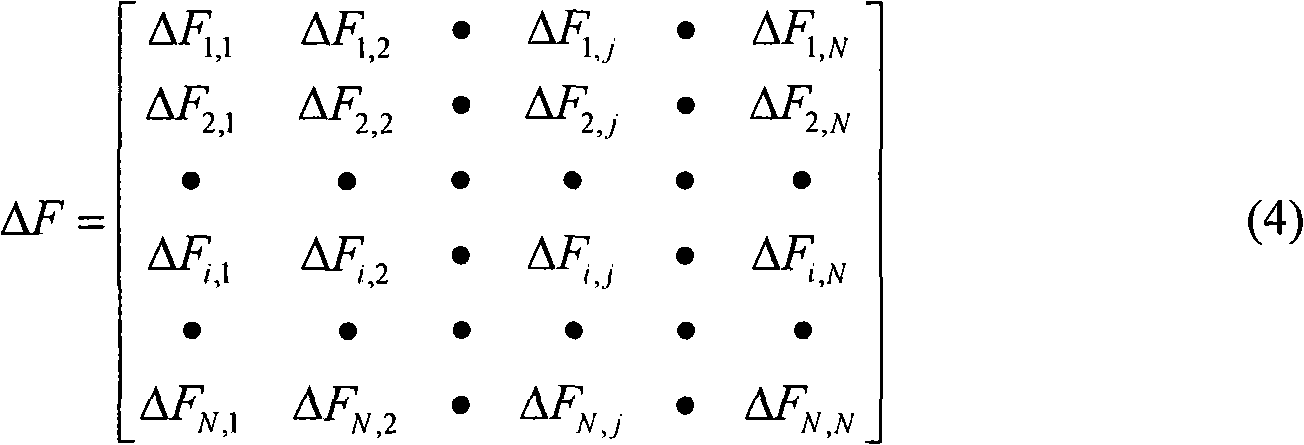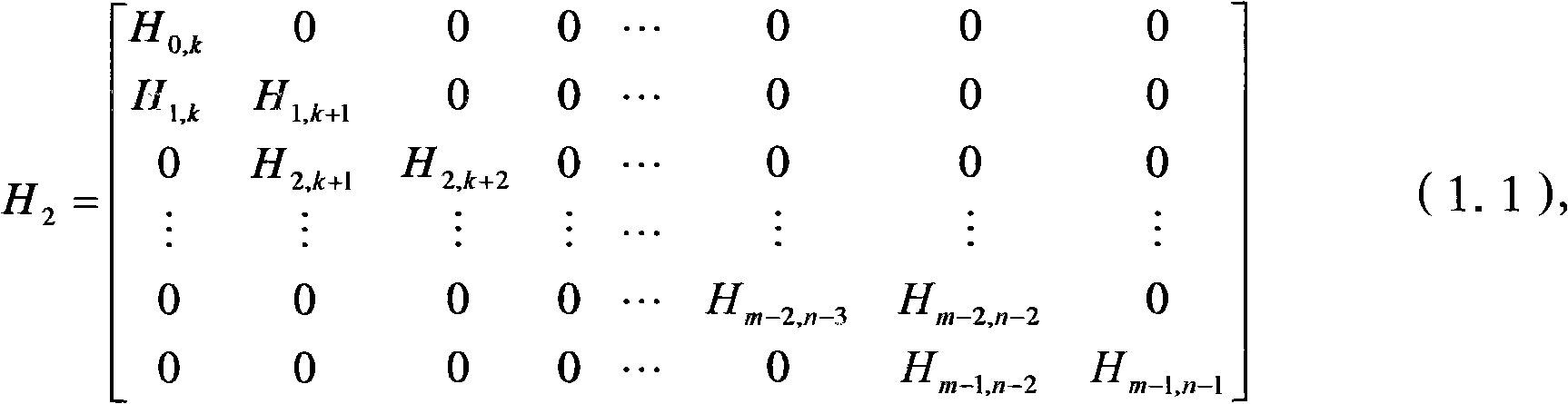Patents
Literature
152 results about "Identity matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
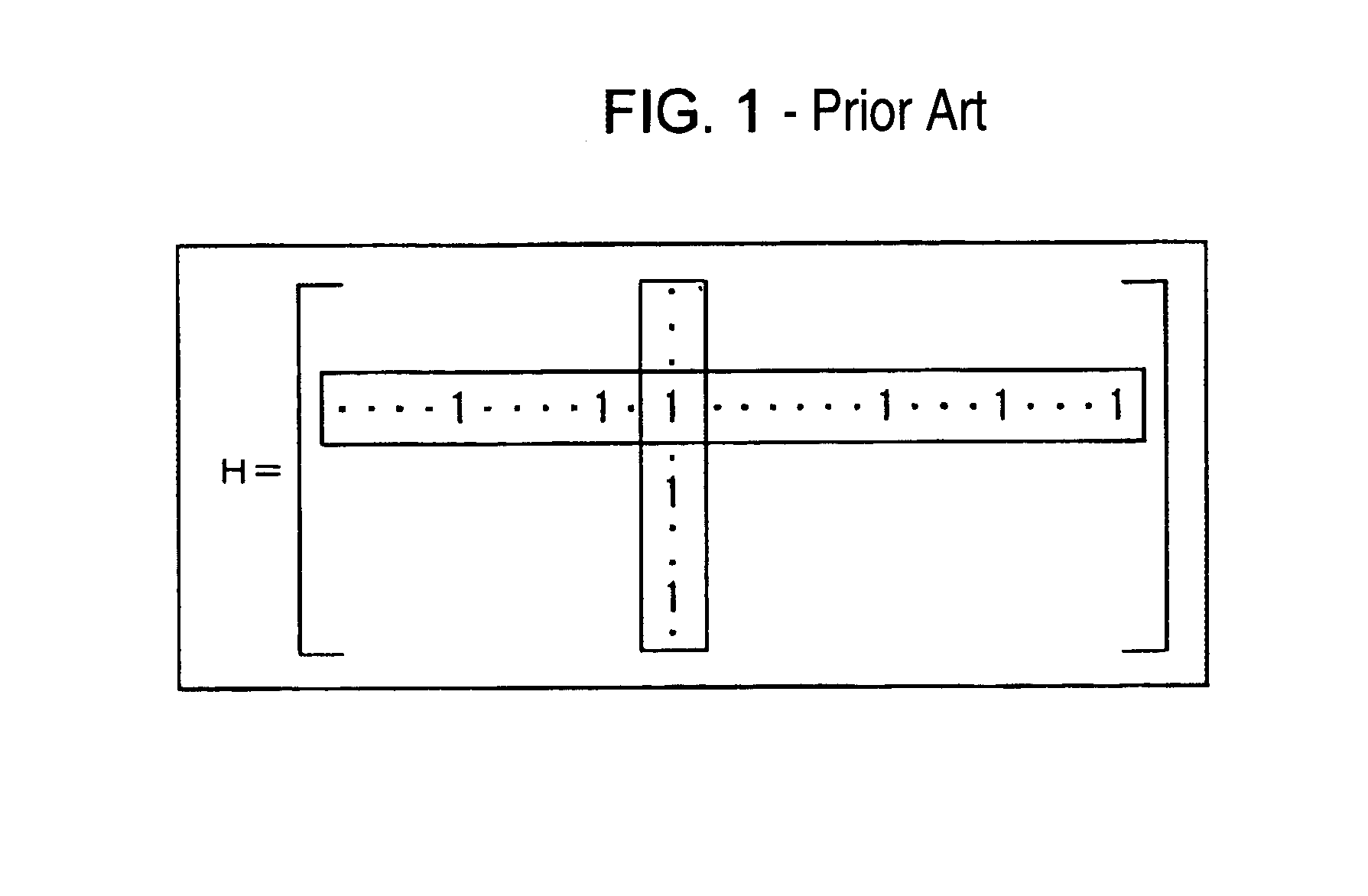
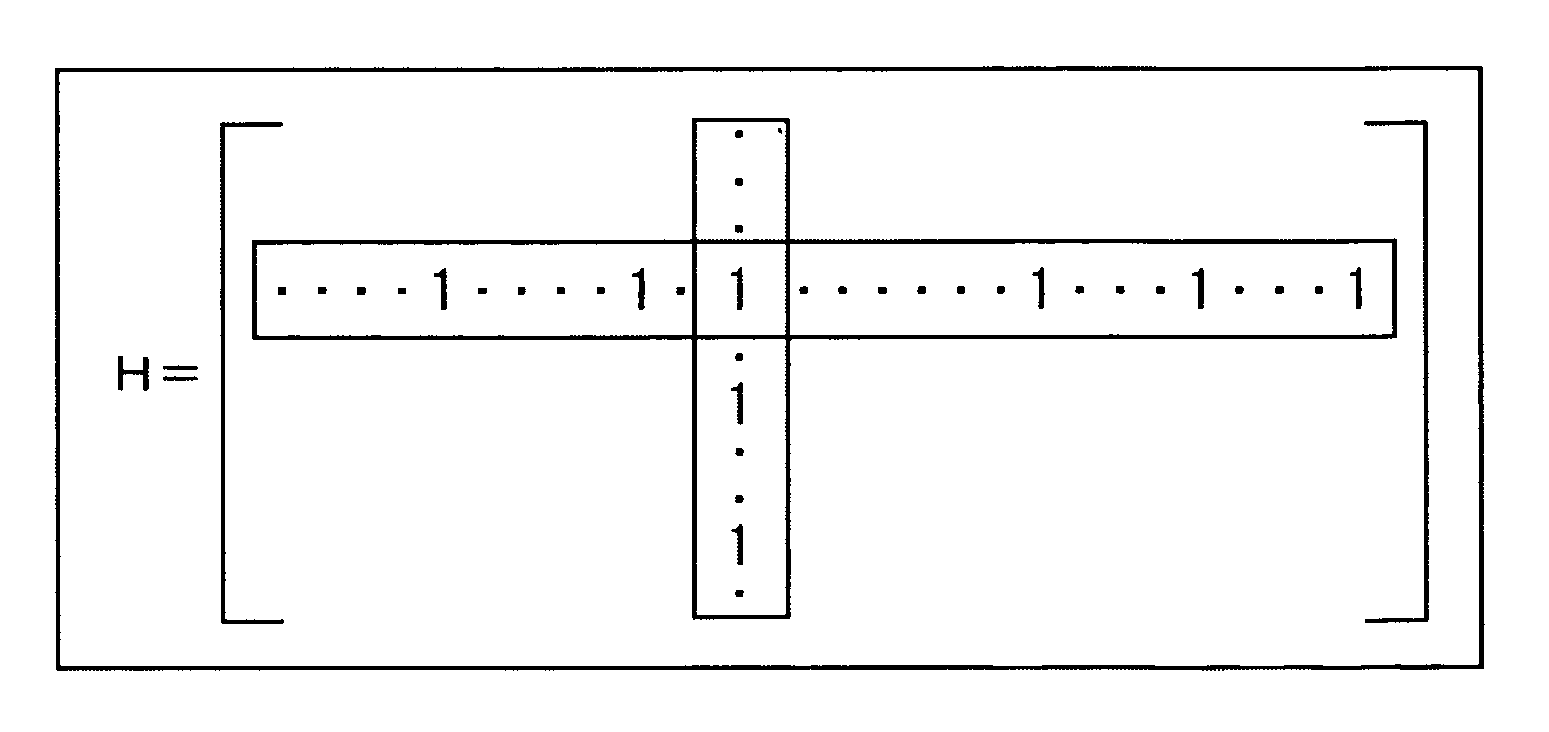
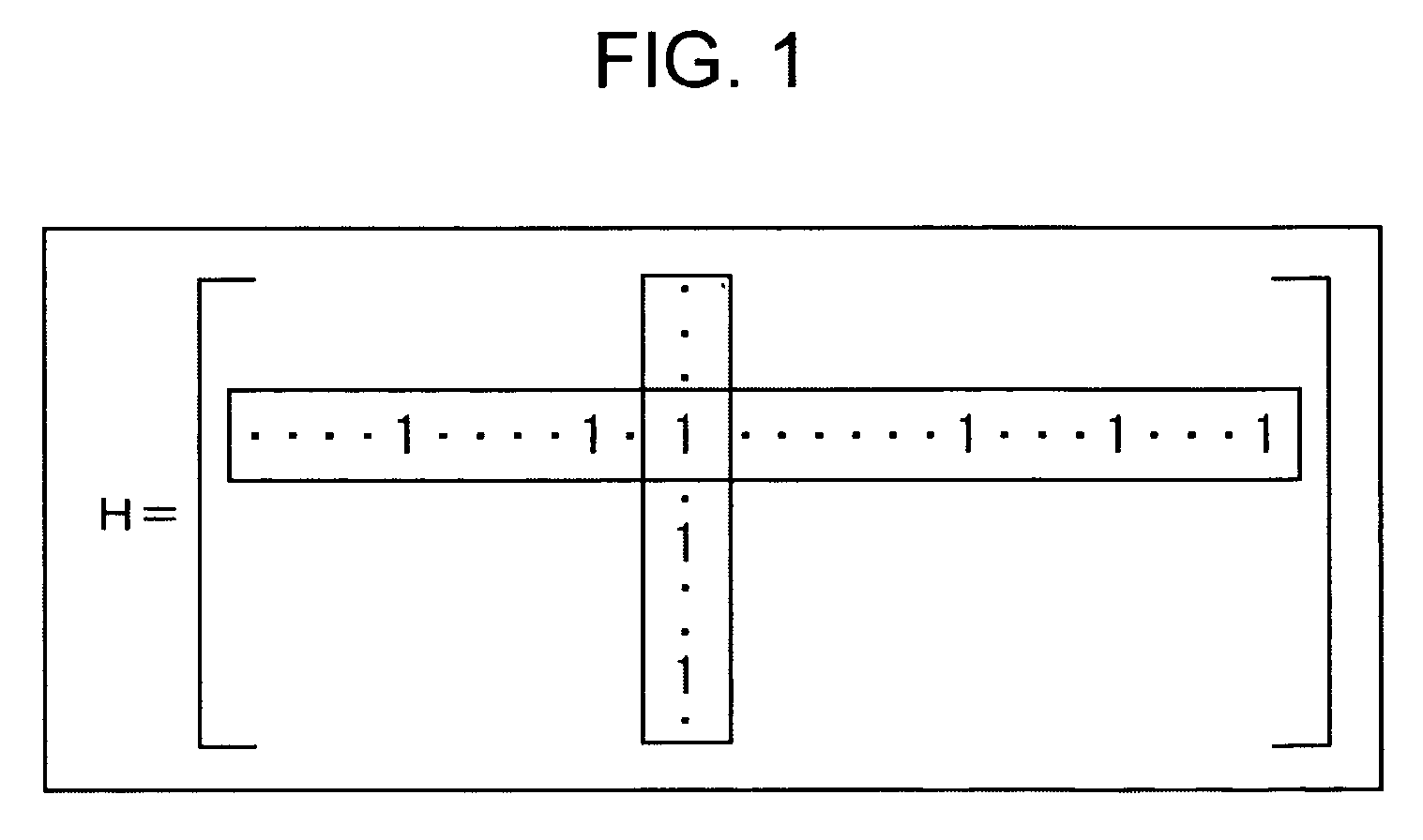
In linear algebra, the identity matrix, or sometimes ambiguously called a unit matrix, of size n is the n × n square matrix with ones on the main diagonal and zeros elsewhere. It is denoted by Iₙ, or simply by I if the size is immaterial or can be trivially determined by the context. (In some fields, such as quantum mechanics, the identity matrix is denoted by a boldface one, 1; otherwise it is identical to I.) Less frequently, some mathematics books use U or E to represent the identity matrix, meaning "unit matrix" and the German word Einheitsmatrix respectively.
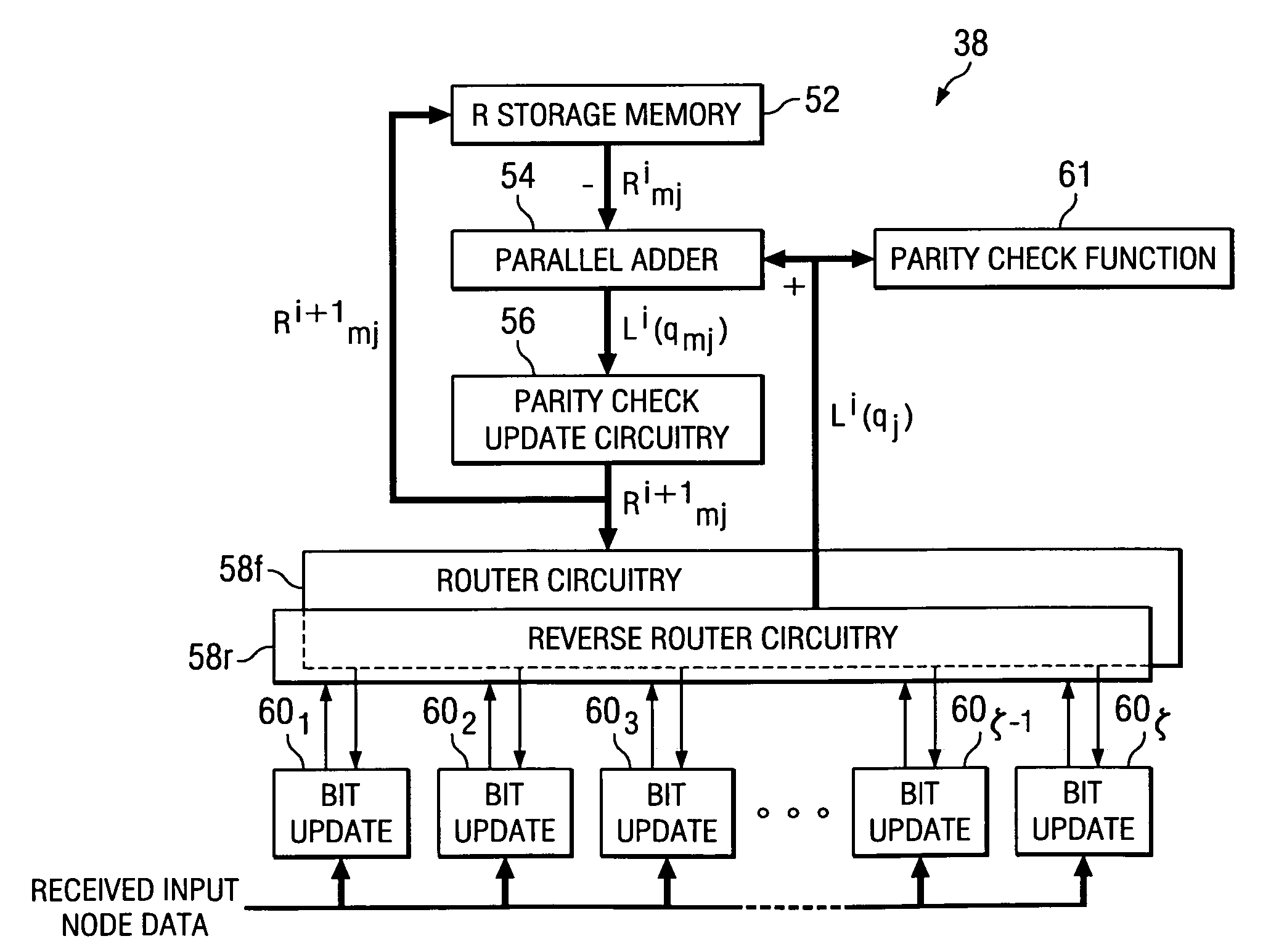
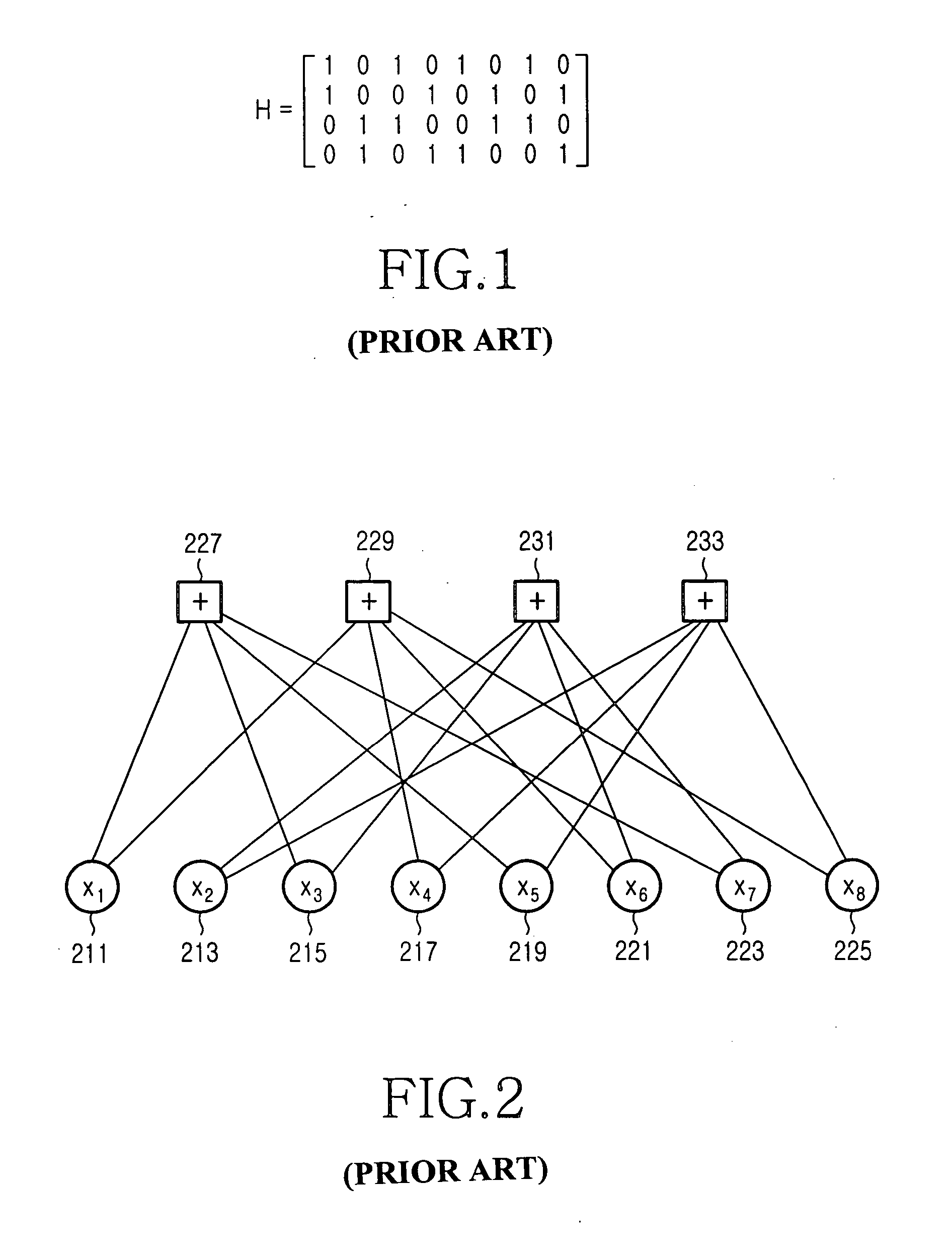
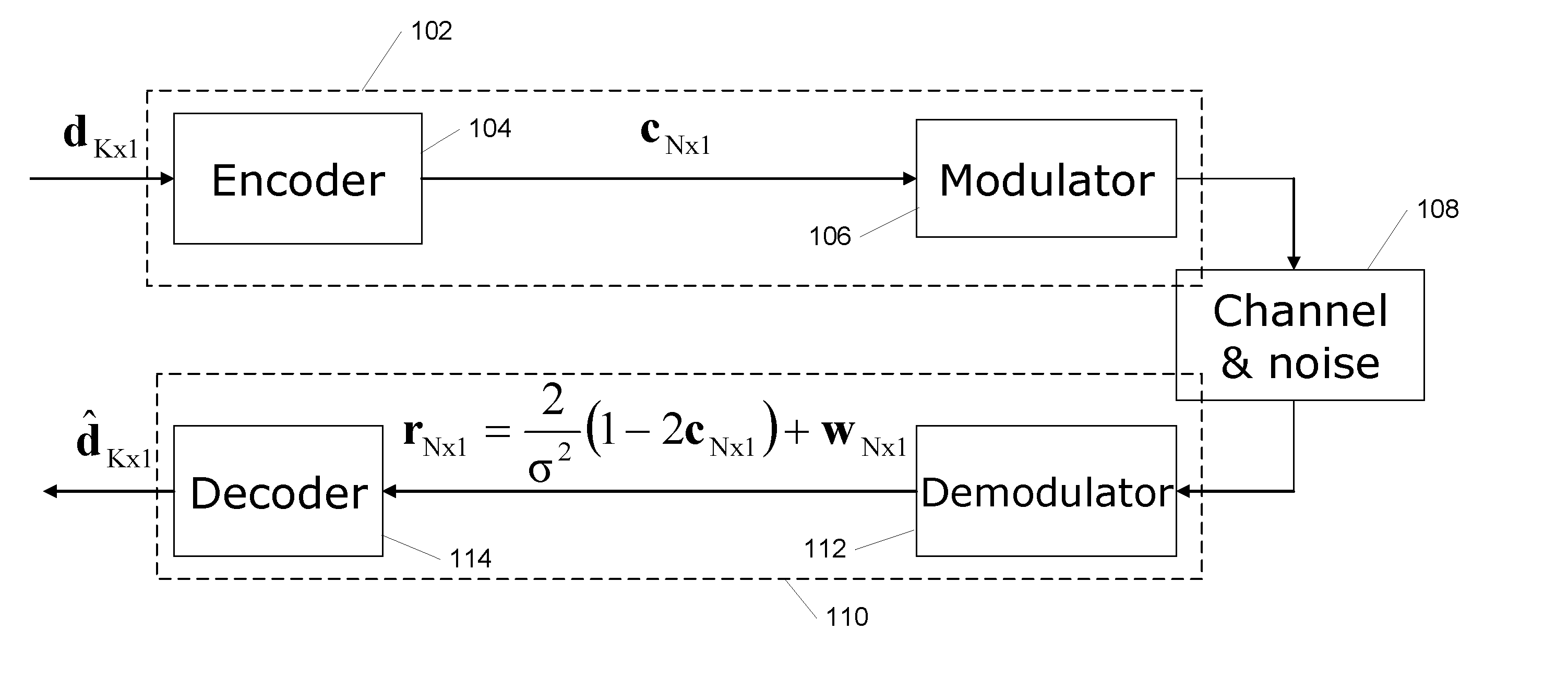
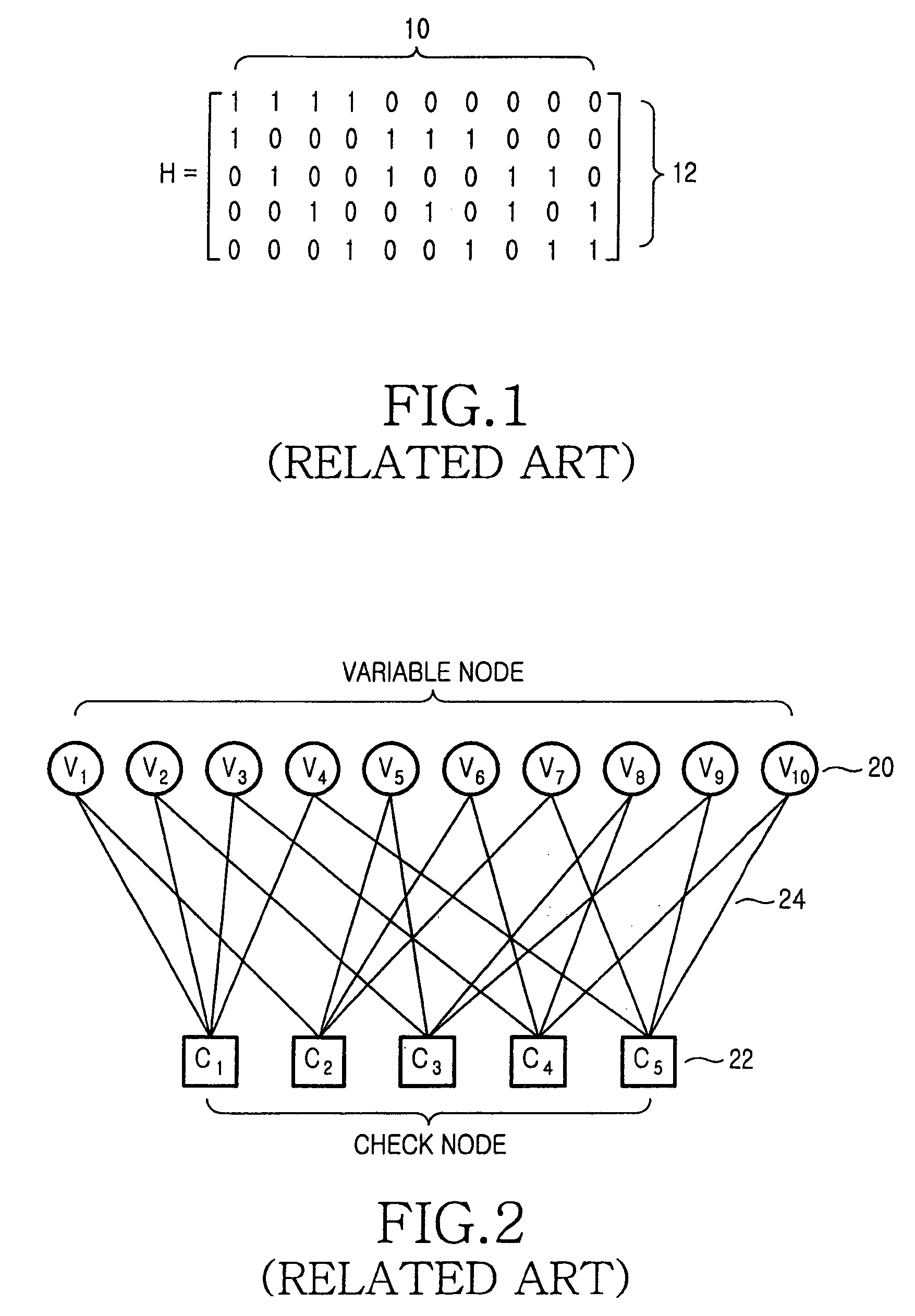
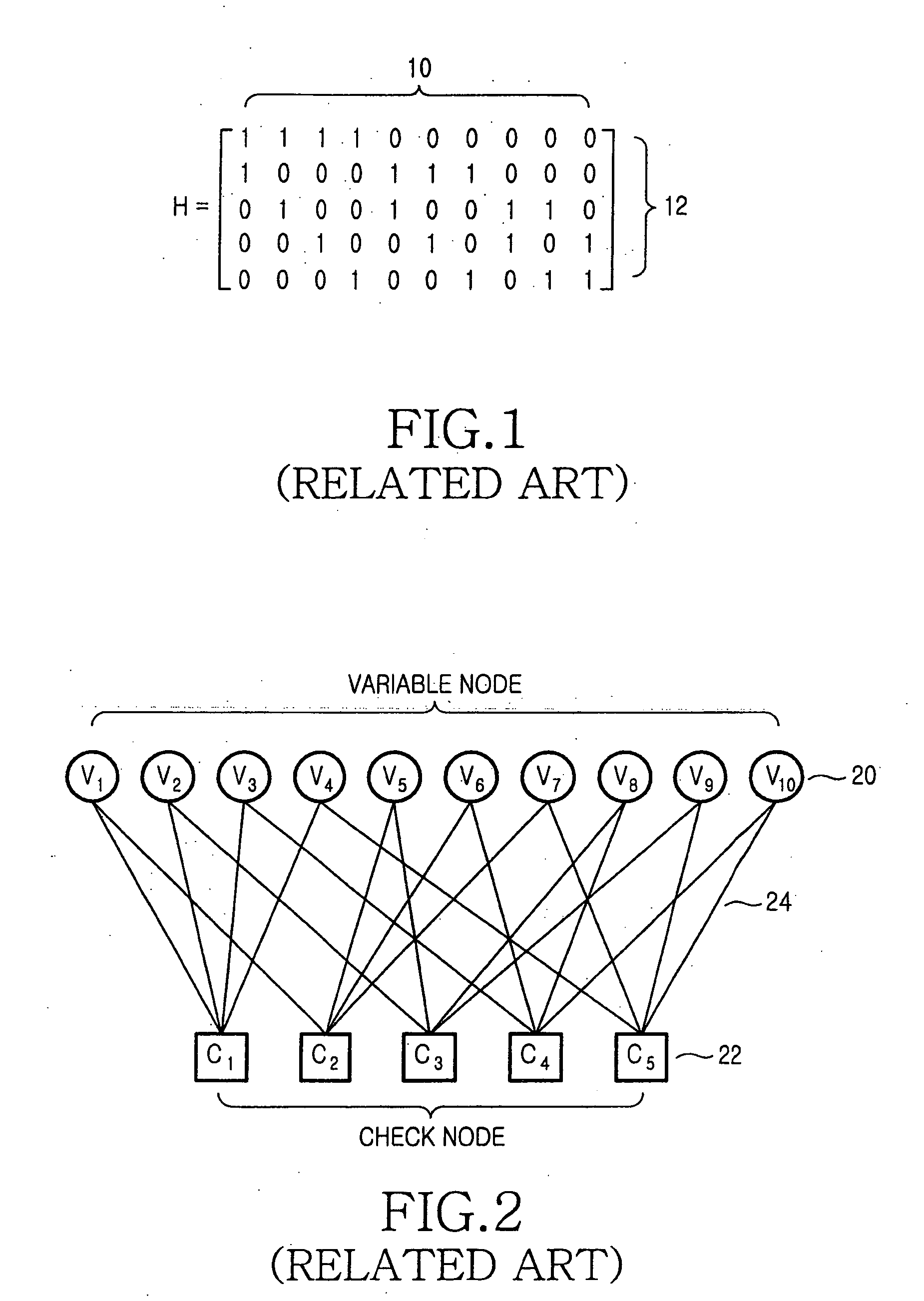
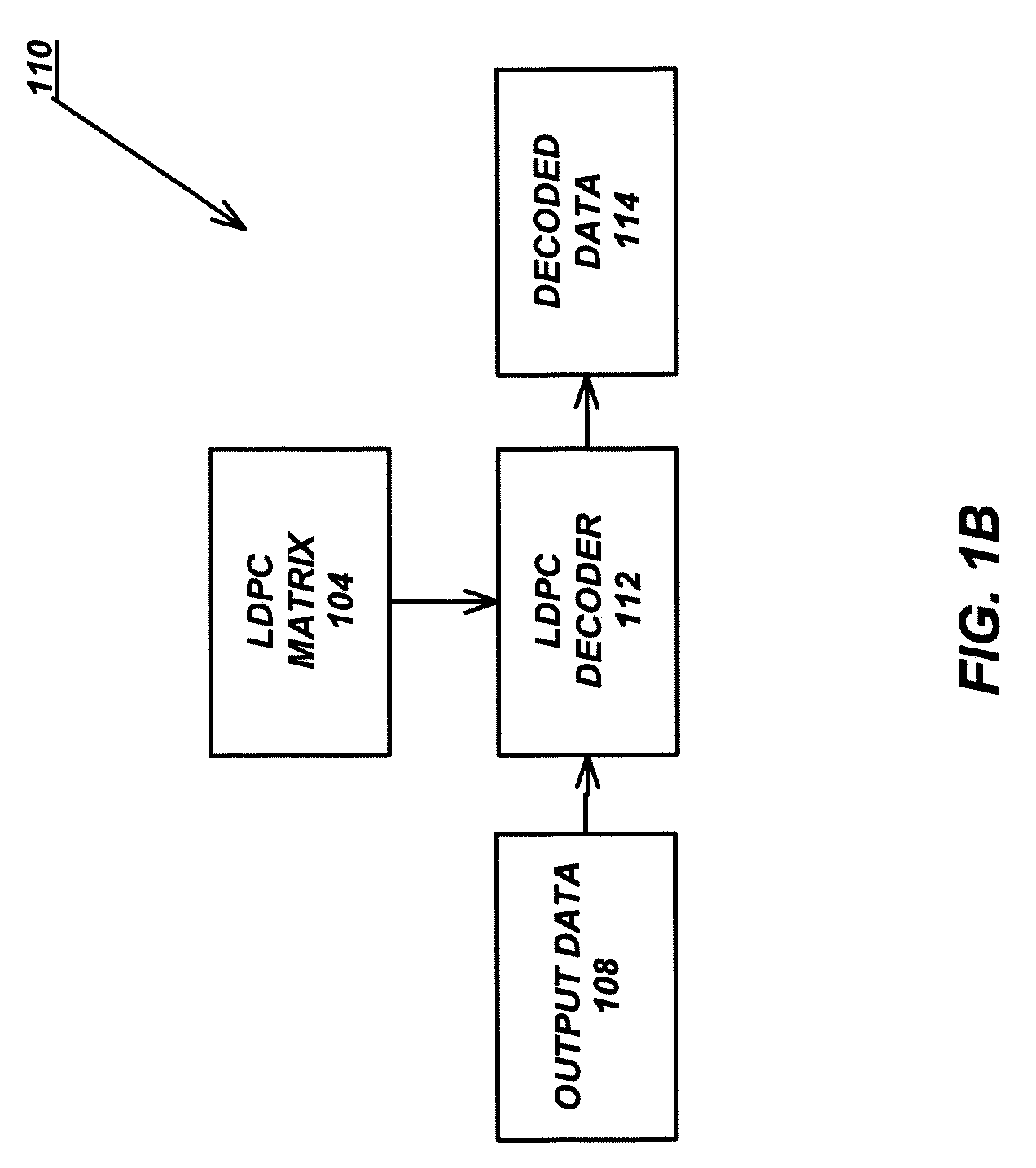
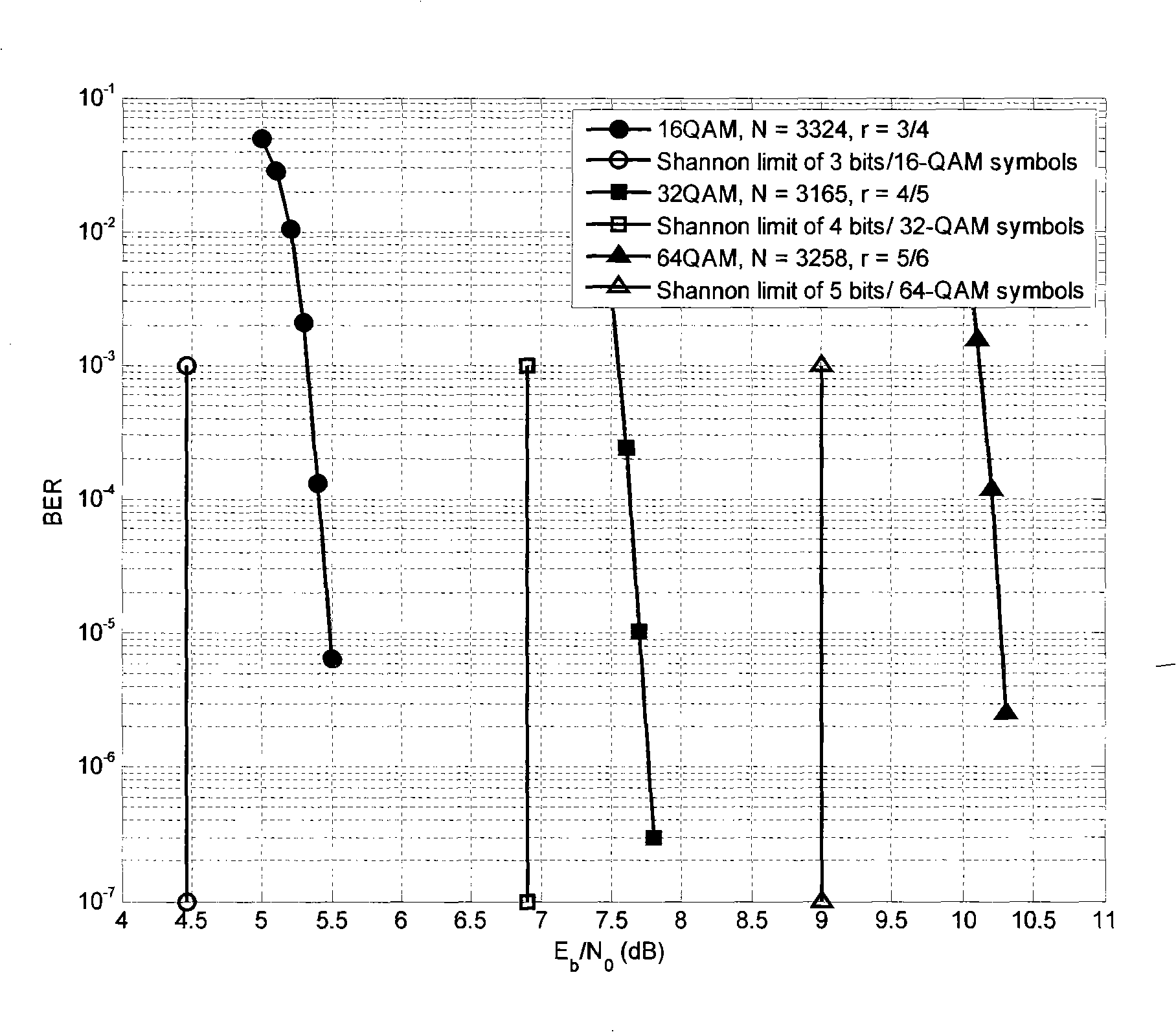
Hardware-efficient low density parity check code for digital communications
ActiveUS7178080B2Efficient implementationEfficient constructionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionMatrix groupParity-check matrix
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
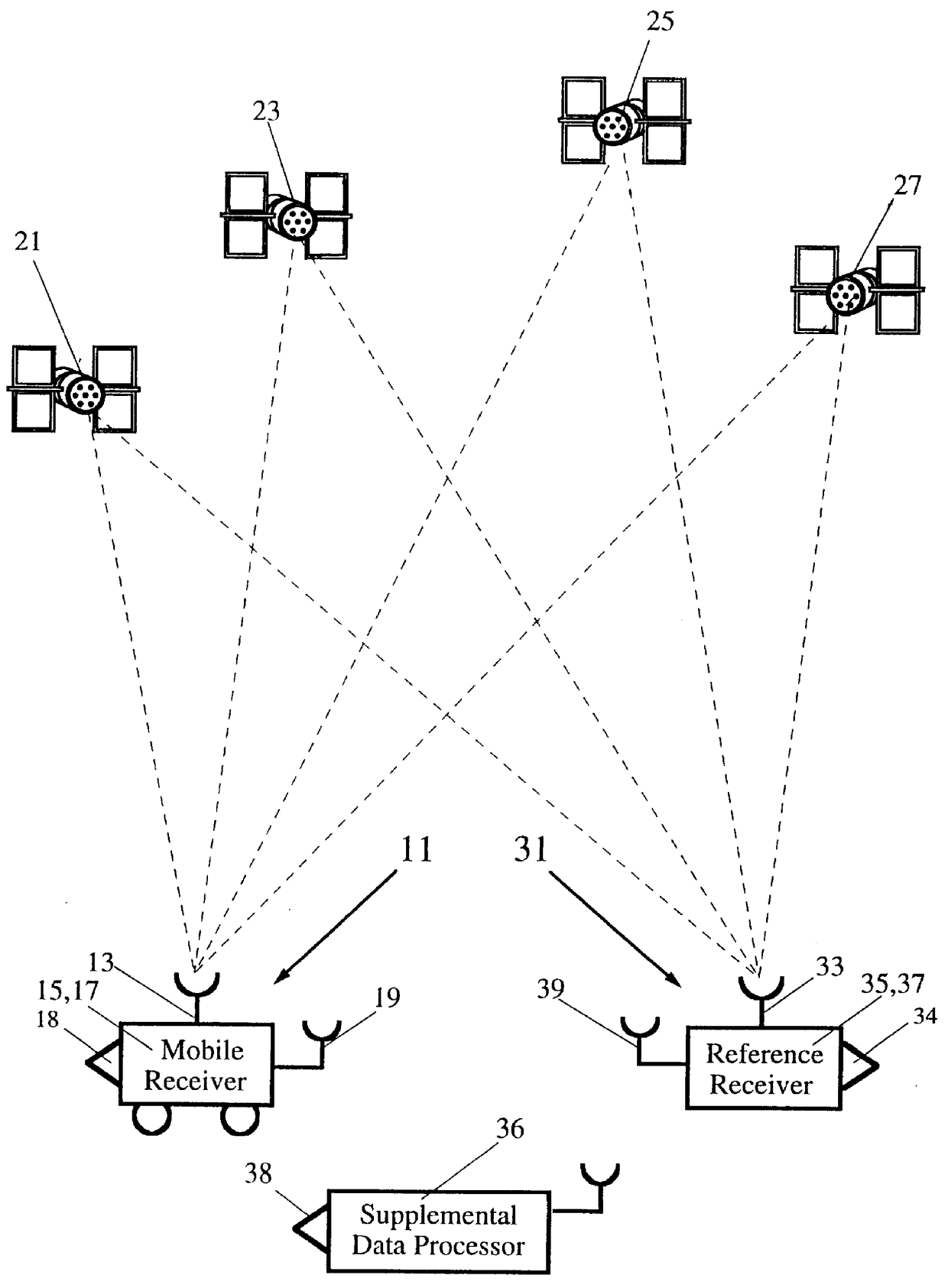
Post-processing of inverse DGPS corrections
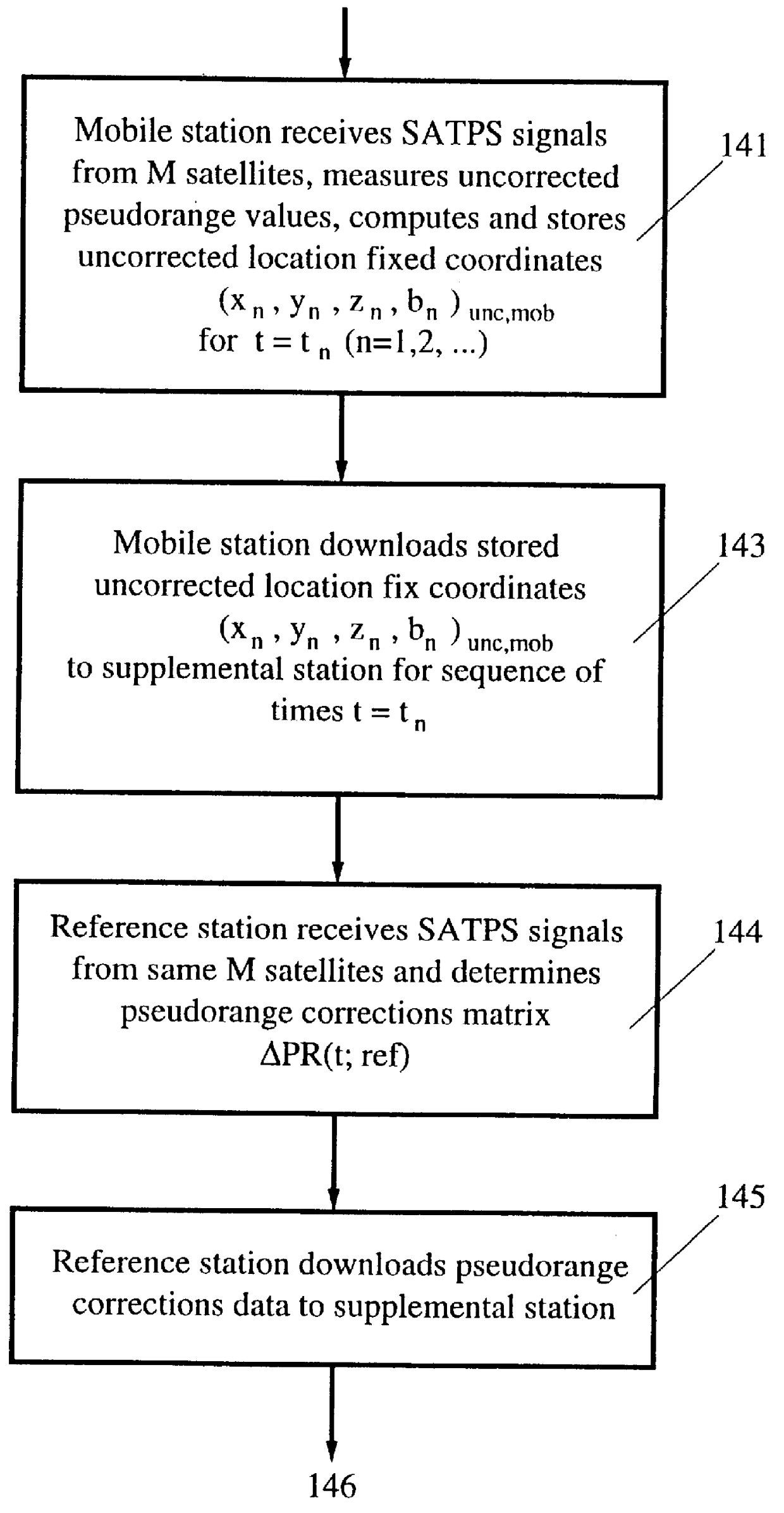
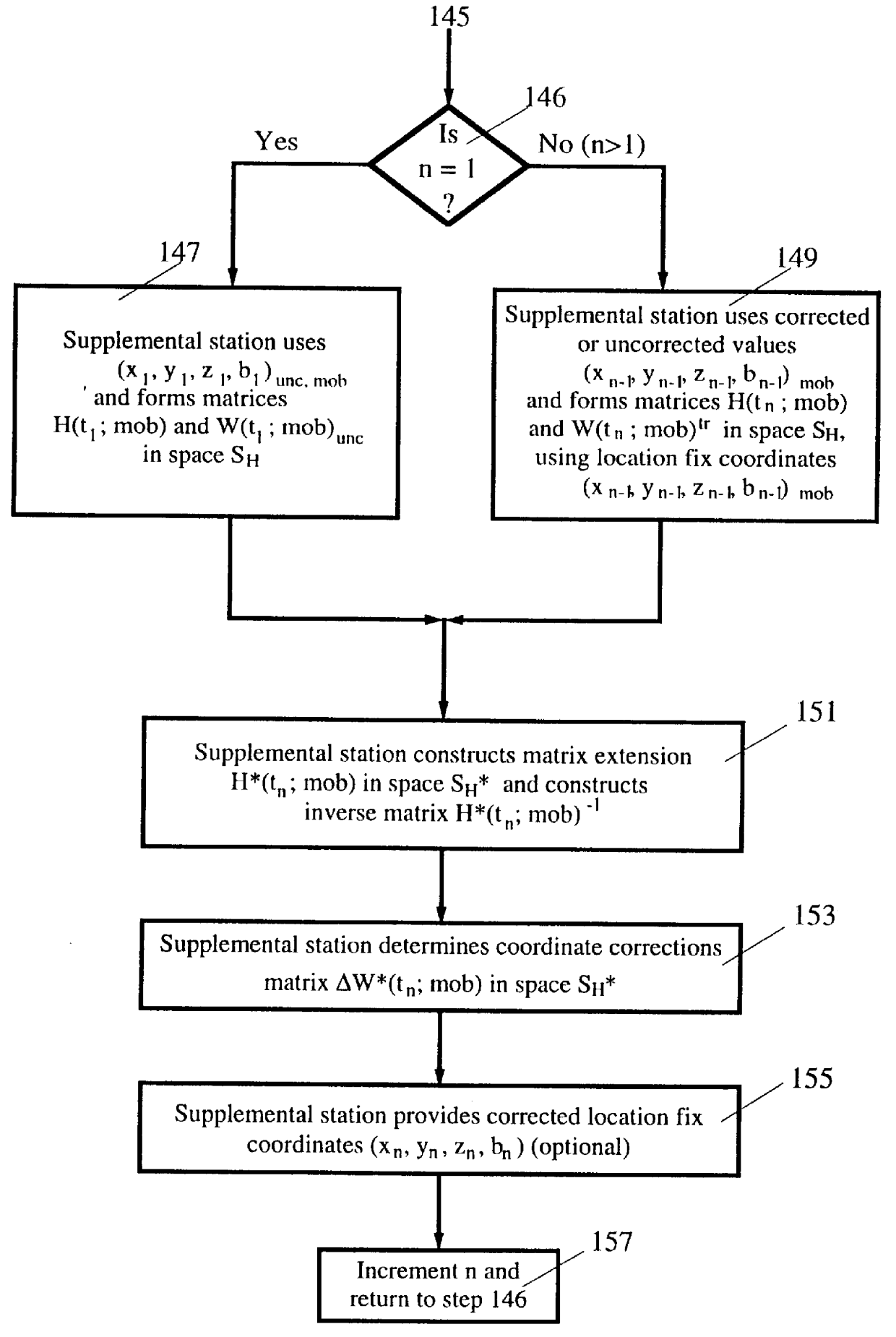
A method for enhancing the accuracy of location coordinates and / or clock bias computed for a mobile user station that is part of a Satellite Positioning System (SATPS), such as GPS or GLONASS. A data processing station is provided with pseudorange corrections PRC(t;j;ref) for an SATPS reference station for each of M SATPS satellites (j=1, . . . , M; M> / =3) and with uncorrected location fix coordinates x'(tf), y'(tf)', z'(tf)' and / or b'(tf) for the mobile station for a selected location fix time tf. A matrix equation H(tf;mob) DELTA W(tf;mob)=PRC(tf;ref) relates a matrix DELTA W of location fix coordinate corrections for the mobile station to a matrix PRC(t;ref) of the pseudorange correction values, where H(tf;mob) is an MxN matrix (M< / =N; N=3 or 4) with known entries computed from mobile station data. An inverse or pseudo-inverse matrix H(tf;mob)(-1) is formed satisfying the relation H(tf;mob)(-1)H(tf;mob)=the identity matrix I, and the matrix DELTA W(tf;mob)=H(tf;mob)(-1)PRC(tf;ref) is computed. The entries of the matrix DELTA W(tf) are interpreted as additive corrections for the location fix coordinates x'(tf), y'(tf)', z'(tf)' and / or b'(tf) for the mobile station. Post-processing can be performed to apply the pseudorange corrections to the mobile station data.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
