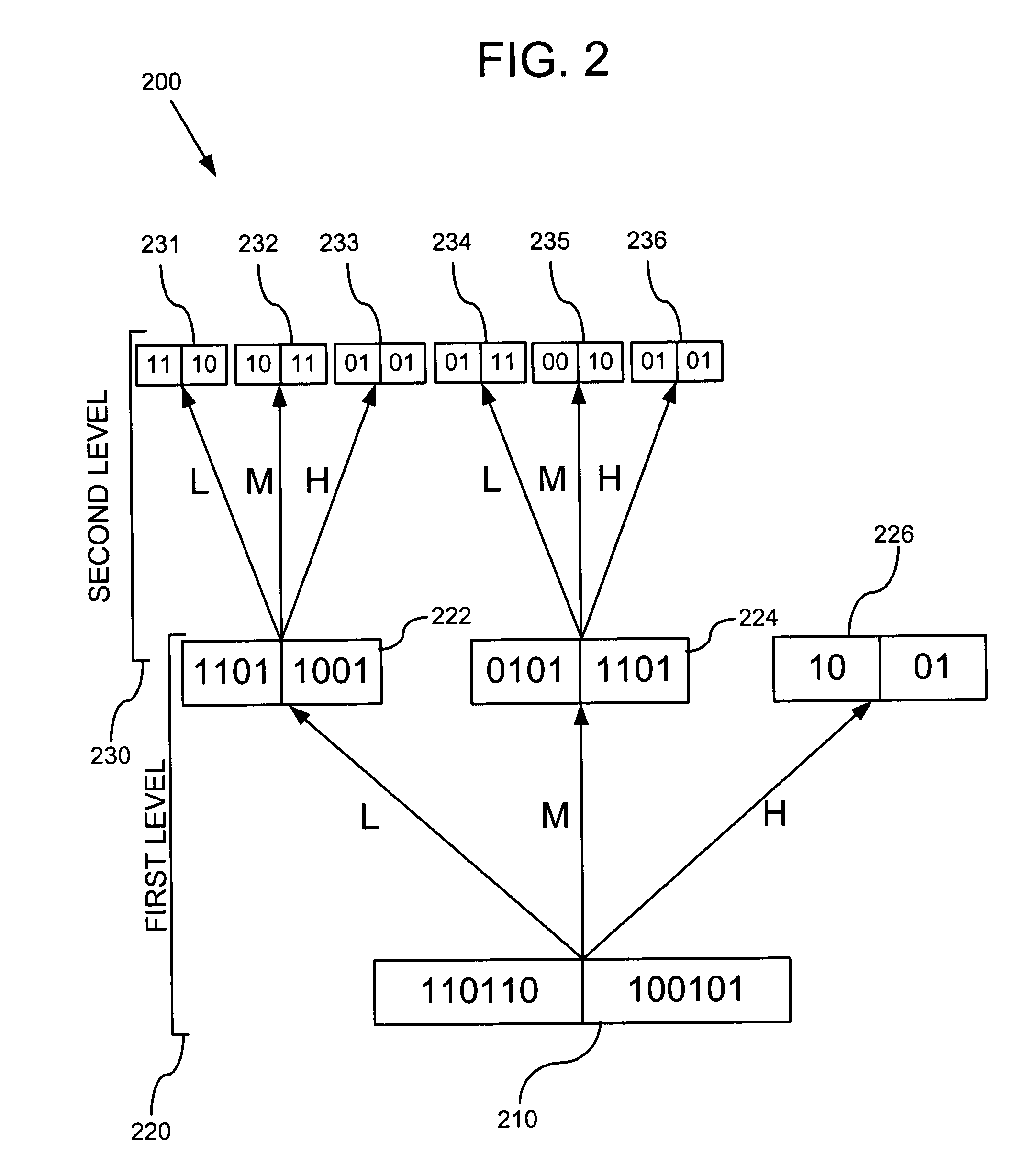
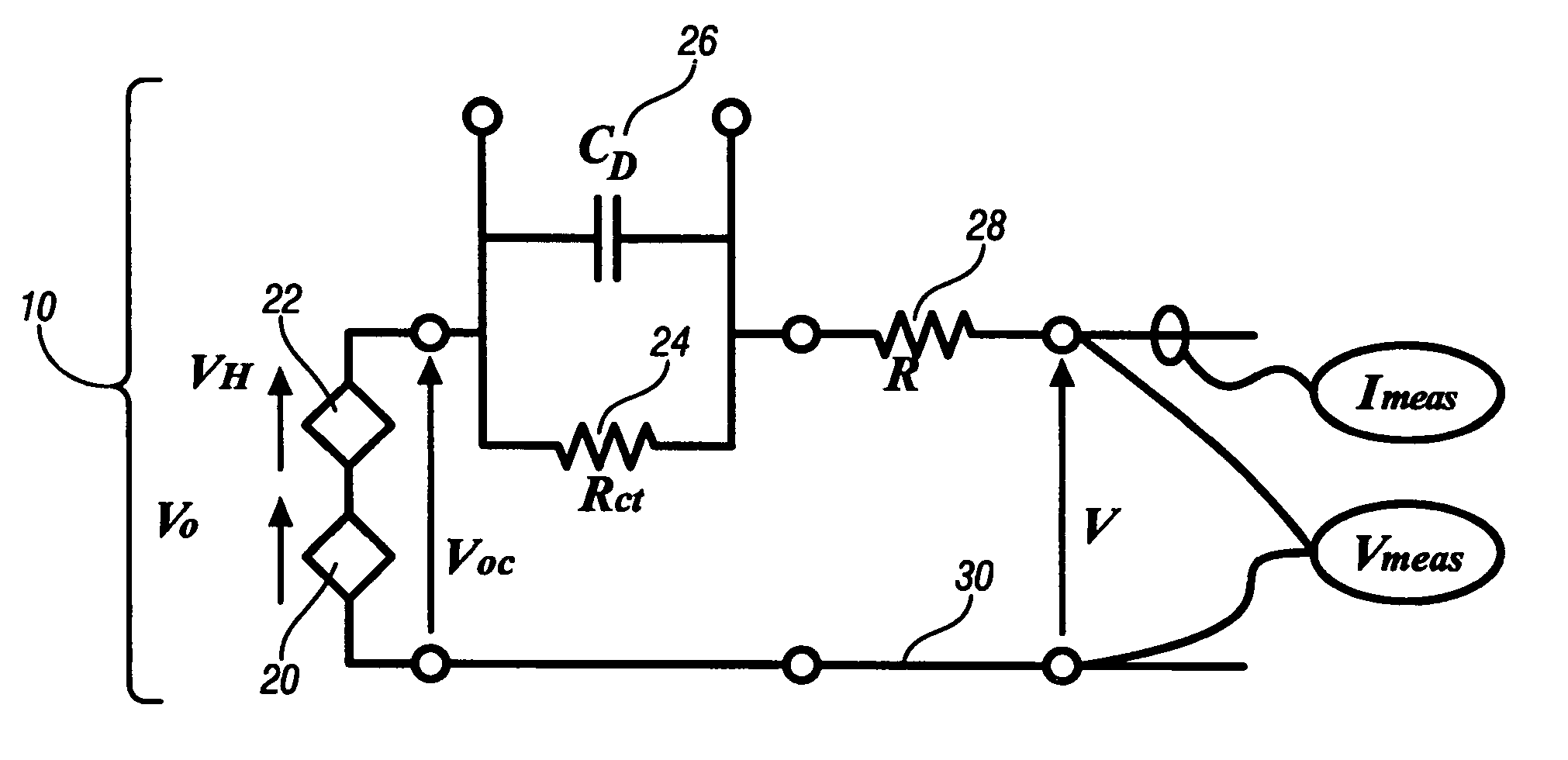
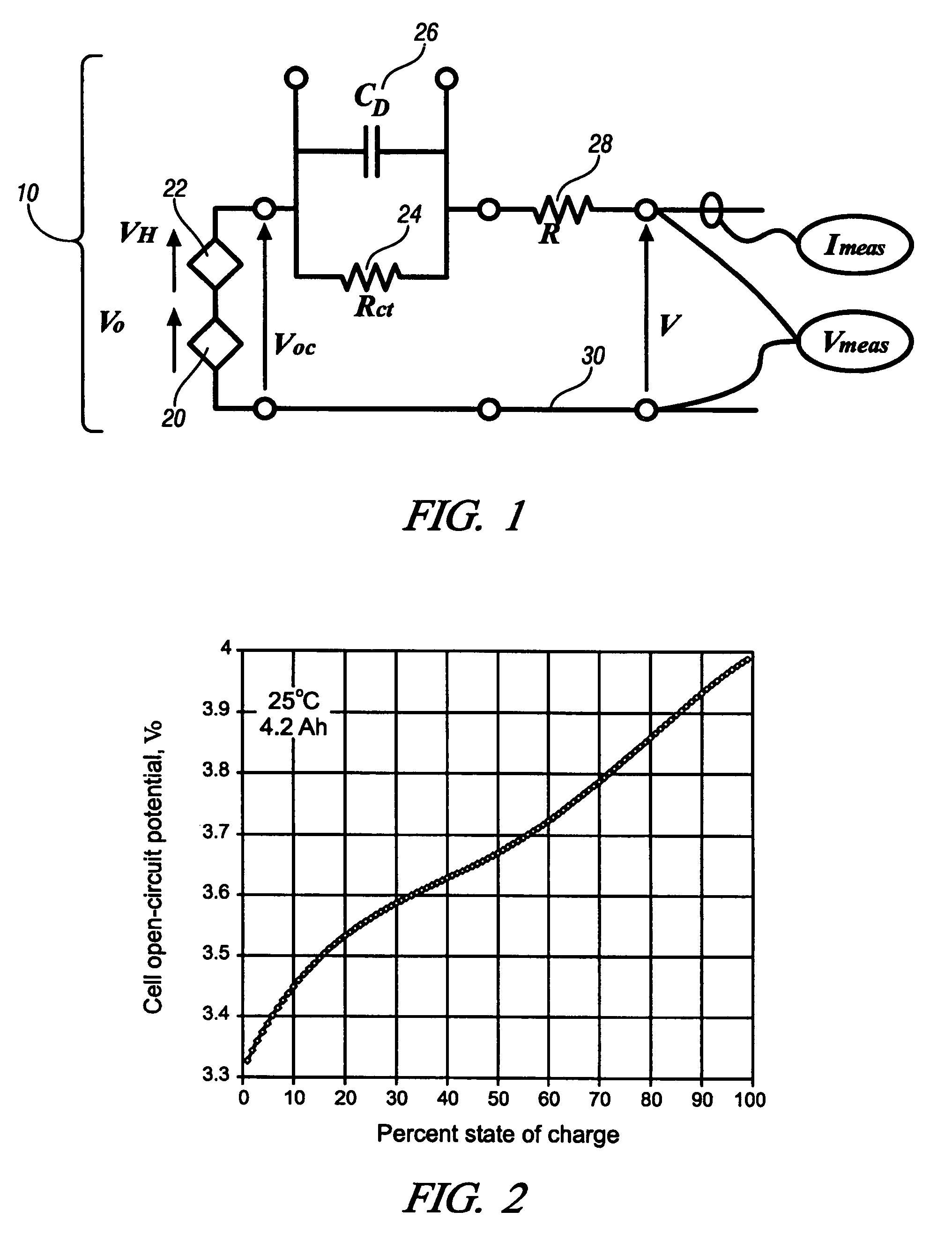
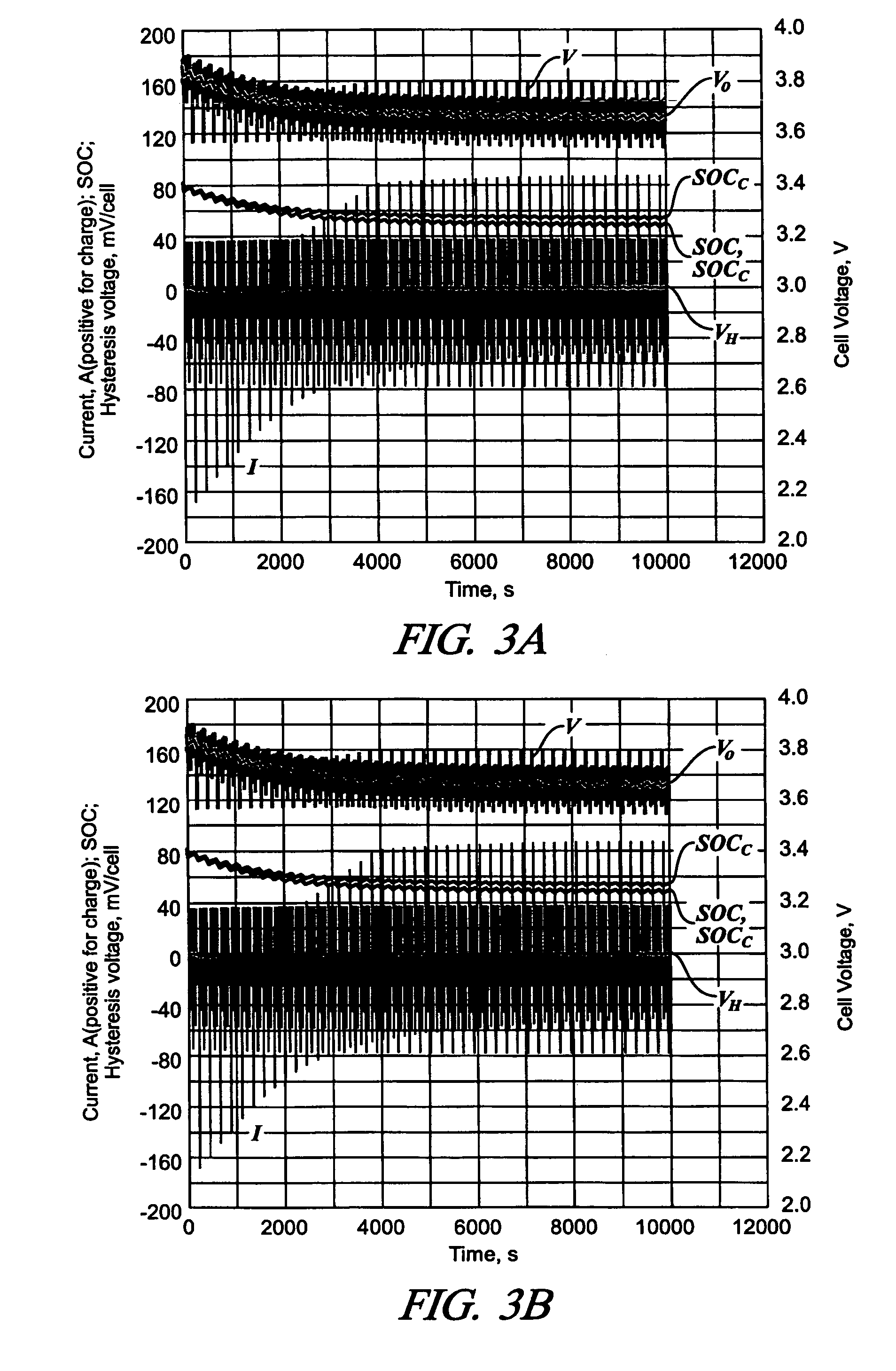
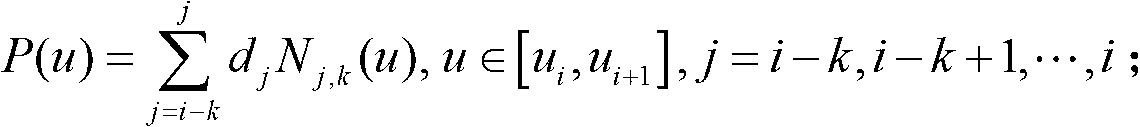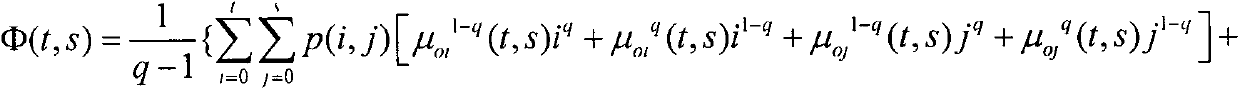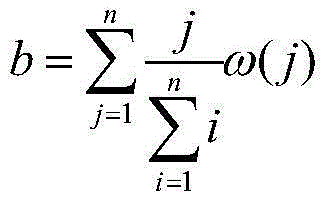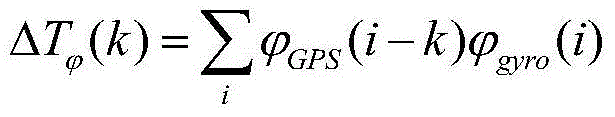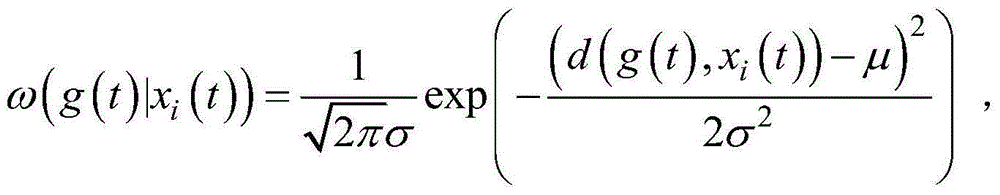Patents
Literature
340 results about "Recursive algorithms" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Recursive algorithm. A recursive algorithm is a function that tells itself to do something, resulting in it running over and over on smaller and smaller inputs. At the end, it gives back a value. This short article about mathematics can be made longer. You can help Wikipedia by adding to it.
Recursive sparse reconstruction
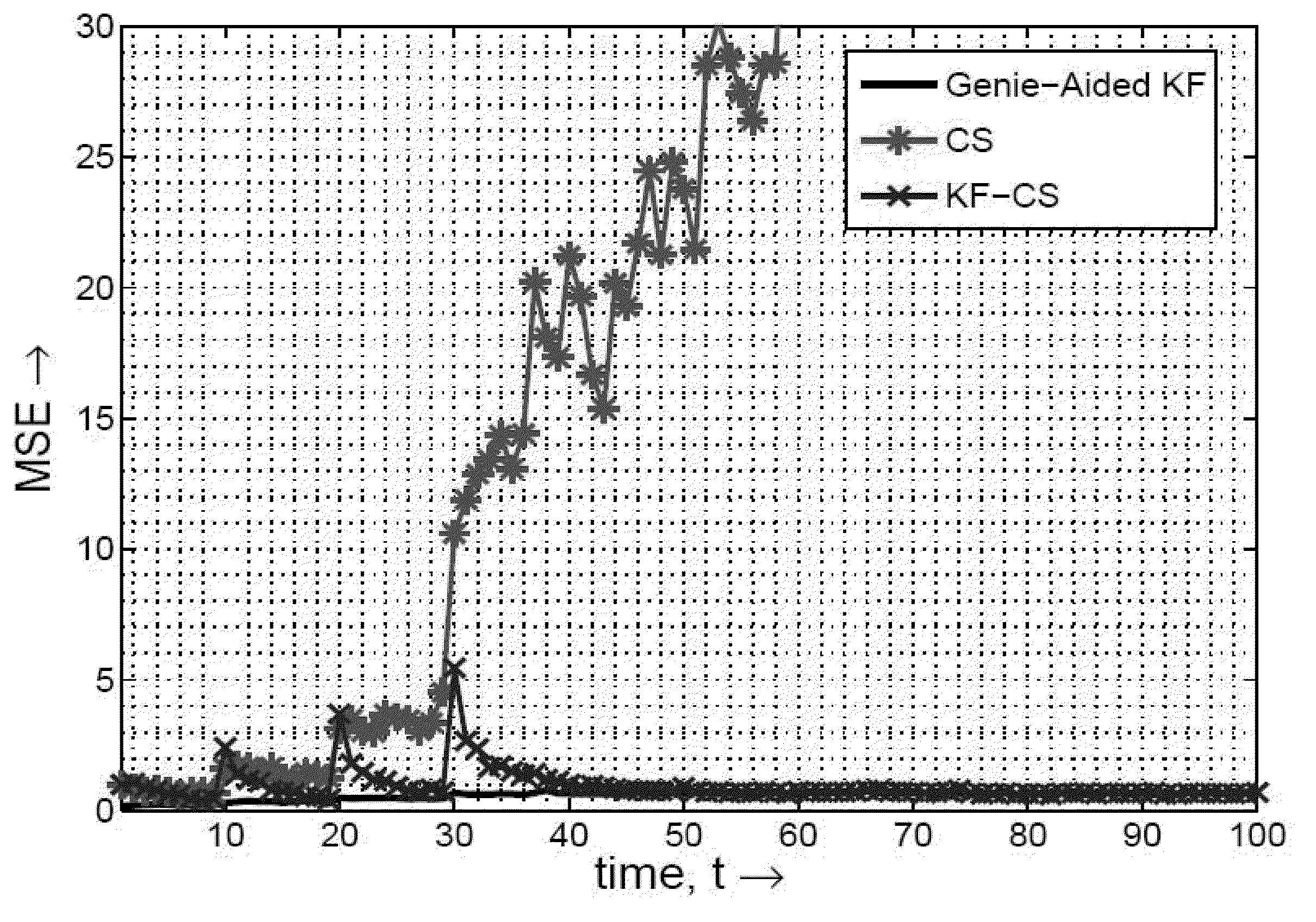
A method for real-time reconstruction is provided. The method includes receiving a sparse signal sequence one at a time and performing compressed sensing on the sparse signal sequence in a manner which causally estimates a time sequence of spatially sparse signals and generates a real-time reconstructed signal. Recursive algorithms provide for causally reconstructing a time sequence of sparse signals from a greatly reduced number of linear projection measurements.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
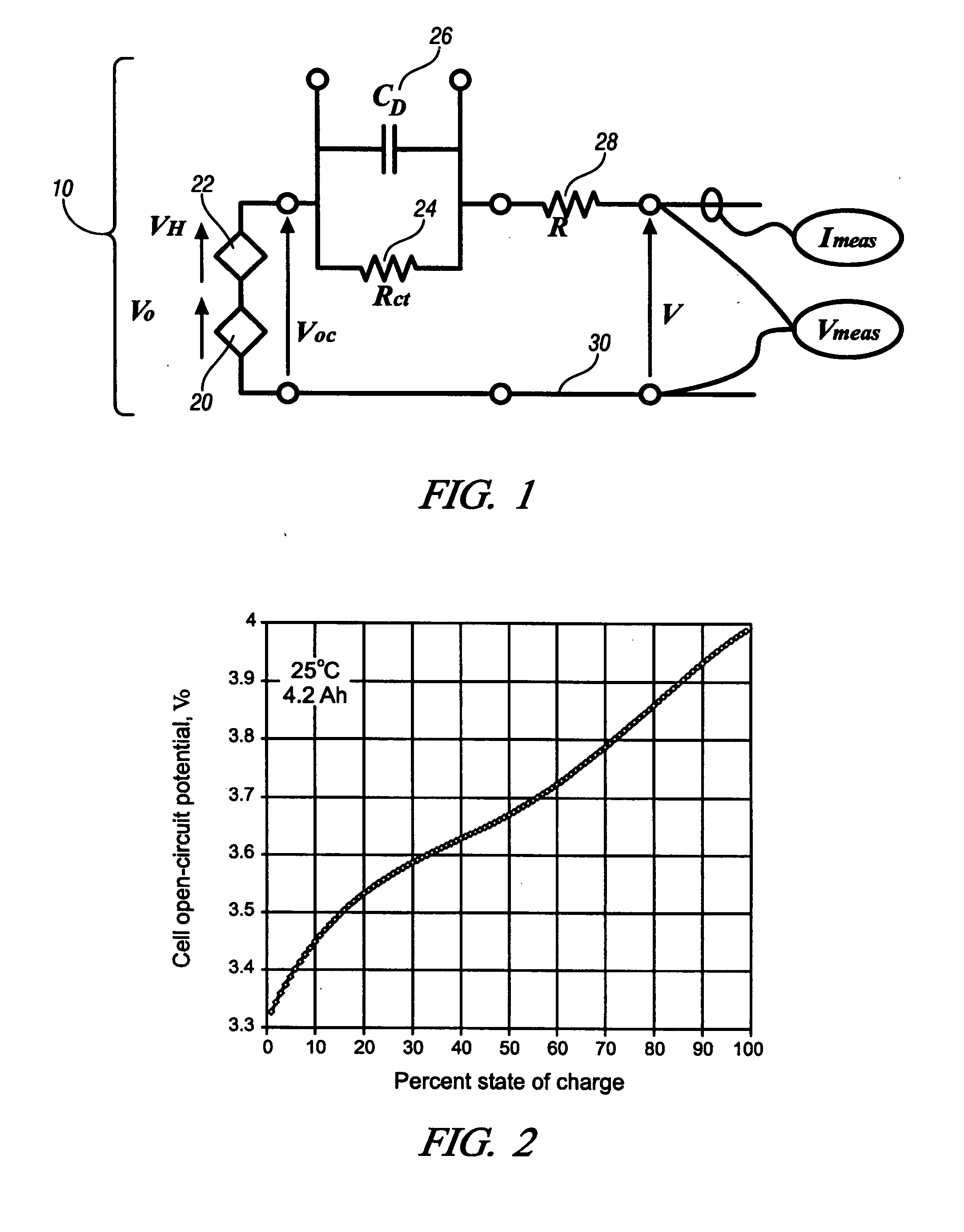
Method for control and monitoring using a state estimator having variable forgetting factors
ActiveUS20060284600A1Stable resistance valueImprove accuracyBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrical testingAlgorithmForgetting factor
A recursive algorithm is provided for adaptive multi-parameter regression enhanced with forgetting factors unique to each regressed parameter. Applications of this algorithm can include lead acid batteries, nickel-metal hydride batteries, and lithium-ion batteries, among others. A control algorithm is presented, having an arbitrary number of model parameters, each having its own time-weighting factor. A method to determine optimal values for the time-weighting factors is included, to give greater effect to recently obtained data for the determination of a system's state. A methodology of weighted recursive least squares is employed, wherein the time weighting corresponds to the exponential-forgetting formalism. The derived mathematical result does not involve matrix inversion, and the method is iterative, i.e. each parameter is regressed individually at every time step.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
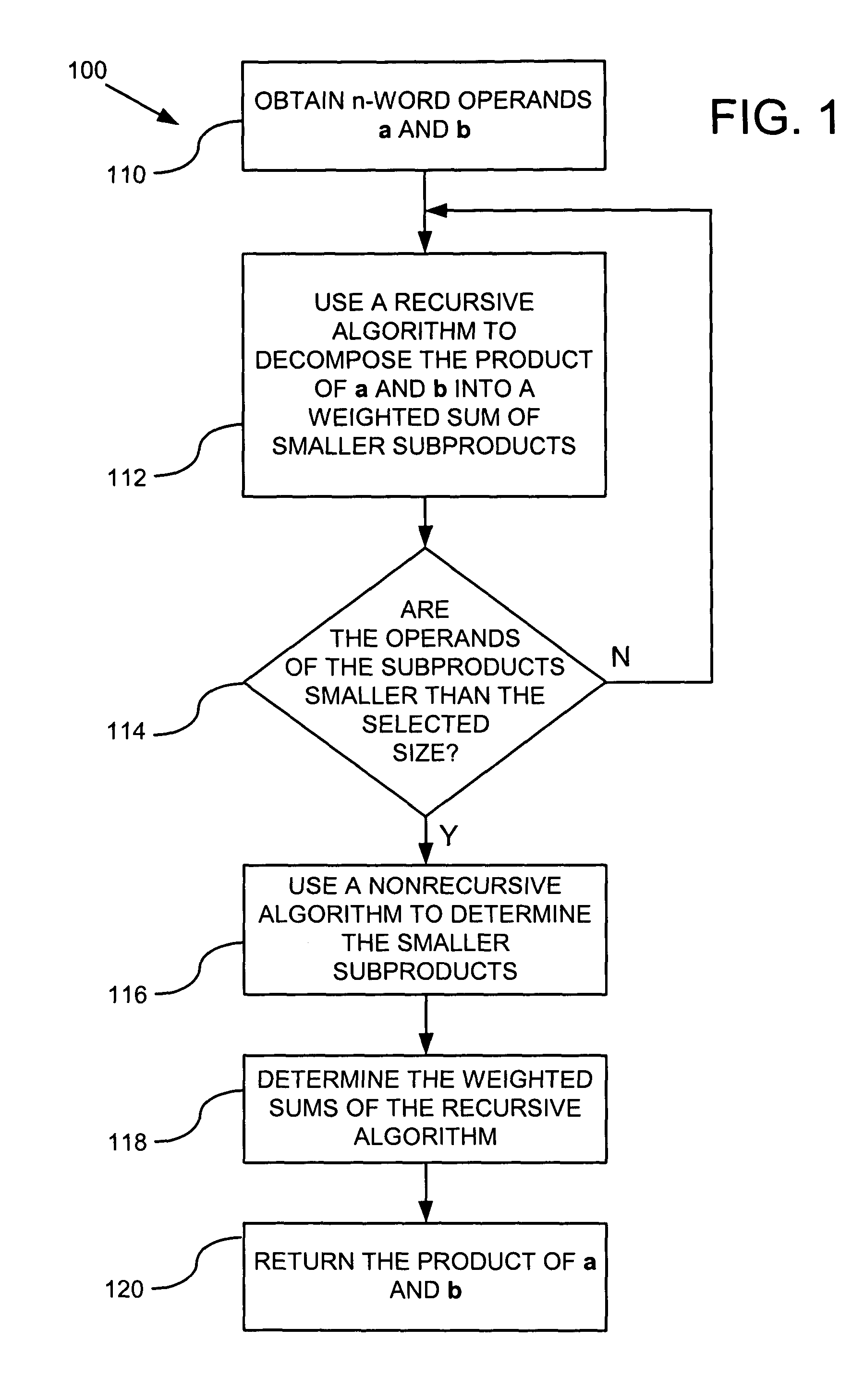
Lean multiplication of multi-precision numbers over GF(2m)
InactiveUS7447310B2Digital data processing detailsPublic key for secure communicationAlgorithmRecursive algorithms
Multi-precision multiplication methods over GF(2m) include representing a first polynomial and a second polynomial as an array of n words. A recursive algorithm may be used to iteratively decompose the multiplication into a weighted sum of smaller subproducts. When the size of the smaller subproducts is less than or equal to a predetermined size, a nonrecursive algorithm may be used to complete the multiplication. The nonrecursive algorithm may be optimized to efficiently perform the bottom-end multiplication. For example, pairs of redundant subproducts can be identified and excluded from the nonrecursive algorithm. Moreover, subproducts having weights in a special form may be efficiently calculated by a process that involves storing and reusing intermediate calculations.
