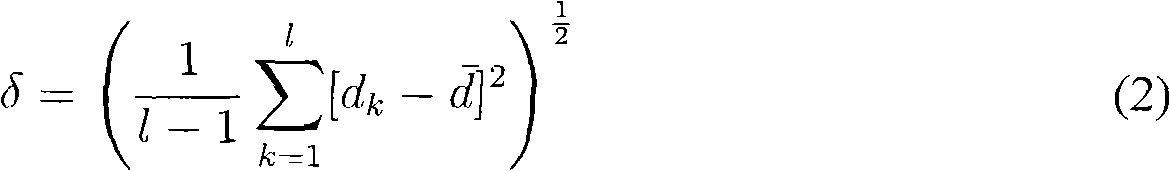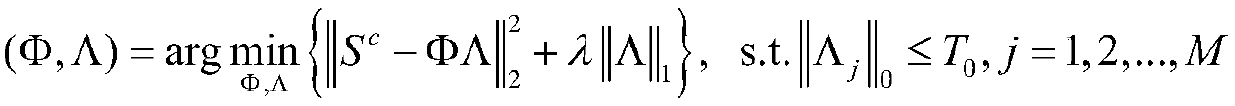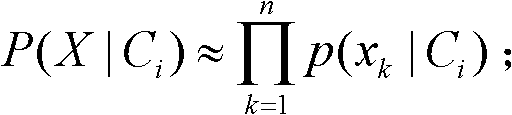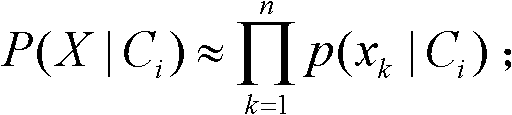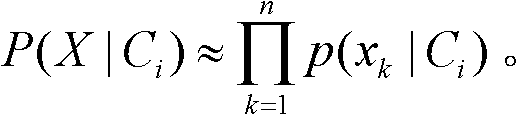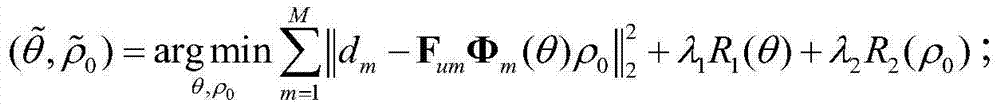Patents
Literature
290 results about "Maximum a posteriori estimation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In Bayesian statistics, a maximum a posteriori probability (MAP) estimate is an estimate of an unknown quantity, that equals the mode of the posterior distribution. The MAP can be used to obtain a point estimate of an unobserved quantity on the basis of empirical data. It is closely related to the method of maximum likelihood (ML) estimation, but employs an augmented optimization objective which incorporates a prior distribution (that quantifies the additional information available through prior knowledge of a related event) over the quantity one wants to estimate. MAP estimation can therefore be seen as a regularization of ML estimation.
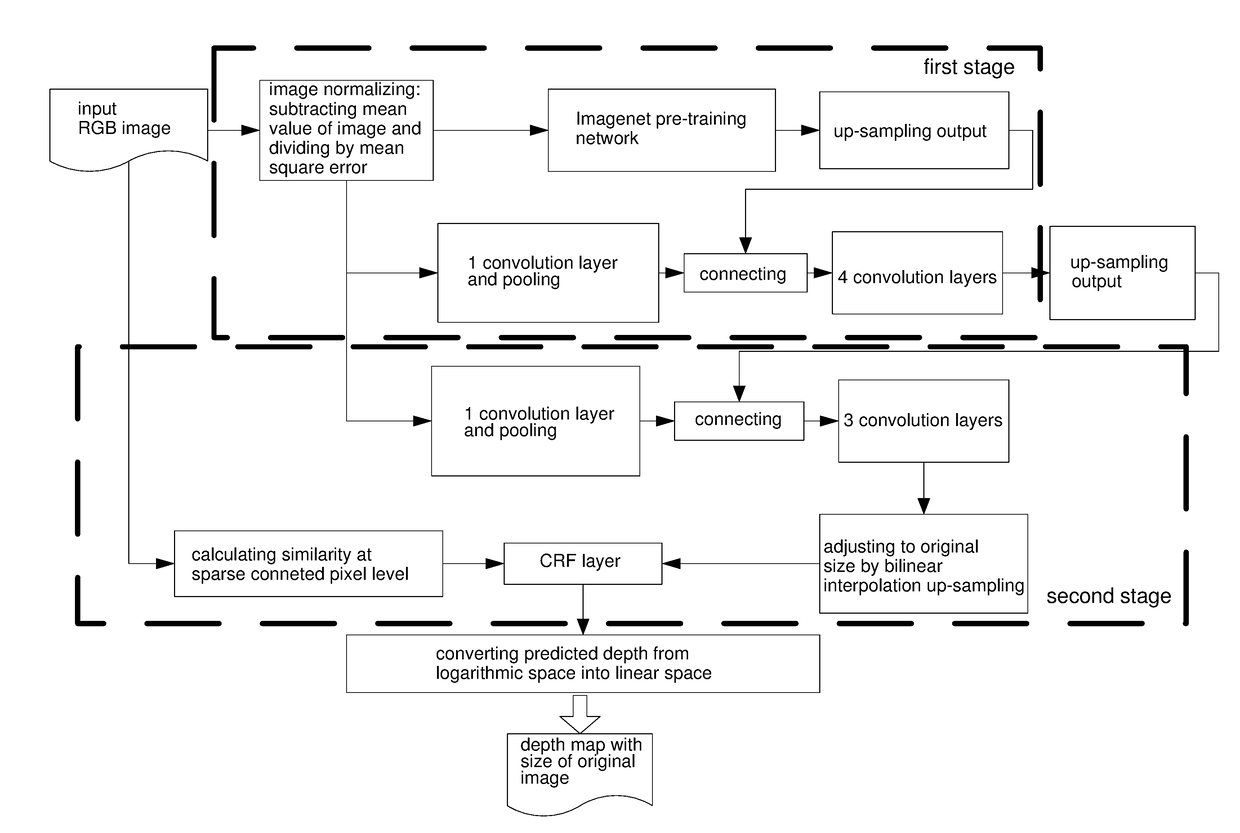
Depth estimation method for monocular image based on multi-scale CNN and continuous CRF
ActiveUS20180231871A1Improve accuracyClear outlineImage enhancementMathematical modelsRgb imageMaximum a posteriori estimation
A depth estimation method for a monocular image based on a multi-scale CNN and a continuous CRF is disclosed in this invention. A CRF module is adopted to calculate a unary potential energy according to the output depth map of a DCNN, and the pairwise sparse potential energy according to input RGB images. MAP (maximum a posteriori estimation) algorithm is used to infer the optimized depth map at last. The present invention integrates optimization theories of the multi-scale CNN with that of the continuous CRF. High accuracy and a clear contour are both achieved in the estimated depth map; the depth estimated by the present invention has a high resolution and detailed contour information can be kept for all objects in the scene, which provides better visual effects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Apparatus and method using reduced memory for channel decoding in a software-defined radio system
InactiveUS20080123781A1Data representation error detection/correctionFault responseSoftware define radioMaximum a posteriori estimation
A maximum a posteriori probability (MAP) block decoder for decoding a received data block of input samples. The MAP block decoder segments the received data block into at least a first segment and a second segment and calculates and stores alpha values during forward processing of the first segment. The MAP block decoder uses a first selected alpha value calculated during forward processing of the first segment as initial state information during forward processing of the second segment. The first and second segments may overlap each other, such that the last M samples of the first segment are the same as the first M samples of the second segment.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Carbonate rock physical parameter seismic inversion method
ActiveCN104516017AAchieve simultaneous inversionReduce credibilitySeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingS-waveMaximum a posteriori estimation
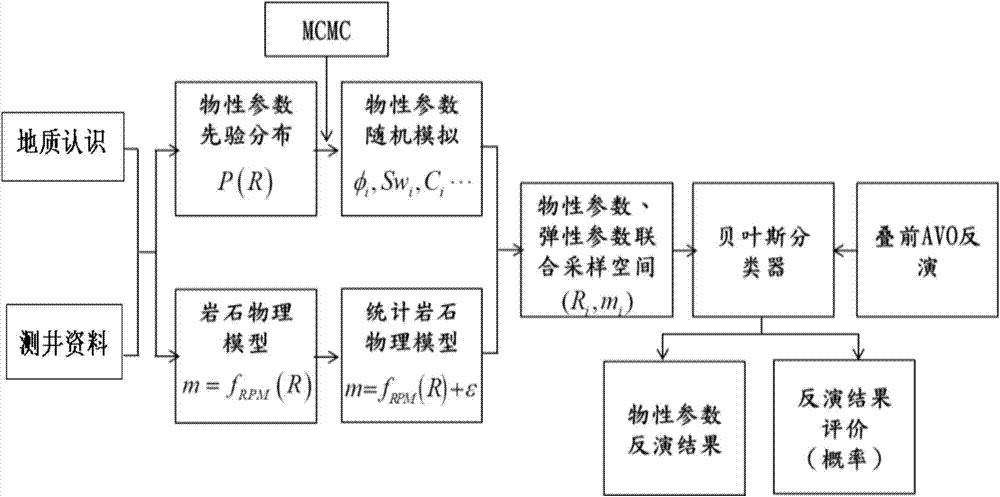
The invention provides a carbonate rock physical parameter seismic inversion method, which belongs to the field of petroleum geophysical exploration. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out pre-stack AVO three-parameter inversion based on a pre-stack angle gather to obtain formation elasticity parameters M, wherein M includes P-wave velocity, S-wave velocity and density; (2) establishing a statistical rock physical model based on logging data; (3) randomly simulating physical conditions of a reservoir based on the rock physical model obtained from step (2) to obtain a random simulation result; and (4) carrying out Bayes classified simulation on the random simulation result obtained from step (3) to obtain a posterior probability distribution, and taking the M obtained from step (1) as the input of inversion to find a R with the maximum posteriori probability distribution, wherein R is the final inversion result.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
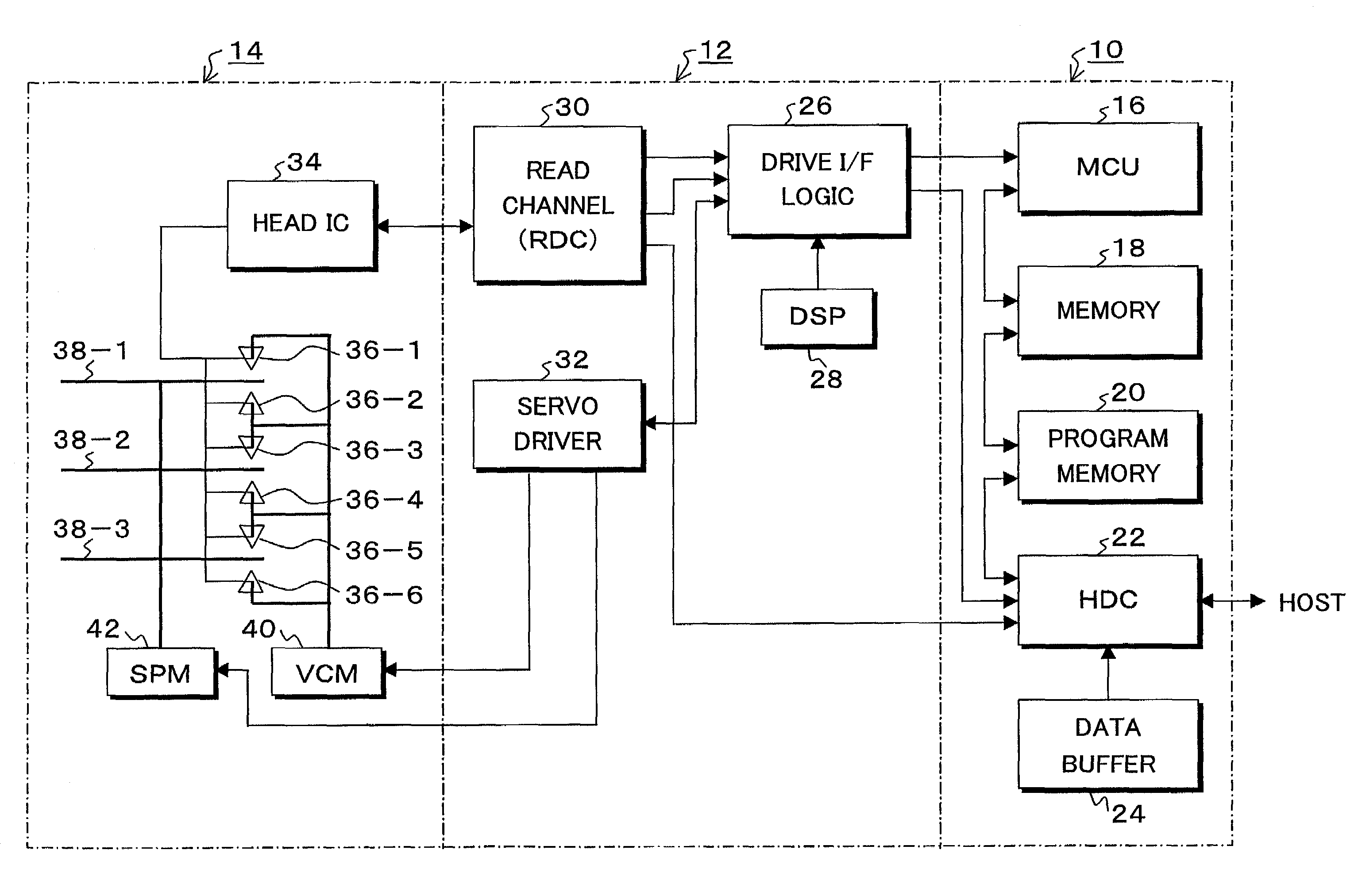
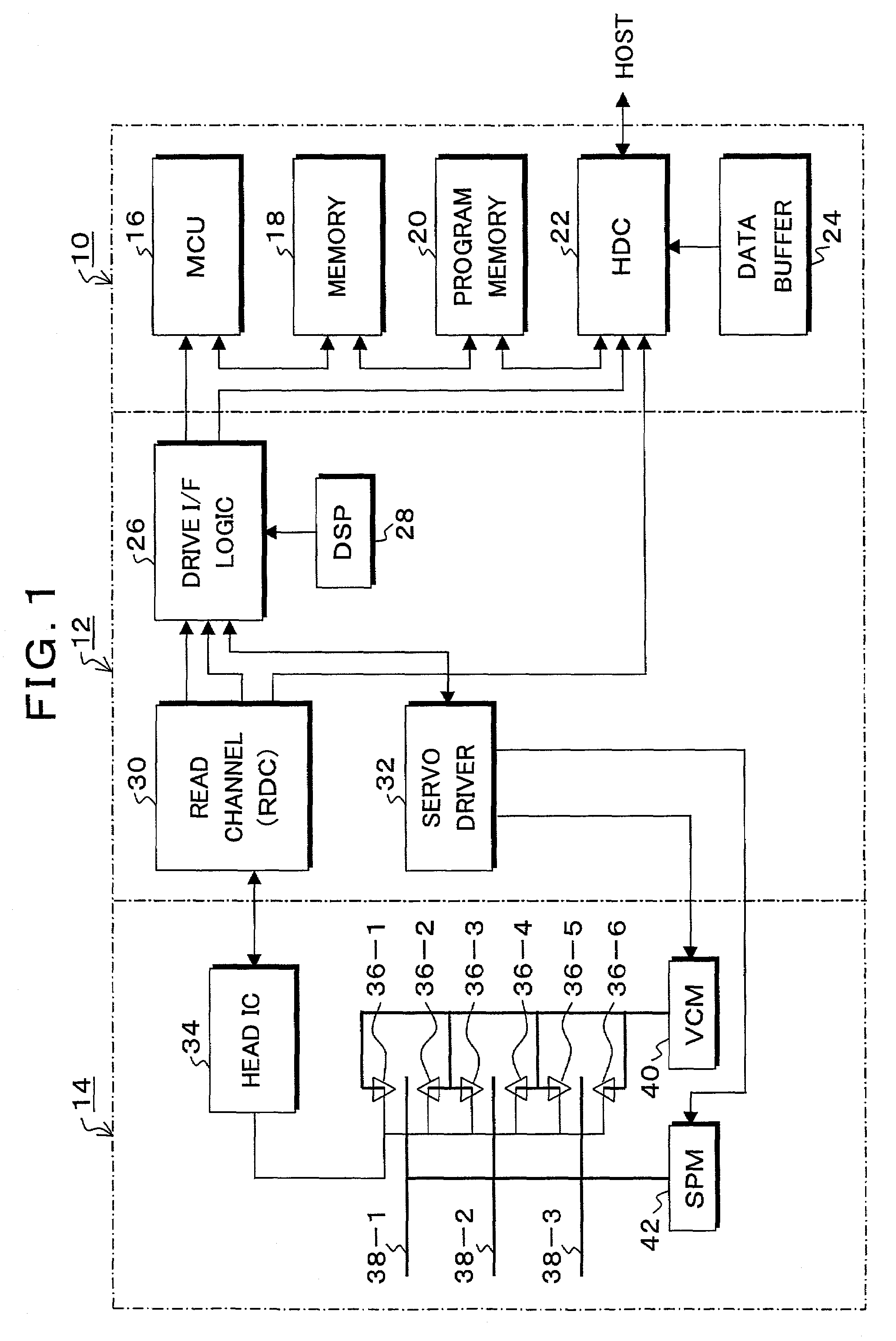
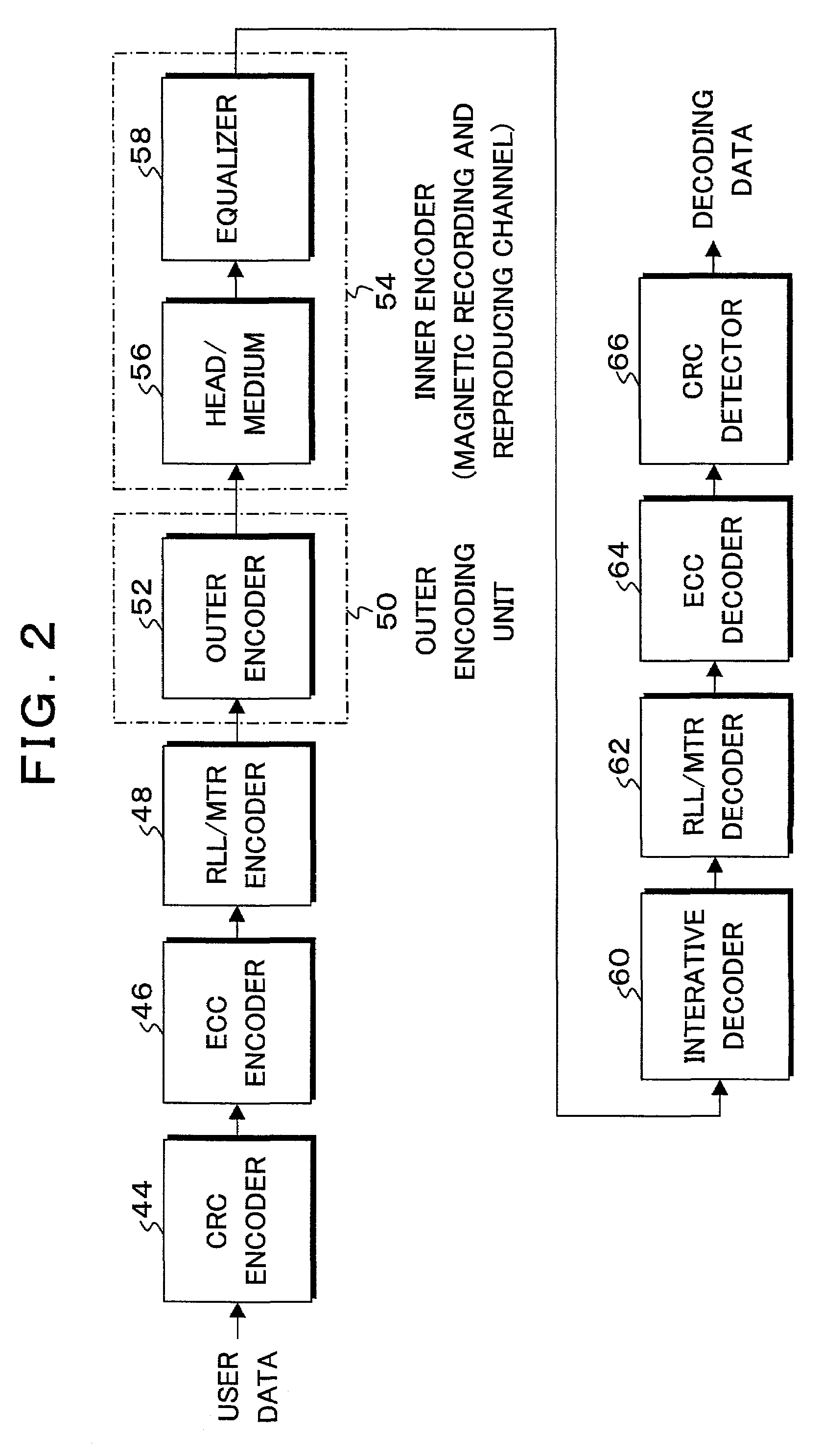
Information recording and reproducing apparatus and method and signal decoding circuit having improved noise processing characteristics
InactiveUS7031090B2Effective applicationImprove decoding performanceModification of read/write signalsOther decoding techniquesMaximum a posteriori estimationComputer science
In a Maximum A posteriori Probability decoding (MAP decoding), a correlation and a deviation of noises for past and future states which depend on input signal patterns in past N bits and future Q bits are calculated by training by a noise correlation arithmetic operating unit 84 and they are stored. Upon reproduction, in a white noise arithmetic operating unit 91, white noise values for the past and future states in which colored noises are converted into white noises are obtained by using the stored correlation and deviation of the noises. In an input signal arithmetic operating unit 92, an input signal (channel information) Λc(yk|Smk) of the MAP decoding is calculated from the white noise values and the deviation for the past and future states. A likelihood in the MAP decoding is obtained from the input signal.
