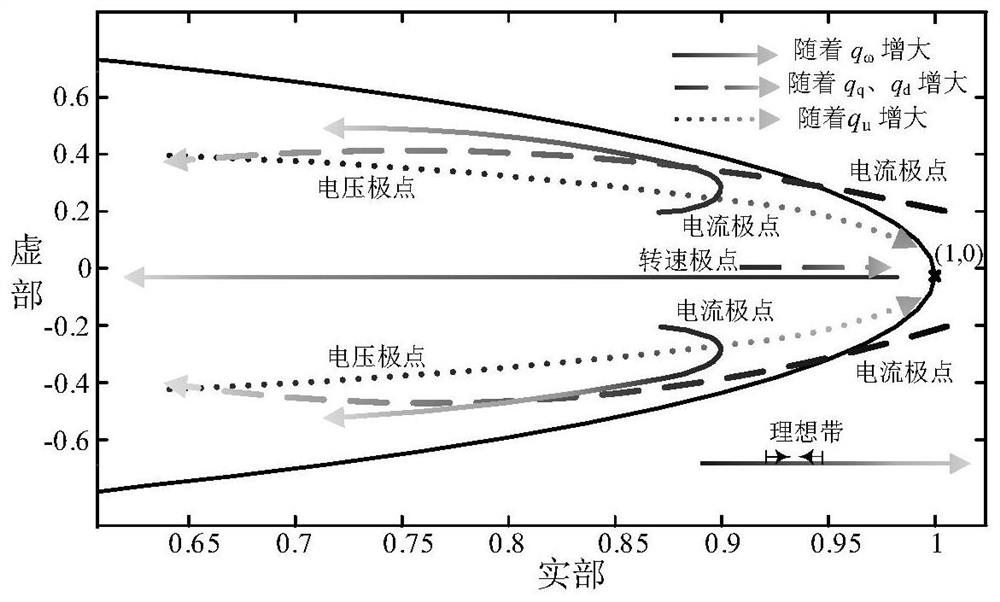
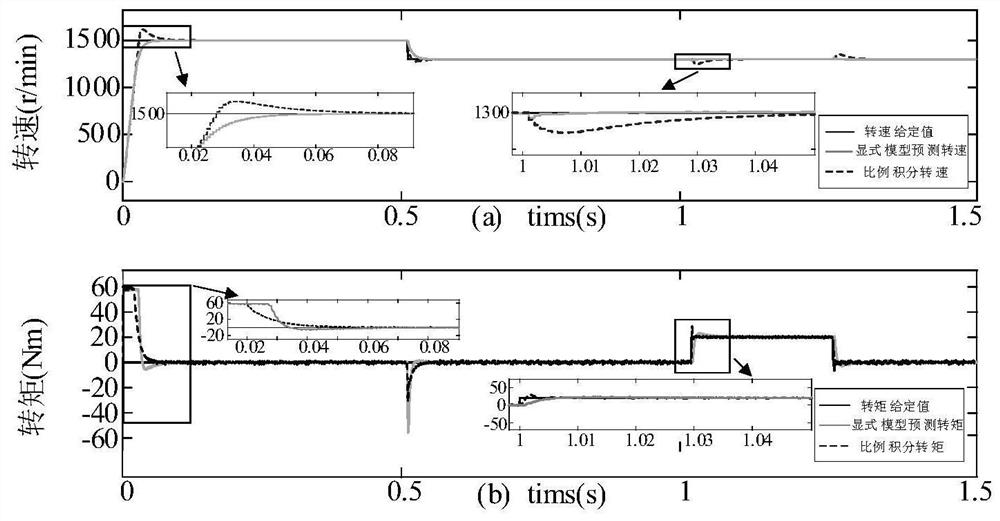
ActiveCN113556073AAvoid trial and errorReliable controlElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlExplicit modelControl system
The invention discloses an implementation method for explicit model predictive control of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The method comprises the steps of: constructing a controller for explicit model predictive control of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, processing and generating an optimal control sequence, and extracting an optimal control quantity from the optimal control sequence and applying the optimal control quantity to a control system of the permanent magnet synchronous motor; calculating an optimal control quantity and a closed-loop transfer equation of a control system under a typical working condition according to an optimal control sequence generated by a controller, taking a solution of the closed-loop transfer equation as a closed-loop pole, drawing a closed-loop pole trajectory diagram, determining an ideal band, and configuring the closed-loop pole to the ideal band so as to obtain each optimal weight coefficient; and substituting into a value function solution to carry out optimal control. According to the method, the problems that a control system is difficult to consider multiple control performances and the stability under different working conditions is difficult to guarantee are solved, the steps are simplified, the excellent control performance is obtained, and meanwhile, the method has very high universality and practicability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV ADVANCED ELECTRICAL EQUIP INNOVATION CENT +1
System and method for explicit model predictive control
A method for controlling a system using an explicit model predictive control (EMPC) evaluates, with respect to a state of the system, each inequality in a set of inequalities defining a set of regions of a state space of the system to produce a set of Boolean results. At least some of the inequalities are evaluated concurrently, and a size of the set of Boolean results equals a size of the set of inequalities. The method determines a region including the state by applying a Boolean function to elements of the set of Boolean results corresponding to inequalities forming boundaries of the region and determines a control for the system based on the state and a gain associated with the region. At least some Boolean functions are applied to corresponding elements concurrently after all elements in the set of Boolean results are evaluated.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
