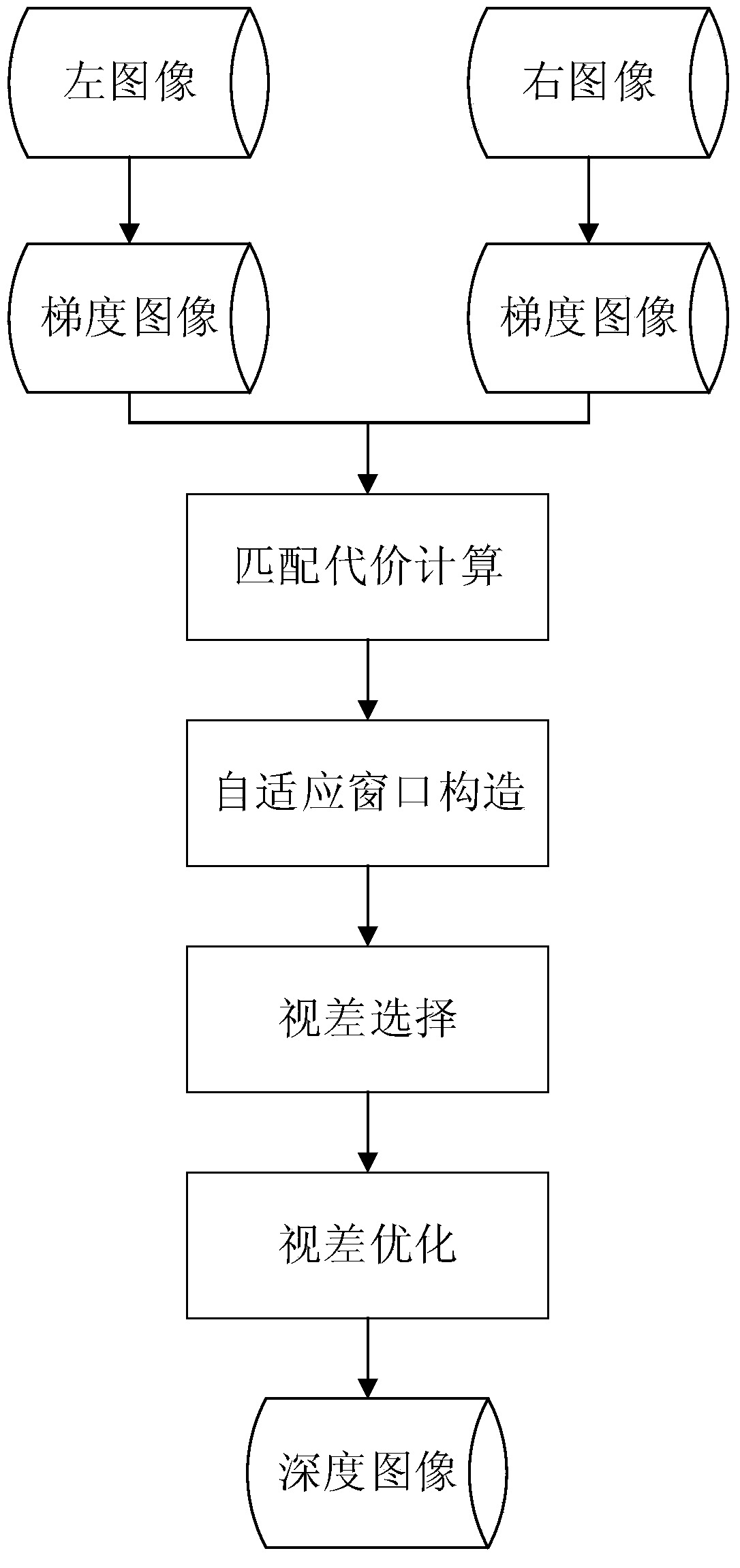
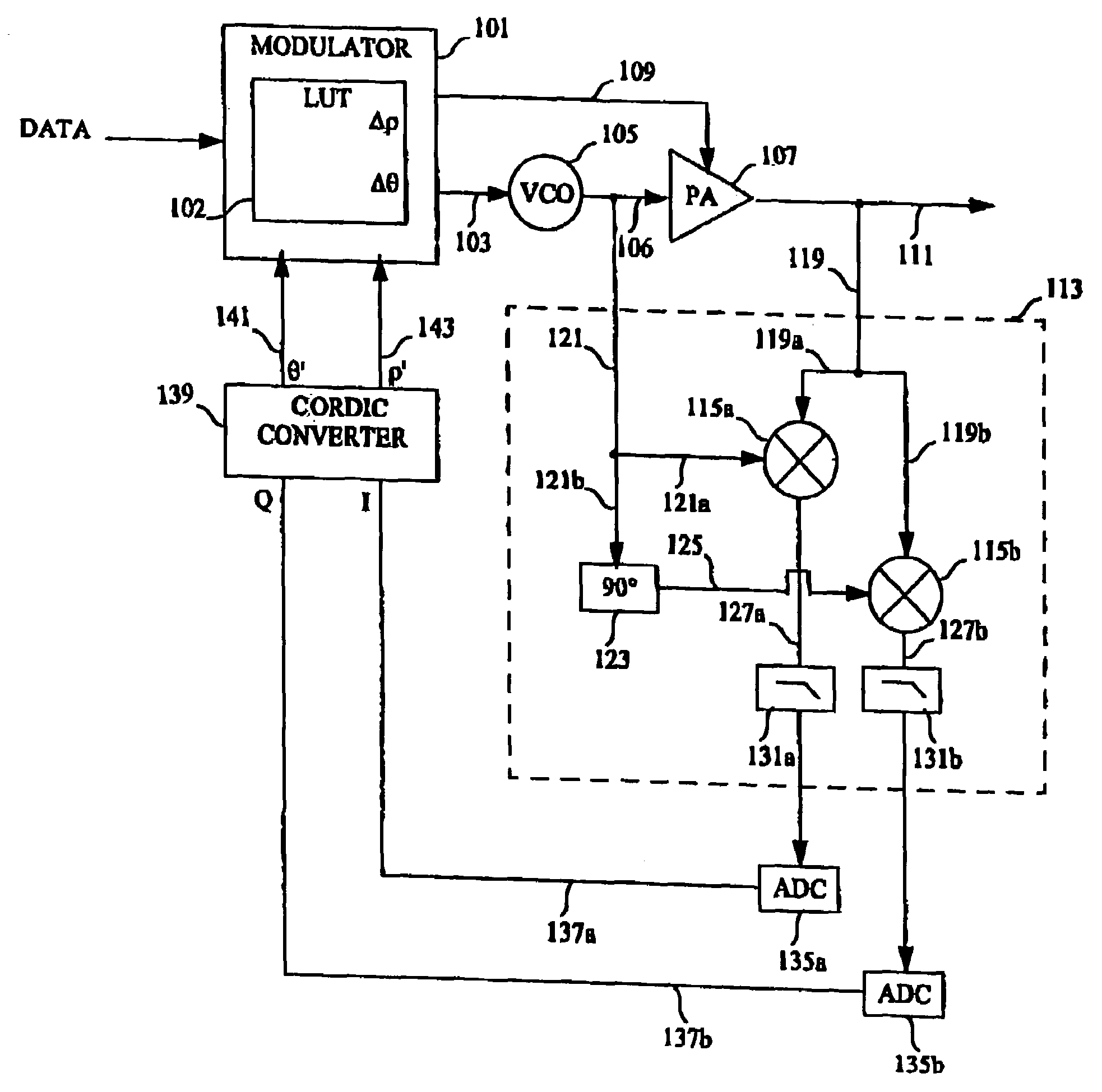
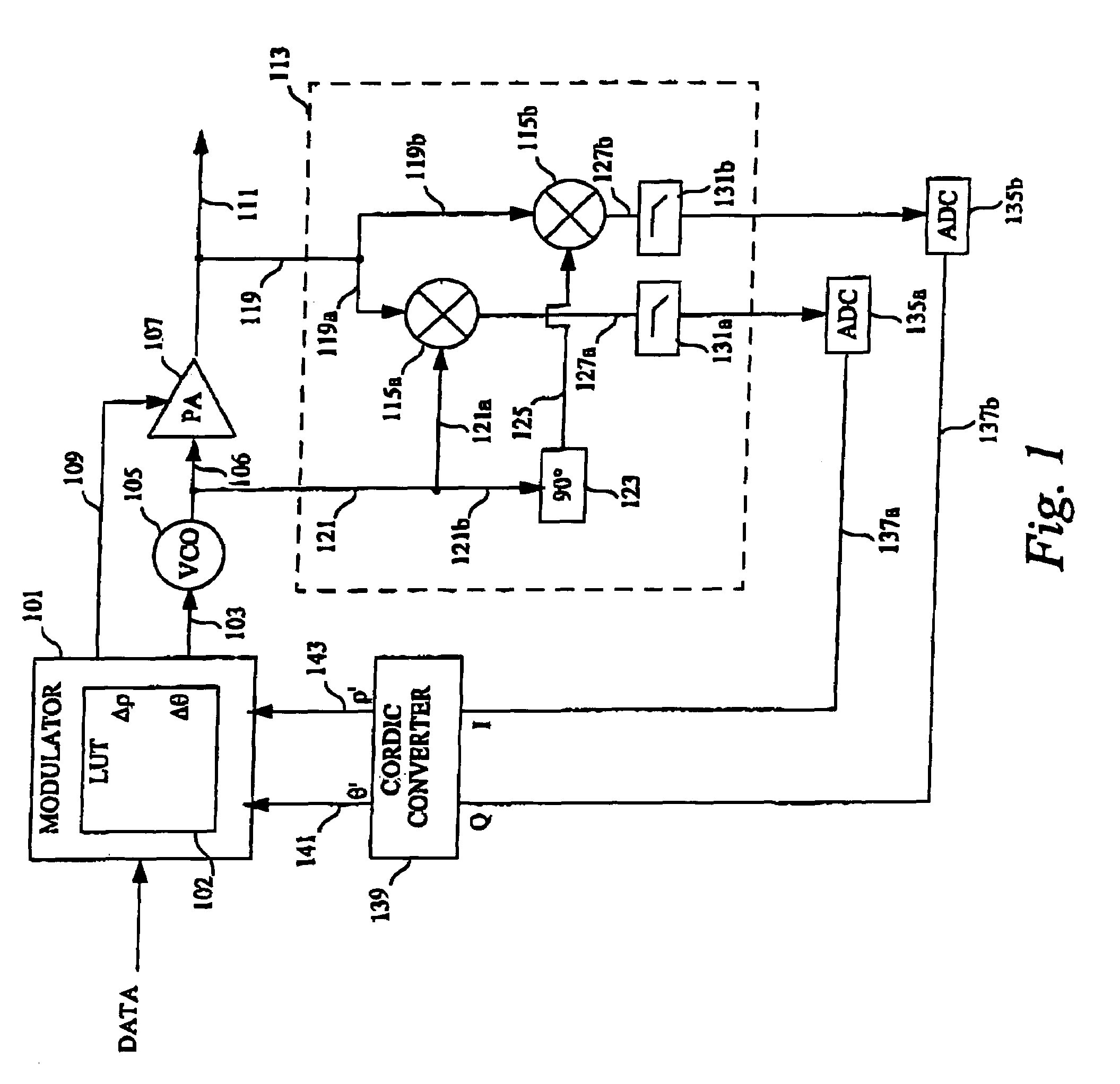
Patents
Literature
119 results about "Amplitude distortion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
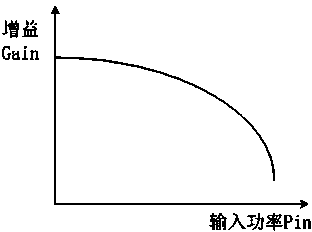
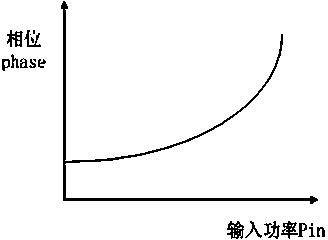
Amplitude distortion is distortion occurring in a system, subsystem, or device when the output amplitude is not a linear function of the input amplitude under specified conditions. Generally, output is a linear function of input only for a fixed portion of the transfer characteristics. In this region, Ic=βIb where Ic is collector current and Ib is base current, following linear relation y=mx.
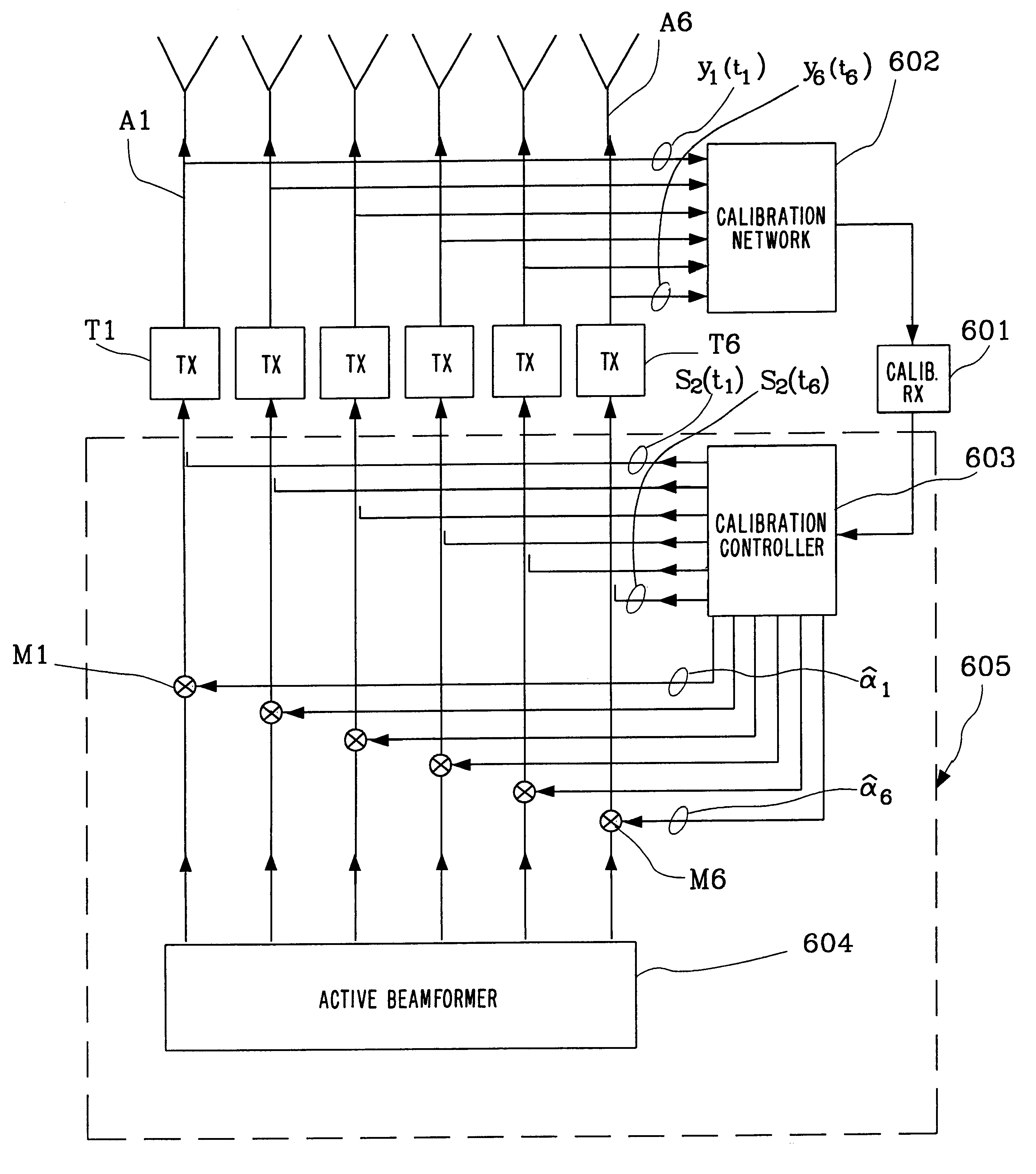
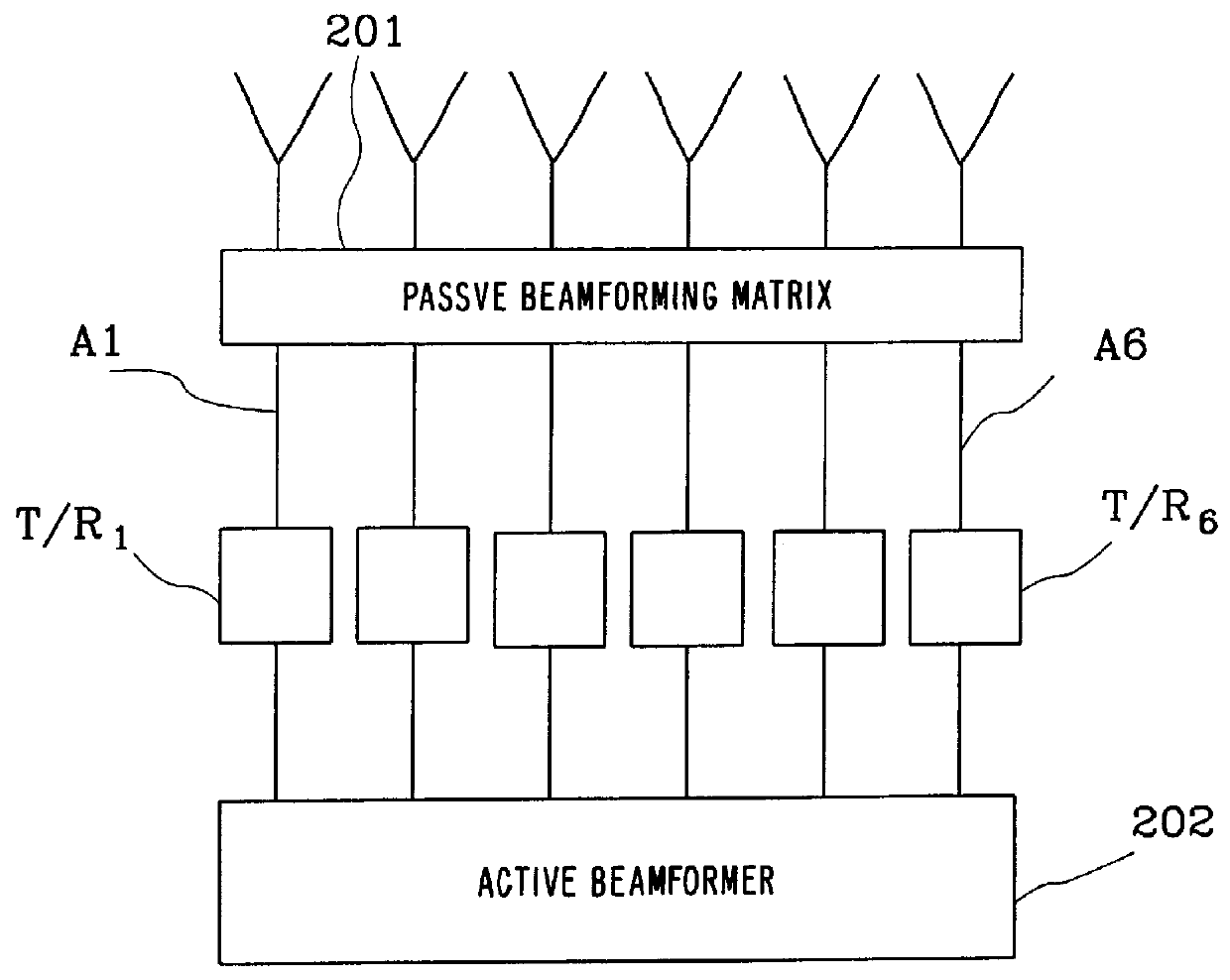
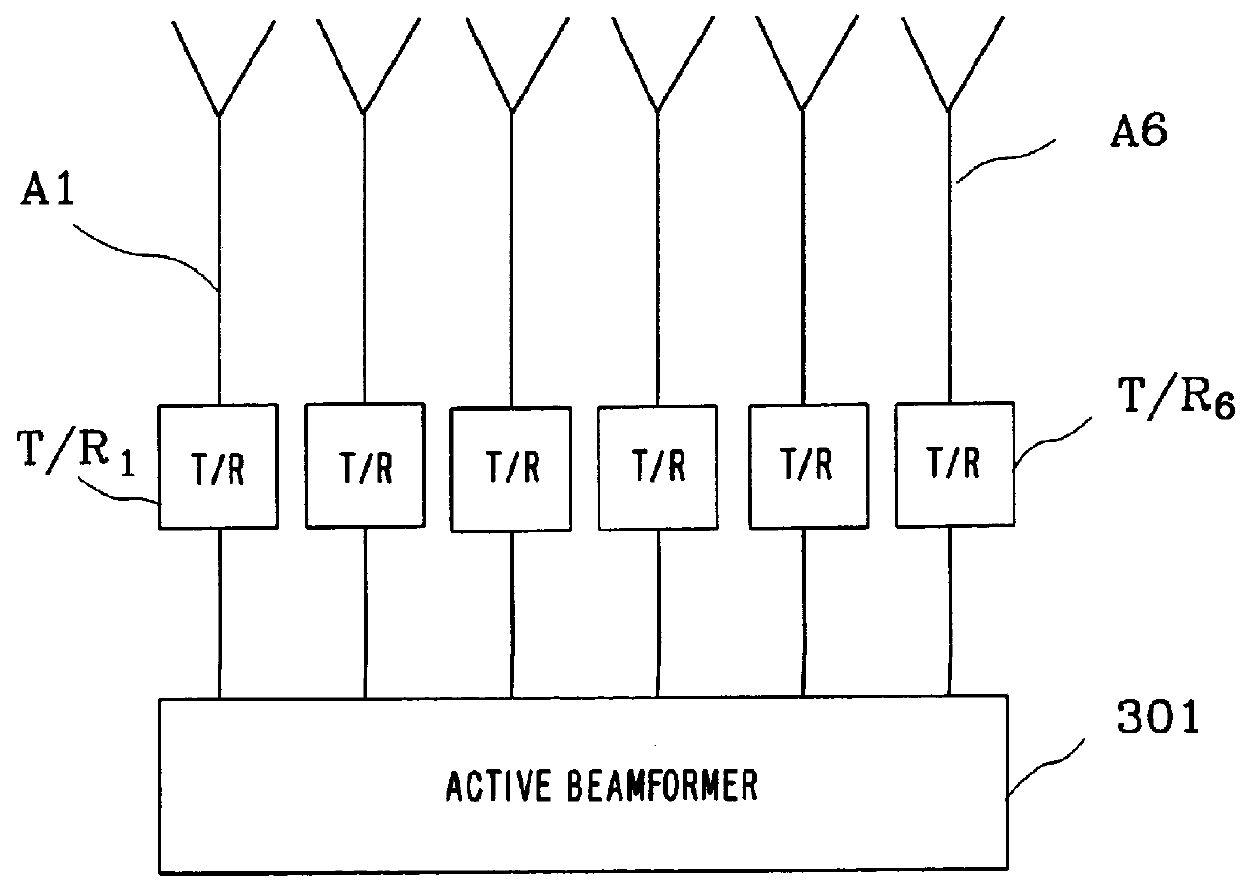
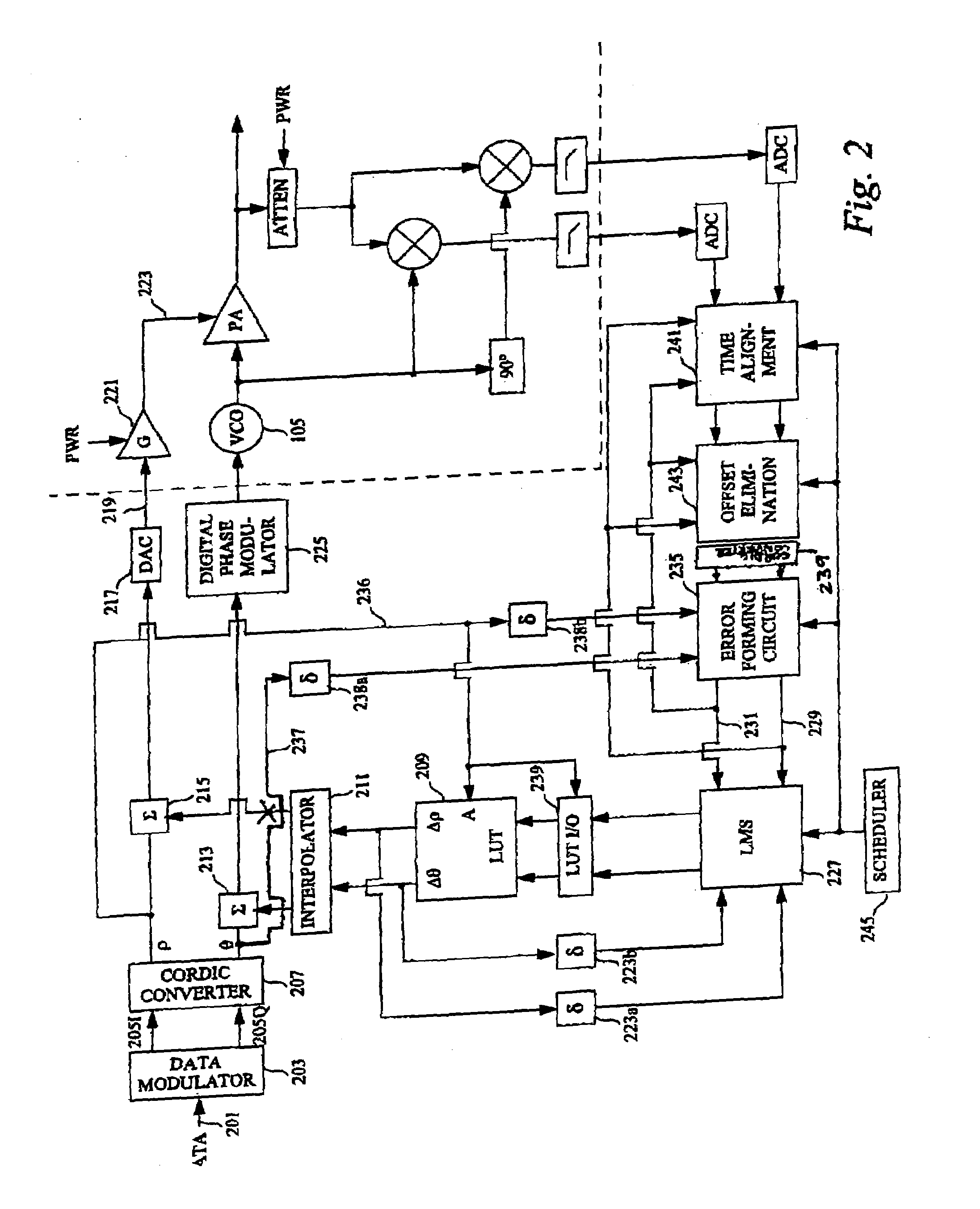
Antenna array calibration
InactiveUS6339399B1Improve performanceImprove accuracyWave based measurement systemsAntennasAmplitude distortionCellular communication systems
A method and a system for calibrating the reception and transmission of an antenna array for use in a cellular communication system is disclosed. The calibration of the reception of the antenna array is performed by injecting a single calibration signal into each of a number of receiving antenna sections, in parallel. The signals are collected after having passed receiving components that might have distorted the phase and amplitude. Correction factors are generated and applied to received signals. The calibration of the transmission of the antenna array is preformed in a similar way. A single calibration signal is generated and injected into each of a number of transmitting antenna sections, one at a time. The signals are collected, one at a time, after having passed transmitting components that might have distorted the phase and amplitude. Correction factors are generated and applied to signals that are to be transmitted.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Antenna array calibration
InactiveUS6157343AImprove radio communication performanceImprove accuracyWave based measurement systemsAntennasAmplitude distortionCellular communication systems
A method and a system for calibrating the reception and transmission of an antenna array for use in a cellular communication system is disclosed. The calibration of the reception of the antenna array is performed by injecting a single calibration signal into each of a number of receiving antenna sections, in parallel. The signals are collected after having passed receiving components that might have distorted the phase and amplitude. Correction factors are generated and applied to received signals. The calibration of the transmission of the antenna array is performed in a similar way. A single calibration signal is generated and injected into each of a number of transmitting antenna sections, one at a time. The signals are collected, one at a time, after having passed transmitting components that might have distorted the phase and amplitude. Correction factors are generated and applied to signals that are to be transmitted.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
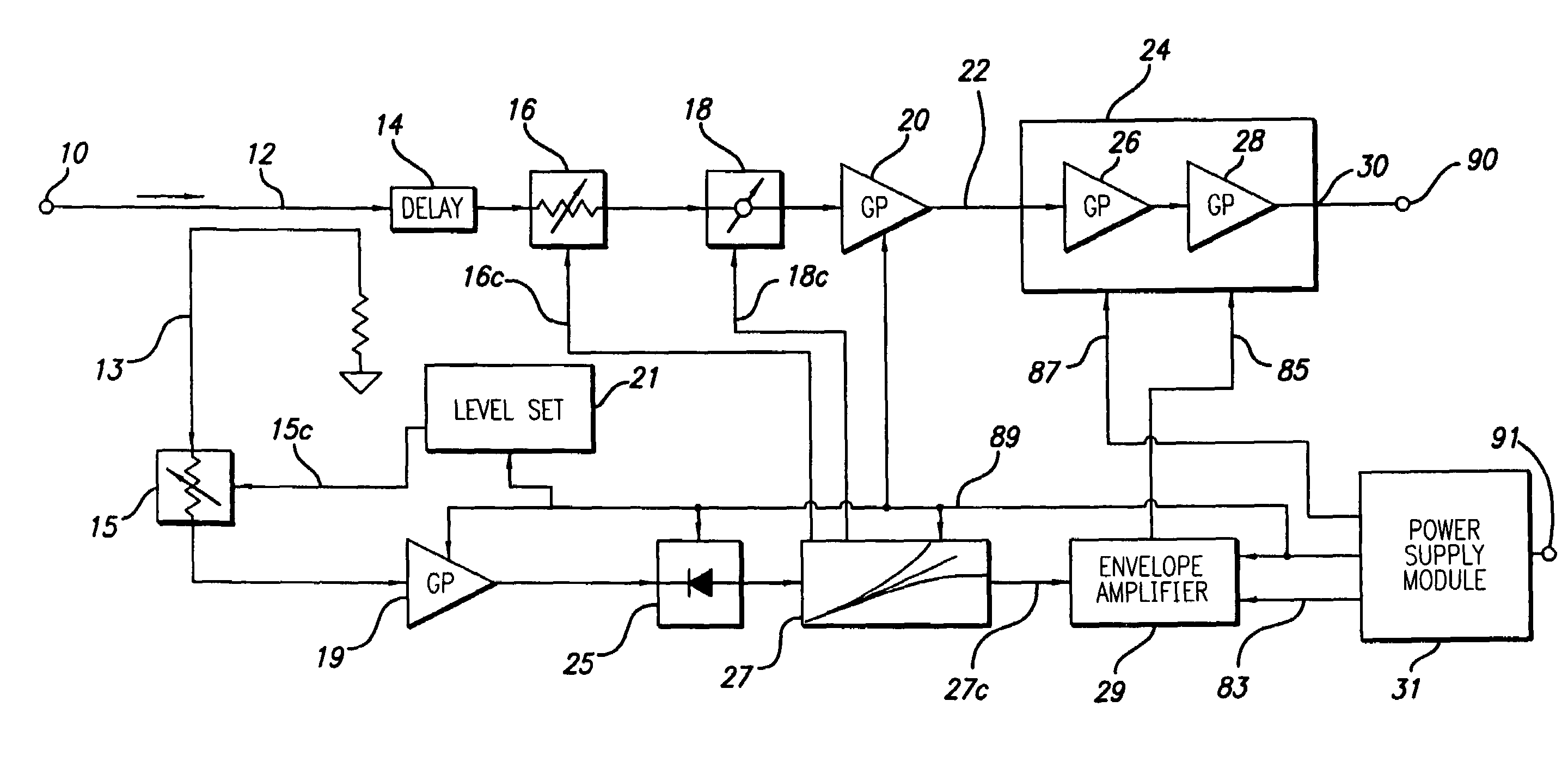
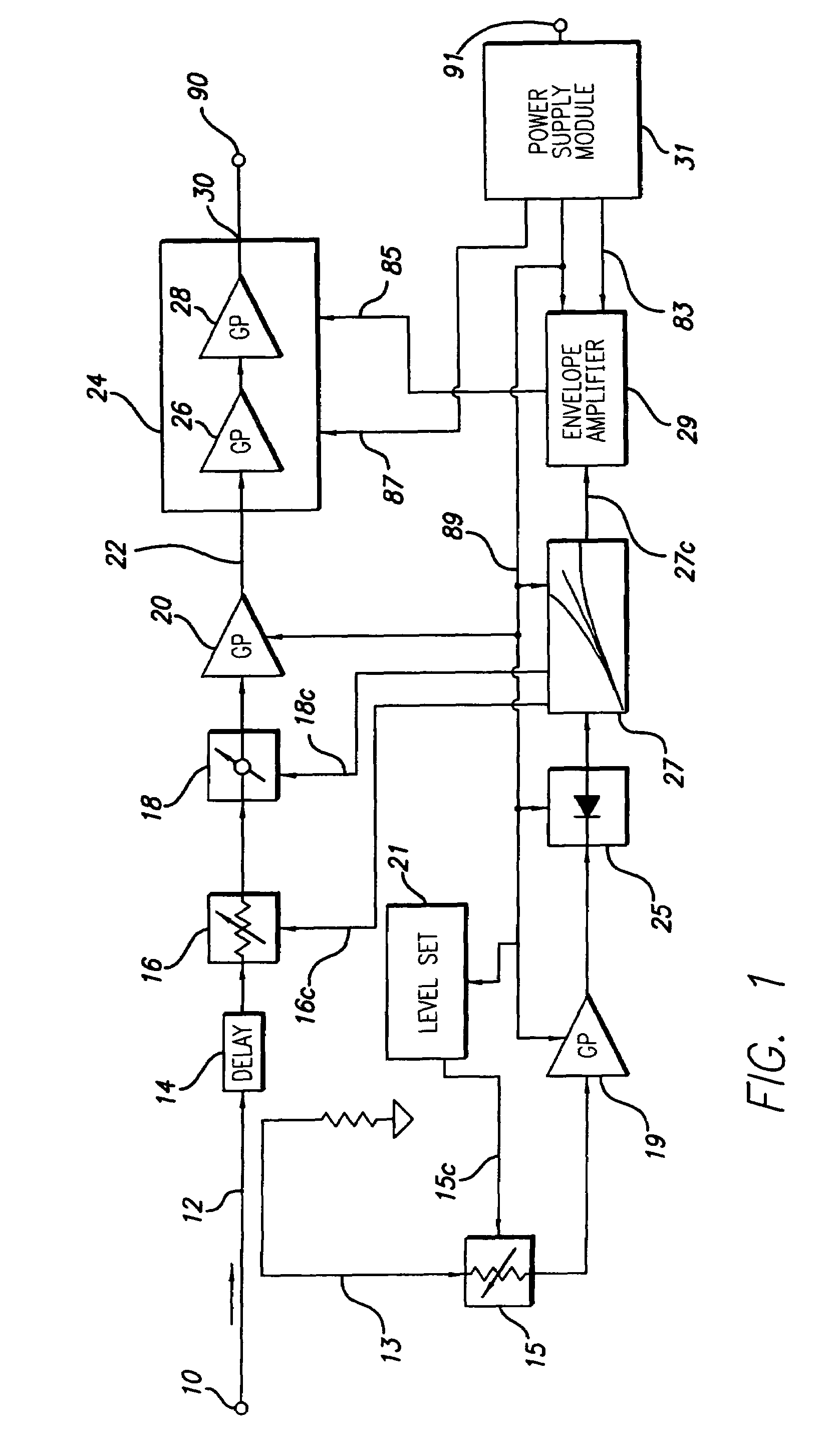
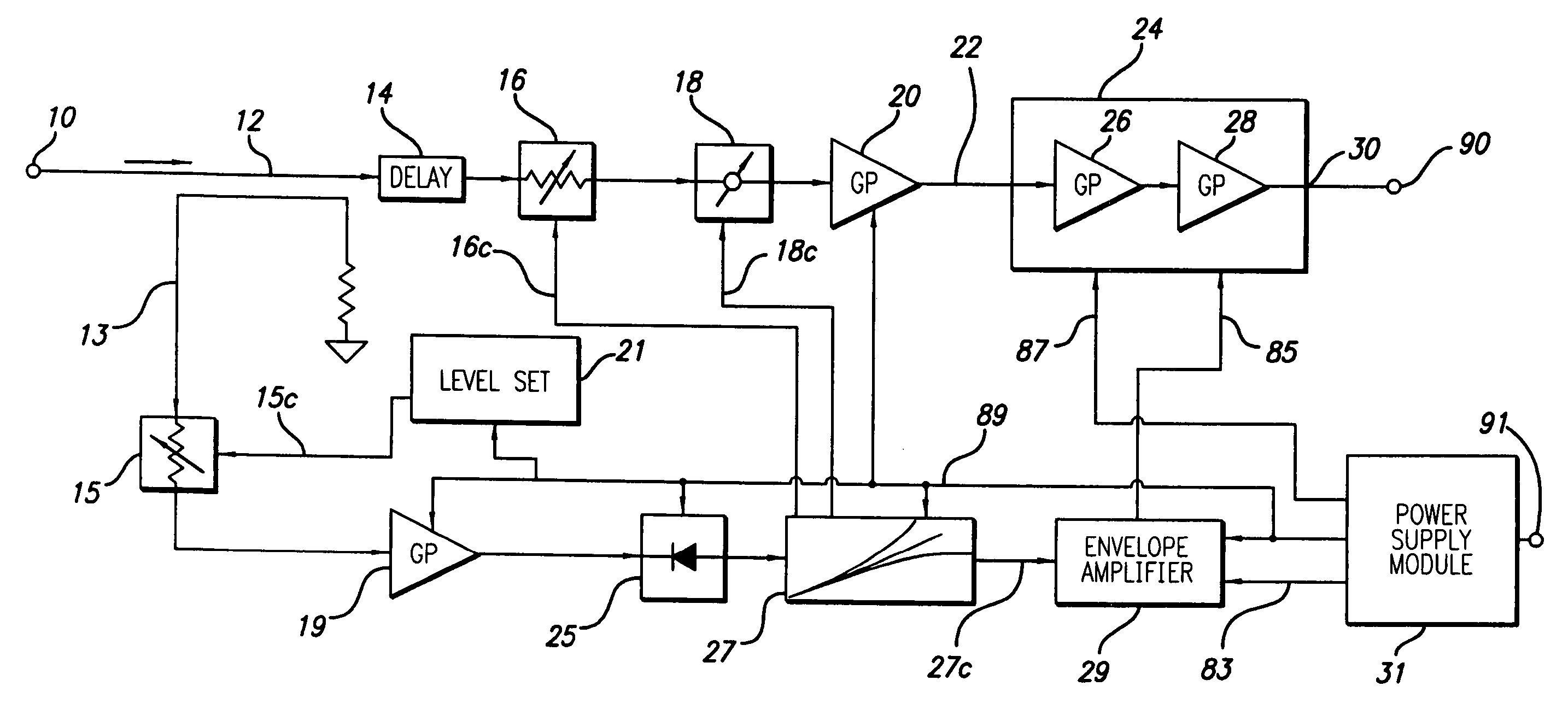
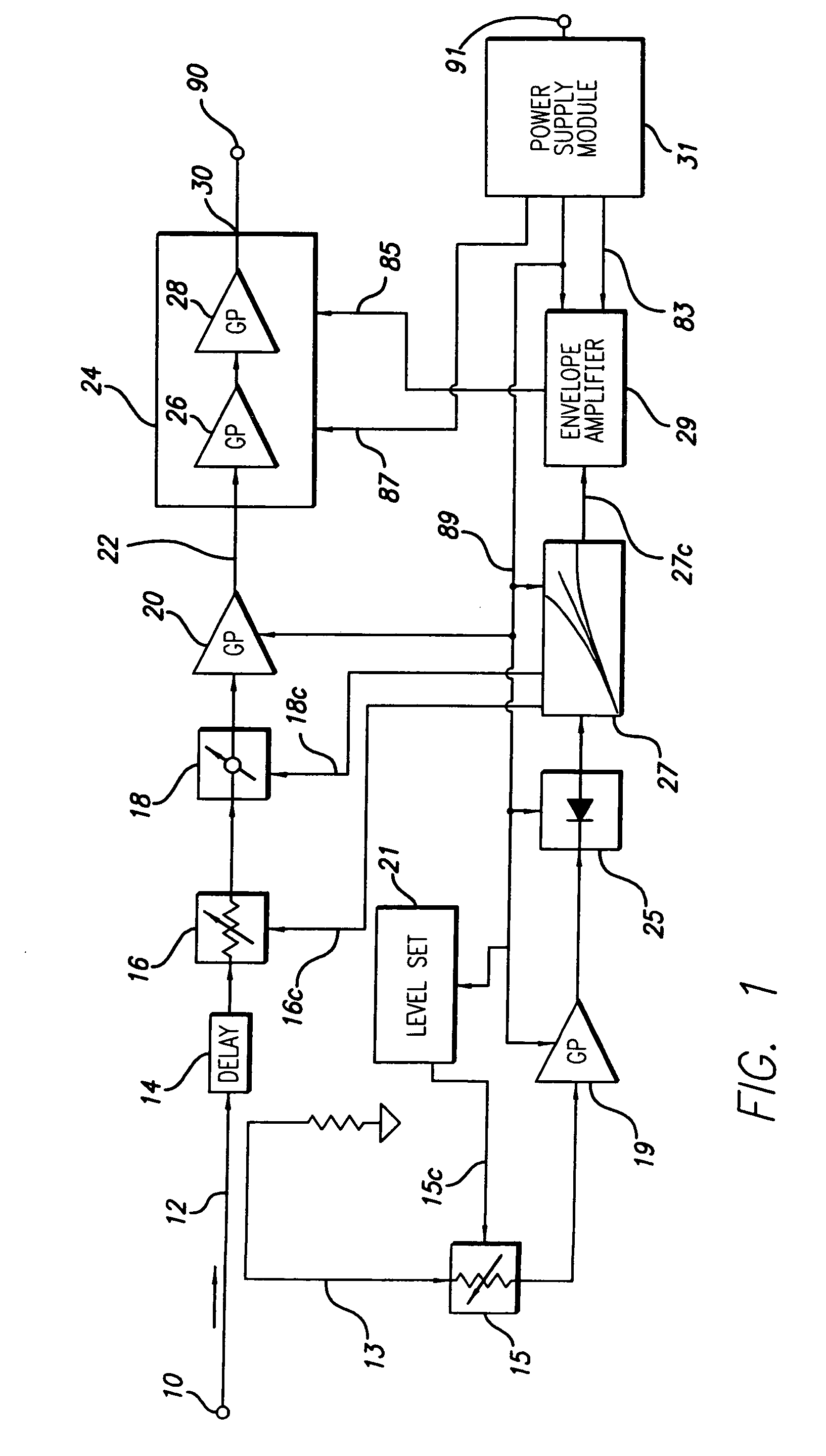
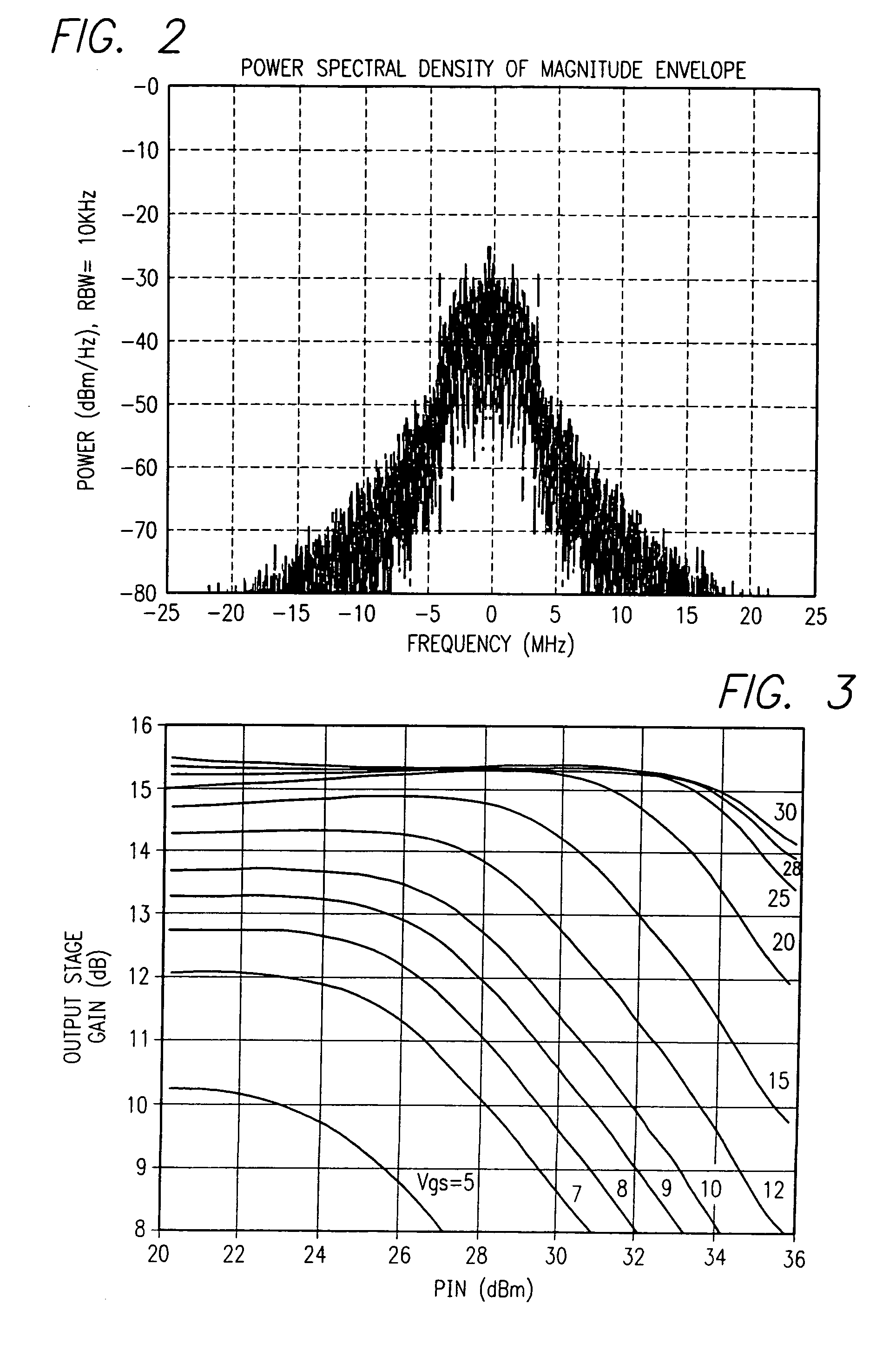
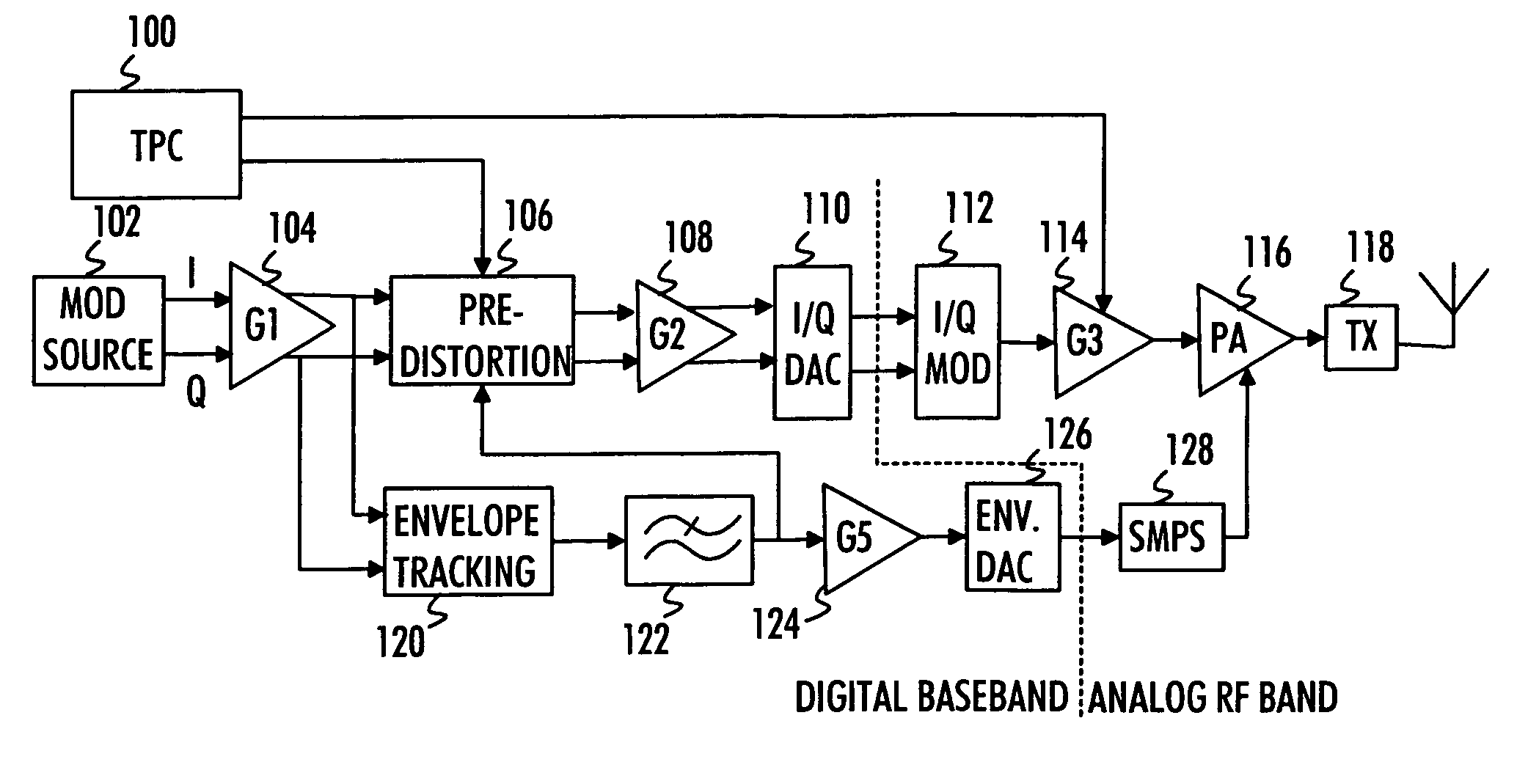
Constant gain nonlinear envelope tracking high efficiency linear amplifier
ActiveUS7440733B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasSignal processing circuitsConstant power
An envelope tracking radio frequency (RF) power amplifier having an adaptive envelope signal processing circuit is disclosed. An RF input voltage is sampled by the adaptive envelope signal processing circuit which provides control signals to the power supply which supplies voltages to RF power devices in order to simultaneously satisfy two operating conditions: a) provide best possible efficiency of the power amplifier stages depending on the input signal characteristics and b) provide compensation for RF transistor AM-AM and AM-PM distortion compensation across the power range. In particular, the voltage control provides for constant power amplifier gain across the input signal dynamic range, thus minimizing power amplifier amplitude distortions and extending the useful power amplifier linear dynamic range up to saturation point. The power amplifier thus exhibits better linearity and efficiency than offered by conventional techniques and topologies.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