Owner:TOSHIBA STORAGE DEVICE CORP
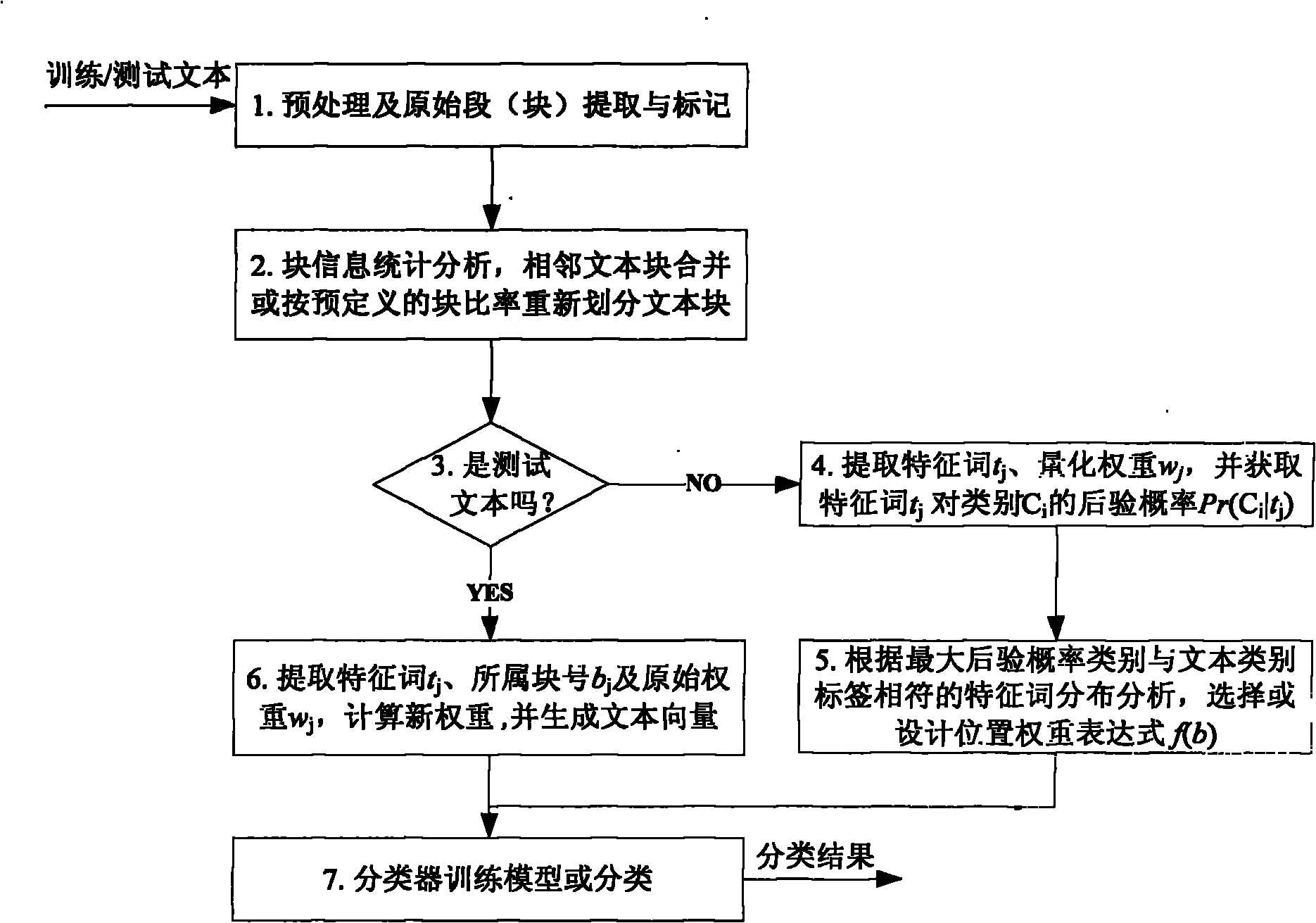
Text classification method based on block partition and position weight
InactiveCN102033964AImprove classification performanceReduce occupancySpecial data processing applicationsText categorizationMaximum a posteriori estimation
The invention discloses a text classification method based on block partition and position weight. The method comprises the following steps of: after performing basic pre-processing on an input training or test text, extracting section information from the text; performing statistical analysis on block information by taking one section as a basic text block; performing block partition on the text content again, according to the block size distribution or pre-defined block ratio, including operation, such as combining text blocks; extracting characteristic words and quantized weight, acquiring the posterior probability of the characteristic words on class, analyzing the distribution of the characteristic words having the biggest posterior probability class and according with a text class label, and generating a text vector; and finishing classification model training or text classification with a classifier. The method can be applied to a text representation stage of a text classification system. The text classification effect is improved through the rich and traditional expression of the text content when the text vector is created by using the characteristic words.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
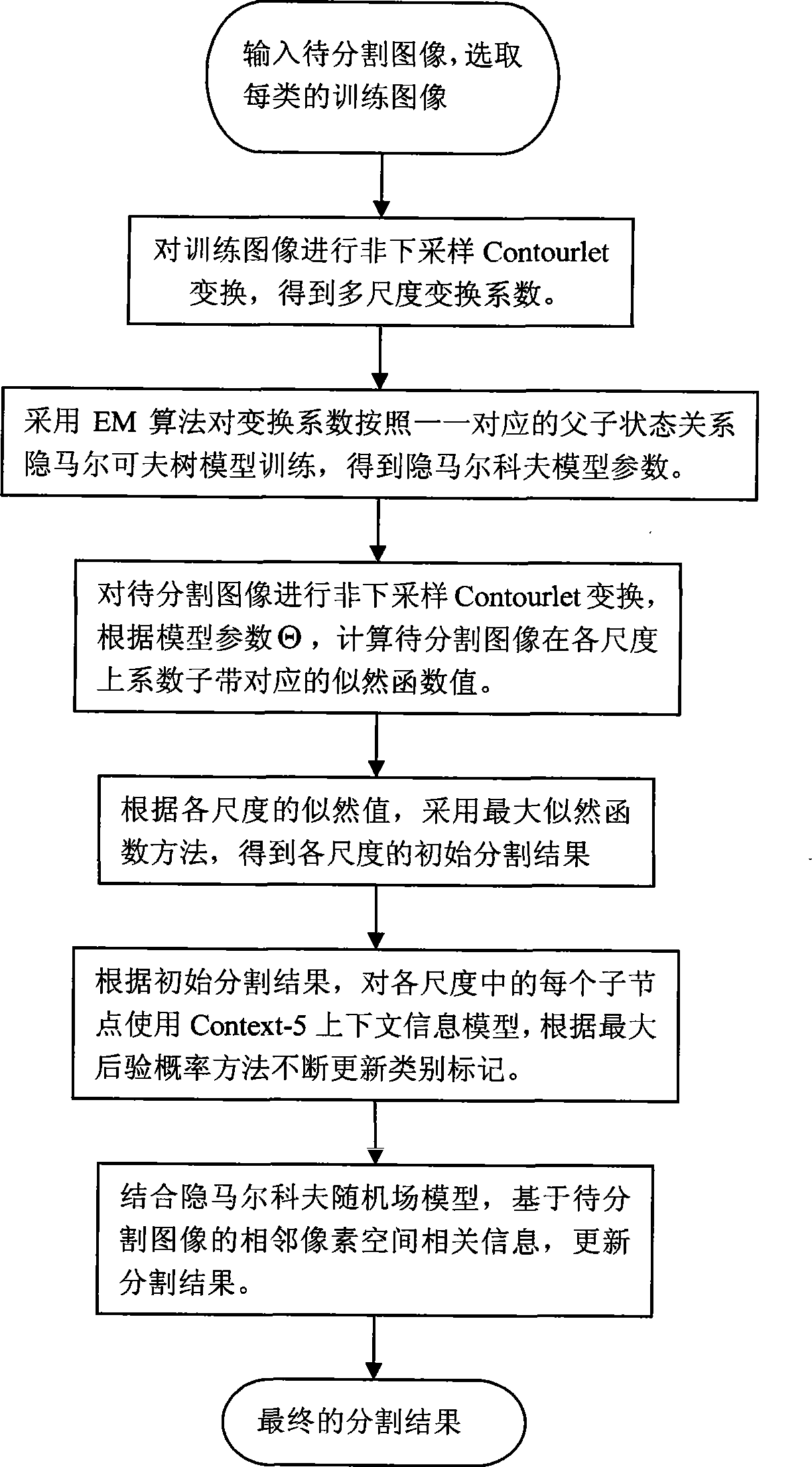
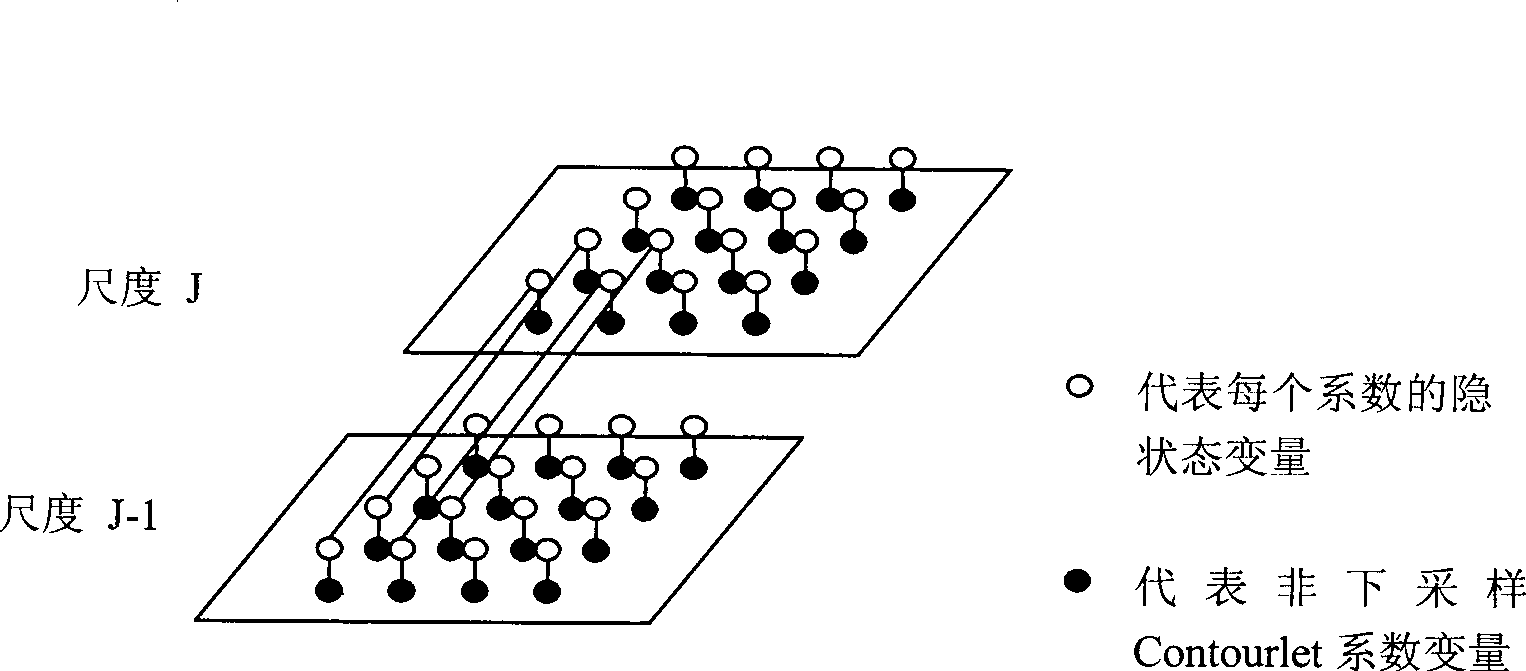
Method for segmenting HMT image on the basis of nonsubsampled Contourlet transformation
ActiveCN101447080AGood segmentation effectAvoid the Gibbs PhenomenonImage analysisRelationship - FatherMaximum a posteriori estimation
The invention discloses a method for segmenting HMT images which is based on the nonsubsampled Contourlet transformation. The method mainly solves the problem that the prior segmentation method has poor area consistency and edge preservation, and comprises the following steps: (1) performing the nonsubsampled Contourlet transformation to images to be segmented and training images of all categories to obtain multi-scale transformation coefficients; (2) according to the nonsubsampled Contourlet transformation coefficients of the training images and the hidden markov tree which represents the one-to-one father and son state relationship, reckoning the model parameters; (3) calculating the corresponding likelihood values of the images to be segmented in all scale coefficient subbands, and classifying by examining possibility after integrating a labeled tree with a multi-scale likelihood function to obtain the maximum multi-scale; (4) updating category labels for each scale based on the context information context-5 model; and (5) with the consideration of the markov random field model and the information about correlation between two adjacent pixel spaces in the images to be segmented, updating the category labels to obtain the final segmentation results. The invention has the advantages of good area consistency and edge preservation, and can be applied to the segmentation for synthesizing grainy images.