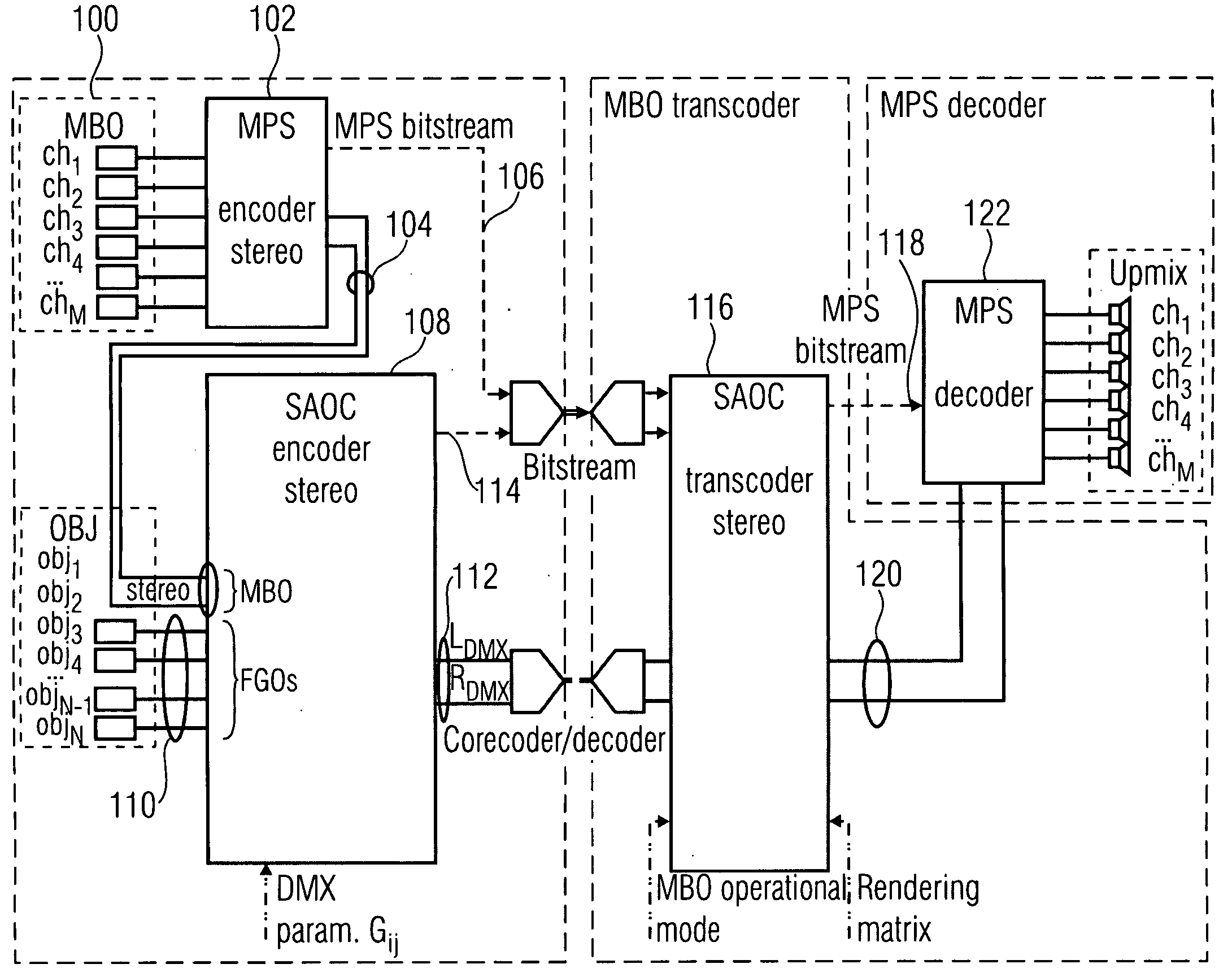
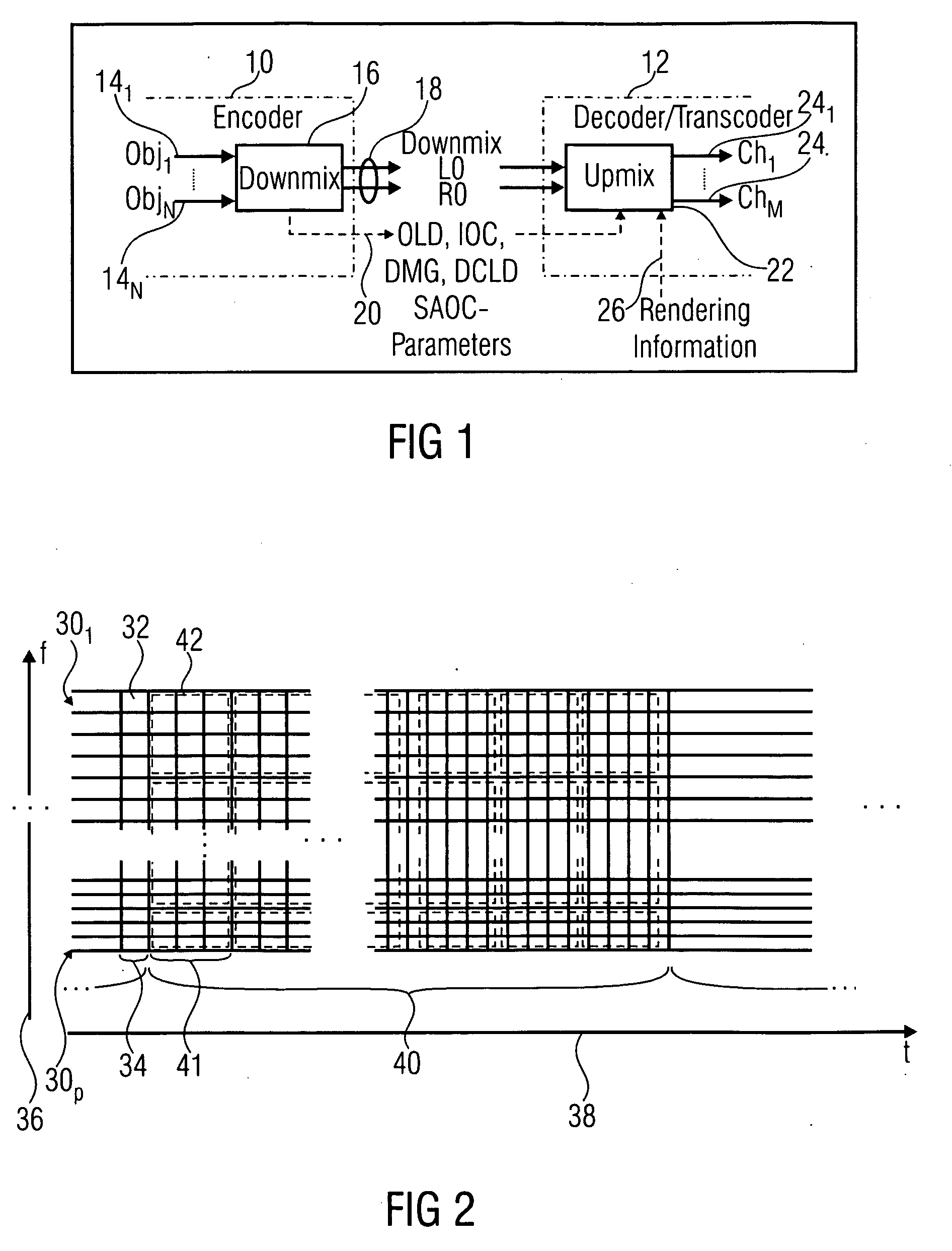
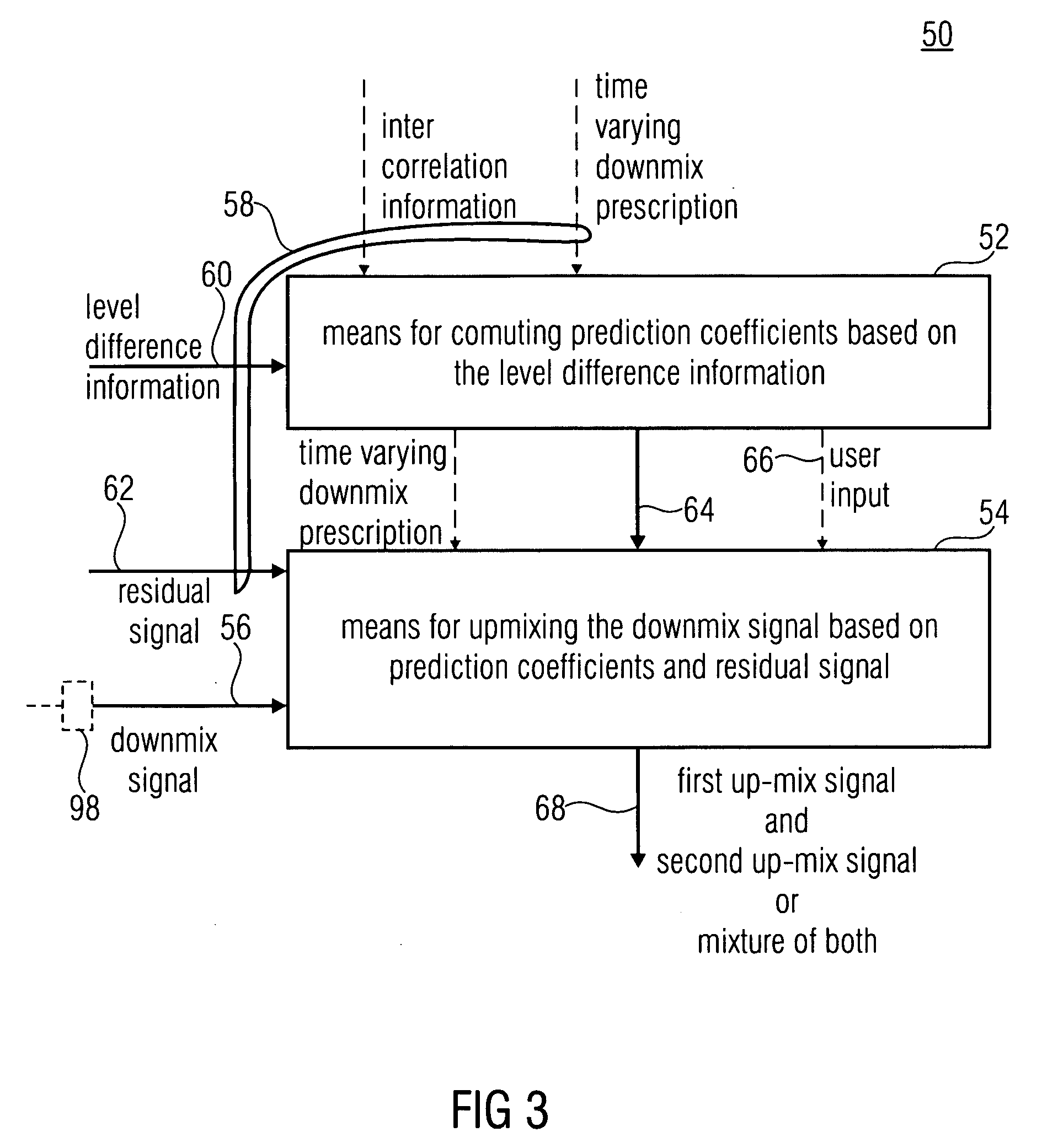
Audio coding using upmix
A method for decoding a multi-audio-object signal having audio signals of first and second types encoded therein, the multi-audio-object signal having a downmix signal and side information having level information of the audio signals of the first and second types in a first predetermined time / frequency resolution, the method including computing a prediction coefficient matrix C based on the level information; and up-mixing the downmix signal based on the prediction coefficients to obtain a first and / or a second up-mix audio signal approximating the audio signals of the first and second types, respectively, wherein up-mixing yields the first and / or second up-mix signals S1 and S2 from the downmix signal d according to a computation representable by(S1S2)=D-1{(1C)d+H},with “1” denoting—depending on the number of channels of d—a scalar, or an identity matrix, and D−1 being a matrix uniquely determined by a downmix prescription according to which the audio signals of the first and second types are downmixed into the downmix signal, and which is also included by the side information, and H being a term independent from d.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Health monitoring method for cable system in cable structure
InactiveCN101319962AMonitor and evaluate health statusReduce distortionMachine part testingTension measurementEngineeringLinearity
The invention relates to a health monitoring method used for a cable system in a cable structure which carries out a plurality of mechanical calculations based on the mechanical calculation benchmark model of a structure; the calculation times are equal to the quantities of the cables. In each calculation, one cable is supposed to have unit damage; the result for each calculation forms vector for calculating a current cable force; a cable force change vector is obtained by using the vector for calculating the current cable force to subtract an initial cable force vector; all the cable force change vectors form a cable force change identity matrix. The noninferior solution of the current damage vector of the cable can be fast calculated by utilizing proper arithmetic such as multi-target optimizing arithmetic according to the approximating linear relation of the current cable force vector (formed by all the current cable forces that are actually detected), the cable force change identity matrix, a unit damage scalar and the current cable damage vector (formed by all the current damage quantities), thus being capable of more accurately confirming the position and the damage degree of the damaged cable.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