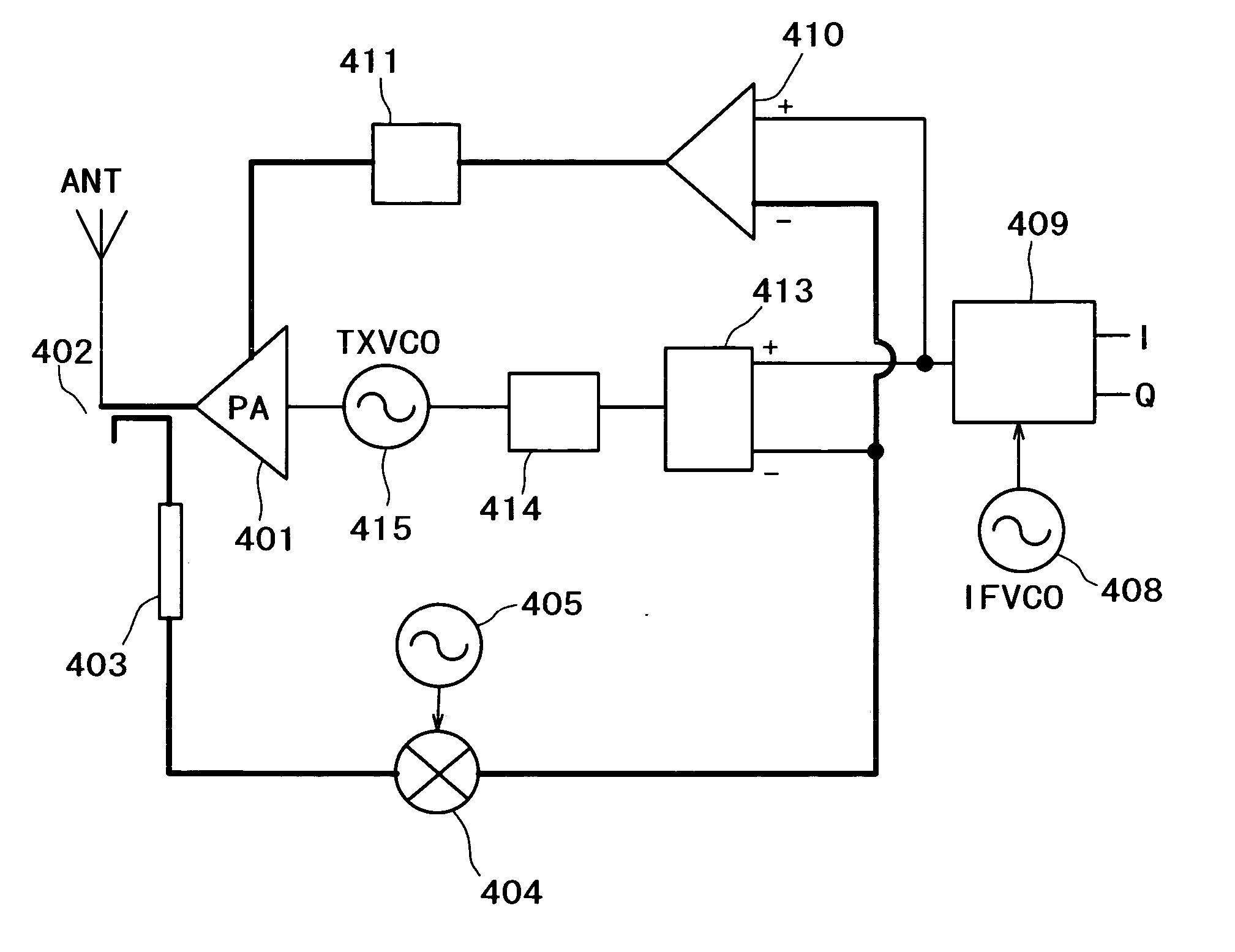
Wireless communication apparatus and receiving method
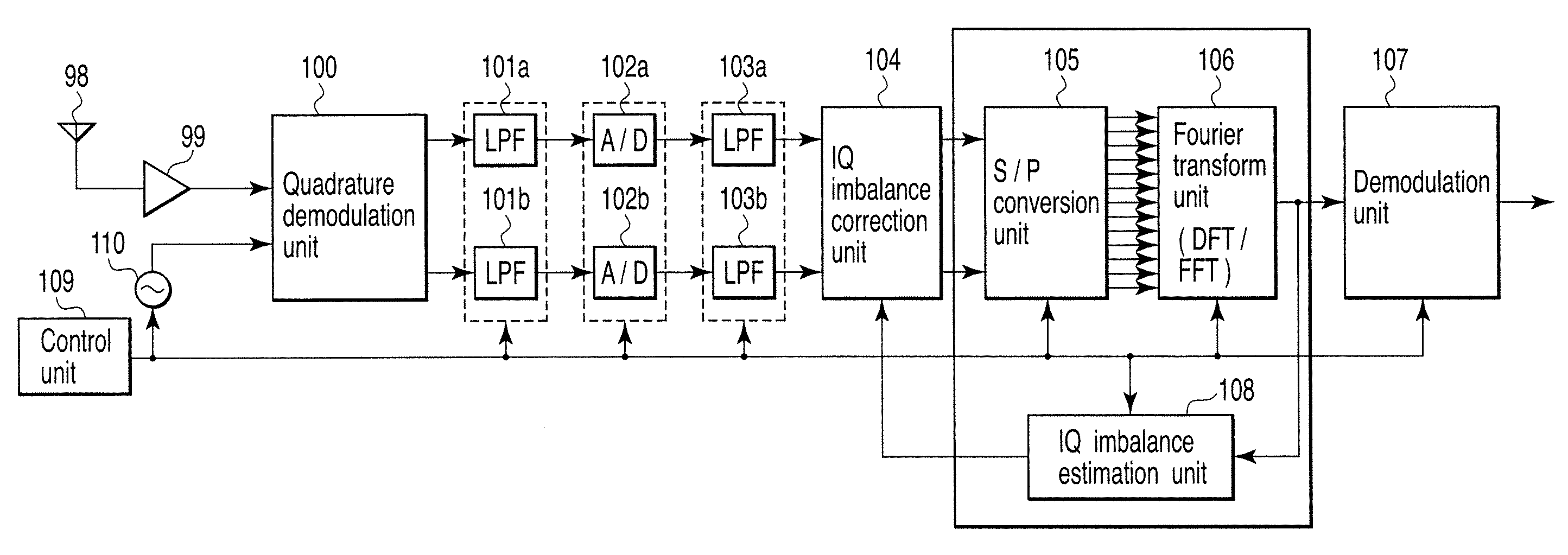
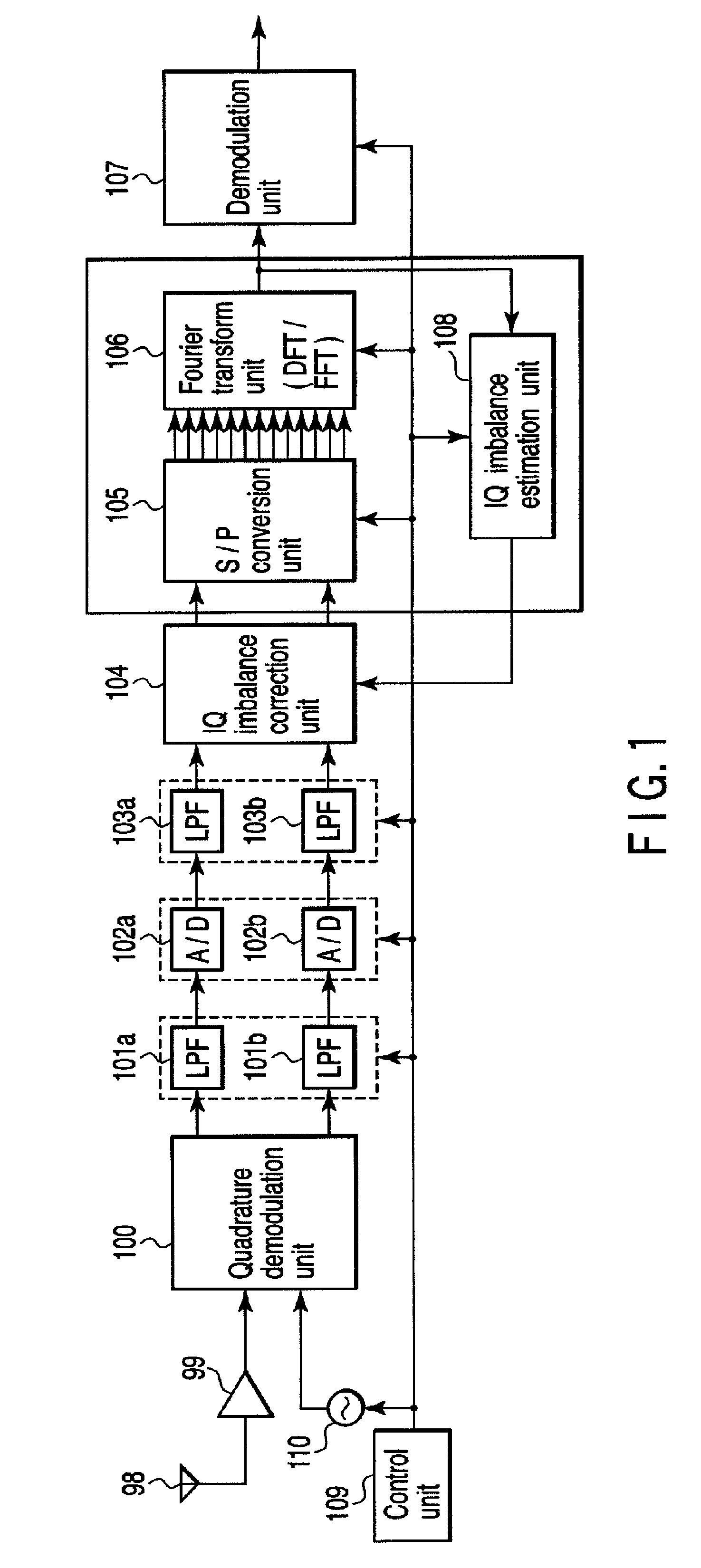
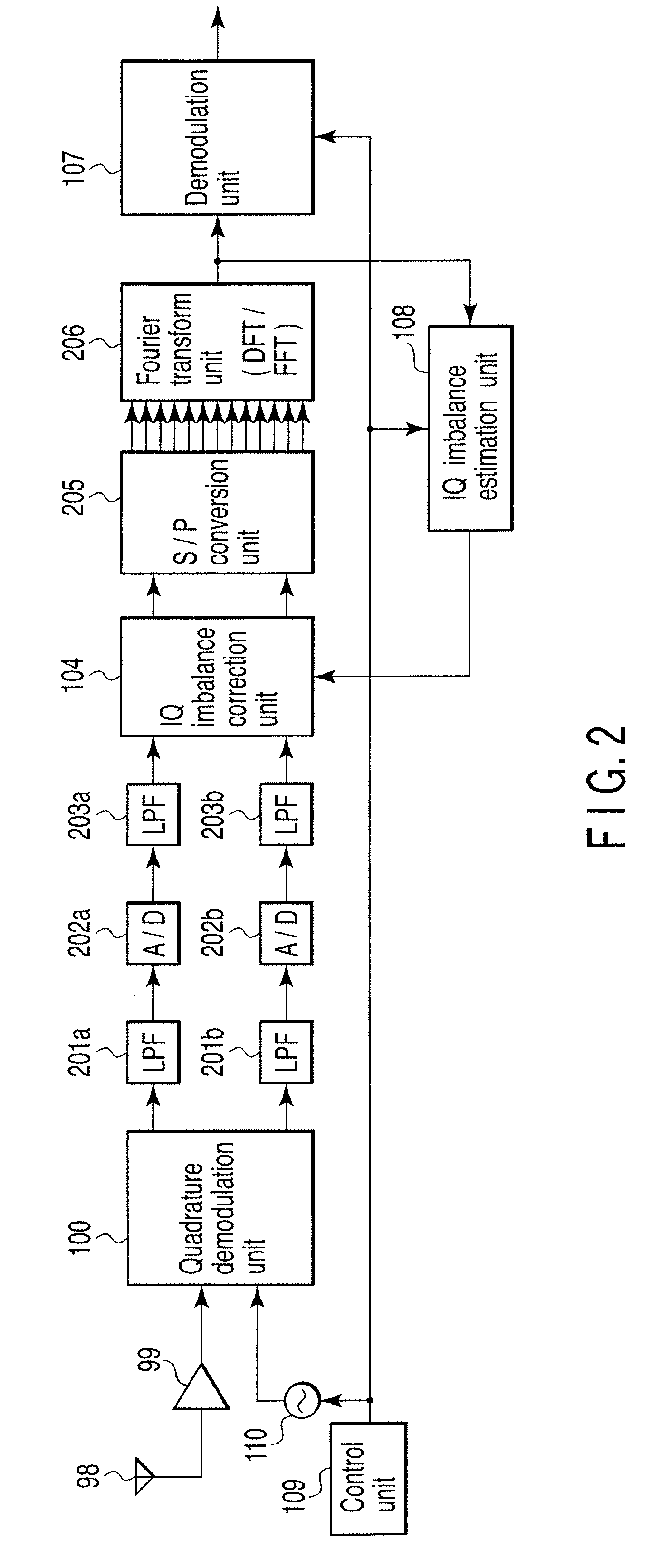
InactiveUS20080159442A1Single output arrangementsElectric pulse generatorAmplitude distortionTelecommunications
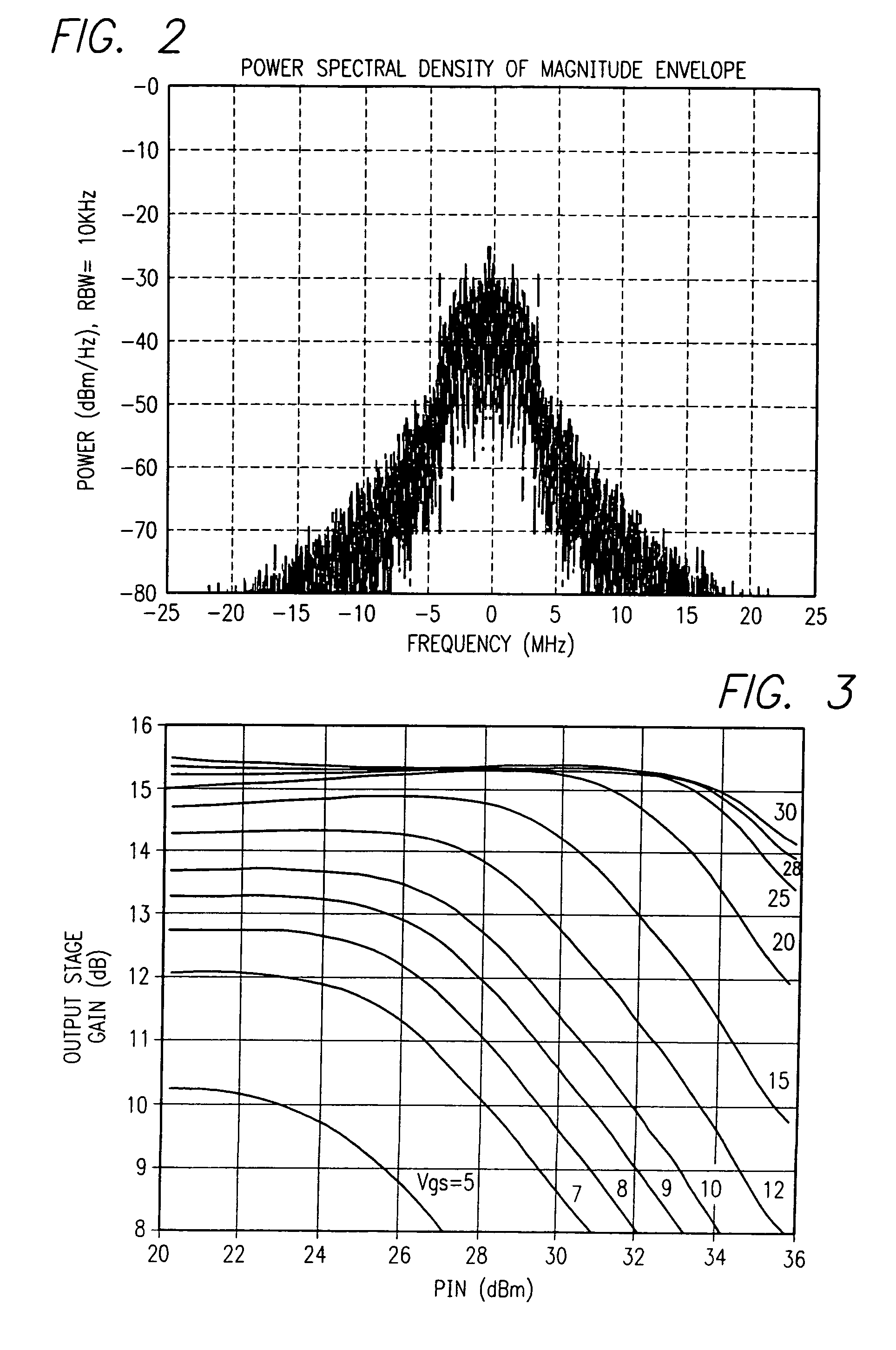
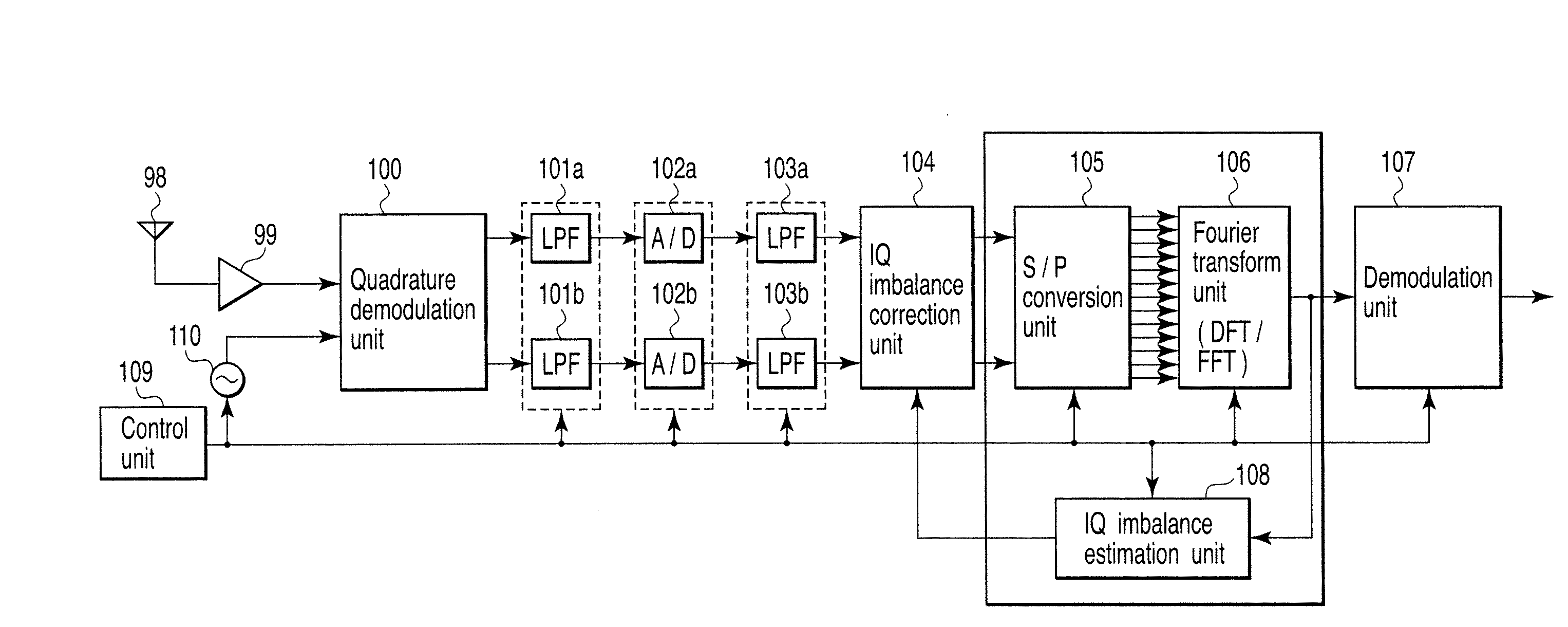
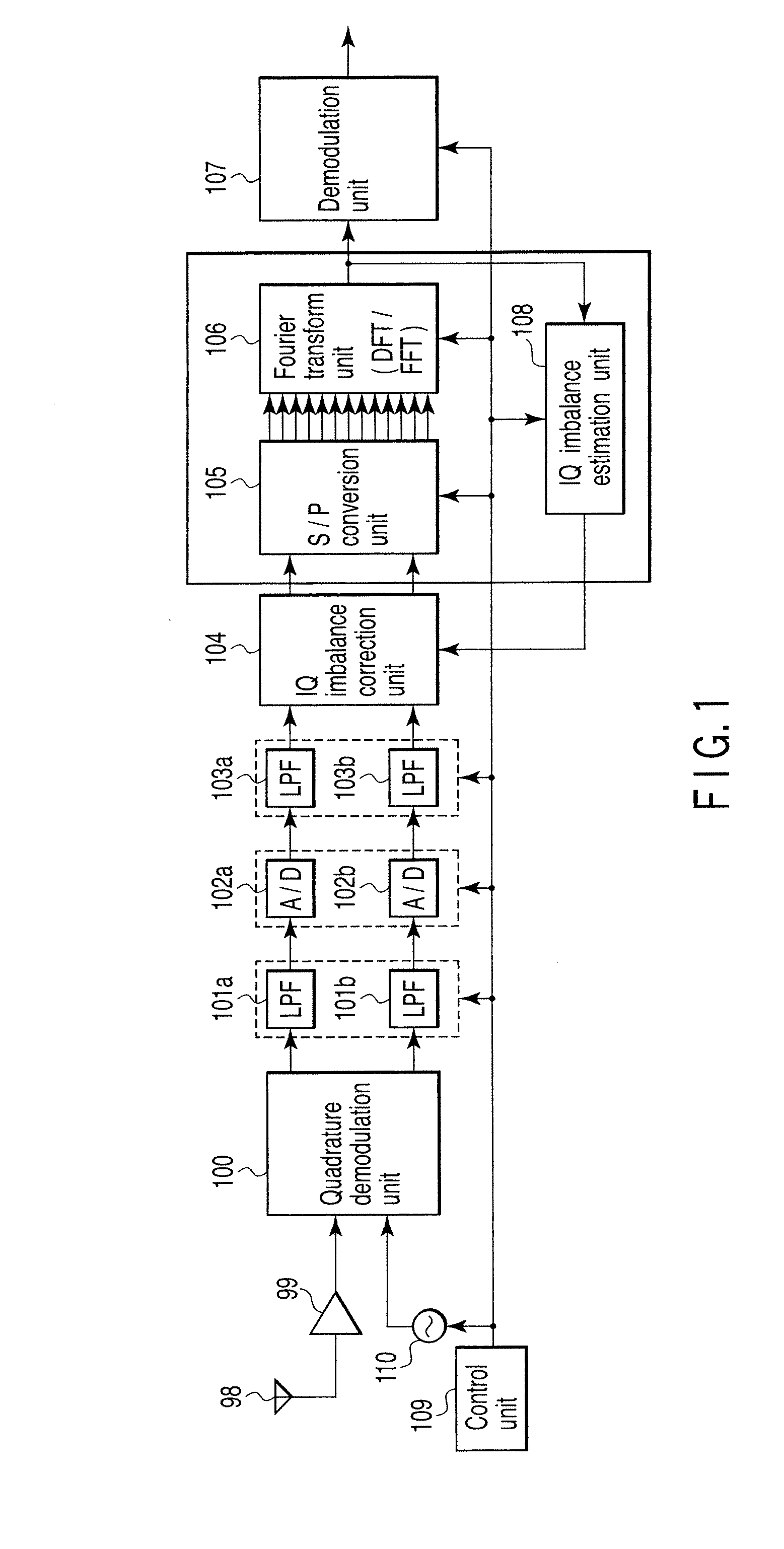
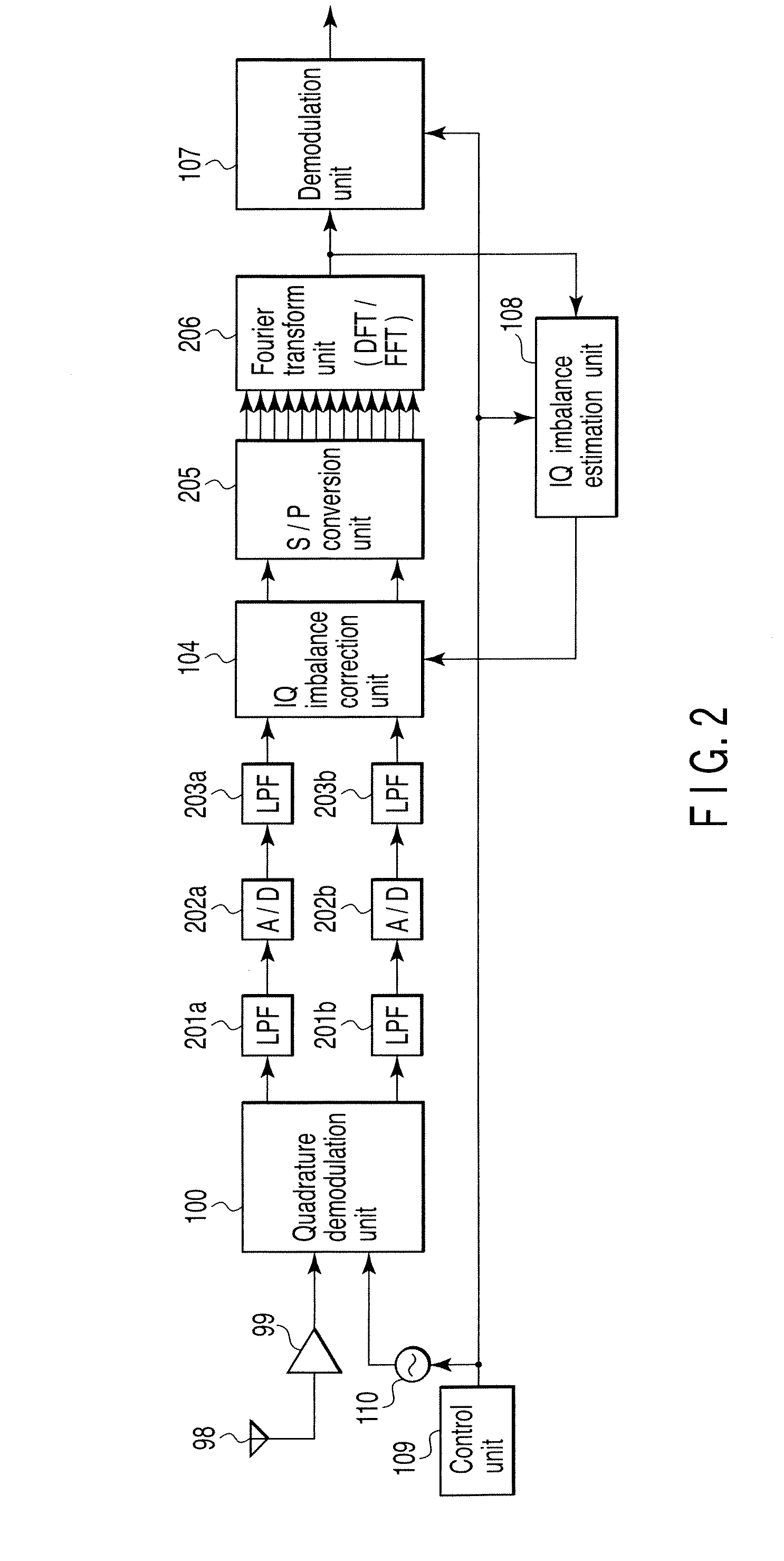
A wireless communication apparatus receives an quadrature modulated signal, generate a local signal having a frequency different from a center frequency of the quadrature modulated signal, performs quadrature demodulation on the quadrature modulated signal by using the local signal, to obtain an I channel signal and a Q channel signal, performs Fourier transform on the I channel signal and the Q channel signal, to obtain signals in a frequency domain, and calculates a first correction coefficient for correcting phase distortion and amplitude distortion caused by the quadrature demodulation by using pairs of signals among the signals, each of the pairs are located at symmetrical frequency positions with respect to the frequency of the local signal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Constant gain nonlinear envelope tracking high efficiency linear amplifier
ActiveUS20050227644A1Constant gainHigh power supply voltageAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasConstant powerSignal processing circuits
An envelope tracking radio frequency (RF) power amplifier having an adaptive envelope signal processing circuit is disclosed. An RF input voltage is sampled by the adaptive envelope signal processing circuit which provides control signals to the power supply which supplies voltages to RF power devices in order to simultaneously satisfy two operating conditions: a) provide best possible efficiency of the power amplifier stages depending on the input signal characteristics and b) provide compensation for RF transistor AM-AM and AM-PM distortion compensation across the power range. In particular, the voltage control provides for constant power amplifier gain across the input signal dynamic range, thus minimizing power amplifier amplitude distortions and extending the useful power amplifier linear dynamic range up to saturation point. The power amplifier thus exhibits better linearity and efficiency than offered by conventional techniques and topologies.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
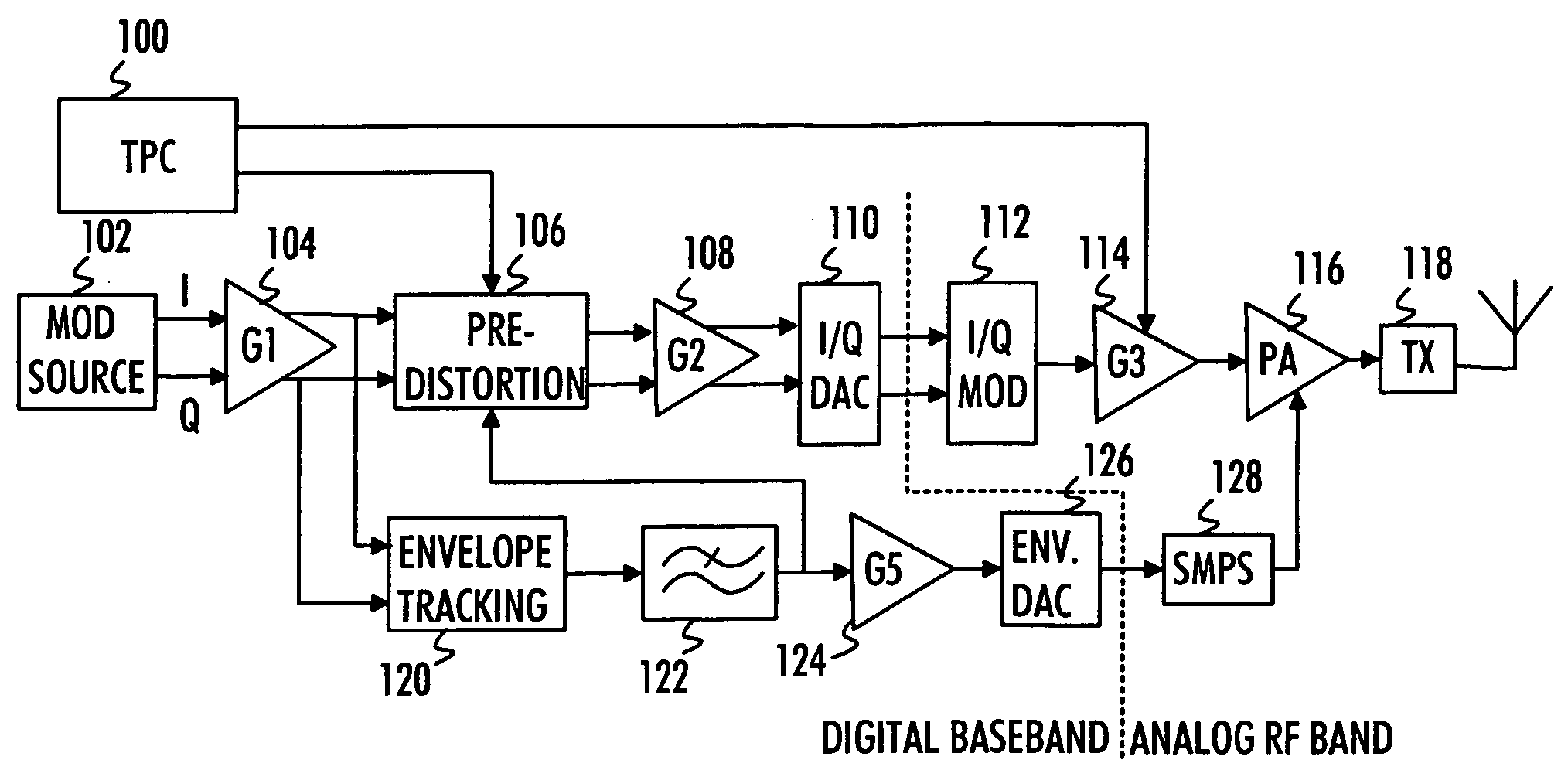
Signal predistortion in radio transmitter
ActiveUS20080139140A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAmplitude distortionAudio power amplifier
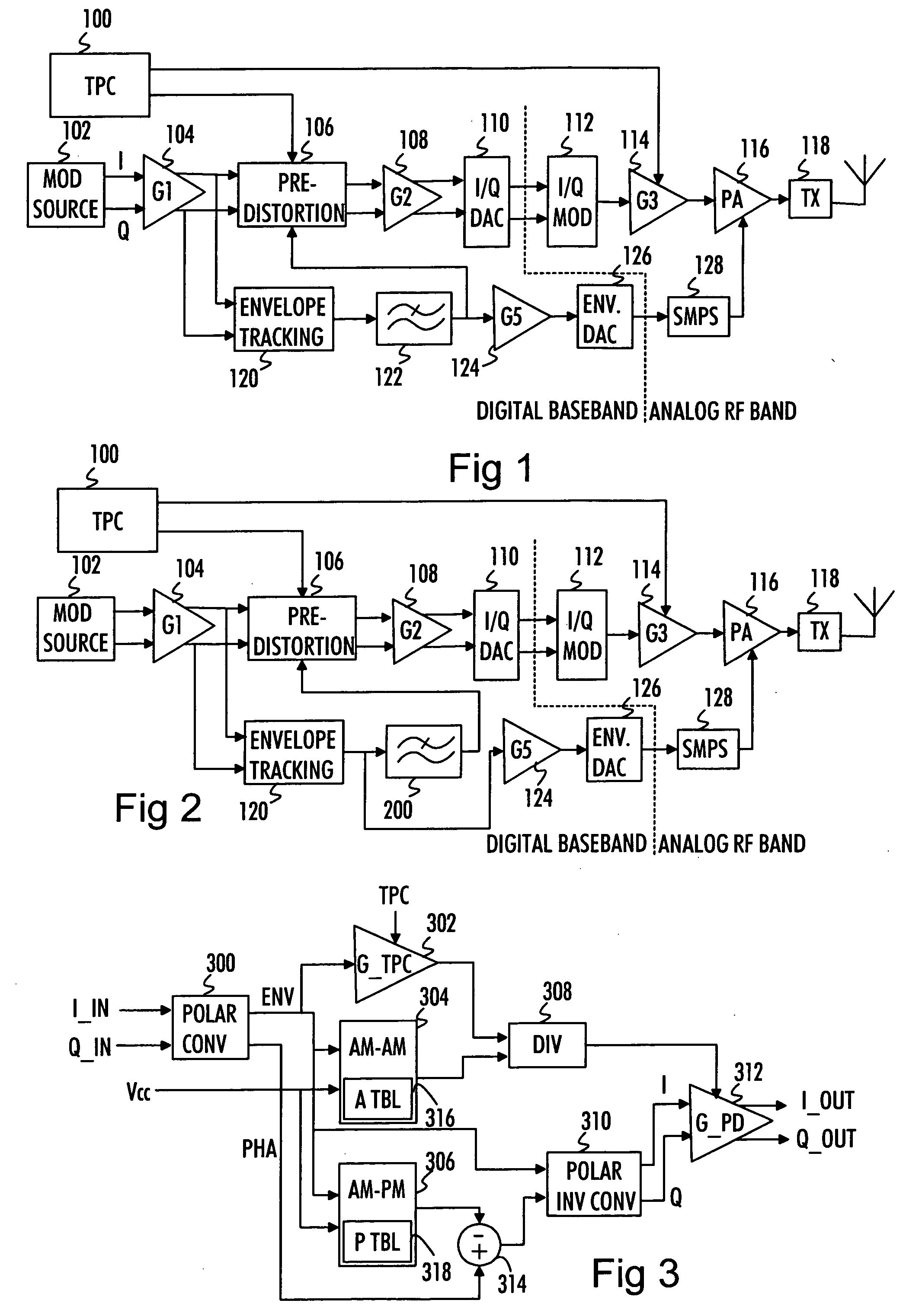
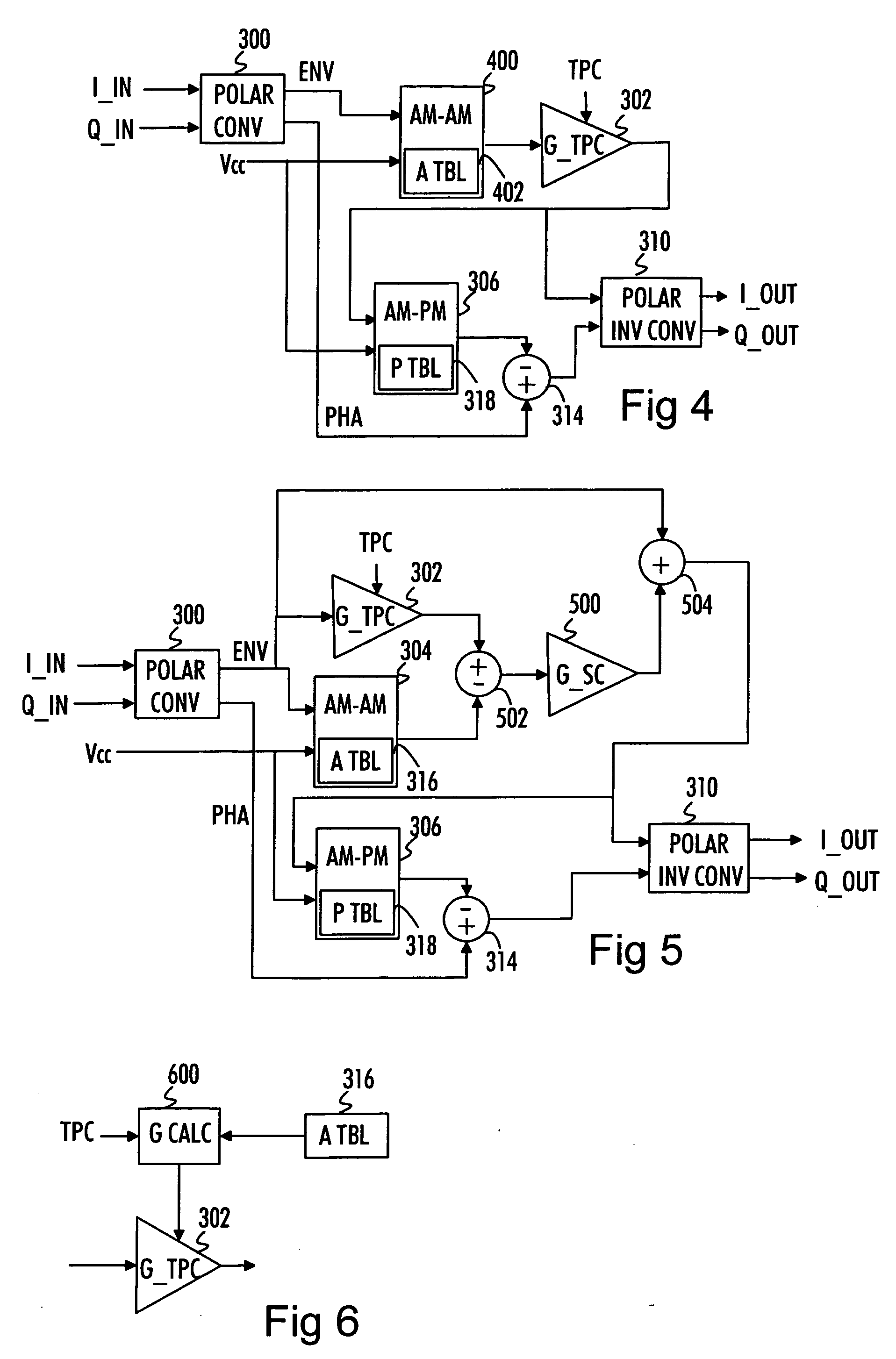
A transmission signal to be transmitted from a radio transmitter is predistorted in order to compensate for the signal distortion caused by a power amplifier. The transmission signal and a signal modeling a power supply voltage applied to the power amplifier are compared with distortion properties of the power amplifier using these signals. The distortion information is comprised in an amplitude distortion lookup table and a phase distortion lookup table. Transmission signal and power supply signal values are associated with envelope and phase predistortion information comprised in the respective lookup tables and the envelope and the phase of the transmission signal is predistorted accordingly.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
System and method for applying multi-tone OFDM based communications within a prescribed frequency range
ActiveUS20090307540A1Modulated-carrier systemsPower distribution line transmissionUltrasound attenuationAmplitude distortion
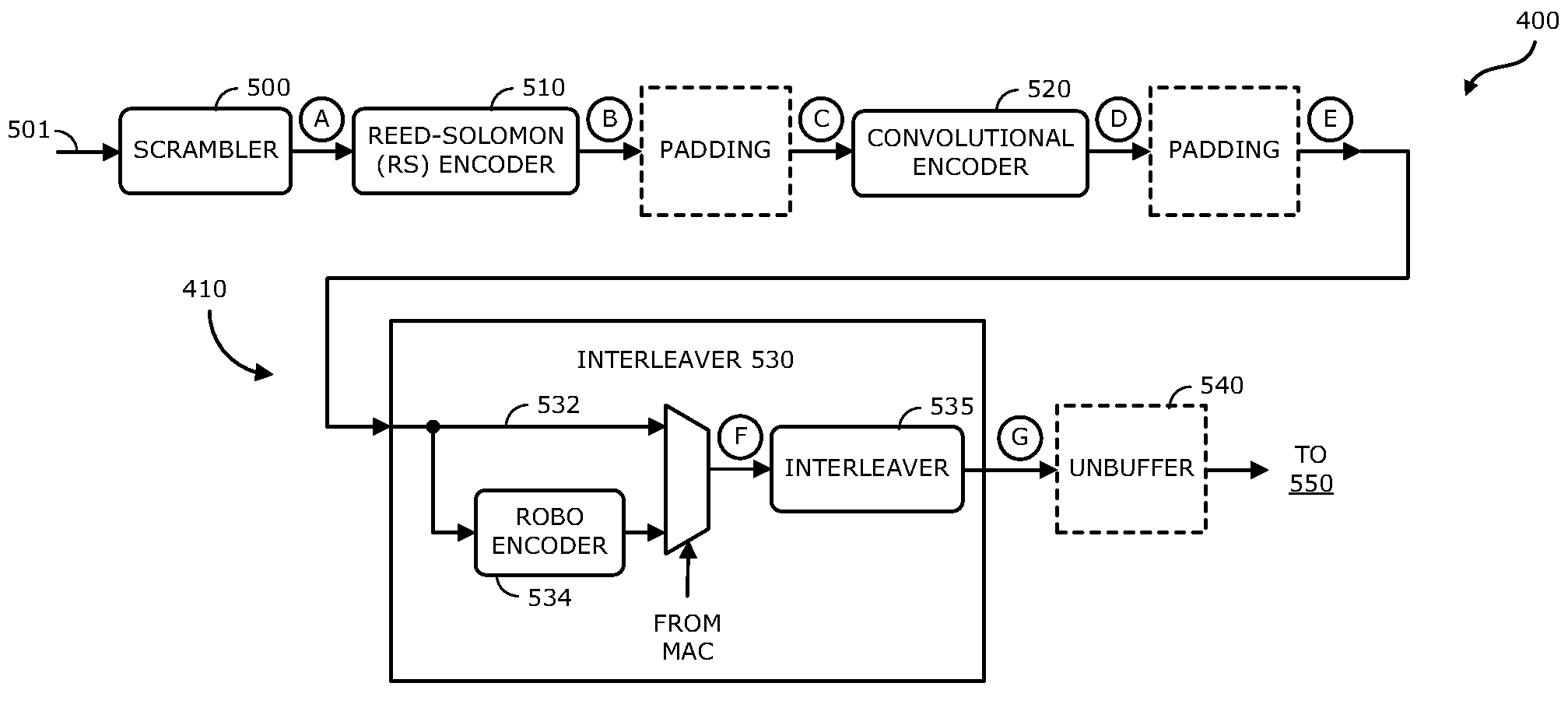