Owner:探知图灵科技(西安)有限公司
Regularized parameter adaptive sparse representation image reconstruction method
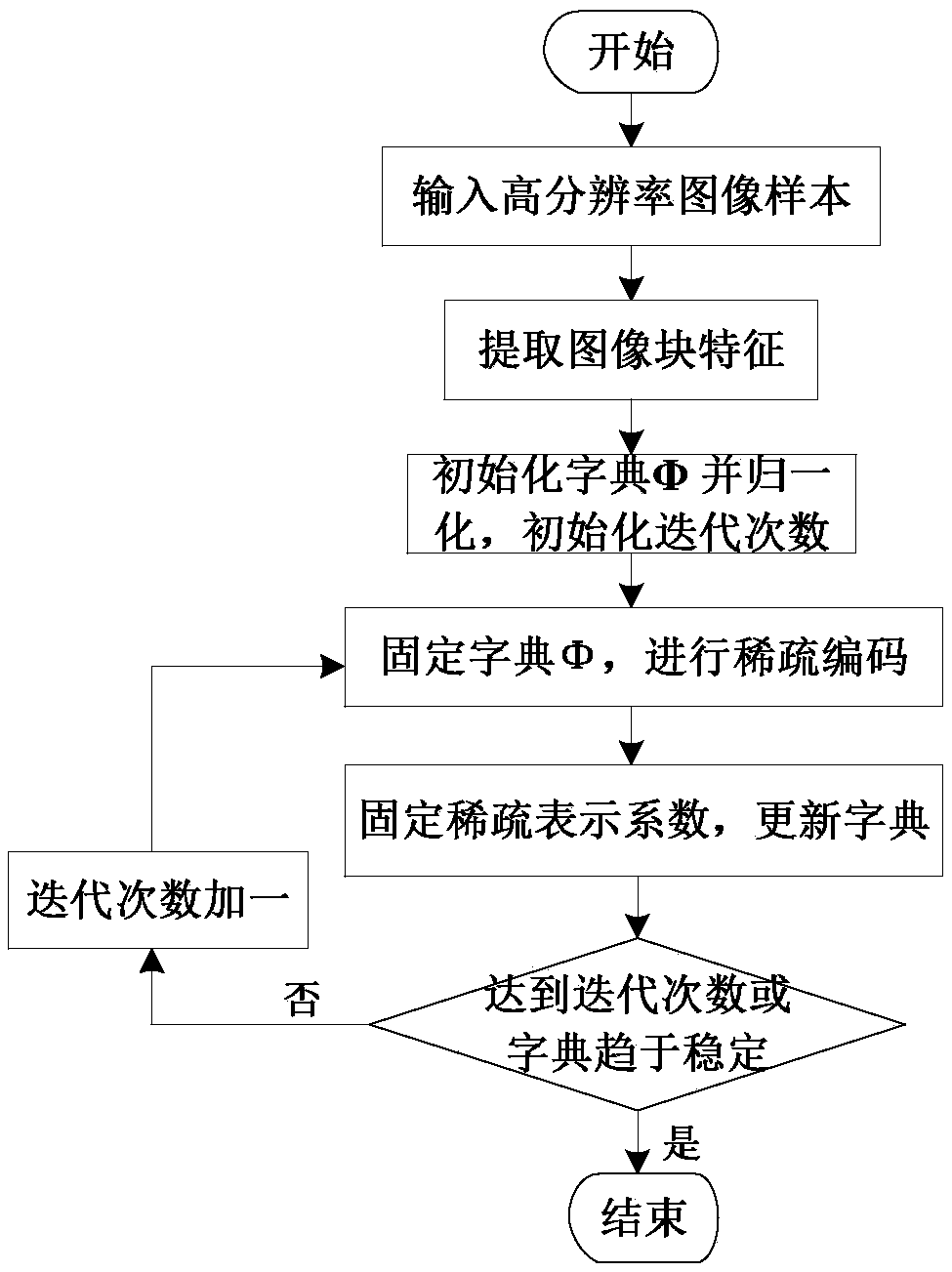
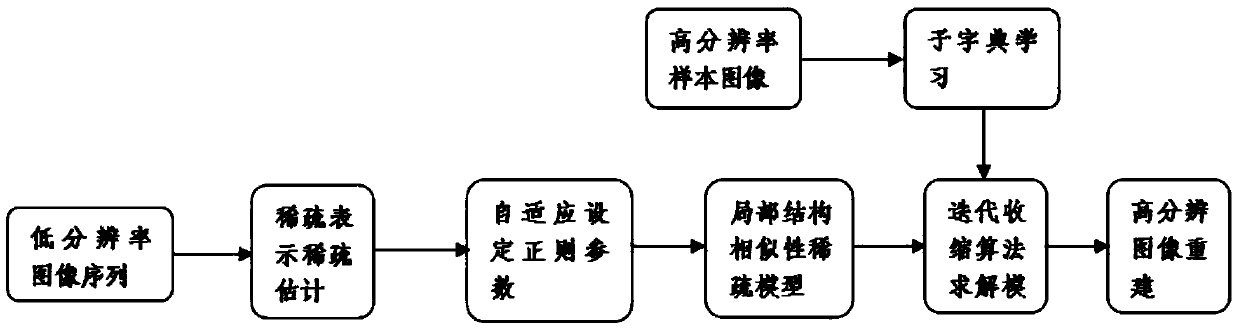
PendingCN109064406AImprove effectivenessMaintain structureGeometric image transformationDictionary learningMaximum a posteriori estimation
The invention provides a regularized parameter adaptive sparse representation image reconstruction method, comprising the following steps: adopting a sparse dictionary learning algorithm, extracting image edge features to train a compact sparse dictionary, and adaptively allocating sub-dictionaries to each image block for sparse coding; Learning the Sparse Estimation of Sparse Coding from an Overcomplete Dictionary; Making full use of the local structure similarity of images, the regularization parameters are adaptively solved by using the method based on the maximum a posteriori probability.Adaptive sparse representation model of regularized parameters is established. The invention improves the effectiveness of sparse representation by utilizing the local structure similarity, and the edge and the structure of the image are well maintained. Adaptively adjusting the regularization parameters based on the maximum a posteriori probability, updating the regularization parameters in eachiteration process, better adapting to the current situation, greatly reducing the workload of manual selection of the regularization parameters; It has good image reconstruction effect and strong robustness to noise and motion blur.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
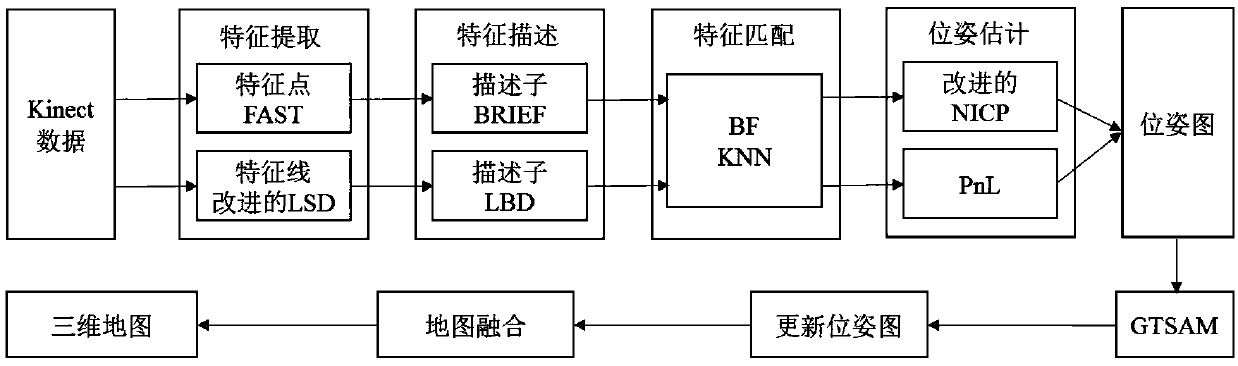
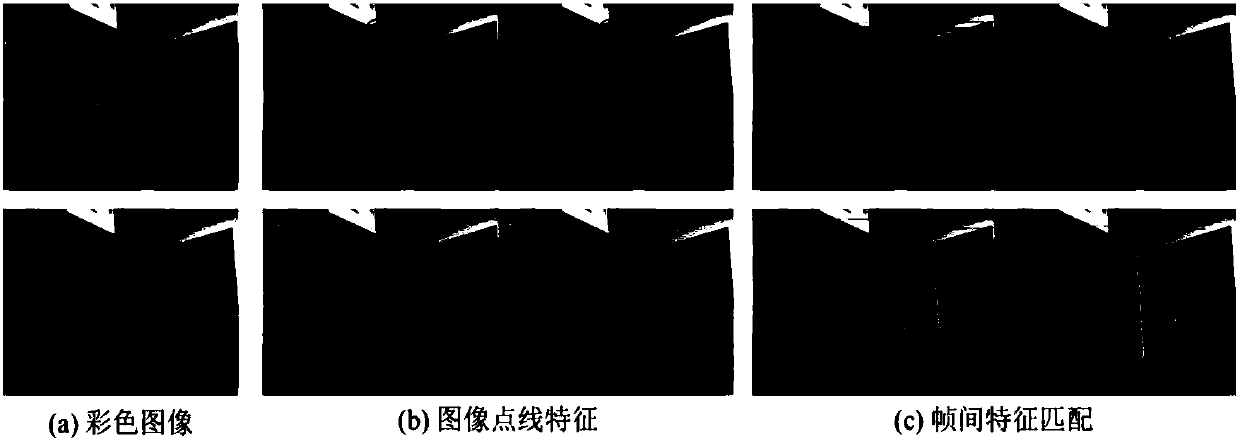
VSLAM method based on multi-characteristic visual odometer and graph optimization model
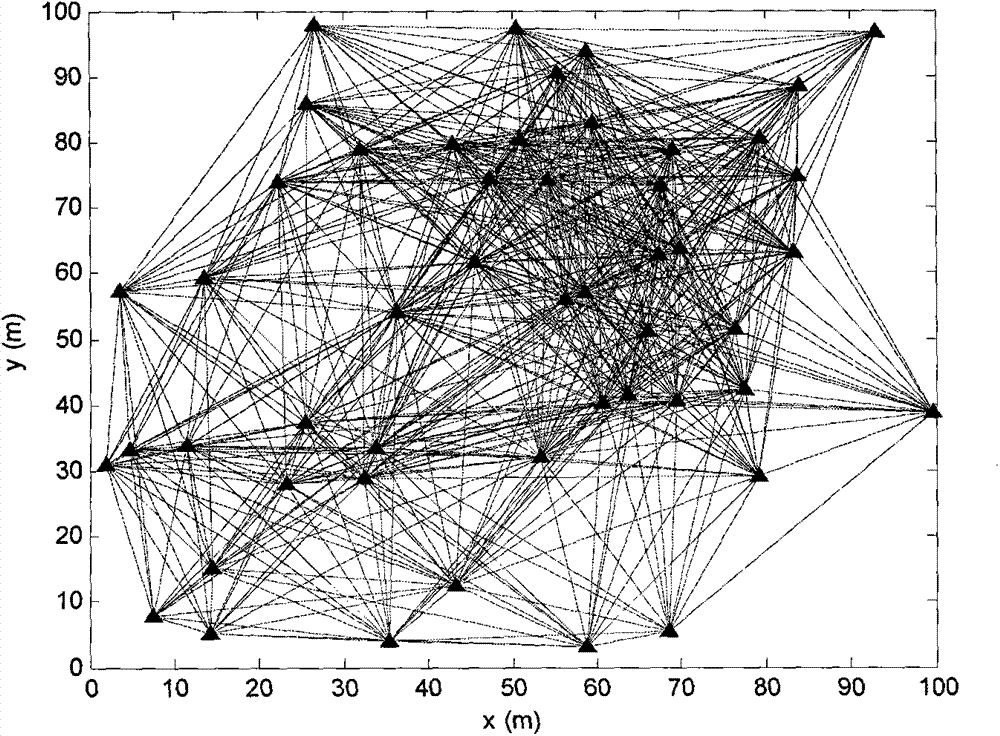
The invention discloses a VSLAM method based on a multi-characteristic visual odometer and a graph optimization model, and belongs to the robot SLAM field; the method comprises the following steps: firstly using a FAST (features from accelerated segment test) and an improved LSD algorithm to extract point and line features in a color image; further using different descriptors to describe characteristics; then carrying out characteristic matching; finally using an improved NICP (normal iterative closest point) algorithm and a PnL (perspective n line) algorithm to estimate a robot initial posture. The method can extract image line features so as to enlarge algorithm application scenes, can obtain a well robot initial posture, uses a Bayes network to express a multi-characteristic visual odometer, obtains a factor graph on the basis of the Bayes network, uses a maximum posterior probability to estimate a robot global posture in the factor graph, and uses a Gauss-Newton method to solve themaximum posterior probability to obtain the updated posture graph; finally, the posture graph and three dimensional points of corresponding frames are fused to obtain a reconstructed three dimensional map.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
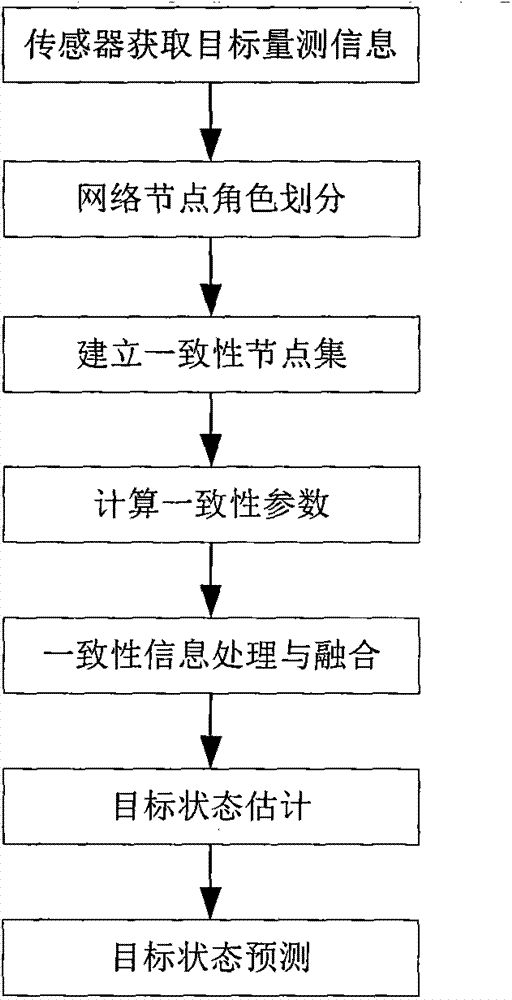
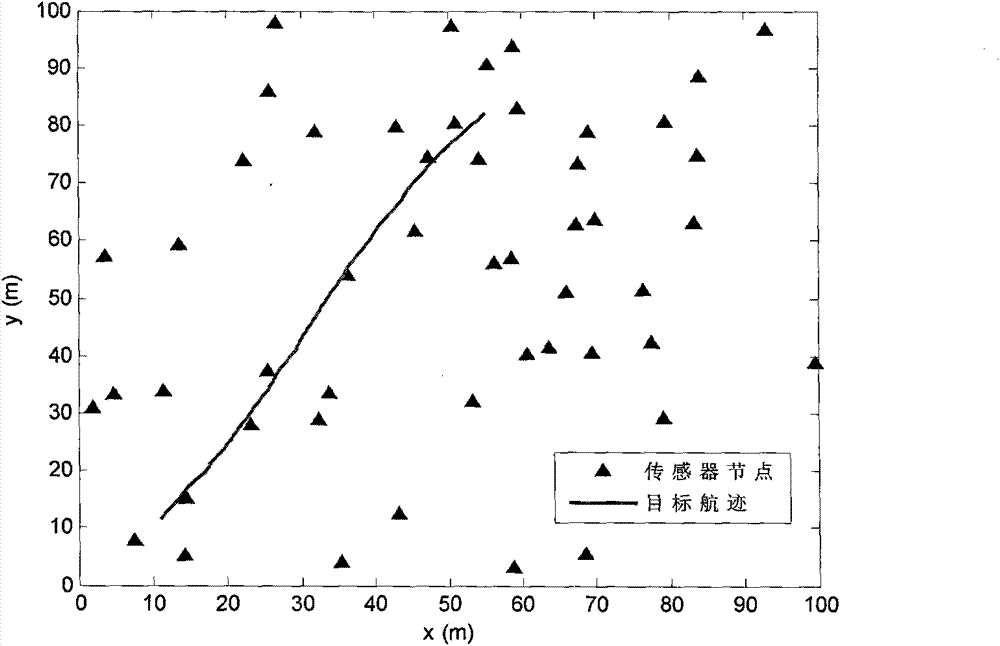
Sensor network distributed consistency object state estimation method
ActiveCN103648108AImprove estimation accuracyNetwork topologiesPrior informationInformation transmission
The invention provides a sensor network distributed consistency object state estimation method. The method, based on information transmission between observation nodes of a sensor network, enables dynamic function division to be carried out on sensor nodes in the network, and observation node sets participating in consistency state estimation are adaptively optimized and selected in real time; on the basis of a distributed maximum a posteriori theory, weighting processing is performed on object prior information and measurement information; and with the influence of covariance of state estimation errors of different observation nodes on the calculation of average consistency state taking into consideration, and effective information consistency processing is performed, the distributed state estimation accuracy of each observation node can rapidly approach to the centralized estimation accuracy, state maintenance of blind nodes on an object is guaranteed, and the cases of endless emergence of new tracks and uncertainty of the tracks and the like can be effectively prevented.
Owner:NAVAL AERONAUTICAL & ASTRONAUTICAL UNIV PLA
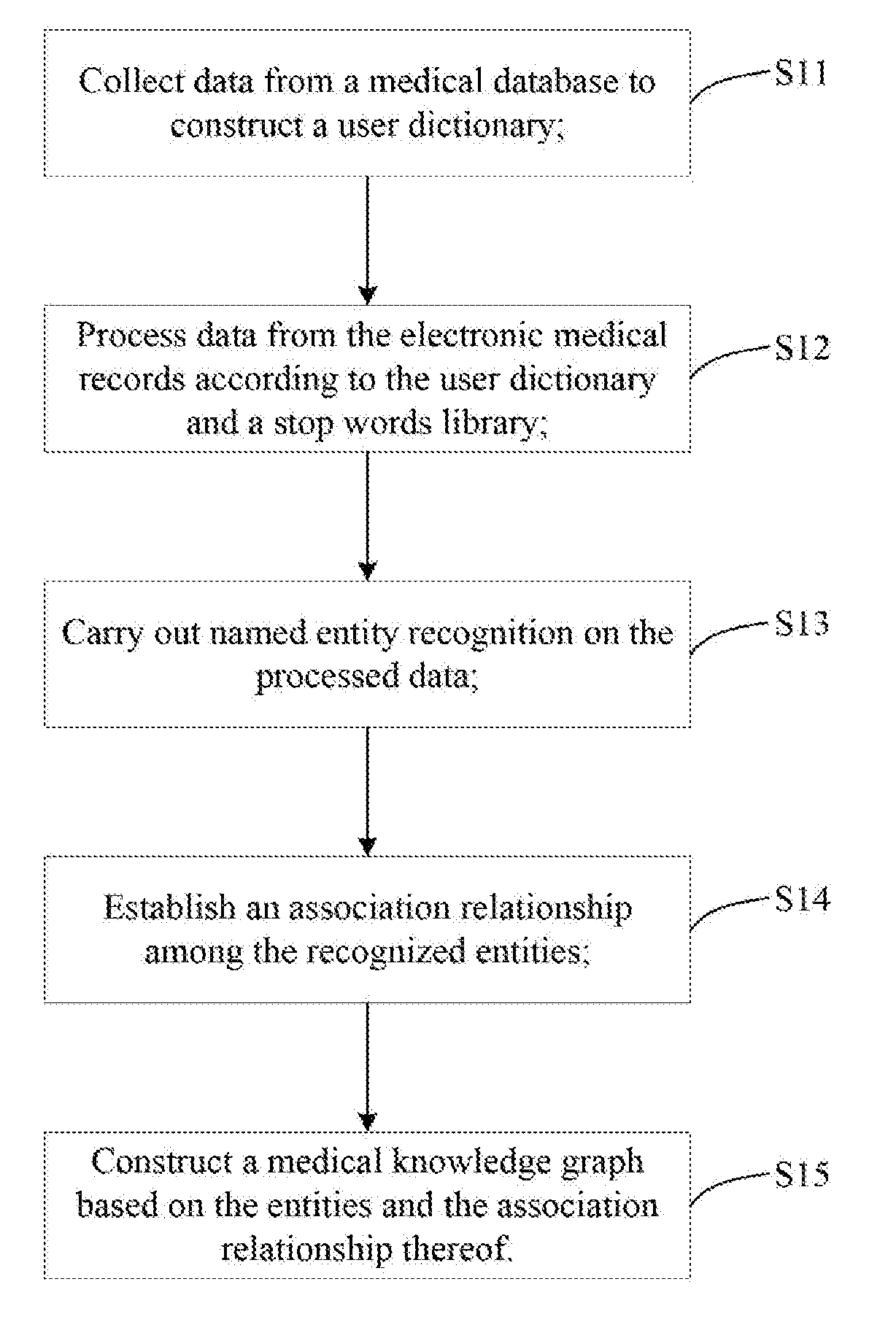
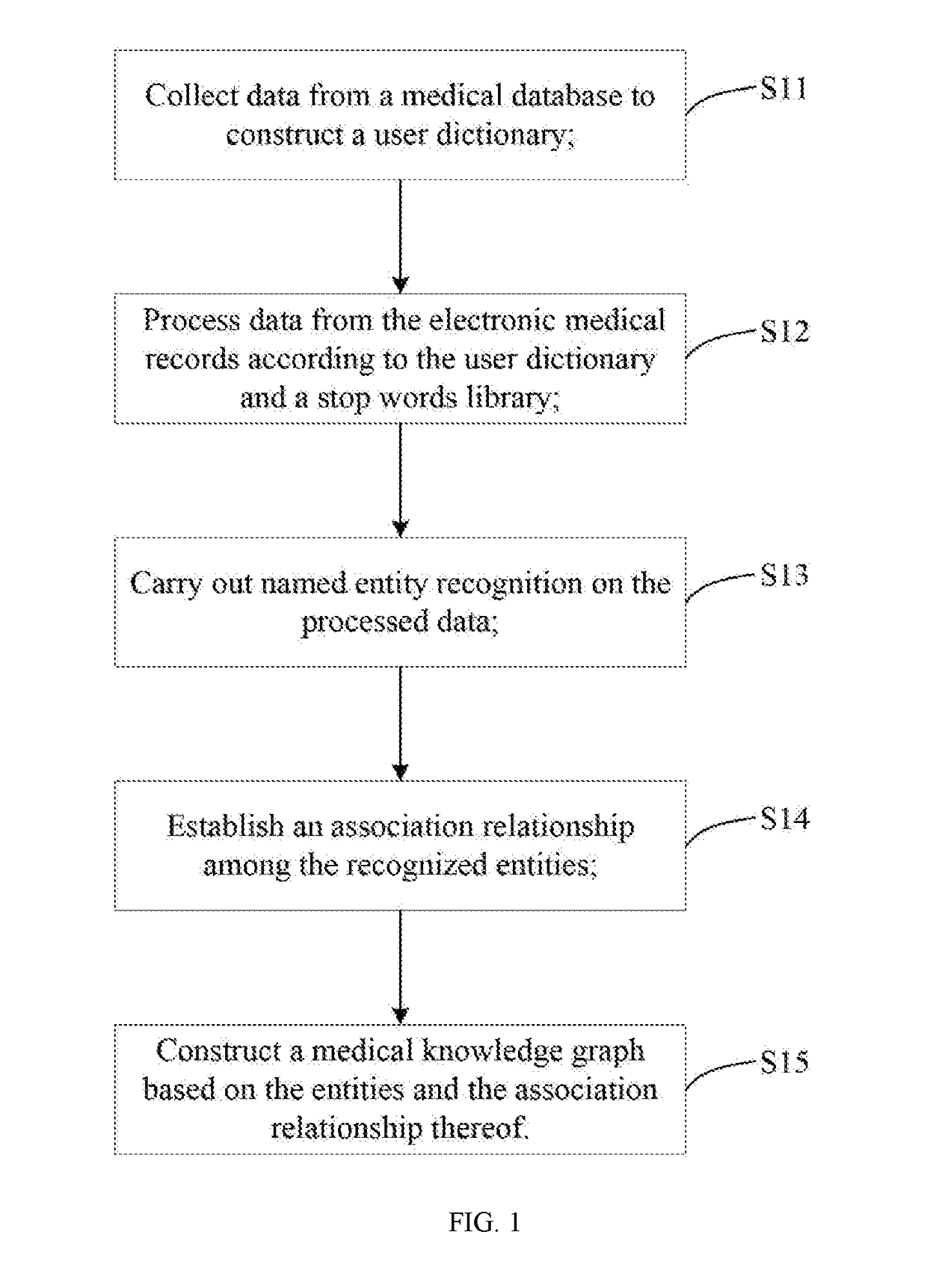
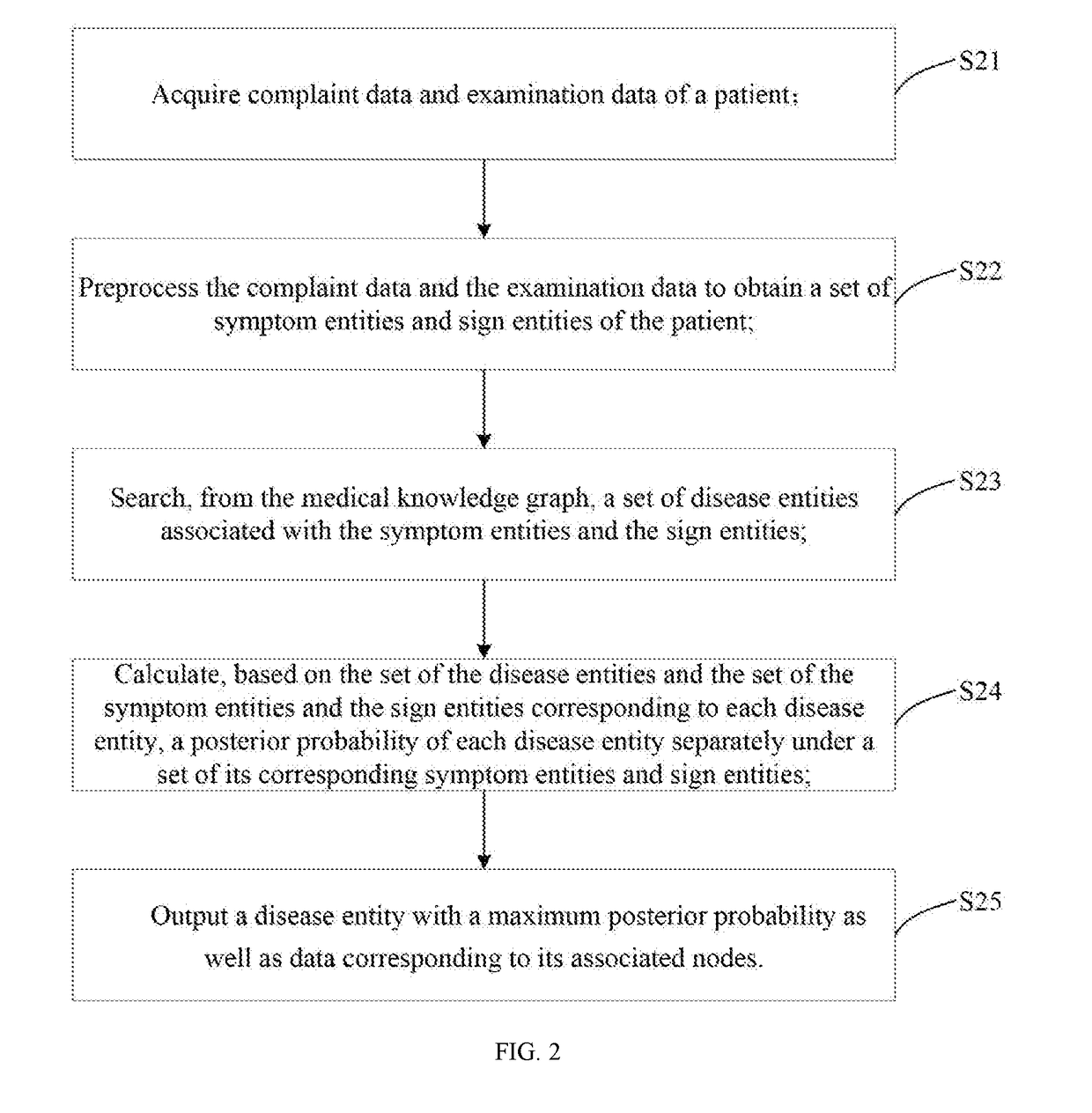
Method and device for constructing medical knowledge graph and assistant diagnosis method
InactiveUS20180322954A1Reduce workloadRelieve pressureMedical data miningMedical automated diagnosisNODALMaximum a posteriori estimation
