Patents
Literature
813 results about "Content-addressable storage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
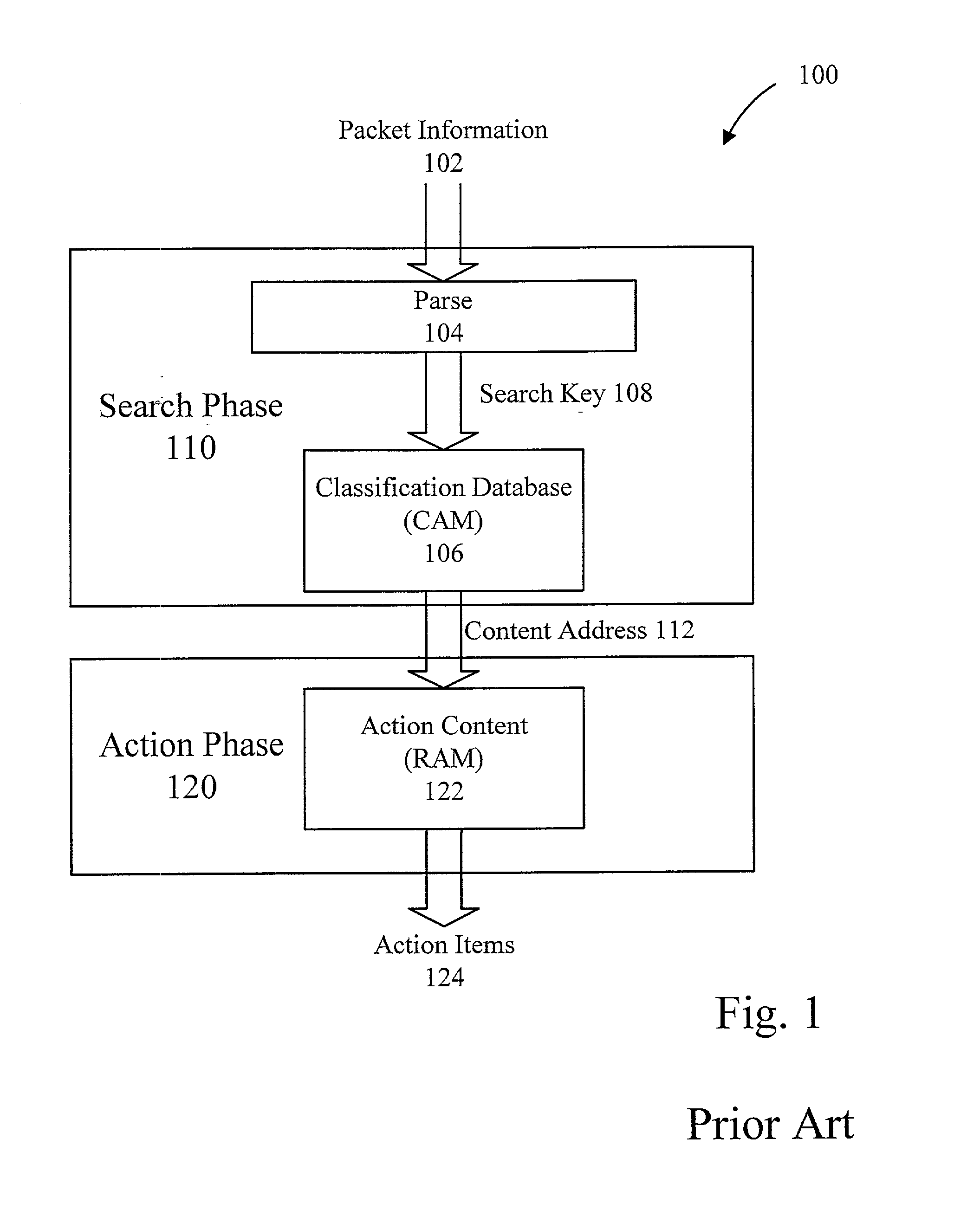
Content-addressable storage, also referred to as content-addressed storage or abbreviated CAS, is a way to store information so it can be retrieved based on its content, not its location. It has been used for high-speed storage and retrieval of fixed content, such as documents stored for compliance with government regulations. Content-addressable storage is like content-addressable memory.
Using storage cells to perform computation
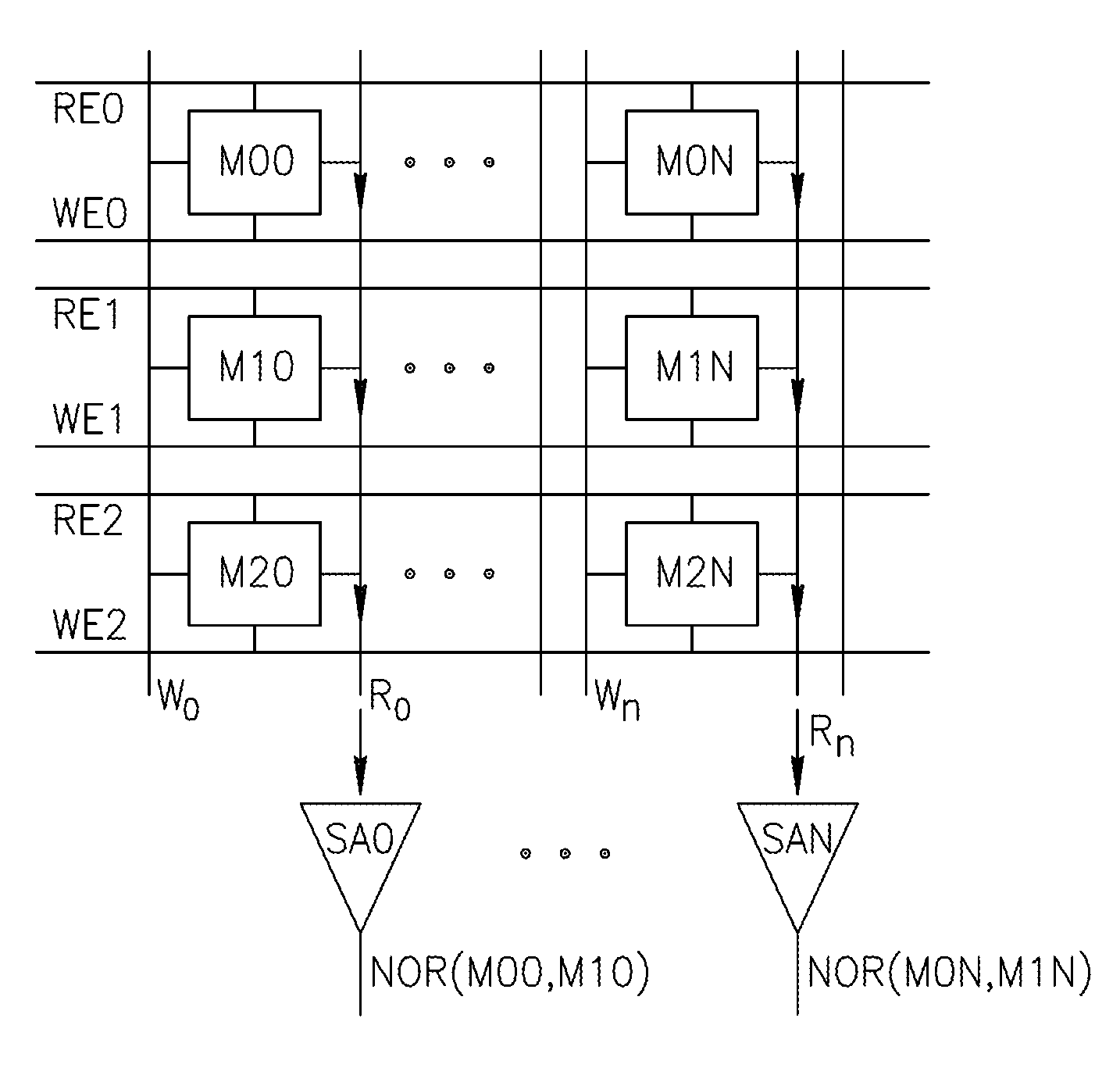
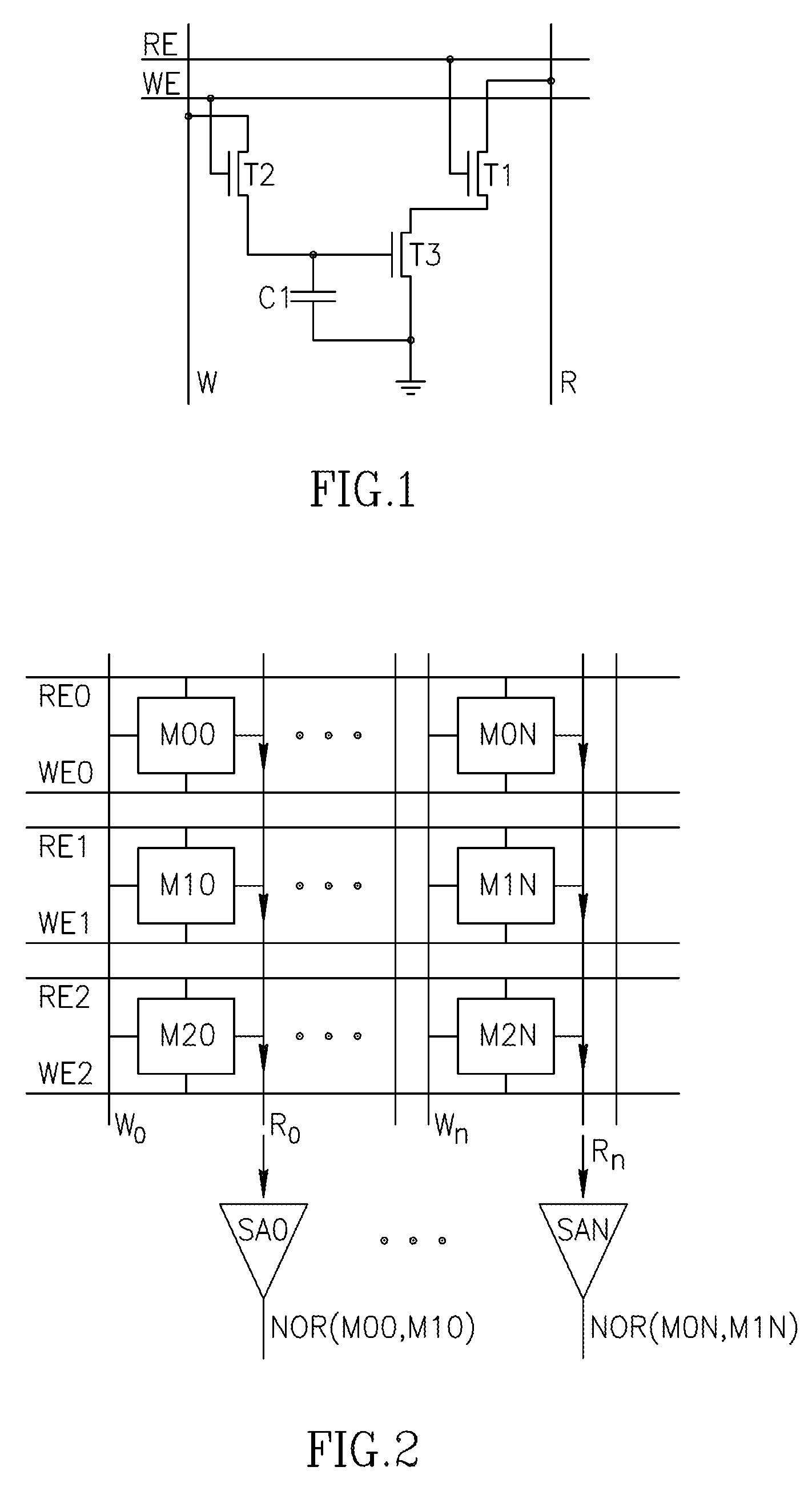
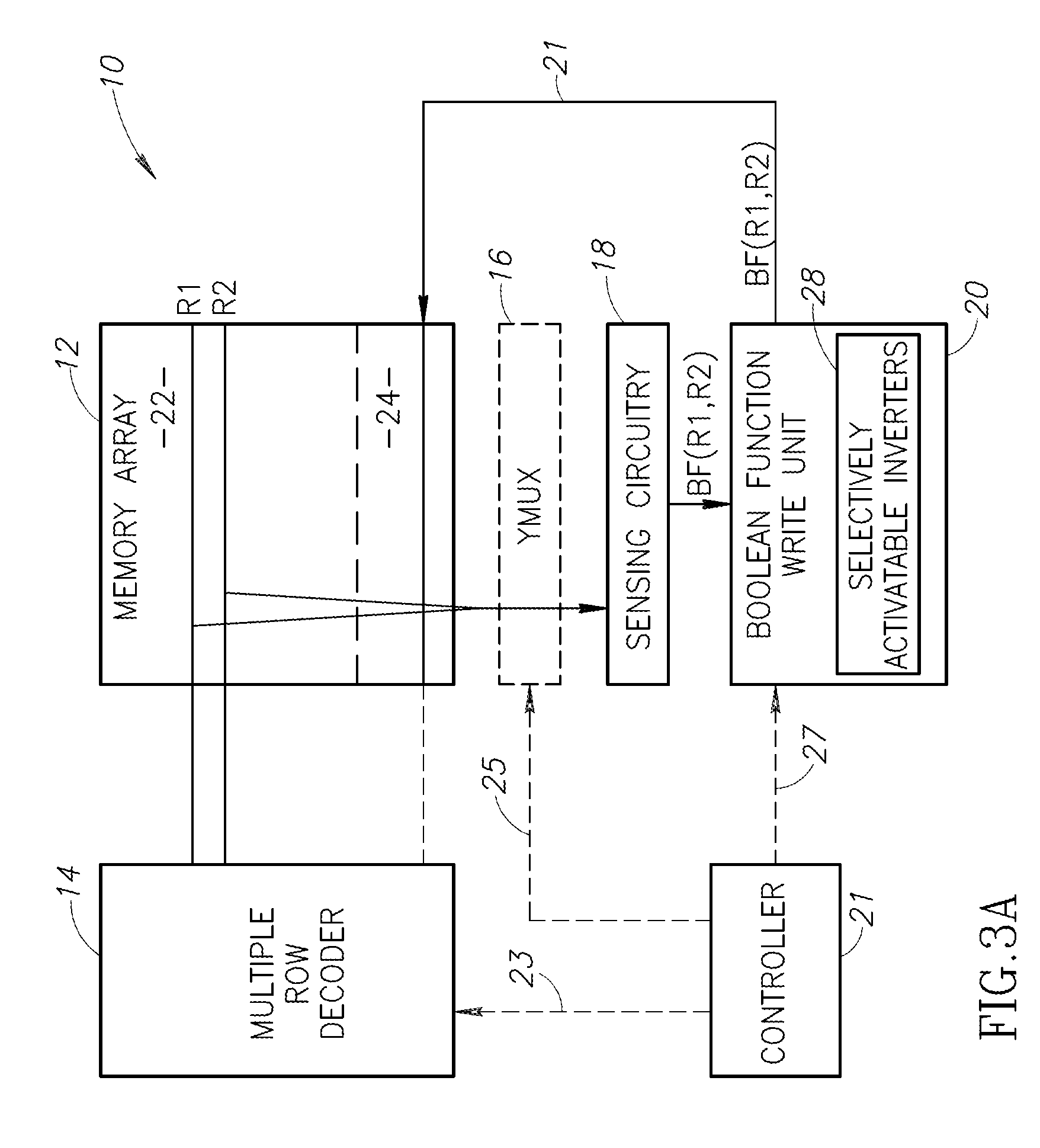
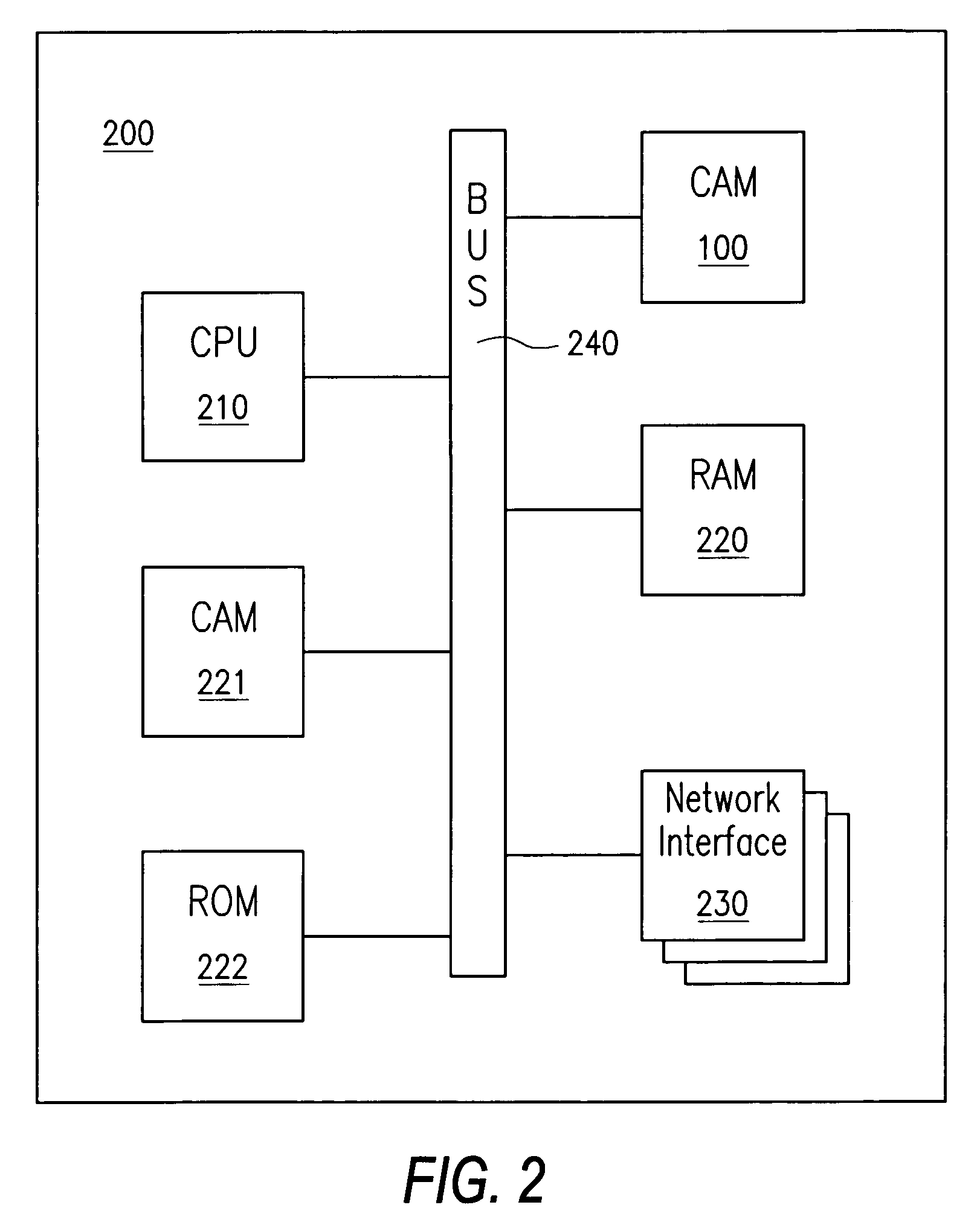
An in-memory processor includes a memory array which stores data and an activation unit to activate at least two cells in a column of the memory array at generally the same time thereby to generate a Boolean function output of the data of the at least two cells. Another embodiment shows a content addressable memory (CAM) unit without any in-cell comparator circuitry.
Owner:GSI TECH
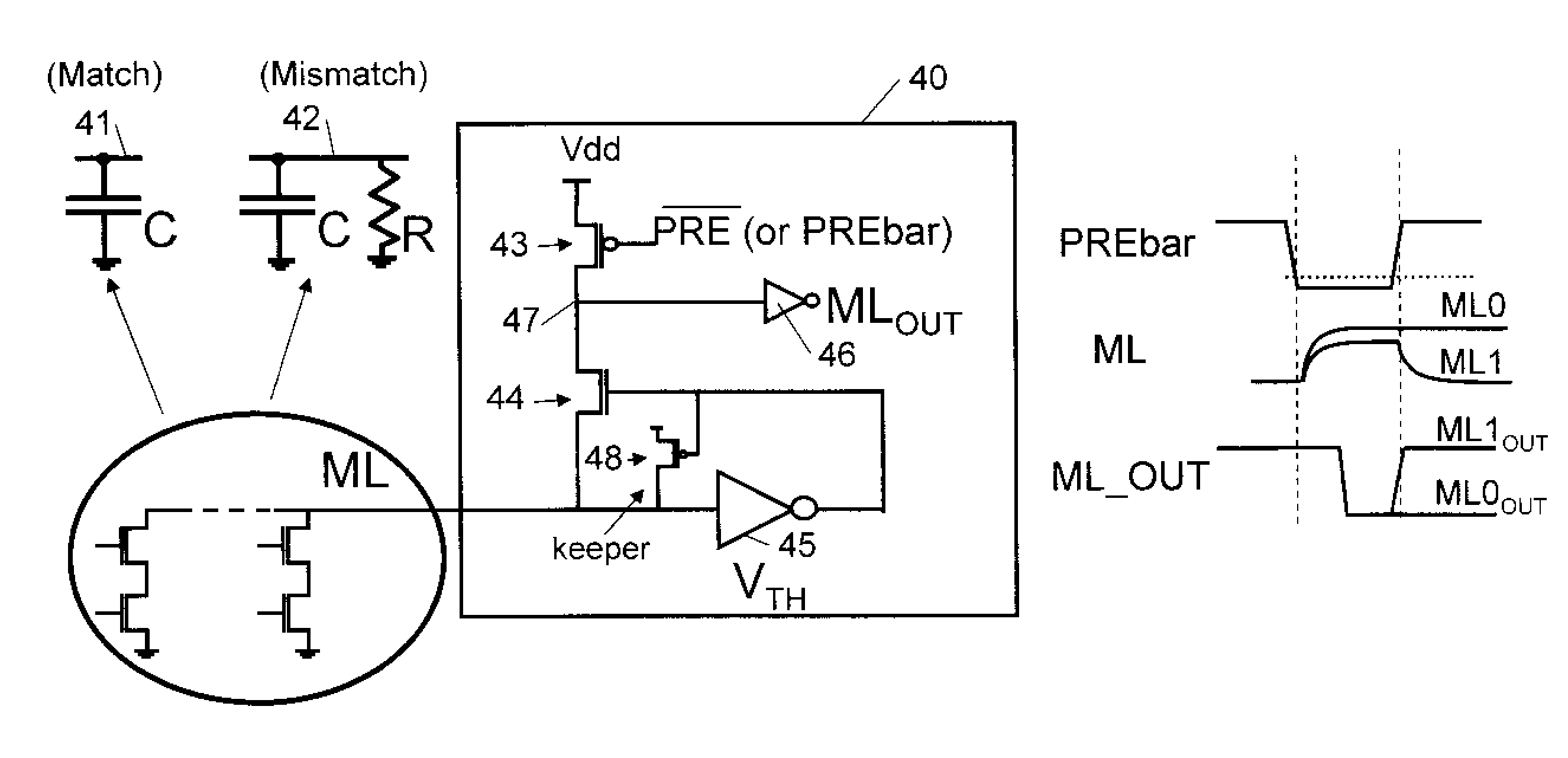
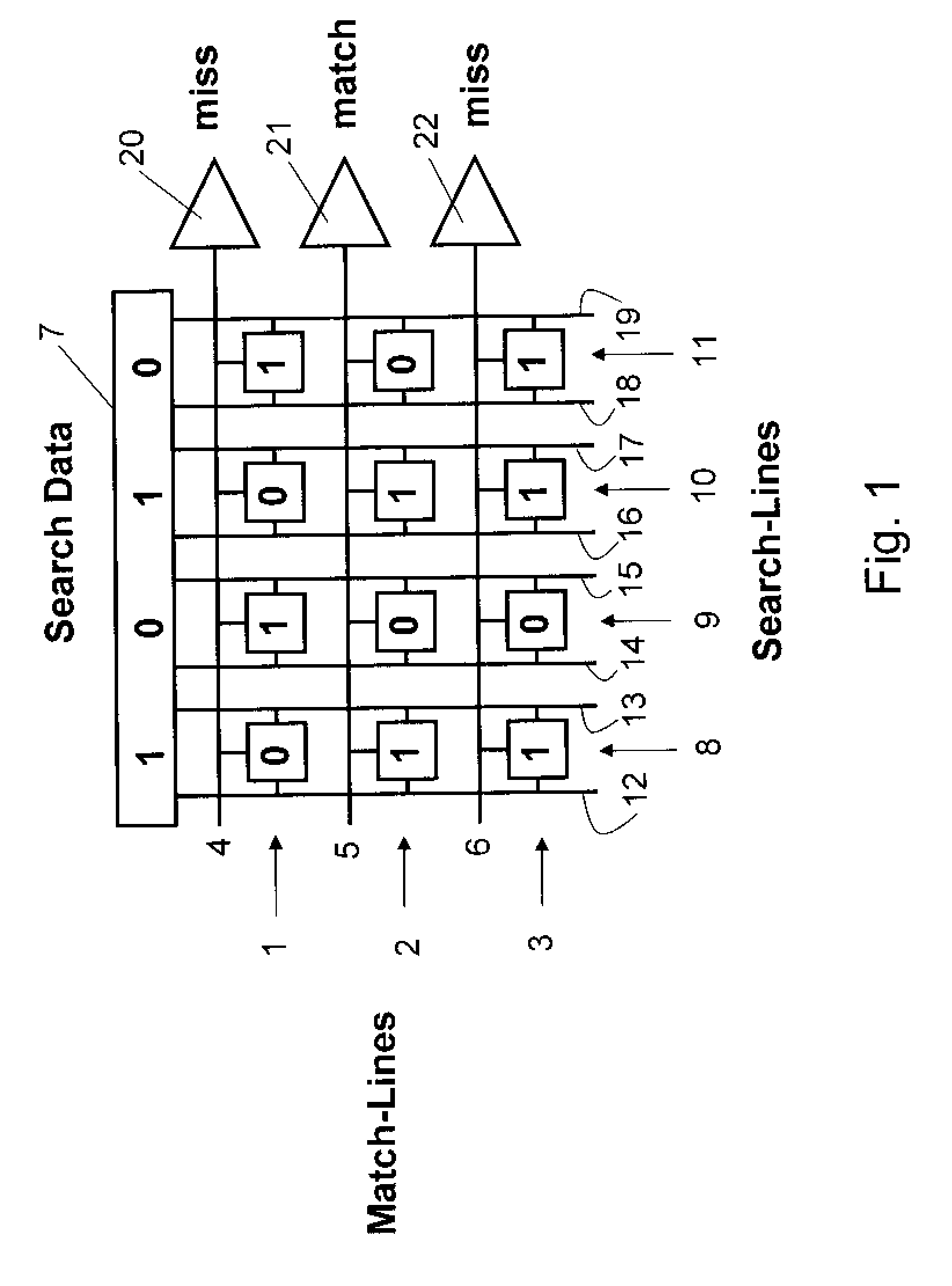
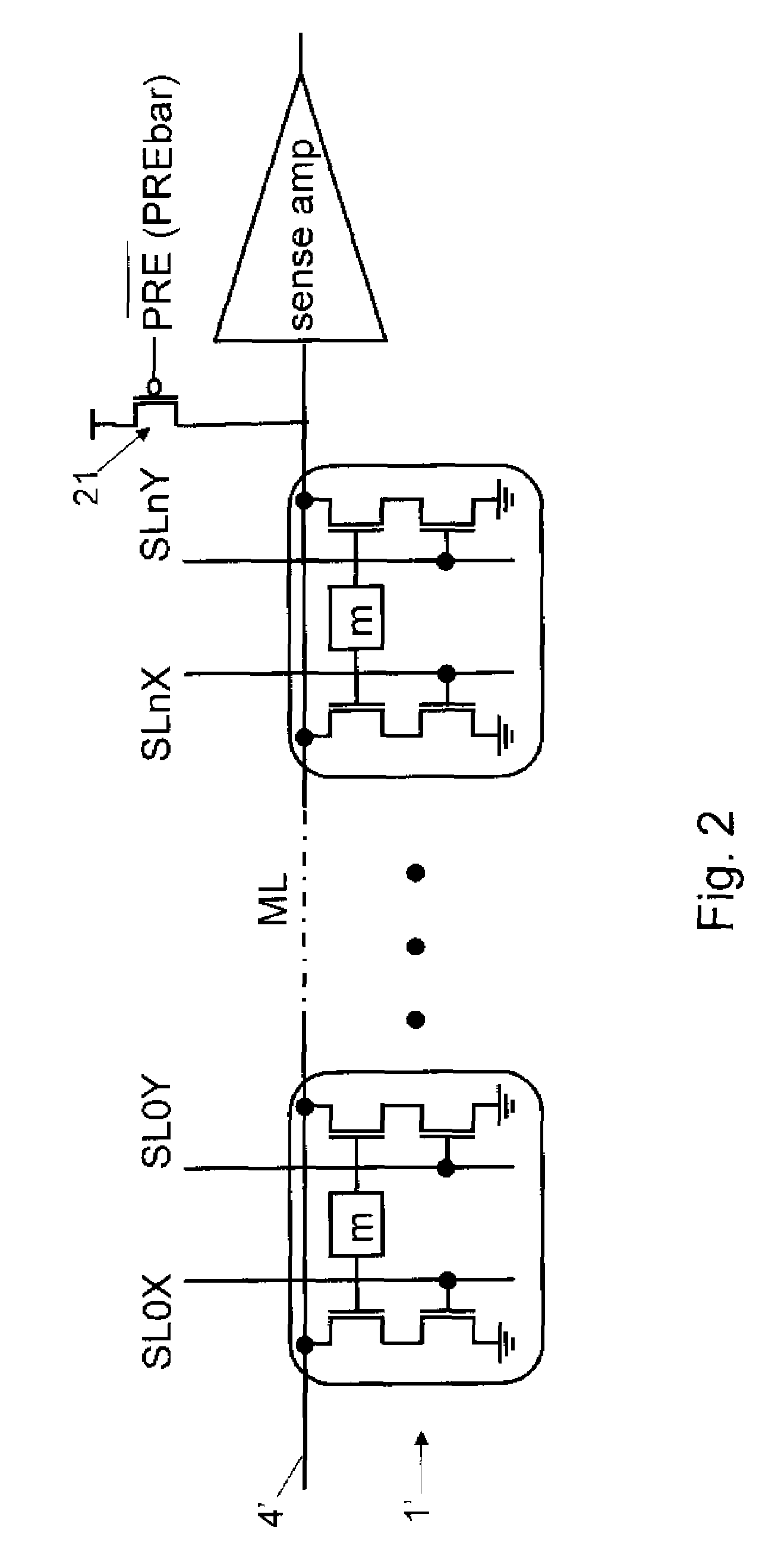
Self-Referenced Match-Line Sense Amplifier For Content Addressable Memories
ActiveUS20080025073A1Reduce the impactReduce impactCurrent/voltage measurementDigital storageAudio power amplifierComputer science
A content addressable memory (CAM) device and process for searching a CAM. The CAM device includes a plurality of CAM cells, match-lines (MLs), search lines, and ML sense amplifiers. The ML sense amplifiers are capable of self-calibration to their respective thresholds to reduce effects of random device variation between adjacent sense amplifiers.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
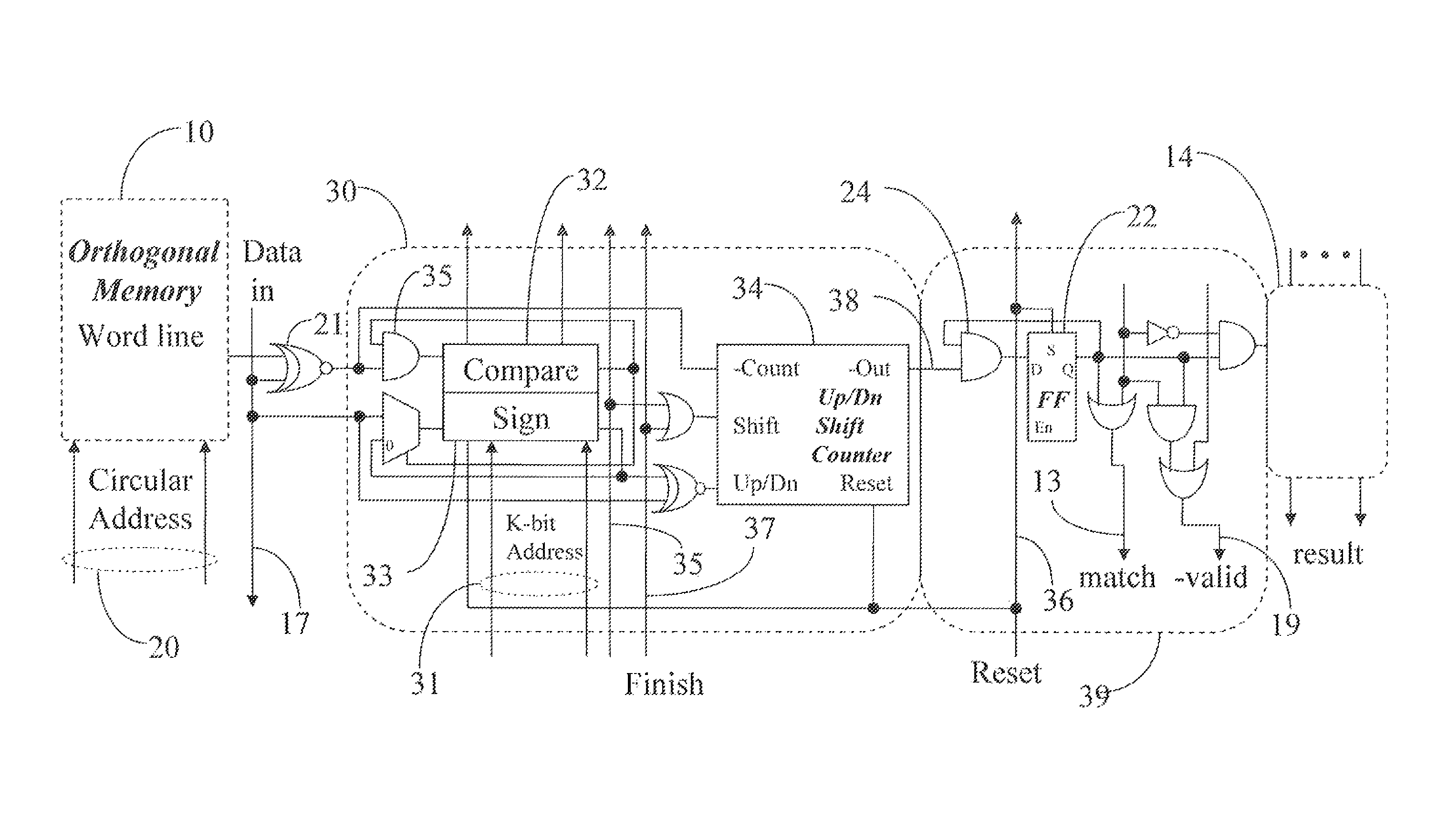
Nearest neighbor serial content addressable memory
A digital design and technique may be used to implement a Manhattan Nearest Neighbor content addressable memory function by augmenting a serial content addressable memory design with additional memory and counters for bit serially accumulating in parallel and subsequently comparing in parallel all the Manhattan distances between a serially inputted vector and all corresponding vectors resident in the CAM. Other distance measures, besides a Manhattan distance, may optionally be used in conjunction with similar techniques and designs.