Owner:THE STATE OF OREGON ACTING BY & THROUGH THE OREGON STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF OREGON STATE UNIV
Method for controlling and monitoring using a state estimator having variable forgetting factors
ActiveUS7612532B2Stable resistance valueImprove accuracyBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrical testingAlgorithmForgetting factor
A recursive algorithm is provided for adaptive multi-parameter regression enhanced with forgetting factors unique to each regressed parameter. Applications of this algorithm can include lead acid batteries, nickel-metal hydride batteries, and lithium-ion batteries, among others. A control algorithm is presented, having an arbitrary number of model parameters, each having its own time-weighting factor. A method to determine optimal values for the time-weighting factors is included, to give greater effect to recently obtained data for the determination of a system's state. A methodology of weighted recursive least squares is employed, wherein the time weighting corresponds to the exponential-forgetting formalism. The derived mathematical result does not involve matrix inversion, and the method is iterative, i.e. each parameter is regressed individually at every time step.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
System and method for reconstructing pathways in large genetic networks from genetic perturbations
InactiveUS20030023388A1Reduce research costsPrecise positioningDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsGraphicsGenetic network
A system and method for reconstructing pathways in large genetic networks from genetic perturbations comprises an analysis method and system that applies a recursive algorithm for determining the path between every gene pair in an arbitrarily large genetic network from large-scale gene perturbation data and reconstructs all direct and indirect regulatory gene interactions in the network. Graph theory mathematics is applied to genetic network reconstruction in the following manner: Genetic perturbation data is used to identify all genes accessible from a perturbed gene to generate an accessibility list for the gene. Graph theory mathematics is applied to the accessibility list and its graph to determine a condensation of the graph as defined by the condensation's accessibility list. Graph theory mathematics is applied to the accessibility list, such as through a recursive algorithm performed on a desktop computer, to obtain an adjacency list for the gene that characterizes a genetic network.
Owner:STC UNM
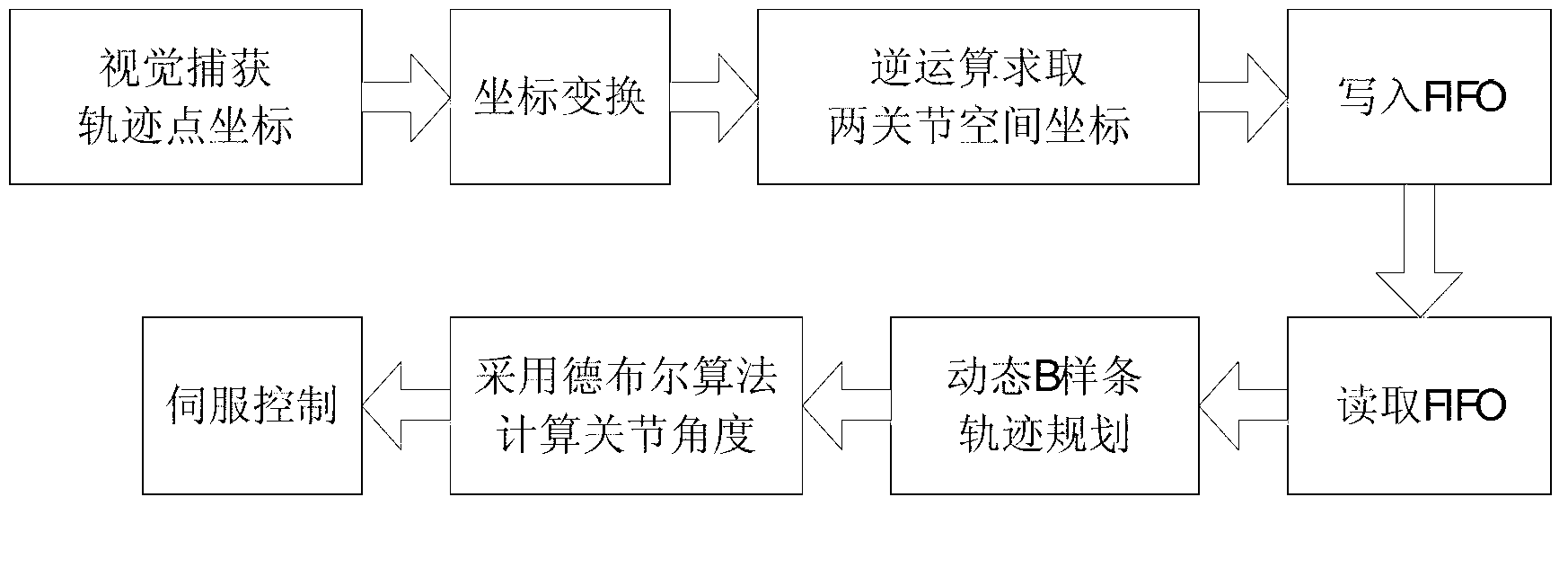
B spline track planning method of robot joint space guided by vision
ActiveCN102794767AImprove trajectory tracking accuracyTrack Motion SmoothingProgramme-controlled manipulatorNODALDegrees of freedom
The invention relates to a B spline track planning method of a robot joint space guided by vision, which comprises the following steps: firstly, a 2-DOF (degree of freedom) robot is arranged in a stereoscopic support, an industrial camera is arranged at the front end of the stereoscopic support, and the moving direction of a conveyor belt is perpendicular to the moving plane of the 2-DOF robot; secondly, after the industrial camera obtains a first track point on the conveyor belt, a B spline curve is constructed according to the obtained time node sequence of joints within the time the 2-DOF robot moves to the first track point; thirdly, the constructed B spline curve is prolonged by adding a node vector and a control vertex to allow the B spline curve to go through an added joint position point; and fourthly, a position point on the B spline curve is calculated by adopting a De Boor recursive algorithm, so as to drive the 2-DOF robot to move. The B spline track planning method can realize smooth movement of the robot guided by the vision, and improve the track following precision of the robot.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
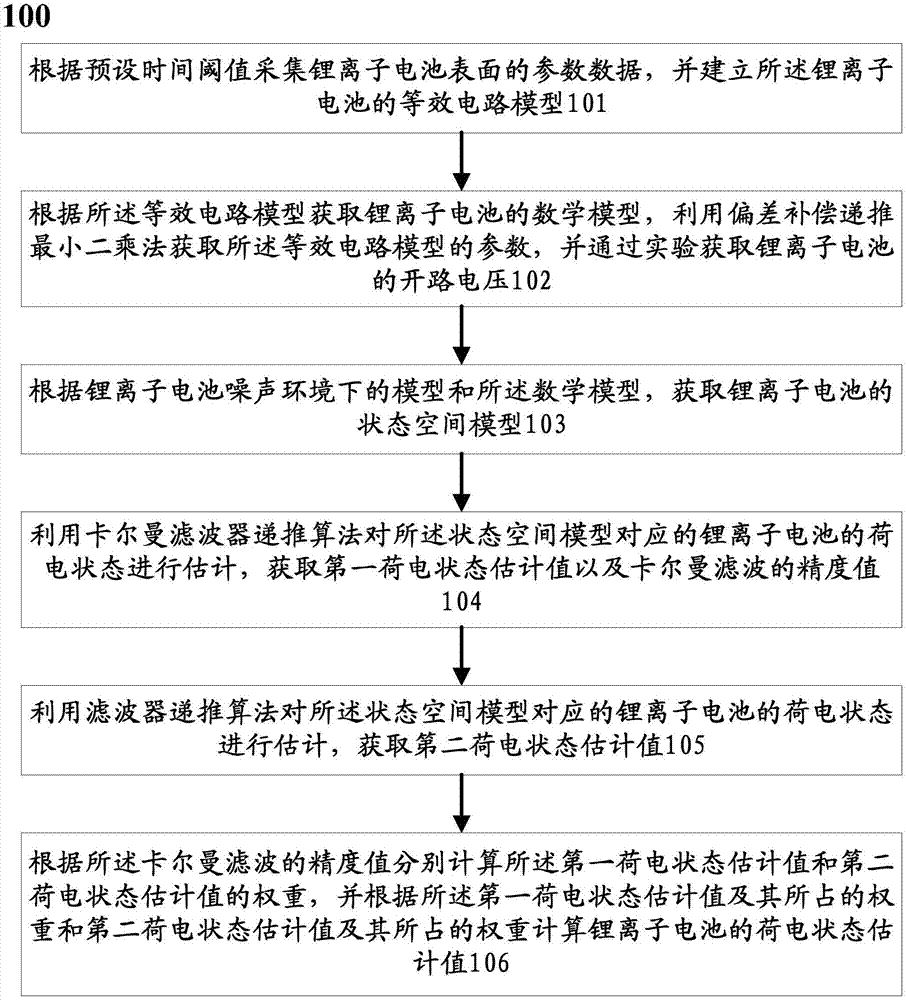
Method and system for carrying out filtering estimation on charged states of lithium ion battery
ActiveCN107402353AIncrease redundancyHigh precisionElectrical testingVehicular energy storageKaiman filterMathematical model
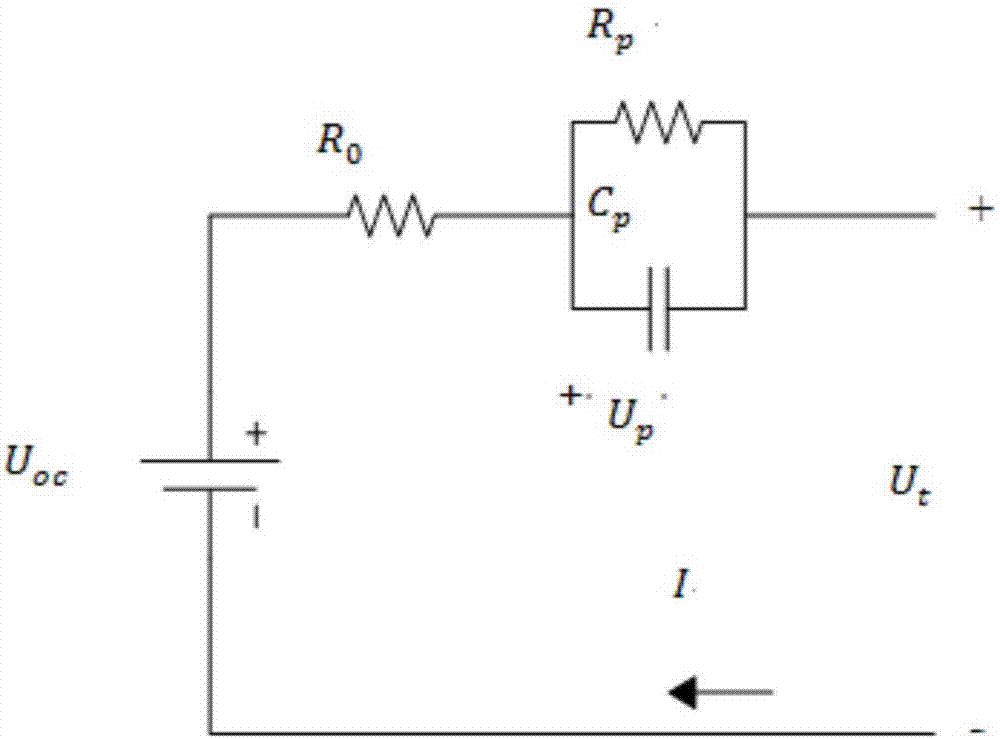
The invention discloses a method for carrying out filtering estimation on charged states of a lithium ion battery. The method comprises steps of acquiring parameter data of the surface of the lithium ion battery according to a preset time threshold, and establishing an equivalent circuit model of the lithium ion battery; acquiring a mathematical model of the lithium ion battery according to equivalent circuit model, acquiring parameters of the equivalent circuit model by use of a deviation compensation recursive least square algorithm and acquiring open-circuit voltage of the lithium ion battery; acquiring a state space model according to a model and the mathematical model of the lithium ion battery in a noise environment; estimating the charged states of the lithium ion battery by use of a Kalman filter recursive algorithm and acquiring a first charged state estimation value and a precision value of the Kalman filter; acquiring a second charged state estimation value by use of the H-infinite filter recursive algorithm; and calculating weights of the first charged state estimation value and the second charged state estimation value, and calculating a charged state estimation value of the lithium ion battery according to the weights.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
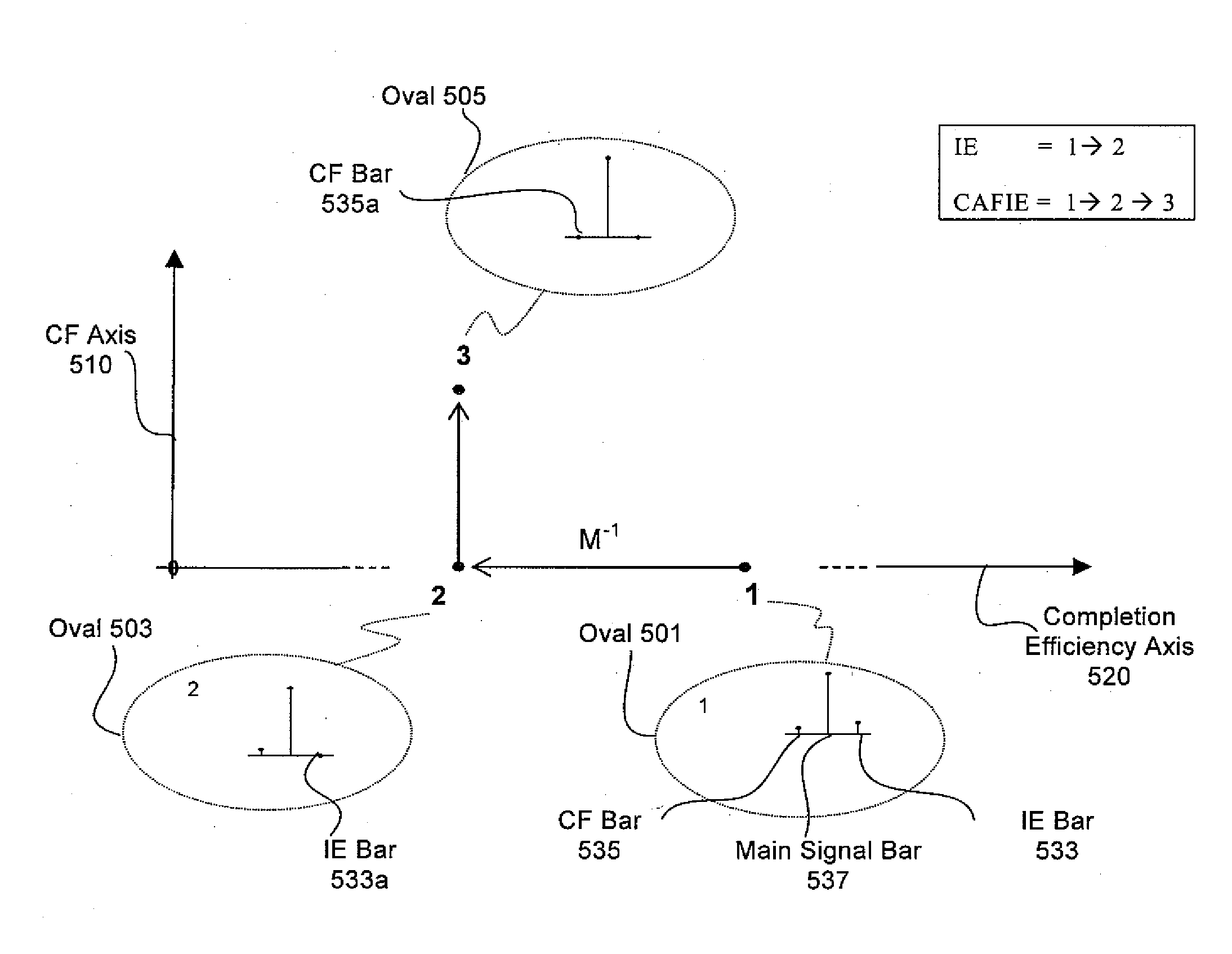
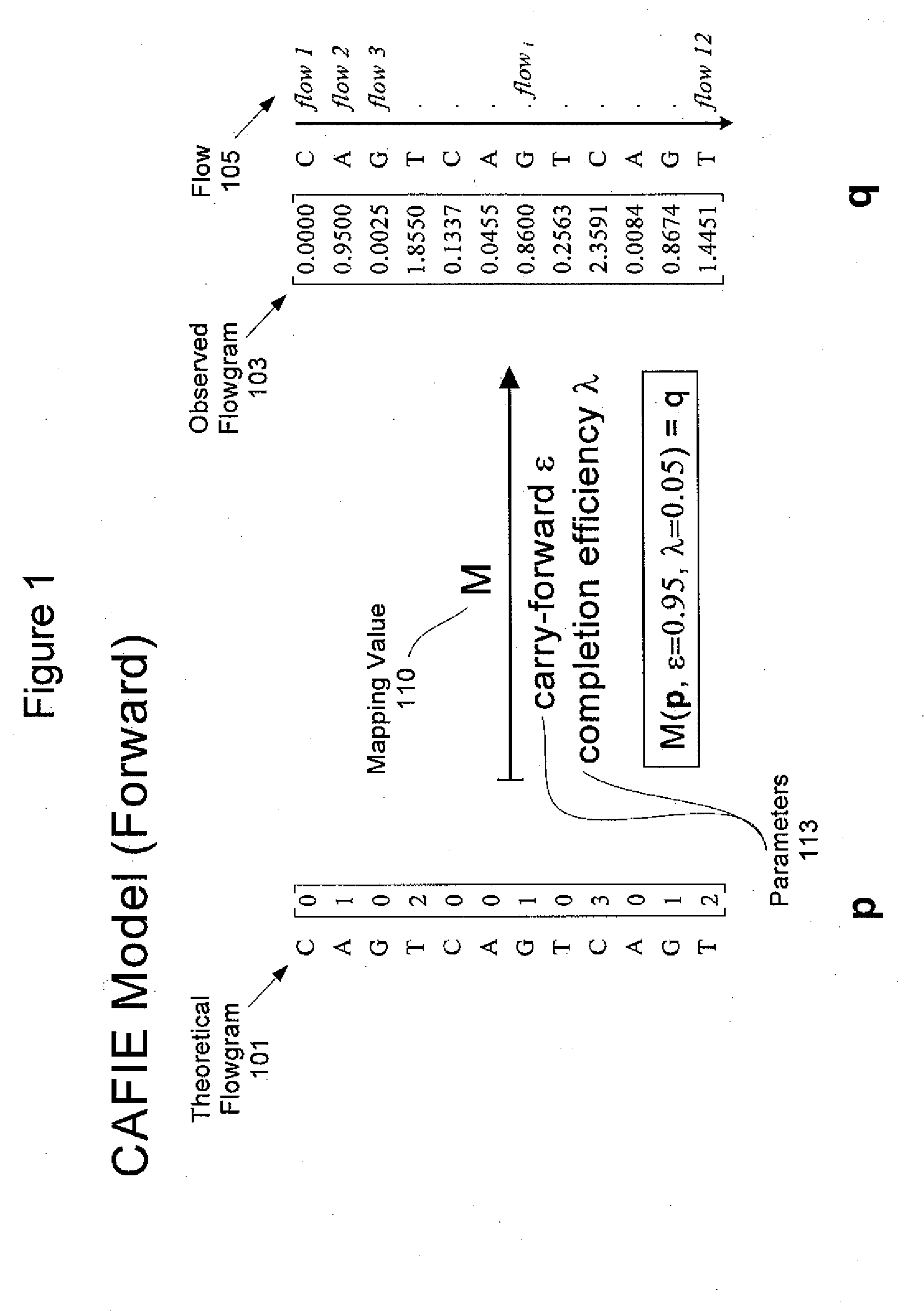
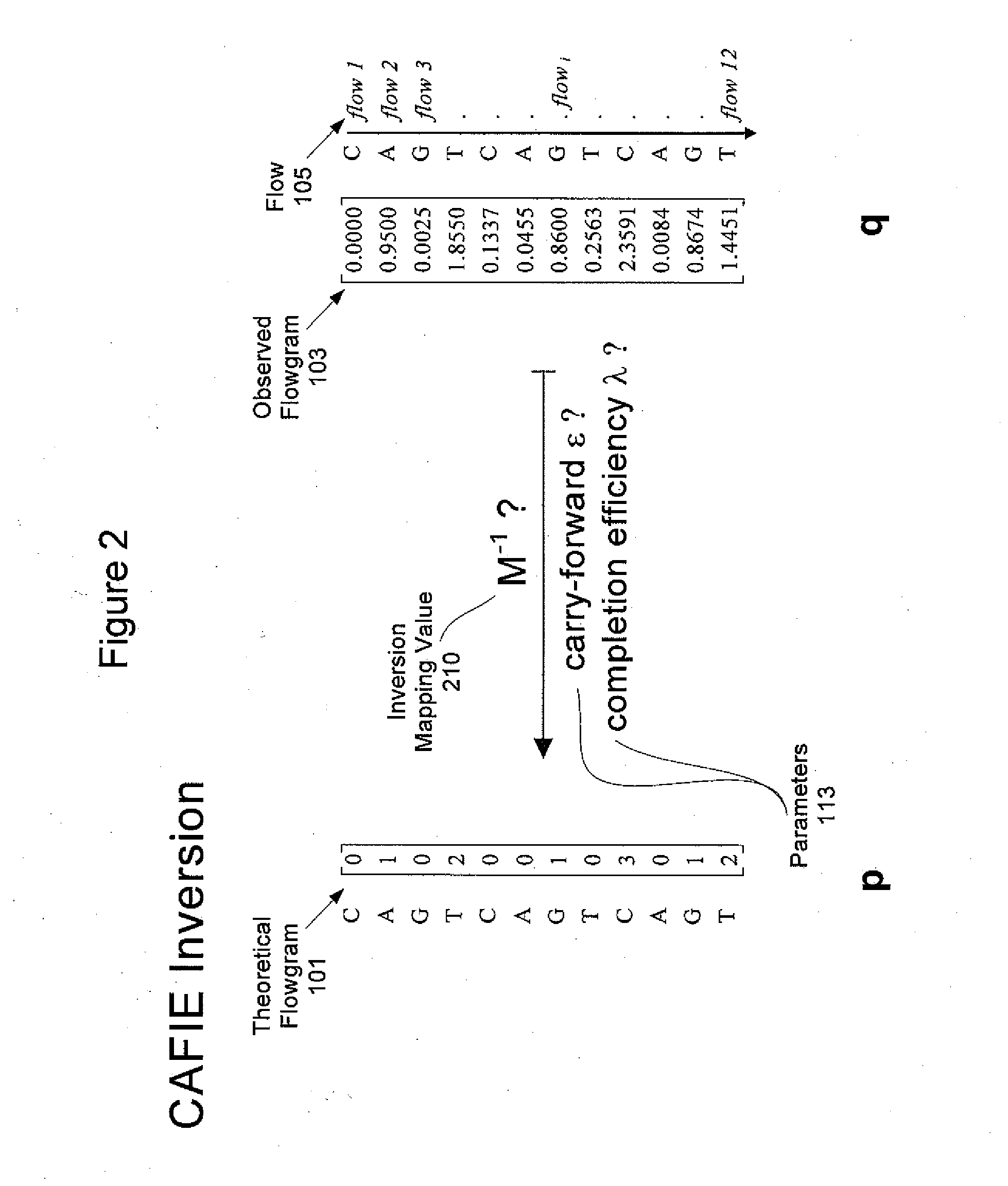
System and method to correct out of phase errors in DNA sequencing data by use of a recursive algorithm
InactiveUS20110213563A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsAlgorithmErrors and residuals
An embodiment of a method for correcting an error associated with phasic synchrony of sequence data generated from a population of template molecules is described that comprises the steps of detecting signals generated in response to nucleotide species introduced during a sequencing reaction; generating an observed value for the signal detected from each of the nucleotide species; defining positive incorporation values and negative incorporation values from the observed values using a carry forward value and an incomplete extension value; revising the carry forward value and the incomplete extension value using a noise value that is derived from observed values associated with the negative incorporation values; re-defining the positive incorporation values and the negative incorporation values using the revised carry forward value and the revised incomplete extension value; and repeating the steps of revising and re-defining until convergence of the positive incorporation values and the negative incorporation values
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
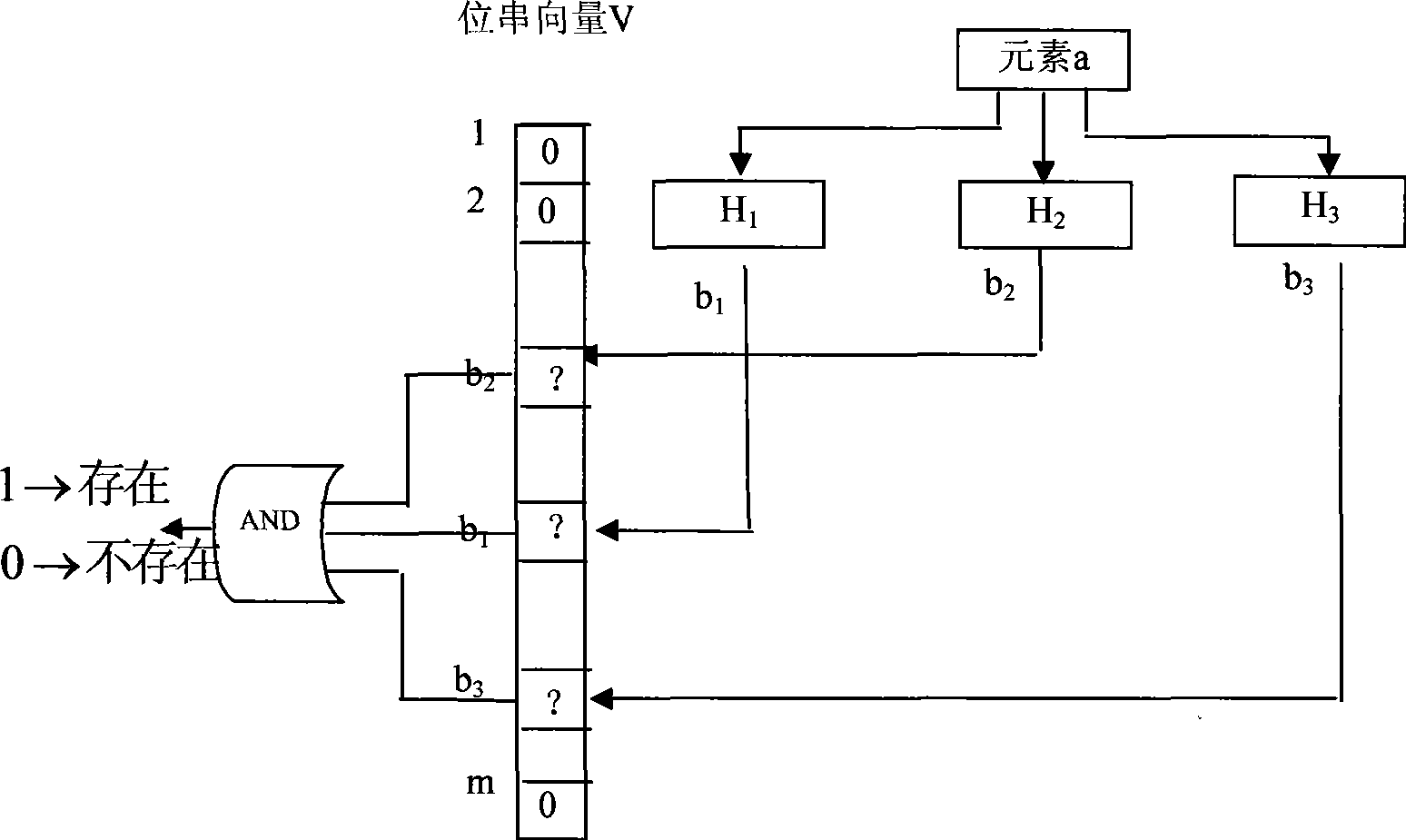
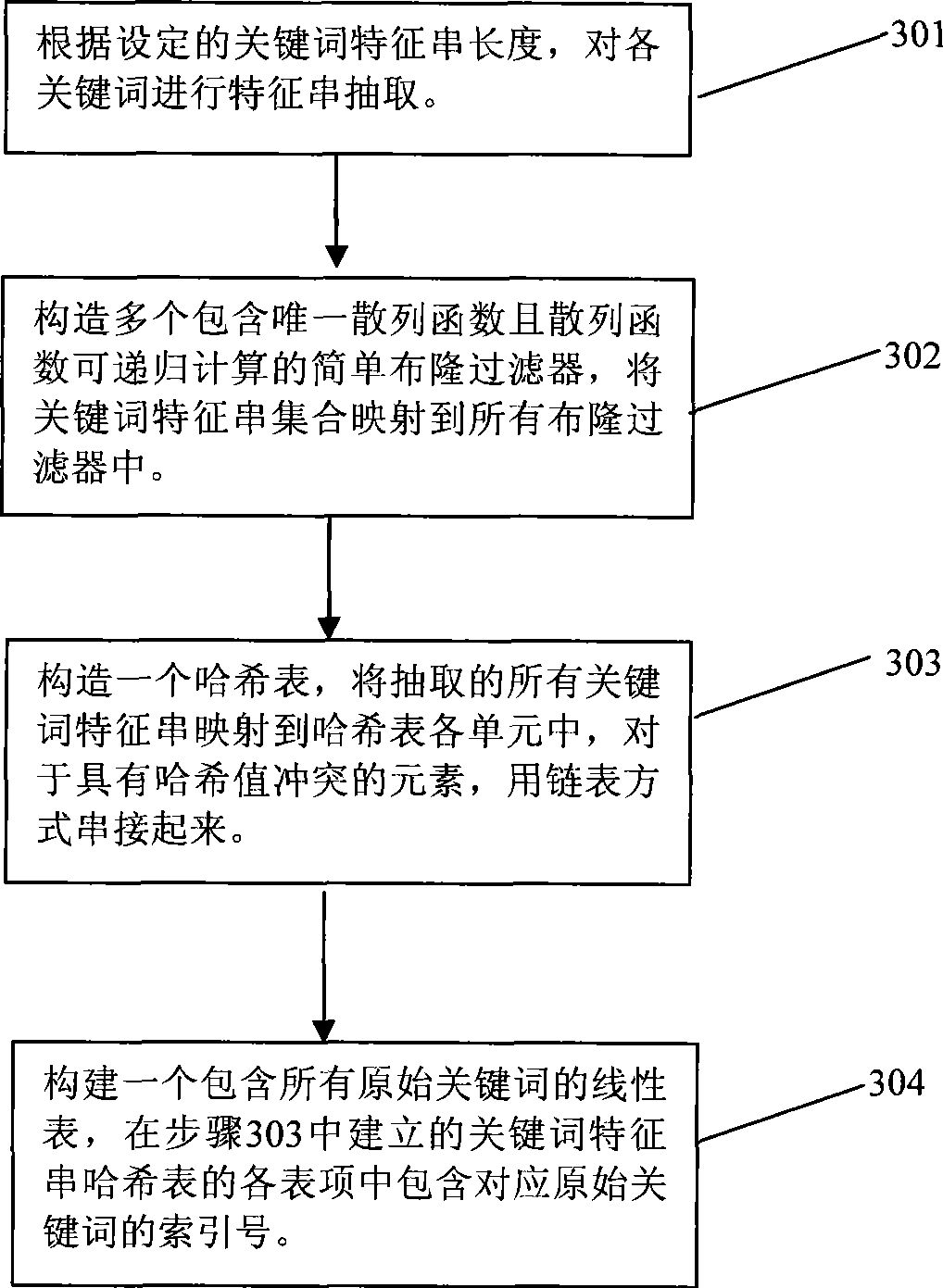
Large scale key word matching method
InactiveCN101398820AReduce the problem of high false alarm rateImprove retrieval efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsExact matchPattern matching
The invention provides a matching method used for large-scale key words, comprising a pre-processing stage and a mode matching stage; the pre-processing stage comprises a key word characteristic string cutter, the structure of a plurality of simple bloom filter based on key word characteristic string sets, and a Hash table structure based on the key word characteristic string sets; the mode matching stage comprises the steps as follows: quick judgment that the text string in the current window is not matched with any key word characteristic string is achieved by the simple bloom filter series of previous structure; the precise match with candidate key words is executed under a failed judgment condition; during the text scanning process, current hash values of the current text corresponding to all simple bloom filters are quickly calculated by a recursive algorithm. The matching method sufficiently uses the characteristics that the match success rate of the text to be matched and the key words is extremely low and the recursive hash arithmetic has high efficiency, can realize the high-speed match under the condition of large-scale key words, and is extremely suitable for online virus scanning application such as virus detection and the like.
