Patents
Literature
147 results about "Boolean function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics and logic, a (finitary) Boolean function (or switching function) is a function of the form ƒ : B → B, where B = {0, 1} is a Boolean domain and k is a non-negative integer called the arity of the function. In the case where k = 0, the "function" is essentially a constant element of B.
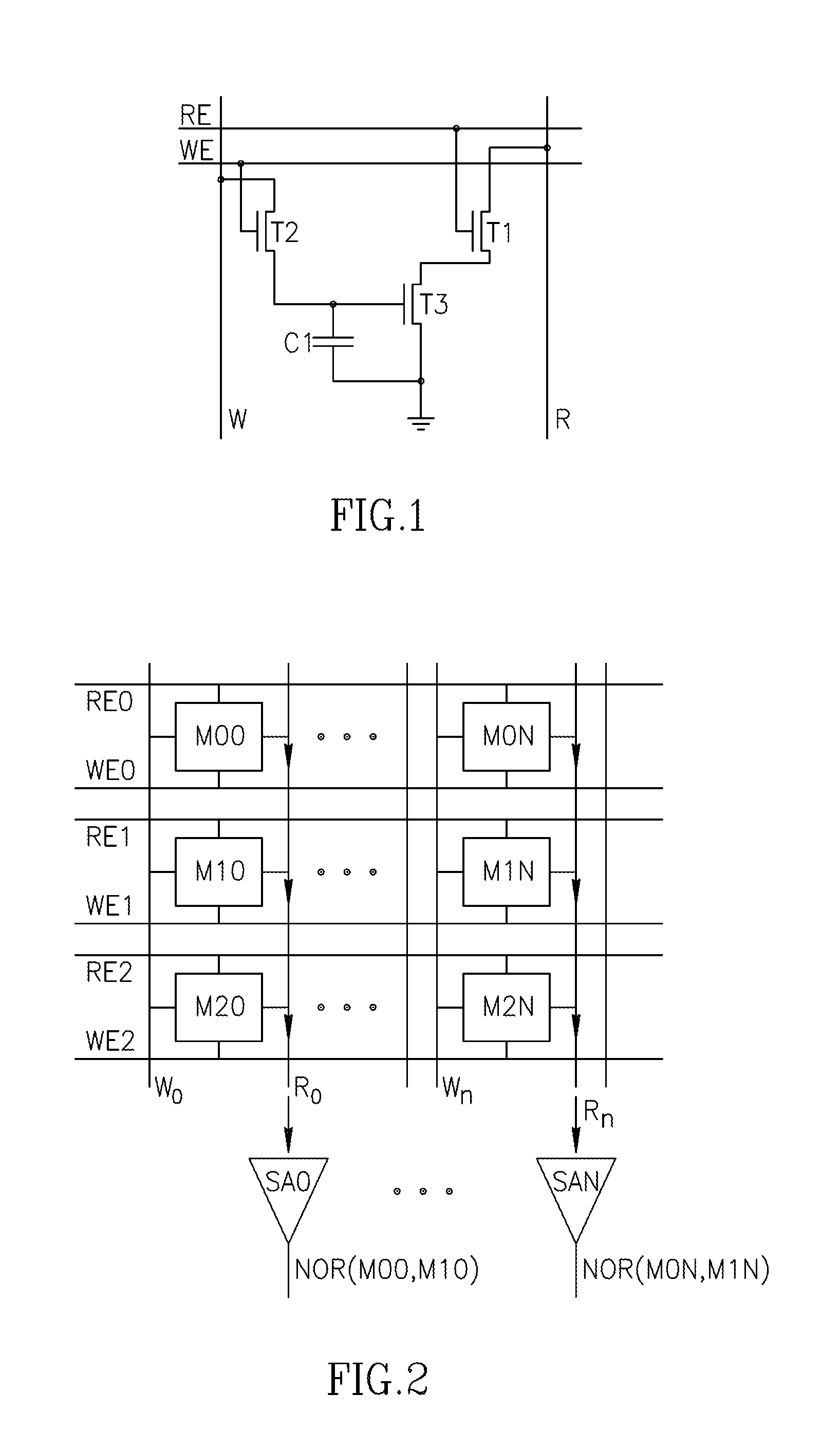
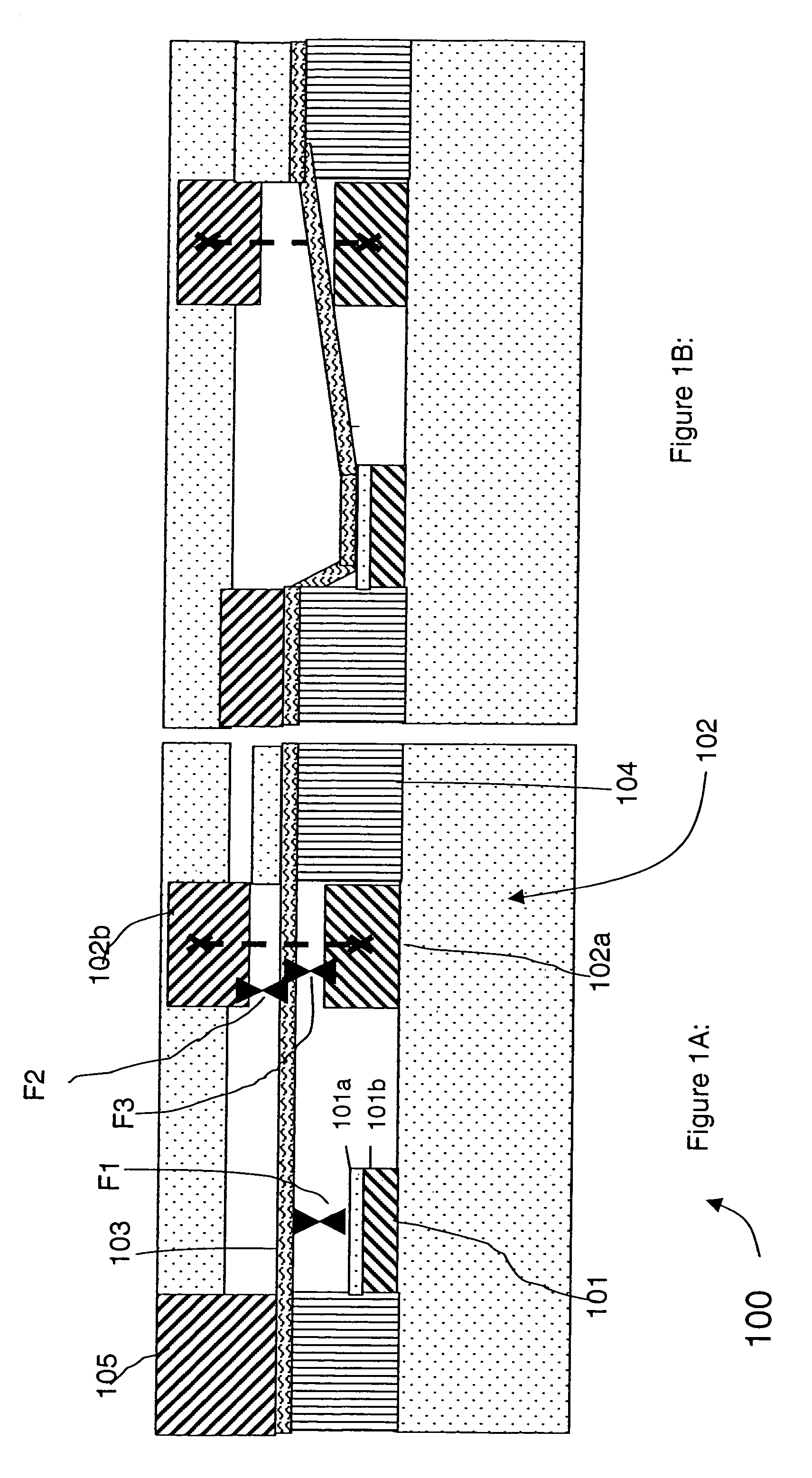
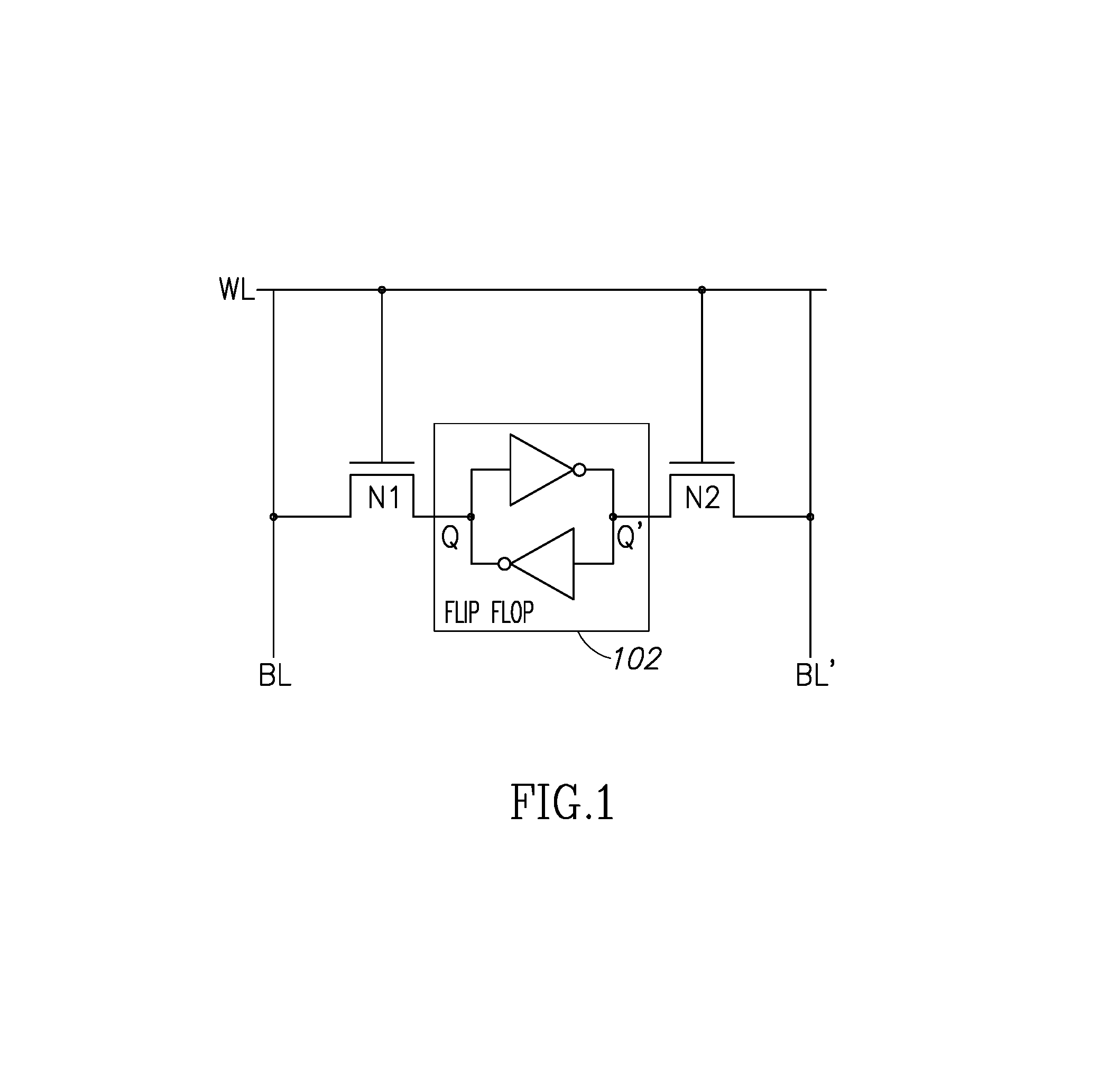
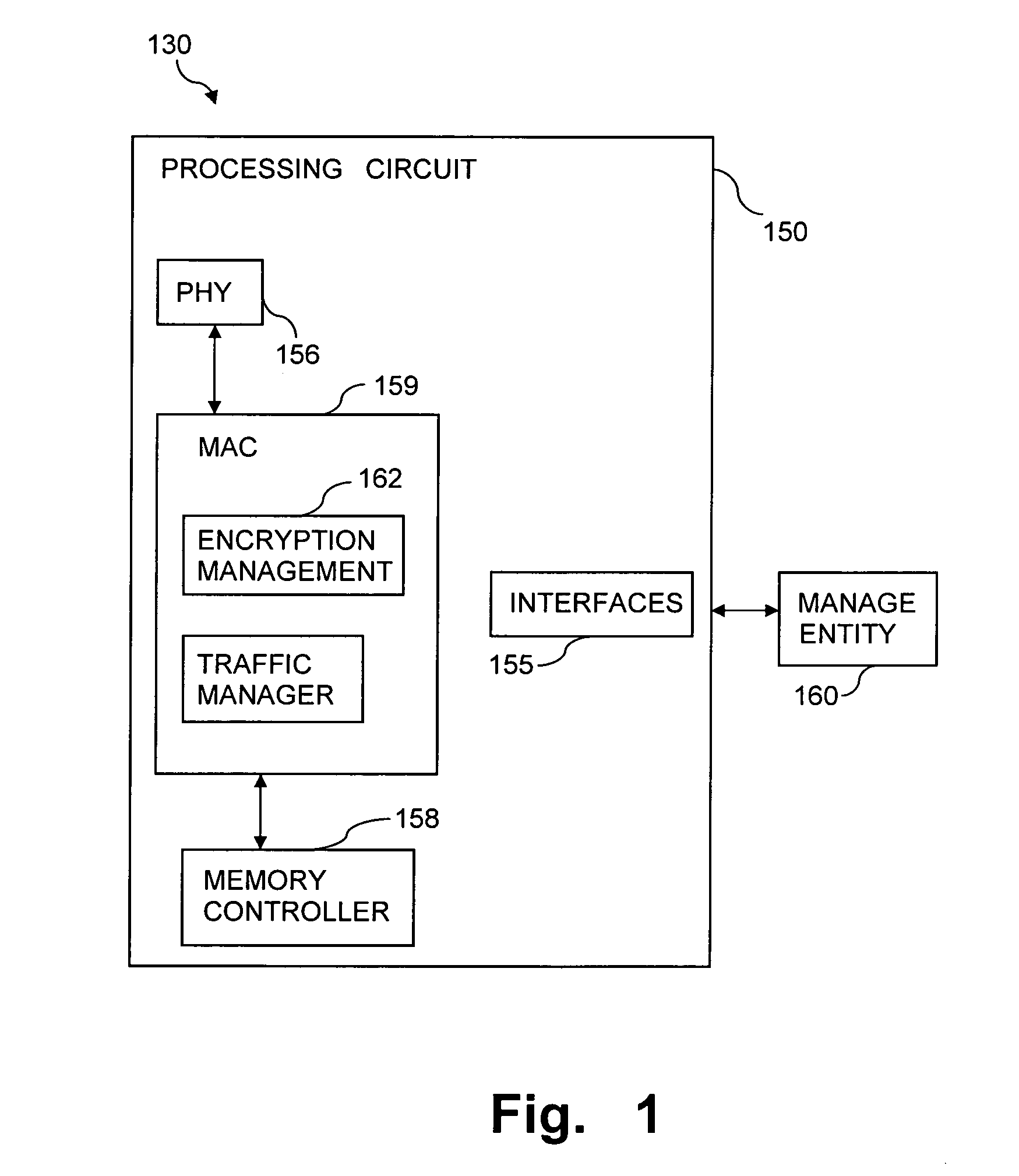
Using storage cells to perform computation
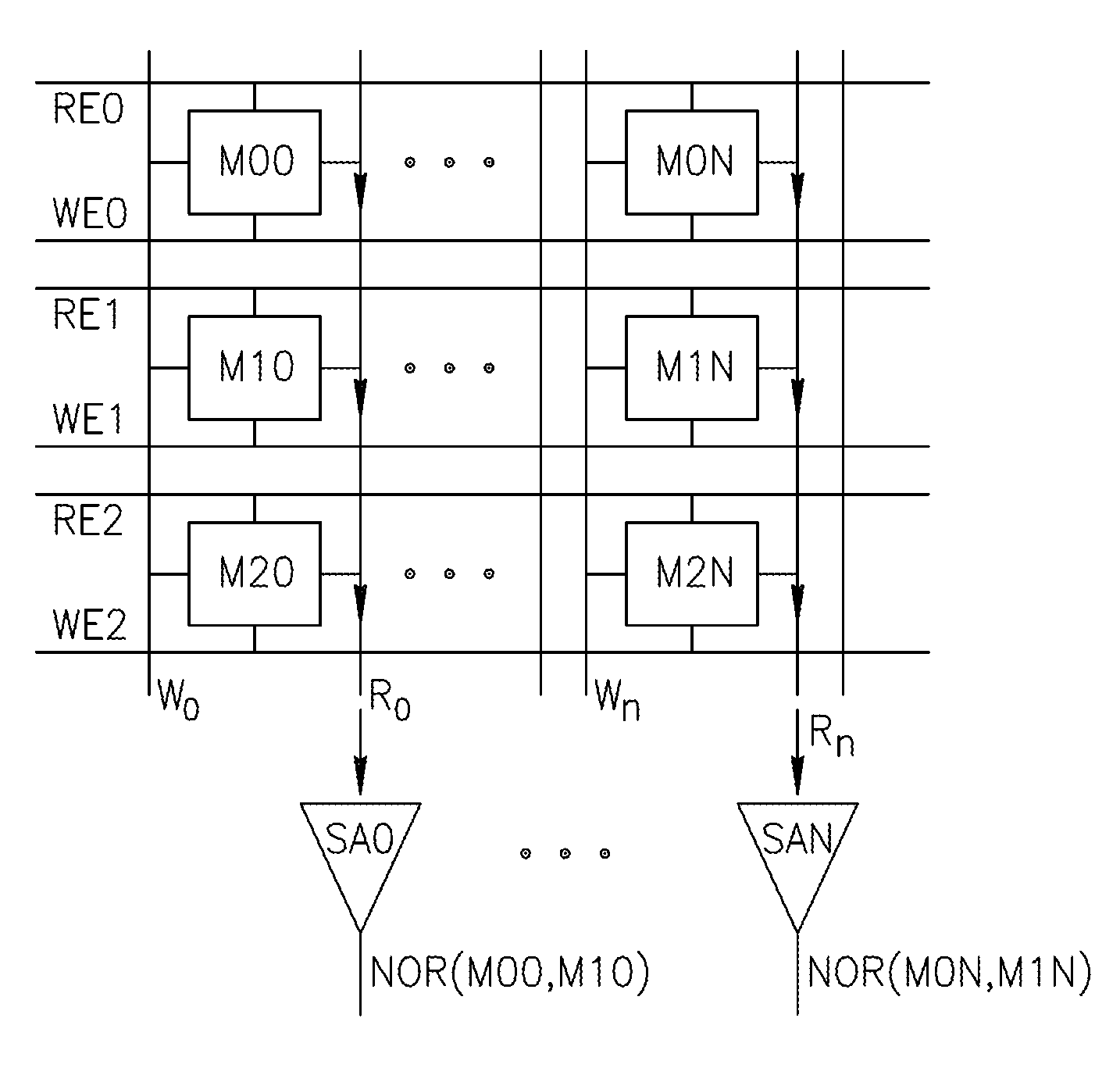
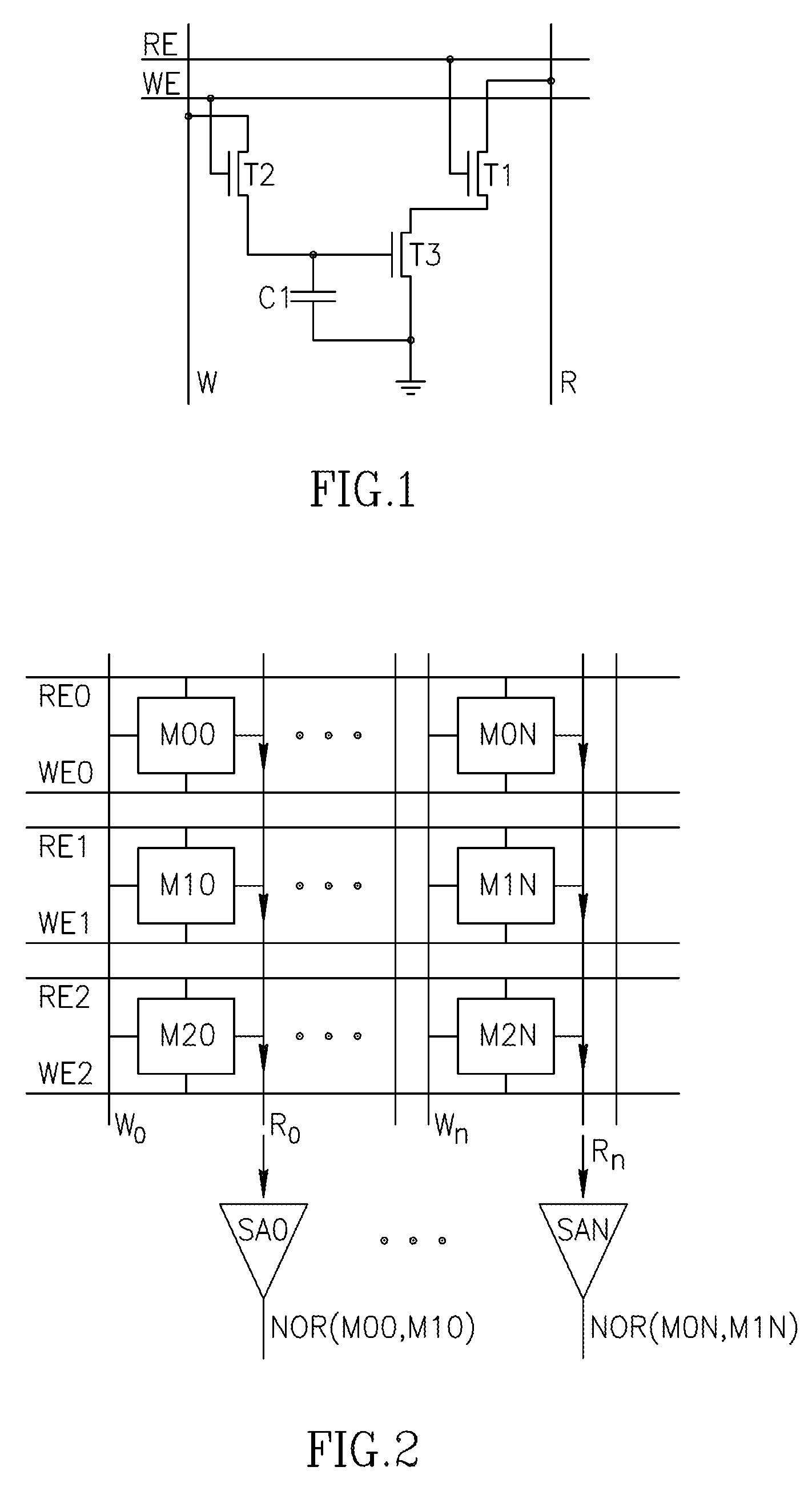
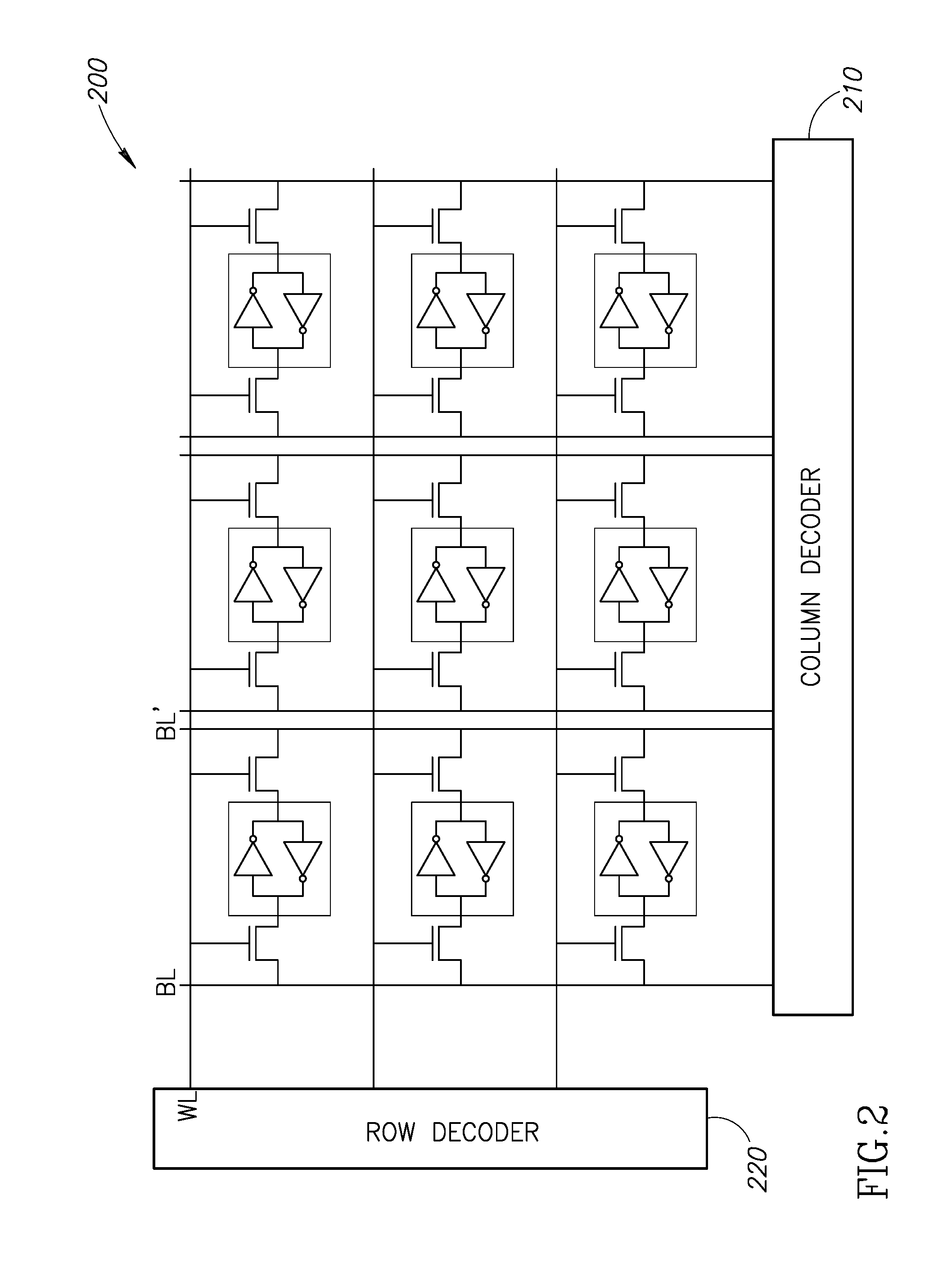
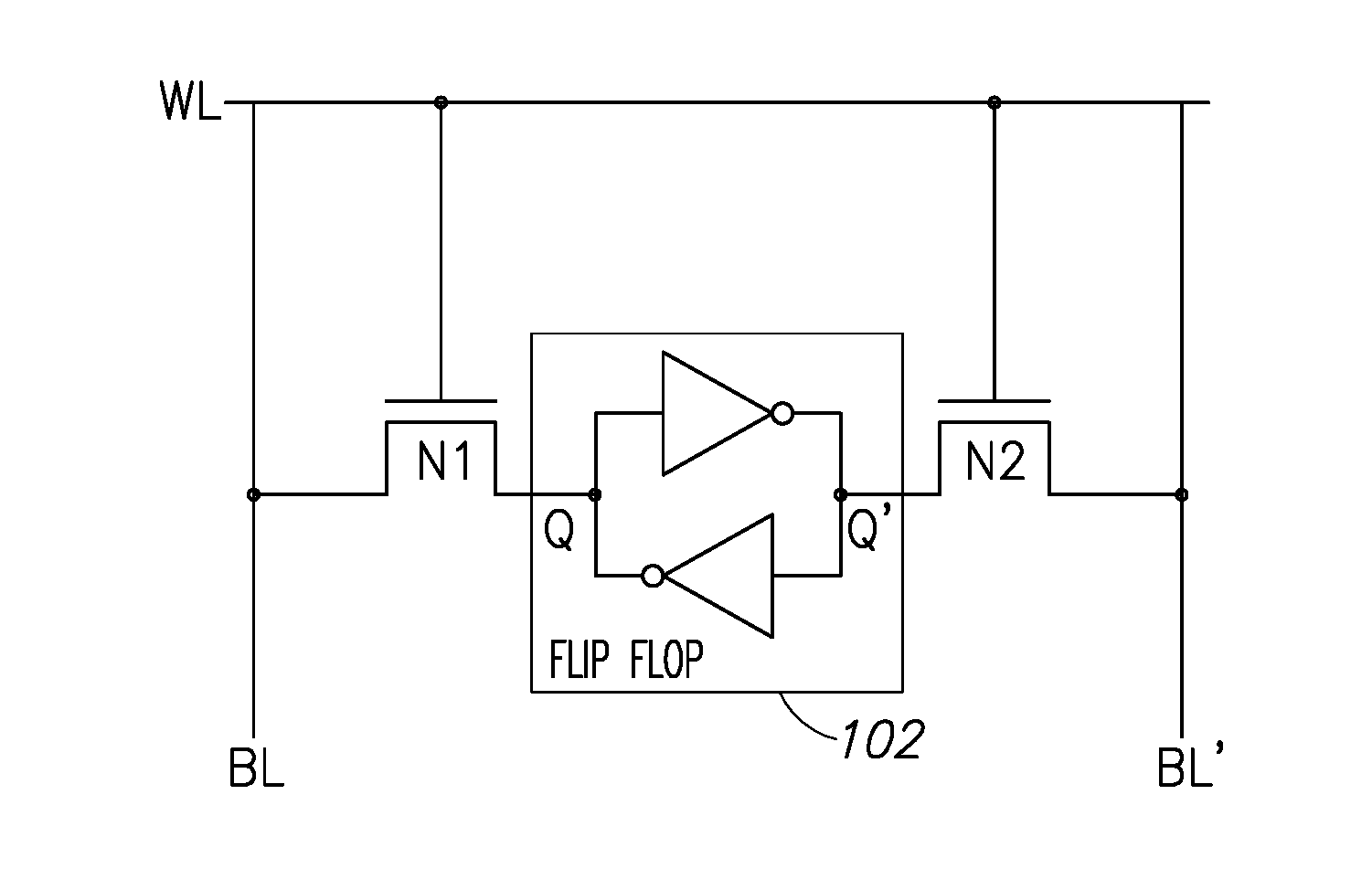
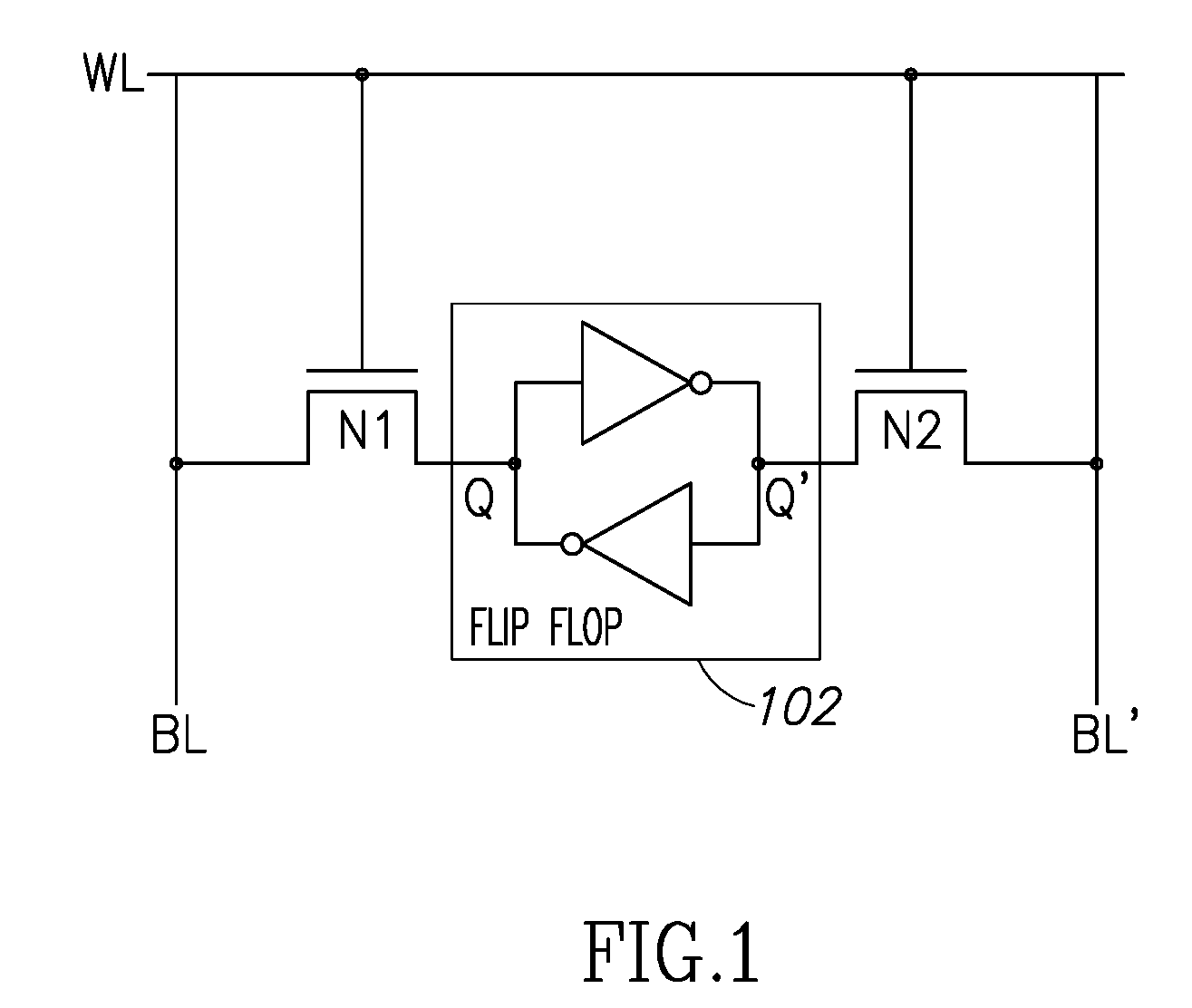
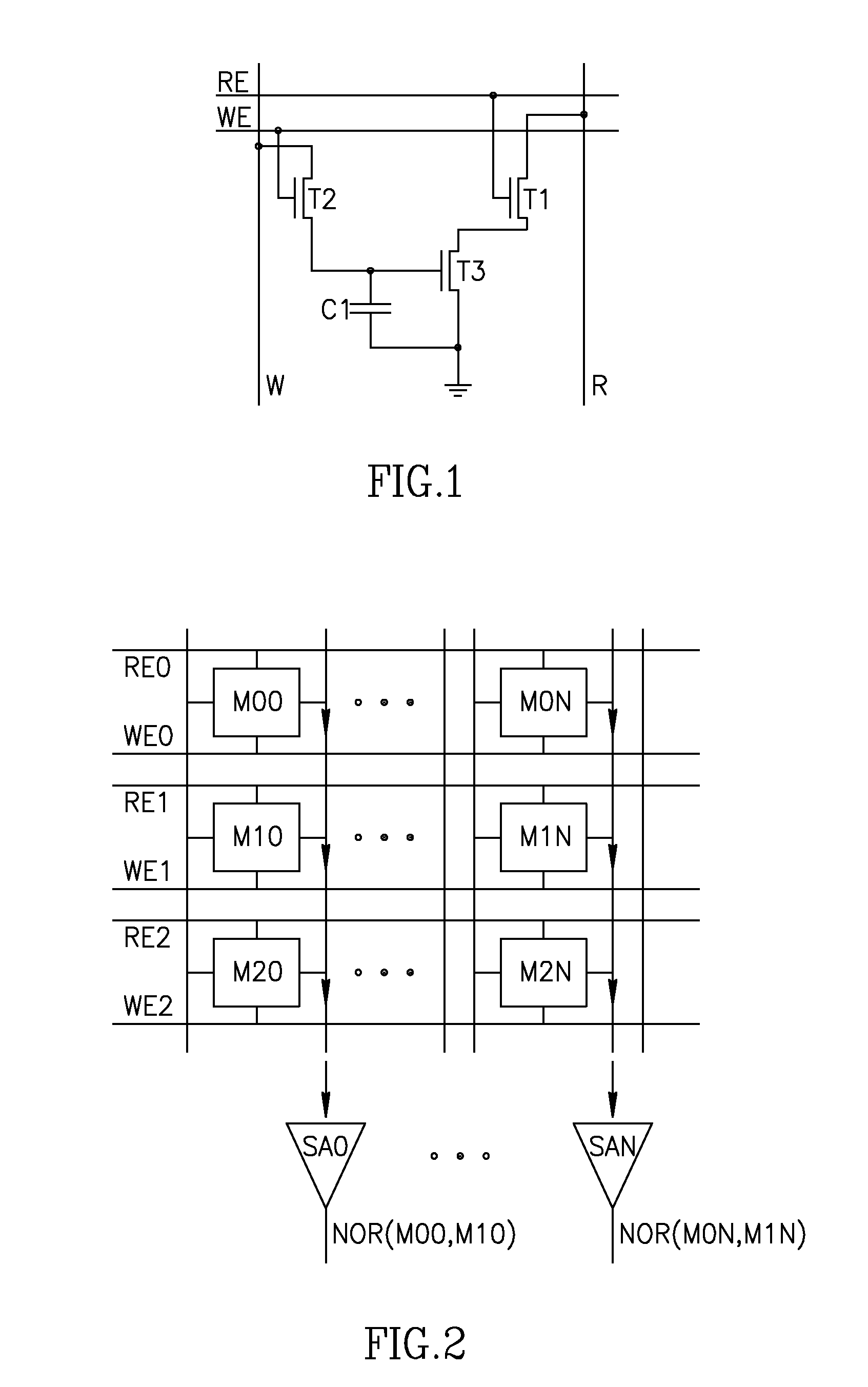
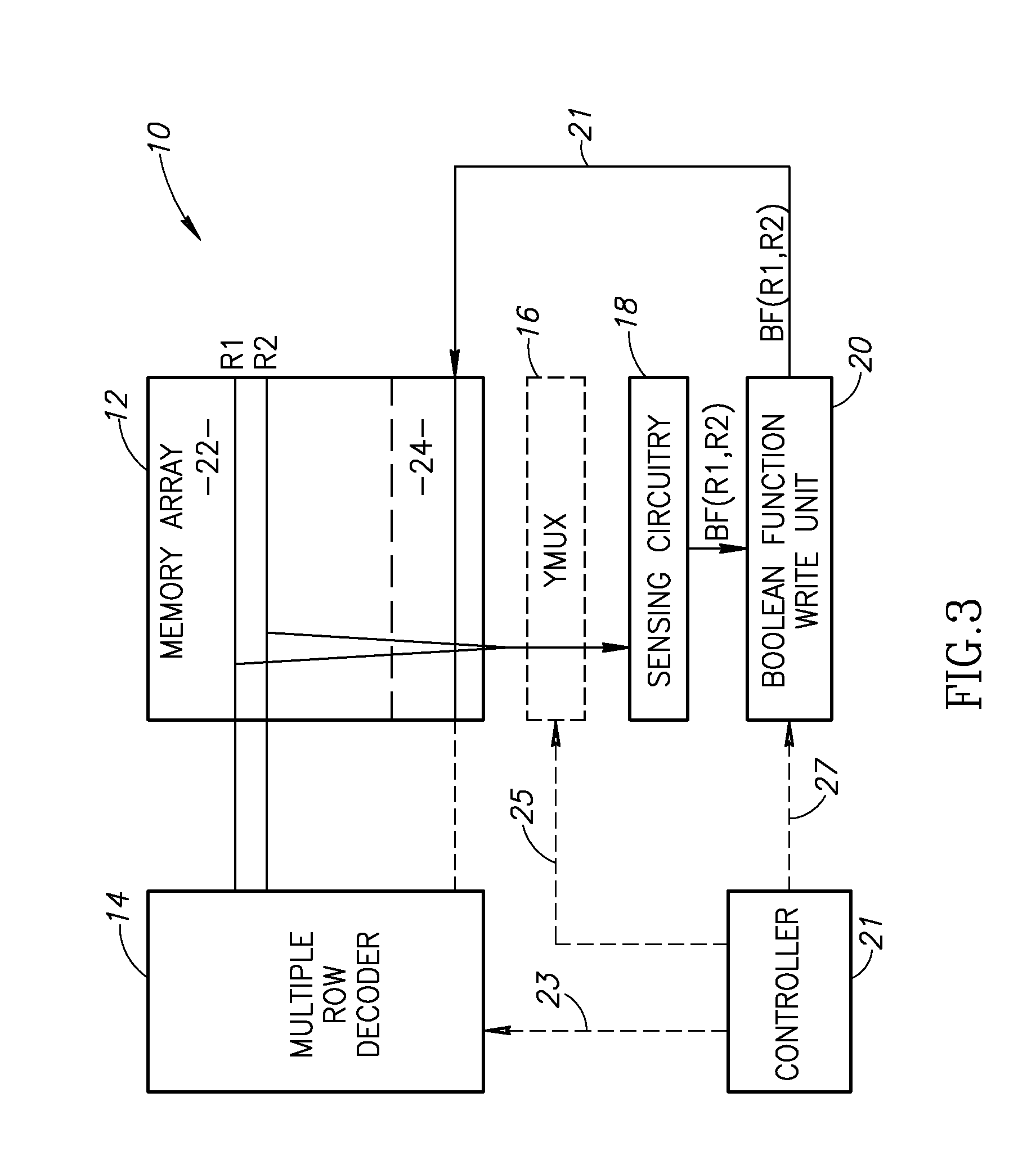
An in-memory processor includes a memory array which stores data and an activation unit to activate at least two cells in a column of the memory array at generally the same time thereby to generate a Boolean function output of the data of the at least two cells. Another embodiment shows a content addressable memory (CAM) unit without any in-cell comparator circuitry.
Owner:GSI TECH
Charge sharing in a tcam array
A memory cell includes a storage capacitor, a read line, and a storage transistor, where the storage transistor is connected to the read line and is subject to activation by a charge in the storage capacitor. An in-memory processor includes a memory array which stores data, and an activation unit to activate at least two cells in a column of the memory array at generally the same time, thereby to generate a Boolean function output of the data of the at least two cells, wherein each of the at least two cells includes at least a storage capacitor, a storage transistor and a read line, where the storage transistor is connected to the read line and subject to activation by a charge in the storage capacitor.
Owner:GSI TECH
Nanotube-based switching elements
Nanotube-based switching elements and logic circuits. Under one embodiment of the invention, a switching element includes an input node, an output node, a nanotube channel element having at least one electrically conductive nanotube, and a control electrode. The control electrode is disposed in relation to the nanotube channel element to controllably form an electrically conductive channel between the input node and the output node. The channel at least includes said nanotube channel element. The output node is constructed and arranged so that channel formation is substantially unaffected by the electrical state of the output node. Under another embodiment of the invention, the control electrode is arranged in relation to the nanotube channel element to form said conductive channel by causing electromechanical deflection of said nanotube channel element. Under another embodiment of the invention, the output node includes an isolation structure disposed in relation to the nanotube channel element so that channel formation is substantially invariant from the state of the output node. Under another embodiment of the invention, the isolation structure includes electrodes disposed on opposite sides of the nanotube channel element and said electrodes produce substantially the same electric field. Under another embodiment of the invention, a Boolean logic circuit includes at least one input terminal and an output terminal, and a network of nanotube switching elements electrically disposed between said at least one input terminal and said output terminal. The network of nanotube switching elements effectuates a Boolean function transformation of Boolean signals on said at least one input terminal. The Boolean function transformation includes a Boolean inversion within the function, such as a NOT or NOR function.