Owner:COOKE LAURENCE H
System and method for performing regular expression matching with high parallelism
InactiveUS7225188B1Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsPattern matchingTheoretical computer science
A system and method for searching data strings, such as network messages, for one or more predefined regular expressions is provided. Regular expressions are programmed into a pattern matching engine so that multiple characters, e.g., 32, of the data strings can be searched at the same time. The pattern matching engine includes a regular expression storage device having one or more content-addressable memories (CAMs) whose rows may be divided into sections. Each predefined regular expression is analyzed so as to identify the “borders” within the regular expression. A border is preferably defined to exist at each occurrence of one or more predefined metacharacters, such as “.*”, which finds any character zero, one or more times. The borders separate the regular expression into a sequence of sub-expressions each of which may be one or more characters in length. Each sub-expression is preferably programmed into a corresponding section of the pattern matching engine. The system may also be configured so as to search multiple regular expressions in parallel.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
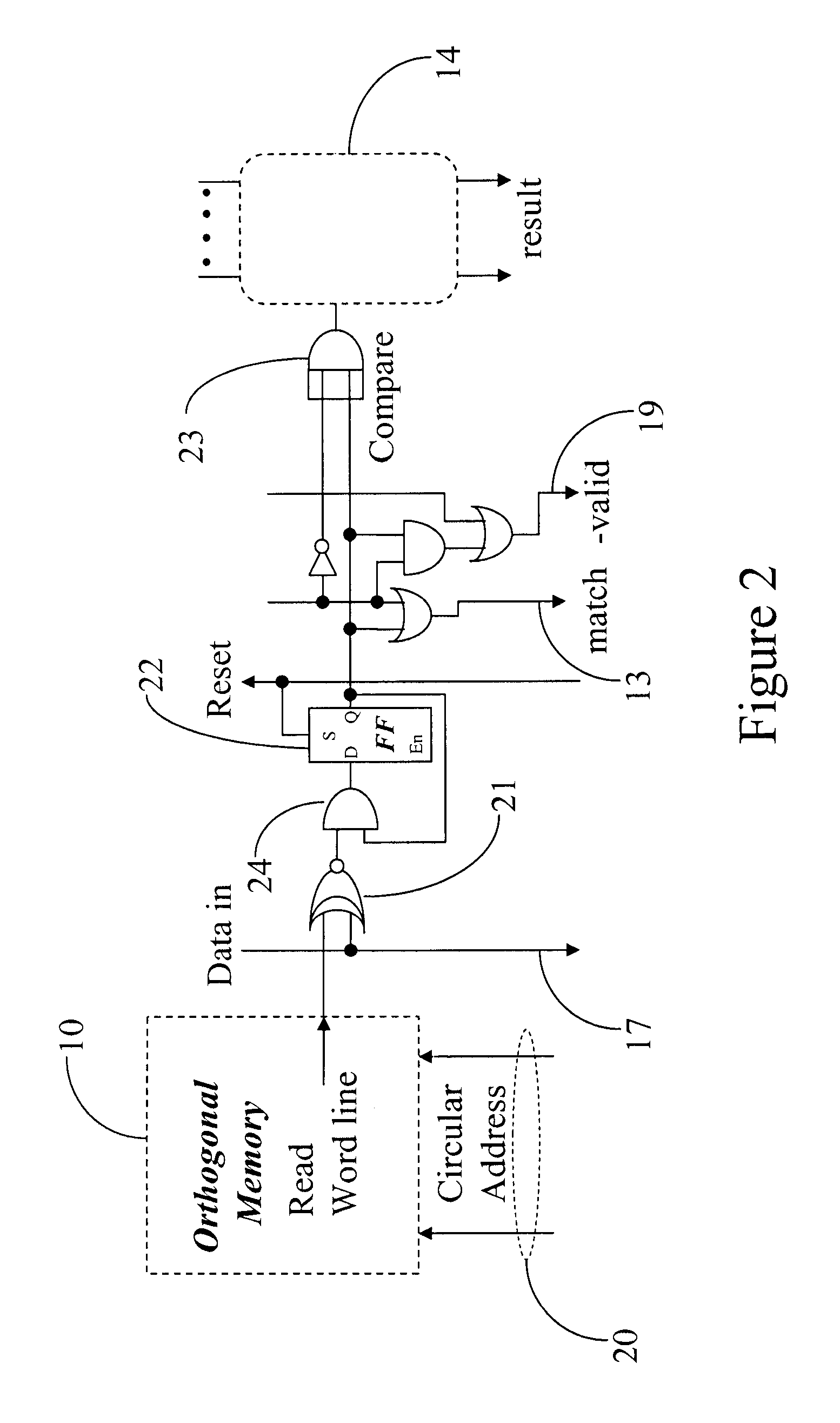
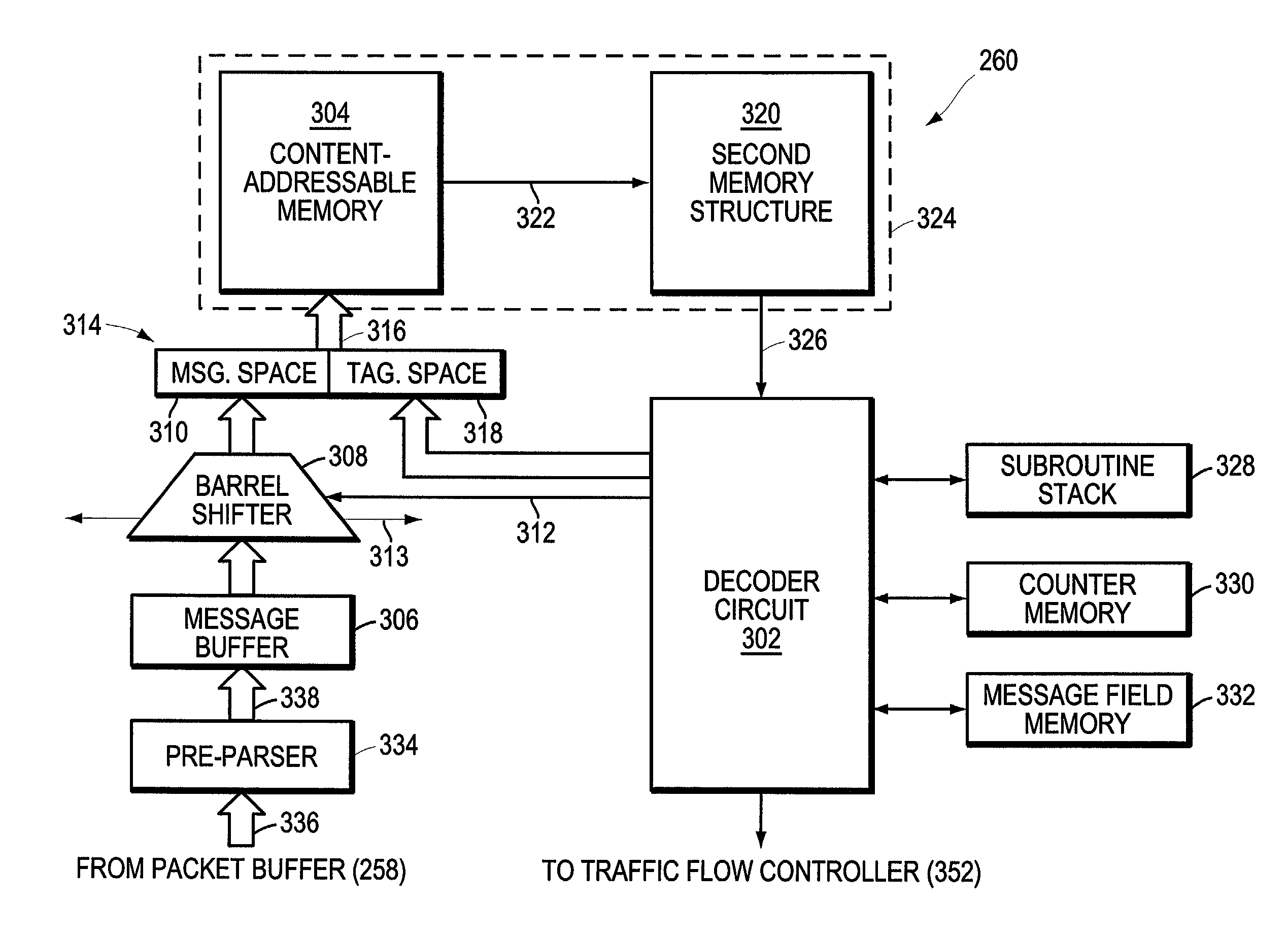
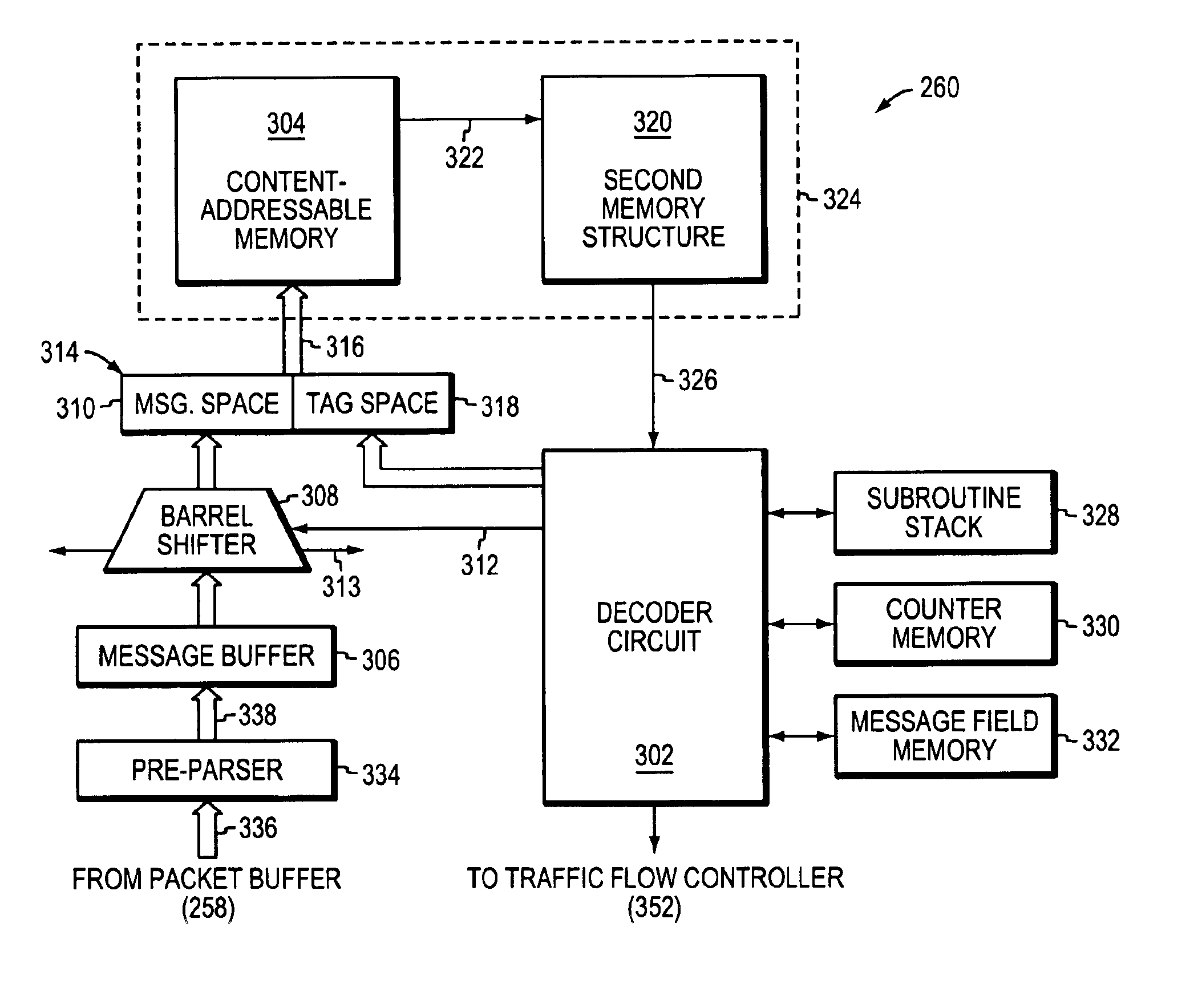
Method and apparatus for high-speed parsing of network messages
InactiveUS6892237B1Efficient analysisIncrease speedMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksPattern matchingRandom access memory
A programmable pattern matching engine efficiently parses the contents of network messages for regular expressions and executes pre-defined actions or treatments on those messages that match the regular expressions. The pattern matching engine is preferably a logic circuit designed to perform its pattern matching and execution functions at high speed, e.g., at multi-gigabit per second rates. It includes, among other things, a message buffer for storing the message being evaluated, a decoder circuit for decoding and executing corresponding actions or treatments, and one or more content-addressable memories (CAMs) that are programmed to store the regular expressions used to search the message. The CAM may be associated with a second memory device, such as a random access memory (RAM), as necessary, that is programmed to contain the respective actions or treatments to be applied to messages matching the corresponding CAM entries. The RAM provides its output to the decoder circuit, which, in response, decodes and executes the specified action or treatment.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
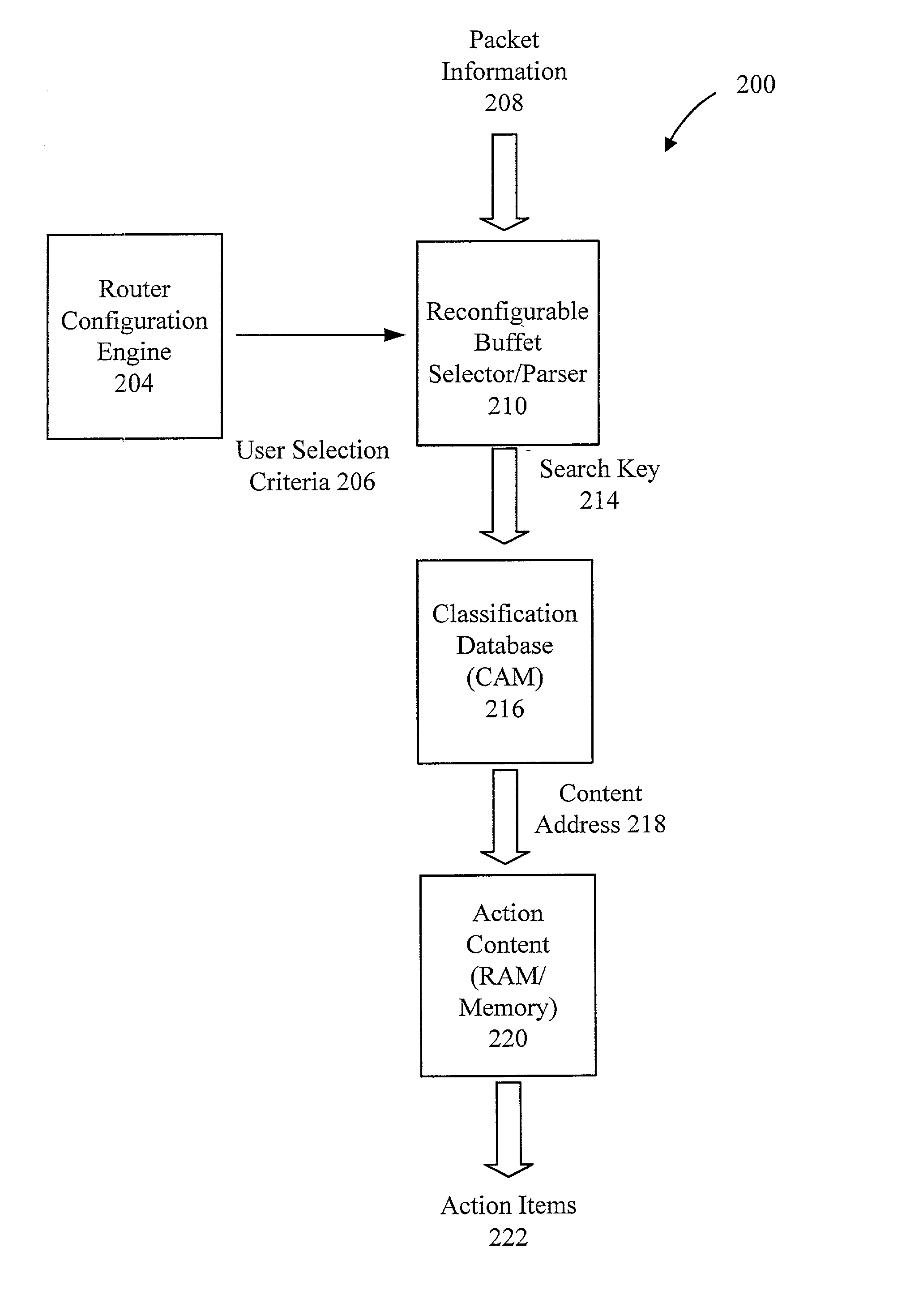
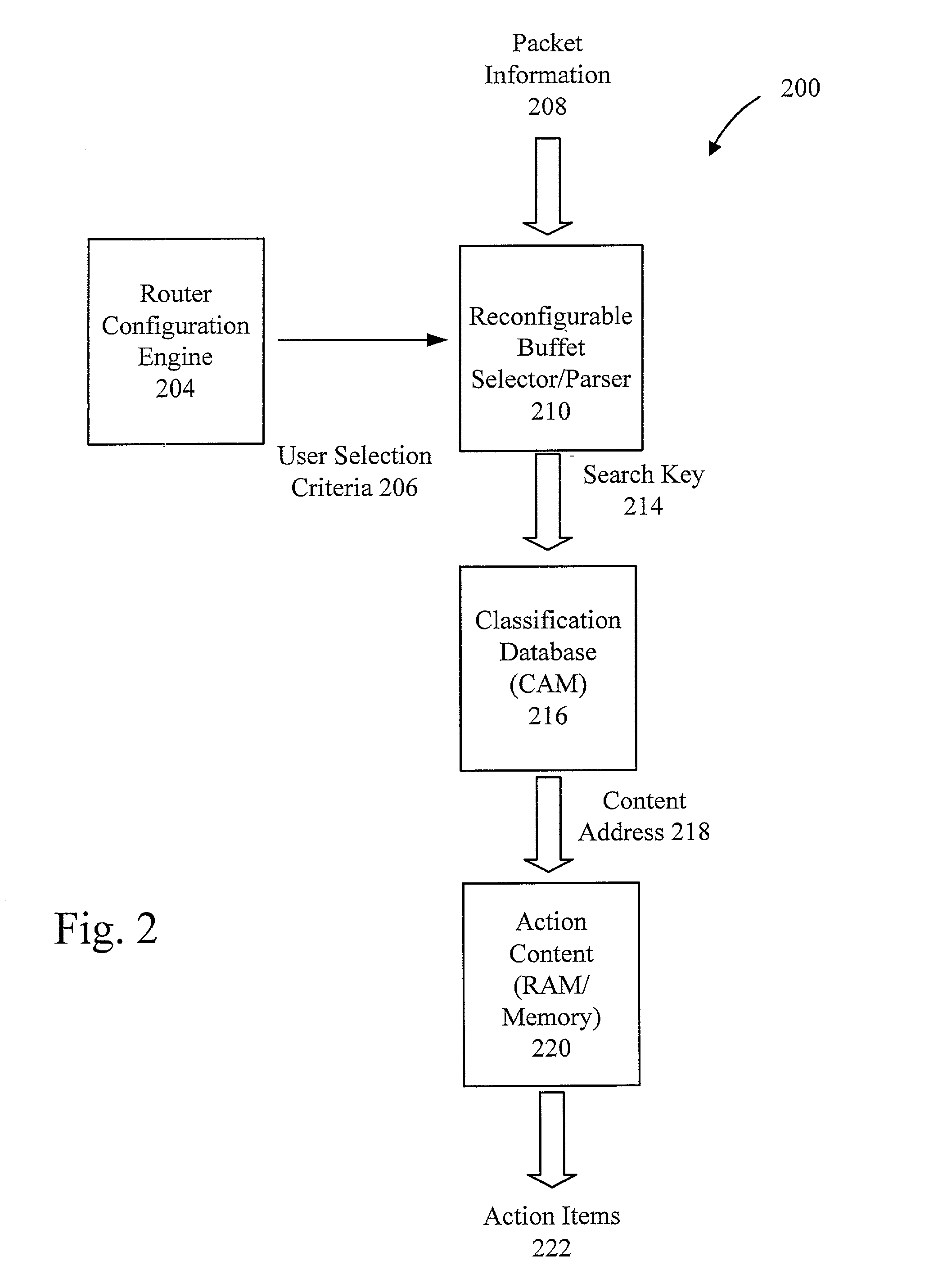
Method and apparatus for a flexible and reconfigurable packet classifier using content addressable memory
InactiveUS20020126672A1Low costFlexibility of deploymentData switching by path configurationSecuring communicationCustomer requirementsTernary content addressable memory
The present invention provides for a reconfigurable packet classifier using CAM. The invention is directed to packet classification for switching / routing systems where the router's system resources are limited and the customer requirements from the router are variable. The invention addresses the CAM constraint (e.g. search key width) problems of CAM-based classification systems, by allowing a reconfigurable selection of packet fields and / or payload bits to be used in the definition of the search key. For any given incoming packet, a subset of that incoming packet may be statically chosen to fit that particular CAM architecture and to create a particular CAM search key. This provides router deployment flexibility within networks and, thus, cuts costs.