Owner:BEIJING VENUS INFORMATION TECH
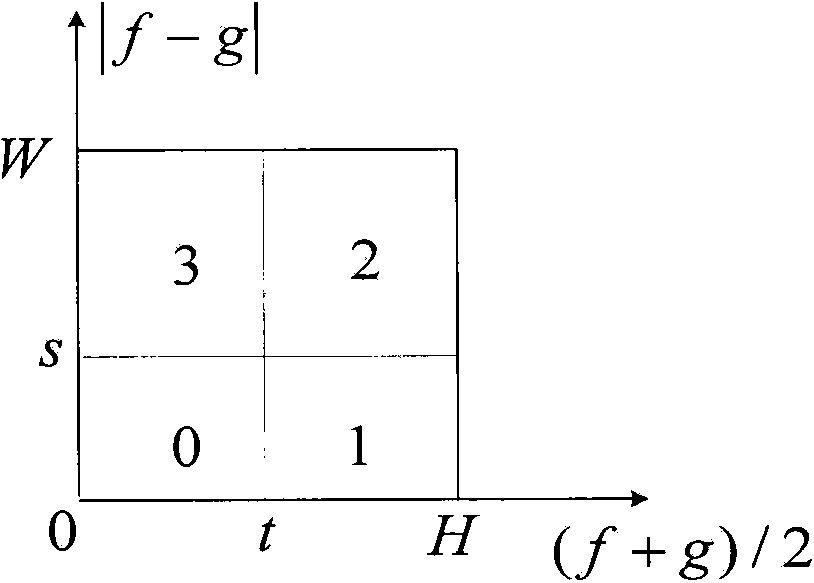
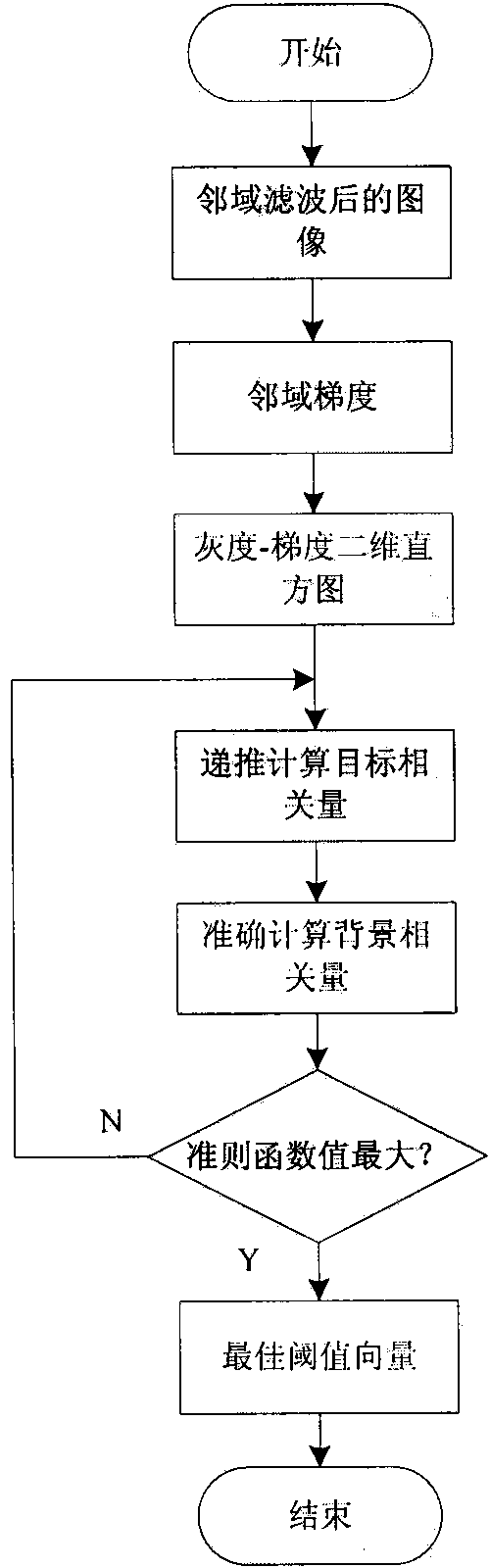
Rapid threshold segmentation method based on gray level-gradient two-dimensional symmetrical Tsallis cross entropy
The invention relates to a rapid threshold segmentation method based on gray level-gradient two-dimensional symmetrical Tsallis cross entropy, aims at the problems that approximate assumption exists in a conventional gray level-average gray level histogram and a whole solution space is required to be searched by calculation, so that segmentation is inaccurate and the efficiency is not high, and provides improved two-dimensional symmetrically Tsallis cross entropy threshold segmentation and a rapid recursive method thereof. The threshold segmentation method is higher in universality and accurate in segmentation; in order to realize accurate segmentation of a gray image, a new gray level-gradient two-dimensional histogram is adopted, and a two-dimensional symmetrical Tsallis cross entropy theory with a superior segmentation effect is combined with the histogram, so that the gray level image segmentation accuracy is effectively improved; the requirement for on-line timeliness of an industrial assembly line is met at the same time, a novel rapid recursive algorithm is adopted, and redundant calculation is reduced; and after a gray level image of the industrial assembly line is processed, the inside of an image zone is uniform, the contour boundary is accurate, the texture detail is clear, and at same time, good universality is provided.
Owner:WUXI XINJIE ELECTRICAL +1
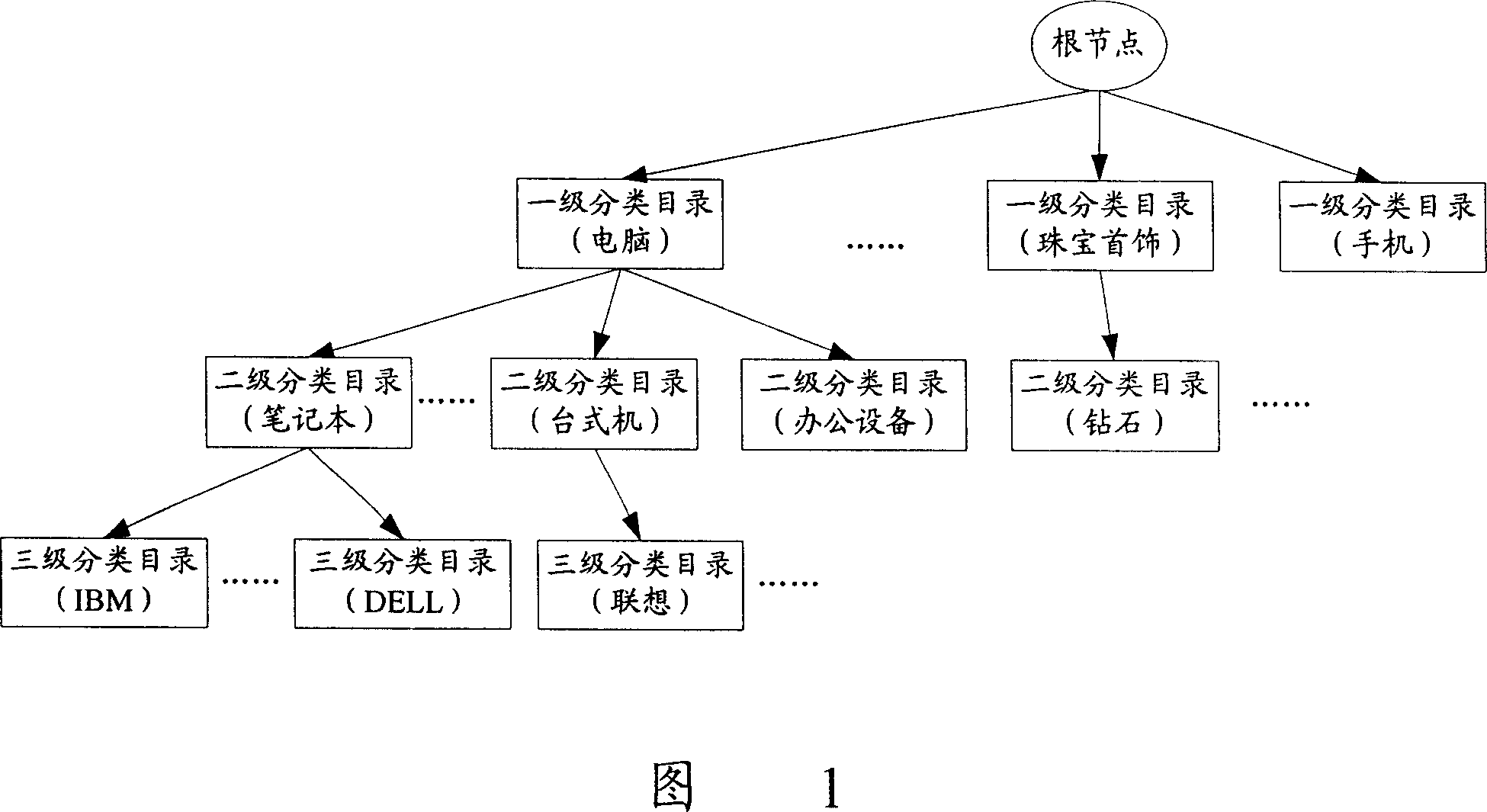
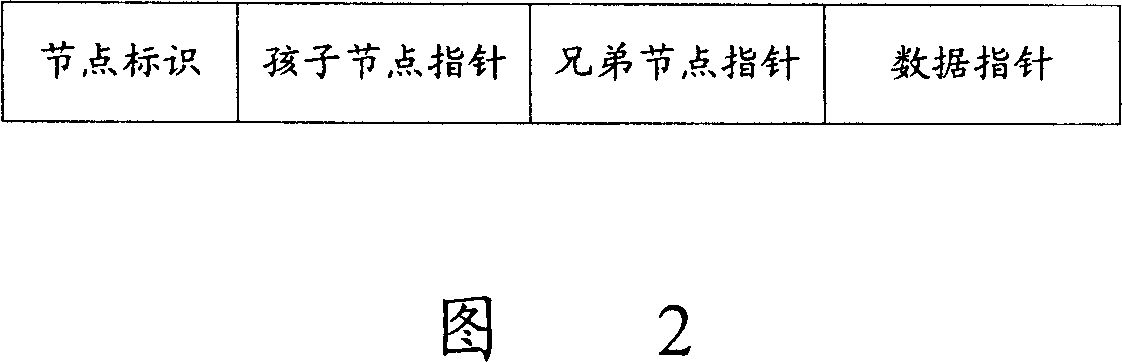
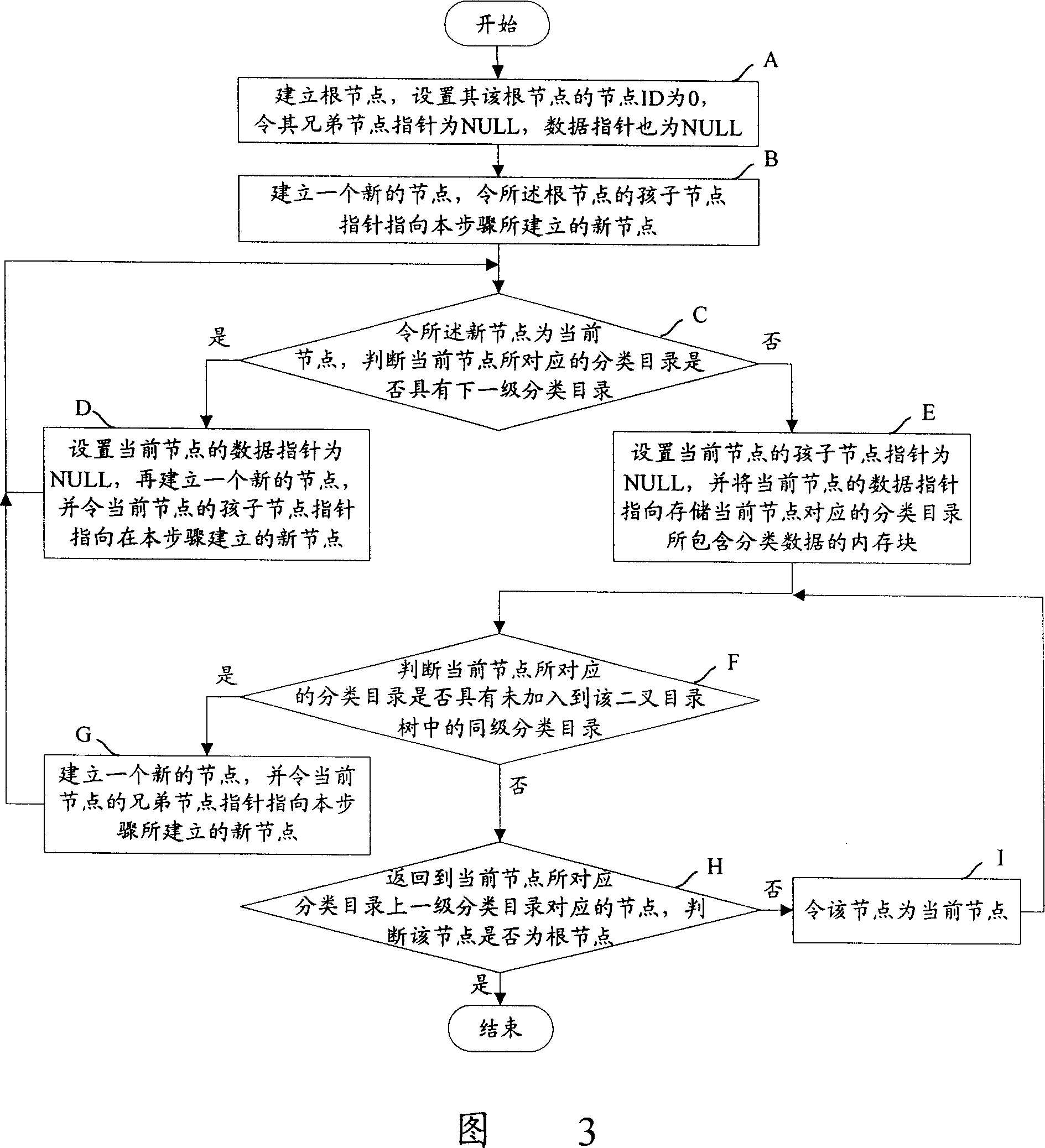
Sort data storage and split catalog inquiry method based on catalog tree
ActiveCN1955958AImprove storage efficiencyStorage moreSpecial data processing applicationsTheoretical computer scienceRecursive algorithms
A method for storing classified data based on catalogue tree includes setting up root node of catalogue tree, making brother node pointer of root node be idle and making data pointer be idle then setting up a new node to let sun node pointer of root node point to set up new node being used to correspond to one grade classification catalogue of classified data, utilizing recursive algorithm to separately set up mapping node to correspond to each grade classification catalogue of classified data. The catalogue querying method based on said catalogue tree is also disclosed.
Owner:BEIJING JINGDONG SHANGKE INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
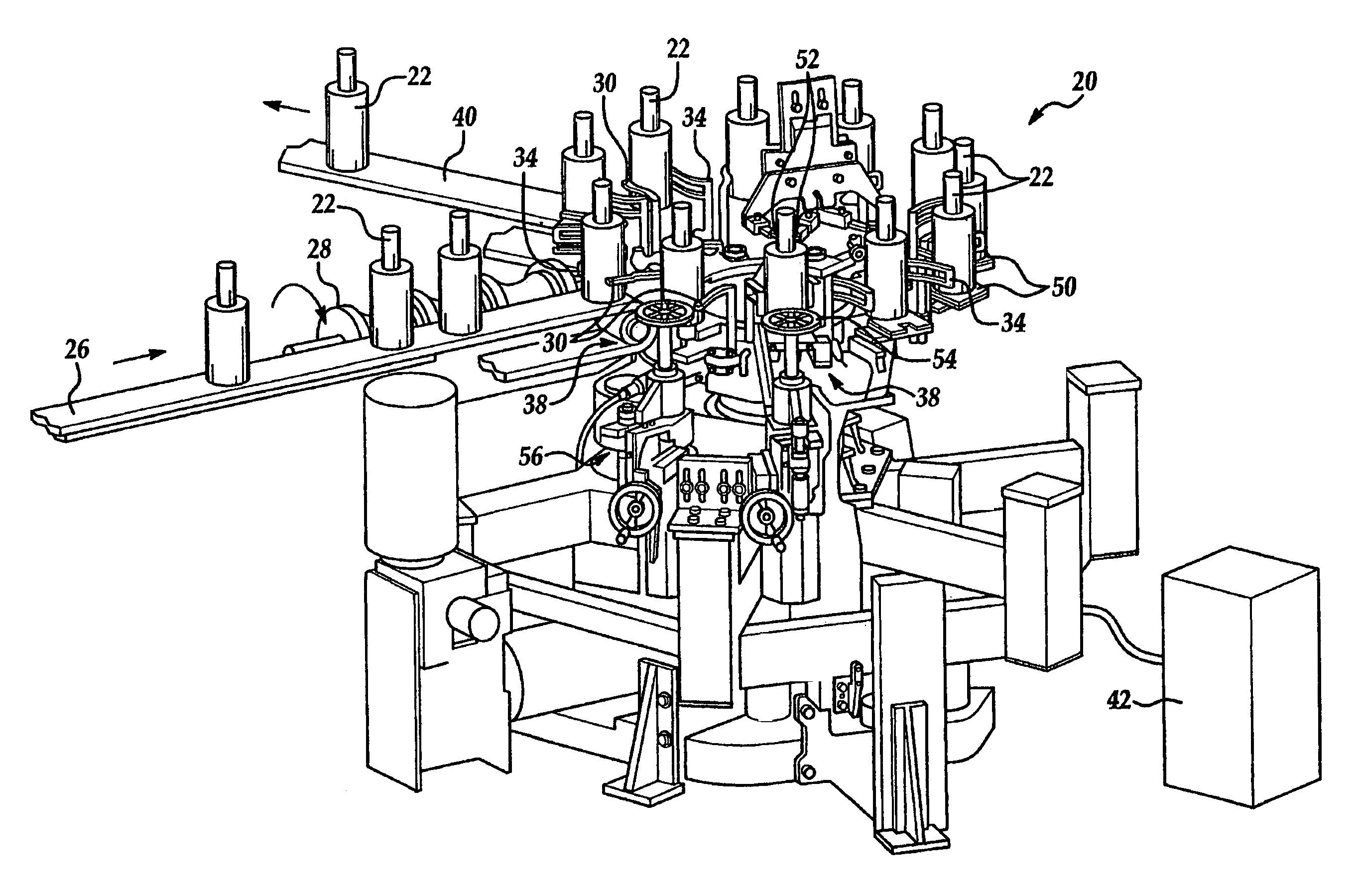
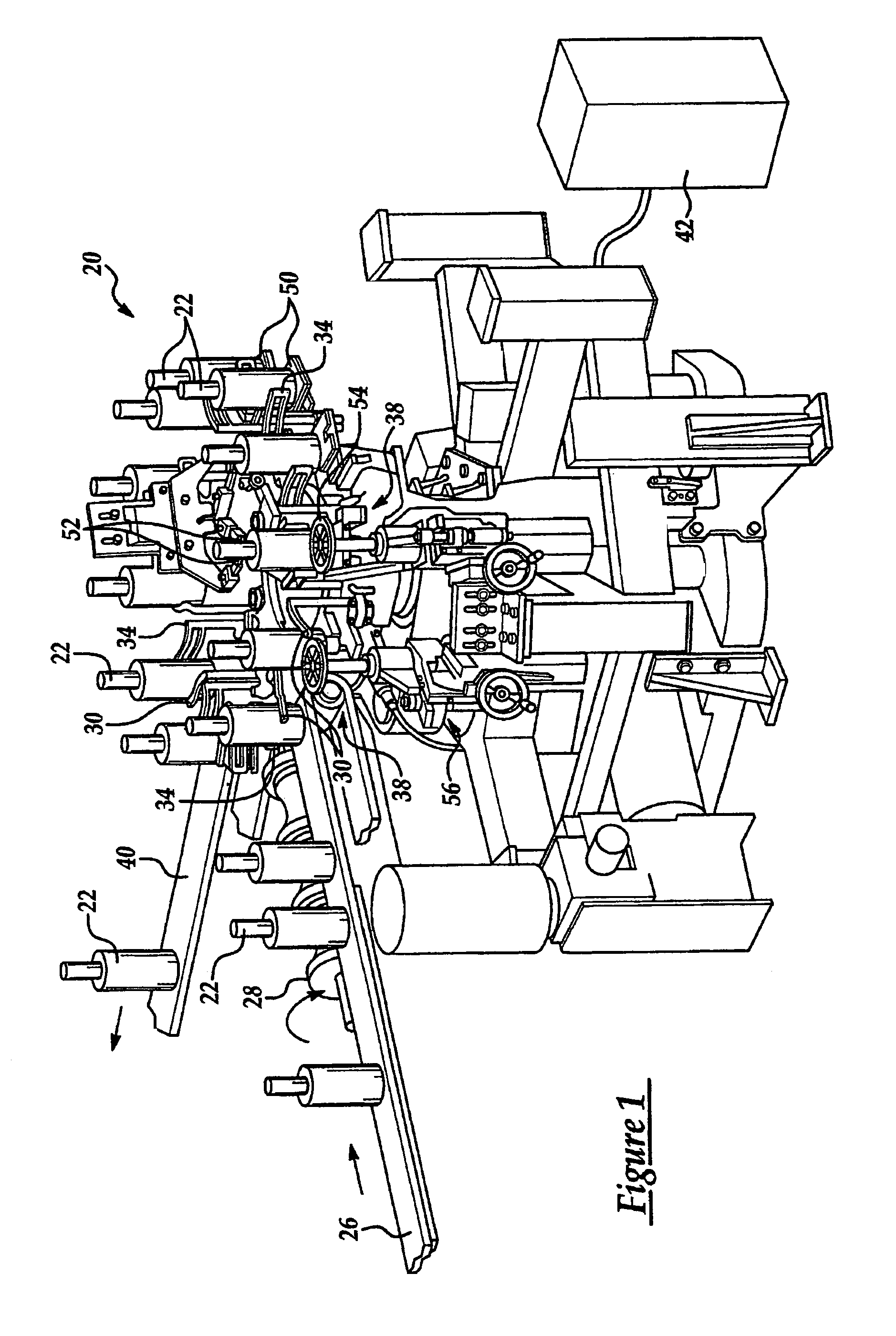
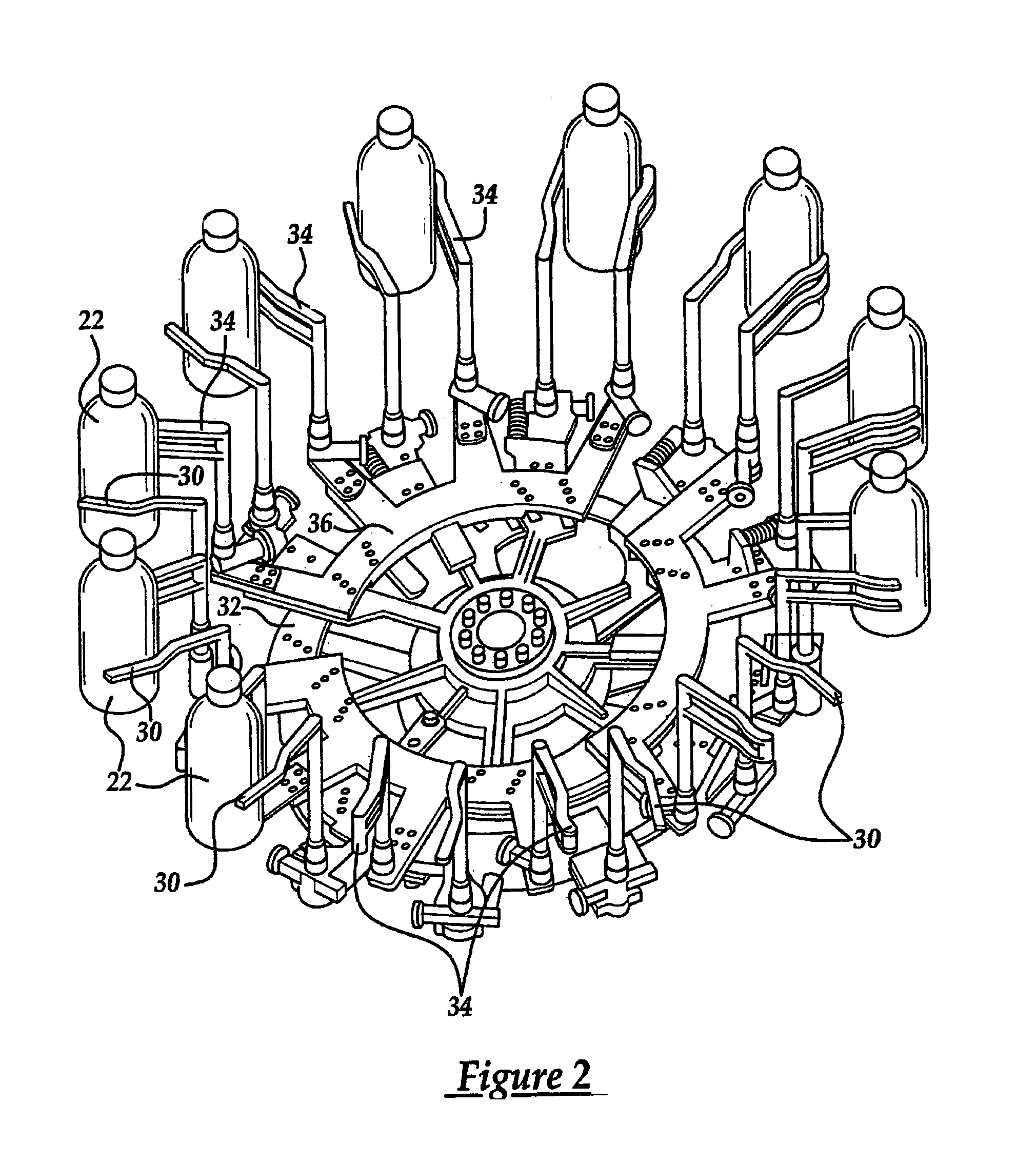
Electronic control system for container indexing and inspection apparatus
A glassware inspection apparatus that includes an electronic control system and method for optimum control of indexing and inspecting glass containers. The control system generally includes a driver circuit for each servo motor of the apparatus, an electronic control unit, and an operator interface. Information about the apparatus and the particular containers being inspected is entered into the control system through the operator interface. The electronic control unit executes a recursive algorithm that utilizes the inputted information, as well as predetermined constraints of the apparatus, to develop an optimum motion profile for each servo motor. The optimum motion profiles provide the overall apparatus with coordinated control and increased container throughput speed, while efficiently distributing cycle time and thermal energy between the various servo motors.