Owner:NANTERO
Nanotube-based switching elements
Nanotube-based switching elements and logic circuits. Under one embodiment of the invention, a switching element includes an input node, an output node, a nanotube channel element having at least one electrically conductive nanotube, and a control electrode. The control electrode is disposed in relation to the nanotube channel element to controllably form an electrically conductive channel between the input node and the output node. The channel at least includes said nanotube channel element. The output node is constructed and arranged so that channel formation is substantially unaffected by the electrical state of the output node. Under another embodiment of the invention, the control electrode is arranged in relation to the nanotube channel element to form said conductive channel by causing electromechanical deflection of said nanotube channel element. Under another embodiment of the invention, the output node includes an isolation structure disposed in relation to the nanotube channel element so that channel formation is substantially invariant from the state of the output node. Under another embodiment of the invention, the isolation structure includes electrodes disposed on opposite sides of the nanotube channel element and said electrodes produce substantially the same electric field. Under another embodiment of the invention, a Boolean logic circuit includes at least one input terminal and an output terminal, and a network of nanotube switching elements electrically disposed between said at least one input terminal and said output terminal. The network of nanotube switching elements effectuates a Boolean function transformation of Boolean signals on said at least one input terminal. The Boolean function transformation includes a Boolean inversion within the function, such as a NOT or NOR function.
Owner:NANTERO
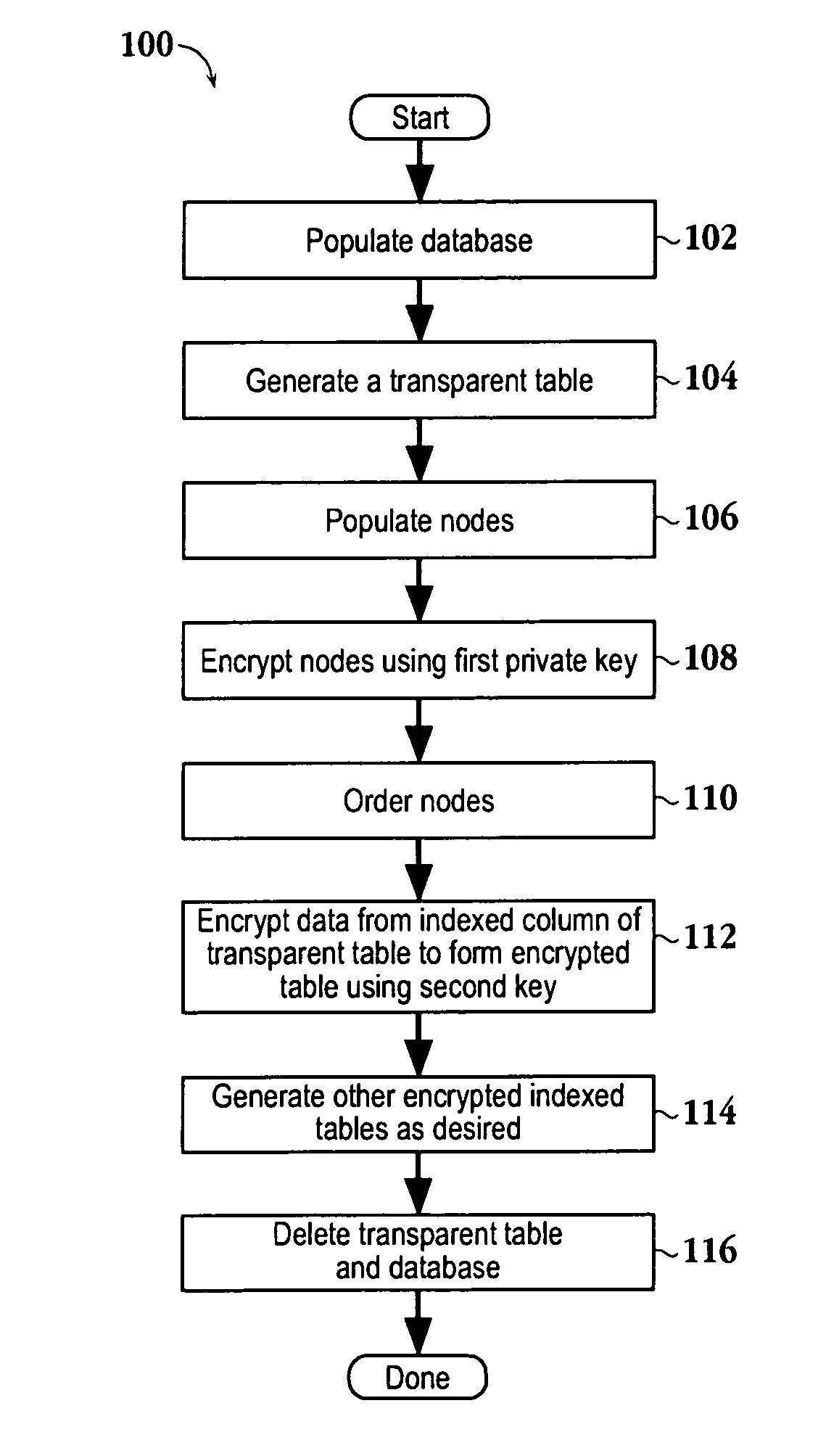
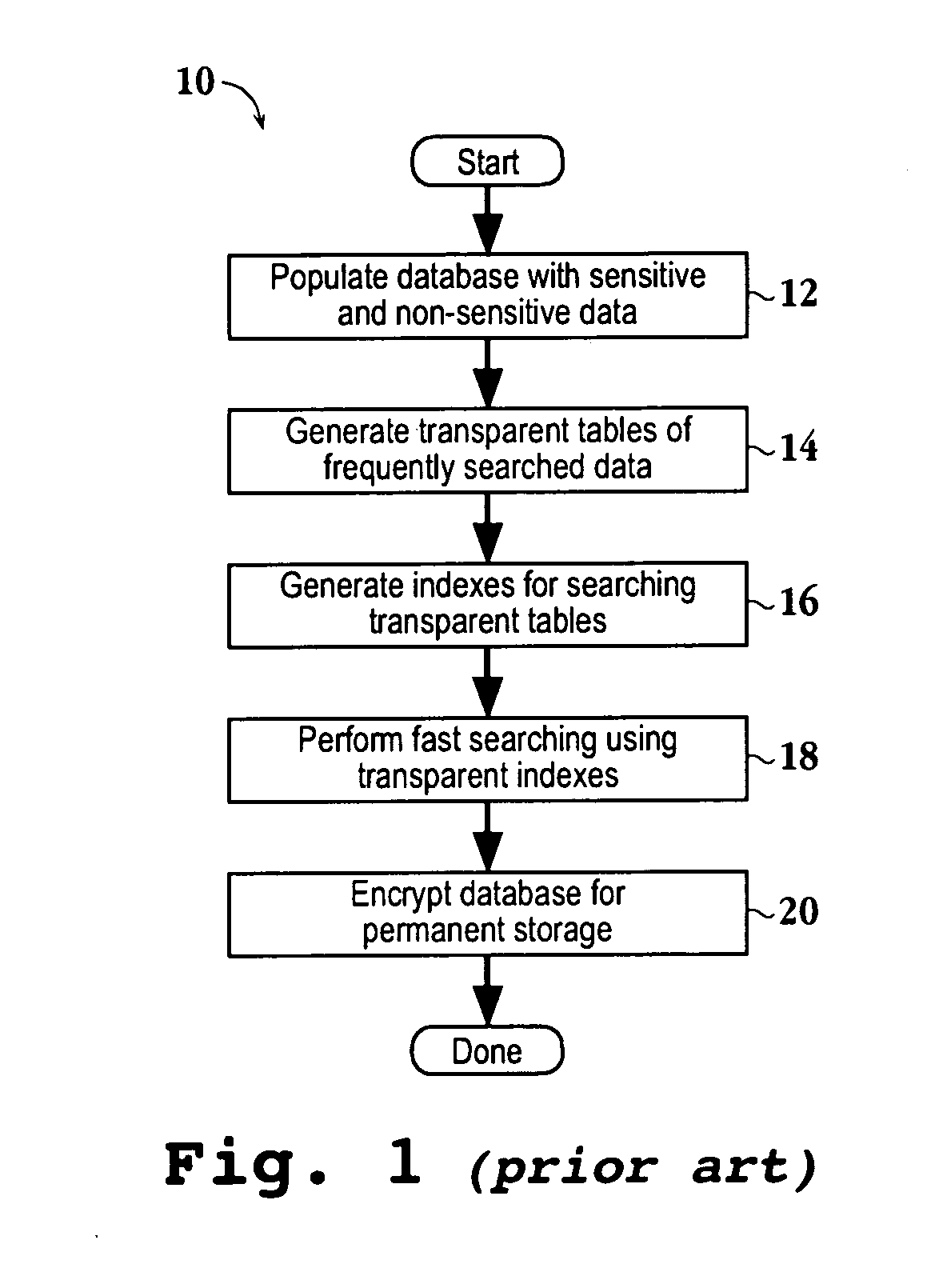
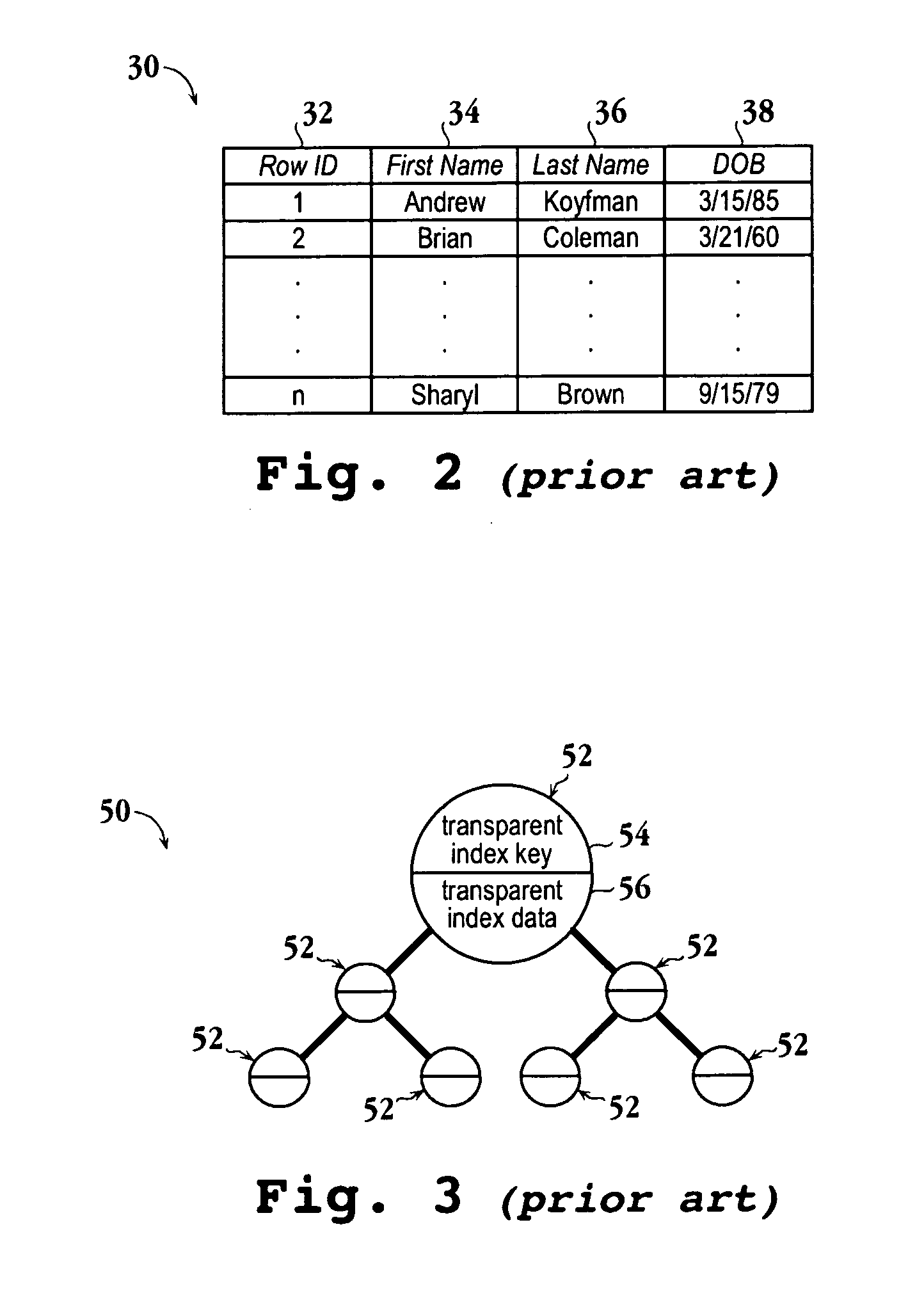
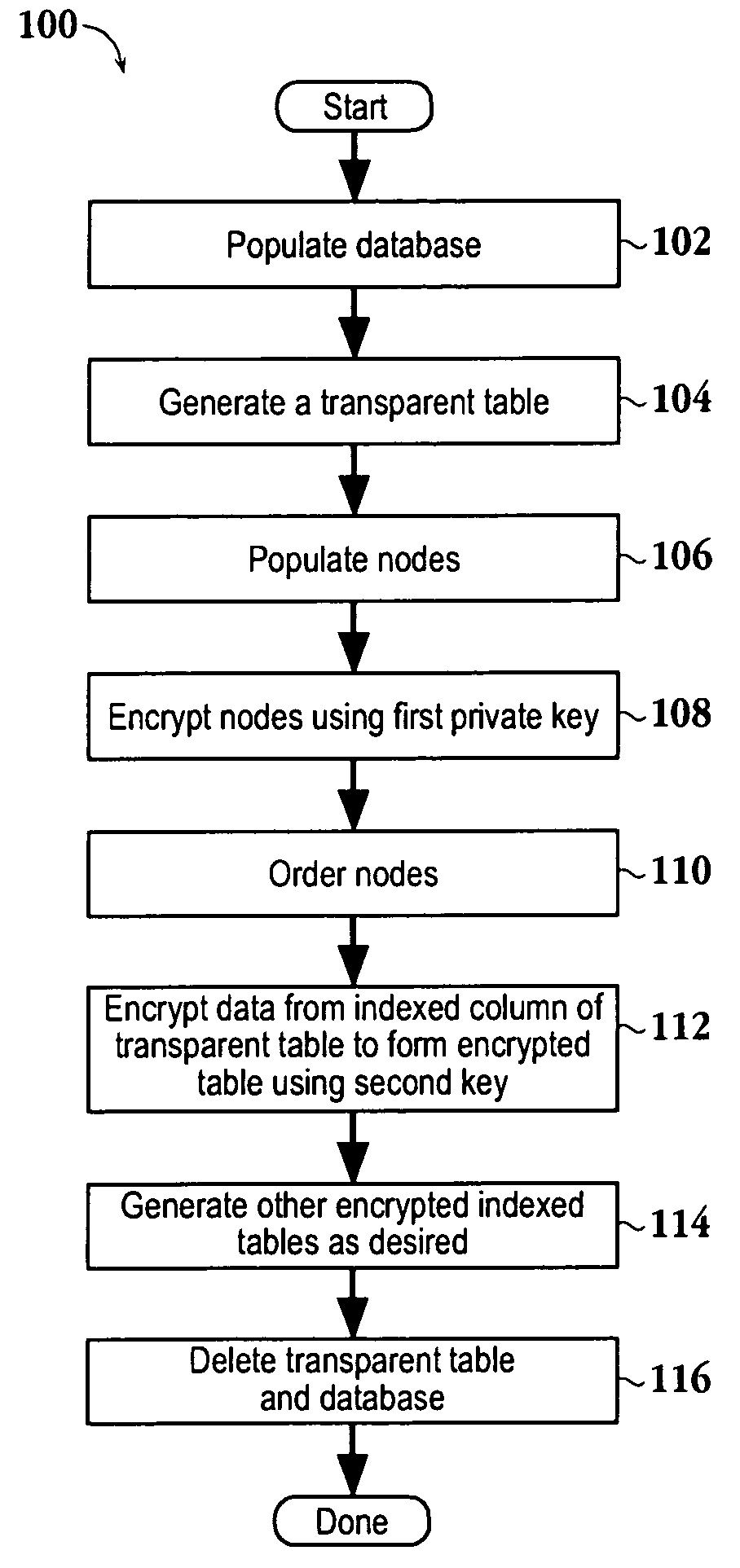
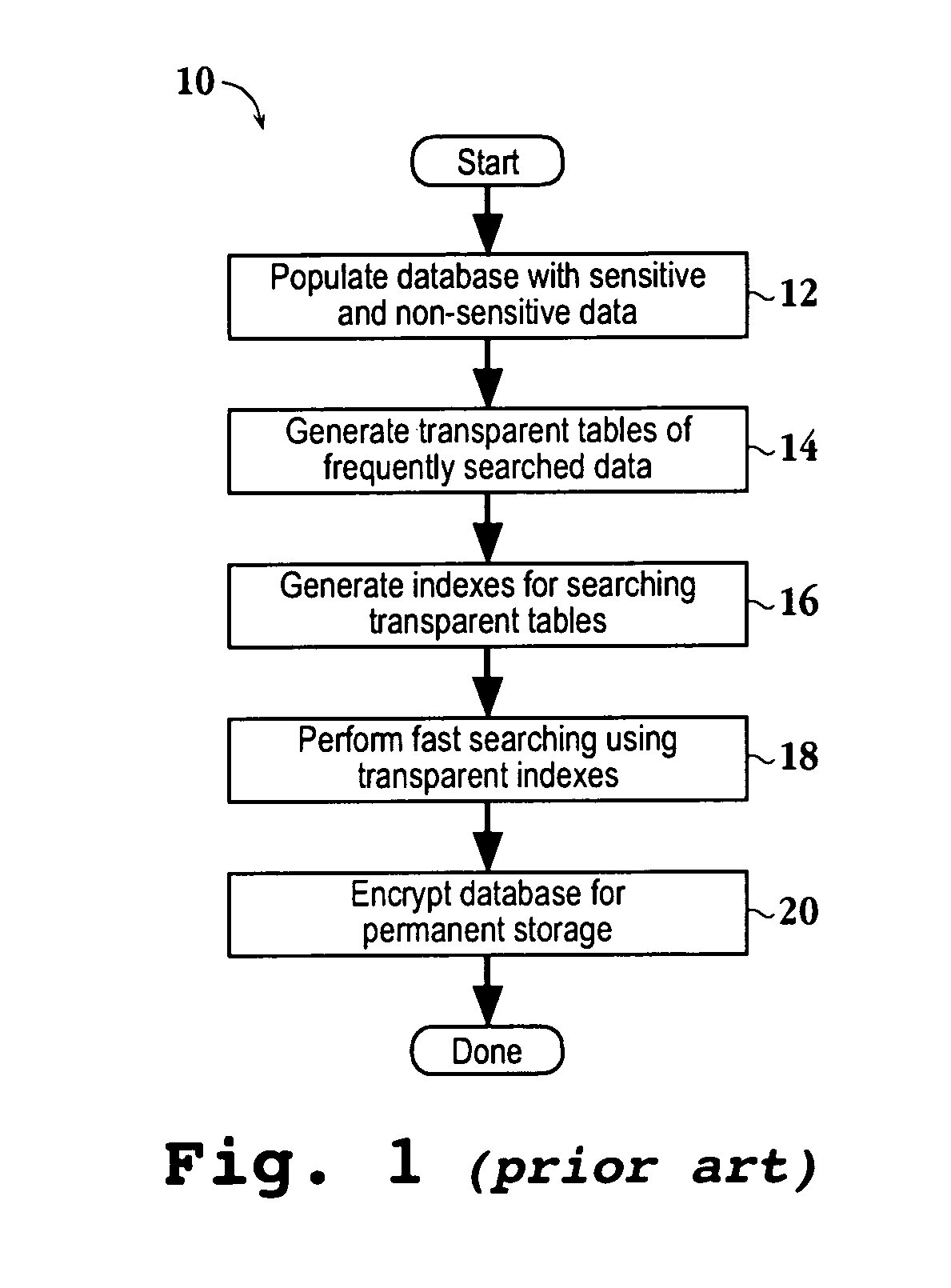
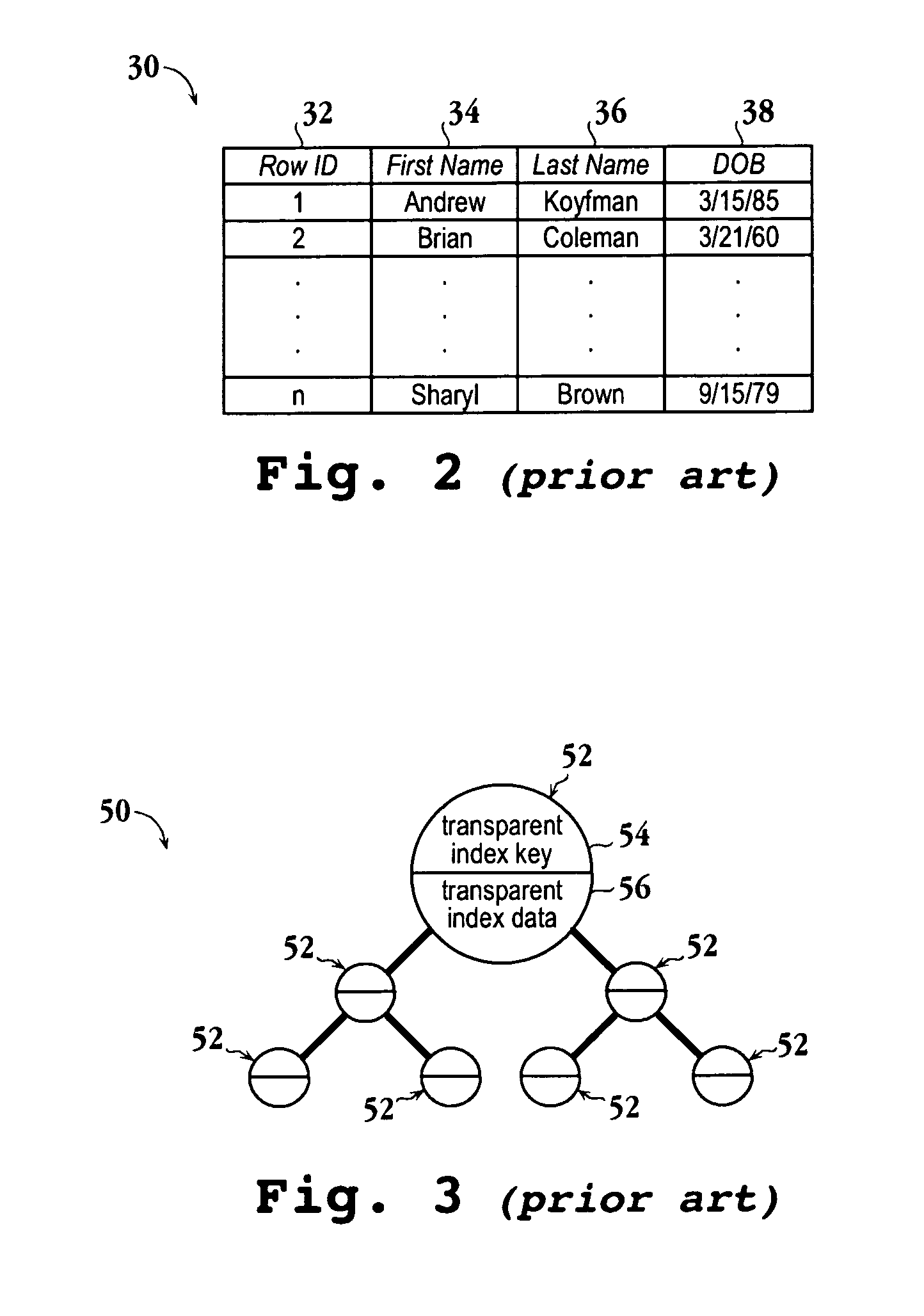
Encrypted table indexes and searching encrypted tables
The present invention teaches a variety of methods for building and searching secure, indexed database tables. Sensitive portions of the database tables and database indexes are encrypted, ordered and searched according to Boolean functions arranged to work with encrypted data. Also disclosed is a database management system that allows authorized users to build and search encrypted tables.
Owner:THALES DIS CPL USA INC
Nanotube-based switching elements and logic circuits