Owner:ACUTE COMM CORP
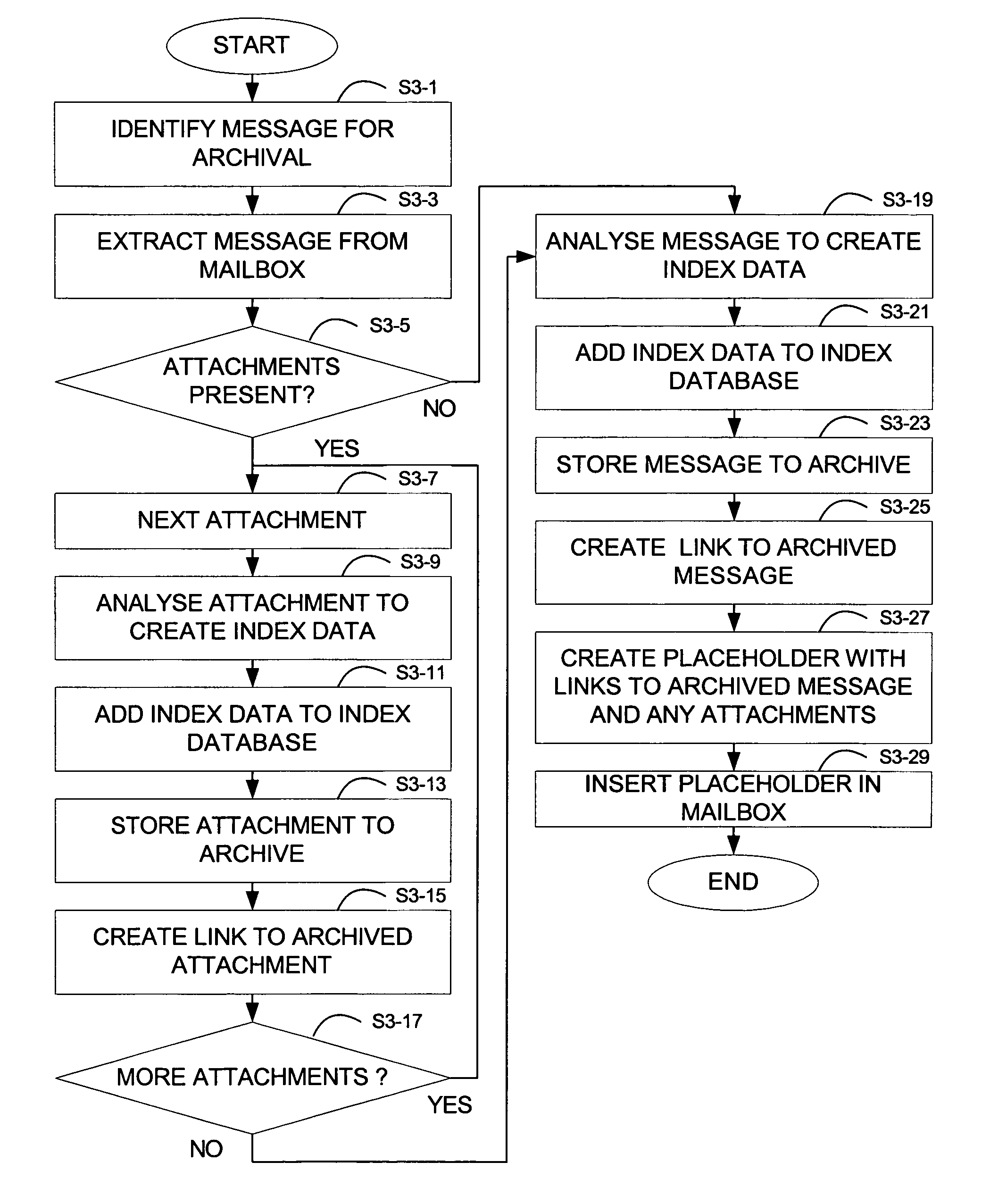
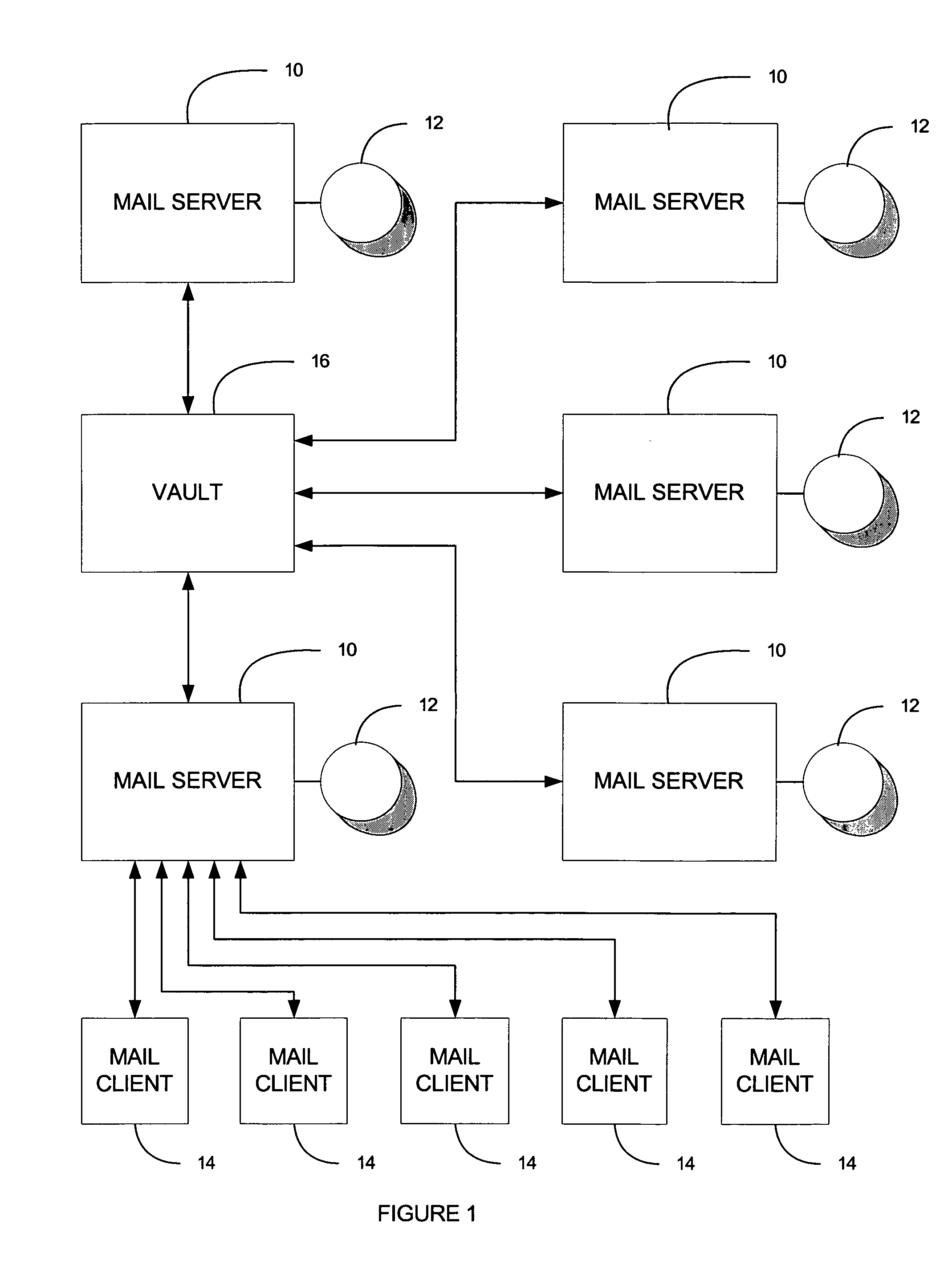
System and method for archival of messages in size-limited containers and separate archival of attachments in content addressable storage
InactiveUS7913053B1Increase storage spaceEasy to useConstructionsRotary drillingContent-addressable storageWorld Wide Web
A method for archival of messages in content addressable storage can be provided. The method can comprise identifying a plurality of messages for archival. The identified messages can be subjected to extraction of attachments therefrom. The messages, minus any removed attachments, can then be concatenated into a container file. Finally, the container file and the extracted attachments are stored in a content addressable storage system.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
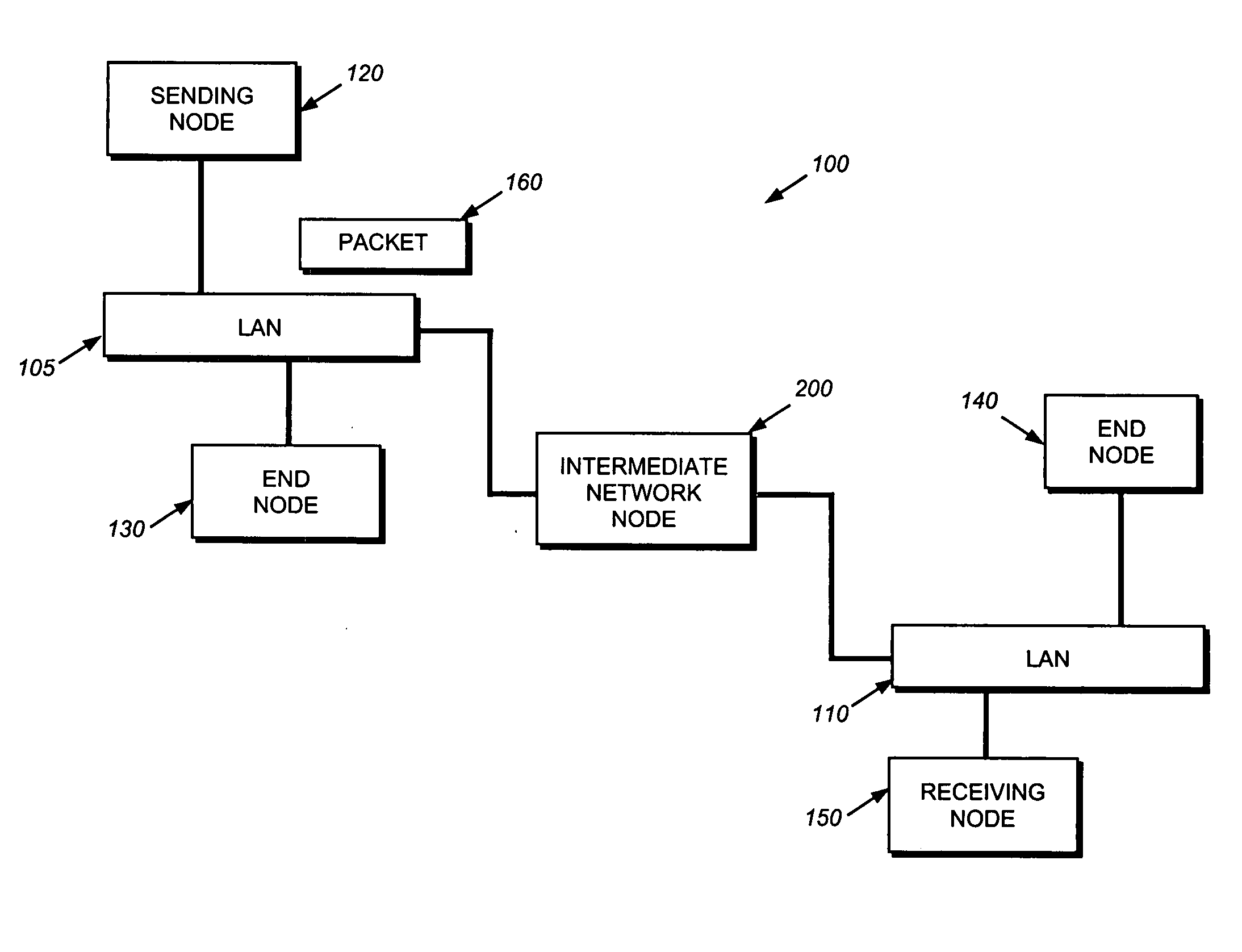
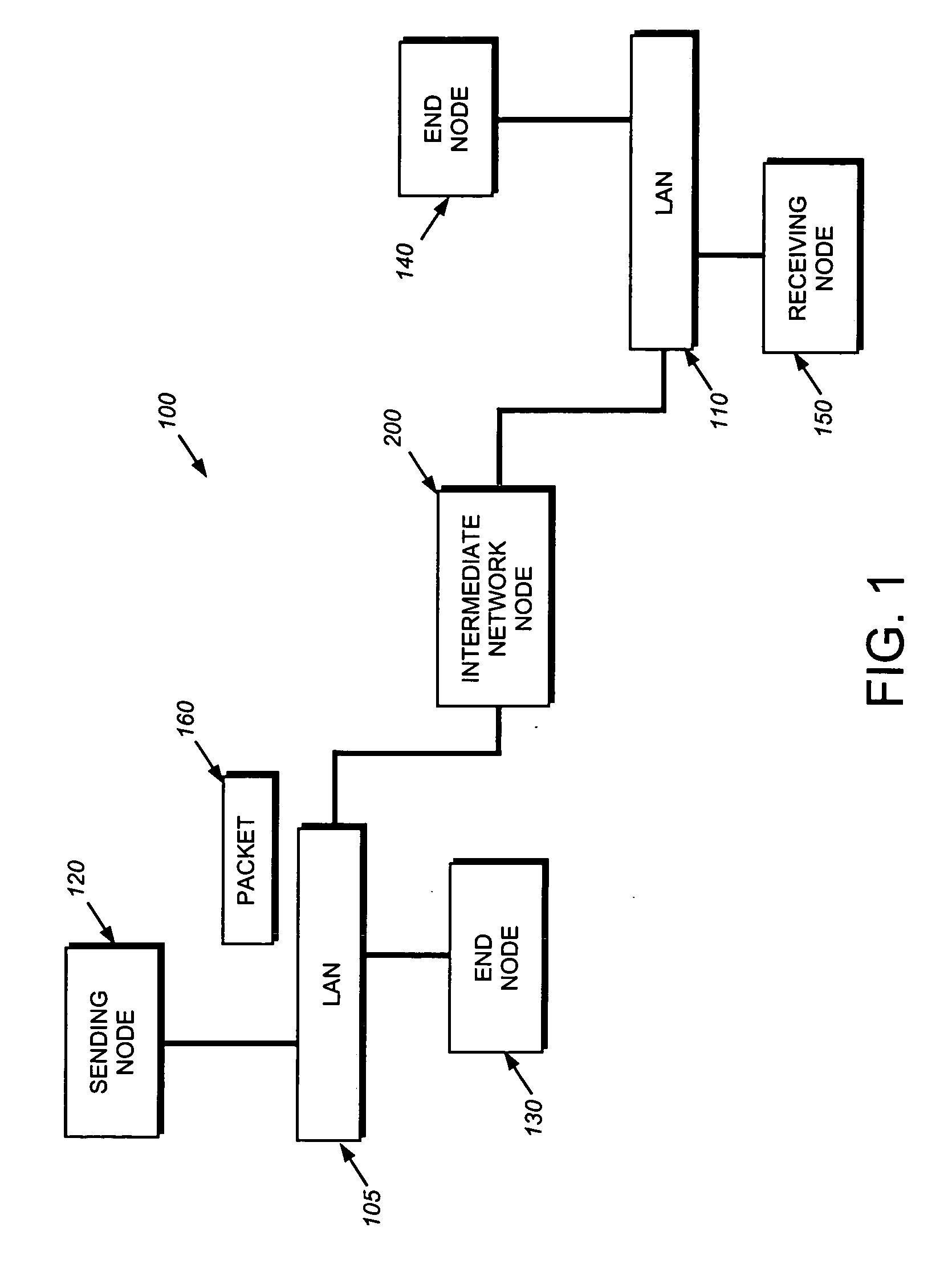
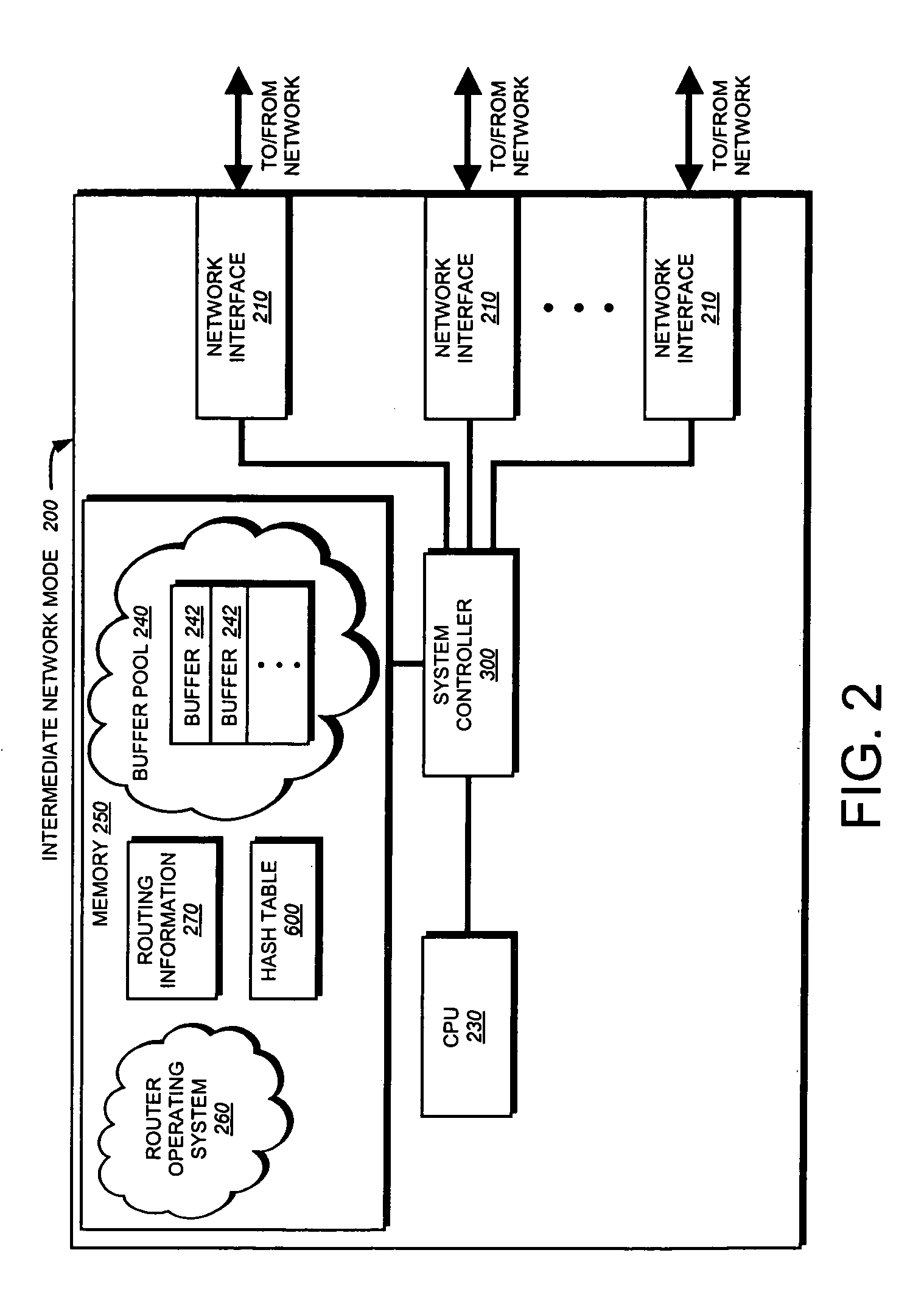
Hardware filtering support for denial-of-service attacks
InactiveUS20050213570A1Processing bandwidthOvercome disadvantagesData switching by path configurationNetwork packetLookup table
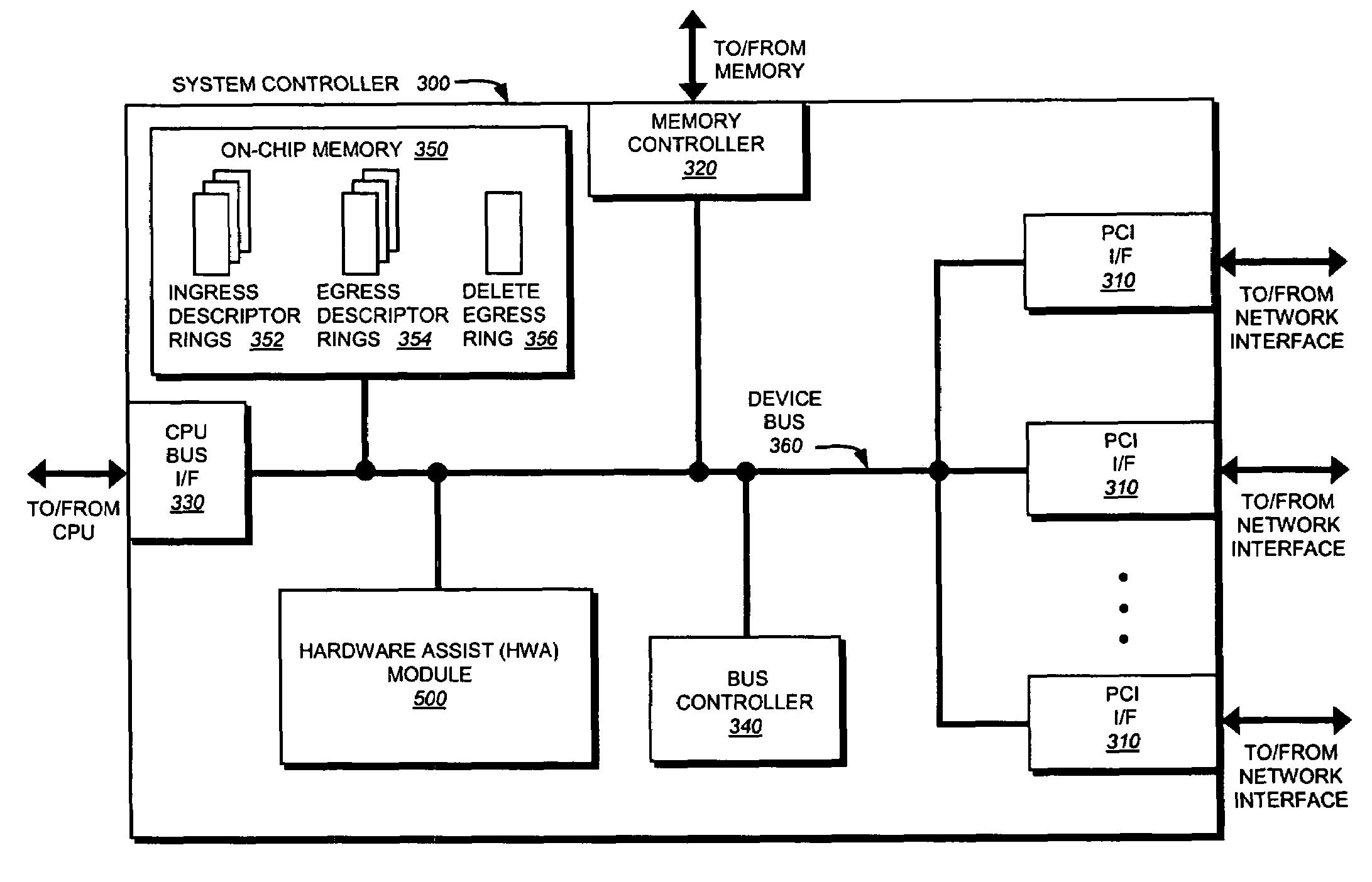
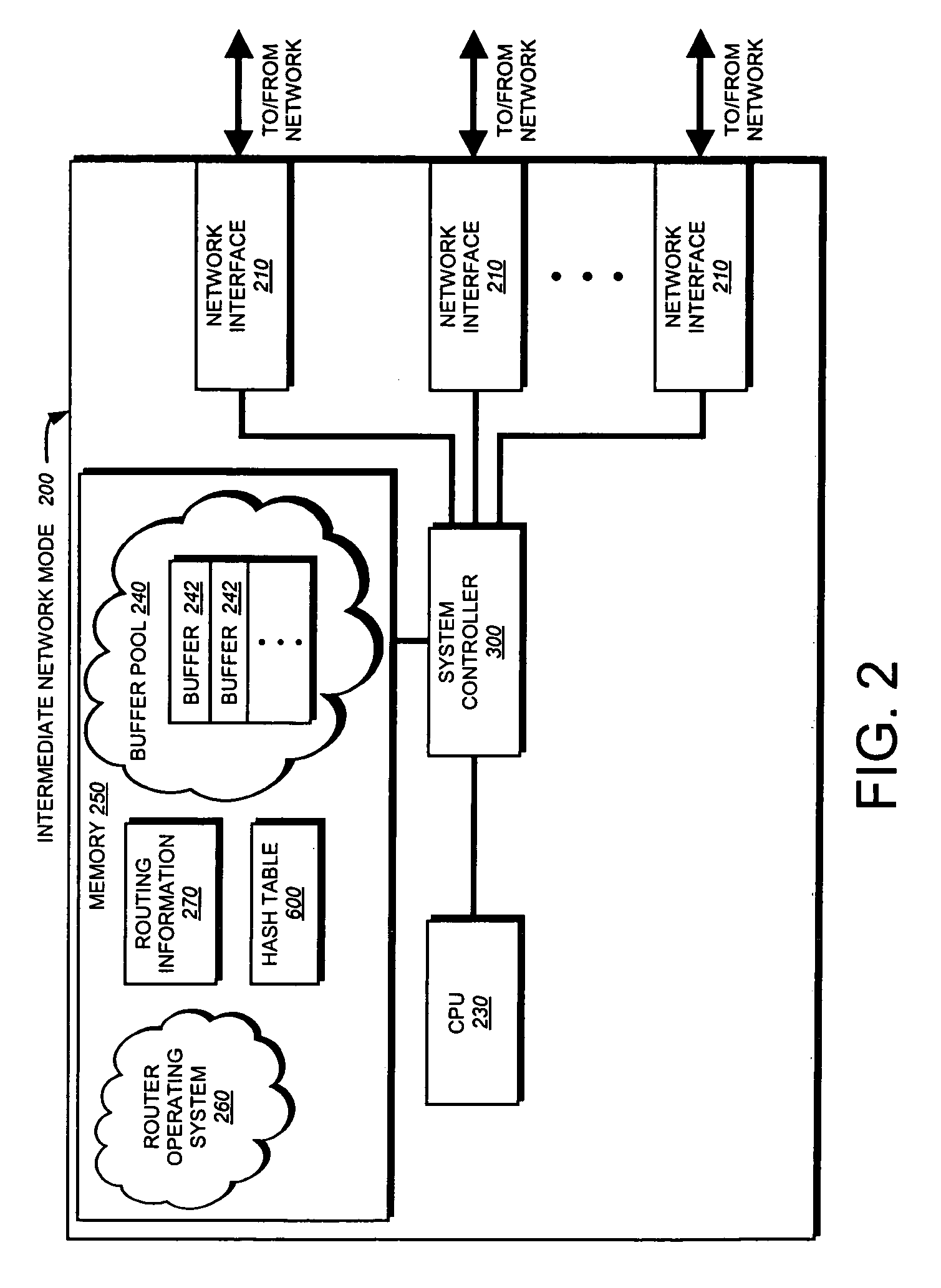
A system and method is provided for automatically identifying and removing malicious data packets, such as denial-of-service (DoS) packets, in an intermediate network node before the packets can be forwarded to a central processing unit (CPU) in the node. The CPU's processing bandwidth is therefore not consumed identifying and removing the malicious packets from the system memory. As such, processing of the malicious packets is essentially “off-loaded” from the CPU, thereby enabling the CPU to process non-malicious packets in a more efficient manner. Unlike prior implementations, the invention identifies malicious packets having complex encapsulations that can not be identified using traditional techniques, such as ternary content addressable memories (TCAM) or lookup tables.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
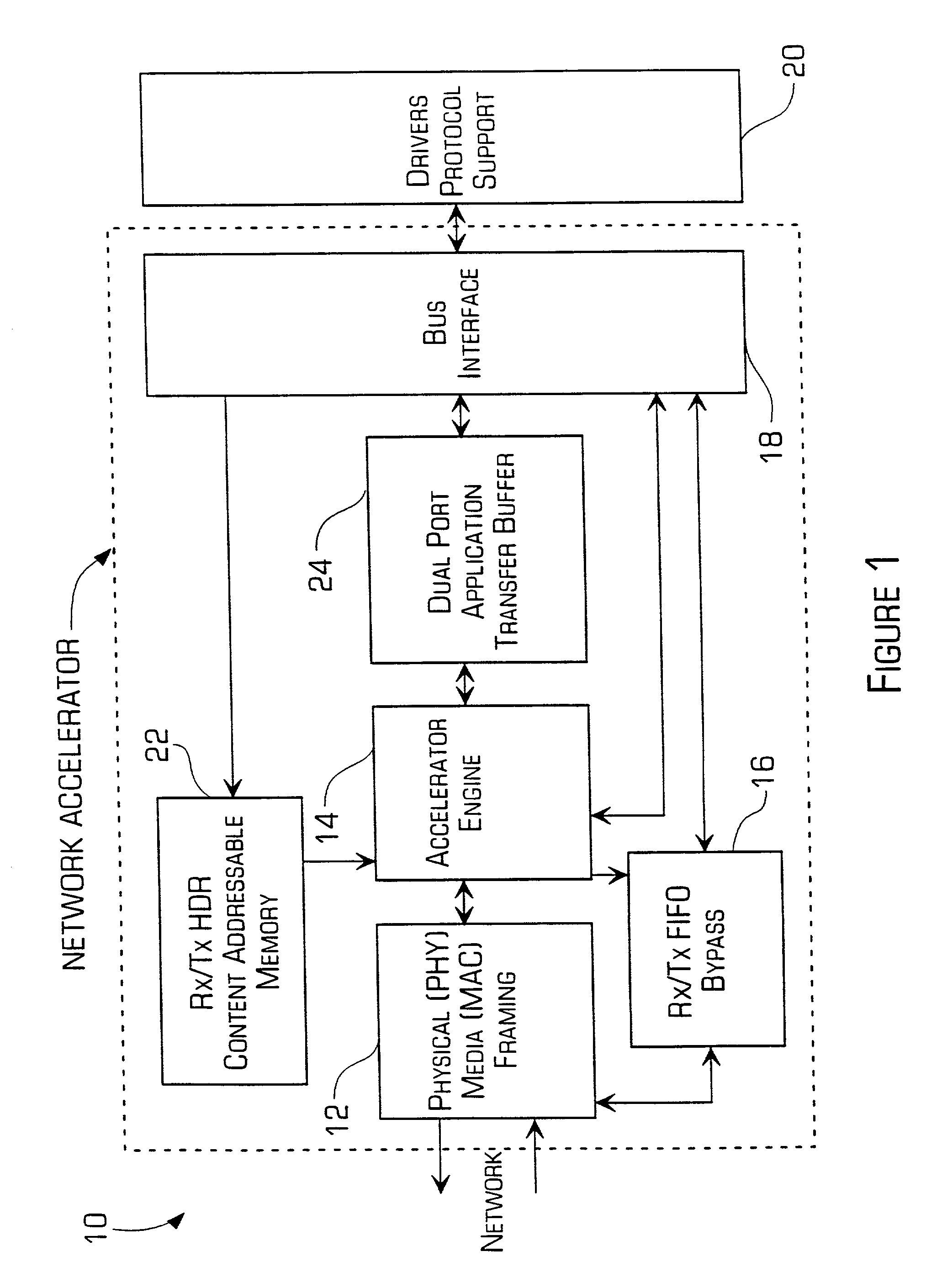
Accelerator system and method
InactiveUS20010004354A1Improve throughputFaster and less-expensive to constructTime-division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmission protocolComputer hardware
A network accelerator for TCP / IP includes programmable logic for performing transparent protocol translation of streamed protocols for audio / video at network signaling rates. The programmable logic is configured in a parallel pipelined architecture controlled by state machines and implements processing for predictable patterns of the majority of transmissions which are stored in a content addressable memory, and are simultaneously stored in a dual port, dual bank application memory. The invention allows raw Internet protocol communications by cell phones, and cell phone to Internet gateway high capacity transfer that scales independent of a translation application, by processing packet headers in parallel and during memory transfers without the necessity of conventional store and forward techniques.