According to one embodiment of the invention, an integrated circuit comprises an encoding module, a modulation module and a spectral shaped module. The encoding module includes an interleaver that adapted to operate in a plurality of modes including a first mode and a second mode. The interleaver performs repetitive encoding when placed in the second mode. The modulation module is adapted to compensate for attenuations that are to be realized during propagation of a transmitted signal over the power line. The spectral shaped module is adapted to compensate for amplitude distortion and further compensates for attenuations that will be realized during propagation of the transmitted signal over the power line.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
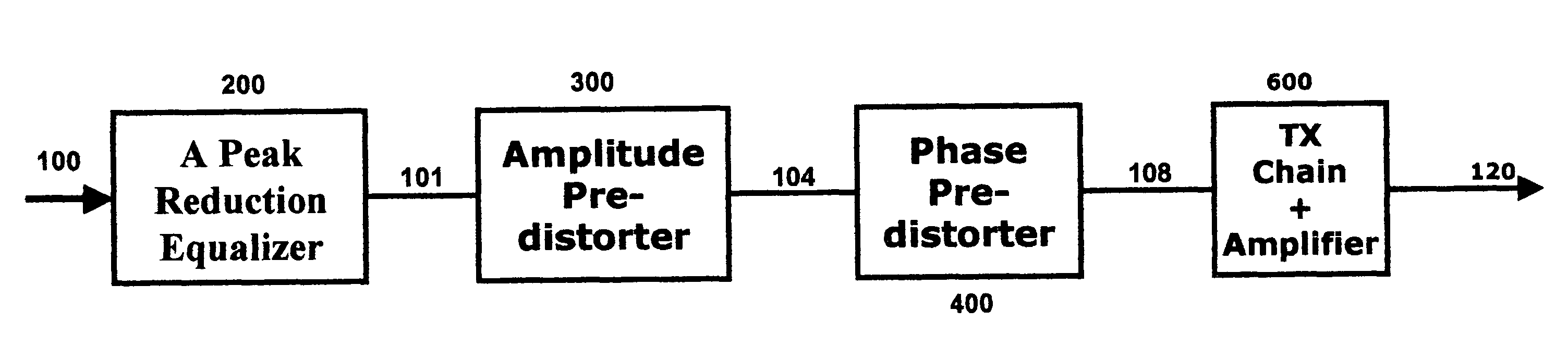
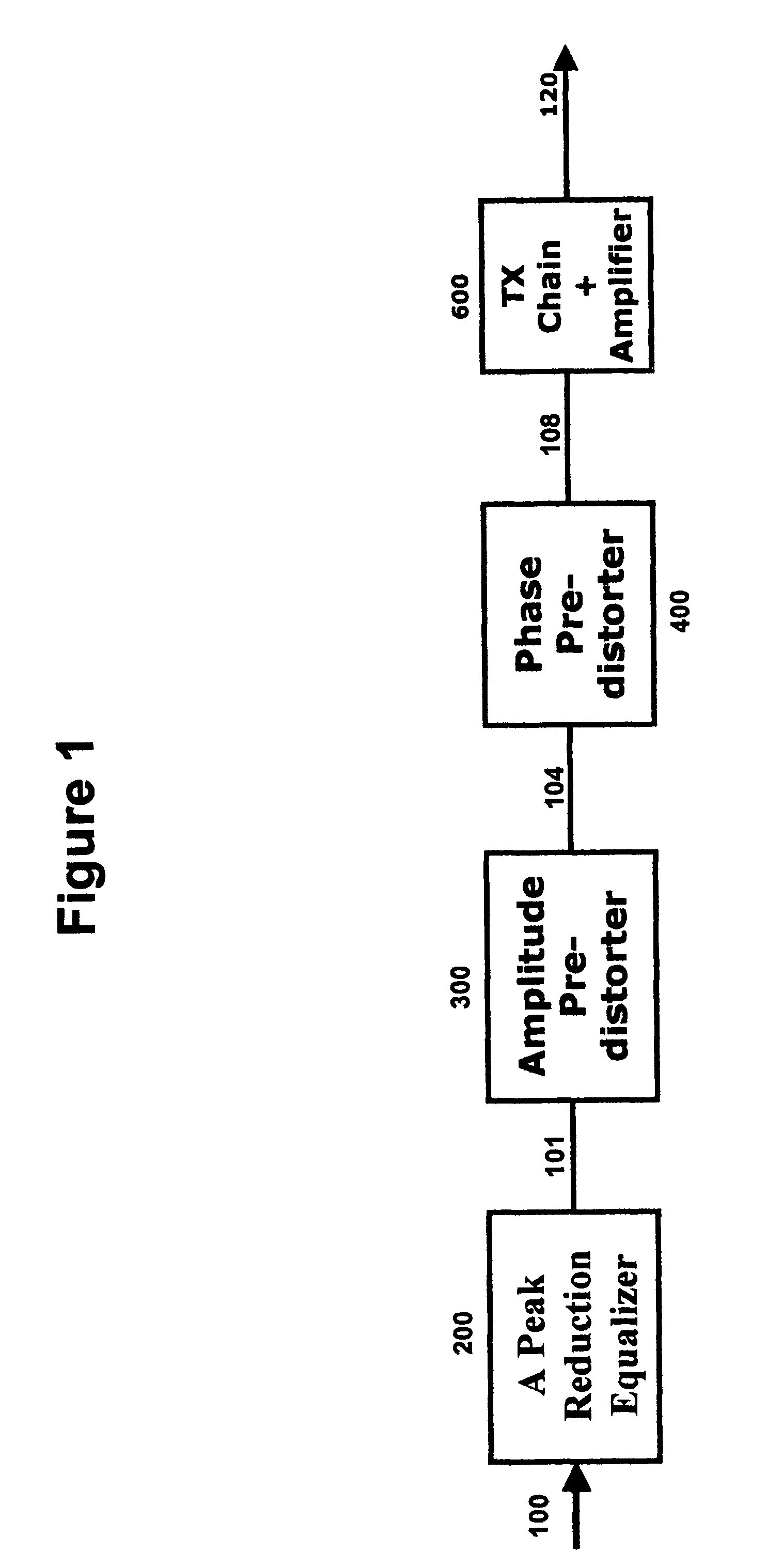
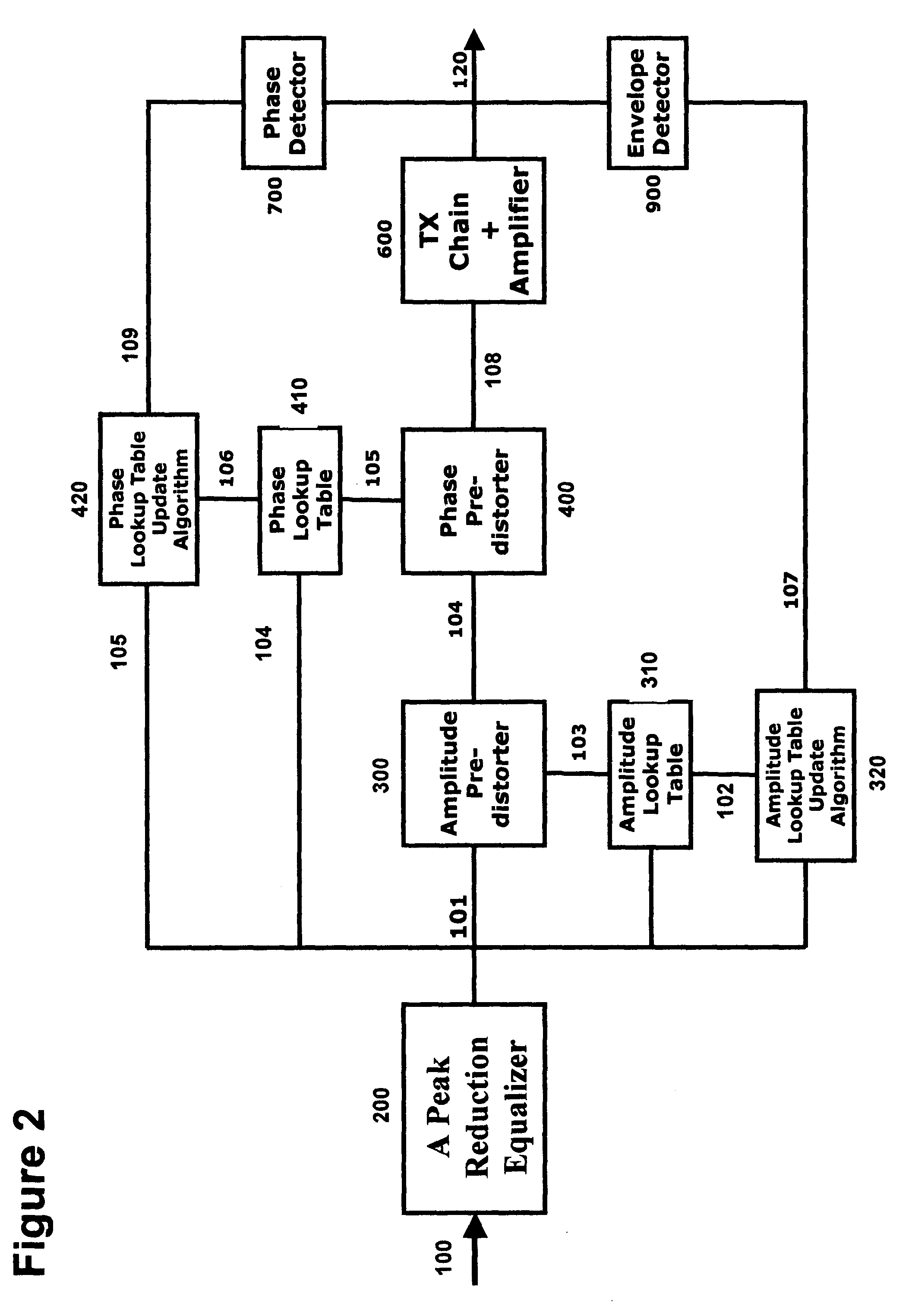
Combined peak reduction equalizer and phase/amplitude pre-distortion
InactiveUS7787564B1Simple signal processingBoost power handlingAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAmplitude distortionDifferential phase
A technique for a combined peak reduction equalizer filter and phase / amplitude pre-distortion is described. The input to a transmitter chain is modified by a combined equalizer filter and pre-distorter, prior to being applied to the transmitter chain. The equalizer filter modifies and smoothen the amplitude of the signal followed by pre-distorter to compensate for phase and amplitude distortion from transmitter chain or power amplifier. The modified and smoothen signal has its peaks reduced before being pre-distorted. The baseband signal pre-distortion results in cancellation of the distortion being introduced by the power amplifier or the transmitter chain. The amplitude pre-distortion is applied to the amplitude of the peak reduced baseband signal using the envelope information from the output of the transmitter chain or power amplifier and the phase pre-distortion is applied to the phase of the peak reduced baseband signal using the differential phase information between input and output of the power amplifier or the transmitter chain.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Variable gain amplifier for use in communications
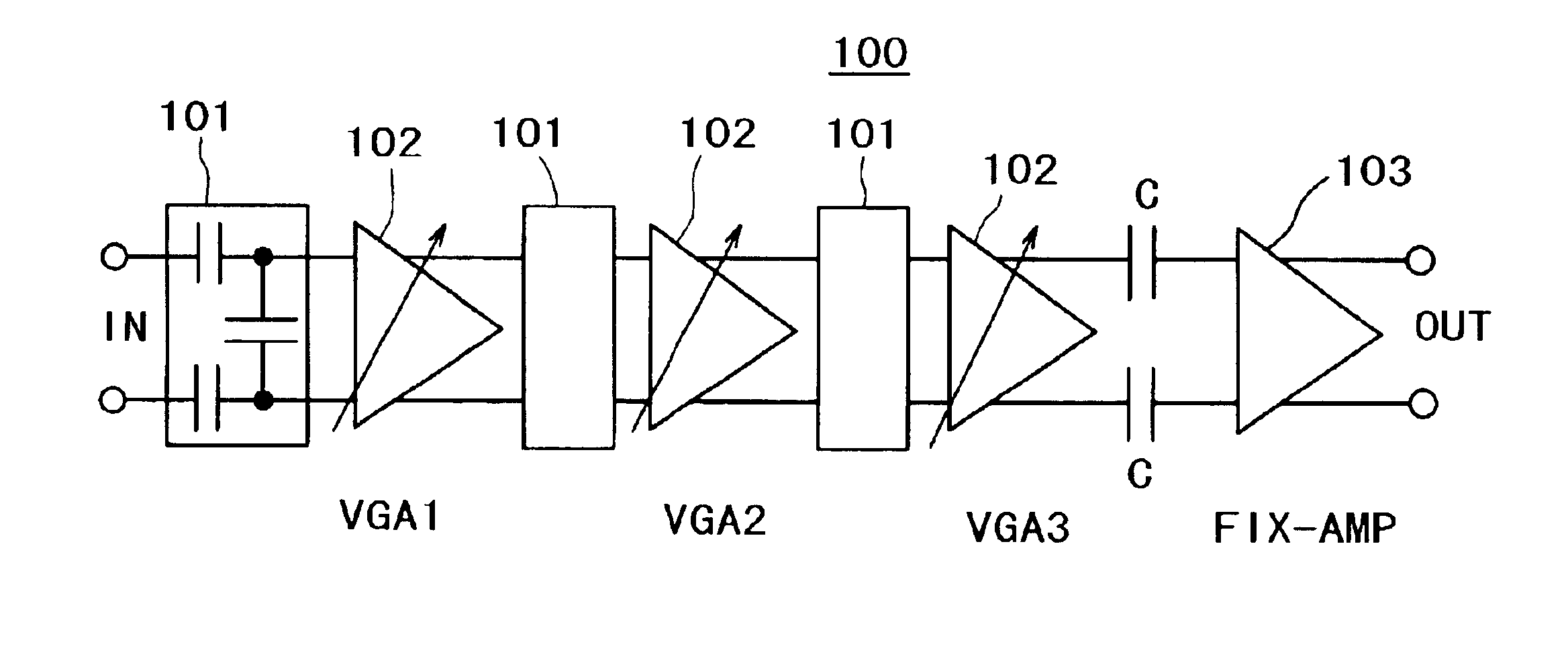
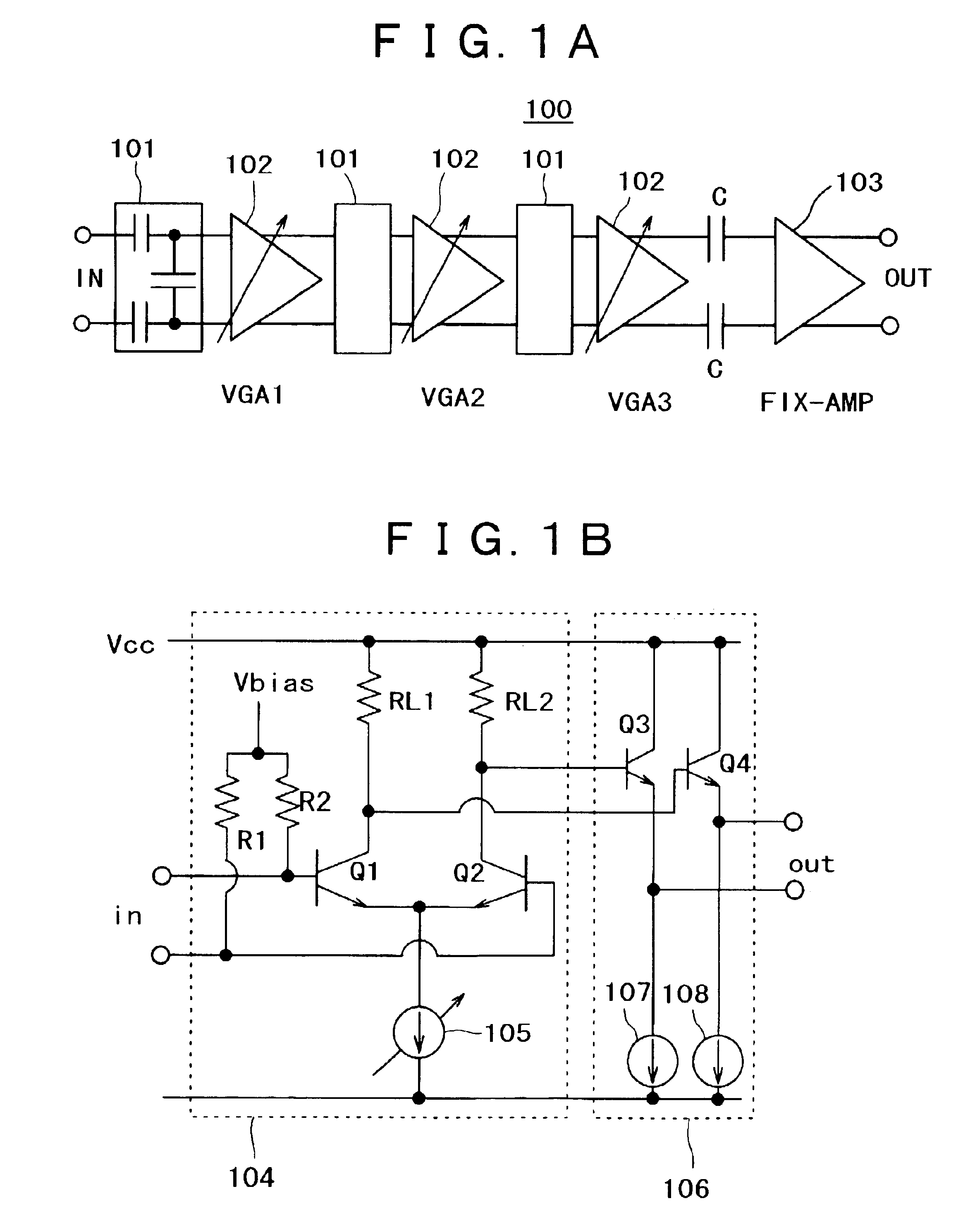
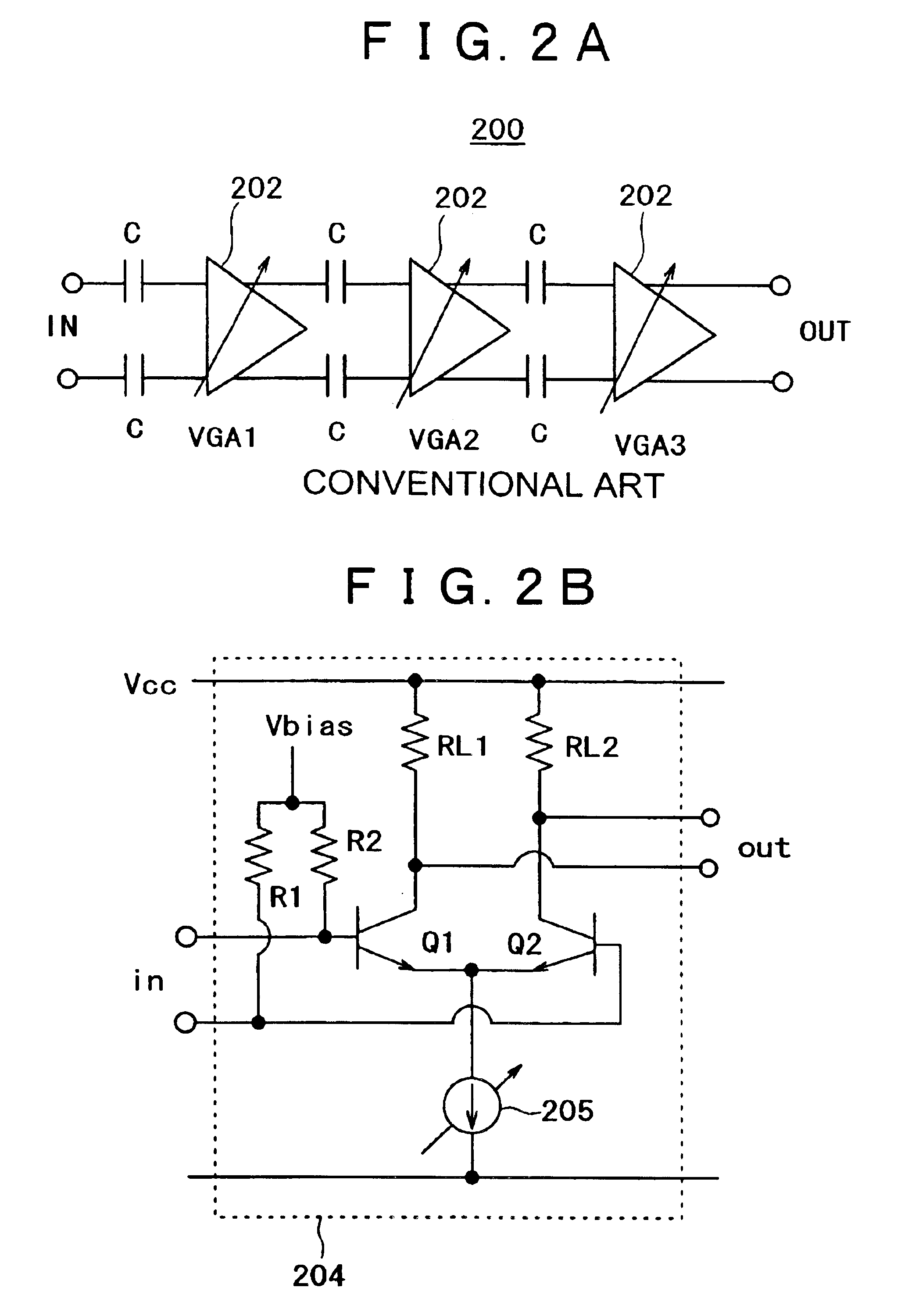
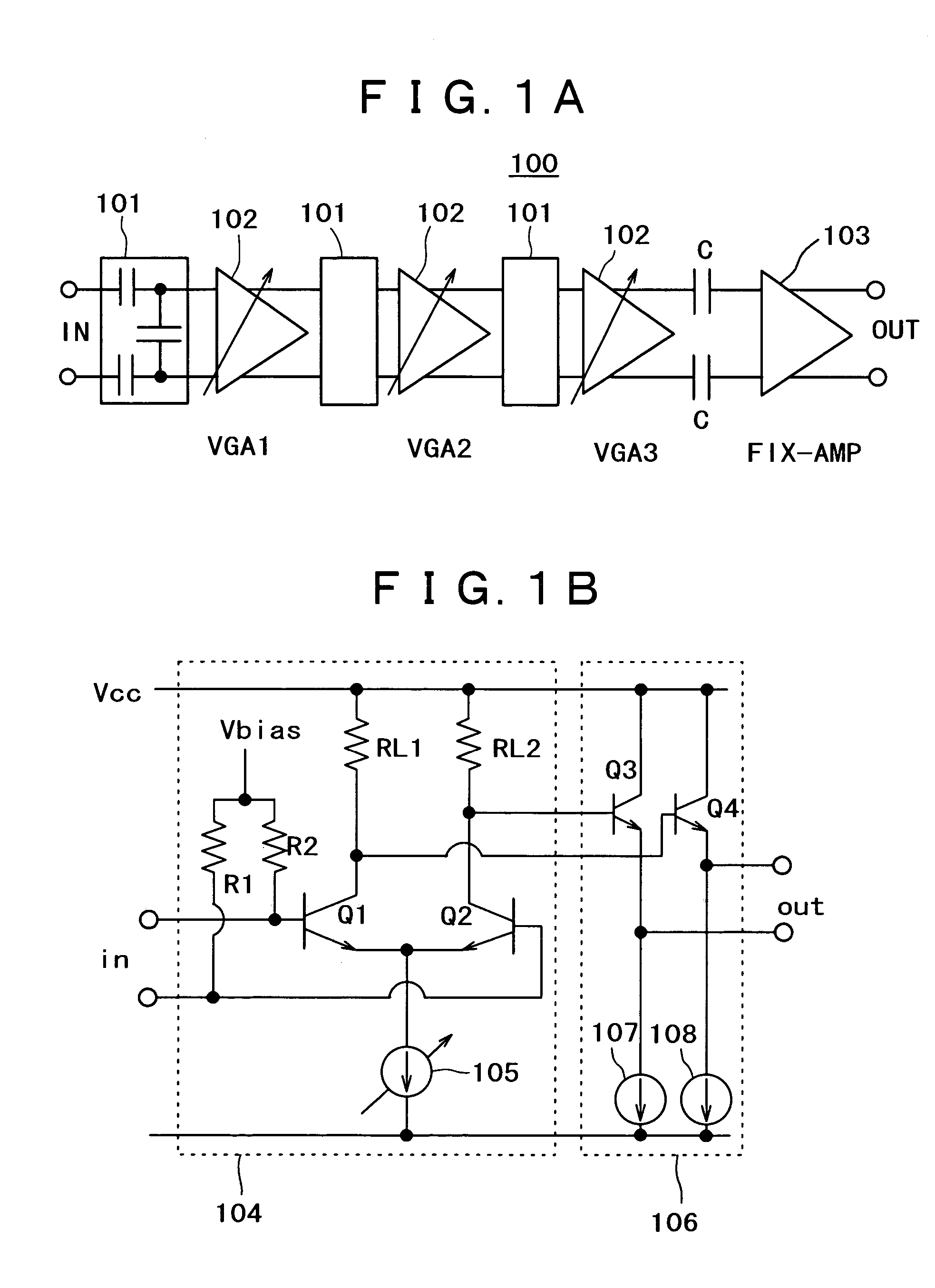
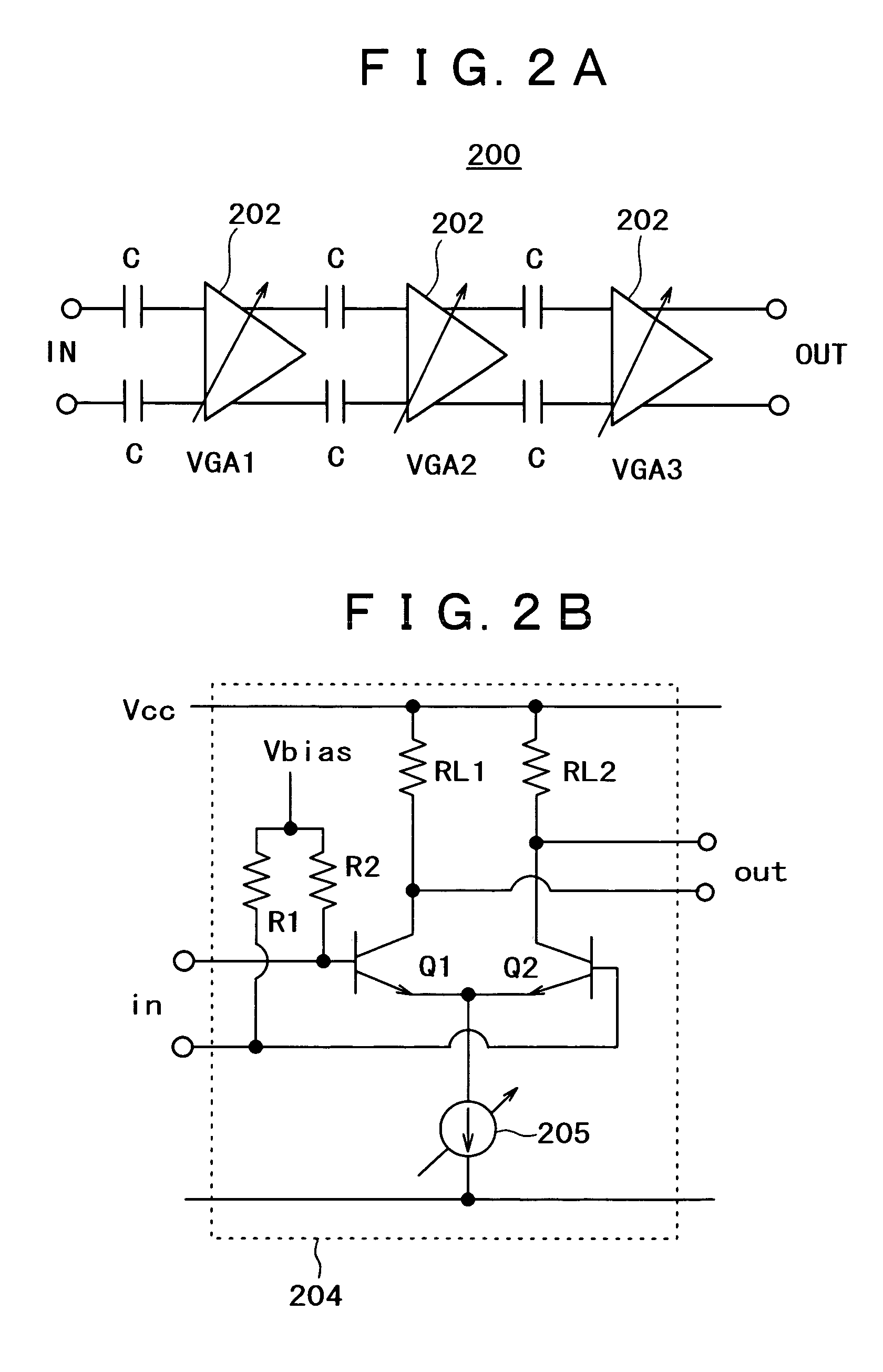
InactiveUS6930549B2Excellent low noise characteristicLimited functionGain controlAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlLow noiseAmplitude distortion
A variable gain amplifier of low amplitude distortion, and low noise, having a large variable range, is provided. A variable gain differential amplifier that controls a gain by use of bias current is used as each of unit amplifiers (VGAs) making up the variable gain amplifier. A large variable gain range is obtained by series-connecting a plurality of the variable gain differential amplifiers. An attenuator is installed on the input side of the unit amplifier (VGA) at least in the initial stage. By doing so, it becomes possible to prevent amplitude distortion from occurring to the respective VGAs. An attenuator utilizing voltage division by capacitors, generating no noise, is used for lowering noise. Further, the variable gain amplifier is provided with a fixed gain amplifier installed in the final stage as necessary in order to obtain a total gain as desired. With the use of the variable gain amplifier as a variable gain amplifier for output power control of a polar loop transmitter, an excellent function for output power control can be achieved without causing significant deterioration in distortion characteristic and noise characteristic thereof.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
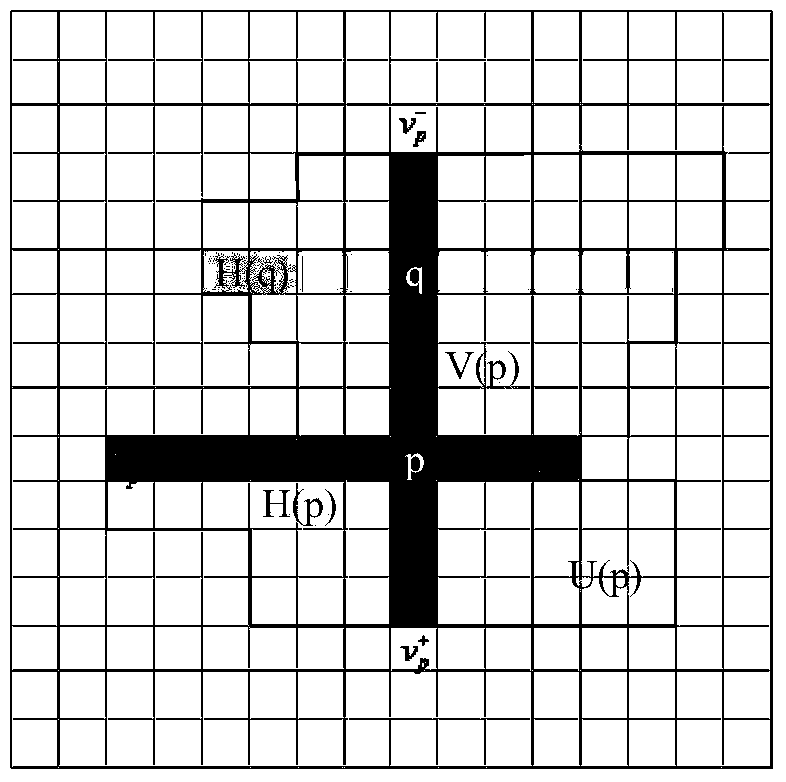
Stereo matching method based on improved gradient and adaptive window
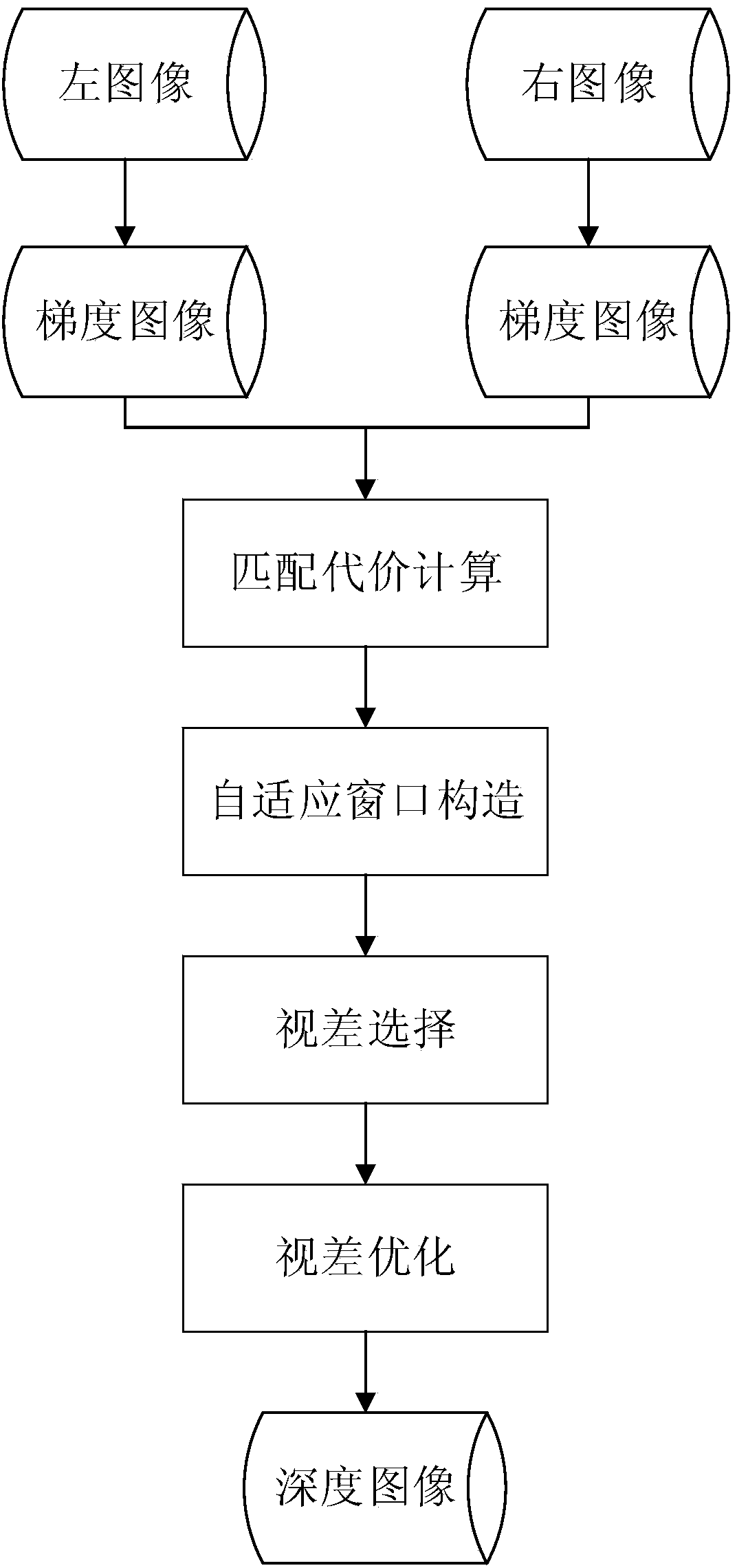