Nanotube-based switching elements and logic circuits. Under one embodiment of the invention, a switching element includes an input node, an output node, a nanotube channel element having at least one electrically conductive nanotube, and a control electrode. The control electrode is disposed in relation to the nanotube channel element to controllably form an electrically conductive channel between the input node and the output node. The channel at least includes said nanotube channel element. The output node is constructed and arranged so that channel formation is substantially unaffected by the electrical state of the output node. Under another embodiment of the invention, the control electrode is arranged in relation to the nanotube channel element to form said conductive channel by causing electromechanical deflection of said nanotube channel element. Under another embodiment of the invention, the output node includes an isolation structure disposed in relation to the nanotube channel element so that channel formation is substantially invariant from the state of the output node. Under another embodiment of the invention, the isolation structure includes electrodes disposed on opposite sides of the nanotube channel element and said electrodes produce substantially the same electric field. Under another embodiment of the invention, a Boolean logic circuit includes at least one input terminal and an output terminal, and a network of nanotube switching elements electrically disposed between said at least one input terminal and said output terminal. The network of nanotube switching elements effectuates a Boolean function transformation of Boolean signals on said at least one input terminal. The Boolean function transformation includes a Boolean inversion within the function, such as a NOT or NOR function.
Owner:NANTERO
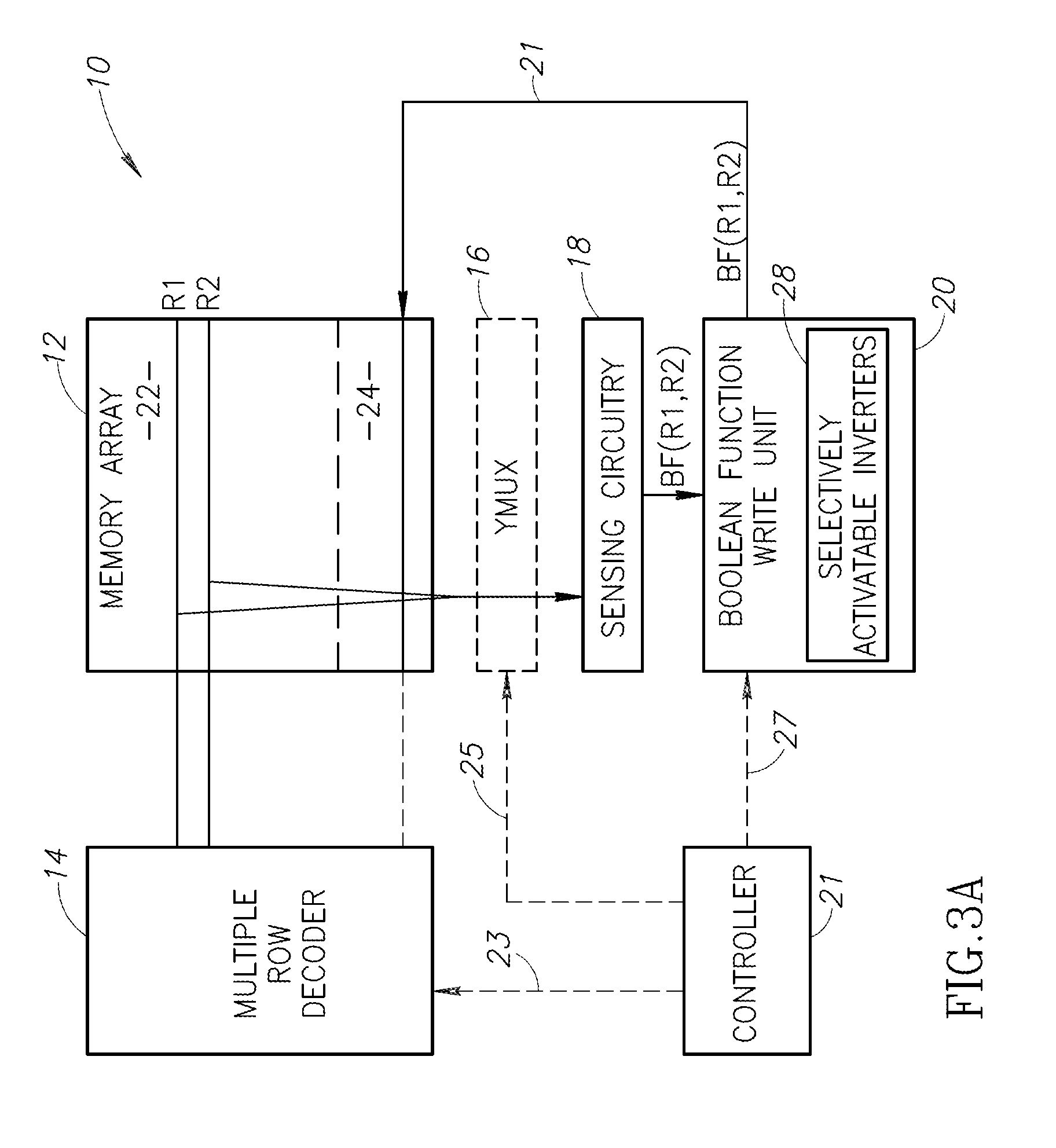
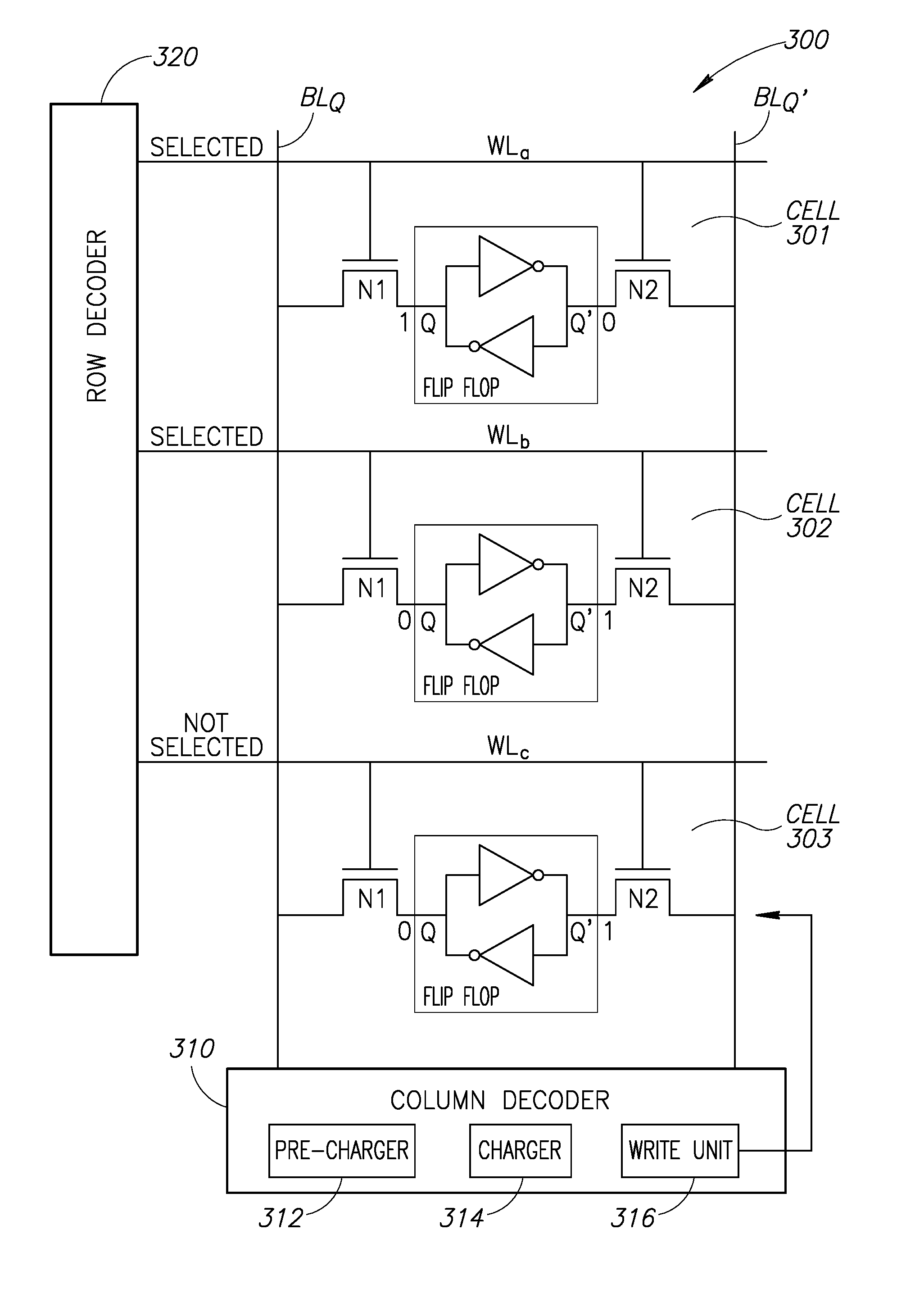
SRAM multi-cell operations
Owner:GSI TECH
Method and system for non-linear state based satisfiability
InactiveUS6912700B1Reduce settingsGenetic modelsDigital computer detailsSatisfiabilityBoolean function
A computerized method and system for solving non-linear Boolean equations is disclosed comprising at least partially solving a Boolean function; developing at least one inference regarding said Boolean function and saving said inference to a state machine; and accessing said inference from said state machine to develop at least one heuristic for determining whether said Boolean function is satisfiable.
Owner:CINCINNATI UNIV OF +1
SRAM multi-cell operations
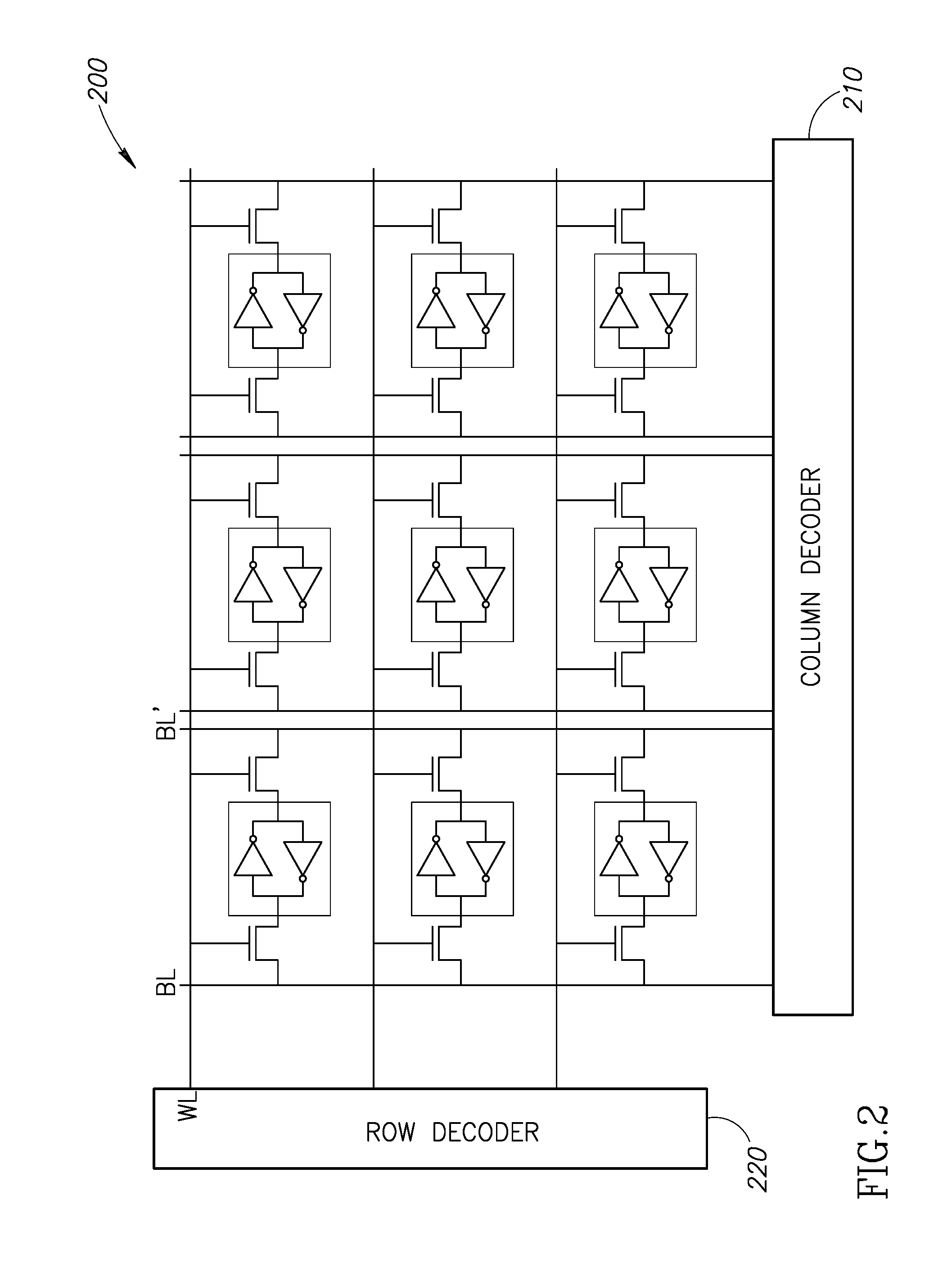
A multi-memory cell operator includes a non-destructive memory array, an activation unit and a multiple column decoder. The non-destructive memory array has first and second bit lines per column. The activation unit activates at least two cells in a column of the memory array at the same time thereby to generate multiple Boolean function outputs of the data and of complementary data of the at least two cells on the first bit line and different multiple Boolean function outputs of the data and of the complementary data on the second bit line. The multiple column decoder at least activates the first and second bit lines of multiple selected columns for reading or writing. The multiple column decoder also includes a write unit to write the output of the first bit line, the second bit line or both bit lines of the selected columns into the memory array.
Owner:GSI TECH
Using storage cells to perform computation
An in-memory processor includes a memory array which stores data and an activation unit to activate at least two cells in a column of the memory array at generally the same time thereby to generate a Boolean function output of the data of the at least two cells. Another embodiment shows a content addressable memory (CAM) unit without any in-cell comparator circuitry.