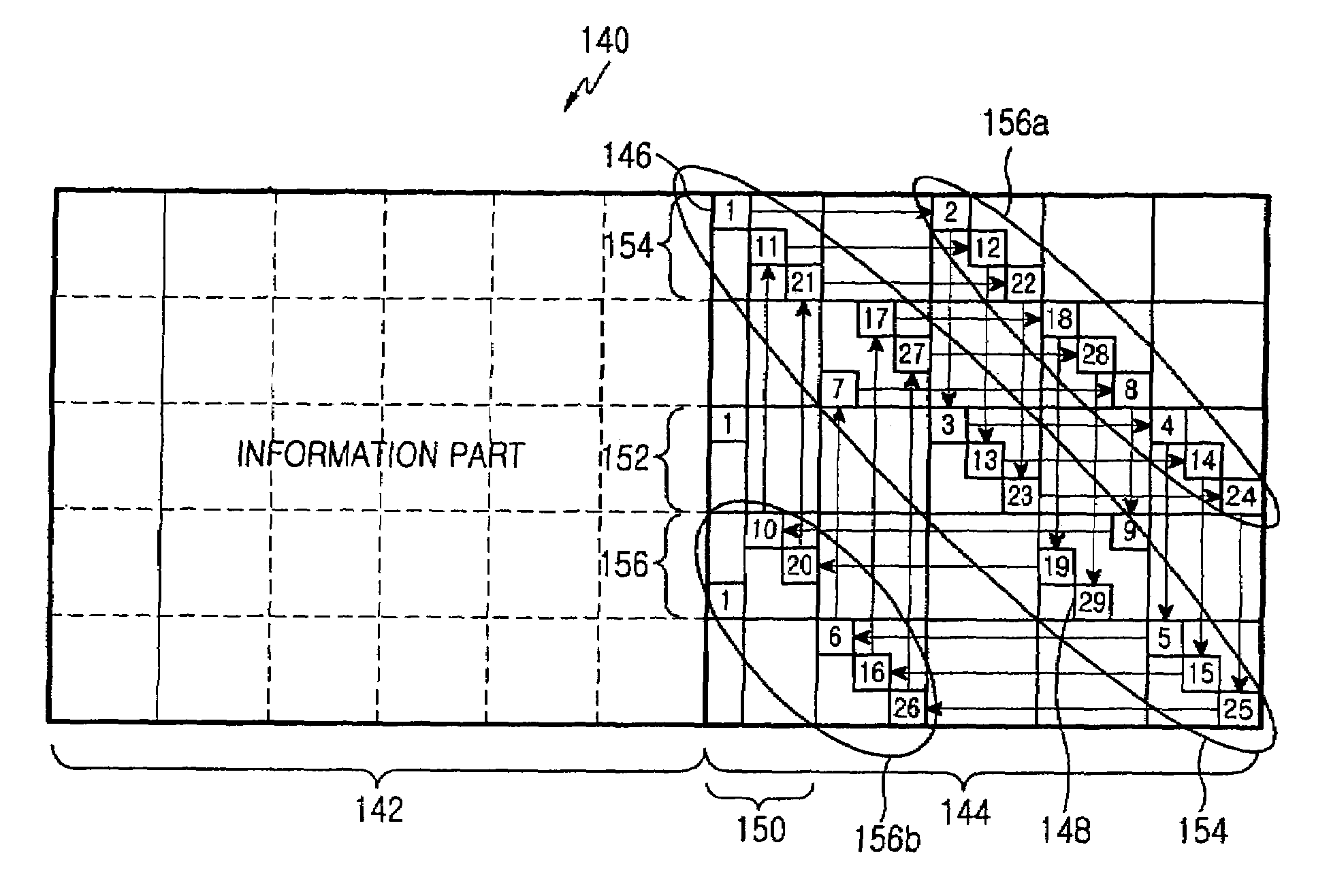
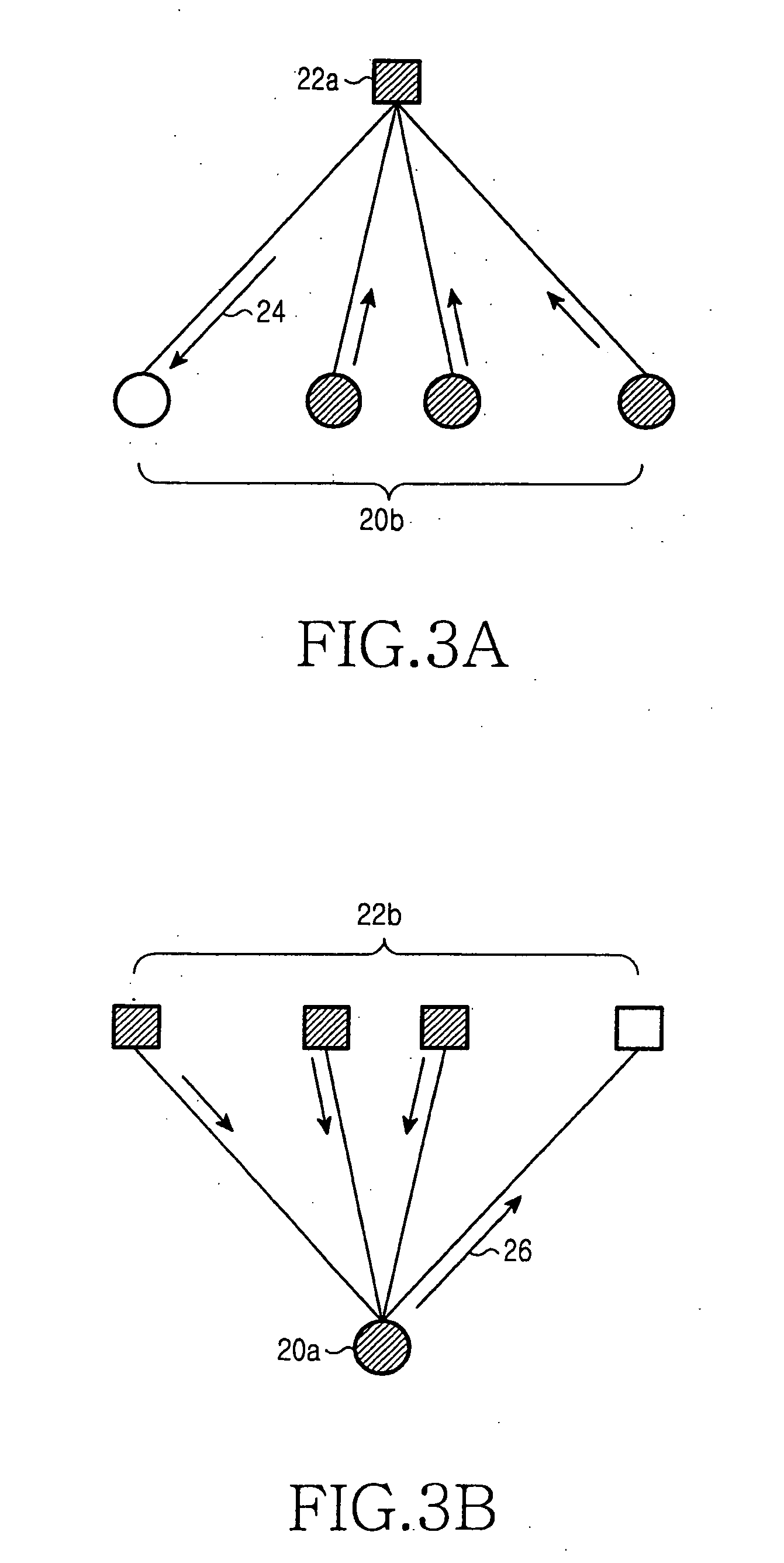
Apparatus and method for coding/decoding block low density parity check code in a mobile communication system
ActiveUS20050050435A1Maximized error correction capabilityMaximized minimum cycle lengthError preventionError detection/correctionTheoretical computer scienceParity-check matrix
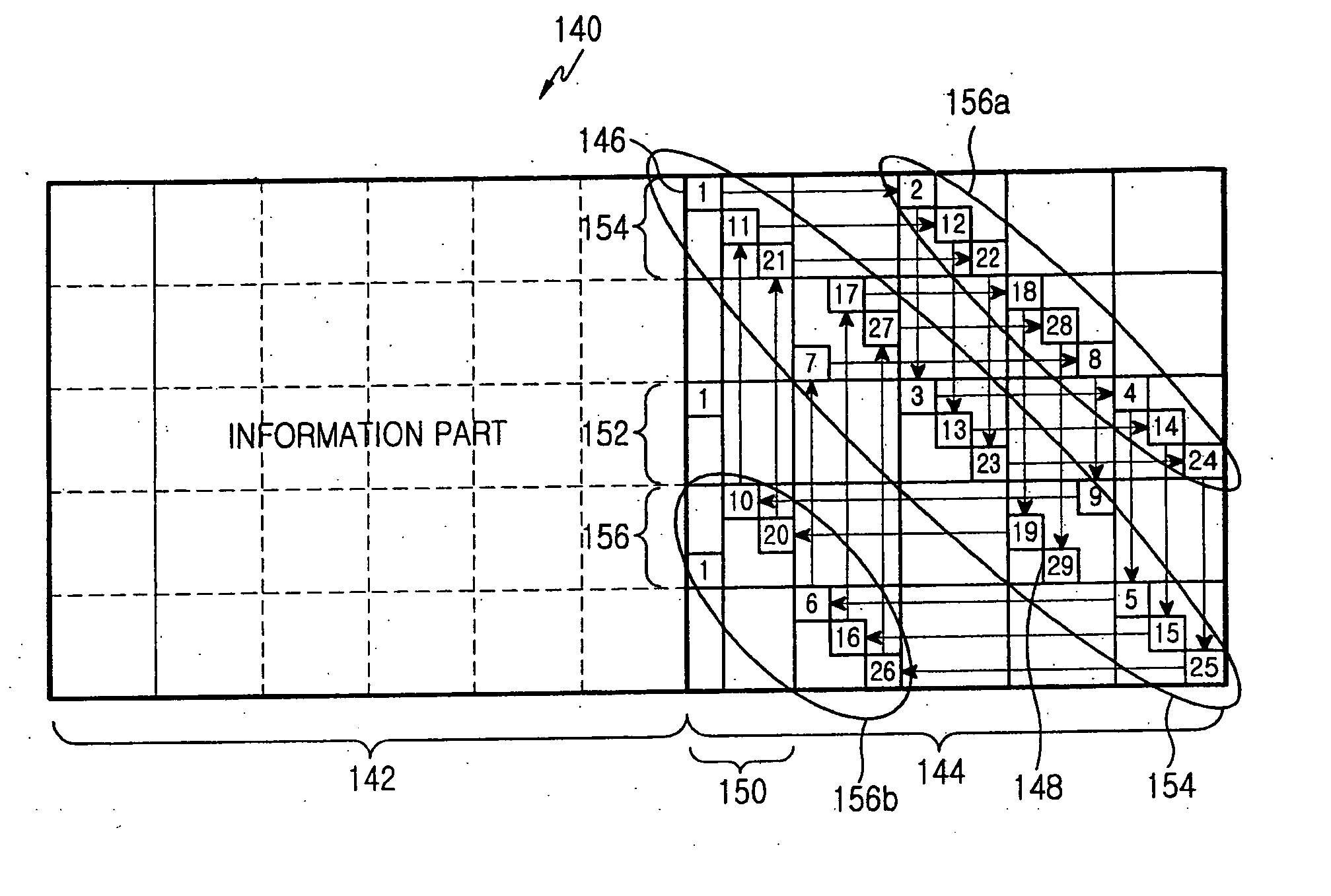
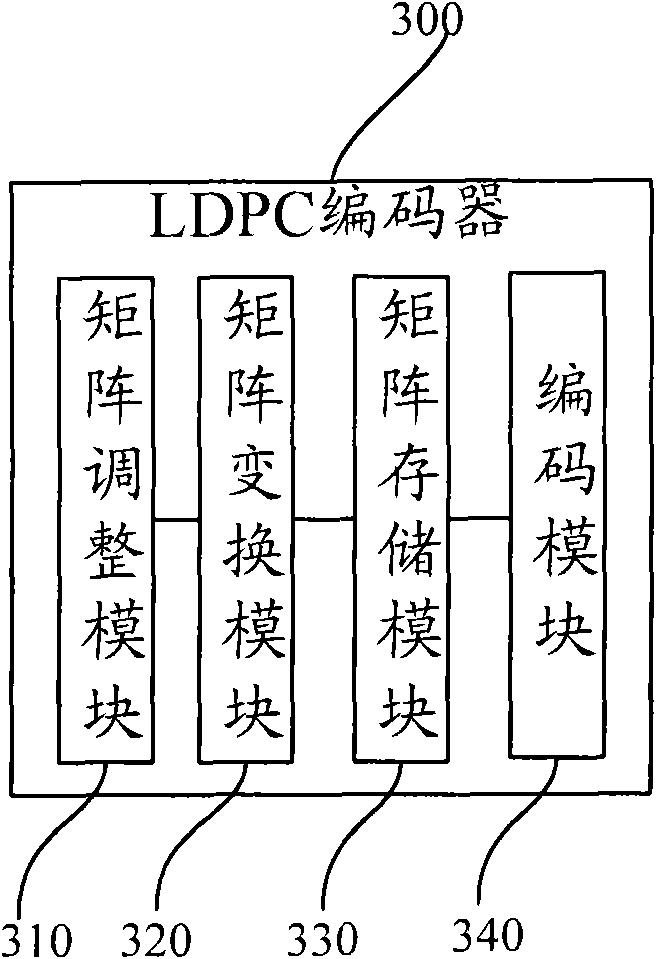
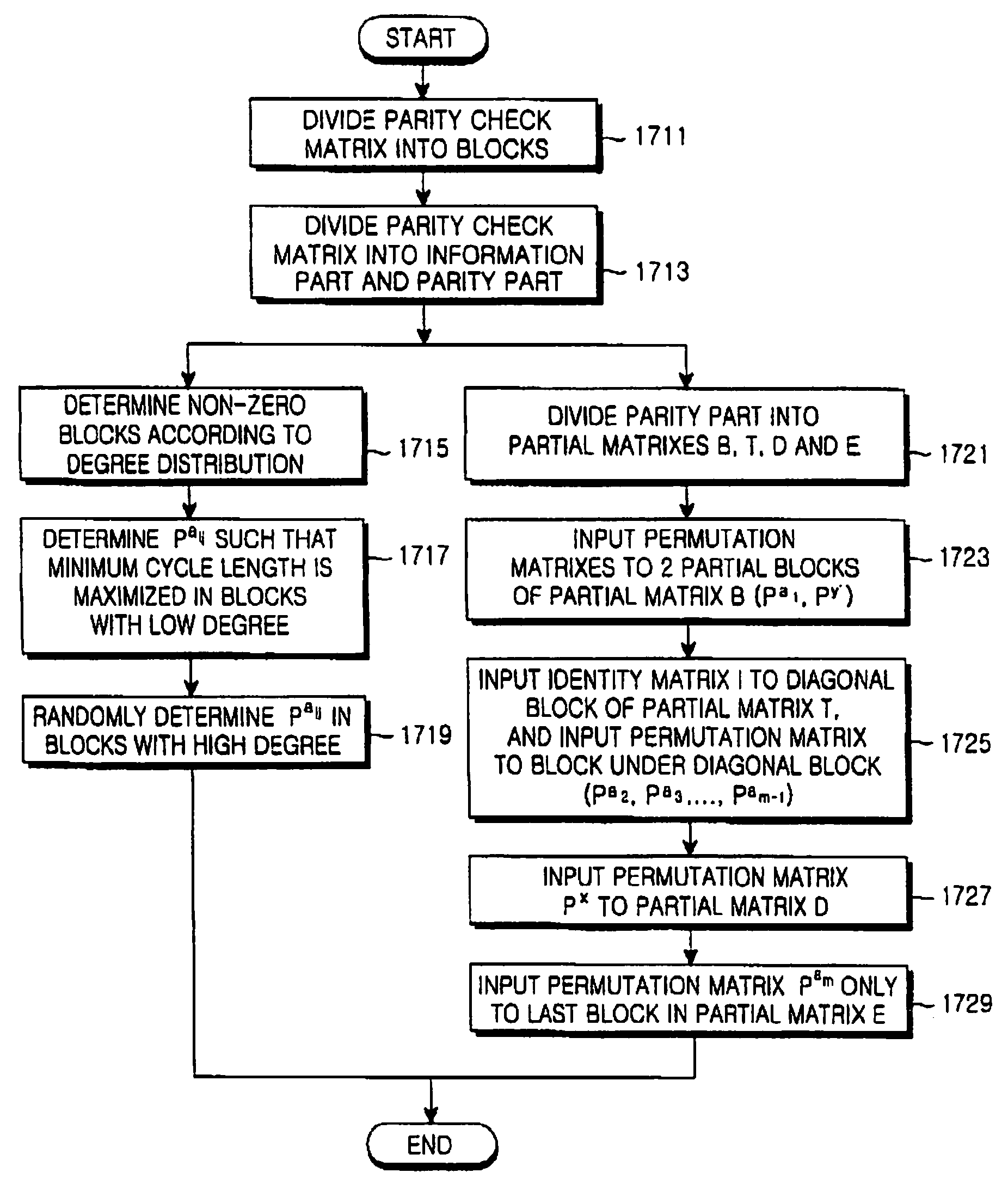
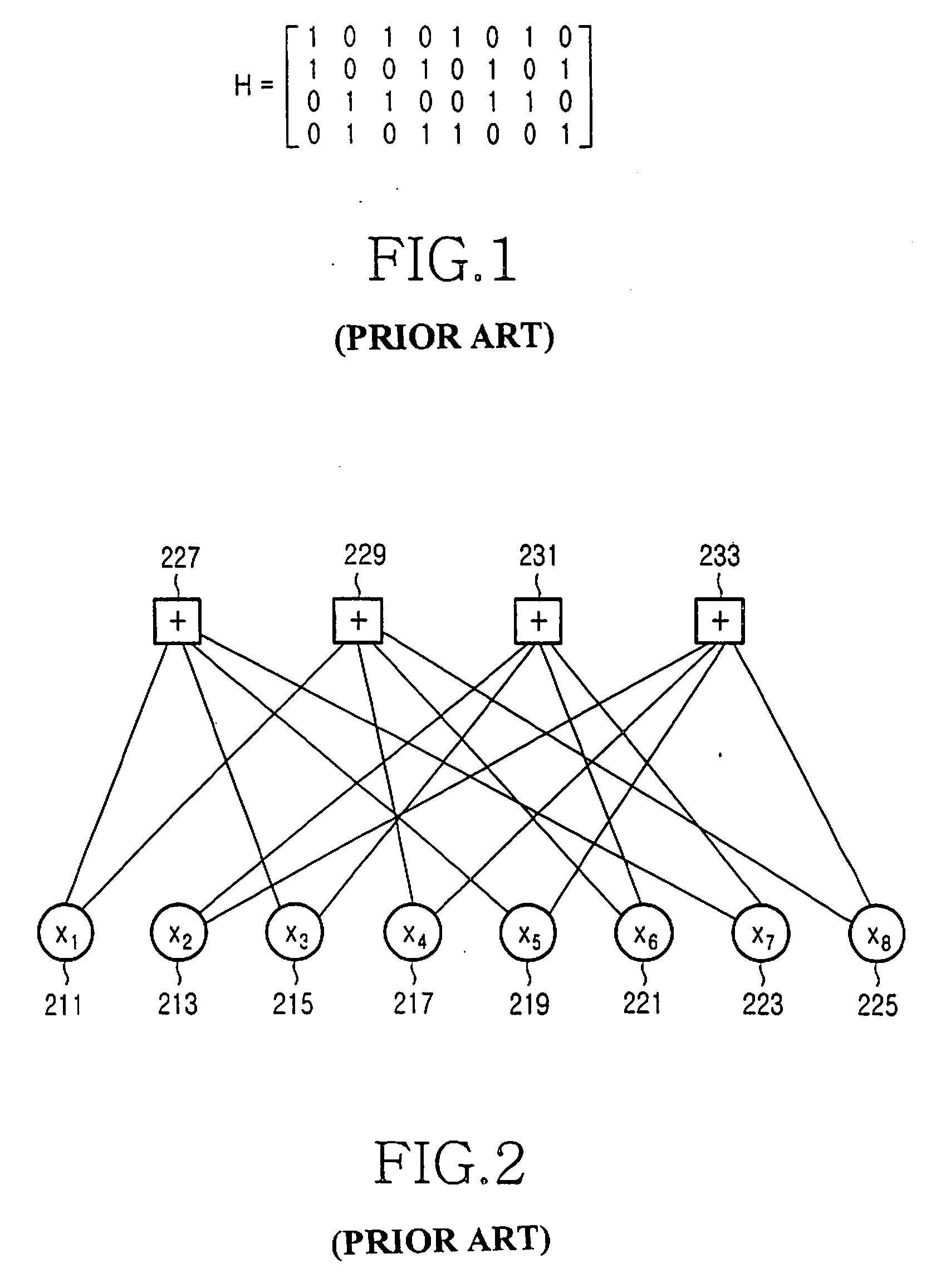
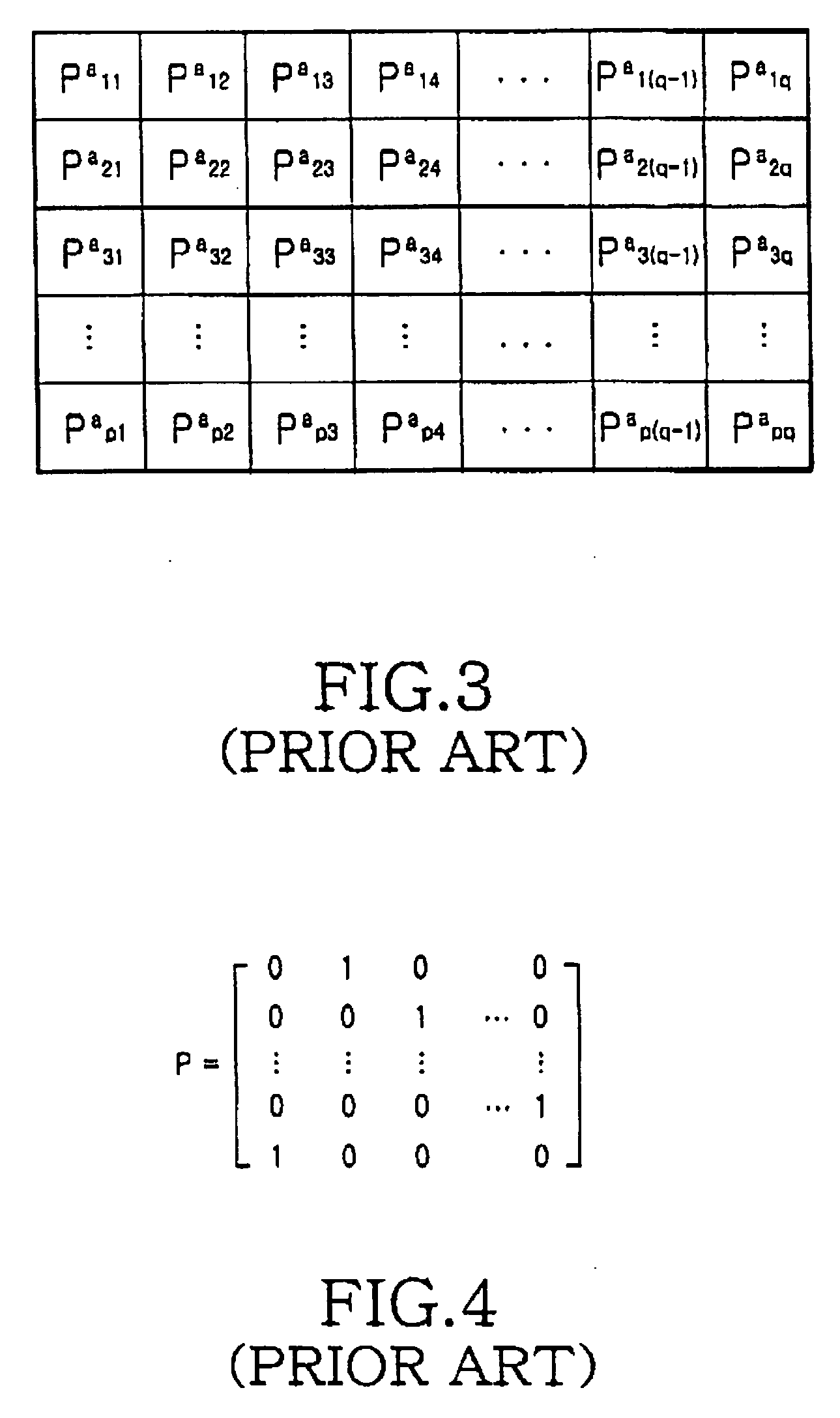
A method for generating a parity check matrix of a block LDPC code is disclosed. The parity check matrix includes an information part corresponding to an information word and a first parity part and a second parity part each corresponding to a parity. The method includes determining a size of the parity check matrix based on a coding rate applied when coding the information word with the block LDPC code, and a codeword length; dividing a parity check matrix with the determined size into a predetermined number of blocks; classifying the blocks into blocks corresponding to the information part, blocks corresponding to the first parity part, and blocks corresponding to the second parity part; arranging permutation matrixes in predetermined blocks from among the blocks classified as the first parity part, and arranging identity matrixes in a full lower triangular form in predetermined blocks from among the blocks classified as the second parity part; and arranging the permutation matrixes in the blocks classified as the information part such that a minimum cycle length is maximized and weight values are irregular on a factor graph of the block LDPC code.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Hardware-Efficient Low Density Parity Check Code for Digital Communications
InactiveUS20070011568A1Efficient implementationEfficient constructionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionMatrix groupMemory bank
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Systems and methods for a turbo low-density parity-check decoder
ActiveUS20070043998A1Control complexityReduce in quantityError detection/correctionCode conversionParity-check matrixData rate