Owner:OWENS-BROCKWAY GLASS CONTAINER INC
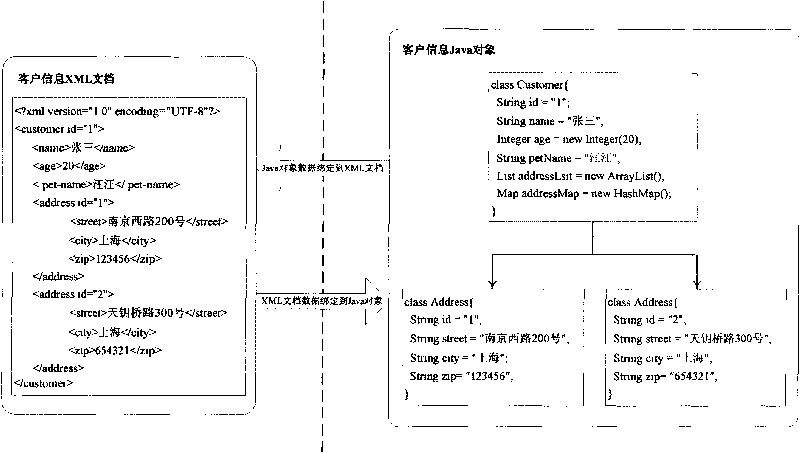
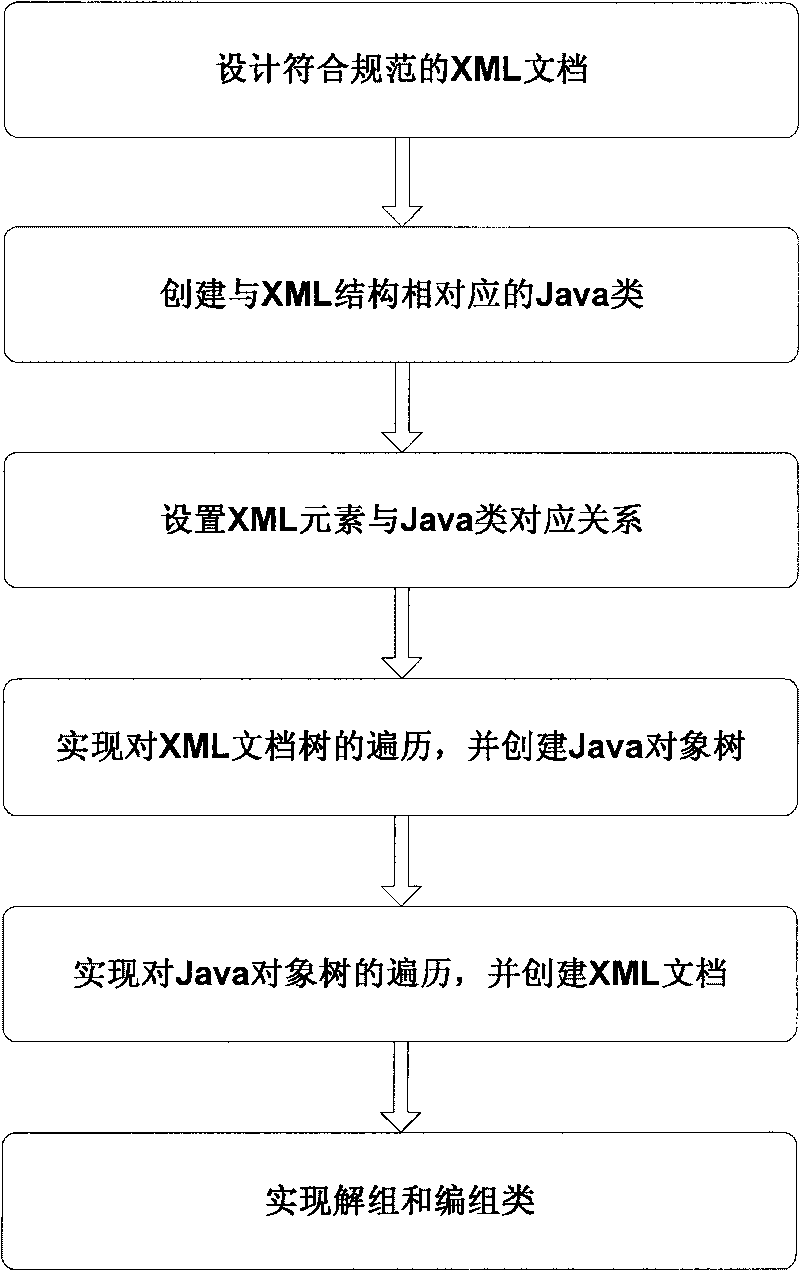
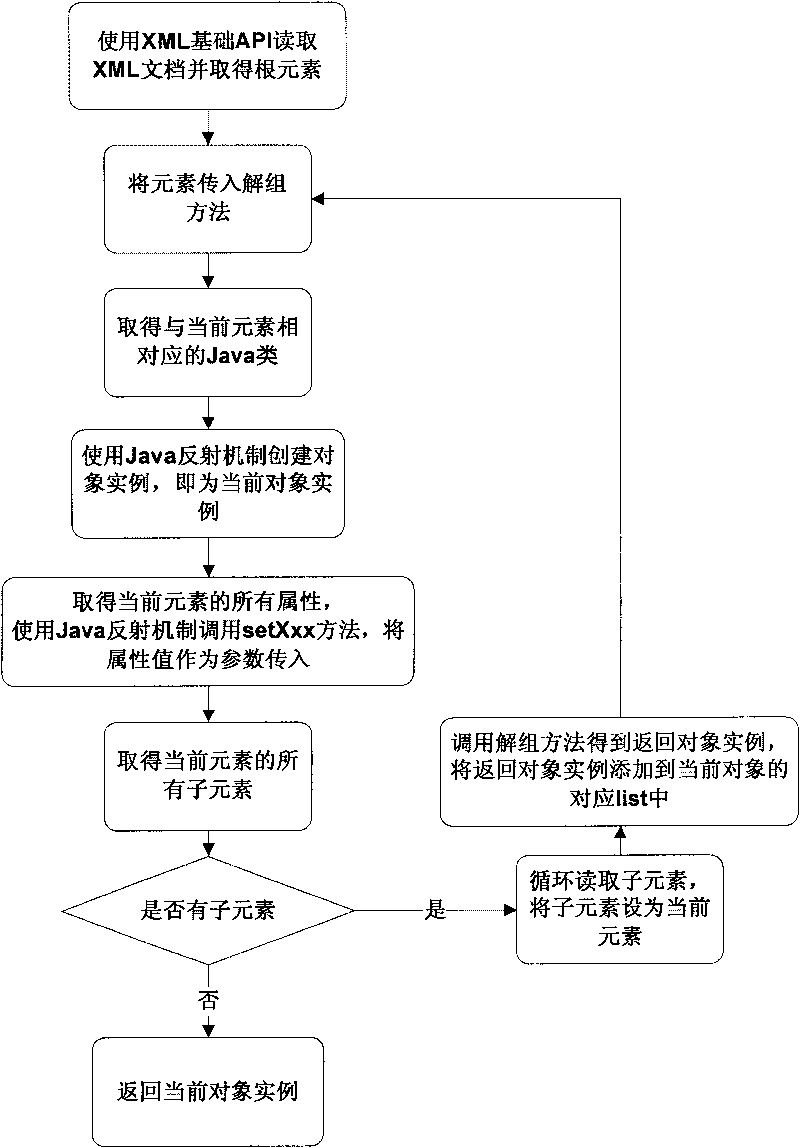
Method for binding Java and XML data
ActiveCN101699397ASimplify development workReduce development difficultySpecial data processing applicationsSpecific program execution arrangementsTree traversalJava classes
The invention discloses a method for binding Java and XML data, which comprises the following steps of: 1) designing an XML document; 2) creating a Java class corresponding to an element according to the structure of the XML document; 3) setting a corresponding relationship between the XML element and the Java class; 4) realizing a disorganization algorithm, adopting a recursive algorithm to transverse an XML document tree, and creating a Java object corresponding to the structure of the XML document; 5) realizing a grouping algorithm, adopting the recursive algorithm to transverse a Java object tree, and creating an XML document corresponding to the whole Java object tree; and 6) realizing a disorganization class and a grouping class. The method realizes bidirectional data mapping binding between the Java object and the XML document, simplifies development work by using the XML, realizes an automation process from resolving the XML document to creating the Java object, and can write the modified Java object back to the XML document and conveniently adapt to the change of the structure of the XML document by modifying few Java codes.
Owner:SHANGHAI BAOSIGHT SOFTWARE CO LTD
Method for detecting braking property of vehicle in road test based on improved Kalman filtering
InactiveCN102175463AMeet the measurement requirementsHigh measurement accuracyVehicle testingFully developedFiltering theory
The invention discloses a method for detecting braking property of a vehicle in a road test based on improved Kalman filtering, which comprises the following steps: on the basis of referring a 'current' statistical model of an engine driven carrier in the navigation field, establishing a system motion model in the vehicle braking process; according to the Kalman filtering theory, using a speed and an azimuth angle outputted by a single-frequency carrier phase single-point GPS (global position system) receiver as the system observed volumes; and high frequently and precisely calculating a plane motion coordinate and the speed in the vehicle braking process, by utilizing the improved Kalman filtering recursive algorithm, thereby calculating and confirming a vehicle braking distance and a mean fully developed deceleration MFDD.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and system for determining offering combinations in a multi-product environment
A multi-product environment is analyzed to identify combinations of products or services which represent strategic offerings of a company. For a multi-product environment and a set of client accounts, a segmentation tree is constructed to identify the offering groups of interest. The tree is first initialized as a root representing all offerings, all clients and an empty offering set. A recursive algorithm is then applied to grow the tree at each node by segmenting the clients based on whether a particular offering is purchased. The selection of the offering to use for segmentation at each node is determined by a mathematical algorithm that considers two factors: 1) the offering should have high pulling power, meaning it is likely to produce high revenue in combination with other offerings, and 2) the offering should be unlikely to cause fragmentation, meaning nodes representing a very small amount of revenue. The algorithm terminates when each leaf node reaches one of the two limits: 1) Representation limit which is reached when a significant portion of revenue is accounted for by offerings in a particular grouping and 2) Significance limit which is reached when the revenue represented by a node is too small to be considered significant. At this point all leaf nodes representing significant revenue are collected as the offering groups.
Owner:IBM CORP
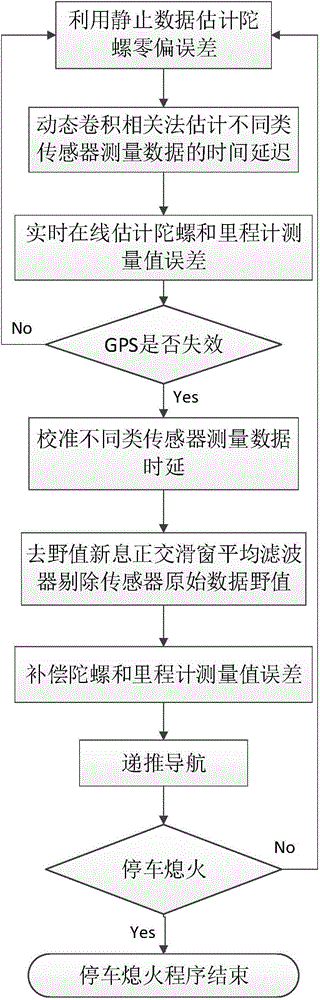
Vehicle-mounted integrated navigation method of resisting to failure of global positioning system
InactiveCN103983997AImprove estimation accuracySmall dispersionNavigation by terrestrial meansSatellite radio beaconingGyroscopeTime delays
The invention provides a vehicle-mounted integrated navigation method of resisting to failure of a global positioning system, and relates to a GPS-failure-resisting integrated navigation method suitable for a vehicle-mounted low-cost integrated navigation system. The vehicle-mounted integrated navigation method of resisting to failure of the GPS comprises the following steps that firstly, relative time delay of measurement data of different types of sensors is estimated with the dynamic convolution correlation method, and output data of three types of sensors which are the GPS, a gyroscope and the speed sensor are corrected according to the relative time delay; secondly, outliers of original data of the three types of sensors are removed through an outlier-removing innovation orthogonality sliding window average filter, and the discrete degree of the data is reduced; thirdly, error coefficients of the gyroscope and the speed sensor are estimated online in real time in the effective status of the GPS, and compensation for the error coefficients is conducted; fourthly, when failure of the GPS occurs, the recursive algorithm is started and the position information and course information are given. According to the vehicle-mounted integrated navigation method of resisting to failure of the GPS, the problem that error drifting of the vehicle-mounted low-cost gyroscope and the speed sensor is rapid is solved, position and course accuracy is improved obviously, and the vehicle-mounted integrated navigation method of resisting to failure of the GPS can be used for various vehicle-mounted navigation systems comprising GPSs, gyroscopes and speed sensors.