Owner:GSI TECH
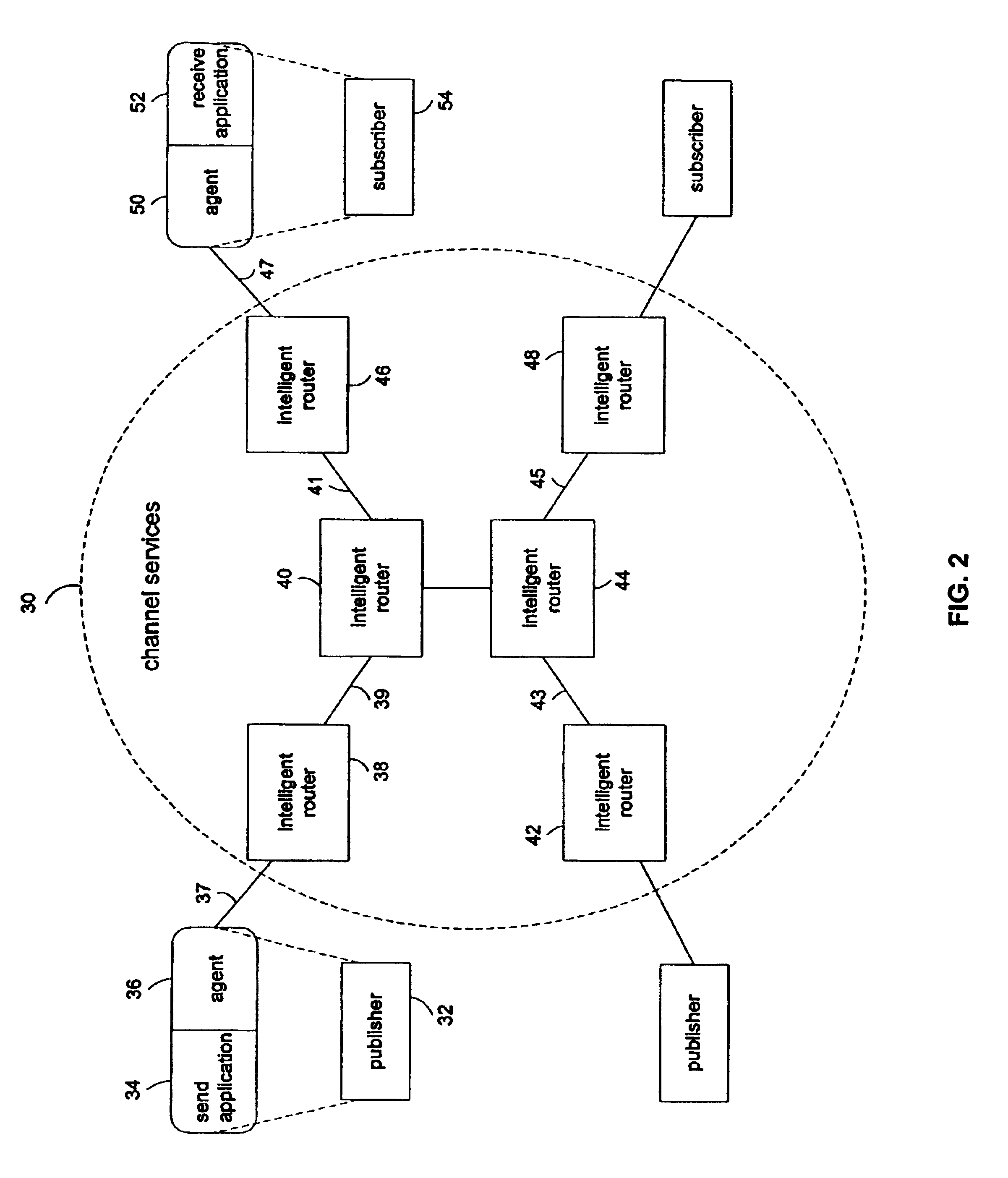
Method for storing Boolean functions to enable evaluation, modification, reuse, and delivery over a network
InactiveUS6910033B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsNetwork packetTheoretical computer science
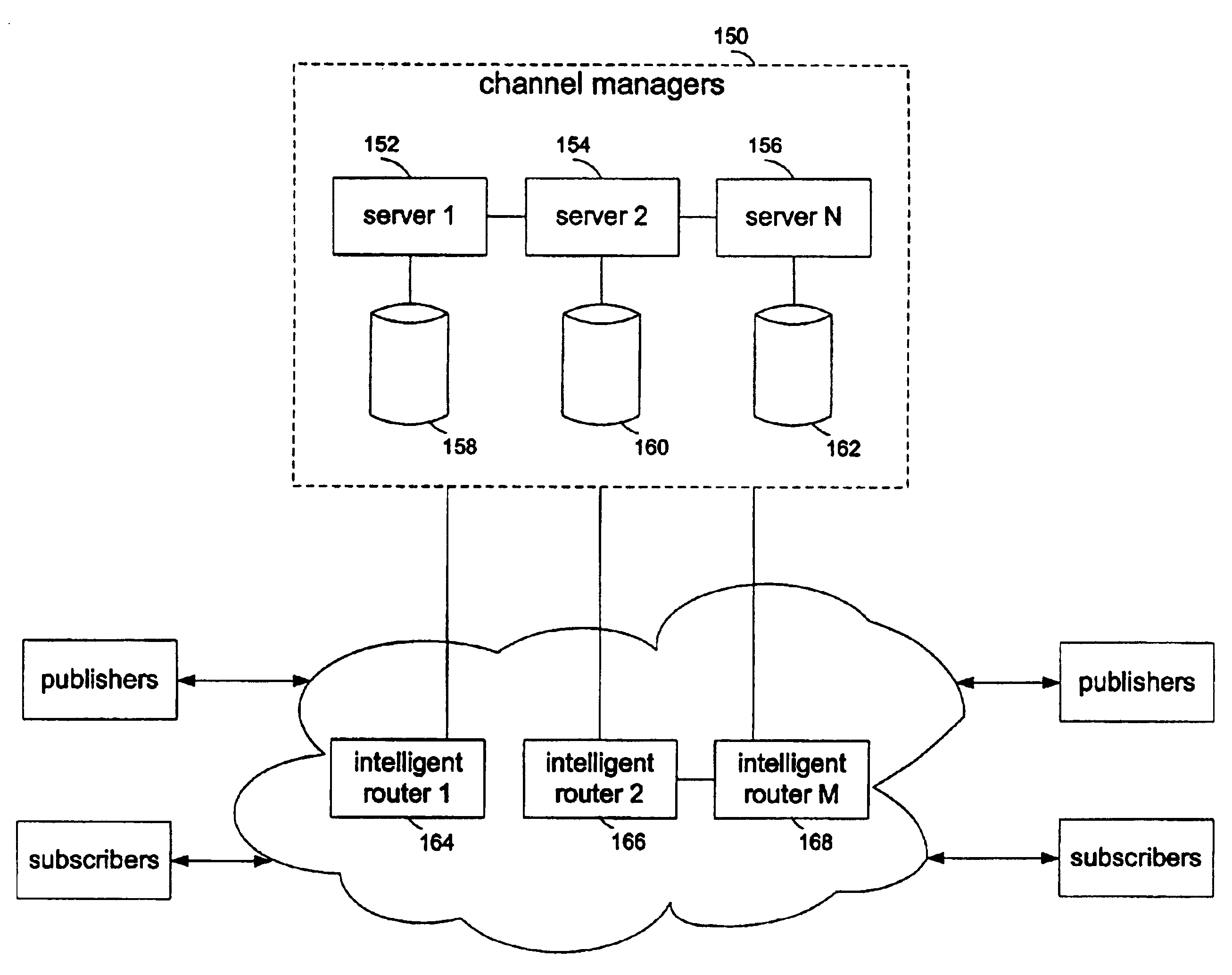
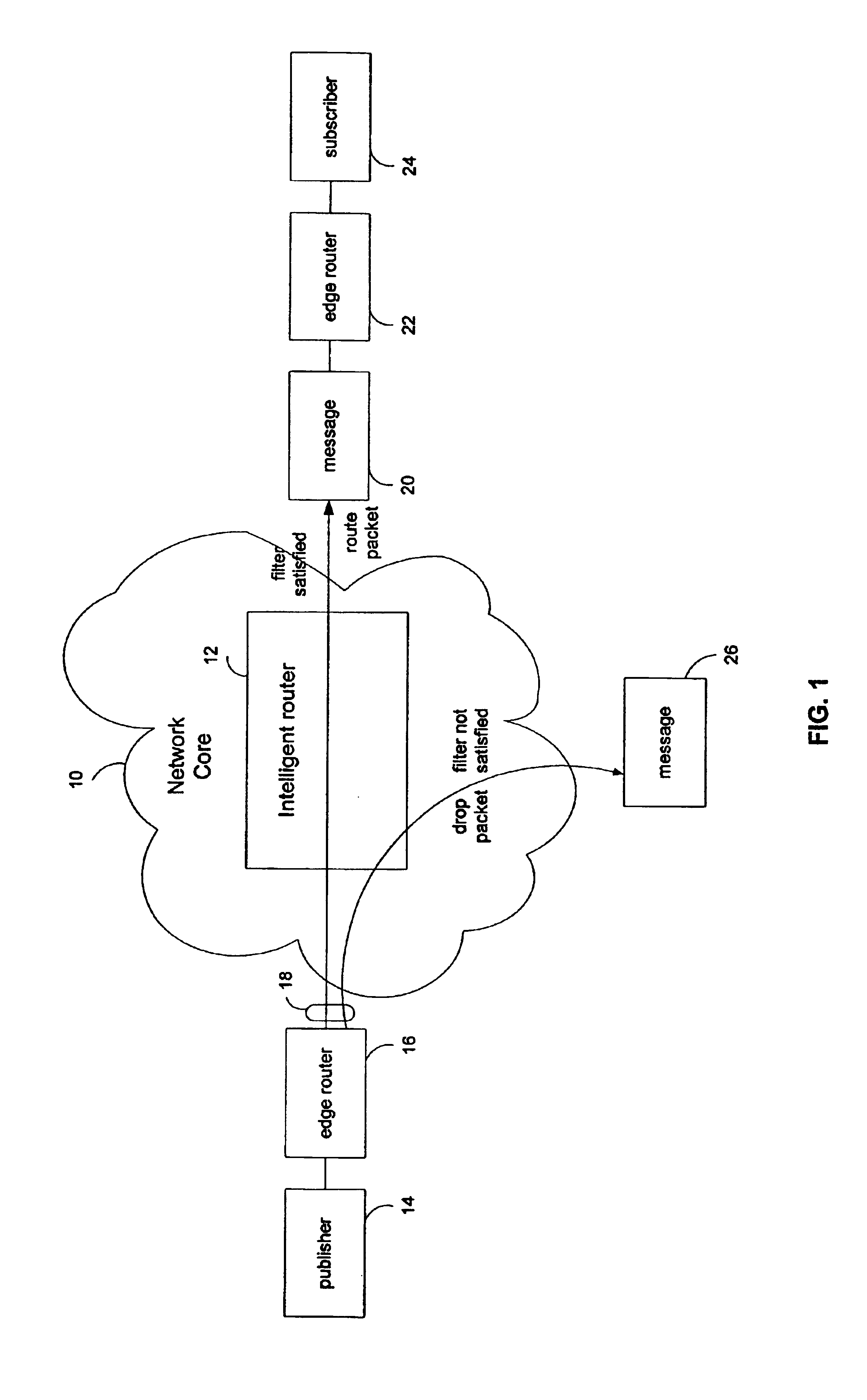
Data structures for storing subscription predicates for transmission in a publish-subscribe network. Subscriptions include Boolean-valued predicates defining content desired by a subscriber. An agent application converts the predicates into a suitable form for storing them in a common data structure. The predicates are used to generate filters to encapsulate the subscriptions, and the filters are specified in the data structure in addition to the Boolean relationships of the predicates. Routers in a network core use the data structure for content-based routing, which involves applying attributes in received packets to the filters.
Owner:PRECACHE
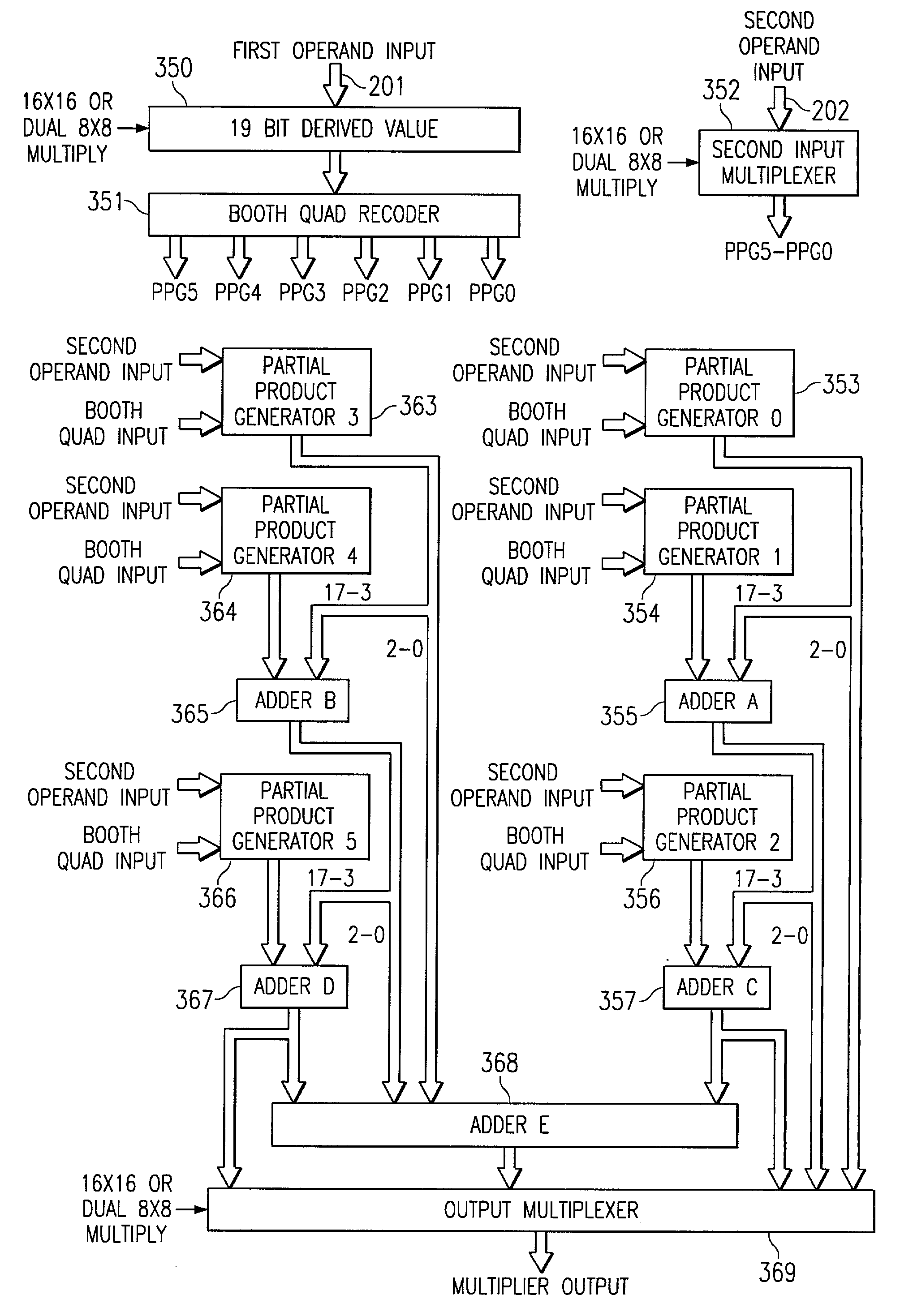
Long instruction word controlling plural independent processor operations
InactiveUS7389317B2Instruction analysisComputation using non-contact making devicesArithmetic logic unitLeast significant bit
A data processing apparatus including a multiplier unit forming a product from L bits of each two data buses of N bits each N is greater than L. The multiplier forms a N bit output having a first portion which is the L most significant bits of the of product and a second portion which is M other bits not including the L least significant bits of the product, where N is the sum of M and L. In the preferred embodiment the M other bits are derived from other bits of the two input data busses, such as the M other bits of the first input data bus. An arithmetic logic unit performs parallel operations (addition, subtraction, Boolean functions) controlled by the same instructions. This arithmetic logic unit is divisible into a selected number of sections for performing identical operations on independent sections of its inputs. The multiplier unit may form dual products from separate parts of the input data. A single instruction controlling both the multiplier unit and the arithmetic logic unit permits addition of dual products. The dual products are temporarily stored in a data register permitting the multiply and add operations to be pipelined. The dual products are formed in one data word and added by a rotate / mask and add operation in a three input arithmetic unit.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
In memory matrix multiplication and its usage in neural networks
ActiveUS20170277659A1Input/output to record carriersDigital storageArray data structureParallel computing
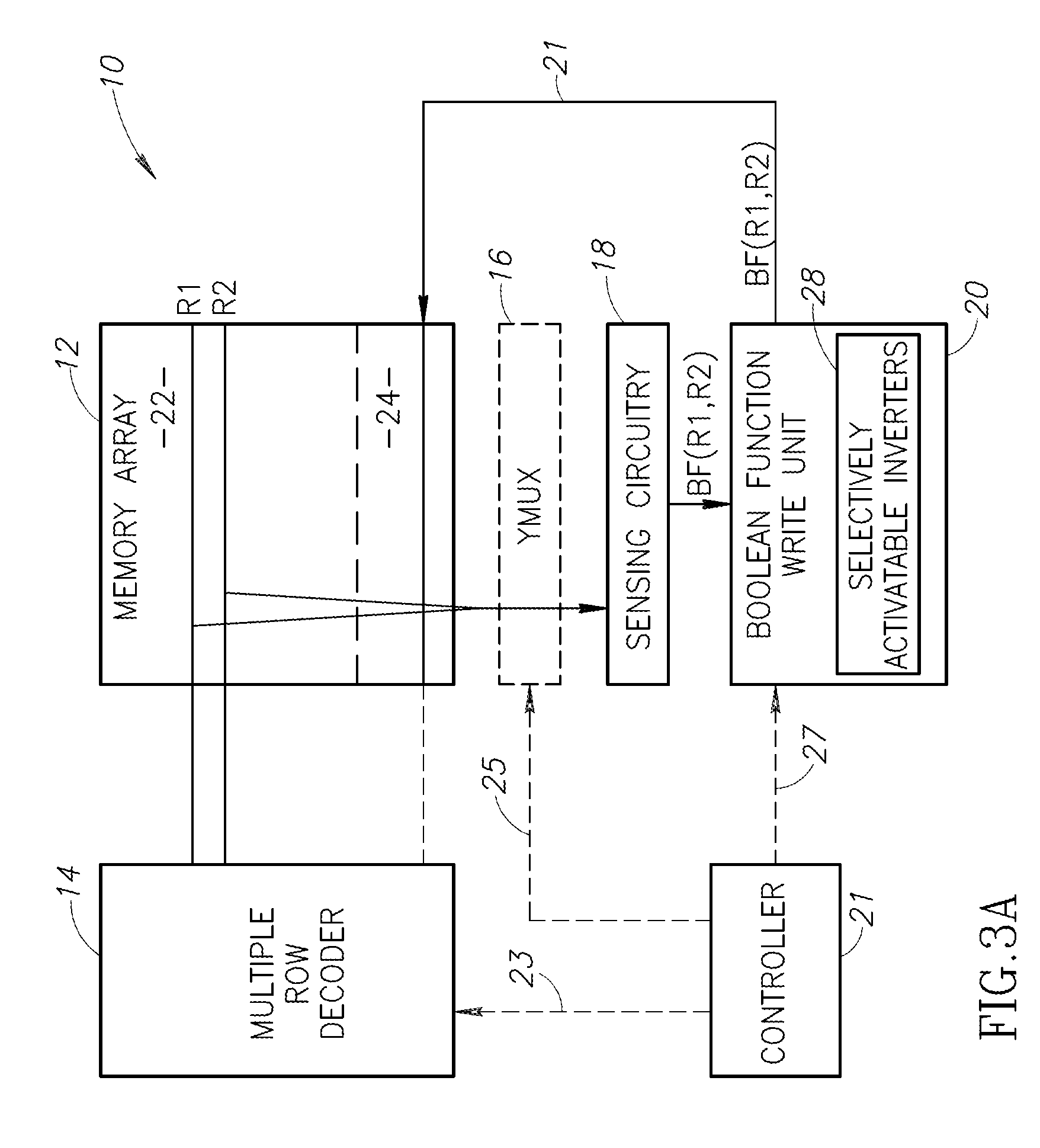
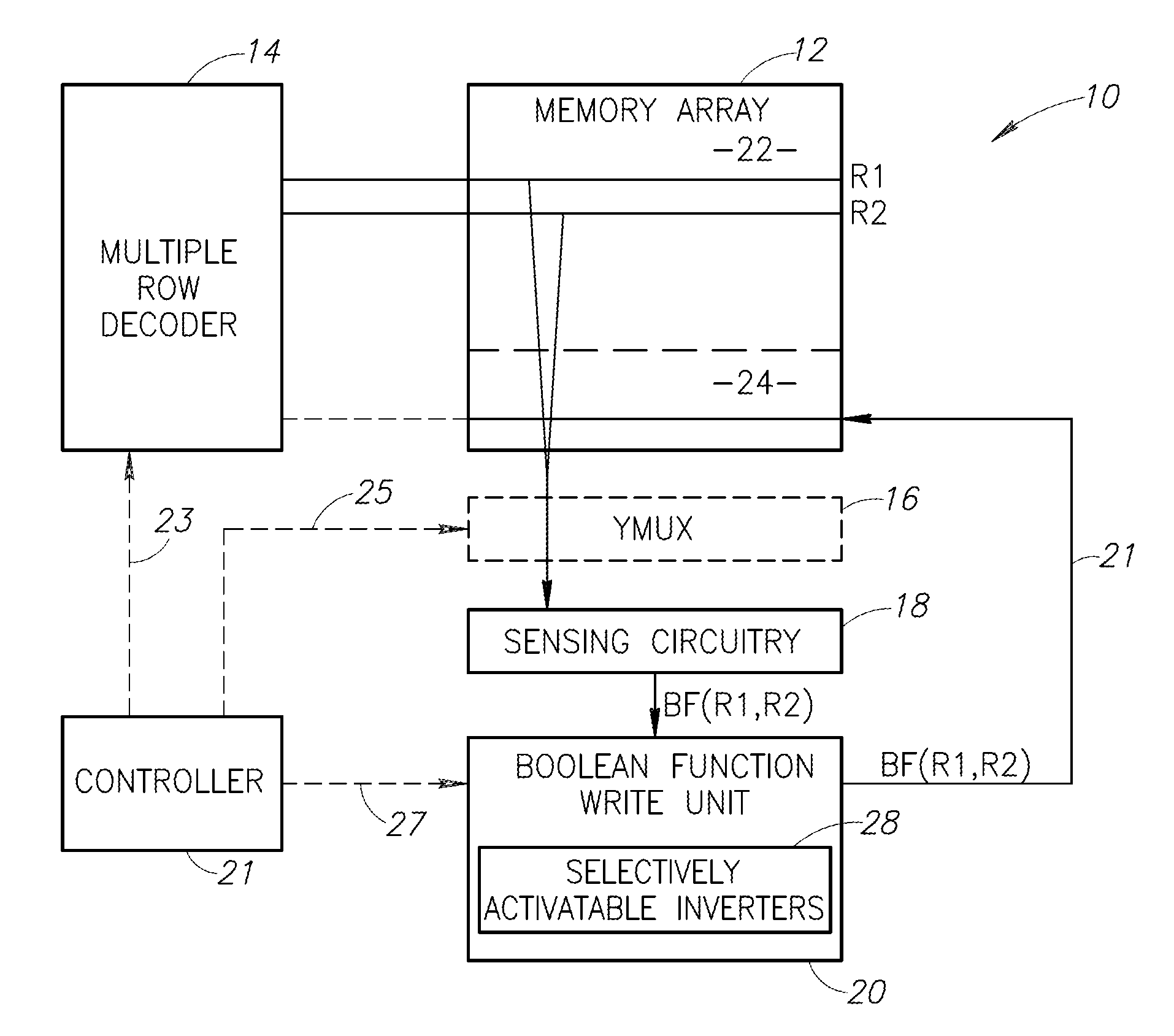
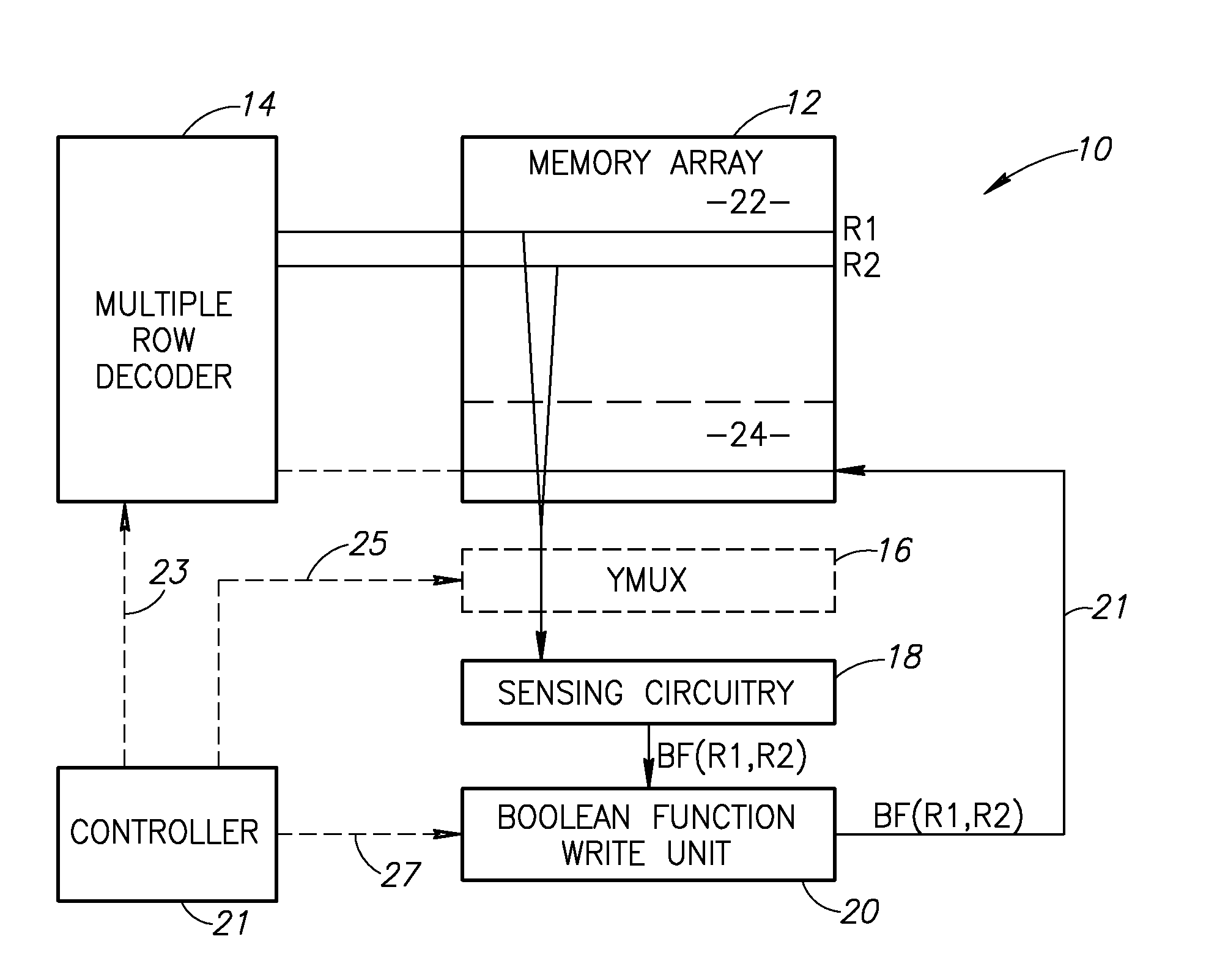
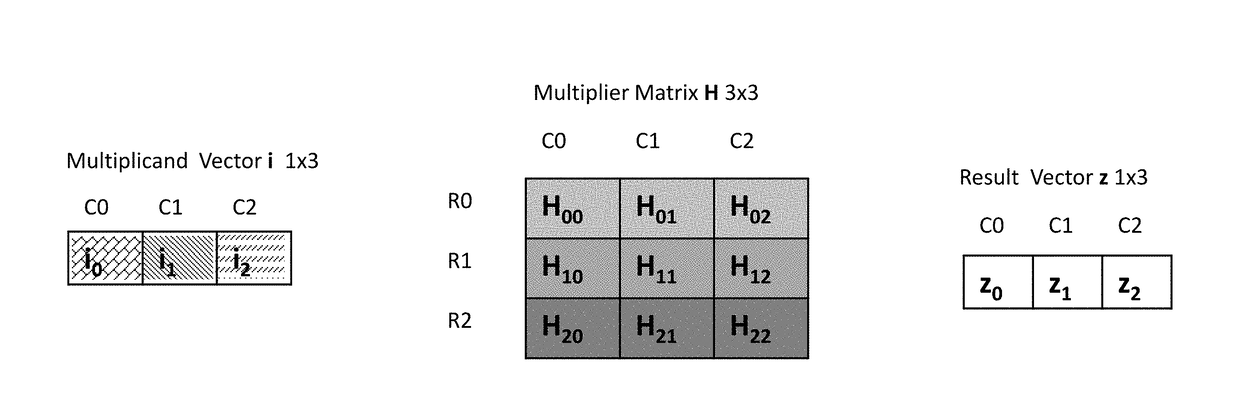
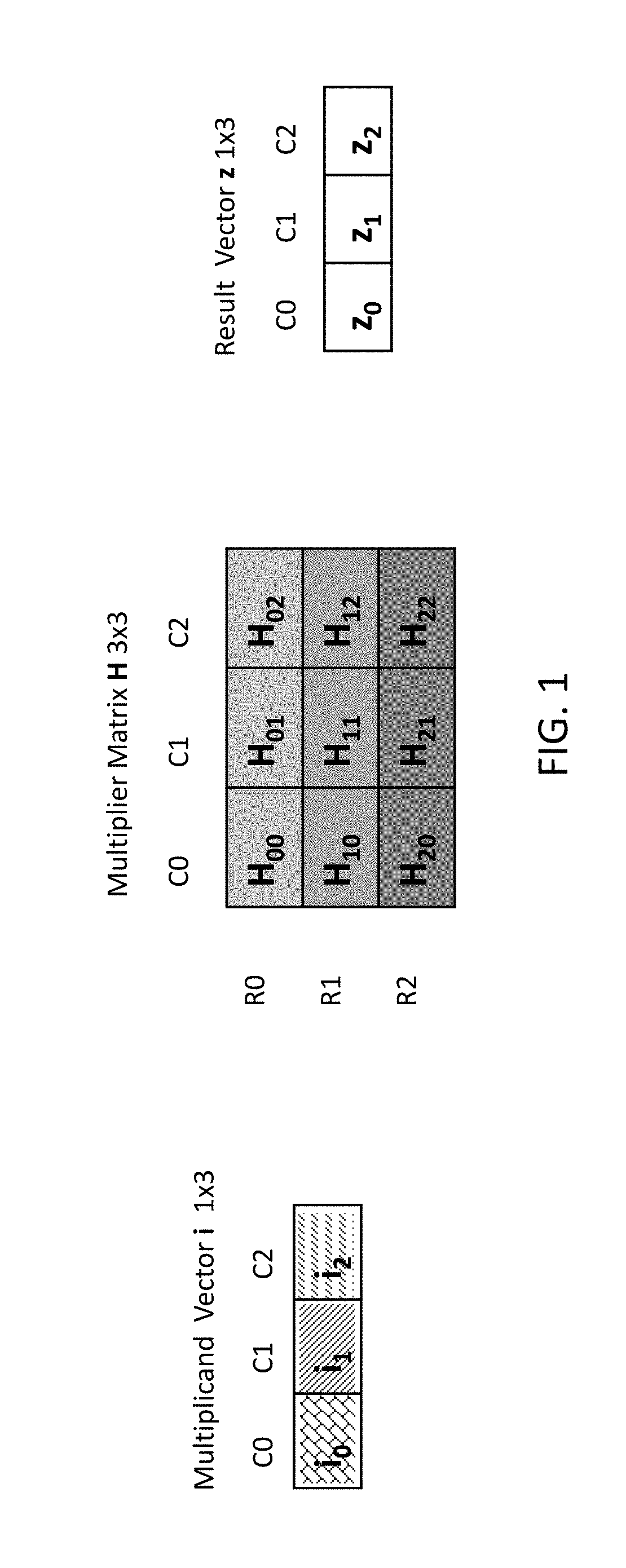
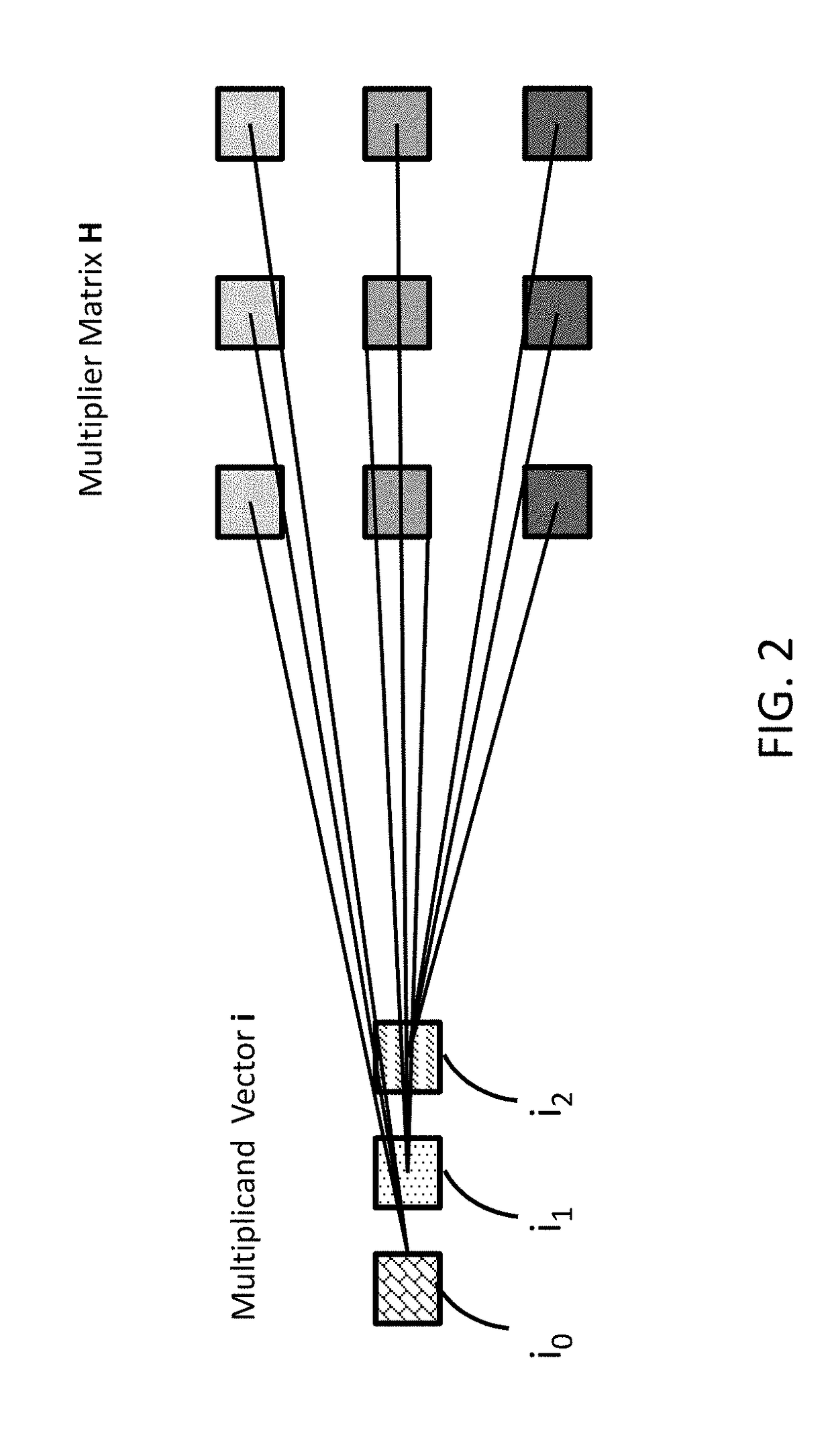
A method for an associative memory array includes storing each column of a matrix in an associated column of the associative memory array, where each bit in row j of the matrix is stored in row R-matrix-row-j of the array, storing a vector in each associated column, where a bit j from the vector is stored in an R-vector-bit-j row of the array. The method includes simultaneously activating a vector-matrix pair of rows R-vector-bit-j and R-matrix-row-j to concurrently receive a result of a Boolean function on all associated columns, using the results to calculate a product between the vector-matrix pair of rows, and writing the product to an R-product-j row in the array.