The present invention discloses a method and a device for constructing a medical knowledge graph and an assistant diagnosis method. The assistant diagnosis method based on a medical knowledge graph comprises the steps of: acquiring complaint data and examination data of a patient and processing the data to obtain symptom entities and sign entities of the patient; searching, from the medical knowledge graph, disease entities associated with the symptom entities and the sign entities, calculating a posterior probability of each disease entity separately under a set of its corresponding symptom entities and sign entities; and outputting a disease entity with a maximum posterior probability as well as data corresponding to its associated nodes. The present invention provides an intelligent assistant diagnosis for clinical medicine to reduce the work burden of medical staff, relieve the medical pressure and reduce medical accidents.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Binocular vision stereo matching method
InactiveCN103440653ASuppressing the Effect of Stereo MatchingImprove stereo matching accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisParallaxStereo matching
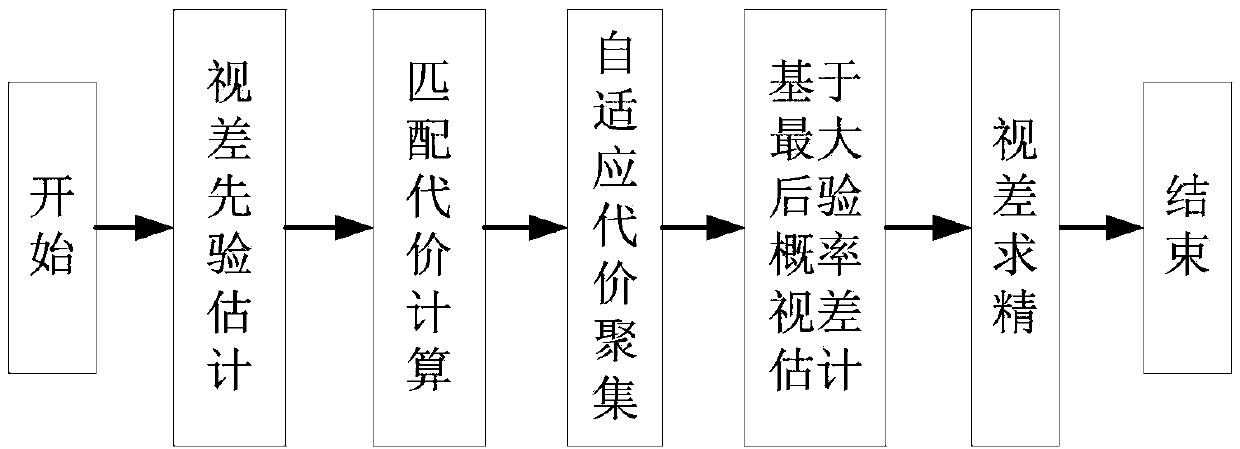
Provided is a binocular vision stereo matching method. Parallax error prior estimation based on a dense characteristic description method is carried out on points to be matched in a view group at first, matching cost of candidate matching points in the view group is calculated by means of a hamming distance method, then cost gathering values of the candidate matching points are solved through a cost gathering method based on self-adaptive windows, parallax error values of pixel points in the view group are calculated by using a parallax error estimation method based on a maximum posterior probability model, and precision processing is carried out on stereo matching results at last. According to the binocular vision stereo matching method, influences on stereo matching due to different illuminations of a left view and a right view or different exposure time periods can be effectively restrained, higher stereo matching precision is obtained, and an algorithm is quick, stable and reliable.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for super-resolution imaging of foresight array SAR based on sparse representation
InactiveCN103869316AQuality improvementOvercoming problems constrained by array lengthRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImaging algorithmMaximum a posteriori estimation
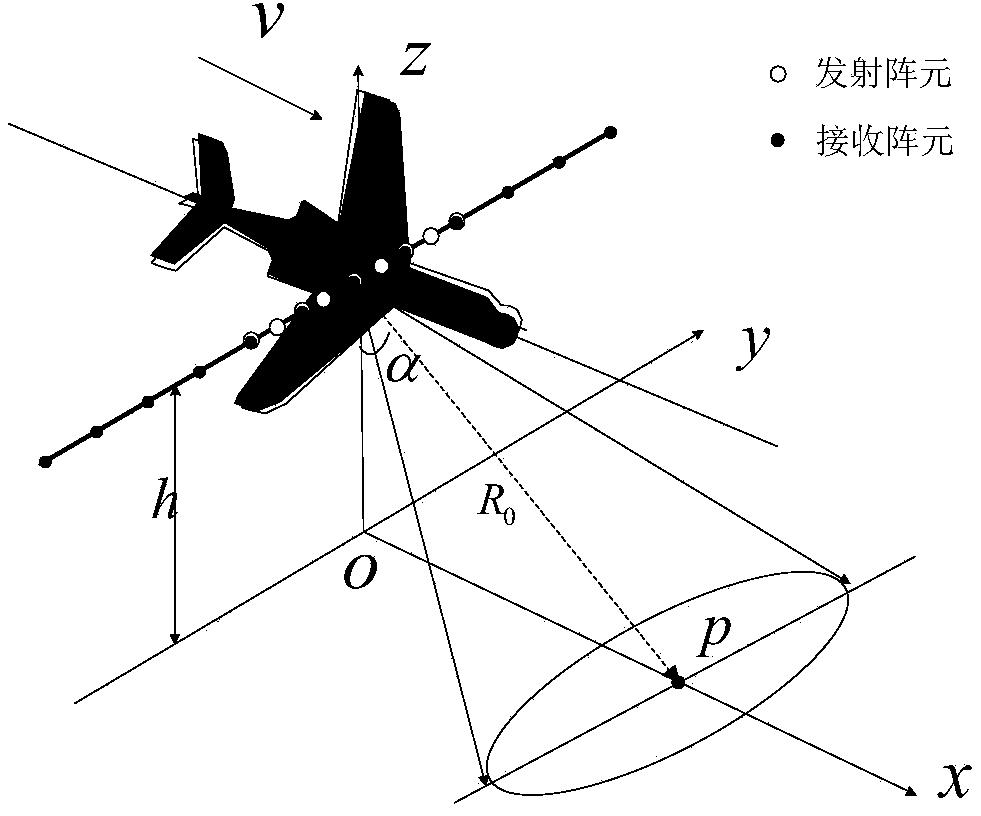
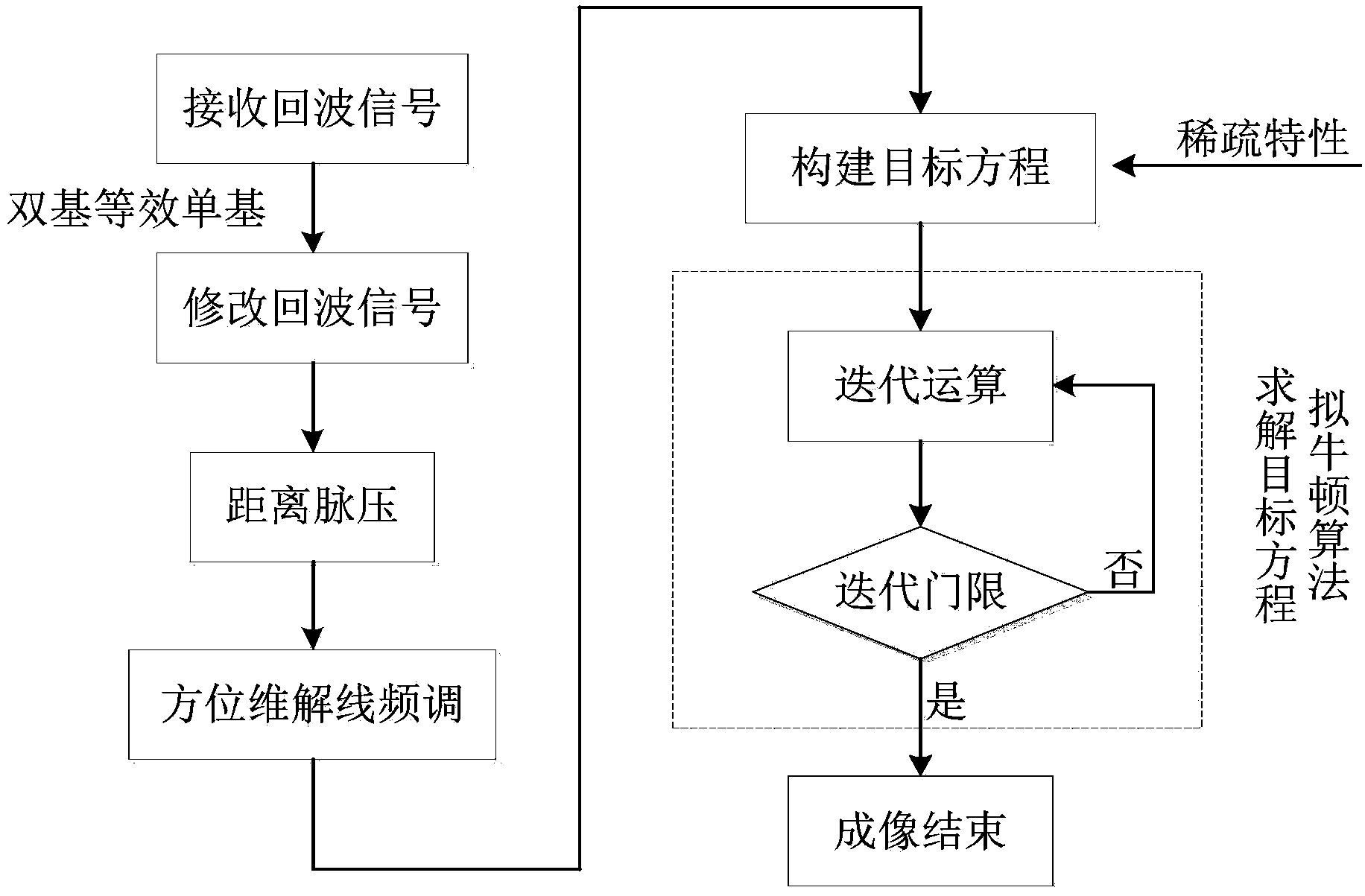
The invention discloses a method for super-resolution imaging of a foresight array SAR based on sparse representation. The method mainly solves the problems that an existing foresight imaging algorithm is difficult to achieve physically, and system cost is high. The method comprises the steps that (1) SAR echo data are received in a double-base mode, and echo signals are modified in a single-base mode; (2) range pulse compression and direction dimension unbinding and frequency modulation are conducted on the modified echo signals; (3) according to the observation scene and the sparse characteristic of an imaging target, a cost function of SAR imaging of the processed signals is established through the maximum posterior probability estimation method; (4) the updated quasi-Newton algorithm is used for solving the cost function, and then a super-resolution imaging result of the foresight array SAR is obtained. By means of the method, a high-resolution foresight imaging result can be obtained under the condition of a limited array length, the cost and complexity of a system are effectively lowered, and the method can be applied to target detection, topographic reconnaissance, guidance, city planning and environment surveys.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Bayesian algorithm-based content filtering method
InactiveCN101996241AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed uptimeSpecial data processing applicationsWireless communicationMaximum a posteriori estimationProbit
The invention discloses a Bayesian algorithm-based content filtering method. Content filtering is performed for text information in a 3rd generation mobile communication core network, text classification is performed by using a double threshold-based Bayesian algorithm, C1 is set to be normal information, C2 is set to be junk information, a classifier estimates the probability that a characteristic vector X which represents a data sample belongs to each class Ci, and a Bayesian formula for the estimation is that: P(Ci / X) = P(X / Ci) P(Ci) / P(X), wherein i is more than or equal to 1 and less than or equal to 2, the maximum value of a posterior probability is called the maximum posterior probability, for an error (a reference source is not found) of each class, the error (a reference source is not found) only needs to be calculated, a characteristic vector X of an unknown sample is assigned to the Ci class of the error (a reference source is not found) with the minimum risk value. Characteristic selection is performed by adopting document frequency (DF), and classification is performed by using minimum risk-based double threshold Bayesian decision. In a time division-synchronous code division multiple access (TD-SCDMA) mobile internet content monitoring system, the algorithm has higher controllability and can realize real-time high-efficiency classification of mass text information.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
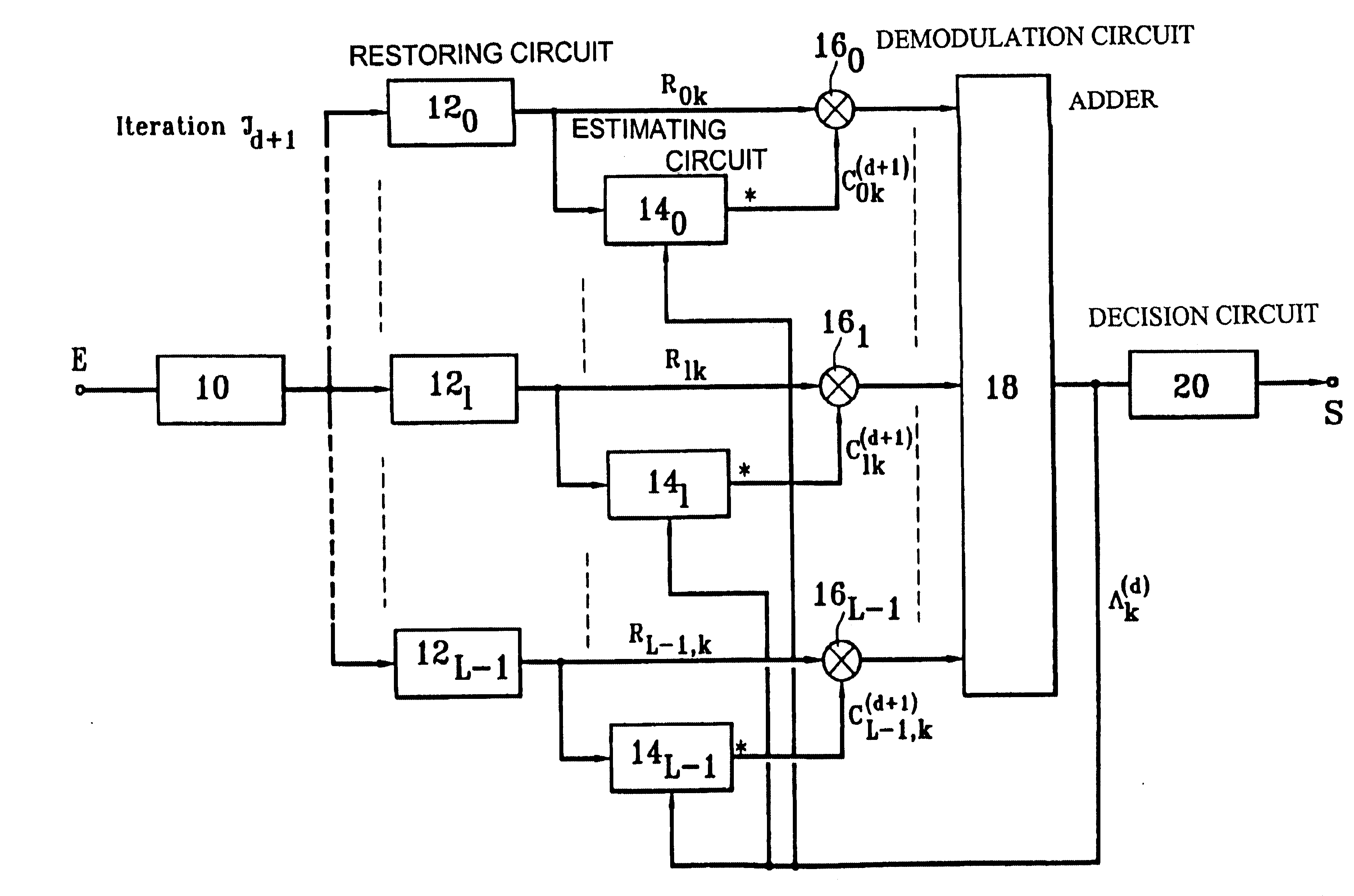
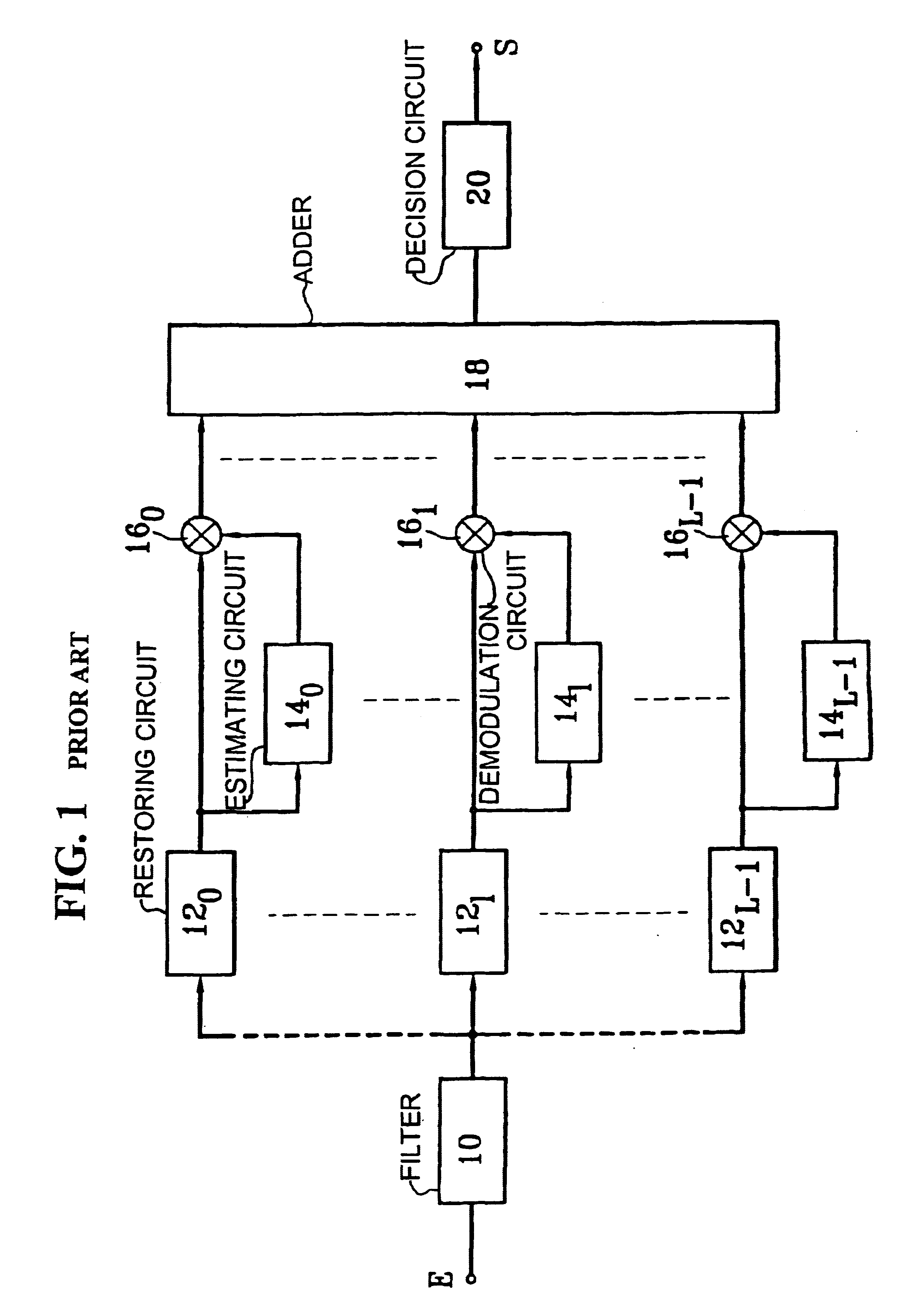
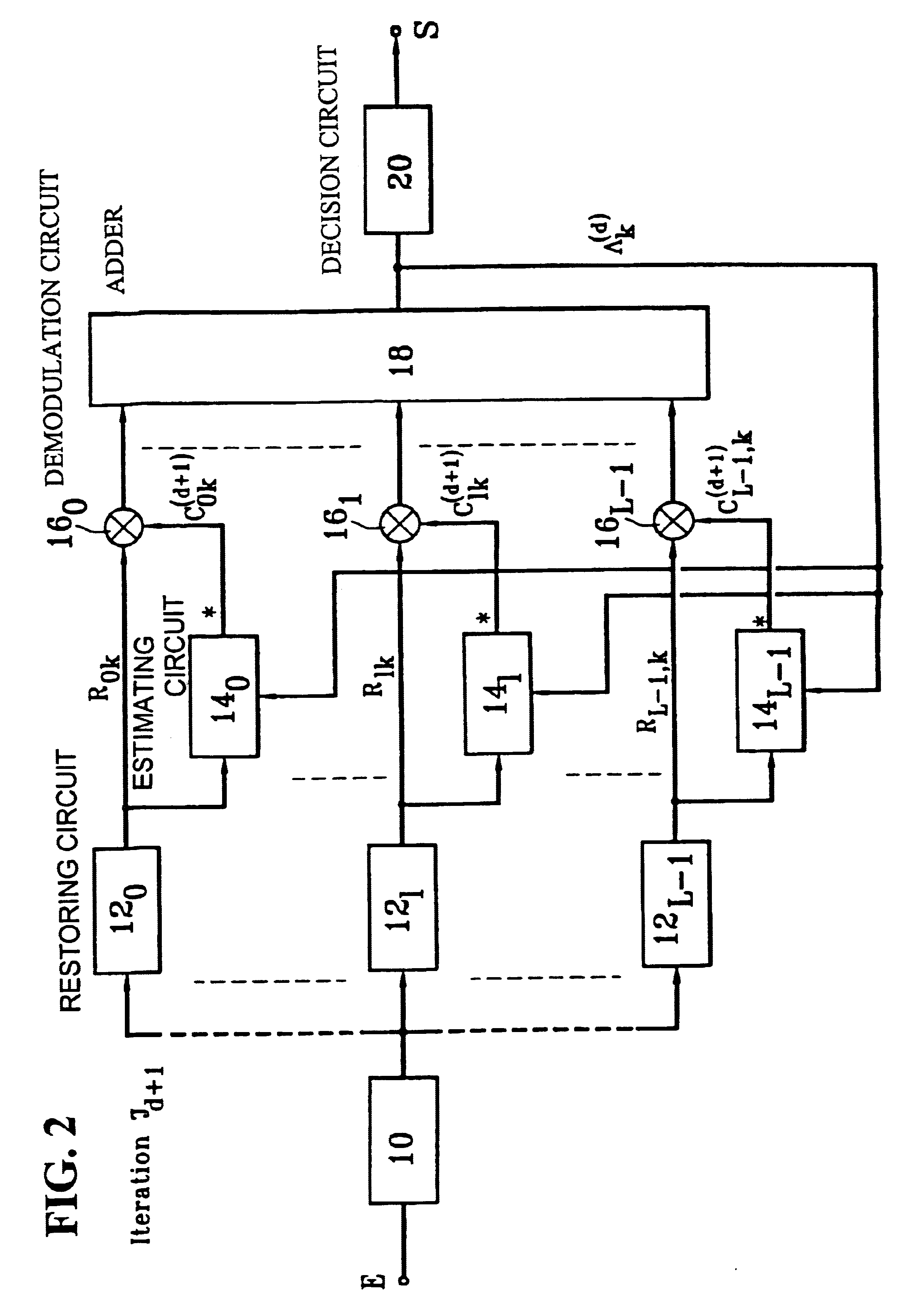
Iterative rake receiver and corresponding reception process