A method for forming a plurality of parity check matrices for a plurality of data rates for use in a Low-Density Parity-Check (LDPC) decoder, comprises establishing a first companion exponent matrix corresponding to a first parity check matrix for a first data rate, and partitioning the first parity check matrix and the first companion exponent matrix into sub-matrices such that the first parity check matrix is defined using a cyclical shift of an identity matrix.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
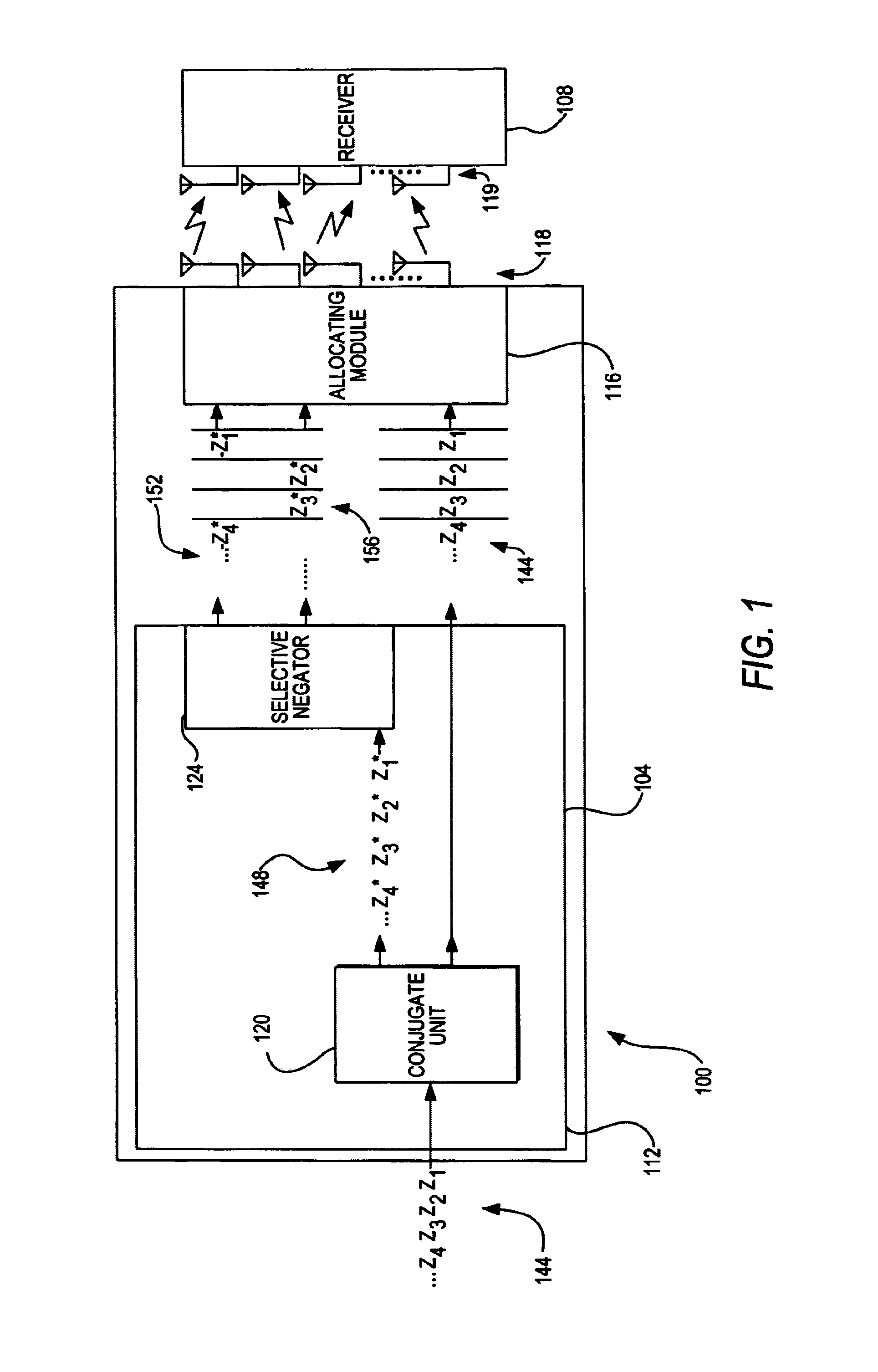
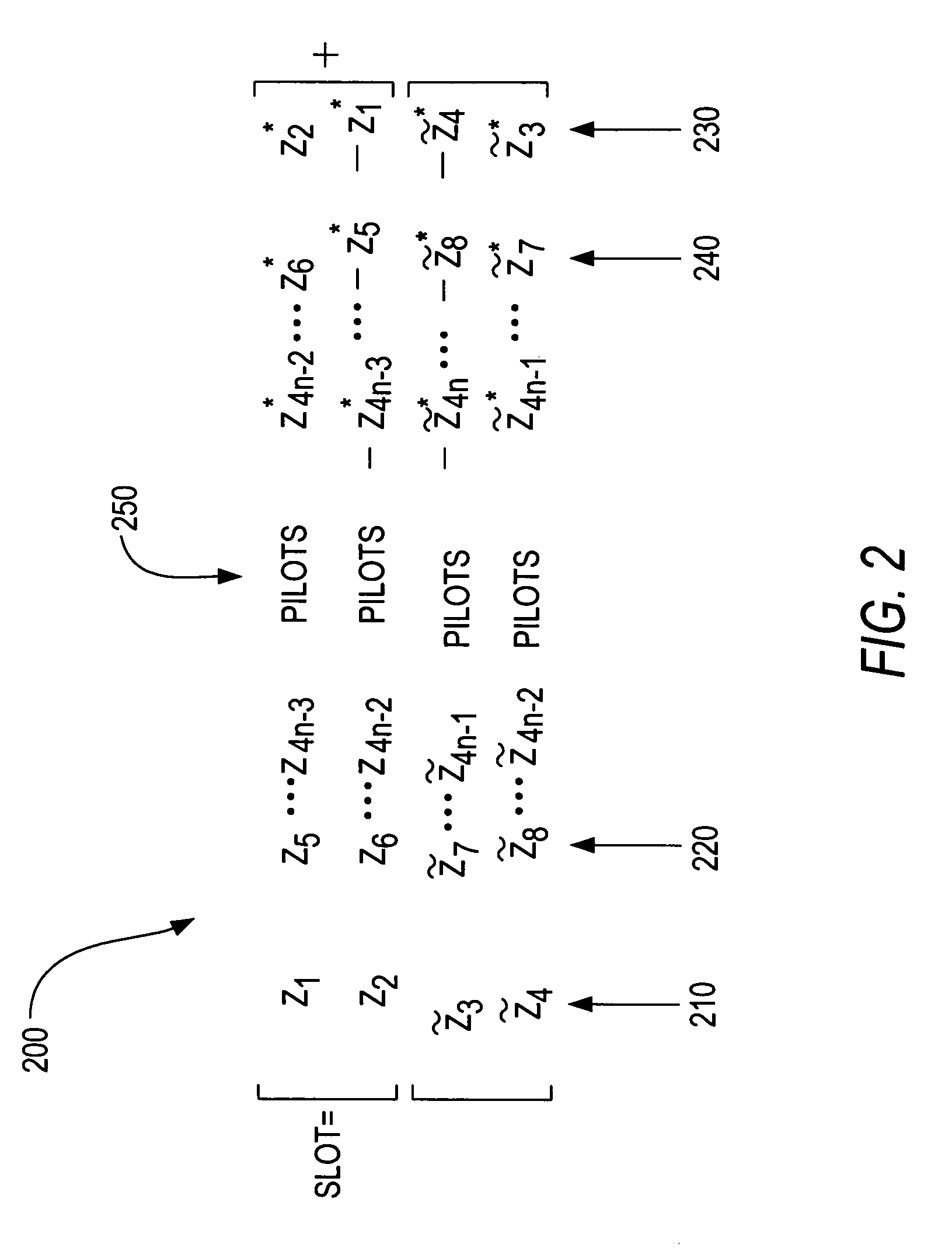
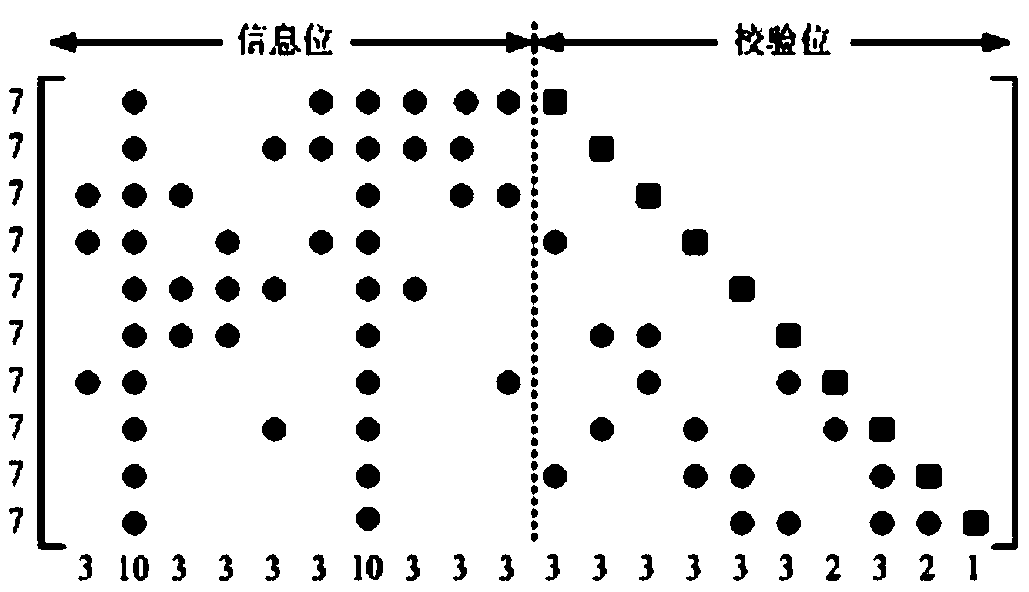
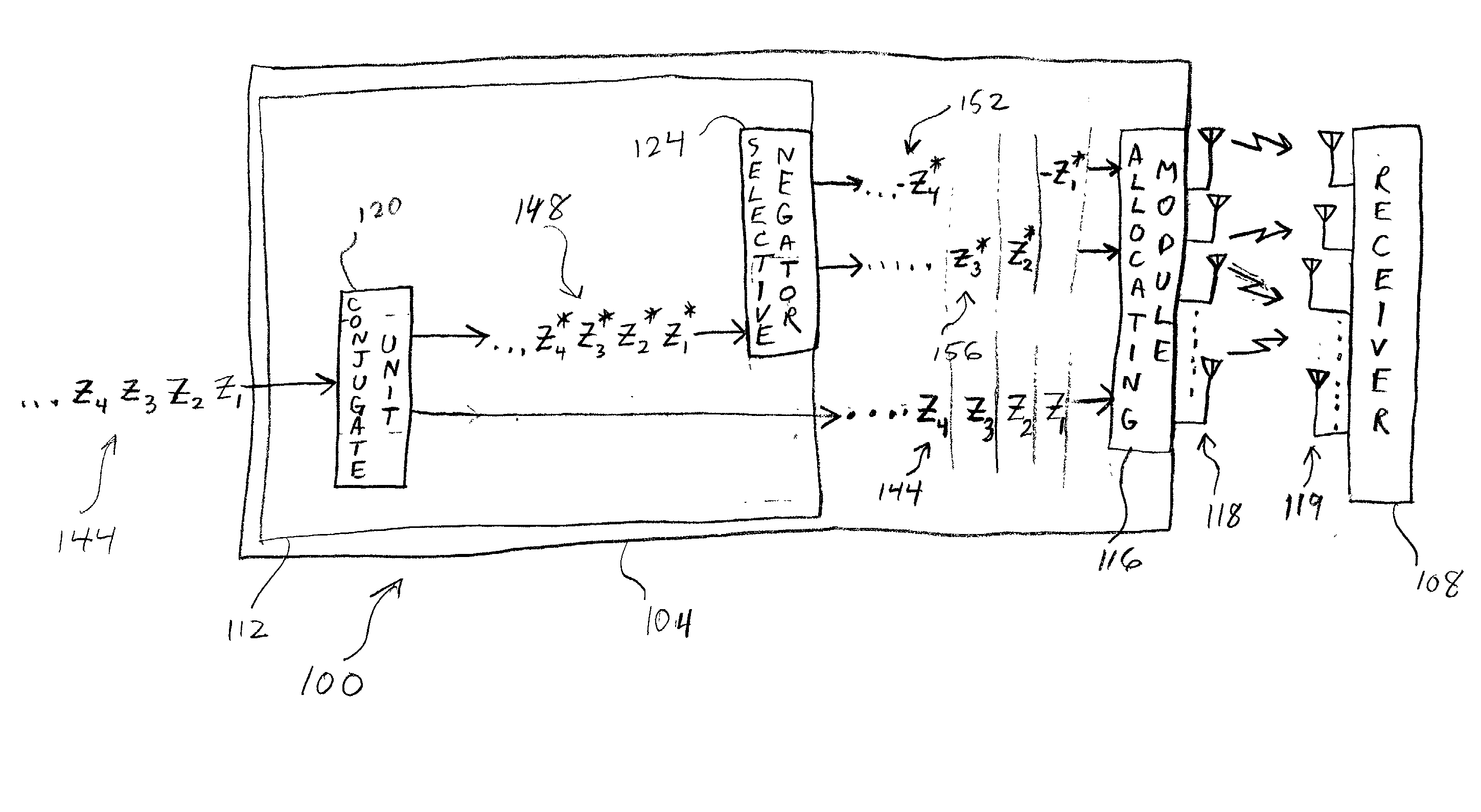
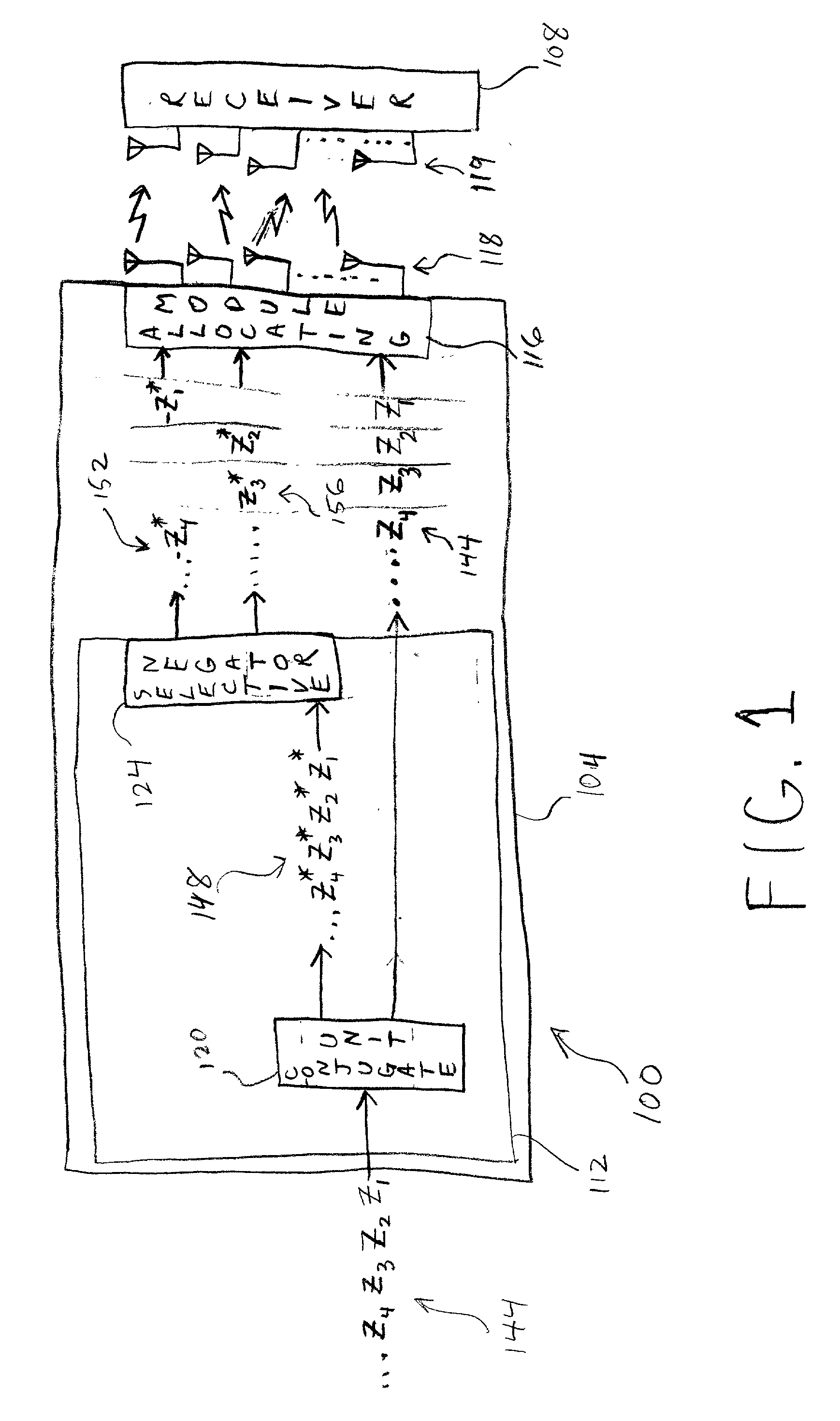
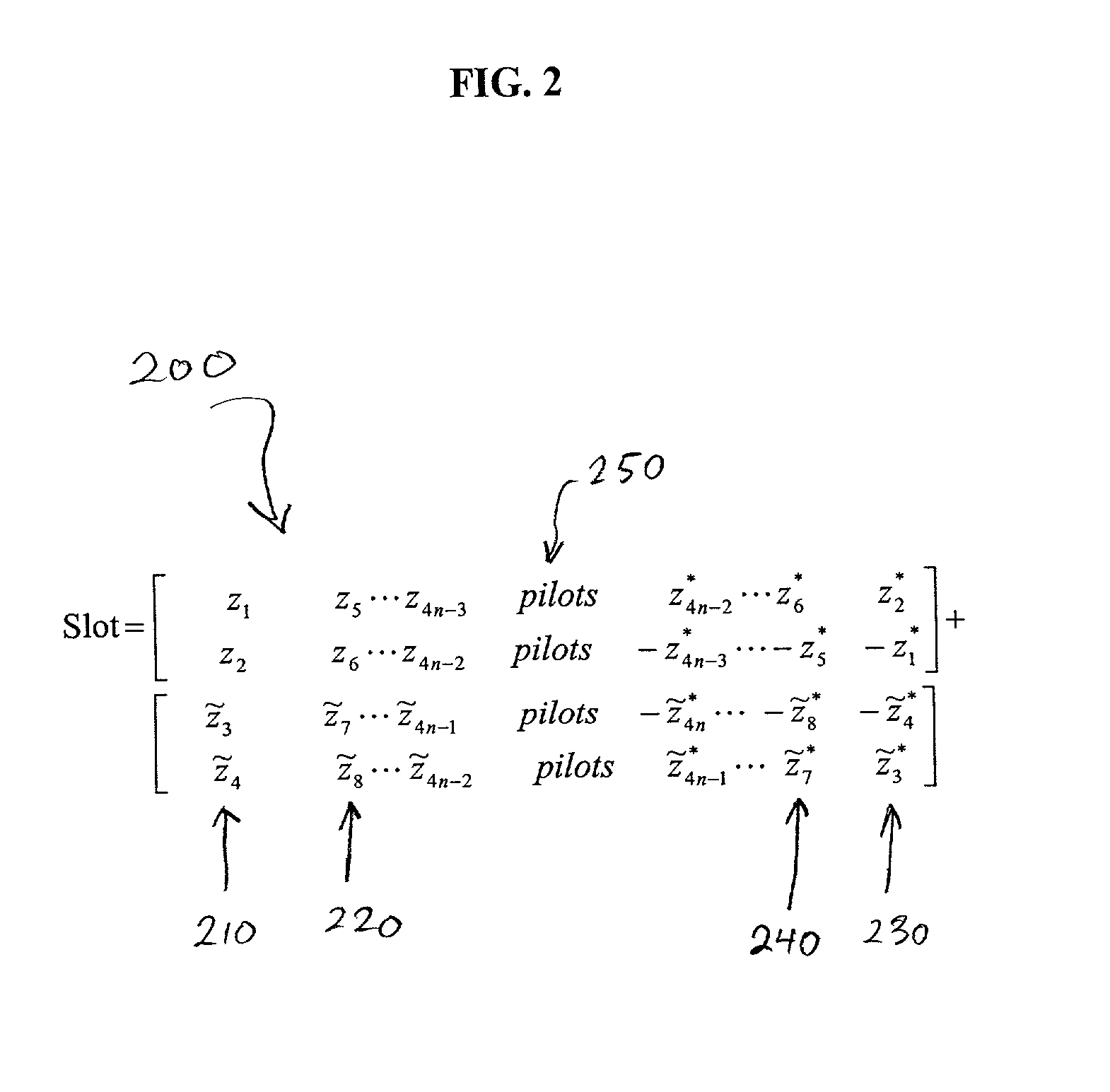
ISI-robust slot formats for non-orthogonal-based space-time block codes
Owner:UNWIRED BROADBAND INC
Method and apparatus for generating a low-density parity check code
ActiveUS7536623B2Low density parity check (LDPC)Simple codingError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionTheoretical computer scienceDiagonal
A low density parity check (LDPC) code generating method and apparatus are provided. A parity check matrix with (N−K) rows for check nodes and N columns for variable nodes are formed to encode an information sequence of length K to a codeword of length N. The parity check matrix is divided into an information part matrix with K columns and a parity part matrix with (N−k) columns. The parity part is divided into P×P subblocks. P is a divisor of (N−K). First and second diagonals are defined in the parity part matrix and the second diagonal is a shift of the first diagonal by f subblocks. Shifted identity matrices are placed on the first and second diagonals and zero matrices are filled elsewhere. An odd number of delta matrices each having only one element of 1 are placed in one subblock column of the parity part matrix. The parity check matrix is stored.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System, Method, and Computer Program Product for Translating an Element of a Static Encoded Image in the Encoded Domain
InactiveUS20100118972A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionImaging quality
A computer-implemented method for creating in the encoded domain one or more video frames from a compressed still video image wherein image content in the created video frames is translated in location by panning or scrolling or a combination thereof on a non-block basis (i.e. pixel-level). A new block formed from portions of two other blocks is created by processing the original two blocks with identity matrices based upon the shift amount. By performing the creation process in the encoded domain processing power requirements are reduced and image quality is increased.