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
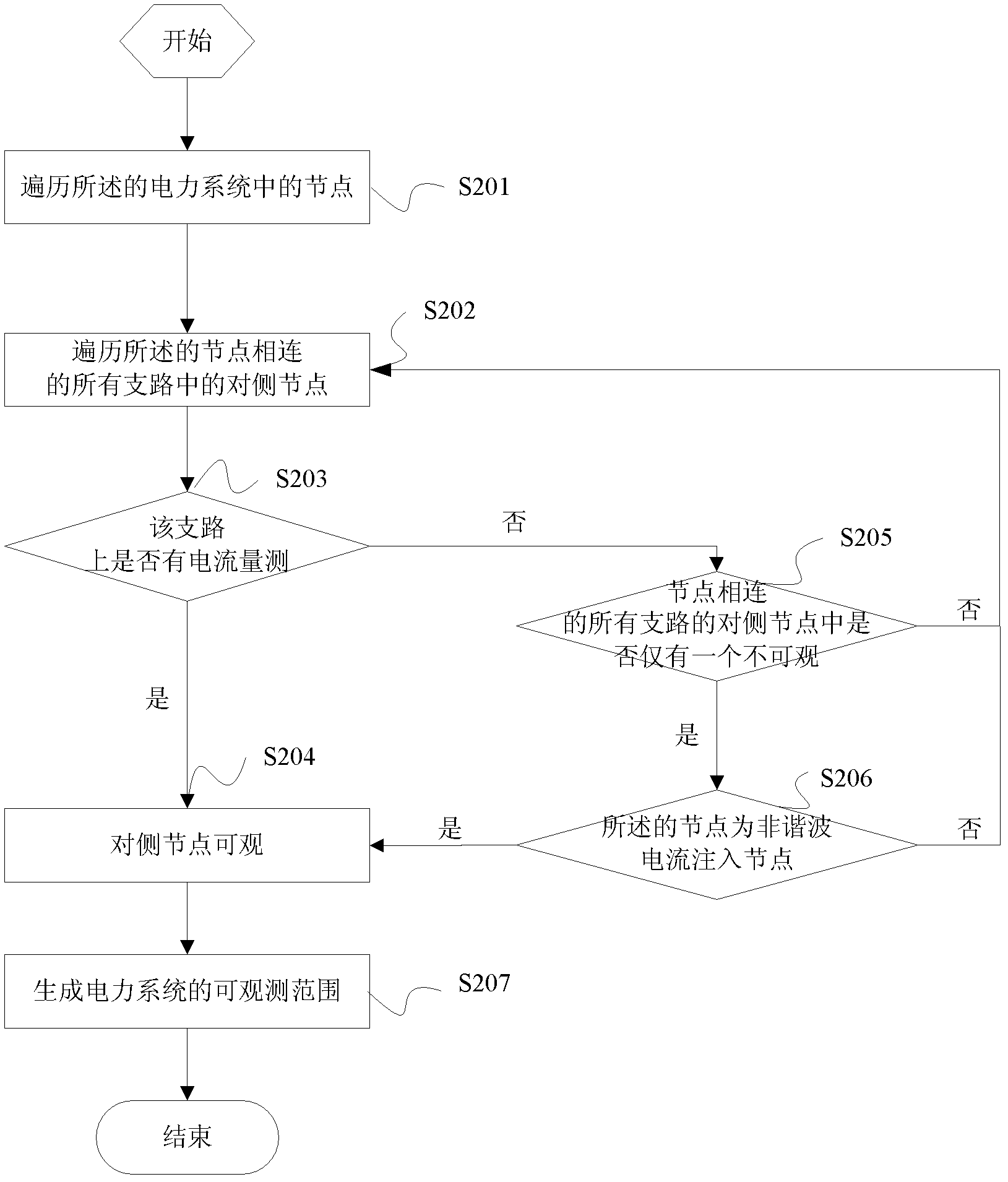
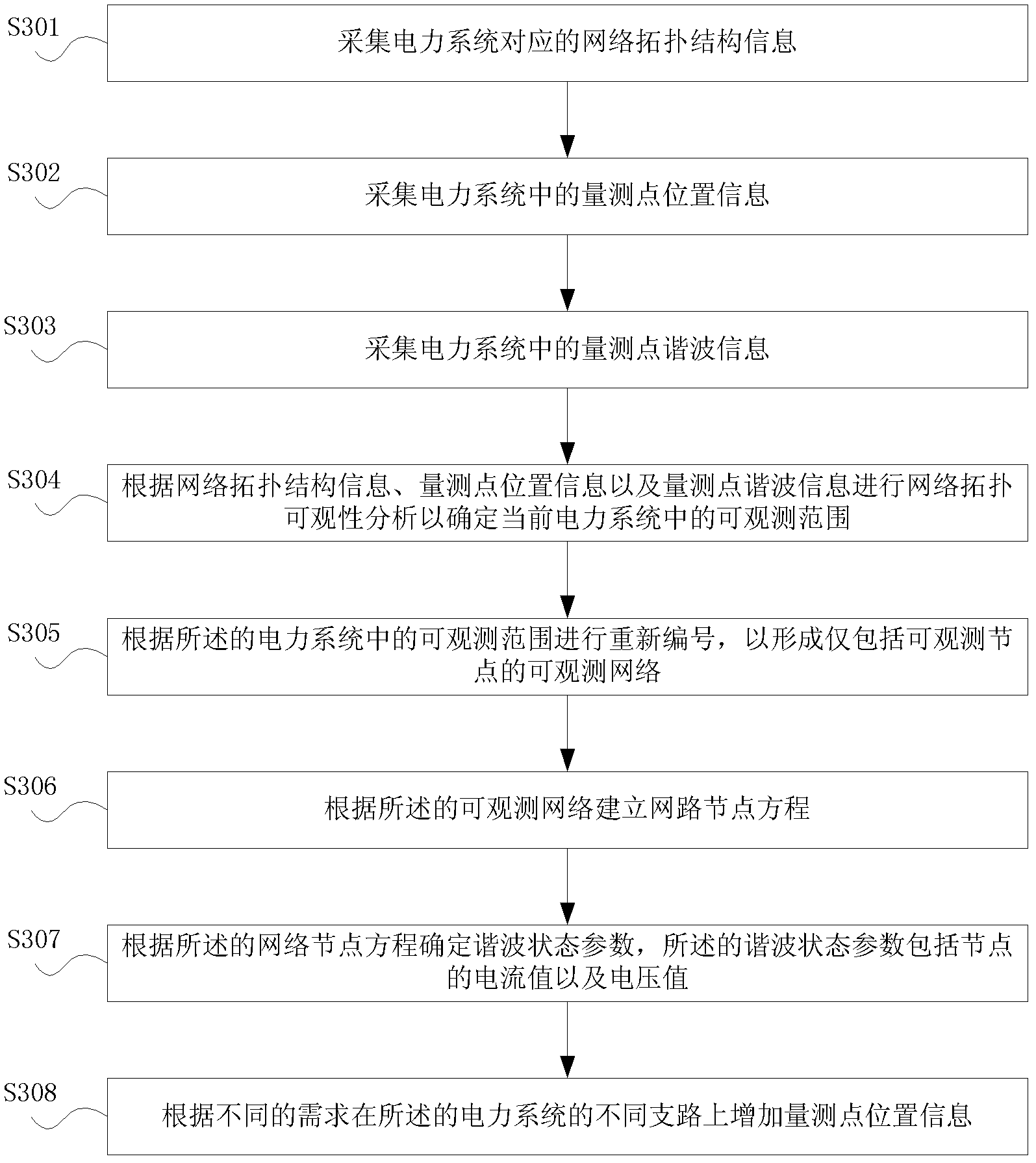
Method and device for estimating harmonic state of electric power system
ActiveCN103323688AIncrease the number ofSmall amount of calculationSpectral/fourier analysisElectrical testingUser needsMeasurement device
The invention provides a method and device for estimating the harmonic state of an electric power system. The method includes the steps of collecting network topology information corresponding to the electric power system, collecting measuring point position information in the electric power system, collecting measuring point harmonic information in the electric power system, making network topology observability analysis and determining the observability range in the current electric power system according to the network topology information, the measuring point position information and the measuring point harmonic information, and determining a harmonic state parameter corresponding to the current electric power system according to the observability range in the current electric power system. Suspicious harmonic injection nodes are led to an observability analytic logical judgment method, the whole network analysis is achieved by the adoption of a recursive algorithm, measuring point optimal allocation is achieved according to different user needs, and the problems that the algorithm is complex, the calculated quantity is large, and the fact that a measurement device has voltage and current measuring capacity at the same time is not considered in the prior art are solved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRICAL POWER RES INST
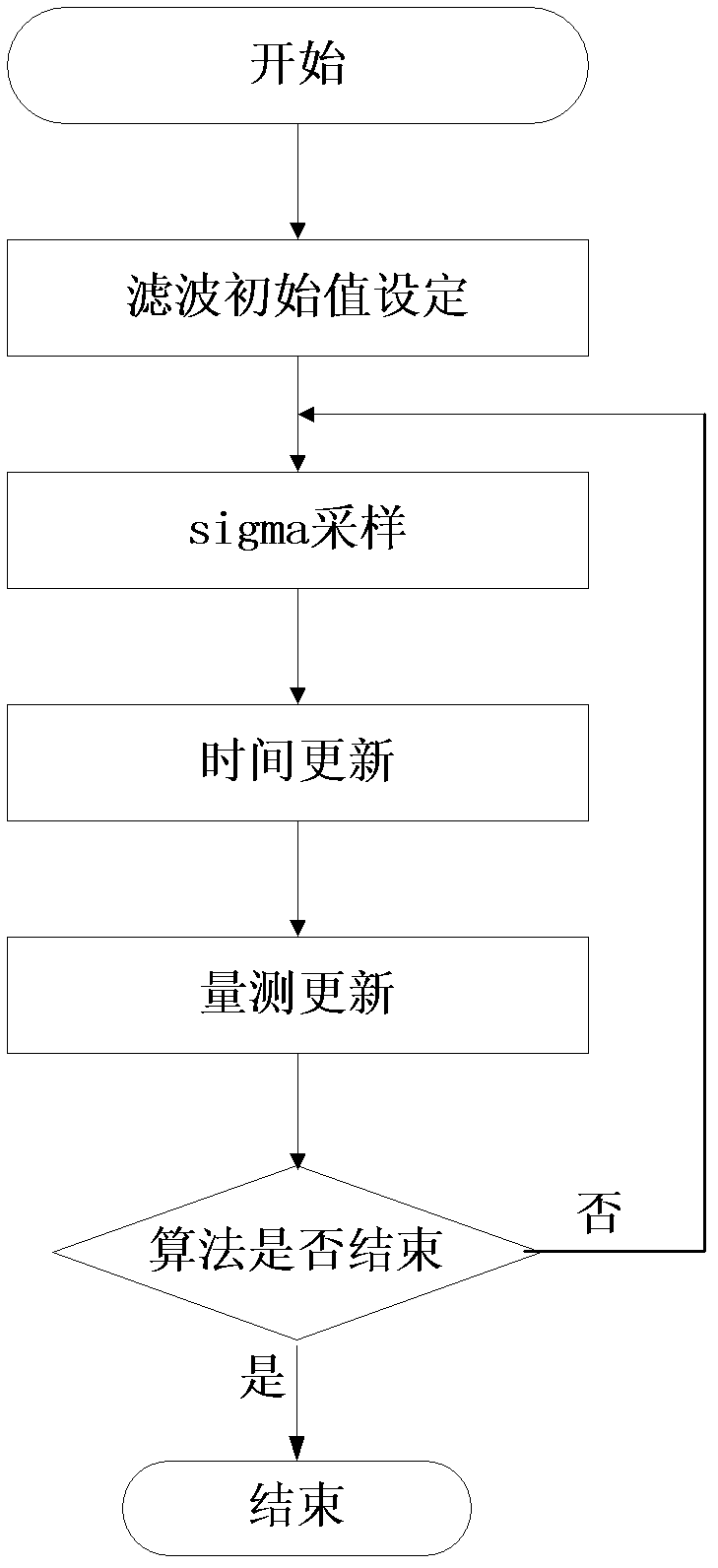
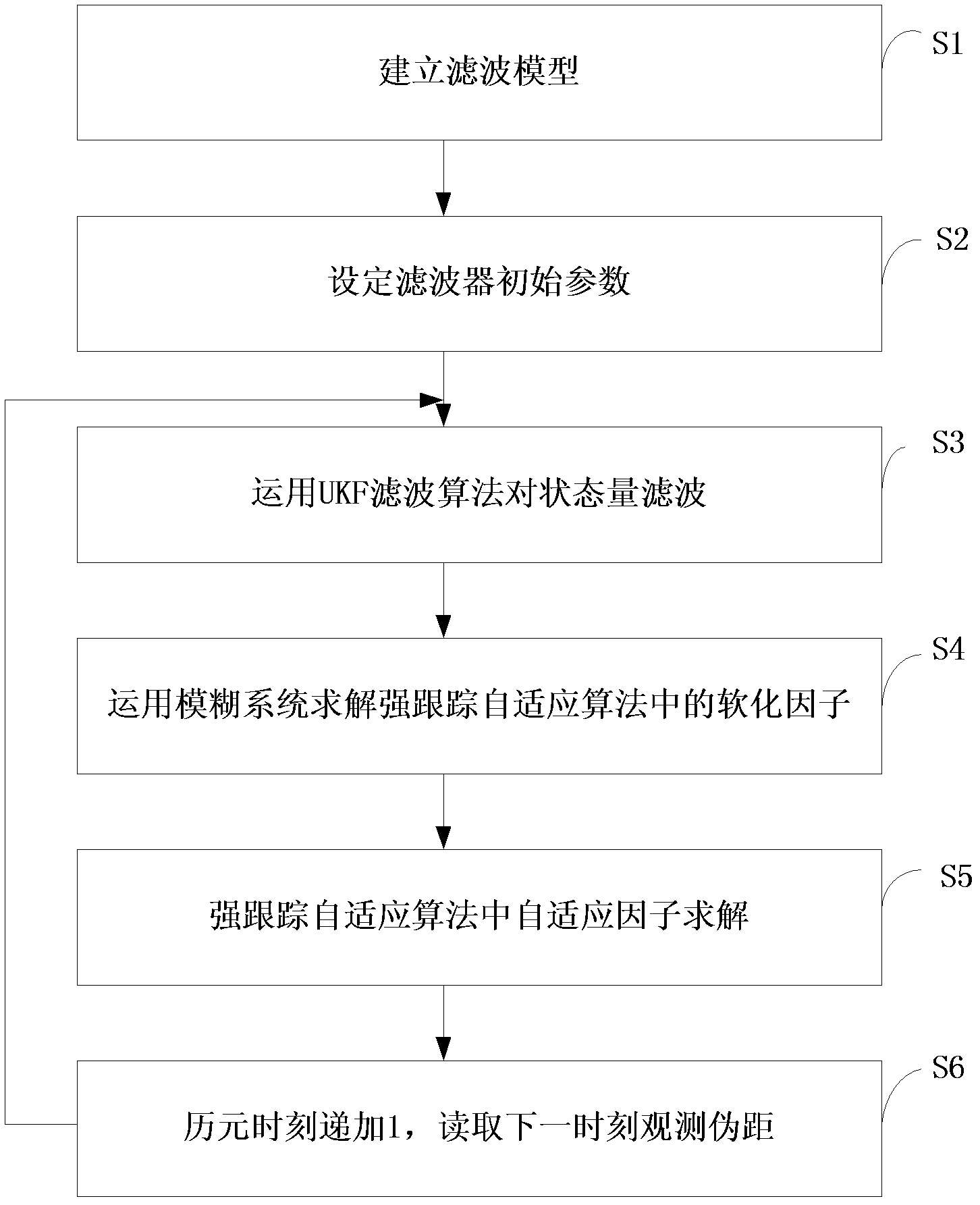
Self-adaption strong tracking unscented kalman filter (UKF) positioning filter algorithm based on fuzzy logic
InactiveCN102608631AReduce estimation errorHigh precisionSatellite radio beaconingFuzzy logic inferenceFilter algorithm
The invention discloses a self-adaption strong tracking unscented kalman filter (UKF) positioning filter algorithm based on fuzzy logic. The self-adaption strong tracking UKF positioning filter algorithm comprises the steps that: (1) a positioning filter model is built; (2) initial parameters of a filter are set; (3) the state quantity is subjected to filtering by adopting the UKF filter algorithm; (4) a fuzzy logic system is used for solving softening factors in the self-adaption tracking algorithm; (5) the self-adaption factors in the strong tracking self-adaption algorithm are solved; and (6) the epoch moment is increased by 1, the next moment observation is read, and the operation returns to the step (4) until the operation is completed. The strong tracking self-adaption algorithm in introduced on the basis of the UKF filter algorithm, in addition, a novel recursive algorithm is adopted in the strong tracking self-adaption algorithm for estimating the information covariance matrix, and the softening factors in the strong tracking algorithm are solved through a fuzzy logic reasoning system and are estimated in real time according to the work state of an epoch moment filter. The estimation is carried out in satellite navigation user receiver position estimation, and the positioning performance and the capability of carriers adapting to the dynamics can be greatly improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
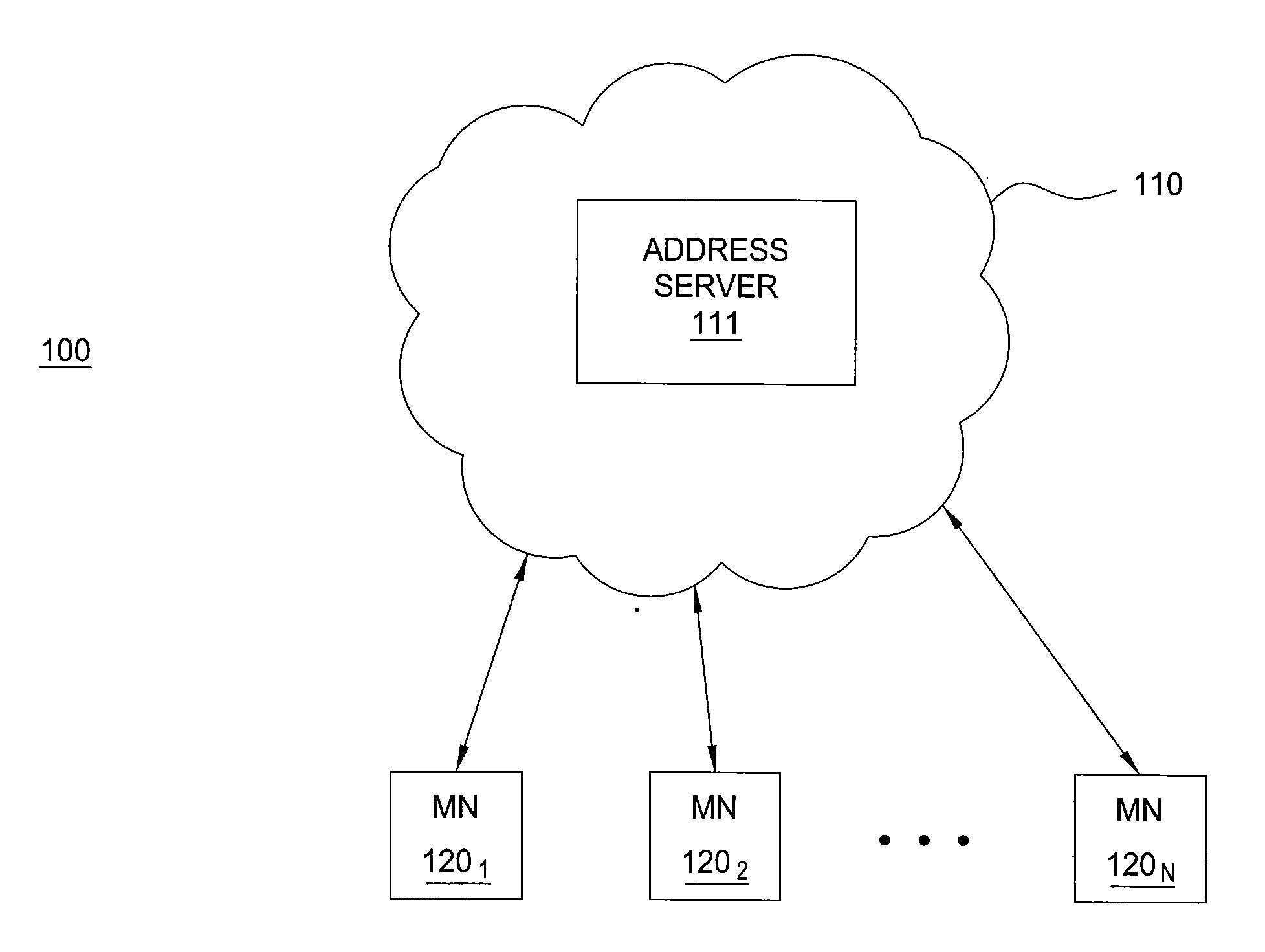
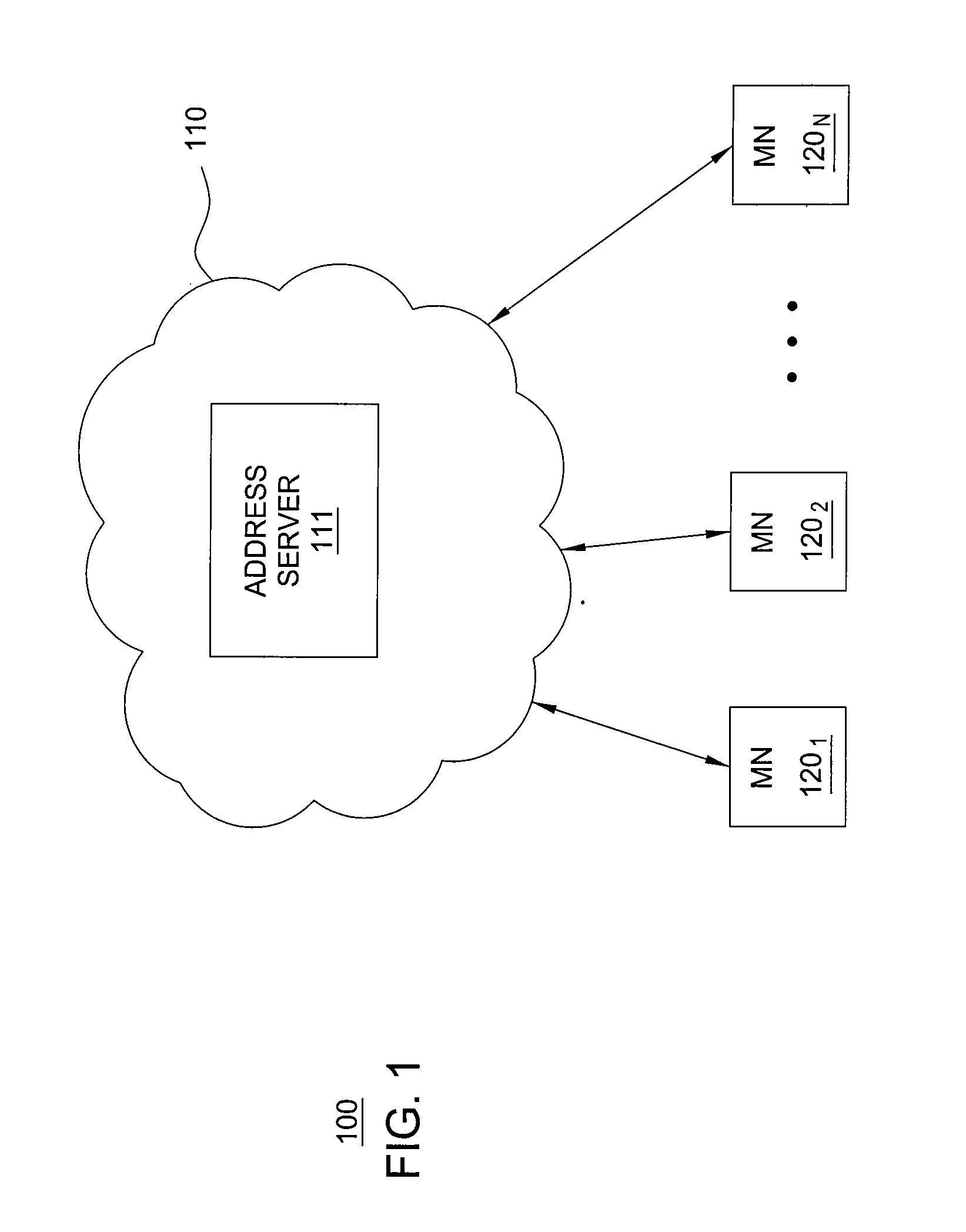
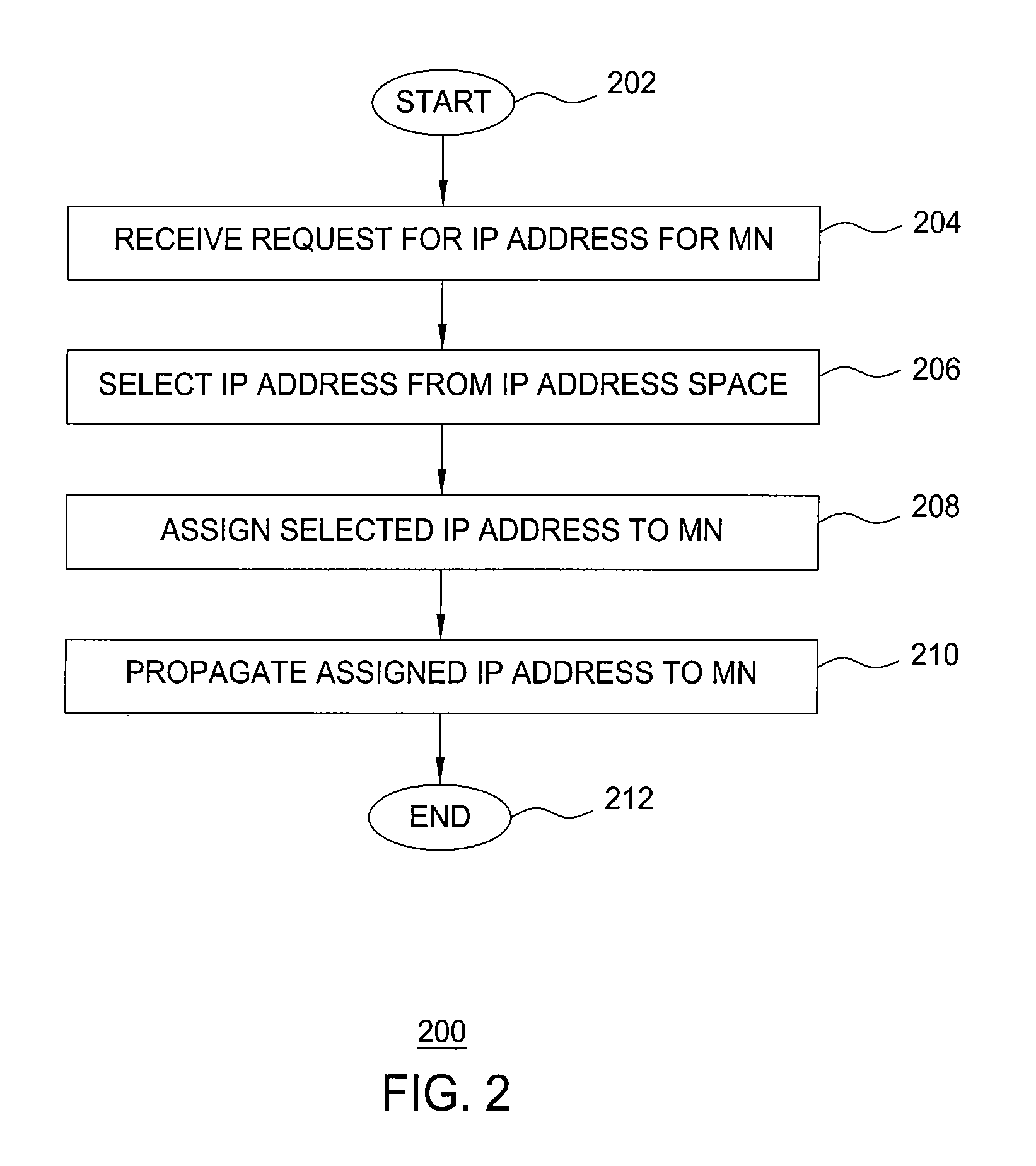
Method and apparatus for assigning IP addresses
The invention includes a method and apparatus for assigning an IP address to a mobile node (MN) from an IP address space represented using an address aggregation tree. A method includes receiving a request for an IP address for the MN, identifying each of a plurality of sub-tree gaps in the address aggregation tree, selecting one of the identified sub-tree gaps, and assigning an available IP address from the selected sub-tree gap to the MN. The sub-tree gaps of the address aggregation tree are identified using a recursive algorithm that traverses the address aggregation tree. The selected one of the sub-tree gaps is selected based on respective sizes of the identified sub-tree gaps. The assigned IP address is communicated to the MN for use by the MN in accessing various services.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
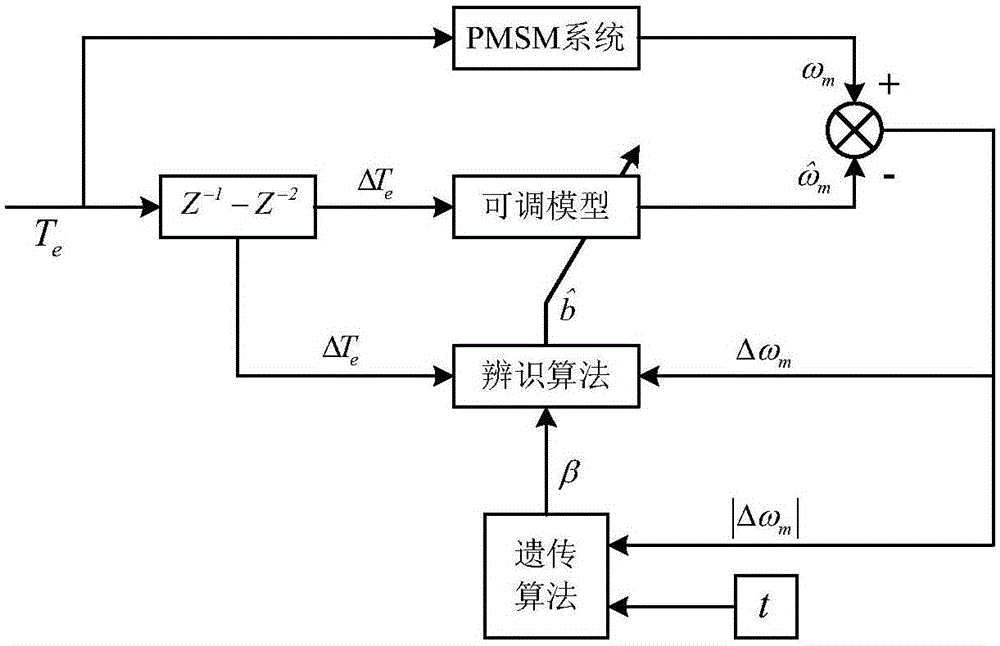