The invention provides a stereo matching method based on an improved gradient and an adaptive window, and aims to solve the problem that an existing local stereo matching algorithm is low in precision and is influenced by amplitude distortion easily. Firstly, on the basis that a traditional gradient vector only contains amplitude information, phase information is introduced, conversion is carried out on the original matching cost, and abnormal values are further eliminated. Then, the adaptive window can be built through the criss-cross adaptive window generation method according to the color and spatial position relation between adjacent pixels, wherein a large window is provided for a low-texture area to improve matching precision, a small window is generated in a high-texture area to protect detail information of the edge of an object and the like, and the aggregated cost is selected according to the Winner-Takes-All strategy so that a disparity value corresponding to the minimum value of the total cost can serve as an initial matching result. Finally, a disparity refinement method based on a local disparity histogram is provided, and a high-precision disparity map is obtained. As is shown in experimental results, the stereo matching method is high in machining precision and has high robustness under the condition of amplitude distortion.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Luminosity insensitivity stereo matching method based on self-adapting Census conversion
InactiveCN102136136ARetain robustnessAdapt to real navigation scenariosImage enhancementAmplitude distortionParallax
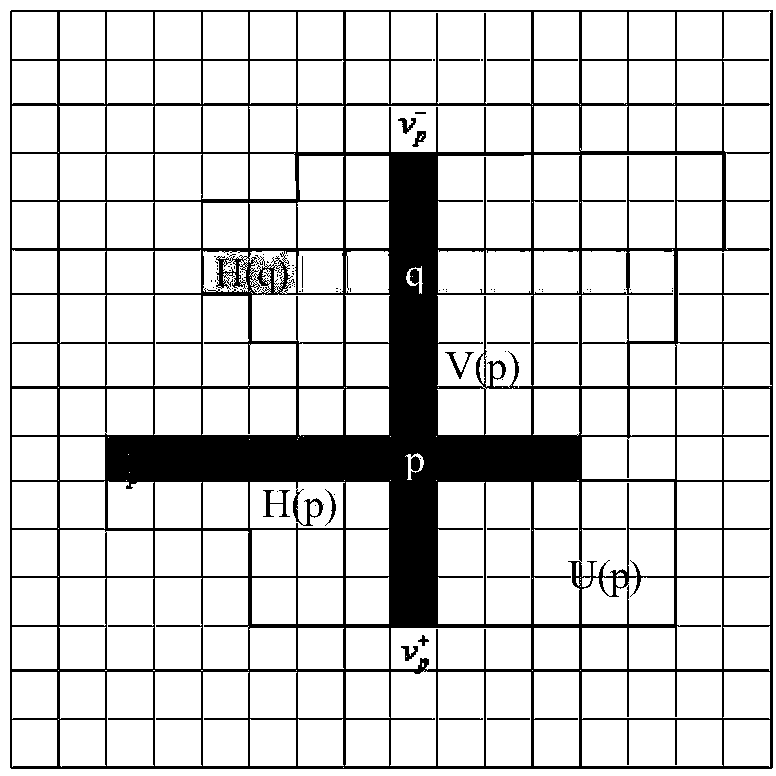
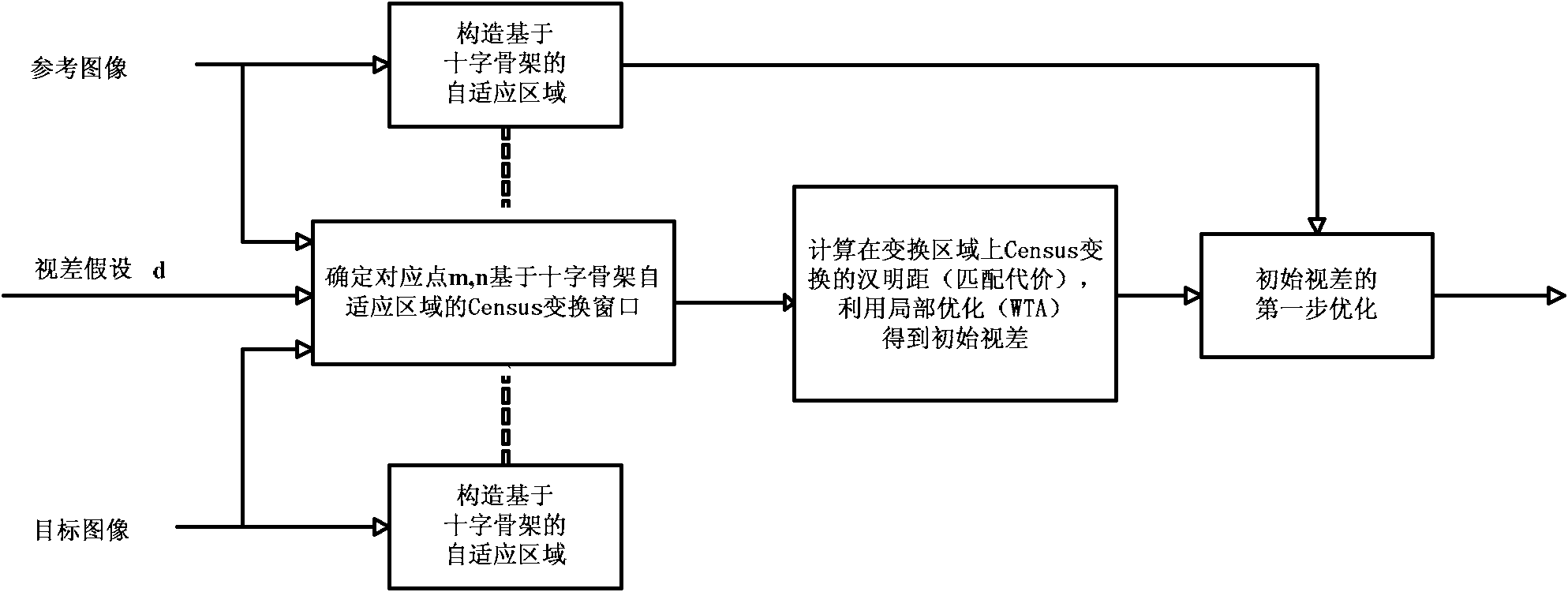
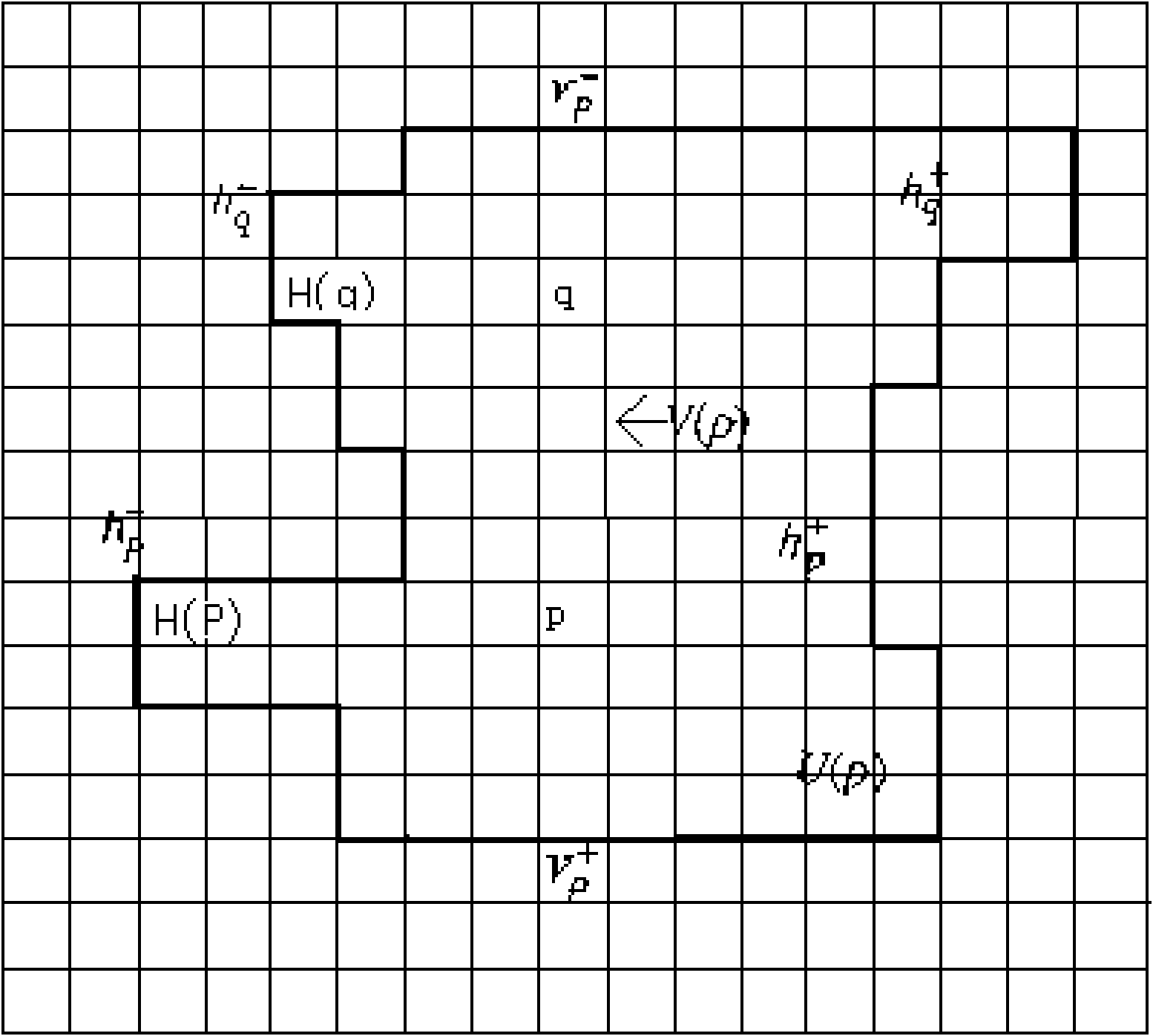
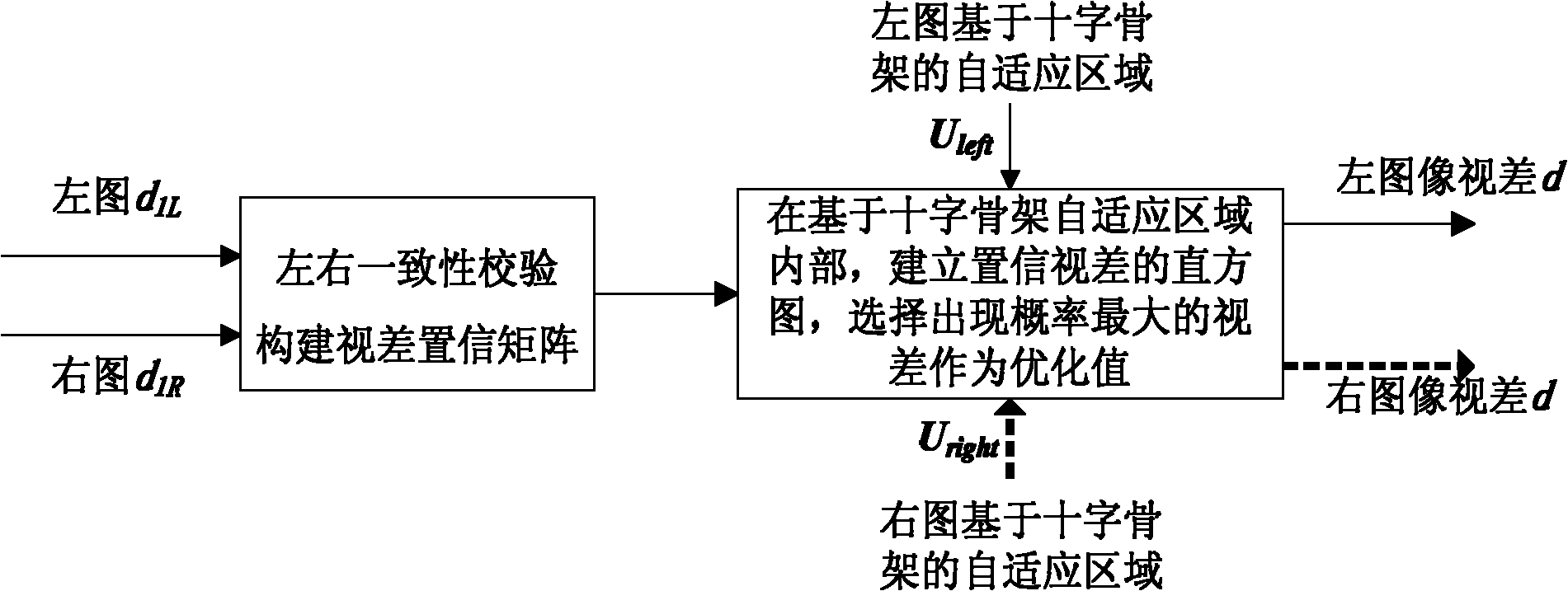
The invention discloses a luminosity insensitivity stereo matching method based on self-adapting Census conversion. Firstly, a self-adapting area based on a cross skeleton is determined according to the structure and color information of an image so as to obtain Census conversion windows of any shape and any size; secondarily, the hamming distance after Census conversion is used as a matching cost and a local optimization method is adopted to calculate an initial parallax; finally, a two-step extracting method based on parallax statistics column diagram and left-right consistency verifying is disclosed to organically integrate the self-adapting area of the cross skeleton into the extracting process to obtain a high-precision parallax diagram. The luminosity insensitivity stereo matching method based on self-adapting Census conversion can obtain the high-precision parallax diagram from a stereo image pair with differences in illumination intensity and exposure time, integrate the matching precision and robustness on amplitude distortion, and be better adapted to application context of visual navigation for unmanned planes.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Stereo matching method based on hybrid matching cost and adaptive window
The invention provides a stereo matching method based on the hybrid matching cost and an adaptive window. Firstly, as an improvement on the traditional gradient matching cost, gradient phase information is introduced, wherein to further improve the robustness of the algorithm, the new hybrid matching cost is provided by normalizing the gray level SAD cost through an exponential function. Then, the adaptive window can be built based on the criss-cross adaptive window generation method according to the color and spatial position relation between adjacent pixels, wherein a large window is provided for a low-texture area to improve matching precision, a small window is generated in a high-texture area to protect detail information of the edge of an object and the like, and the aggregated cost is selected according to the Winner-Takes-All strategy so that a disparity value corresponding to the minimum value of the total cost can serve as an initial matching result. Finally, a disparity refinement method based on a local disparity histogram is provided, and a high-precision disparity map is obtained. As is shown in experimental results, the stereo matching method is high in machining precision and has high robustness under the condition of amplitude distortion.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
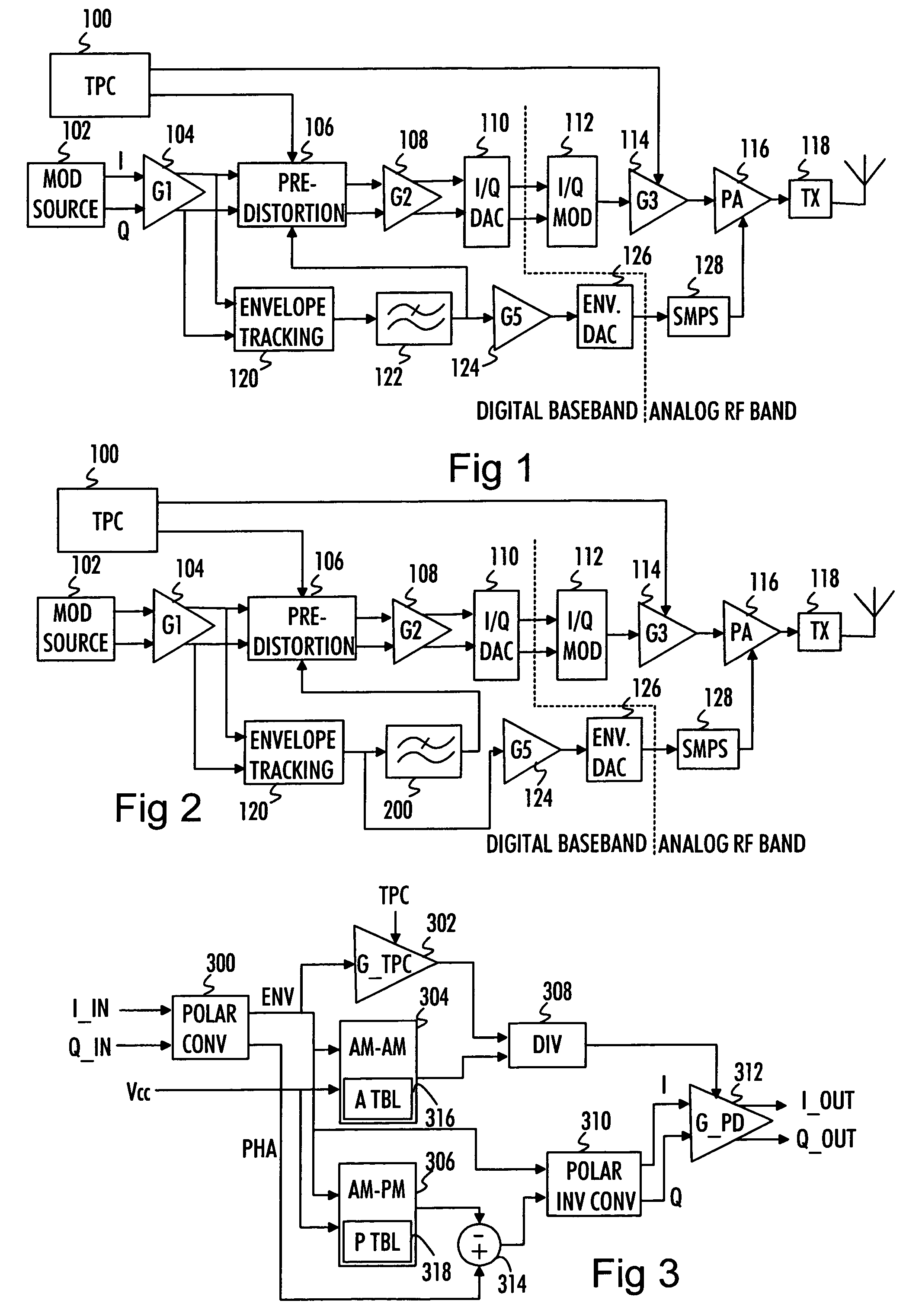
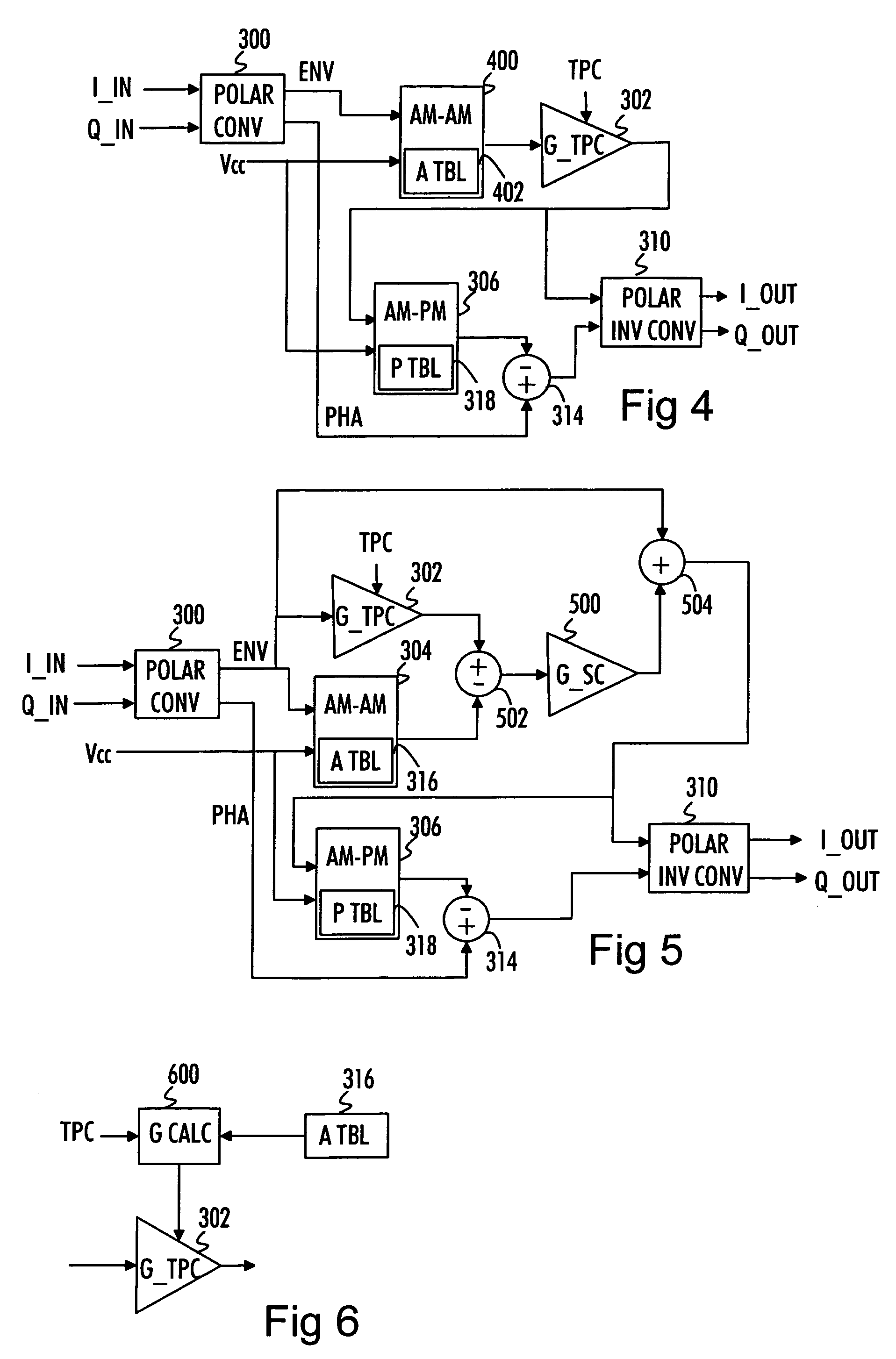
Hybrid polar modulator differential phase Cartesian feedback correction circuit for power amplifier linearization
ActiveUS7409004B2Accurate estimateAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionMemory effect compensationAmplitude distortionAudio power amplifier