InactiveUS6674740B1Code division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsDecision circuitFrequency spectrum
A CDMA radiocommunication signals receiver for receiving signals obtained from spectrum symbols spread using pseudo-random sequences and having been propagated along a number of paths. The receiver includes a filter configured to restore L unspread signals for each symbol, corresponding to L different paths, a calculating circuit configured to calculate L estimates of the L different paths, and a demodulator configured to process each of the L unspread signals using the corresponding L estimates to obtain L path contributions. Also included is an adder configured to form a sum of the L path contributions and for outputting an estimate of a received symbol, and a decision circuit configured to make a decision about a value of the received symbol based on a value of the estimate of the received symbol output by the adder. Further, the receiver processes blocks of N symbols, each block having data symbols and control symbols, each symbol being identified by a rank k that it occupies in the block, where k varies from 0 to N-1. Also, for each path identified by an index l, where l varies from 0 to L-1, and for each block, the receiver considers a vector Cl with N components that characterizes the path during the block, and the receiver defines a vector base BK, vectors of the vector base BK being N eigenvectors of the matrix E [ClCl<.T>], each vector Cl being decomposed in the vector base, where decomposition coefficients denoted GlK form independent random Gaussian variables. In addition, coefficients GlK, define a vector Gl with N components for each path l, and the calculating circuit estimates each vector Gl, using an iterative process based on EM estimation-maximization algorithm based on a maximum a posteriori probability criterion.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
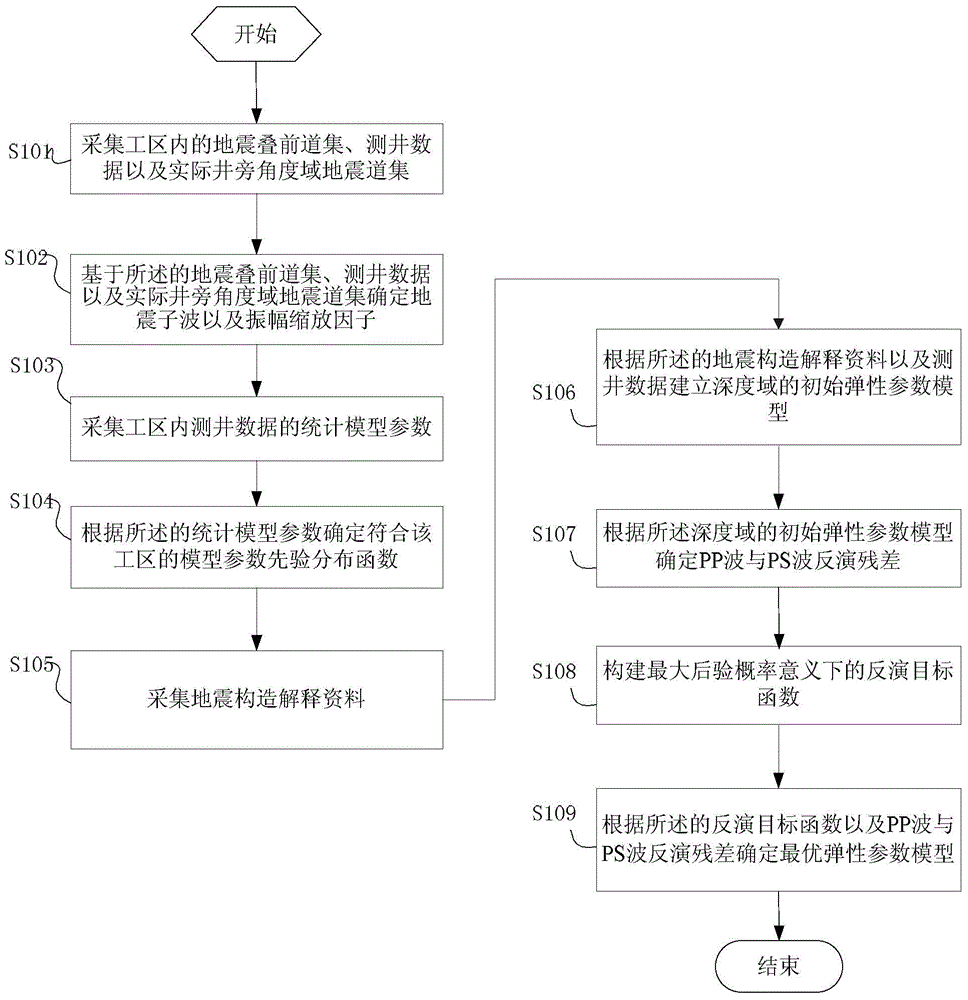
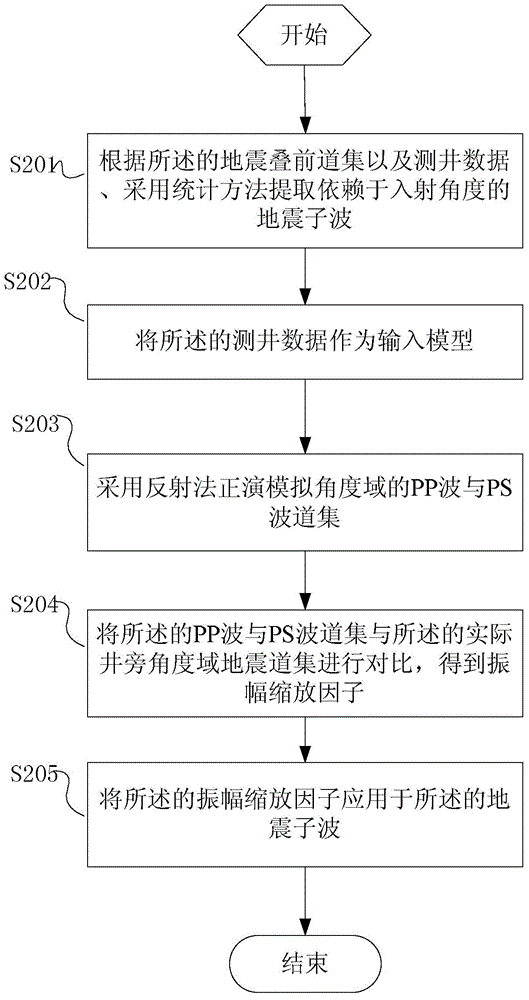
Method and system for inverting elastic parameters of multi-wave AVO reservoir based on reflectivity method
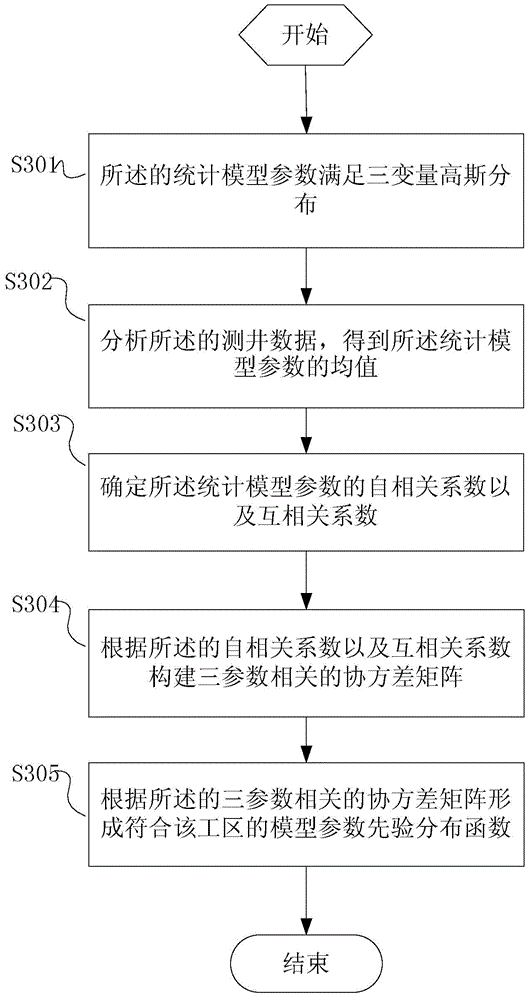
ActiveCN104614763AImprove stabilityHigh precisionSeismic signal processingMaximum a posteriori estimationModel parameters
The invention provides method and system for inverting elastic parameters of multi-wave AVO reservoir based on the reflectivity method. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a seismic prestack gather, log data and an actual seismic gather of an angle area beside the well; determining seismic wavelet and amplitude extension factors according to the eismic prestack gather, the log data and the actual seismic gather of the angle area beside the well; acquiring statistical model parameters of the log data; determining model parameter prior distribution functions meeting the working area according to the statistical model parameters; acquiring seismotectonics interpreting data; building an initial elastic parameter model of a depth area according to the seismotectonics interpreting data and the log data; determining inversion residuals of PP wave and PS wave according to the initial elastic parameter model; creating the inversion target function under the maximum posterior probability significance; determining an optimal elastic parameter model according to the inversion target function and the inversion residuals of PP wave and PS wave. According to the scheme, the method meets the requirements on inversing to recognize the characterization of a seismic prestack oil and gas reservoir, in particular a shale gas reservoir.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING) +1
Acoustic vector array DOA estimation method
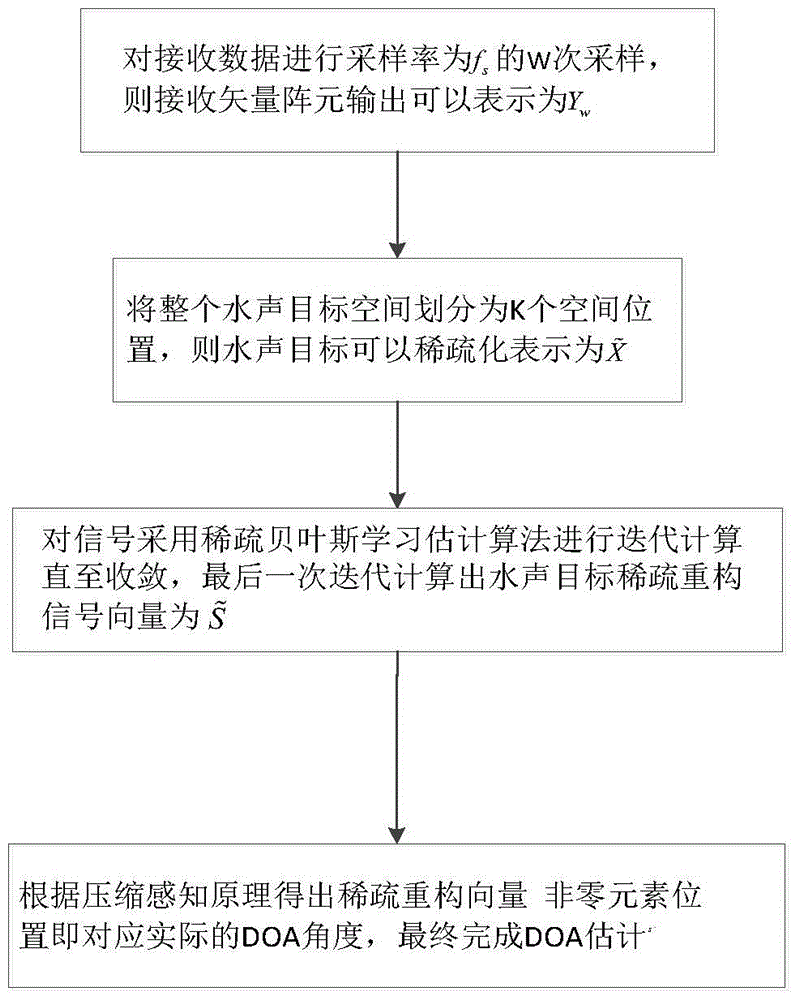
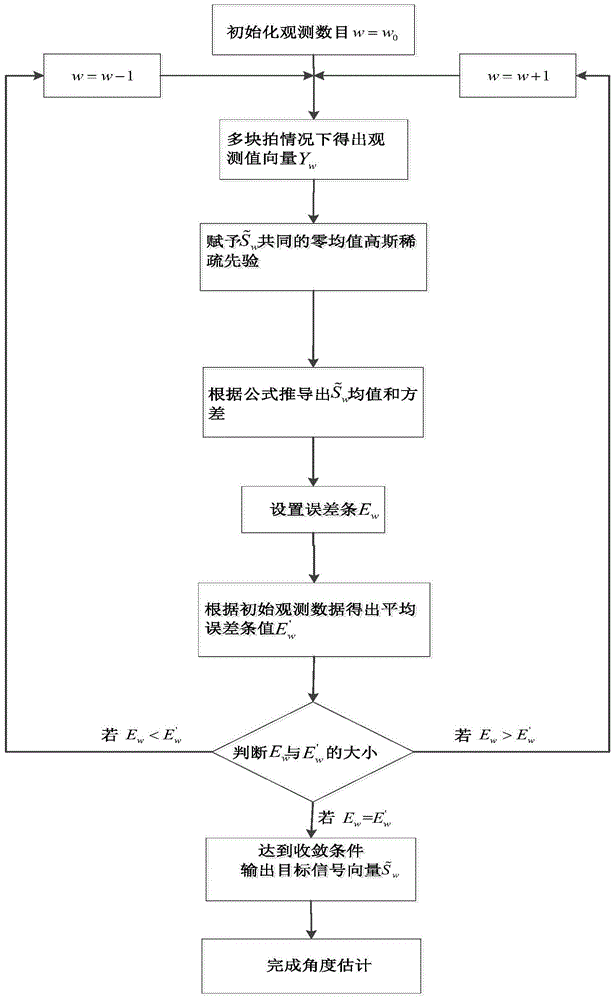
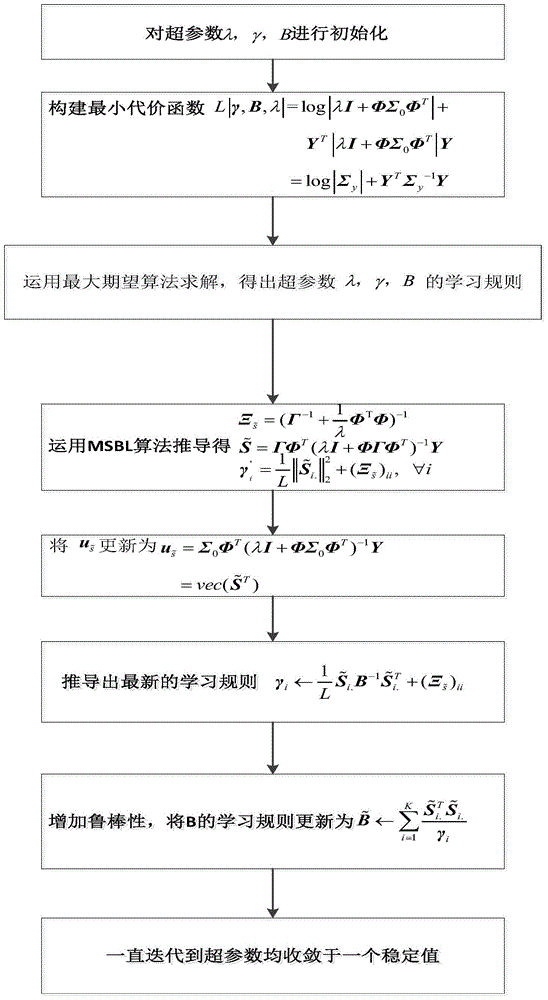
ActiveCN105676168AReduce sidelobeHigh precisionDirection/deviation determination systemsMaximum a posteriori estimationArray element
The invention discloses an acoustic vector array DOA estimation method, which comprises the steps that: signals sent by L remote underwater acoustic targets are narrowband signals at frequency f, a receiving signal array is a uniform linear array comprising M vector sensor array elements, and an array element distance is half wavelength of the transmitted signals; an entire underwater acoustic target space is divided into K spatial positions, and each spatial position corresponds to one directional angle; a sparse bayesian learning DOA estimation algorithm is adopted for the signal Sw<~>, a maximum posterior probability of a signal source is obtained to achieve azimuth angle estimation of the targets through solving a value of a hyper-parameter, the hyper-parameter is subjected to iterative calculation till convergence, and an underwater acoustic target sparse reconstructed signal vector is calculated to be Si<~> through the final iterative calculation; a position of a S<~> non-zero row is determined, a non-zero element position of the sparse reconstructed vector S<~> corresponds to an actual DOA angle, and the DOA estimation is completed finally. The acoustic vector array DOA estimation method can improve DOA estimation accuracy, obtains more incisive directional beams and lower side lobes, and achieves omnibearing DOA estimation.