Owner:GSI TECH
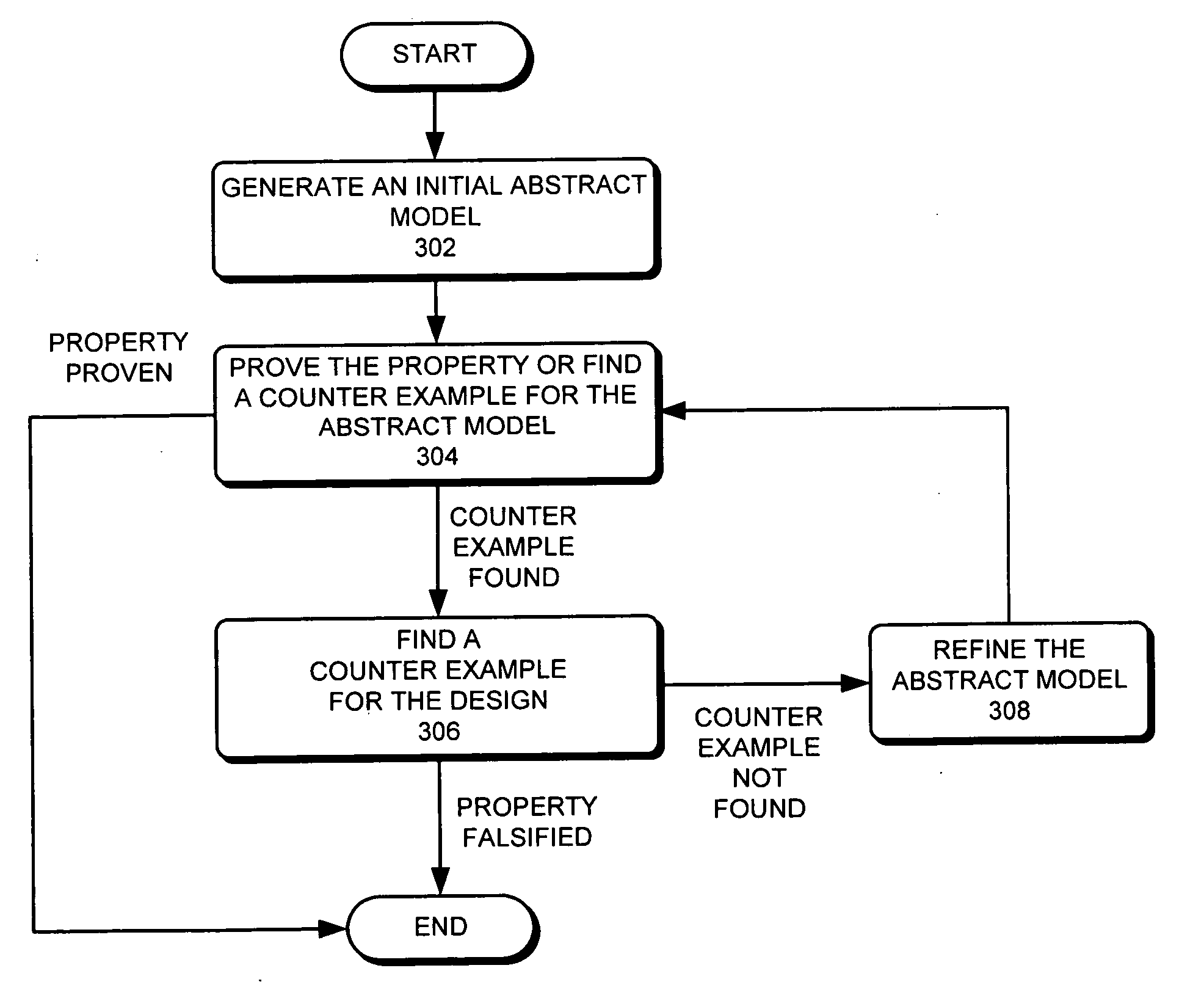
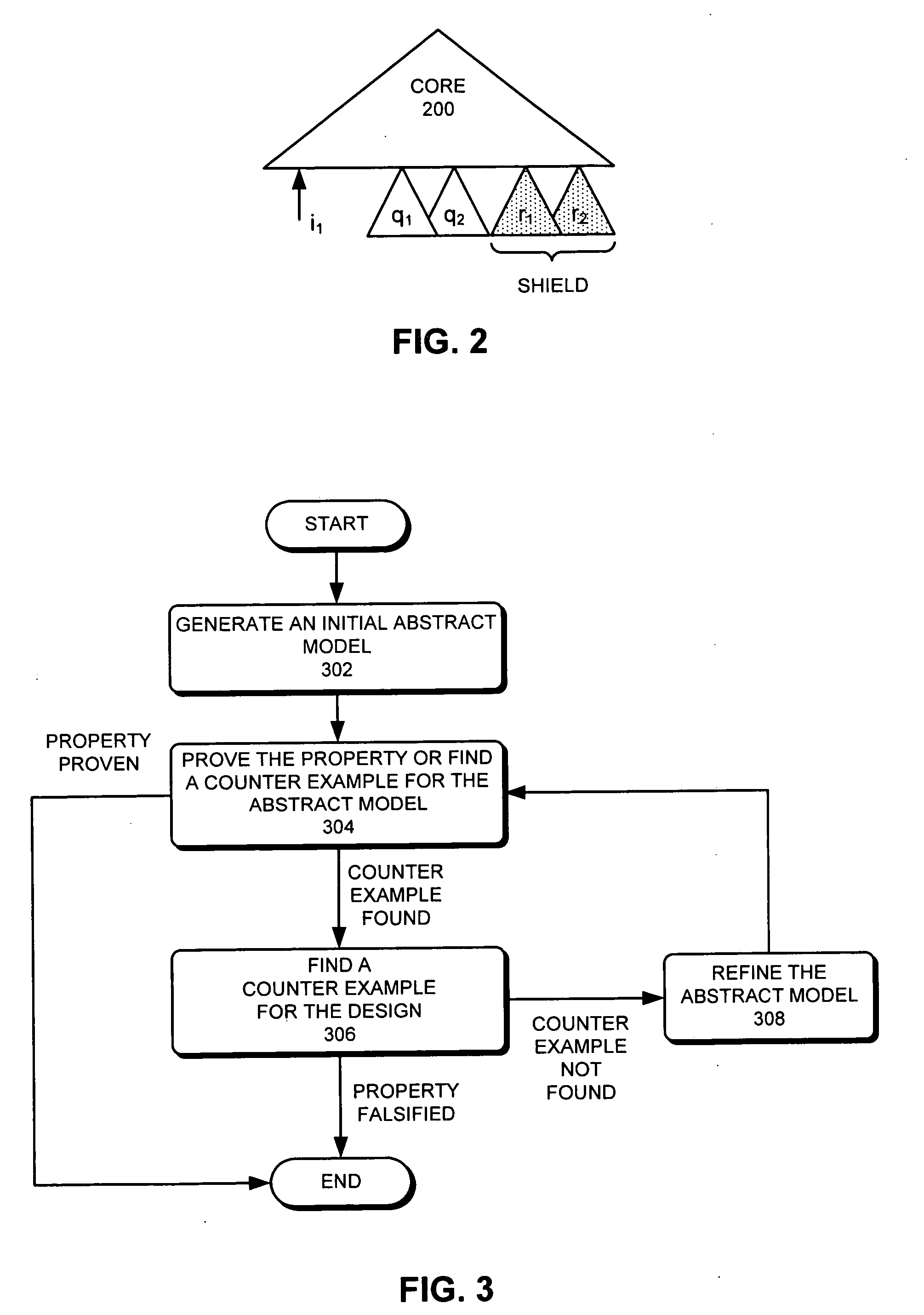
Abstraction refinement using controllability and cooperativeness analysis
InactiveUS20060129959A1Analogue computers for electric apparatusComputer aided designTheoretical computer scienceSecurity properties
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that refines an abstract model. Note that abstraction refinement is commonly used in formal property verification. During operation, the system receives an abstract model which is a subset of a logic design which can be represented using a set of variables and a set of Boolean functions. Next, the system receives a safety property for the logic design which is desired to be proven. The system also receives a set of counter-examples. A counter-example is a sequence of states that violates the safety property. Note that a state is an assignment of values to the variables, which are determined using the set of Boolean functions and the variable values in the previous state. The system then determines a set of cooperative variables using the set of counter-examples. A cooperative variable is a variable that can help invalidate all counter-examples. The system then refines the abstract model using the set of cooperative variables.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
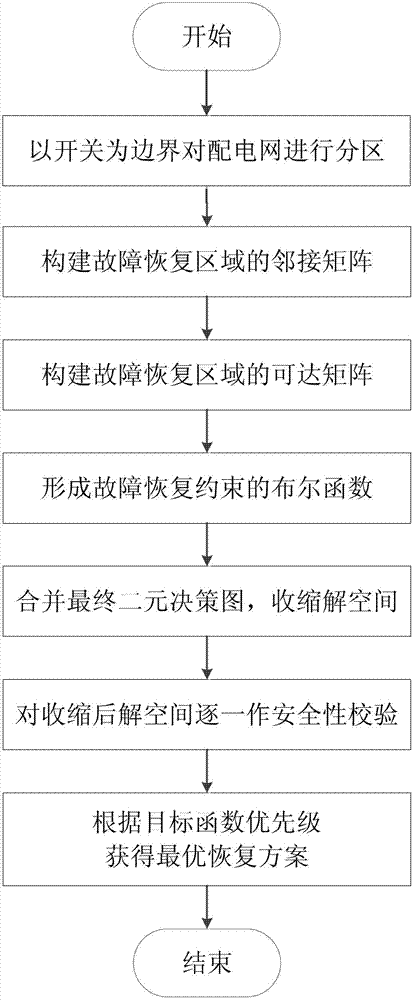
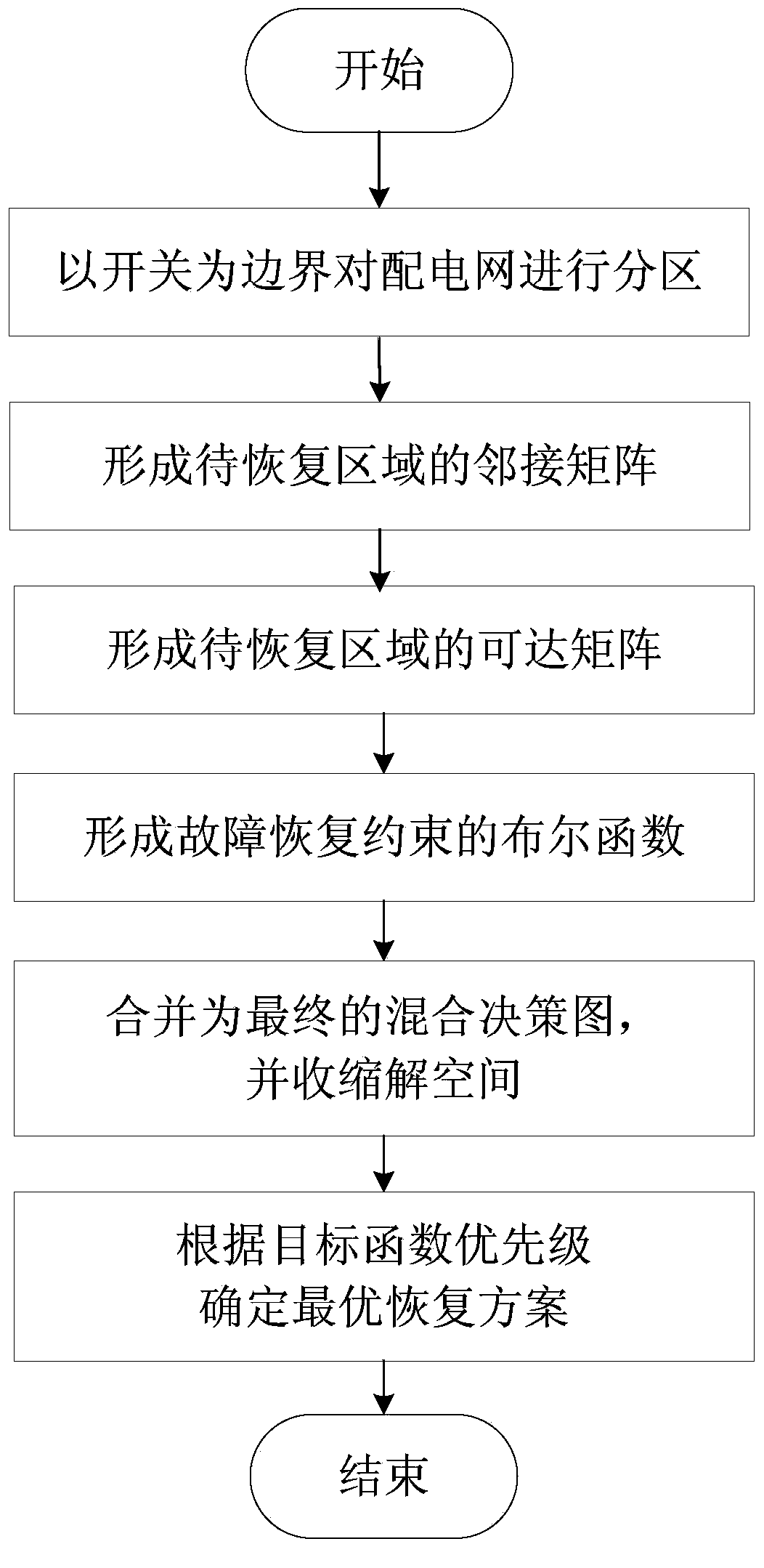
Ordered binary decision diagram modeling method for distribution network fault recovery
InactiveCN103199510AThe principle is simpleEasy to implementEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionLocal optimumUndirected graph
The invention discloses an ordered binary decision diagram modeling method for distribution network fault recovery. The method includes a first step of carrying out partition on a power distribution network, and using an on-off state as a decision variable, a second step of forming an adjacent matrix of the power distribution network according to a forming method of the adjacent matrix of an undirected graph, a third step of forming a reachable matrix of the power distribution network, a fourth step of forming boolean functions of each restriction of fault recovery, a fifth step of combining to generate a final binary decision diagram, and obtaining a contractive solution space, a sixth step of carrying out load flow calculation on feasible solutions one by one in the solution space after contraction, and carrying out safety verification, and a seventh step of obtaining an optimal recovery scheme according to priority levels of optimized objective functions. The modeling method has the advantages of effectively reducing the solution complexity of fault recovery problems, overcoming the defect that a traditional artificial intelligence algorithm is prone to premature convergence in local optimal solution, and improves understanding reliability and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
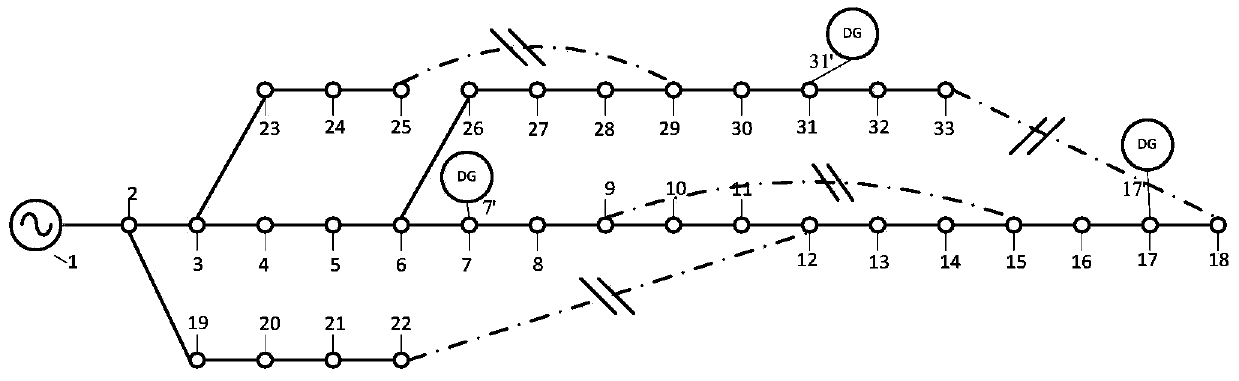
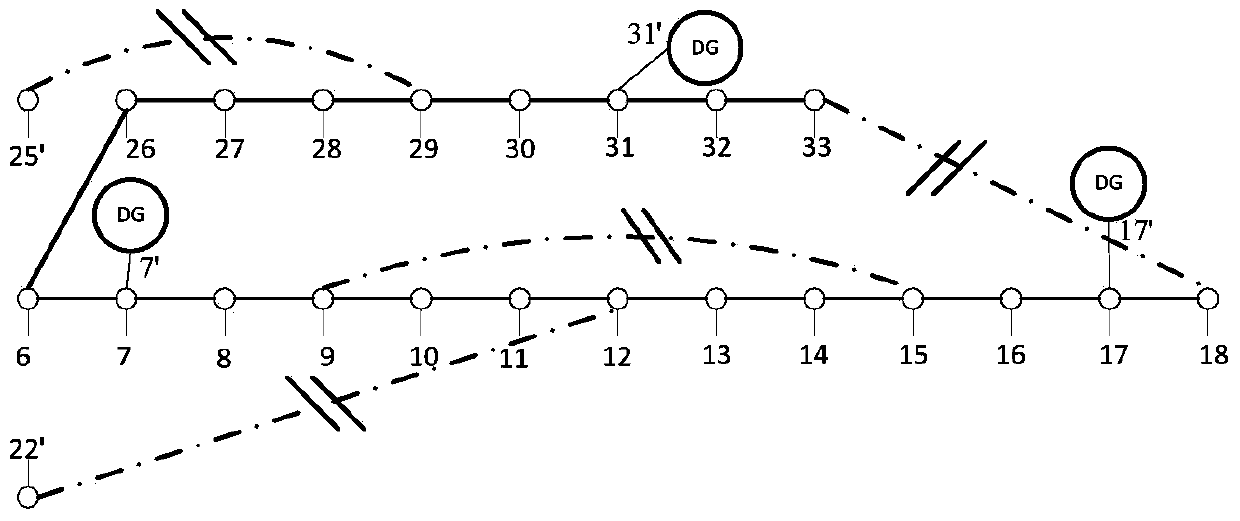
Distributed-generation-contained power distribution system fault recovery method based on mixed decision diagram
ActiveCN103579990AThe principle is simpleEasy to implementEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionSpecial data processing applicationsRecovery methodRestoration method
The invention discloses a modeling method for achieving distributed-generation-contained power distribution system fault recovery. The modeling method comprises the following steps of (1) reading original data of a distribution network, using a switch as the boundary to carry out partition on the distribution network, and using the switch as a decision variable; (2) forming an adjacency matrix of a region to be recovered; (3) forming a reachable matrix of the region to be recovered; (4) forming the Boolean function about various fault recovery constraints; (5) carrying out merging to form a final mixed decision diagram, carrying out conversion to form an orderly binary decision diagram, and contracting a solution space; (6) determining an optimal fault recovery scheme for the contracted solution space according to a priority of an objective function. The modeling method for achieving distributed-generation-contained power distribution system fault recovery can effectively reduce the complexity for solving the distributed-generation-contained power distribution network fault recovery problem, and can have the advantages of being high in computation speed, high in credibility of solutions, good in actual operability of projects and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
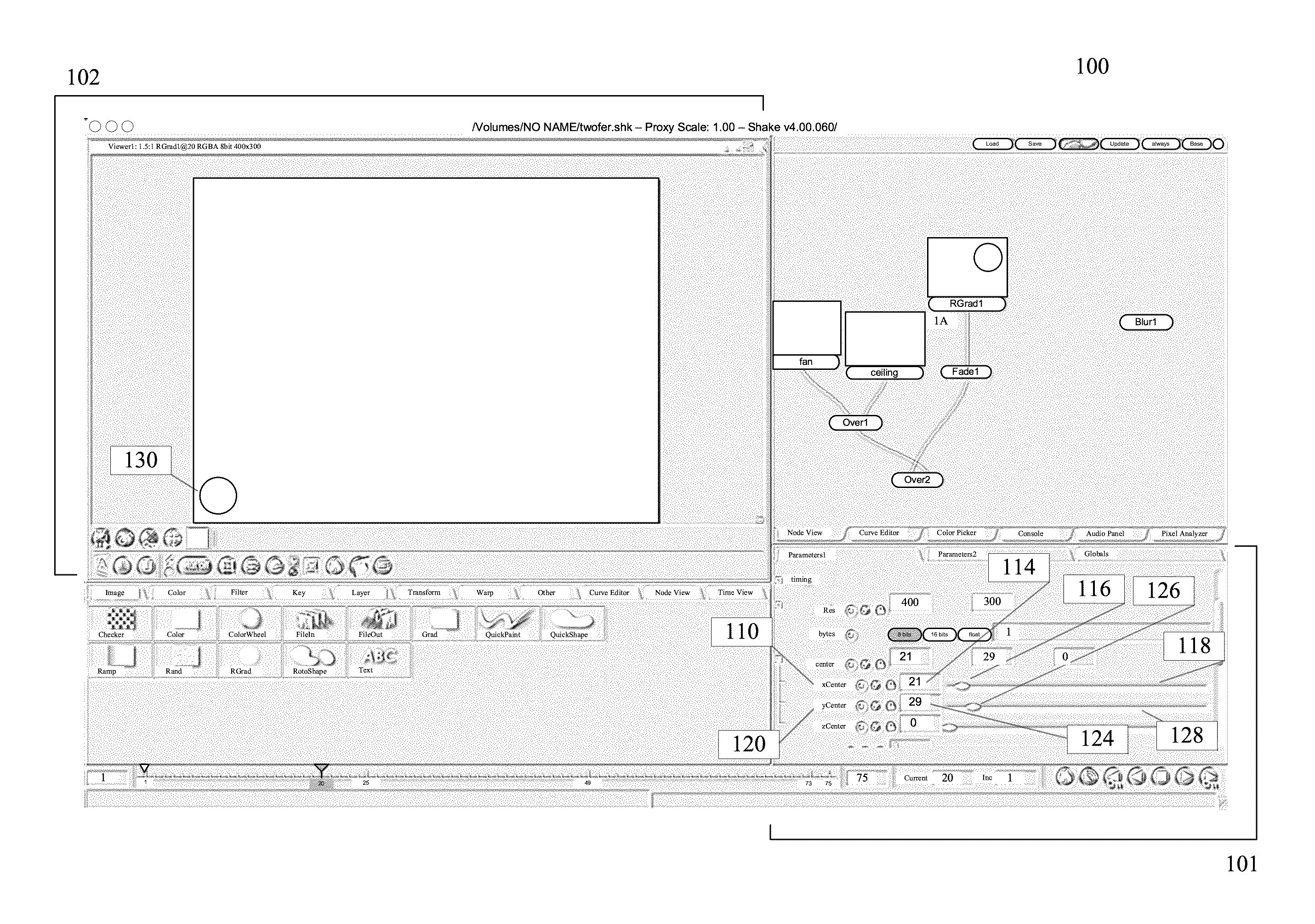
Locking relationships among parameters in computer programs
InactiveUS20110145743A1Input/output processes for data processingTheoretical computer scienceLookup table
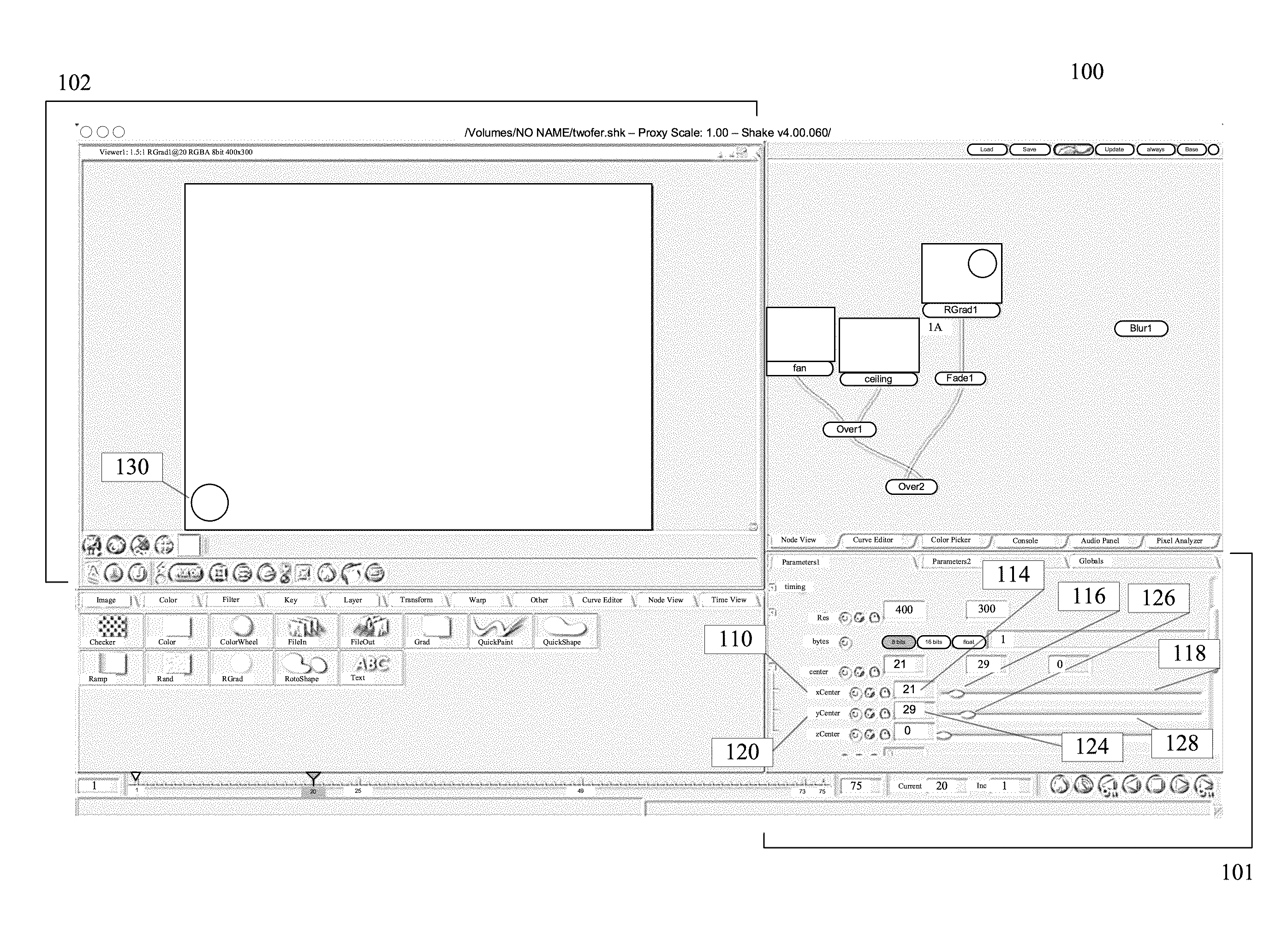
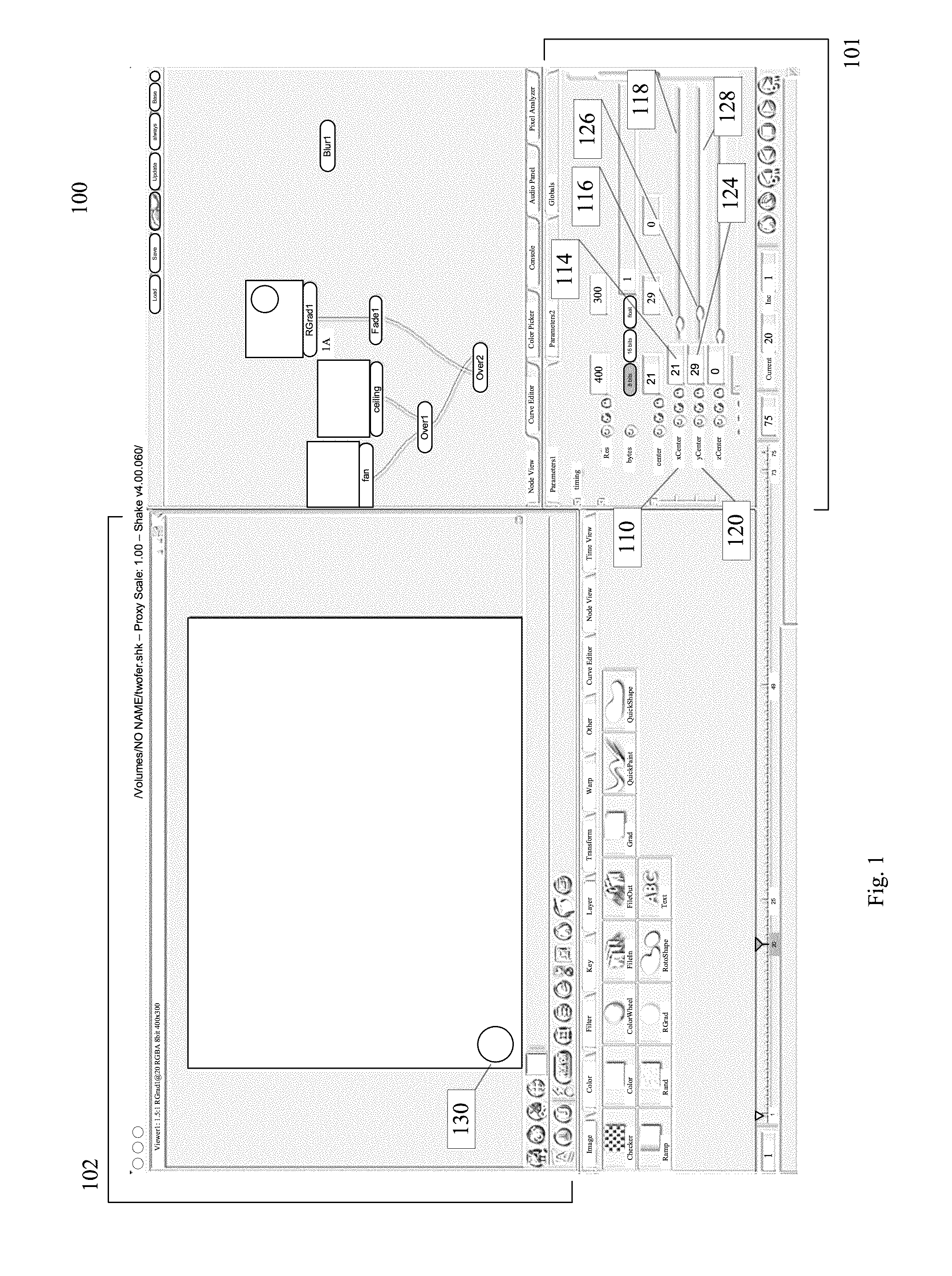
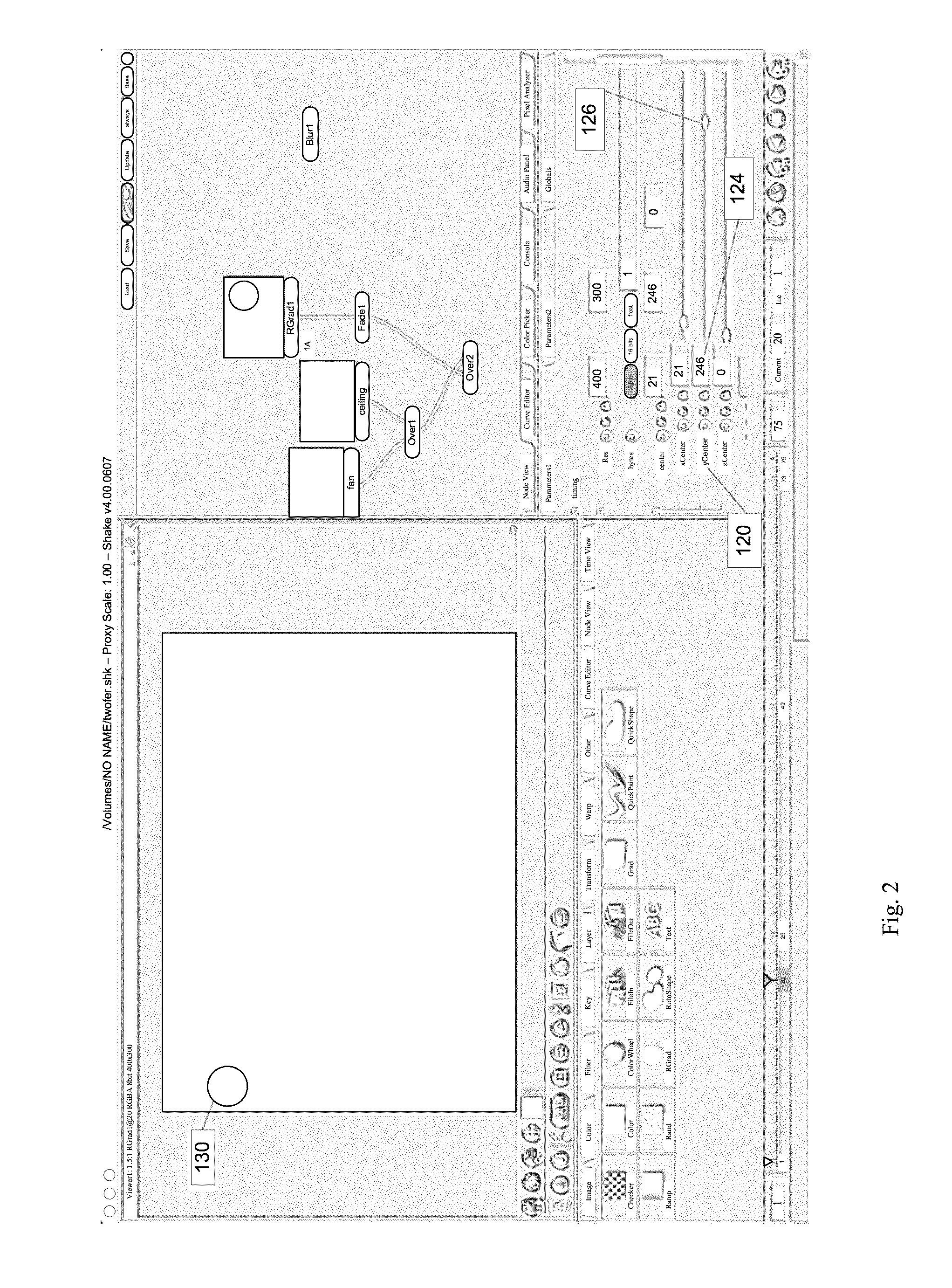
Some embodiments provide a method for locking in a mathematical relationship between a set of at least two parameters in a computer program. The method selects a first parameter. The method defines a mathematical relationship that ties the value of the first parameter to the value of a second parameter. In some embodiments, the mathematical relationship can be a mathematical function, a Boolean function, or a lookup table. The relationship could be directly entered by the user, or the computer program itself could derive it from the user's actions. In some embodiments, the first parameter can be locked to the mathematical relationship. The lock prevents the value of that parameter from being changed, except by changing the value of the second parameter. Some embodiments implement this method by using a GUI with an intuitive set of controls.