Owner:ACTIVE VIDEO NETWORKS INC
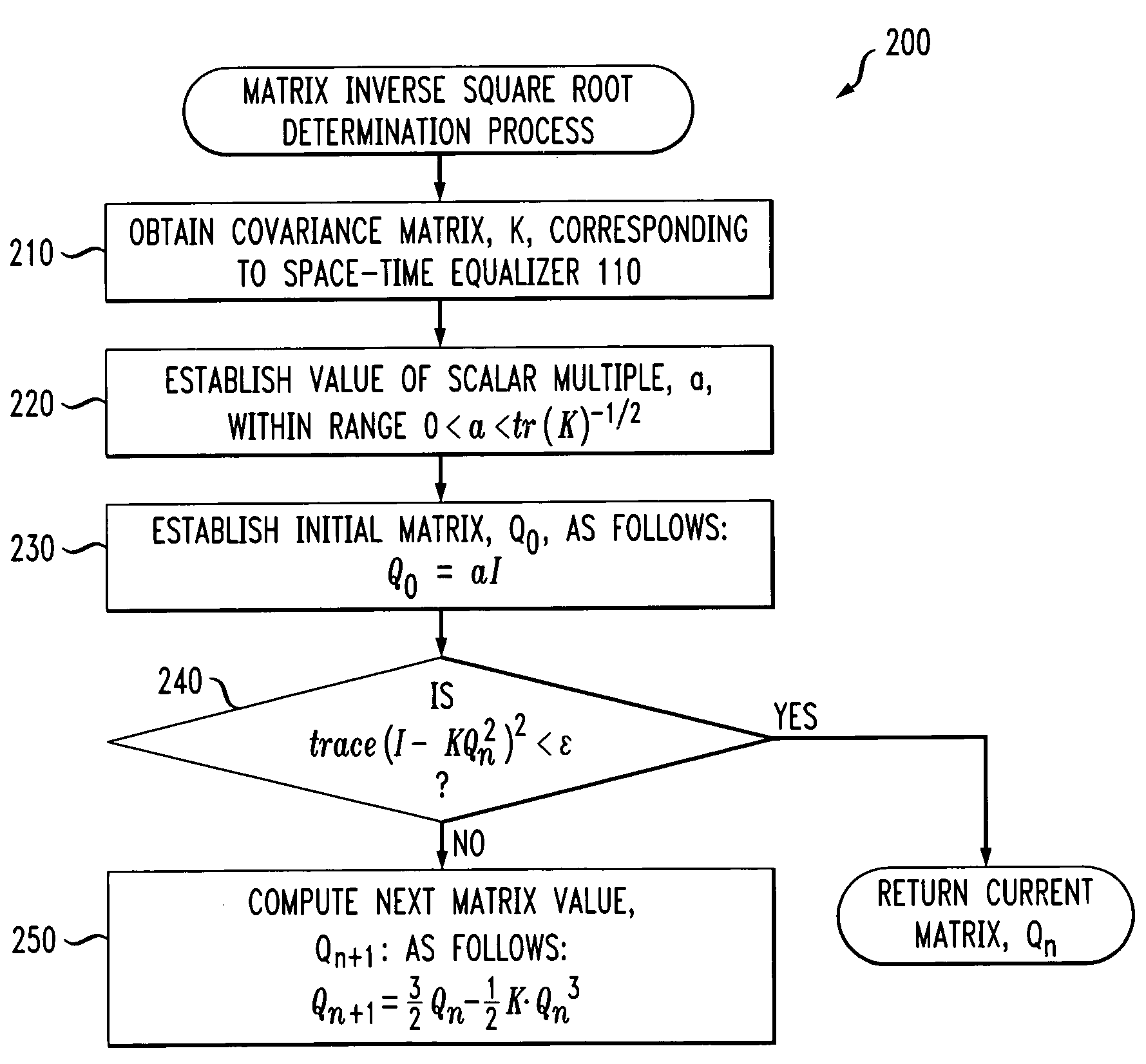
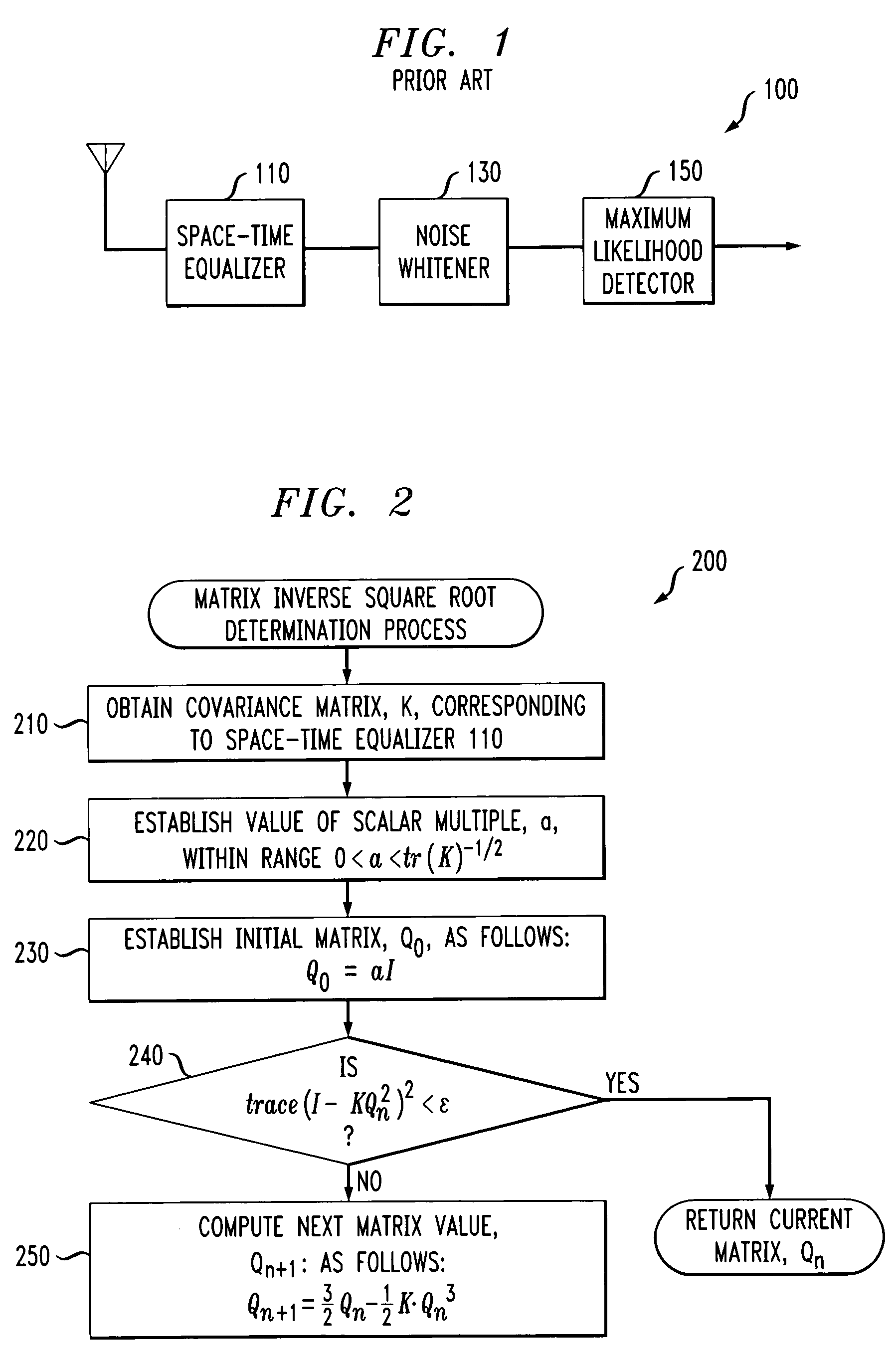
Method and apparatus for determining an inverse square root of a given positive-definite hermitian matrix
Generally, a method and apparatus are provided for computing a matrix inverse square root of a given positive-definite Hermitian matrix, K. The disclosed technique for computing an inverse square root of a matrix may be implemented, for example, by the noise whitener of a MIMO receiver. Conventional noise whitening algorithms whiten a non-white vector, X, by applying a matrix, Q, to X, such that the resulting vector, Y, equal to Q·X, is a white vector. Thus, the noise whitening algorithms attempt to identify a matrix, Q, that when multiplied by the non-white vector, will convert the vector to a white vector. The disclosed iterative algorithm determines the matrix, Q, given the covariance matrix, K. The disclosed matrix inverse square root determination process initially establishes an initial matrix, Q0, by multiplying an identity matrix by a scalar value and then continues to iterate and compute another value of the matrix, Qn+1, until a convergence threshold is satisfied. The disclosed iterative algorithm only requires multiplication and addition operations and allows incremental updates when the covariance matrix, K, changes.
Owner:LGS INNOVATIONS +1
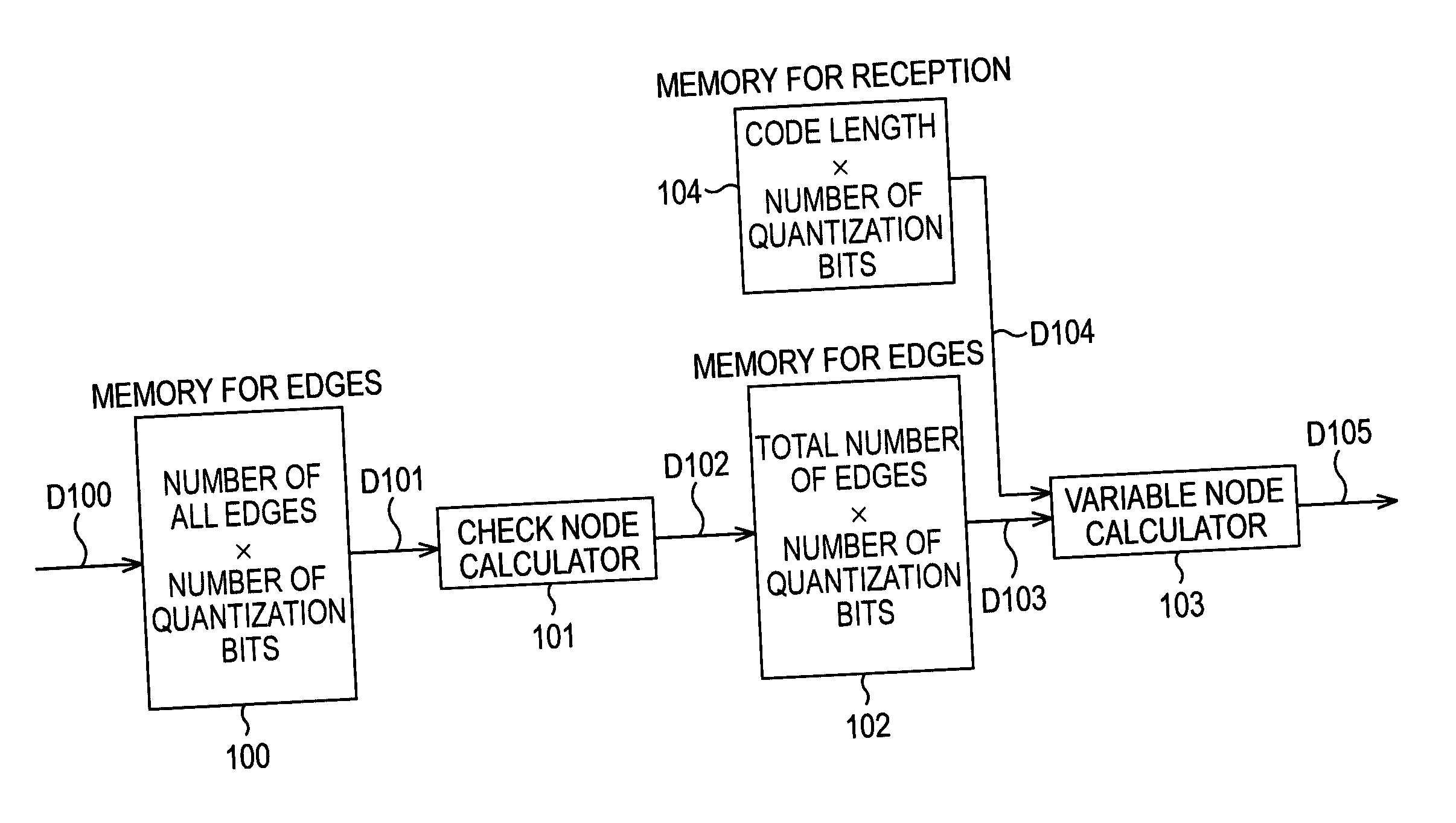
Decoding device, decoding method, and program
ActiveUS20050240853A1Suppress operating frequencyEasy to controlError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionDecoding methodsComputer architecture
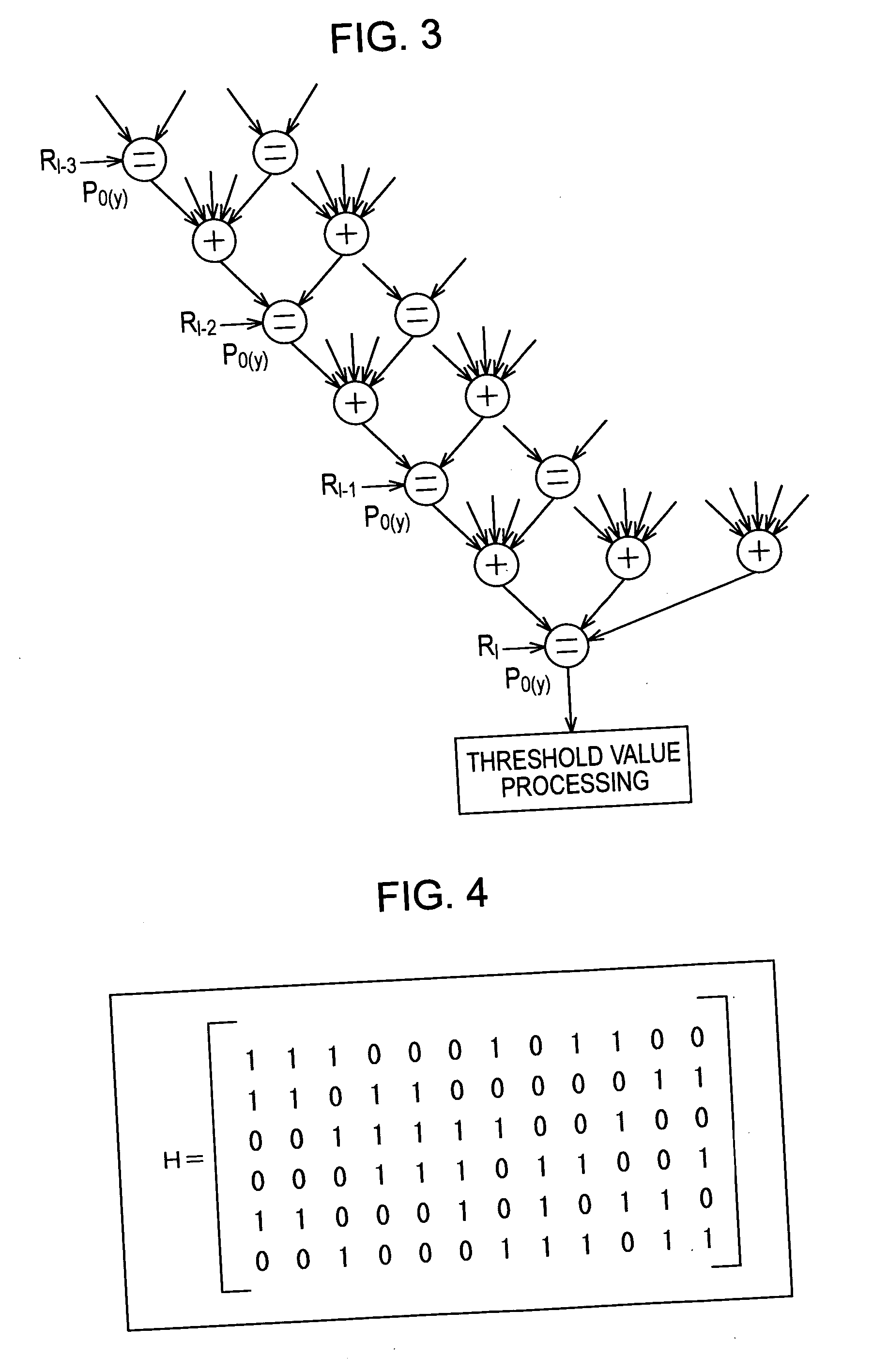
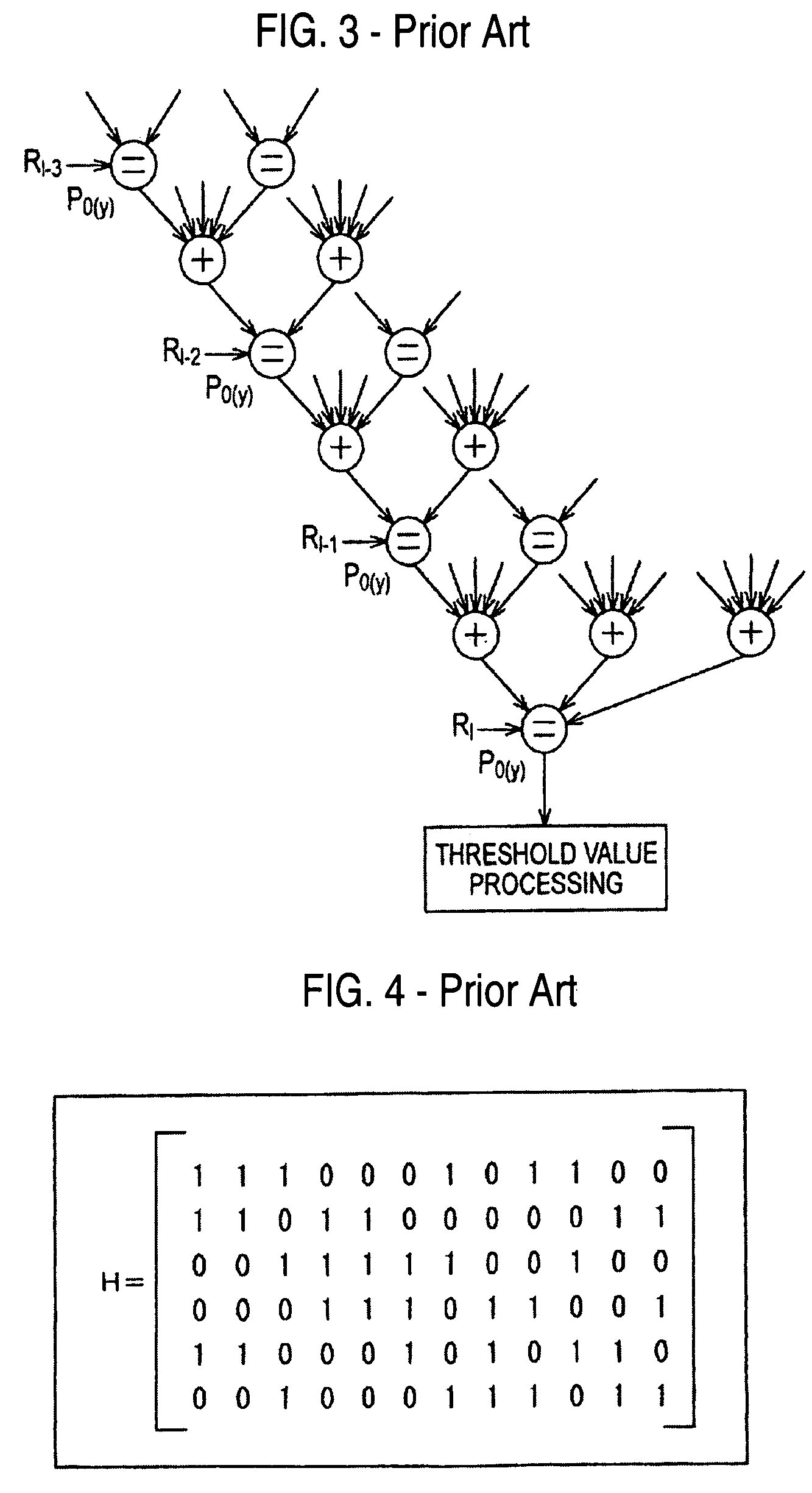
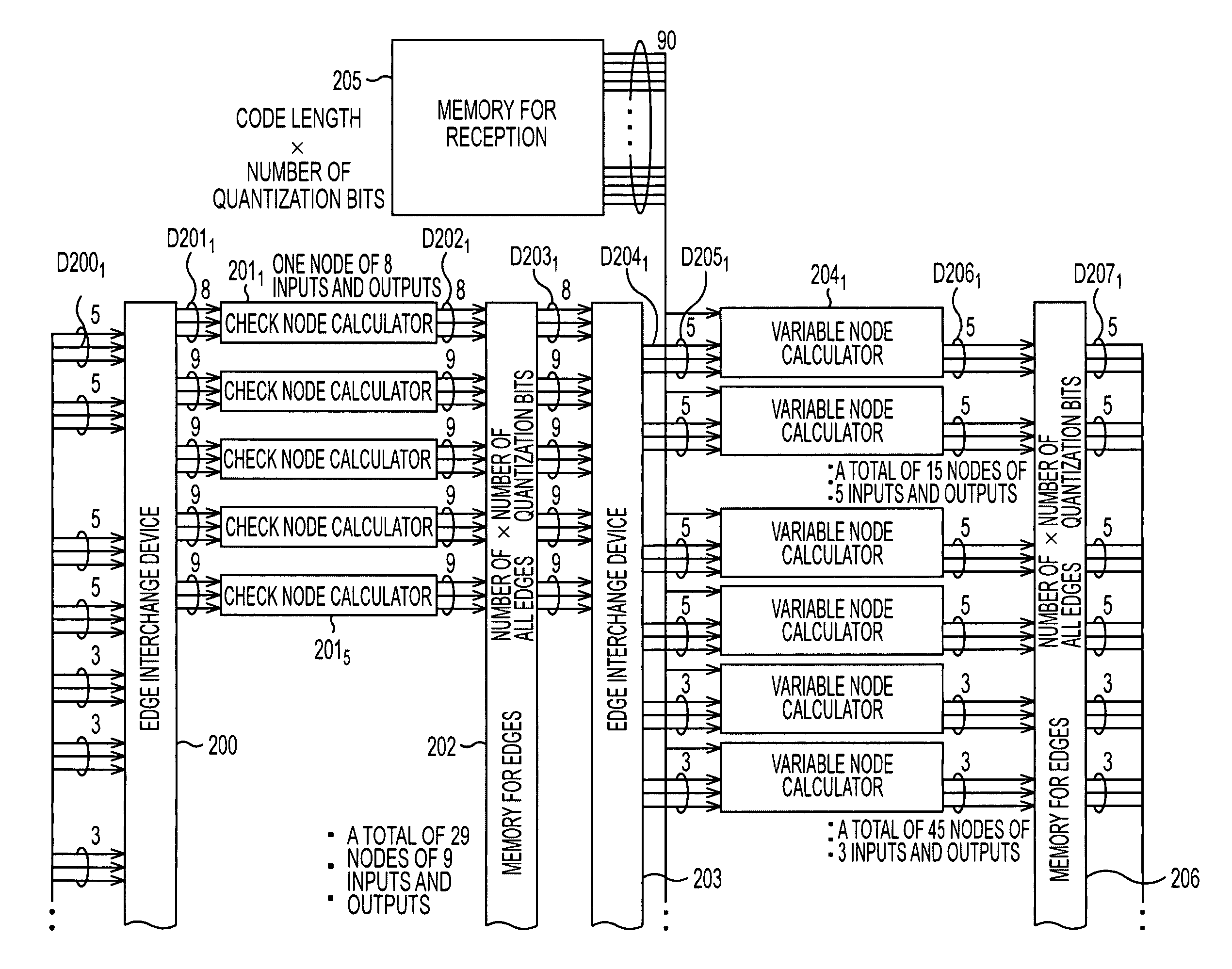
The present invention relates to a decoding apparatus and a decoding method for realizing the decoding of LDPC codes, in which, while the circuit scale is suppressed, the operating frequency can be suppressed within a sufficiently feasible range, and control of memory access can be performed easily, and to a program therefor. A check matrix of LDPC codes is formed by a combination of a (P×P) unit matrix, a matrix in which one to several 1s of the unit matrix are substituted with 0, a matrix in which they are cyclically shifted, a matrix, which is the sum of two or more of them, and a (P×P) 0-matrix. A check node calculator 313 simultaneously performs p check node calculations. A variable node calculator 319 simultaneously performs p variable node calculations.
Owner:SONY CORP
Decoding apparatus, decoding method, and program to decode low density parity check codes
ActiveUS7299397B2Easy to controlSuppression frequencyError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionComputer architectureLow density
The present invention relates to a decoding apparatus and a decoding method for realizing the decoding of LDPC codes, in which, while the circuit scale is suppressed, the operating frequency can be suppressed within a sufficiently feasible range, and control of memory access can be performed easily, and to a program therefor. A check matrix of LDPC codes is formed by a combination of a (P×P) unit matrix, a matrix in which one to several 1s of the unit matrix are substituted with 0, a matrix in which they are cyclically shifted, a matrix, which is the sum of two or more of them, and a (P×P) 0-matrix. A check node calculator 313 simultaneously performs p check node calculations. A variable node calculator 319 simultaneously performs p variable node calculations.