Owner:HUAWEI TEHCHNOLOGIES CO LTD
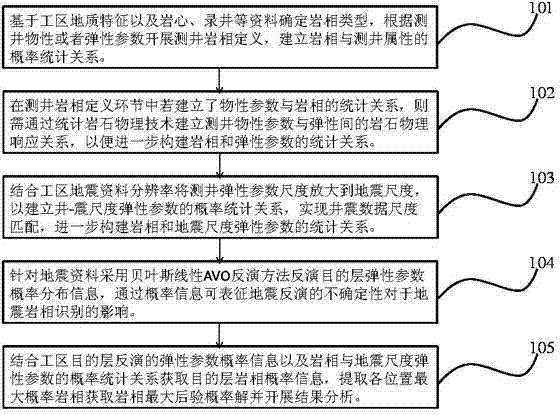
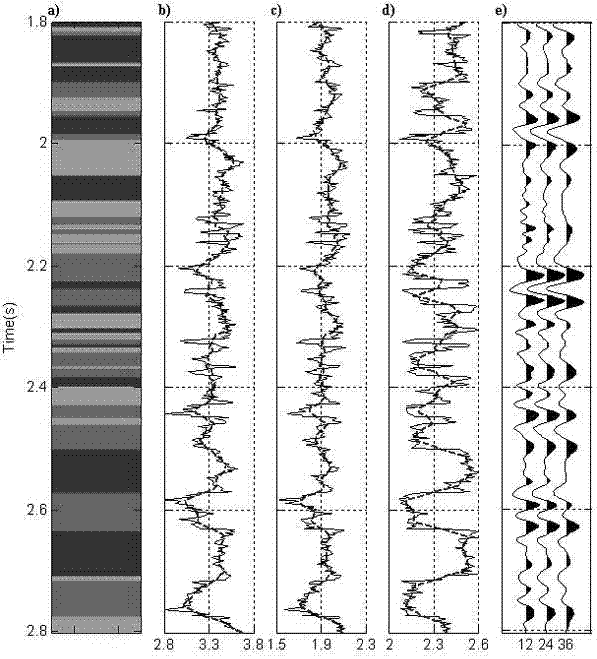
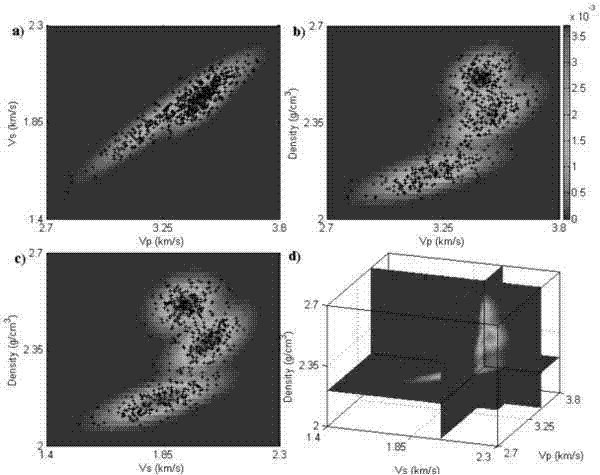
Method for synchronously realizing seismic lithofacies identification and quantitative assessment of uncertainty of seismic lithofacies identification
ActiveCN104749624AUncertainty objective realityReduce evaluation riskSeismic signal processingApplicability domainMaximum a posteriori estimation
The invention relates to a method for synchronously realizing seismic lithofacies identification and quantitative assessment of uncertainty of the seismic lithofacies identification. The method comprises the steps of determining the type of the lithofacies and performing logging lithofacies definition, establishing a rock physical response relation between logging physical parameters and elasticity, establishing a probability statistical relation between the lithofacies and logging attributes, establishing the probability statistical relation of well-seismic scale elasticity parameters and constructing the statistical relation of the lithofacies and the seismic scale elasticity parameters, inverting the information of the probability distribution of the elasticity parameters of a target layer, obtaining the lithofacies probability information of the target layer by combining the inverted probability information of the elasticity parameters of the target layer and the statistical relation of the lithofacies and the seismic scale elasticity parameters, obtaining the maximum posterior probability solution of the lithofacies distribution according to the probability information of the lithofacies and outputting final model parameters. The method is capable of quantitatively characterizing the uncertainty of each link of lithofacies identification and the propagation and accumulation characteristics of the uncertainty in the lithofacies identification process, and also capable of performing uncertainty analysis on the seismic lithofacies identification; as a result, the reservoir evaluation risk is reduced; in short, the method is wide in application range.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
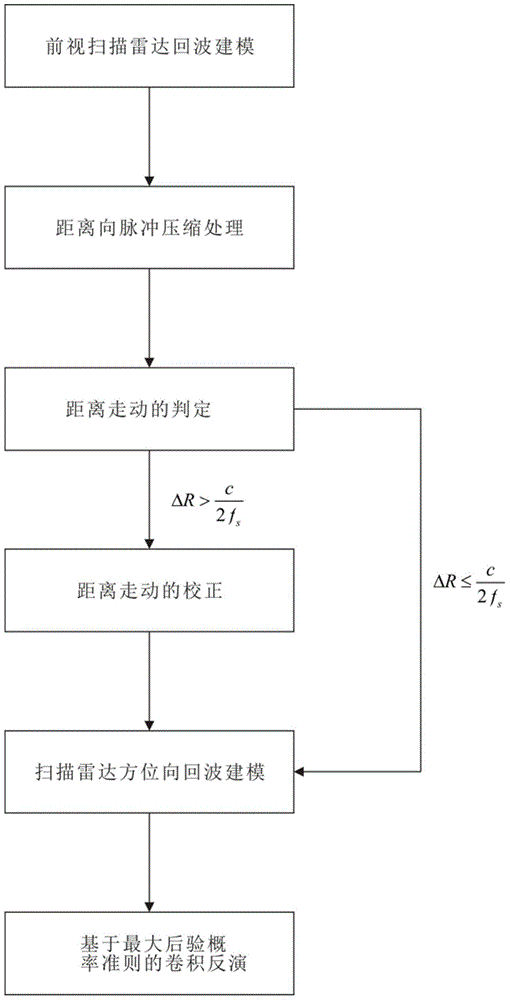
Deconvolution method for realizing scanning radar azimuth super-resolution imaging
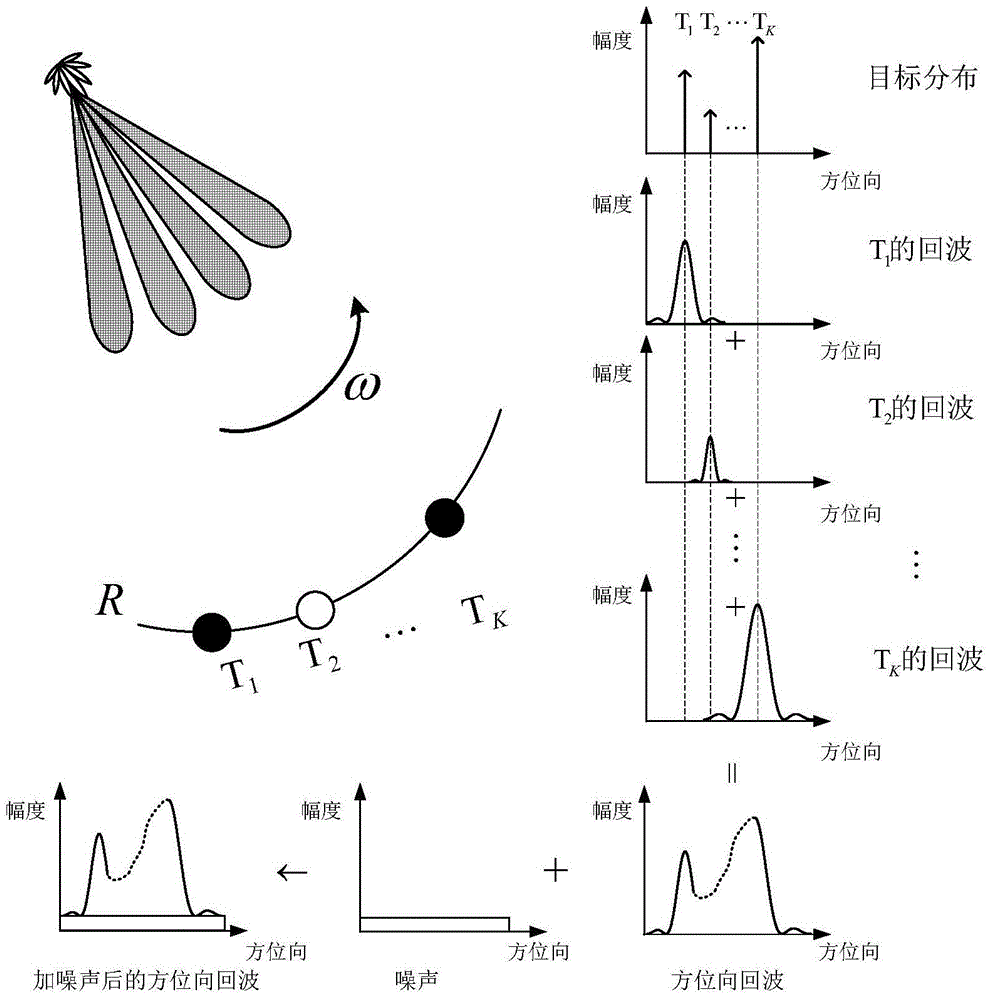
ActiveCN104977582AAchieving super-resolution imagingOvercome Spectrum LossRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumMaximum a posteriori estimation
The invention discloses a deconvolution method for realizing scanning radar azimuth super-resolution imaging. Step one, forward-looking scanning radar echo modeling is performed; step two, range direction pulse compression processing is performed; step three, range wall determination is performed; step four, range walk correction is performed; step five, scanning radar azimuth direction echo modeling is performed; and step six, convolution inversion based on the maximum posterior probability criterion is performed. The beneficial effects are that an azimuth echo convolution model is established, an algorithm iteration expression is derived based on the maximum posterior probability criterion through combination of prior information and a likelihood function, low frequency is reconstructed, high frequency is recovered, an iterative solution is obtained by utilizing frequency spectrum extrapolation property, a problem of spectrum loss caused by noise and antenna low-pass property is overcome, a high-frequency component is acquired by utilizing nonlinear operation separation and super-resolution imaging is realized. Besides, frequency domain spectrum width and a change trend diagram of frequency domain integral sidelobe comparison number of iterations are provided by utilizing the frequency spectrum extrapolation property, and finally convolution inversion is realized and the inversion result is used for realizing scanning radar super-resolution imaging.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
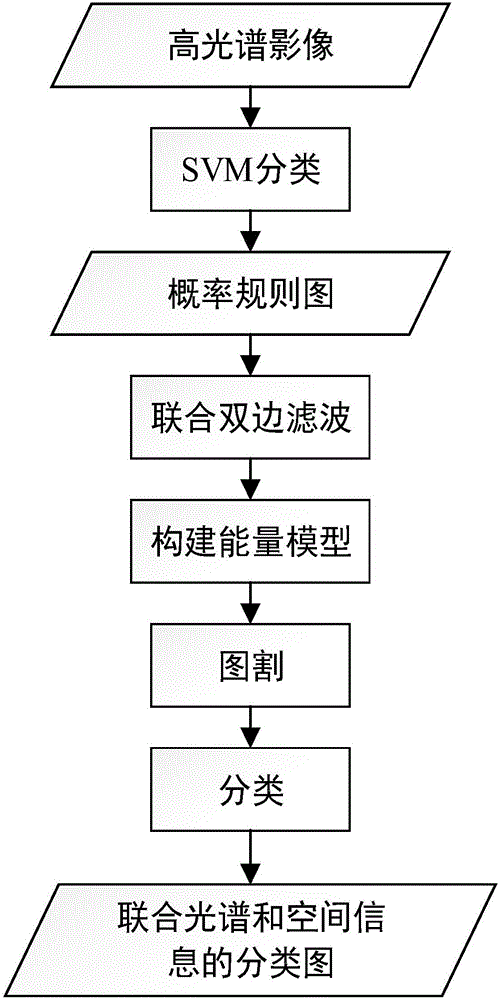
Hyperspectral image classification method based on edge preservation and graph cut model
InactiveCN106339674AAchieve fine classificationBorder keepingScene recognitionTest sampleMaximum a posteriori estimation
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image classification method based on edge preservation and a graph cut model. The hyperspectral image classification method comprises the following steps that S1, hyperspectral images to be classified are inputted; S2, the image elements of the corresponding coordinate positions of the original hyperspectral images are extracted to form a reference data sample set; S3, a supervised classification training sample set is selected; and the rest reference data samples act as a test sample set; S4, pixel level image classification operation is performed so that a probability membership distribution graph of each corresponding class is acquired; S5, filtering is performed so that the optimized class probability membership distribution graph is acquired; S6, all the ground targets are extracted: the optimized class probability membership distribution graph is cut by using the graph cut model so that the cut result of each class is acquired; and the final tag result is acquired from the cut result of each class by using the merging rule and the maximum posterior probability estimation; and S7, the final classification graph is outputted. A new strategy for area tagging is provided so that the hyperspectral image classification accuracy can be effectively enhanced.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
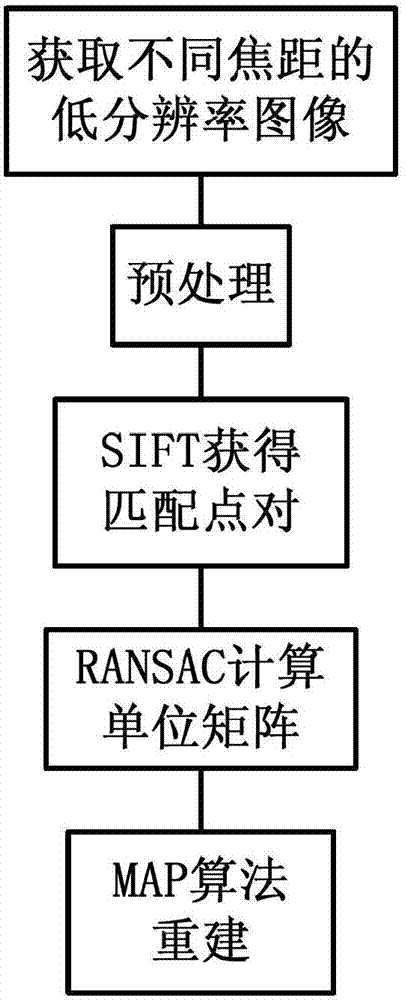
Image super-resolution rebuilding method based on variable focal length video sequence
InactiveCN103034982ASolve the reconstruction problem with scale scalingImage enhancementMaximum a posteriori estimationVideo sequence