Owner:JOLITZ LYNNE G
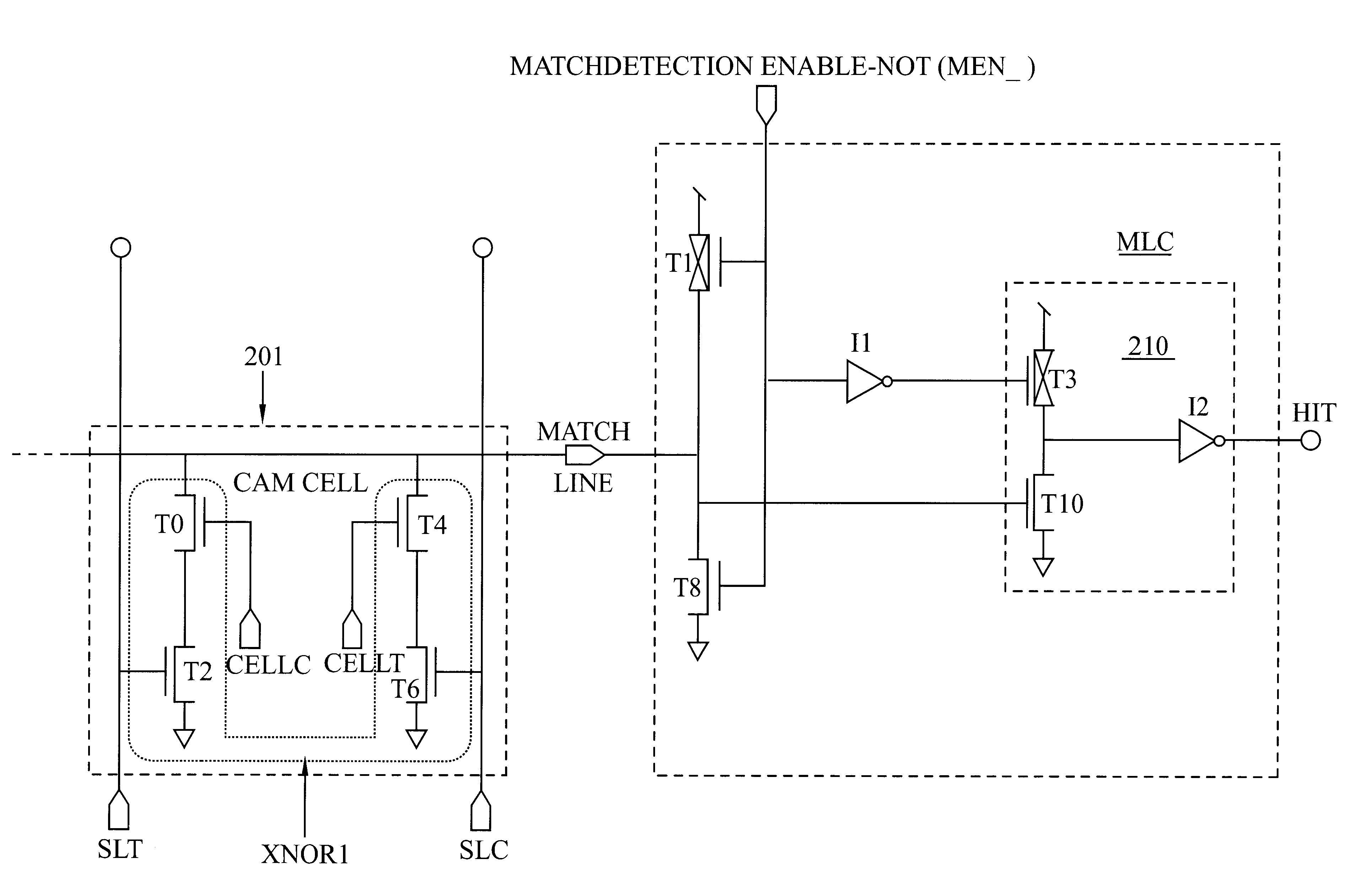
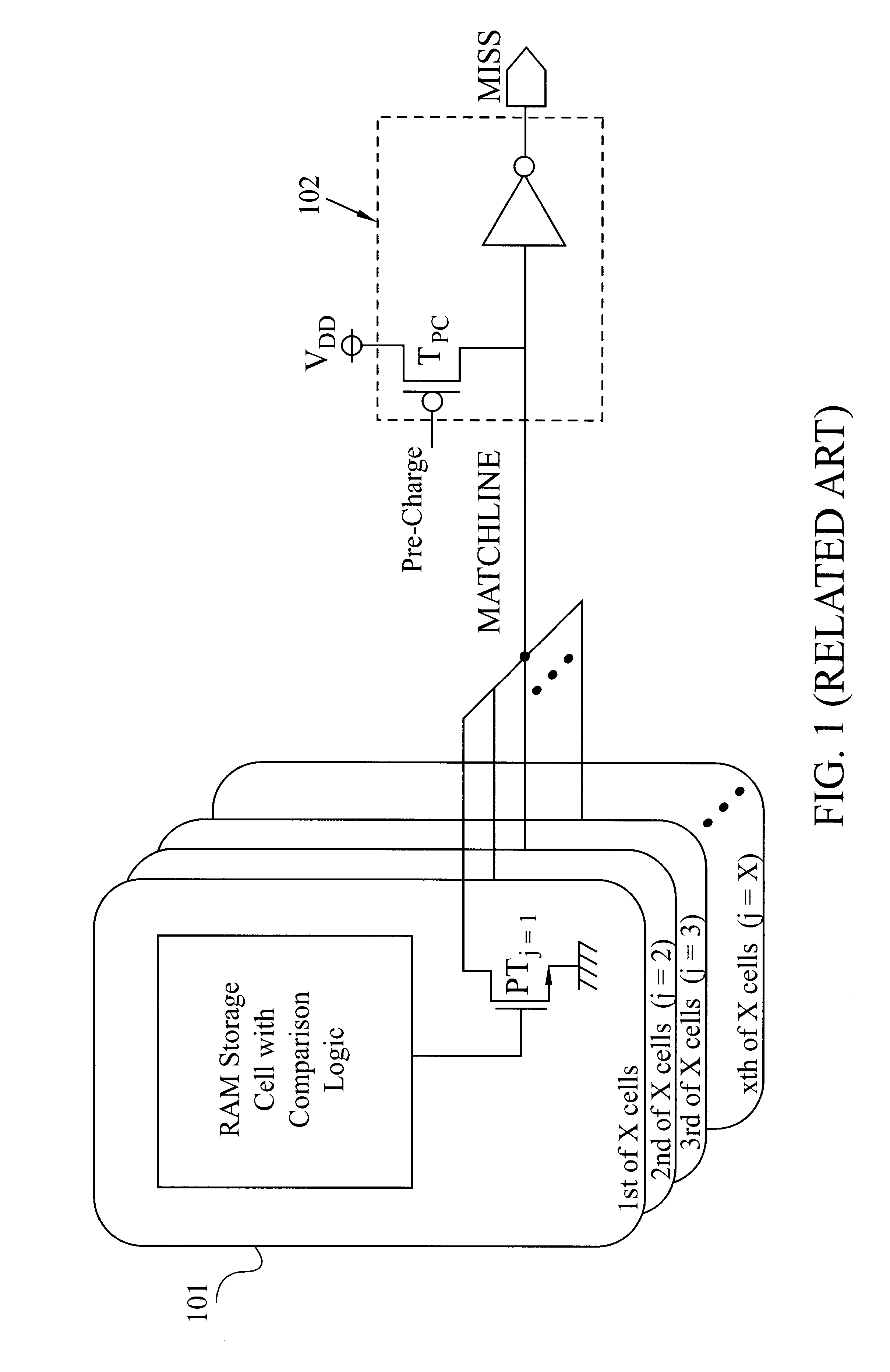
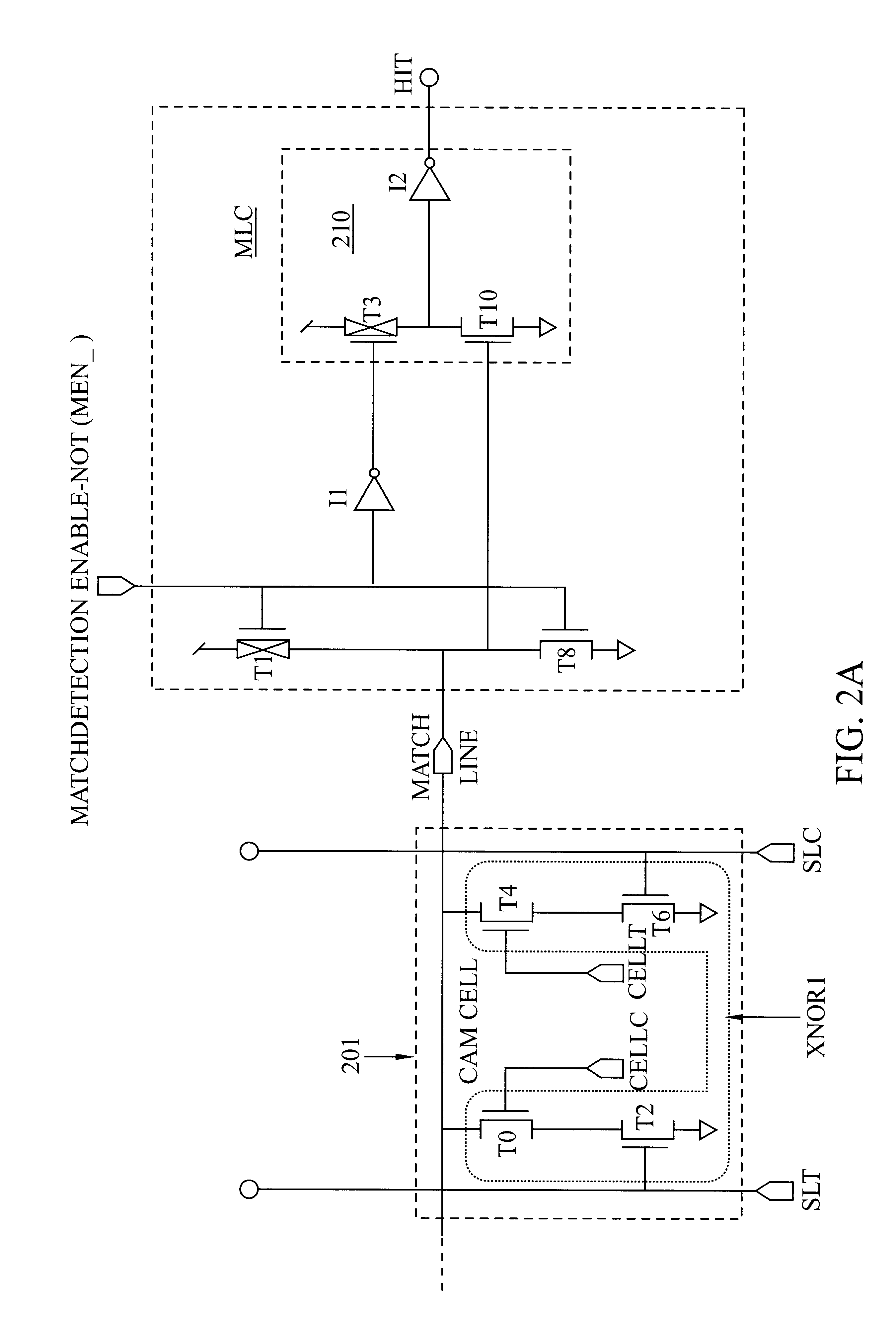
Low power CAM match line circuit
A Match-Detection Circuit and Match-Detection method, for low-power-consuming searches in a Content Addressable Memory. A HIT is output when the Match Line rises from a Low voltage level to a higher Match Detection Voltage. The Match Detection Voltage is approximately the conducting threshold voltage of an N-channel Field Effect Transistor (FET), and is normally less than One Half of the Power Supply Voltage. Circuits and methods to turn of the through-current in each MISS-ing entry by a carefully timed control signal at the end of a brief Match Detection Period, are disclosed.
Owner:IBM CORP
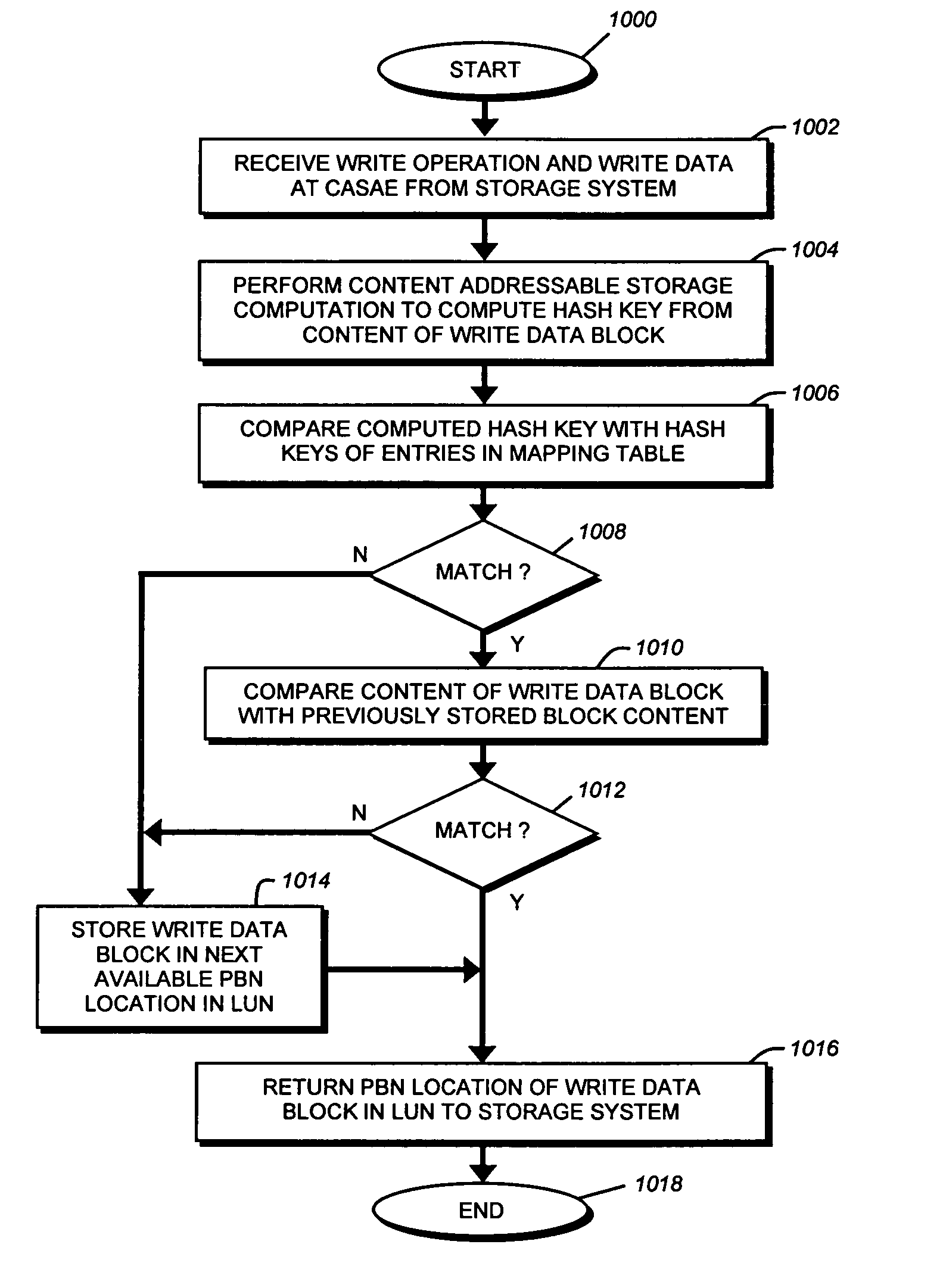
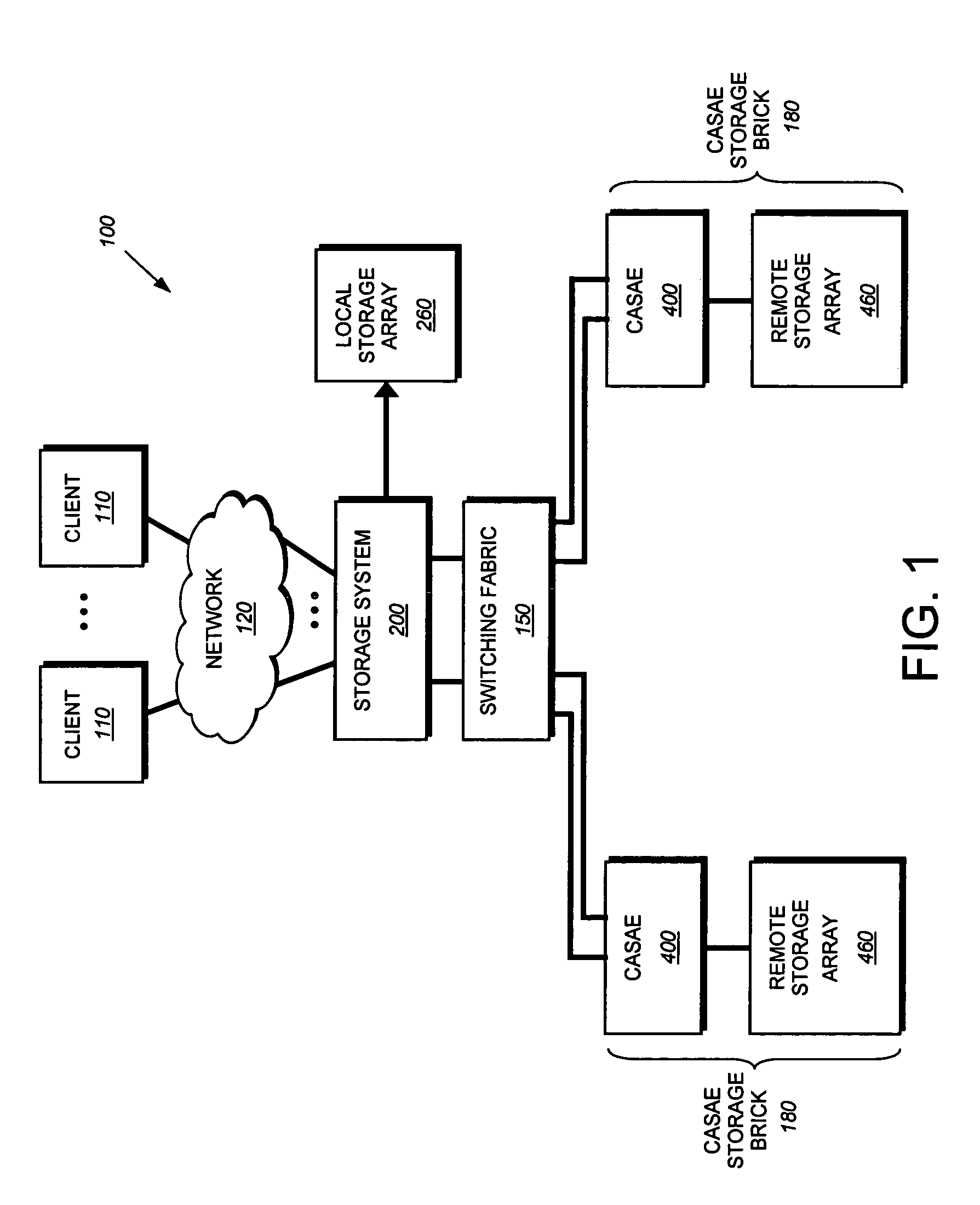
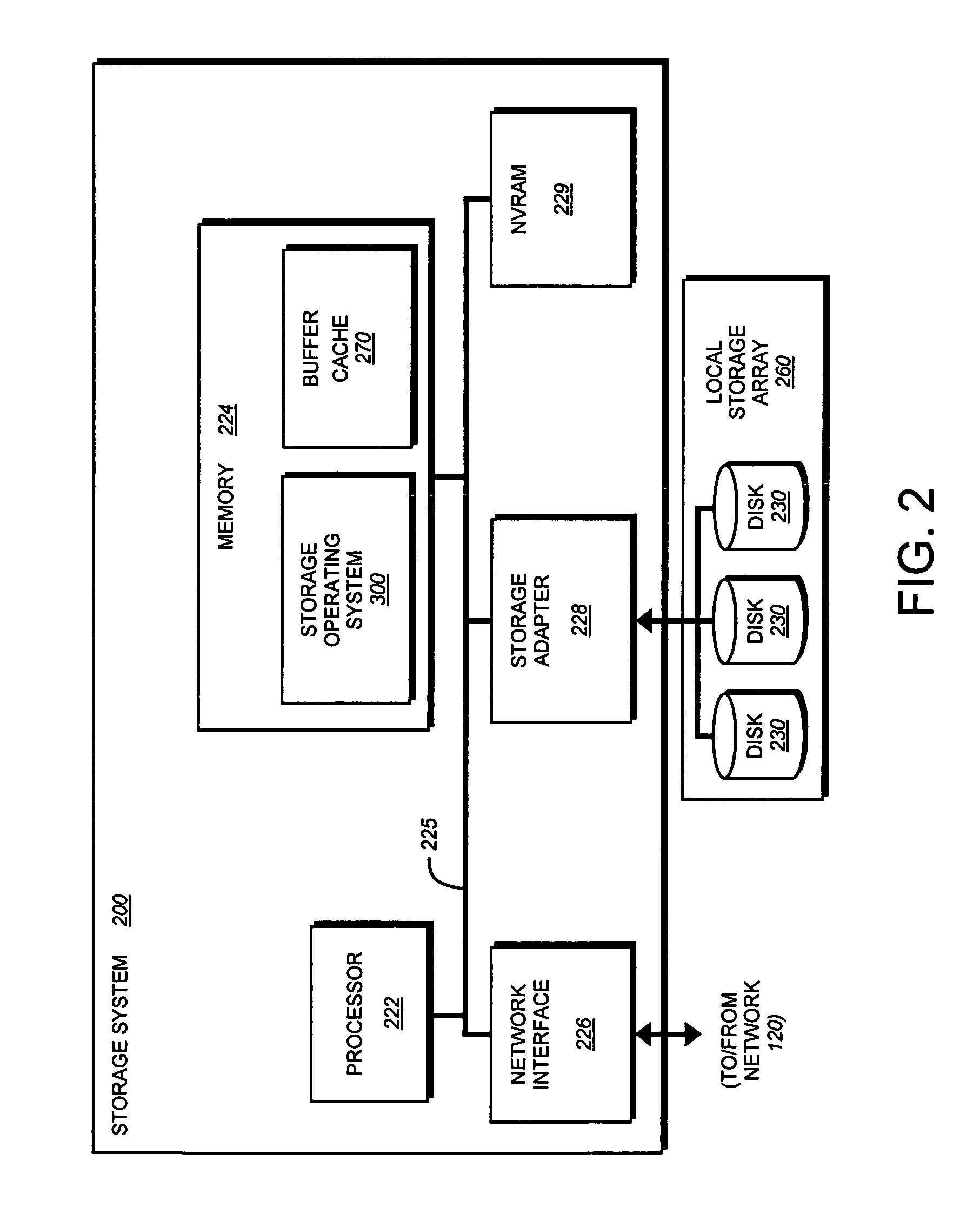
Content addressable storage array element
ActiveUS7734603B1Improve reliabilityDigital data processing detailsCode conversionContent-addressable storageFile system
A content addressable storage array element (CASAE) of a storage system is configured to eliminate duplicate data stored on its storage resources. The CASAE independently determines whether data associated with a write operation has already been written to a location on its storage resources. To that end, the CASAE performs a content addressable storage computation on each data block written to those resources in order to prevent storage of two or more blocks with the same data. If data of a block has been previously stored on the resources, the CASAE cooperates with a file system executing on the system to provide a reference (block pointer) to the same data block rather than duplicate the stored data. Otherwise, the CASAE stores the data block at a new location on the resources and provides a block pointer to that location.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
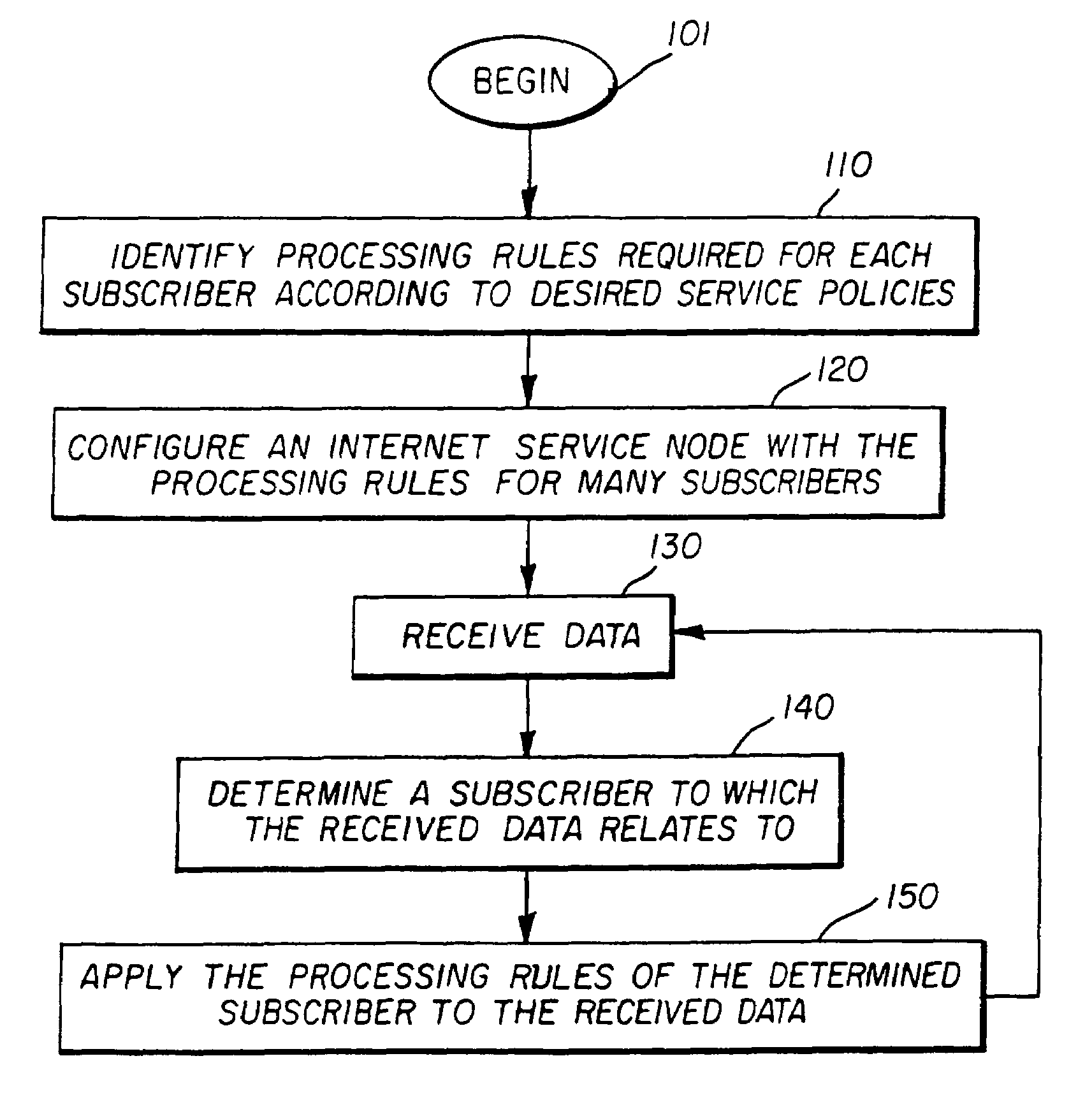
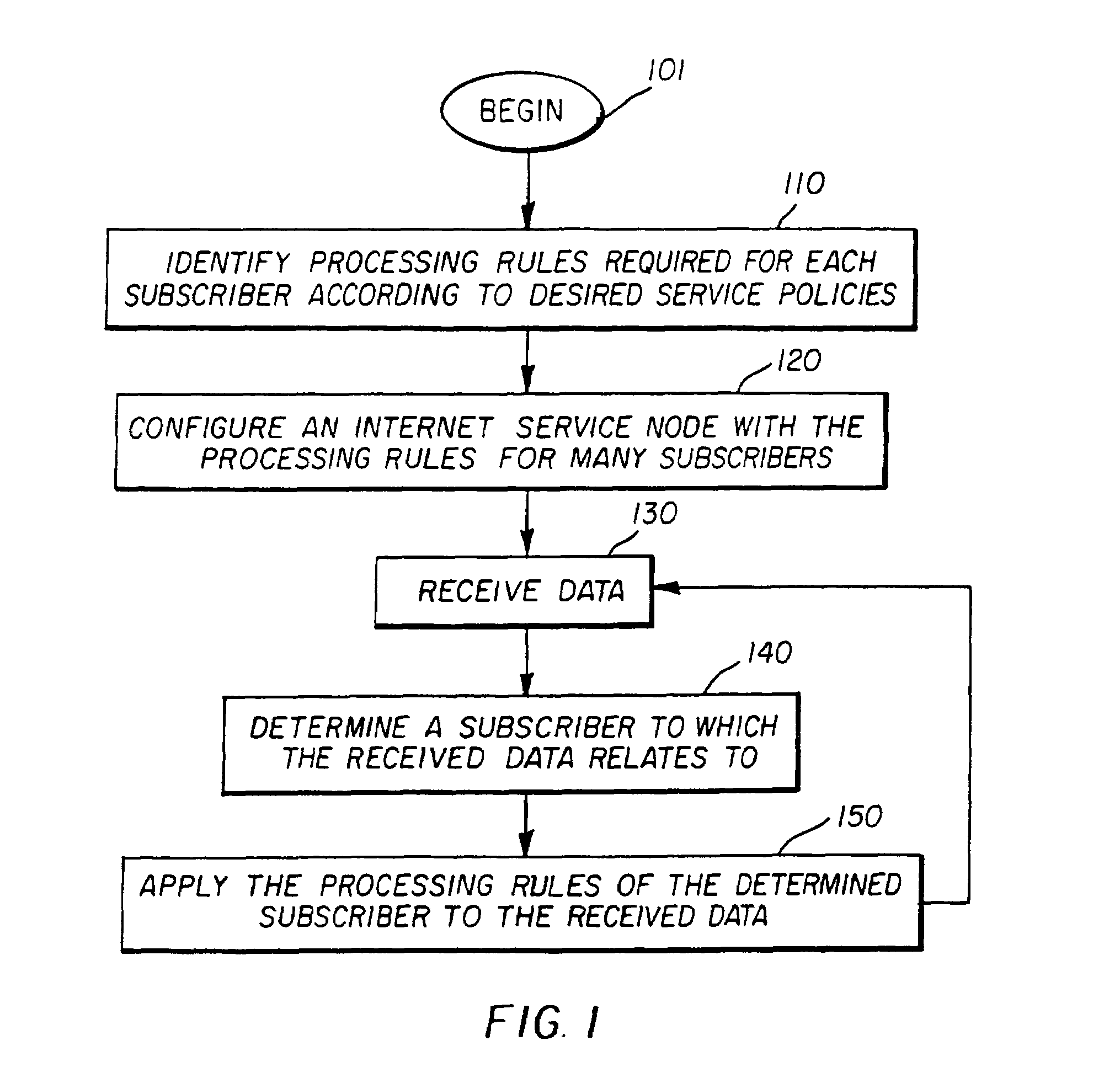
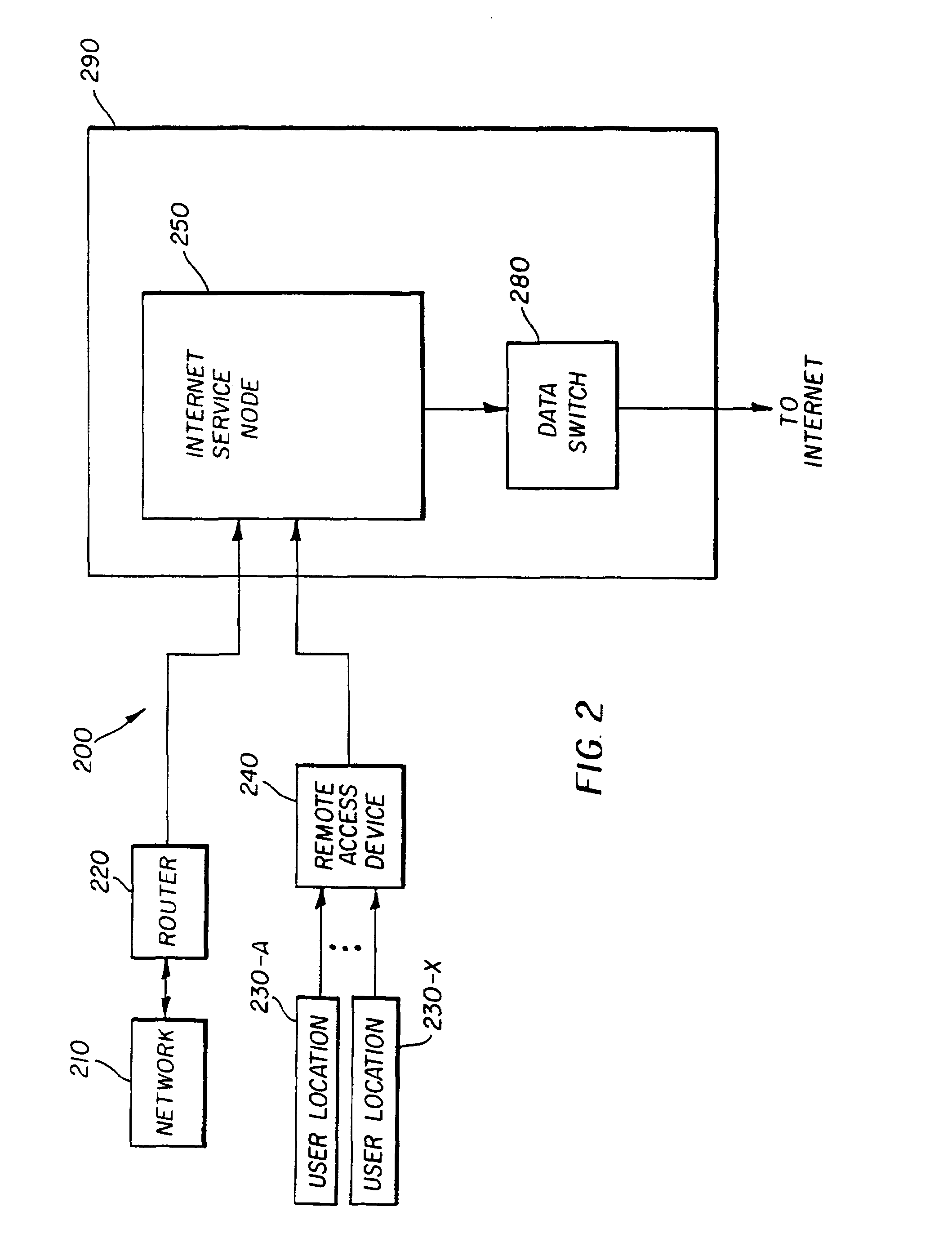
Providing desired service policies to subscribers accessing internet
InactiveUS6952728B1Minimize the numberFast forwardMultiple digital computer combinationsElectric digital data processingAccess networkContent-addressable storage
An internet service node (ISN) enabling the provision of desired service policies to each subscriber. The ISN may contain multiple processor groups, with each subscriber being assigned to a processor group. The assigned processor group may be configured with the processing rules, which provide the service policies desired, by a subscriber. A port may determine the specific processor group to which received data is to be forwarded. A content addressable memory with masks for individual locations may be implemented to quickly determines the processor group to which received data is to be assigned to. Due to the features of the present invention, an ISN may be able to serve a large number of subscribers efficiently. The ISN may be used at the edge of an access network.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Hardware filtering support for denial-of-service attacks
InactiveUS7411957B2Processing bandwidthOvercome disadvantagesUser identity/authority verificationHardware monitoringNetwork packetLookup table
