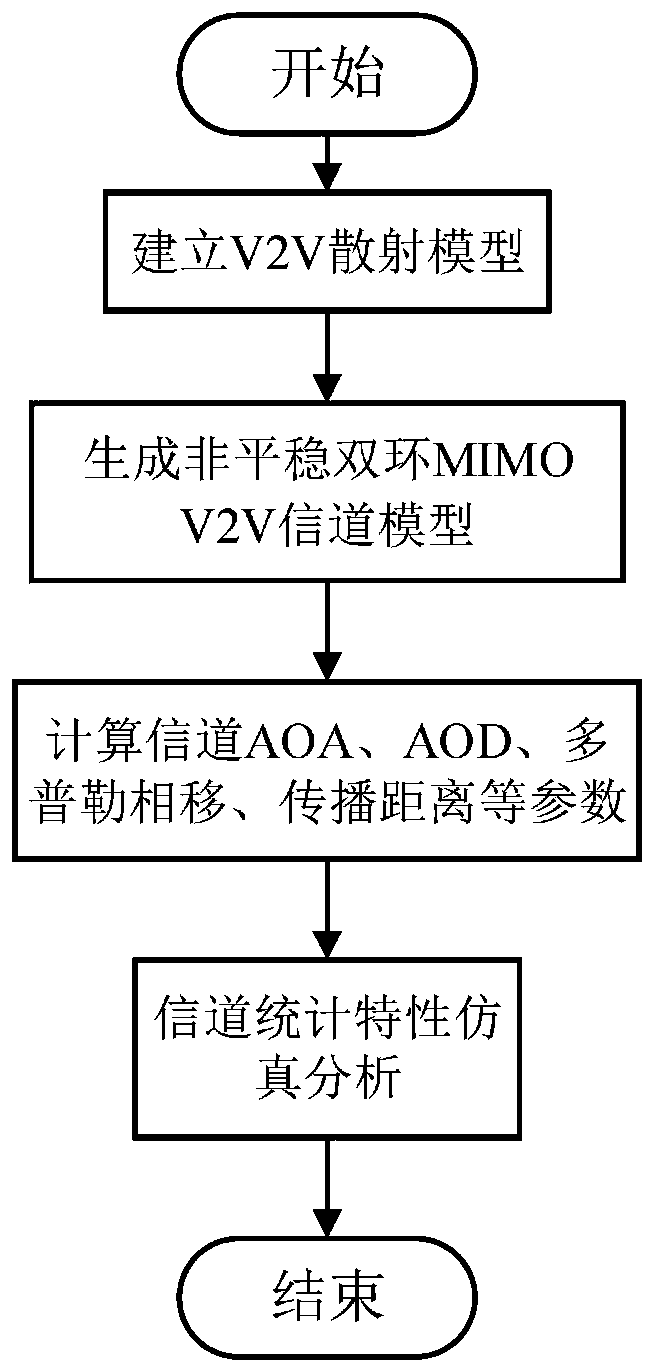
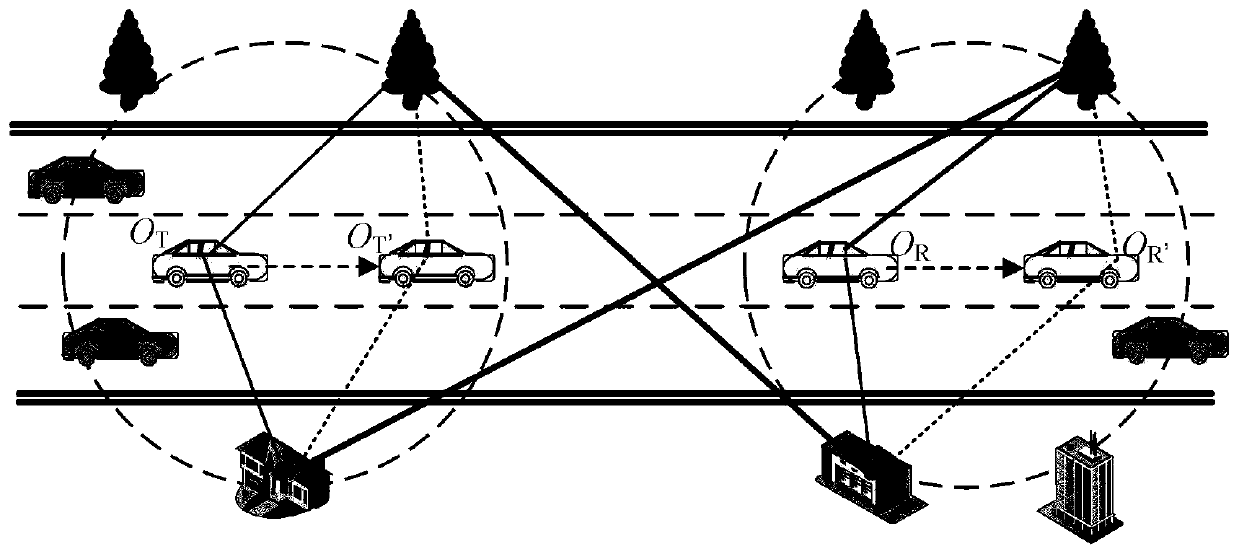
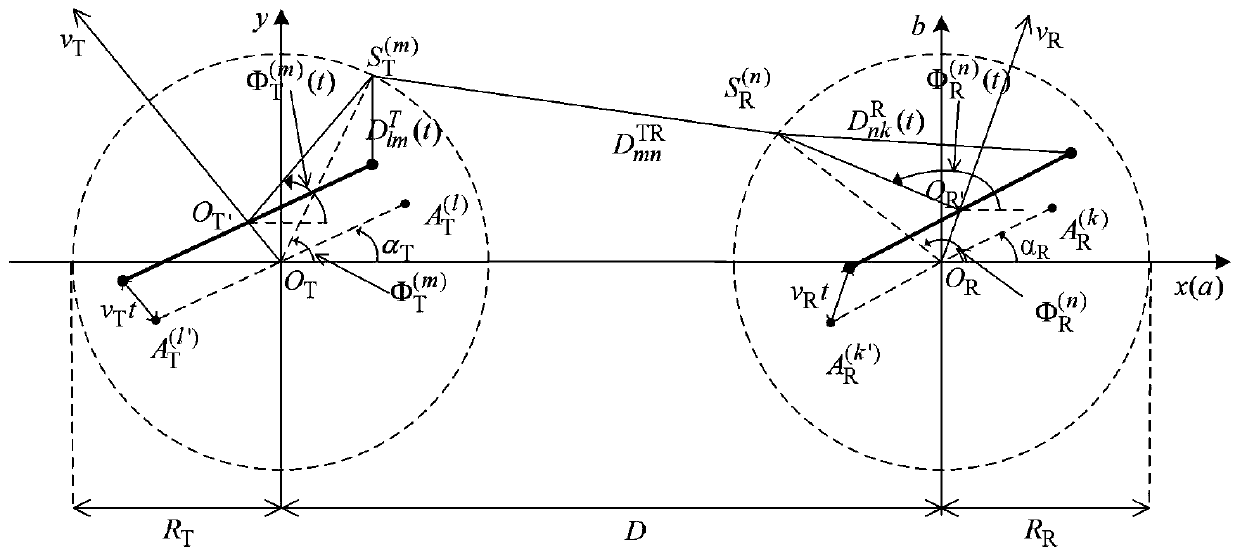
Non-stationary V2V MIMO channel modeling method based on geometry
A channel modeling, non-stationary technology, used in specific environment-based services, vehicle-to-vehicle communication, vehicle wireless communication services, etc.
Inactive Publication Date: 2020-06-19
HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
View PDF2 Cites 18 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
The above model assumes that the scatterers are distributed with a von Mises probability density function, so that the Angle of Arrival (AOA) and the Angle of Departure (AOD) are time-invariant. However, in the
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
 Login to View More
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
The invention relates to a non-stationary V2V MIMO channel modeling method based on geometry. The method comprises the following steps in sequence: establishing a V2V double-loop scattering model; establishing a channel impulse response between the V2V MIMO channel transmitting antenna 1 and the V2V MIMO channel receiving antenna k according to the V2V double-loop scattering model; and according to the geometrical relationship among the mobile transmitting end, the mobile receiving end and the scatterer, time-varying channel parameters of the arrival angle, the departure angle, the Doppler phase shift and the propagation distance of the electric wave are derived. The non-WSS channel model established in the invention is the extension of a stationary double-loop model, and can simulate thenon-stationarity of a V2V channel