Owner:BRINKMANN RON +2
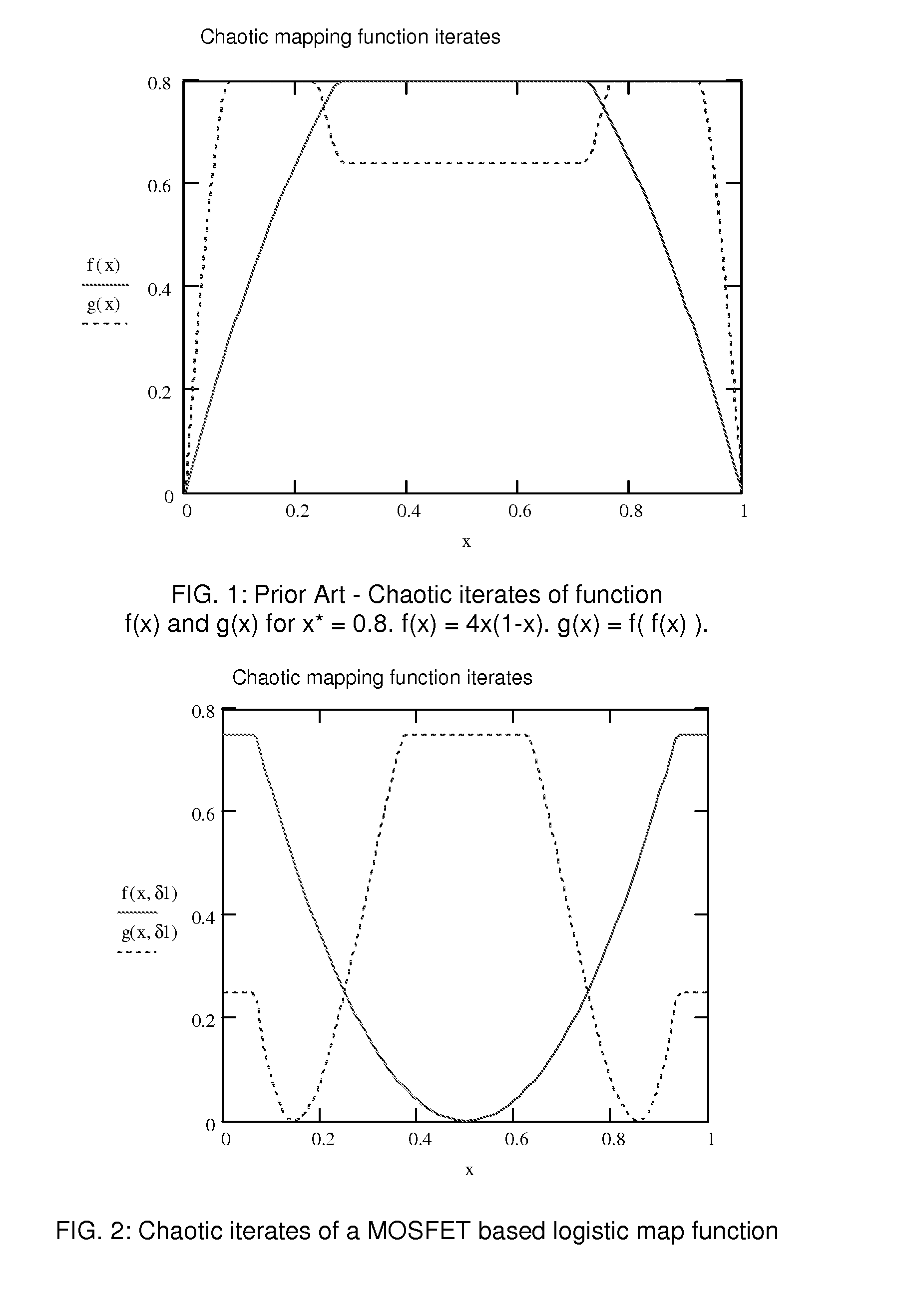
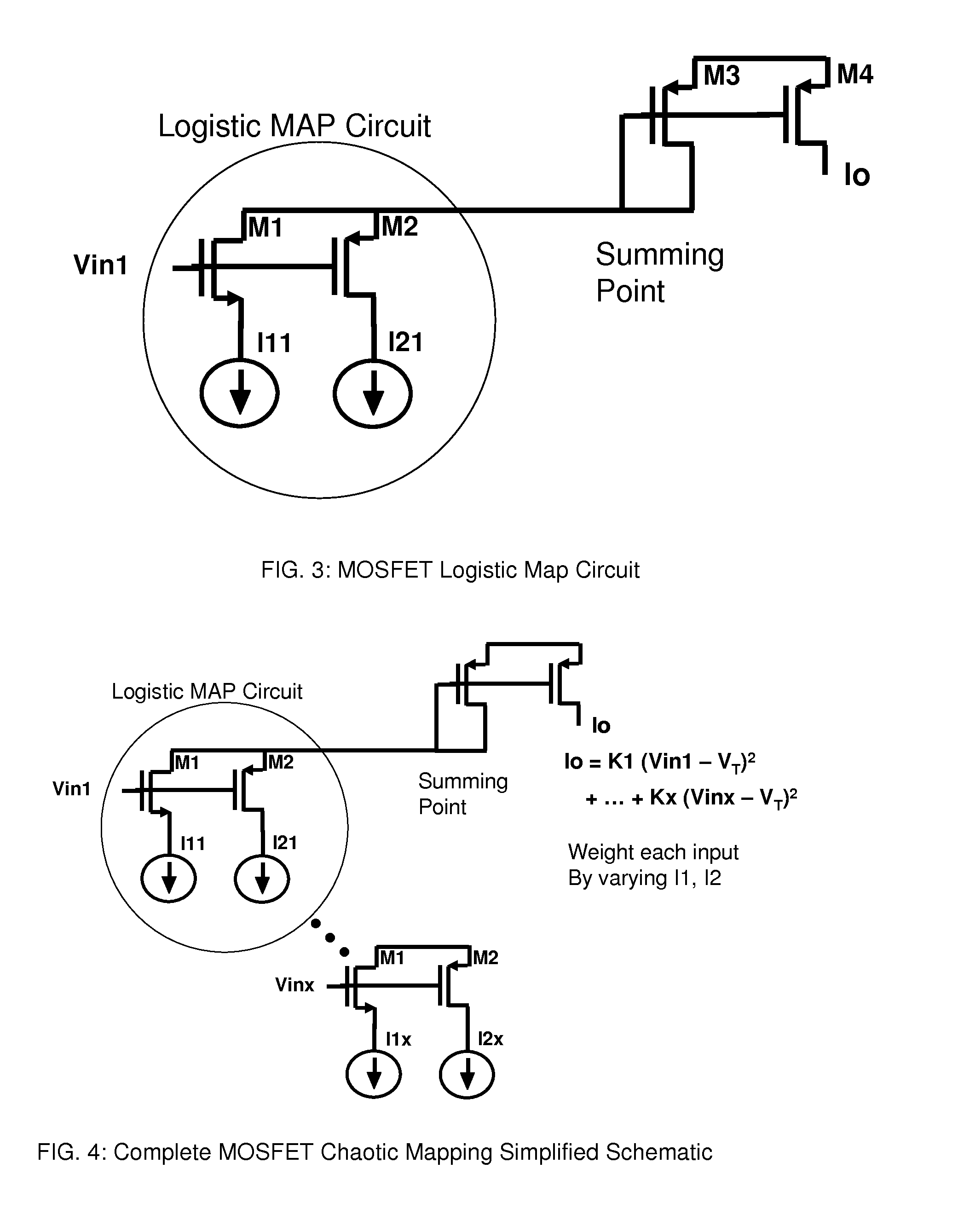
High utilization universal logic array with variable circuit topology and logistic map circuit to realize a variety of logic gates with constant power signatures
ActiveUS20110085662A1Avoid detectionPower reduction in field effect transistorsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionMulti inputConstant power
Disclosed is a novel circuit able to generate any logic combination possible as a function of the input logic signals. The circuit is described as a 2 input logistic map circuit but may be expanded to 3 or more inputs as required. Further disclosed is a universal logic array with variable circuit topology. A metallization layer and / or a via interconnection between cells in the array elements produce a circuit topology that implements a Boolean function and / or chaotic function and / or a logic function. The novel circuit provides a circuit topology for secure applications with no obvious physical correspondence between control signal values and input to output mapping. Further disclosed is a network which has a power signature independent of input signal state and output transition. This provides a very useful circuit to protect data from decryption from power signature analysis in secure applications.
Owner:CHAOLOGIX INC
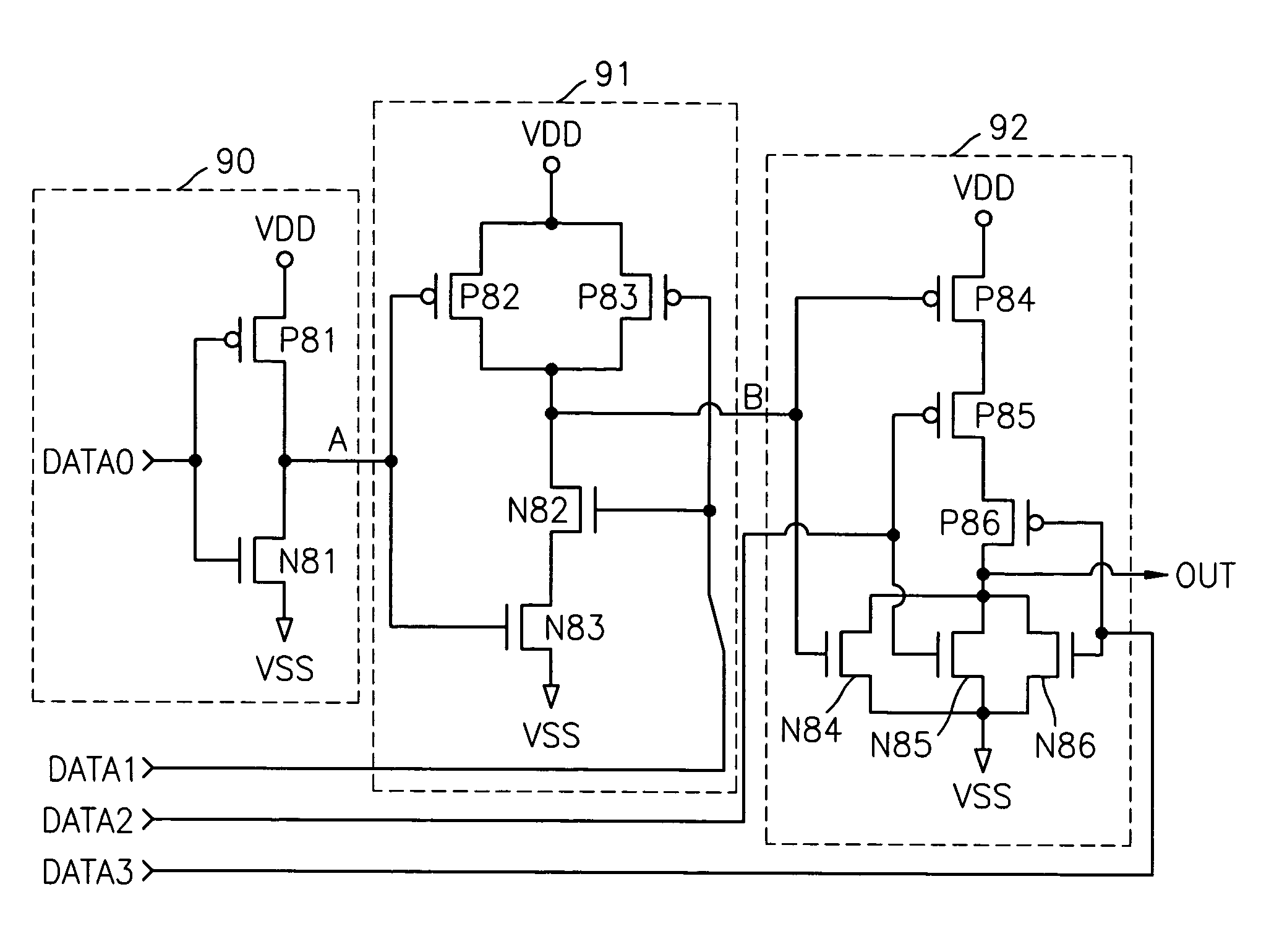
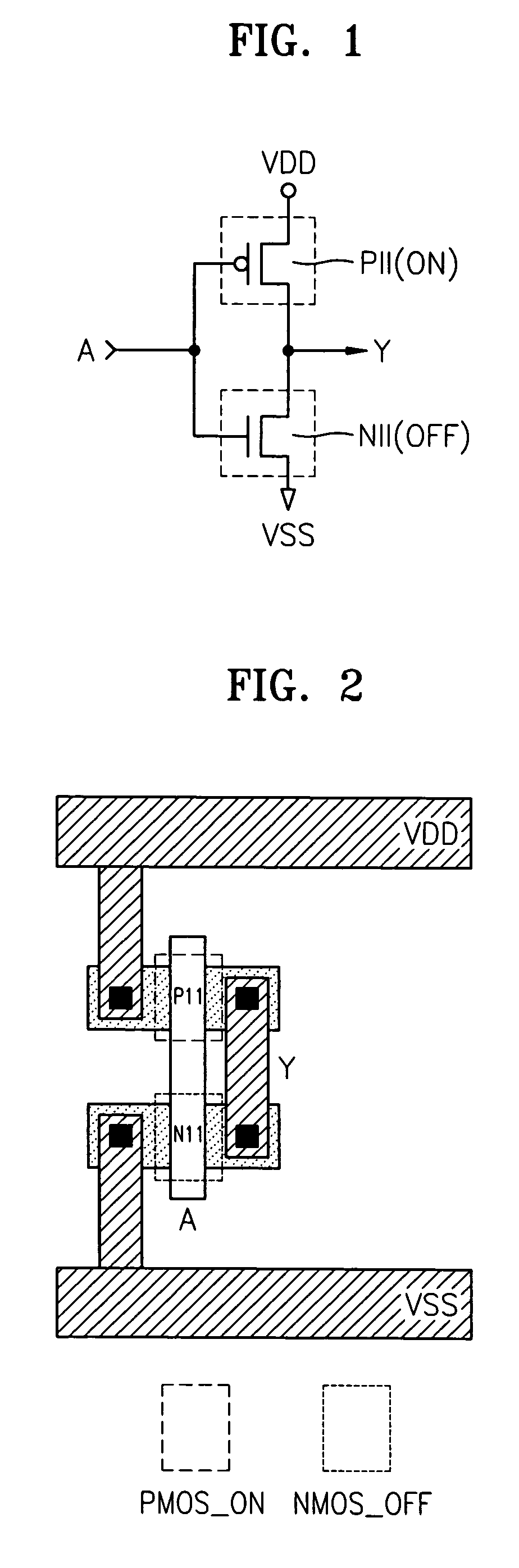
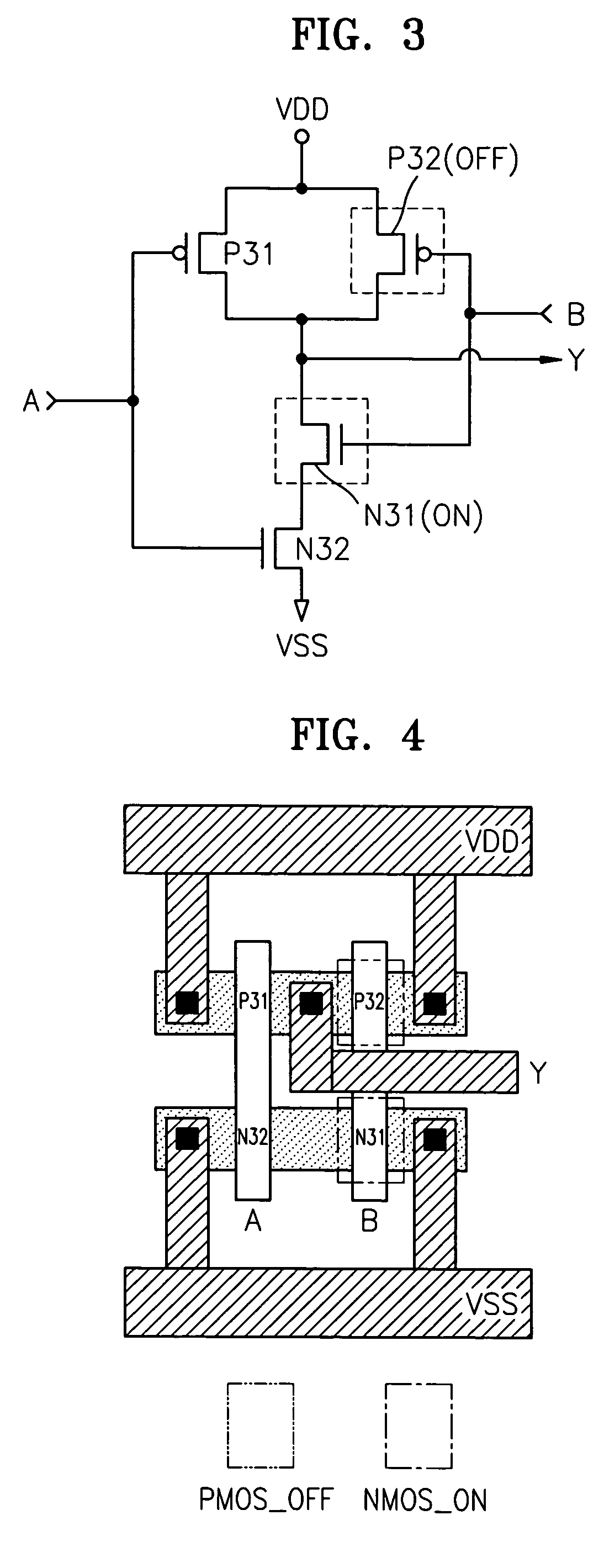
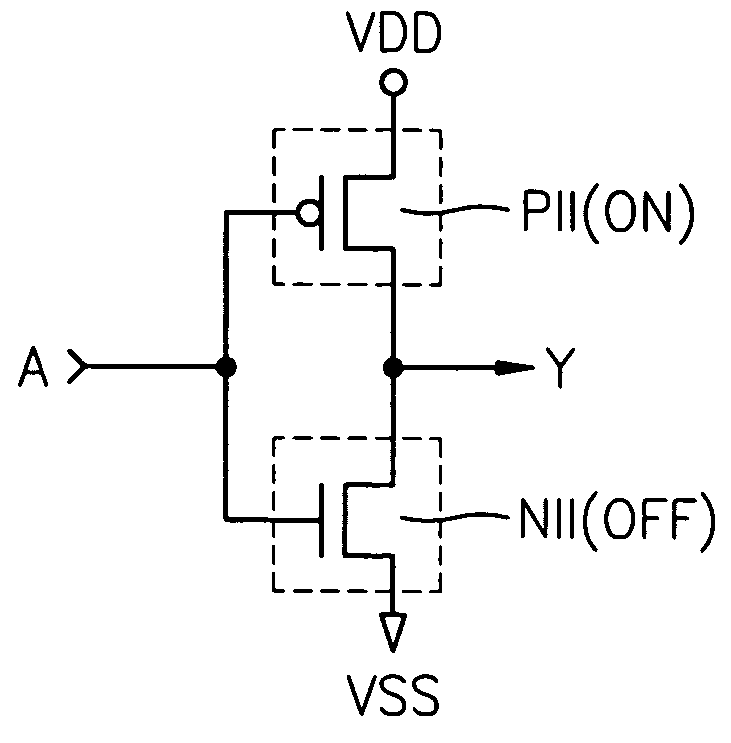
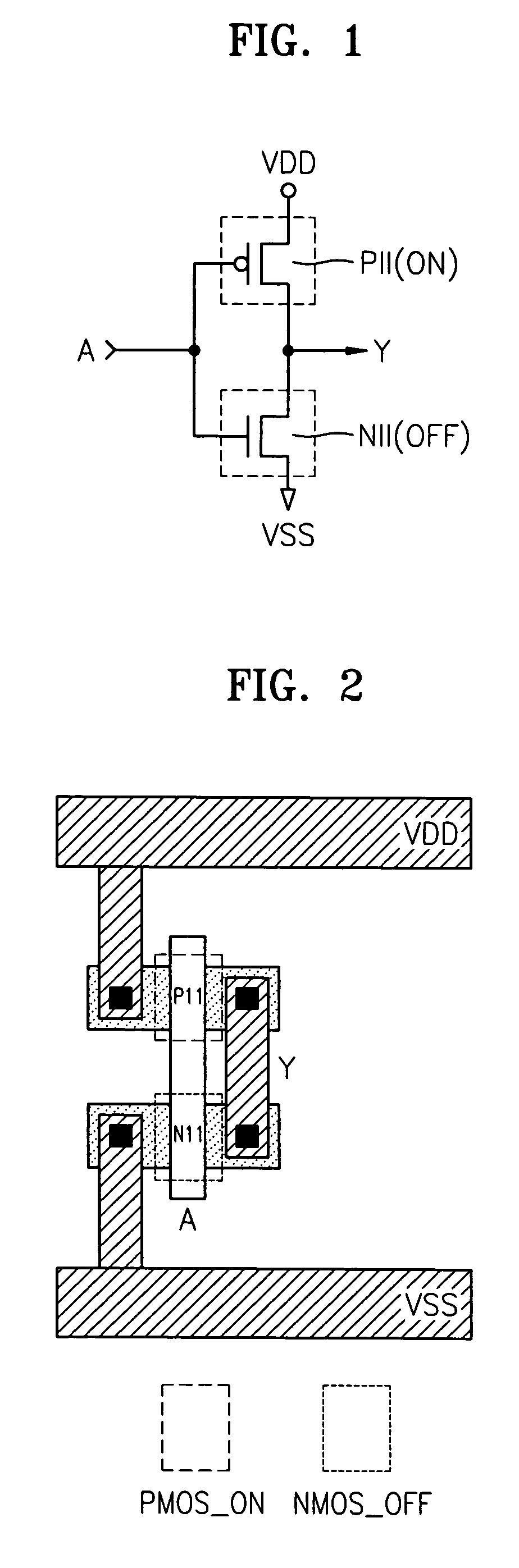
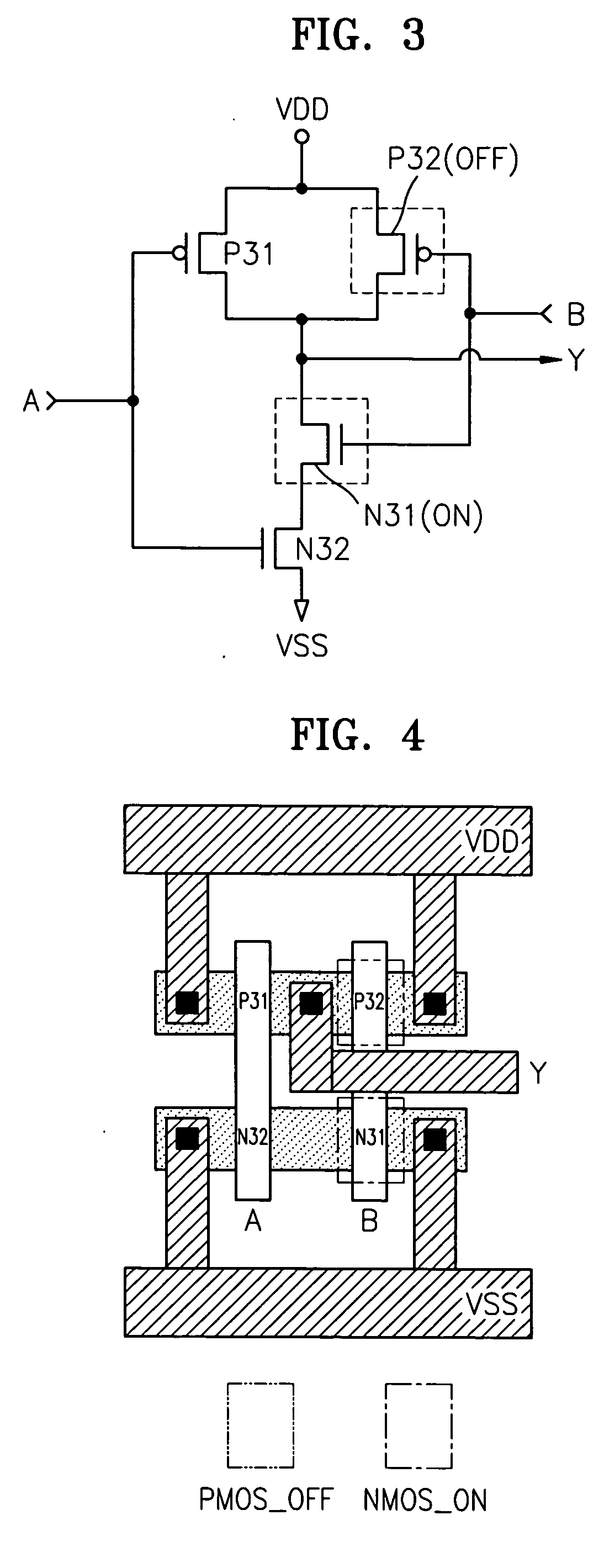
Semiconductor integrated circuit and methods for protecting the circuit from reverse engineering
A semiconductor integrated circuit having a reverse engineering protection part that can be easily implemented without additional circuitry or process using a method for protecting against reverse engineering of the semiconductor integrated circuit. The semiconductor integrated circuit includes a logic gate and a reverse engineering protection part. The reverse engineering protection part alters the apparent Boolean functions of a logic gate. Further, the reverse engineering protection part includes at least one PMOS transistor and at least one NMOS transistor. The PMOS and NMOS transistors are constructed to remain in a state of constant on or off irrespective of an input signal applied to their gates. The PMOS transistors and the NMOS transistors are included in transistors forming the logic gate. The PMOS transistors and the NMOS transistors that remain in a state of constant on or off are formed by implanting ions into their gate channels or blocking ion implantation into their gate channels during manufacturing.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Locking relationships among parameters in computer programs
ActiveUS20070113183A1Recording carrier detailsRecord information storageMethod selectionTheoretical computer science
Some embodiments provide a method for locking in a mathematical relationship between a set of at least two parameters in a computer program. The method selects a first parameter. The method defines a mathematical relationship that ties the value of the first parameter to the value of a second parameter. In some embodiments, the mathematical relationship can be a mathematical function, a Boolean function, or a lookup table. The relationship could be directly entered by the user, or the computer program itself could derive it from the user's actions. In some embodiments, the first parameter can be locked to the mathematical relationship. The lock prevents the value of that parameter from being changed, except by changing the value of the second parameter. Some embodiments implement this method by using a GUI with an intuitive set of controls.