Owner:SONY CORP
Decoding method, decoding apparatus, and program to decode low density parity check codes
ActiveUS7318186B2Easy to controlSuppression frequencyError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionFormation matrixPartition of unity
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and apparatus for generating a low-density parity check code
ActiveUS20060156183A1Low density parity check (LDPC)Simple codingError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionTheoretical computer scienceDiagonal
A low density parity check (LDPC) code generating method and apparatus are provided. A parity check matrix with (N−K) rows for check nodes and N columns for variable nodes are formed to encode an information sequence of length K to a codeword of length N. The parity check matrix is divided into an information part matrix with K columns and a parity part matrix with (N−k) columns. The parity part is divided into P×P subblocks. P is a divisor of (N−K). First and second diagonals are defined in the parity part matrix and the second diagonal is a shift of the first diagonal by f subblocks. Shifted identity matrices are placed on the first and second diagonals and zero matrices are filled elsewhere. An odd number of delta matrices each having only one element of 1 are placed in one subblock column of the parity part matrix. The parity check matrix is stored.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
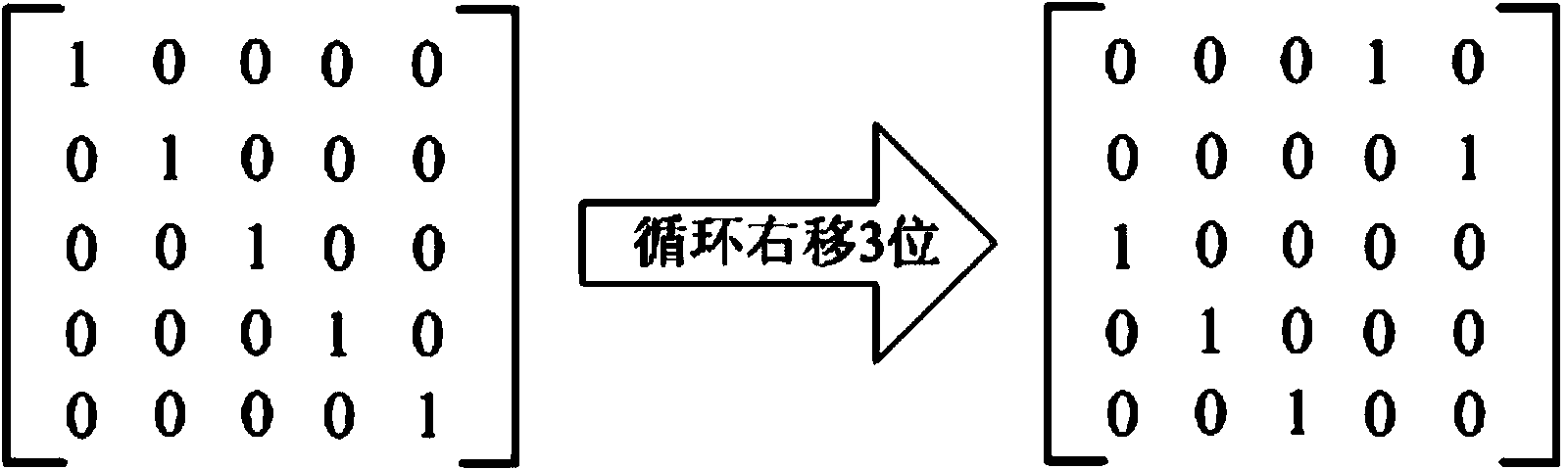
Construction method and encoding method for check matrix of LDPC code
ActiveCN104333390ASimple structureEasy to storeError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsLow-density parity-check codeComputational physics
The invention belongs to the construction technology field of LDPC code (low-density parity-check code) check matrix, and in particular relates to a construction method and encoding method for check matrix of LDPC code. The construction method for check matrix of LDPC code comprises the steps as follows: building the base matrix HB of the LDPC code check matrix, aiming at the base matrix HB, detecting and eliminating the four ring to obtain the base matrix after removing the four ring; in the base matrix after removing the four ring, using z*z whole zero matrix for replacing the 0 element, z expresses the set extension factor; F expresses the number of the non-zero element in the base matrix after removing the four ring, HB(f) expresses the f(th) non-zero element in the base matrix after removing the four ring, obtaining the matrix Iz(HB(f)) of the unit matrix with size of z*z for ring shift right of HB(f), in the base matrix after removing the four ring, replacing the f(th) non-zero element HB(f) by the matrix Iz(HB(f)); obtaining LDPC code check matrix, the LDPC code check matrix is the new matrix after replacing each element for the base matrix after removing the four ring.
Owner:西安烽火电子科技有限责任公司
ISI-robust slot formats for non-orthogonal-based space-time block codes
InactiveUS20020126648A1Modulated-carrier systemsRadio transmissionSymbol of a differential operatorTranspose
The transmit diversity and symbol rate in a wireless mobile system are increased by allocating the complex symbols to be transmitted in accordance with a time-space slot format that incorporates non-orthogonal-based matrices, defined as matrices whose format is such that the product of the matrix and its Hermitian transpose is other than the identity matrix times a real number other than unity. The non-orthogonal-based matrices are indexed by antenna and by symbol period. Copies and complex conjugates (or negative complex conjugates) of the same symbol that are transmitted from different antennas are mutually separated into non-adjacent parts of the slot. Each non-orthogonal-based "space-time" matrix is composed of orthogonal-based matrices, i.e., matrices other than non-orthogonal-based matrices. Preferably, sequences of complex conjugates are time-reversed in the slot.
Owner:UNWIRED BROADBAND INC
LDPC constructing method with short ring or low duplicate code
InactiveCN101488761ASolve the problem of low-code repeated code wordsCode majorError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsLinear codingShort loop
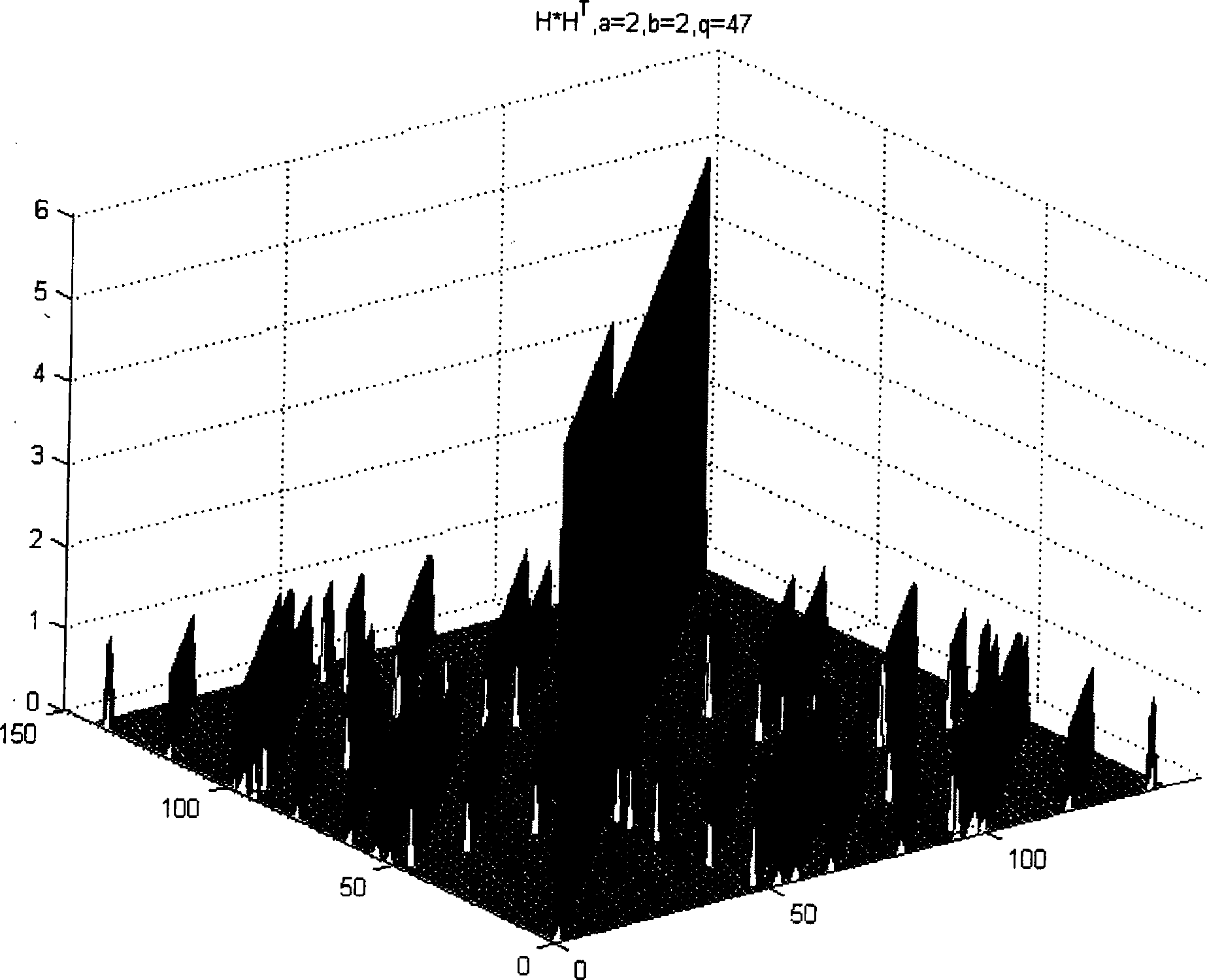
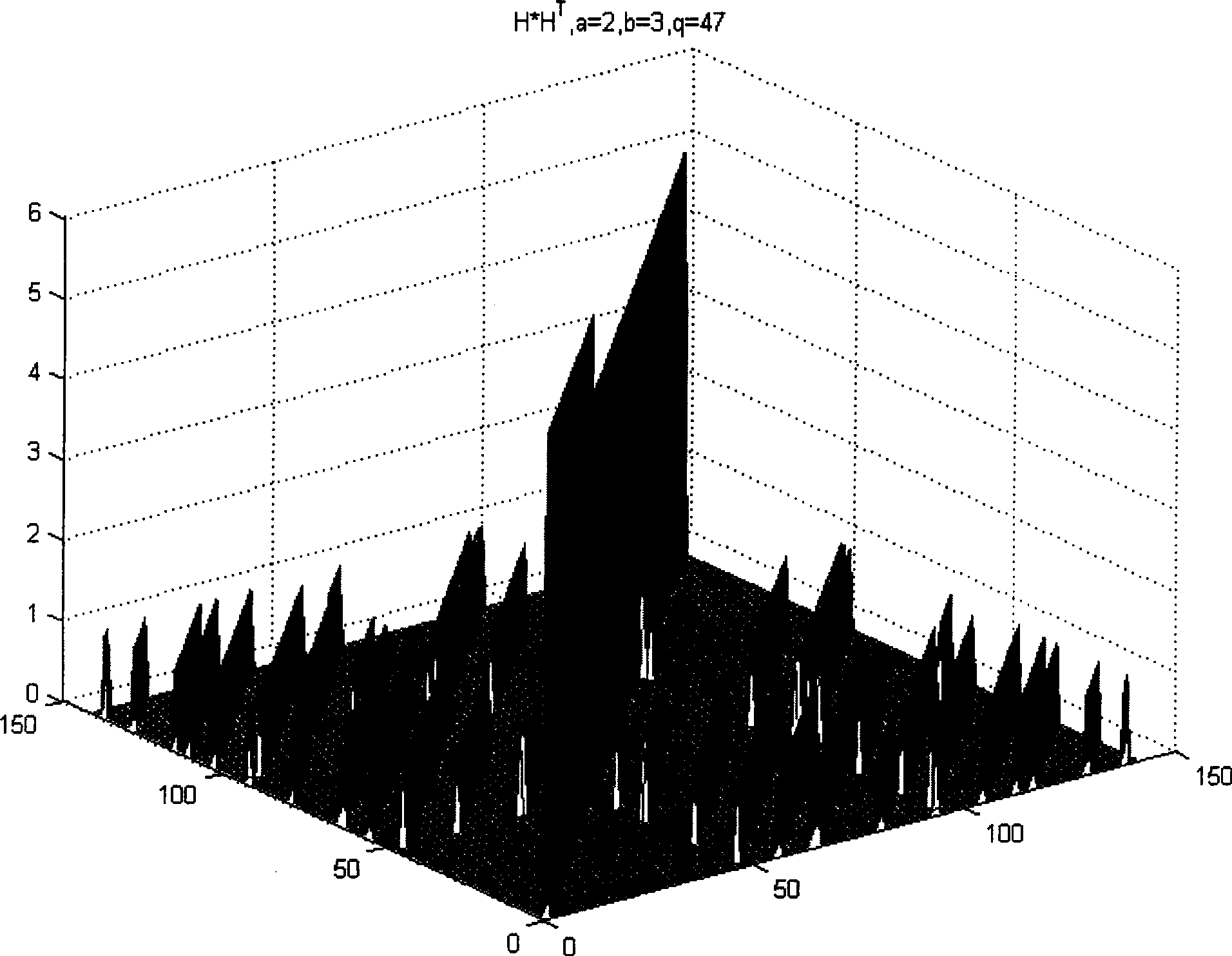
The invention discloses an algebraic construction method of LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) code based on cyclic matrixes; design parameters of cyclic matrixes are adjusted by short-loop check and minimum code weight check, which are nonnegative prime numbers a and b meeting two constraint conditions, and dimension q of an identity matrix, wherein the magnitude of dimension q of a shift identity matrix and whether the error rate characteristics of the designed LDPC code are influenced by prime numbers. The invention solves the problems of short-loop and low code coincident code word appearing in the existing QC LDPC code design. The method can check the existence of low code coincident code word in the designed code, thereby checking the existence of 4-loop. An irregular quasi-cyclic LDPC code structure disclosed by the invention divides the check matrix H into two submatrixes A and B, the nonsingular structure of the submatrix A is disclosed, and a matrix is generated by the two submatrixes A and B. Direct linear coding is carried out by generating the matrix. The embodiment validates the efficiency and good bit rate performance of the method disclosed by the invention.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Low cost, high performance error detection and correction
InactiveUS20080059869A1Low costReduce complexityError detection/correctionCode conversionTheoretical computer scienceLow density
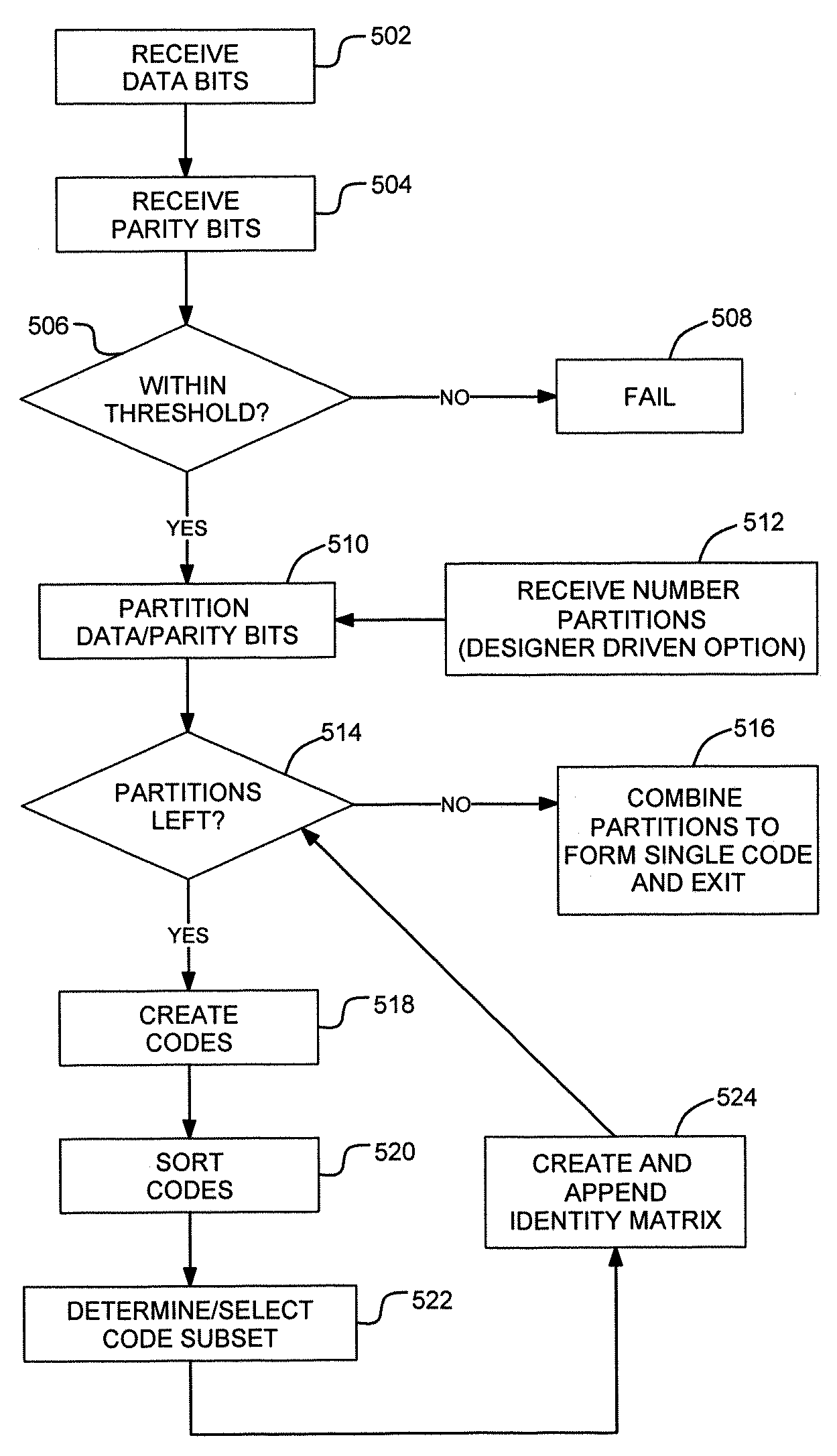
A method and apparatus provides the ability to build and use low-density linear parity-check (LDPC) codes for implementing error detection and correction (EDC). A number of data bits and a number of parity bits are received. While the number of data bits and number of parity bits are within a defined threshold with respect to each other, codes are created. The codes are based on the number of parity bits as combinations of values for the parity bits. The codes are sorted into weight subsections with each subsection containing having the same weight. A subset of each subsection is determined based on the number of data bits with the subset containing codes representing a lowest number of inputs to a parity tree for a given parity bit. An identity matrix of a size of the number of data bits is appended to the subset.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
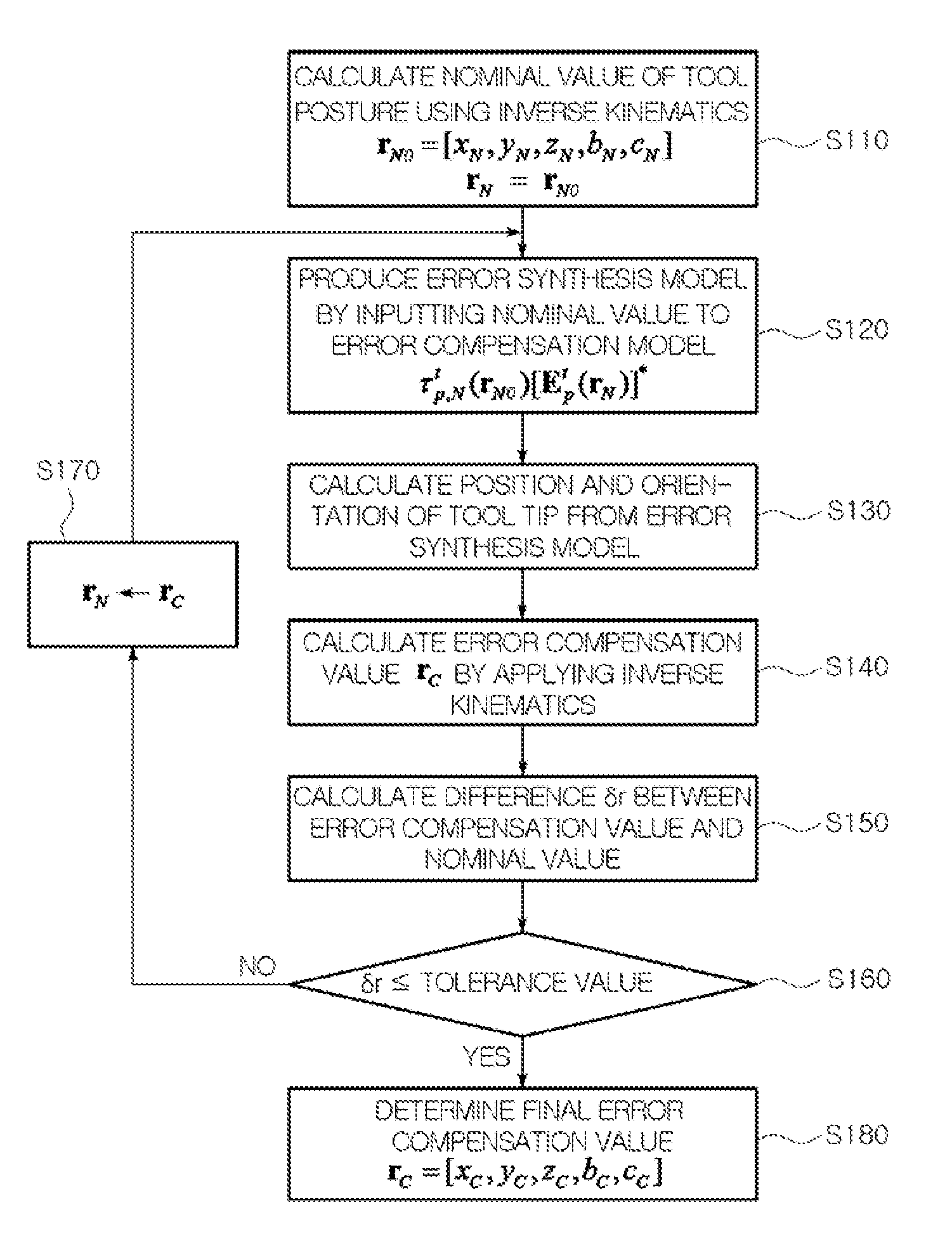
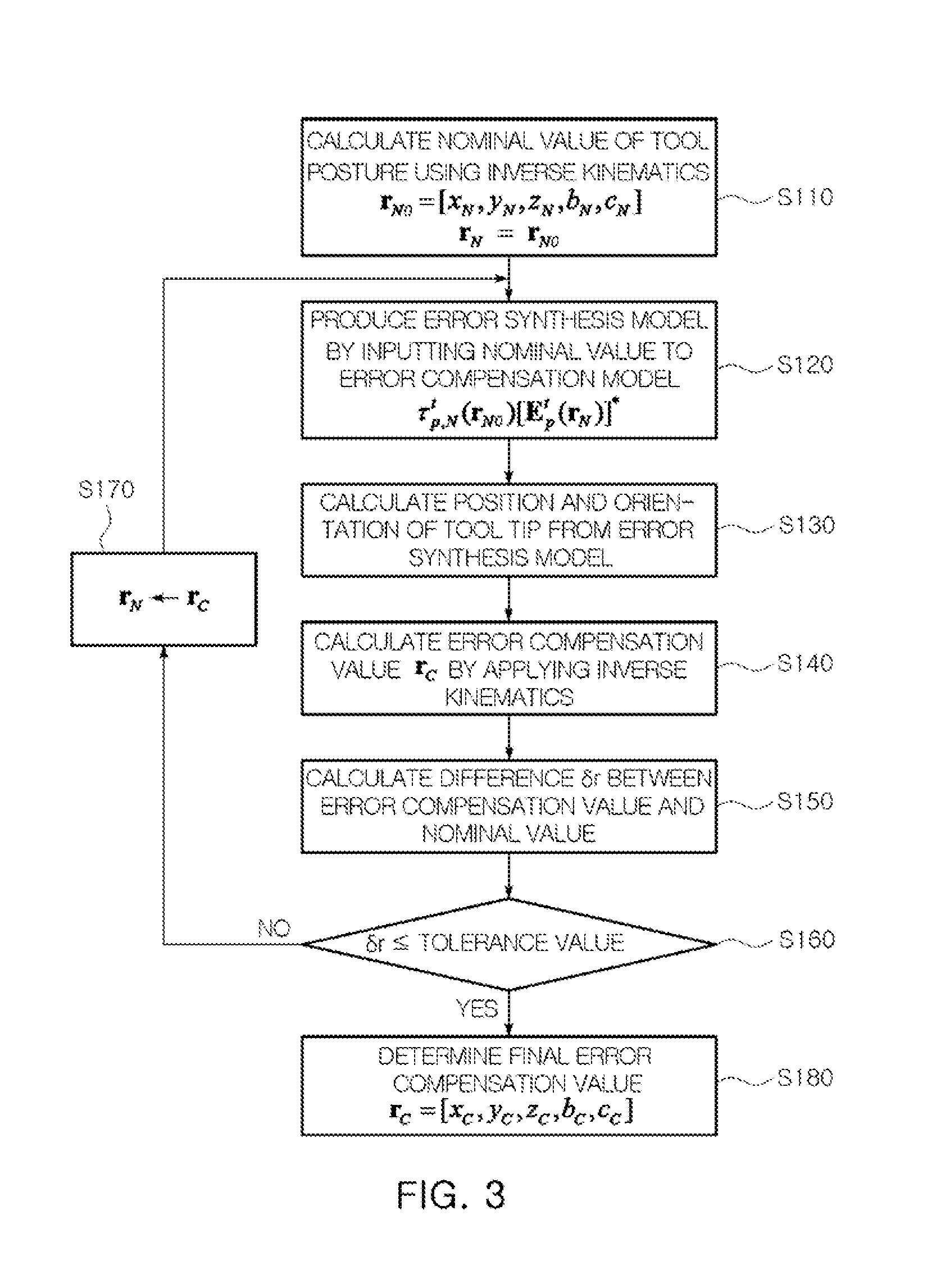
Error compensation method for multi-axis controlled machines
ActiveUS20110224958A1Efficient productionReduce errorsProgramme controlMeasurement devicesGeometric errorPartition of unity
An error compensation method for multi-axis controlled machines generates an error compensation model for compensating for geometric error of a multi-axis controlled machine by separating an error matrix of a tool tip from an error synthesis model of a multi-axis controlled machine and calculates an error compensation value using the error compensation model and an inverse kinematic model so that the error matrix becomes an identity matrix. The error compensation method can reduce calculation error and calculation time due to complicated numerical analysis and compensate for error in the multi-axis controlled machine, regardless of its configuration.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
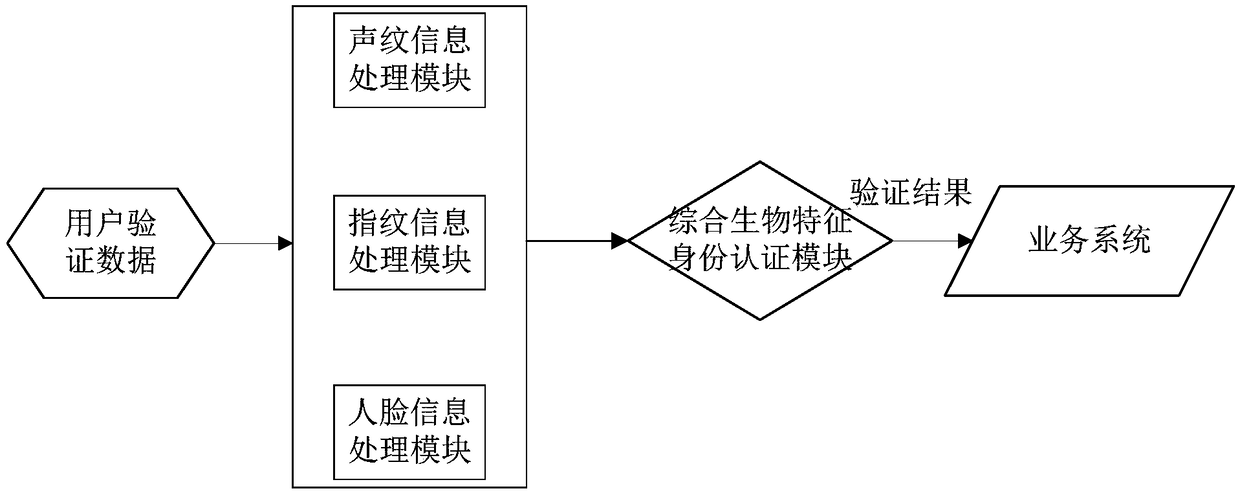
Identity authentication method and system
InactiveCN108429619AImprove security strengthEnsure safetyUser identity/authority verificationDigital data authenticationFrequency spectrumBiometric data
The invention provides an identity authentication method and system. The method comprises the steps of collecting voice signals, fingerprint image data and face image data of a user; extracting spectrum features of the voice signals to obtain voiceprint feature information; converting the voiceprint feature information, the fingerprint image data and the face image data into a voiceprint matrix, afingerprint image matrix and a face image matrix of preset dimensions; splicing the three matrixes to obtain identity matrix data; inputting the identity matrix data into a preset neural network model to obtain first biological feature data of the user; calculating the similarity between the first biological feature data and second biological feature data of pre-registered users; determining a target user corresponding to the highest similarity; returning a verification result showing that the target user passes the identity authentication if the highest similarity is greater than a preset similarity threshold; and returning the verification result showing that the target user does not pass the identity authentication if the highest similarity is smaller than or equal to the preset similarity threshold.