in a time delay domain and a space domain; parameters such as a scatterer concentration factor, an angle mean value, a vehicle moving speed and an antenna array direction angle comprehensively act on channel statistical characteristics and non-stationary characteristics; the V2V non-stationary channel modeling method is enriched, and the statistical property and non-stationary research of the channel has a practical application value for V2V communication system design and evaluation.
Description
technical field [0001] The invention relates to the technical field of V2V non-stationary channel modeling, in particular to a geometry-based non-stationary V2V MIMO channel modeling method. Background technique [0002] A V2V channel model that effectively describes the characteristics of the communication environment and signal transmission characteristics is crucial for the optimization and evaluation of the wireless communication system of the Internet of Vehicles. However, there are serious differences between the traditional Fixed-to-Mobile (F2M) cellular wireless channel model and the V2V channel model in application scenarios: one is that the vehicles at both ends of the V2V communication system are in motion, and the other is that The antenna height of the mobile transmitter in the V2V communication system is much lower than that of the F2M system. Therefore, the traditional F2M cellular model cannot be directly used to analyze the channel transmission characterist...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): H04B17/391H04B7/0413H04W4/46
CPCH04B7/0413H04B17/3912H04W4/46
Inventor 尹柏强侯金波王署东何怡刚李兵佐磊
Owner HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com