Servo system inertia identification method adopting genetic algorithm for optimization
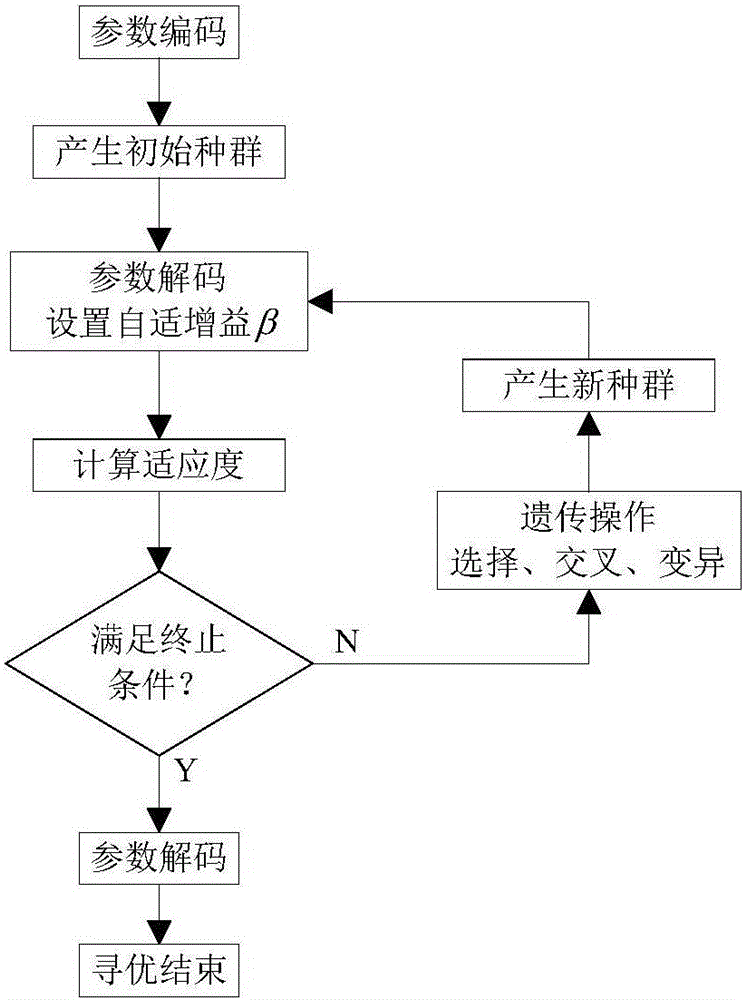
ActiveCN105915121ARealize online adjustmentEasy to identifyElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlRotary inertiaSelf adaptive
The invention discloses a servo system inertia identification method adopting a genetic algorithm for optimization. Based on a model reference self-adaption theory, the self-adaption rule of inertia identification is designed according to a Landau discrete time recursive algorithm. The global searching capability of the genetic algorithm is utilized, a model reference self-adaption system is used as a control object, an output difference between a motor practical angular speed and an estimated angular speed is used as a control error, the integration of the product of time and an error absolute value is used as an optimization target, the self-adaption gain [beta] in the inertia identification is dynamically adjusted, and the online optimization of control parameters is realized. According to the invention, both the higher convergence speed and the higher identification precision are realized in inertia identification, and the relatively high self-adaption capability to the change of rotary inertia is achieved.
Owner:无锡超通智能制造技术研究院有限公司
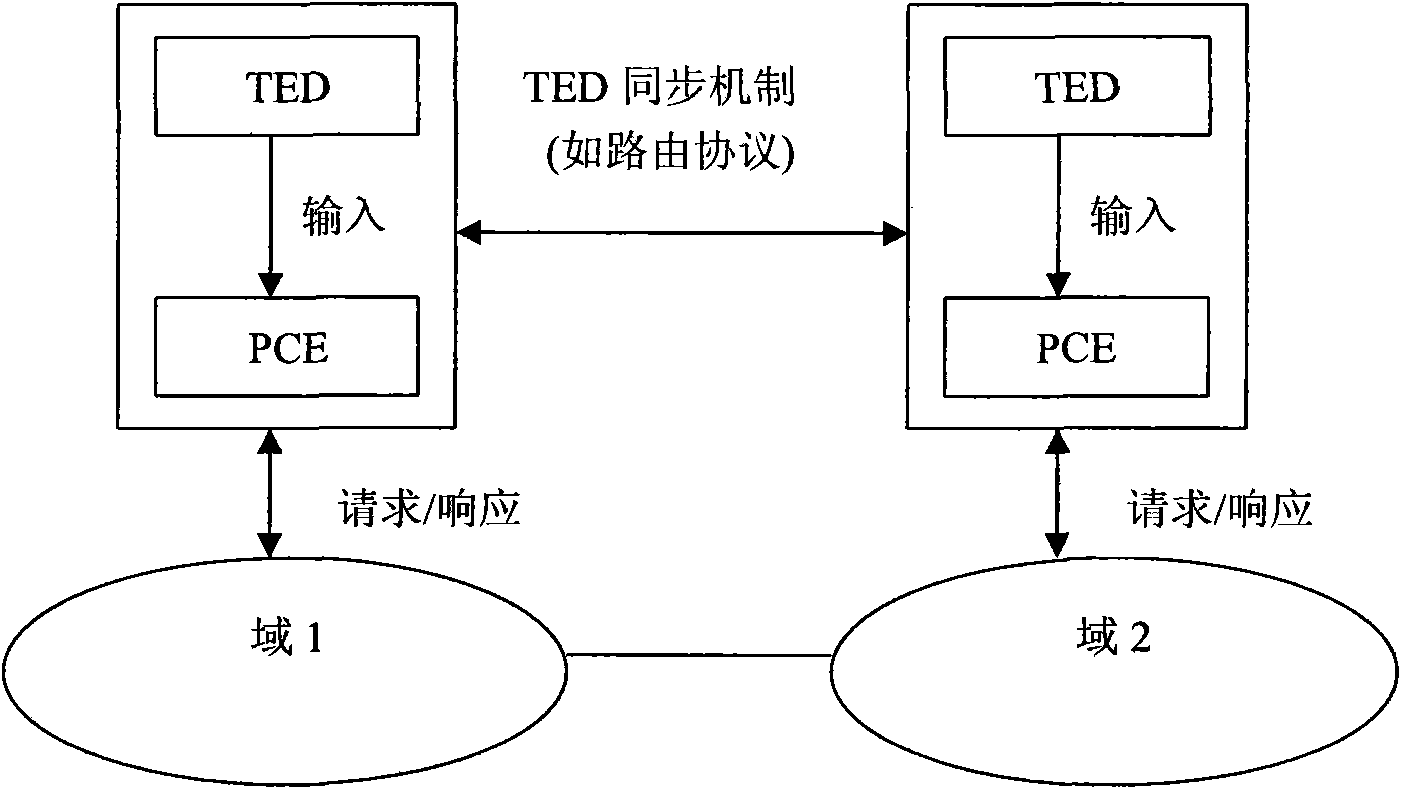
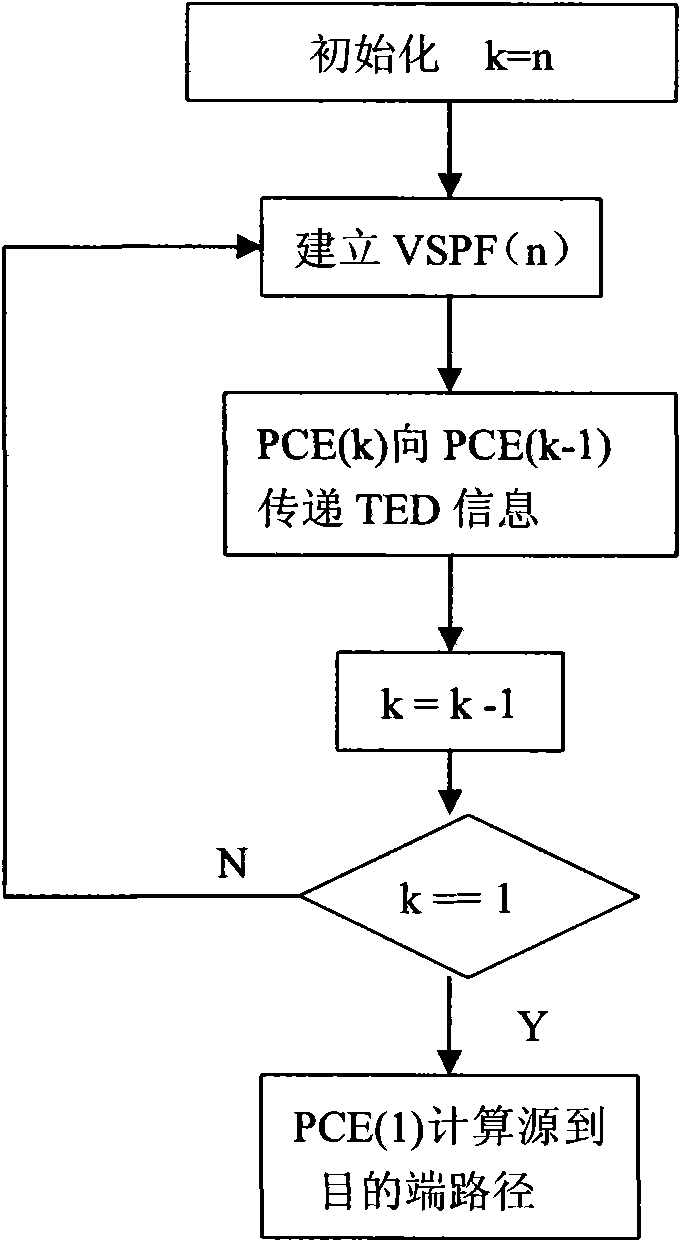
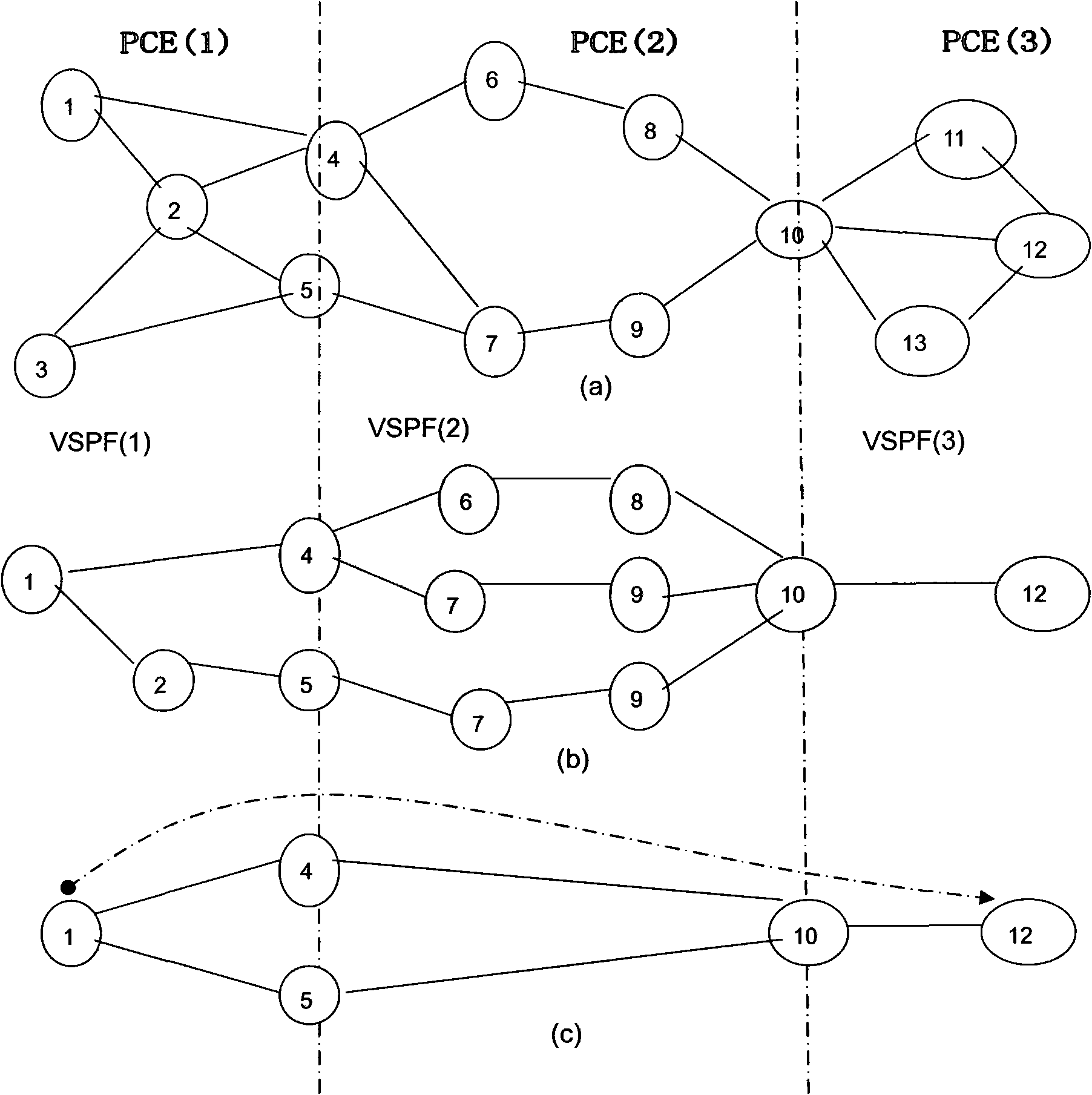
Optical internet cross-domain reliable route calculating method based on PCE backtracking recursion
InactiveCN101552934ACapable of topology visualizationReduce computational complexityMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksThe InternetDependability
The invention discloses an optical internet cross-domain reliable route creating method based on PCE backtracking recursion, applied to calculating cross-domain reliable path using path calculation element (PCE), including: improving PCE backtracking recursion algorithm through setting threshold and adding protection path to certain domains; and creating a virtual path tree meeting reliability constraint in a group of given cascaded domains. Existing reliable constraint path usually calculates the most reliable path from source end to destination end, and then adds a protection path to certain domains so as to enhance end-to-end path reliability, thereby meeting reliability requirement. The invention determines whether creating protection path according to reliability threshold while creating virtual path tree meeting reliability constraint through improving PCE backtracking recursion algorithm, thereafter, source PCE selects a cross-domain path meeting the reliability restriction and with the minimum cost.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
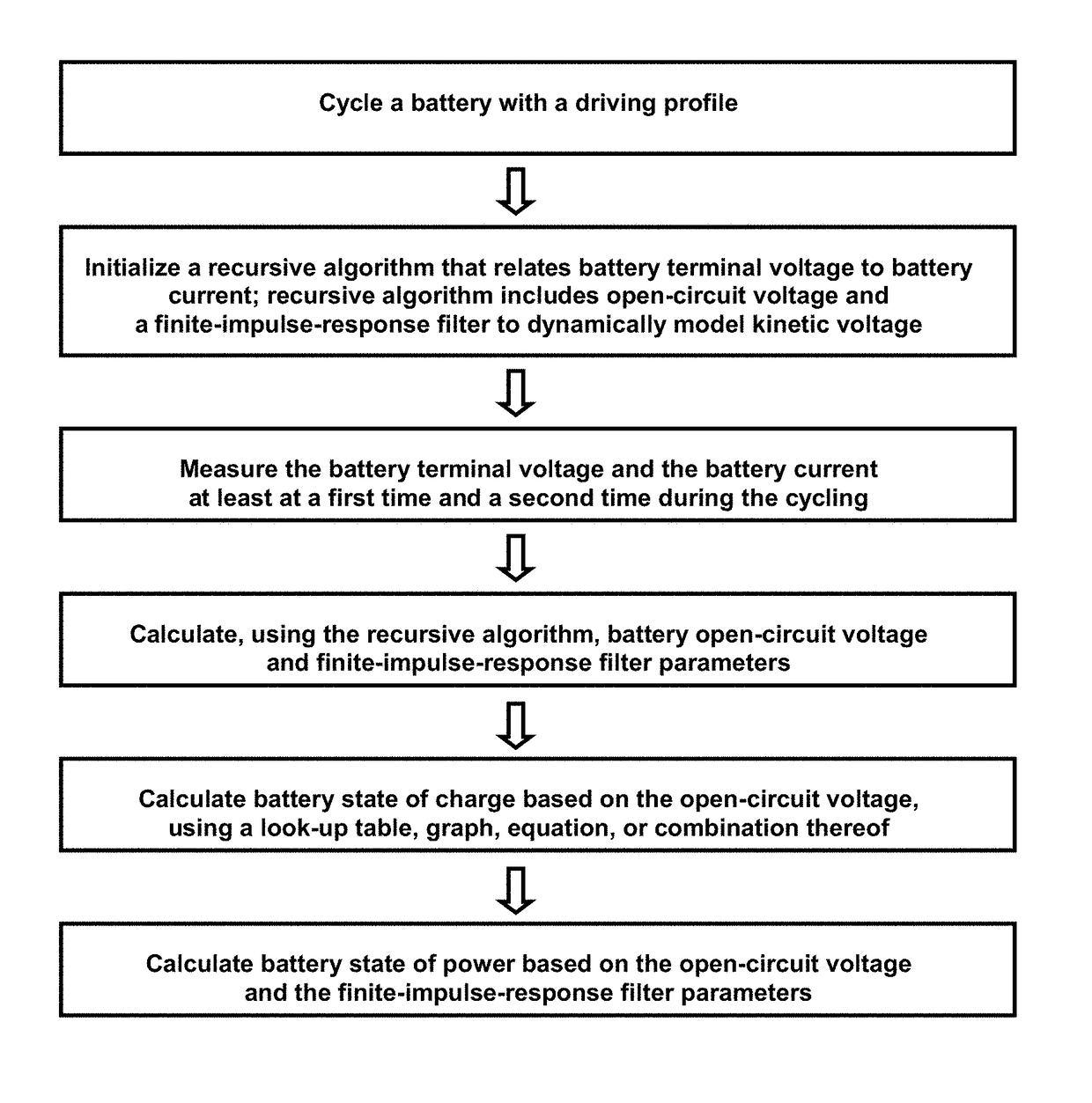
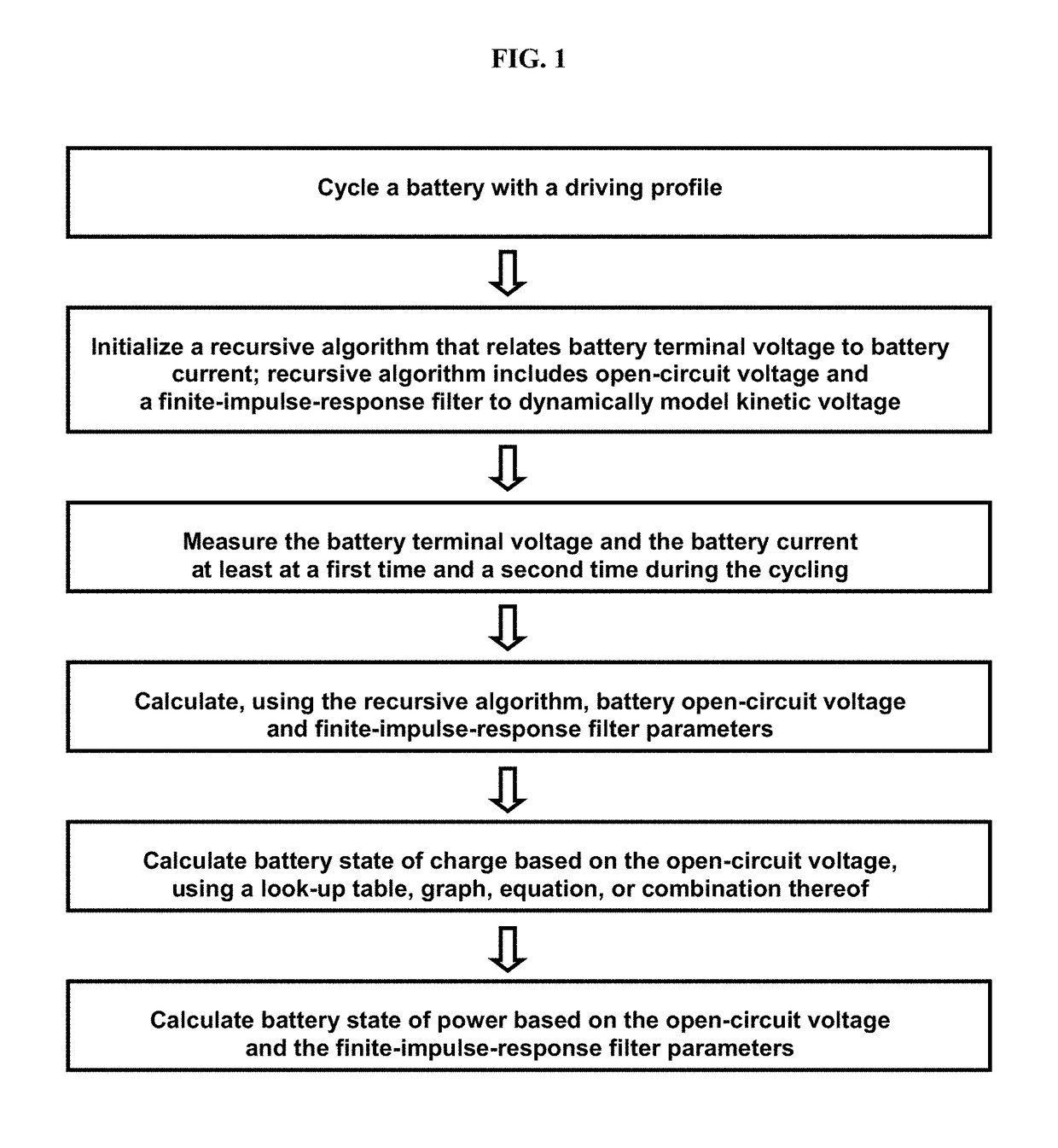
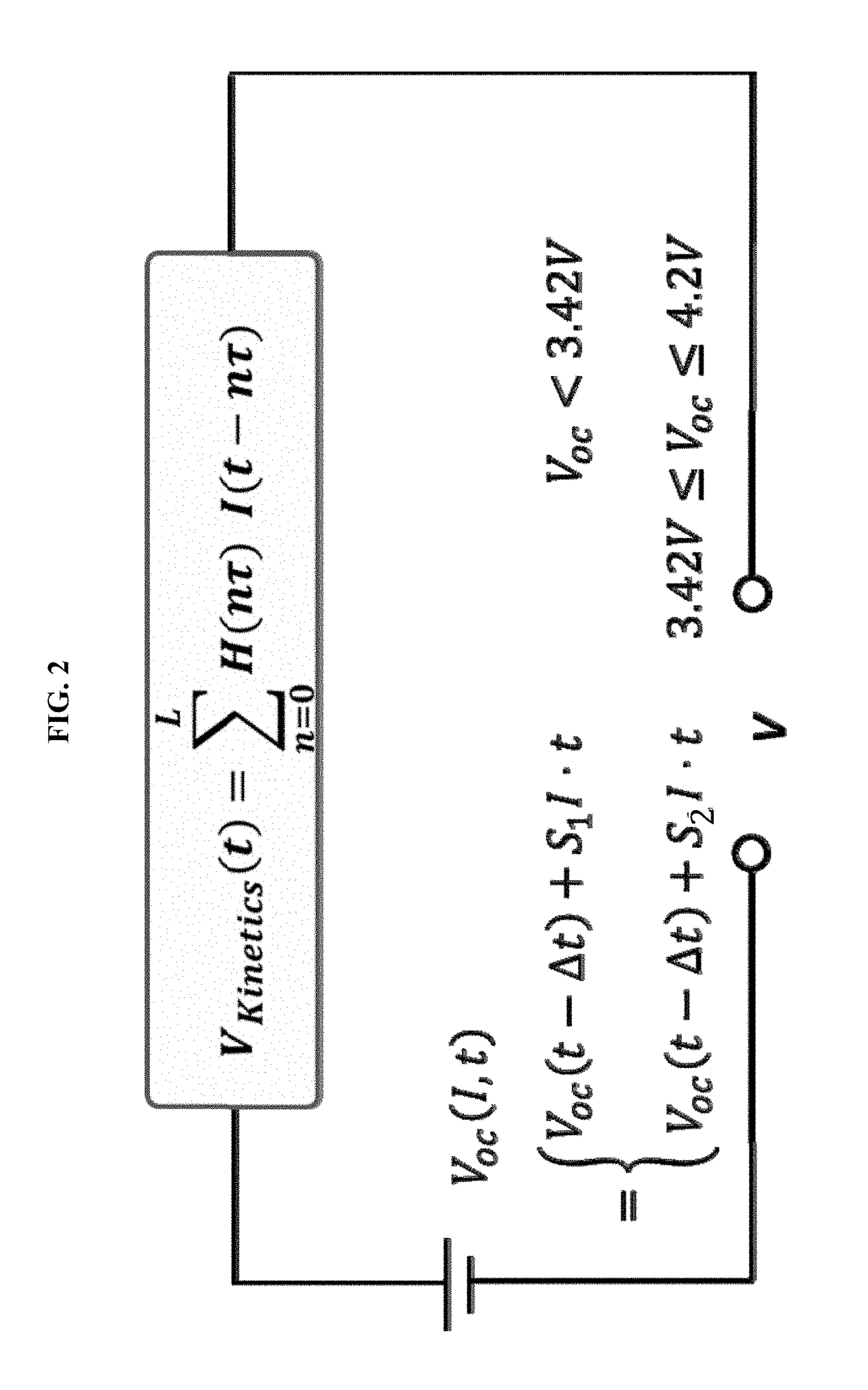
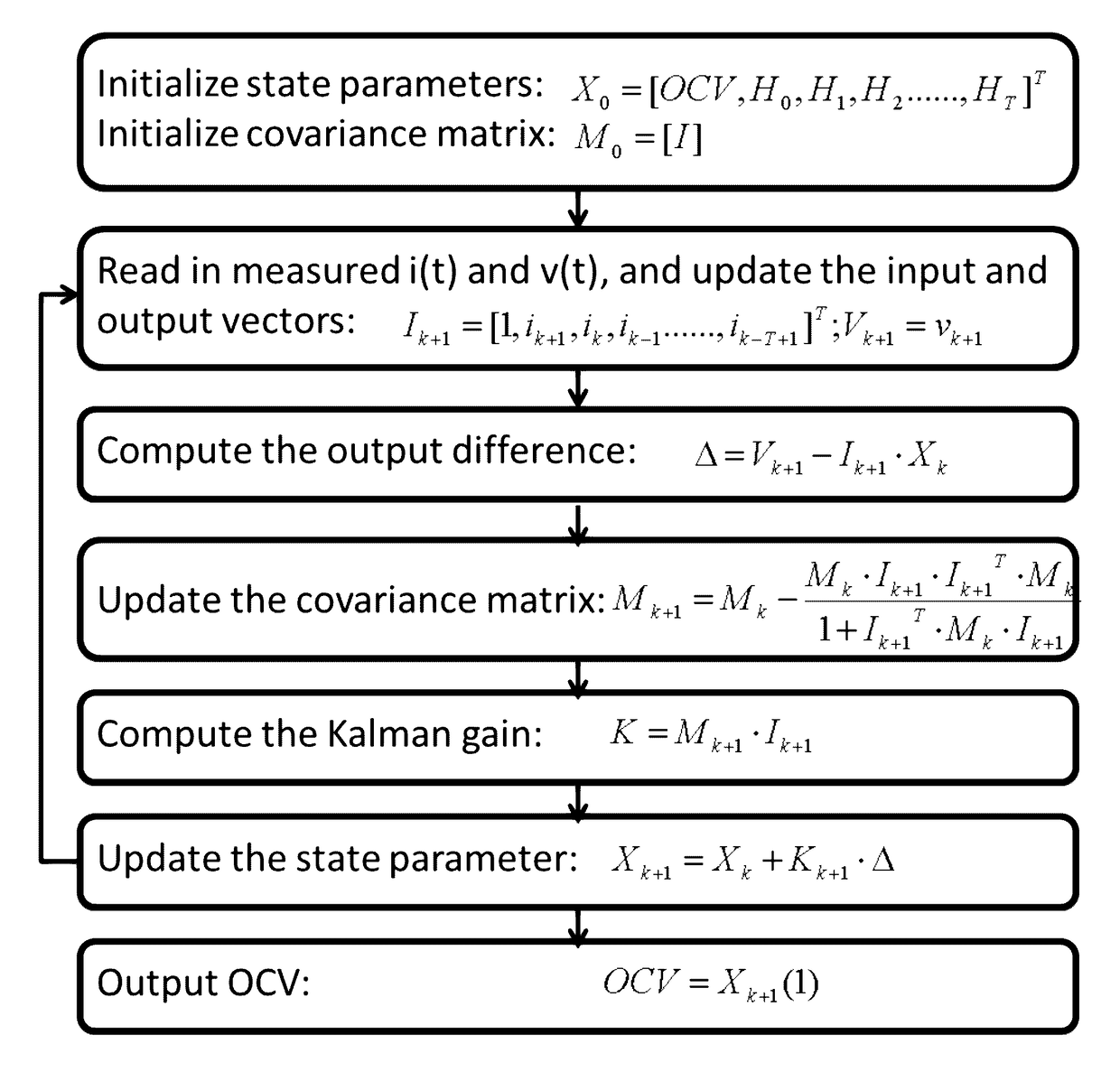
Methods for on-line, high-accuracy estimation of battery state of power
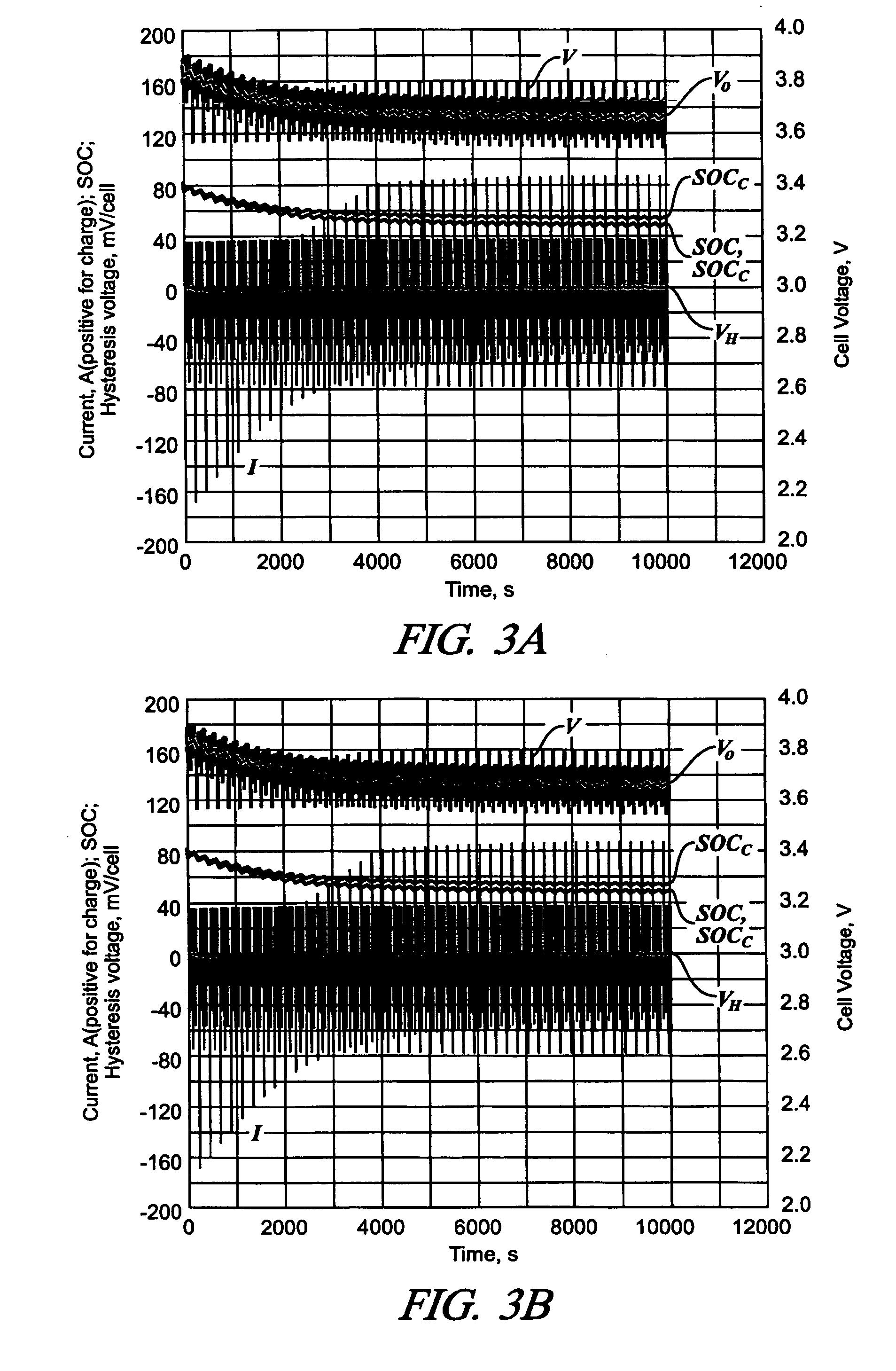
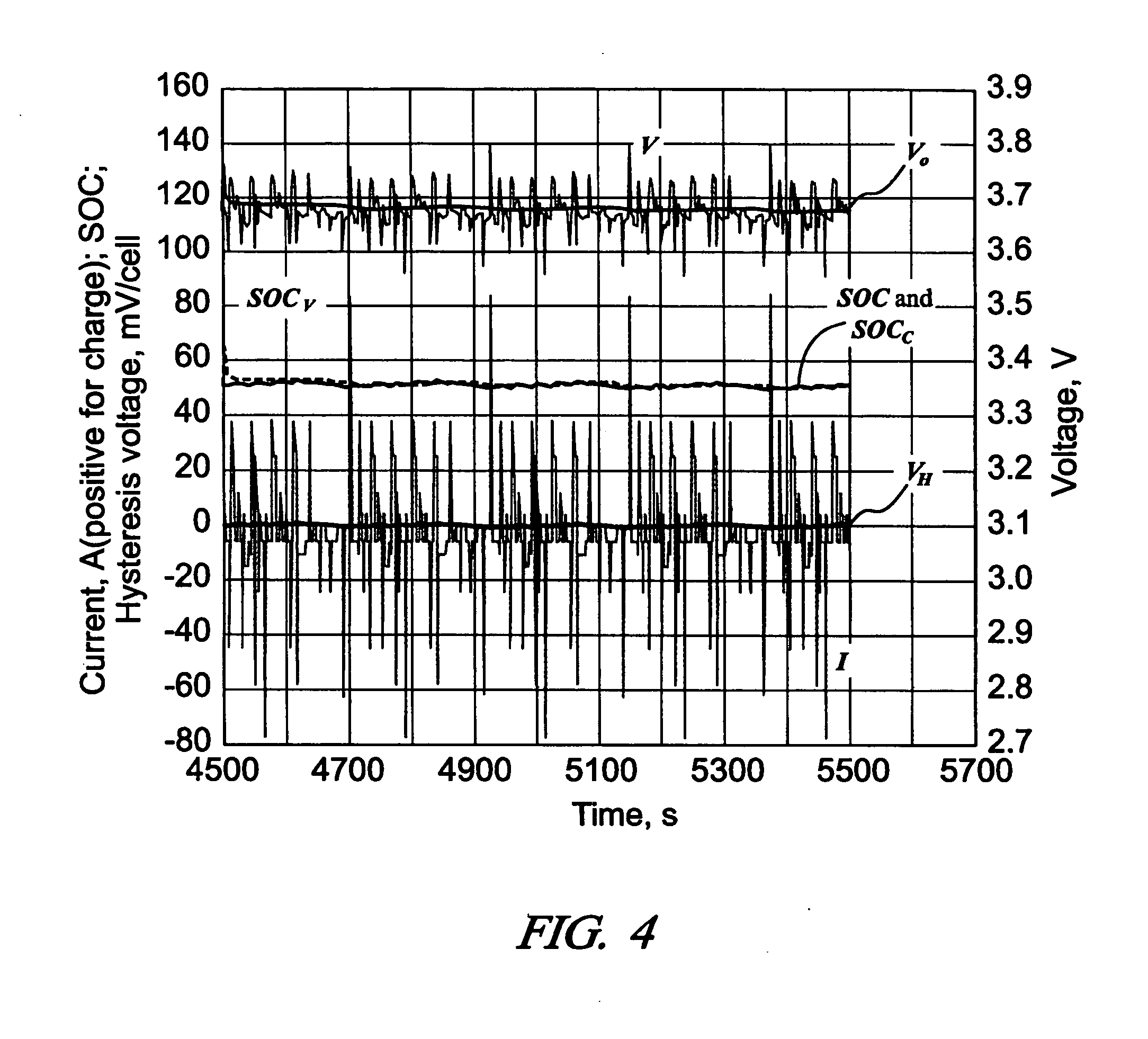
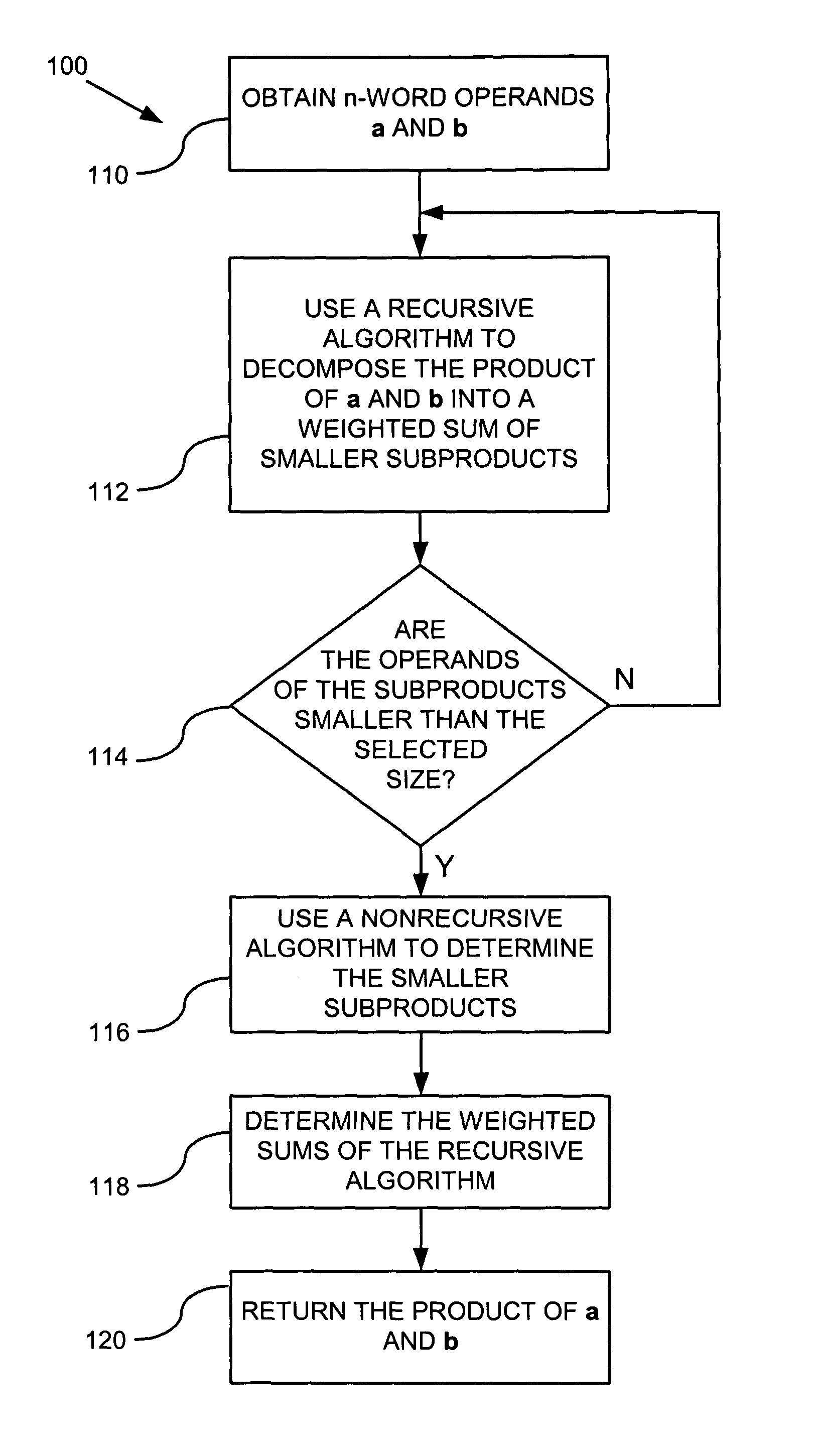
Some variations provide a method for real-time estimation of state of charge and state of power of a battery, comprising: (a) cycling a battery with a driving profile; (b) utilizing a recursive algorithm that relates battery terminal voltage to battery current, wherein the algorithm includes open-circuit voltage and a finite-impulse-response filter to dynamically model kinetic voltage; measuring the battery terminal voltage and the battery current at least at a first time and a second time during cycling; calculating battery open-circuit voltage and finite-impulse-response filter parameters; calculating battery state of charge based on the open-circuit voltage; and calculating battery state of power based on the open-circuit voltage and the finite-impulse-response filter parameters. An extended Kalman filtering technique is incorporated for real-time updating of FIR model parameters. Only a single FIR filter is necessary, making these methods applicable for battery-powered systems with limited computing and storage capabilities.
Owner:HRL LAB
Methods and apparatus for dynamic estimation of battery open-circuit voltage
ActiveUS9658291B1Improve stabilityElectrical testingCells structural combinationPower capabilityState of health
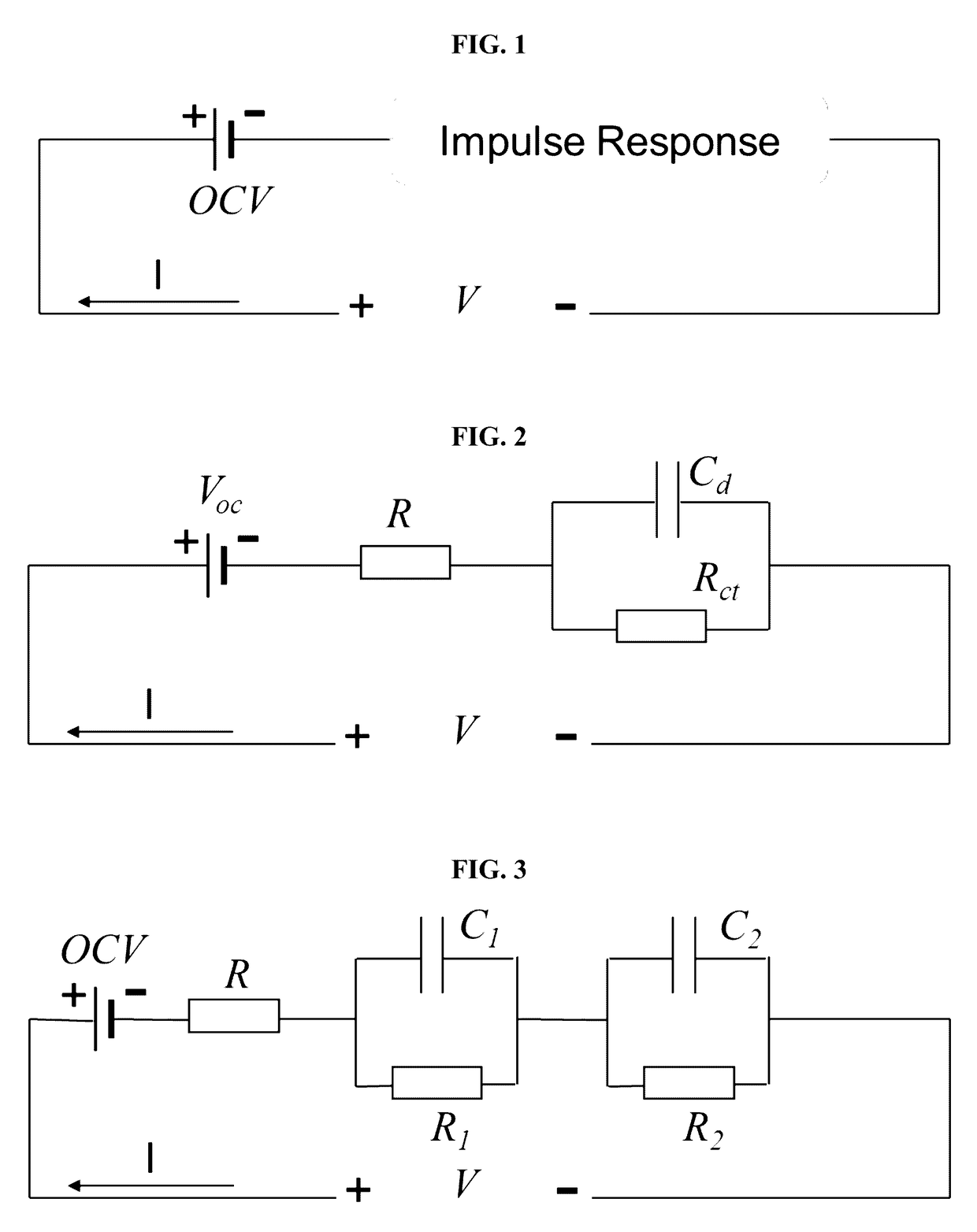
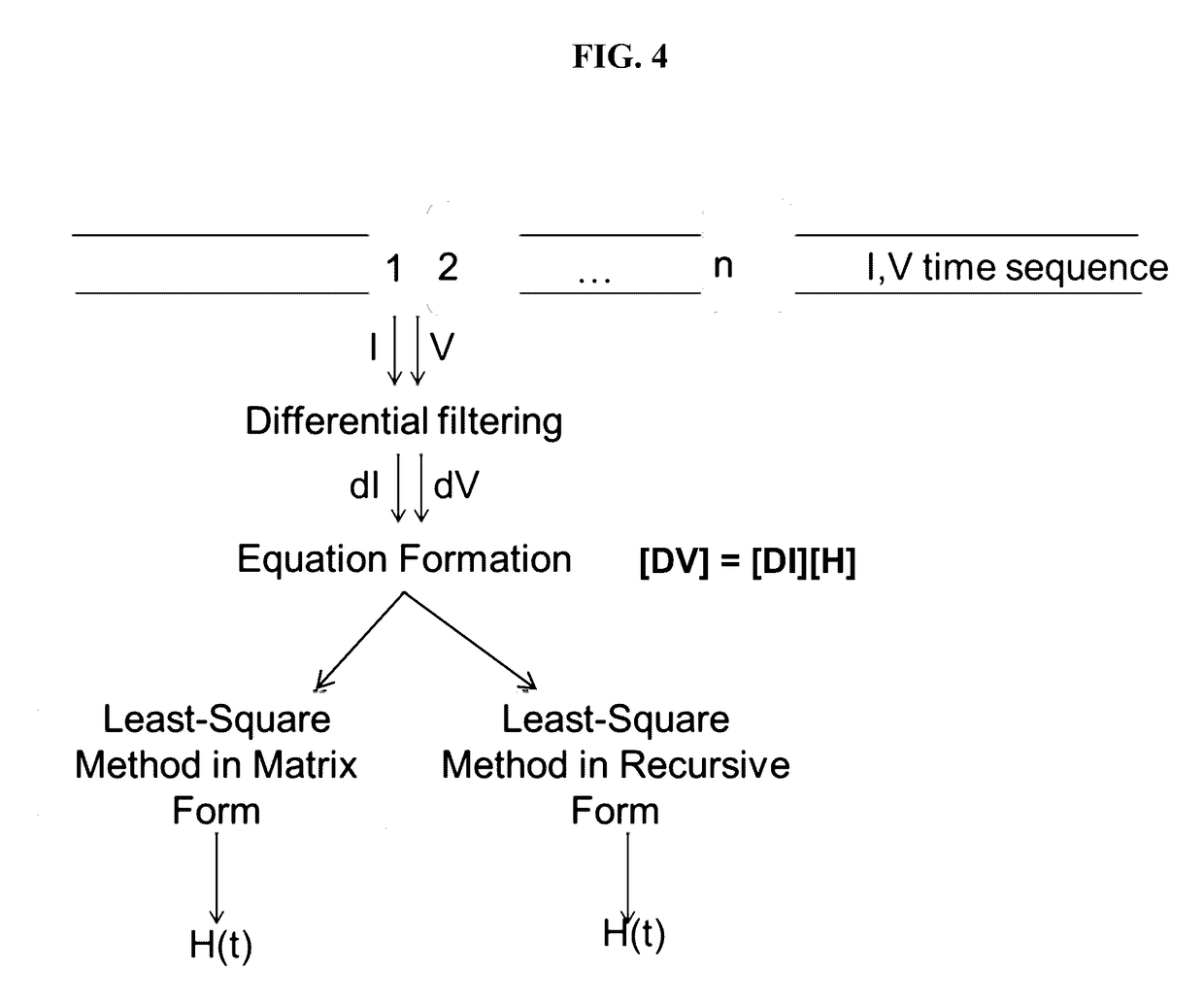
This invention provides methods for dynamic estimation of the open-circuit voltage of a battery. In some embodiments, an impulse response is calculated using a matrix-based algorithm or a recursive algorithm. Then, a current response is calculated by convolving the impulse response with the measured current. The open-circuit voltage of the battery is derived by subtracting the current response from the measured voltage. Using the principles disclosed to estimate OCV, a lithium-ion battery may be managed with a battery-state estimator that allows accurate and timely estimation of the state of charge, the charge and the discharge power capabilities, and the state of health of the battery. These methods are able to accept various exciting signals, are stable and robust against noises, even when diffusion is a limiting kinetic factor in the battery.