A system and method is provided for automatically identifying and removing malicious data packets, such as denial-of-service (DoS) packets, in an intermediate network node before the packets can be forwarded to a central processing unit (CPU) in the node. The CPU's processing bandwidth is therefore not consumed identifying and removing the malicious packets from the system memory. As such, processing of the malicious packets is essentially “off-loaded” from the CPU, thereby enabling the CPU to process non-malicious packets in a more efficient manner. Unlike prior implementations, the invention identifies malicious packets having complex encapsulations that can not be identified using traditional techniques, such as ternary content addressable memories (TCAM) or lookup tables.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
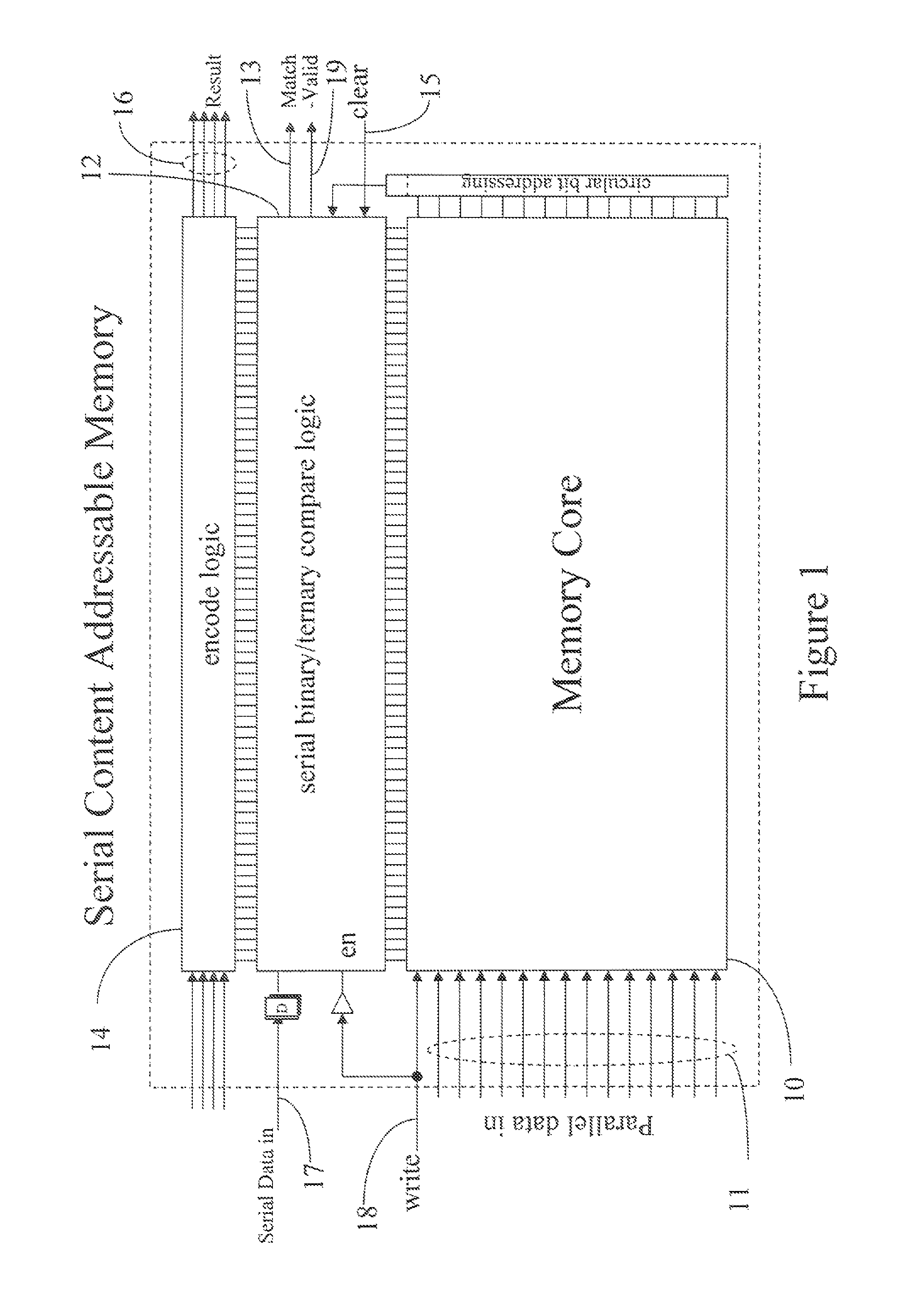
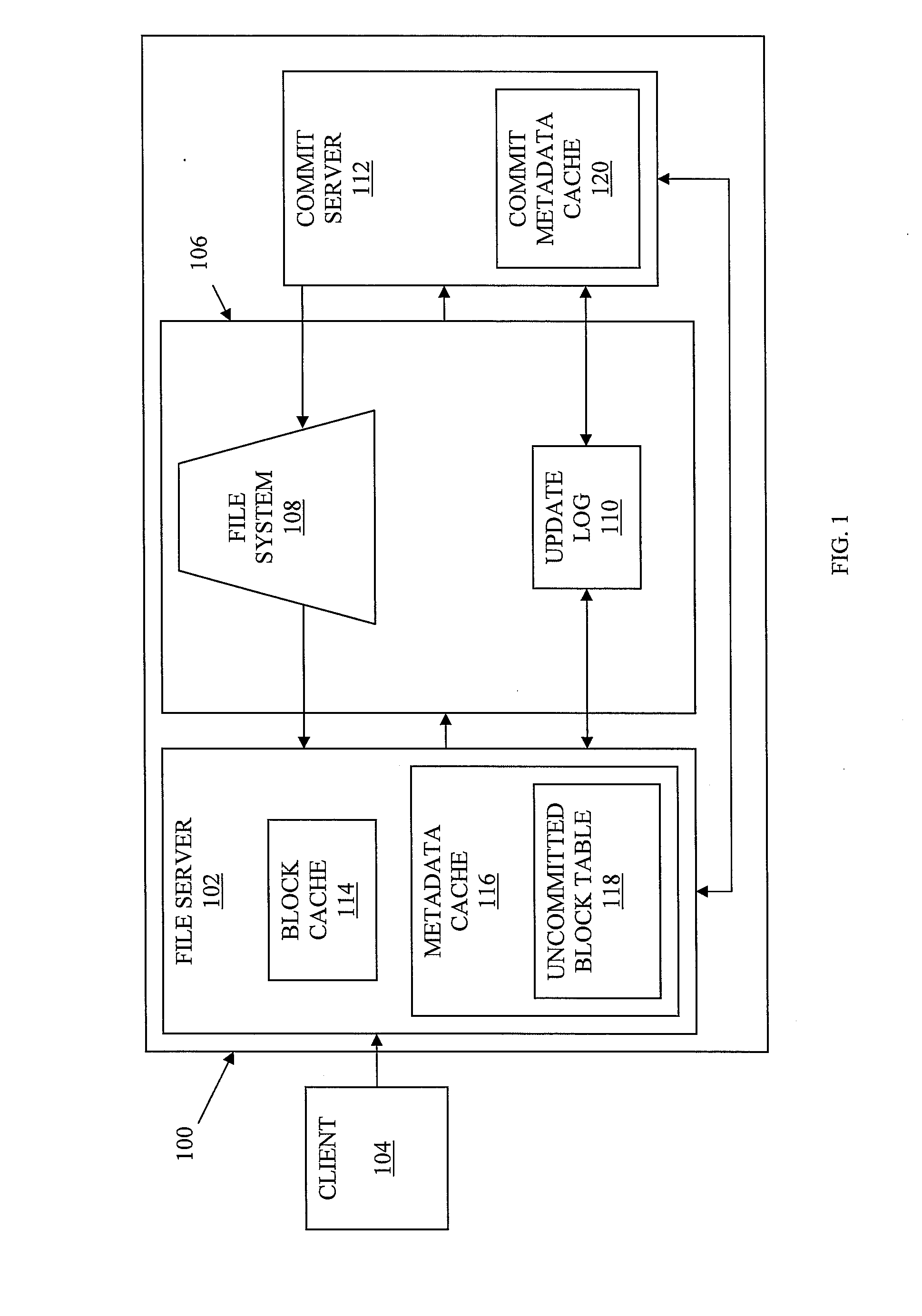
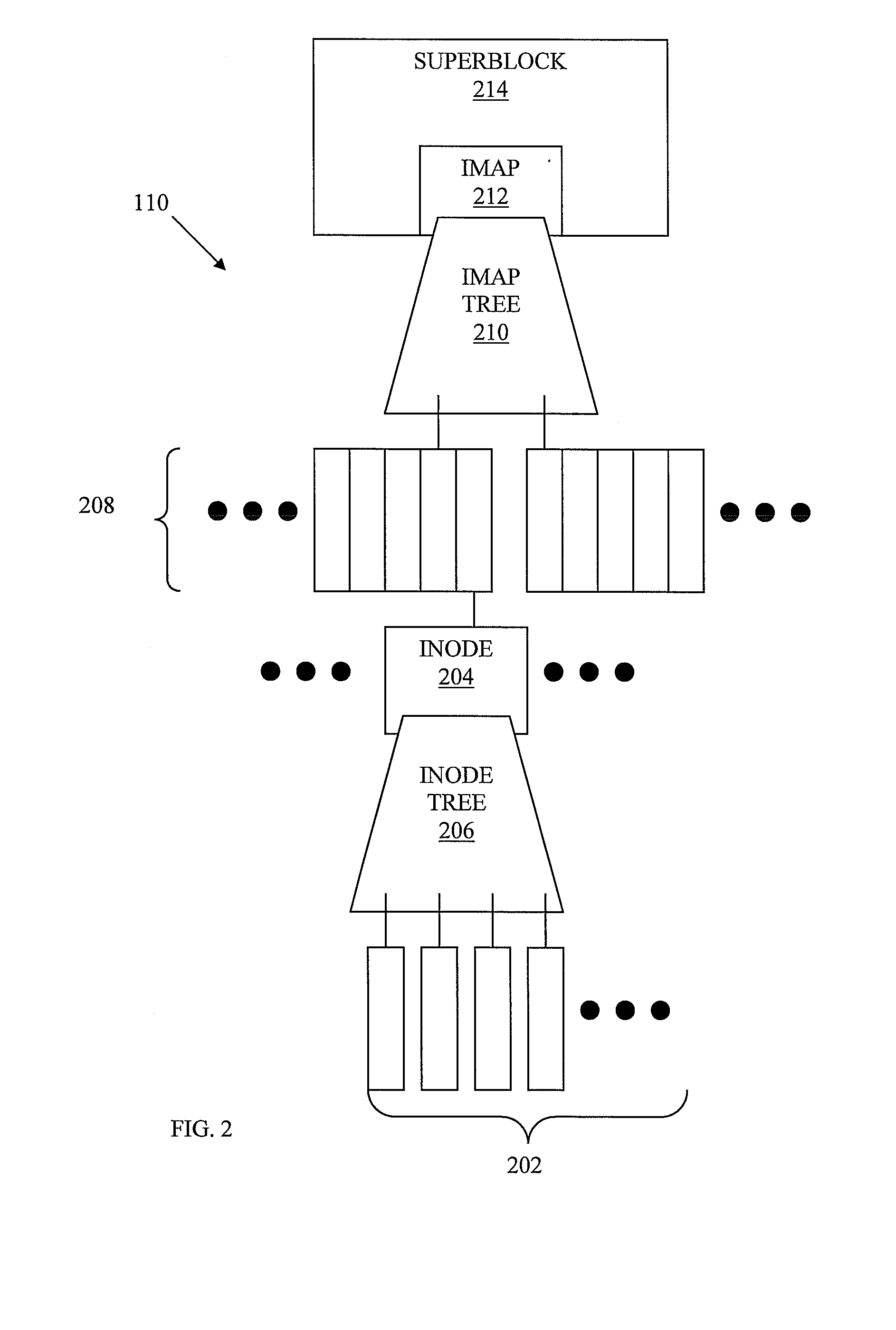
System and Method for Content Addressable Storage
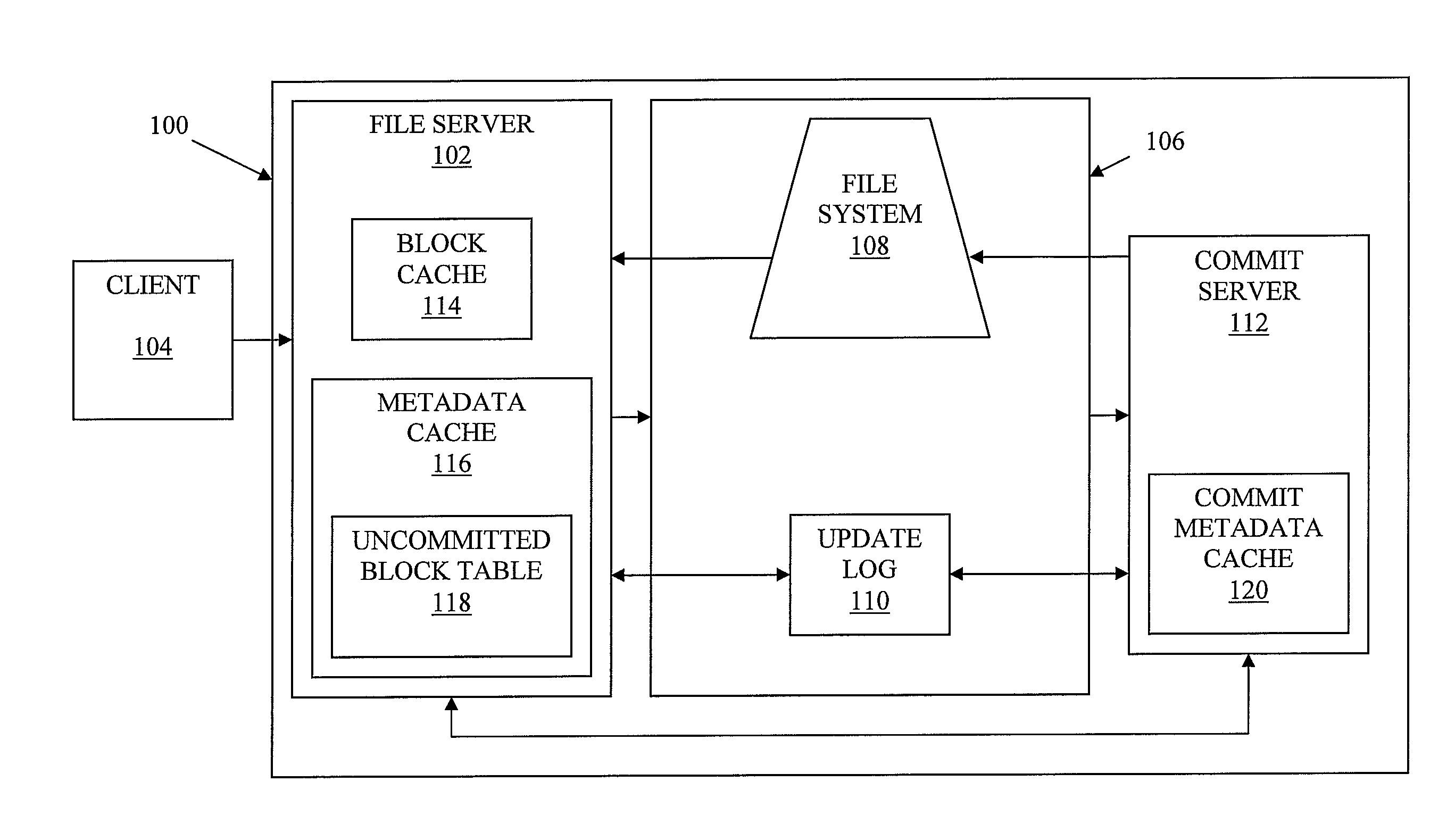
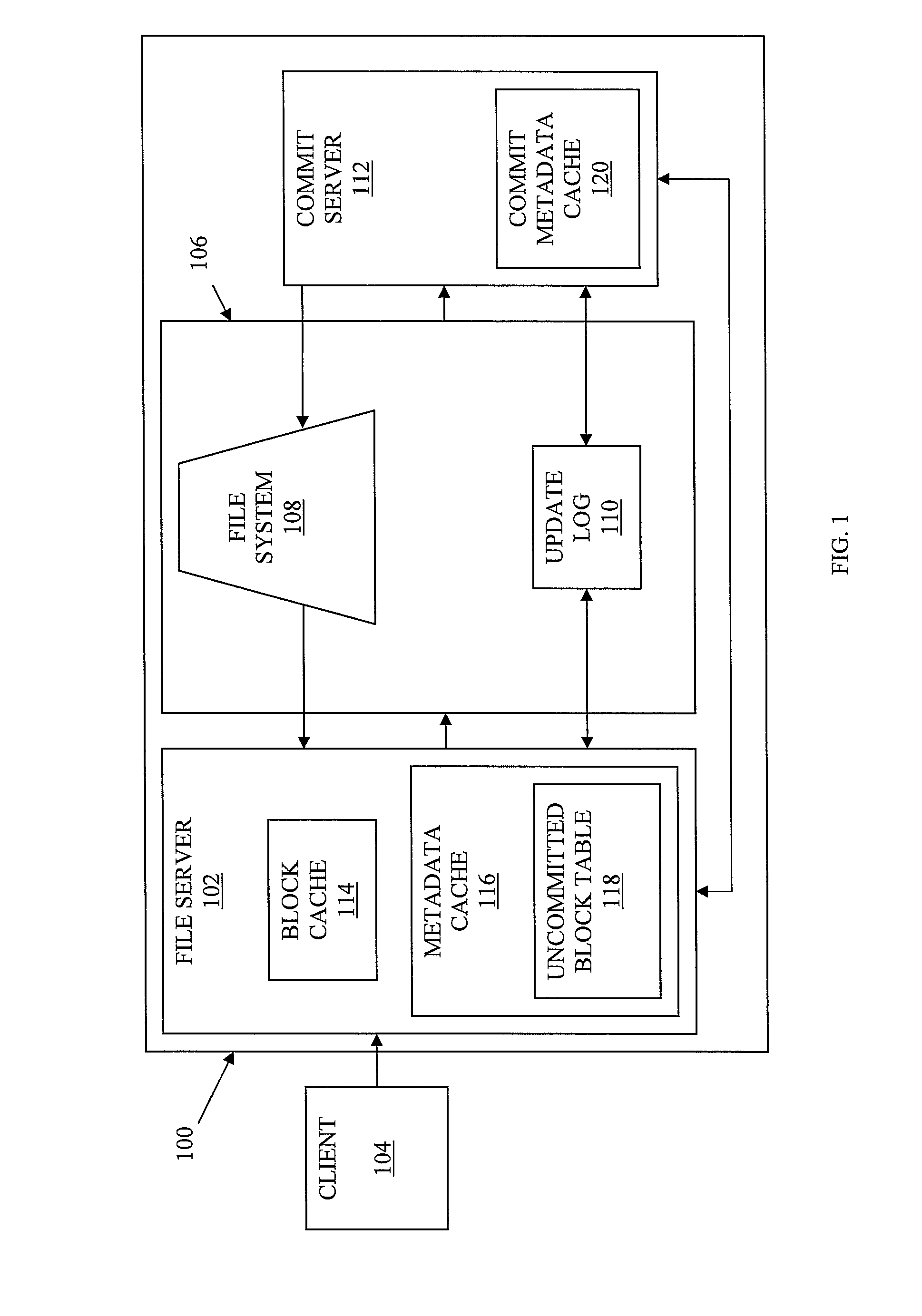
ActiveUS20090228511A1Effectively storing informationEfficient storageDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsClient-sideFile server
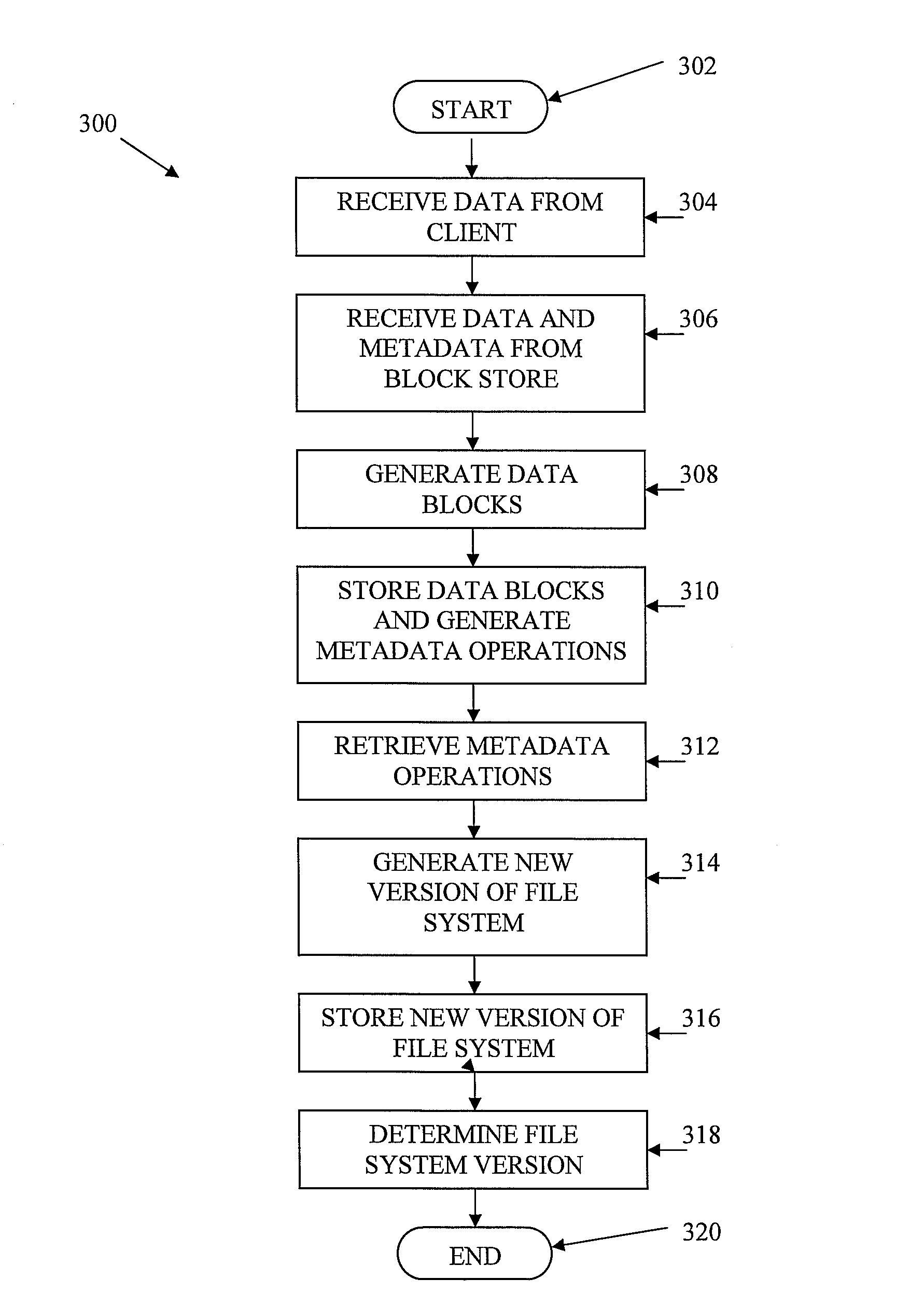
Information, such as files received from a client, etc., is stored in a storage system, such as a content addressable storage system. A file server receives data from a client and chunks the data into blocks of data. The file server also generates metadata for use in forming a data structure. The blocks of data are stored in a block store and a copy of the data blocks and the metadata are locally cached at the file server. A commit server retrieves the metadata. In at least one embodiment, the metadata is retrieved from an update log shared between the file server and the commit server. Based on the retrieved metadata, the commit server generates a version of a data structure. The data structure is then stored at the block store.
Owner:NEC ASIA PACIFIC PTE LTD
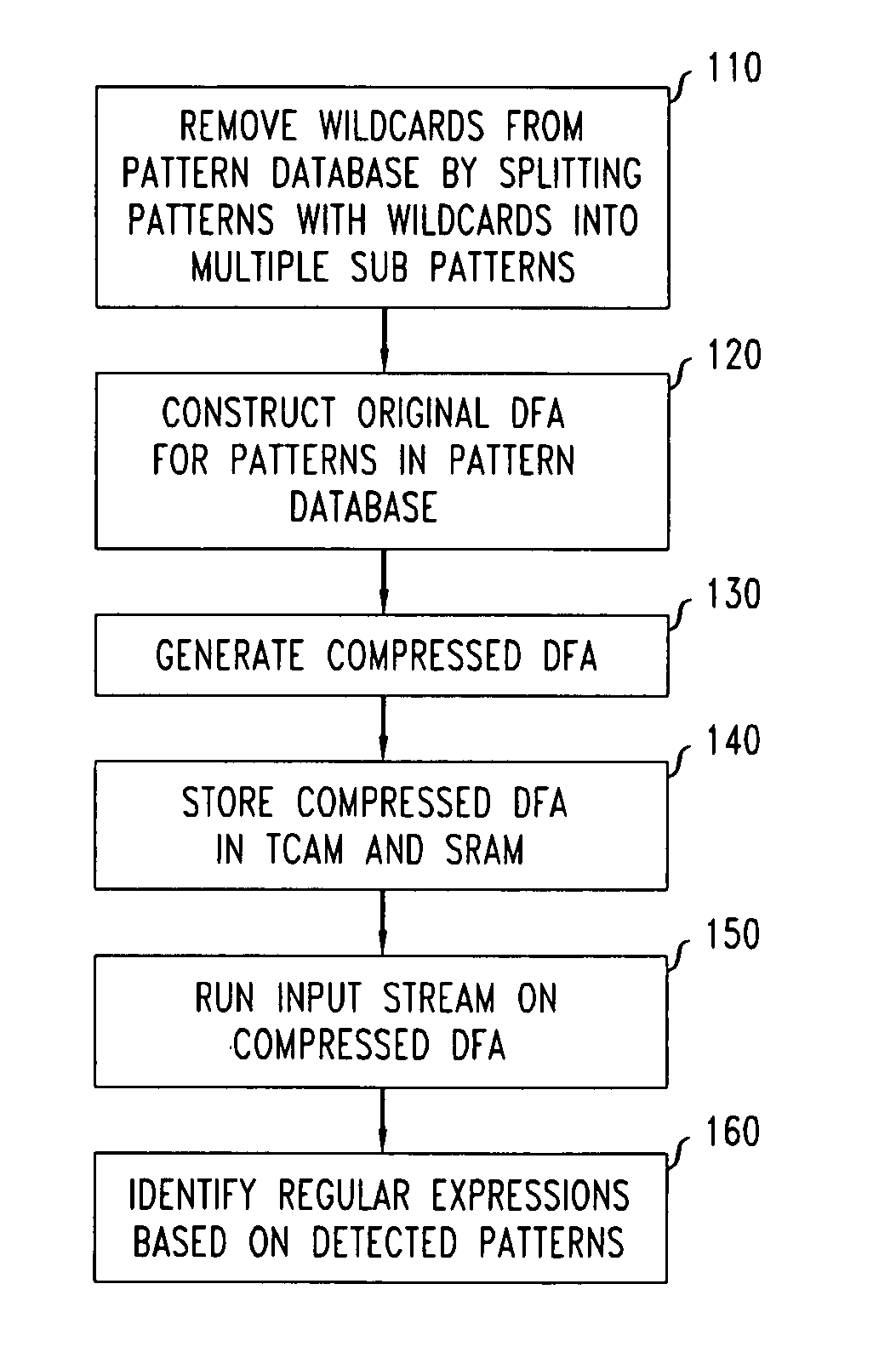
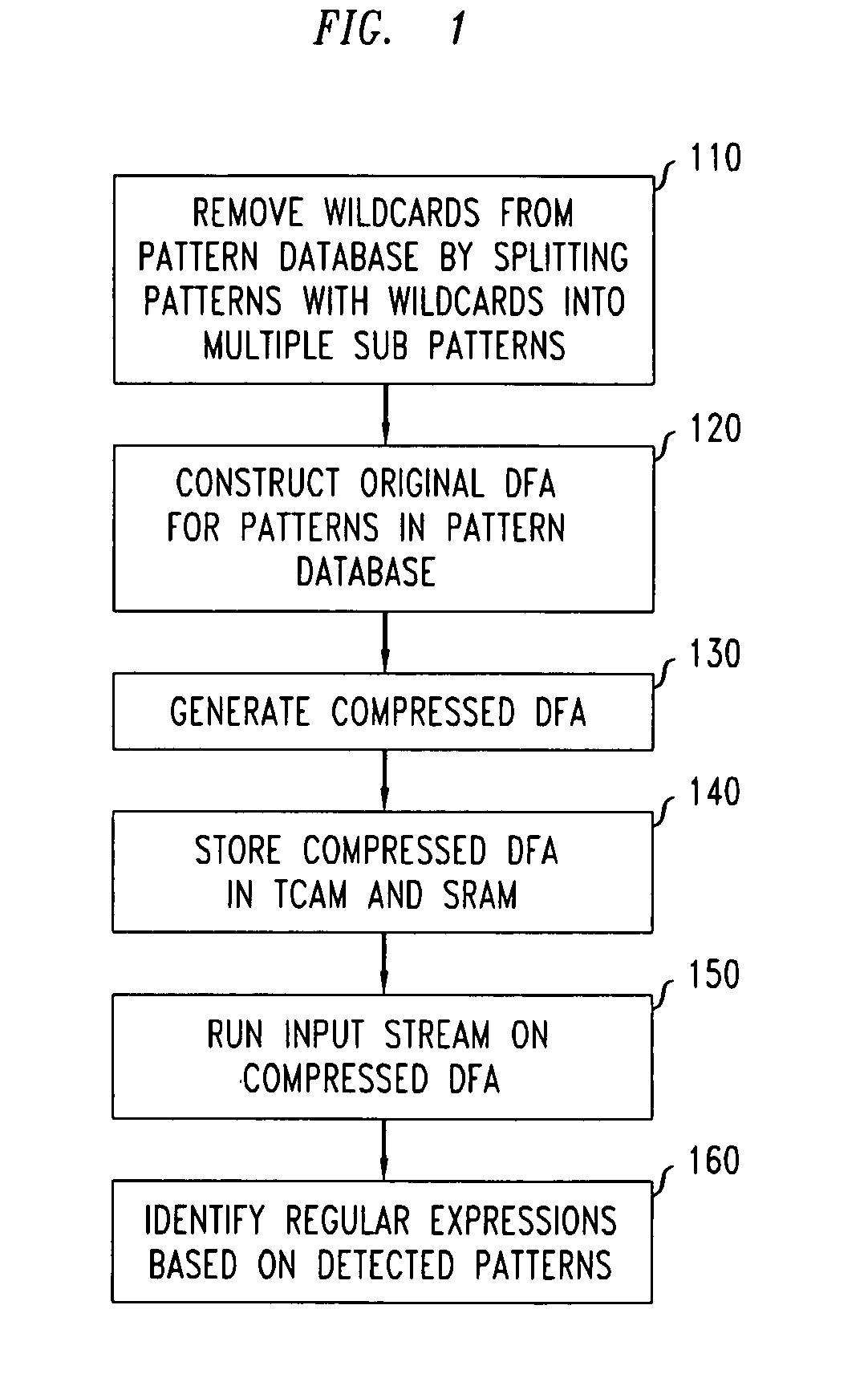
Method and system for multi-character multi-pattern pattern matching
ActiveUS20080046423A1High pattern matching speedEasy to implementData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalPattern matchingTernary content addressable memory
Disclosed is a method and system for multi-character multi-pattern pattern matching. In the multi-character multi-pattern pattern matching method, patterns in an input stream are detected by transitioning between states of a “compressed deterministic finite state automaton (DFA)”, with each transition based on multiple characters of the input stream. The compressed DFA is created by compressing an original DFA, such as an Aho-Corasick DFA, such that each state of the compressed DFA represents multiple consecutive states of the original DFA and each transition between the states of the compressed DFA is a combination of all of the transitions between the multiple consecutive states of the original DFA. This method can be implemented using a Ternary Content-Addressable Memory (TCAM) to store the transitions of the compressed DFA and compares the transitions with multiple characters of an input stream at a time to detect patterns in the input stream.