The present invention, generally speaking, provides a method of obtaining very accurate estimates of the phase and amplitude distortions introduced by radio frequency or microwave power amplifiers even where polar modulation is used.
Owner:APPLE INC
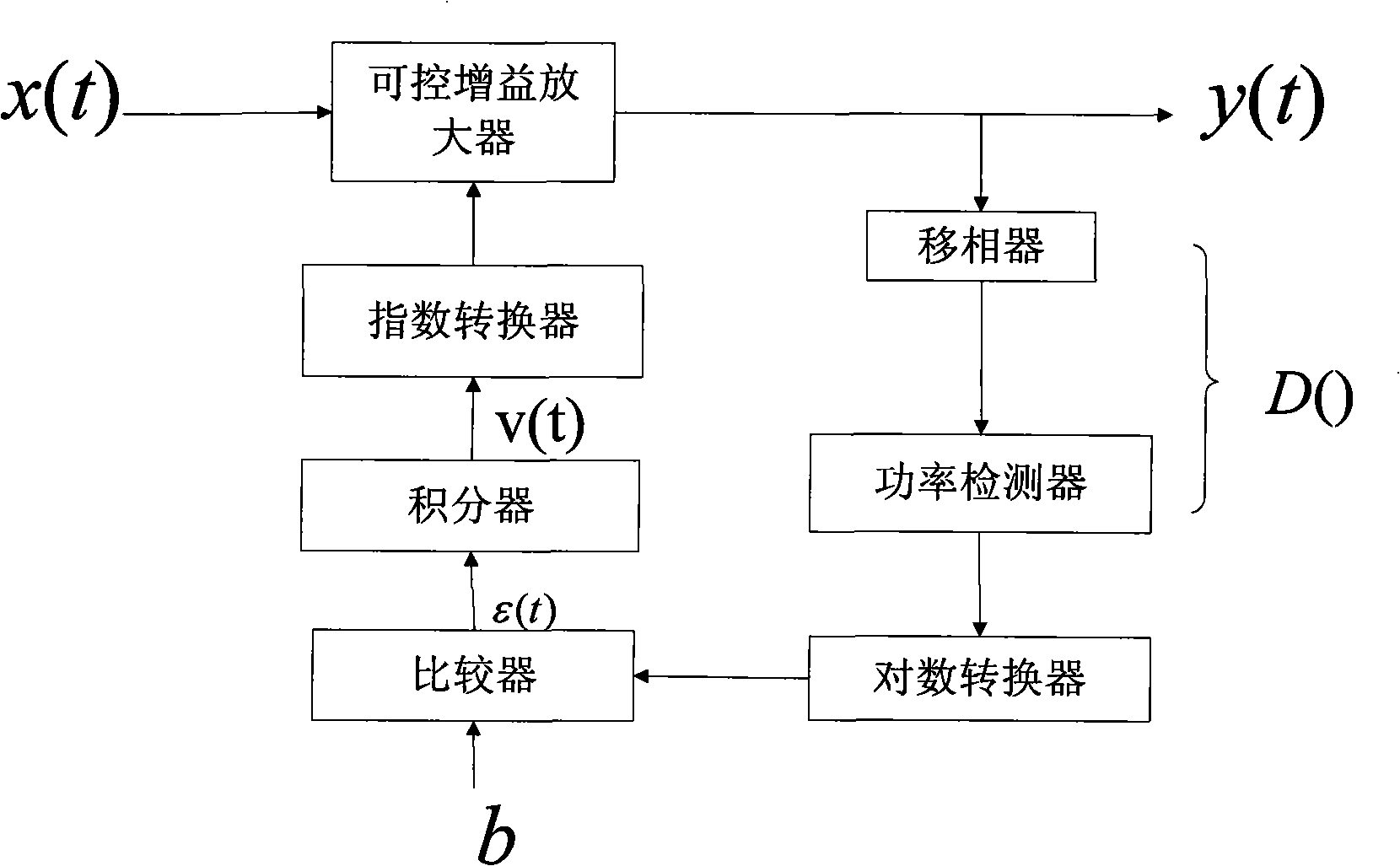
Complete digital logarithm automatic gain control device and method
InactiveCN101257319AEasy to handleHigh control precisionGain controlTransmissionDigital signal processingIntegrator
The invention discloses an all-digital logarithm automatic gain control device and a method thereof. A phase shifter extracts an equidirectional branch data I and a quadrature branch data Q of instantaneous outcoming signal, then a power detector obtains the power of outcoming signal, a logarithmic converter performs the linearizing process to the outcoming signal, compares the results with a system preset parameter b to form an error signal, finally an integrator removes the high-frequency component, an index converter performs the reverse-linearizing process to the error signal, a controllable gain amplifier forms a feedback loop. When the outcoming signal power is larger than the preset value,the gain of the controllable gain amplifier is reduced, and when the outcoming signal power is smaller than the preset value,t he gain of the controllable gain amplifier is enhanced, therefore outputting the digit signal with constant power. The invention avoids the limiting amplitude distortion, considerably reduces the complexity of back-end digital signal processing, enhances the anti-interference and stability of the system and effectively reduces the consumption of hardware system resources.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
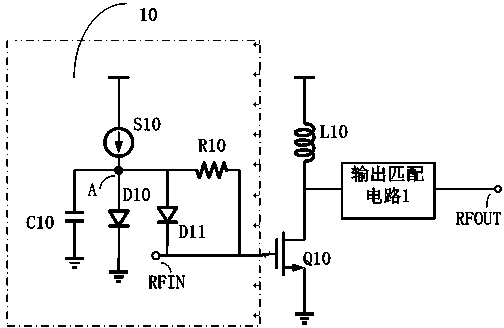
Circuit capable of improving linearity of power amplifier
ActiveCN103715997ACompensation rangeCompensate for phase distortionPower amplifiersAmplitude distortionAudio power amplifier
The invention relates to a circuit capable of improving the linearity of a power amplifier. The circuit comprises a power amplifier circuit, wherein a linearity compensating circuit is arranged at the front end of the power amplifier circuit and comprises a current source, a voltage clamp transistor, a state compensating transistor and an isolation resistor, the current source and the voltage clamp transistor are connected to the ground in series and provide bias voltage for the power amplifier circuit, the isolation resistor is connected between the current source and the signal input end of the power amplifier circuit in series, the state compensating transistor is connected between the current source and the signal input end of the power amplifier circuit in series, and the voltage clamp transistor and the state compensating transistor can be diodes, audios, NMOS tubes and the like. The amplitude distortion and phase distortion generated by the power amplifier can be compensated effectively through the simulated predistortion technology. The circuit is simple in structure, convenient to control, and easy to integrate and implement, and the effect of improvement on the linearity of the power amplifier is remarkable.
Owner:北京昂瑞微电子技术股份有限公司
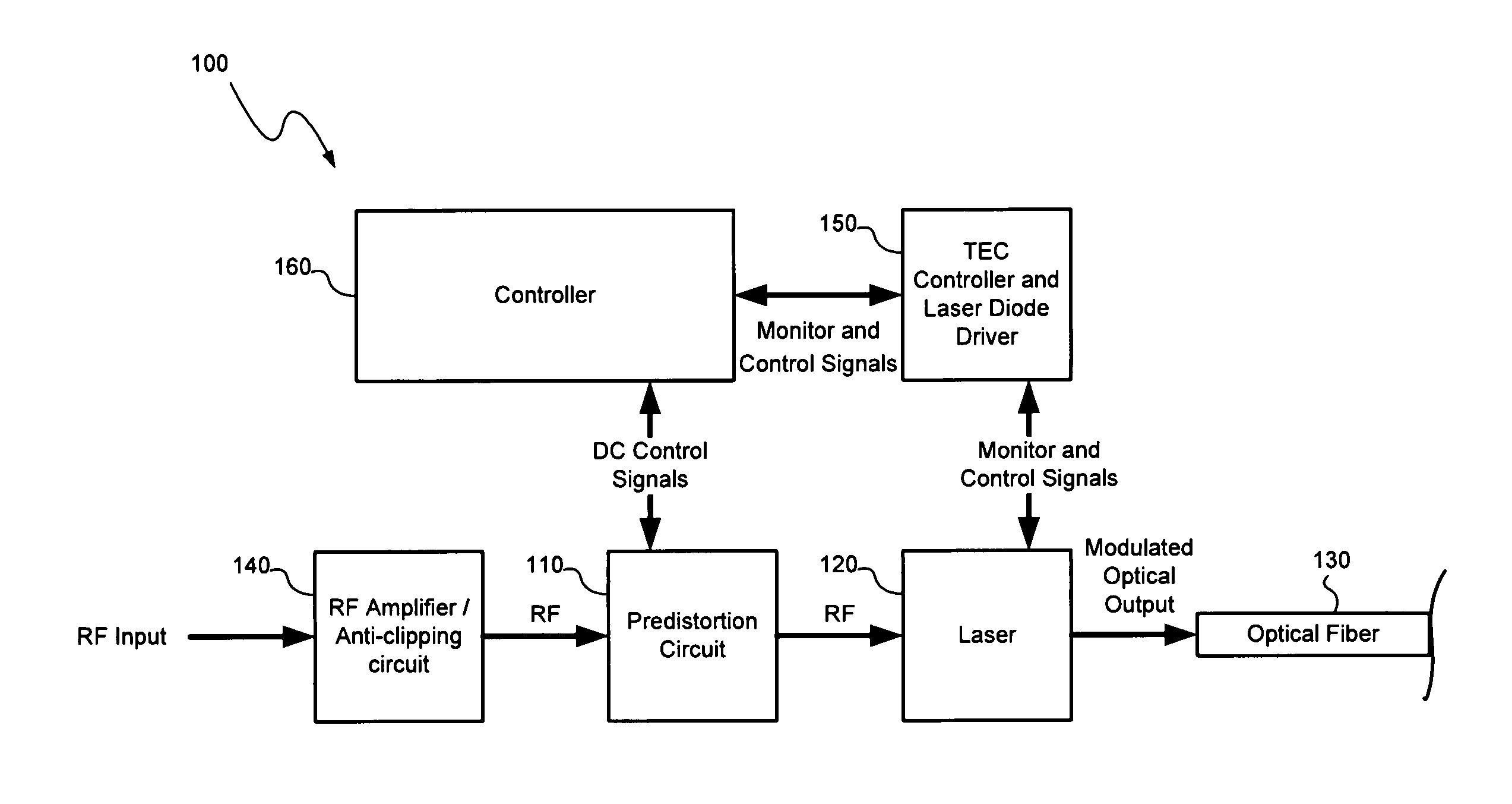
Distortion compensation circuit and method based on orders of time dependent series of distortion signal
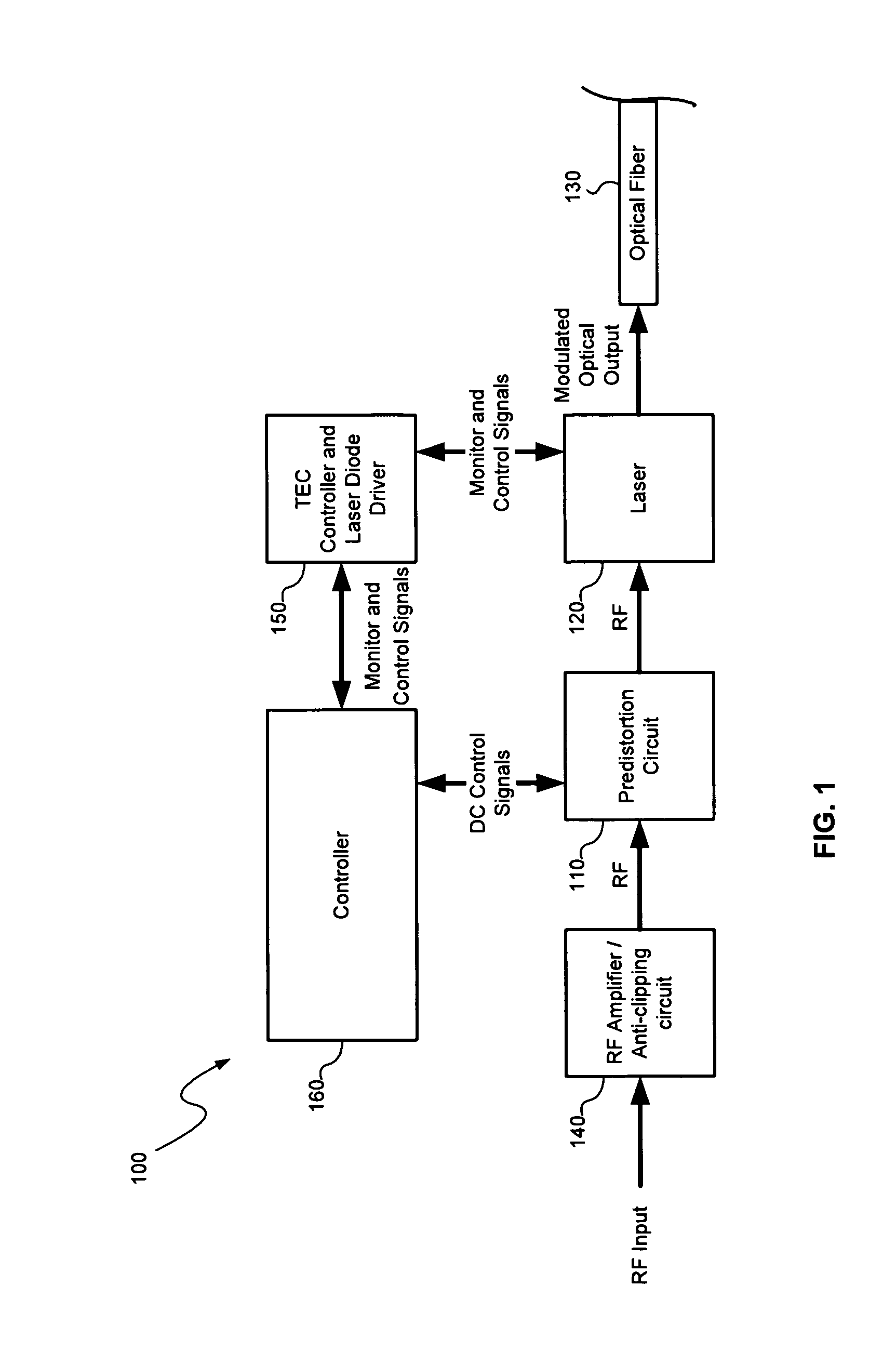
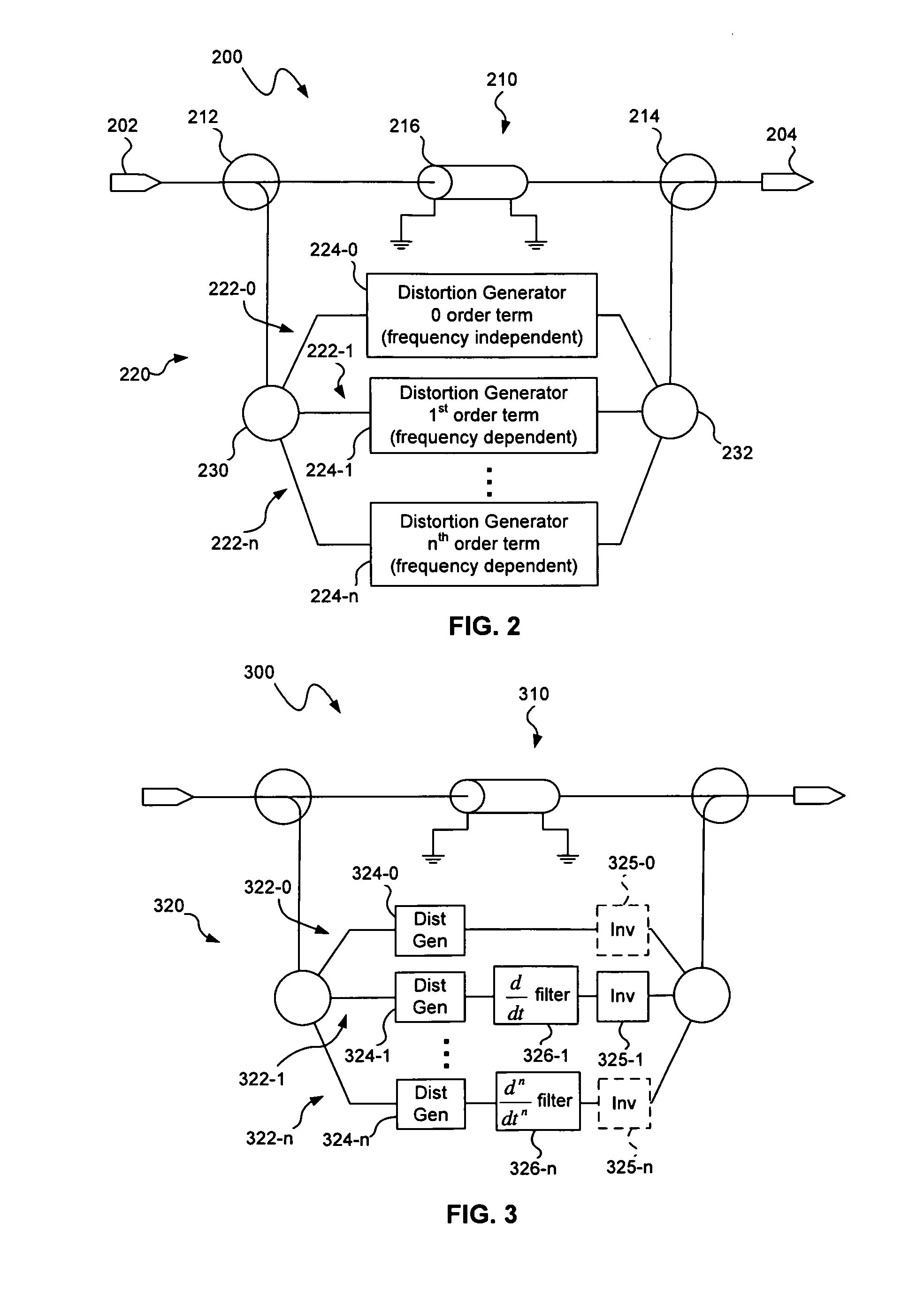
A distortion compensation circuit compensates for distortion generated by one or more non-linear elements such as a laser device. The distortion compensation circuit may be used in an optical transmitter, such as a laser transmitter used for forward path CATV applications. The distortion compensation circuit may include a primary signal path and a secondary signal path that receive an input signal. The secondary signal path produces distortion of a magnitude corresponding to the magnitude of, but at an opposite phase to, the distortion generated by the non-linear amplifier. The secondary signal path includes a plurality of distortion sub-paths with each of the distortion sub-paths configured to produce intermodulation distortion products of the same distortion order but for different frequency dependent orders in a time dependent series representative of the distortion produced by the non-linear amplifier.