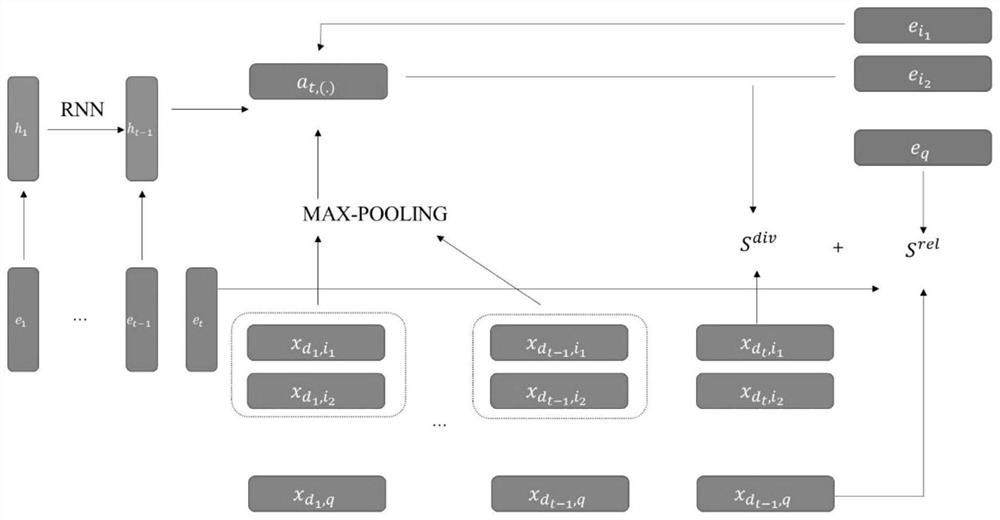
Search result diversification method based on generative adversarial network
ActiveCN112182155AHard to getIncrease coverageCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesExplicit modelAlgorithm
In the invention, a search result diversified training method based on the generative adversarial network is realized through a method in the field of artificial intelligence. The method comprises thefollowing steps: after giving out a query word, defining a corresponding candidate document set, and a sampler, a generator and a determiner unit which are sequentially arranged for a logic path; setting diversified scoring functions in the determiner and the generator, and carrying out training through a positive feedback process; introducing a generative adversarial network, and combining an explicit model and an implicit model through the generative adversarial network, wherein the final generator can generate better diversified document sequences through the means.
Owner:RENMIN UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
Attitude control method of direct lateral force and aerodynamic composite missile based on hybrid predictive control
The invention relates to an attitude control method of direct lateral force and aerodynamic composite missile attitude control based on hybrid predictive control, which belongs to the field of aircraft control. The invention solves the problem that the existing attitude control design method cannot simultaneously solve the problem of model nonlinearity and control input mixed characteristics. The technical gist of the present invention is: establish the complete attitude control model and the direct lateral force model of direct lateral force and aerodynamic compound missile, and through the analysis of aerodynamic characteristics, transform the nonlinear dynamic model into a segmented affine model; Based on the equivalence between the piecewise affine model and the hybrid logic dynamic model, and considering the hybrid characteristics of the control input, a hybrid logic dynamic model for compound control missiles is established; based on the hybrid logic dynamic model, an explicit model predictive control law is designed to determine the aerodynamic rudder Control law and attitude control engine opening law. The method of the invention is applicable to the field of aircraft guidance and control.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com