Owner:ALGOGENE FINANCIAL TECHNOLOGY COMPANY LIMITED
CAM memory architecture and a method of forming and operating a device according to a CAM memory architecture
InactiveUS6906938B2Lower requirementOptimized areaDigital storageMemory systemsControl signalControl data
A method for a content addressable memory that includes receiving a first data value for evaluation at a first memory block during a first time interval, receiving a second data value for evaluation at a second memory block during a second time interval and evaluating said both the first and second data values during a third time interval. According to one embodiment of the invention the first and second time intervals are separate so that the first and second data blocks receive unique data out of phase with one another from a single address bus. Evaluation of both data values takes place substantially simultaneously in the respective memory blocks. Also included is a device architecture and a device adapted to control data transfer to two CAM memory blocks in response to alternate phase transitions of a control signal.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Non-volatile memory-based mass storage devices and methods for writing data thereto
ActiveUS20130067138A1Need for goodMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesMass storageComputer science
A non-volatile solid state memory-based mass storage device having at least one non-volatile memory component and methods of operating the storage device. In one aspect of the invention, the one or more memory components define a memory space partitioned into user memory and over-provisioning pools based on a P / E cycle count stored in a block information record. The storage device transfers the P / E cycle count of erased blocks to a host and the host stores the P / E cycle count in a content addressable memory. During a host write to the storage device, the host issues a low P / E cycle count number as a primary address to the content addressable memory, which returns available block addresses of blocks within the over-provisioning pool as a first dimension in a multidimensional address space. Changed files are preferably updated in append mode and the previous version can be maintained for version control.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
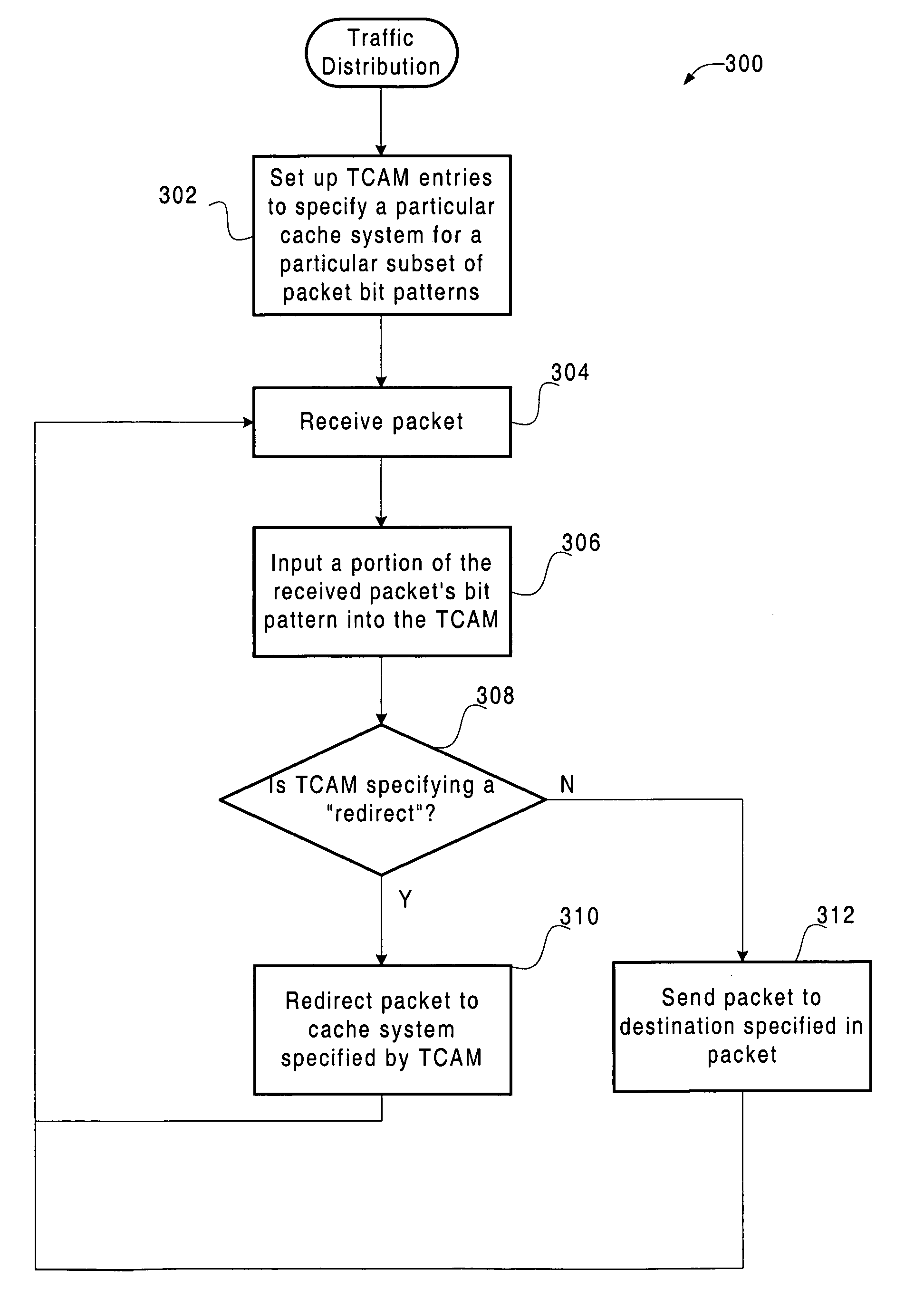
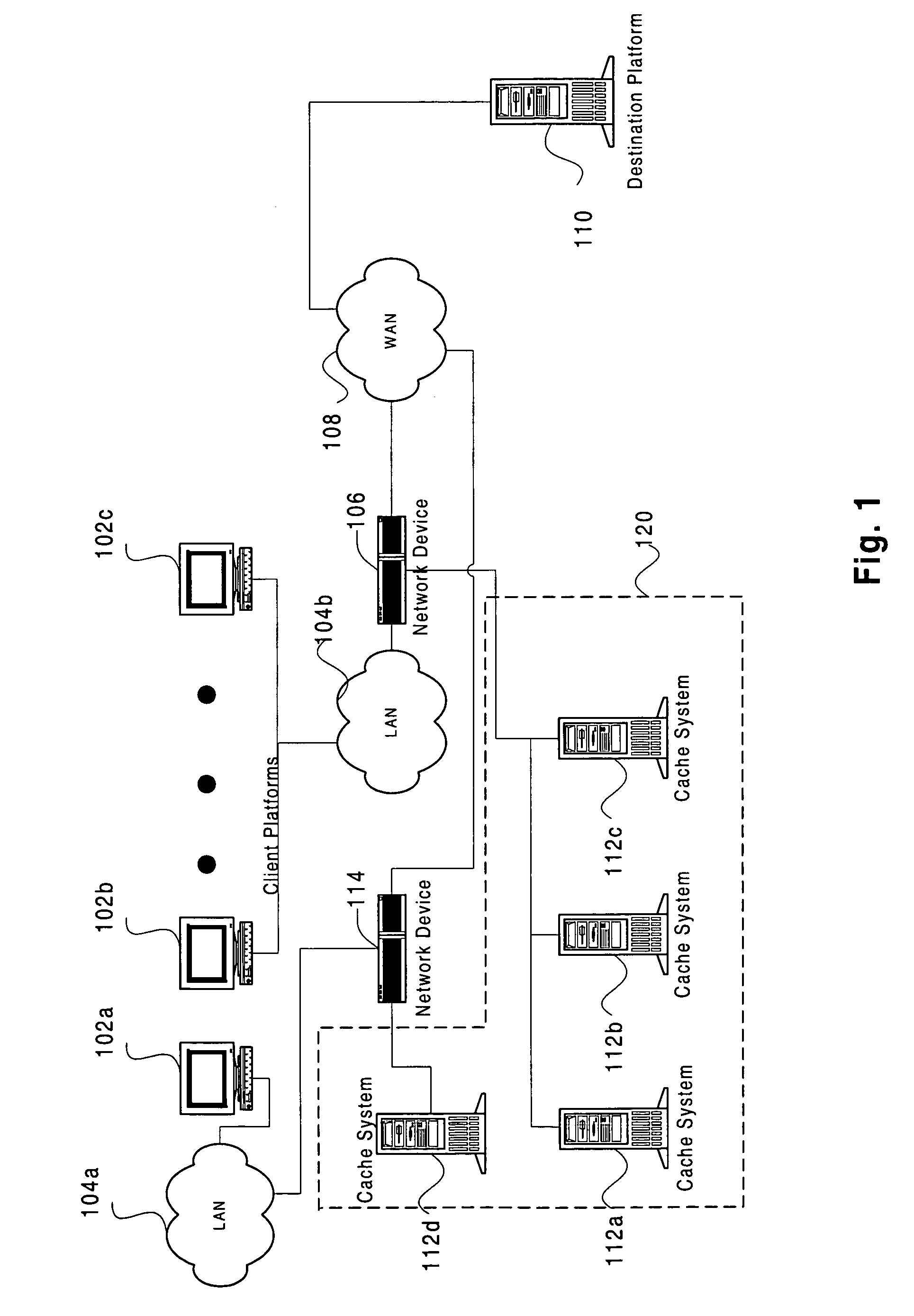
Efficient IP load-balancing traffic distribution using ternary CAMs
InactiveUS7062571B1Digital computer detailsTransmissionTraffic capacityTernary content addressable memory
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for distributing traffic to one or more selected cache systems or servers. In general terms, a content addressable memory (e.g., a TCAM) is utilized to distribute traffic among a plurality of cache systems or servers. The content addressable memory is populated with a plurality of entries. Each entry within the content addressable memory generally indicates an action to be performed on a packet, such as to redirect the packet or to forward the packet to its original destination. When the action indicated by the content addressable memory is to redirect the packet, the content addressable memory also indicates where (e.g., to which cache system) to redirect the packet.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
CAM modified to be used for statistic calculation in network switches and routers
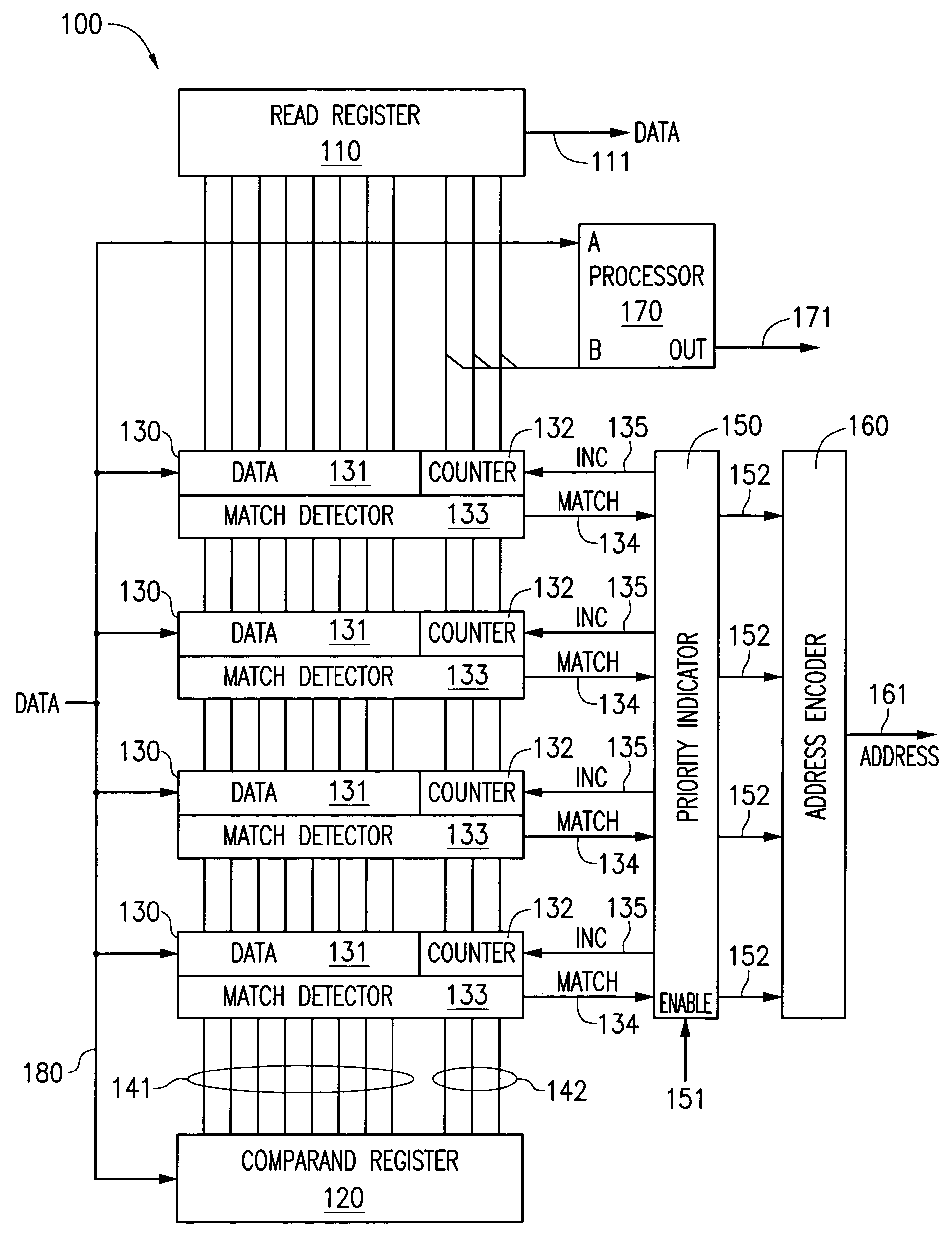
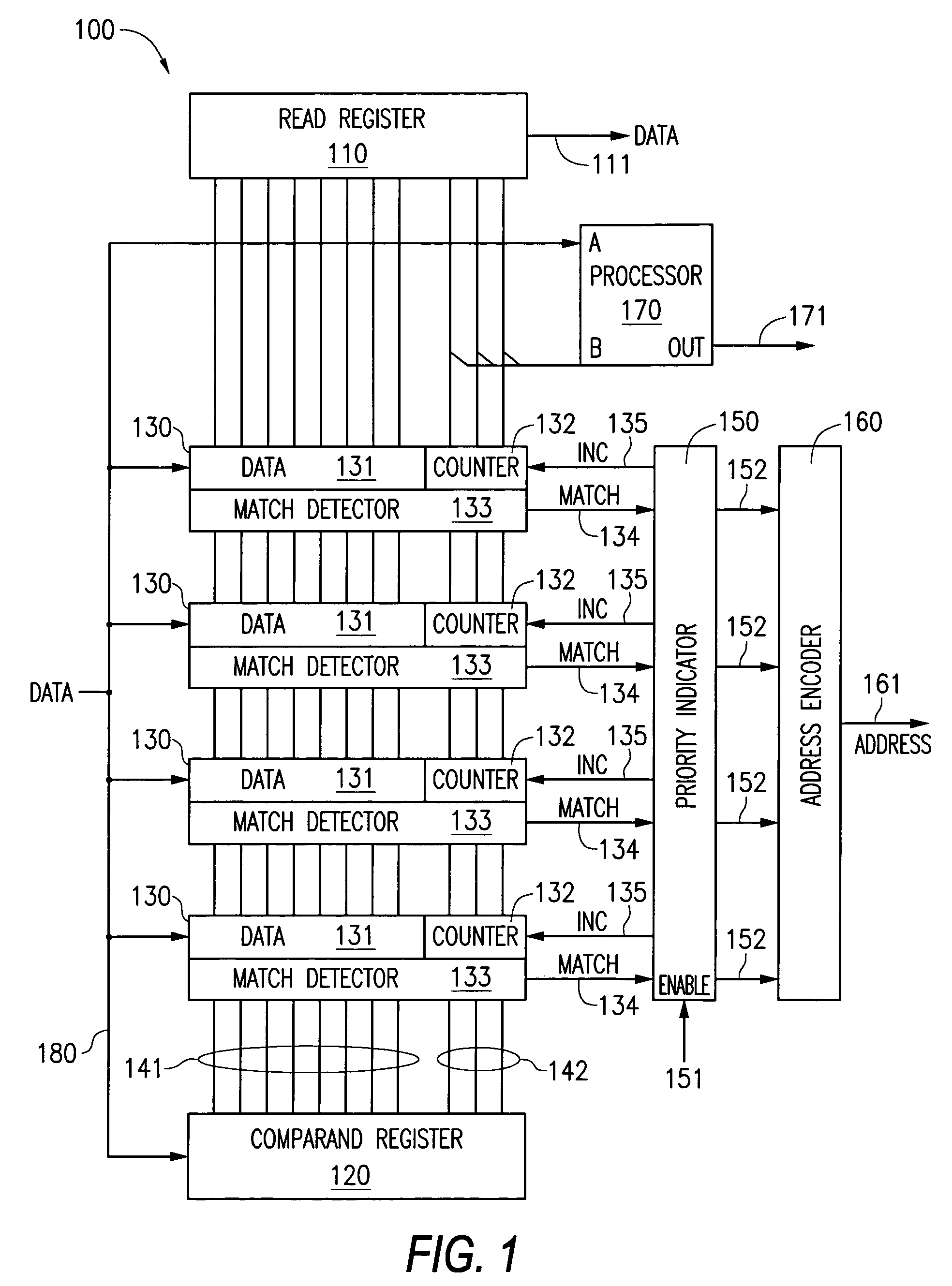
A content addressable memory (CAM) device includes a plurality of entries each having an associated counter. When a CAM entry matches a search word stored in the comparand register of the CAM device, the matching entry's counter may be incremented. Alternatively, if there are multiple matching entries, in some instances only one matching entry has its counter incremented. The counter value can be written or read as part of either the least significant or most significant bits of the CAM entry.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Method and apparatus for span and subspan sorting rendering system
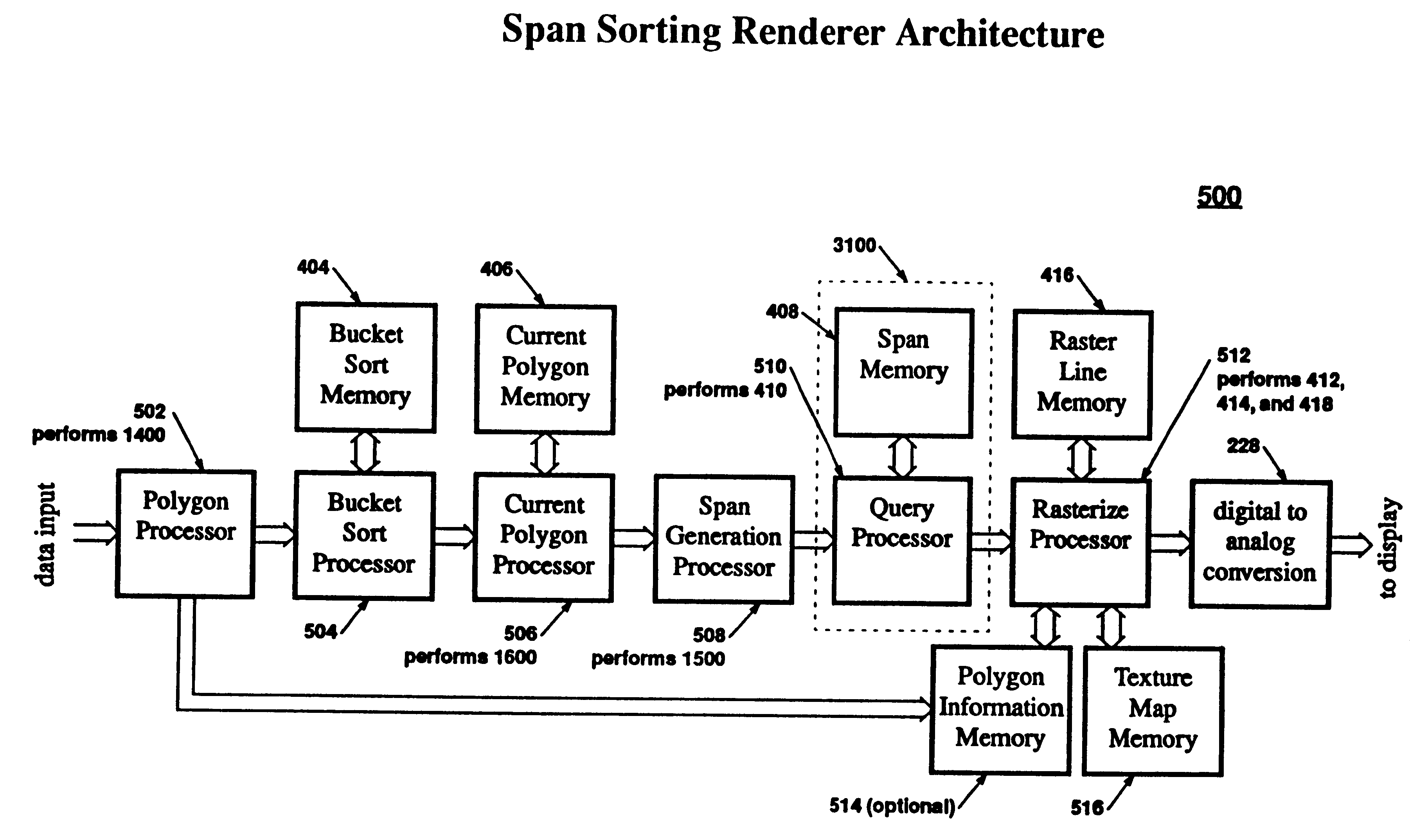
InactiveUS6285378B1Improve compatibilitySimplifies downstream processingDrawing from basic elementsDigital computer detailsGraphicsGrating
A data shifting capability that permits sorting the data in addition to searching for obtaining real-time performance in color, with high quality imagery through a simple search of a spacial database based on a rectangularly shaped search region or range search. A sorting Magnitude Comparison Content Addressable Memory (SMCCAM) performs a range search, introducing a conservative approximation of the idea Occluding Region, and provides a MCCAM wherein the data words stored in the fields are shifted to corresponding fields in an adjacent word, based on the magnitude comparisons. The 3D graphics method stores the parameters of a polygon span in a spatial database and a query operation is performed on the database to determine which of those spans, or portions of spans, are visible, and applies a rule for comparing a new span portion to an old span portion on a subspan-by-subspan basis, thereby providing additional polygon edge information within a raster line, providing anti-aliasing.