Owner:HRL LAB
Map matching method based on conditional random fields and low-sampling-frequency floating car data
ActiveCN105203116AHigh precisionReduce computational complexityInstruments for road network navigationConditional random fieldComputation complexity
The invention discloses a map matching method based on conditional random fields and low-sampling-frequency floating car data. The map matching method includes the steps that according to the low-sampling-frequency floating car data, on the basis of a road network model, a candidate projection point set possibly matched with GPS observing points and the observing probability of the candidate projection points in the set are firstly calculated, and then a candidate route set of the adjacent GPS observing points and the transmission probability between every two adjacent candidate projection points are calculated; according to the candidate projection points and candidate routes, in a sliding window, based on a condition random field model, the optimal matched projection points of the observing points are selected through a front-and-back-direction recursive algorithm. According to the map matching method, under the condition of the low sampling frequency, the topological structure of a road network and related information between the GPS observing points are both considered so that the calculation complexity can be low, and map matching accuracy is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
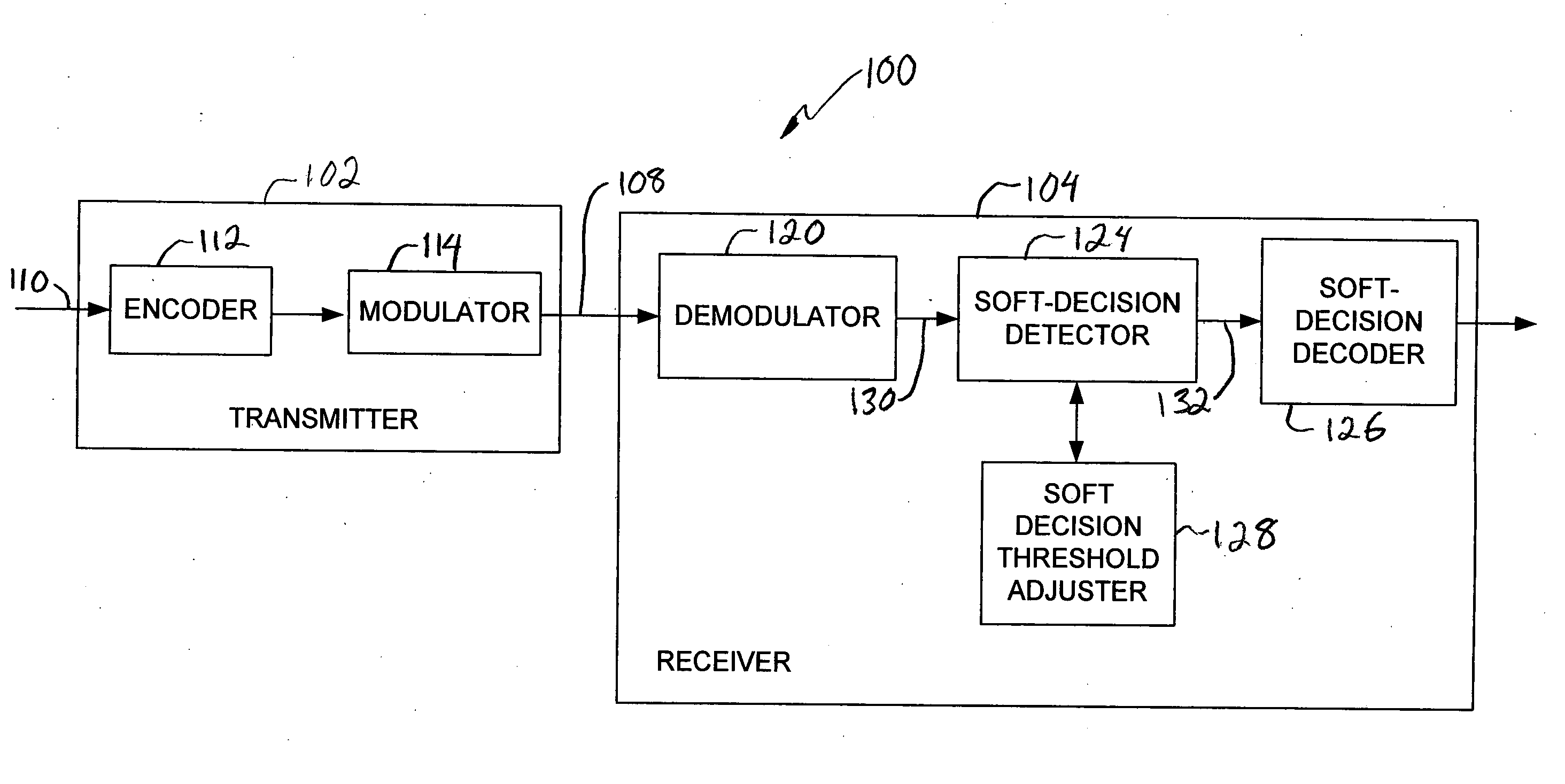
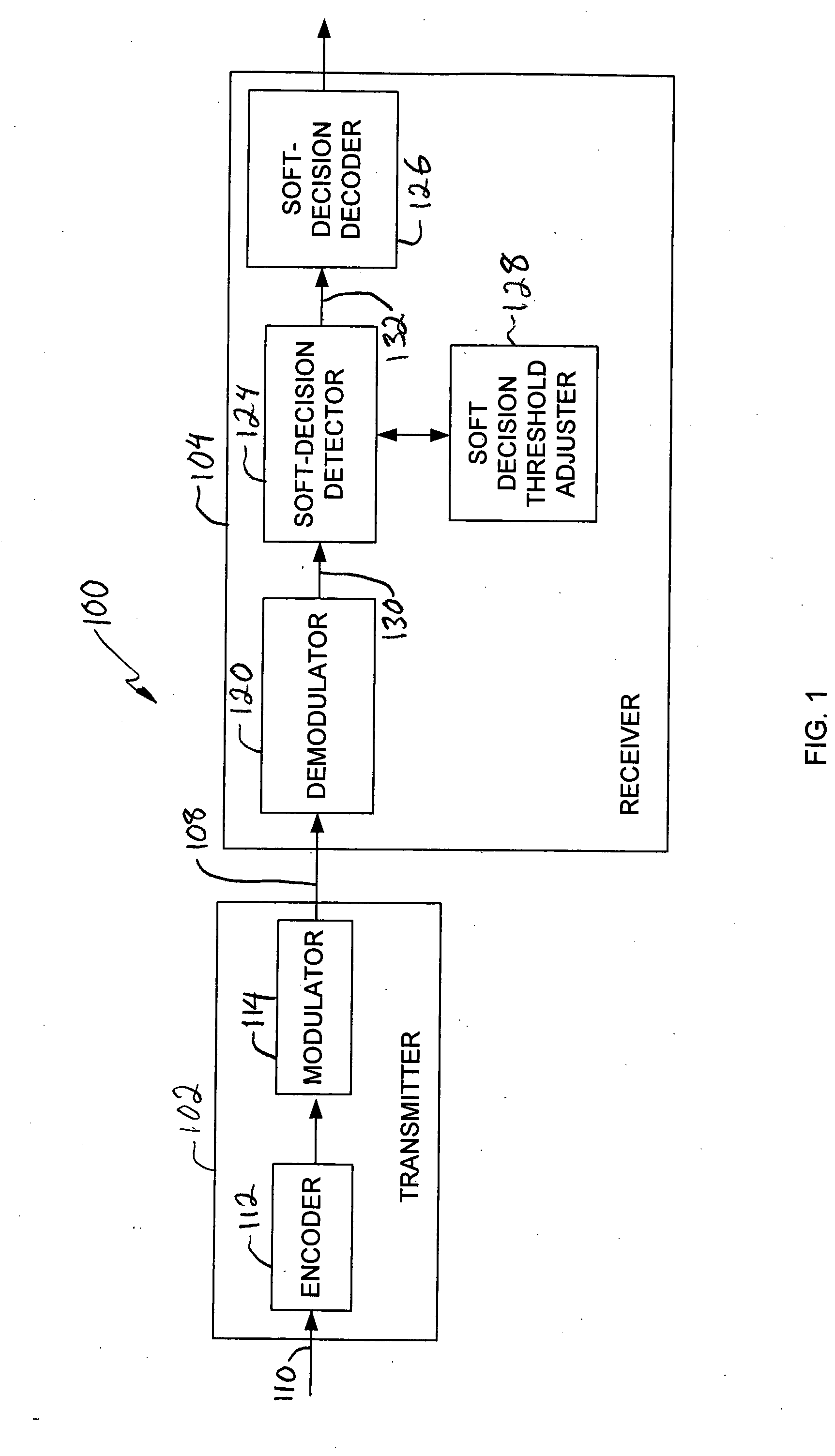
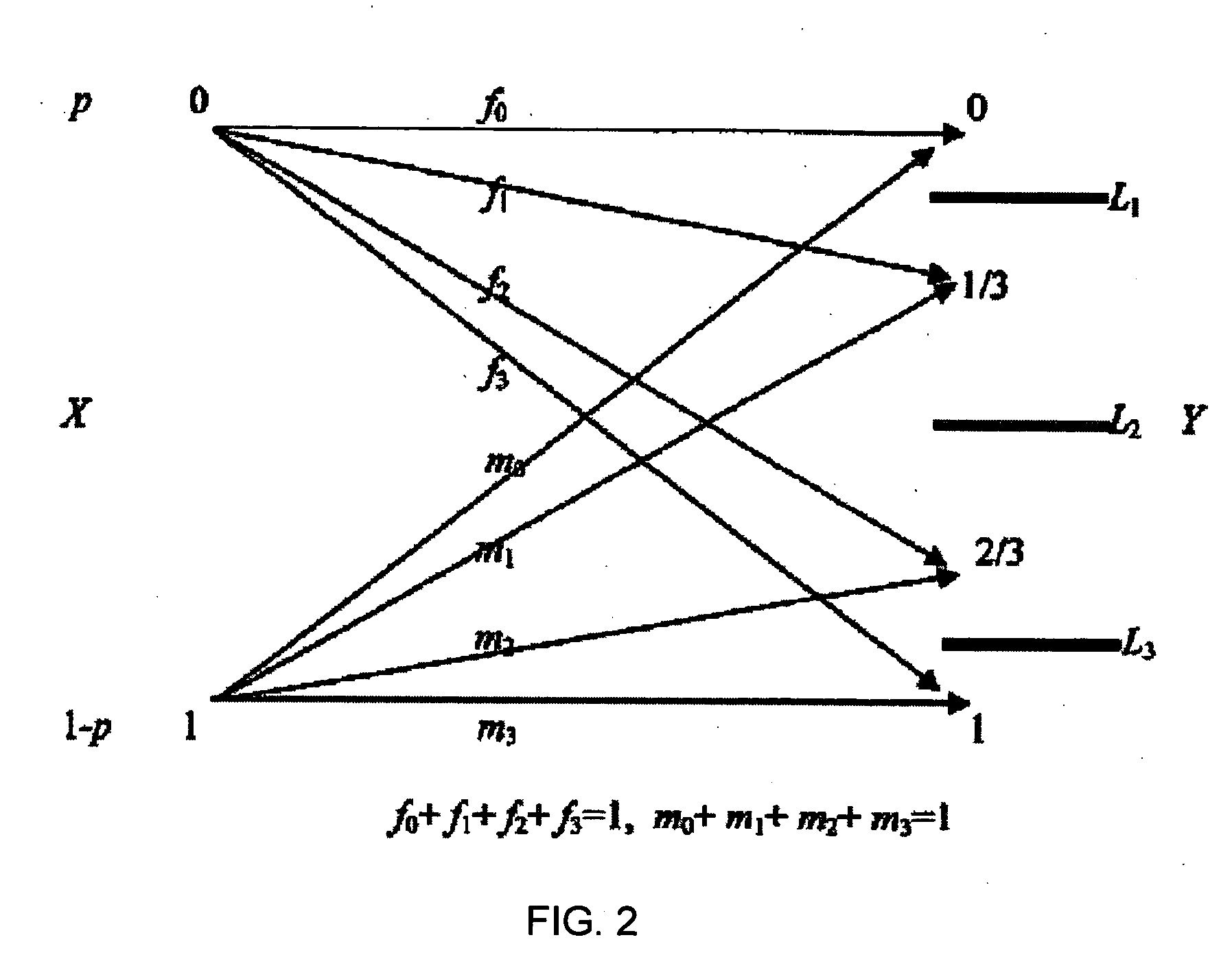
System and method for adjusting soft decision thresholds in a soft-decision error correction system
InactiveUS20050154955A1Error preventionTransmission systemsForward error correctionDecision threshold
The soft decision thresholds in a soft decision forward error correction (FEC) system may be adjusted based on mutual information of a detected signal. In one embodiment, a recursive algorithm may be used to optimize threshold values by maximizing the mutual information. In another embodiment, an adaptive scheme may be used to optimize threshold values based on a pre-knowledge of the noise in the channel. In a further embodiment, an adaptive scheme may be used to optimize threshold values by without pre-knowledge of the noise in the channel.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS SUBSEA COMM LLC
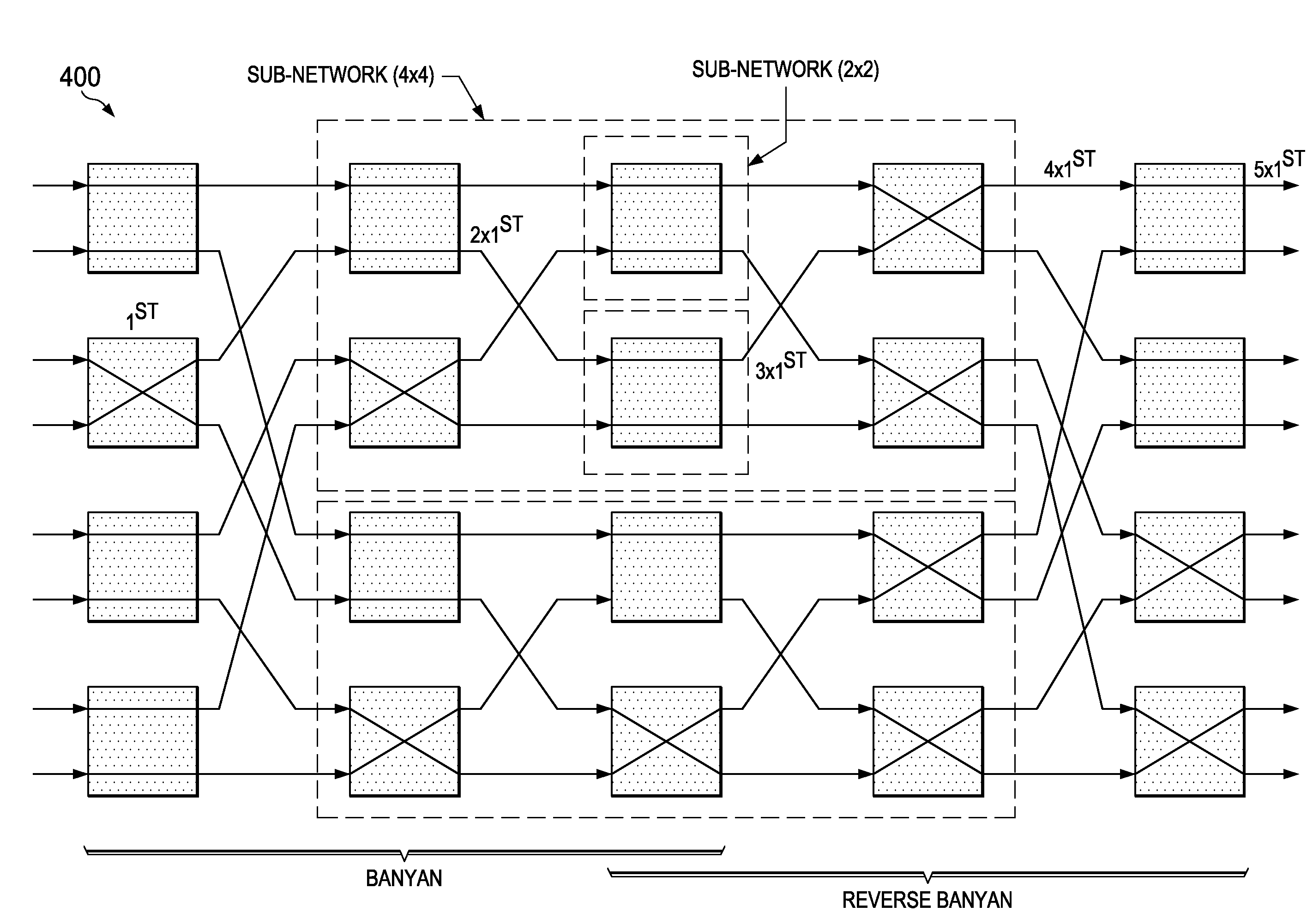
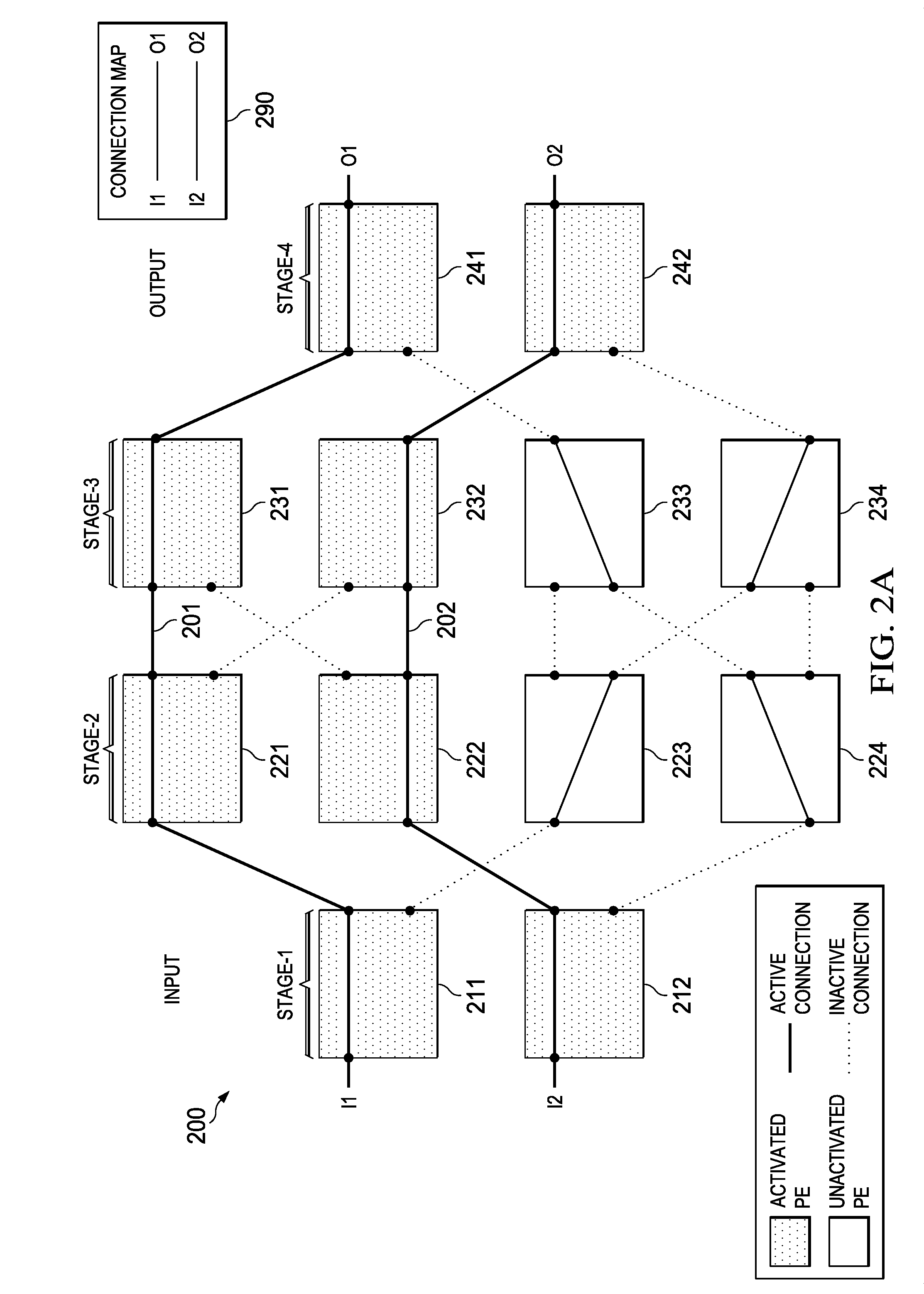
Method for Crosstalk and Power Optimization in Silicon Photonic Based Switch Matrices
InactiveUS20140328154A1Avoid spreadingMultiplex system selection arrangementsFrequency-division multiplex detailsPhotonicsSilicon
Crosstalk can be suppressed in photonic switching fabrics by activating unused photonic elements in a manner that manipulates the inactive connections and inhibits the propagation of cross-talk over the switching fabric. For example, unused photonic elements can be set to a cross or bar configuration to block first and second order crosstalk from propagating to the output ports, thereby reducing noise in the output signals. All of the unused elements can be activated in order to maximize crosstalk suppression. Alternatively, fewer than all of the unused elements may be activated to achieve a balance between crosstalk suppression and power conservation. Photonic switch architectures can be configured to use pre-determined cross-talk suppression maps (e.g., patterns of activated unused cells) for the various switching configurations, which may be computed using a recursive algorithm.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
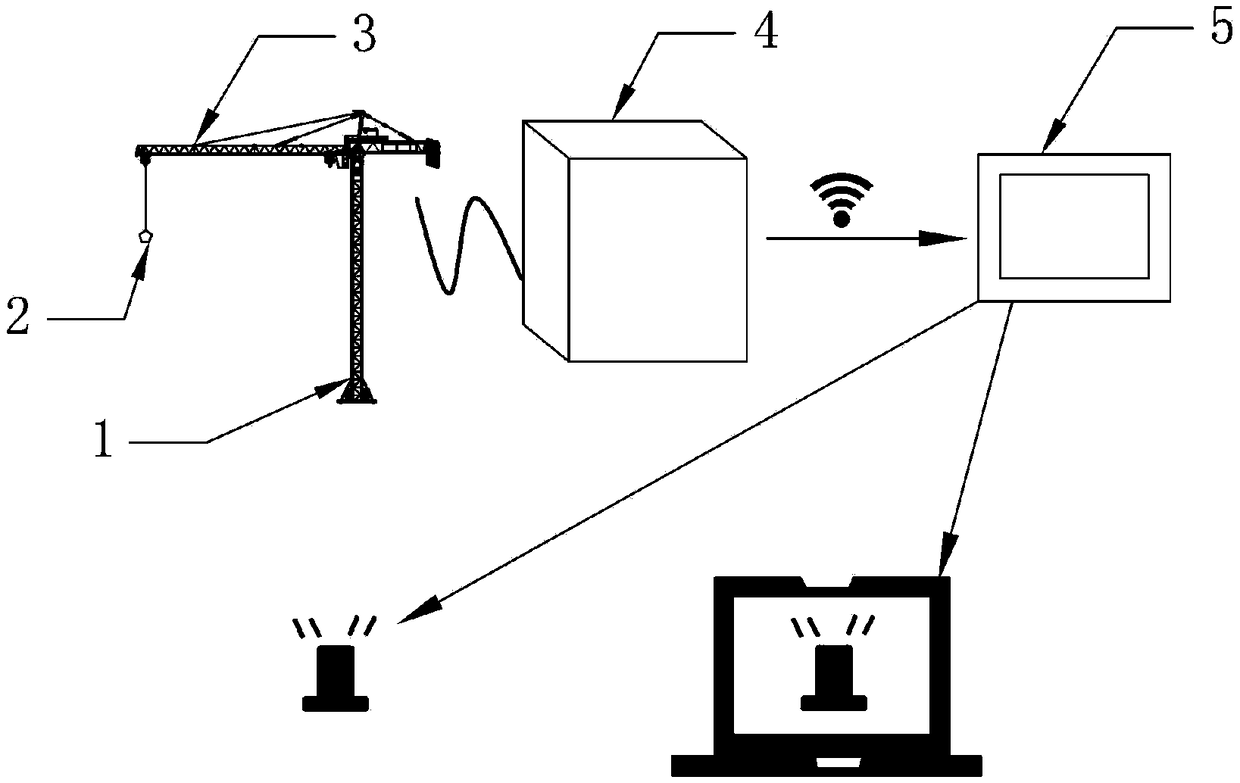
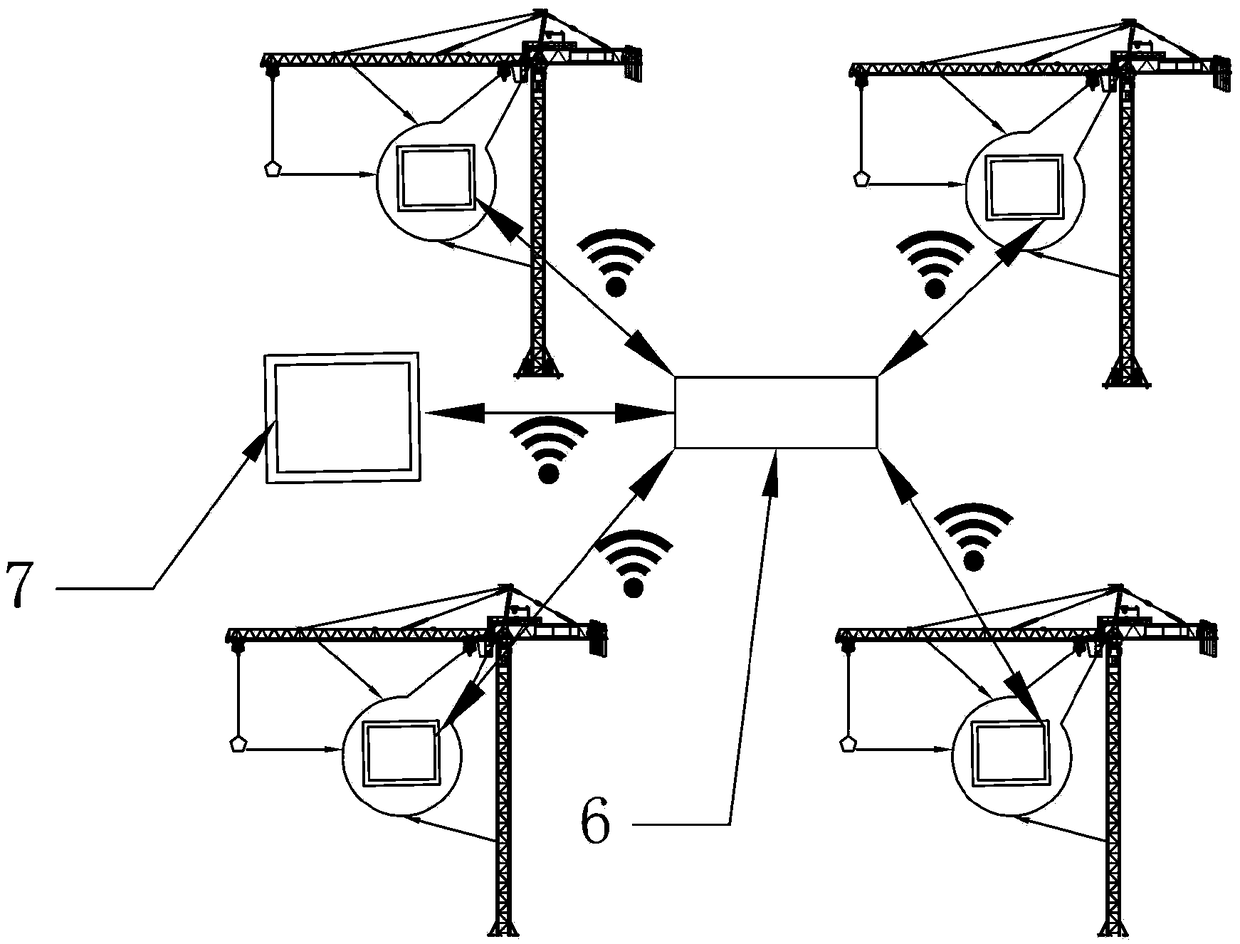
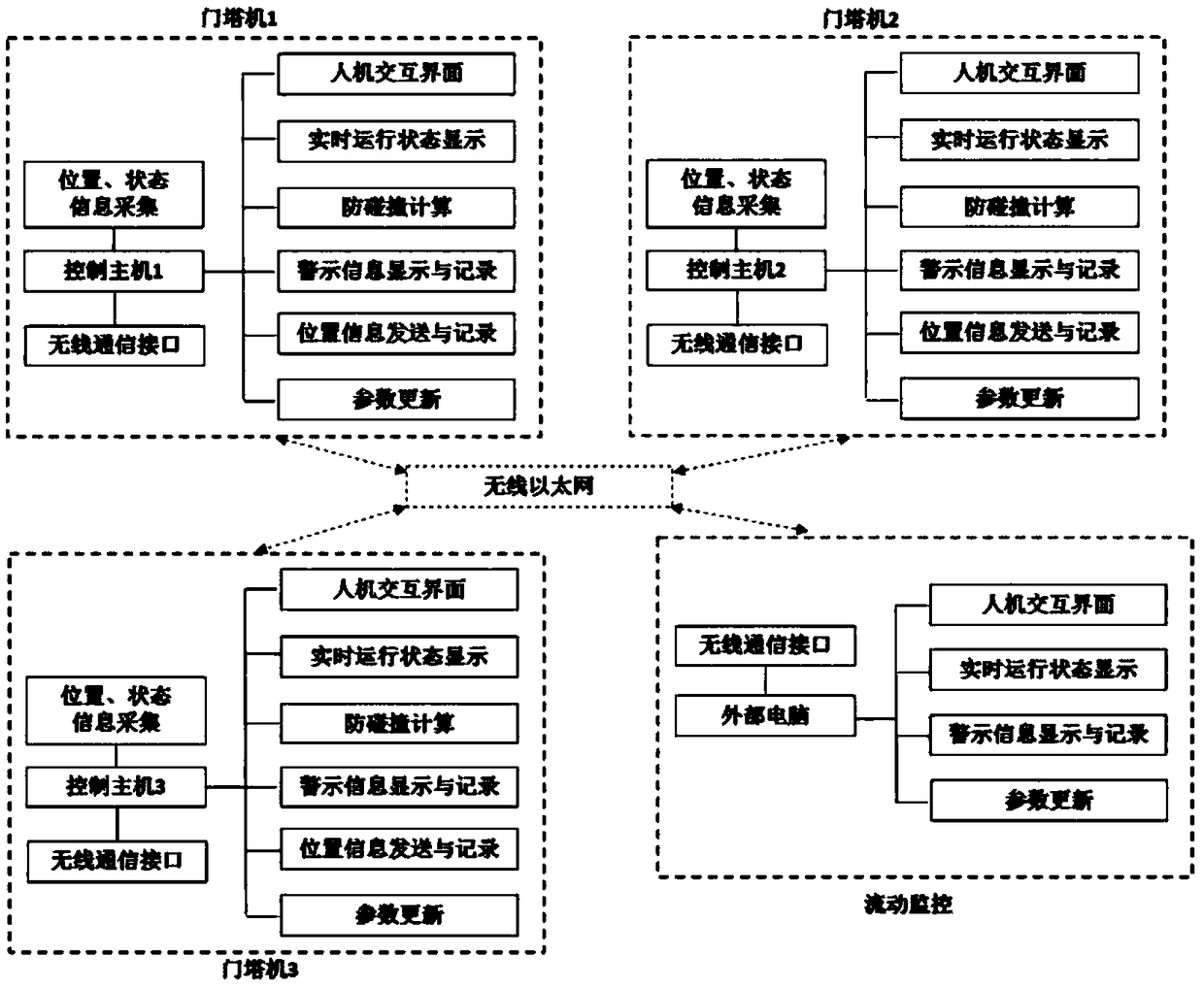
Anti-collision pre-warning system and method for hoisting equipment
InactiveCN109052201AGuaranteed anti-collision prediction accuracyReduce storage requirementsCranesLoad-engaging elementsCollection systemSimulation
The invention discloses an anti-collision pre-warning system and method for hoisting equipment. The anti-collision pre-warning system is based on a distributed type modular framework, and comprises aninformation collection system, an information transmission system and a field control system which are arranged in a distributed modularity mode, and all equipment and fixed obstacles are placed in the same coordinate system. The anti-collision pre-warning method includes the steps that the real-time position, the moving direction and speed information of moving parts of all the equipment are collected and preliminarily calculated by all the hoisting equipment in the field, then relevant information exchange is carried out, the probability of collision is calculated and pre-warning is carriedout, and the steps are cycled and repeated every 0.1 second. According to the anti-collision pre-warning system and method for the hoisting equipment, the distributed type anti-collision system framework is built, anti-collision calculation rules are made, the problem of collision among the hoisting equipment is decomposed into the problem of collision between the moving parts, a binary tree traversal recursive algorithm is adopted to ensure the prediction accuracy of the collision phenomenon, then the collision phenomenon is subjected to commonness processing, a collision pre-warning algorithm is compiled, and collision pre-warning is realized according to the anti-collision rules and algorithm compilation.