Owner:APPLIED OPTOELECTRONICS
Linearity Evaluation Method Using Integrations Weighted by Probability Density Function, and Circuit simulator, Evaluation Device, Communication Circuit, andvProgram Using the Method
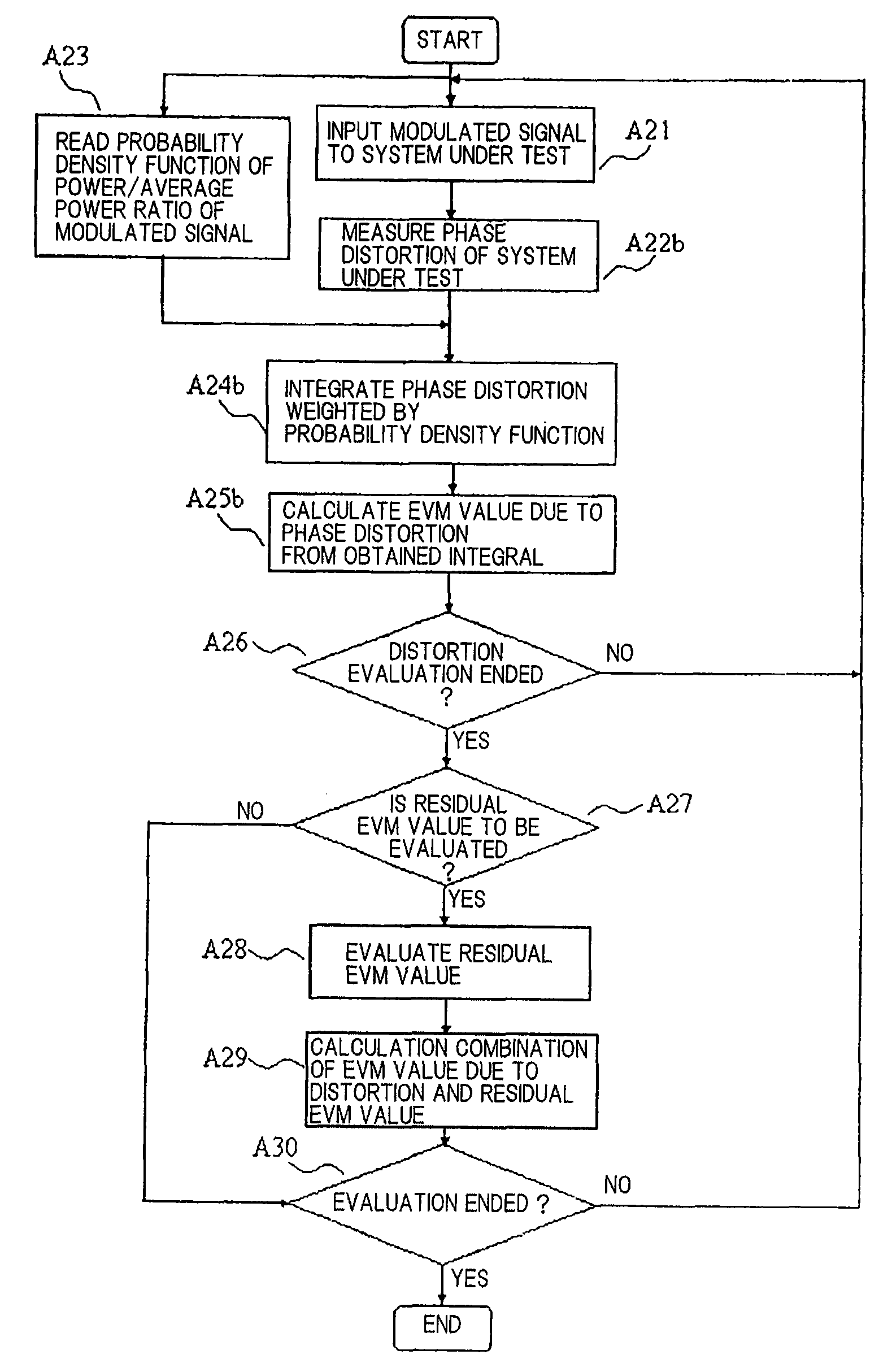
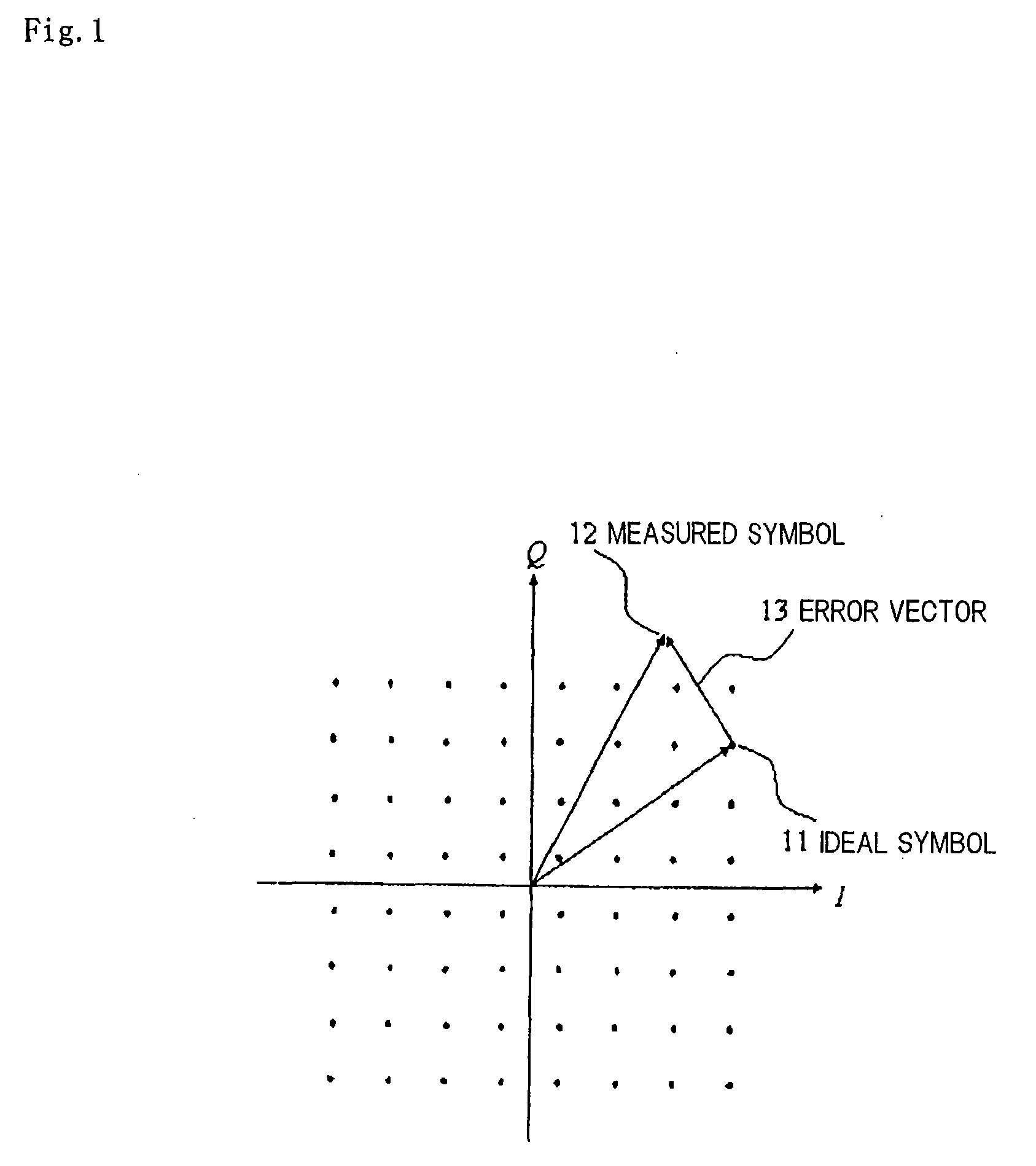
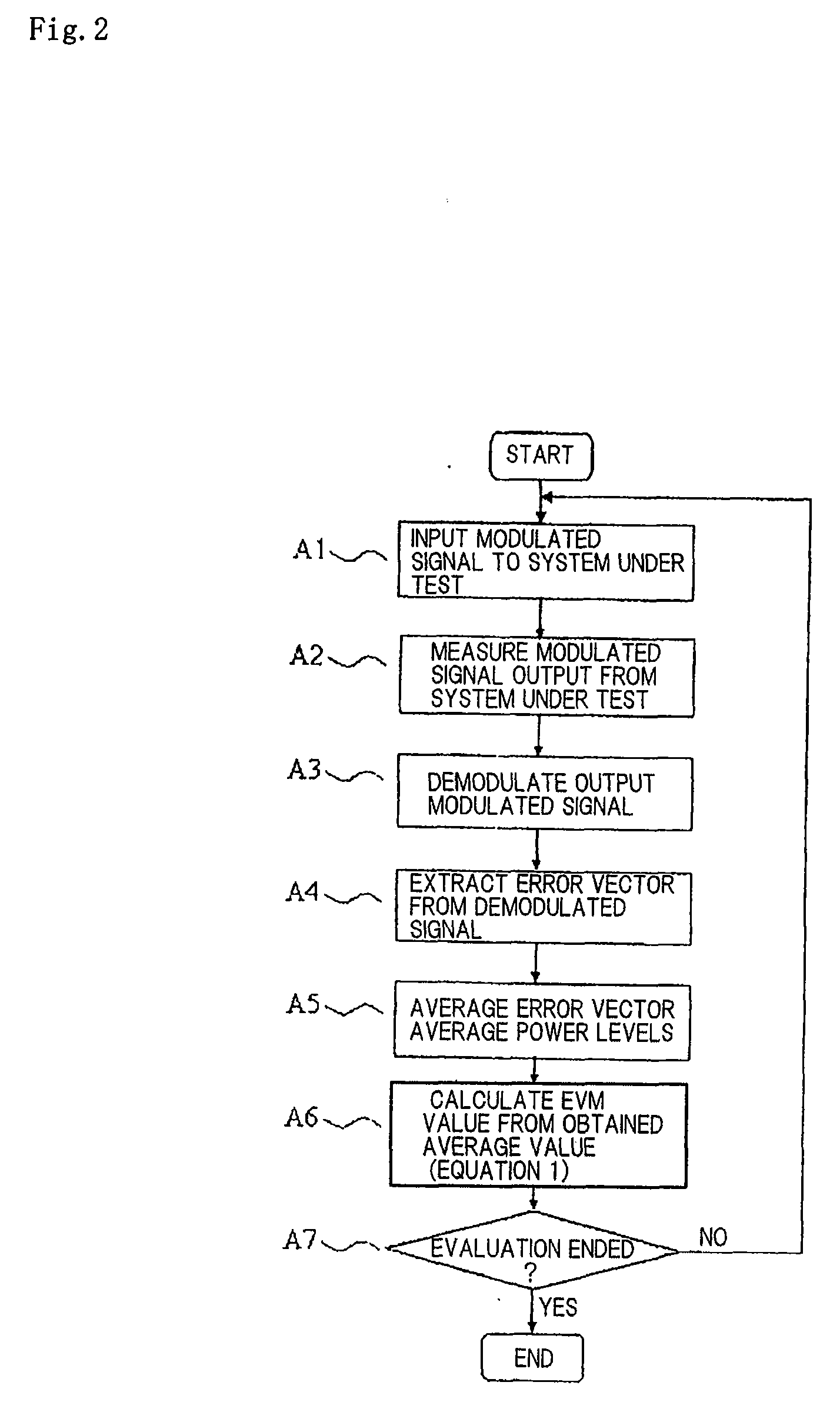
An evaluation method for linearity evaluations neither performing calculations of error vectors at multiple sampling points nor using a demodulator corresponding to a desired modulation scheme. Measuring devices (164 and 165) measure the input signal and the output signal of an evaluation object (1), to which a predetermined evaluation signal has been inputted. An evaluation unit (166) uses the input signal and the output signal of the evaluation object (1), to determine at least one of an amplitude distortion or a phase distortion of the output signal. An integration unit (169) uses the distortions to perform the integrations weighted by the probability density function of the power-to-average ratio of a predetermined modulated signal. A linearity index calculation unit (170) calculates a linearity index from the results of processing by the integration unit (169).
Owner:NEC CORP
Signal predistortion in radio transmitter
ActiveUS7742748B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAmplitude distortionAudio power amplifier
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Radio-frequency circuit having a transcoupling element
InactiveUS8798561B2Reduced insertion lossReduce areaMultiple-port networksResonant long antennasAmplitude distortionOperational costs
An RF circuit having a transcoupler, a multifunctional RF-circuit element that can operate both as an impedance inverter and as a signal coupler. When connected to a fixed load impedance, the transcoupler can also operate as an impedance transformer. The impedance-transformer / inverter functionality of the transcoupler can be used, e.g., to modulate the load of a power amplifier. The signal coupler functionality of the transcoupler can be used, e.g., to generate a corresponding feedback signal indicative of phase and / or amplitude distortions in the amplifier. The use of various embodiments of the transcoupler in an RF circuit can be advantageous, for example, because the transcoupler has a lower insertion loss than a cascade consisting of a prior-art impedance inverter and a prior-art directional coupler, occupies a relatively small area on the printed circuit board, and helps to reduce the per-unit fabrication and operating costs.
Owner:RPX CORP
Predistortion linearization device of millimeter wave power amplifier
ActiveCN103414435AEasy to adjustAdjustable featuresAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersHigh resistanceAmplitude distortion
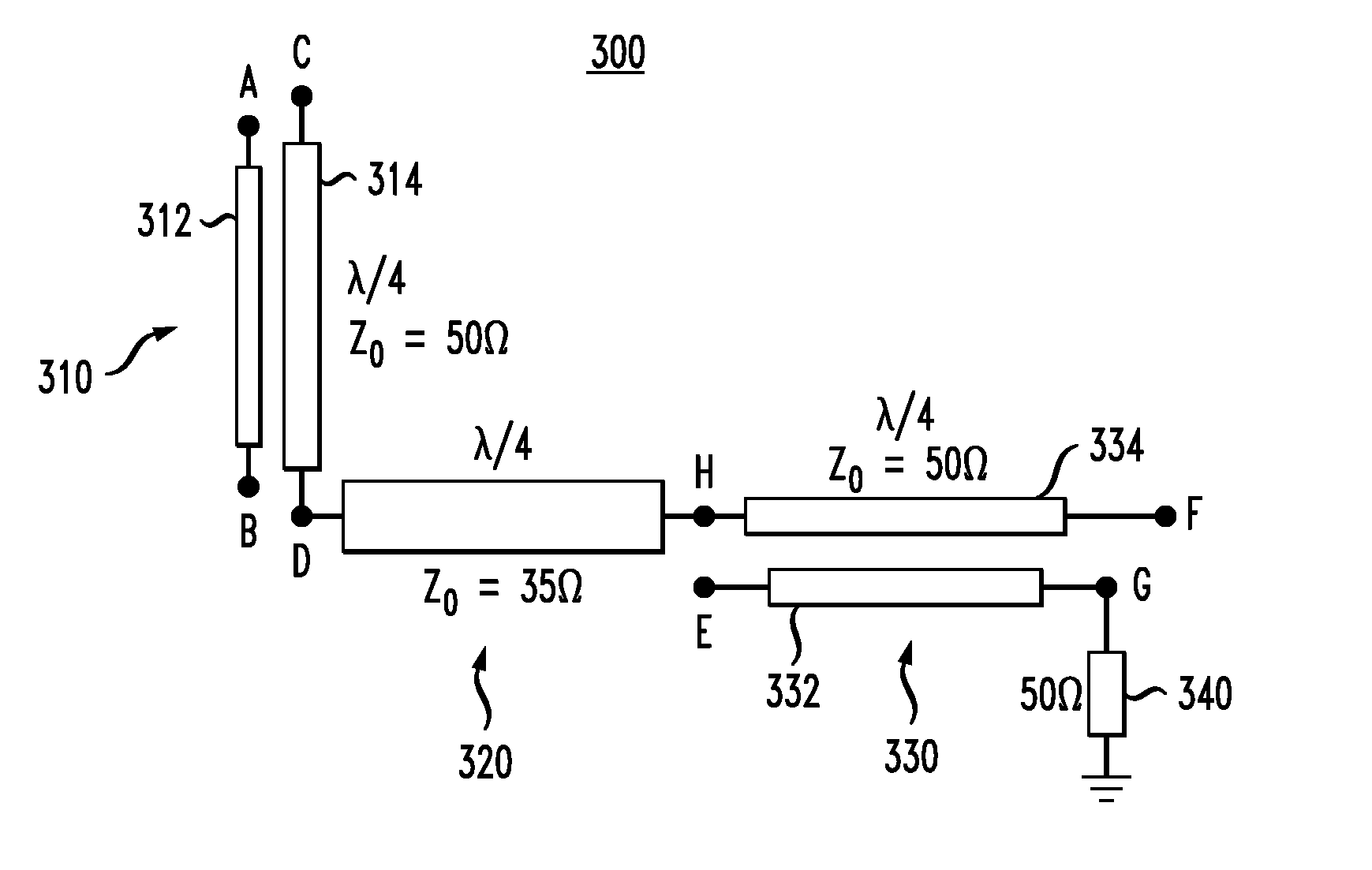
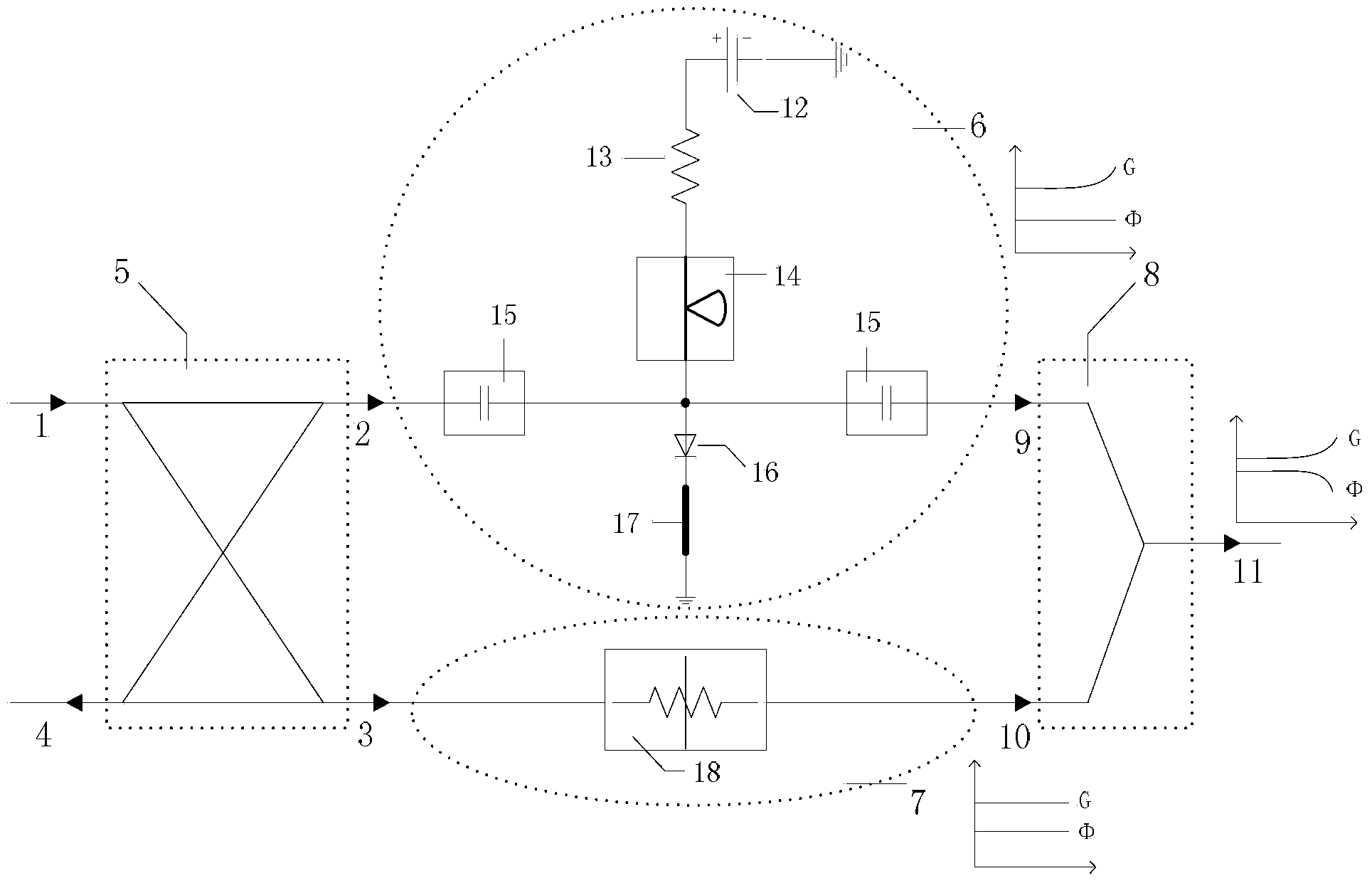
The invention discloses a predistortion linearization device of a millimeter wave power amplifier and aims at providing the predistortion linearization device which is simple in structure, wide in bandwidth, good in stability and suitable for the millimeter wave high-power amplifier, wherein gain and phase are respectively adjustable. According to the technical scheme, a radio frequency signal is input to the input end of an orthocoupler through a radio frequency input port (1), and two paths of orthogonal signals are produced. The signal of one path enters a path I (6) through the straight end (2) of the orthocoupler, bias voltage is adjusted through a DC feed power supply (12), a component with the phase of non-linear conditions not distorted and amplitude distorted is obtained through a high-resistance wire (17) connected with a diode (16), and a signal with the characteristic of gain expansion is output. The signal of the other path enters a path Q (7) by being connected with the isolation end (4) of the orthocoupler and the coupling end of the orthocoupler of a matched load, and a signal with controllable amplitude is output. The two signals finally pass through a power synthesizer (8), then a signal with amplitude and phase both distorted is output, and the amplitude and the phase are respectively adjustable.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Joint carrier synchronization and channel equalization method for OFDM systems
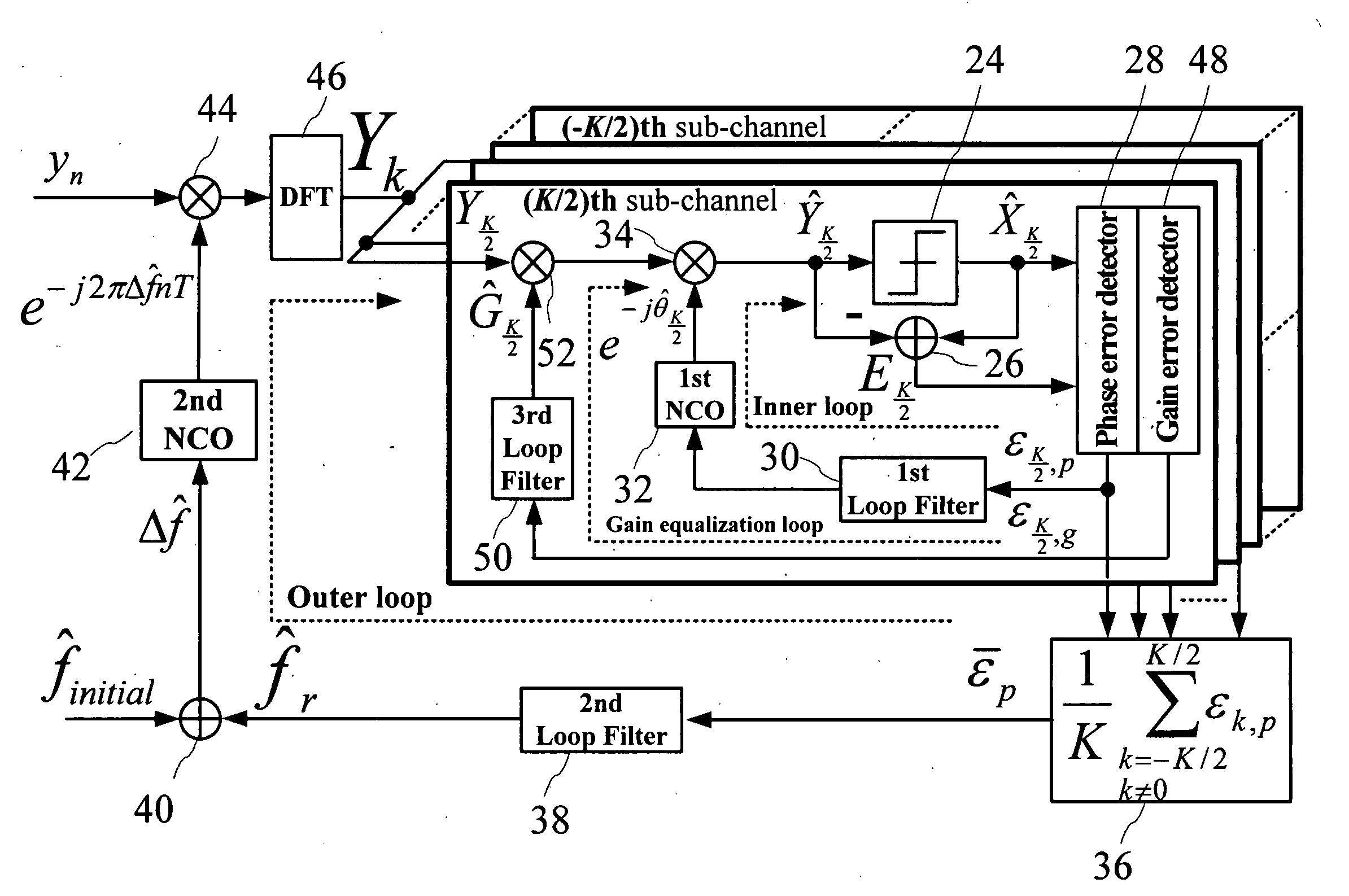
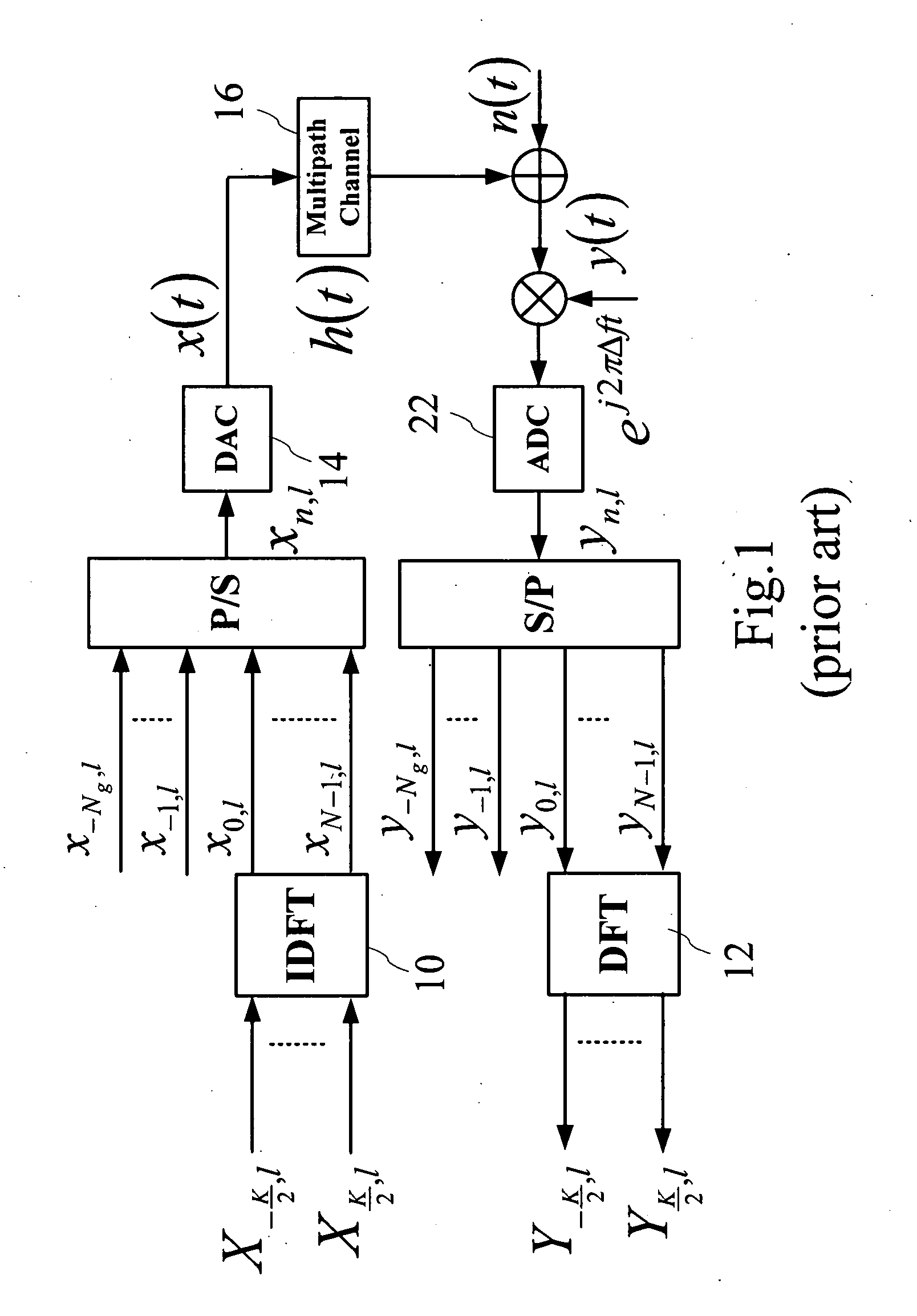