Owner:BEIJING SINOVOICE TECH CO LTD
Decoding method, decoding device, and program
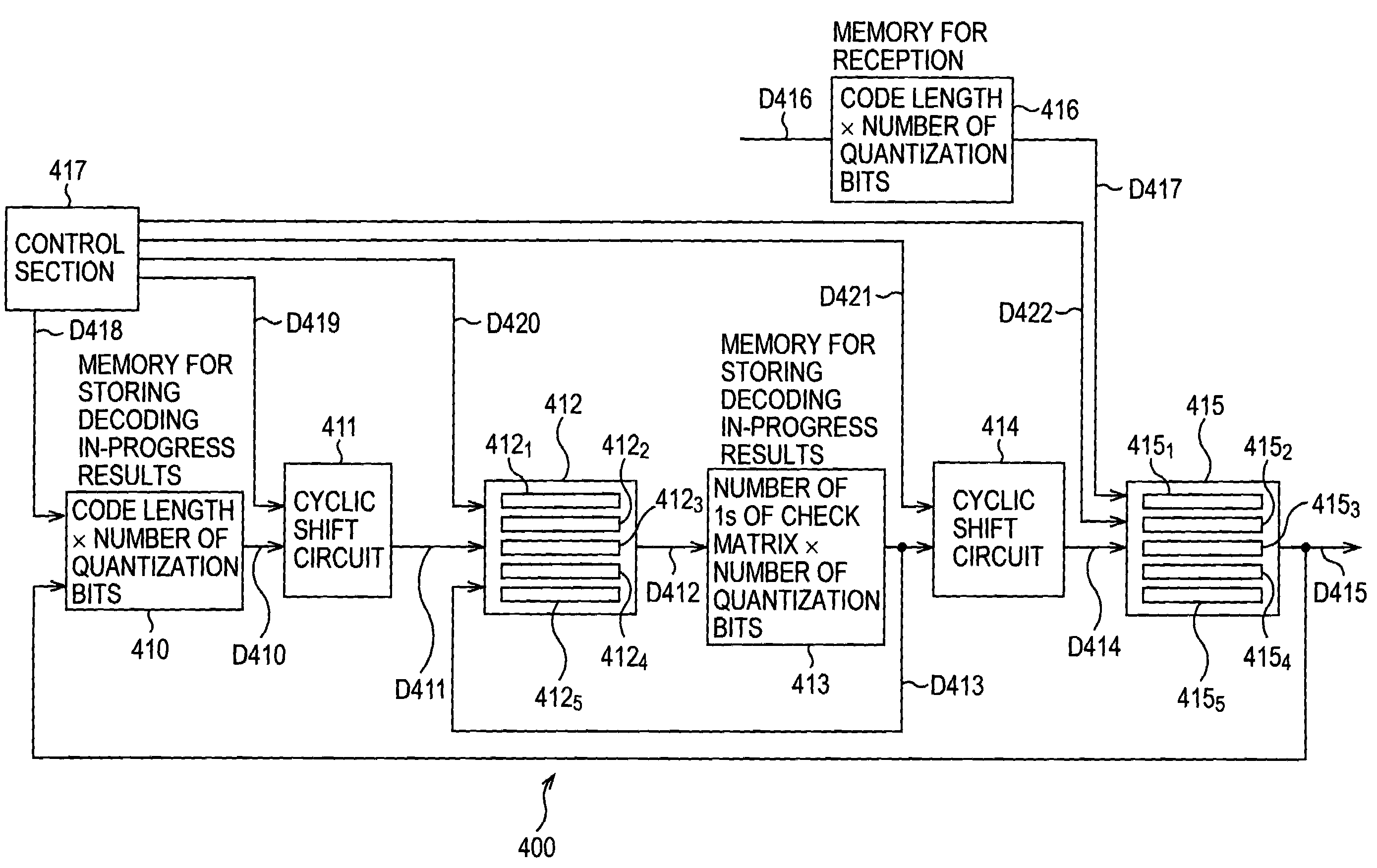
ActiveUS20050278604A1Suppress operating frequencyEasy to controlError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionDecoding methodsFormation matrix
The present invention relates to a decoding method and a decoding apparatus in which, while the circuit scale is suppressed, the operating frequency can be suppressed within a sufficiently feasible range, and control of memory access can be performed easily, and to a program therefor. By using a transformation check matrix obtained by performing one of or both a row permutation and a column permutation on an original check matrix of LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) codes, the LDPC codes are decoded. In this case, by using, as a formation matrix, a P×P unit matrix, a quasi-unit matrix in which one or more is, which are elements of the unit matrix, are substituted with 0, a shift matrix in which the unit matrix or the quasi-unit matrix is cyclically shifted, a sum matrix, which is the sum of two or more of the unit matrix, the quasi-unit matrix, and the shift matrix, and a P×P 0-matrix, the transformation check matrix is represented by a combination of a plurality of the formation matrices. A check node calculator 302 simultaneously performs p check node calculations. A variable node calculator 304 simultaneously performs p variable node calculations.
Owner:SONY CORP
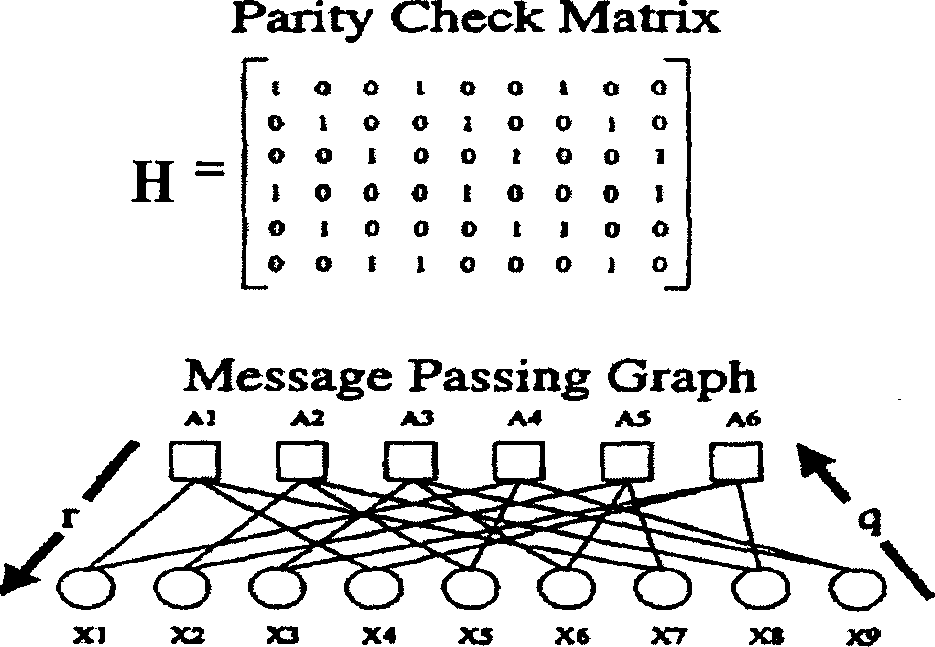
Construction method of non-regular permutation matrix LDPC code and its device
InactiveCN1794621ASimple designSimplify implementation complexityError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsRing circuitH matrix
This invention relates to a method for constructing new non-standard replacement matrix LDPC codes characterizing that under the principle of optimizing the smallest ring circuit, it takes each sub-block as the smallest unit and utilizes a binary chart with weight to determine the position of the sub-block and the deviation of circulation shift: simplifying the binary chart with bit as the unit of the LDPC code to that with a sub-block as the unit based on the property of the matrix of a replacement unit, then applying the traditional PEG algorithm with the bit as the unit to the new chart with the sub-block as the unit to determine the position of every replacement unit matrix of the H matrix and finally utilizing the ring circuit property of the LDPC code to decide the deviation of circular shift of each replacement unit matrix.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
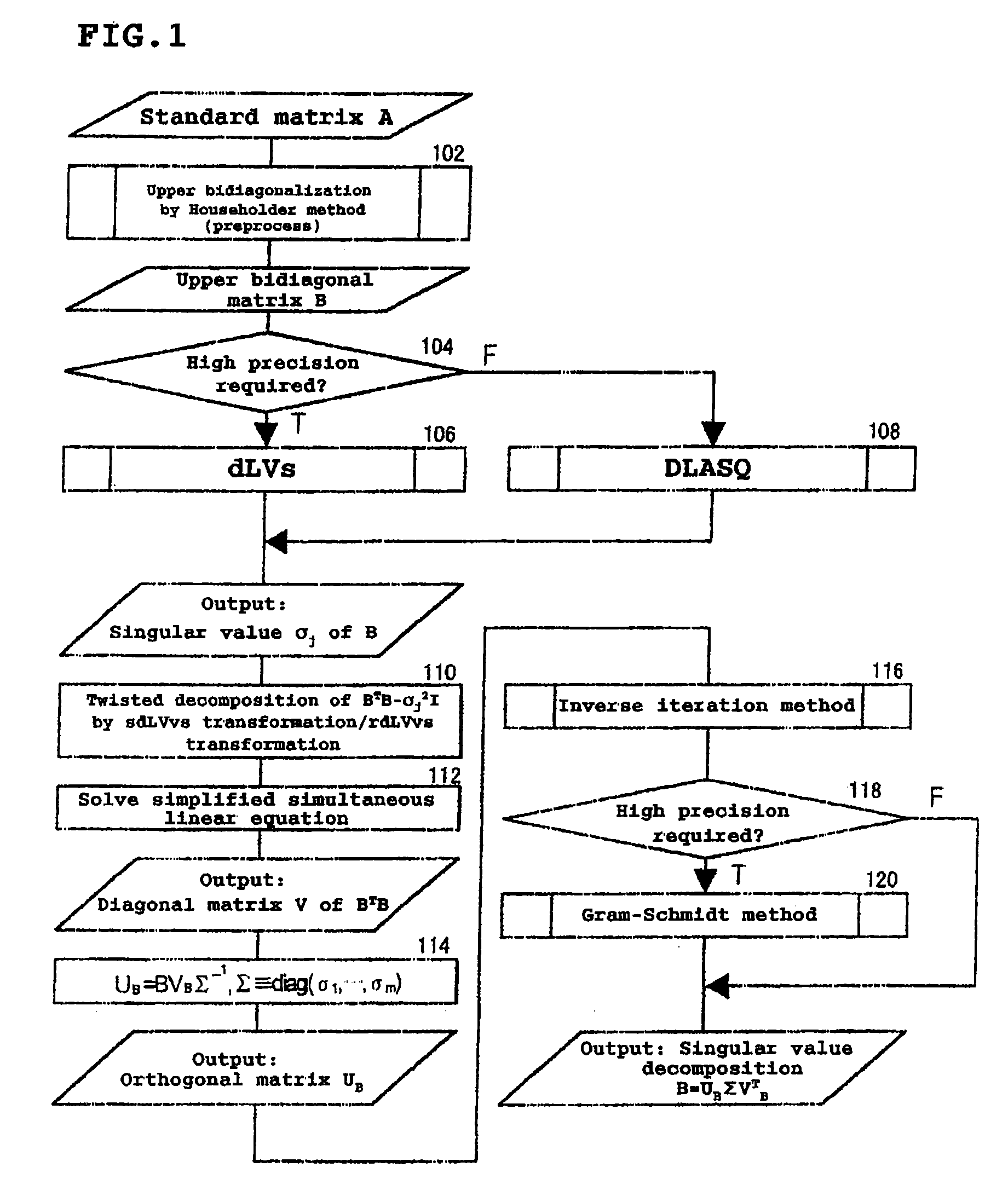
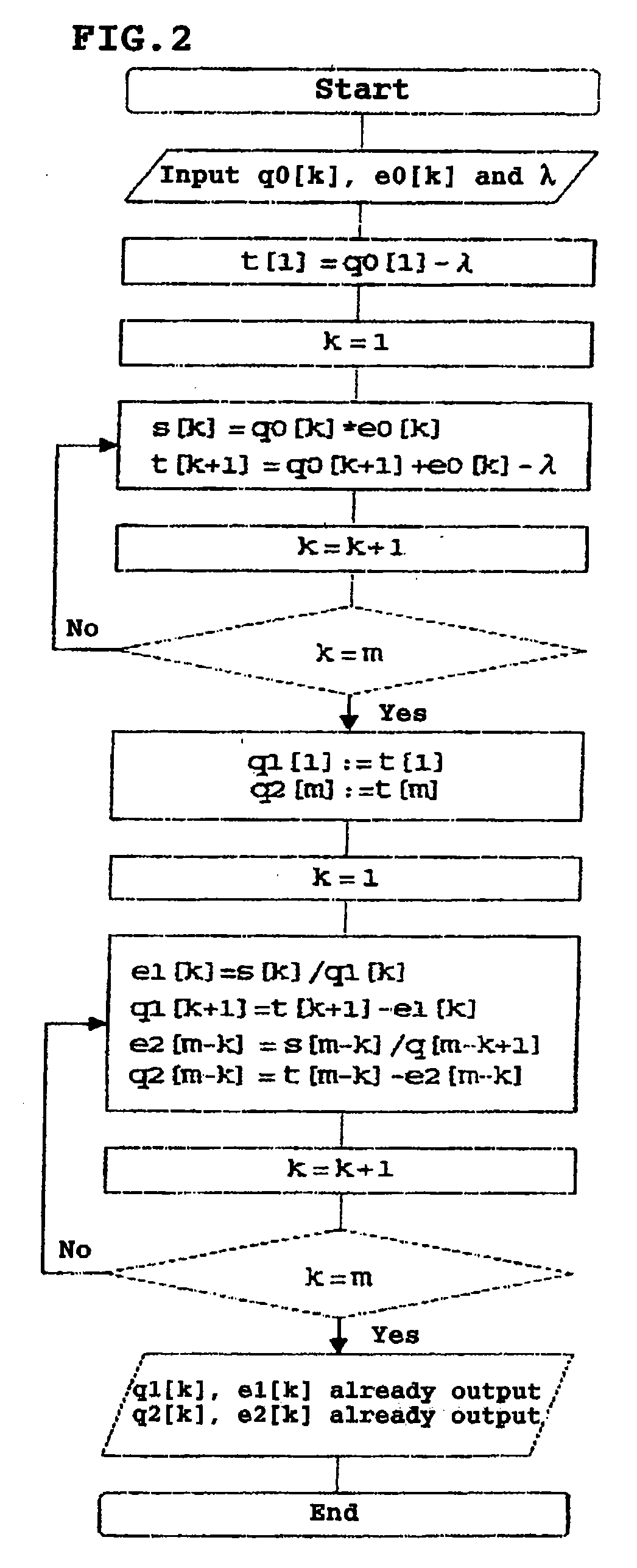
High-speed high-accuracy matrix singular value decomposition method, program, and device
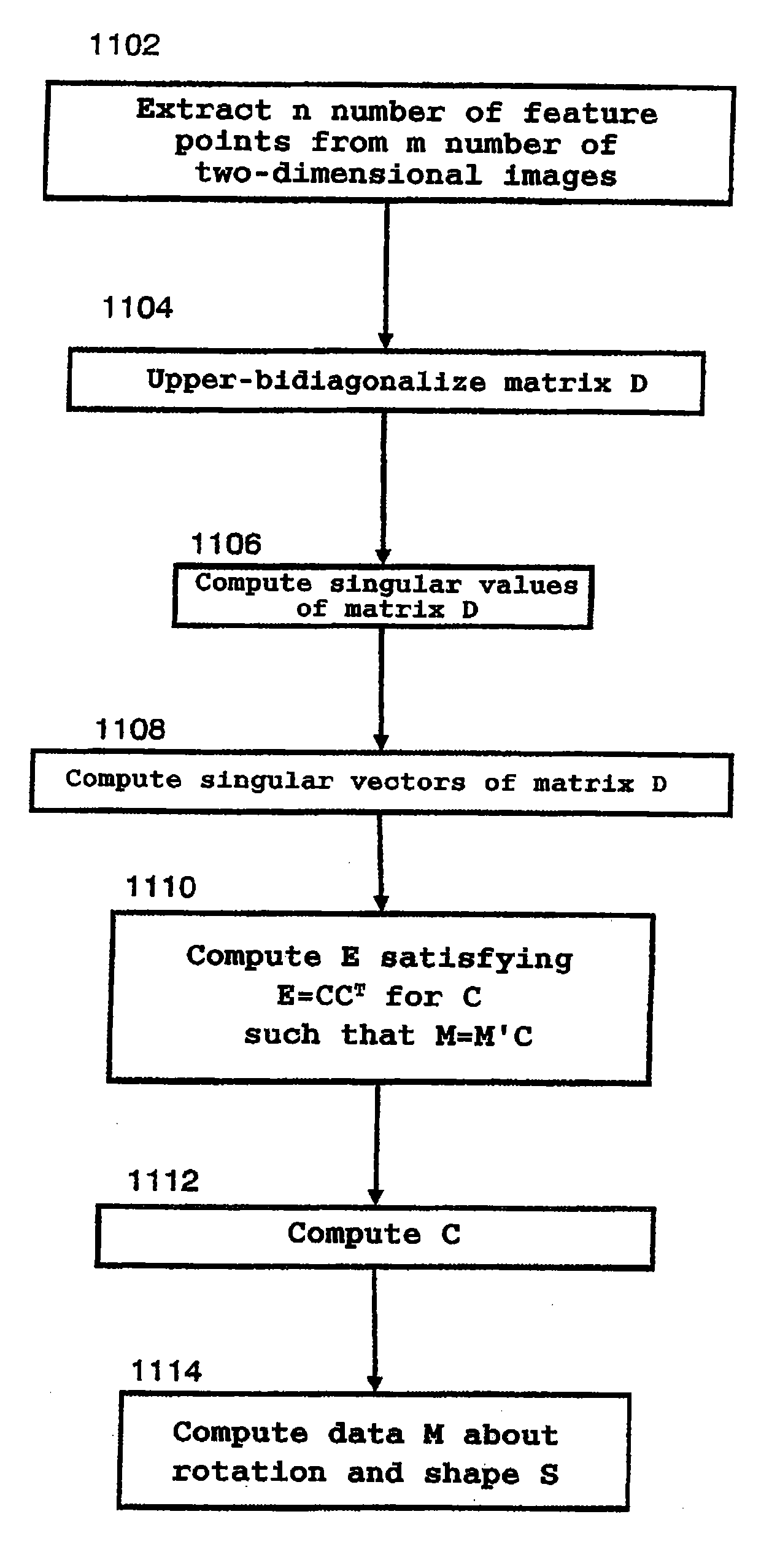
ActiveUS20090028455A1Shorten the timeAmount of timeImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmDecomposition
A singular value decomposition method according to the present invention is a method for performing a singular value decomposition on an arbitrary matrix A using a computer, the method including the steps of: performing an upper bidiagonalization on the matrix A so as to obtain an upper bidiagonal matrix B of the matrix A; obtaining at least one singular value σ of the matrix B as singular values of the matrix A; and obtaining a singular vector of the matrix A for the σ. The step of obtaining a singular vector of the matrix A includes a step of performing a Twisted decomposition on a matrix BTB−σ2I (where I is a unit matrix) by using a Miura inverse transformation, an sdLVvs transformation, an rdLVvs transformation and a Miura transformation so as to diagonalize a matrix BTB.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Encoding method of LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) code and encoder
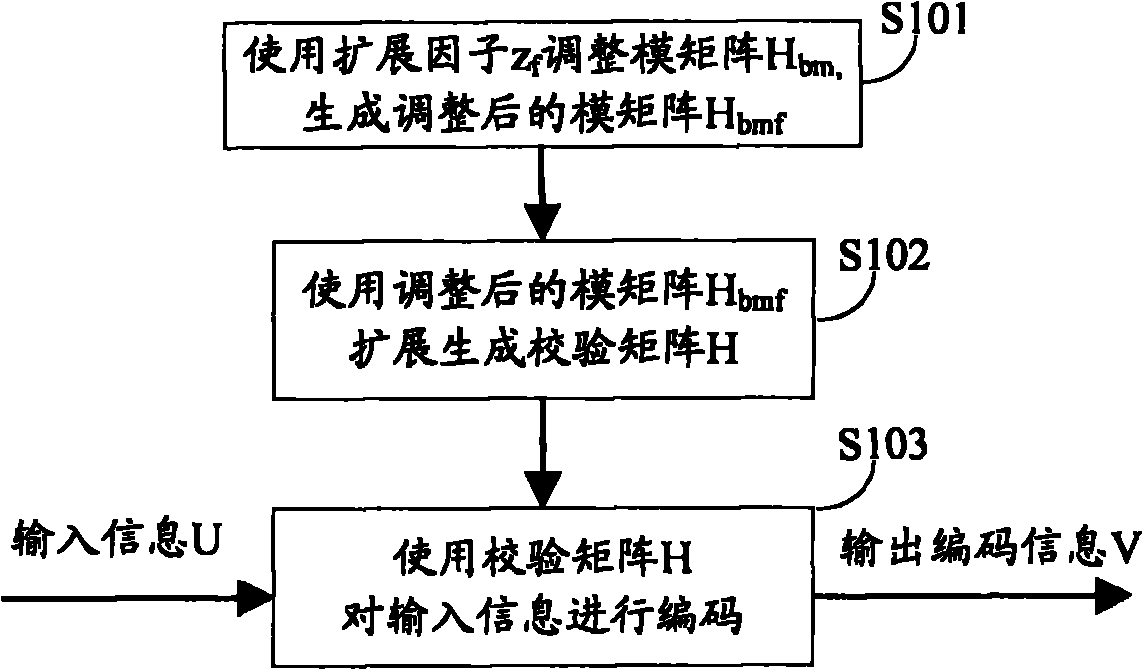
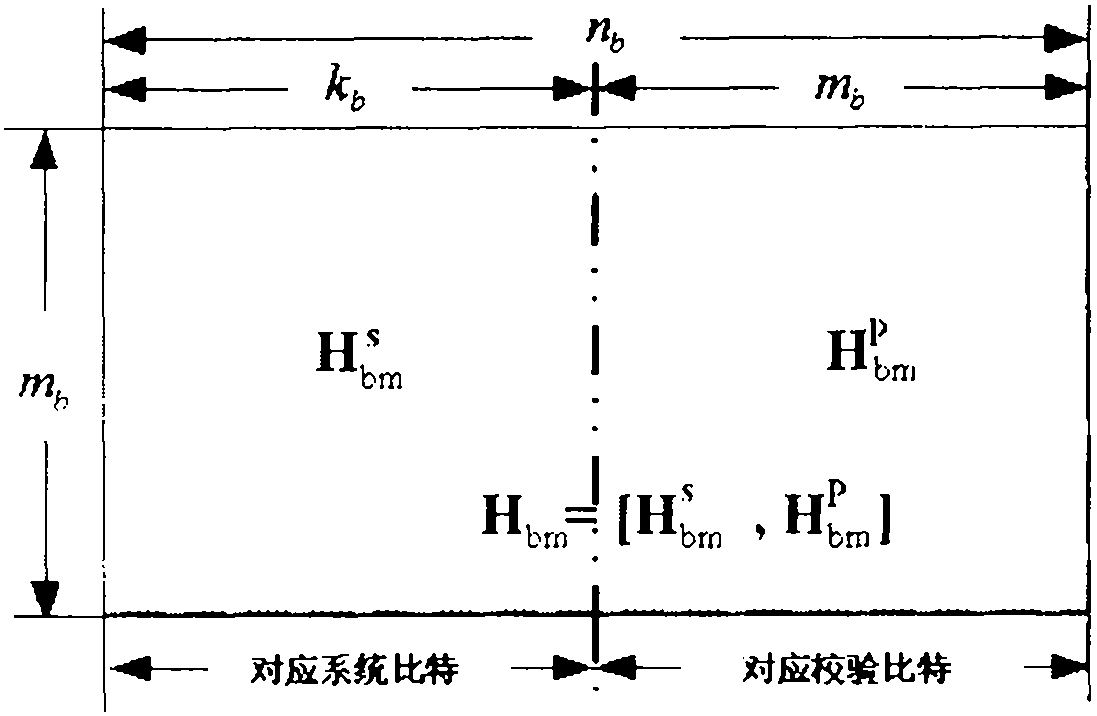
ActiveCN101834613AReduced Quantization BitsProcessing speedError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsRound complexityTheoretical computer science
The invention provides an encoding method of an LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) code. The encoding method comprises the following steps of: adjusting elements of a modular matrix Hbm by using an expanding factor zf to generate an adjusted modular matrix Hbmf; expanding by using the modular matrix Hbmf to generate a check matrix H, wherein the expanding mode is as follows: sub-matrixes Pi and j in the check matrix H expand according to the value of the modular matrix Hbmf, and each of the sub-matrixes Pi and j is a full zero matrix, a unit matrix or a unit matrix for left and right cyclic shifting according to a line direction; and encoding input information U by using the check matrix H and outputting encoding information V. The invention also provides an encoder of the LDPC code. According to the technical scheme proposed by the invention, through increasing the quantity of zero elements of the modular matrix Hbm, the processing complexity and the implementation complexity of the encoding and the decoding of the LDPC code can be reduced, and the processing speed of the encoding and the coding can be improved.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Apparatus and method for coding/decoding block low density parity check code in a mobile communication system
ActiveUS20070283221A1Maximized error correction capabilityMaximized minimum cycle lengthError preventionError detection/correctionTheoretical computer scienceParity-check matrix