Owner:APPLE INC
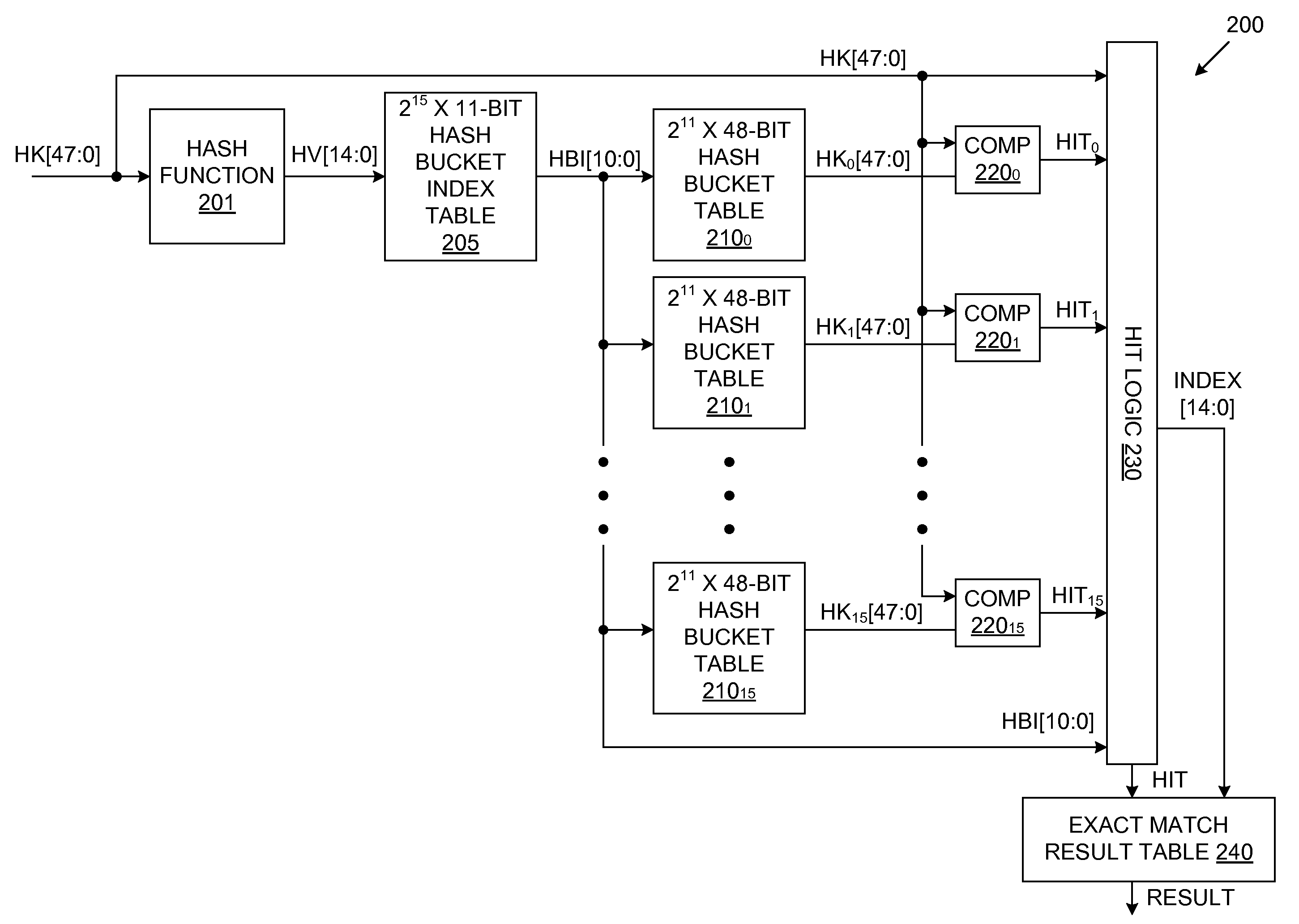
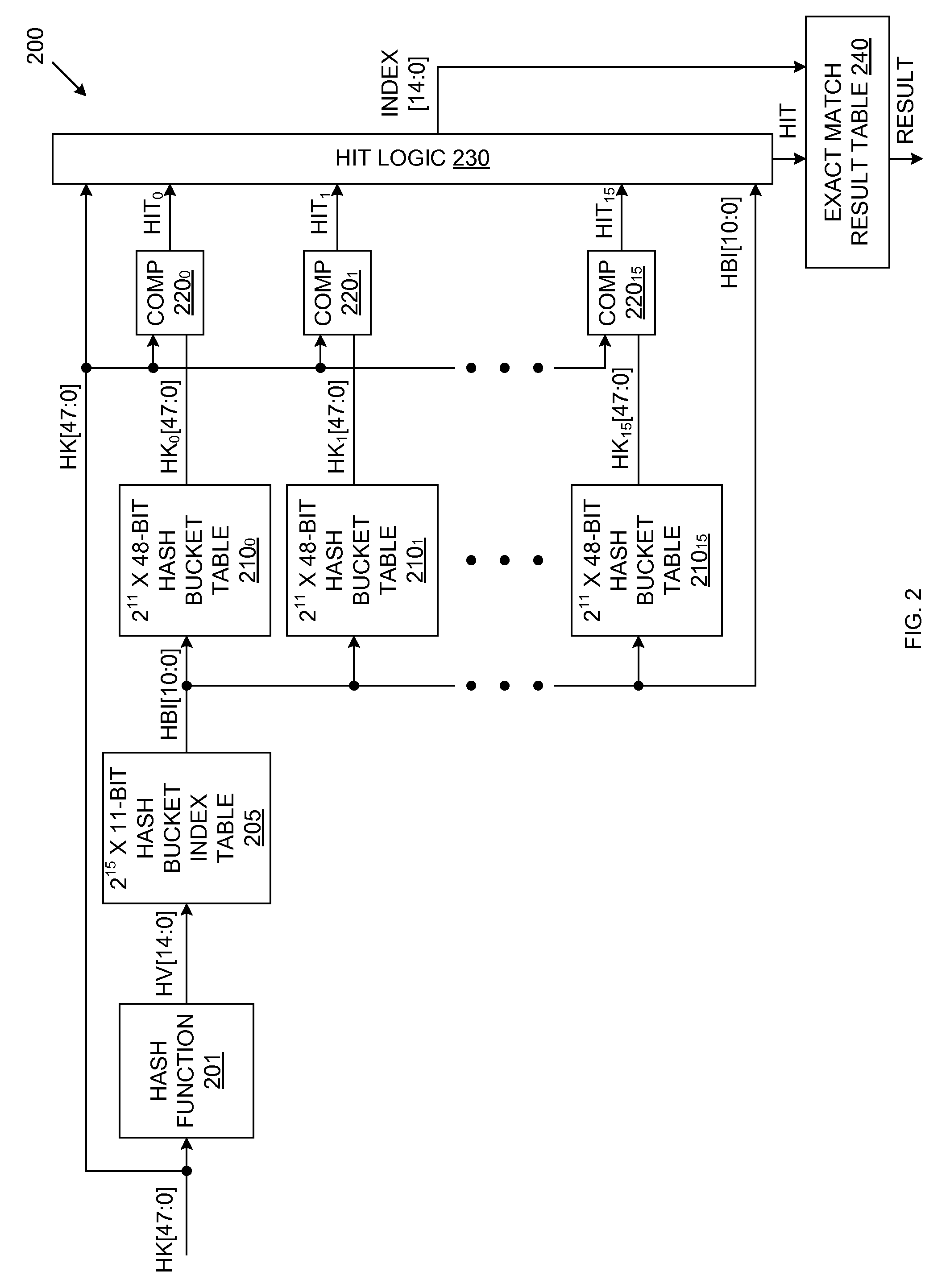
Exact Match Lookup Scheme
InactiveUS20110060876A1Digital data information retrievalData switching networksExact matchHash table
An exact match lookup system includes a hash function that generates a hash value in response to an input hash key. The hash value is used to retrieve a hash bucket index value from a hash bucket index table. The hash bucket index value is used to retrieve a plurality of hash keys from a plurality of hash bucket tables, in parallel. The retrieved hash keys are compared with the input hash key to identify a match. Hit logic generates an output index by concatenating the hash bucket index value with an address associated with the hash bucket table that provides the matching hash key. An exact match result is provided in response to the output index. A content addressable memory (CAM) may store hash keys that do not fit in the hash bucket tables.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
L4 lookup implementation using efficient CAM organization
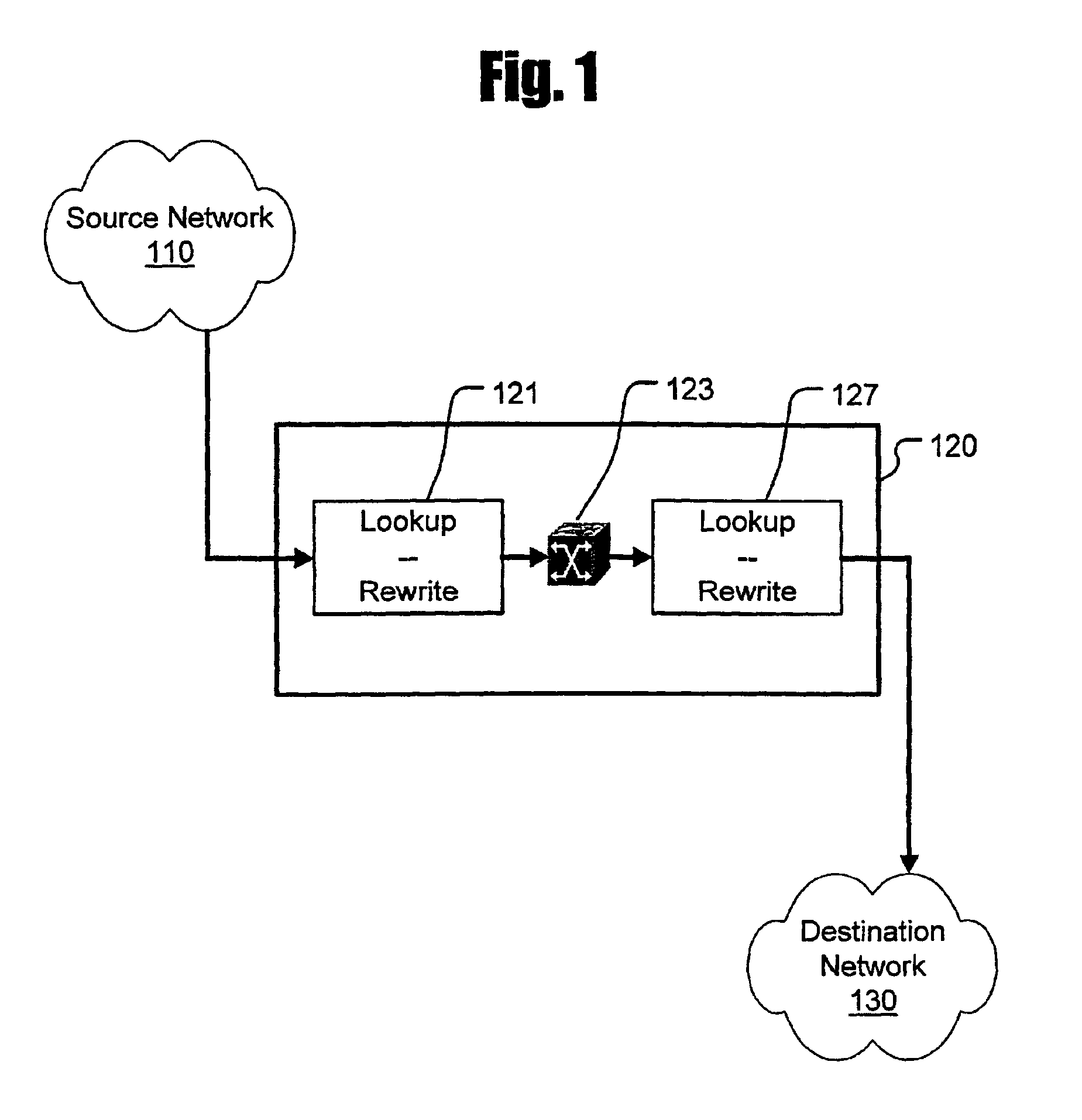
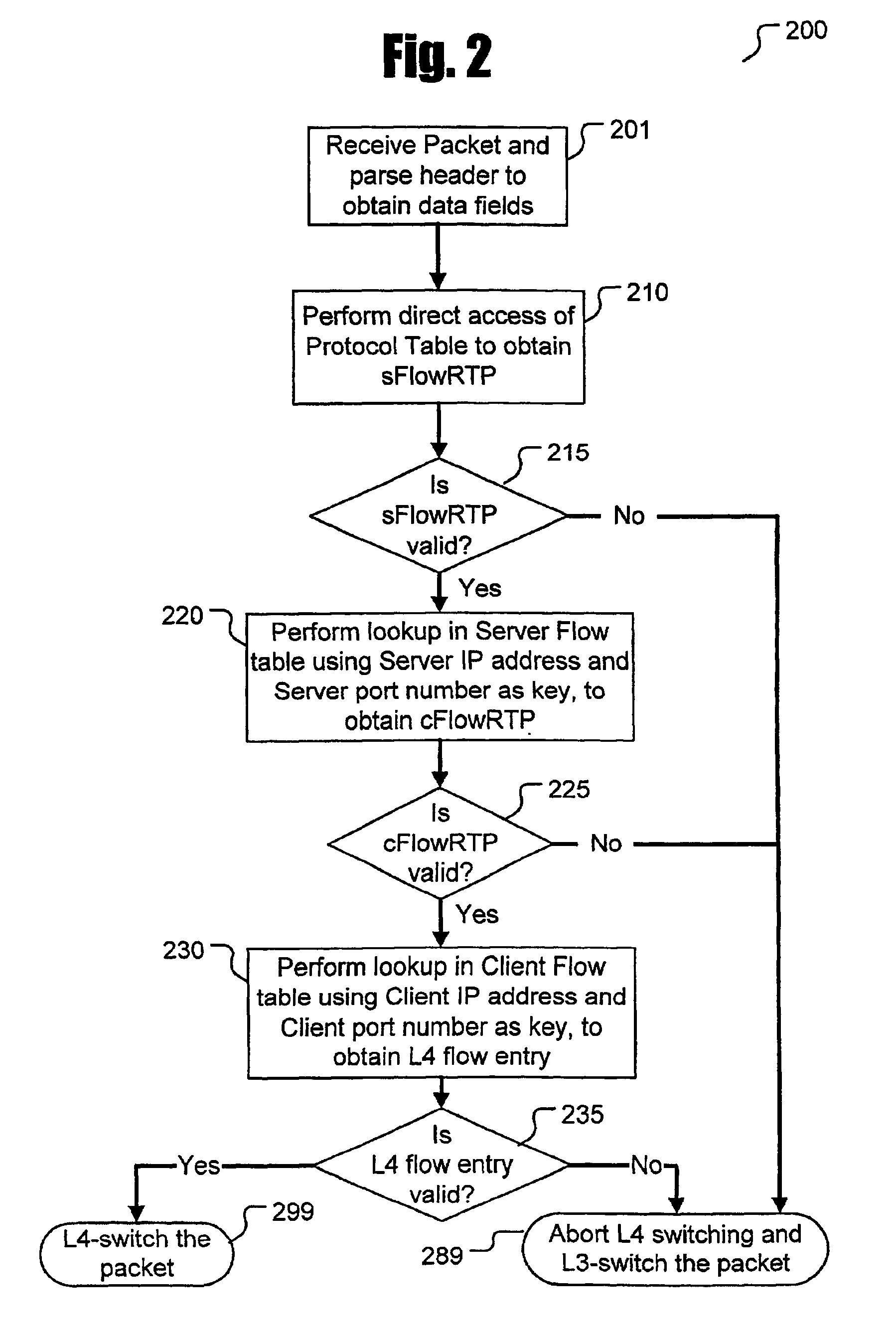
ActiveUS6862281B1Faster and efficient useIncrease speedData switching by path configurationMemory systemsContent-addressable storageTime-division multiplexing
A method of segmenting Layer 4 packet routing lookups into multiple levels for sequential search in multiple tables provided in a specially organized memory device, such as a content addressable memory (CAM). Using a sequence of limited-width keys, a single CAM (or length-cascaded bank of CAMs) can be tuned to provided faster and more efficient use of limited CAM space. Lookups used to process continuous streams of packets (such as those in the Internet Protocol [IP] format) can be performed with the present invention in either one-packet-at-a-time sequential order or in a pipelined fashion. Packet streams arriving on multiple ports of the switch device can also take advantage of time division multiplexing to employ a single search engine embodying the present invention.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
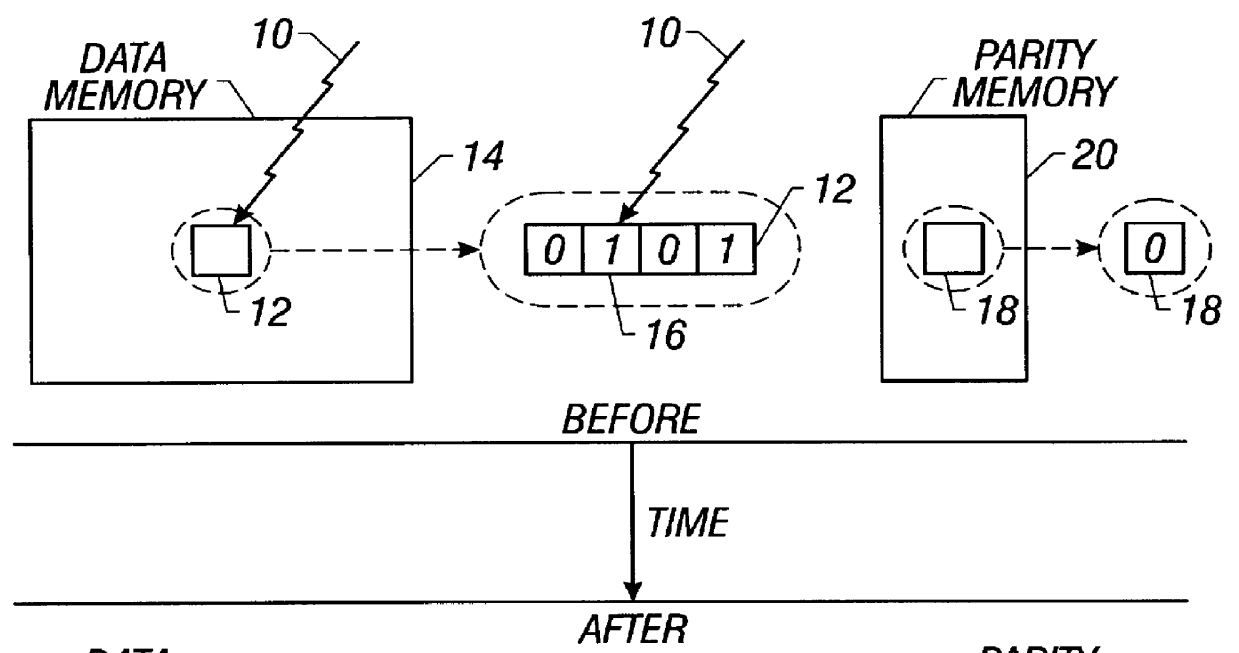
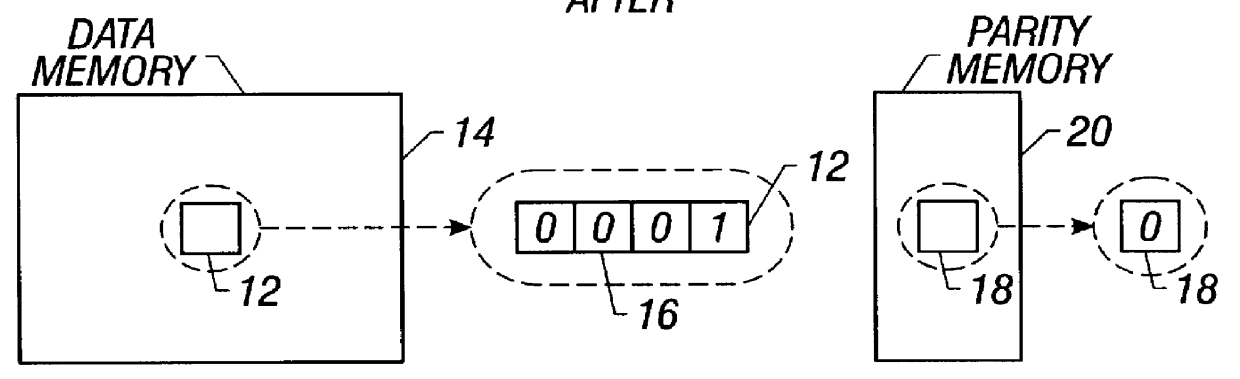
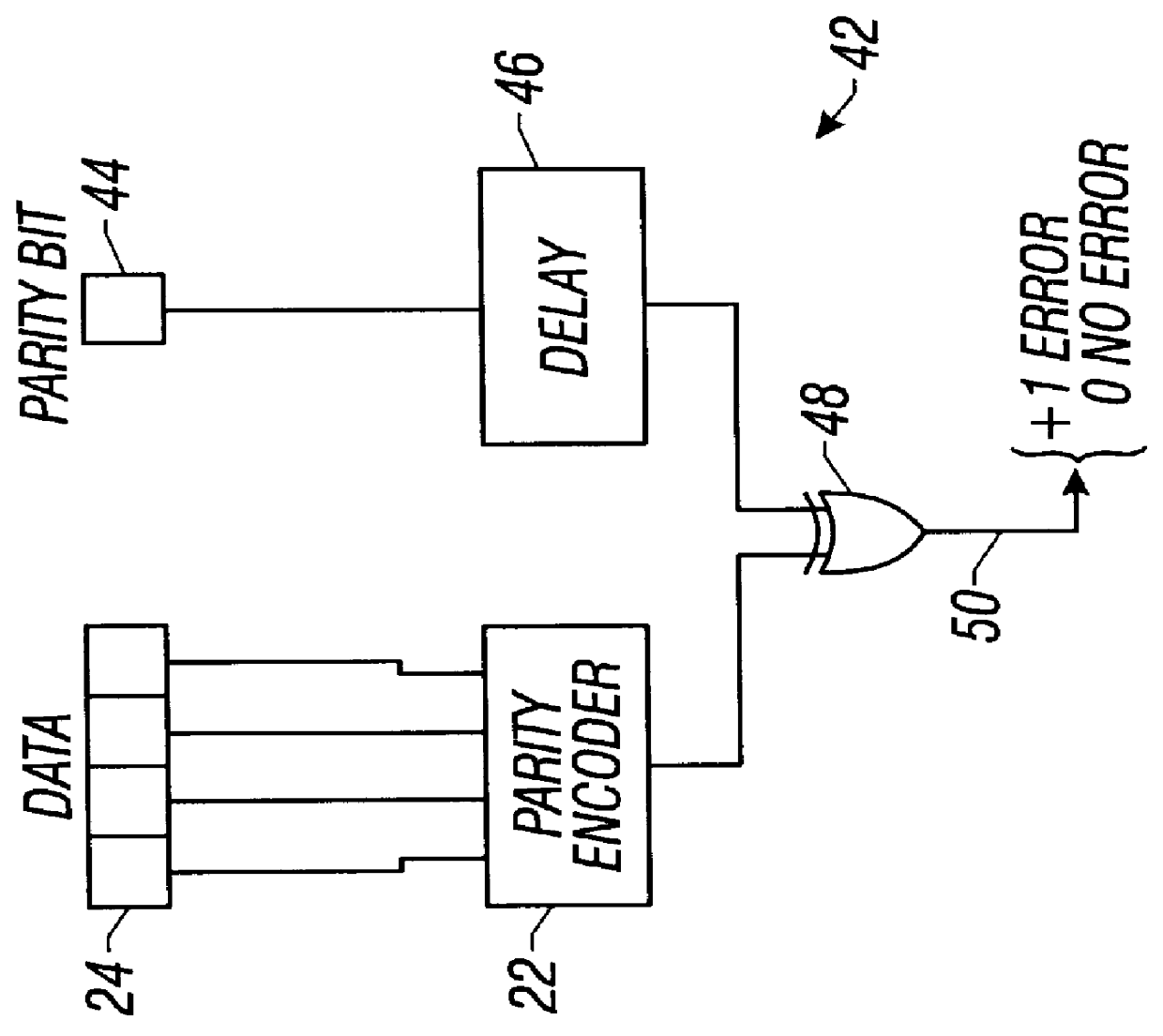
Method and apparatus for detecting soft errors in content addressable memory arrays
The invention comprises, in one aspect, a content addressable memory array having a plurality of memory locations to store tag words. The content addressable memory array includes a parity encoder and a parity comparator. The parity encoder has a first input terminal to receive an input data signal and a first output terminal to deliver a signal representative of the parity of the input data signal. The parity comparator has a second input terminal, a third input terminal connected to the first output terminal, and a plurality of memory cells to store original parities of the tag words. The parity comparator compares the original parity of a first tag word to the parity of the input data signal in response to a receiving a match signal. The content addressable memory array includes a fourth input terminal to receive the input data signal, and a second output terminal to send the match signal in response to one of the tag words matching the input data signal. The second output terminal connects to the second input terminal.
Owner:INTEL CORP
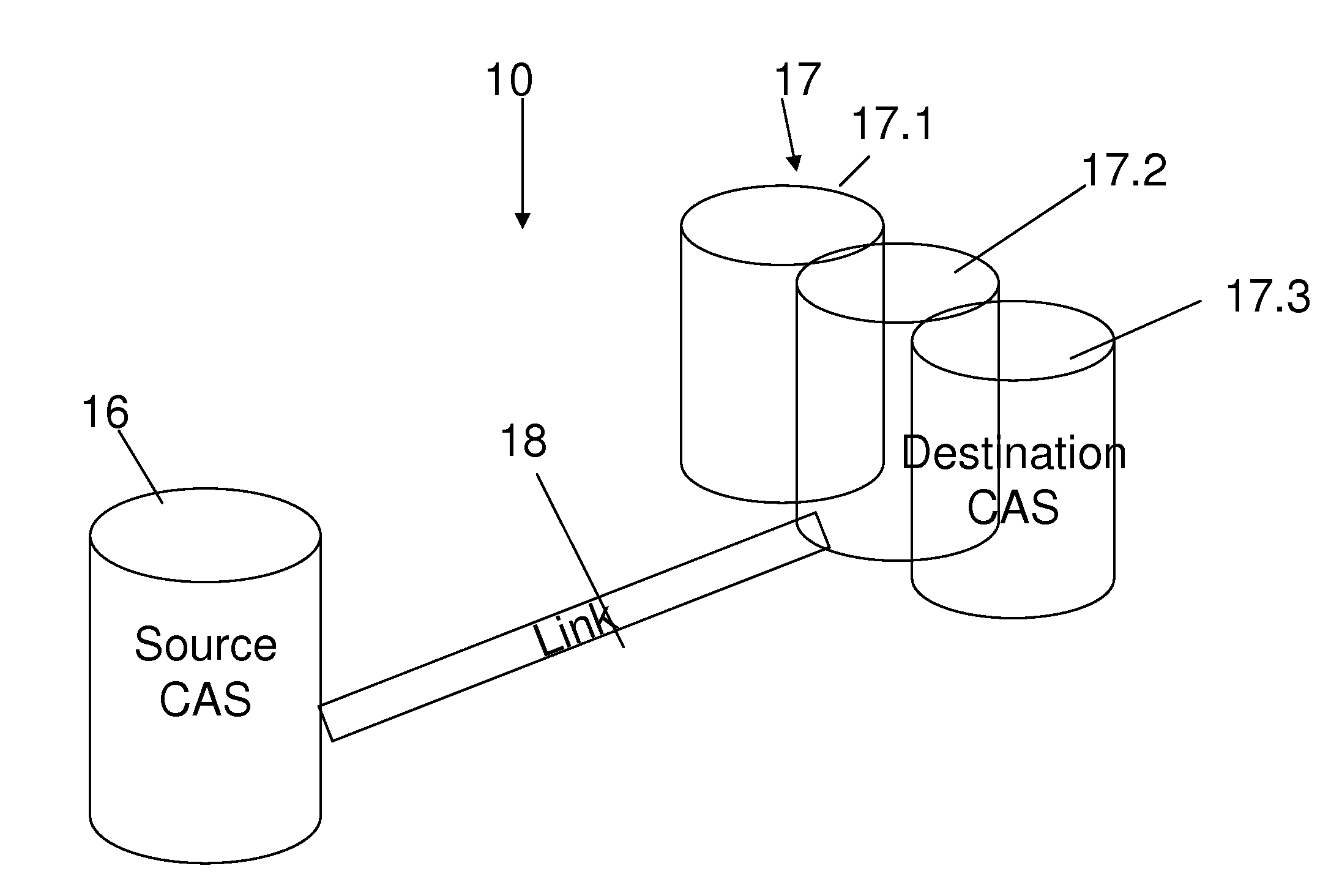
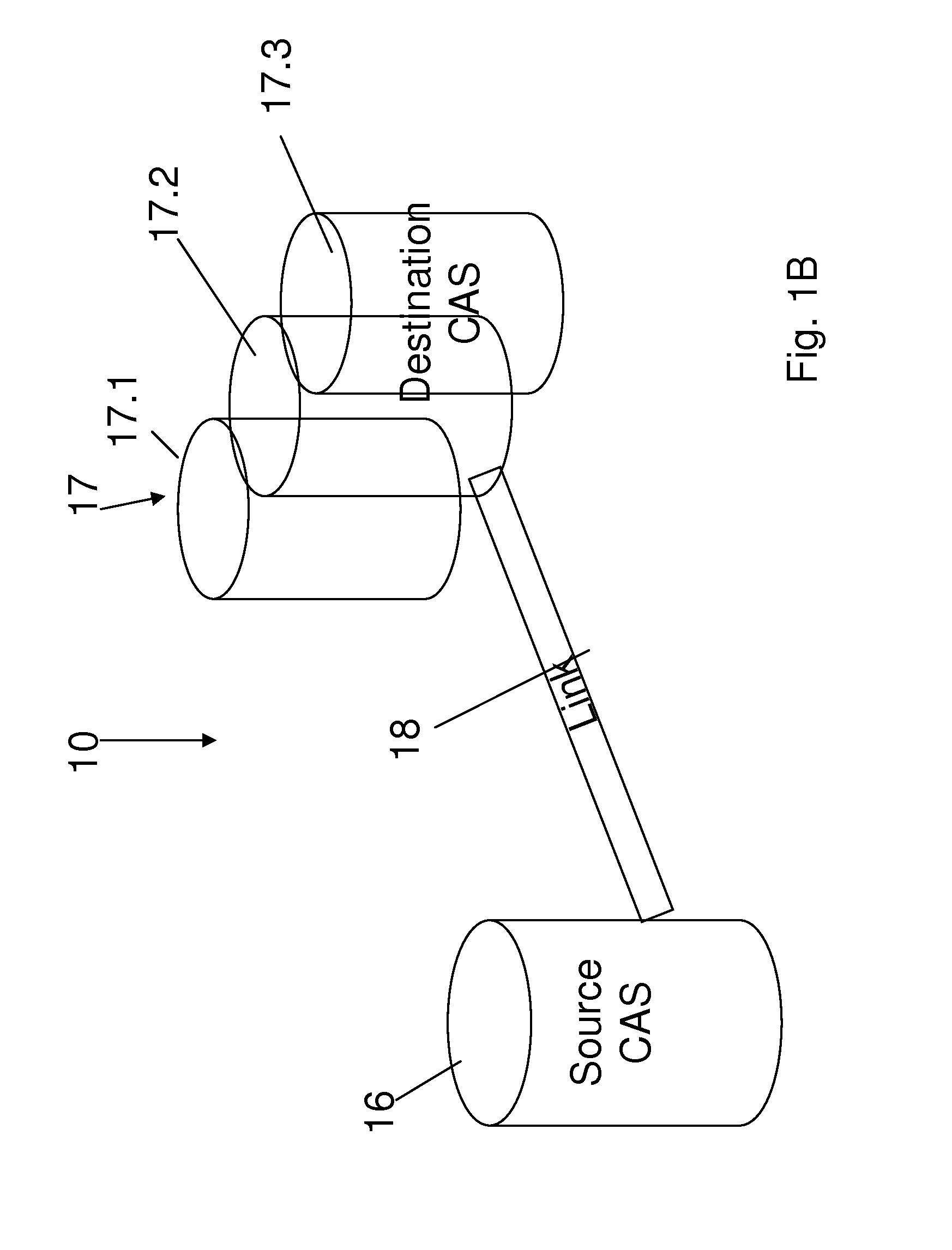
Replication techniques with content addressable storage
ActiveUS20120317353A1Memory systemsInput/output processes for data processingComputer hardwareContent-addressable storage
A CAS data storage system with one or more source CAS data storage spaces and one or more destination CAS data storage spaces, and a communication line therebetween, receives input data at the source storage space for local storage and for replication to the destination CAS storage space. CAS metadata is used in the replication procedure between the two separate CAS storage spaces. Thus, data at the source storage space is used to form an active buffer for transfer to the destination storage space, the active buffer holding a hash result of the respective data item and a storage address. The system detects whenever there is more than one data item in said active buffer sharing a same storage address and upon such detection transfers a respective hash result of only the last of the data items.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
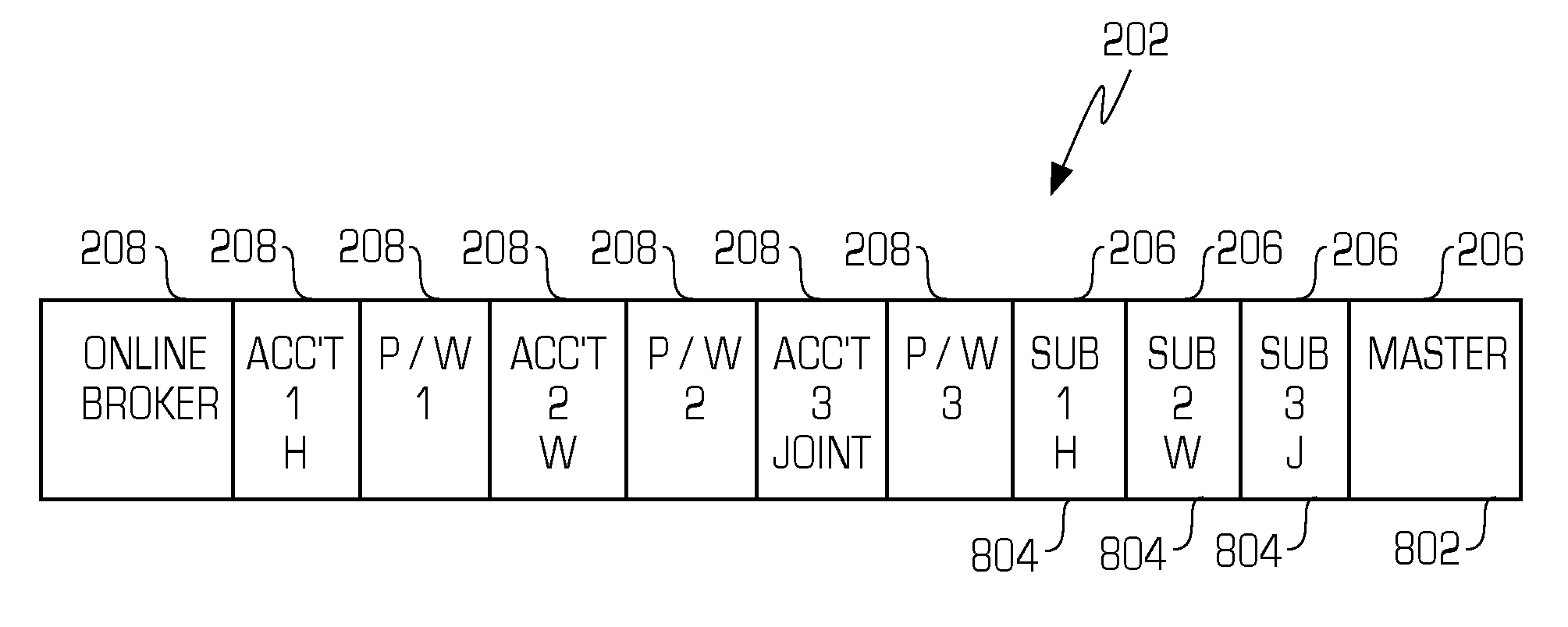
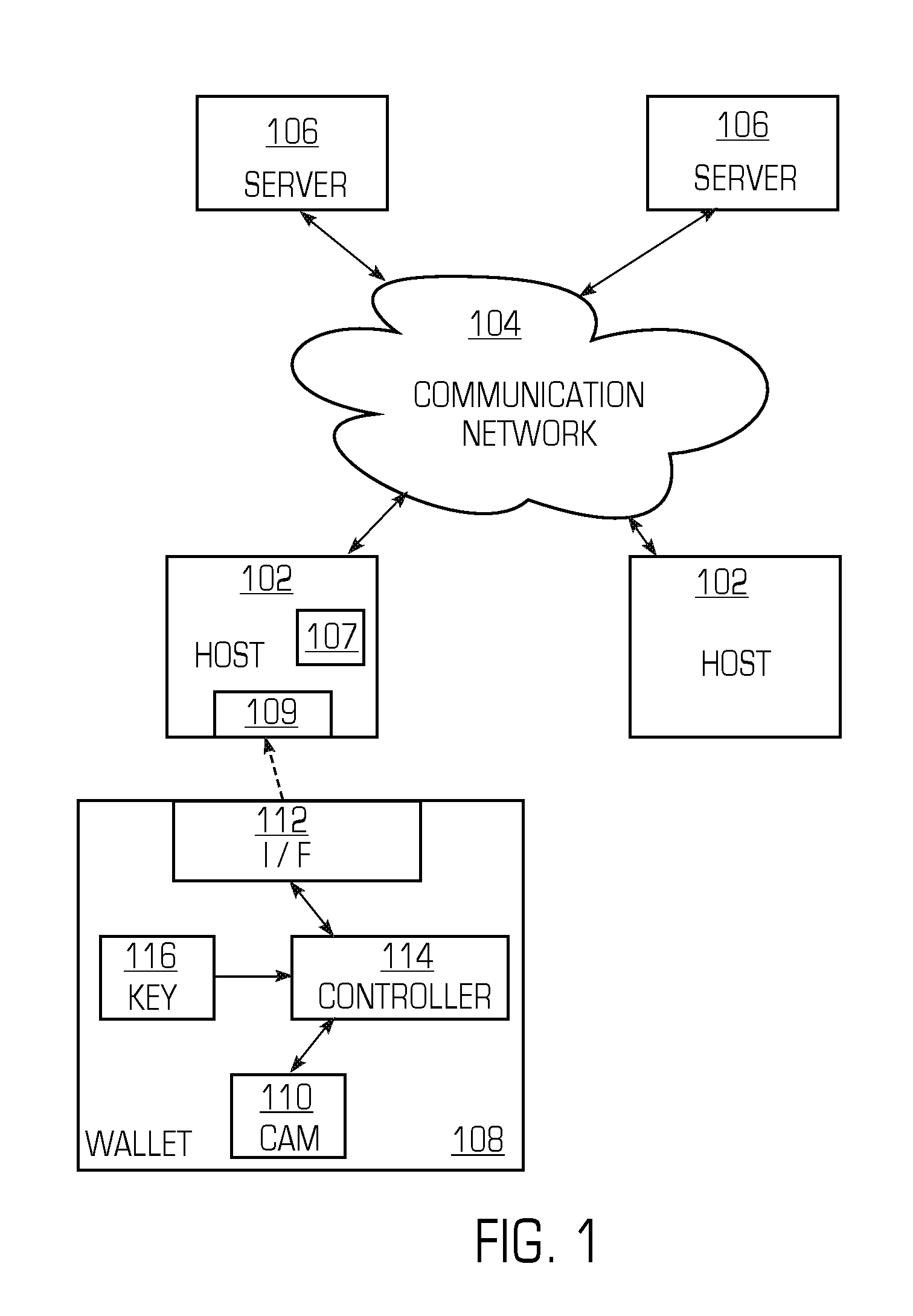
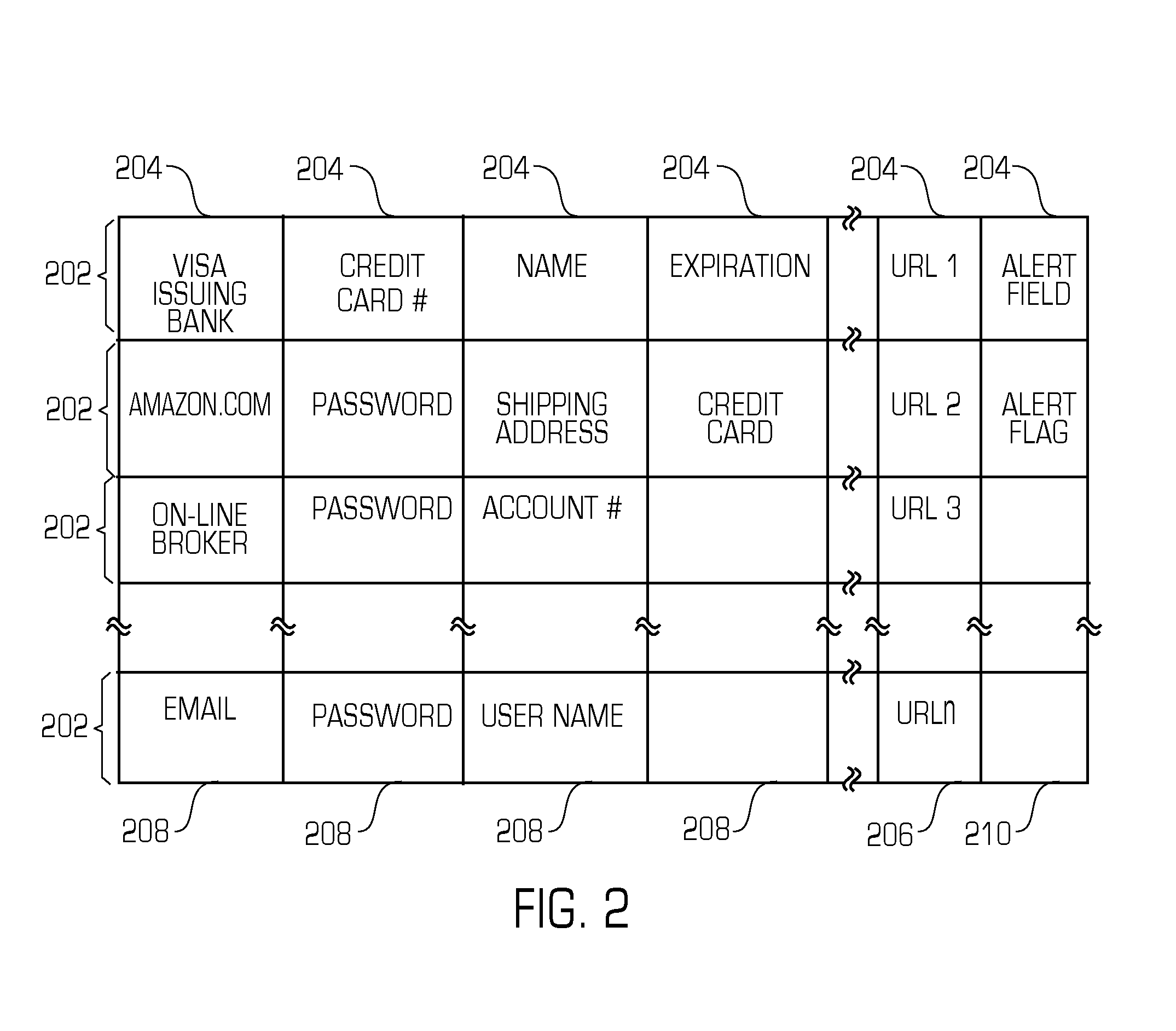
Smart memory card wallet
InactiveUS7533063B2Coded identity card or credit card actuationProtocol authorisationUser inputPassword
A system includes at least one server and at least one host computer coupled to a communication network. A memory card wallet includes a content addressable memory that stores server identifiers, such as URLs, and user information associated with the resource provider, such as user identification numbers and passwords. The user inserts the memory card wallet into the host computer, and instead of entering user identifiers and passwords, the memory card wallet can provide such information to the server. When the user enters a server identifier that matches a server identifier stored in the content addressable memory, the memory card wallet provides the user information associated with the matched sever identifier.