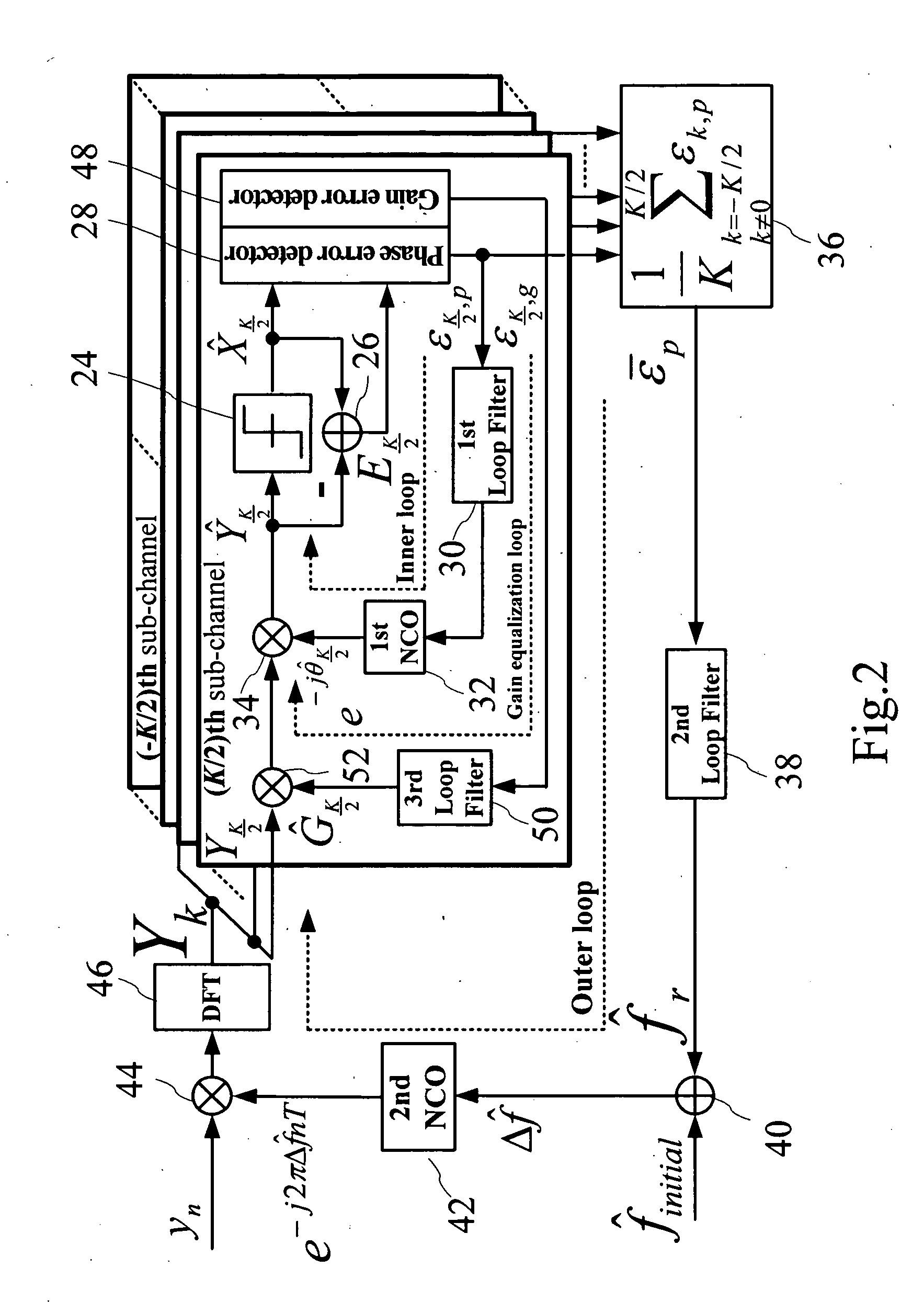
InactiveUS20100239033A1Minimize error powerImprove system performanceSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsFactor baseSignal on
A joint carrier synchronization and channel equalization method for OFDM systems, that is suitable for use in a receiver of said orthogonal frequency division multiplexer (OFDM) systems, comprising the following steps: firstly, receiving a reception signal sample of an OFDM symbol, and obtaining simultaneously a phase error and a gain error on each sub-channel in a frequency domain, through outputting a sub-channel signal on each said sub-channel in said frequency domain; next, obtaining an execution carrier frequency offset factor, an execution phase compensation factor, and an execution gain compensation factor based on said phase error and said gain error; and finally, eliminating a phase offset of said reception signal sample of a next symbol in a time domain based on said factors, and compensating a magnitude distortion and a phase distortion on each said sub-channel in said frequency domain for said reception signal of said next symbol.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
Directional hearing given binaural hearing aid coverage
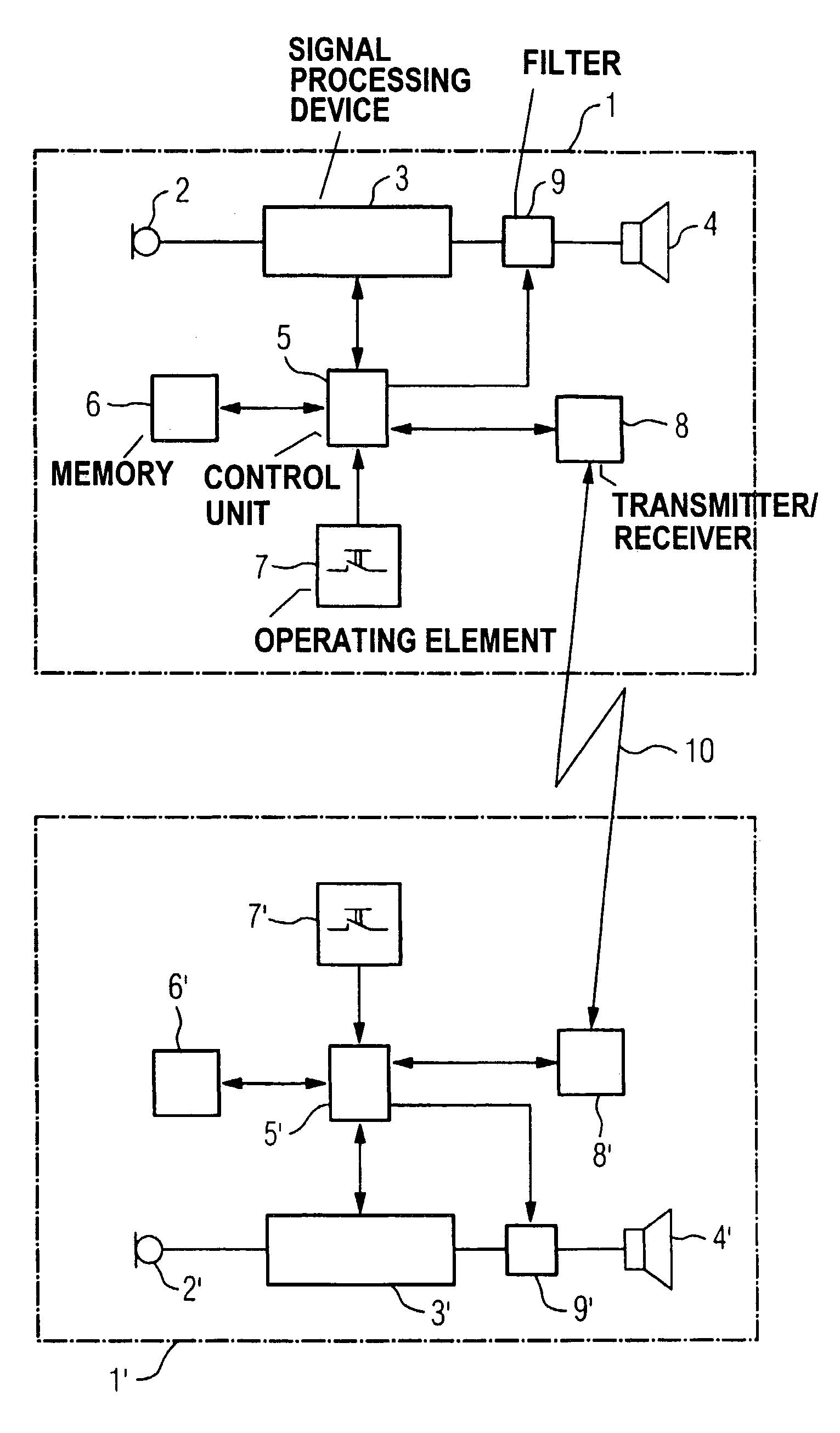
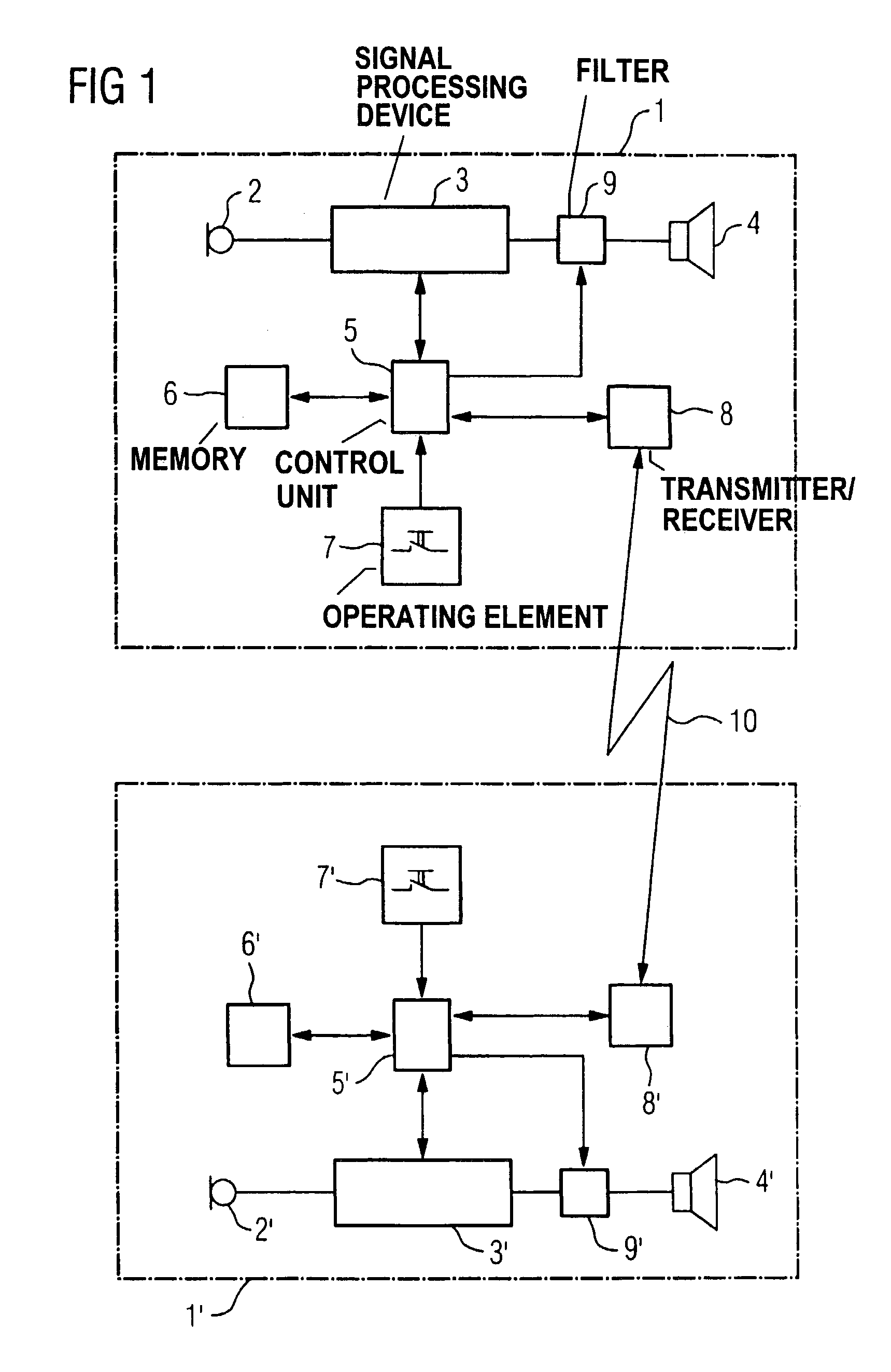
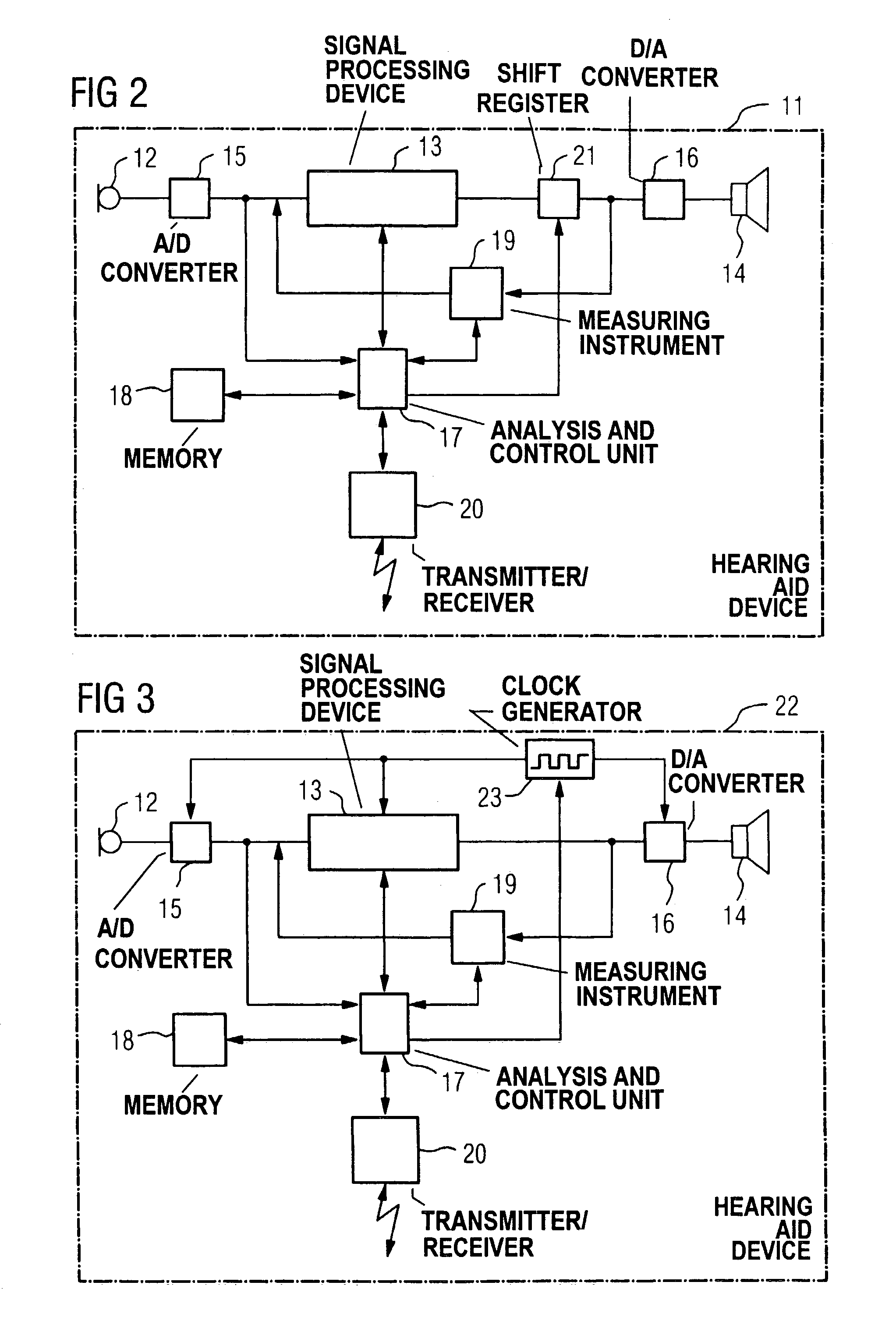
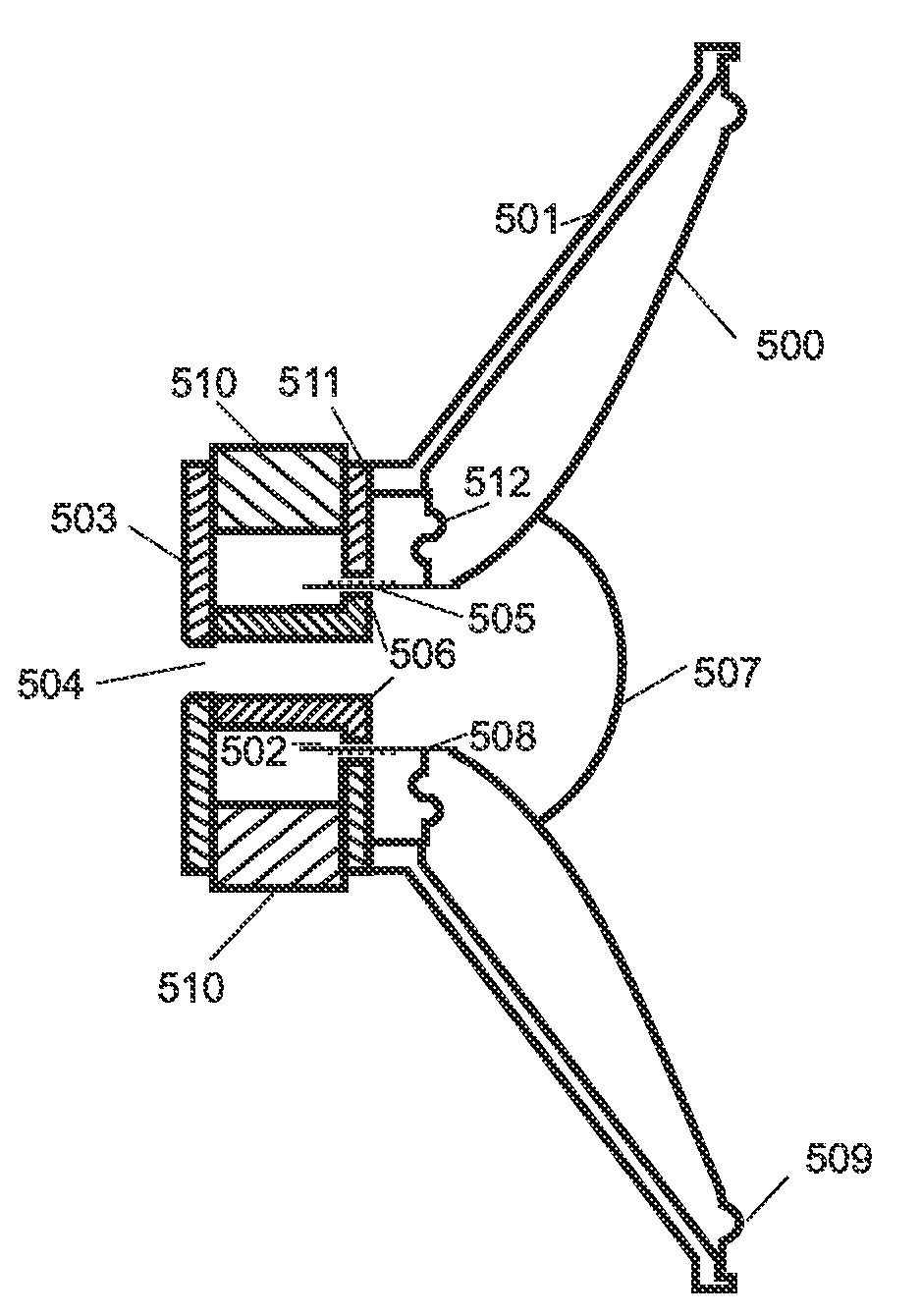
InactiveUS7474758B2Minimize the additional computing outlayDeaf-aid setsAmplitude distortionTransducer
Directional hearing is improved given the binaural coverage for a hearing aid user with two hearing aid devices wearable at the ears. The respective signal transit times and / or signal amplitudes and / or amplifications of an electrical signal are respectively measured in a signal path between an input transducer and an output transducer and that data with respect to the measured signal transit times and / or signal amplitudes and / or gains is transmitted onto the respectively other hearing aid device. As a result, the signal transit times and the signal amplitudes of the electrical signals through the two hearing aid devices can be matched to one another. The hearing aid devices thus cause no phase or amplitude distortion, and the natural phase shift as well as the natural amplitude difference of a sound signal incident from a specific direction are thus preserved. The directional information is thus also preserved for the hearing aid user.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
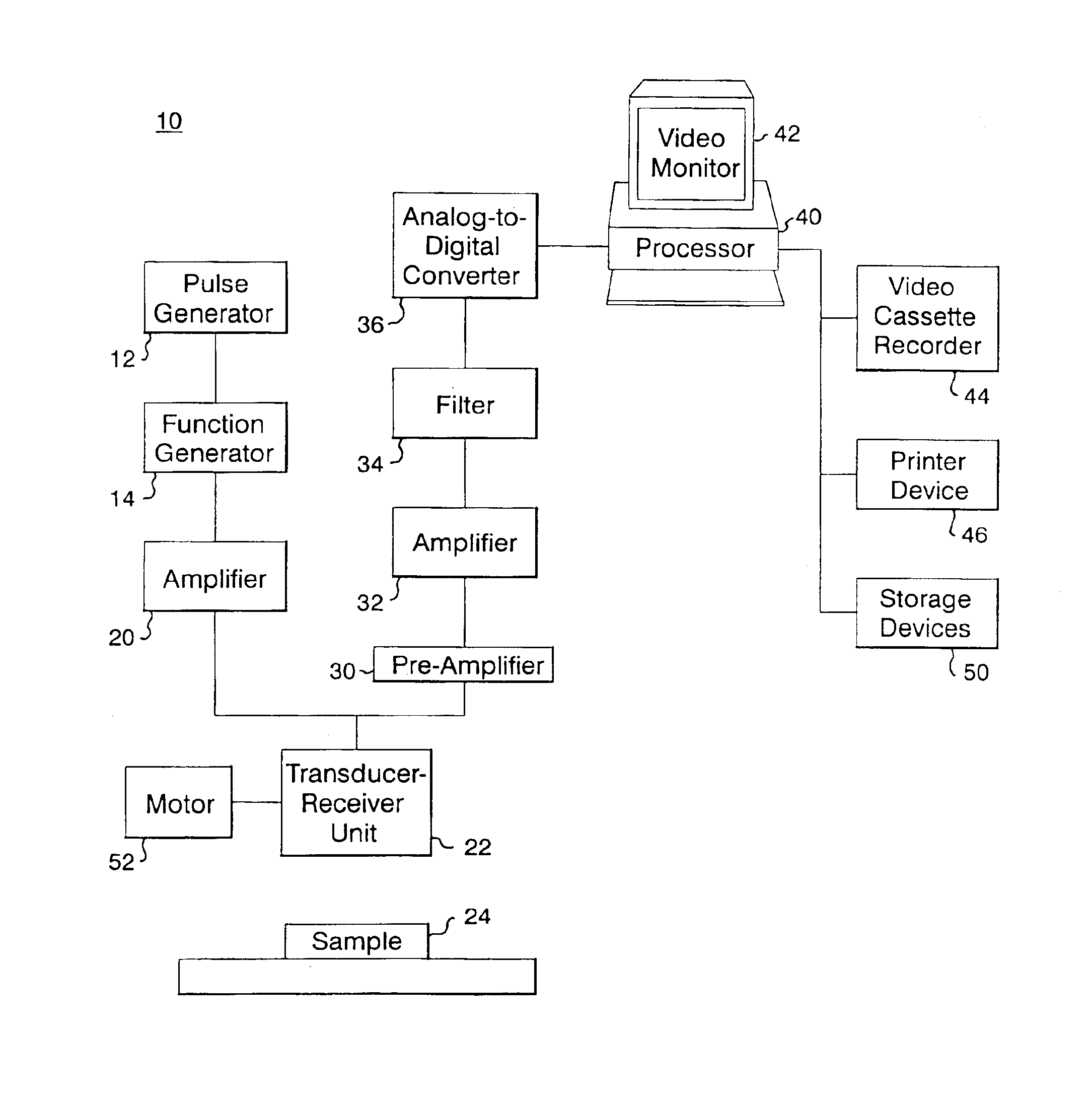
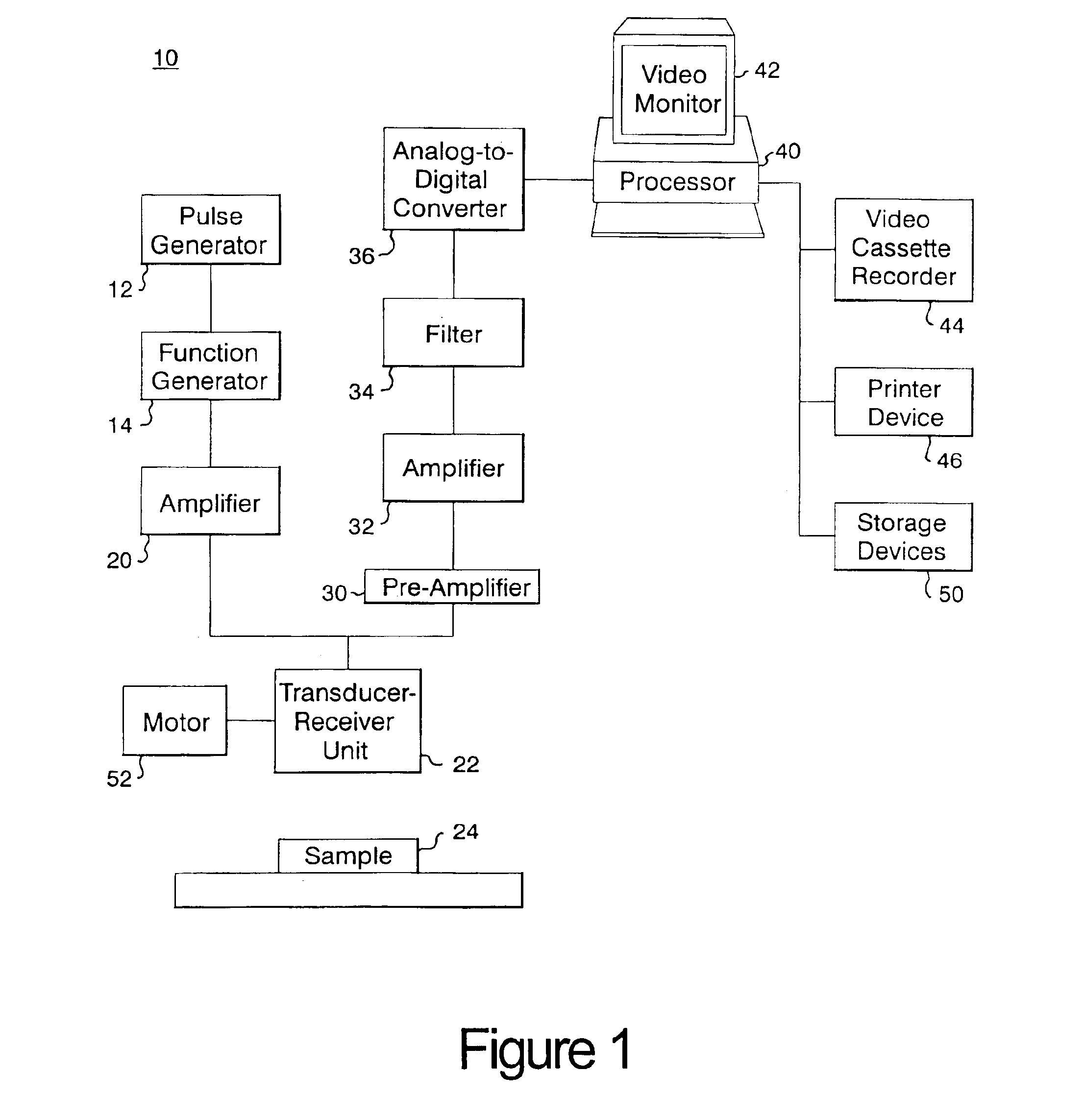
Finite amplitude distortion-based inhomogeneous pulse echo ultrasonic imaging
InactiveUS7004905B2Improve imaging resolutionEnhanced inhomogeneous focusing propertyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsAmplitude distortionSonification
A method and system for imaging a sample. The method includes the steps of generating an ultrasonic signal, directing the signal into a sample, which signal is distorted and contains a first order and higher order component signals at first and higher frequencies respectively. The received distorted signal is processed, and an image is formed, and then displayed, from one of the higher order component signals of the received distorted signal.
Owner:RES CORP TECH INC
Automatic gain control method and device
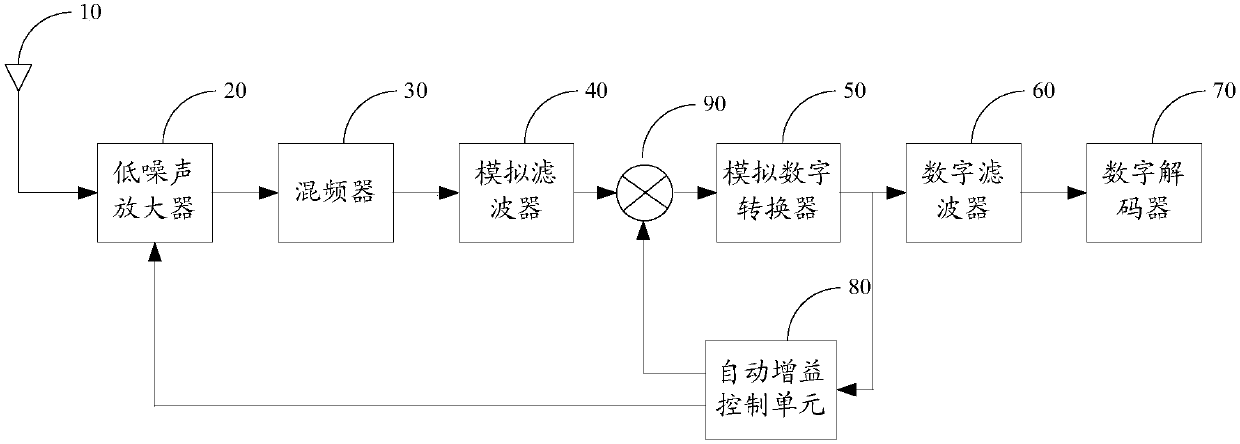
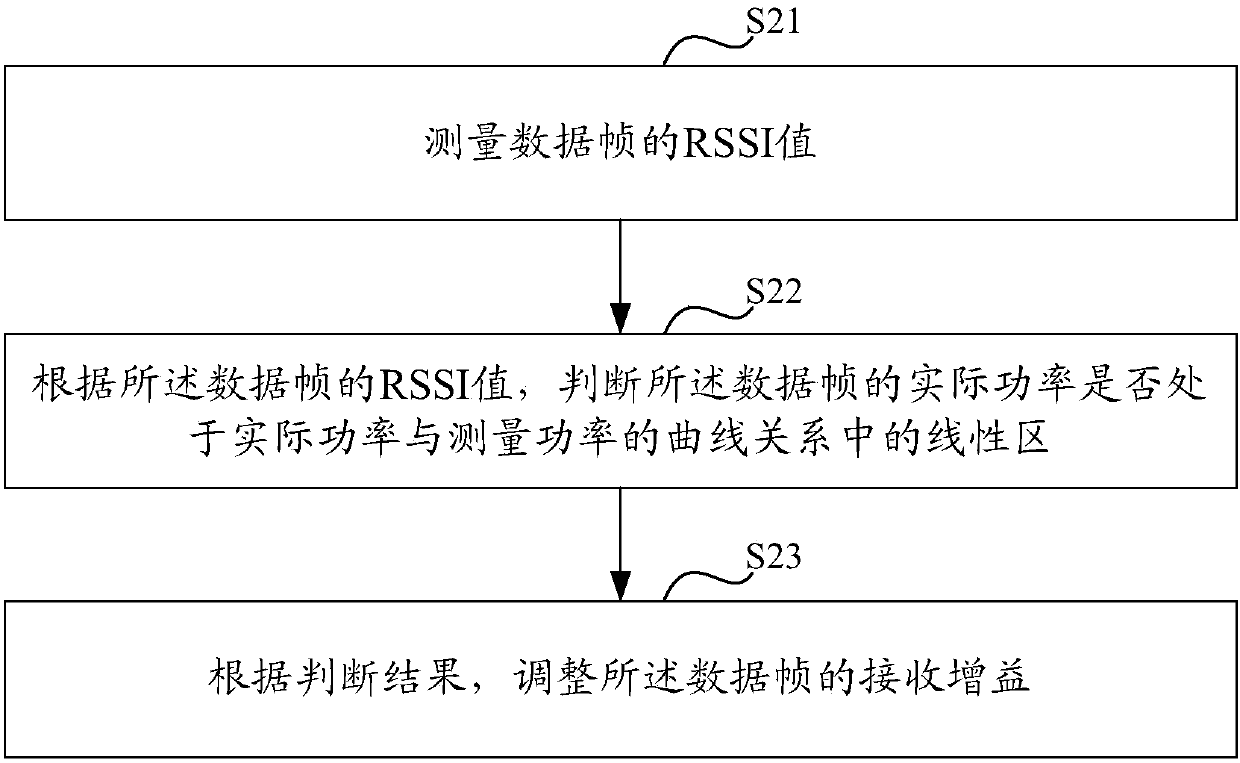
ActiveCN107645283AImplement Automatic Gain ControlImprove receiver sensitivityGain controlNear-field systems using receiversAmplitude distortionFrame based
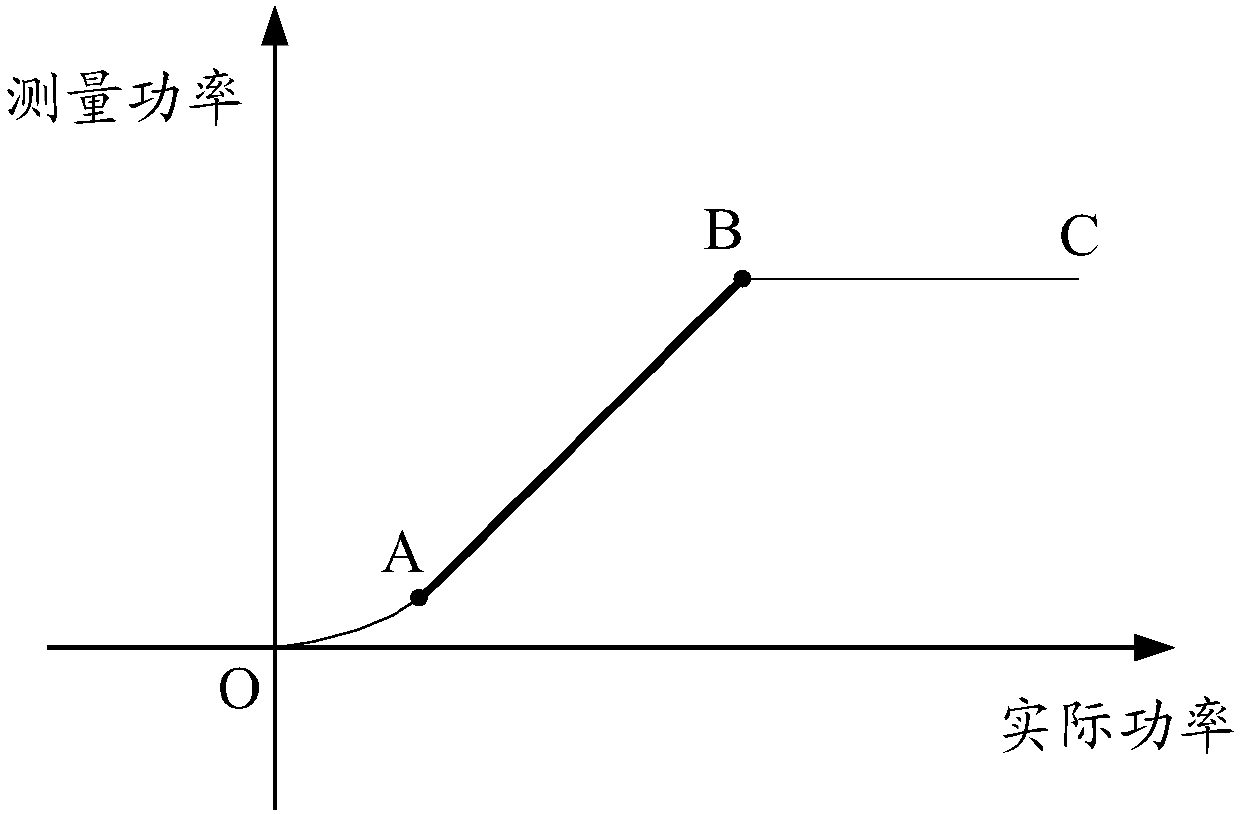
The invention discloses an automatic gain control method and device, which are used for resolving the problem that the conventional automatic gain control method may lead to in-band amplitude distortion and greatly reduce the function of a Bluetooth device. The method comprises the steps of measuring the RSSI value of a data frame; determining whether the actual power of the data frame is within alinear zone of curve relationship between the actual power and the measuring power or not based on the RSSI value of the data frame; adjusting the receiving gain of the data frame based on the judging result. The invention is advantageous in that the device can work at the best gain point, and the receiving sensitivity and anti-interference performance can be bettered.