The invention discloses an image super-resolution rebuilding method based on a variable focal length video sequence. The image super-resolution rebuilding method includes the following steps: a first step is that a group of low-resolution images with different focal lengths are shot to form one video sequence, all the images are changed into gray level images and subjected to image preprocessing, and reference images are selected from the gray level images; a second step is that matching point pairs between the reference images and the remaining unselected images are acquired by using the scale invariant feature transformation algorithm; a third step is that a homography matrix between the reference images and the remaining unselected images is calculated according to the matching point pairs by using the random sampling consensus algorithm; and a fourth step is that the reference images are subjected to super-resolution rebuilding by using the maximum posterior probability algorithm. Through the sub pixel precision image registration algorithm, the image super-resolution rebuilding method allows that translation, rotation, zooming and other situations exist among the images, has an outstanding effect in the super-resolution rebuilding of the variable focal length video sequence, and has certain innovativeness.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Airborne scanning radar imaging method in iteration compression mode
ActiveCN103487803AAchieving super-resolution imagingEfficient integrationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPrior informationMaximum a posteriori estimation
The invention discloses an airborne scanning radar imaging method in an iteration compression mode. The airborne scanning radar imaging method is characterized in that an azimuth-direction super-resolution imaging back model is built under the Bayesian theory framework, and the model built under the Bayesian theory can effectively fuse prior information of a target. When the super-resolution imaging back model is built, the assumption of a radar imaging basic idea on the noise statistical property is followed, and the Gaussian distribution function is adopted in the model to describe the noise statistical property. Due to the fact that target scattering has sparsity relative to an imaging background, the prior information of target scattering is described through the Laplace distribution function, radar super-resolution imaging is precisely converted into the maximum posterior probability problem in mathematics, corresponding target information when the posterior probability is maximum is solved, then the target information is reconstituted, and therefore the radar super-resolution imaging is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Cooperative modulation signal identifying method based on data fusion of decision layer
InactiveCN102647391AReduce in quantityImprove classification efficiencyMultiple carrier systemsNODALMaximum a posteriori estimation
The invention discloses a cooperative modulation signal identifying method based on data fusion of a decision layer, belonging to the technical field of wireless communication. According to the cooperative modulation signal identifying method provided by the invention, a judging result of each receiving node is obtained by obtaining characteristic values of sample signals collected by a plurality of receiving nodes and using a support vector machine based on a binary tree decision; and a data fusion center uses a decision with a maximum posterior probability, so as to finally determine a modulation manner of signals to be identified. With the adoption of the cooperative modulation signal identifying method provided by the invention, the quantity of the support vector machines to be trained is reduced by using the SVM (Support Vector Machine) based on a binary tree, so as to improve the classification efficiency. An error caused by single-user detection is corrected by multi-user cooperative identification, particularly the identification rate at a low signal-to-noise ratio can be improved; and compared with the traditional voting fusion decision, the fusion decision with the maximum posterior probability has higher reliability of an identifying result by considering influences caused by a prior identification condition in a system and the judging results of the receiving nodes.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
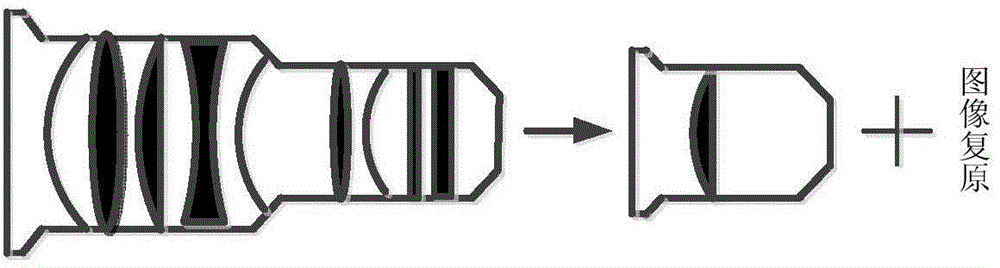
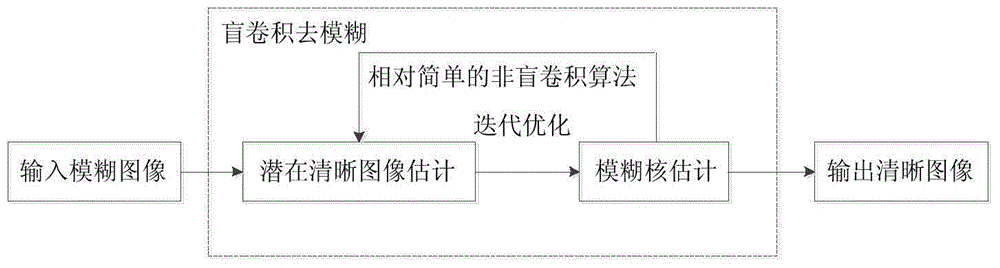
Single lens imaging method for extracting blurring kernel priori according to image spectrum information
The invention relates to the field of image processing, and particularly discloses a single lens imaging method for extracting a blurring kernel priori according to image spectrum information. The method comprises the steps that a single lens camera is used for acquiring a blurred image; an l1 / l2 image priori and the blurring kernel priori extracted according to the information of the blurred image are added in an existing target optimization function; then a blind convolution algorithm based on maximum posterior probability is used for estimating the blurring kernel of the single lens camera; combined with the estimated blurring kernel, a non-blind convolution algorithm is used for obtaining a clear image. According to the single lens imaging method for extracting the blurring kernel priori according to the image spectrum information, single lens high-quality computational imaging can be achieved, the blurred image information can be fully used by the adopted blurring kernel, and therefore a good deblurring effect is achieved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
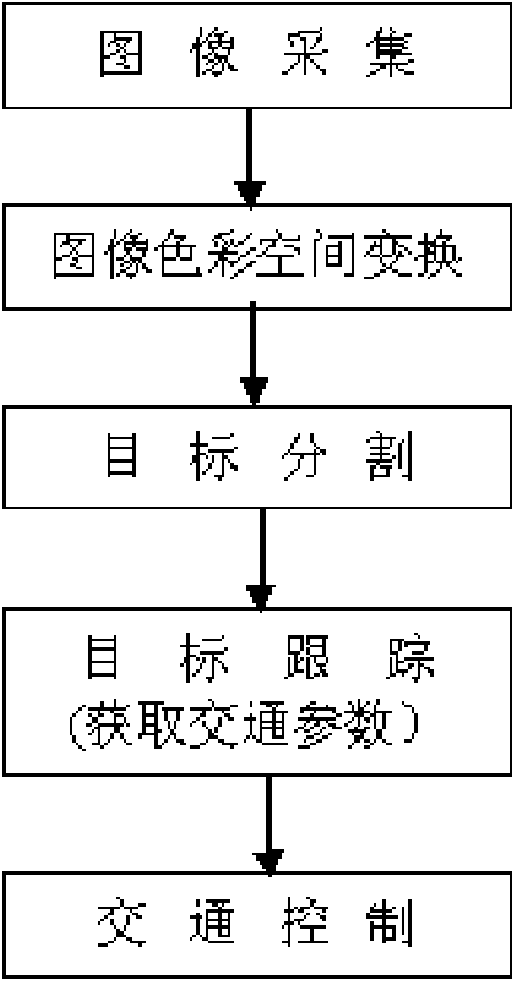
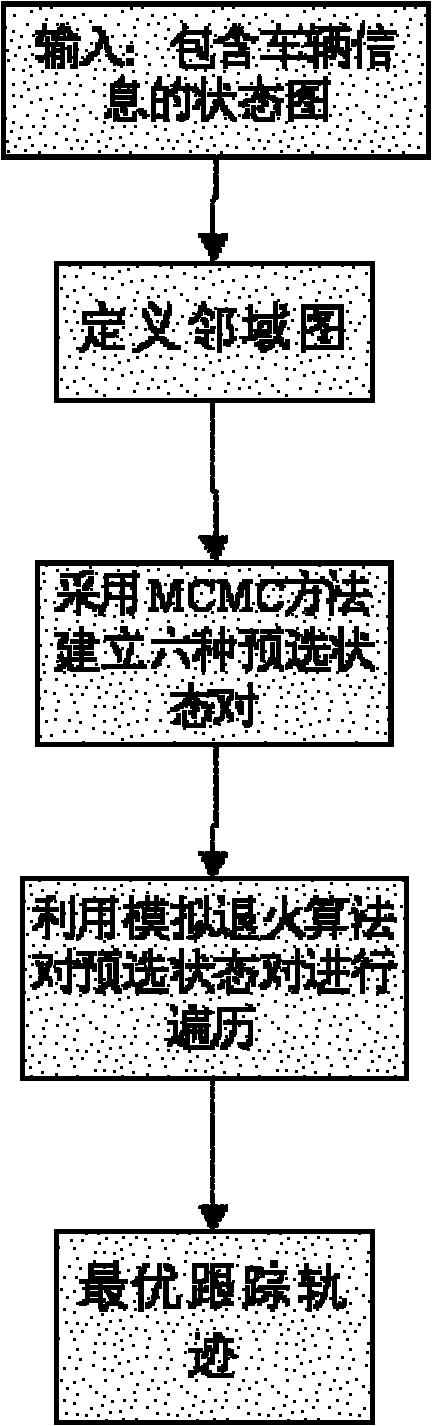
Method for tracking multi-target vehicles by adopting MCMC (Markov Chain Monte Carlo) algorithm
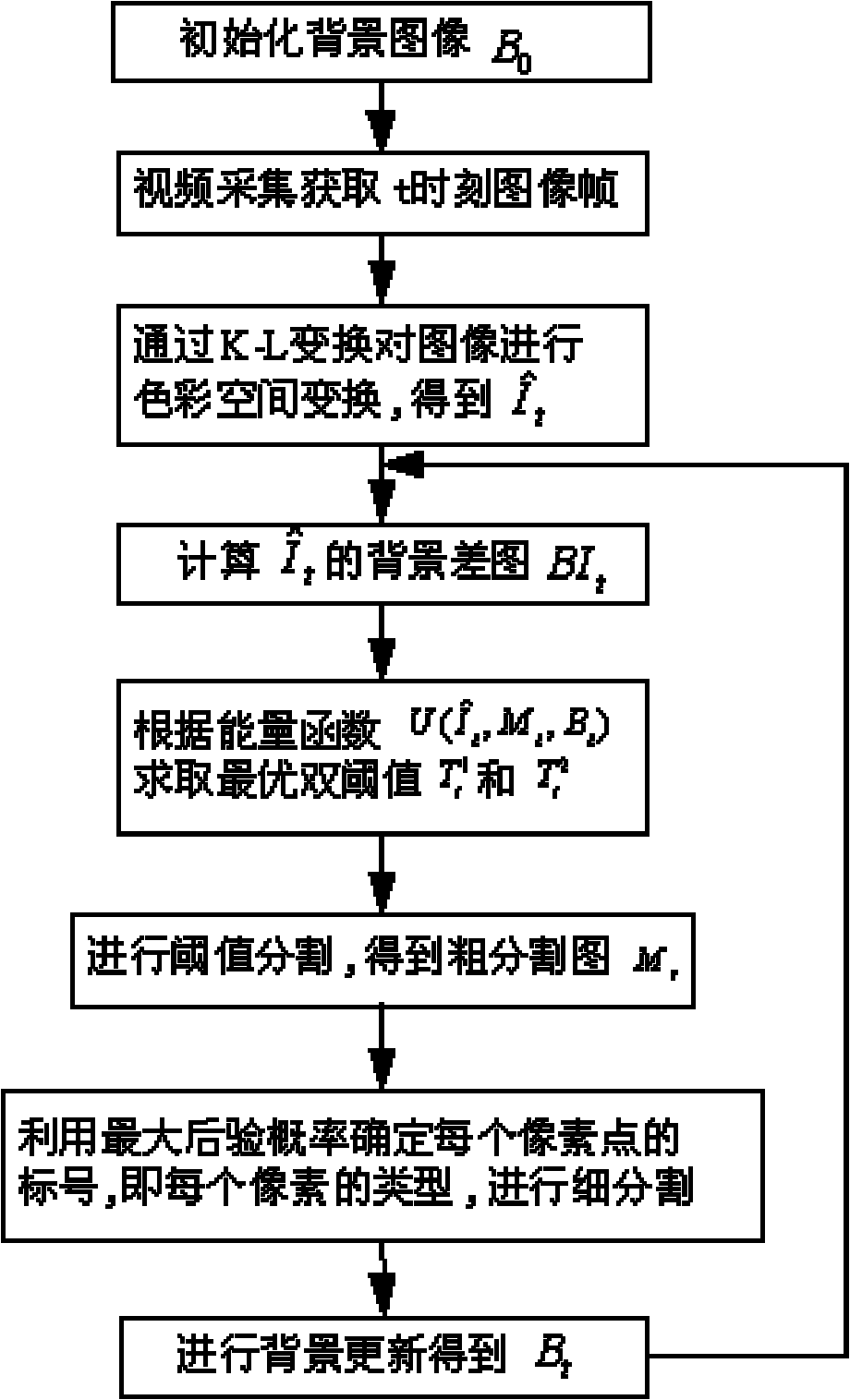
InactiveCN102073853AAccurate trackingSolve the problem of occlusion splittingImage analysisRoad vehicles traffic controlMaximum a posteriori estimationPosteriori probability
The invention relates to a method for tracking multi-target vehicles by adopting the MCMC (Markov Chain Monte Carlo) algorithm, comprising the following steps: modeling the multi-target vehicle tracking process by adopting the MCMC algorithm, establishing various preselection states, traversing the preselection states by using the Metropolis-Hastings sampling based simulated annealing algorithm, and selecting the preselection state with the maximum connection probability as the optimal solution. In the method, a limit is set to the transfer equivalence for the first time, and the parameters in the data association are estimated by the experimental data regression fitting, thus the optimal vehicle motion trajectory with maximum posteriori probability significance is obtained, and the vehicles are tracked. The invention solves the problems of frequent shielding splitting of the multi-target vehicles and has the advantages of high multi-target vehicle tracking precision and good real-time performance.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