Owner:SILICON STORAGE TECHNOLOGY
Content Addressable Memory Device Having Electrically Floating Body Transistor
A content addressable memory cell includes a first floating body transistor and a second floating body transistor. The first floating body transistor and the second floating body transistor are electrically connected in series through a common node. The first floating body transistor and the second floating body transistor store complementary data.
Owner:LAW OFFICE OF ALAN W CANNON +1
System and method for ecmp load sharing
A packet classifier and a method for routing a data packet are provided. The packet classifier includes a content addressable memory, a translation table and a parameter memory. The method includes looking up a content addressable memory for a base address into a parameter memory using a header of the data packet. The base address is related to the routes under ECMP for forwarding the data packet. From among these addresses, using multiple headers of the data packet, an adjustment to the base address is computed. The adjustment specifies an actual address to the parameter memory corresponding to a selected route for forwarding the data packet. The parameter memory is then accessed using the actual address to obtain parameter values relevant to the selected route. The data packet is then forwarded according to the parameter values thus obtained.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
Content addressable memory system with cascaded memories and self timed signals
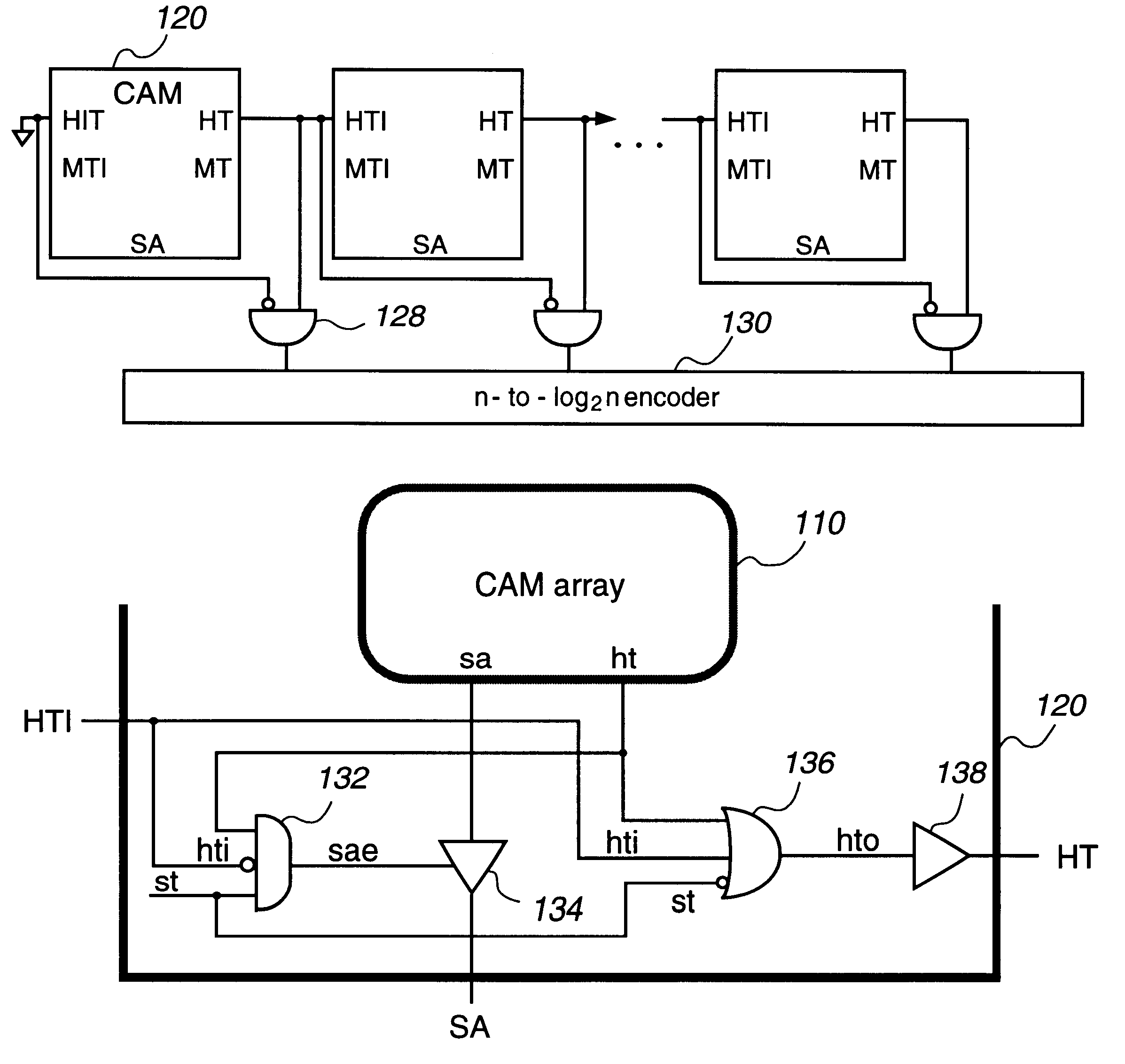
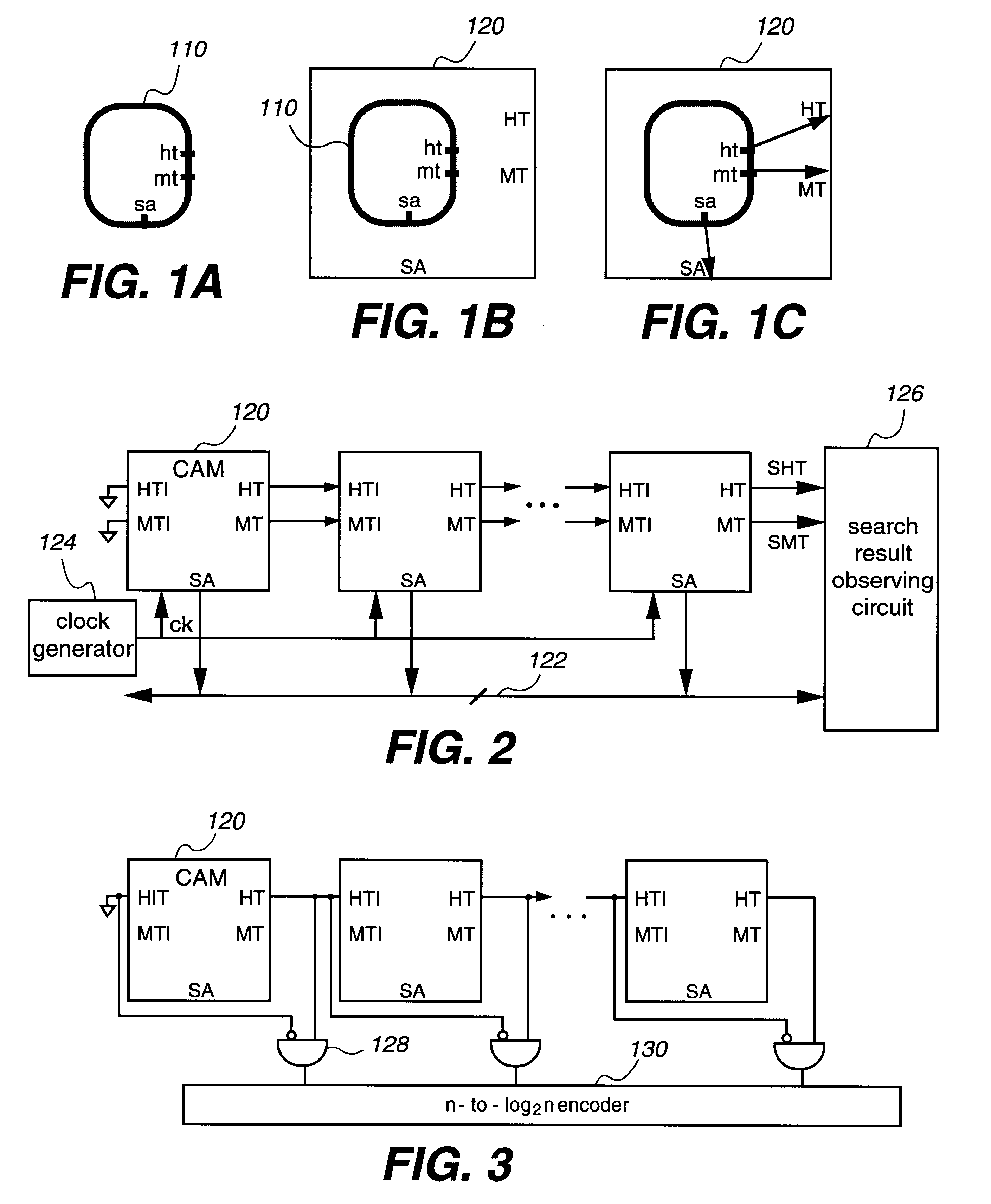
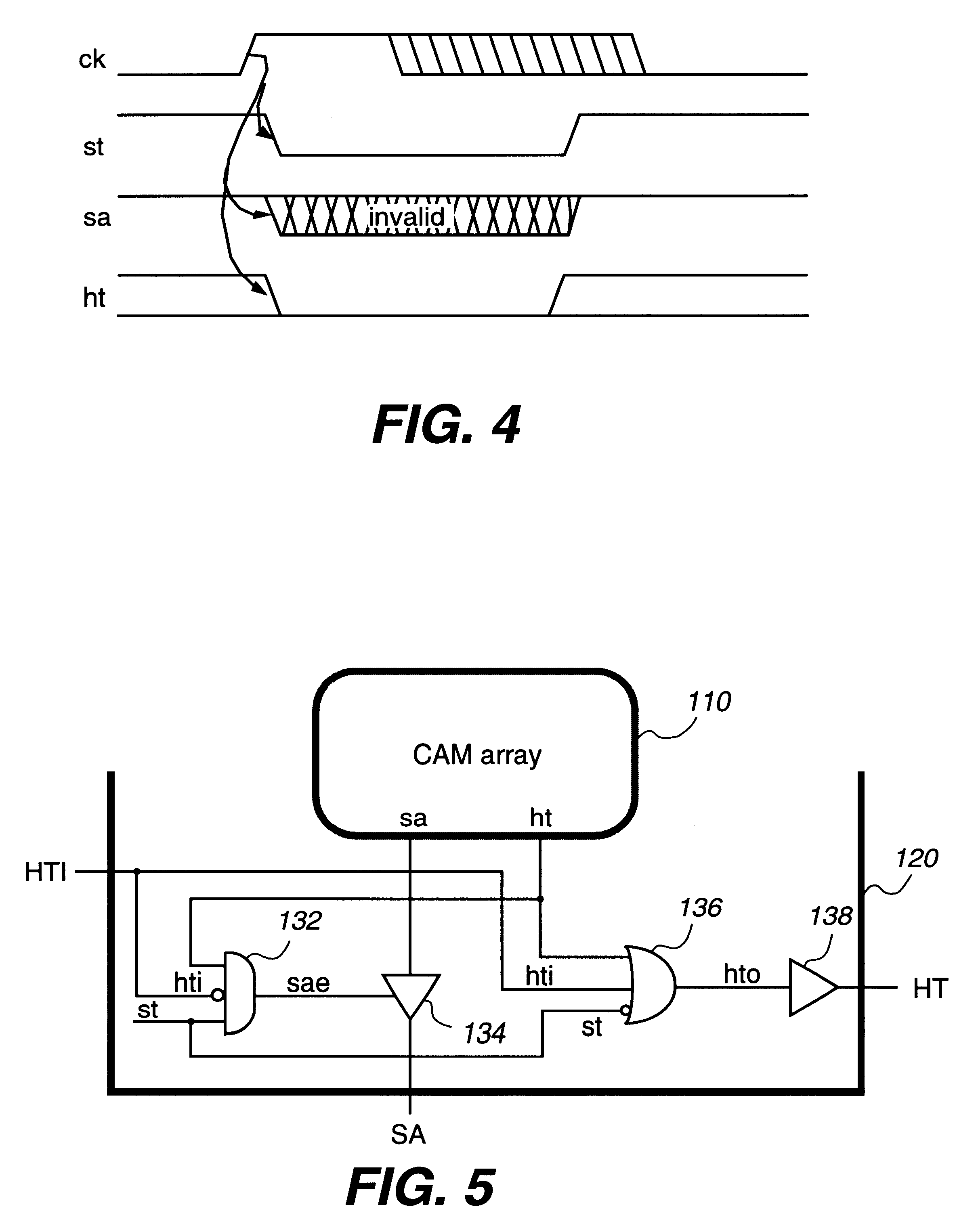
InactiveUS6301636B1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageHemt circuitsSignal generator
A system includes cascaded content addressable memory (CAM) chips connected to a common bus. Each CAM chip includes a CAM array, a self-timed signal generator and hit propagation and match address transfer circuits. Each CAM array including an array of core cells provides, through its encoder, hit and match address signals resulting from a search operation in response to a clock signal. Each match address transfer circuit transfers the match address signal to the common bus, in response to a self-timed signal, the hit signal and a propagation-in hit signal provided from an upstream CAM chip, so that more than one CAM chip is prevented from providing the match address signal to the common bus simultaneously. Each hit propagation circuit provides a propagation-out hit signal to a downstream CAM chip, in response to the self-timed signal, the hit signal and the propagation-in hit signal from the upstream CAM chip, so that a hit signal is propagated from an upstream CAM chip to a downstream CAM chip. Each CAM chip may include an extra row for providing a modelmiss signal or a modelhit signal which is used for a generating self-timed signal. Each word may be divided into two halves and two match lines of the two halves are coupled by a logic circuit. The system may also observe a multiple match status and the highest priority chip indicating a match.
Owner:FOOTHILLS IP LLC +1
Packet classification
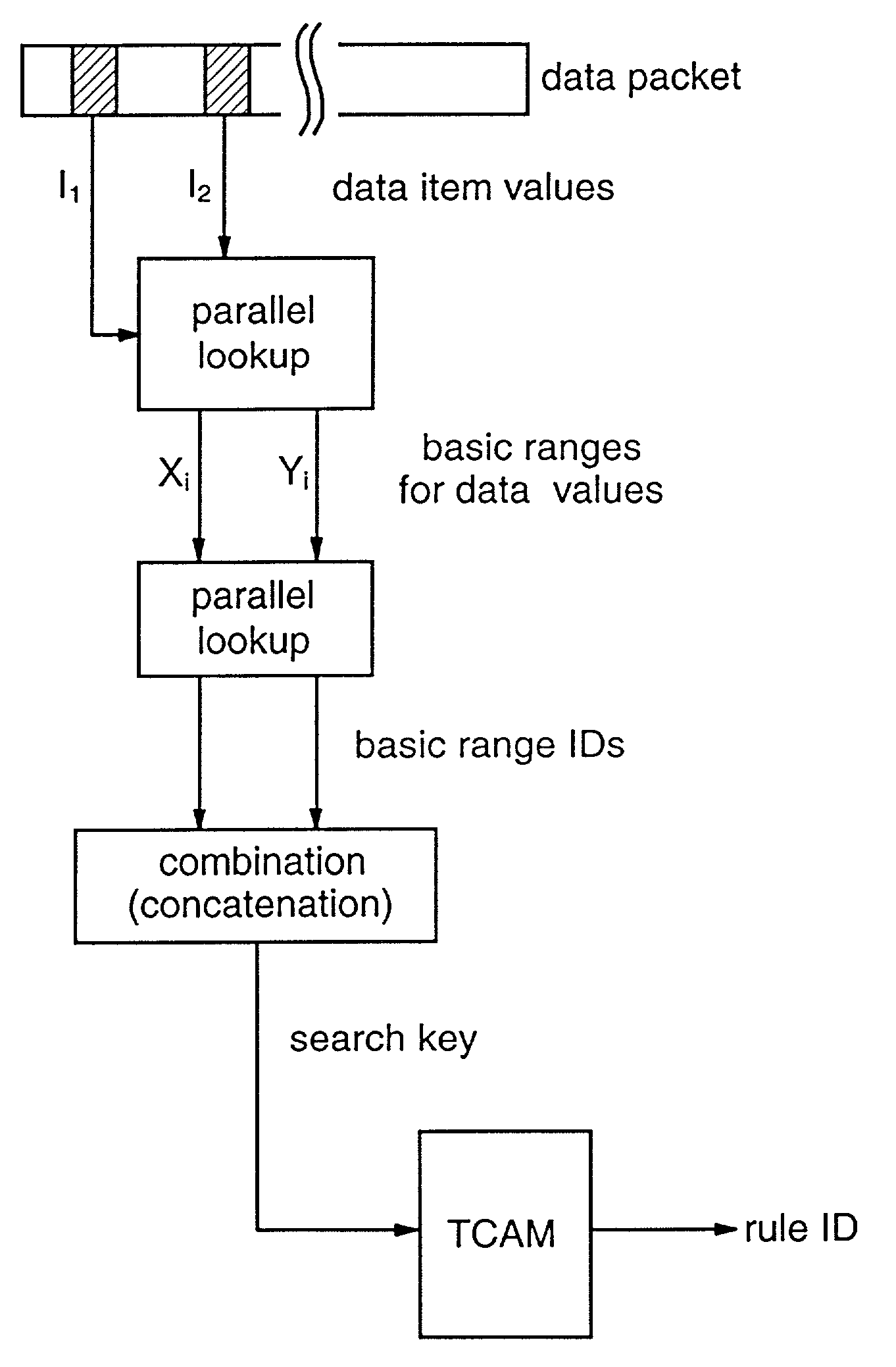
InactiveUS7193997B2Efficient use ofEffective structureData switching by path configurationSecuring communicationData processing systemClassification methods
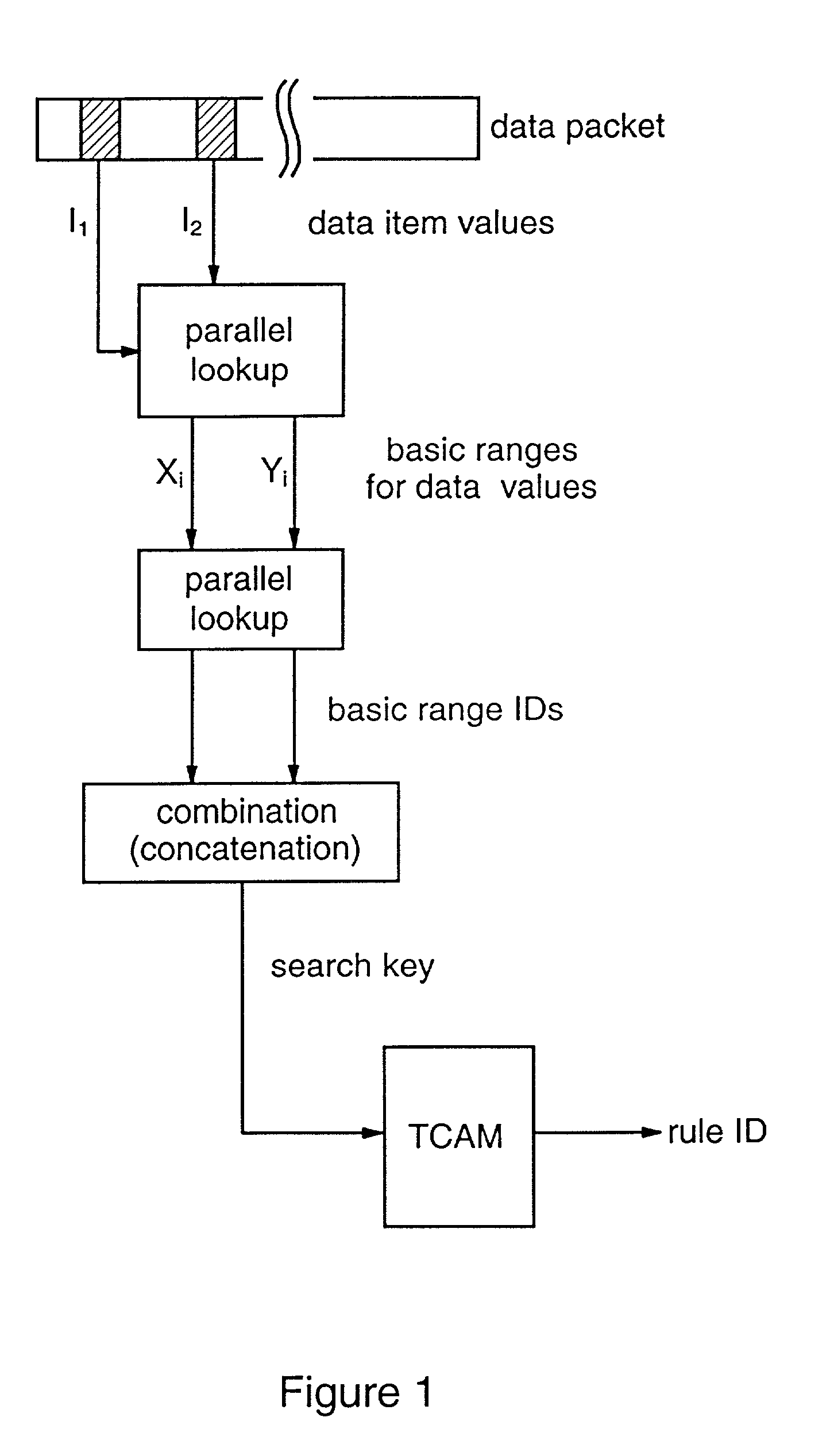
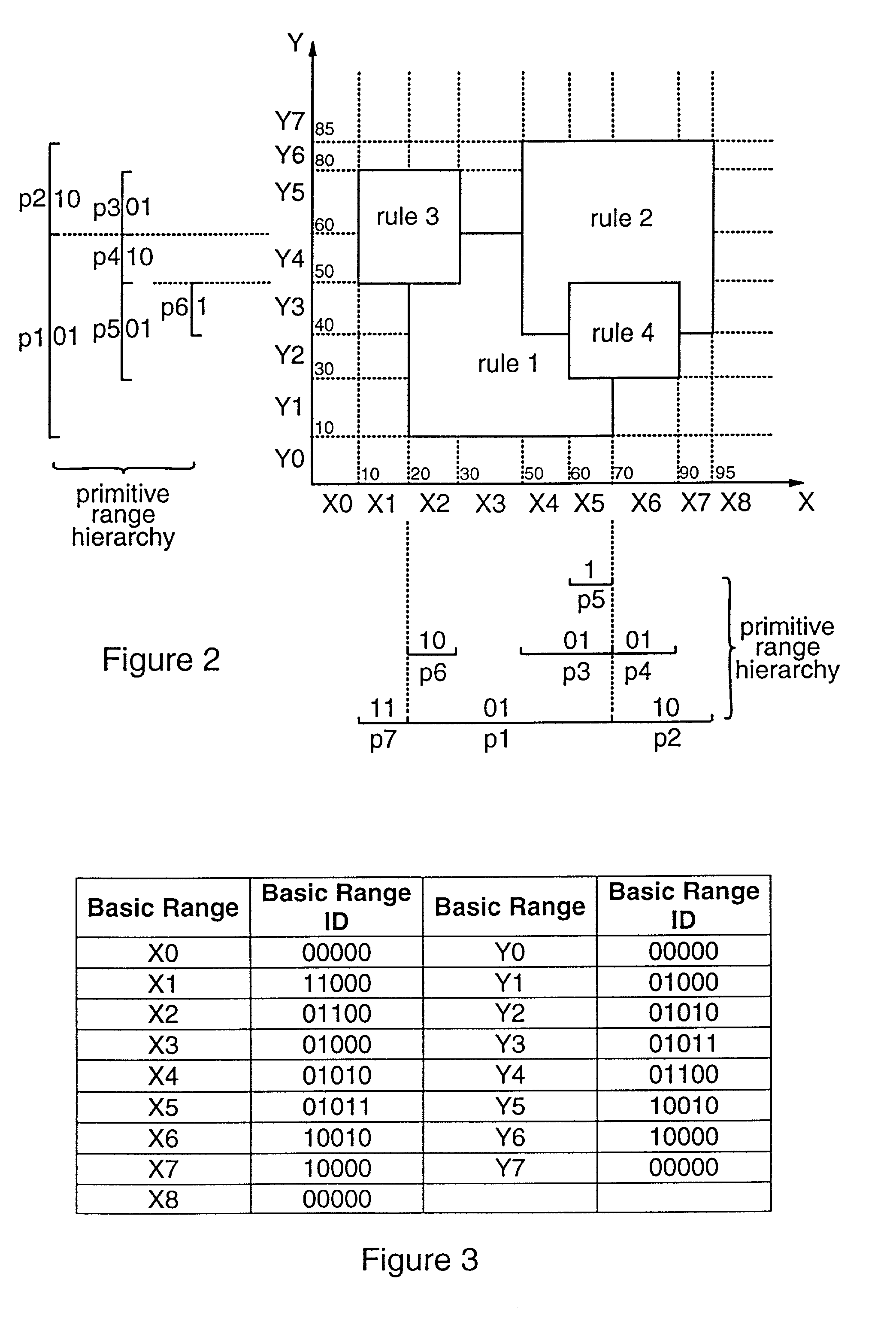
Methods and apparatus are provided for classifying data packets in data processing systems. A first packet classification method determines which of a plurality of predefined processing rules applies to a data packet, where each rule is associated with a range of possible data values in each of a plurality of dimensions (X,Y) corresponding to respective data items in the packet format. For each dimension (X,Y), it is determined which of a set of predefined basic ranges contains the corresponding data value (I1, I2) from the packet, where the basic ranges correspond to respective non-overlapping value ranges between successive rule range boundaries in the dimension. For the basic range so determined for each dimension, a corresponding basic range identifier is selected from a set of predefined basic range identifiers corresponding to respective basic ranges in that dimension. For each of at least two dimensions (X,Y), the basic range identifiers comprise respective pD-bit strings generated independently for that dimension by a process of deriving a primitive range hierarchy based on the rule ranges in that dimension. The resulting basic range identifiers, one for each dimension, are then combined to produce a search key which is supplied to a ternary content-addressable memory (5). In the memory (5), the search key is compared with a set of ternary rule vectors, each associated with a particular rule and derived for that rule from the aforementioned hierarchies, to identify at least one rule which applies to the data packet. A second method classifies data packets according to the values in respective data packets of a single, predetermined data item (DA) in the data packet format, where a plurality of classification results are predefined for respective ranges of values of the data item (DA). Here the data item (DA) in the packet is first segmented. The resulting segments are then equated to different dimensions (X,Y) of a multidimensional packet classification problem and are processed in a similar manner to identify a classification result for the packet.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for content addressable storage
ActiveUS7747663B2Effectively storing informationEfficient storageDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsClient-sideFile server
Information, such as files received from a client, etc., is stored in a storage system, such as a content addressable storage system. A file server receives data from a client and chunks the data into blocks of data. The file server also generates metadata for use in forming a data structure. The blocks of data are stored in a block store and a copy of the data blocks and the metadata are locally cached at the file server. A commit server retrieves the metadata. In at least one embodiment, the metadata is retrieved from an update log shared between the file server and the commit server. Based on the retrieved metadata, the commit server generates a version of a data structure. The data structure is then stored at the block store.
Owner:NEC ASIA PACIFIC PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com