A method for generating a parity check matrix of a block LDPC code. The parity check matrix includes an information part corresponding to an information word and a first parity part and a second parity part each corresponding to a parity. The method includes determining a size of the parity check matrix based on a coding rate applied when coding the information word with the block LDPC code, and a codeword length; dividing a parity check matrix with the determined size into a predetermined number of blocks; classifying the blocks into blocks corresponding to the information part, blocks corresponding to the first parity part, and blocks corresponding to the second parity part; arranging permutation matrixes in predetermined blocks from among the blocks classified as the first parity part, and arranging identity matrixes in a full lower triangular form in predetermined blocks from among the blocks classified as the second parity part; and arranging the permutation matrixes in the blocks classified as the information part such that a minimum cycle length is maximized and weight values are irregular on a factor graph of the block LDPC code.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Low-complexity quick parallel matrix inversion method
ActiveCN104298649AImprove efficiencyReduce complexityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksComplex mathematical operationsSubstitution methodSignal processing
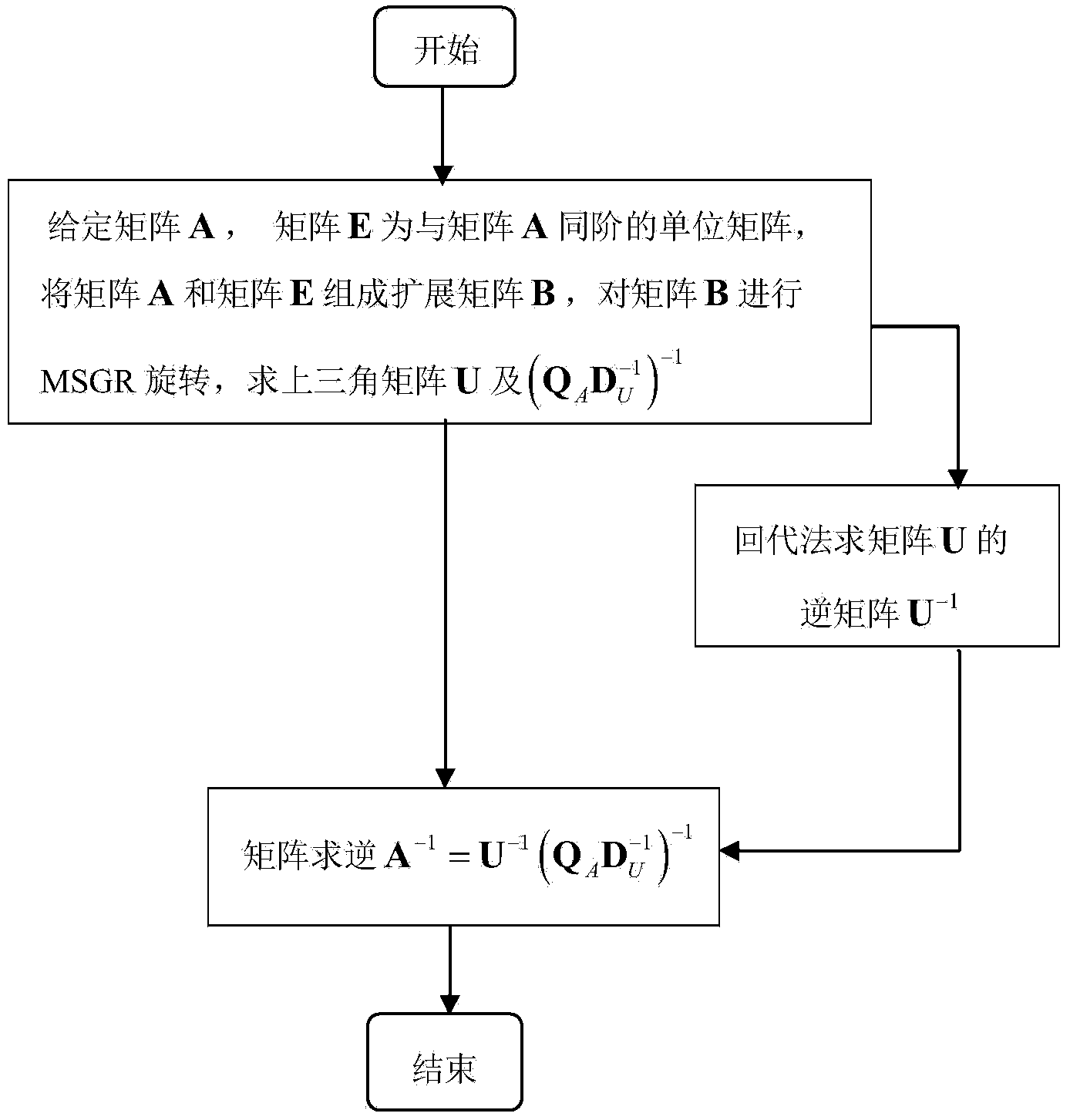
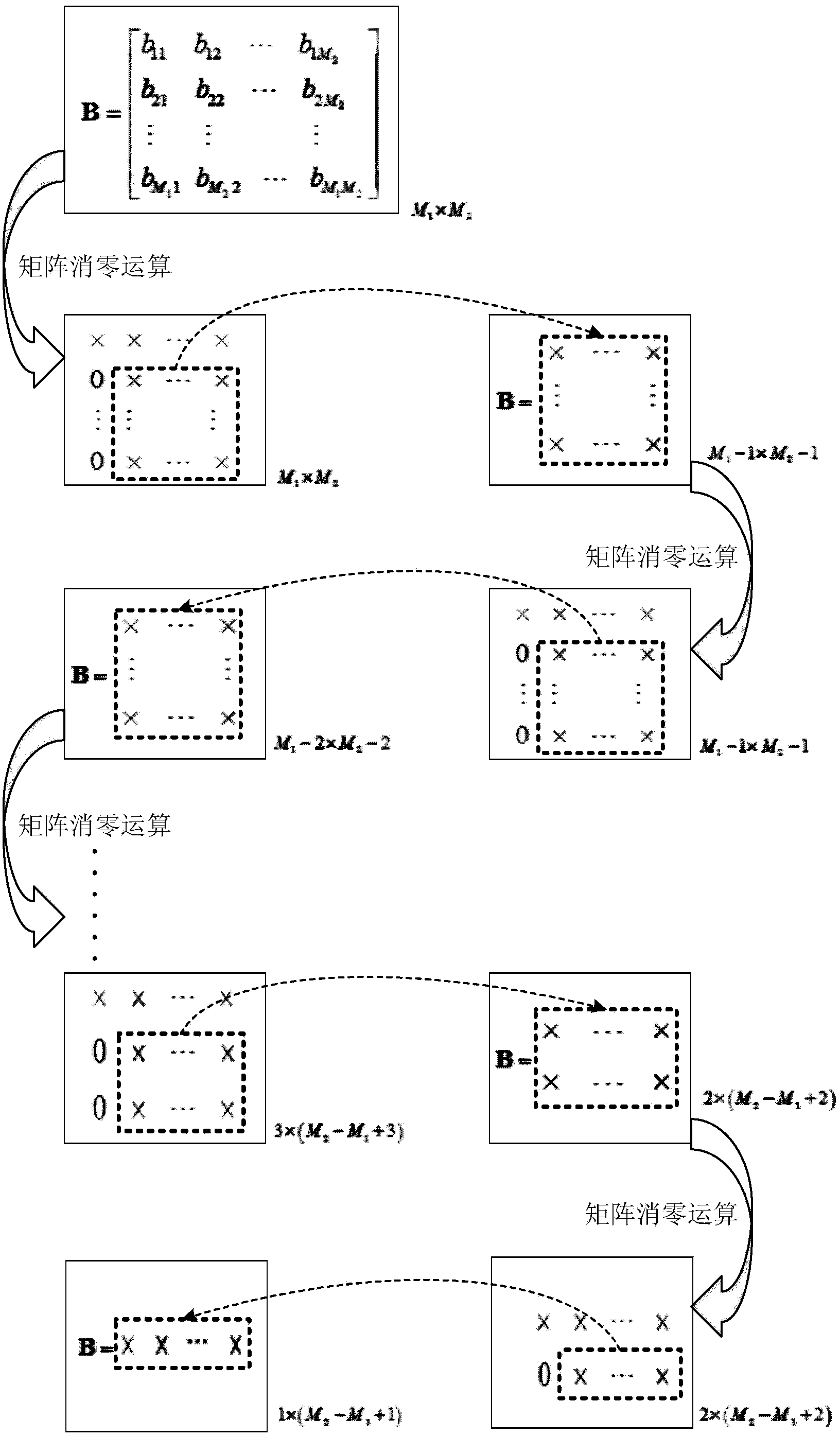
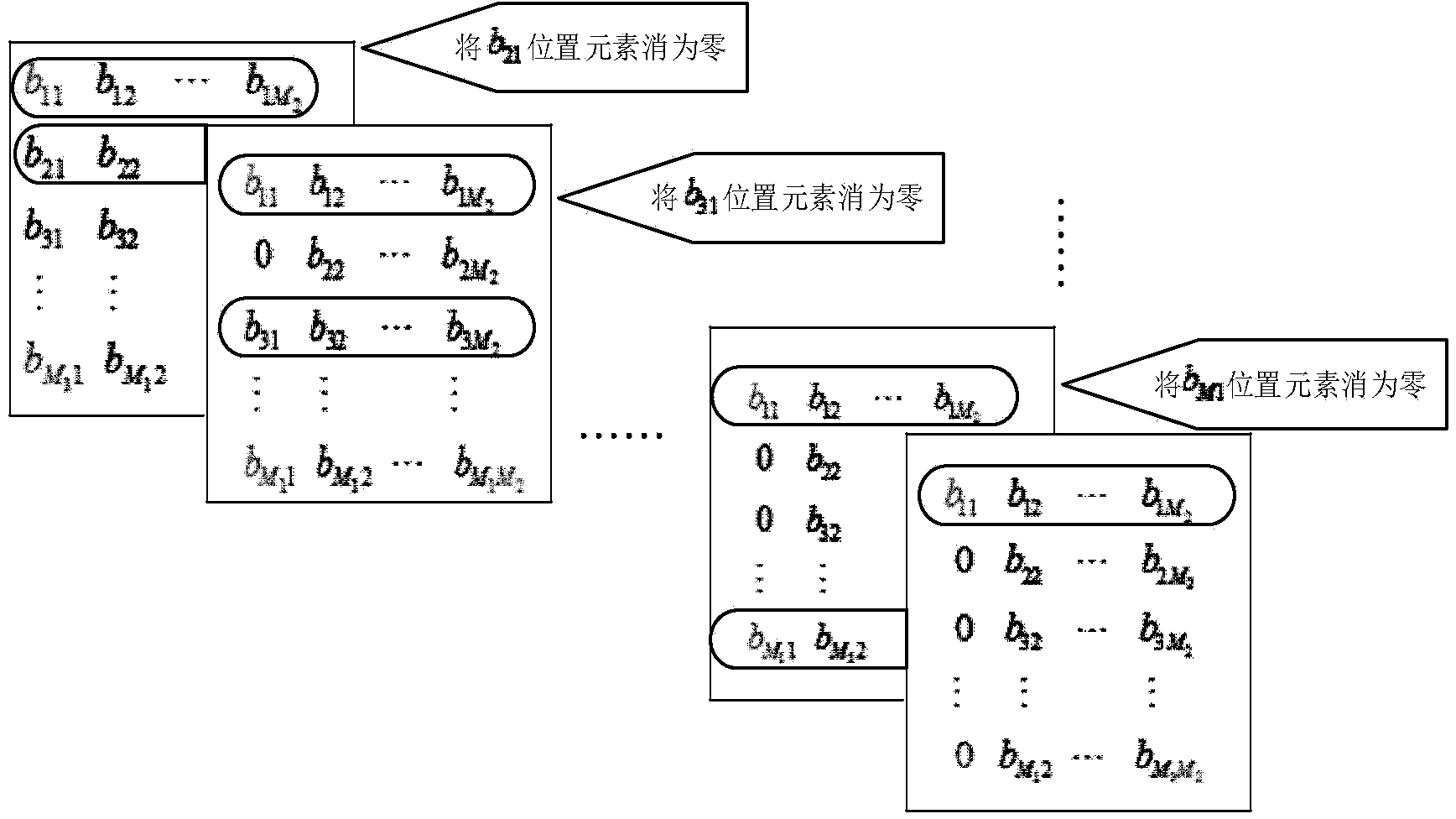
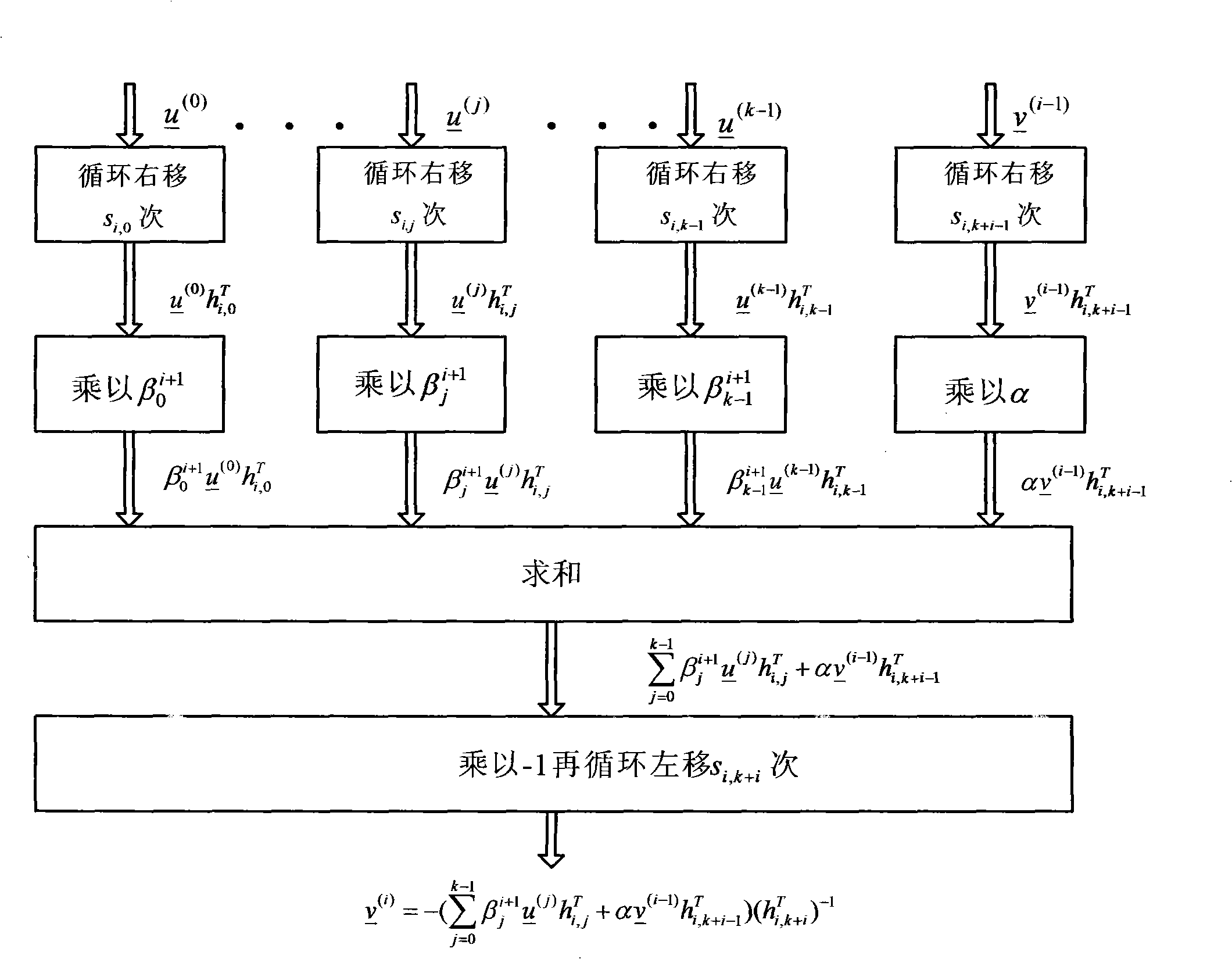
The invention discloses a low-complexity quick parallel matrix inversion method. The method comprises the following steps that first, a matrix A is given, a matrix E is made to be a unit matrix with the same order as the matrix A, the matrix A and the matrix E form an expanding matrix B, modified Givens rotation (MSGR, Modified Square Givens Rotations) is carried out on the matrix B, an upper triangular matrix U and , wherein according to the define of the matrix U and , an SGR (Squared Givens Rotations) method is used for deforming the QR division of the matrix A according to the equation, and the relation between the QR division and original QR division meets the equations , , , and ; according to the MSRG method, the square root operation in the process of Givens rotation can be omitted while division operation is reduced, and algorithm complexity is obviously reduced; second, a back substitution method is used for working out the inverse matrix U-1 of the upper triangular matrix U; third, matrix inversion is carried out according to the equation . According to the low-complexity quick parallel matrix inversion method, a large amount of division operation and a large amount of square root operation are omitted, algorithm complexity is reduced, and the method can be used for matrix inversion of the fields of wireless communication, signal processing and numerical calculation.
Owner:南京易太可通信技术有限公司
Construction method and encoding method for multiple LDPC code
InactiveCN101335528ASave storage spaceEfficient and Fast Coding MethodError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsPartition of unityTheoretical computer science
The invention belongs to the communication technology field, particularly relates to a structuring method of a multi-LDPC code. The method comprises steps as follows: the check matrix H of the multi-LDPC code is a partitioned matrix which consists of (m multiplying n) sub-matrixes of H<i, j>, and each sub-matrix H<i, j> is obtained from that a scale factor beta<i, j> epsilon GF(q) is multiplied by a unit matrix of (1 multiplying 1) and then left moved by s<i, j> times according to a line cycle; wherein, GF(q) is a finite field having q elements; the check matrix H of the multi-LDPC code can be divided into two parts, namely, H is equal to (H1H2); wherein, the H2 is a dual partitioned diagonal matrix with a size of m multiplying m and the H1 consists of sub-matrixes left in the H; the H1 corresponds to information symbols and the H2 corresponds to check symbols. In addition, the invention also provides a fast coding method applicable to the invented multi-LDPC code.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
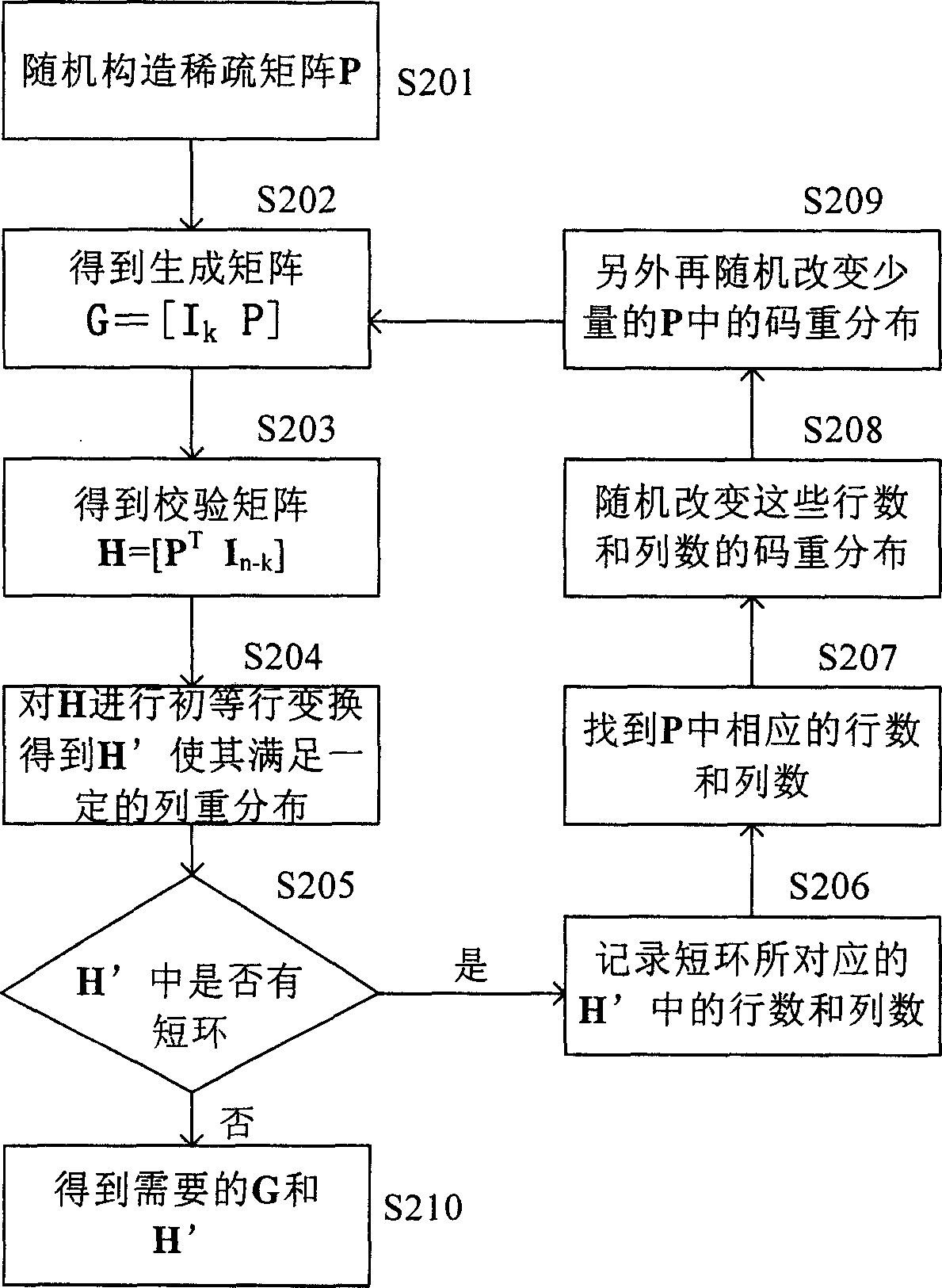
Method for consitituting sparse generative matrix and method for coding low-density block check code
InactiveCN1889367ASimple codingError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsPartition of unityAlgorithm
This invention discloses a method for generating matrixes including: a, randomly generating a sparse matrix P of k lines and n-k columns, b, getting a generated matrix G=[Ik P] from said sparse matrix P, checking the matrix H=[PT In-k], in which, Ik is the unit matrix of k lines and k columns, the PT is the transposed matrix of P, c, carrying out initial transformation to said checked matrix H to let it meet the preset re-distribution of columns to get the transformed check matrix H, d, checking if there are short rings in the matrix H, e, recording the corresponding lines and columns of the short rings in H to further get the numbers corresponding to said short rings in H so as to further find out numbers corresponding to those in the random matrix P and H, f, regulating the code re-distribution corresponding to said line and column number in P, g, repeating said step b to f and short rings do not exist in H.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and Apparatus of a Fully-Pipelined Layered LDPC Decoder
ActiveUS20150214980A1Sustain performance levelDissipates low powerError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionComputer architectureConstraint matrix
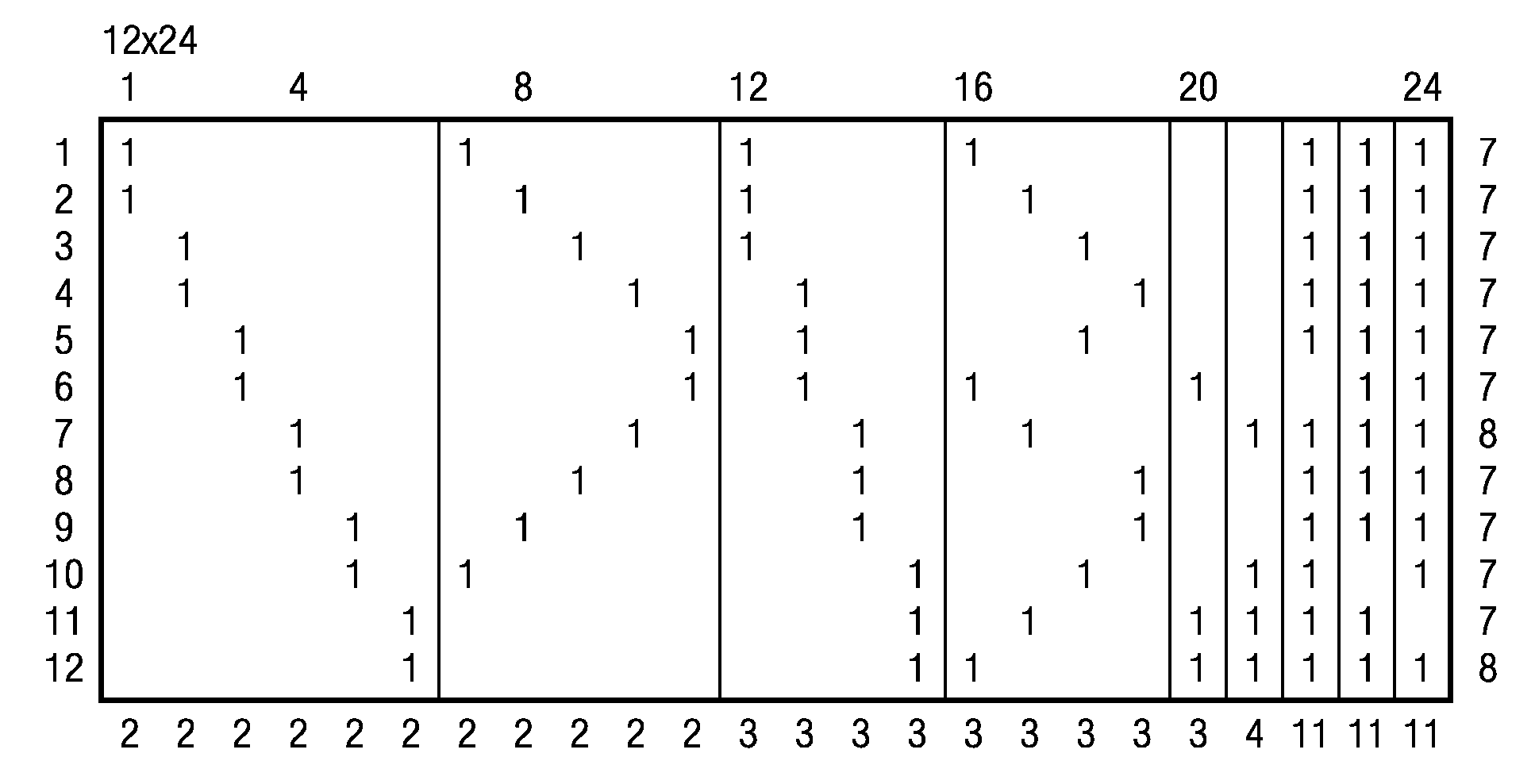
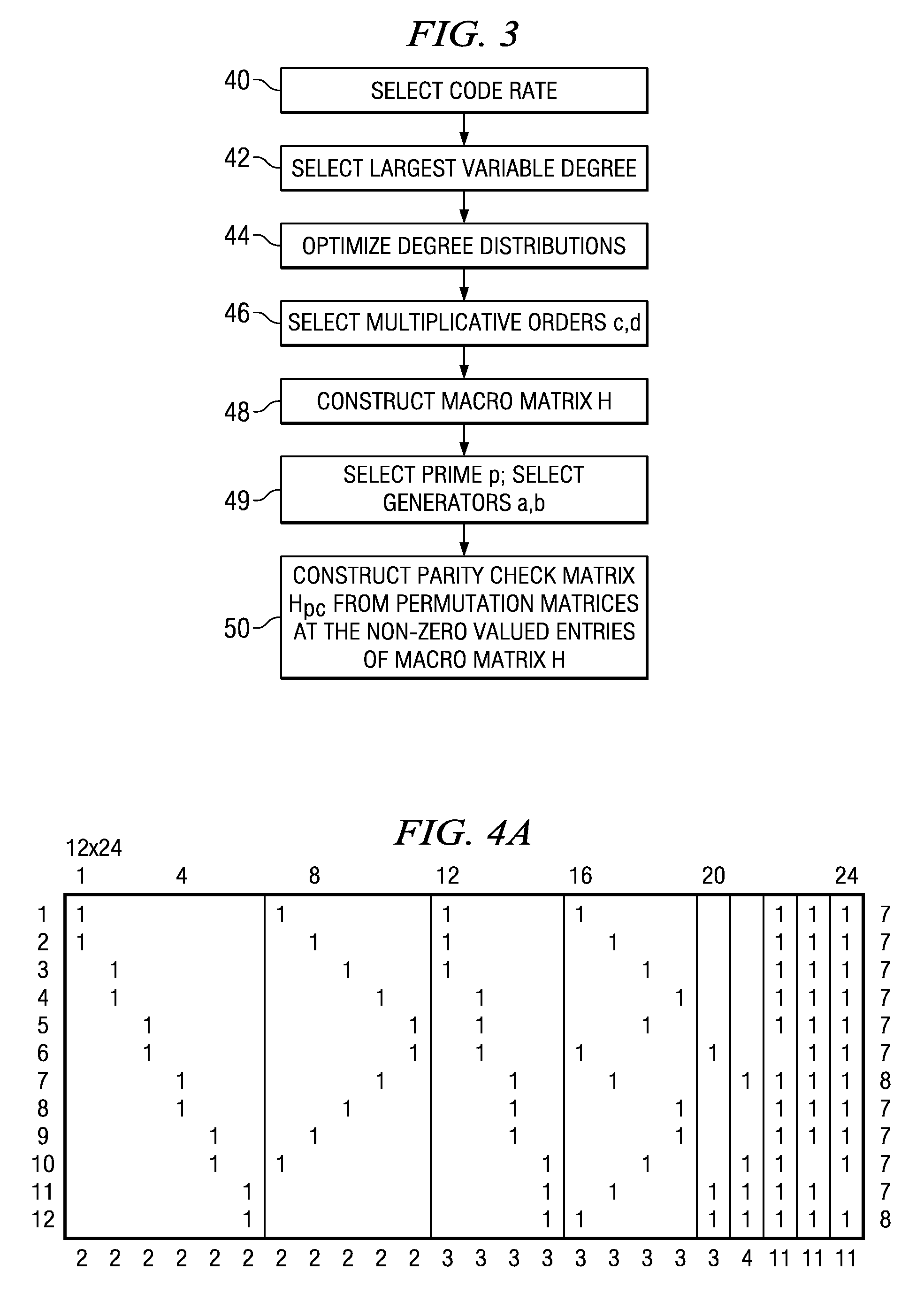
The architecture is able to switch to Non-blocking check-node-update (CNU) scheduling architecture which has better performance than blocking CNU scheduling architecture. The architecture uses an Offset Min-Sum with Beta=1 with a clock domain operating at 440 MHz. The constraint macro-matrix is a spare matrix where each “1’ corresponds to a sub-array of a cyclically shifted identity matrix which is a shifted version of an identity matrix. Four core processors are used in the layered architecture where the constraint matrix uses a sub-array of 42 (check nodes)×42 (variable nodes) in the macro-array of 168×672 bits. Pipeline processing is used where the delay for each layer only requires 4 clock cycles.
Owner:TENSORCOM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com