Owner:APPLE INC
Encrypted table indexes and searching encrypted tables
ActiveUS7519835B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsDatabase indexComputer science
The present invention teaches a variety of methods for building and searching secure, indexed database tables. Sensitive portions of the database tables and database indexes are encrypted, ordered and searched according to Boolean functions arranged to work with encrypted data. Also disclosed is a database management system that allows authorized users to build and search encrypted tables.
Owner:THALES DIS CPL USA INC
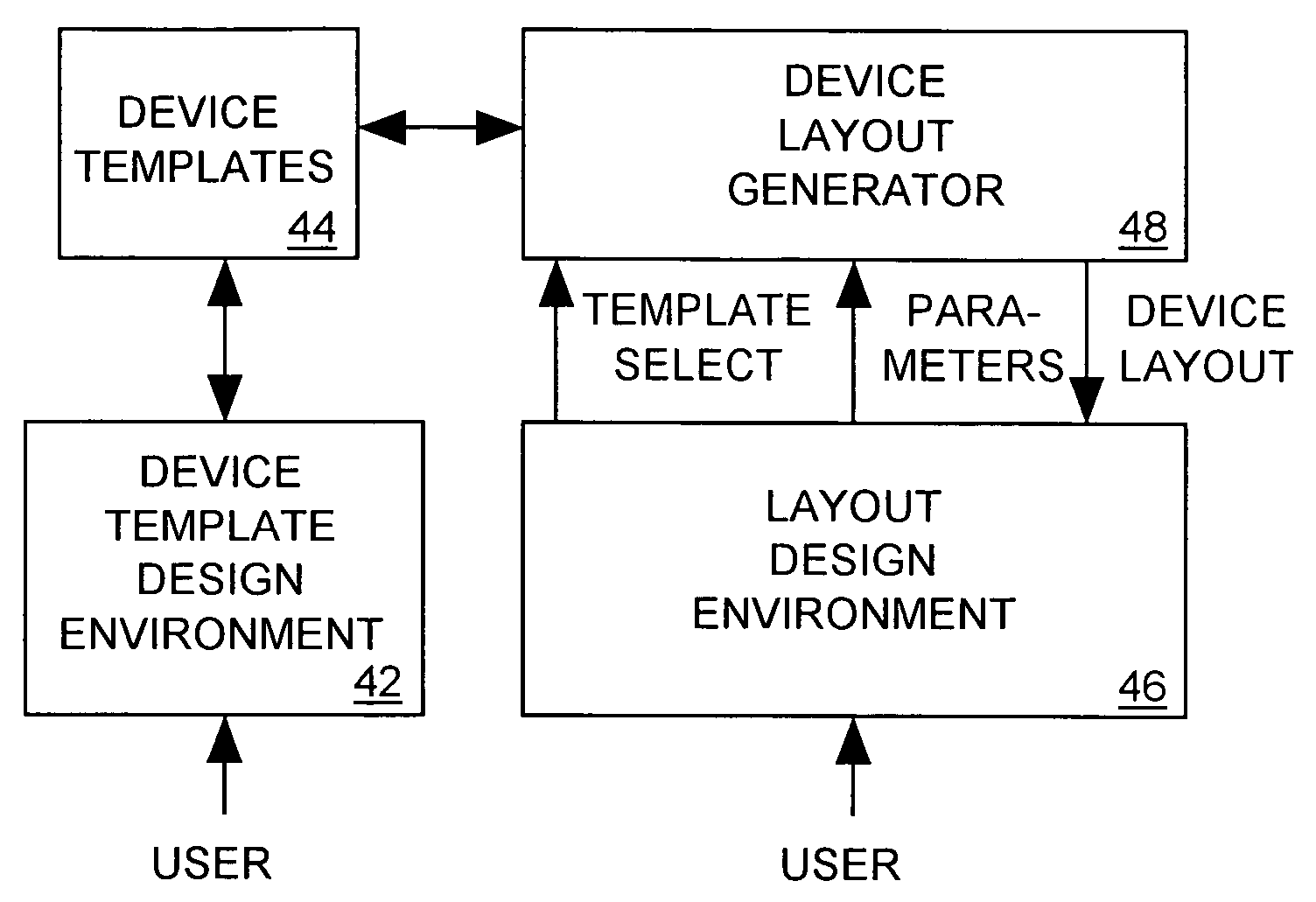
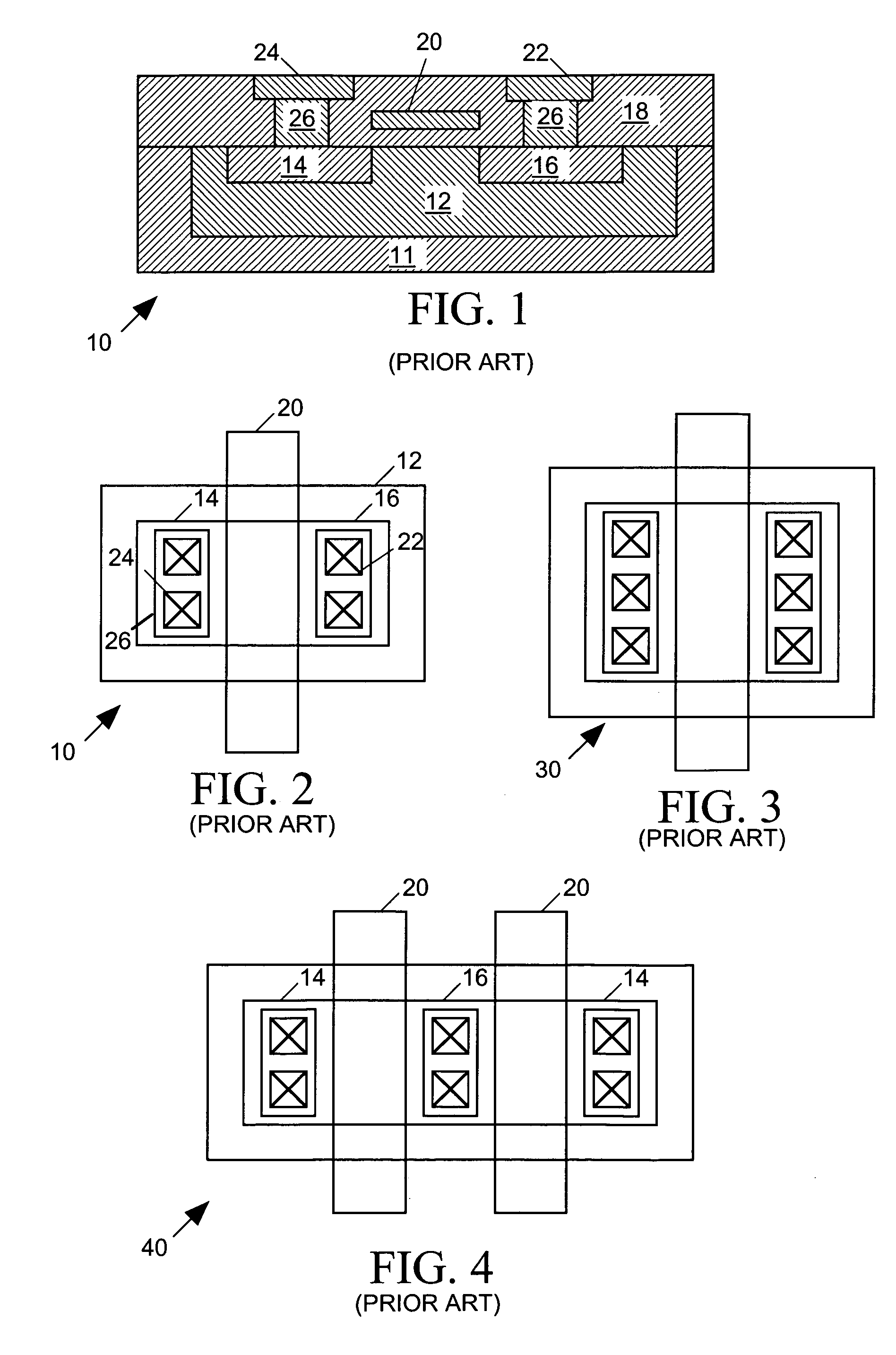
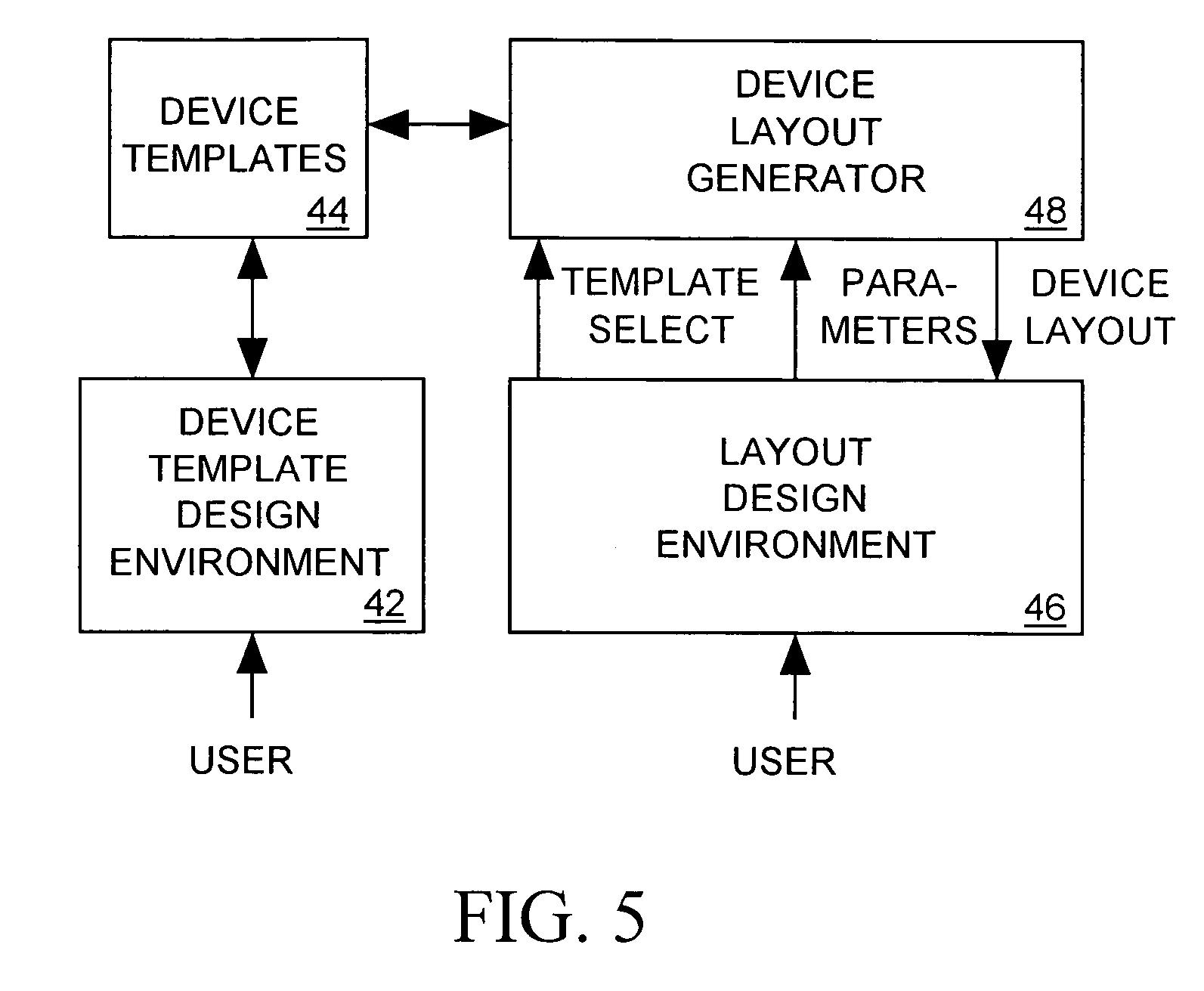
Scripted, hierarchical template-based IC physical layout system
InactiveUS7178114B2Quickly and easily to commandQuickly and easily generateComputer programmed simultaneously with data introductionCAD circuit designComputer Aided DesignTemplate based
A computer-aided design tool for automatically generating a layout for an electronic device to be formed by a set of objects implemented within an integrated circuit, receives input from a user defining a device template specifying shapes, dimensions and relative positions within the layout of the objects forming the device. Some of the object dimensions and / or relative positions are specified as functions of values of input parameters to be supplied by the user. When the user supplies the input parameters, the CAD tool evaluates the functions to determine the object dimensions and / or positions that are functions of the input parameters and then generates a layout for the electronic device wherein object shapes, dimensions and relative positions are as specified in the device template and consistent with the function evaluations. The device template may also include instructions for modifying the layout, for example, indicating that copies of an object are to form an array in the layout, that copies of one object are to fill another object, that an object is to be added to the layout having a shape that is a Boolean function of other objects, and that objects are to be added to or removed from the layout.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
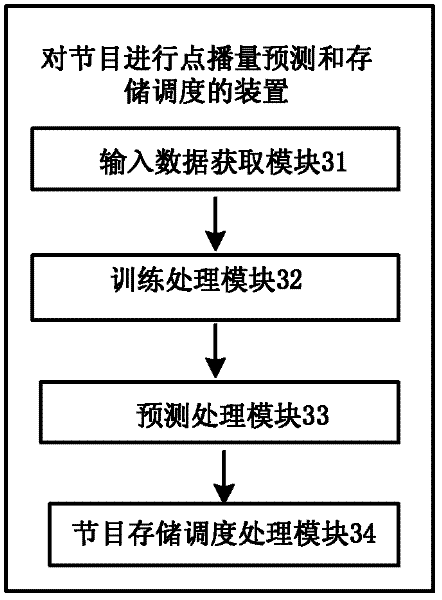
Method for performing on-demand play quantity prediction and memory scheduling on programs
InactiveCN102510529AImprove accuracyImprove forecasting efficiencyBiological neural network modelsSelective content distributionBoolean functionMachine learning
The embodiment of the invention provides a method for performing on-demand play quantity prediction and memory scheduling on programs, which comprises the following steps: acquiring input data of a neural network according to on-demand play quantities of every program in a number of days preset before specific days; training the previously established neural network according to the input data and the on-demand play quantities of every program within the specific days; and acquiring the input data of the trained neural network according to the on-demand play quantities of every program within the number of days preset before the current day, inputting the input data into the trained neural network, and using the computed output data of the trained neural network as the predicted on-demand play quantities of every program within the current day. According to the embodiment of the invention, the on-demand play quantities of the program is predicted by using the neural network, thereby acquiring the heat of every program; and the three-layer neural network approaches to the characteristics of any Boolean function, thereby enhancing the prediction accuracy and prediction efficiency of hot programs.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
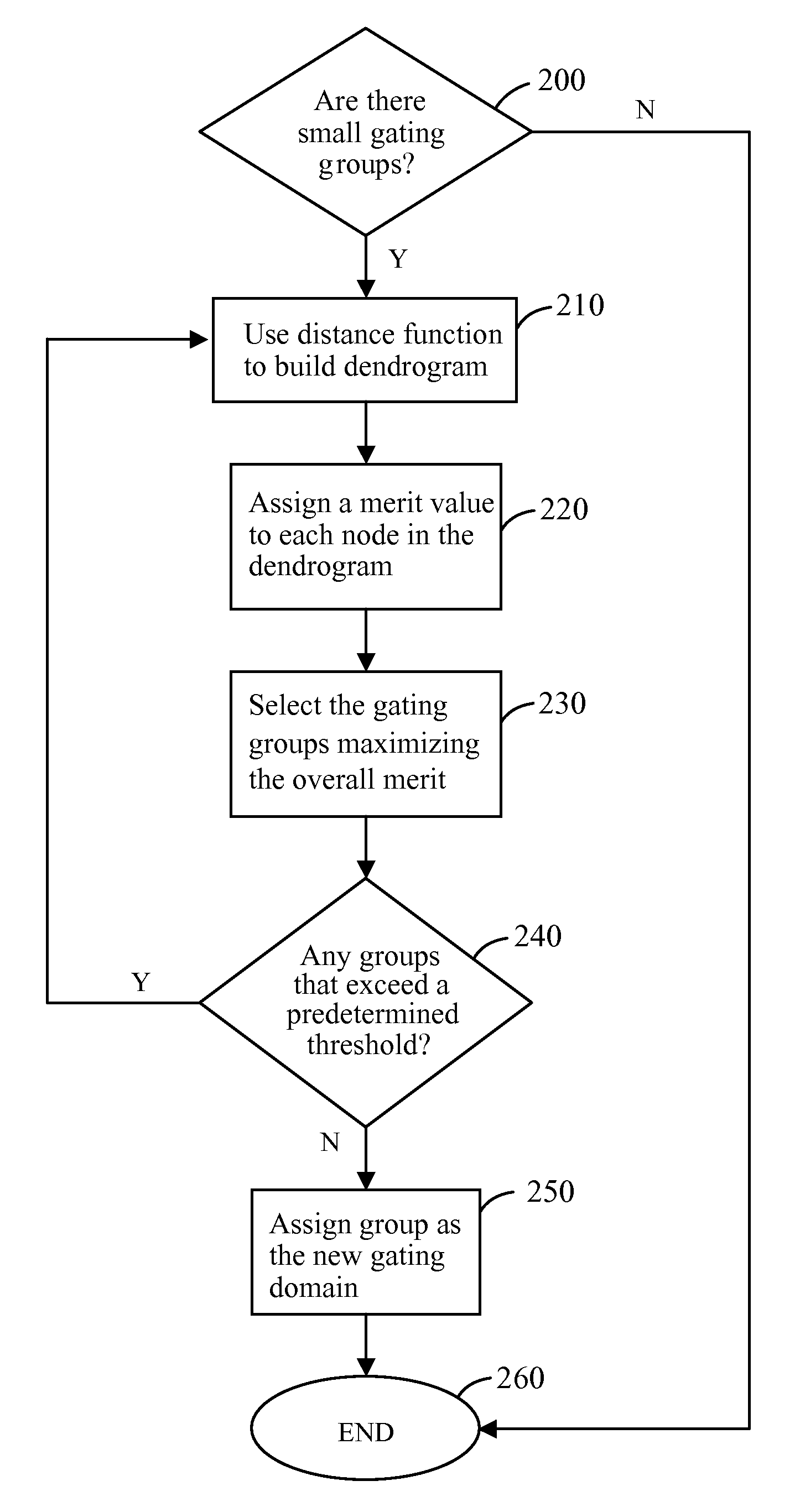
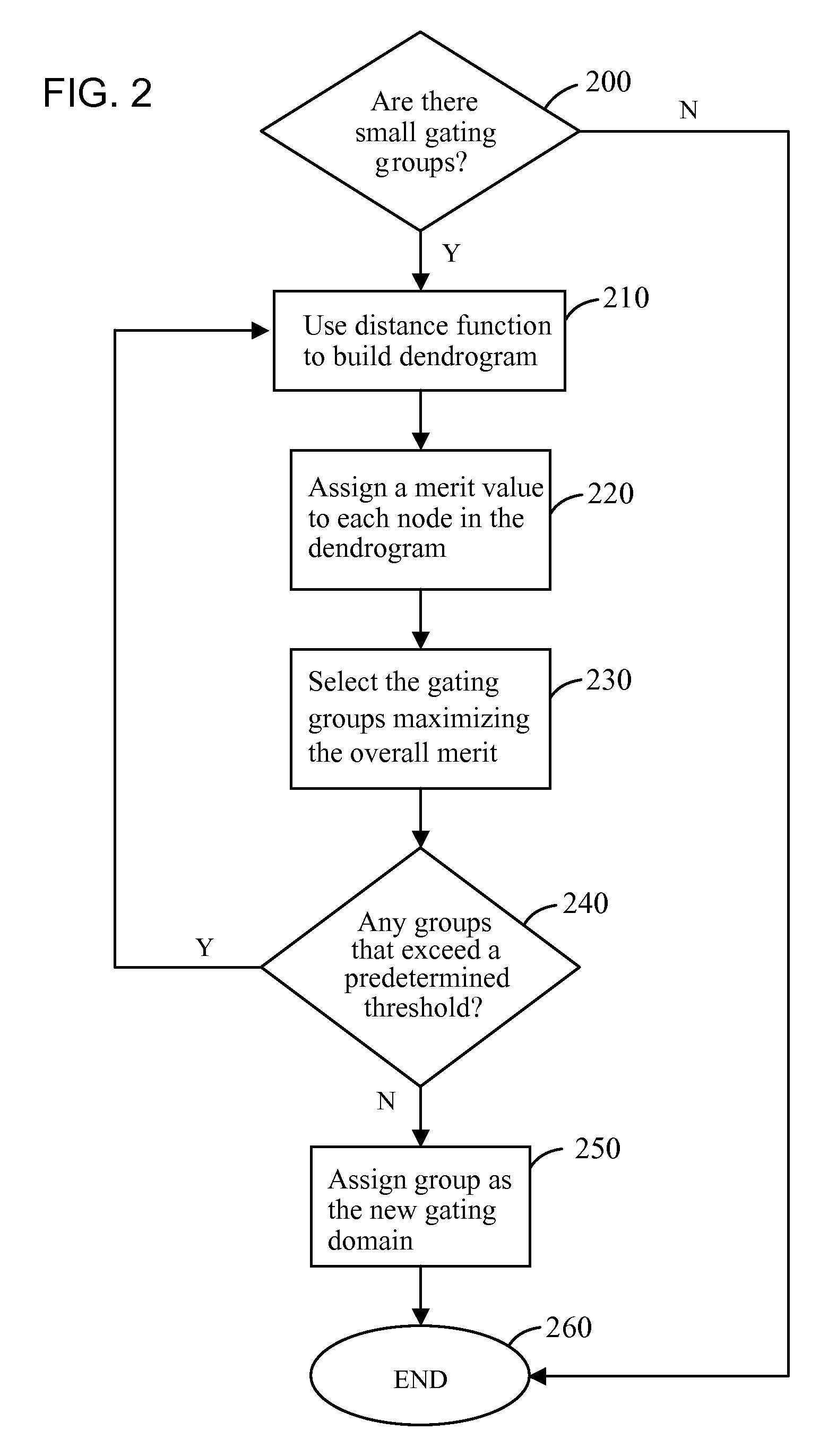
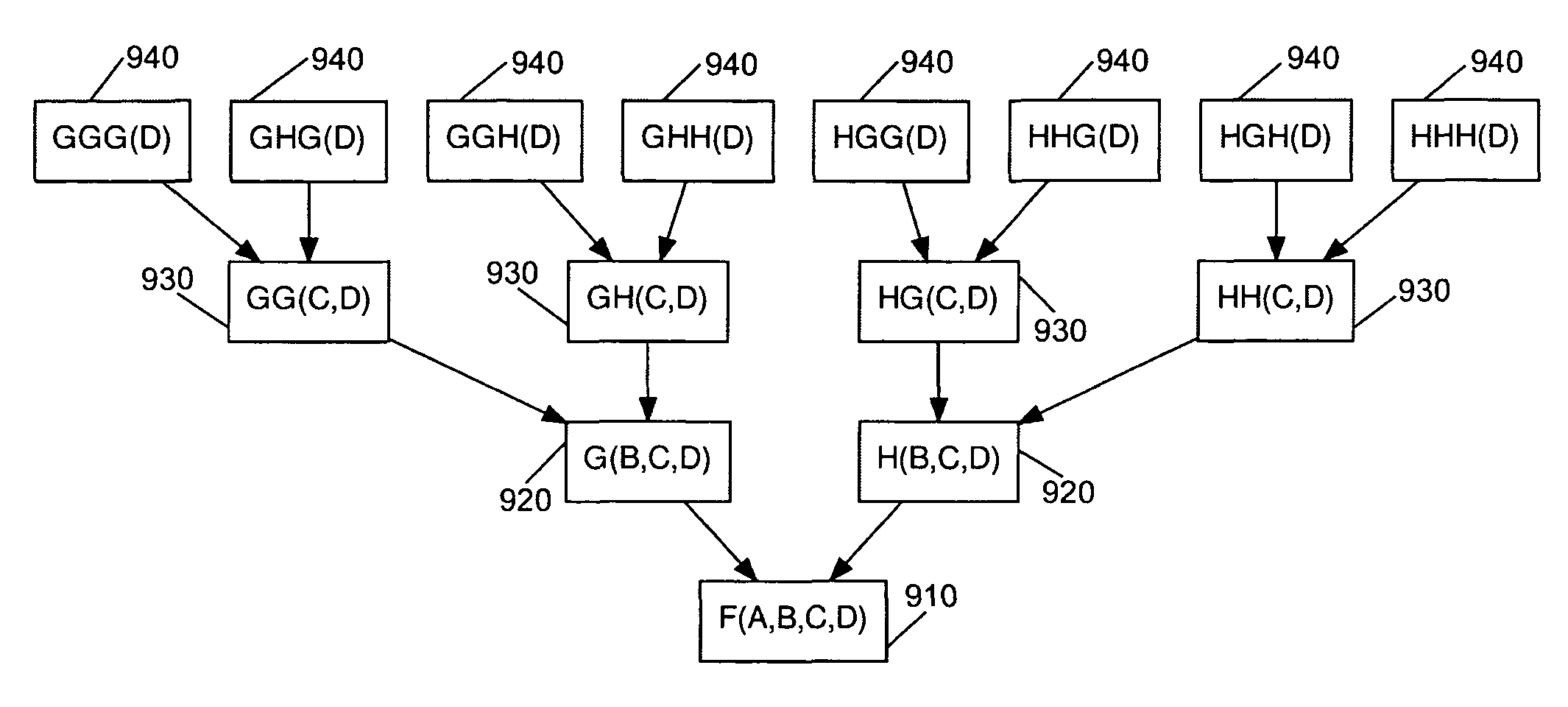
Device to cluster Boolean functions for clock gating
InactiveUS7562325B1Maximizes power savingPower maximizationCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsClock treeData mining
A system for clustering Boolean functions for clock gating according to various exemplary embodiments can include a computer configured to identify at least two small gating groups within a clock tree representative of an electrical network and at least two gating functions of the at least two small gating groups, wherein the at least two gating functions are Boolean functions; perform hierarchical clustering on the at least two gating functions using a similarity measure that describes a distance between the at least two gating functions such that the clustering forms a merge function of a cluster generated and displayed in a form of a dendrogram; assign to each gating domain a merit value according to a power consumption profile of the gating domain using a merit function; and partition the cluster into gating groups using the dendrogram to construct a directed acyclic graph to determine a partition which maximize the overall power saving.