Owner:ACTIONS ZHUHAI TECH CO
Wireless communication apparatus and receiving method
InactiveUS7885360B2Single output arrangementsElectric pulse generatorAmplitude distortionFourier transform on finite groups
A wireless communication apparatus receives an quadrature modulated signal, generate a local signal having a frequency different from a center frequency of the quadrature modulated signal, performs quadrature demodulation on the quadrature modulated signal by using the local signal, to obtain an I channel signal and a Q channel signal, performs Fourier transform on the I channel signal and the Q channel signal, to obtain signals in a frequency domain, and calculates a first correction coefficient for correcting phase distortion and amplitude distortion caused by the quadrature demodulation by using pairs of signals among the signals, each of the pairs are located at symmetrical frequency positions with respect to the frequency of the local signal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Digital signal receiver and method for receiving digital signal
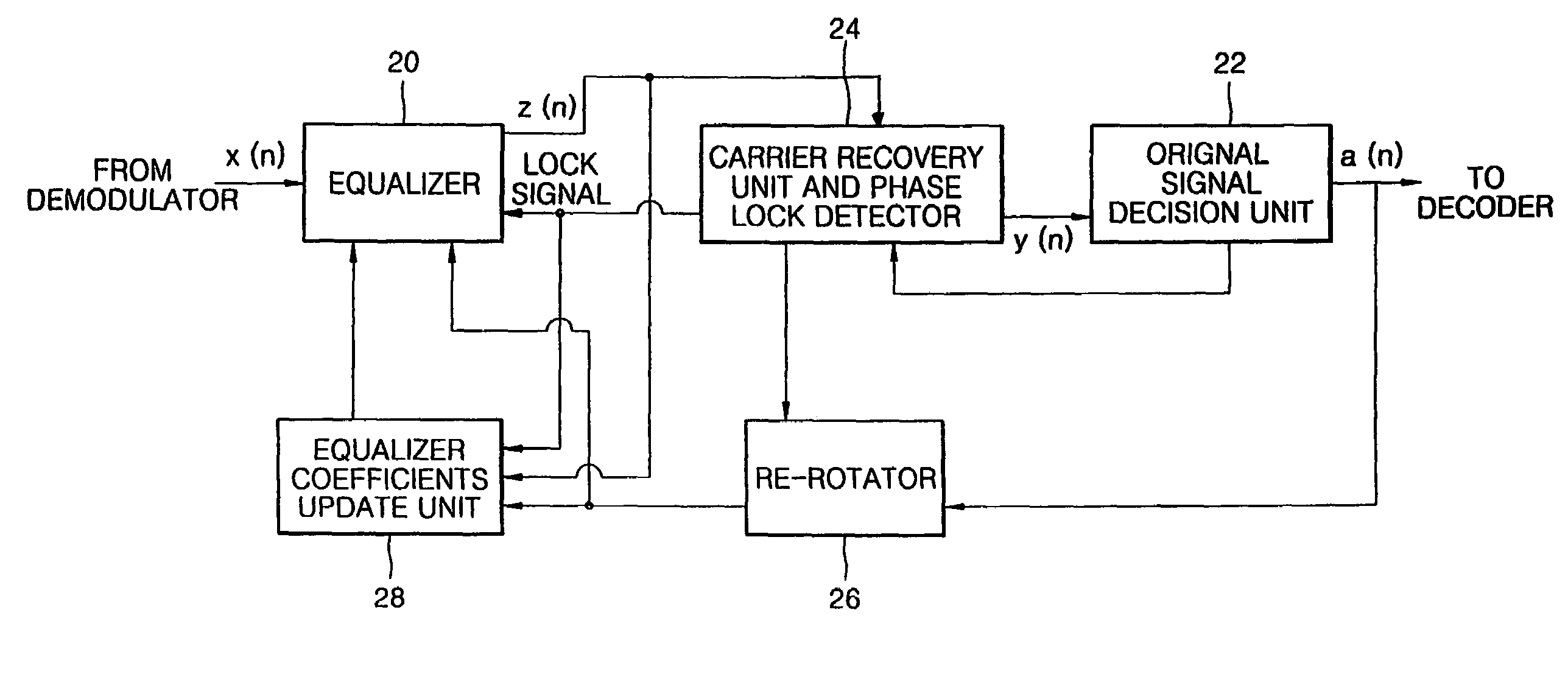
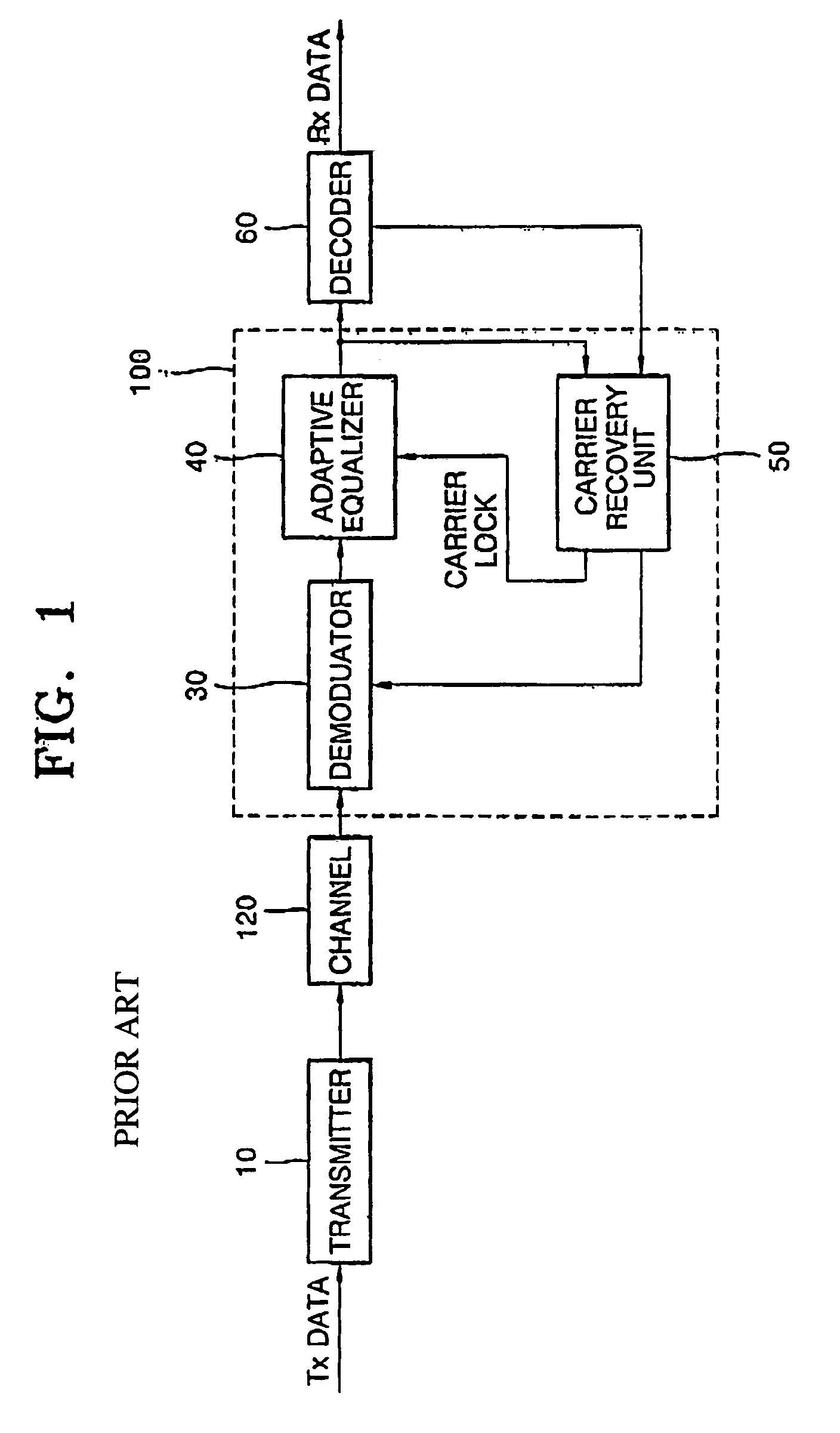
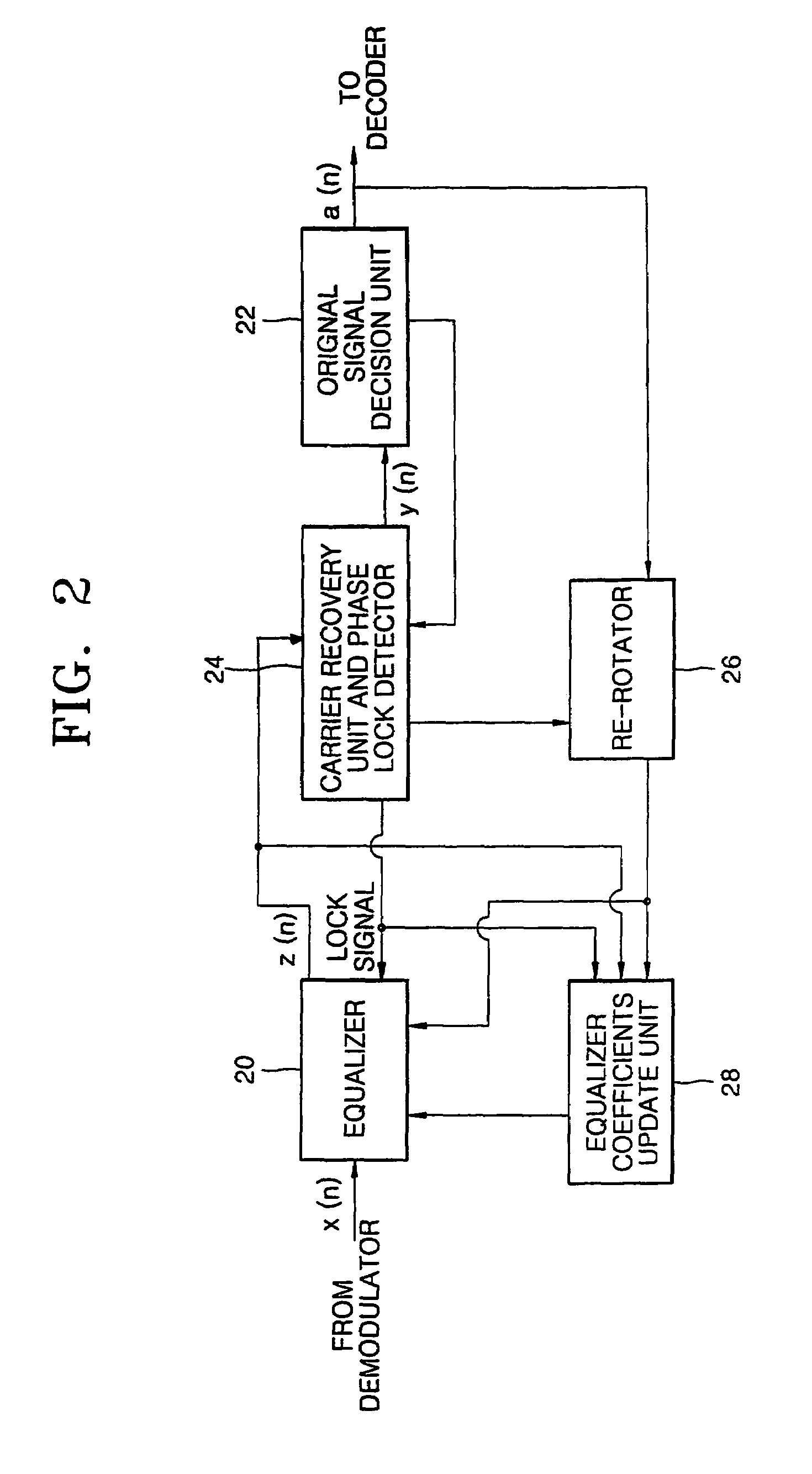
InactiveUS6947497B1Promote recoveryQuick snapTelevision system detailsMultiple-port networksAmplitude distortionSignal restoration
A digital signal receiver and a method for receiving a digital signal. The receiver includes an equalizing unit for compensating for an amplitude distortion of a received signal, an original signal decision unit for deciding an original signal from a signal which is compensated for the amplitude distortion, a carrier recovering and phase lock detecting unit for detecting a phase error between an input of the original signal decision unit and the decided original signal, and outputting a phase lock signal, a re-rotating unit for restoring the signal from the original signal decision unit to its original state and outputting a restored signal to the equalizer, and a coefficients updating unit for receiving the phase lock signal from the carrier recovering and phase lock detecting unit and the restored signal from the re-rotator unit, generating an error for updating the coefficients of the equalizer, and updating the coefficients of the equalizer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of equalization in an OFDM system
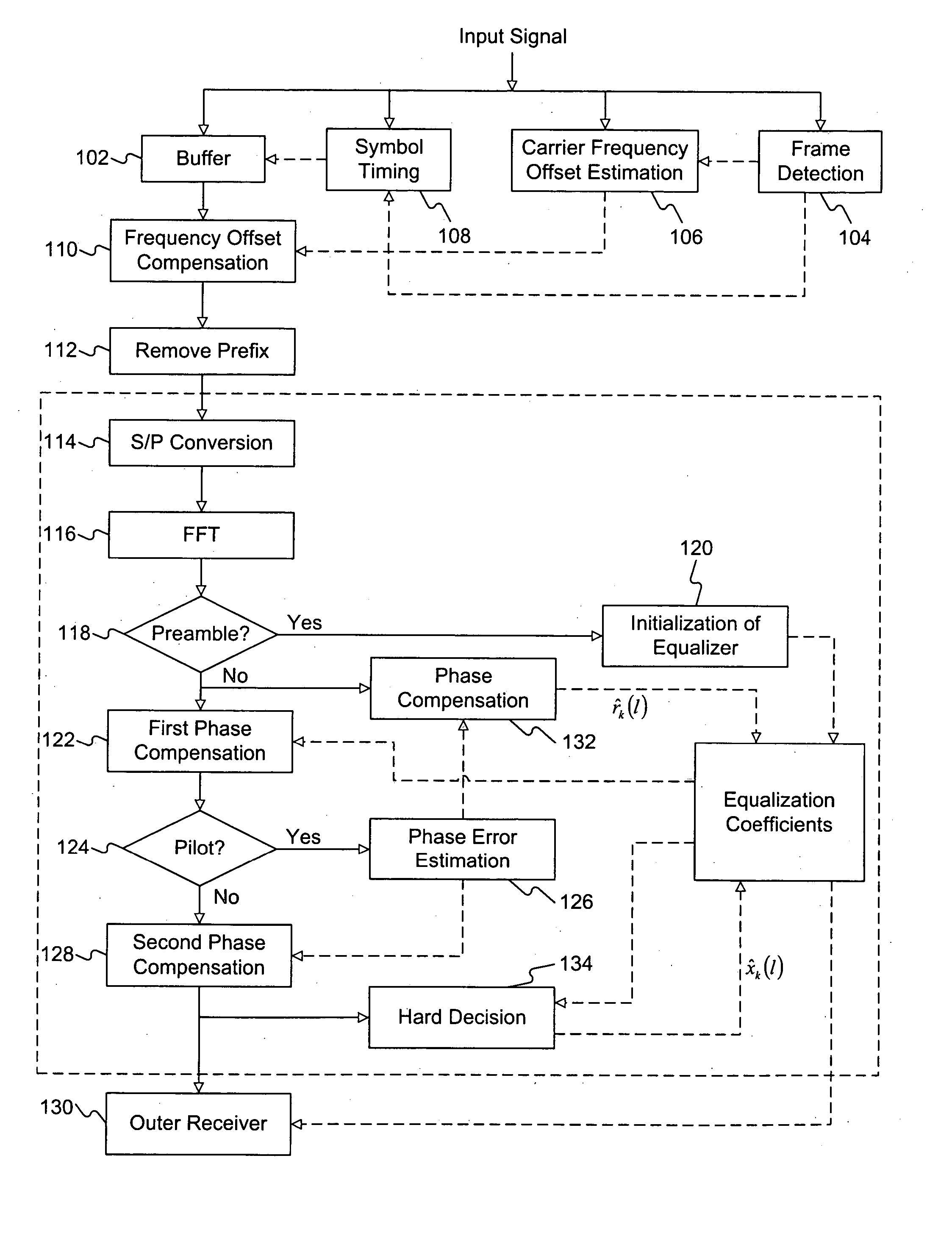
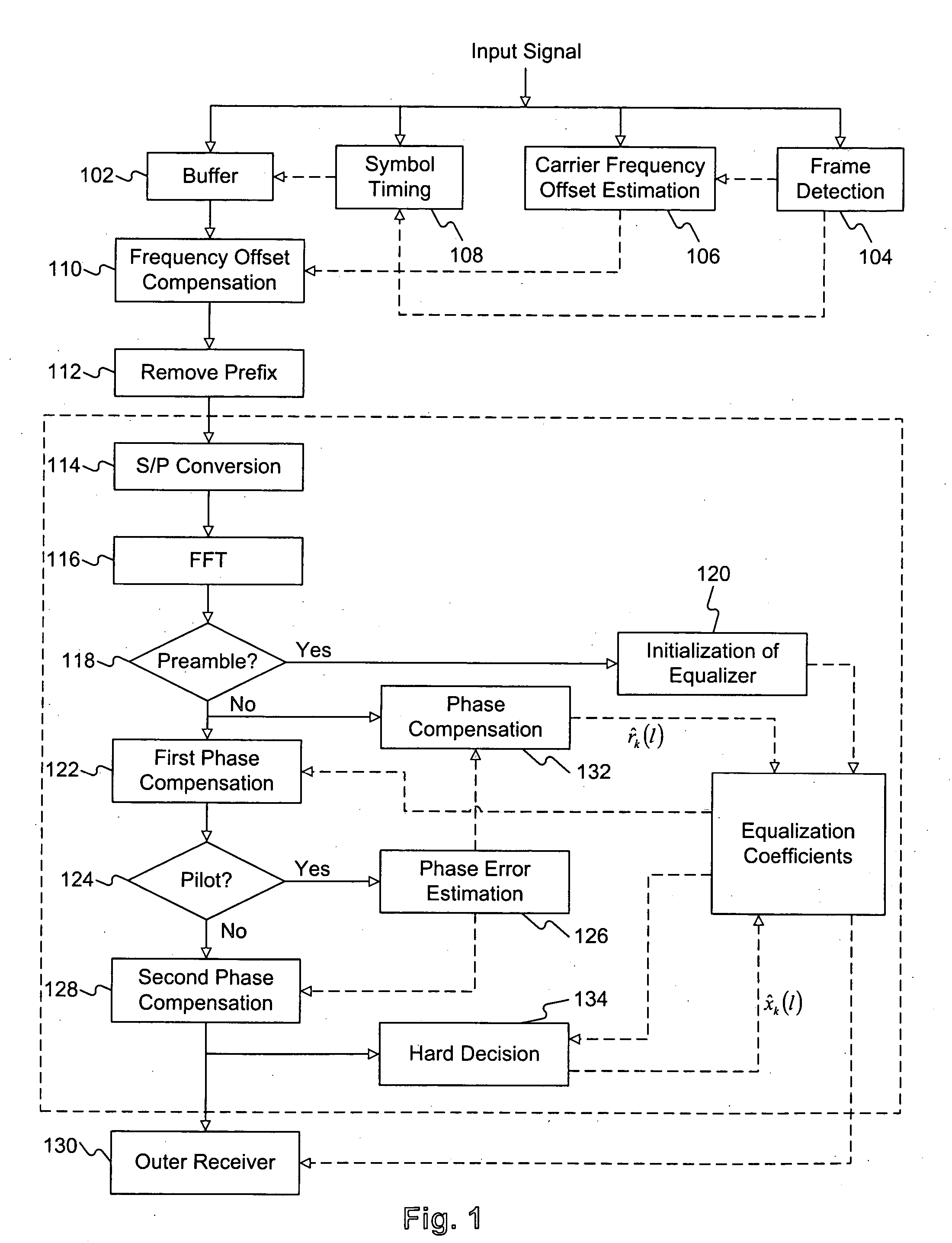
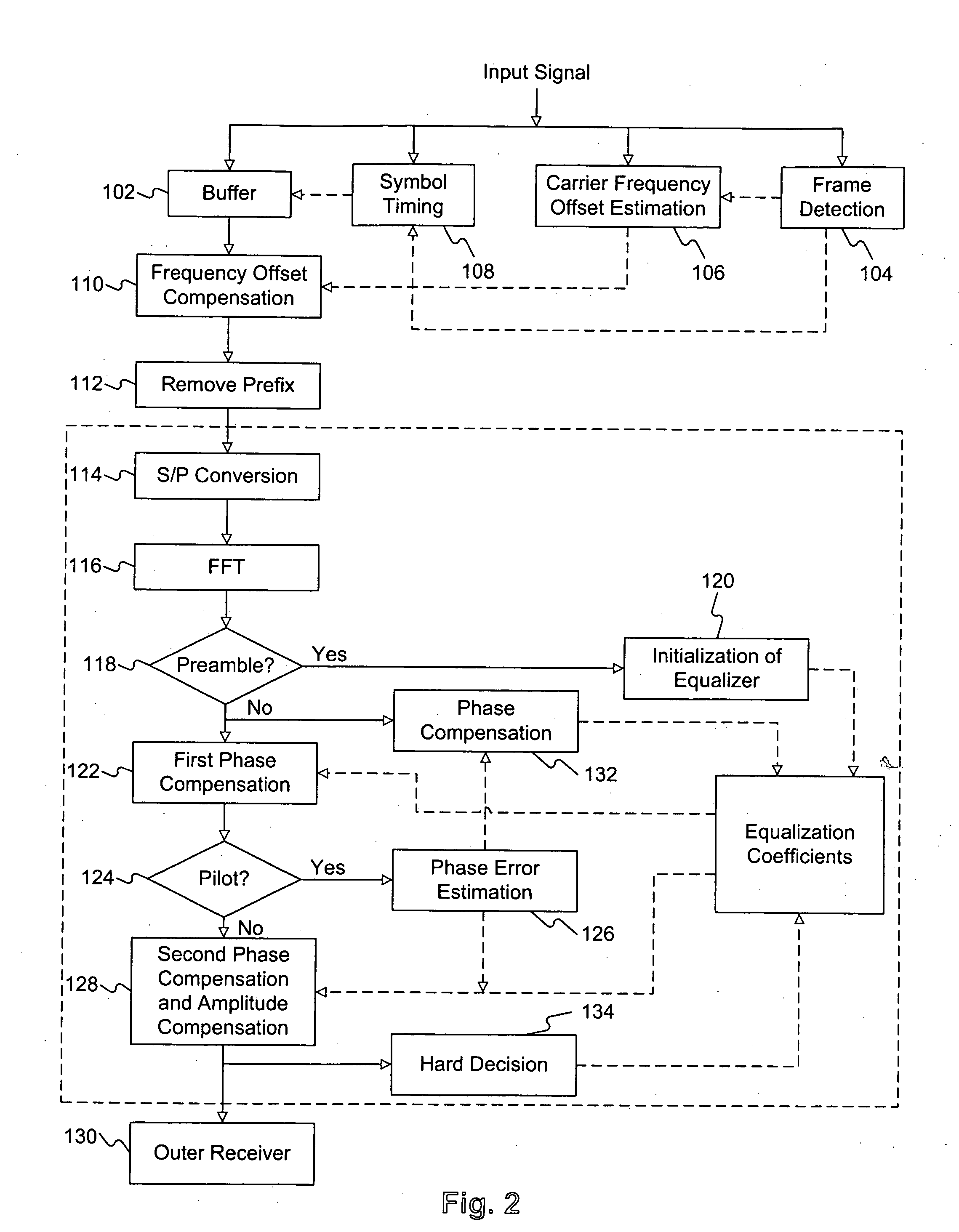
ActiveUS20050180461A1Multiple-port networksDelay line applicationsAmplitude distortionFast Fourier transform
An equalization method suitable for use in a receiver in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system utilizing a plurality of sub-carriers. The receiver includes an outer receiver for decoding. The equalization method includes receiving an input signal including at least one preamble symbol containing a training sequence and a plurality of informative OFDM symbols each containing a serial stream of samples, and performing compensations for each of the informative OFDM symbols. Compensation for each of the informative OFDM symbols includes converting the serial stream of samples into parallel samples, performing a fast Fourier transform (FFT) of the parallel samples to obtain a plurality of data symbols, each data symbol corresponding to a sub-carrier, compensating the data symbols for at least one first phase distortion and at least one second phase distortion, and providing at least one amplitude distortion factor to the outer receiver.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Variable gain amplifier for use in communications
InactiveUS20050233714A1Improve low noiseLimited functionResonant long antennasGain controlLow noiseAmplitude distortion
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Fetal communication system
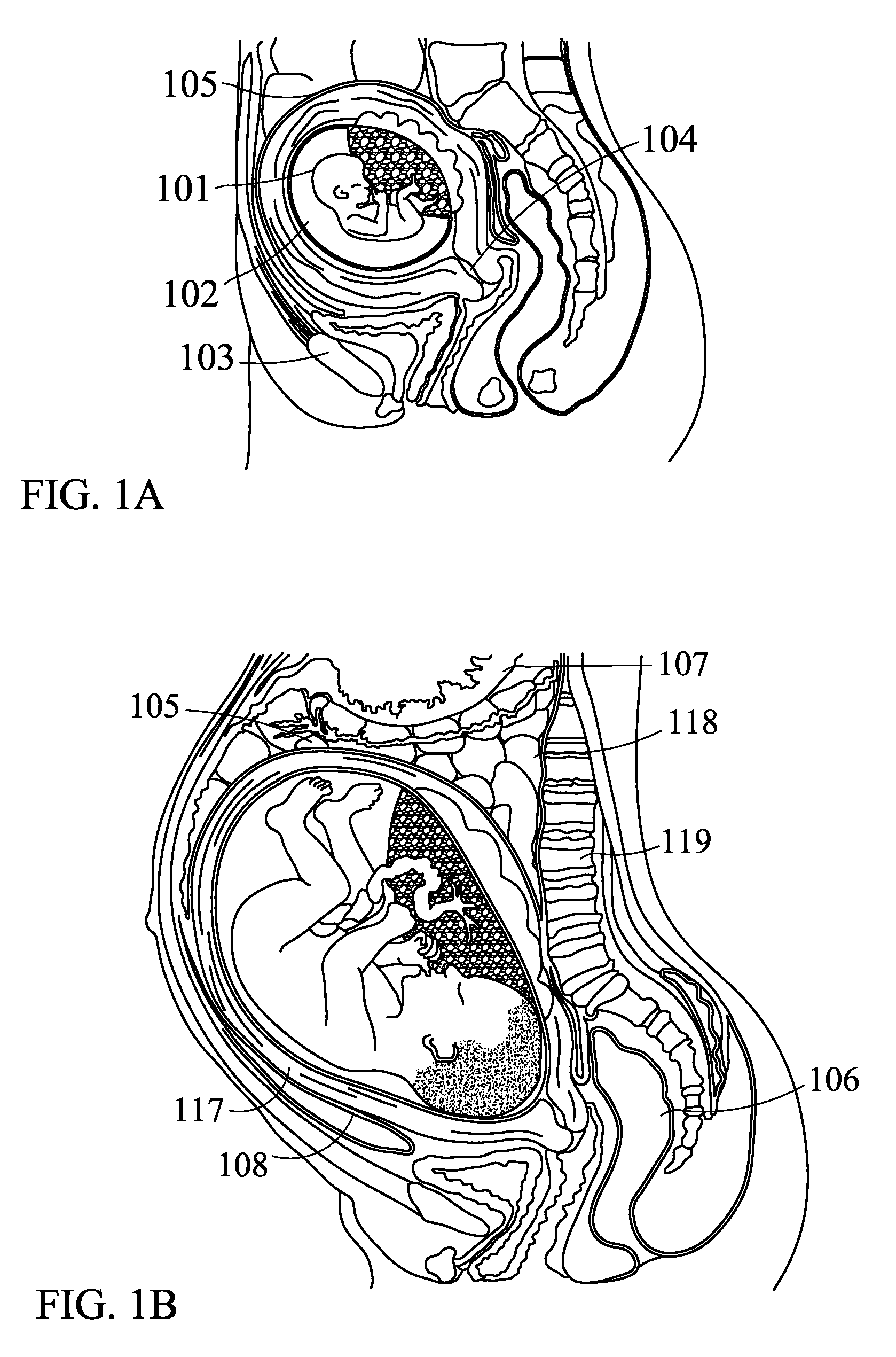
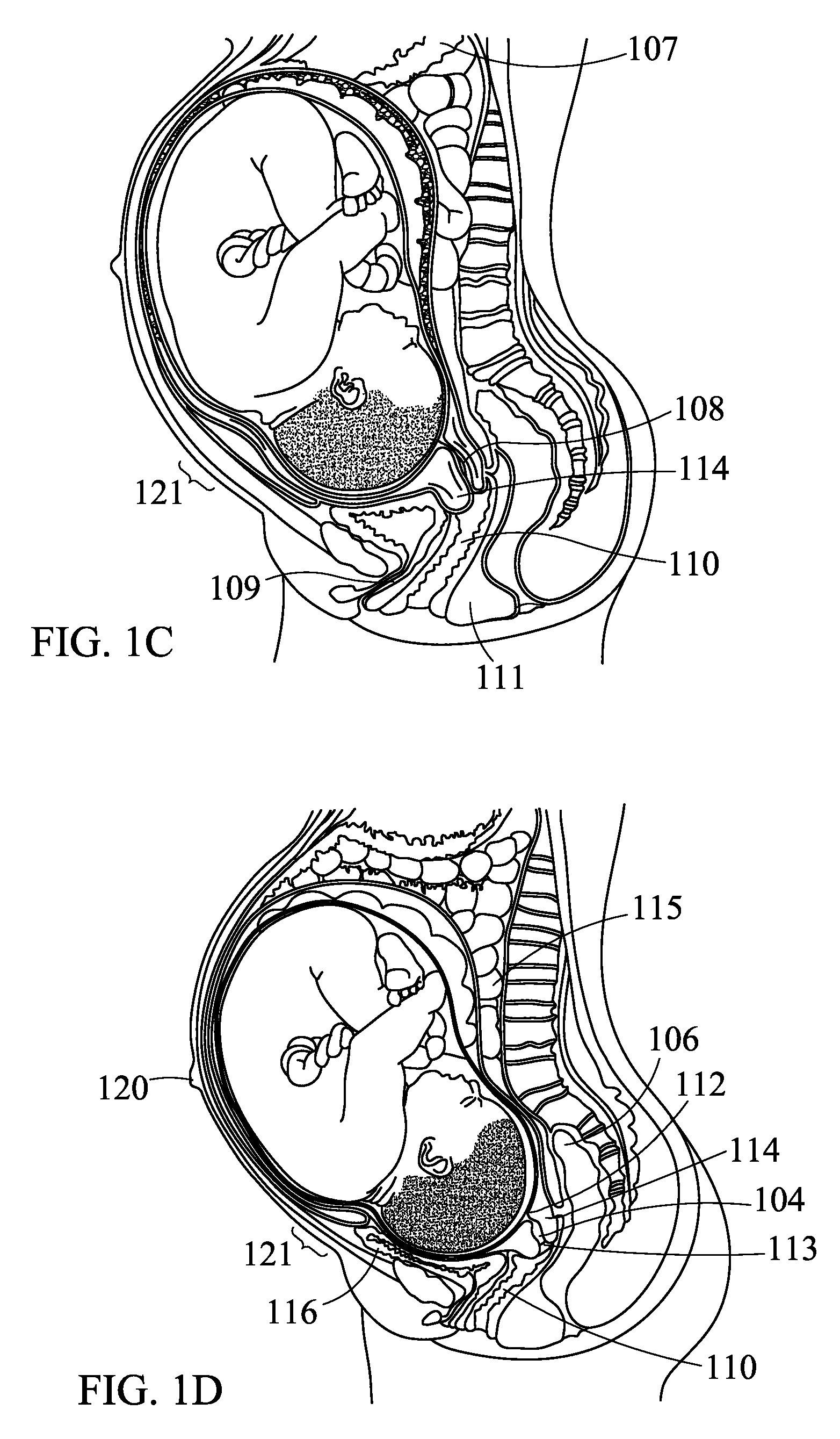
InactiveUS20090161892A1Small sizeReduce weightMicrophonesLoudspeakersDigital signal processingFrequency spectrum
A compact fetal sound system delivers high-fidelity sound to a fetus in utero through a miniature, abdominally mounted driver with a convex diaphragm. No gel is necessary at the interface between the diaphragm and the mother's abdomen. Digital signal processing shapes the frequency spectrum of the sound transmitted to the fetus, so that after traveling through the attenuative tissue of the expectant mother the desired volume of sound and frequency content reach the ears of the fetus. As the term of pregnancy progresses, the frequency shaping provided by the digital signal processing automatically varies to compensate for changes in uterine lining thickness and the like. Preferred embodiments also include a microphone attached to the abdomen of the mother and signal processing to correct for frequency and amplitude distortions of sound eminating from the womb. Embodiments also include an elastic belt to maintain the transducer and microphone against the abdomen.
Owner:JENNIFER SEVELLO +1
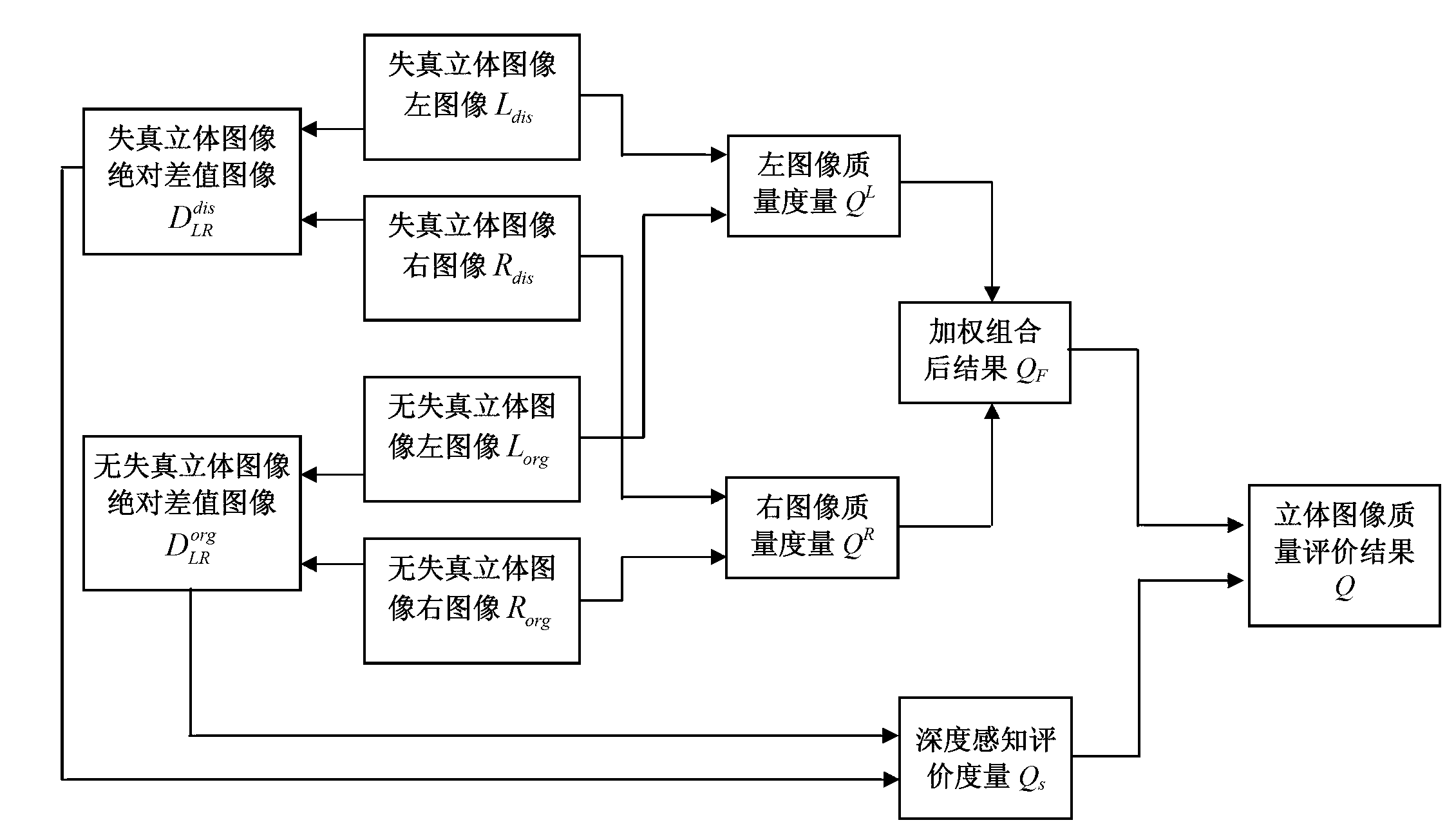
Stereoscopic image objective quality evaluation method on basis of structural distortion
The invention discloses a stereoscopic image objective quality evaluation method on the basis of the structural distortion, which comprises the following steps: firstly, respectively carrying out regional division on left and right viewpoint images of an undistorted stereoscopic image and a distorted stereoscopic image to obtain an eye sensitive region and a corresponding nonsensitive region and then respectively obtaining evaluation indexes of the sensitive region and the nonsensitive region from two aspects of the structural amplitude distortion and the structural direction distortion; secondly, acquiring quality evaluation values of the left and right viewpoint images; thirdly, sampling singular value difference and a mean deviation ratio of residual images of which singular values are deprived to evaluate the distortion condition of the depth perception of a stereoscopic image so as to obtain an evaluation value of stereoscopic perceived quality; and finally, combining the quality of the left and right viewpoint images with the stereoscopic perceived quality to obtain a final quality evaluation result of the stereoscopic image. The method disclosed by the invention avoids simulating each composition part of an eye vision system, but sufficiently utilizes structure information of the stereoscopic image, so the consistency of the objective evaluation result and the subjective perception is effectively improved.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com