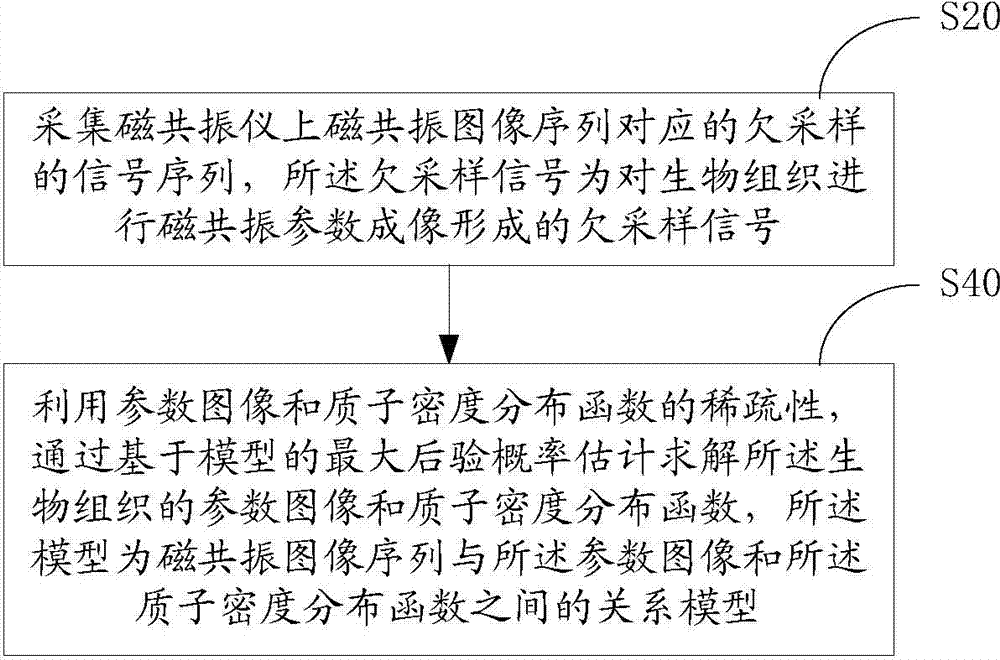
Magnetic resonance parameter imaging method and system
ActiveCN103705239AImaging is fast and accurateAvoid error propagationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRelational modelMaximum a posteriori estimation
A magnetic resonance parameter imaging method includes the steps of acquiring an under-sampling signal corresponding to a magnetic resonance image sequence on a magnetic resonance imager; estimating and solving a parameter image and proton density distribution function of biological issue through sparsity in parameter image and proton density distribution functions and model-based maximum posterior probability. The under-sampling signal is formed by application of magnetic resonance parameter imaging on the biological issue. A model for maximum posterior probability is a model of relation between the magnetic resonance image sequence and the parameter image and proton density distribution function. The method has the advantages that the parameter image and proton density distribution function of the biological tissue is directly estimated through the under-sampling signal and error propagation caused by the application of an under-sampling rebuilt magnetic resonance image in estimating biological tissue parameters is avoided. The sparsity in the parameter image and proton density distribution function is introduced, and image artifacts caused by under-sampling can be effectively suppressed. In addition, the invention further provides a magnetic resonance parameter imaging system.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
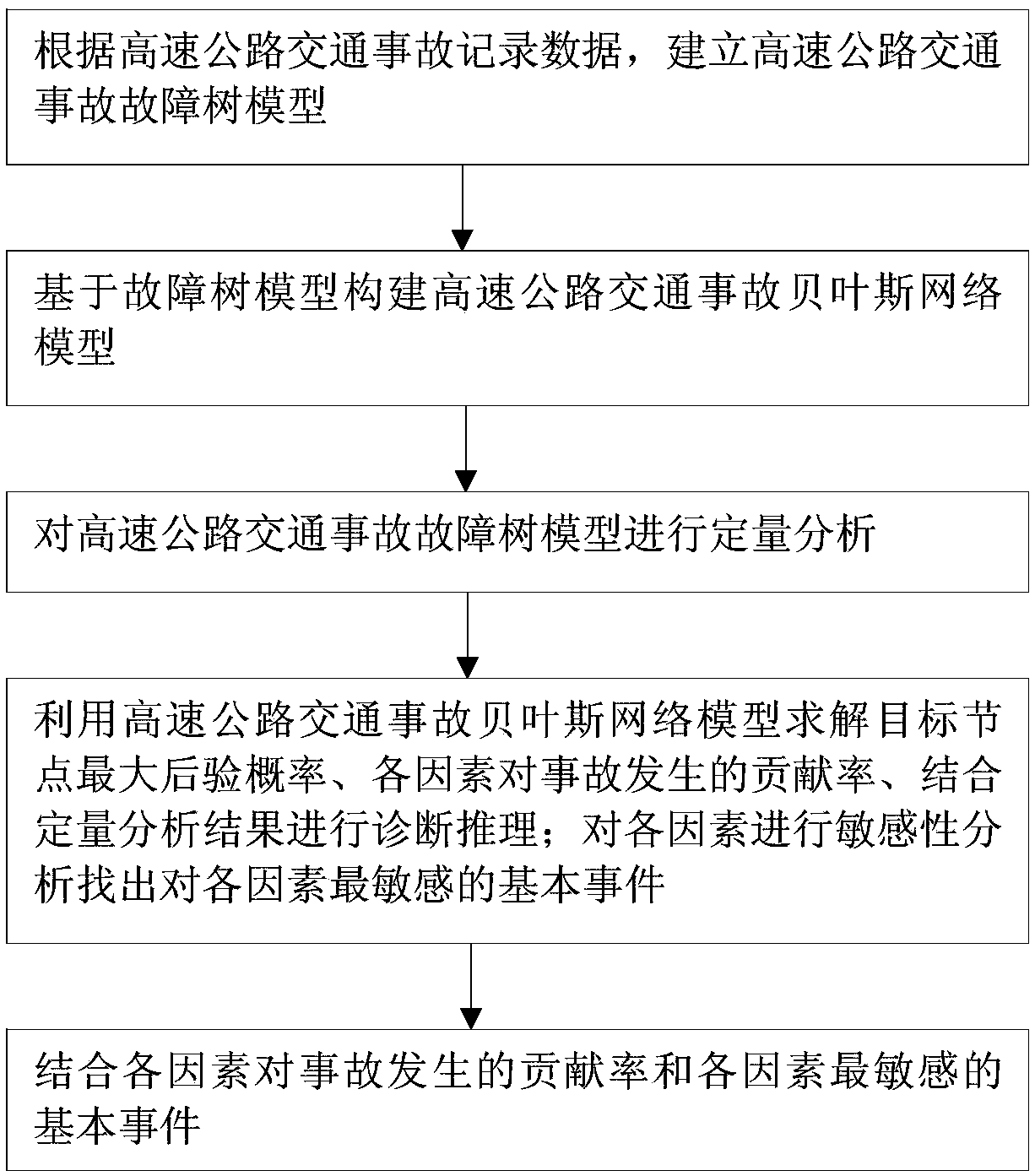
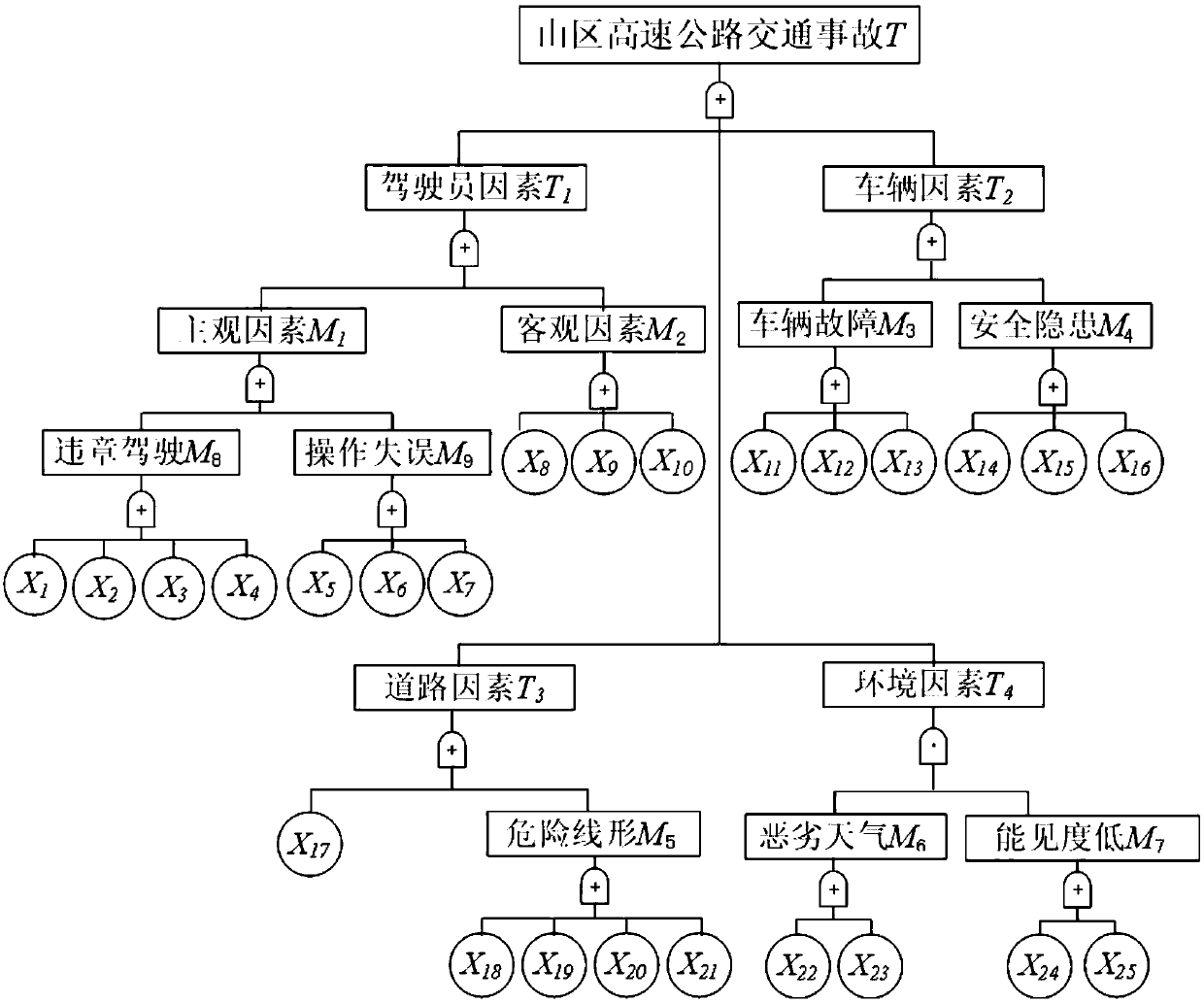
Method for analyzing cause of highway traffic accident
InactiveCN109523786AImprove efficiencyHigh precisionDetection of traffic movementMaximum a posteriori estimationTraffic accident
The invention provides a method for analyzing the cause of a highway traffic accident, and belongs to the technical field of traffic safety management and control. The method comprises a step of establishing a highway traffic accident fault tree model based on highway traffic accident record data, a step of constructing a highway traffic accident Bayesian network model based on the fault tree model, a step of quantitatively analyzing the highway traffic accident fault tree model, a step of solving the maximum posterior probability of a target node and the contribution rate of each factor to the accident by using the highway traffic accident Bayesian network model and performing diagnostic reasoning with the combination of a quantitative analysis result, a step of performing sensitivity analysis on each factor to find a basic event which is most sensitive to each factor, and a step of combining the contribution rate of each factor to the accident and the basic event which is most sensitive to each factor. According to the method, the problem of a large calculation amount or an inaccurate analysis result of the reason analysis of the highway traffic accident at present is solved. Themethod can be used for analyzing the highway traffic accident.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
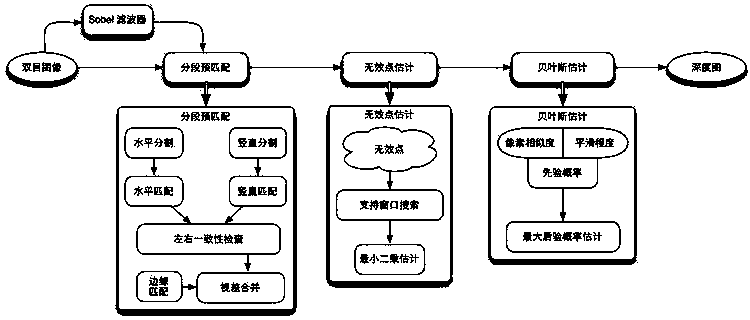
Progressive type three-dimensional matching algorithm based on sectional matching and bayes estimation
InactiveCN103383776AReduce the occurrence of mismatchesImage analysisStereo matchingMaximum a posteriori estimation
The invention discloses a progressive type three-dimensional matching algorithm based on sectional matching and bayes estimation. The progressive type three-dimensional matching algorithm includes: 1) dividing an image into an edge area and a sectional area on the basis of responding of a Sobel filter, matching through a three-dimensional matching strategy based on a window and a sectional matching strategy, and combining to obtain a pre-matching depth image; 2) for invalid points in the pre-matching depth image, fitting a least square plane through effective points in a support window, estimating the depth of the invalid point position, and thickening the pre-matching image; 3) for the obtained pre-matching image, revising the depth of each point through a bayes maximum posterior probability method, considering using pre-matching values as the prior probability, and considering using smoothness of similarity and depth of the image as the posterior probability. By means of the progressive type three-dimensional matching algorithm, extraction of depth images from thick to dense and from coarse to fine can be finished through a progressive structure, and meanwhile, edge characteristics and smoothness are considered, so that the accurate and smooth depth images can be obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
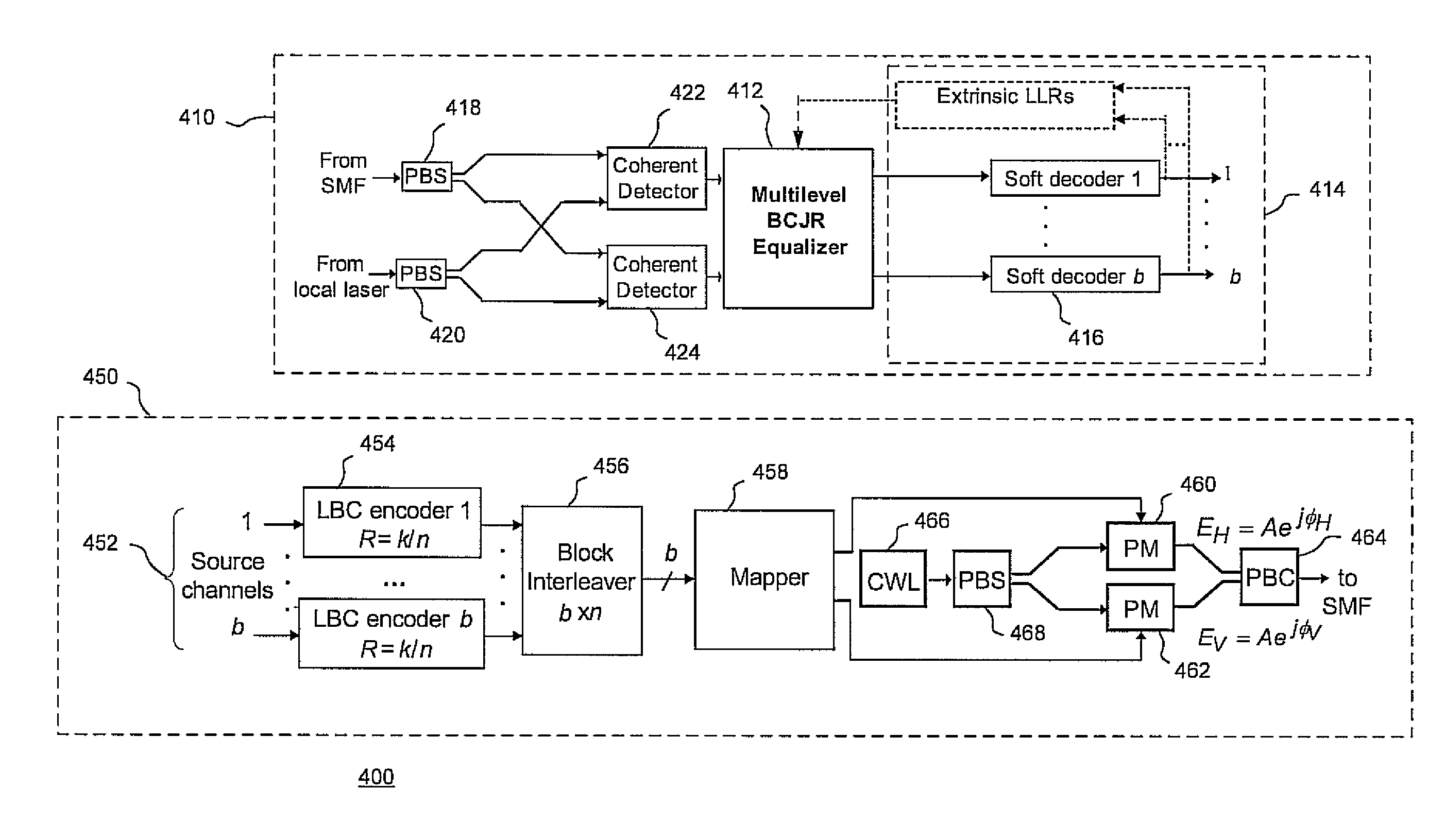
Methods and systems for polarization multiplexed multilevel modulation for optical communication
ActiveUS20100232804A1Reduce the impactReduce impactMultiple-port networksPolarisation multiplex systemsMaximum a posteriori estimationPolarization multiplexed
Multilevel soft-equalizer detectors, such as a maximum a posteriori probability (MAP) detector, suitable for use in polarization multiplexed optical communications using multilevel modulations and coherent detection are disclosed. Detection systems and methods may consider two symbols transmitted over two orthogonal polarization states as a two-component symbol, which is effective in eliminating the bit error ratio (BER) floor phenomenon introduced by conventional soft equalizers.
Owner:NEC CORP
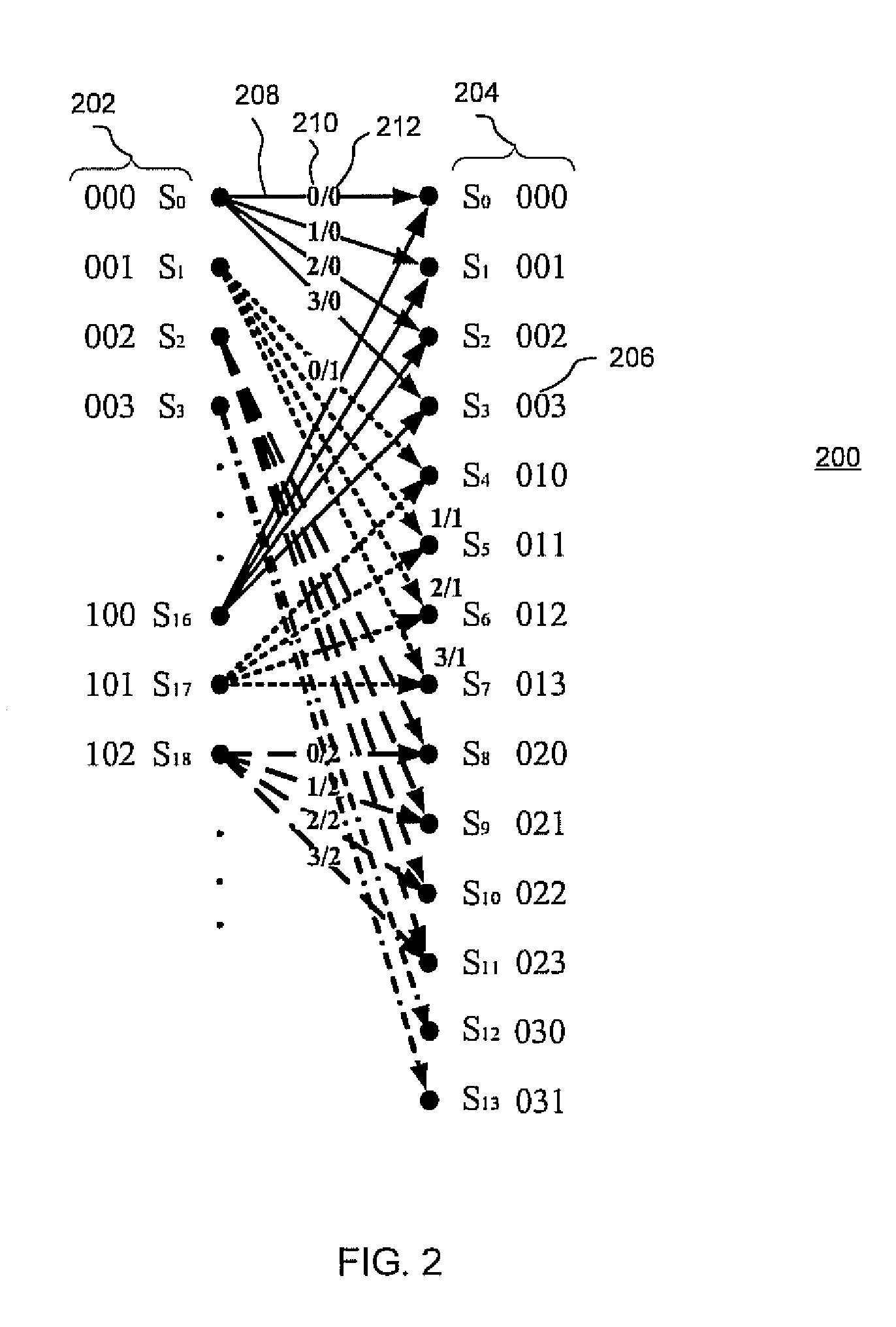
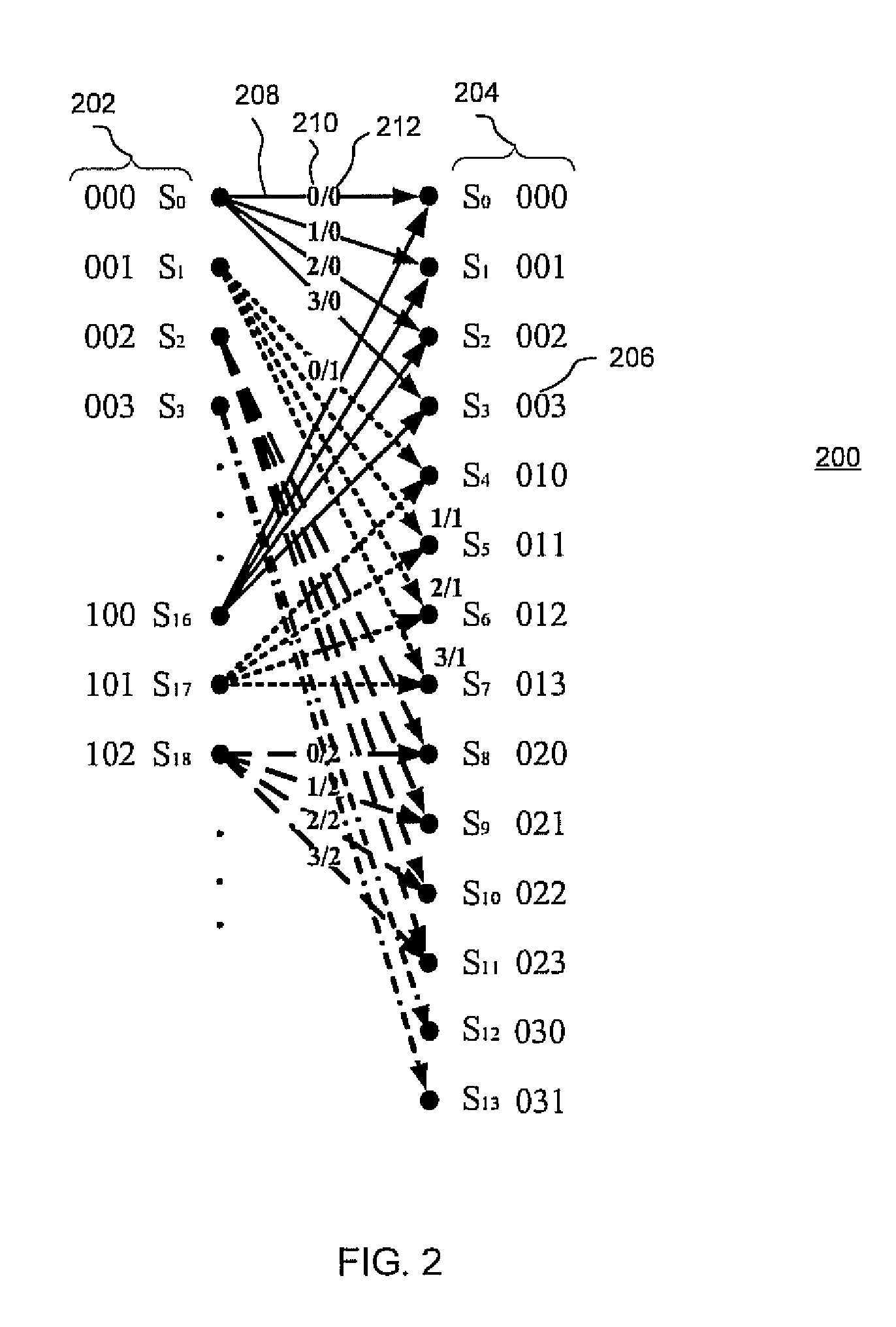
Methods and systems for polarization multiplexed multilevel modulation for optical communication
ActiveUS8175466B2Reduce impactBit error ratio floor phenomenon can be eliminatedMultiple-port networksPolarisation multiplex systemsMultilevel modelMaximum a posteriori estimation
Multilevel soft-equalizer detectors, such as a maximum a posteriori probability (MAP) detector, suitable for use in polarization multiplexed optical communications using multilevel modulations and coherent detection are disclosed. Detection systems and methods may consider two symbols transmitted over two orthogonal polarization states as a two-component symbol, which is effective in eliminating the bit error ratio (BER) floor phenomenon introduced by conventional soft equalizers.
Owner:NEC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com