Owner:IBM CORP
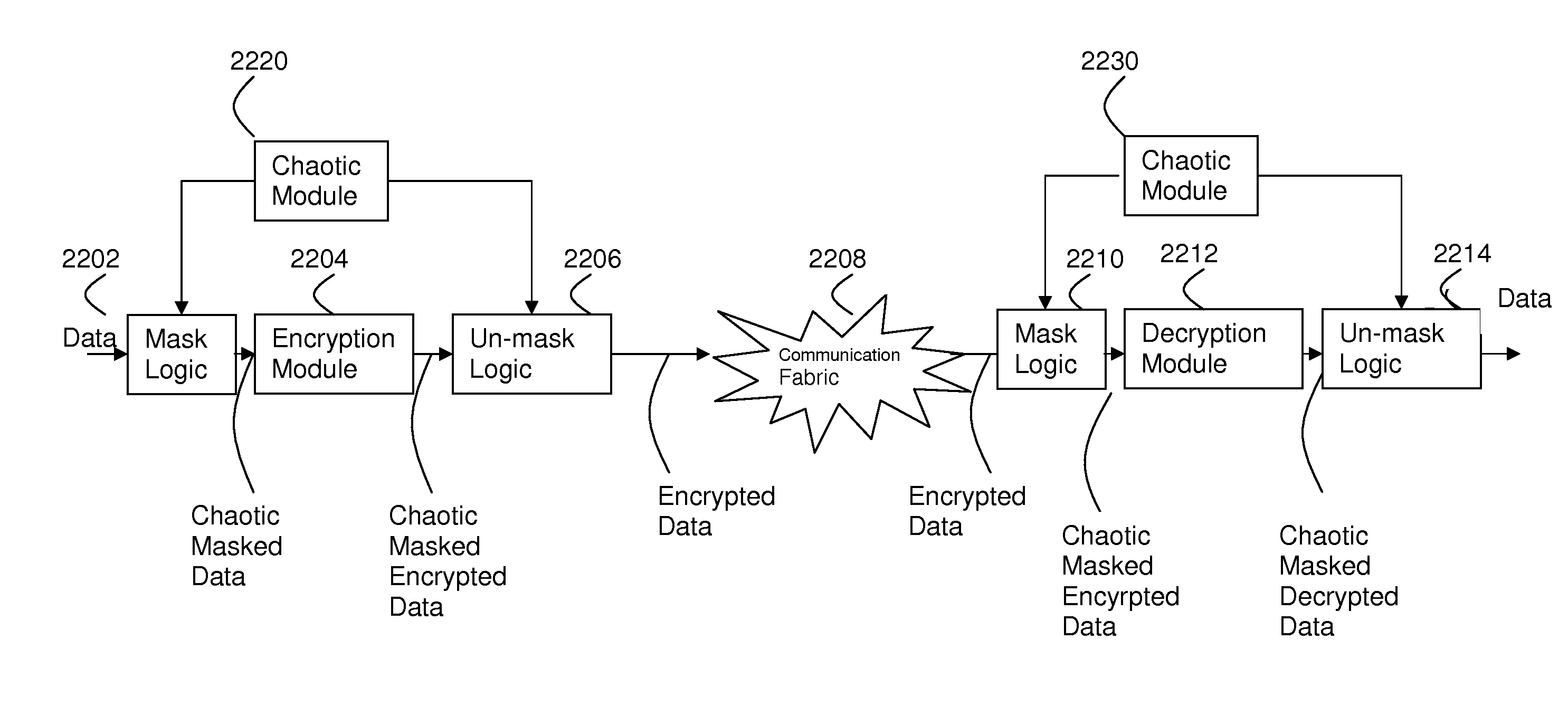
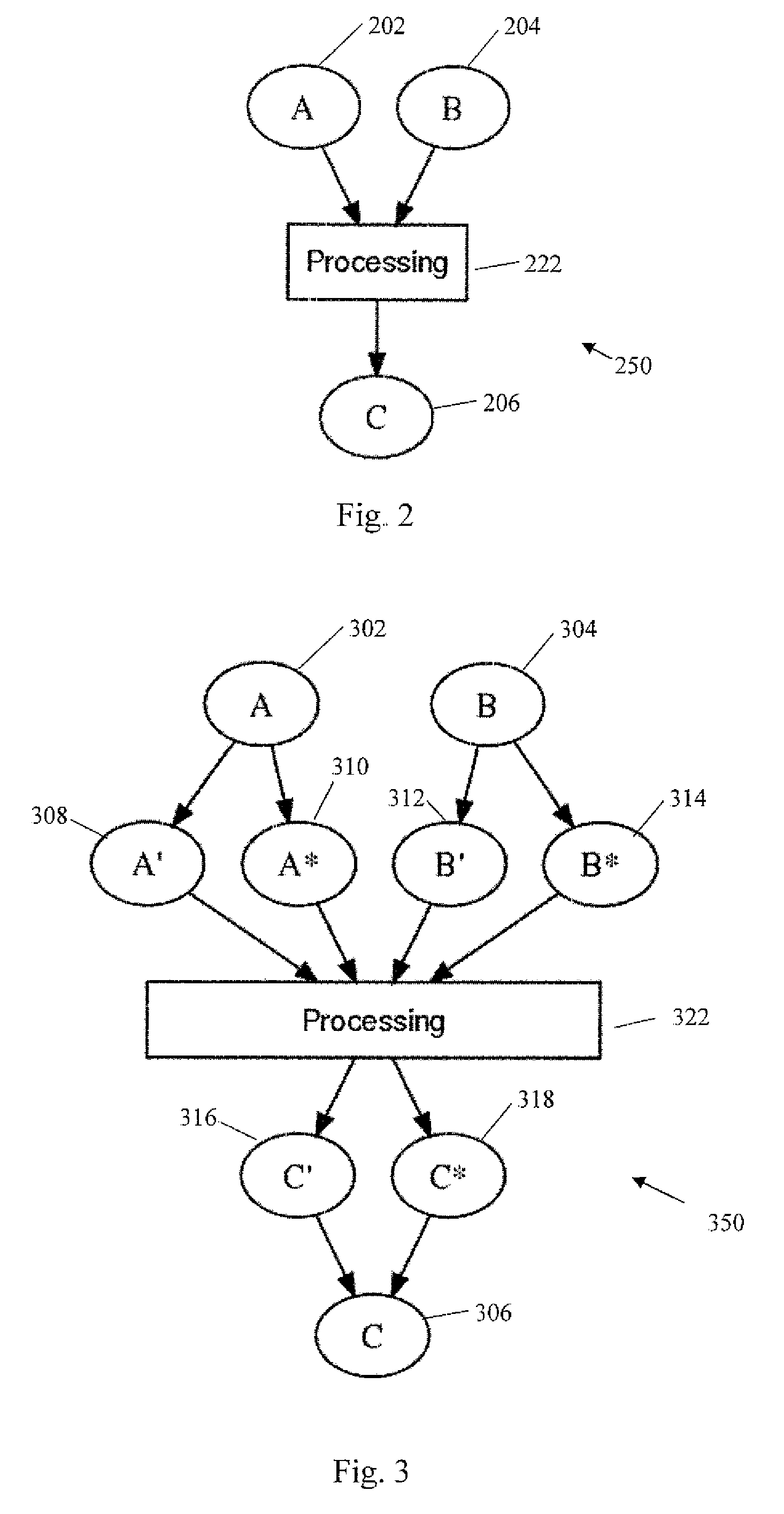
System and method for masking arbitrary Boolean functions
ActiveUS8091139B2Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionBoolean functionSide channel attack
A method is disclosed for protecting secret data, which is intended to be processed by an original function, from being deduced by a side-channel attack upon execution of the original function by an electronic computing device. The method includes creating hardware circuitry which replaces the original function with one or more pairs of replacement functions, by applying a predetermined masking algorithm which performs a recursive protection process. Further disclosed is an apparatus for protecting secret data, which is intended to be processed by an original function, from being deduced by a side-channel attack upon execution of the original function by an electronic computing device.
Owner:ARM LTD
Locking relationships among parameters in computer programs
ActiveUS7873917B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsComputation using non-denominational number representationTheoretical computer scienceLookup table
Owner:APPLE INC
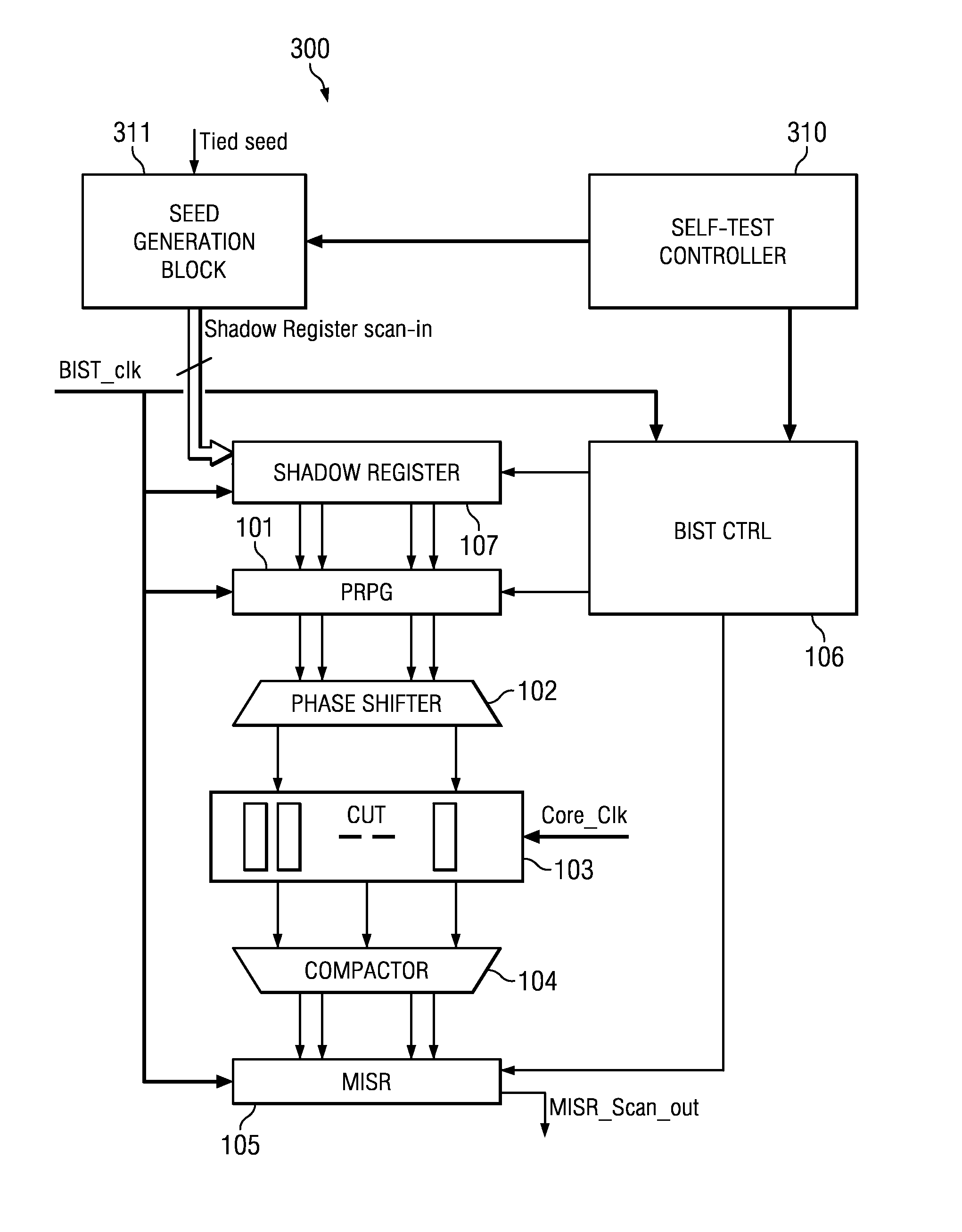
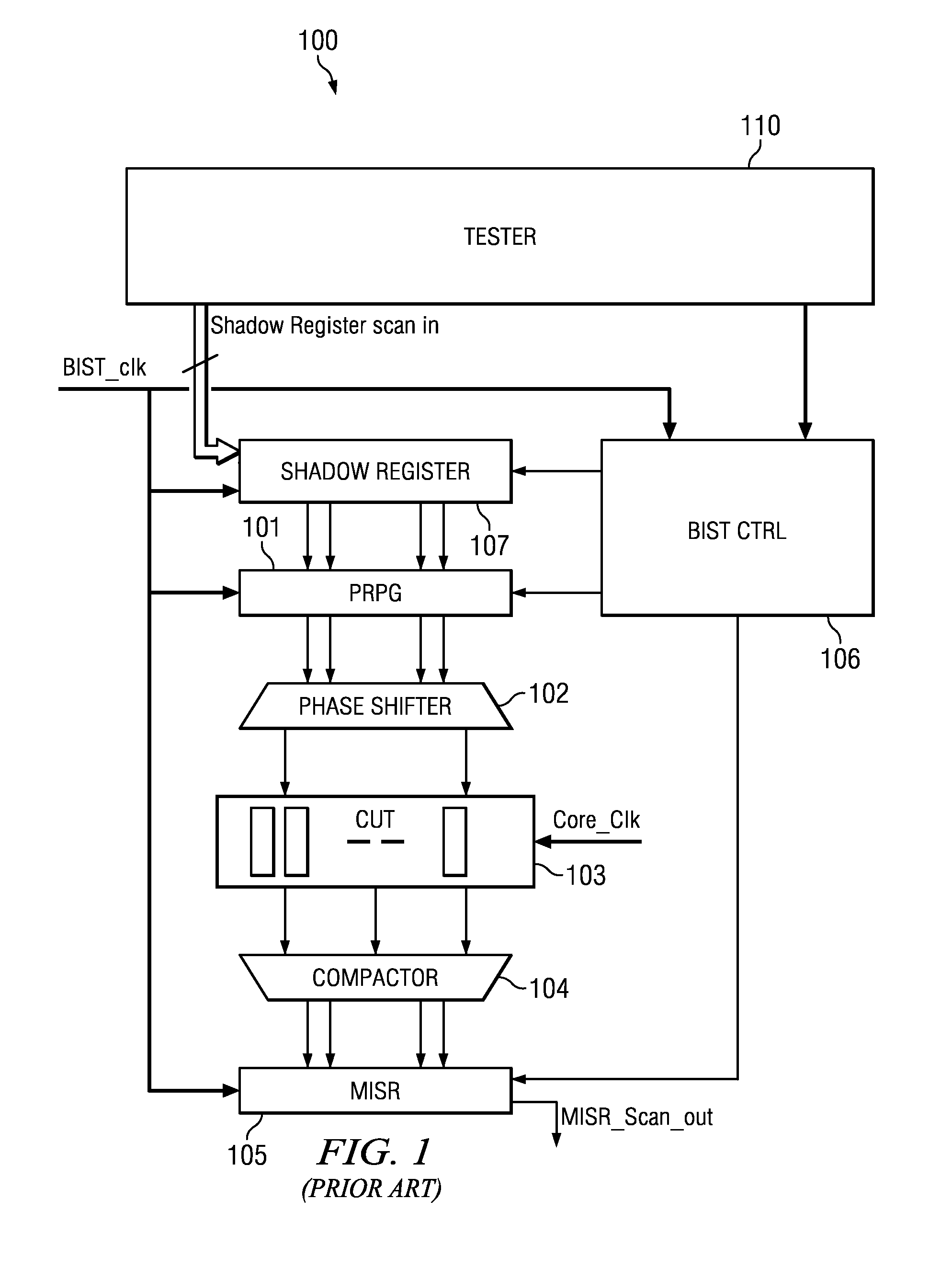
On-chip seed generation using boolean functions for LFSR re-seeding based logic BIST techniques for low cost field testability
ActiveUS8286042B2Reduce area requirementsFunction increaseElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionRandom seedFinite-state machine
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method for foresting demand of wind generating set for spare parts based on fault tree analysis
The invention discloses a method for forecasting the demand of a wind generating set for spare parts based on fault tree analysis. The method comprises the steps of firstly building an abstract model of a wind generating set fault tree; then acquiring the daily annual fault probability of components corresponding to each bottom event in the fault tree; building a fault tree simulation model by using a Simulink platform, and simplifying a Boolean function expression of a top event; solving a minimum cutest of the fault tree; compiling a numerical operation sub-function for calculating the probability importance degree and key importance indexes of each bottom event; inputting the daily annual fault probability of each bottom event by a user, and calling the sub-function to output the probability importance degree and key importance indexes; and calculating the number of spare parts of each component in a future stage. The method disclosed by the invention is based on the wind generating set fault tree, adjustable in model parameter, capable of adapting to product differentiation of different manufacturers and different working conditions, fault reasons of the wind generating set are detailed, the utilization efficiency of the spare parts is improved, the inventory cost is reduced, and so that the objective of reducing the operation and maintenance cost of wind power generation enterprises is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and system for smart card chip personalization
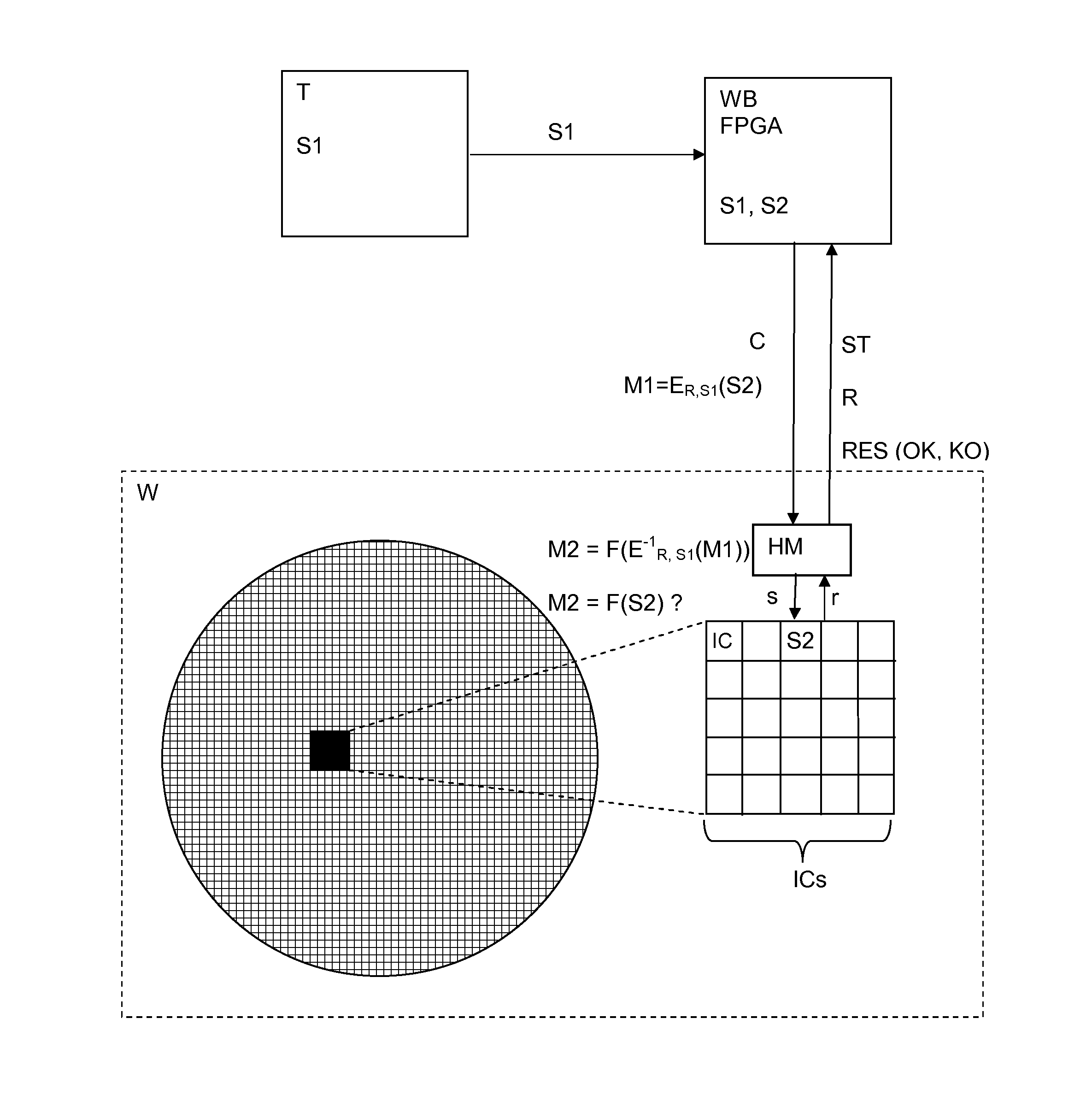
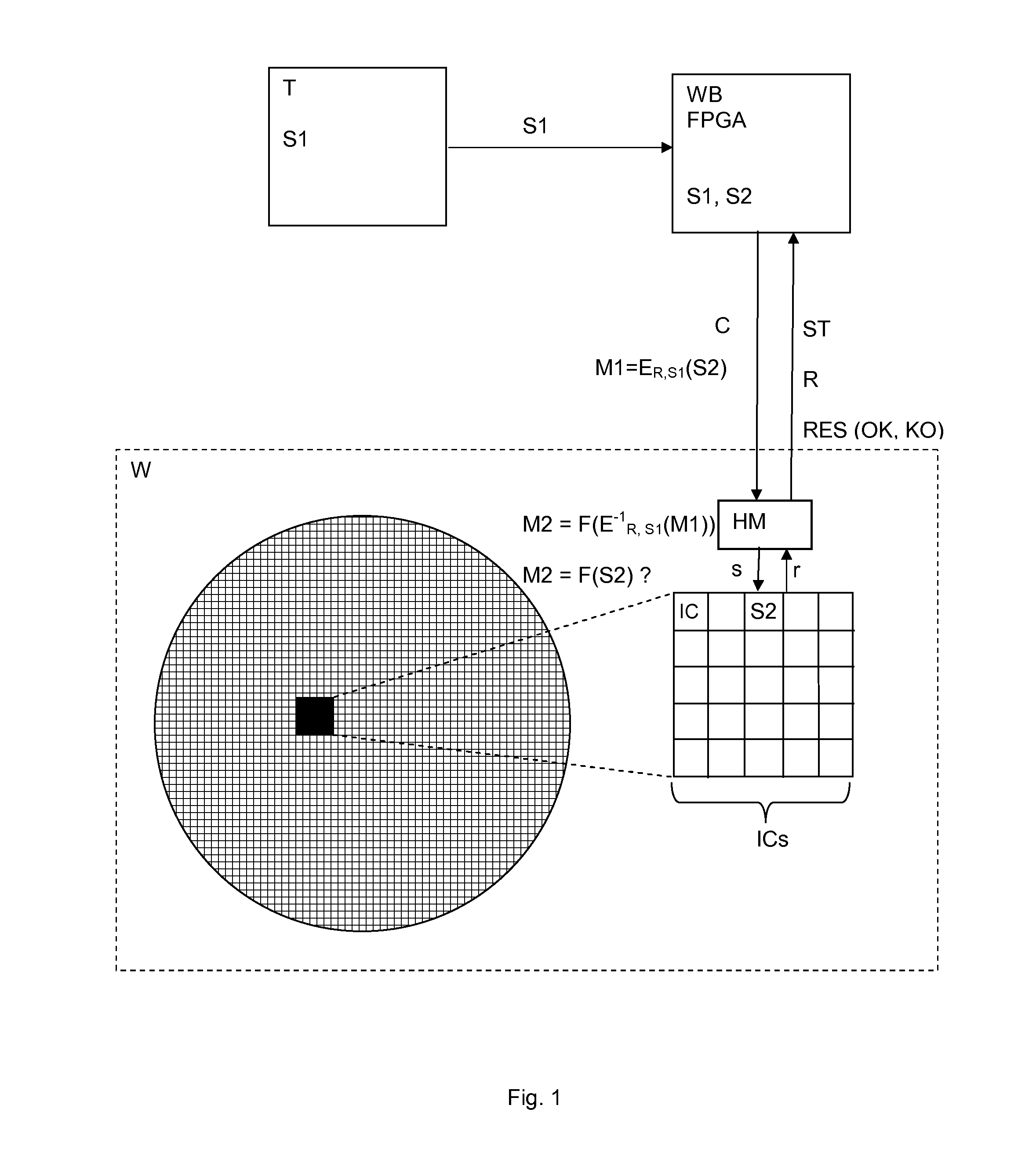
InactiveUS20150270962A1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usagePersonalizationTester device
Method and system for personalizing a chip, intended to be integrated into a smart card, comprising a tester associated to an FPGA device connected to the chip, the chip being part of a wafer comprising a plurality of chips and a disposable hardware module for verifying presence of the chip on the wafer. The tester sends a first secret code to the FPGA device, which commands the chip to initiate a test mode activation. The FPGA device encrypts a second secret code by using a secret encryption algorithm parameterized with a random number received from the chip and the first secret code to obtain a first cryptogram which is sent to the chip. The chip determines a second cryptogram by carrying out a Boolean function over a result obtained by decryption of the first cryptogram using the inverse algorithm parameterized with the random number and the first secret code. The second cryptogram is compared with a result obtained by carrying out the Boolean function over the second secret code temporarily stored on the chip. The FPGA device personalizes the chip only if the second cryptogram matches the calculated result.
Owner:NAGRAVISION SA
Semiconductor integrated circuit and methods for protecting the circuit from reverse engineering
A semiconductor integrated circuit having a reverse engineering protection part that can be easily implemented without additional circuitry or process using a method for protecting against reverse engineering of the semiconductor integrated circuit. The semiconductor integrated circuit includes a logic gate and a reverse engineering protection part. The reverse engineering protection part alters the apparent Boolean functions of a logic gate. Further, the reverse engineering protection part includes at least one PMOS transistor and at least one NMOS transistor. The PMOS and NMOS transistors are constructed to remain in a state of constant on or off irrespective of an input signal applied to their gates. The PMOS transistors and the NMOS transistors are included in transistors forming the logic gate. The PMOS transistors and the NMOS transistors that remain in a state of constant on or off are formed by implanting ions into their gate channels or blocking ion implantation into their gate channels during manufacturing.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com