Owner:SINOHYDRO BUREAU 7 CO LTD
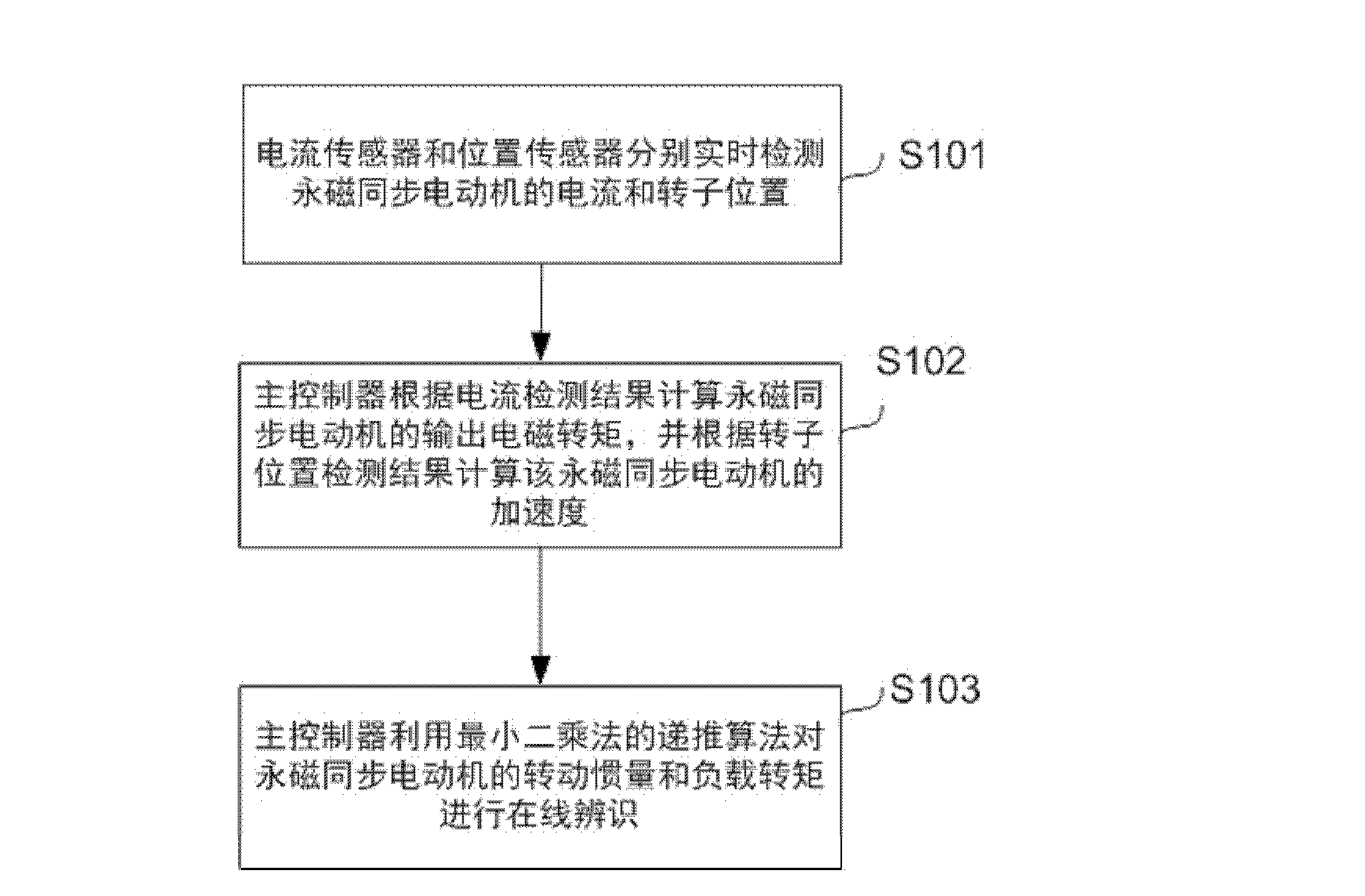
Method for identifying permanent magnetic synchronous motor load parameters
ActiveCN103178758AImprove anti-disturbance abilityStrong real-timeSingle motor speed/torque controlElectronic commutatorsSynchronous motorLoad torque
The invention discloses a method for identifying permanent magnetic synchronous motor load parameters. The method includes that input current and rotor positions of a permanent magnetic synchronous motor are detected in real time respectively through a current sensor and a position sensor, and a detecting result is sent to a main controller; the main controller calculates output electromagnetic torque of the permanent magnetic synchronous motor according to a current detecting result, and rotation speed and acceleration of the permanent magnetic synchronous motor according to a rotor position detecting result; and the main controller conducts online identification on rotational inertia and load torque of the permanent magnetic synchronous motor through a recursive algorithm of a least square method according to the calculated output electromagnetic torque and acceleration. By means of the load parameter identifying method of the least square method, the rotational inertia and the load torque of the permanent magnetic synchronous motor can be identified online, and a correct identification result can be obtained.
Owner:NINGBO CHIKEWEI ELECTRONICS CO LTD
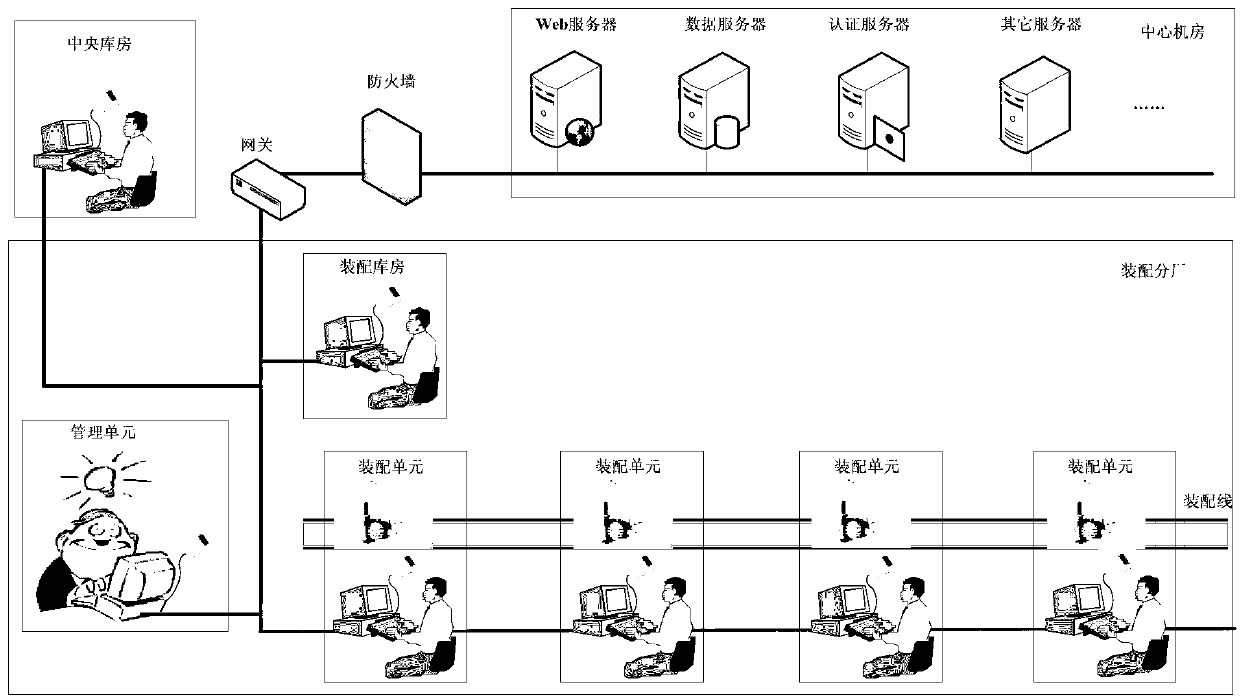
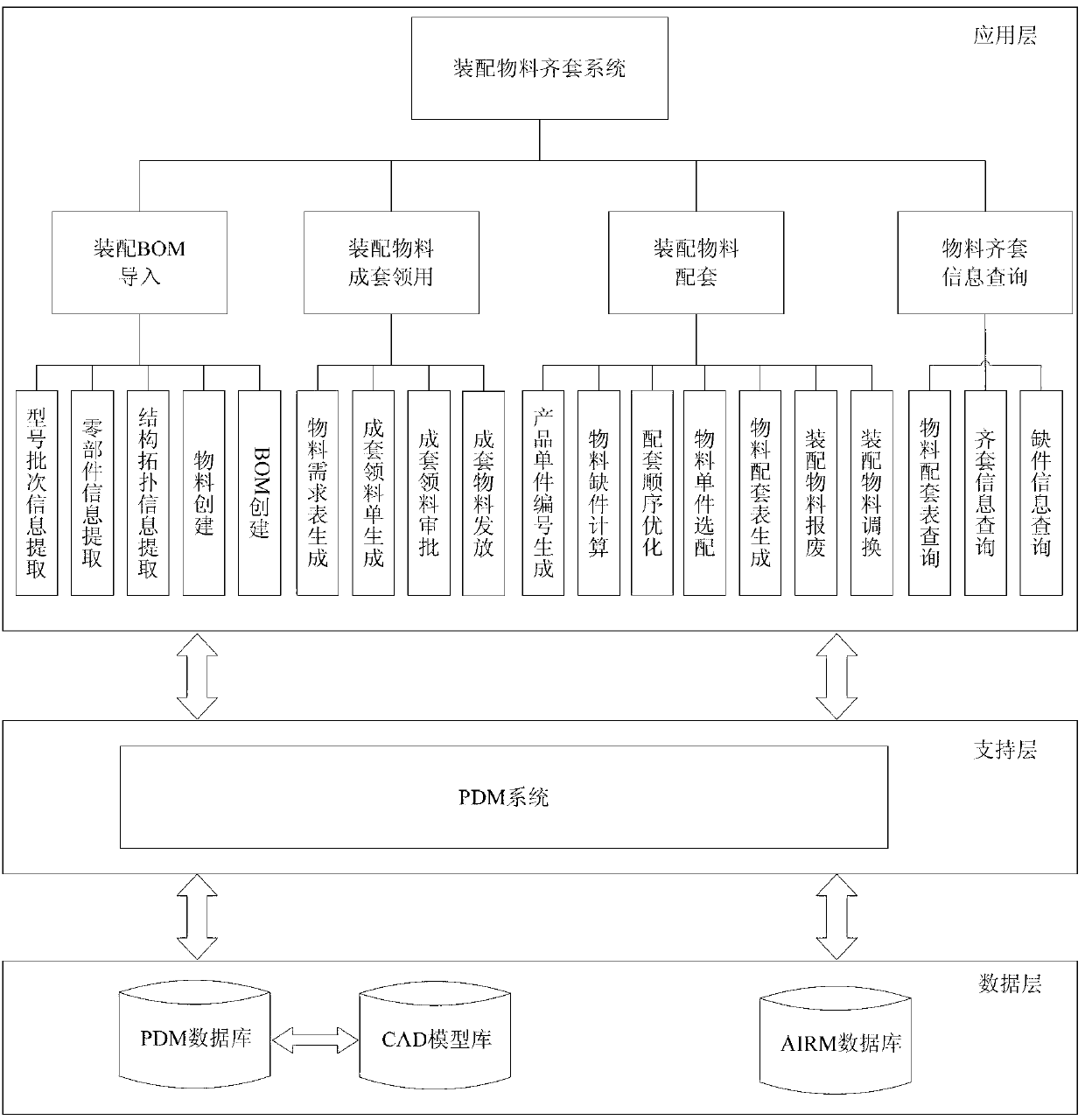
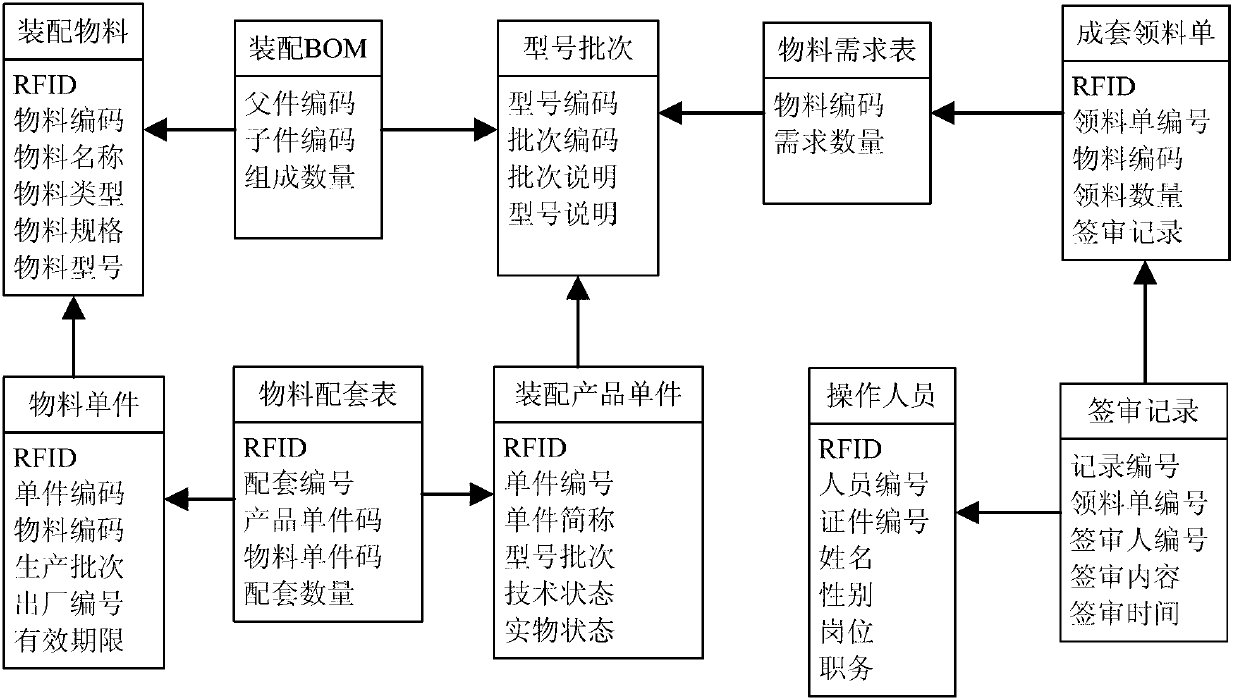
Automatic matching method for high-precision complex product assembling materials
ActiveCN103279613AQuick searchFully automatedSensing record carriersLogisticsComputer Aided DesignBill of materials
The invention discloses an automatic matching method for high-precision complex product assembling materials. The method is characterized by including: traversing and extracting unstructured assembling CAD (computer-aided design) model information through recursive algorithm, and automatically fast building a structured product assembling BOM (bill of material); iterating node layers of the assembling BOM to automatically calculate independent material requirements and related material requirements, and fast and accurately generating material requirement tables; acquiring materials in a matched manner through material requirement table separation, automatic material acquisition list circulation, online signing and examining, single material acquisition registration, and FRID (radio frequency identification); automatically and accurately calculating material shortage lists through assembling BOM iteration and reading of matched material acquisition lists and material matching lists; intelligently optimizing matching sequence through particle swarm optimization, and fast performing optimized material matching; automatically acquiring material information and automatically tracking single material through convenient RFID; and fast inquiring product material matching information through multi-condition optional combination vague inquiry. By the method, automation and intelligence of assembling material matching is increased, and assembling time is shortened.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS +1
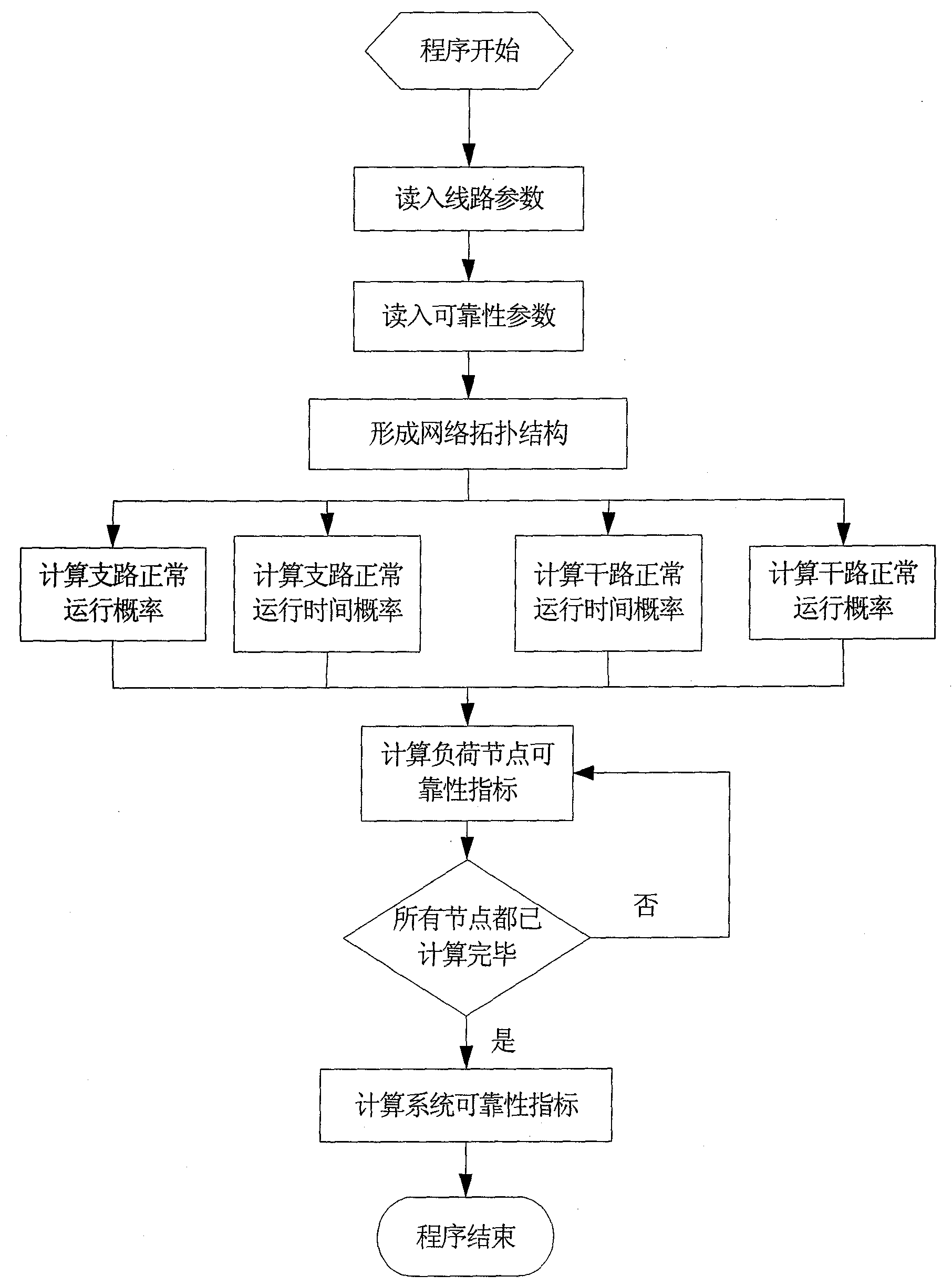
Reliability index calculating method of power distribution system based on successful flow
InactiveCN101562339AImprove reliabilityData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsTransformerDistribution power system
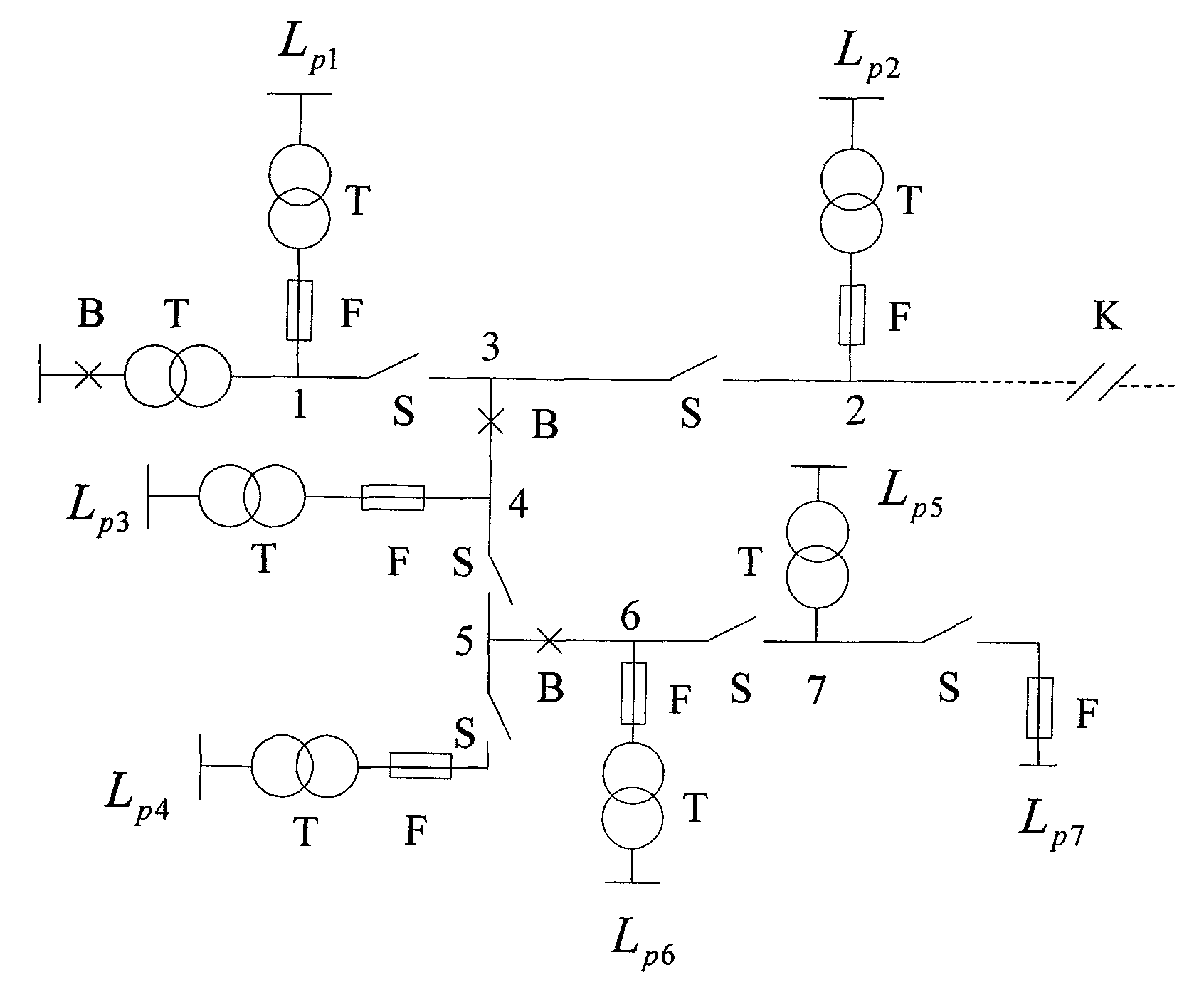
The invention relates to a reliability index calculating method of a power distribution system based on a successful flow, and the method is characterized by simple model, less time consumption for calculation, high calculation precision, ability of being used for the system with larger scale and the ability of calculating indexes of all load points and further providing a basis for the management of micro-limits of individual reliability. The method comprises the following steps: step 1: reading network parameters: including the element parameters of a circuit, a transformer, a fuse, an isolation switch and a circuit breaker; step 2: reading reliability data: including fault rate of the circuit, troubleshooting time of the circuit, operation time of the circuit breaker, the fault rate of the circuit breaker, the operation time of the isolation switch, the fault rate of the fuse, the fault rate of the transformer, and fault maintenance time of the transformer; step 3: forming a network topological structure and forming the element connection relationship; step 4: utilizing the recursive algorithm to calculate the reliability indexes of all complicated branches; step 5: calculating the reliability indexes of all the load points; step 6: calculating the total reliability indexes of the system.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com